Exhibition dates: 26th November 2014 – 15th March 2015
The Eyal Ofer Galleries
Artists: Jules Andrieu, Pierre Antony-Thouret, Nobuyoshi Araki, George Barnard, Adam Broomberg and Oliver Chanarin, Luc Delahaye, Ken Domon, Roger Fenton, Ernst Friedrich, Jim Goldberg, Toshio Fukada, Kenji Ishiguro, Kikuji Kawada, An-My Lê, Jerzy Lewczyński, Emeric Lhuisset, Agata Madejska, Diana Matar, Eiichi Matsumoto, Chloe Dewe Mathews, Don McCullin, Susan Meiselas, Kenzo Nakajima, Simon Norfolk, João Penalva, Richard Peter, Walid Raad, Jo Ratcliffe, Sophie Ristelhueber, Julian Rosefeldt, Hrair Sarkissian, Michael Schmidt, Ursula Schulz-Dornburg, Indre Šerpytyte, Stephen Shore, Harry Shunk and János Kender, Taryn Simon, Shomei Tomatsu, Hiromi Tsuchida, Marc Vaux, Paul Virilio, Nick Waplington, Jane and Louise Wilson, and Sasaki Yuichiro.
Curators: Simon Baker, Curator Photography and International Art, Shoair Mavlian, Assistant Curator, and Professor David Alan Mellor, University of Sussex
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
The Valley of the Shadow of Death
1855
Another fascinating exhibition. The concept, that of vanishing time, a vanquishing of time – inspired by Kurt Vonnegut’s 1969 novel Slaughterhouse-Five and the Japanese photographer Kikuji Kawada’s 1965 photobook The Map – is simply inspired. Although the images are not war photography per se, they are about the lasting psychological effects of war imaged on a variable time scale.
While the images allow increasing passages of time between events and the photographs that reflect on them – “made moments after the events they depict, then those made days after, then months, years and so on” – there settles in the pit of the stomach some unremitting melancholy, some unholy dread as to the brutal facticity and inhumanness of war. The work which “pictures” the memory of the events that took place, like a visual ode of remembrance, are made all the more powerful for their transcendence – of time, of death and the immediate detritus of war.