Exhibition dates: 13th October 2023 – 4th February 2024
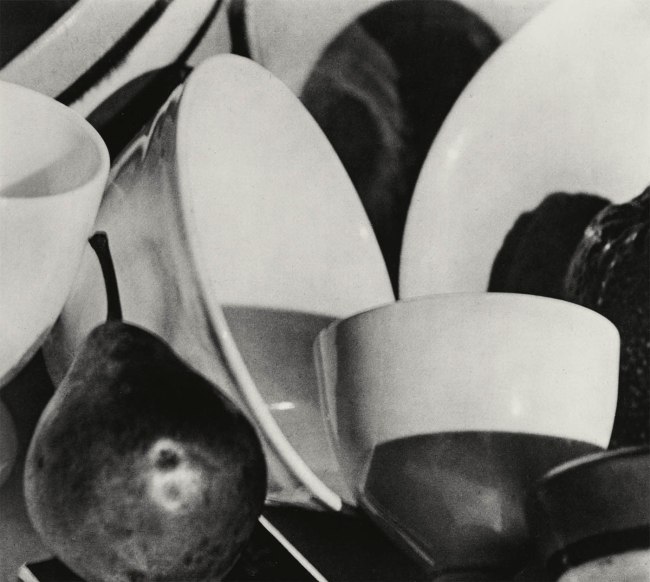
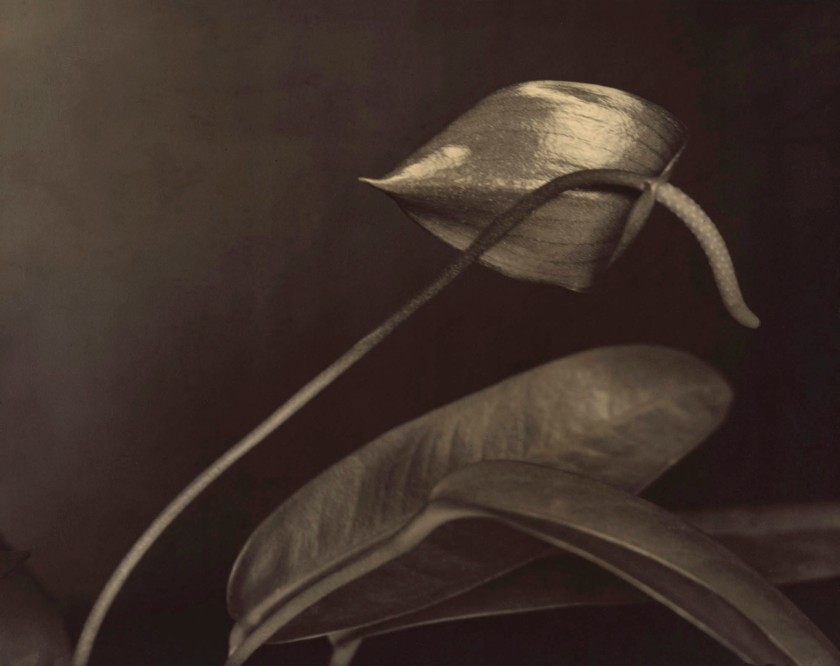
Paul Strand (American 1890-1976, France 1951-1976)
Still life, pear and bowls, Twin Lakes, Connecticut
1916, printed 1983
From the Paul Strand: The Formative Years 1914-1917 portfolio photogravure
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1984
Public domain
“I feel that photographs can either document or record reality or they can offer images as an alternative to everyday life: places for the viewer to dream in.”
Francesca Woodman, 1980
Smoke and mirrors, smoke and mirrors…
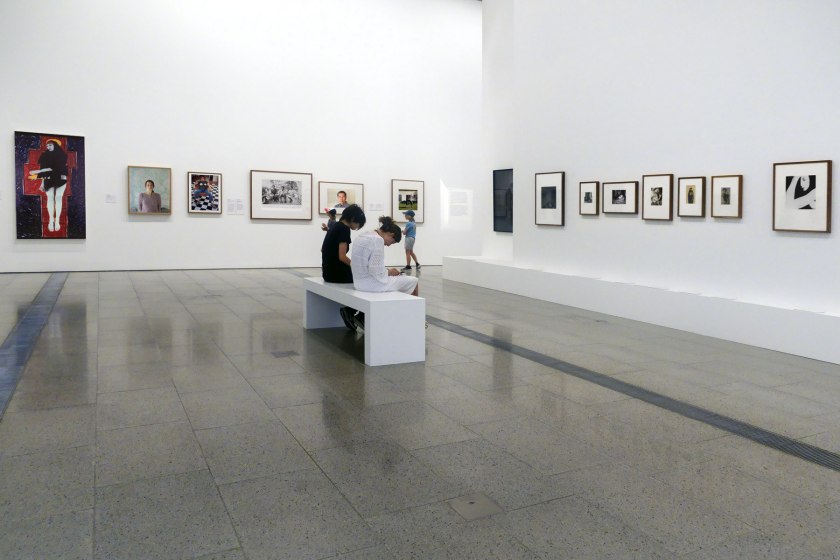
In many ways the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia can be seen as a summation of all that is good and bad with the photography collection and the photography exhibition program at the National Gallery of Victoria.
Since the sad and unfortunate demise of the small but important dedicated photography gallery, photography exhibitions at the NGV (other than the large Patrick Pound exhibition all those years ago in 2017) have been in a state of deep freeze. I MISS that little third floor gallery… it’s all we had for photography at the NGV on a regular basis and there were some interesting shows there. It’s been gone for years and photography has been lumped in with contemporary art. And then, and now, nothing for years.
Therefore, as a fellow photographic artist observed to me, “It was great to see the NGV finally give photography a large exhibition after so many years of neglect.” Never a truer word said.
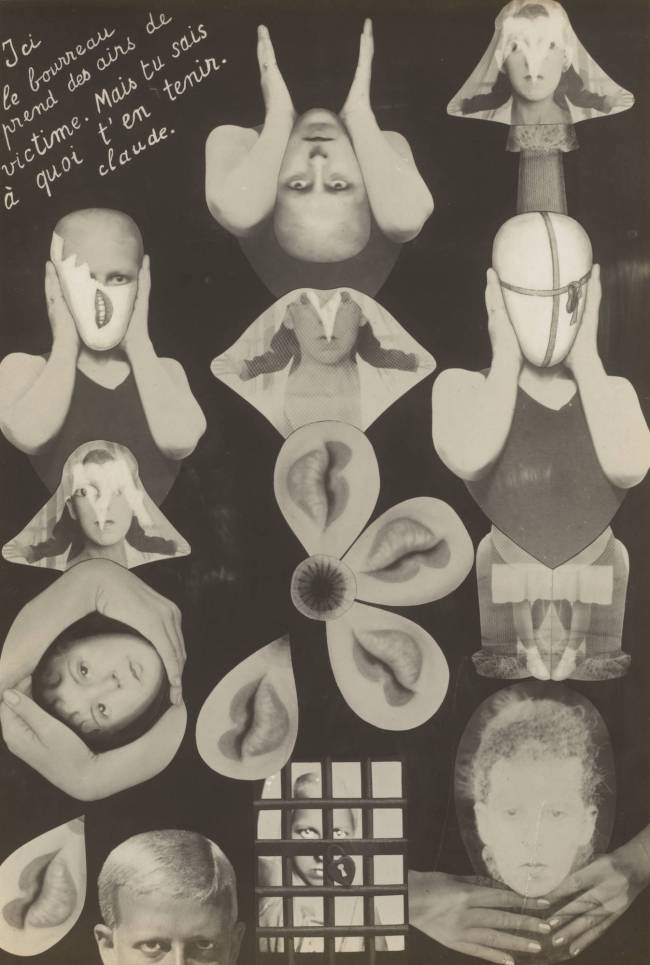
Let’s get the good stuff about the exhibition out of the way first. Whoever curated the exhibition (unknown, unnamed) really knew how to pull an installation of photographs together. There was some sophisticated sequencing of the images on the various themes from Australian and International artists, very intelligently and beautifully rendered which I enjoyed tremendously. I also enjoyed seeing the glorious display of photobooks: I was in heaven seeing in one display cabinet Man Ray’s book Photographs by Man Ray Paris 1920-1934 (published 1934), Claude Cahun and Marcel Moore’s book Aveux non Avenus (Disavowals or Cancelled Confessions) (published 1930), Bill Brandt’s book Perspective of Nudes (published 1961), and Germaine Krull’s book Nude studies (Études de nu) (published 1930). What a selection!
And it was finally great to see Australian and international work displayed together on such a large scale, something I can’t remember happening in the 35 years I have being viewing photography exhibitions in Australia. This is something that the NGV should have been promoting for many years, the placement of Australian photography in an international context… even taking this concept overseas, to promote Australian photography internationally. But no, nothing of this kind of forward thinking has ever happened in insular Australia.
Now to the not so good stuff. The most glaring anomaly about the exhibition was its over ambitious structure. While the concept ‘Real & Imagined’ was very strong – an exhibition of photographs picturing a version of reality captured by the camera (for it can never capture reality itself) / photographs created by the imagination of human beings – this robust concept was overwhelmed by too many thematic sections in the exhibition.
These sections included ‘Light’ and ‘Systems and Surface’ and ‘Surreal’ and ‘Narrative’ and ‘Work and Play’ and ‘Movement’ and ‘Studio and Things’ and ‘Display’ and ‘Consumption’ and ‘Self’ and ‘Skin’ and ‘Community and Touch’ and ‘Environment’ and ‘Place and Built’ and ‘Nineteenth-century photography’ and ‘Conflict’ and ‘Death’. I’m exhausted already…
And then, walking around the exhibition, the wall texts used to identify and illuminate these sections became totally irrelevant as through their placement on the wall I had no idea to which area they were referring. It was totally confusing and in the end I just ignored them.
As I observed people wandering around the exhibition, most had no idea of the importance of some of the images on display… why would they? They are not photography aficionados but the viewing public. If I found the exhibition confusing imagine how they viewed it. What the NGV should have done was have a guided tour on the hour, every hour, to talk about the seminal works in the exhibition and about how the exhibition had been structured. Imagine someone explaining the importance of the four photobooks in a display cabinet mentioned earlier in the history of photography and how by putting them together you were creating a sophisticated dialogue over time about identity and gender issues.
As the aforementioned colleague observed to me, “the exhibition felt like a data dump with a tacked on theme that strained (and failed) to resonate.” I wouldn’t go that far for the overall concept was strong and vibrant but like much of what has happened with the photography collection at the NGV, the overall outcome was confused and piecemeal.
This can no better be illustrated than through the comments of the Director of the NGV, Tony Ellwood, when he said in the press release, “This exhibition celebrates the collections and achievements of the NGV’s photography department, which has presented more than 180 exhibitions in its 55-year history. The exhibition is a testament to the strength of the NGV Collection, with so many key examples of the history of photography represented, from the earliest examples from the 19th century, through to contemporary images being produced right now in the twenty-first century.”
I note that when the head of the NGV boasts about the number of photography exhibitions over the last 55 years (180, about 3 a year mainly small exhibitions) and the “strength” of the NGV Photography Collection… you know that he is proselytising.
Most of the large photography exhibitions have been brought in from outside sources in the last 30 years and little research has been done into Australian photography and its relationship to world photography in house. And while the NGV collection has “strength” in certain areas it is woefully lacking in others. Again, the word “piecemeal” springs to mind, like Swiss cheese full of the biggest holes … and this exhibition only serves to reinforce that idea, often displaying the only photograph by an important artist that the collection holds. Smoke and mirrors, smoke and mirrors!
For example I picked a few photographic artists off the top of my head as I thought of them – and the NGV collection possesses some in reasonable depth:
Edward Steichen 23
Paul Strand 51
Brassai 17
André Kertesz 45
Eugène Atget 143
Frank Hurley 20
Max Dupain 94
Bill Brandt 44
Bill Henson 108
Lee Friedlander 31
David Goldblatt 15
Dorothea Lange 28
August Sander 16
Other important photographers the NGV have nothing or next to nothing at all:
Joseph Sudek 1
Stephen Shore 0
William Eggleston 0
Julia Margaret Cameron 3
Robert Mapplethorpe 1
Ansel Adams 4
Hiroshi Sugimoto 1
Daido Moriyama 0
Raja Deen Dayal 0
Aleksandr Rodchenko 1
Olive Cotton 9
Berenice Abbott 7
Diane Arbus 2
Roger Ballen 1
Bernd and Hiller Becher 1
Thomas Ruff 2
Manuel Álvarez Bravo 0
Edward Weston 6
Henri Cartier-Bresson 2
Robert Frank 11
Garry Winogrand 0
Nan Goldin 3
Gordon Parks 3
Lewis Hine 9
Peter Hujar 0
Imogen Cunningham 6
Not exactly an institution that has “strength” in their photography collection. And over the last 30 years seemingly nothing much has been done to plug these enormous holes in the collection…. instead, for example, buying one work by Jeff Wall for a million dollars.
The NGV needs to improve the photography collection and its photography exhibition program. After too many years of stagnation an injection of new ideas and a new direction for exhibition programming is needed. A couple of focused photography exhibitions per year would be a good start, as would the purchasing of historic photographs to fill huge gaps in the collection rather than the purchasing of contemporary work. Non-vintage prints of the masters can still be bought at affordable prices. And therein lies just one of the problems: money.
Investment in photography at the NGV in terms of people and money is much needed, otherwise the deep freeze and dance of smoke and mirrors will continue well into the future.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
For more information on the early collecting practices for the NGV photography collection please see my research paper Beginnings: The International Photographic Collection at the National Gallery of Victoria (2105)
Many thankx to the NGV for allowing me to publish the media images in the posting. All other installation images are by Marcus Bunyan.
Photography: Real and Imagined examines two perspectives on photography; photography grounded in the real world, as a record, a document, a reflection of the world around us; and photography as the product of imagination, storytelling and illusion. On occasion, photography operates in both realms of the real and the imagined.
Highlighting major photographic works from the NGV Collection, including recent acquisitions on display for the very first time, Photography: Real and Imagined examines the complex, engaging and sometimes contradictory nature, of all things photographic. The NGV’s largest survey of the photography collection, the exhibition includes more than 300 works by Australian and international photographers and artists working with photo-media from the nineteenth, twentieth and twenty-first centuries.
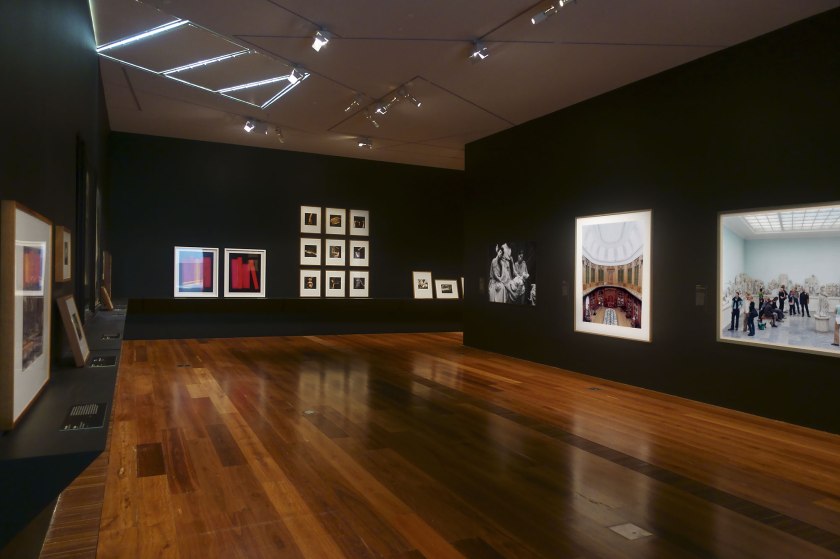
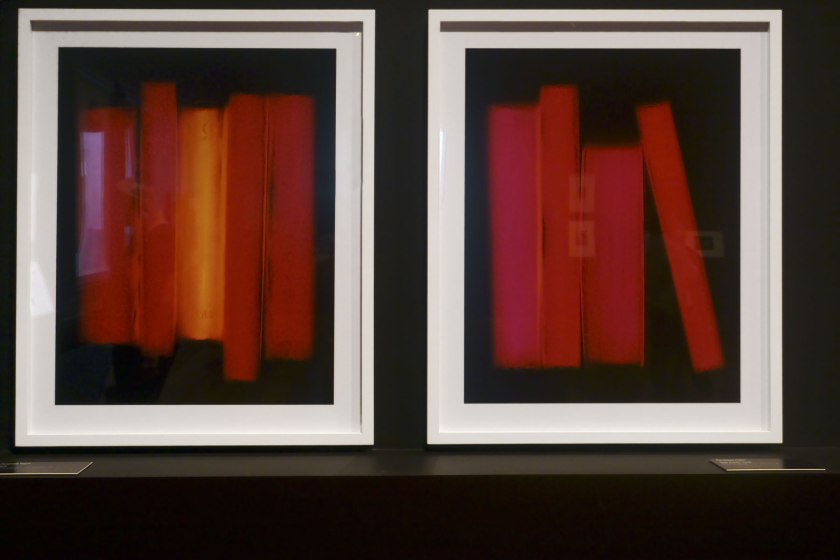
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at rear left, Penelope Davis’ Shelf (2008) and Non-fiction (red) (2008, below); at third right, Anne Ferran’s Scenes on the death of nature, III (1986); at second right, Candida Höfer’s Teylers Museum Haarlem II (2003, below); and at right, Thomas Struth’s Pergamon Museum IV, Berlin (2001)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Penelope Davis’ Shelf (2008) and Non-fiction (red) (2008) from the Fiction-Non-Fiction series 2007-2008
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
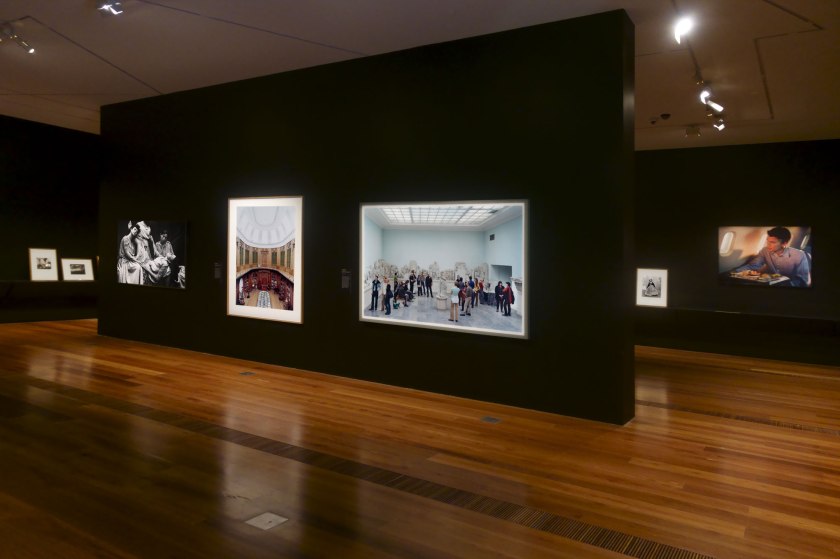
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at middle left, Anne Ferran’s Scenes on the death of nature, III (1986); at centre, Candida Höfer’s Teylers Museum Haarlem II (2003, below); and at middle right, Thomas Struth’s Pergamon Museum IV, Berlin (2001)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The luminous photograph by Thomas Struth shows museum visitors immersed in observing the Telephos frieze within a room of the Pergamon Museum in Berlin. Struth draws our attention to the fact that viewing a work of art in a public gallery is rarely a private experience. The visit is usually shared by other visitors, museum staff, security guards and tour guides. There is also the omnipresent gaze of security cameras. Struth seems to be emulating the technical innovations of the Telephos frieze in his arrangement of the viewers. Similarities between the poses of the audience members and the poses of the carved relief figures gradually emerge, suggesting an unconscious dialogue between the viewers and the objects they regard.
Wall text from the exhibition
Candida Höfer (German, b. 1944)
Teylers Museum Haarlem II
2003
Type C photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 2004
This photograph shows the famous Oval Room within Teylers Museum, the oldest public museum in the Netherlands. Candida Höfer photographed the space bathed in a brilliant, even light that illuminates its architecture, objects and famed mineralogical cabinet. The highly structured museological ordering of the objects and the Neoclassical architecture that contains them are exaggerated by the formal, symmetrical composition of the photograph. This image invites reflection of the ways in which cultural institutions direct our engagement with materials. As the artist has said, ‘There are no people there, but you understand that the places were made specially for them. This is very meaningful for me, and it’s exactly what I want to express’.
Wall text from the exhibition
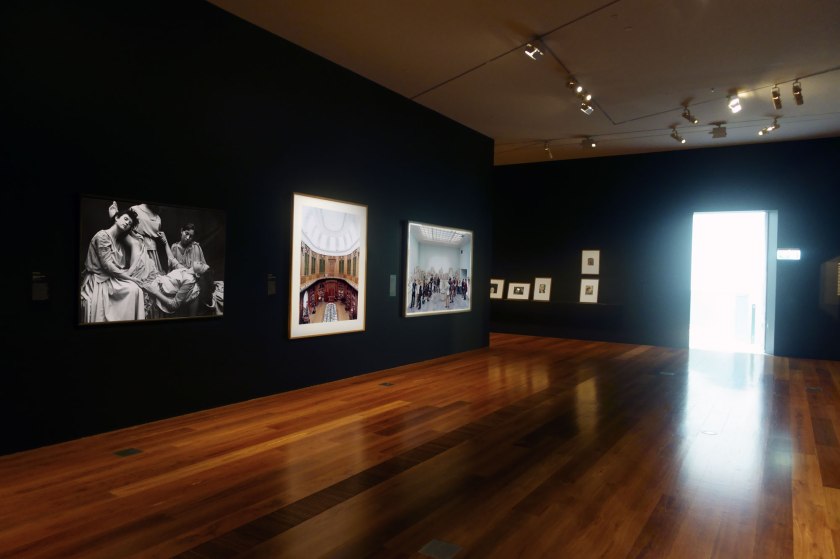
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left, Anne Ferran’s Scenes on the death of nature, III (1986); at centre, Candida Höfer’s Teylers Museum Haarlem II (2003, above); and at right, Thomas Struth’s Pergamon Museum IV, Berlin (2001).
In the distance can be seen Lotte Jacobi’s Head of a dancer (1929, below); Man Ray’s Head of a dancer (1929, below); and Lee Miller’s Nimet Eloui Bey (c. 1930, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Lotte Jacobi (German 1896-1990, United States 1935-1990)
Head of a dancer
1929, printed c. 1970
Gelatin silver photograph
26.4 × 33.2cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2021
Public domain
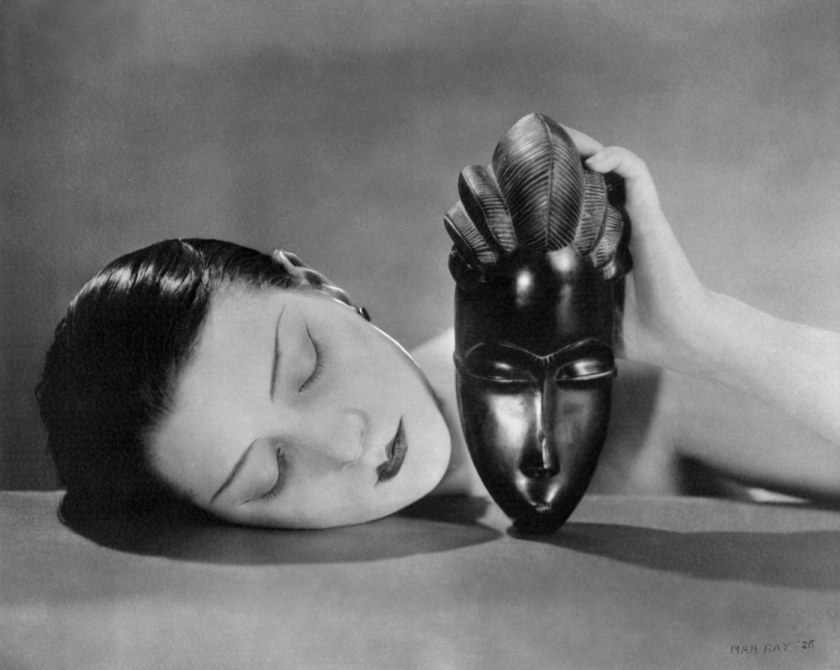
Man Ray (Emmanuel Radnitzky) (American, 1890-1976)
Kiki with African mask
1926
Gelatin silver photograph
21.1 x 27.6cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of Miss Flora MacDonald Anderson and Mrs Ethel Elizabeth Ogilvy Lumsden, Founder Benefactors, 1983
Public domain
Kiki with African mask is one of Man Ray’s most celebrated photographs and an iconic image of the Art Deco period. First published in Vogue in 1926, it is an elegant image, but it also speaks to the impact of European colonialism in Africa. In this pared-back studio photograph all extraneous detail is excluded from the image, focusing our attention on the exquisitely made-up face of Kiki in juxtaposition with the perfectly polished ebony of the mask. This photograph invites us to delight in the physical beauty of Man Ray’s celebrated model but offers nothing about the mask or its maker.
