Exhibition dates: 8th December 2020 – 9th May 2021
Curator: Alexander Moore
The exhibition will include work by the following 41 artists (in alphabetical order):
Nobuyoshi Araki, Anna Atkins, Alois Auer, Cecil Beaton, Karl Blossfeldt, Adolphe Braun, Jan Brueghel the Elder, Mat Collishaw, Imogen Cunningham, Roger Fenton, Adam Fuss, Ori Gersht, Cecilia Glaisher, Joy Gregory, William Henry Fox Talbot, Sir John Herschel, Gyula Holics, Jan van Huysum, Henry Irving, Charles Jones, Sarah Jones, André Kertész, Nick Knight, Lou Landauer, Richard Learoyd, Pradip Malde, Robert Mapplethorpe, John Moffat, Sarah Moon, James Mudd, Kazumasa Ogawa, T Enami, Dr Albert G Richards, Scowen & Co., Scheltens & Abbenes, Helen Sear, Edward Steichen, Josef Sudek, Lorenzo Vitturi, Edward Weston, Walter Woodbury.
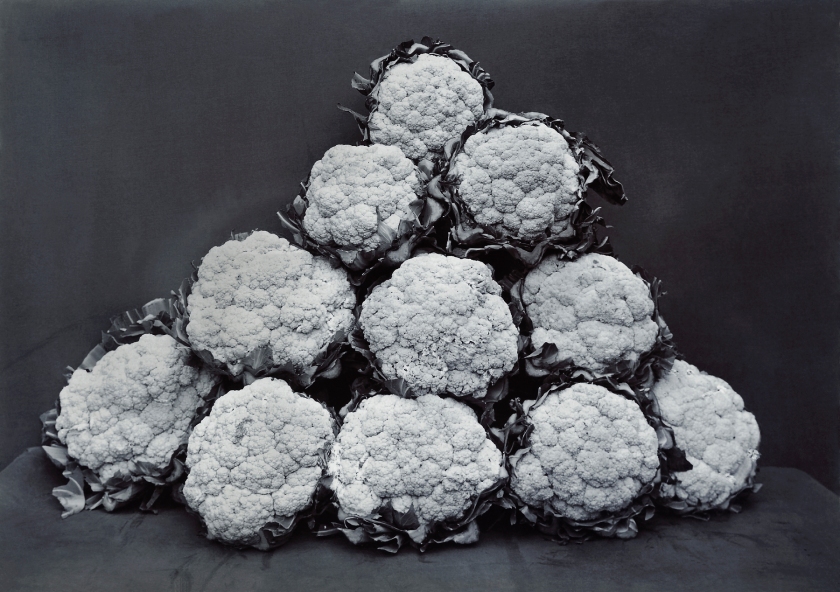
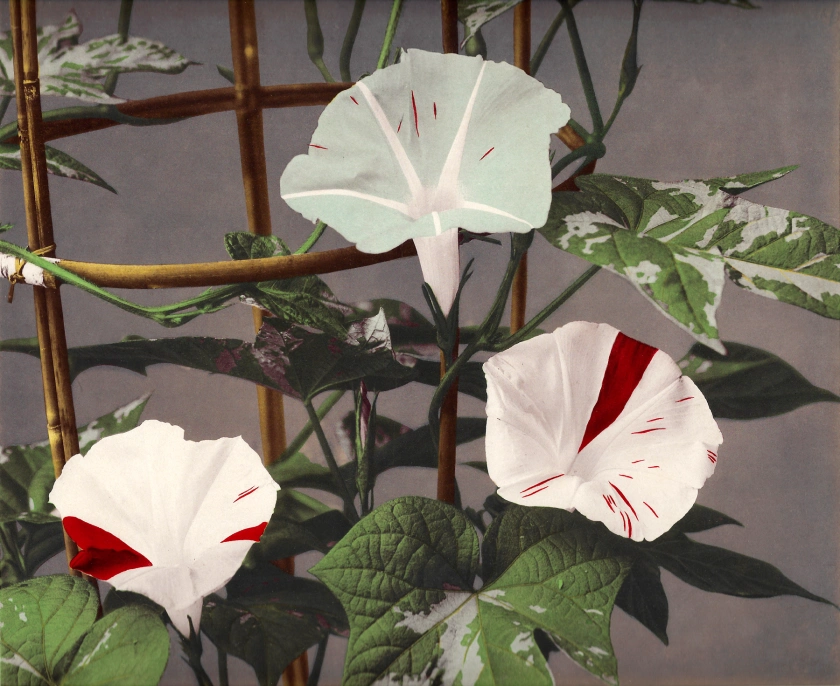
Charles Jones (British, 1866-1959)
Broccoli Leamington
c. 1895-1910
© Sean Sexton
Photo copyright Dulwich Picture Gallery
A difficult thing said simply
What a wonderful selection of photographs to start the year 2021.
As Laura Cumming observes, there is a profound connection between photography and photosynthesis – both created through light, both constructed and political. For the photograph is ALWAYS the choice of the photographer, and the landscape has ALWAYS been shaped and constructed since human beings emerged on this earth. Nothing in the natural world is ever “natural” but always mediated by time, space, context, power and desire. Desire to control the direction of a river, desire for food and shelter, desire for Lebensraum or living space as a practice of settler colonialism, desire to celebrate the “natural” world, desire to procreate, desire to propagate the (genetically modified) vegetable. A desire to desire.
Photography’s symbiotic relationship with the natural world is the relationship of photography and transmutation (the action of changing or the state of being changed into another form), photography and transmogrification (the act or process of changing or being changed completely). The natural world, through an action (that of being photographed), changes its state (flux) and, further, changes its state to a completely different form (fixed in liquid fixer; fixed, saved, but fluid, in the digital pixel). Flowers and vegetables are alive then wither and die, only to remain “the same” in the freeze frame of the death-defying photograph.
Photography’s fluidity and fixity – of movement, time, space, context, representation – allows “the infinite possibility of experimentation” not, as Cumming argues, “without the interference of humanity, accident, sound or movement” but through their very agency. It is the human hand that arranges these pyramidal broccoli, the accident of light in the photogram that allows us to pierce a clump of Bory’s Spleenwort root structure. It is human imagination, the movement of the human mind, that allows the artist Charles Jones to darken the Bean Longpod cases so that these become seared in the mind’s eye, fixed in all time and space as iconic image: the “transformation of an earthy root vegetable into an abstracted object worthy of adulation.”
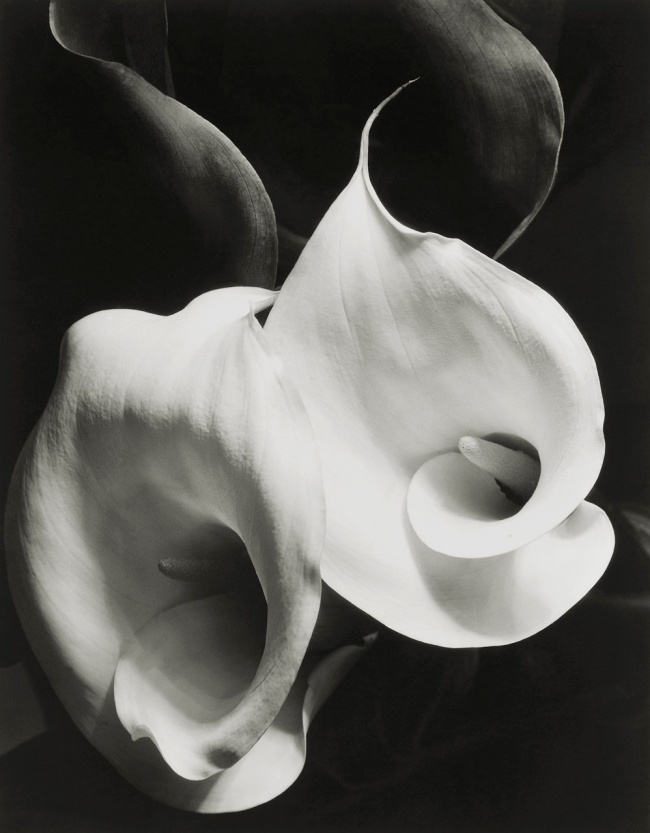
While the process of photographing flower and vegetable may well be due to the interference of humanity, accident, sound or movement, contemplation or decisive moment, the final outcome of the image – the representation of the natural in the physicality of the print – usually attempts to hide these processes in images that are frozen in time, images that play on the notion of memento mori and the transient nature of life. In the presence of a triple death (ie. the death of the plant or flower, the time freeze or death moment of the photograph, and our knowledge that these plants and flowers in the photograph have already died), it is the abstraction of the death reality in images of flowers, plants and vegetables that allows for a touch of the soul. These photographs “provide a glimpse into the terrain of the unseen, or what German philosopher and cultural critic Walter Benjamin coined the “optical unconsciousness”.”1 Here, photography allows us to capture the realm of the unseen and also allows us to glimpse the expansive terrain of the human imaginary. The camera reveals aspects of reality that register in our senses but never quite get processed consciously. (Is there anything “real” about Cunningham’s Two Callas 1929 other than a vibration of the energy of the cosmos?)
Still, still, still we are (unconsciously) aware of all that is embedded within a photograph for photography makes us feel, makes us remember “that which lies beyond the frame, or what photographs compel us to remember and forget, what they enable us to uncover and repress…”. Like any great work of art, when we look at a great photograph it is not what we BELIEVE that matters when we look, but how the art work makes us FEEL, how it touches the depths of our soul. These are the roots of photography, un/earthed, in the languages of image – (sub)conscious stories of the human imagination which seek to make sense of our roots in Earth.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Footnotes
1/ A different nature presents itself to the movie camera than to the naked eye. Instead of being something we enter into unconsciously or vaguely, in film we enter nature analytically. While a painter lovely caresses the surfaces of nature, the cameraman chucks a piece of dynamite at it, then reassembles the pieces:
“Our taverns and our metropolitan streets, our offices and furnished rooms, our railroad stations and our factories appeared to have us locked up hopelessly. Then came the film and burst this prison-world asunder by the dynamite of the tenth of a second, so that now, in the midst of its far-clung ruins and debris, we calmly and adventurously go travelling.”
A movie camera can be mounted on a speeding locomotive, dropped down a sewer, or secreted in a valise and carried surreptitiously around a city. The camera reveals aspects of reality that register in our senses but never quite get processed consciously. Film changed how we view the least significant minutiae of reality just as surely as Freud’s Psychopathology of Everyday Life changed how we look at incidental phenomenon like slips of the tongue. In other words, film serves as an optical unconscious. Benjamin asserts the film camera “introduces us to unconscious optics as does psychoanalysis to unconscious impulses.
“Richard Prouty. “The optical unconsciousness,” on the One-Way Street website Oct 16, 2009 [Online] Cited 03/01/2021
Many thankx to the Dulwich Picture Gallery for allowing me to publish the artwork in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
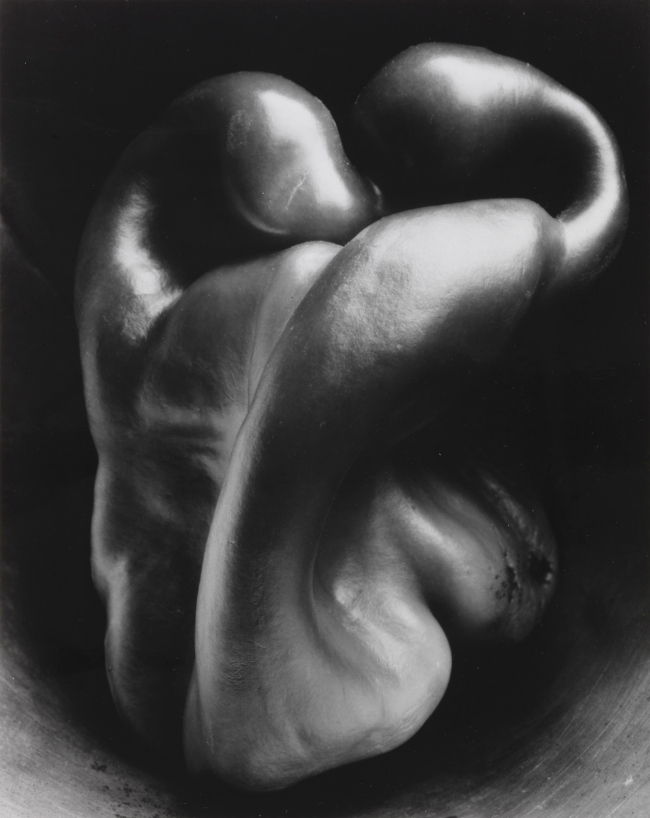
“The Dulwich show amounts to a political history of photography by other means. Should it aspire to nothing more than the fictions of painting? Should it be a catalogue, a document, a celebration of the natural life? Where Glaisher records the precise difference between two varieties of fern, Jones observes the Sputnik-like eccentricity of a plucked turnip. Where Imogen Cunningham sees the perfect abstraction of a calla lily, Edward Weston anthropomorphises a pepper, so that it momentarily resembles the torso of a body-builder. …
Perhaps the desire to photograph the vegetable world brings its own peace, as well as the infinite possibility of experimentation without the interference of humanity, accident, sound or movement. But perhaps it also has something to do with the profound connection between photography and photosynthesis. The very light that gives life to a rose, before its petals drop, is the same light that preserves it in a death-defying photograph.”
Laura Cumming. “Unearthed: Photography’s Roots review – cauliflowers saying cheese…” on the Guardian website Sun 29 Nov 2020 [Online] Cited 23/12/2020
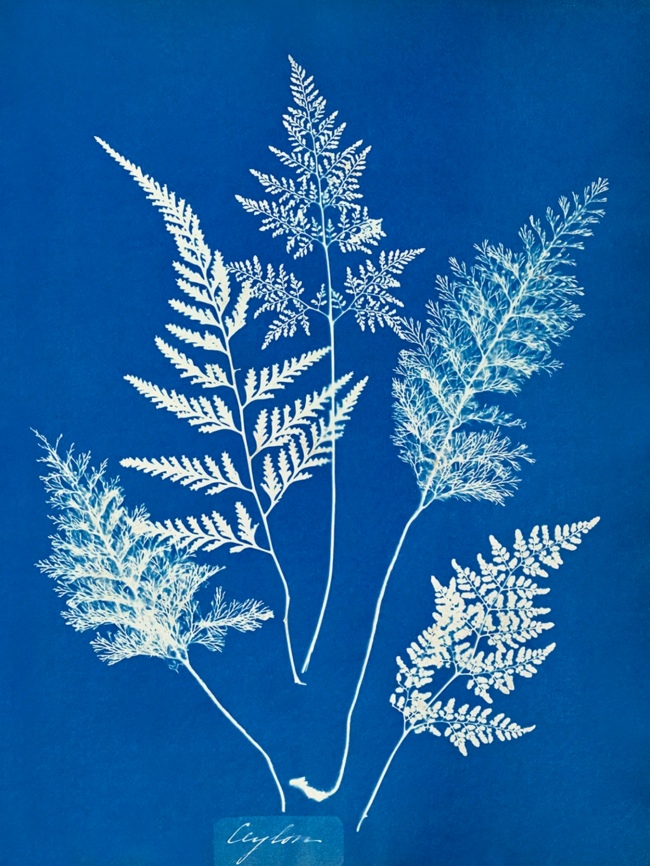
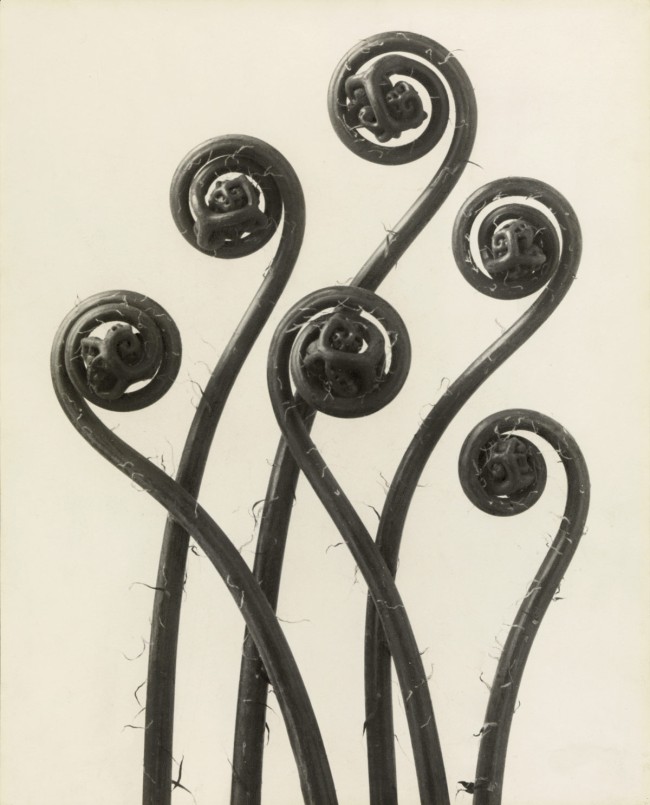
Anna Atkins (English, 1799-1871)
Ceylon [examples of ferns]
c. 1850
Cyanotype
After publishing her own book of cyanotype photograms of British algae in the 1840s, Atkins collaborated with her childhood friend and fellow scholar Anna Dixon on a second book of photograms. The book, Cyanotypes of British and Foreign Ferns, was published in 1853 and now resides in the J. Paul Getty Museum in Los Angeles.