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Tate Modern for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“… taking its cue from Vonnegut, ‘Conflict, Time, Photography’ is arranged differently, following instead the increasing passages of time between events and the photographs that reflect on them. There are groups of works made moments after the events they depict, then those made days after, then months, years and so on – 10, 20, 50, right up to 100 years later.”
Simon Baker
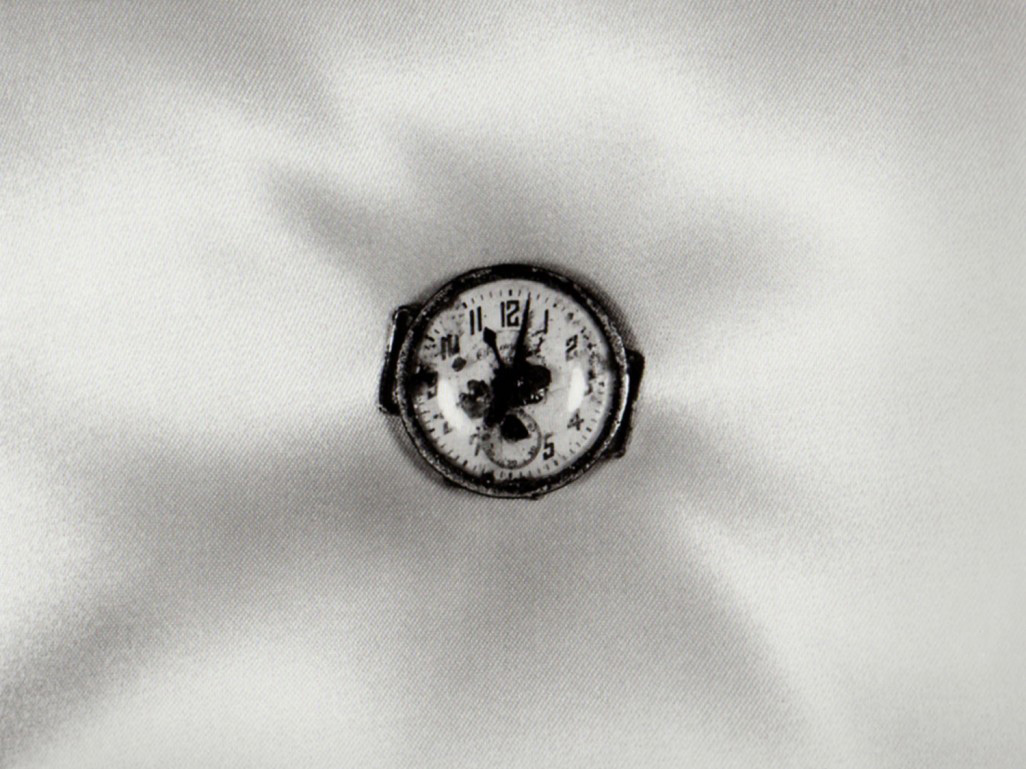
Shomei Tomatsu (Japanese, 1930-2012)
Atomic Bomb Damage – Wristwatch Stopped at 11.02, August 9, 1945, Nagasaki
1961
Gelatin silver print on paper
253 x 251mm
Tokyo Metropolitan Museum of Photography, Tokyo
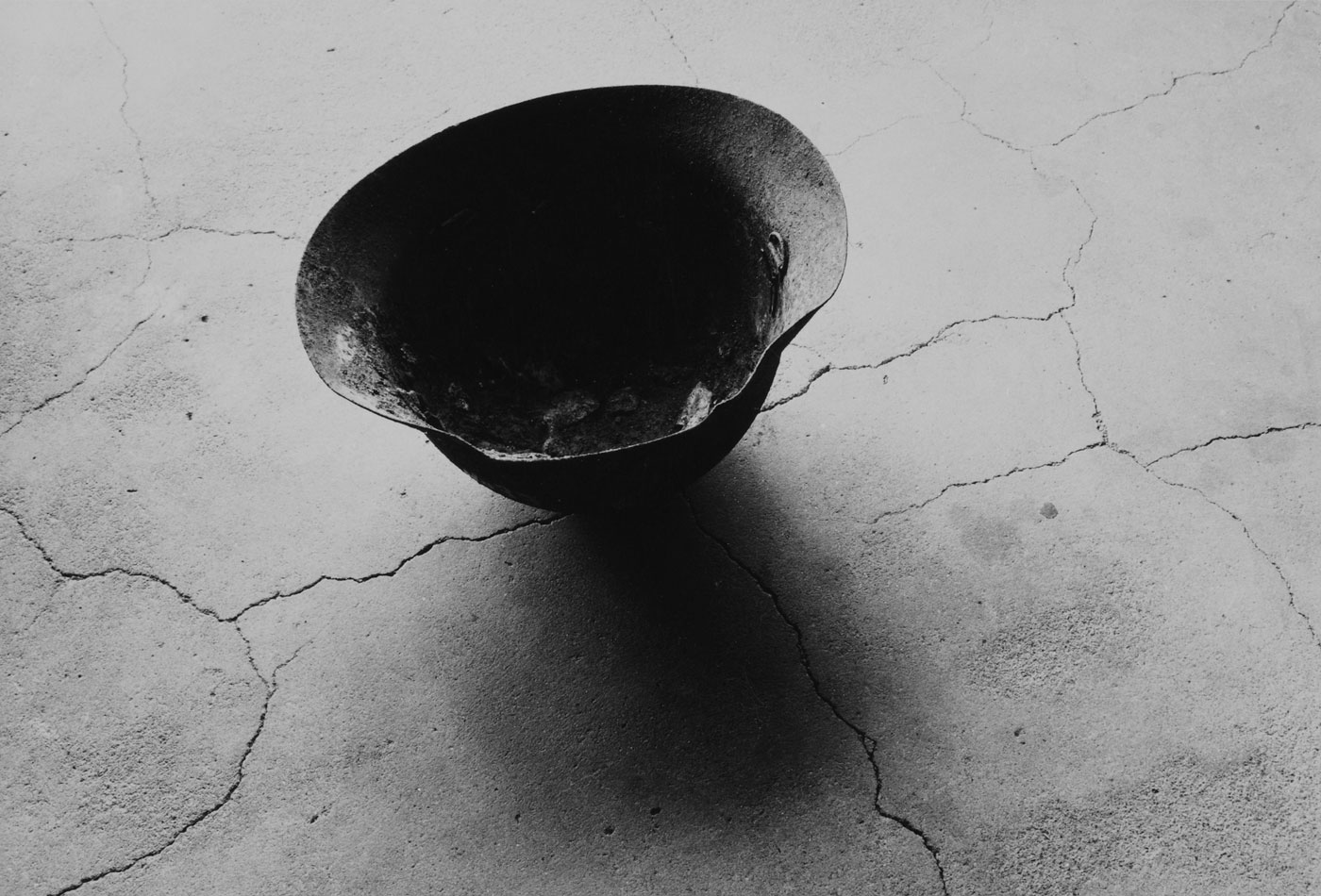
Shomei Tomatsu (Japanese, 1930-2012)
Steel Helmet with Skull Bone Fused by Atomic Bomb, Nagasaki
1963
Gelatin silver print on paper
226 x 303mm
Tokyo Metropolitan Museum of Photography, Tokyo
Shomei Tomatsu (Japanese, 1930-2012)
Melted bottle
Nagasaki, 1961
from the series Nagasaki 11:02
Silver Gelatin print
20 x 21cm
© Shomei Tomatsu
“From the seconds after a bomb is detonated to a former scene of battle years after a war has ended, this moving exhibition focuses on the passing of time, tracing a diverse and poignant journey through over 150 years of conflict around the world, since the invention of photography.
In an innovative move, the works are ordered according to how long after the event they were created from moments, days and weeks to decades later. Photographs taken seven months after the fire bombing of Dresden are shown alongside those taken seven months after the end of the First Gulf War. Images made in Vietnam 25 years after the fall of Saigon are shown alongside those made in Nakasaki 25 years after the atomic bomb. The result is the chance to make never-before-made connections while viewing the legacy of war as artists and photographers have captured it in retrospect…
The exhibition is staged to coincide with the 2014 centenary and concludes with new and recent projects by British, German, Polish and Syrian photographers which reflect on the First World War a century after it began.”