Wall text from the exhibition
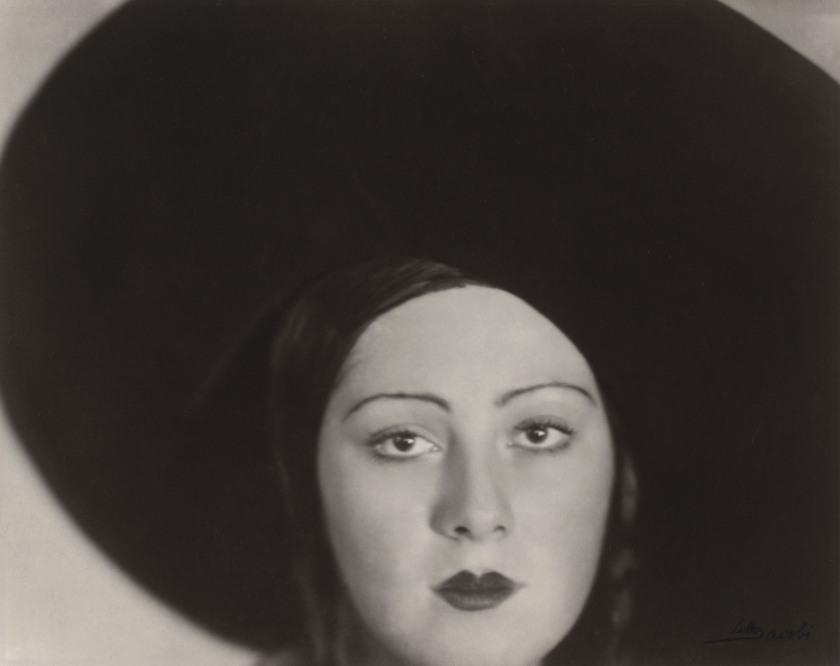
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Lee Miller’s Nimet Eloui Bey (c. 1930)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
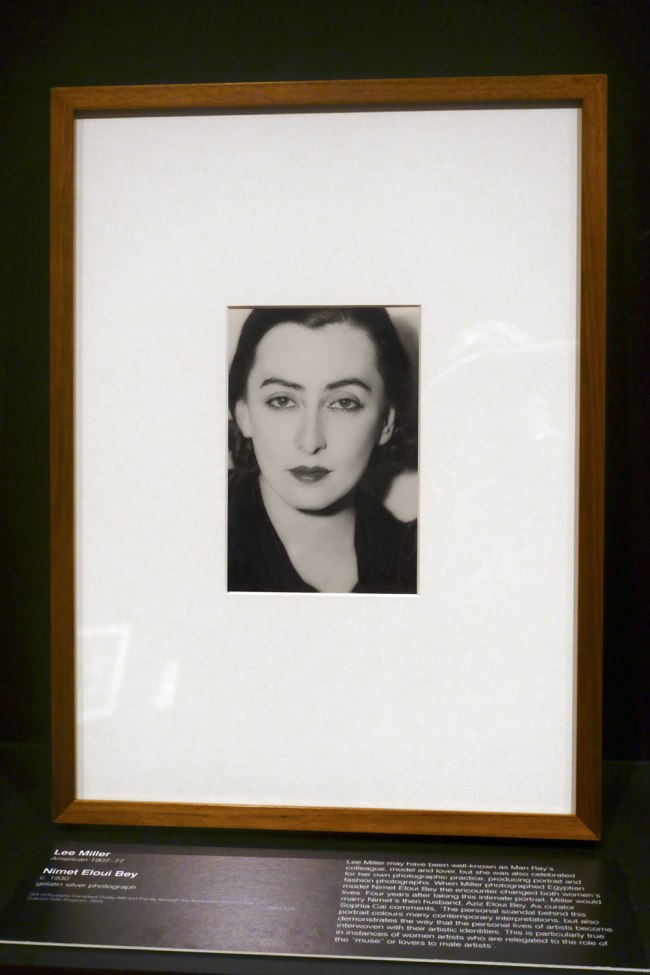
Lee Miller (American 1907-1977)
Nimet Eloui Bey (installation view)
c. 1930
Gelatin silver photograph
23.0 × 15.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of Krystyna Campbell-Pretty AM and Family through the Australian Government’s Cultural Gifts Program, 2022
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Lee Miller may have been well-known as Man Ray’s colleague, model and lover, but she was also celebrated for her own photographic practice, producing portrait and fashion photographs. When Miller photographed Egyptian model Nimet Eloui Bey the encounter changed both women’s lives. Four years after taking this intimate portrait, Miller would marry Nimet’s then husband, Aziz Eloui Bey. As curator Sophia Cai comments, ‘The personal scandal behind this portrait colours many contemporary interpretations, but also demonstrates the way that the personal lives of artists become interwoven with their artistic identities. This is particularly true in instances of women artists who are relegated to the role of the “muse” or lovers to male artists’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at centre, Fiona Pardington’s Portrait of a life-cast of Koe, Timor (2010) and Portrait of a life cast of Matoua Tawai, Aotearoa New Zealand (2010); and at right, Linda Judge’s Victoria and Albert Museum 20/4/94 (1994, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Fiona Pardington’s photograph shows a life cast of the tattooed head of a Māori man, Matoua Tawai. The cast, held in a museum collection, is one of many made by Pierre- Marie Alexandre Dumoutier of Māori peoples in the 1830s. Pardington, who is of Māori and Scottish descent, has spoken of her desire to reconsider the complex history of these life casts and find a state of continuum between the past and present, to, as she says, ‘find the faces of the living people presenting and manifesting in the object’. Printing the photograph at larger-than-life scale provokes a physical encounter, an opportunity to look again and reconsider the histories of the person, the object and the image.
Wall text from the exhibition
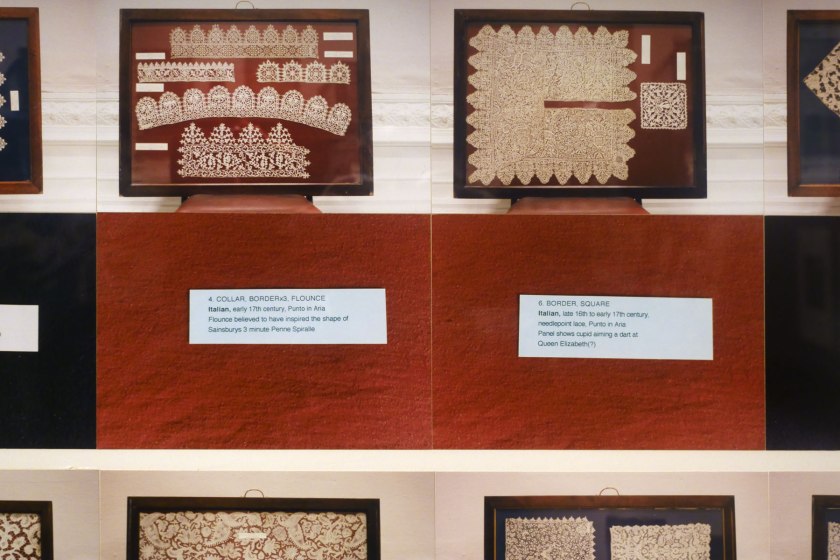
Linda Judge (Australian, b. 1964)
Victoria and Albert Museum 20/4/94 (detail)
1994
Type C photographs
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Margaret Stewart Endowment, 1994
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
In this image, Linda Judge wittily creates new narratives and resurrects otherwise ‘mummified’ museum objects. Concerned with the open-ended nature of archives and their ability to slip between fiction and reality, Judge presents photographs of historical lace from the collection of the Victoria and Albert Museum, London. Beneath each photograph, Judge has provided a range of both ‘plausible’ captions (’12. collar, cuff, border: Italian, late 17th century, Tape lace with needlepoint fillings and brides’) and fanciful ones (’51. veil: Brussels, end 18th century, needlepoint on bobbin ground. Worn by Madonna, for Like a Virgin in her Brussels tour ’91’). Judge humorously invites the viewer to interrogate the expectations of truth in the presentation of archival content.
Wall text from the exhibition
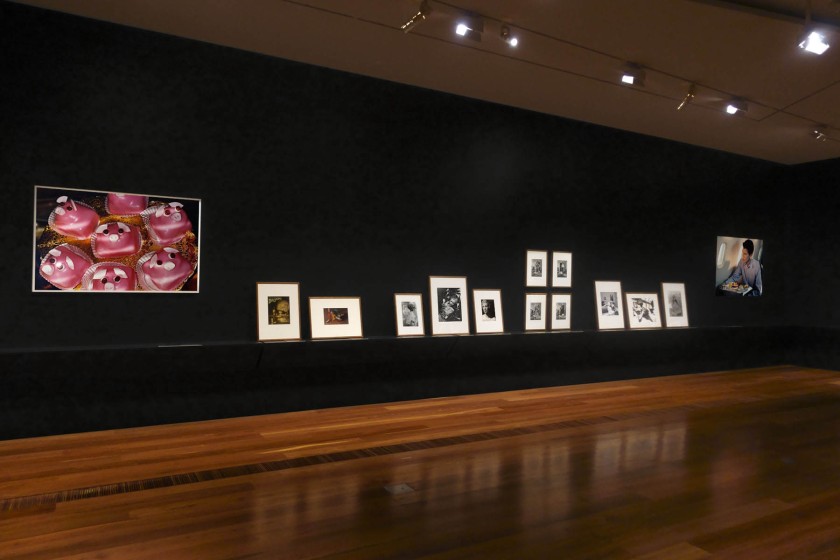
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left, Martin Parr’s Pink pig cakes from Common Sense (1995-1999); at fourth left, ringl+pit’s Komol (1931, below); at fifth left, Ilse Bing’s Salut de Schiaparelli (1934, below); and at sixth left, Dora Maar’s Untitled (Study of Beauty) (1936, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
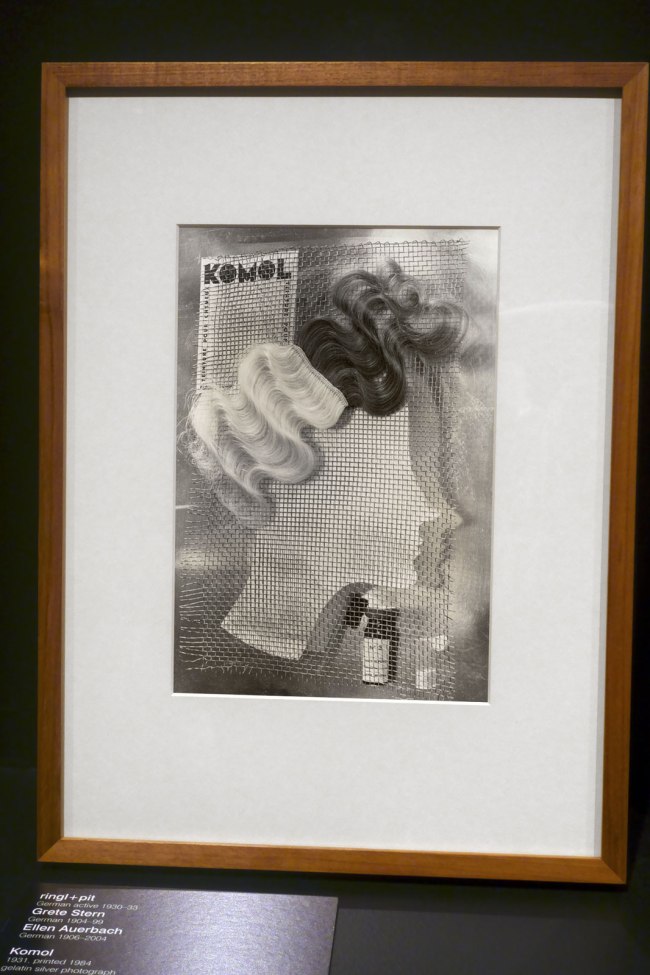
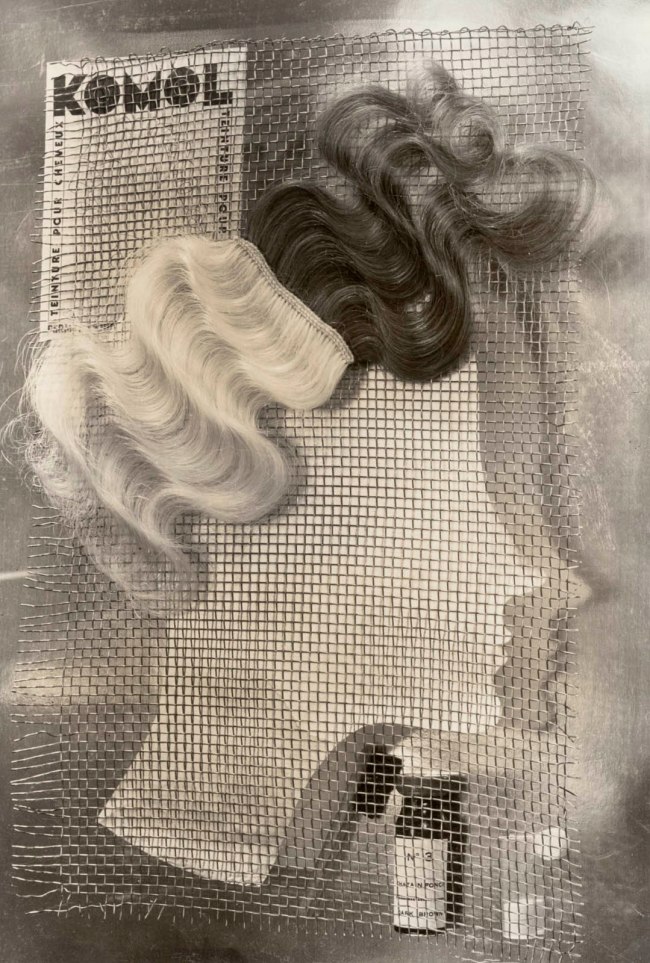
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing ringl+pit’s Komol (1931, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
ringl+pit (German active 1930-1933)
Grete Stern (German, 1904-1999)
Ellen Auerbach (German 1906-2004)
Komol
1931, printed 1984
Gelatin silver photograph
34.4 × 23.3cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2022
© ringl+pit
Dora Maar (French 1907-1997)
Untitled (Study of Beauty)
1936
Gelatin silver photograph
33.0 x 24.1cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2021
© Dora Maar. Licensed by Copyright Agency, Australia
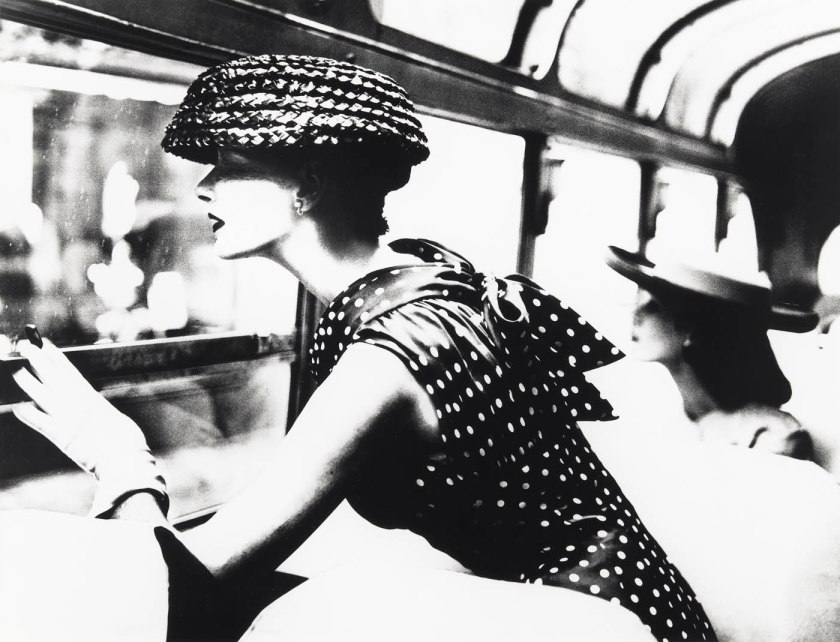
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left, Martin Parr’s Pink Pig Cakes, Bristol, UK (1995); at third right, Lillian Bassman’s More fashion mileage per dress, Barbara Vaughn, Harper’s Bazaar, New York (1956); at second right, and at right, Darren Sylvester’s On Holiday (2010)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Darren Sylvester builds and photographs hyperreal tableaux using the visual language of advertising – beautiful models, perfect lighting and considered ‘product’ placement – to construct a familiar yet illusionary reality. Here Sylvester’s model plays the role of a handsome businessman. ‘Against a sunrise, a business traveller gazes at an unknown destination’, Sylvester once wrote of this image. ‘The composition plays on stereotypes of luxury aspirations and aeroplane advertisements. For example, no-one ever flies into darkness or storms in an ad.’ In this lush, seductive photograph, Sylvester explores the slippery space between reality and illusion, aspiration and irrelevance, as we move on to the next shiny thing.
Wall text from the exhibition
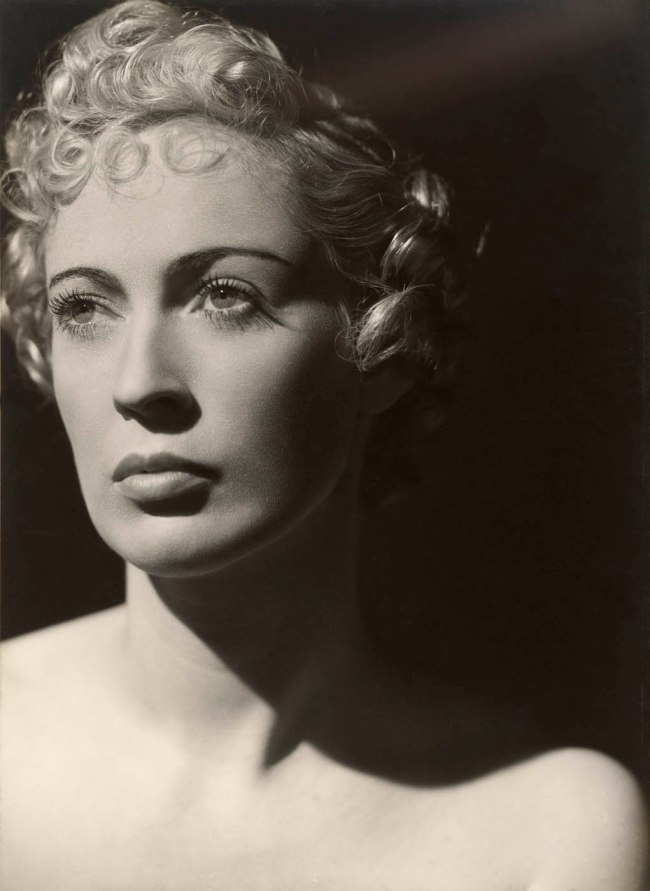
Lillian Bassman (American, 1917-2012)
More fashion mileage per dress, Barbara Vaughn, Harper’s Bazaar, New York
1956, printed later
Gelatin silver photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of Krystyna Campbell-Pretty AM and Family through the Australian Government’s Cultural Gifts Program, 2023
In the late 1930s, Lillian Bassman studied fashion illustration and textile design at the Pratt Institute, New York. In 1940 she began working with Alexey Brodovitch, art director of Harper’s Bazaar magazine, which soon led to her appointment as art director of the subsidiary publication Junior Bazaar. In this capacity she worked with photographers, including Richard Avedon and Robert Frank, and in 1947 began working as a freelance fashion and advertising photographer. In an interview later in her life Bassman played down her directorial role as photographer, stating, ‘It is part of the nature of a woman to be unconsciously graceful … I try to record that natural grace with a camera’.
Wall text from the exhibition
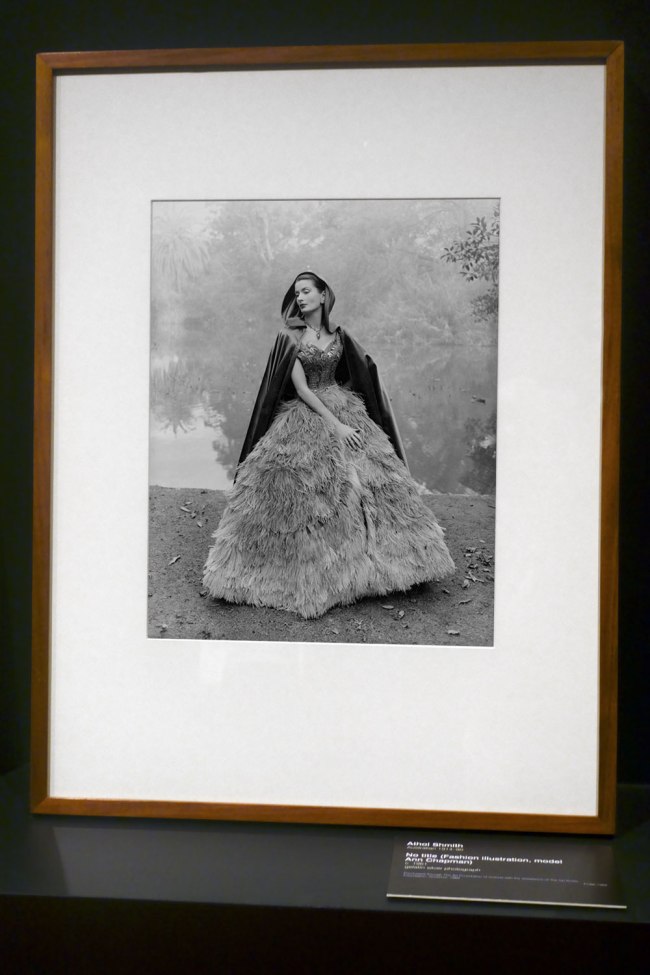
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Athol Shmith’s Fashion illustration, model Ann Chapman (c. 1961)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
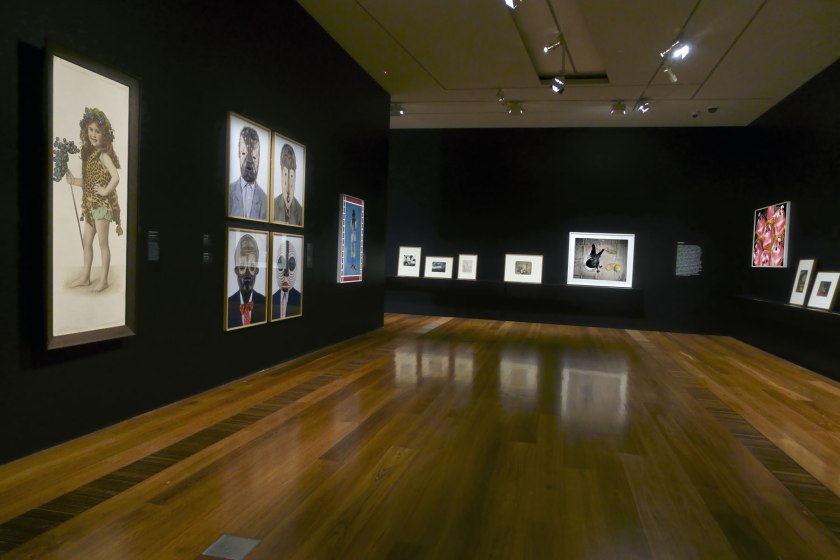
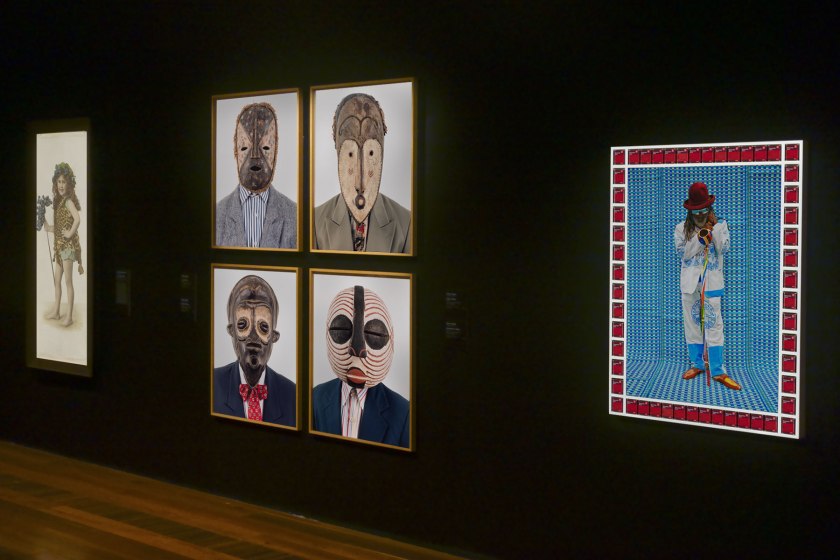
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left, Alice Mills’ Joan Margaret Syme (c. 1918, below); at second left, works by Edson Chagas from his Tipo Passe series (2014); and at third left, Hassan Hajjaj’s Master Cobra Mansa (2013, below) with at right, Martin Parr’s Pink Pig Cakes, Bristol, UK (1995)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
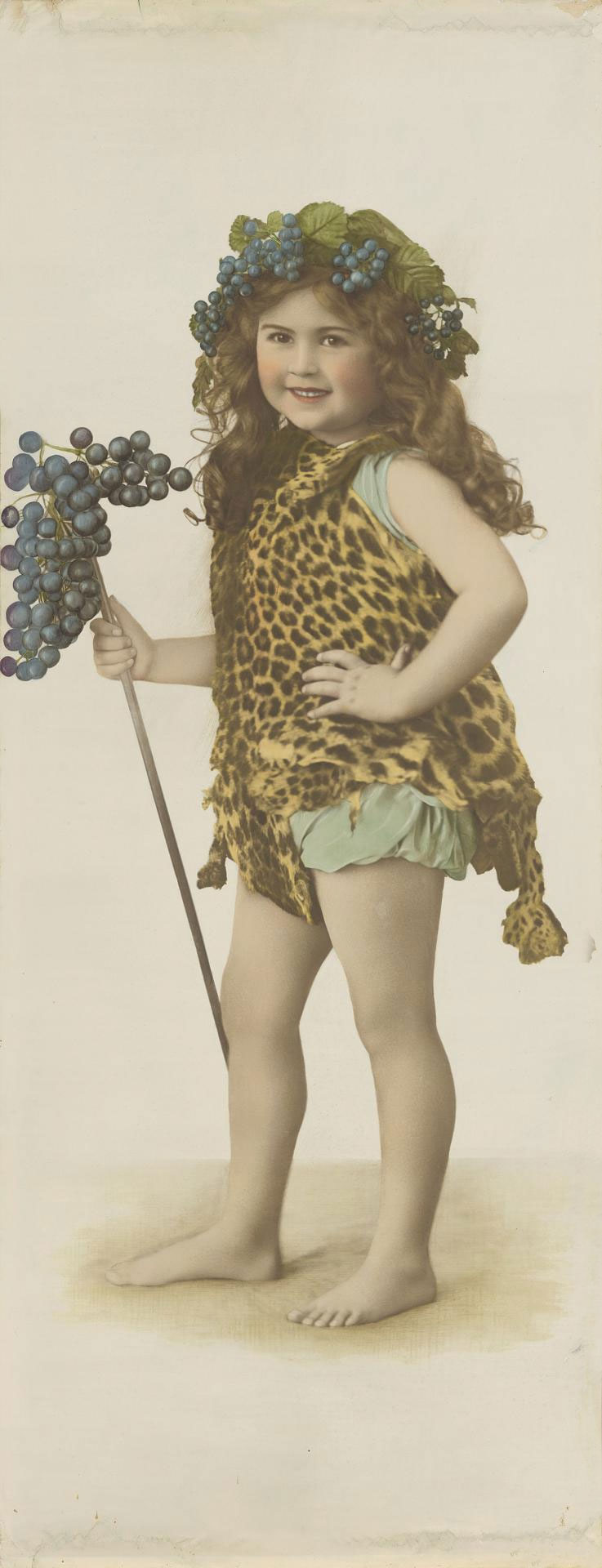
Alice Mills (attributed to) (Australian, 1870-1929)
Joan Margaret Syme
c. 1918
Gelatin silver photograph, coloured dyes
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented through the NGV Foundation by Michael Hayne, 2005
Public domain
Alice Mills set up her first studio in Melbourne in 1900. She was highly regarded as a portrait photographer and in 1907 was invited to exhibit in the Australian Exhibition of Women’s Work. Her portrait of five-year-old Joan Margaret Syme dressed in a leopard-skin robe is an outstanding example of studio portraiture. It shows the skilled application of hand colouring, which was used to transform black-and-white photographs in the era before colour photography, bringing a life-like quality to the portrait. At almost two metres high, this is no only a charming study of a young child, but one of the largest photographs from the early twentieth century in the NGV Collection.