This particular image [above] is a selection from Cyanotypes of British and Foreign Ferns. A collection of four distinct ferns, it’s simply captioned “Ceylon”. At the time these cyanotypes were being made, the island of Ceylon – modern day Sri Lanka – was under British rule. It would be nearly another century before the island declared independence from Atkins’ home country. Despite the abundant difficulties of travel in the 1850s, Atkins’s many scientific and business connections no doubt helped her obtain several foreign specimens for this book of fern cyanotypes.
Anonymous text on the 20 x 200 website [Online] Cited 24/12/2020
This unique camera-less photograph was part of an extensive project to document plants from Great Britain and British colonies like Ceylon (now Sri Lanka), and illustrates an early example of how important photography would become in our attempts to learn about and protect the natural world. Anna Atkins (British, 1799-1871) was a trained botanist who adopted photographic processes in order to describe, analyse, and, in a manner of speaking, preserve plant specimens from around the world. She is widely considered the first person to use photographs to illustrate a book, her British Algae: Cyanotype Impressions published in 1843. This particular photograph was produced with Anna Dixon for a later compilation: Cyanotypes of British and Foreign Flowering Plants and Ferns in 1854. With these and other projects, Atkins helped establish photography as an important tool in scientific and ecological observation. …
Atkins made all of her cyanotypes in England, often receiving specimens through imperial trade. This image, therefore, was produced over 5,000 miles away from where the plant originated
Brian Piper. “Object Lesson: Ceylon cyanotype by Anna Atkins,” on the New Orleans Museum of Art website March 23, 2020 [Online] Cited 24/12/2020.
Anna Atkins (English, 1799-1871)
Plate 55 – Dictyota dichotoma, in the young state and in fruit
1853
From Photographs of British Algae: Cyanotype Impressions Volume 1 (Part 1)
Cyanotype
Photo copyright Horniman Museum and Gardens
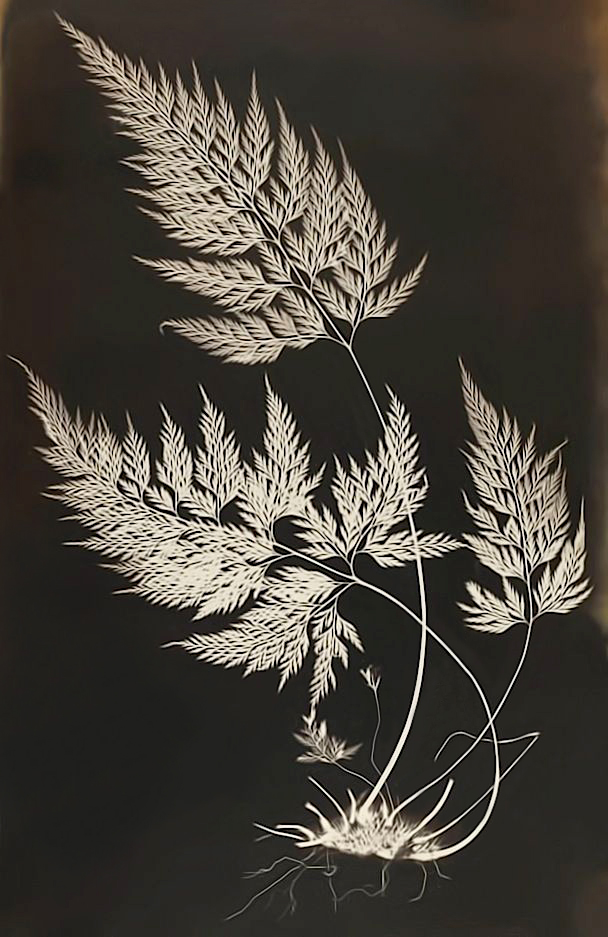
Cecilia Glaisher (British, 1828-1892)
Bory’s Spleenwort (Asplenium onopteris)
c. 1853-1856
Salted paper print
Cecilia Glaisher (British, 1828-1892)
Cecilia Glaisher (20 April 1828 – 28 December 1892) was an English amateur photographer, artist, illustrator and print-maker, working in the 1850s world of Victorian science and natural history. …
The British Ferns – Photographed from Nature by Mrs Glaisher was planned as an illustrated guide to identifying ferns, with the entomologist Edward Newman (1801-1876), a fern expert and publisher. Made using William Henry Fox Talbot’s photogenic drawing process during what has come to be known as the Victorian fern craze, it was to be published in a number of parts and intended to appeal to the growing number of fern collectors whose enthusiasm was fuelled by increasingly informative and magnificently illustrated fern publications. The use of photography, according to the printed handbill produced by Newman to promote the work, would allow fern specimens to be “displayed with incomparable exactness, producing absolute facsimiles of the objects, perfect in artistic effect and structural details”. A portfolio of ten prints, in mounts embossed with Newman’s publishing details, was presented by him to the Linnean Society in London in December 1855. However, perhaps due to an inability to raise sufficient subscriptions, or difficulties in producing prints in consistent quantities, the project appears to have been abandoned by 1856.
Text from the Wikipedia website
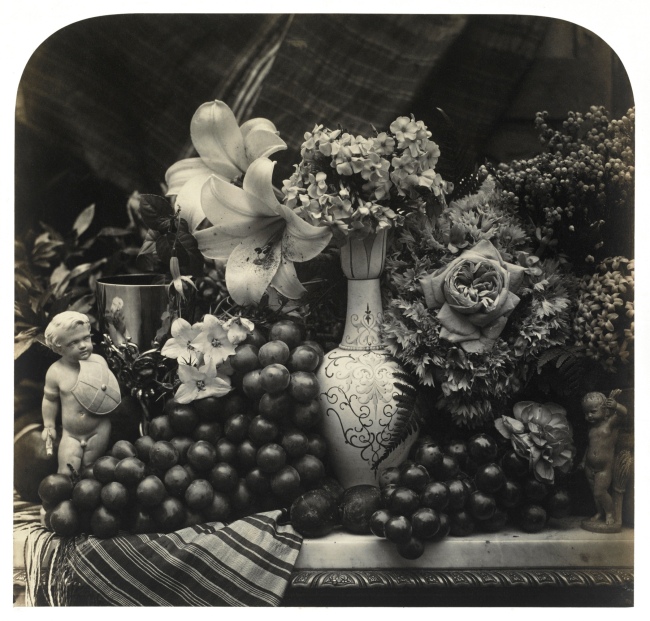
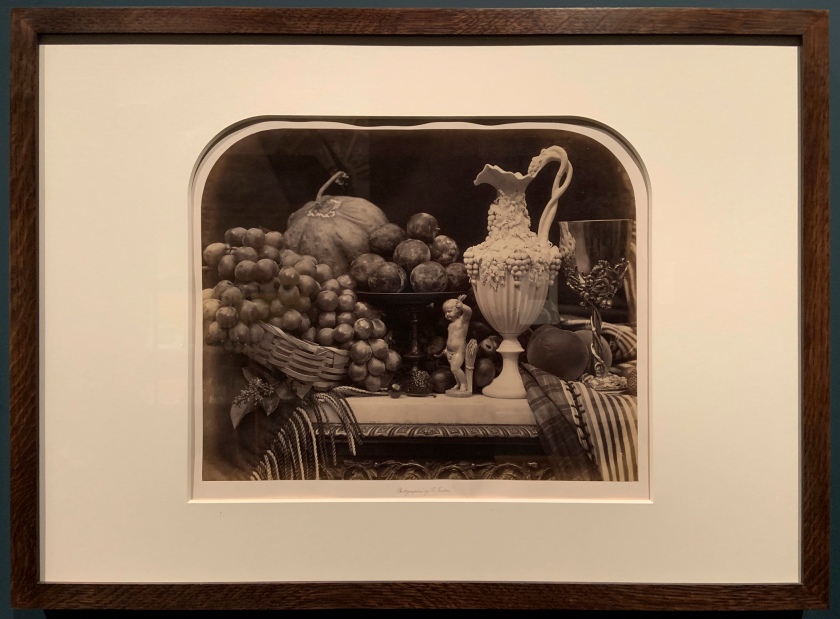
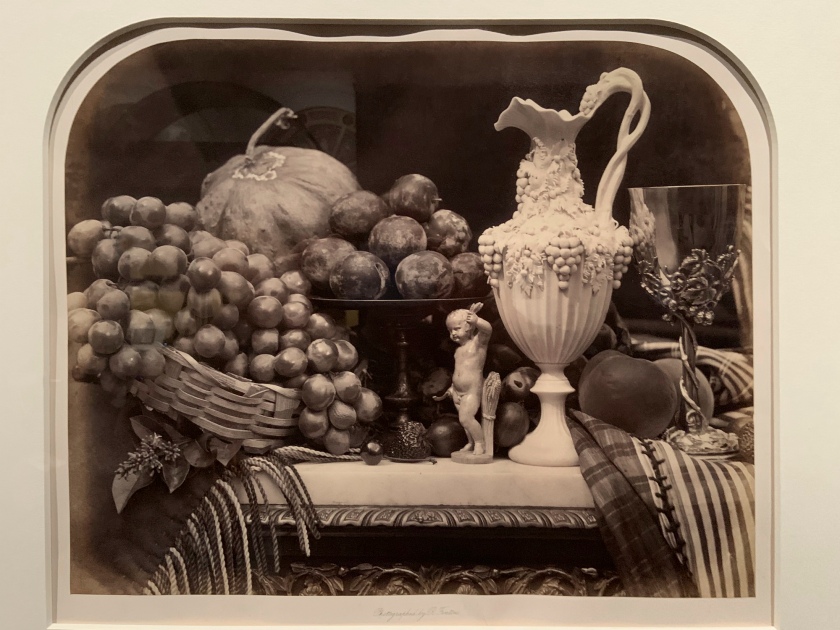
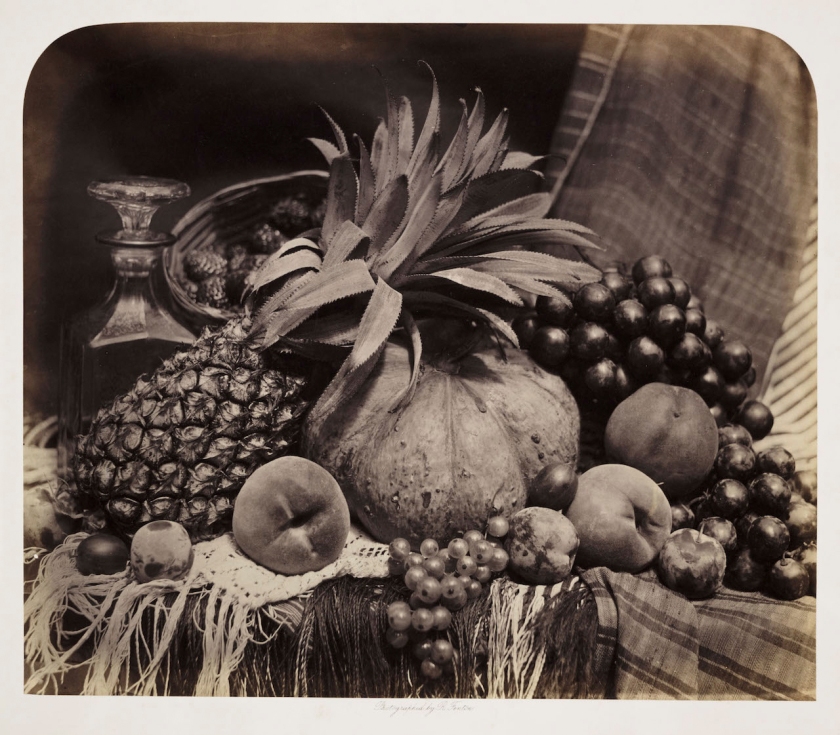
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Fruit and Flowers
1860
Albumen print from a collodion negative
Victoria & Albert Museum
In tackling still lifes, Roger Fenton gave form to his ardent belief that no subject was off limits to photography, even one intimately linked to the history of painting and seemingly so dependent on colour. Faced with terrible weather in 1860 that curtailed his ability to photograph landscapes, Fenton drew upon the skills he had perfected earlier in the decade while photographing the collection of the British Museum and trained his lens on carefully balanced still-life arrangements. Cleverly massing and juxtaposing forms and tonal values, and brazenly taking advantage of photography’s ability to convey detail, Fenton quickly produced a series of unprecedented vivaciousness that convincingly demonstrated why photography should be counted as an art. Fruit and Flowers is among the last images this towering figure in the history of photography made before quitting photography for good at age 41.
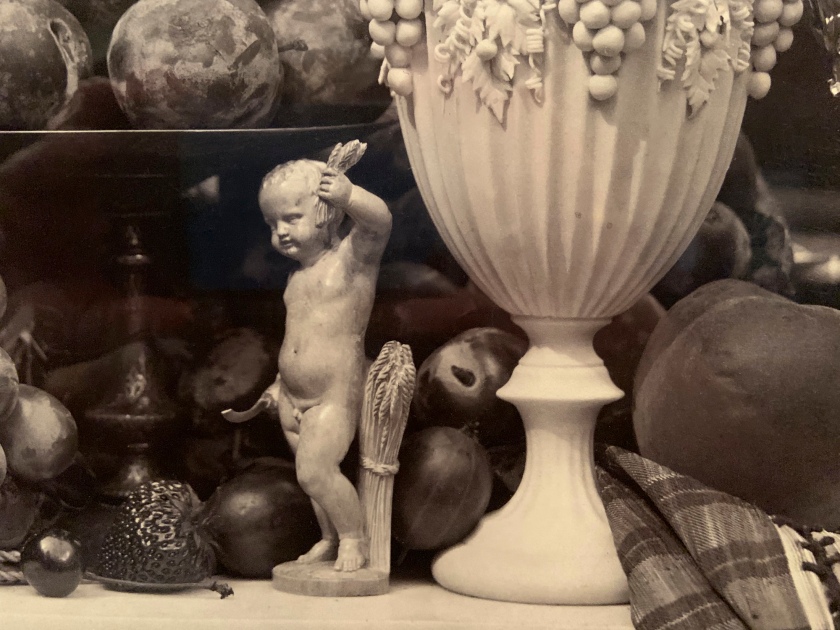
Fruit and Flowers is an ebullient, in-your-face celebration of summer’s bounty. Shot head on and close up, the densely packed arrangement seems ready to tumble from the large, glossy 14- by nearly 17-inch albumen print made from a collodion negative. Dozens of juicy, sensuous grapes flank a tall, centred vase decorated with a tendril pattern; the vase holds pansies at its top while plums nestle at the base. At right, a few grapes dangle over the edge of a marble tabletop, falling into the viewer’s space, as does a striped, tasseled cloth at left. Star-shaped hoyas are reflected in a chased silver goblet, and two immense lilies, their stems obscured, appear to hover untethered above. The lilies are balanced compositionally by a large rose that faces the viewer, while a second rose, near the bottom, separates the grapes and a nude figurine. Ferns and lily of the valley complete the floral medley.