Text from the Tate Modern website
“The original idea for the Tate Modern exhibition Conflict, Time, Photography came from a coincidence between two books that have captivated and inspired me for many years: Kurt Vonnegut‘s classic 1969 novel Slaughterhouse-Five and the Japanese photographer Kikuji Kawada’s 1965 photobook The Map. Both look back to hugely significant and controversial incidents from the Second World War from similar distances.
Vonnegut was a prisoner of war in Dresden when what he called ‘possibly the world’s most beautiful city’ was destroyed by incendiary bombs, and struggled to write his war book for almost 25 years. Kawada was a young photographer working in post-war Hiroshima when he began to take the strange photographs of the scarred, stained ceiling of the A-bomb Dome – the only building to survive the explosion – that he would eventually publish on August 6 1965, 20 years to the day since the atomic bomb was dropped on the city.
It may seem odd that these great works of art and literature took so long to emerge from the aftermath of the events they concern. But many of the most complex and considered accounts of conflict have taken their time. To Vonnegut’s painfully slow response to the war, for example, we might add Joseph Heller’s brilliantly satirical Catch-22, published in 1961, and, even more significantly, JG Ballard’s memorial masterpiece Empire of the Sun, which did not see the light of day until 1984.
And today, in 2014, 100 years since the start of the First World War, it seems more important than ever not only to understand the nature and long-term effects of conflict, but also the process of looking back at the past…”