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left Alice Mills’ Joan Margaret Syme (c. 1918, above); at centre, works by Edson Chagas from his Tipo Passe series (2014); and at right, Hassan Hajjaj’s Master Cobra Mansa (2013, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
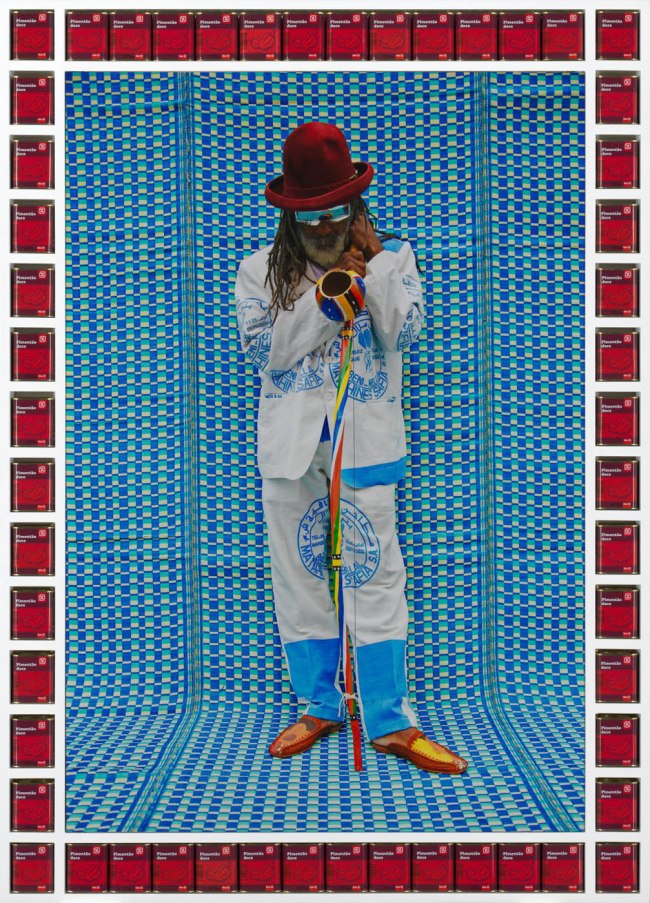
Hassan Hajjaj (Moroccan, b. 1961)
Master Cobra Mansa
2013
Metallic inkjet print, timber frame, cans
76.2 x 111.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Orloff Family Charitable Trust, 2019
© Hassan Hajjaj
Multidisciplinary artist Hassan Hajjaj’s portraits show London’s Moroccan diaspora; as a designer he also creates stylish street fashion and playful interiors that are a contemporary take on Moroccan tea houses and riads. Hajjaj came to professional photography by happenstance, taking pictures both for fun and as a tool while working as a stylist on music videos. It soon became a cornerstone of his creative practice. From the outset Hajjaj wanted his photography to show ‘another side of Moroccan culture’, something that, as he says, was not ‘camels, dates and drinking mint tea!’
Wall text from the exhibition
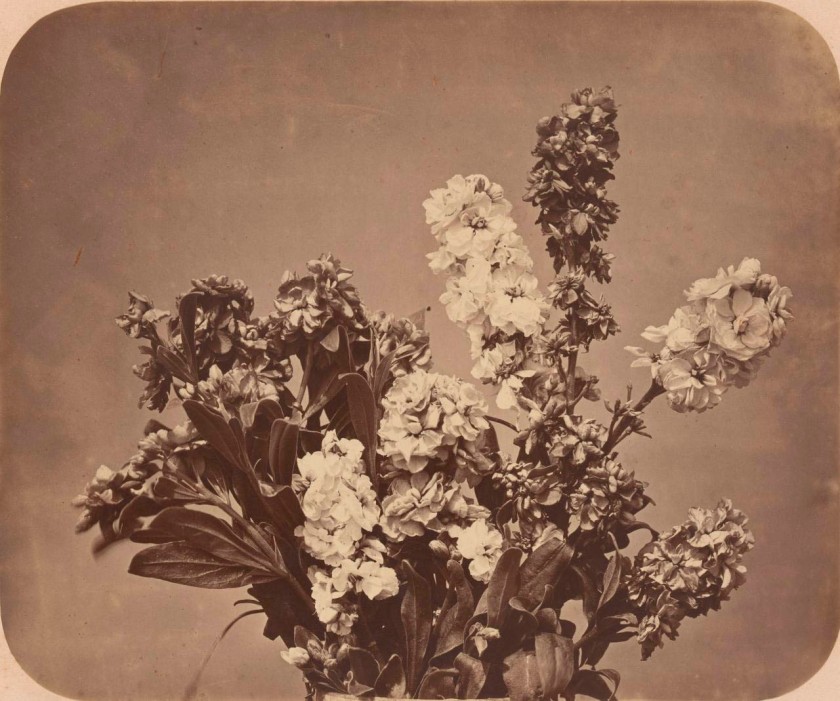
Adolphe Braun (French 1811-1877)
No title (Flower study)
c. 1854
Albumen silver photograph
31.0 × 37.3cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased NGV Foundation, 2017
Public domain
Adolphe Braun arrived in Paris in 1828 to study drafting and decorative design and within six years had established a textile design studio. Around 1853 he began to make photographs using the recently invented collodion process. The following year Braun commenced a project to photograph an extensive series of flower studies with the intent of providing documentary source material for artists and designers. He produced 300 of these photographs and in 1854 published his images in a six-volume series titled Fleurs photographiés. When they were exhibited in the 1855 Universal Exhibition in Paris, Braun was awarded a gold medal for his work’s usefulness to the fabric and decorating industries.
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left Julie Rrap’s Persona and shadow: Madonna (1984, below)
Julie Rrap (Australian, b. 1950)
Persona and shadow: Madonna
1984
Cibachrome photograph
194.7 × 104.6cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Michell Endowment, 1984
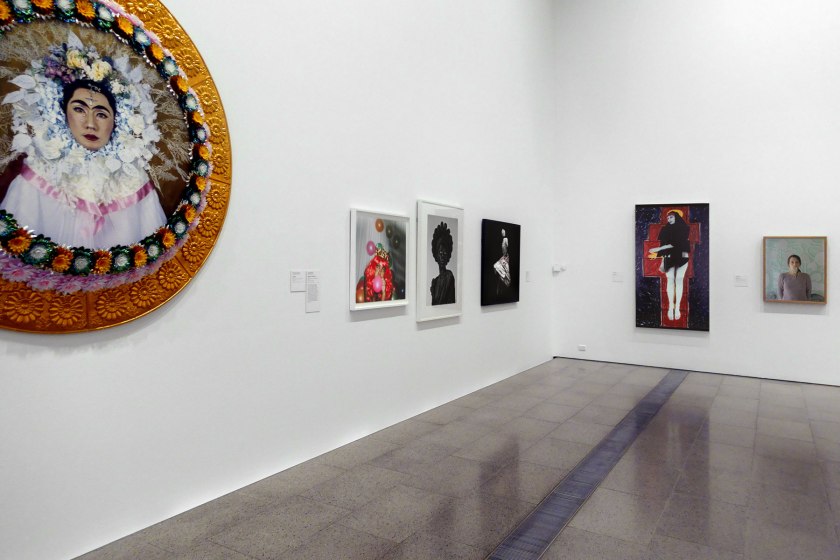
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Yasumasa Morimura’s An inner dialogue with Frida Kahlo (Flower wreath and tears) (2001, below); Phumzile Khanyile’s Untitled (2016); Zanele Muholi’s Ntozkhe II (Parktown) (2016, below); Ayana V. Jackson’s How sweet the song (2017); Julie Rrap’s Madonna (1984, above); and Siri Hayes Spilling pearls (2012)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
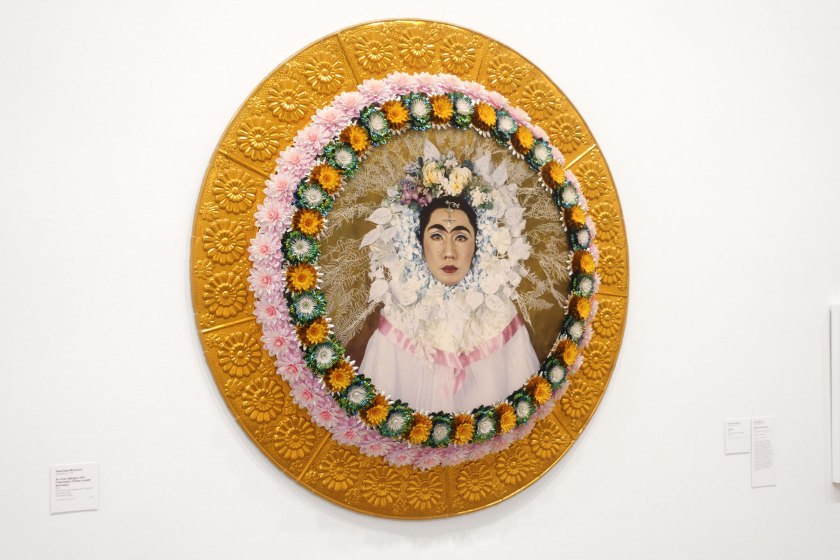
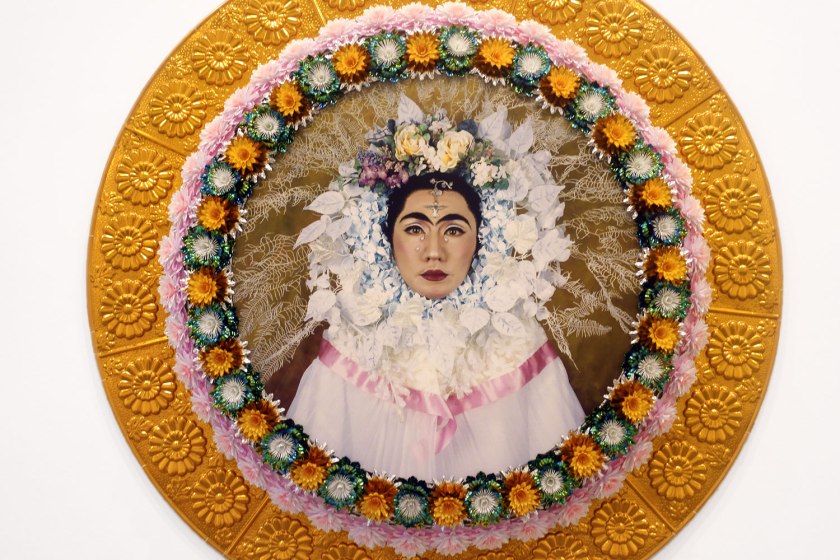
Yasumasa Morimura (Japanese, b. 1951)
An inner dialogue with Frida Kahlo (Flower wreath and tears) (installation views)
2001
From the An Inner Dialogue with Frida Kahlo series 1991-2001
Photograph, plastic
213.4cm diameter
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased NGV Foundation, 2022
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
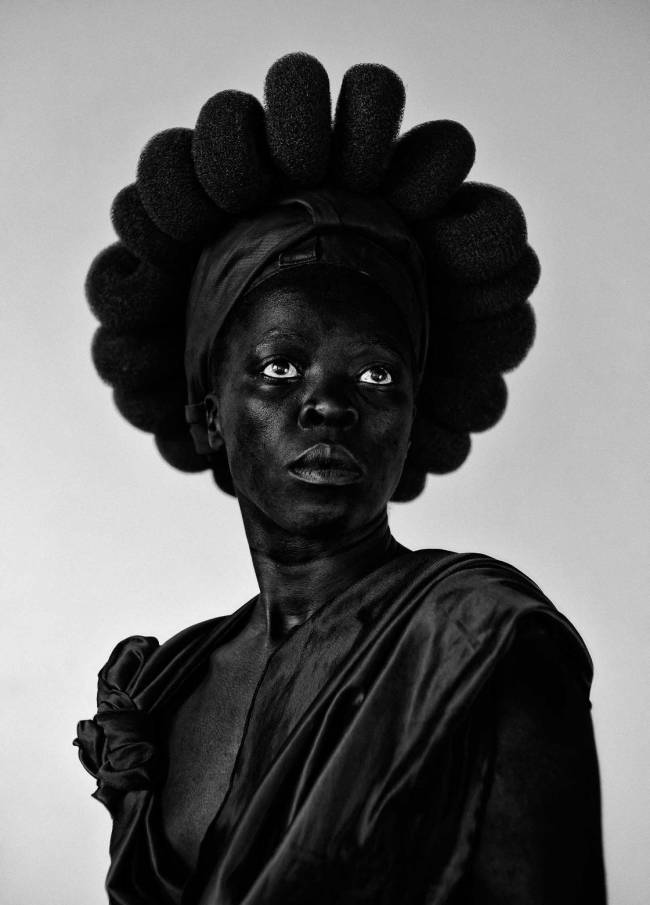
Zanele Muholi (South African, b. 1972)
Ntozkhe II (Parktown)
2016
From the Somnyama Ngonyama series 2015-2016
Gelatin silver photograph
99.0 x 74.0cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2017
© Zanele Muholi. Courtesy of the artist and Yancey Richardson, New York
Using found props – in this instance a ‘crown’ of scouring pads – Zanele Muholi has photographed themself to confront racial stereotypes and examine concepts of self-representation while honouring generations of women who have worked domestically. Discussing this work the artist wrote, ‘In some ways, yes: Ntozakhe is based on the Statue of Liberty, representing the idea of freedom – the freedom all women should have – as well as pride: pride in who we are as black, female-bodied beings. But what kind of freedom are we talking about? What is the colour of the Statue of Liberty? What race is the figure monumentalised as Lady Liberty?’
Wall text from the exhibition
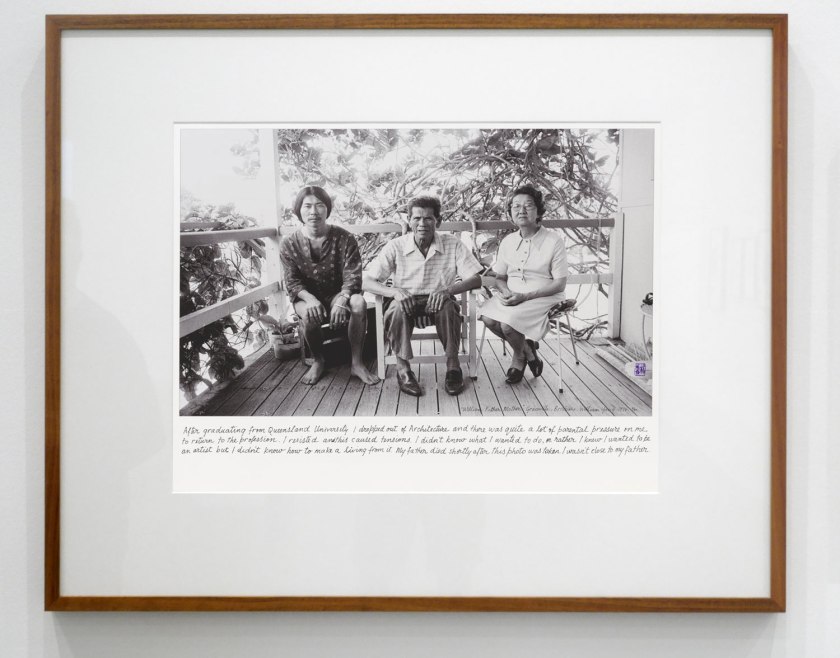
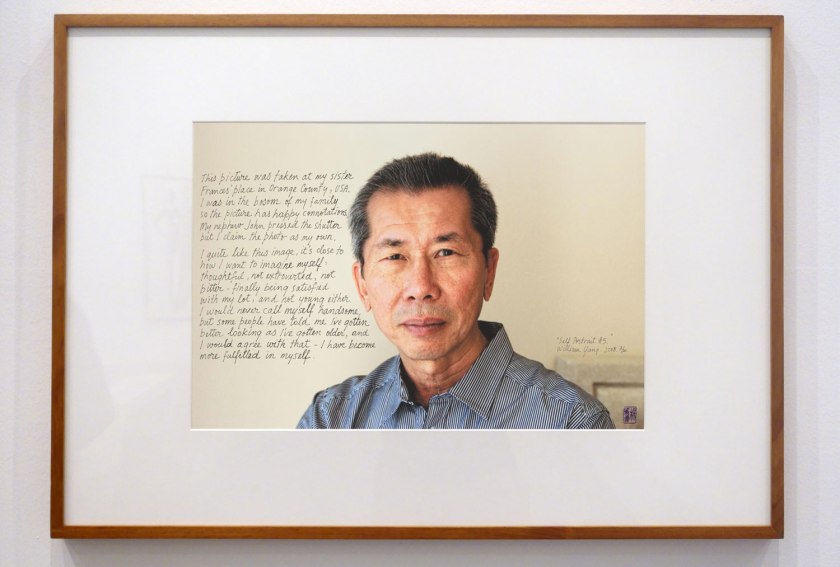
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left, Julie Rrap’s Madonna (1984, above); at second left, Siri Hayes’ Spilling pearls (2012); at third left, Sarah Lucas’ Self-portrait with fried eggs (1999); at fourth left, William Yang’s William, Father, Mother, Graceville, Brisbane (1974, below) and then his Self Portrait #5 (2008, below)
William Yang (Australian, b. 1943)
William, Father, Mother, Graceville, Brisbane (installation view)
1974, printed 2014
Inkjet print
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2014
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
William Yang’s autobiographical photographs combine photographs and handwritten text to tell the stories of Yang’s family, his childhood, and his experiences of being Chinese in an Australia that was not always welcoming to him. In one of these photographs Yang points to the difficulties he faced as a young man torn between his parents’ aspirations for him and his own wish for a different life. In the other, he describes himself as more content, at ease with himself and the choices he has made in his life. Together they form part of a powerful account of his life and sense of self.
Wall text from the exhibition
William Yang (Australian, b. 1943)
Self Portrait #5 (installation view)
2008; printed 2014
From the Self Portrait series
Inkjet print
43 × 65cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2014
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
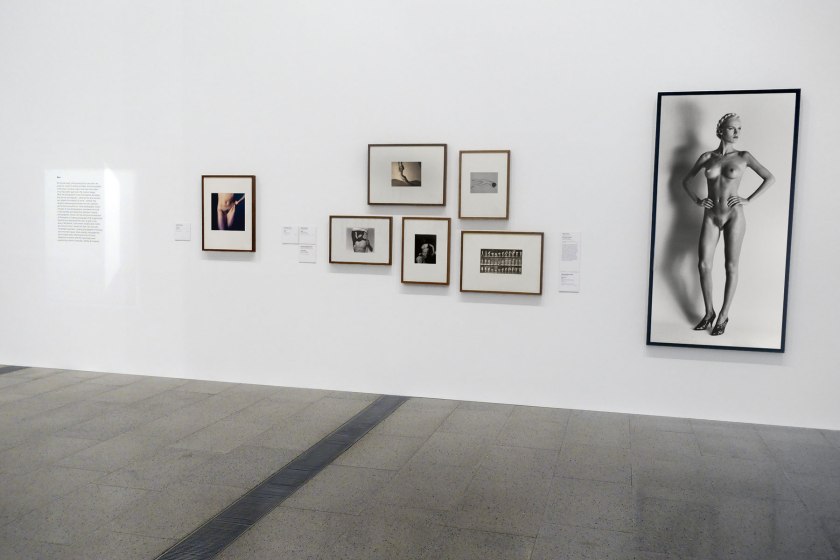
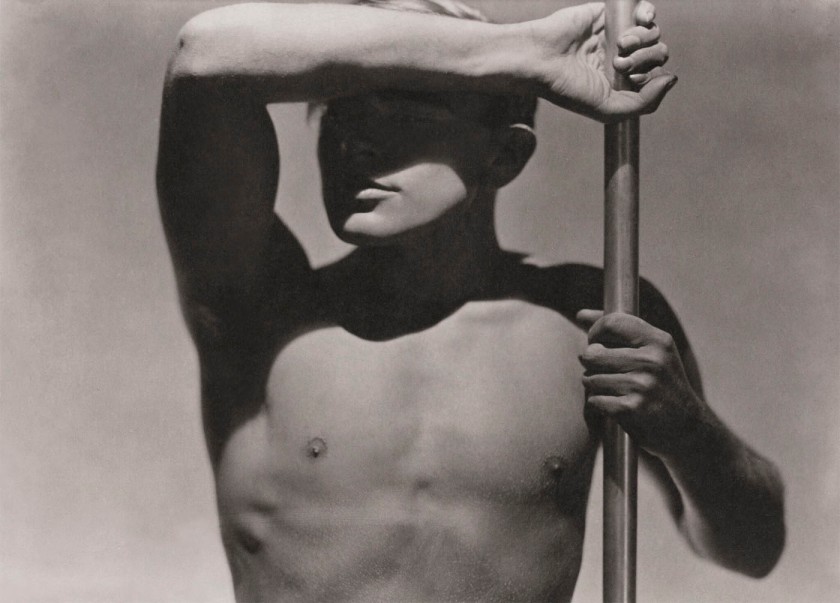
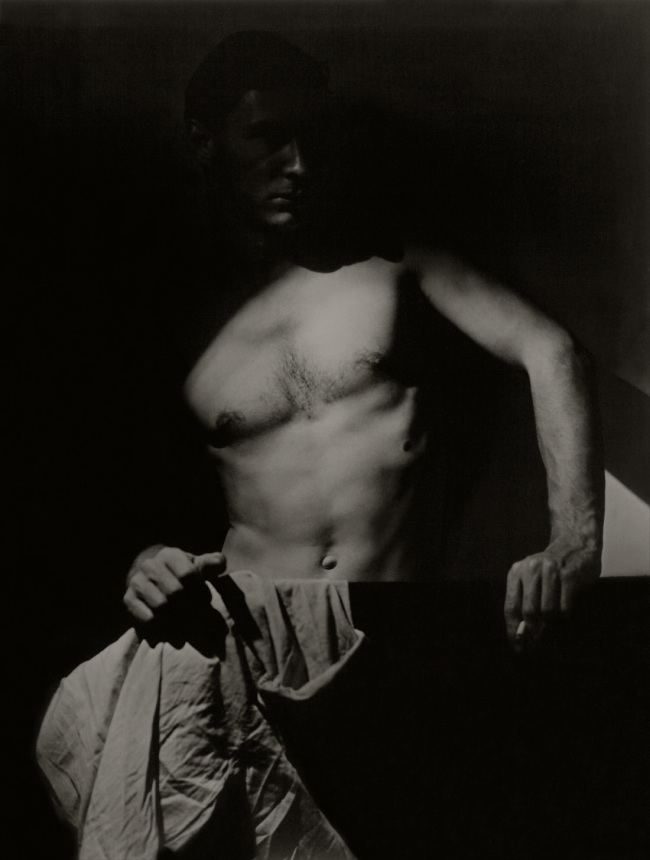
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Virginie Grange’s Untitled (1990); George Hoyningen-Huene’s Horst torso (1931, below); František Drtikol’s Nude (1927-1929); Olive Cotton’s Max after surfing (1937, below); Edward Weston’s Nude (1936, below); Eadweard Muybridge’s Plate 227 from Animal Locomotion series 1887; and Helmut Newton’s Big nude I (1980)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
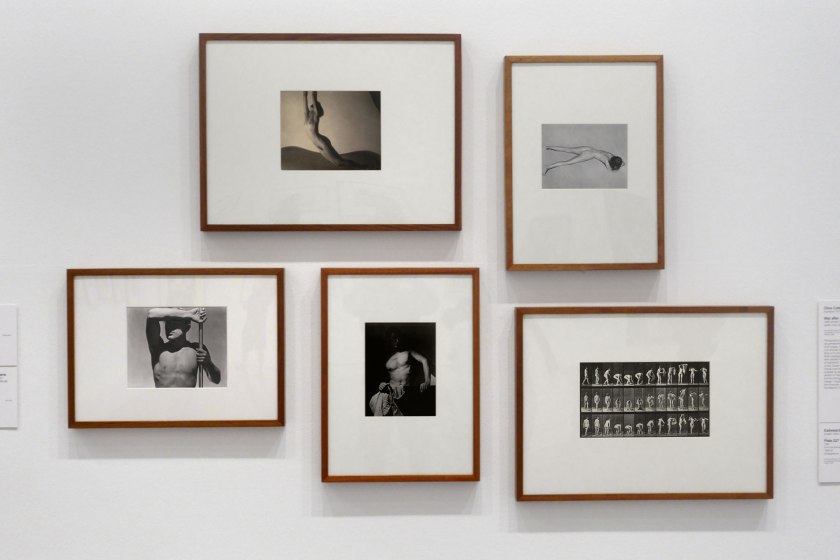
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, George Hoyningen-Huene’s Horst torso (1931, below); František Drtikol’s Nude (1927-1929); Olive Cotton’s Max after surfing (1937, below); Edward Weston’s Nude (1936, below); Eadweard Muybridge’s Plate 227 from Animal Locomotion series 1887
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The František Drtikol was the first fine art photograph to enter the National Gallery of Victoria collection.