The prominent roses and lilies may allude to the sacred, as both are associated with the Virgin Mary, but myriad wine references, such as the grapes, the chalice decorated with grape vines, and especially the impish figurine, whose physical attributes link him to bacchanalian Roman festivals, point decidedly to the profane. At the same time, the withering rose, drooping leaves, and tired-looking plums remind the viewer that such pleasures are ephemeral.
Anonymous. “Fruit and Flowers: Roger Fenton,” on the National Gallery of Art website [Online] Cited 24/12/2020.
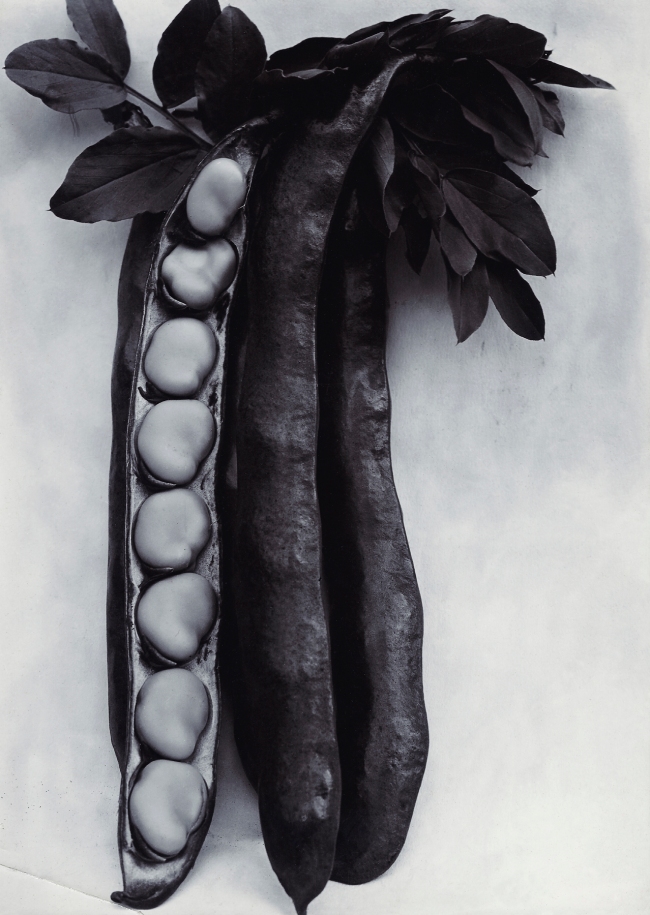
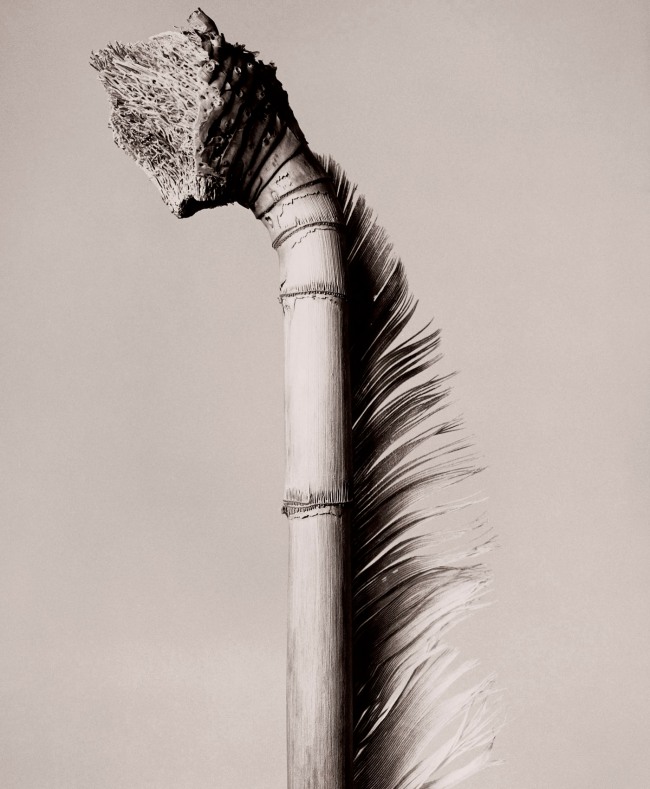
Charles Jones (British, 1866-1959)
Bean Longpod
c. 1895-1910
© Sean Sexton
Photo copyright Dulwich Picture Gallery
In Bean Longpod (1895-1910), now on view in “Unearthed,” the titular plant cuts through the centre of the composition, leaving little room for anything else. Other works play with their subjects’ placement: Broccoli Leamington (1895-1910), for instance, finds large broccoli heads sitting atop one another in a pyramid-like formation. The overall effect of this unusual treatment, notes the Michael Hoppen Gallery, is the “transformation of an earthy root vegetable into an abstracted” object worthy of adulation. …
According to the Michael Hoppen Gallery, which hosted a 2015 exhibition on Jones, “[t]he extraordinary beauty of each Charles Jones print rests in the intensity of focus on the subject and the almost portrait-like respect with which each specimen is treated.”
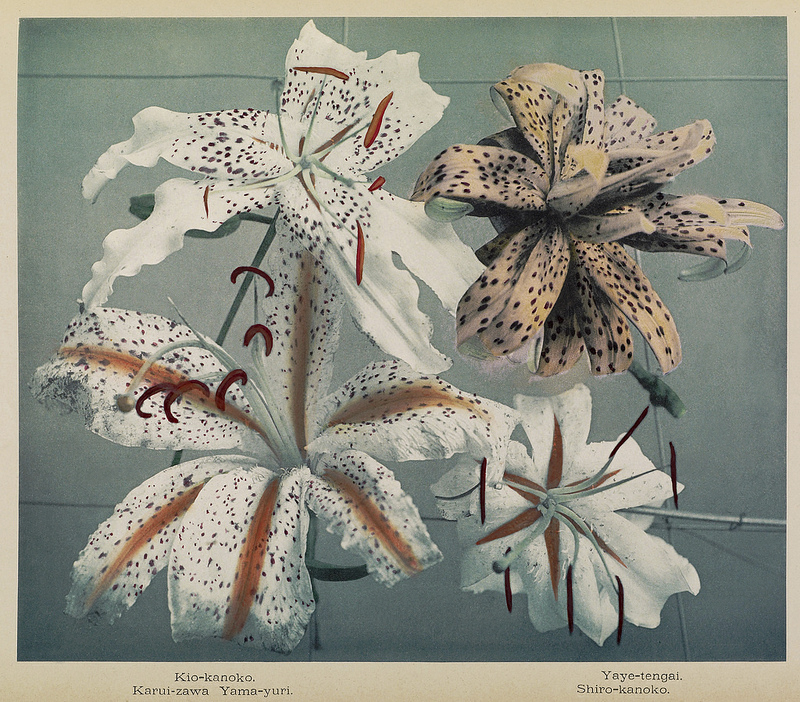
Ogawa Kazumasa (Japanese, 1860-1929)
Iris Kaempferi
c. 1894
From Some Japanese Flowers
Chromo-collotype
Hand-coloured photograph
Photo copyright Dulwich Picture Gallery
Ogawa Kazumasa (Japanese, 1860-1929)
Japanese Lilies
c. 1894
From Some Japanese Flowers
Chromo-collotype
Hand-coloured photograph
Photo copyright Dulwich Picture Gallery
Ogawa Kazumasa lived from the 1860s to almost the 1930s, surely one of the most fascinating 70-year stretches in Japanese history. Ogawa’s homeland “opened” to the world when he was a boy, and for the rest of his life he bore witness to the sometimes beautiful, sometimes strange, sometimes exhilarating results of a once-isolated culture assimilating seemingly everything foreign – art, technology, customs – all at once. Naturally he picked up a camera to document it all, and history now remembers him as a pioneer of his art. During the 1890s he published Some Japanese Flowers, a book containing his pictures of just that.
The following year, Ogawa’s hand-coloured photographs of Japanese flowers also appeared in the American books Japan, Described and Illustrated by the Japanese, edited by the renowned Anglo-Irish expatriate Japanese culture scholar Francis Brinkley and published in Boston, the city where Ogawa had spent a couple of years studying portrait photography and processing.
Ogawa’s varied life in Japan included working as an editor at Shashin Shinpō (写真新報), the only photography journal in the country at the time, as well as at the flower magazine Kokka (国華), which would certainly have given him the experience he needed to produce photographic specimens such as these. Though Ogawa invested a great deal in learning and employing the highest photographic technologies, they were the highest photographic technologies of the 1890s, when colour photography necessitated adding colours – of particular importance in the case of flowers – after the fact.
… Even as everything changed so rapidly all around him, as he mastered the just-as-rapidly developing tools of his craft, Ogawa nevertheless kept his eye for the natural and cultural aspects of his homeland that seemed never to have changed at all.
Colin Marshall. “Beautiful Hand-Colored Japanese Flowers Created by the Pioneering Photographer Ogawa Kazumasa (1896),” on the Open Culture website March 22nd, 2019 [Online] Cited 24/12/2020.
The stunning floral images … are the work of Ogawa Kazumasa, a Japanese photographer, printer, and publisher known for his pioneering work in photomechanical printing and photography in the Meiji era. Studying photography from the age of fifteen, Ogawa moved to Tokyo aged twenty to further his study and develop his English skills which he believed necessary to deepen his technical knowledge. After opening his own photography studio and working as an English interpreter for the Yokohama Police Department, Ogawa decided to travel to the United States to learn first hand the advance photographic techniques of the time. Having little money, Ogawa managed to get hired as a sailor on the USS Swatara and six months later landed in Washington. For the next two years, in Boston and Philadelphia, Ogawa studied printing techniques including the complicated collotype process with which he’d make his name on returning to Japan.
In 1884, Ogawa opened a photographic studio in Tokyo and in 1888 established a dry plate manufacturing company, and the following year, Japan’s first collotype business, the “K. Ogawa printing factory”. He also worked as an editor for various photography magazines, which he printed using the collotype printing process, and was a founding member of the Japan Photographic Society.
Anonymous. “Ogawa Kazumasa’s Hand-Coloured Photographs of Flowers (1896),” on The Public Domain Review website [Online] Cited 24/12/2020.
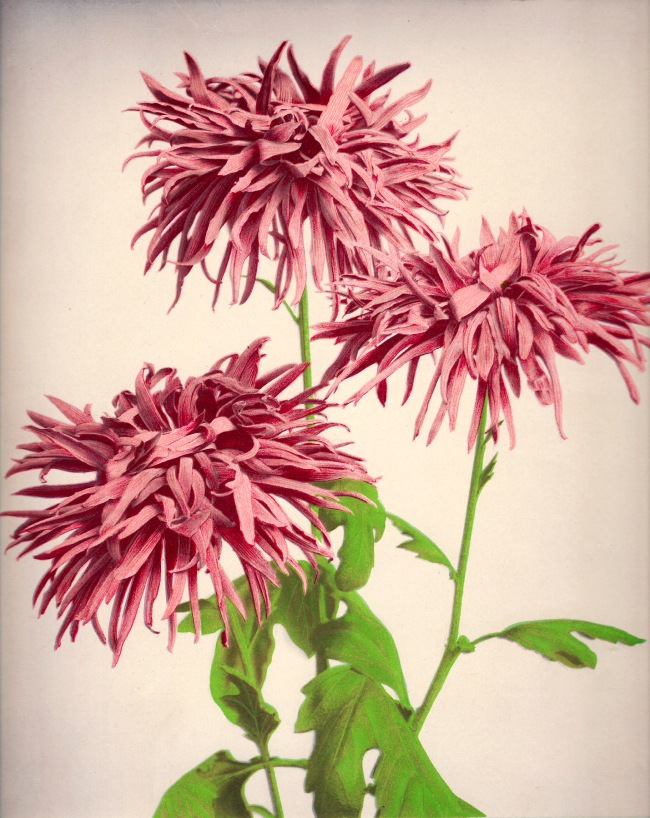
Ogawa Kazumasa (Japanese, 1860-1929)
Chrysanthemum
c. 1894
From Some Japanese Flowers
Chromo-collotype
Hand-coloured photograph
Photo copyright Dulwich Picture Gallery
Ogawa Kazumasa (Japanese, 1860-1929)
Morning Glory
c. 1894
From Some Japanese Flowers
Chromo-collotype
Hand-coloured photograph
Photo copyright Dulwich Picture Gallery
A central focus for the show and a truly rare opportunity for visitors will be a display of 11 works by the inventor and pioneer, Kazumasa Ogawa, whose effectively coloured photographs were created 30 years before colour film was invented. Ogawa combined printmaking and traditions in Japan to create truly original and pioneering photographs. By developing up to 16 different colour plates per image from expertly hand coloured prints he made Japan the world’s leading producer of coloured photographs, the display of which is hoped to be a revelation for many.