Extract from Simon Baker. “War photography: what happens after the conflict?” on The Telegraph website, 7th November 2014 [Online] Cited 09/02/2015
An-My Lê (Vietnamese-American, b. 1960)
Untitled, Hanoi
1994-1998
Gelatin silver print on paper
508 x 609mm
Courtesy the artist and Murray Guy, New York
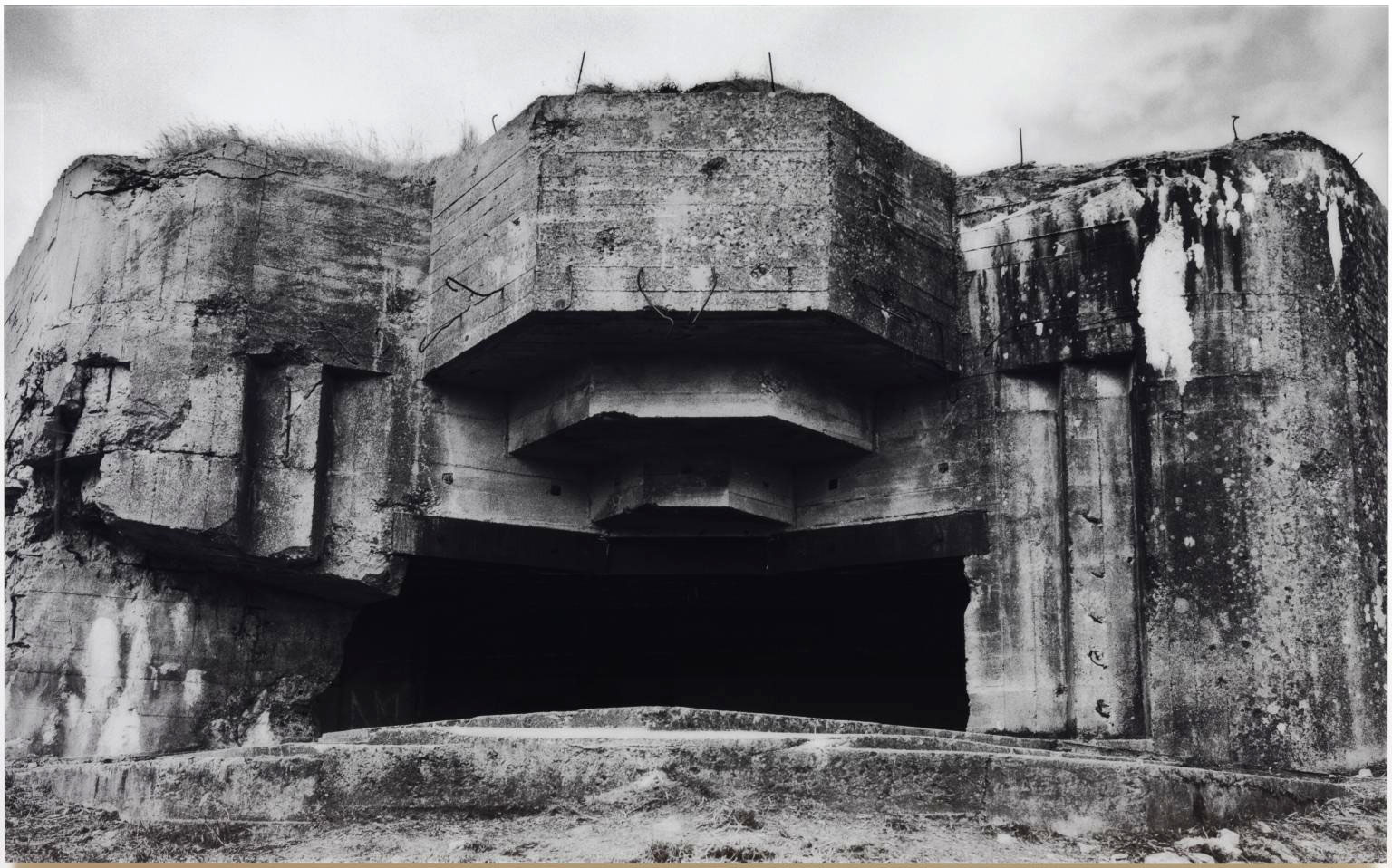
Jane Wilson (British, b. 1967)
Louise Wilson (British, b. 1967)
Urville
2006
Gelatin silver print, mounted onto aluminium
1800 x 1800mm
Tate
Purchased 2011
Jane Wilson (British, b. 1967)
Louise Wilson (British, b. 1967)
Azeville
2006
Gelatin silver print, mounted onto aluminium
1800 x 2900mm
Tate
Purchased 2011
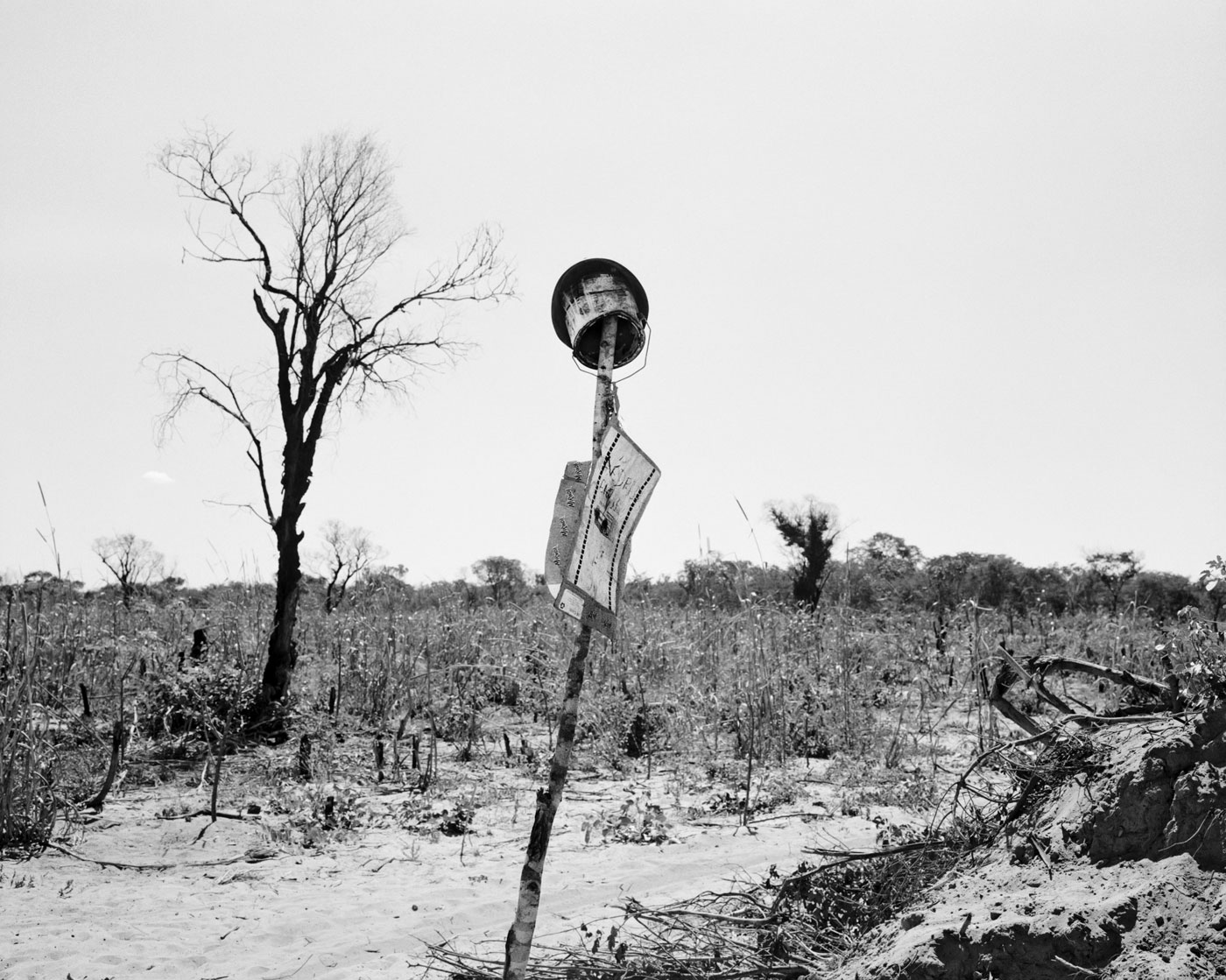
Jo Ractliffe (South African, b. 1961)
As Terras do fim do Mundo (The Lands of the End of the World)
2009-2010
Courtesy Mark McCain collection
“At first glance, Jo Ractliffe’s black-and-white shots of sun-baked African landscapes look random and bland: rocks, dirt, scrubby trees; some handwritten signs but no people. Only when reading the titles – “Mass Grave at Cassinga,” “Minefield Near Mupa” – do you learn where the people are, or once were, and the pictures snap into expressive focus.
Ms. Ractliffe, who lives in Johannesburg, took the photographs in 2009 and 2010 in Angola on visits to now-deserted places that were important to that country’s protracted civil war and to the intertwined struggle of neighbouring Namibia to gain independence from South Africa’s apartheid rule. South Africa played an active role in both conflicts, giving military support to insurgents who resisted Angola’s leftist government, and hunting down Namibian rebels who sought safety within Angola’s borders.