George Hoyningen-Huene (Russian 1900-1968, England 1917-1921, France 1921-1935, United States 1935-1968)
Horst torso
1931, printed 1980s
Gelatin silver photograph
23.1 × 27.9cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2017
Edward Weston (American 1886-1958)
Nude
1936, printed 1976
Gelatin silver photograph
17.8 × 23.8cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased from Agfa and B. H. P. donation, 1977
Public domain
Olive Cotton (Australian, 1911-2003)
Max after surfing
1937, printed 1998
Gelatin silver photograph
26.0 × 19.7cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of Optus Communications Pty Limited, Member, 1998
Photographs of lovers, family and friends are perhaps the most emotionally charged of all images, not because the subject is monumental or dramatic, but because they allow us to see into intimate relationships. When photographs show subjects nude, or even partially naked, the sense of familiarity is heightened. Olive Cotton’s photograph of Max Dupain is an image that reveals intimacy and tenderness. His body is sculpted by raking side lighting and the allusion to Classical sculpture is apparent, but this photograph also carries an erotic charge – Dupain is shown as being tanned and muscular, movie-star handsome and the object of Cotton’s desire.
Wall text from the exhibition
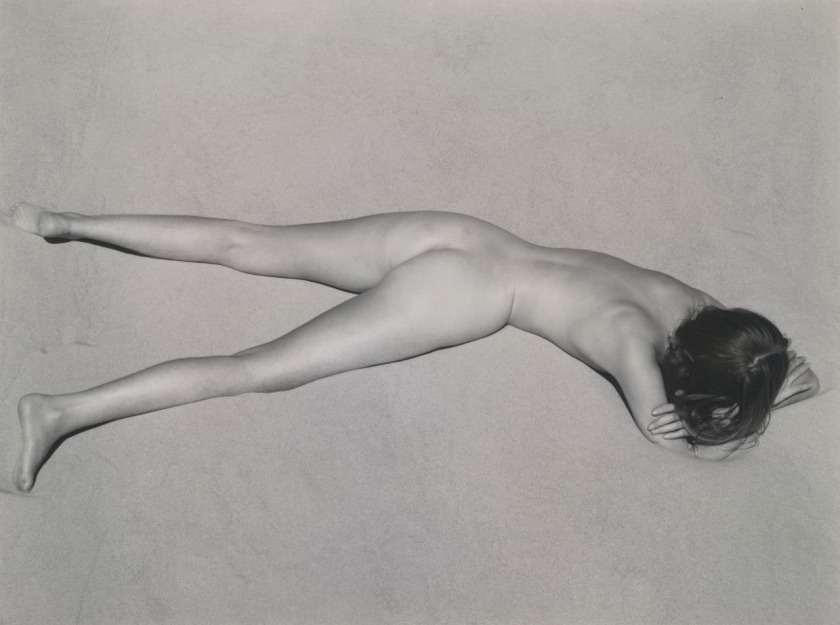
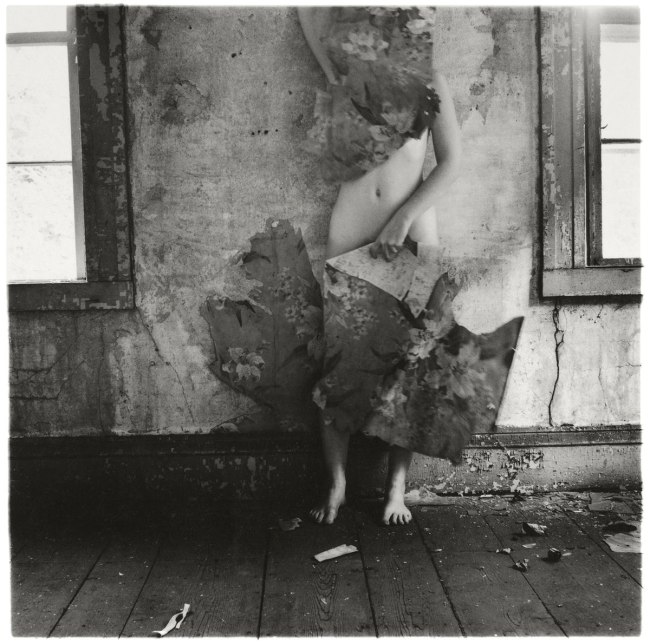
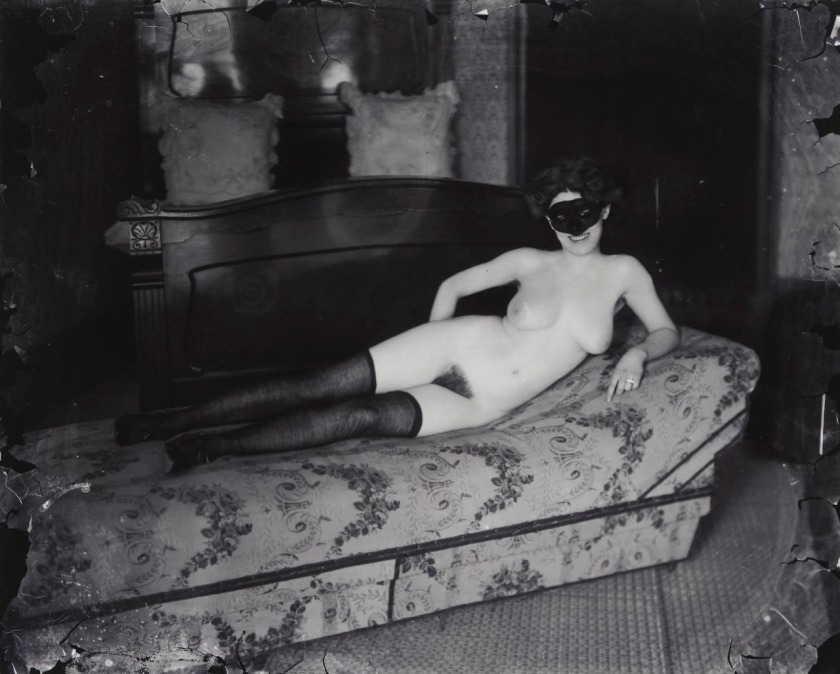
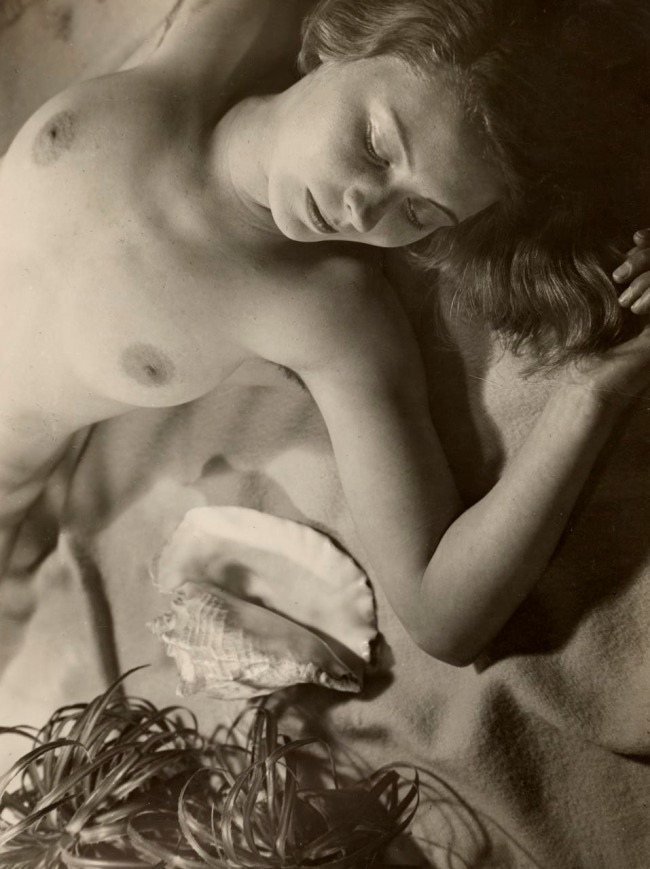
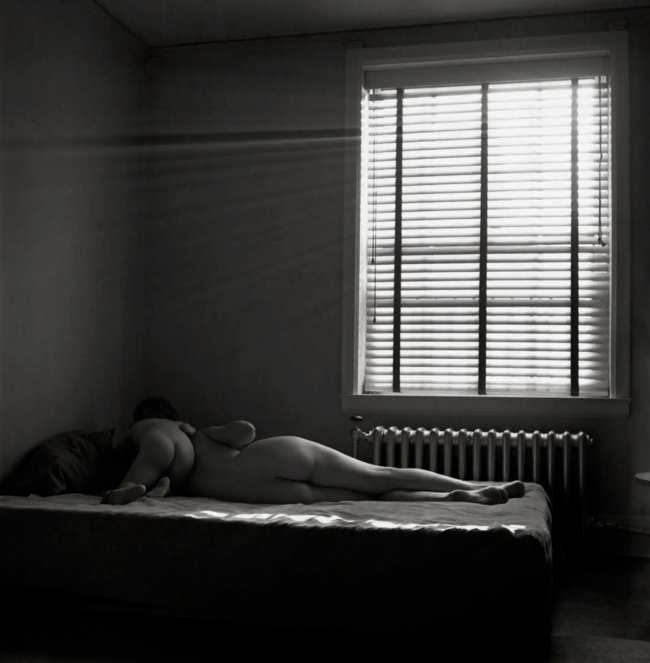
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Francesca Woodman’s Space², Providence, Rhode Island, 1976 (1976, below); E. J. Bellocq’s Woman reclining with mask (c. 1912, below); Florence Henri’s Nude composition (c. 1930, below); an anonymous American photographer’s image Kaloma (1914); and Germaine Krull’s Daretha (Dorothea) Albu (c. 1925)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Francesca Woodman (American, 1958-1981)
Space², Providence, Rhode Island, 1976
1976, printed c. 2000
Gelatin silver photograph
16.3 × 16.3cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Ruth Margaret Frances Houghton Bequest, 2021
Francesca Woodman once stated, ‘I want my pictures to have a certain timeless, personal but allegorical quality like they do in many Ingres history paintings, but I like the rough edge that photography gives a nude’. Woodman was only twenty-three when she died, her work has had a profound impact on other artists, including Cindy Sherman, who wrote, ‘[Woodman] had few boundaries and made art out of nothing: empty rooms with peeling wallpaper and just her figure … Her process struck me more the way a painter works, making do with what’s right in front of her, rather than photographers like myself who need time to plan out what they’re going to do’.
Wall text from the exhibition
E. J. Bellocq (American, 1873-1949)
No title (Woman reclining with mask)
c. 1912, printed c. 1981
From the Storyville Portraits series c. 1911-1913
Gelatin silver photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1981
Public domain
Florence Henri (American, 1893-1982)
Nude composition (Nu composition)
c. 1930
Gelatin silver photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of Krystyna Campbell-Pretty AM and Family through the Australian Government’s Cultural Gifts Program, 2021
Public domain
This photograph is a beautiful example of the way in which Florence Henri combined the elements of New Objectivity in photography, including sharp focus and unexpected vantage points, with her exploration of identity and sexuality. The presentation of the woman is unashamedly erotic: her naked form is presented for the pleasure of the viewer, but she does not conform to conventional modes of softcore pornography. The woman’s gaze excludes the viewer; she reclines on a coarse cloth backdrop, crumpled to suggest a beach as she looks at a perfect conch shell symbolising female fertility and an eloquently beautiful indicator of the artist’s object of desire.
Wall text from the exhibition
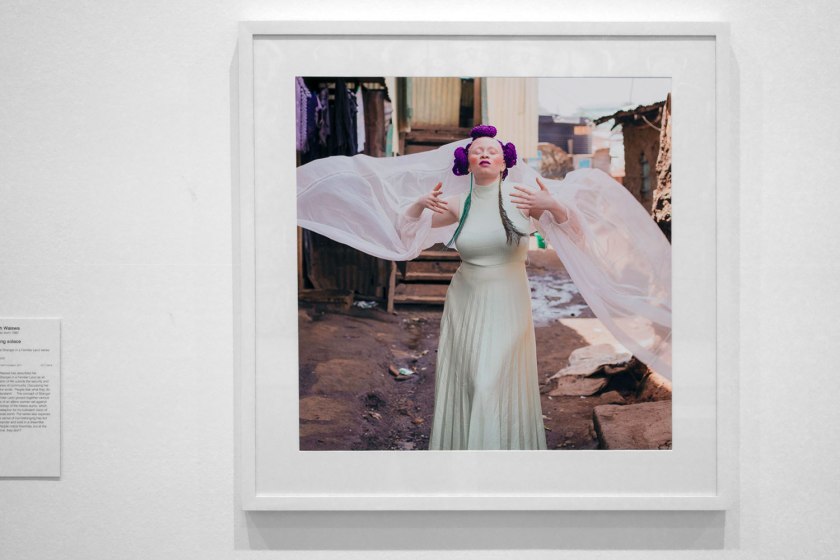
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left, Sophie Calle’s The giraffe (2012); and centre right, Lynne Roberts-Goodwin’s Al Hammadi Desert Saqar #1 and #3; and at right, Sarah Waiswa’s Finding solace (2016)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Sarah Waiswa (Ugandan, b. 1980)
Finding solace (installation view)
2016
From the Stranger in a Familiar Land series 2016
Inkjet print
79.5 × 79.5cm
Purchased NGV Foundation, 2017
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Sarah Waiswa has described her series Stranger in a Familiar Land as an exploration of life outside the security and boundaries of community. Discussing her work, she wrote, ‘People fear what they do not understand … The concept of Stranger in a Familiar Land groups together various portraits of an albino woman set against the backdrop of the Kibera slums, which are a metaphor for my turbulent vision of the outside world. The series also explores how the sense of non-belonging has led her to wander and exist in a dreamlike state. People notice Kisombe, but at the same time, they don’t’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at right, Lynne Roberts-Goodwin’s Al Hammadi Desert Saqar #1 and #3
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
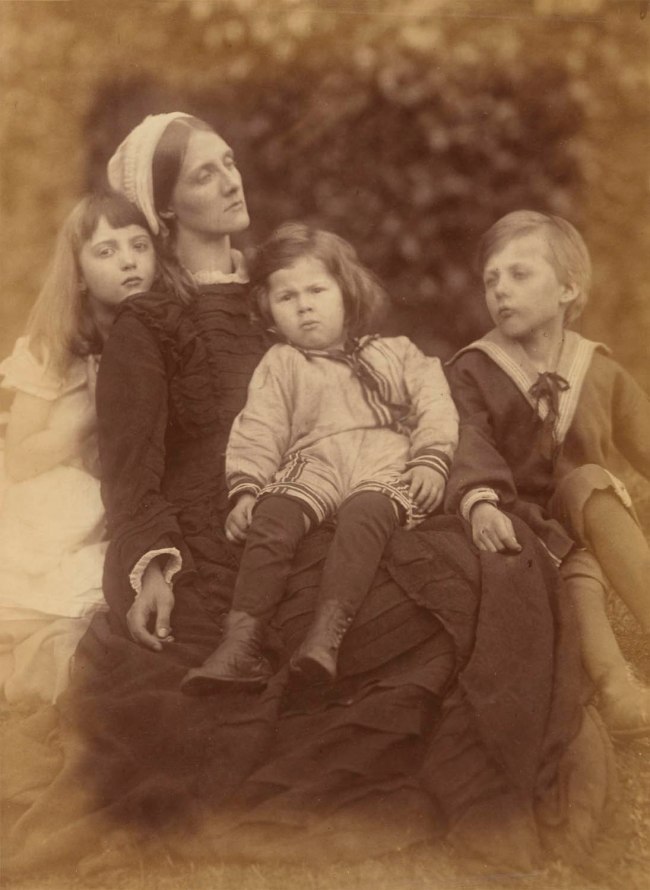
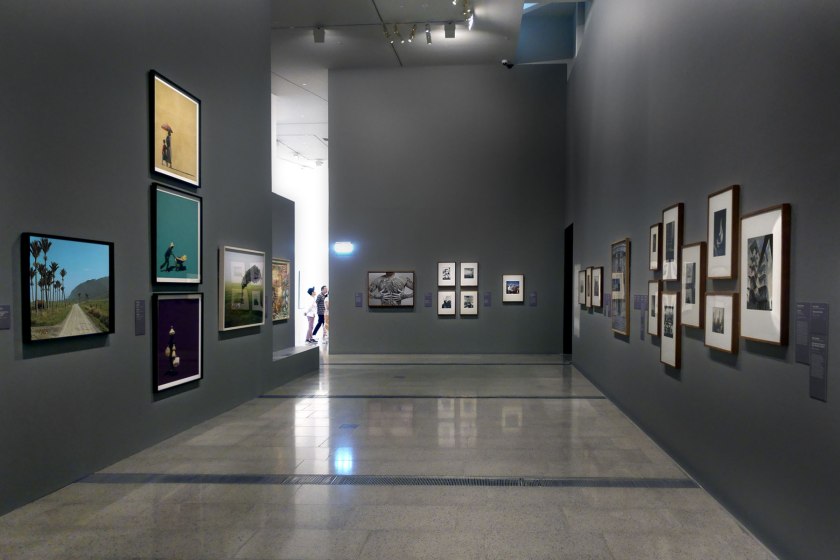
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Jan Groover’s Untitled (1981); August Sander’s Bohemians (Willi Bongard and Gottfried Brockman) (1922-1925, below); Julia Margaret Cameron’s Mrs Herbert Duckworth, her son George, Florence Fisher and H. A. L. Fisher (c. 1871, below); Harry Callahan’s Eleanor and Barbara, Chicago (1954); Gordon Parks’ Big Mama and boy, 1961 (1961); Micky Allan’s Man holding his daughter (1982, below); Brenda L. Croft’s In my mother’s garden (1998); and Angela Lynkushka’s Zühre Yildirim from Turkey with grand-daughter Nurahan Gundogdu, born in Australia. De Carle Street, Brunswick (1982)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
August Sander (German, 1876-1964)
Bohemians (Willi Bongard and Gottfried Brockman)
1922-1925, printed 1973
From the People of the Twentieth Century project 1920s-1964
Gelatin silver photograph
23.3 × 30.5cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1974
Gottfried Waldemar Brockmann (1903-1983) was a German artist, educator, publisher, and served as a cultural advisor for the city of Kiel, Germany. He taught at Muthesius Academy of Art in Kiel.
Julia Margaret Cameron (English, 1815-1879, Ceylon (Sri Lanka) 1875-1879)
Mrs Herbert Duckworth, her son George, Florence Fisher and H. A. L. Fisher
c. 1871
Albumen silver photograph
31.0 × 22.7cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of the Herald & Weekly Times Limited, Fellow, 1979
Public domain
In this portrait, Julia Duckworth sits for her aunt, Julia Margaret Cameron, one of the nineteenth century’s most esteemed photographers. As curator Elisa deCourcy notes, ‘Julia Duckworth’s lackadaisical pose and her flailing hand cast her as somewhat of a Pre-Raphaelite heroine, very much in the style of Cameron’s broader oeuvre’. DeCourcy adds it is perhaps also a depiction of the experience of maternal exhaustion: ‘Julia’s distant gaze and slouched form makes it hard for us not to read this photograph as depicting fatigued motherhood. Through touch, the children seem to demonstrate a sentimental connection to Julia while also laying claim to her attention and energy’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Harry Callahan (American, 1912-1999)
Eleanor and Barbara
1954, printed 1970s
Gelatin silver photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1979
Harry Callahan began photographing his wife Eleanor shortly after they married in 1936 and continued to do so for almost fifty years. Discussing their relationship as artist and muse in a 1983 film, Callahan said, ‘I felt very natural photographing Eleanor. I didn’t feel like there were any obstacles of any kind’. Following the birth of their daughter Barbara in 1950 he began to photograph mother and child and, as can be seen in this image, often captured moments of family life in pictures of great intimacy.
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Micky Allan’s Man holding his daughter (1982) from the People of Elizabeth series 1982-1983
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The application of hand-colouring to photographs was generally the work of women in photography studios until the 1950s. In the 1970s and 80s these superseded processes experienced a revival as some feminist photographers applied the historic treatment to their images of contemporary life. As art historian Elisa deCourcy observes, ‘Micky Allan’s vibrant hand-colouring radically alters the topography of this otherwise monochrome photographic portrait of a young father and daughter from the 1980s … The application of colour to the father’s and daughter’s faces and the “retouching” of their hair, eyes and lips with colour offers an illuminated realism to each subject’.
Wall text from the exhibition
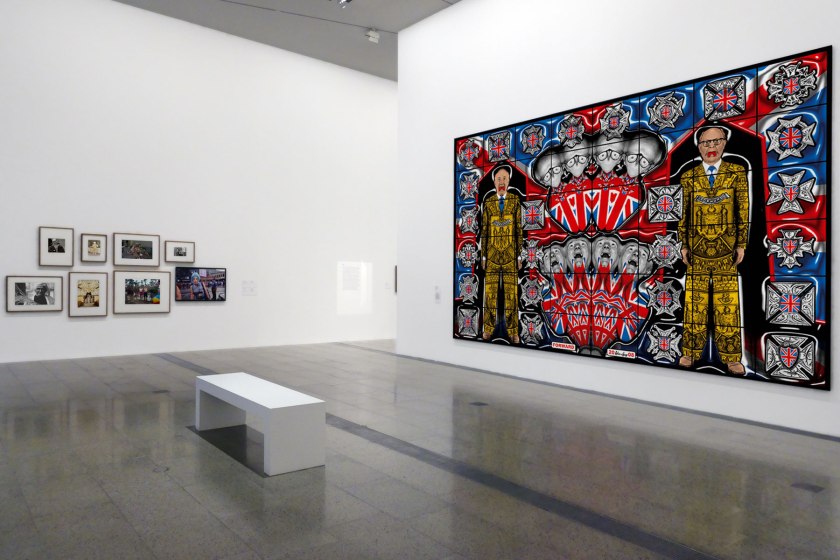
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at right Gilbert & George’s FORWARD (2008, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gilbert & George (active 1967- )
Gilbert Proesch (Italian, b. 1943
George Passmore (English, b. 1942)
FORWARD
2008
from the Jack Freak series
Inkjet print
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Professor AGL Shaw AO Bequest, 2021
Writer Michael Bracewell described the Jack Freak series as being ‘among the most iconic, philosophically astute and visually violent works that Gilbert & George have ever created’. In this picture the Union Jack, an internationally familiar flag and politically charged symbol whose significance spans the cultural spectrum from contemporary fashion to aggressive national pride, forms the backdrop to monumental portraits of the artists. In contrast to this visual cacophony the artists appear as rather low-key, neatly dressed, senior statesmen maintaining their central relevance in a community that too often disregards the elderly.