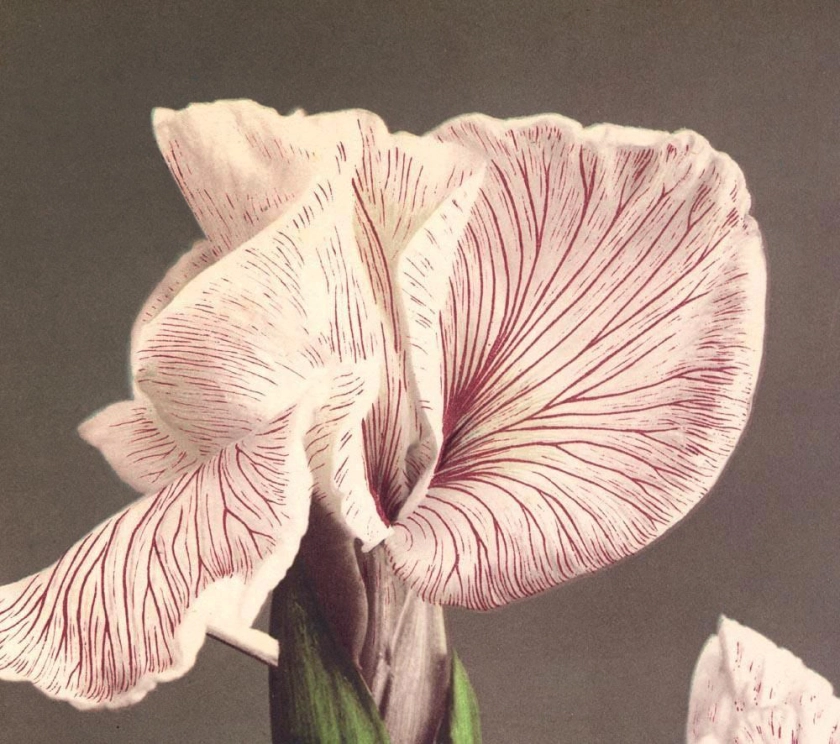
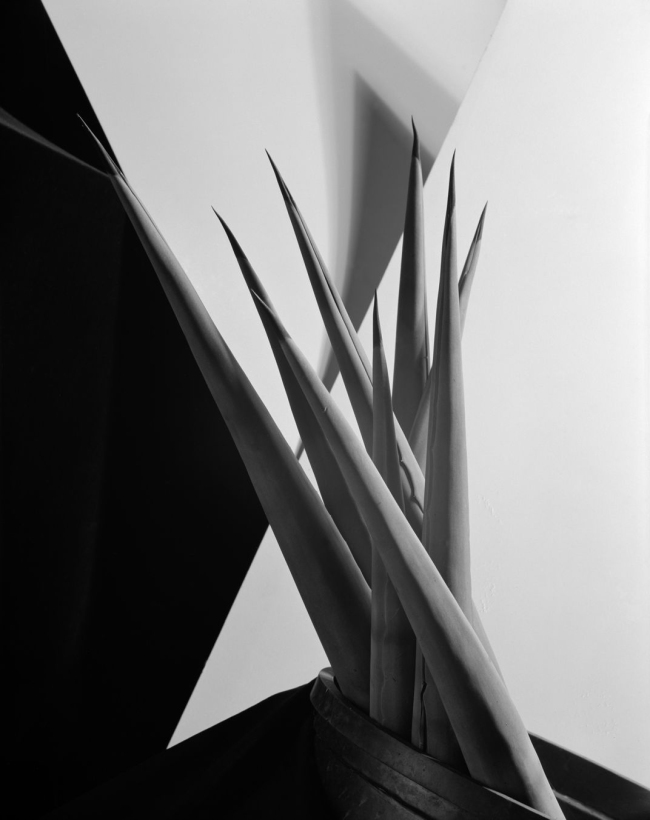
Imogen Cunningham (American, 1883-1976)
Agave Design I
1920s
Gelatin silver print
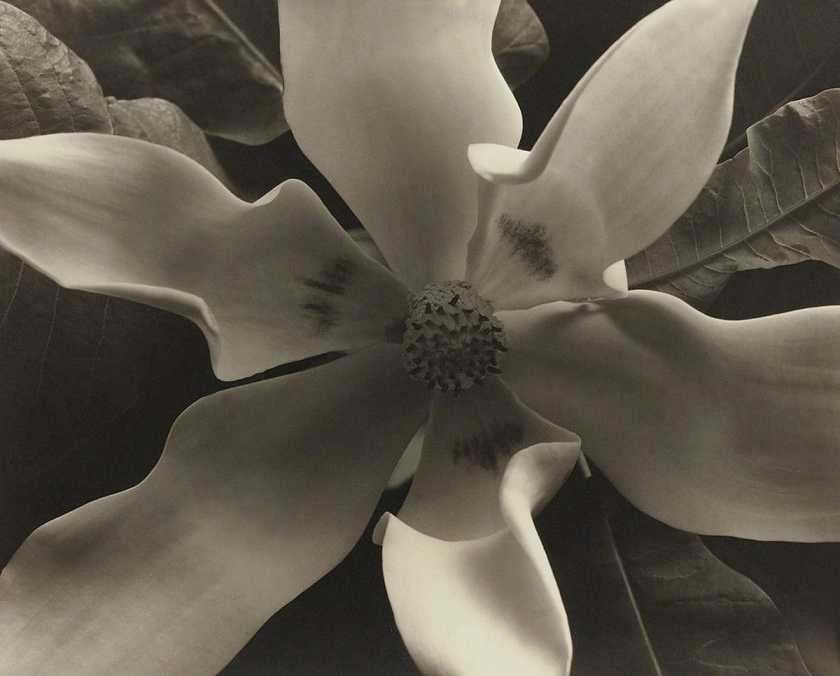
Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973)
Magnolia Blossoms, Voulangis, France
c. 1921
Gelatin silver print
19.4 x 23.8cm
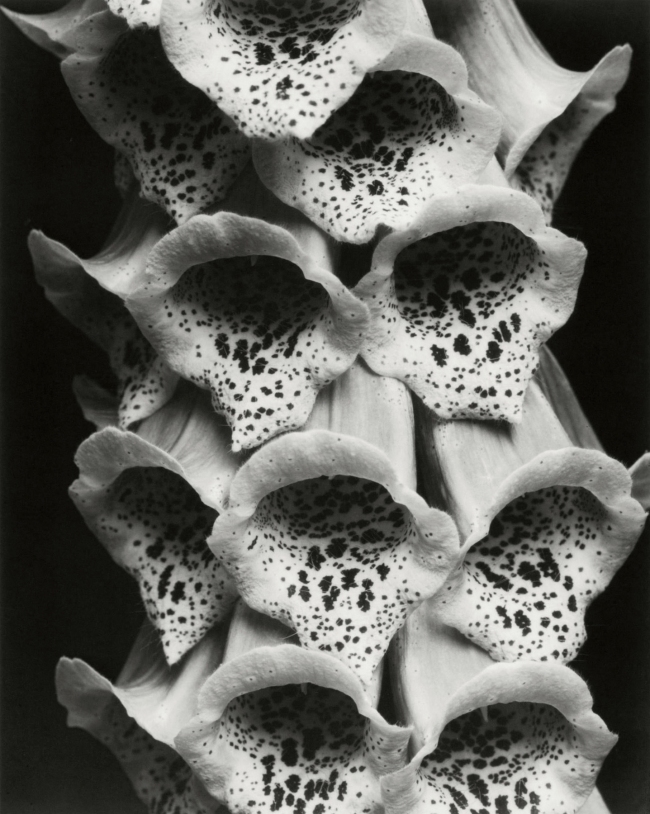
Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973)
Foxgloves, France
1925
Gelatin silver print
Karl Blossfeldt (German, 1865-1932)
Adiantum pedatum. Maidenhair Fern
before 1926
Private Collection, Derbyshire
Karl Blossfeldt (1865-1932)
Impatiens Glandulifera
1928
Gelatin silver print
27 x 20.5cm
Imogen Cunningham (American, 1883-1976)
Two Callas
1929
Gelatin silver print
Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
Pepper No. 30
1930
Gelatin silver print contact print
24.1 × 19.2cm
A year later, during a four-day period from August 2-6, 1930, Weston took at least thirty more negatives of peppers. He first tried again with plain muslin or a piece of white cardboard as the backdrop, but for these images he thought the contrast between the backdrop and the pepper was too stark. On August 3 he found a large tin funnel, and, placing it on its side, he set a pepper just inside the large open end. He wrote:
It was a bright idea, a perfect relief for the pepper and adding reflecting light to important contours. I still had the pepper which caused me a week’s work, I had decided I could go no further with it, yet something kept me from taking it to the kitchen, the end of all good peppers. I placed it in the funnel, focused with the Zeiss, and knowing just the viewpoint, recognizing a perfect light, made an exposure of six minutes, with but a few moments’ preliminary work, the real preliminary was on in hours passed. I have a great negative, – by far the best!
It is a classic, completely satisfying, – a pepper – but more than a pepper; abstract, in that it is completely outside subject matter. It has no psychological attributes, no human emotions are aroused: this new pepper takes one beyond the world we know in the conscious mind.
To be sure, much of my work has this quality… but this one, and in fact all of the new ones, take one into an inner reality, – the absolute, – with a clear understanding, a mystic revealment. This is the “significant presentation” that I mean, the presentation through one’s intuitive self, seeing “through one’s eyes, not with them”: the visionary.”
By placing the pepper in the opening of the funnel, Weston was able to light it in a way that portrays the pepper in three dimensions, rather than as a flat image. It is this light that gives the image much of its extraordinary quality.
Edward Weston (1961). Nancy Newhall (ed.,). The Day-books of Edward Weston, Volume II. NY: Horizon Press. p. 180 quoted on the Wikipedia website.
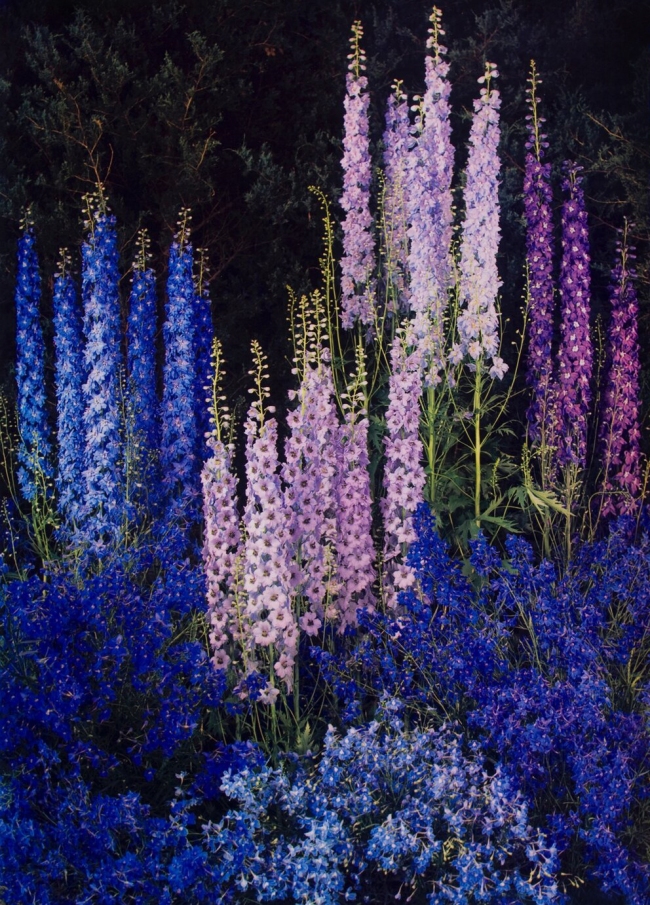
Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973)
Delphiniums
1940
Dye imbibition print
Digital image courtesy of the George Eastman Museum
© 2019 The Estate of Edward Steichen/Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York
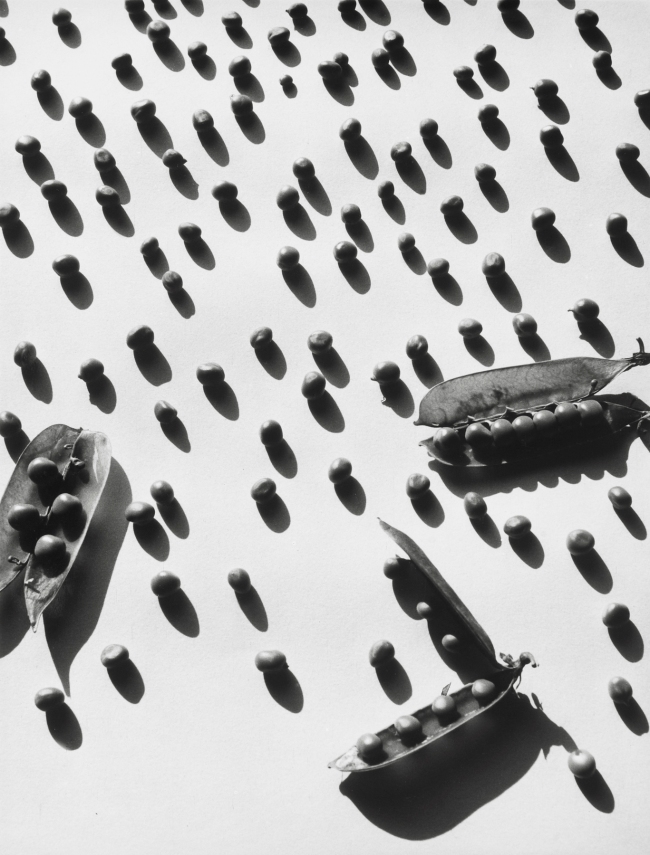
Gyula Holics (Hungarian, 1919-1989)
Peas
1950s
Gelatin silver print
23.8 x 18.1cm
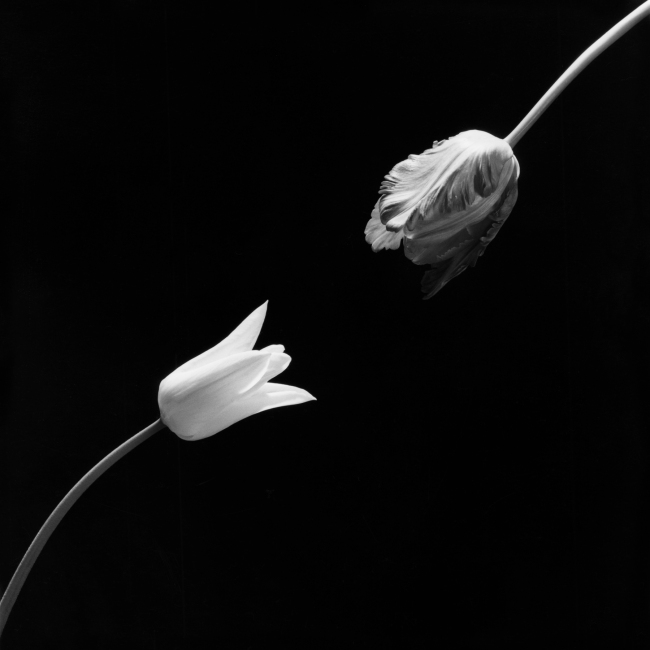
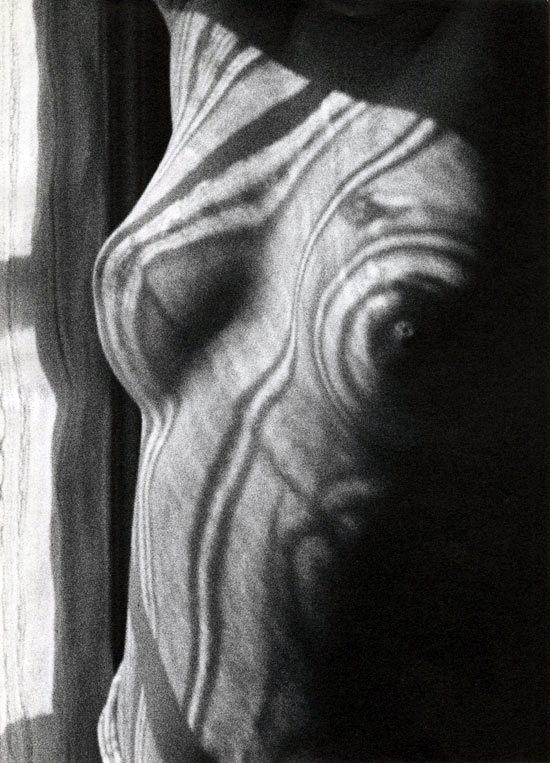
Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Tulip
1984
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission
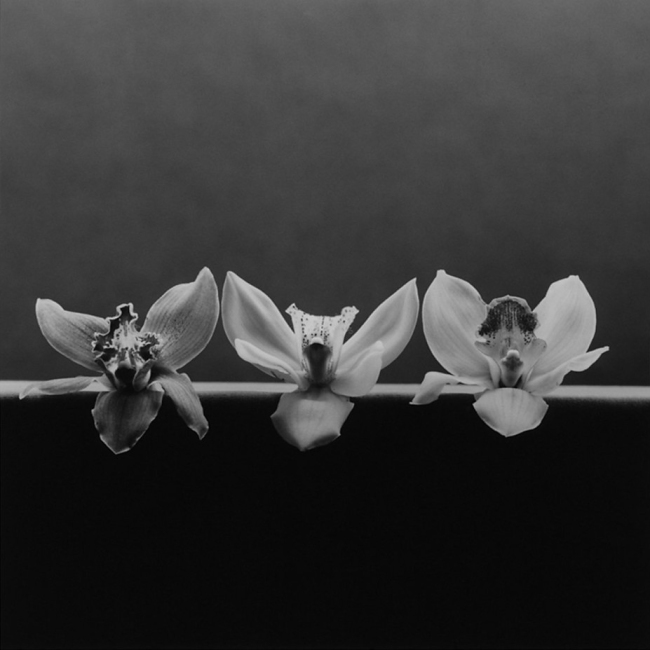
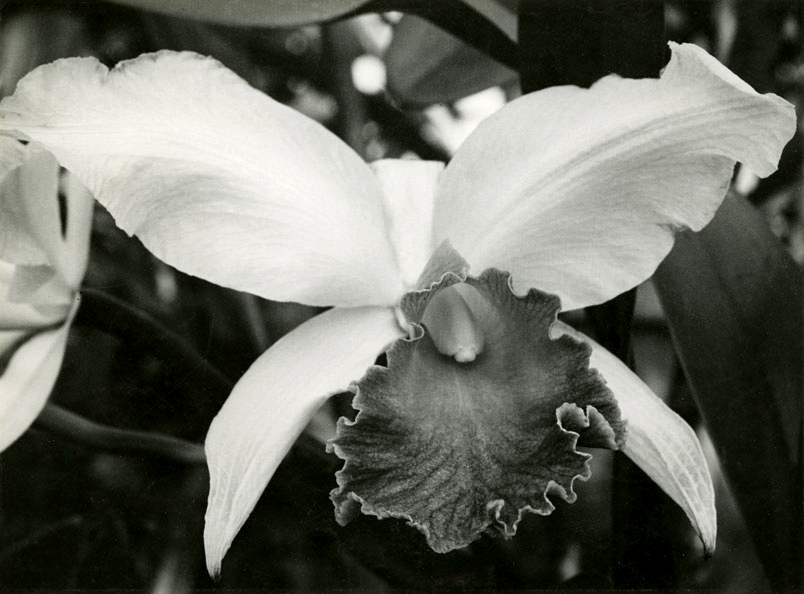
Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Orchid
1985
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation
Used by permission
Trace the history of photography from the 1840s to present day, as seen through depictions of nature. In Summer 2020, we present our first major photography exhibition, tracing the rich history of the medium told through depictions of nature, bringing together over 100 works by 25 leading international photographers.