It’s through this historical lens that Ms. Ractliffe views landscape: as morally neutral terrain rendered uninhabitable by terrible facts from the past – the grave of hundreds of Namibia refugees, most of them children, killed in an air raid; the unknown numbers of land mines buried in Angola’s soil. Some are now decades old but can still detonate, so the killing goes on.”
Holland Cotter. “Jo Ratcliffe: ‘As Terras do Fim do Mundo (The Lands of the End of the World)’,” on The New York Times website May 26, 2011 [Online] Cited 12/07/2021
Kikuji Kawada (Japanese, b. 1933)
Hinomaru, Japanese National Flag
1965
From the series The Map
Gelatin silver print
279 x 355mm
© Kikuji Kawada, courtesy the artist and Photo Gallery International, Tokyo
Kikuji Kawada (Japanese, b. 1933)
Lucky Strike
1962
From the series The Map
© Kikuji Kawada, courtesy the artist and Photo Gallery International, Tokyo
Kikuji Kawada (Japanese, b. 1933)
The A-Bomb Memorial Dome and Ohta River from the series The Map
Hiroshima 1960-1965
Gelatin silver print
© Kikuji Kawada
Points of memory: Kikuji Kawada
My first published photo book, The Map, took me five years to complete, beginning in 1960. In late 1961 a solo show with work from the series was held at Fuji Photo Salon in Tokyo, organised in three parts.
The first featured a ruined castle that was blown up intentionally by the Japanese army during the Second World War. The second comprised photographs taken a decade after the atomic bomb exploded in Hiroshima. They showed the stains and flaking ceilings of the Atomic Bomb Dome, the only structure left standing at the heart of the detonation zone. The third part concerned Tokyo during the period of economic recovery: images of advertising, scrap iron, the trampled national flag and emblems of the American Forces such as Lucky Strike and Coca-Cola, all twisted together, their order shuffled again and again. Some appeared as a montage to be presented as a metaphor. I dare not say the meaning of it.
These works led me to attempt to create this photographic book, using the notion of the map as a clue to the future and to question the whereabouts of my spirit. Discarded memorial photographs, a farewell note, kamikaze pilots – the illusions of various maps that emerge are to me like a discussion with the devil. The stains are situated as a key image of the series by drawing a future stratum and sealing the history, the nationality, the fear and anxiety of destruction and prosperity. It was almost a metaphor for the growth and the fall.
On the back of the black cover box are written rhyming words that are almost impossible to read. The front cover shows that the words are about to burn out. Inside, the pages are laid out as hinged double fold-out spreads. The repetition of the act of opening and closing makes the images appear and disappear. I wanted to have a book design as a new object and something that goes beyond the contents. With the rich and chaotic nature of monochrome, it might be that I tried to find my early style within the illusion of reality by abstracting the phenomenon. As an observer, I would like to keep forcing myself into the future, never losing the sense of danger which emerges in the conflicts of daily life. I wish to harmonise my old distorted maps with the heartbeat of this exhibition at Tate Modern, twisting across the bridges of the centuries through conflicting space and time.
Kikuji Kawada is a photographer based in Tokyo.
Kikuji Kawada. “Points of memory: Kikuji Kawada: Conflict, Time, Photography,” on the Tate Modern website 3 December 2014 [Online] Cited 12/07/2021
Richard Peter (German, 1895-1977)
Dresden After Allied Raids Germany
1945
© SLUB Dresden / Deutsche Fotothek / Richard Peter, sen.
Toshio Fukada (Japanese, 1928-2009)
The Mushroom Cloud – Less than twenty minutes after the explosion (4)