Wall text from the exhibition
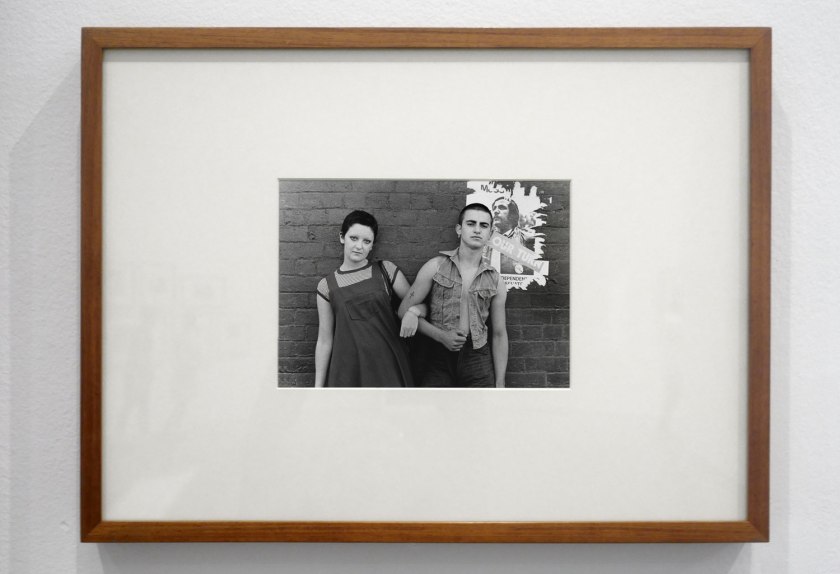
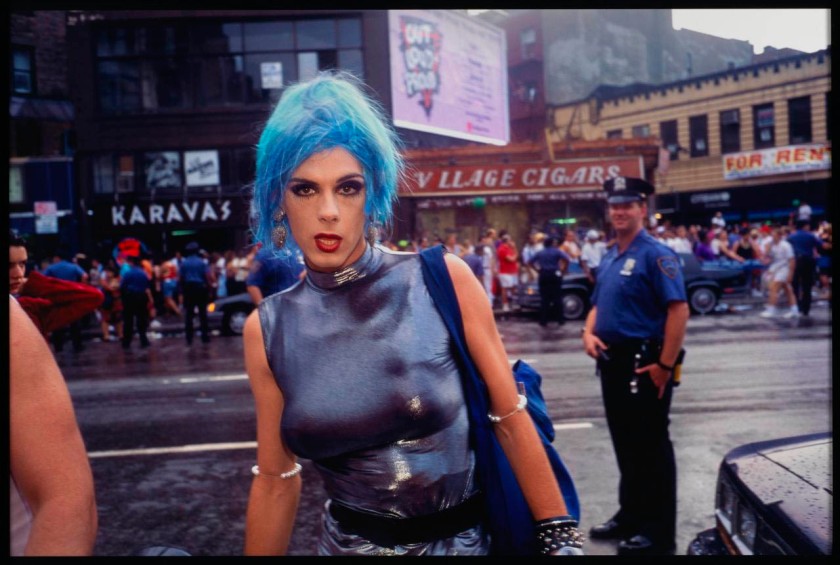
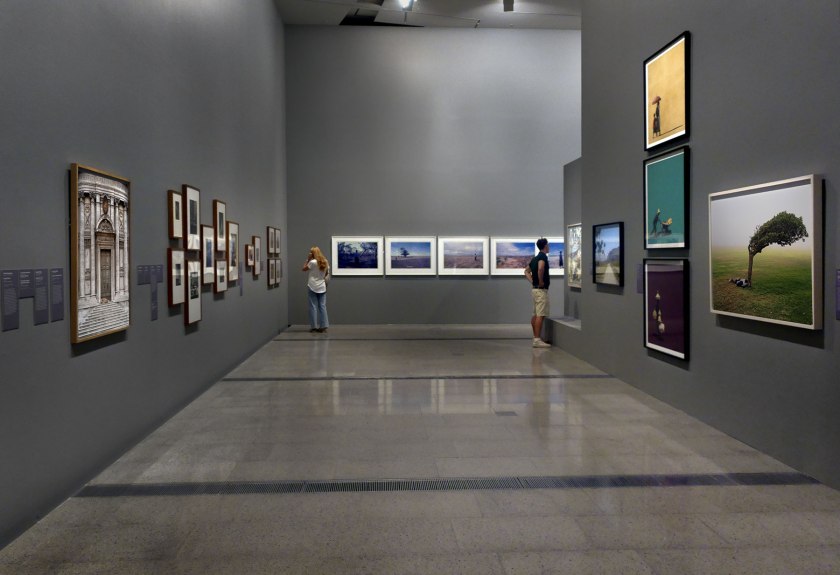
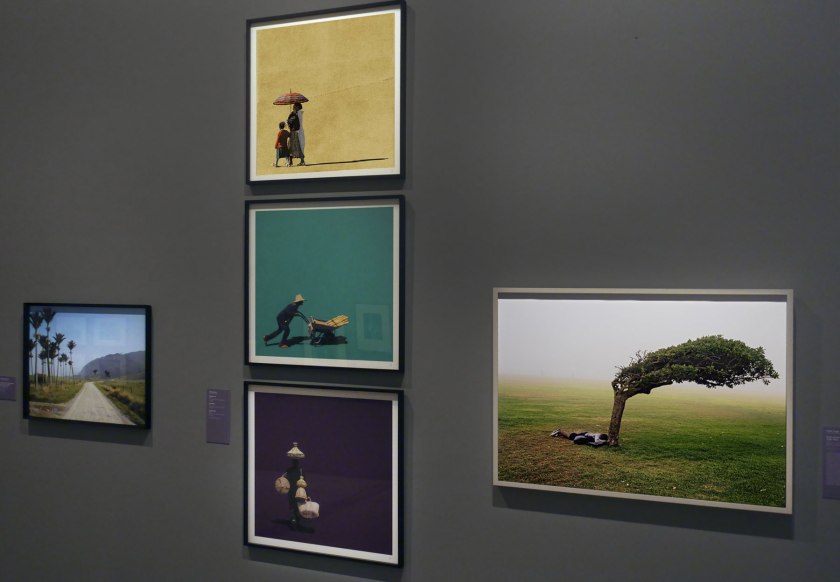
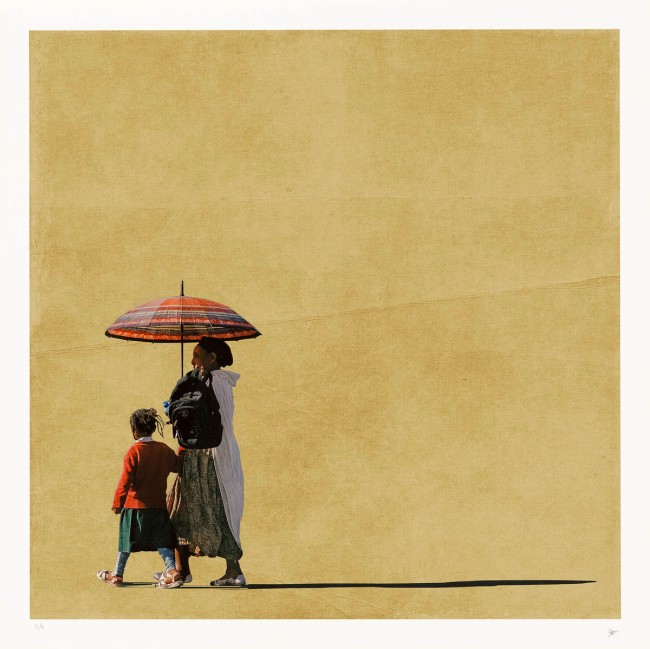
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Ellen José’s Basket Weaver, Lake Tyers (1988); Roman Vishniac’s Grandfather and granddaughter, Warsaw (c. 1935-1938, below); Wolfgang Tillmans’ Lars in tube (1993); Ruth Maddison’s Molly O’Sullivan, 82 (1990); Naomi Hobson’s The God Father (2021); Donna Bailey’s Lush (2002); Carol Jerrems Sharpies (1976, below); and Nan Goldin’s Misty in Sheridan Square, NYC (1991, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Roman Vishniac (Russian, 1897-1990, United States 1940-1990) Grandfather and granddaughter, Warsaw
c. 1935-1938, printed 1977
Gelatin silver photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1978
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Carol Jerrems’ Sharpies (1976)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Nan Goldin (American, b. 1953)
Misty in Sheridan Square, NYC
1991; 2015 {printed}
Cibachrome photograph
76.0 x 102.0cm (sheet)
ed. 20/25
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased NGV Foundation, 2015
© Nan Goldin, courtesy Matthew Marks Gallery
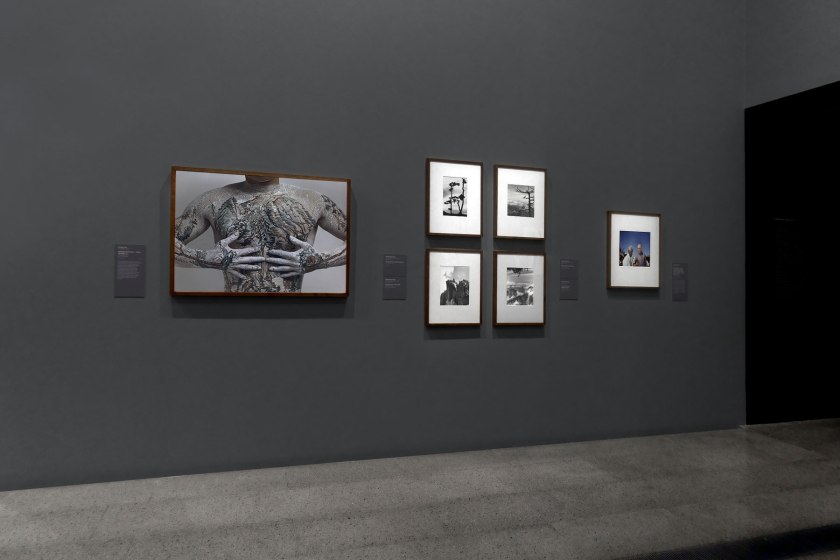
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Huang Yan’s Chinese landscape – Tattoo (Number 1) (1999); four photographs by Hedda Morrison (1935, below); and Mervyn Bishop’s Prime Minister Gough Whitlam pours soil into the hands of traditional land owner Vincent Lingiari, Northern Territory (1975, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
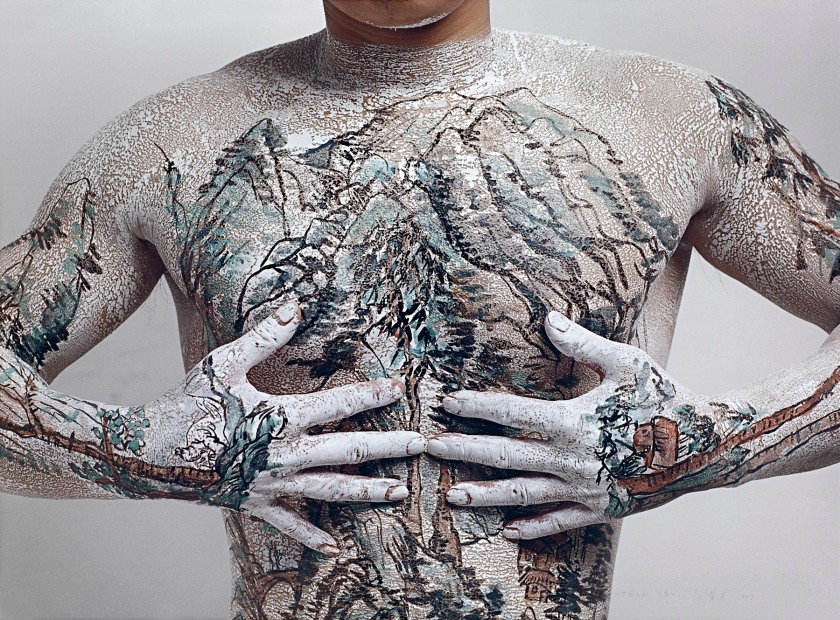
Huang Yan (Chinese, b. 1966)
Chinese landscape – Tattoo (Number 1)
1999, printed 2004
Type C photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 2004
In this photograph Huang Yan uses the human body as a canvas for the traditional shānshuǐ style of Chinese landscape painting. Discussing this image, curator and writer Isobel Crombie observed, ‘The title of the work, Tattoo, implies that landscape traditions are written permanently into the Chinese body, making them alive and active. However, ironically, the scenes painted onto the artist’s torso are clearly fugitive, alerting us to both the fragility of the natural environment and the transience of the body’.
Wall text from the exhibition
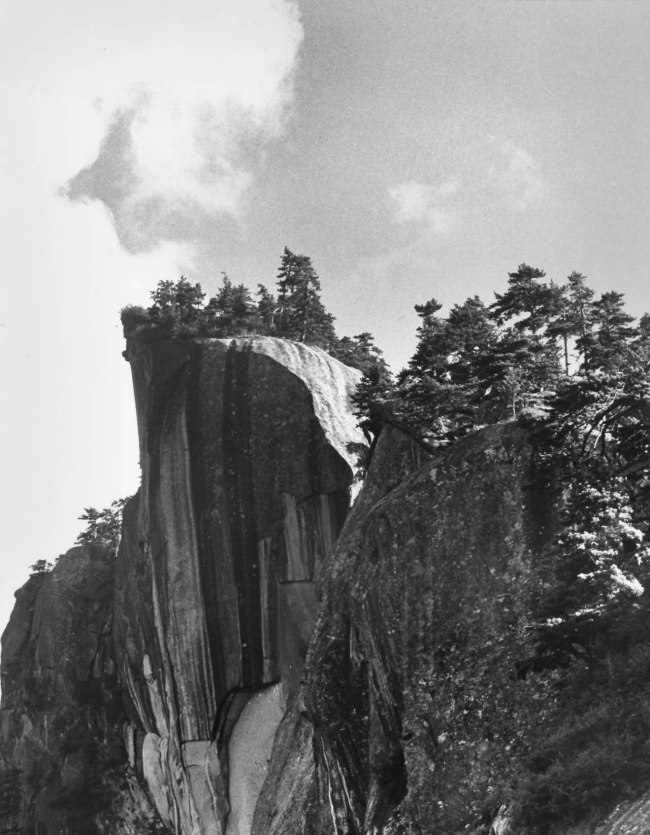
Hedda Morrison (German 1908-1991, China 1933-1946, Australia 1967-1991)
No title (Fairy Palm Cliff)
1935
Gelatin silver photograph
25.3 × 22.8cm
Purchased, 1976
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1976
Public domain
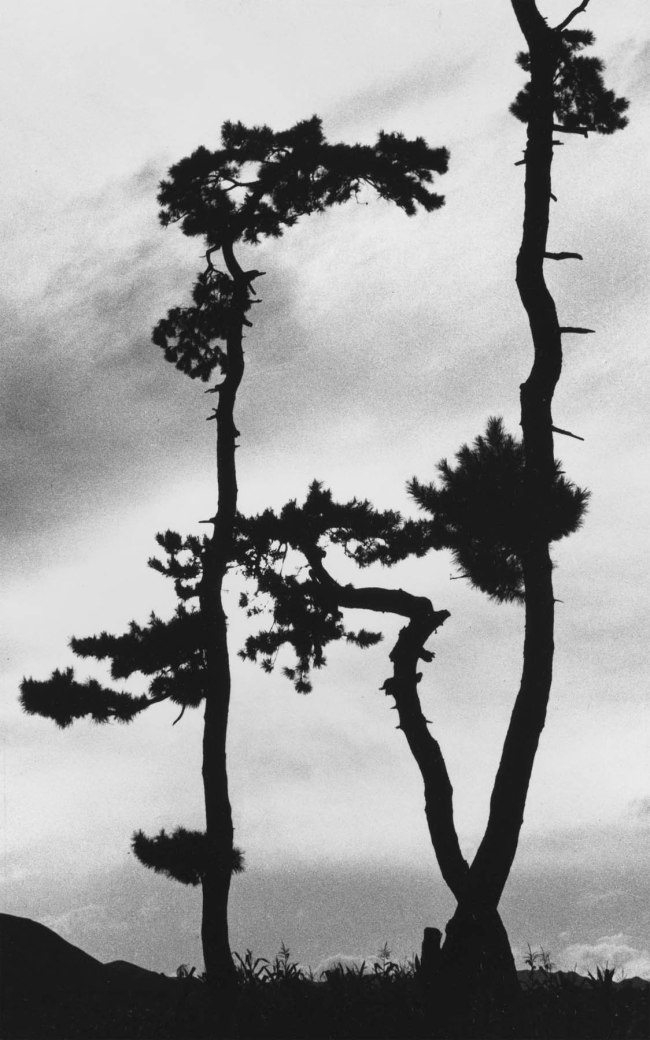
Hedda Morrison (German 1908-1991, China 1933-1946, Australia 1967-1991)
No title (Three gnarled pines)
1935
Gelatin silver photograph
30.6 × 19cm
Purchased, 1976
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1976
Public domain
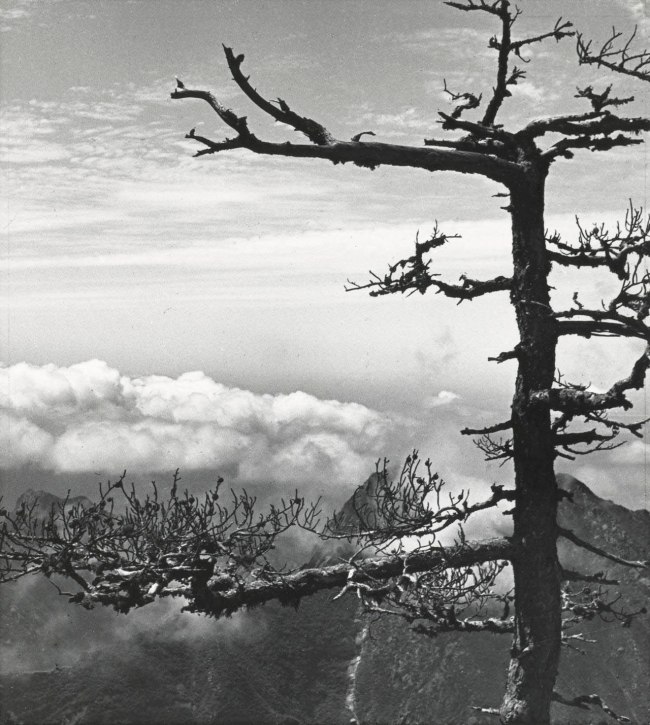
Hedda Morrison (German 1908-1991, China 1933-1946, Australia 1967-1991)
No title (Lone pine against clouds)
1935; printed 1976
Gelatin silver photograph
25.3 × 22.8cm
Purchased, 1976
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1976
Public domain
Hedda Morrison (German 1908-1991, China 1933-1946, Australia 1967-1991)
No title (Morning clouds)
1935; printed 1970s
Gelatin silver photograph
25.3 × 22.8cm
Purchased, 1976
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1976
Public domain
Mervyn Bishop (Australian, b. 1945)
Prime Minister Gough Whitlam pours soil into the hands of traditional land owner Vincent Lingiari, Northern Territory
1975, printed 1990
Cibachrome photograph
35.5 × 35.5cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, NGV Foundation and NGV Supporters of Photography, 2021
© Mervyn Bishop / Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet
In August 1975 Mervyn Bishop travelled to Daguragu, formerly known as Wattie Creek, in the Northern Territory. As a press photographer he captured the moment when then prime minister Gough Whitlam placed a handful of soil into the palm of Gurindji elder and activist Vincent Lingiari. This photograph is an iconic image of the ongoing battle for self-determination for Australia’s traditional owners; however, the photograph is not as straightforward as it appears: the moment was re-staged outside so Bishop could take advantage of better lighting.
Wall text from the exhibition
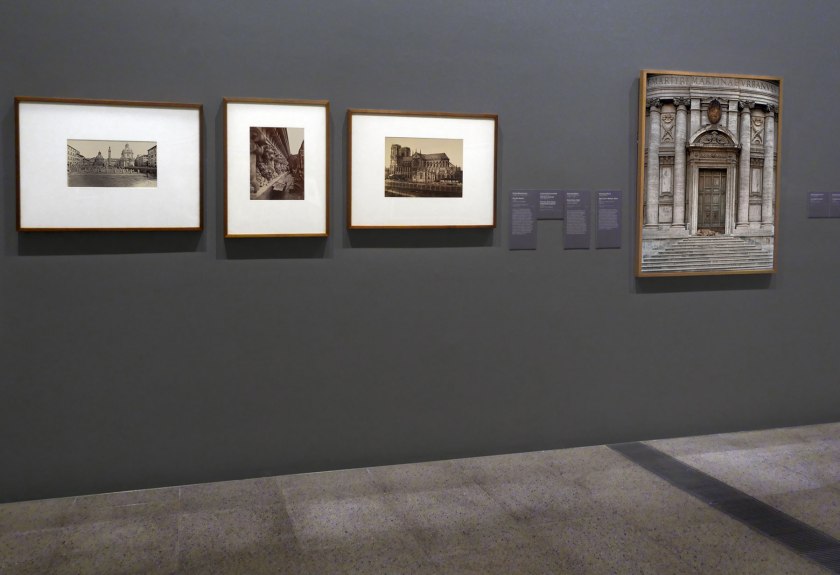
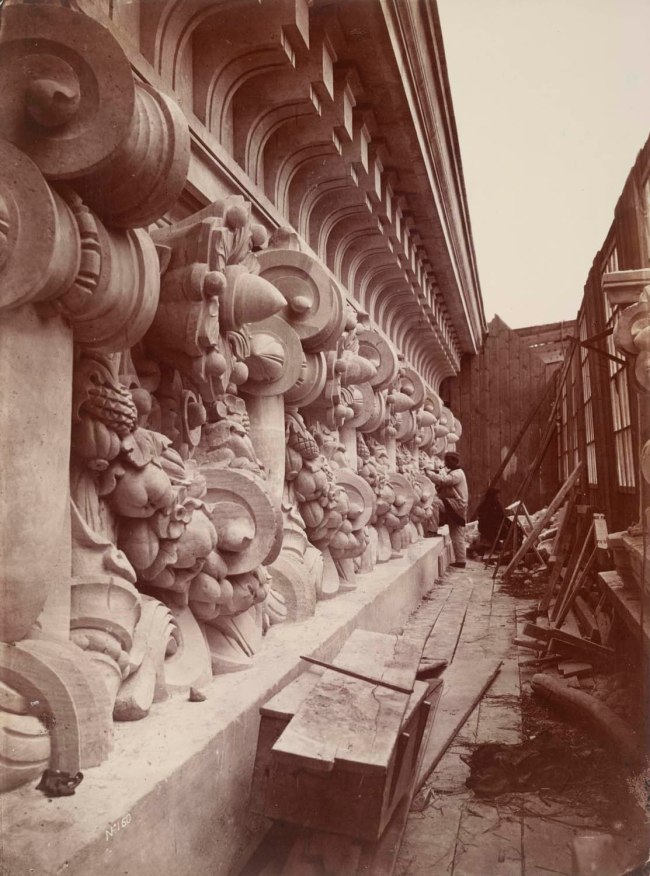
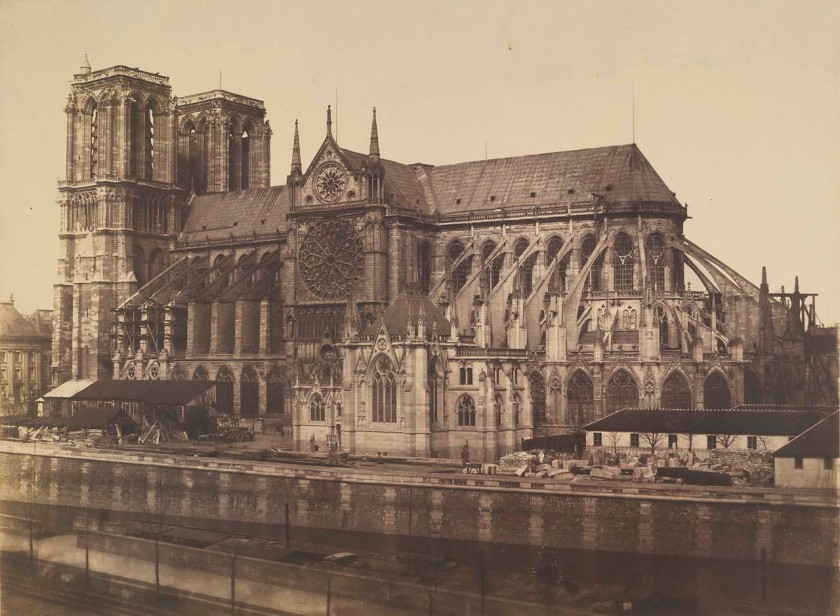
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Robert Macpherson’s Rome (c. 1860); Louis-Emile Durandelle and Clémence Delmaet’s The new Paris Opera, ornamental sculpture (c. 1870, below); Edouard Baldus’ Notre Dame, Paris (c. 1852-1853, below); and Véronique Ellena’s Santi Luca e Martina, Rome (2011)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
In Véronique Ellena’s photograph we see a shrouded figure, draped in a blanket or canvas cloth, lying on the steps of a Baroque church in central Rome. Initially seducing us with the formal beauty of the city and its architecture, the photograph then jolts us as we recognise the harsh reality of the scene. This was a calculated strategy on Ellena’s part, as she acknowledges: ‘At first, we could only perceive the sublime beauty of architecture. But this work tells us something else: the place of some people in this world, who are there but whom we do not see – or not anymore’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Louis-Emile Durandelle (French, 1839-1917)
Clémence Delmaet (French, 1838-1917)
The new Paris Opera, ornamental sculpture
c. 1870
Albumen silver photograph
38.1 × 28.3cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by the Lunn Gallery, Washington D.C, USA, 1982
Public domain
Edouard Baldus (Prussian 1813-1989, France c. 1848 – c. 1869)
Notre Dame, Paris
c. 1852-1853, printed 1880s
Platinum photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by the National Gallery Women’s Association, 1995
Public domain
By the middle of the nineteenth century many of the great historic buildings of Paris, including Notre Dame Cathedral, were in a state of disrepair due to decades of neglect. Under the auspices of the Commission des Monuments Historiques, significant historic buildings underwent extensive restoration. This committee recognised the invaluable role photography could play in documenting the changes occurring to the architectural heritage of Paris. Official Second Empire photographer, Édouard Baldus, captured the splendour of newly commissioned and lavishly restored architectural icons as cultural highlights of the Second Empire.