This autumn, Dulwich Picture Gallery will present the first exhibition to trace the history of photography as told through depictions of nature, revealing how the subject led to key advancements in the medium, from its very beginnings in 1840 to present day. Unearthed: Photography’s Roots will be the first major photography show at Dulwich Picture Gallery, bringing together over 100 works by 35 leading international photographers, many never seen before.
Presenting just one of the many possible histories of photography, this exhibition follows the lasting legacy of the great pioneers who made some of the world’s first photographs of nature, examining key moments in the medium’s history and the influences of sociological change, artistic movements and technological developments, including Pictorialism through to Modernism, experiments with colour and contemporary photography and new technologies.
Arranged chronologically and with a focus on botany and science throughout, the exhibition will highlight the innovations of some of the medium’s key figures, including William Henry Fox Talbot (1800-1877), Imogen Cunningham (1883-1976) and Robert Mapplethorpe (1946-1989) as well as several overlooked photographers including Japanese artist, Kazumasa Ogawa (1860-1929) and the English gardener, Charles Jones (1866-1959). It will be the first show to publicly exhibit work by Jones, whose striking modernist photographs of plants remained unknown until 20 years after his death, when they were discovered in a trunk at Bermondsey Market in 1981.
Questioning the true age of photography, the exhibition will open with some of the first known Victorian images by William Henry Fox Talbot, positioning his experimentation with paper negatives as the very beginning of photography. It will also introduce a key selection of cyanotypes by one of the first women photographers, Anna Atkins (1799-1871), who created camera-less photograms of the algae specimens found along the south coast of England. Displayed publicly for the first time, these works highlight the ground-breaking accuracy of Atkins’ approach, and the remarkably contemporary appearance of her work which has inspired many artists and designers.
The exhibition will also foreground the artists who produced unprecedented photographic art in the twentieth century without artistic intention. The medium allowed for quick documentation of nature’s infinite specimens, making it an important tool for scientists and botanists such as the German photographer and teacher Karl Blossfeldt (1865-1932) who captured close-up views of plant specimens in order to study and share an understanding of nature’s ‘architecture’. A selection of Blossfeldt’s ‘study aids’ will be displayed alongside work by the proud gardener Charles Jones, who used a glass plate camera to keep a meticulously illustrated record of his finest crops. Seen together for the first time, the two artists will be examined for their pragmatic approach that set them apart from the romanticised style of their time.
A central focus for the show and a truly rare opportunity for visitors will be a display of 11 works by the inventor and pioneer, Kazumasa Ogawa, whose effectively coloured photographs were created 30 years before colour film was invented. Ogawa combined printmaking and traditions in Japan to create truly original and pioneering photographs. By developing up to 16 different colour plates per image from expertly hand coloured prints, he made Japan the world’s leading producer of coloured photographs, the display of which is hoped to be a revelation for many.
Unearthed: Photography’s Roots will aim to highlight how nature photography has remained consistently radical, inventive and influential over the past two centuries with the final rooms in the exhibition dedicated to more recent advancements in the medium. A selection of work by the renowned symbolist photographers Imogen Cunningham and Robert Mapplethorpe will highlight the coded language of nature in photography. Both artists used nature to tackle the oppression experienced in their lives by channelling the strength and the sexuality of the natural subjects they photographed. This powerful symbolism, in works such as Mapplethorpe’s Tulips (1984) and Cunningham’s Agave Design I (1920s), allowed both artists to express themselves at a time when homosexuality was criminalised and women artists fought for recognition.
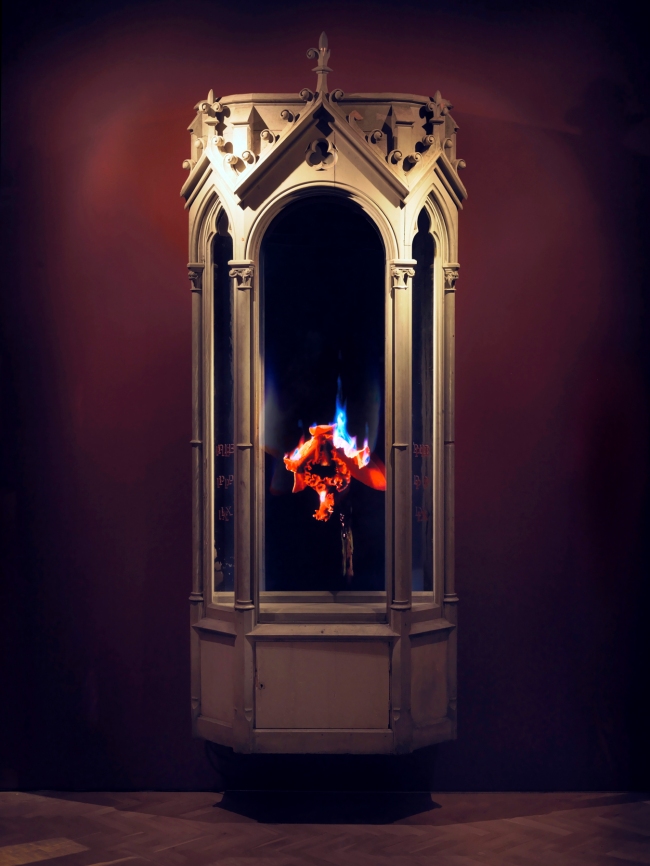
The final room culminates with contemporary works that reveal the enduring influence of early forms of photography and still life, with a spotlight on the artists today who are re-shaping the definition of these mediums through digital processes. Mat Collishaw’s (b.1966) Auto-Immolation (2010) combines new technology and ancient religious ideals, whilst Richard Learoyd’s (b.1966) camera-obscura photographs present a new dimension in the traditional still life genre pioneered by the artists of the Dutch Golden Age. The Gallery’s Mausoleum will host On Reflection (2014), by renowned Israeli video artist, Ori Gersht (b.1967), displayed publicly for the first time in the UK. An homage to the work of Flemish still-life painter Jan Brueghel the Elder, this ambitious work uses modern technolgy to capture the dynamic explosion of mirrored glass reflecting meticulously detailed floral arrangements by the Old Master. Brueghel’s Still Life A Stoneware Vase of Flowers, 1607-08, will also be included in the exhibition, on loan from St John’s College, Oxford for the first time in 300 years.
Unearthed: Photography’s Roots is curated by Alexander Moore, Creative Producer at Dulwich Picture Gallery, and former Head of Exhibitions for Mario Testino. He said:
“I am thrilled to present this extensive survey of photography which celebrates botany in its various guises – from Robert Mapplethorpe’s beautifully shot tulips, to Anna Atkins’ algae specimens. There is beauty to be found in all of the works in the exhibition, which includes some new discoveries. More than anything though, this exhibition reveals nature as the gift that keeps on giving – a conduit for the development of photography, it is also a force for hope and well-being that we have come to depend on so much in recent months. I hope the energy of this timely exhibition provides visitors with a new perspective on the power of the natural world – and perhaps the encouragement to take some pictures themselves!”
The exhibition will include a number of major loans from public and private collections, many never displayed publicly before. Lenders include The Horniman Museum, the Museum of Domestic Design and Architecture, Michael Hoppen Gallery and Blain Southern. A catalogue will accompany featuring essays by Alexander Moore and art historian and 17th-century still life painting specialist, Dr Fred Meijer.
Press release from the Dulwich Picture Gallery
Mat Collishaw (English, b. 1966)
Auto Immolation 002 (still)
2010
Hard Drive, LCD Screen, Steel, Surveillance Mirror, Wood
300 x 113.5 x 52cm
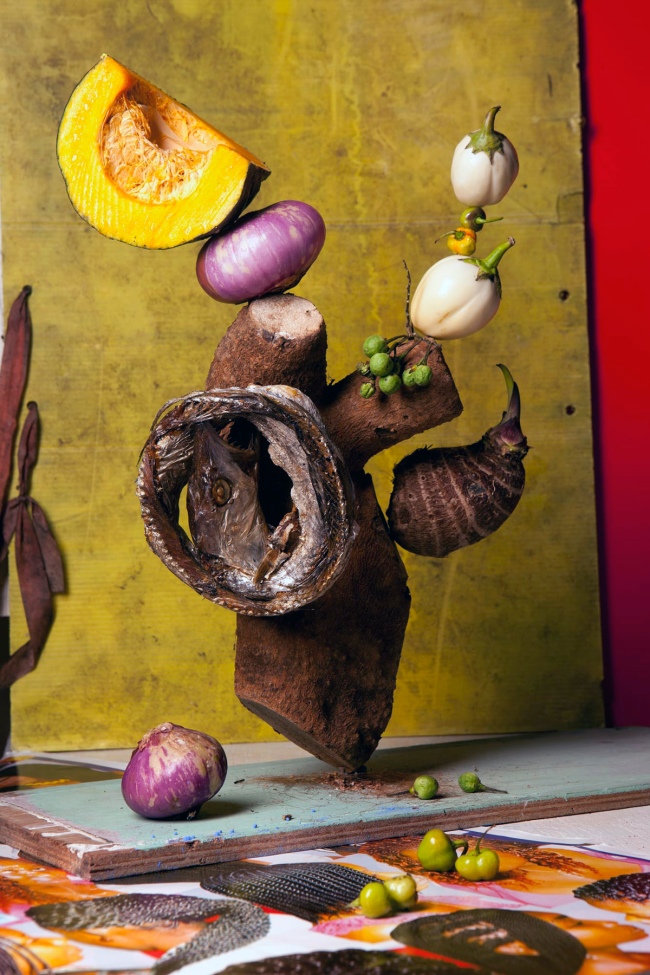
Lorenzo Vitturi (Italian, b. 1980)
Yellow and Red Bokkom Mix #2
2013
Giclee print on Hahnemuhle bamboo paper
29.5 x 44cm
Edition of 7
© Lorenzo Vitturi
Courtesy of Flowers Gallery
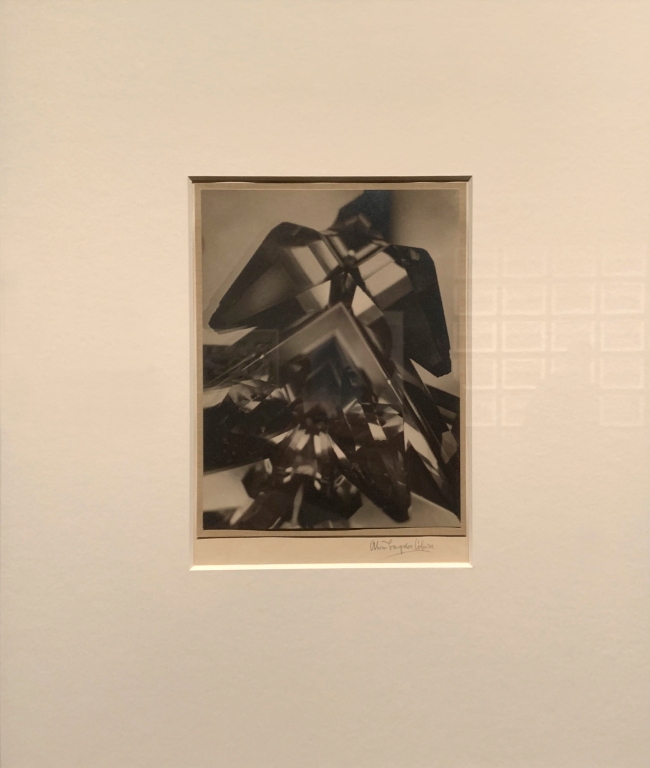
Ori Gersht (Israeli, b. 1967)
On Reflection
2014
© the Artist
Ori Gersht explores the binary oppositions of attraction and repulsion by capturing the moment when “destruction in the exploding mirrors becomes… the moment of creation.”
In the adjacent exhibition rooms, viewers are faced with ten enlarged video stills from the film presented as archival pigment prints. The images somewhat reverse the symbolic value of still-life paintings, or the idea that they are meant to immortalise the experience of nature. Frozen in time, images of the explosion also plays on the notion of memento mori and the transient nature of life. Thanatotic [the name chosen by Freud to represent a universal death instinct] undertones are also seen in the fine network of cracks in the mirrors, which are especially noticeable in On Reflection, Material E01 and On Reflection, Material B02 (both 2014). Gersht’s works provide a glimpse into the terrain of the unseen, or what German philosopher and cultural critic Walter Benjamin coined the “optical unconsciousness.” The outcome is a powerful reminder of the fragility of existence.
Crystal Tong. “On Reflection: Ori Gersht,” on the ArtAsiaPacific website [Online] Cited 24/12/2020.