1945
Tokyo Metropolitan Museum of Photography
© The estate of Toshio Fukada, courtesy Hiroshima Peace Memorial Museum
Jerzy Lewczyński (Polish, 1924-2014)
Wolf’s Lair / Adolf Hitler’s War Headquarters
1960
© Jerzy Lewczyński
Don McCullin (British, b. 1935)
Shell Shocked US Marine, Vietnam, The Battle of Hue
1968, printed 2013
© Don McCullin
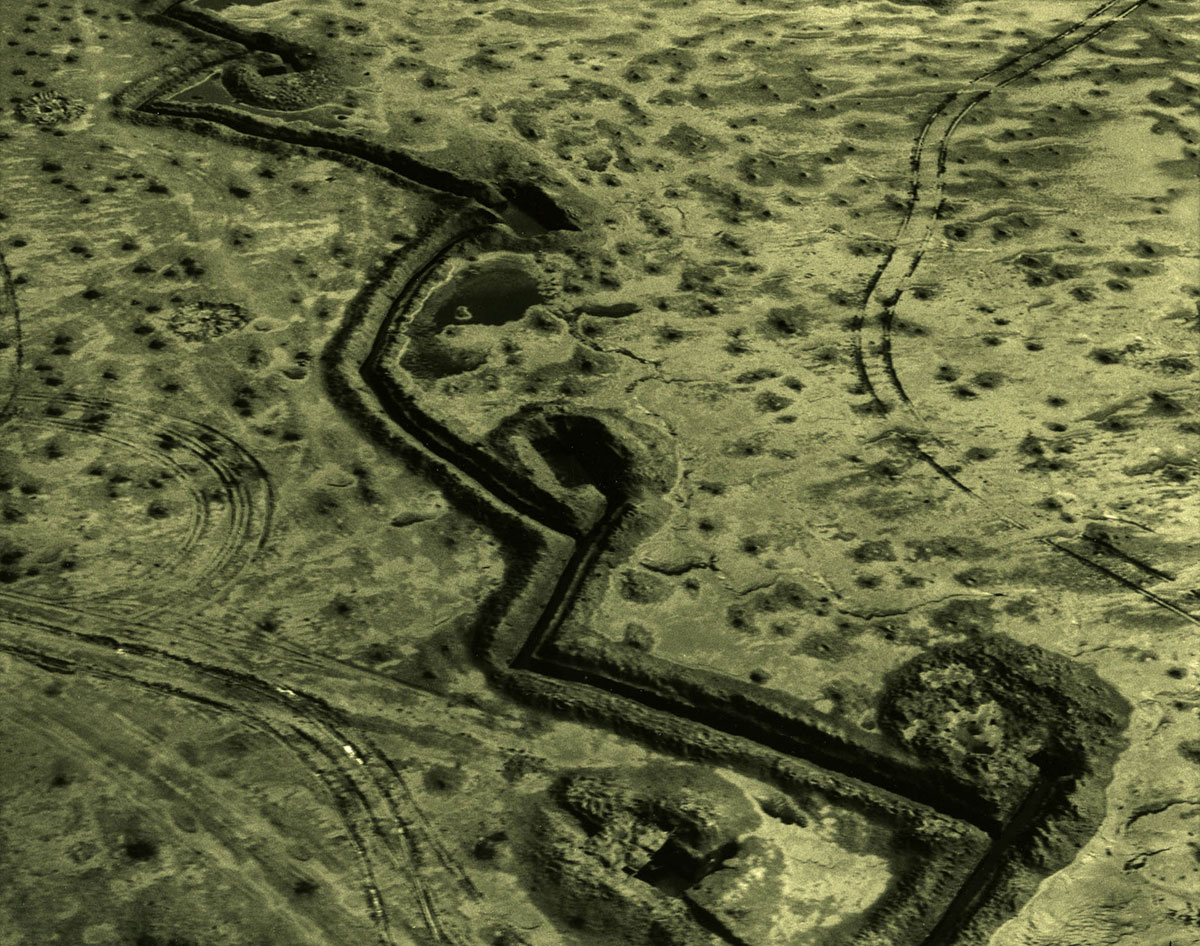
Ursula Schulz-Dornburg (German, b. 1938)
Kurchatov – Architecture of a Nuclear Test Site Kazakhstan. Opytnoe Pole
2012
Courtesy of the artist’s studio
© Ursula Schultz-Domburg
Conflict, Time, Photography brings together photographers who have looked back at moments of conflict, from the seconds after a bomb is detonated to 100 years after a war has ended. Staged to coincide with the centenary of the First World War, this major group exhibition offers an alternative to familiar notions of war reportage and photojournalism, instead focusing on the passing of time and the unique ways that artists have used the camera to reflect on past events.
Conflicts from around the world and across the modern era are depicted, revealing the impact of war days, weeks, months and years after the fact. The works are ordered according to how long after the event they were created: images taken weeks after the end of the American Civil War are hung alongside those taken weeks after the atomic bombs fell on Japan in 1945. Photographs from Nicaragua taken 25 years after the revolution are grouped with those taken in Vietnam 25 years after the fall of Saigon. The exhibition concludes with new and recent projects by British, German, Polish and Syrian photographers which reflect on the First World War a century after it began.
The broad range of work reflects the many different ways in which conflict impacts on people’s lives. The immediate trauma of war can be seen in the eyes of Don McCullin’s Shell-shocked US Marine 1968, while the destruction of buildings and landscapes is documented by Pierre Antony-Thouret’s Reims After the War (published in 1927) and Simon Norfolk’s Afghanistan: Chronotopia 2001-2002. Other photographers explore the human cost of conflict, from Stephen Shore’s account of displaced Jewish survivors of the Second World War in the Ukraine, to Taryn Simon’s meticulously researched portraits of those descended from victims of the Srebrenica massacre.
Different conflicts also reappear from multiple points in time throughout the exhibition, whether as rarely-seen historical images or recent photographic installations. The Second World War for example is addressed in Jerzy Lewczyński’s 1960 photographs of the Wolf’s Lair / Adolf Hitler’s War Headquarters, Shomei Tomatsu’s images of objects found in Nagasaki, Kikuji Kawada’s epic project The Map made in Hiroshima in the 1960s, Michael Schmidt’s Berlin streetscapes from 1980, and Nick Waplington’s 1993 close-ups of cell walls from a Prisoner of War camp in Wales.
As part of Conflict, Time, Photography, a special room within the exhibition has been guest-curated by the Archive of Modern Conflict. Drawing on their unique and fascinating private collection, the Archive presents a range of photographs, documents and other material to provide an alternative view of war and memory.
Conflict, Time, Photography is curated at Tate Modern by Simon Baker, Curator of Photography and International Art, with Shoair Mavlian, Assistant Curator, and Professor David Mellor, University of Sussex. It is organised by Tate Modern in association with the Museum Folkwang, Essen and the Staatliche Kunstsammlungen, Dresden, where it will tour in spring and summer 2015 respectively. The exhibition is also accompanied by a fully-illustrated catalogue from Tate Publishing and a programme of talks, events and film screenings at Tate Modern.