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at left, Véronique Ellena’s Santi Luca e Martina, Rome (2011); at second right, work from Girma Berta’s Moving shadows series (2017); and at right, Pieter Hugo’s Green Point Common, Cape Town (2013)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at centre, Girma Berta’s Untitled IV, VI and XII (2017) at right, Pieter Hugo’s Green Point Common, Cape Town (2013)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Girma Berta (Ethiopian, b. 1990)
Untitled IV
2017
From the Moving shadows series 2017
Inkjet print, ed. 4/4
89.8 x 90.0cm (image)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2018
© Girma Berta
Girma Berta has been photographing people on the streets of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, since around 2014. His earlier photographs were documentary in style, but over time his work has become more refined and stylised.
The five photographs from his Moving Shadows series 2017 … are from an ongoing body of work in which all background detail has been removed. These photographs show isolated figures, and their shadows, on immersive, coloured backgrounds. The works feature individuals photographed on the streets of Addis Ababa going about the daily lives. Using the camera in his phone, Berta is able to work discretely and capture his subjects without them being aware of his presence.
In all his street-based work, Berta is interested in presenting a ‘portrait’ of the people of Addis Ababa. Working in his studio, he has developed a method to extract aspects of the scenes he photographs from the city’s busy streetscapes. Berta explains further: ‘Through my work on Instagram, I wish the world (would) stare into the eyes of a face of Addis Ababa; the city where I was born and where I grew up. The beautiful, the ugly and all that is in between.’
Text from the National Gallery of Victoria website
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing at second left, Girma Berta’s Untitled IV, VI and XII (2017, above); and at right, Dacre Stubbs’ St. George’s Road flats (1953, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
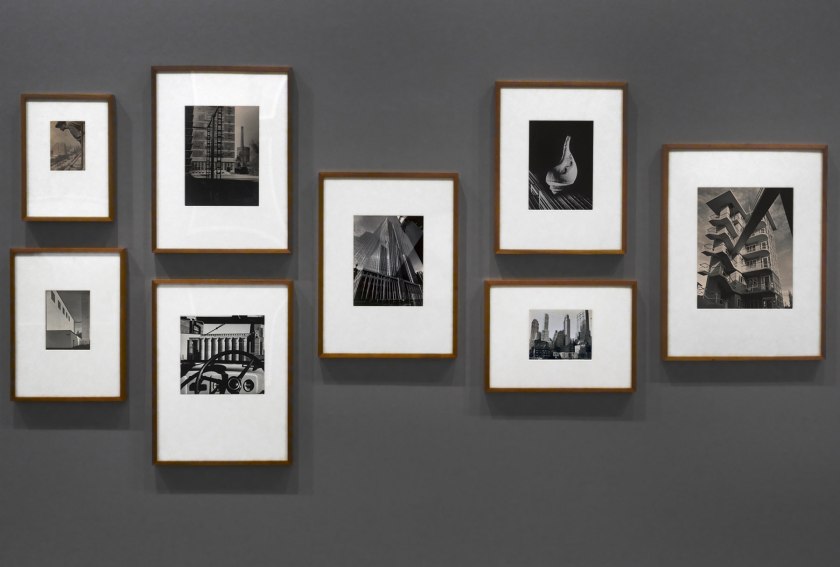
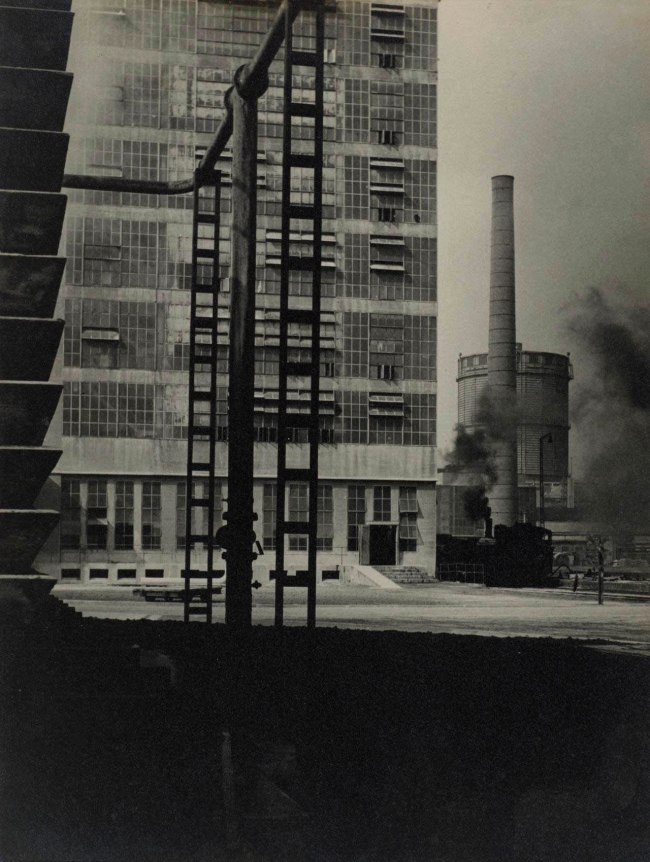
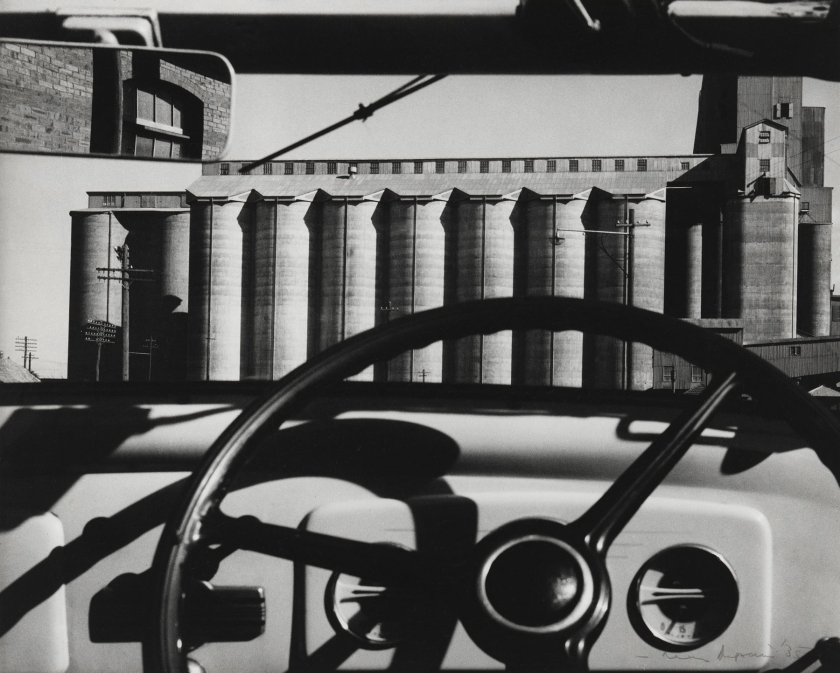
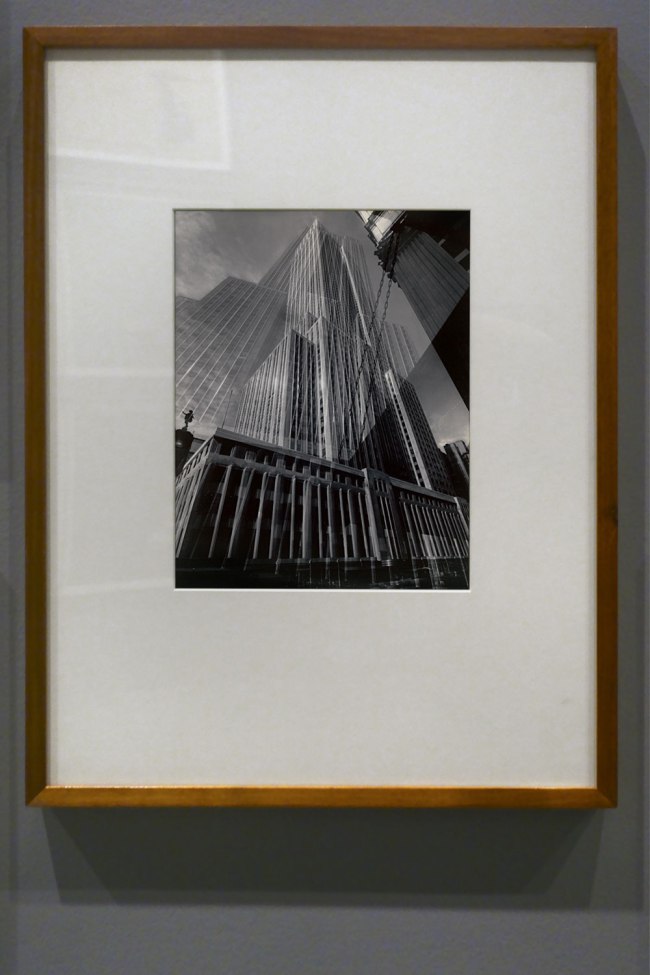
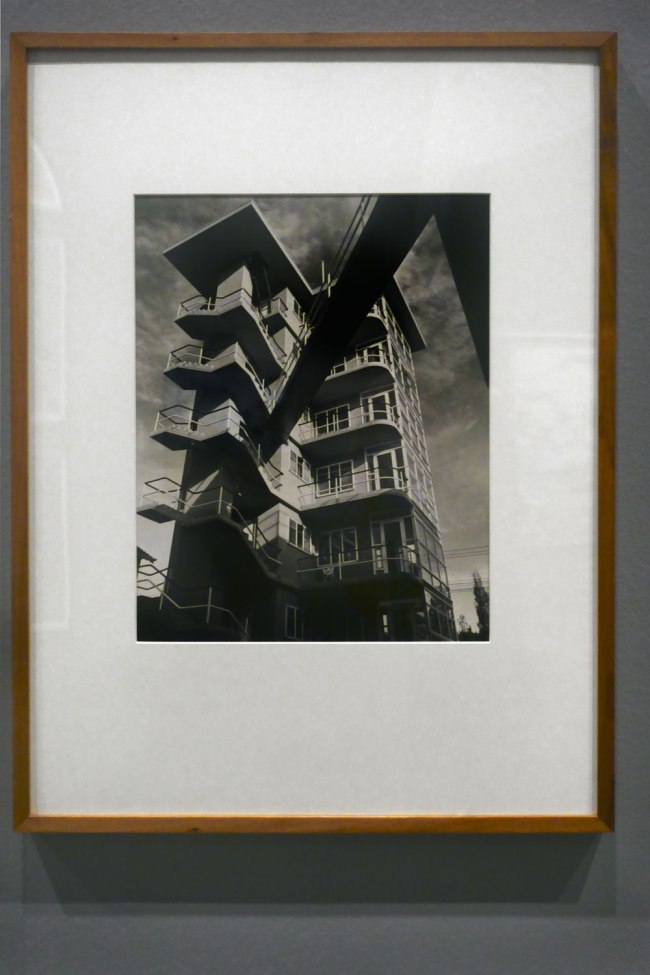
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing from left to right, Gertrude Kasebier’s Gargoyle (1901, top); Albert Renger-Patzsch’s Art d’eglise in Achen (1930s, bottom); Werner Mantz’s Industrial Landscape (1937, top); Max Dupain’s Silos through windscreen (1935, bottom); Edward Steichen’s The maypole (1932); Barbara Morgan’s City shell (1938, top); Berenice Abbott’s Park Avenue and Thirty-ninth Street, Manhattan, October 8 (1936, bottom) and Dacre Stubbs’ St. George’s Road flats (1953)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
For modernist architects in the 1930s there was a natural synergy between their own vision of the constructed environment in the machine age and the work of photographers. In architecture this was manifested in structural clarity and precision, and the use of modern building materials such as steel, glass and unadorned concrete. In photography the use of sharp focus, unexpected vantage points, radical cropping of images and unusual perspectives formed part of the lexicon of the so-called New Objectivity. Photographers like Werner Mantz show a world in which compressed space and unexpected vantages confound our expectations of how buildings should be photographed.
Wall text from the exhibition
Gertrude Kasebier (American, 1852-1934)
Gargoyle
1901
Platinum photograph
20.6 × 13.5cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of the Herald & Weekly Times Limited, Fellow, 1979
Public domain
Werner Mantz (German 1901-1983)
Industrial landscape
1937
Gelatin silver photograph
38.6 × 29.2cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1983
Public domain
Max Dupain (Australian 1911-1992)
Silos through windscreen
1935, printed c. 1985
Gelatin silver photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1986
Public domain
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Edward Steichen’s The maypole (1932)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Barbara Morgan (American, 1900-1992)
City shell
1938, printed 1972
Gelatin silver photograph
34.4 × 25.1cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of Krystyna Campbell-Pretty AM and Family through the Australian Government’s Cultural Gifts Program, 2022
Public domain
Barbara Morgan moved to New York in 1930 and began experimenting with the avant-garde photographic techniques of photograms and photomontage. City shell is an outstanding example of Morgan’s innovative photography from the 1930s. In this image she combined a view from her studio window of the Empire State Building with a shell gifted to her by a friend. The monumental skyscraper is shown tilted on an extreme angle while the shell appears upright in the centre of the photograph – a visual metaphor, according to the artist, for the transient nature of built structures in comparison to those of the natural world.
Wall text from the exhibition
Berenice Abbott (American 1898-1991, France 1921-1929)
Park Avenue and Thirty-ninth Street, Manhattan, October 8
1936
Gelatin silver photograph
19.3 × 24.3cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2021
Public domain
In 1929, after living in Paris for eight years, Berenice Abbott returned to New York and, having noted the rapid change taking place across the city, commenced a project to document New York in photographs. Abbott’s project was funded by the WPA Federal Art Project from 1935 to 1939, which culminated in the 1939 book and exhibition, Changing New York. Discussing her project, Abbott wrote of desiring to capture the ‘spirit’ of the city, driven by the urgent realisation that ‘the tempo of the metropolis is not of eternity, or even time, but of the vanishing instant’.
Wall text from the exhibition
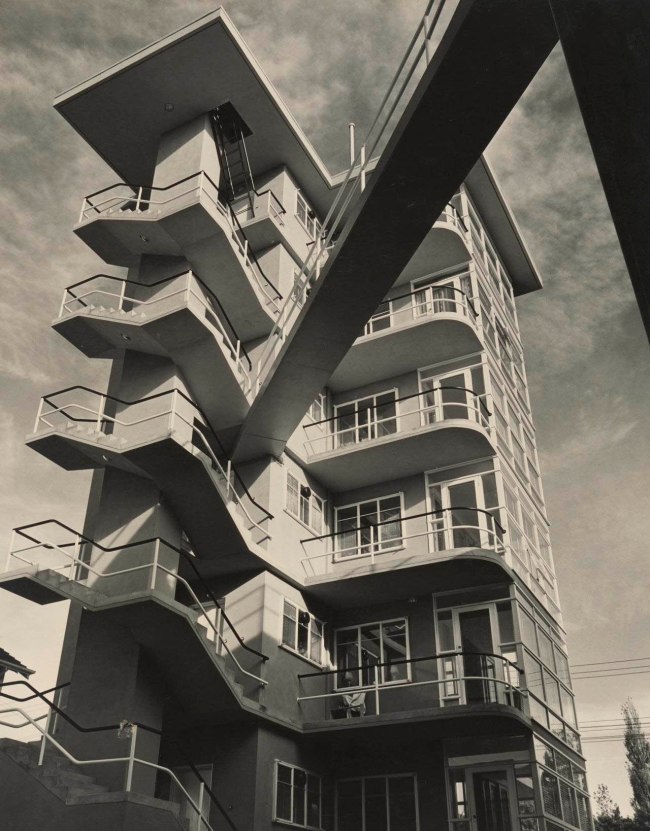
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Dacre Stubbs’ St George’s Road flats (1953, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Dacre Stubbs (English 1910-2001, Australia 1948-2001)
St George’s Road flats
1953
Gelatin silver photograph
47.6 × 38.0cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1993
Public domain
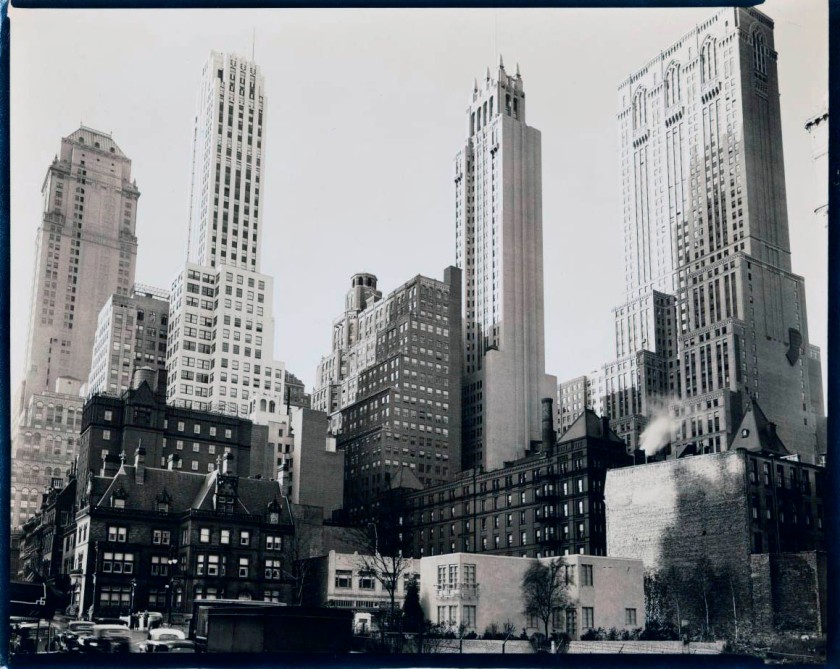
More photographs from the exhibition
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing William Henry Fox Talbot’s Portrait of a man (c. 1844, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
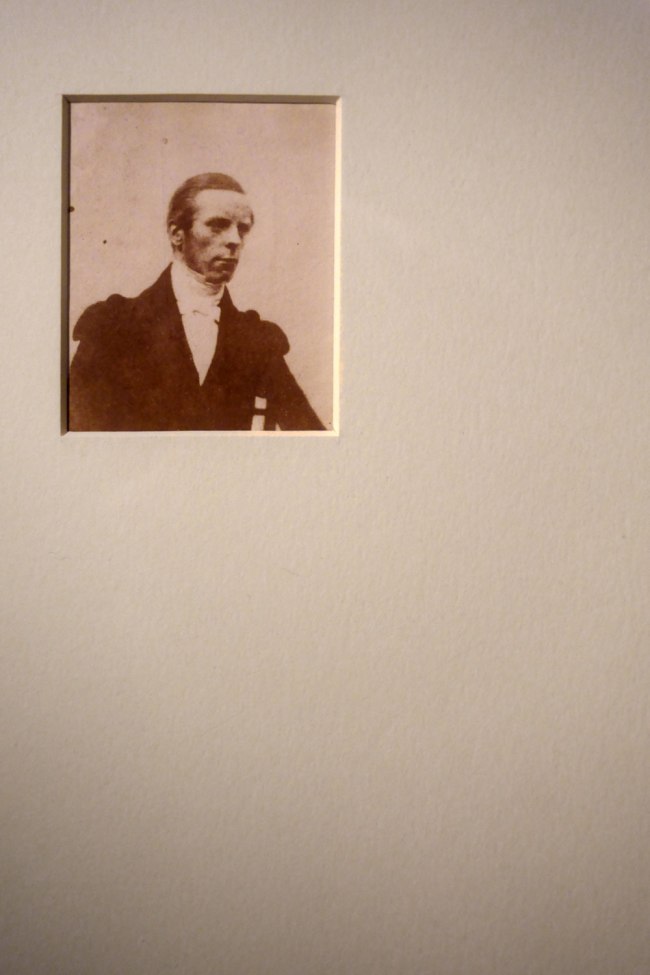
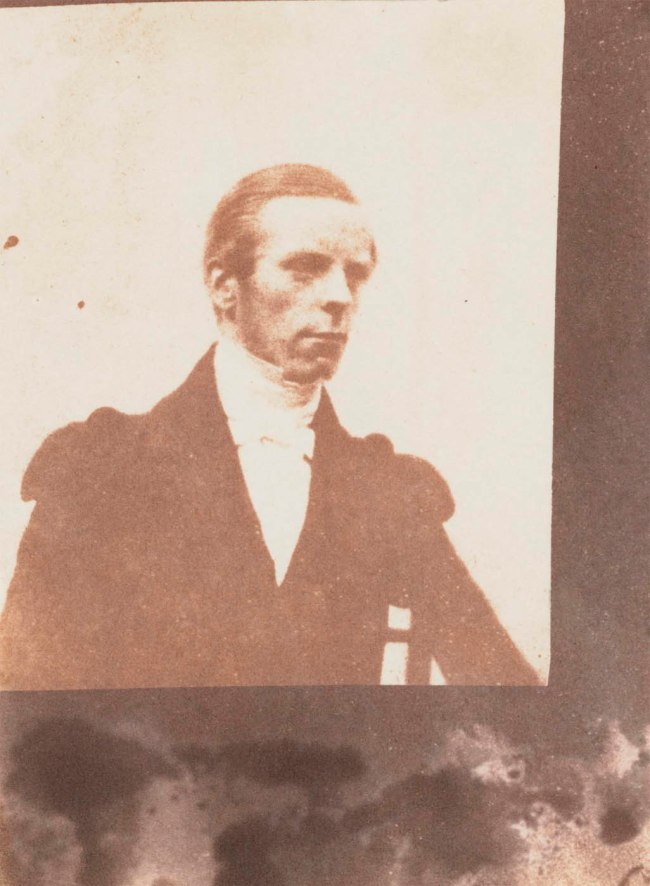
William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877)
No title (Portrait of a man)
c. 1844
Salted paper photograph
7.6 × 6.6cm irreg.