Ori Gersht (Israeli, b. 1967)
On Reflection (detail)
2014
© the Artist
Ori Gersht (Israeli, b. 1967)
On Reflection (detail)
2014
© the Artist
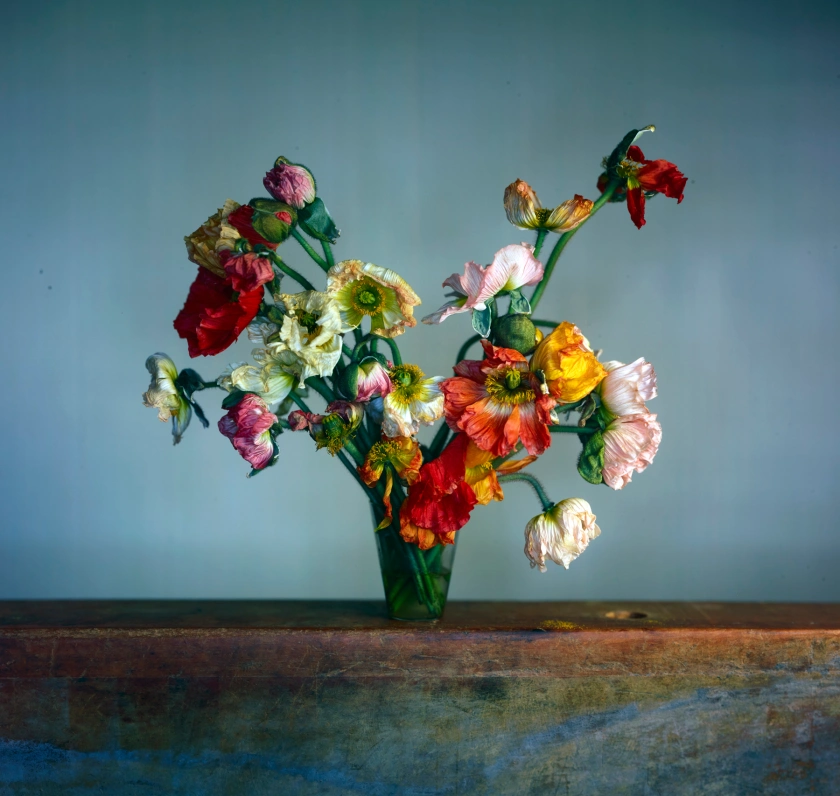
Richard Learoyd (British, b. 1966)
Large Poppies
2019
© the Artist
Image courtesy of Michael Hoppen Gallery
Dulwich Picture Gallery
Gallery Road, London
SE21 7AD
Phone: 020 8693 5254
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Sunday 10am – 5pm
Closed Mondays (except Bank Holiday Mondays)





























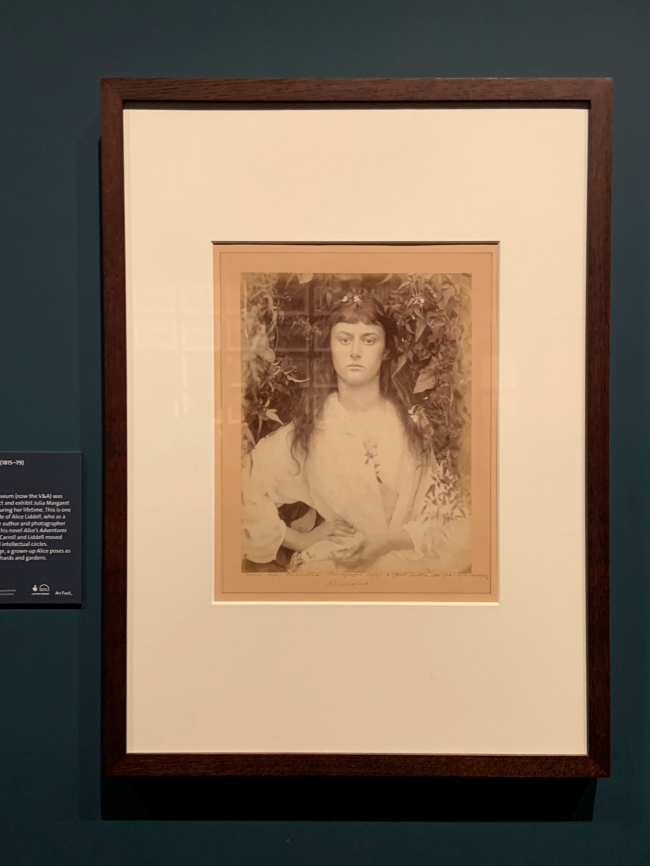
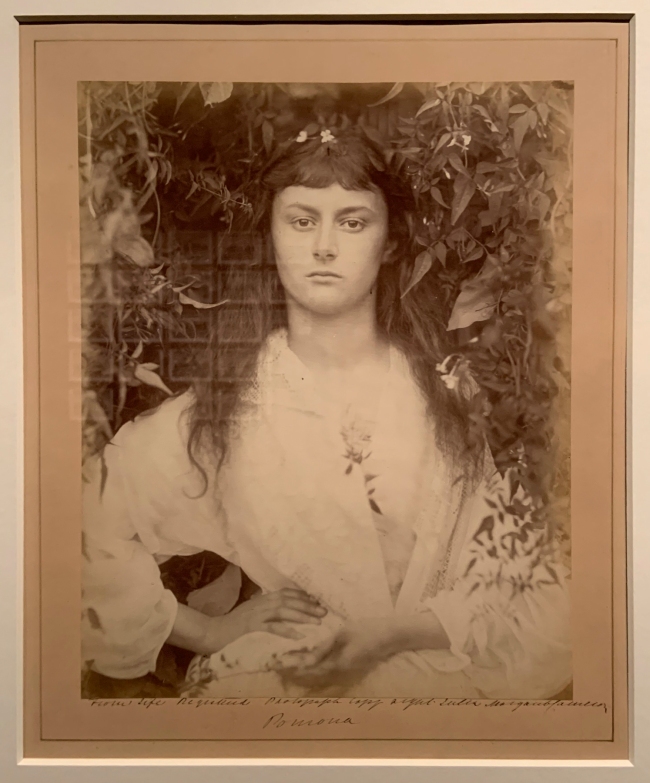
![Lewis Carroll (British, Daresbury, Cheshire 1832 - 1898 Guildford) '[Alice Liddell]' June 25, 1870 Lewis Carroll (British, Daresbury, Cheshire 1832 - 1898 Guildford) '[Alice Liddell]' June 25, 1870](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/lewis-carroll-alice-liddell.jpg?w=650&h=741)
![Unknown photographer (American) '[Surveyor]' c. 1854 Unknown photographer (American) '[Surveyor]' c. 1854](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-surveyor-a.jpg?w=840)
![Unknown photographer (American) '[Surveyor]' c. 1854 Unknown photographer (American) '[Surveyor]' c. 1854](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-surveyor-b.jpg?w=650&h=758)

![Hippolyte Bayard (French, 1801-1887) '[Classical Head]' probably 1839 Hippolyte Bayard (French, 1801-1887) '[Classical Head]' probably 1839](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/bayard-classical-head.jpg?w=650&h=715)

![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-a.jpg?w=650&h=783)
![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-b.jpg?w=650&h=760)
![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-c.jpg?w=650&h=798)
![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-d.jpg?w=650&h=844)
![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-e.jpg?w=650&h=800)
![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-f.jpg?w=650&h=771)
![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-g.jpg?w=650&h=830)
![Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s Unknown artist. '[Carte-de-visite Album of Collaged Portraits]' 1850s-1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/anon-collaged-portraits-h.jpg?w=650&h=761)
![Unknown artist (American) '[Studio Photographer at Work]' c. 1855 Unknown artist (American) '[Studio Photographer at Work]' c. 1855](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/unknown-artist-american-studio-photographer-at-work-c-1855.jpg?w=650&h=807)
![Unknown artist (American) '[Boy Holding a Daguerreotype]' 1850s Unknown artist (American) '[Boy Holding a Daguerreotype]' 1850s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/unknown-american-active-1850s-boy-holding-a-daguerreotype-1850s.jpg?w=650&h=759)