Press release from the Tate Modern website
Simon Norfolk
(British born Nigeria, b. 1963)
Bullet-scarred apartment building and shops in the Karte Char district of Kabul. This area saw fighting between Hikmetyar and Rabbani and then between Rabbani and the Hazaras
2003
© Simon Norfolk
Susan Meiselas (American, b. 1948)
Managua, July 2004
2004
From the series Reframing History
“Cuesto del Plomo,” hillside outside Managua, a well-known site of many assassinations carried out by the National Guard. People searched here daily for missing persons. July 1978, from the series, “Reframing History,” Managua, July 2004
In July 2004, for the 25th anniversary of the overthrow of Somoza, Susan returned to Nicaragua with nineteen mural-sized images of her photographs from 1978-1979, collaborating with local communities to create sites for collective memory. The project, “Reframing History,” placed murals on public walls and in open spaces in the towns, at the sites where the photographs were originally made.
Reframing History: Excerpt, Bus (2004)
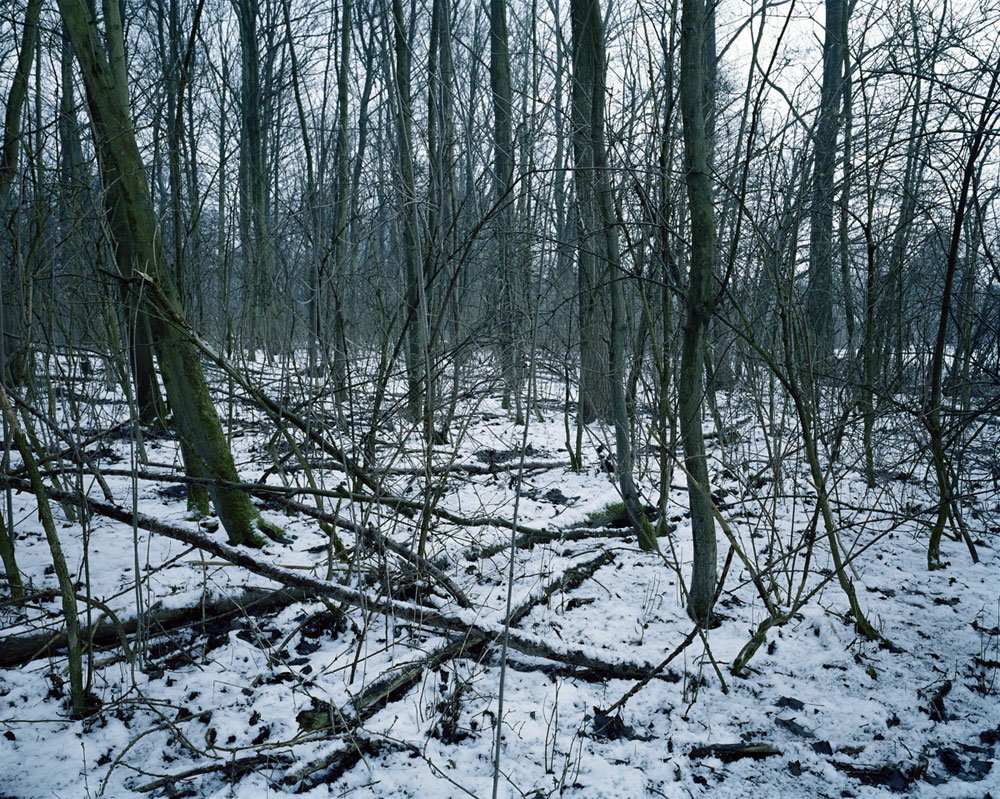
Nick Waplington (British, b. 1965)
Untitled
1993
From the series We Live as We Dream, Alone
Nick Waplington (British, b. 1965)
Untitled
1993
From the series We Live as We Dream, Alone
Nick Waplington’s deeply moving and once controversial photographs of the cells of Barry Island prison, where Nazi SS Officers were held prisoner before the Nuremburg trials, were taken in 1993, almost 50 years after the prisoners had embellished the cell walls with Germanic slogans and drawings of pin-up girls and Bavarian landscapes will be displayed. The half-century that elapsed between the photographs and the creation of their subject is grim testament to the enduring legacy of conflict…
“In 1992 I was commissioned to make work by the Neue galerie in Graz, Austria and the theme was war or “krieg” as it is in German. Graz is on the border with Yugoslavia and there was war in Yugoslavia at the time. I think they were hoping that I would make something to do with the war that was taking place between Croatia and Serbia and Bosnia. I did go to the war; you went to Zagreb and got a UN pass and went in to the war zone. It was very interesting to be taken into the war zone but ultimately I got back to England and I decided – to the annoyance of the gallery – that I was thinking about Austria instead. At the time, the president of Austria, Kurt Waldheim, had been exposed as a member of the SS and had been informing Yugoslavia during the war [World War Two] and the Austrians were very unconcerned about this. I thought I’d much prefer to make work that had the Austrians confronting their Nazi past rather than about the current conflict. I knew about the prison in Barry Island in South Wales where the SS were held before they were sent to Nuremberg for the trial and I started taking a series of photographs in the prison. It was lucky that I did because it was demolished the following year by the MOD. It’s gone now. When I got there, I saw the prisoners had been drawing on the walls. They’re mossy and crumbling but you can see Germanic lettering and Bavarian landscapes and women with 1940s haircuts. They are evocative and powerful given the emotive history. ”
Extract from Elliot Watson. “Nick Waplington: Conflict, Rim, Photography,” on the Hunger TV website, 26th November 2014 [Online] Cited 09/02/2015. No longer available online
Sophie Ristelhueber (French, b. 1949)
Fait #25
1992
71 photographs, gelatin silver prints mounted on aluminium
Object, each: 1000 x 1240 x 50mm
National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa. Purchased 2013
Sophie Ristelhueber (French, b. 1949)
Fait #44
1992
71 photographs, gelatin silver prints mounted on aluminium
Object, each: 1000 x 1240 x 50mm
National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa. Purchased 2013
Sophie Ristelhueber (French, b. 1949)
Fait #46
1992
71 photographs, gelatin silver prints mounted on aluminium
Object, each: 1000 x 1240 x 50mm
National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa. Purchased 2013
Luc Delahaye (French, b. 1962)
US Bombing on Taliban Positions
2001
C-print
238.6 x 112.2cm
Courtesy Luc Delahaye and Galerie Nathalie Obadia, Paris/Bruxelles
Chloe Dewe Mathews (British, b. 1982)
Vebranden-Molen, West-Vlaanderen
2013
Soldat Ahmed ben Mohammed el Yadjizy
Soldat Ali ben Ahmed ben Frej ben Khelil
Soldat Hassen ben Ali ben Guerra el Amolani