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of David Syme & Co. Limited, Fellow, 1982
Public domain
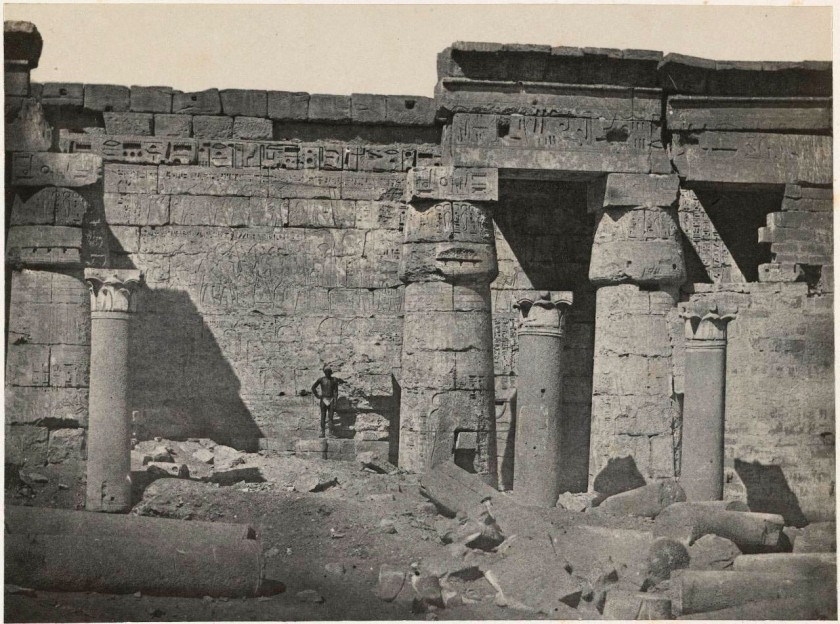
Maxime Du Camp (French 1822-1894)
Peristyle of the Palace of Rameses III, Medinet Habu, Thebes
1849-1851, printed 1852
Salted paper photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1983
Public domain
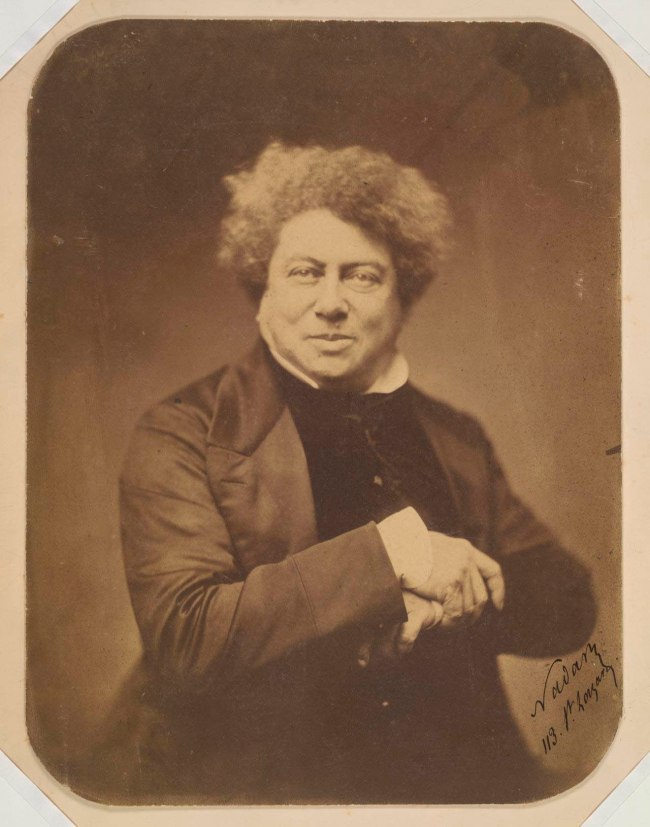
Gaspard-Felix Tournachon Nadar (French, 1820-1910)
Alexander Dumas (père)
1855
Salted paper photograph
24.4 × 18.6cm irreg. (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by the National Gallery Women’s Association, 1995
Public domain
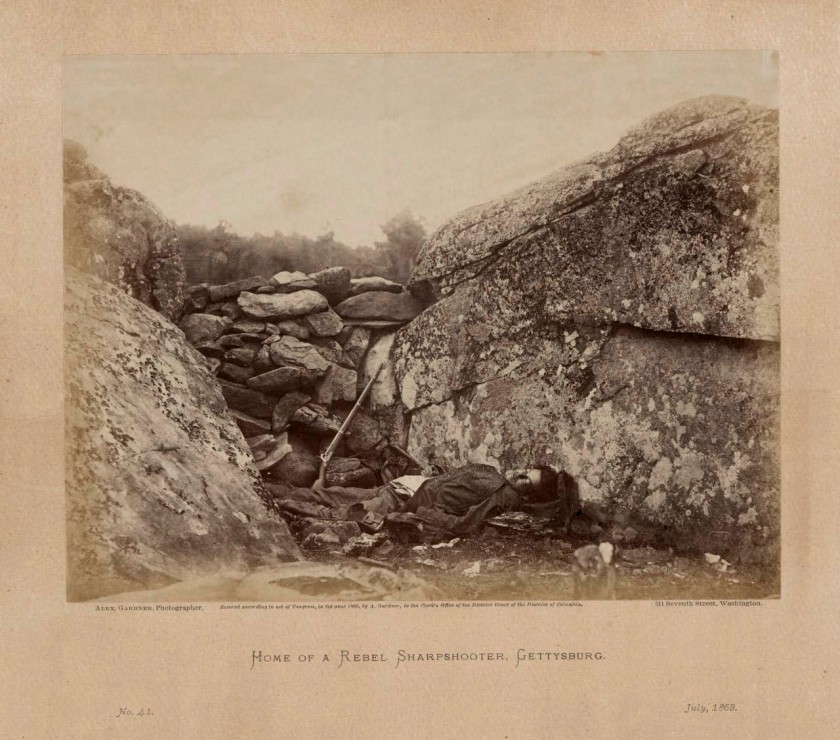
Alexander Gardner (American 1821-1882)
Home of a Rebel sharpshooter, Gettysburg
1863; printed 1865-1866
Plate no. 41 from Gardner’s Photographic Sketch Book of the War, vol. I and II, 1865-1866
Albumen silver photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of the Herald & Weekly Times Limited, Fellow, 1979
Public domain
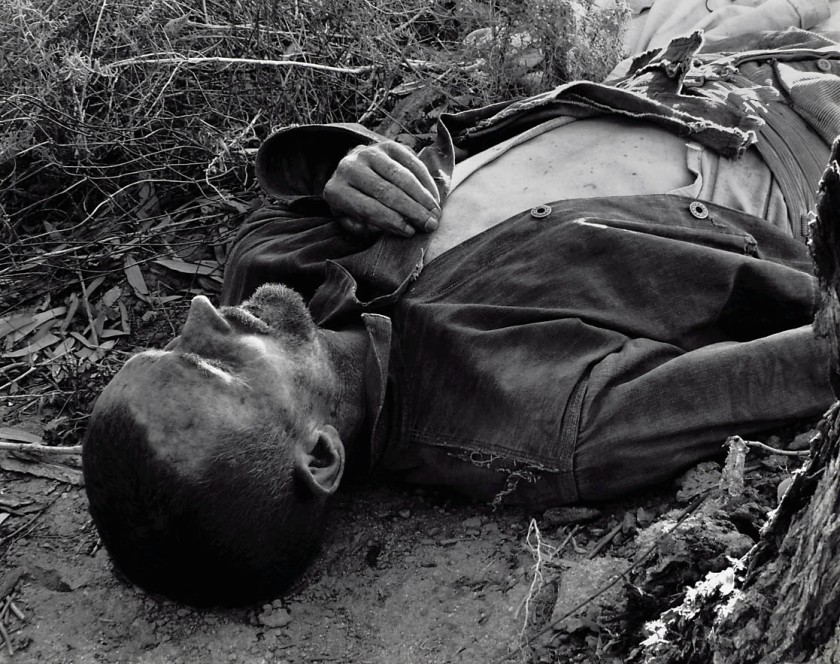
Around 620,000 soldiers are believed to have died during the American Civil War, which was fought from 1861 to 1865. Discussing the war, this photograph, and the work of Alexander Gardner, author and art historian Helen Ennis wrote, ‘The extensive coverage of the war that Gardner and his colleagues achieved – including its often graphic, confronting imagery – is lauded in the history of photography for its pioneering documentary photography and photojournalism. However, war photography has its own disturbing history, one in which photographing the dead has become routine. In Gardner’s photograph the corpse (and his rifle) may have been specially positioned for the photograph, a further reminder that in war death has no dignity’.
Wall text from the exhibition
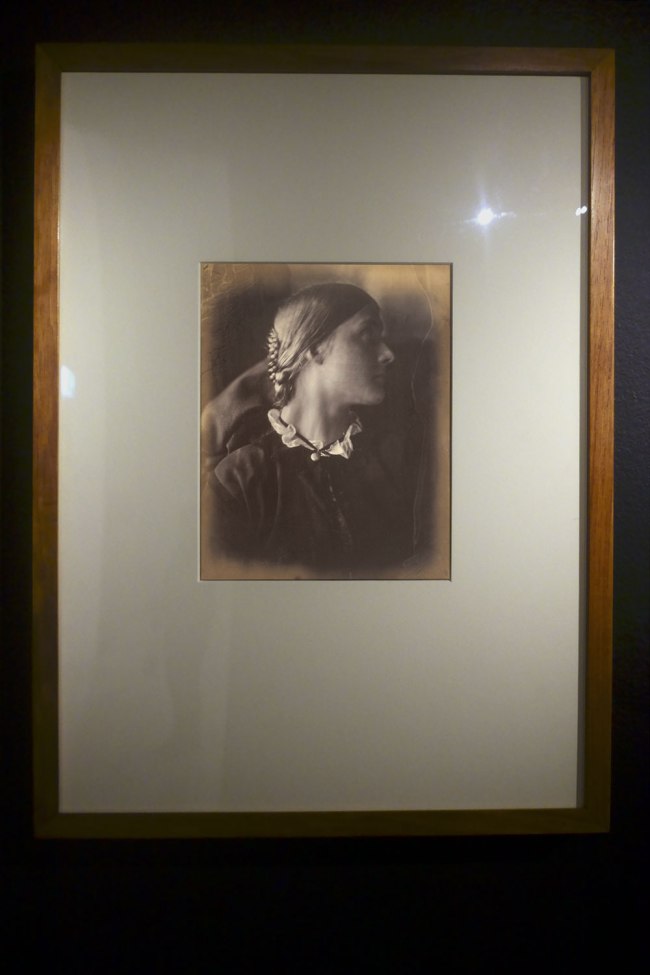
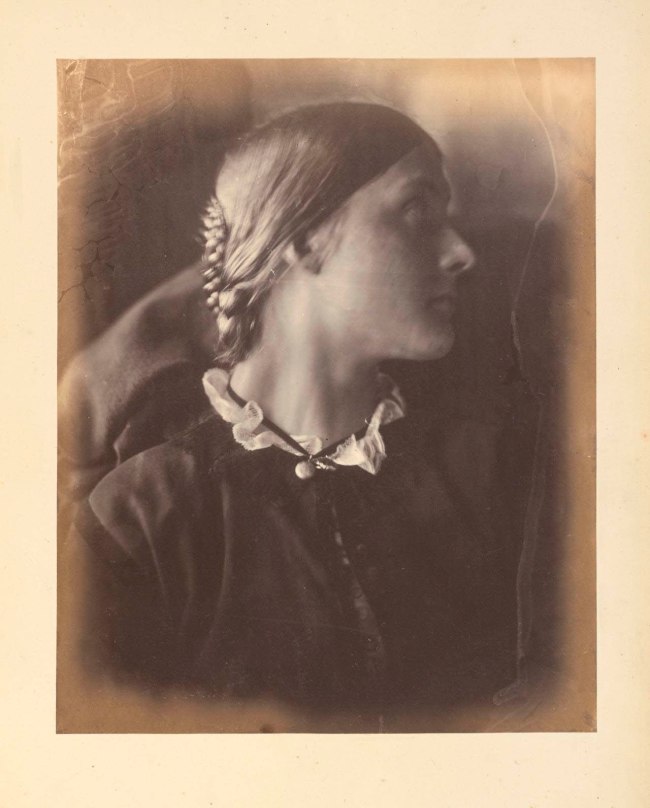
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Julia Margaret Cameron’s Julia Jackson (1864, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Julia Margaret Cameron (English, 1815-1879)
Julia Jackson
1864
Albumen silver photograph
24.0 × 19.1cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of the Herald and Weekly Times Limited, Fellow, 1979
Public domain
Giorgio Sommer (German 1834-1914)
Human imprint, Pompeii (Impronte umare. Pompei)
1873
Albumen silver photograph
19.8 × 25.5cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented through the NGV Foundation by Janice Hinderaker, Member, 2003
Public domain
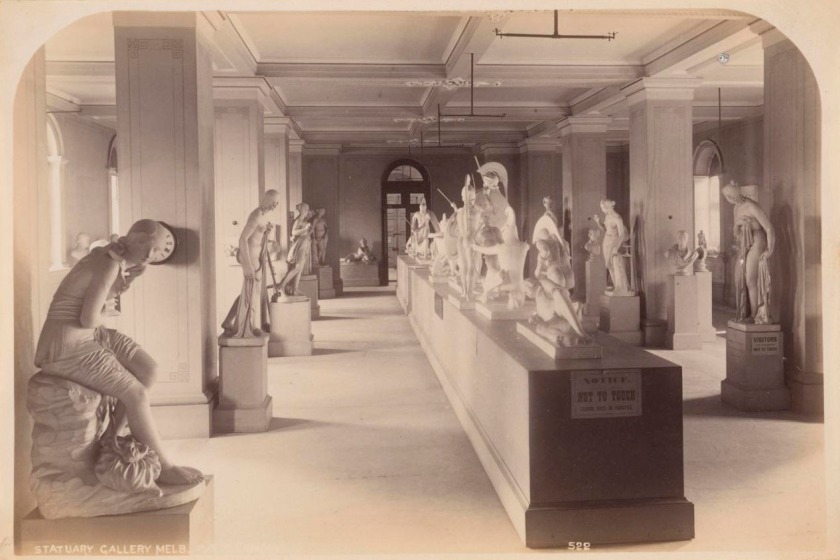
Charles Rudd (Australian 1872-1900)
Statuary Gallery, Melbourne Public Library
1886-1887
From the C. Rudd’s New Views of Melbourne series 1886-1887
Albumen silver photograph
13.6 × 19.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of Terence Lane, 1990
Public domain
F. B. Mendelssohn & Co., Melbourne (Australian, active 1889-1900)
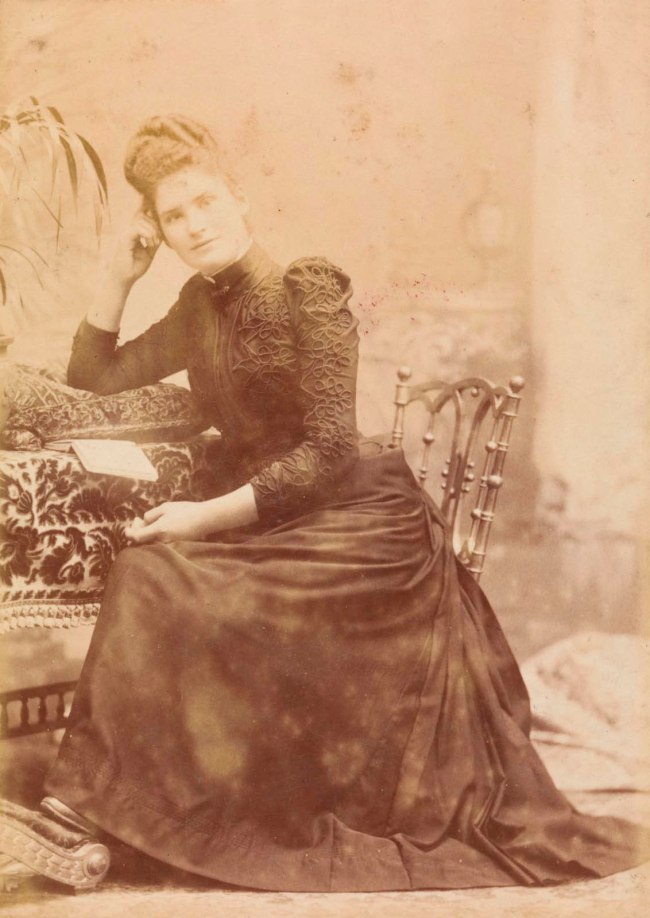
No title (Young woman, full length, seated at plush covered table)
1889
Cabinet print
Albumen silver photograph
14 × 10cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of C. Stuart Tompkins, 1972
Public domain
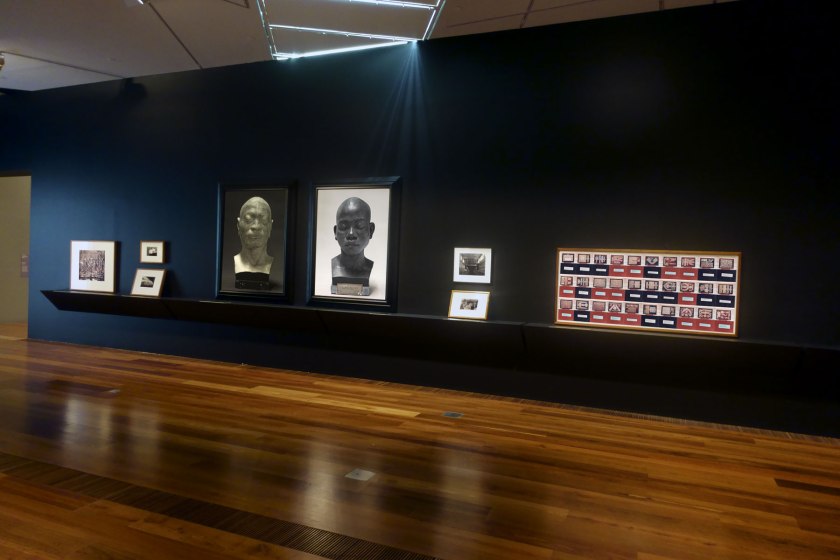
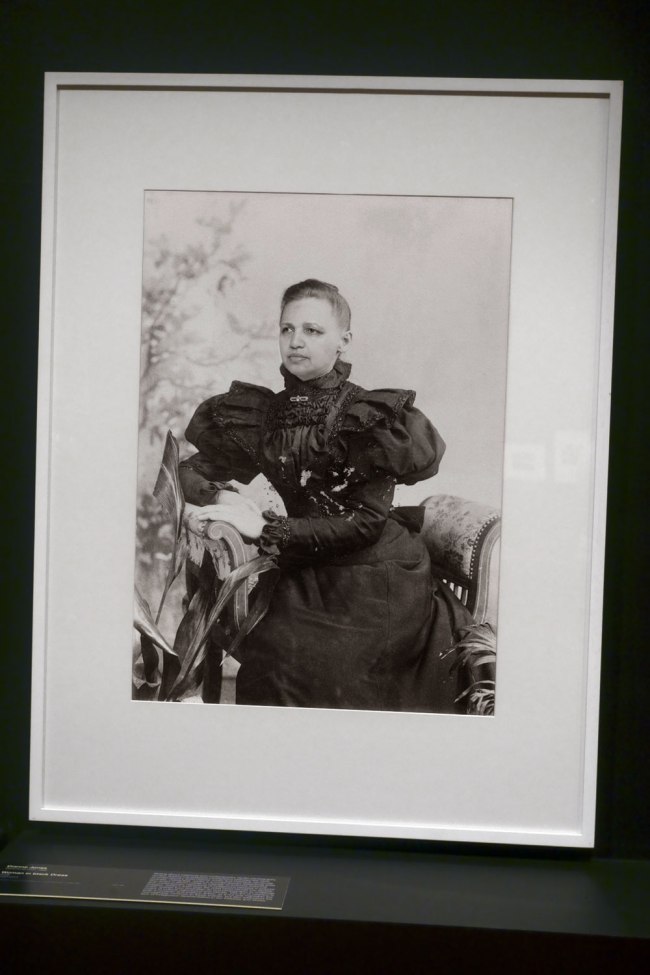
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Diane Jones’ Woman in black Dress (2009)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Writing about historical and contemporary studio photography, curator Sophia Cai explored connections between the work of contemporary artist Dianne Jones and historical vernacular portraits, noting that ‘Jones is a contemporary Balardung artist who works in photo media to critically re-examine historical and contemporary depictions of Indigenous peoples in popular imagery. Jones’s work sees the artist insert herself into familiar, iconic scenes from Australian art and photography to challenge myths of cultural nationhood and identity. This act of insertion is both a comedic and political action, as it not only highlights the homogeneity common to these scenes, but also addresses the lack of Indigenous representation in our histories and stories’.
Wall text from the exhibition
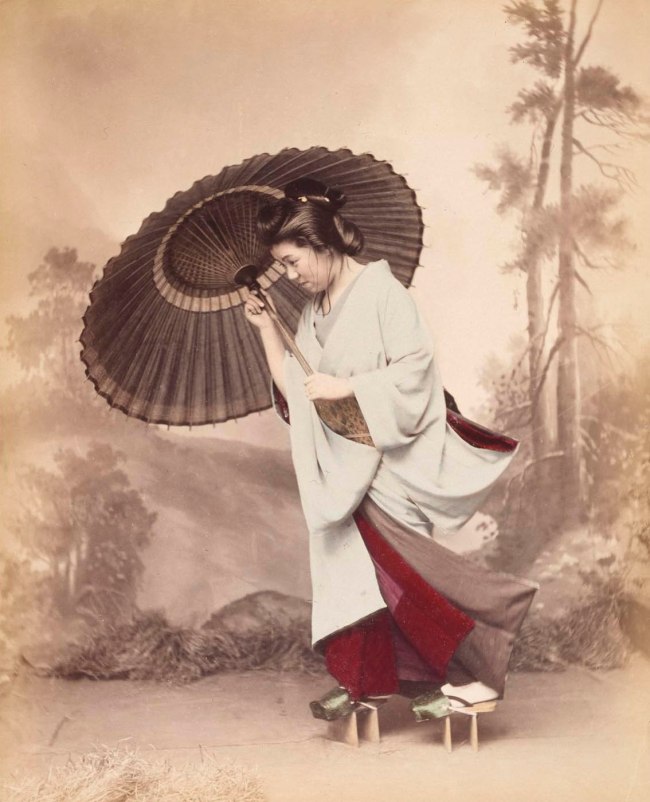
Unknown photographer (Japanese active 1880s)
No title (Woman with umbrella)
1880s
Albumen silver photograph, colour dyes
24.2 x 19.4cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Public domain
In the nineteenth century a distinctive style of photography developed in Japan in which the aesthetics of traditional woodblock prints (ukiyo-e) were translated into photographic practice. The resulting photographs included carefully composed genre images featuring traditional aspects of the life and work of the Japanese middle classes. Typical life scenes, such as this one showing a woman walking through a rainstorm, were recreated in the studio with remarkable attention to detail, as seen in the subject’s ‘windblown’ kimono. As these images were staged for the European market, however, they often diverted from reality in favour of focusing on customs that would have appeared ‘exotic’ to their Western viewers.
Wall text from the exhibition
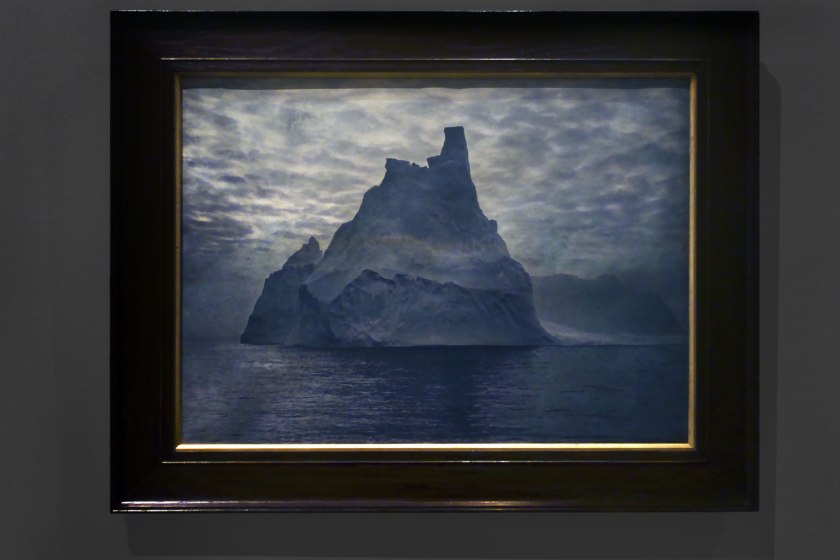
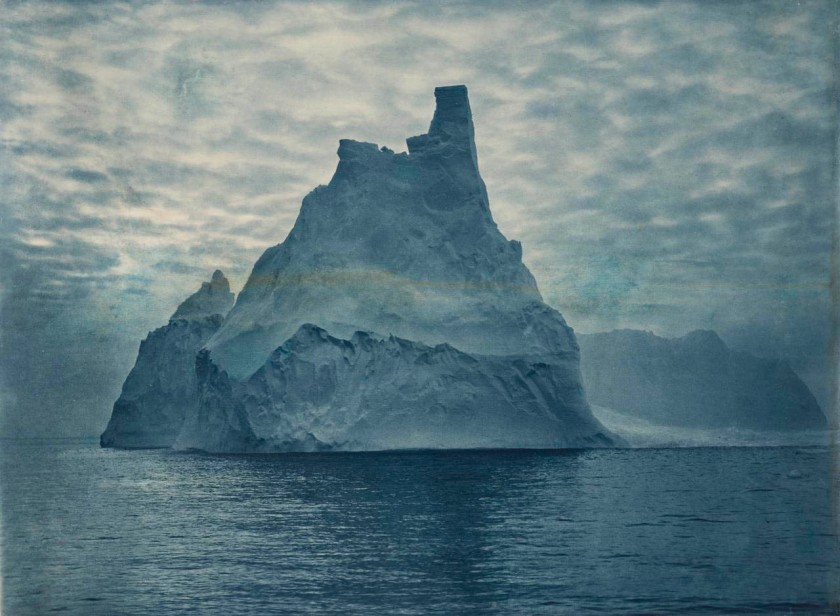
Installation view of the exhibition Photography: Real & Imagined at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne showing Frank Hurley’s A turreted berg (1913, below)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Frank Hurley (Australian, 1890-1962)
No title (A turreted berg)
1913
Carbon print
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1999
Public domain
The photographs produced by Frank Hurley during his time as the official photographer for the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911-1914), and his subsequent texts, dramatically convey the awe-inspiring gargantuan icebergs encountered in the region. ‘No grander sight have I ever witnessed among the wonders of Antarctica’, Hurley wrote of the icebergs in the area where this photograph was taken. ‘We threaded a way down lanes of vivid blue with shimmering walls of mammoth bergs rising like castles of jade on either side.’ This photograph is, at first appearance, a sublimely ‘true’ representation of an iceberg. On closer inspection, however, subtle alterations become apparent. More real than real, Hurley’s constructed image was celebrated at the time and continues to be.
Wall text from the exhibition
André Kertész (Hungarian, 1894-1985)
Chez Mondrian, Paris
1926; c. 1972 {printed}
Gelatin silver photograph
24.7 x 18.5 cm (image) 25.3 x 20.4 cm (sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1973
Public domain
Trude Fleischmann (Austrian 1895-1990, United States 1938-1990)
The actress Sibylle Binder, Vienna
c. 1926
Gelatin silver photograph
21.9 × 16.2cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2022
Public domain
Trude Fleischmann (American born Austria, 1895-1990)
Trude Fleischmann (22 December 1895 – 21 January 1990) was an Austrian-born American photographer. After becoming a notable society photographer in Vienna in the 1920s, she re-established her business in New York in 1940. …
In 1920, at the age of 25, Fleischmann opened her own studio close to Vienna’s city hall. Her glass plates benefitted from her careful use of diffuse artificial light. Photographing music and theatre celebrities, her work was published in journals such as Die Bühne, Moderne Welt, ‘Welt und Mode and Uhu. She was represented by Schostal Photo Agency (Agentur Schostal). In addition to portraits of Karl Kraus and Adolf Loos, in 1925 she took a nude series of the dancer Claire Bauroff which the police confiscated when the images were displayed at a Berlin theatre, bringing her international fame. Fleischmann also did much to encourage other women to become professional photographers.