![Carleton E. Watkins (American, 1829-1916) '[California Oak, Santa Clara Valley]' c. 1863 Carleton E. Watkins (American, 1829-1916) '[California Oak, Santa Clara Valley]' c. 1863](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/watkins-california-oak-santa-clara-valley.jpg?w=650&h=805)
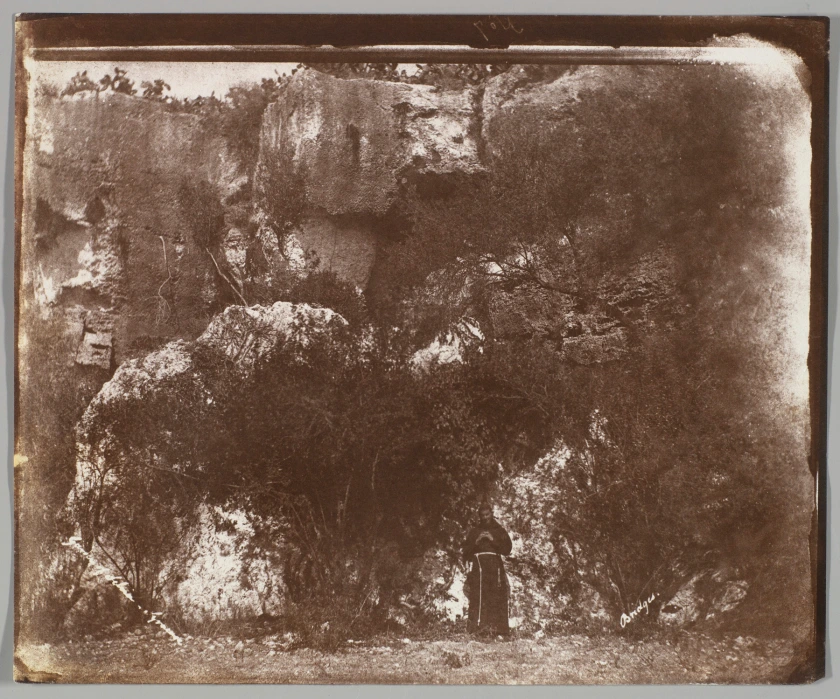

![Pietro Dovizielli (Italian, 1804-1885) '[Spanish Steps, Rome]' c. 1855 Pietro Dovizielli (Italian, 1804-1885) '[Spanish Steps, Rome]' c. 1855](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/dovizielli-spanish-steps.jpg?w=650&h=846)
![Edouard Baldus (French (born Prussia), 1813-1889) '[Amphitheater, Nîmes]' c. 1853 Edouard Baldus (French (born Prussia), 1813-1889) '[Amphitheater, Nîmes]' c. 1853](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/baldus-amphitheater.jpg?w=840)
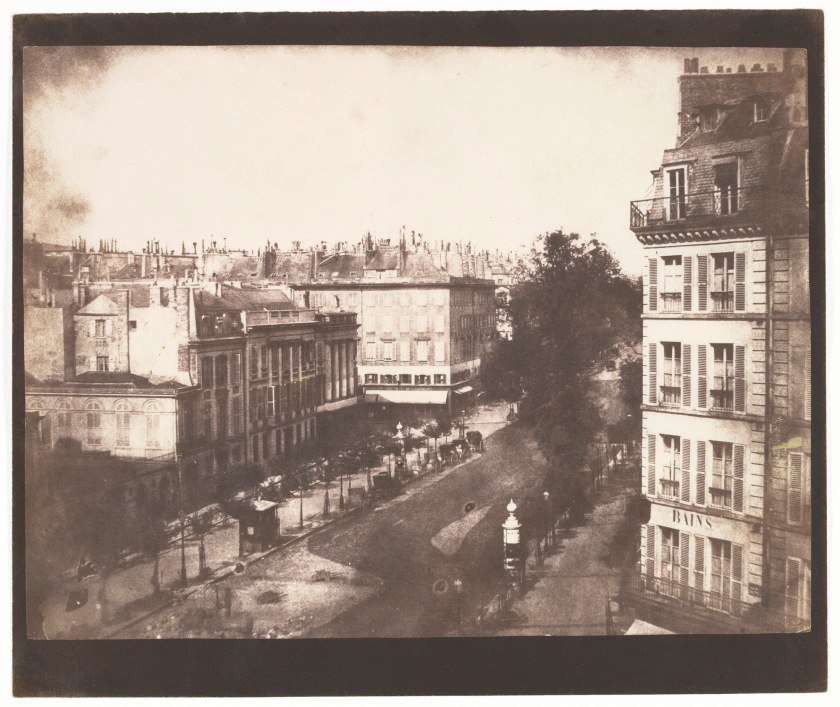

![Lewis Dowe (American, active 1860s-1880s) '[Dowe's Photograph Rooms, Sycamore, Illinois]' 1860s Lewis Dowe (American, active 1860s-1880s) '[Dowe's Photograph Rooms, Sycamore, Illinois]' 1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/lewis-dowe-dowes-photograph-rooms-sycamore-illinois-1860s.jpg?w=840)
![E. & H. T. Anthony (American) '[Specimens of New York Bill Posting]' 1863 E. & H. T. Anthony (American) '[Specimens of New York Bill Posting]' 1863](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/e-h-t-anthony-specimens-of-new-york-bill-posting-1863.jpg?w=840)
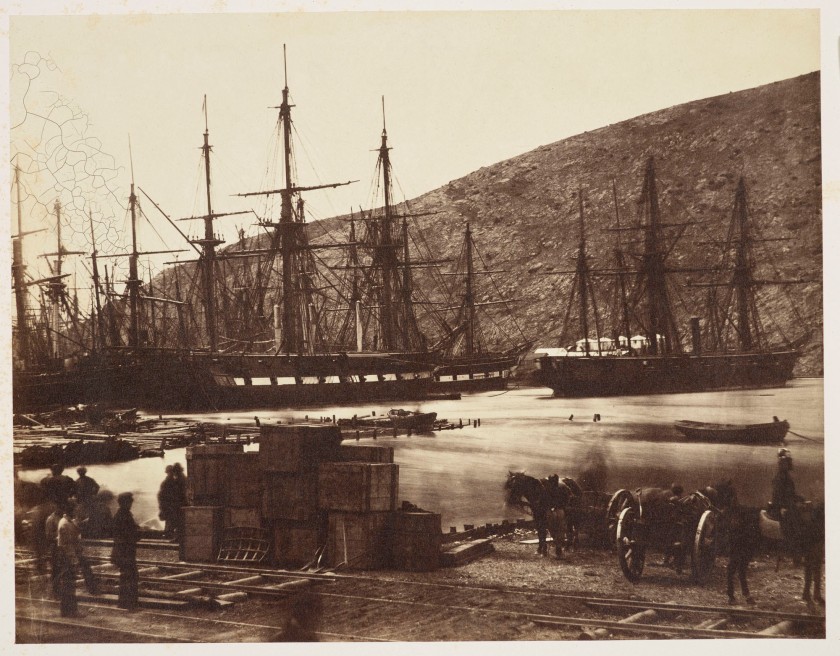


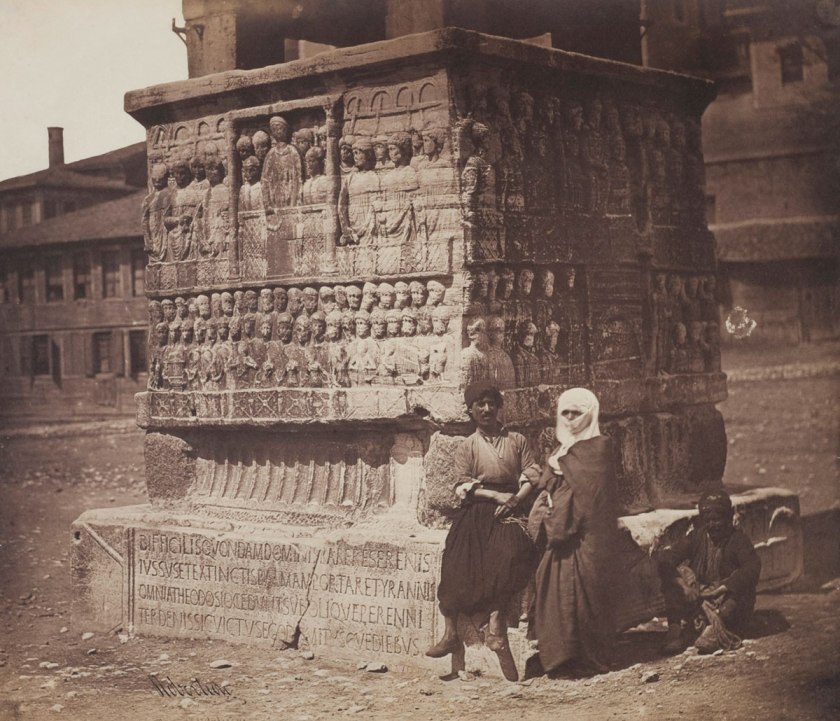
![Felice Beato (British (born Italy), Venice 1832-1909 Luxor) and James Robertson (British, 1813-1881) [Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem] 1856-1857 Felice Beato (British (born Italy), Venice 1832-1909 Luxor) and James Robertson (British, 1813-1881) [Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem] 1856-1857](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/beato-dome.jpg?w=840)
![R.C. Montgomery (American, active 1850s) '[Self-Portrait (?)]' 1850s R.C. Montgomery (American, active 1850s) '[Self-Portrait (?)]' 1850s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/07/r.c.-montgomery-self-portrait-1850s.jpg?w=650&h=1068)
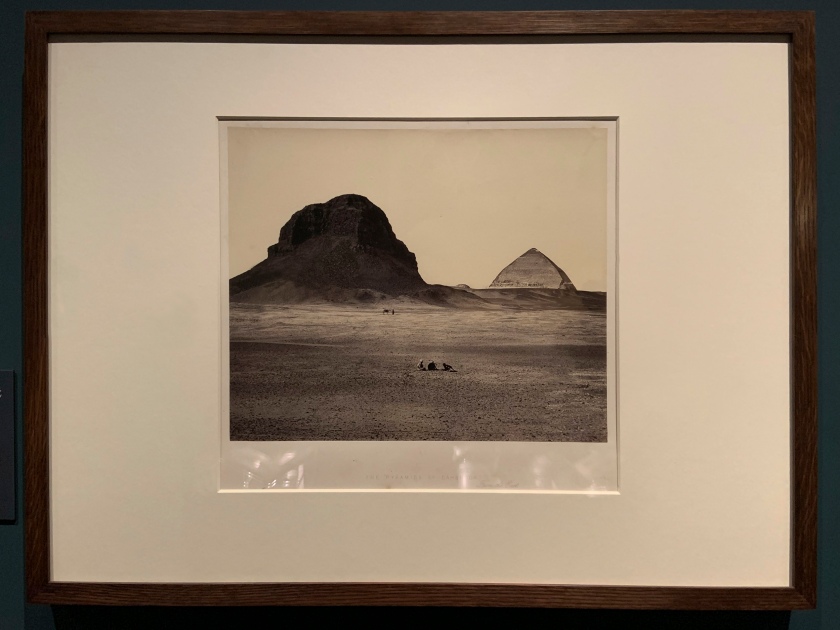
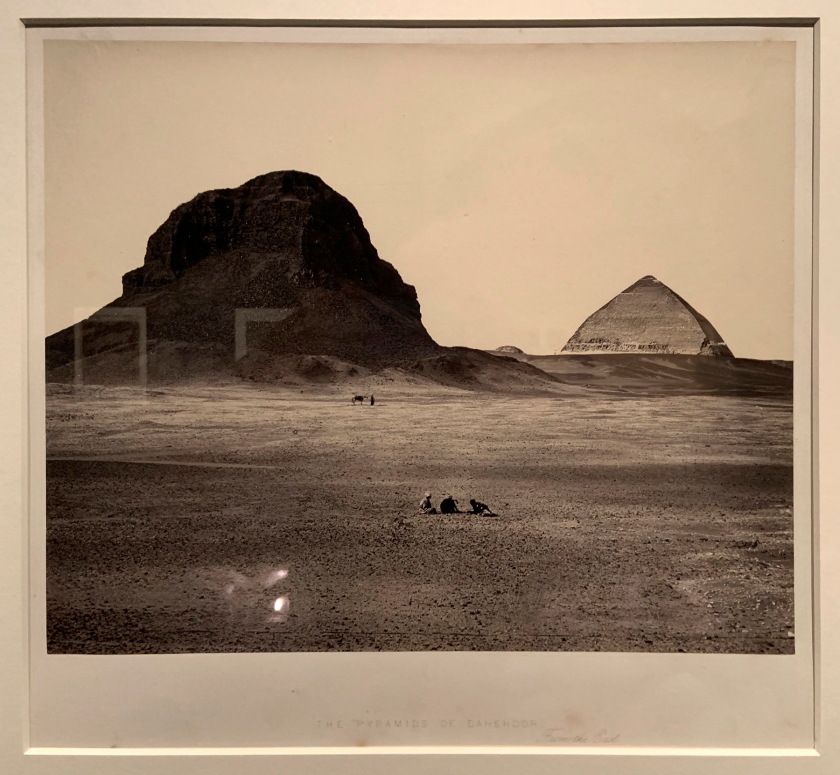





























![Francis Frith (British, 1822-98) 'The Pyramids of Dahshoor [Dahshur], from the East, from Egypt, Sinai, and Jerusalem: A Series of Twenty Photographic Views by Francis Frith' 1858 (published 1860 or 1862) Francis Frith (British, 1822-98) 'The Pyramids of Dahshoor [Dahshur], from the East, from Egypt, Sinai, and Jerusalem: A Series of Twenty Photographic Views by Francis Frith' 1858 (published 1860 or 1862)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/05/frith-the-pyramids-of-dahshoor-web.jpg?w=840)
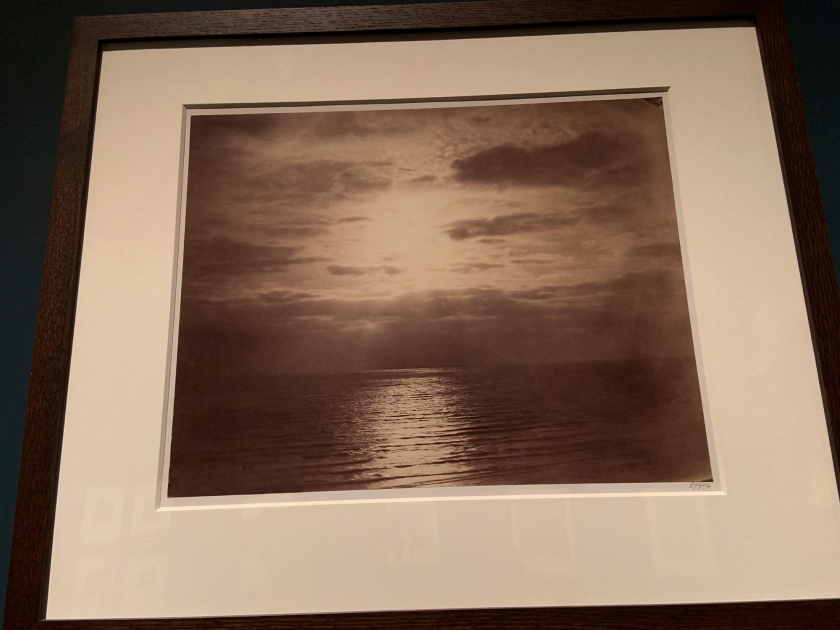
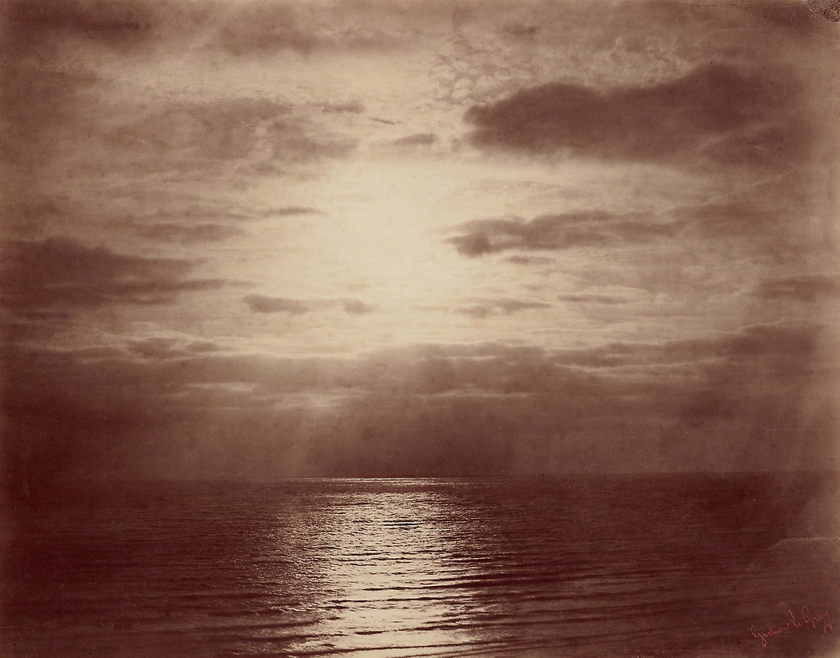
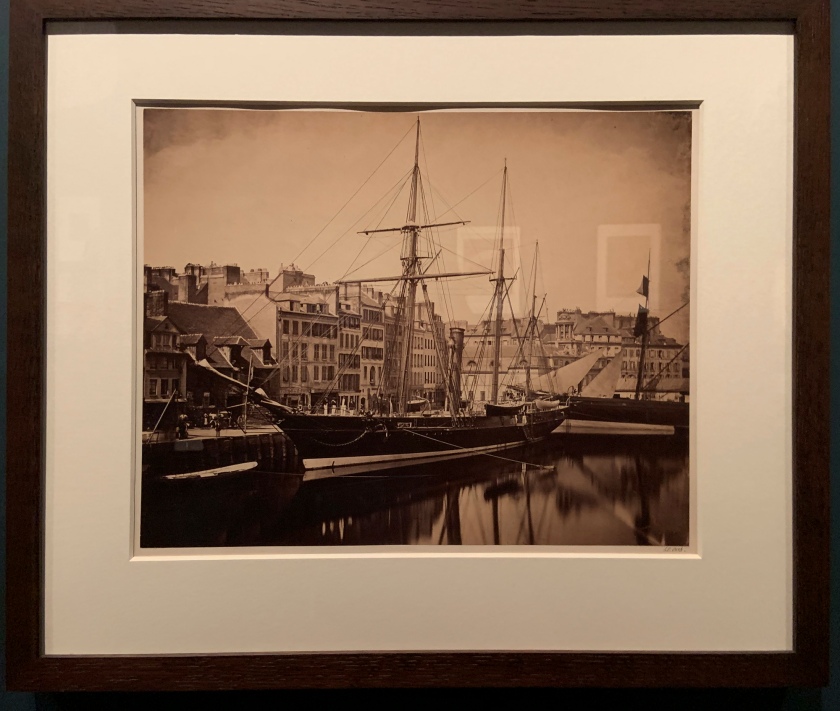