Soldat Mohammed Ould Mohammed ben Ahmed
17:00 / 15.12.1914
From the series Shot at Dawn
© Chloe Dewe Mathews
Chloe Dewe Mathews (British, b. 1982)
Former Abattoir, Mazingarbe, Nord-Pas-de-Calais
2013
Eleven British soldiers were executed here between 1915-1918
From the series Shot at Dawn
© Chloe Dewe Mathews
Seeing what can’t be seen
“This is a challenge still faced by photographers today. Two years ago, the British documentary photographer Chloe Dewe Mathews set about creating a series of her own responding to the World War One. Called Shot at Dawn, it expresses her shock upon discovering that during the conflict around a thousand British, French and Belgian troops were condemned for cowardice or desertion before being executed the following morning by firing squads consisting of comrades from their own battalions. “I never knew this happened,” she tells me. “Until quite recently, no one really talked about it, because the subject was so contentious and taboo.”
Researching her series, Dewe Mathews worked closely with academics to locate the forgotten places along the western front where these unfortunate combatants had been shot. She then travelled to each spot and set up her camera there at dawn, recording whatever could be seen a century after the executions had taken place.
The results are eerie and elegiac – otherwise unremarkable, empty landscapes infused with a powerful sense of mourning, outrage and loss.”
Extract from Alastair Sooke. “Beyond boots and guns: A new look at the horrors of war,” on BBC Culture website, 11 November 2014 [Online] Cited 09/02/2015
For more information please see the excellent article by Sean O’Hagan. “Chloe Dewe Mathews’s Shot at Dawn: a moving photographic memorial” on The Guardian website [Online] Cited 09/02/2015
Chloe Dewe Mathews (British, b. 1982)
Six Farm, Loker, West-Vlaanderen
2013
Private Joseph Byers
Private Andrew Evans
Time unknown / 6.2.1915
Private George E. Collins
07:30 / 15.2.1915
© Chloe Dewe Mathews
Stephen Shore (American, b. 1947)
Tzylia Bederman, Bucha, Ukraine, July 18, 2012
2012
Courtesy of Stephen Shore
Pierre Anthony-Thouret (French, 1861-1926)
Plate I
1927
from Reims after the war. The mutilated cathedral. The devastated city.
Private collection, London
The limits of realism
“So how can photographers respond to conflict if not by employing strategies commonly found in photojournalism about war? One alternative approach is to focus less on documenting the heat of battle and more on remembrance – something that feels relevant this year, which marks the centenary of the start of the World War One.
Some of the most moving evocations of the Great War were captured by commercial photographers who arrived in northeast France in the wake of the conflict, when people began travelling to the region in order to see for themselves the extent of the devastation of local villages, towns, and cities. There was enormous appetite for images recording the destruction, available in the form of cheap guidebooks and postcards.
“This is one of the first episodes of mass tourism in the history of the world,” explains [curator Simon] Baker. “There were 300 million postcards sent from the western front, for instance by people visiting the places where their relatives had died. And the photographers had to make these incredible compromises: making photographs of places that weren’t there anymore.”
In the case of Craonne, which was entirely obliterated by artillery, the village had to be rebuilt on a nearby site, while the ruins of the original settlement were abandoned to nature. As a result, the only way for photographers to identify Craonne was by providing a caption.
“The idea of photographing absence became really important,” says Baker. “War is about destruction, removing things, disappearance. A really interesting photographic language about disappearance in conflict emerged and it is extremely powerful. How does one record something that is gone?””
Extract from Alastair Sooke. “Beyond boots and guns: A new look at the horrors of war,” on BBC Culture website, 11 November 2014 [Online] Cited 09/02/2015
Pierre Anthony-Thouret (French, 1861-1926)
Plate XXXVIII
1927
from Reims after the war. The mutilated cathedral. The devastated city.
Private collection, London
Tate Modern
Bankside
London SE1 9TG
United Kingdom
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 6pm







































You must be logged in to post a comment.