With the Anschluss in 1938, Fleischmann was forced to leave the country. She moved first to Paris, then to London and finally, together with her former student and companion Helen Post, in April 1939 to New York. In 1940, she opened a studio on West 56th Street next to Carnegie Hall which she ran with Frank Elmer who had also emigrated from Vienna. In addition to scenes of New York City, she photographed celebrities and notable immigrants including Albert Einstein, Eleanor Roosevelt, Oskar Kokoschka, Lotte Lehmann, Otto von Habsburg, Count Richard von Coudenhove-Kalergi and Arturo Toscanini. She also worked as a fashion photographer, contributing to magazines such as Vogue. She established a close friendship with the photographer Lisette Model.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Sybille Binder (Austrian, 1895-1962)
Sybille Binder (5 January 1895 – 30 June 1962) was an Austrian actress of Jewish descent whose career of over 40 years was based variously in her home country, Germany and Britain, where she found success in films during the 1940s.
Binder began her stage career in Berlin in 1915, then in 1918 moved to Munich, where she enjoyed success in classical drama. Between 1916 and 1918 she also appeared in a handful of silent films. In 1922, she returned to Berlin and received acclaim for her performance in Frank Wedekind’s Earth Spirit. Over the next few years she performed regularly in Germany and Austria then, in the mid-1930s as war approached and conditions in Germany became difficult, she made the decision to move to England.
Between 1942 and 1950 Binder featured in 13 British films, including several of superior quality. Her first screen appearance in Britain came auspiciously in the highly acclaimed supernatural drama Thunder Rock, playing opposite dramatic heavyweights including Michael Redgrave, James Mason and Frederick Valk. Other notable films in which Binder appeared were war drama Candlelight in Algeria (1944), hugely popular period melodrama Blanche Fury, espionage thriller Against the Wind and amnesia-themed romance Portrait from Life (all 1948).
Binder returned to Germany in 1950, settling in Düsseldorf, where she successfully picked up her stage career but did not attempt to break into the German film industry. She died on 30 June 1962, aged 67.
Text from the Wikipedia website
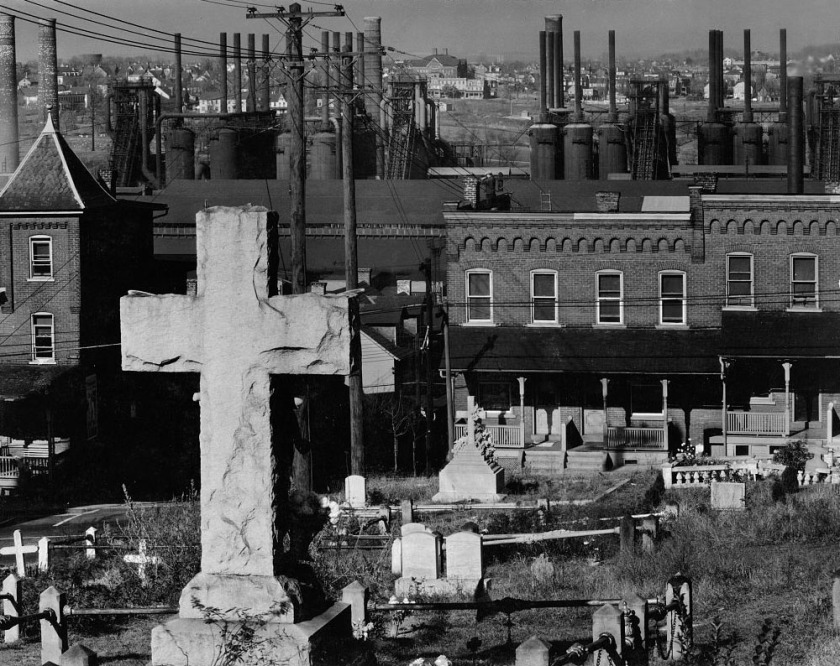
Walker Evans (American 1903-1975)
Graveyard, houses and steel mill, Bethlehem, Pennsylvania
1935, printed c. 1975
Gelatin silver photograph
39.5 × 49.5cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1975
Public domain
Marion Post Wolcott (American, 1910-1990)
Near Wadesboro, North Carolina
1938; c. 1975 {printed}
Gelatin silver photograph
26.4 x 26.5cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1975
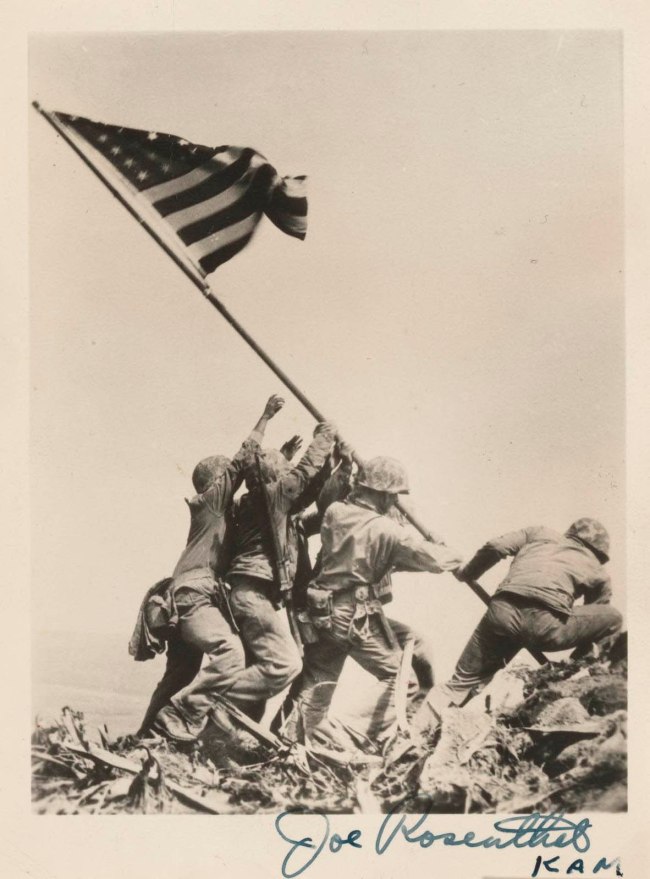
Joe Rosenthal (1911-2006)
Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima
1945; printed (c. 1948)
Gelatin silver photograph
11.5 × 8.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of Francis Reiss, 2014
Public domain
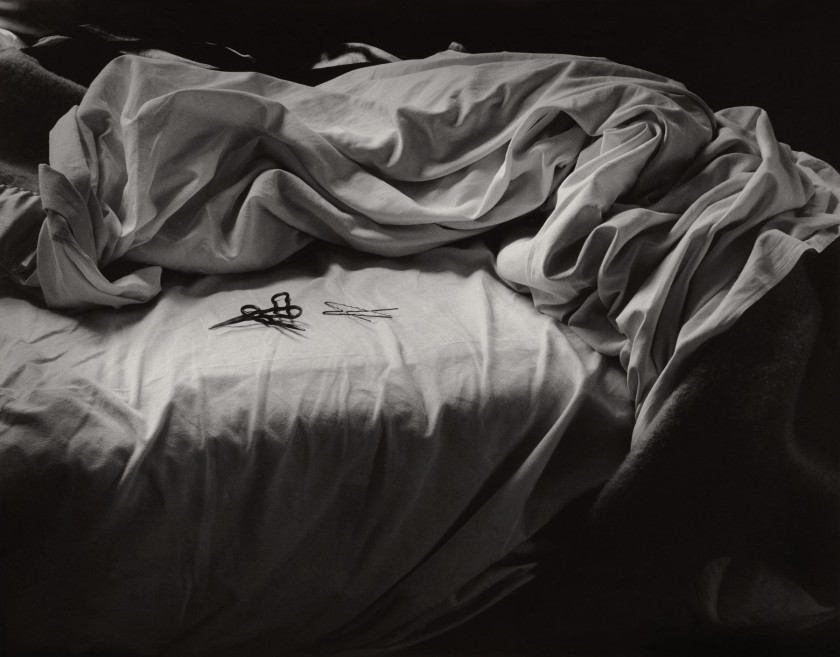
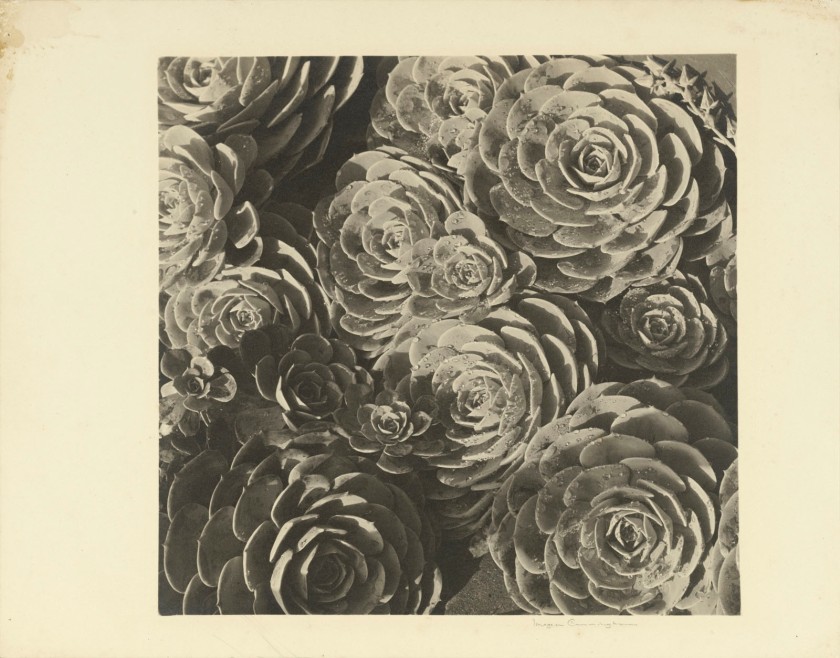
Imogen Cunningham (American, 1883-1976)
The unmade bed
1957
Gelatin silver photograph
24.4 × 32.7cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of Krystyna Campbell-Pretty AM and Family through the Australian Government’s Cultural Gifts Program, 2023
In 1957, while teaching at the California School of Fine Arts in San Francisco, Imogen Cunningham overheard her colleague Dorothea Lange set a task for her students to photograph an ordinary object that they used every day. Cunningham is said to have set the same task for herself. The resulting photograph, The unmade bed, is an image constructed with familiar objects, including discarded hairpins and a crumpled bedsheet. In this quiet and unassuming photograph, Cunningham has created both an elegant still life and an unexpectedly tender portrait of a woman recently risen from her sleep.
Wall text from the exhibition
George Bell (Australian 1878-1966, England 1907-1920)
Pain
1966, printed 1991
Gelatin silver photograph
28.2 × 35.6cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1991
Public domain
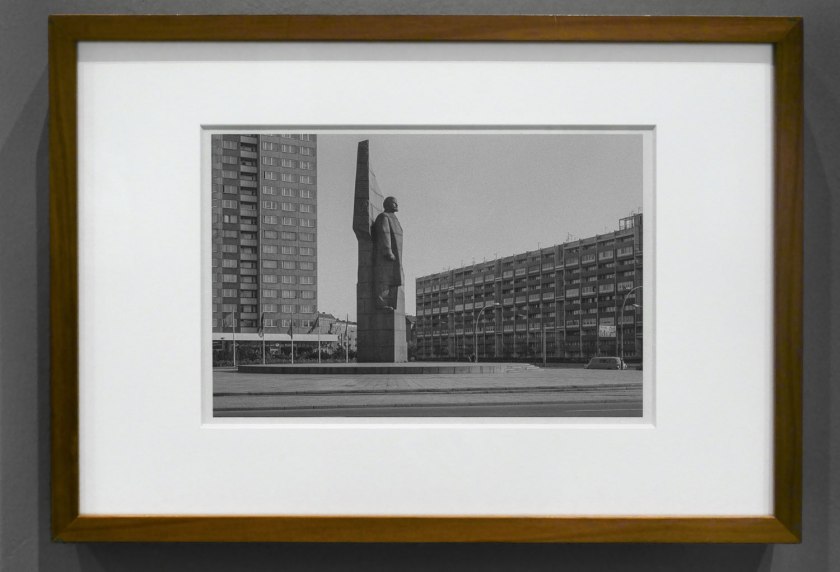
Ulrich Wüst (German, b. 1949)
Berlin (installation view)
1982
From the Cityscapes (Stadtbilder) series 1979-1984
Inkjet print
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased NGV Foundation, 2018
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Hank Willis Thomas (American, b. 1976)
Amelia falling
2014
Photographic print, mirror and glass
166 x 135cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Bowness Family Fund for Photography, 2017
© Hank Willis Thomas. Courtesy of the artist and Jack Shainman Gallery, New York
Hank Willis Thomas’s photographs printed on mirrors are sometimes difficult to look at, but with the viewer’s reflection integrated into the work they are also impossible to ignore. In this work we bear witness to the shockingly violent incursions into what was intended to have been a peaceful civil rights protest in Selma, Alabama. Willis Thomas’s work and its source image, a photograph taken in 1965 by Spider Martin, show civil rights activist Amelia Boynton Robinson being carried by fellow marchers after being gassed and beaten. Through his use of archival images Willis Thomas draws connections between historical moments and contemporary life, leaving little comfortable space to be a dispassionate observer.
Wall text from the exhibition
Malala Andrialavidrazana (Madagascar, b. 1971)
Figures 1850, various empires, kingdoms, states and republics
2015
Inkjet print
110.0 x 138.5cm
ed. 1/5
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Ruth Margaret Frances Houghton Bequest, 2021
© Malala Andrialavidrazana. Courtesy of the artist and AFRONOVA Gallery
Malala Andrialavidrazana’s series Figures are digital photomontages created using images sourced from archival collections of nineteenth-century maps of the African continent, as well as bank notes and stamps. The historical maps are overlaid with portraits of various heads of state and depictions of colonial developments and decorative details showing people, places, plants and animals from across Africa. These photomontages reveal the complex political and cultural histories of maps, cartography and archives, and the changing understanding of the greater African continent by European colonial powers in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries.
Wall text from the exhibition
Section wall texts from the exhibition
Light wall text from the exhibition
Systems and Surface wall text from the exhibition
Surreal wall text from the exhibition
Narrative wall text from the exhibition
Work and Play wall text from the exhibition
Movement wall text from the exhibition
Studio and Things wall text from the exhibition
Display wall text from the exhibition
Consumption wall text from the exhibition
SELF wall text from the exhibition (missing)
Skin wall text from the exhibition
Community and Touch wall text from the exhibition
ENVIRONMENT wall text from the exhibition (missing)
Place and Built wall text from the exhibition
NINETEETH-CENTURY PHOTOGRAPHY wall text from the exhibition (missing)
Conflict wall text from the exhibition
DEATH wall text from the exhibition (missing)
The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia
Federation Square
Corner of Russell and
Flinders Streets, Melbourne
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm















































































































































































































































































![Ansel Adams (American, 1902-1984) '[Dogwood Blossoms, Yosemite National Park]' Negative about 1938; print 1941 Ansel Adams (American, 1902-1984) '[Dogwood Blossoms, Yosemite National Park]' Negative about 1938; print 1941](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2022/05/ansel-adams-dogwood-blossoms-yosemite-national-park.jpg?w=650&h=825)
![Imogen Cunningham (American, 1883-1976) '[Sonya Noskowiak]' 1928 Imogen Cunningham (American, 1883-1976) '[Sonya Noskowiak]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2022/05/cunningham-sonya-noskowiak.jpg?w=650&h=813)
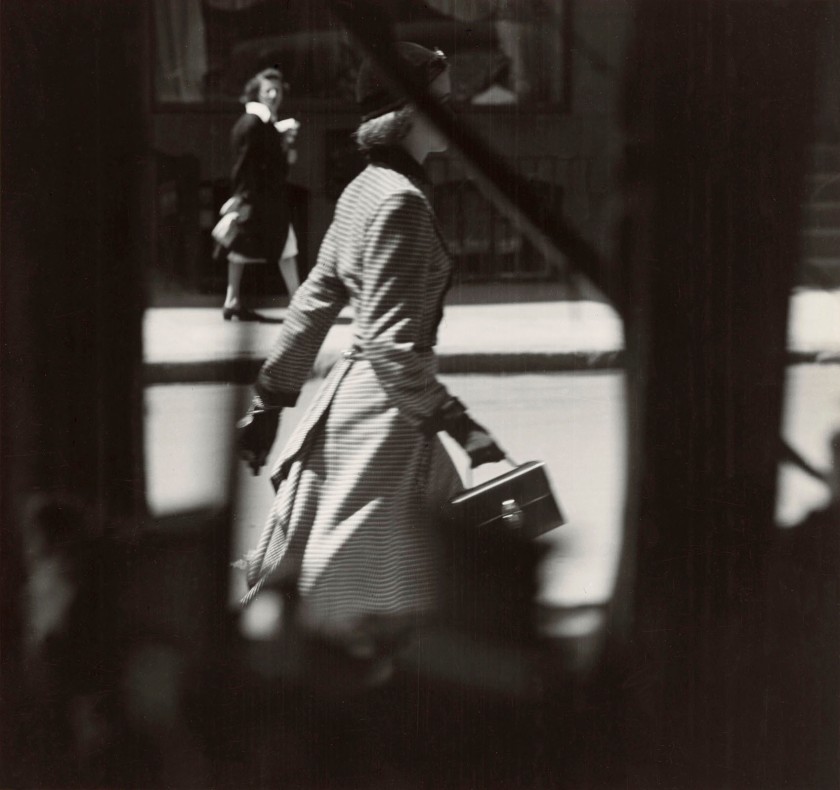
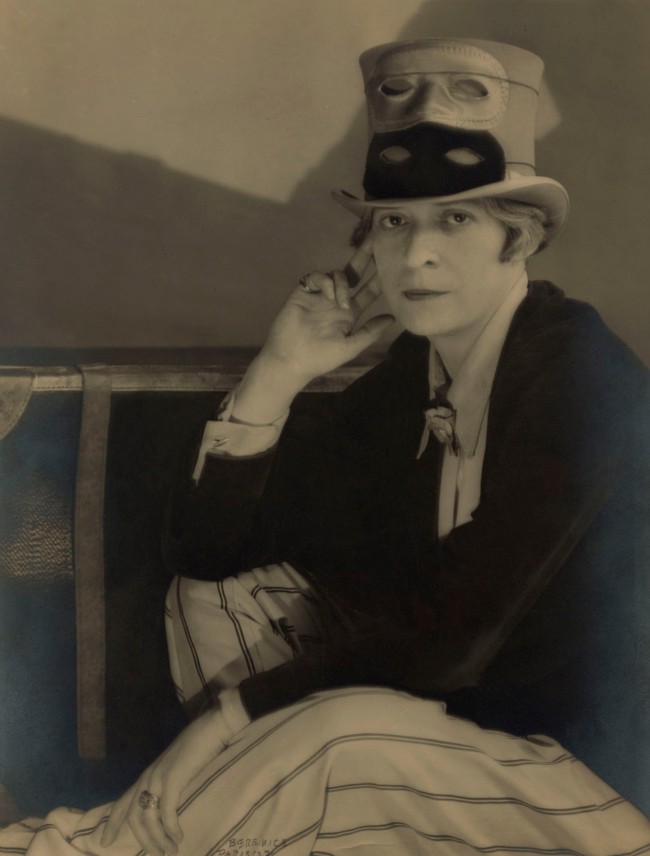












































































































































































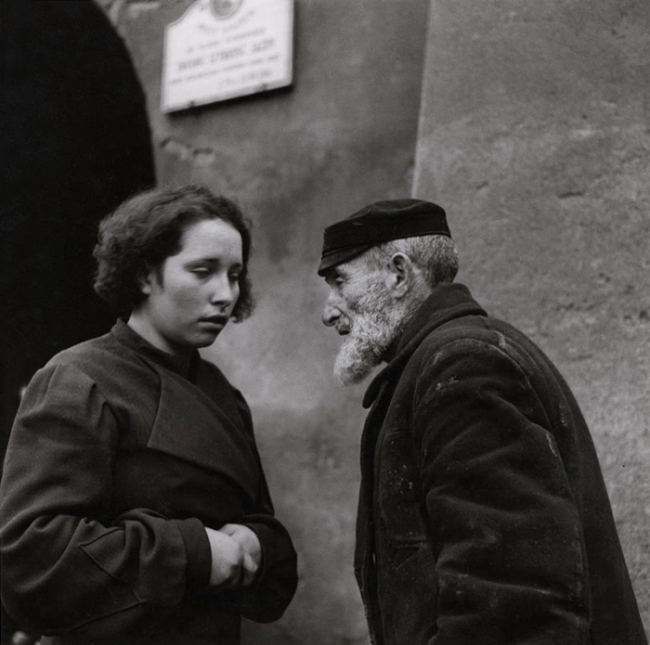
![Emmy Andriesse (Dutch, 1914-1953) 'Amsterdam tijdens de hongerwinter' (Amsterdam during the hunger winter) [1944-1945] book published 1947 Emmy Andriesse (Dutch, 1914-1953) 'Amsterdam tijdens de hongerwinter' (Amsterdam during the hunger winter) [1944-1945] book published 1947](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/11/5280-082-small.jpg?w=840)
![Emmy Andriesse (Dutch, 1914-1953) 'Amsterdam tijdens de hongerwinter' (Amsterdam during the hunger winter) [1944-1945] book published 1947 (detail) Emmy Andriesse (Dutch, 1914-1953) 'Amsterdam tijdens de hongerwinter' (Amsterdam during the hunger winter) [1944-1945] book published 1947 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/11/5280-082-detail1.jpg?w=650&h=804)
![Emmy Andriesse (Dutch, 1914-1953) 'Amsterdam tijdens de hongerwinter' (Amsterdam during the hunger winter) [1944-1945] book published 1947 (detail) Emmy Andriesse (Dutch, 1914-1953) 'Amsterdam tijdens de hongerwinter' (Amsterdam during the hunger winter) [1944-1945] book published 1947 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/11/5280-082-detail2.jpg?w=650&h=750)
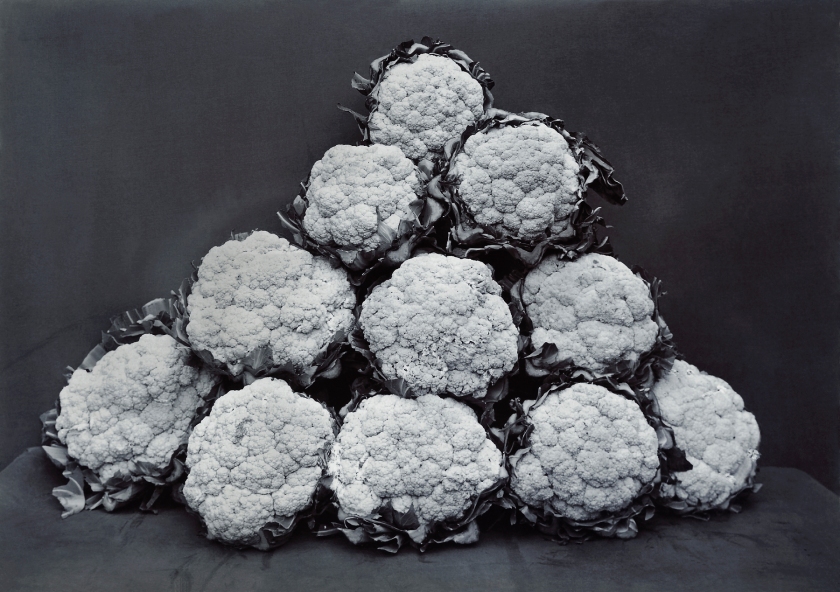
















































You must be logged in to post a comment.