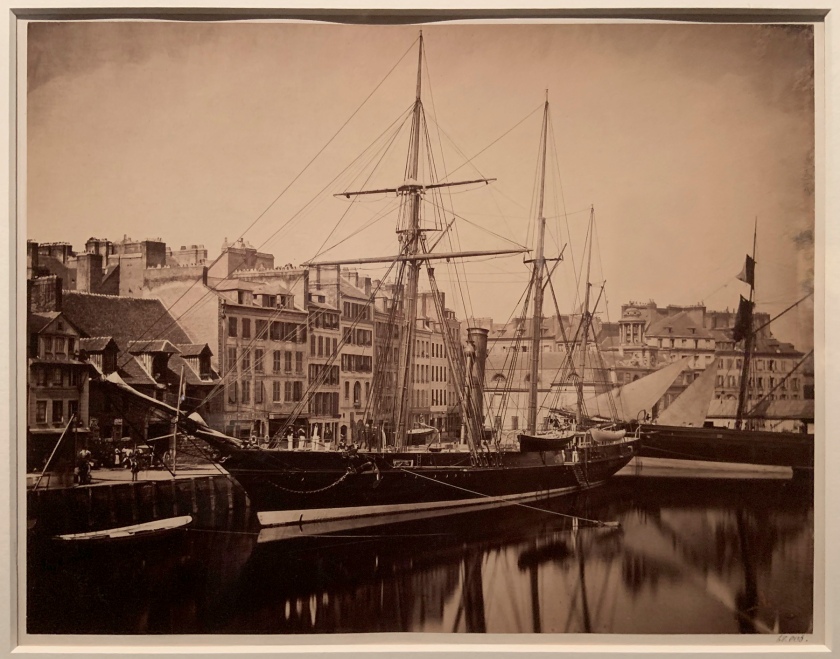
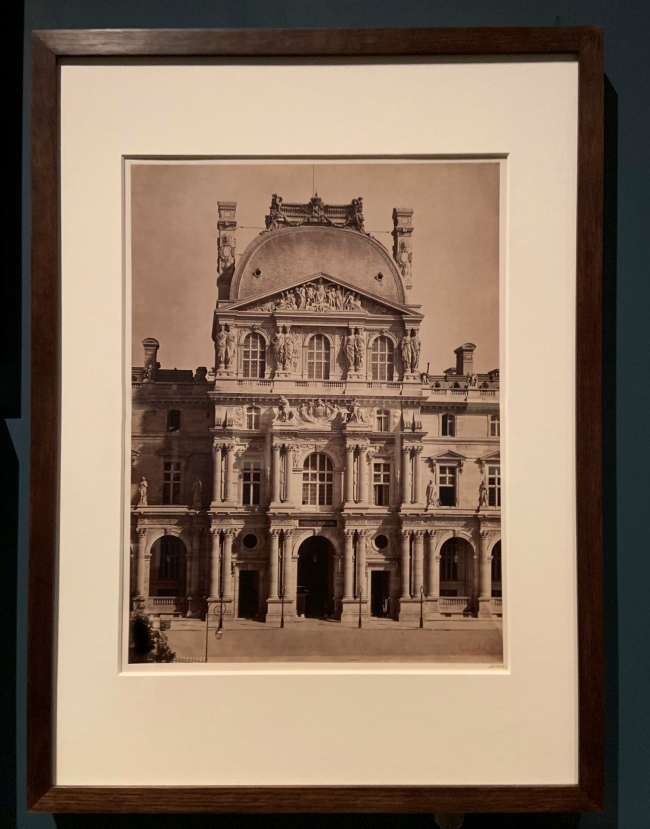
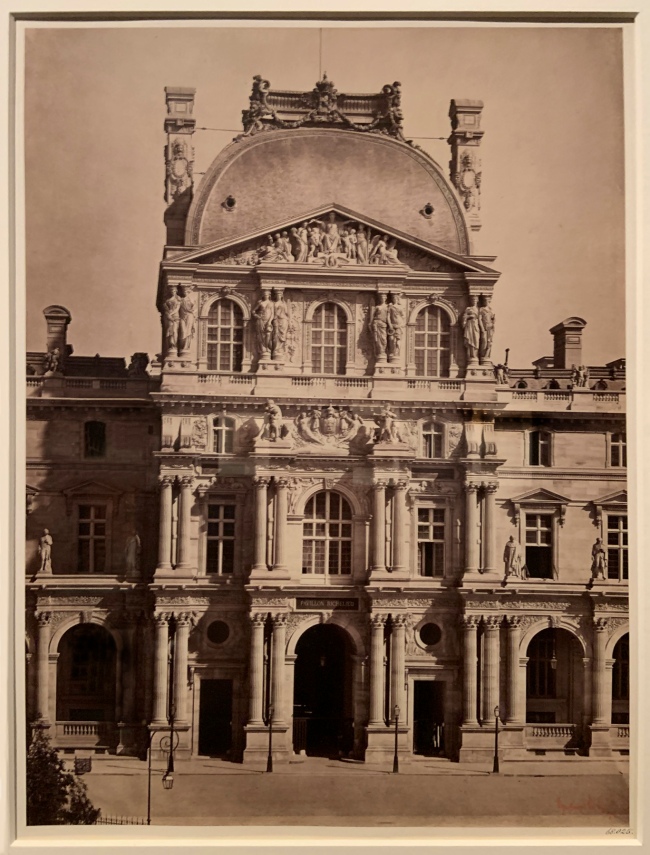
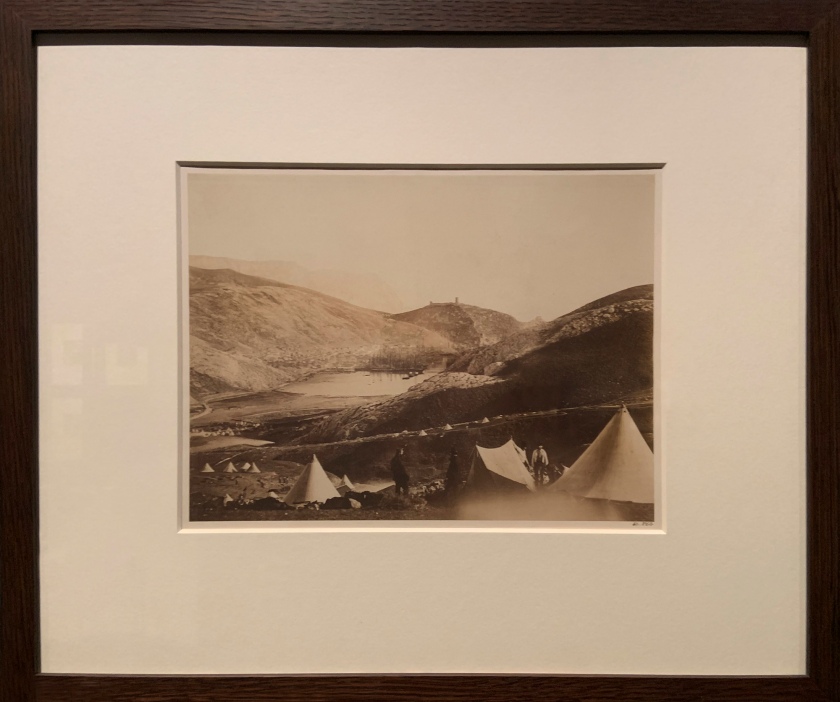
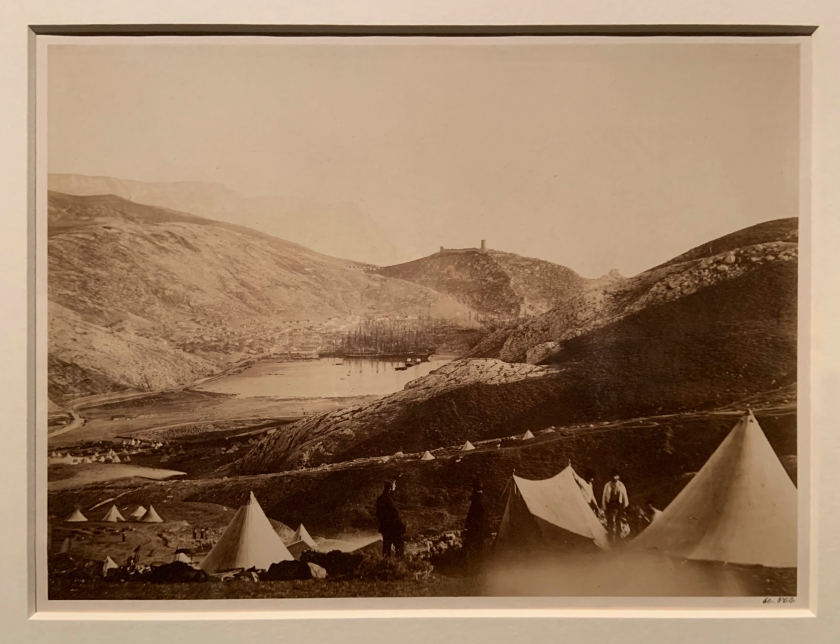
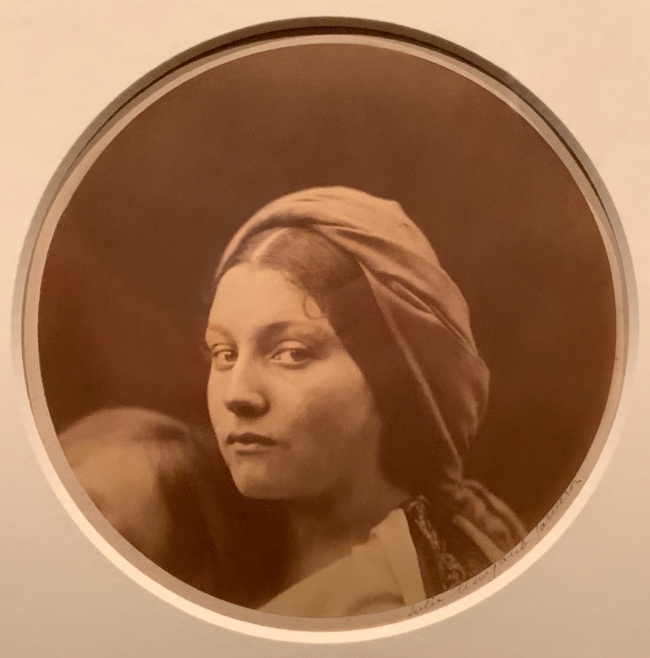
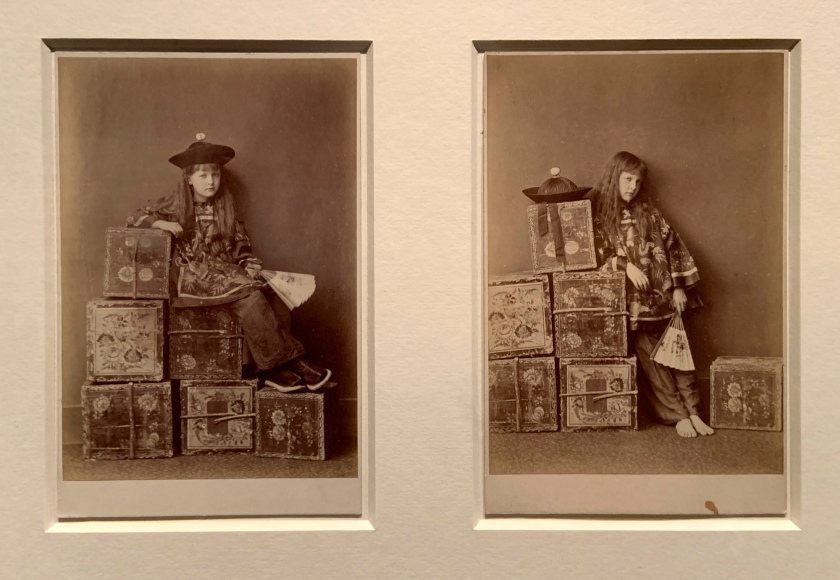
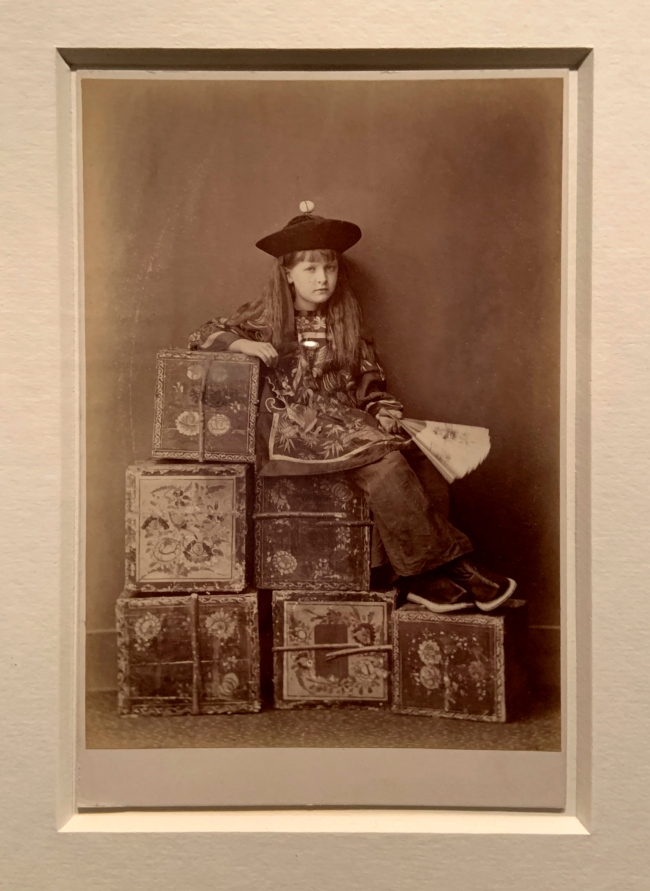
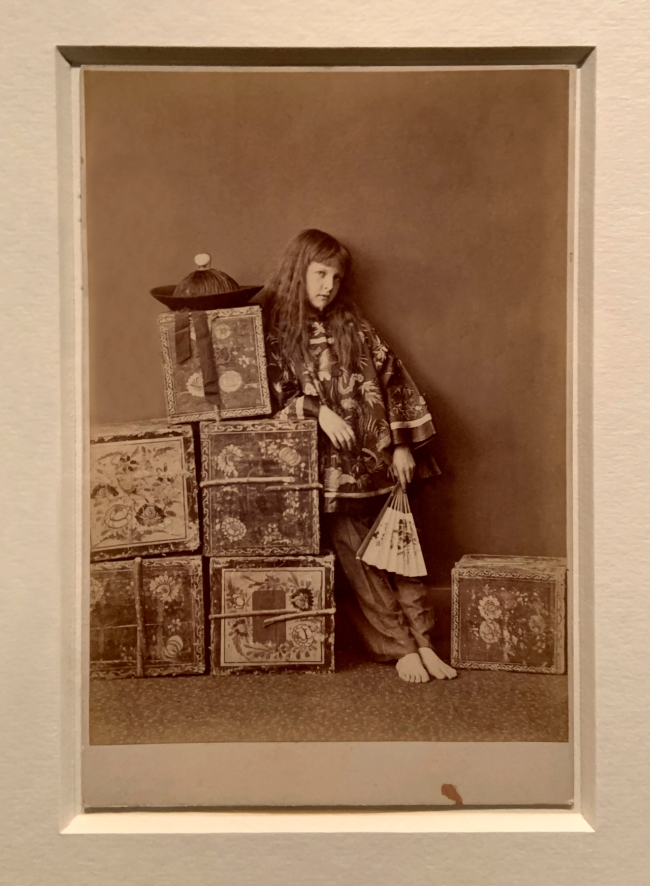
















































































































































































![David Hill and Robert Adamson. 'The Gowan [Margaret and Mary Cavendish]' c. 1843-1848 David Hill and Robert Adamson. 'The Gowan [Margaret and Mary Cavendish]' c. 1843-1848](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/david-hill-and-robert-adamson-the-gowan-margaret-and-mary-cavendish-c-1843-1848-web.jpg?w=840)
























![John S. Johnston. 'One of Dr Kane’s Men [possibly William Morton]' c. 1857 John S. Johnston. 'One of Dr Kane’s Men [possibly William Morton]' c. 1857](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/john-s-johnston-one-of-dr-kanes-men-possibly-william-morton-c-1857-web.jpg?w=650&h=930)







![Platt D. Babbitt. '[Scene at Niagara Falls]' c. 1855](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/platt_d_babbitt_scene_at_niagara_falls-web.jpg?w=840)

![Camille Silvy. 'Group of their Royal Highnesses the Princess Clementine de Saxe Cobourg Gotha, her Sons and Daughter, the Duke d'Aumale, the Count d'Eu, the Duke d'Alencon, and the Duke de Penthievre [in England]' 1864](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/camille-silvy-group-of-their-royal-web.jpg?w=840)
![Camille Silvy. 'Group of their Royal Highnesses the Princess Clementine de Saxe Cobourg Gotha, her Sons and Daughter, the Duke d'Aumale, the Count d'Eu, the Duke d'Alencon, and the Duke de Penthievre [in England]' 1864](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/camille-silvy-group-of-their-royal-detail.jpg?w=840)
![Man Ray. '[Marcel Duchamp and Raoul de Roussy de Sales Playing Chess]' 1925](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/gm_05332701-web.jpg?w=840)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig). '[Summer, The Lower East Side, New York City]' Summer 1937](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/gm_04304601-web.jpg?w=840)
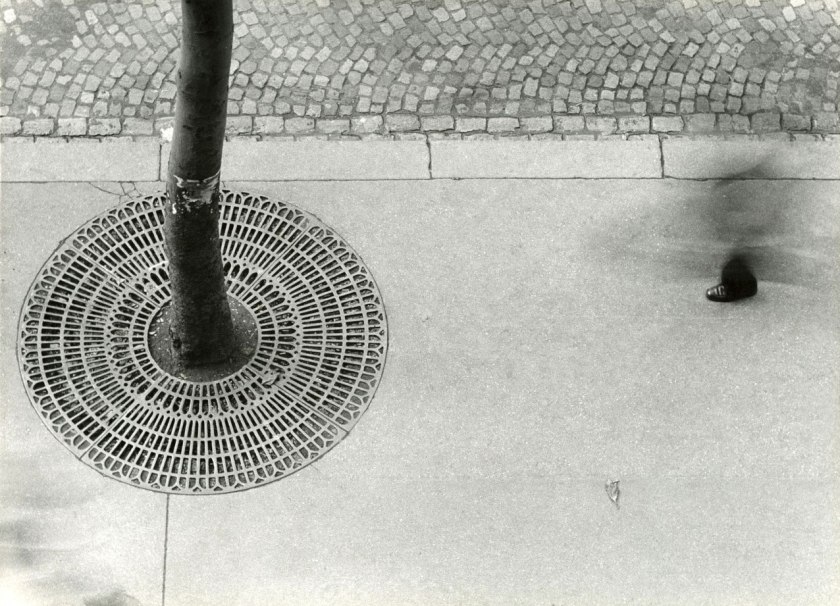
![André Kertész. '[Underwater Swimmer]' Negative 1917; print 1970s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/gm_06225401-web.jpg?w=840)
![Unknown photographer. '[Barnum and Bailey Circus Tent in Paris, France]' 1901-1902](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/gm_05045201-web.jpg?w=840)








































































You must be logged in to post a comment.