Exhibition dates: 31st October, 2021 – 30th January, 2022
Curator: The exhibition is curated by Andrea Nelson, associate curator in the department of photographs, National Gallery of Art, Washington.

Tsuneko Sasamoto (Japanese, b. 1914)
Ginza 4 Chome P.X.
1946, printed 1993
Gelatin silver print
Image: 29.6 x 29.6cm (11 5/8 x 11 5/8 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 41 x 51.2 x 2.5cm (16 1/8 x 20 3/16 x 1 in.)
Collection of Tokyo Photographic Art Museum
Abstract
Using the media images from the exhibition The New Woman Behind the Camera at the National Gallery of Art, Washington (31st October, 2021 – 30th January, 2022) as a starting point, this text examines the (in)visibility of the “New Woman” behind the camera. The text briefly investigates the disenfranchisement of women in 19th century through the work of George Sand and Camille Claudel; the role of the female flâneuse and the rise of the suffragettes; the relationship between two women and two men; a story; the work of two women photographers (Germaine Krull and Claude Cahun) who through photography challenged the representation of gender identity; a Zen proposition, and the particular becomes universal – in order to understand how artists, both female and male, find integrity on their chosen path.
Keywords
New Woman, photography, art, integrity, George Sand, Camille Claudel, female flâneuse, suffragette, camera, Germaine Krull, Claude Cahun, Leni Reifenstahl, Georgia O’Keeffe, Alfred Stieglitz, female emancipation, gender identity, representation, Sabine Weiss, Susan Sontag, self recognition, patriarchal society.
Download the complete text of Finding Integrity: “New Woman” artists and female emancipation in the first half of the twentieth-century (5.6Mb Word docx)
“The world doesn’t like independent women, why, I don’t know, but I don’t care.”
Berenice Abbott
Finding Integrity: “New Woman” artists and female emancipation in the first half of the twentieth-century
After thousands of years of human existence, woman still do not have equality. They have to fight for equal pay for the same job, they fight for equal opportunity in many jobs and top level positions, they fight for control of their body, and they fight against misogyny, discrimination and the aggression of hypermasculinity. They, and their children, fight not to be killed by jealous and enraged (x)lovers or (x)husbands – where x in mathematics is a variable number which is not yet known (in 2021 in Australia 43 women died at the hands of men) – whose ego and possessiveness cannot bear the thought of a vibrant, free thinking woman living beyond their control. I know of these things having grown in the womb, having grown up for the first 18 years of my life feeling my mother being abused, and then being abused myself trying to protect my mother.
My mother wanted to study music at Cambridge after graduating from the Royal College of Music but because she got married and had children she never had the opportunity. Her struggle, as with many women still, was to find her place in a man’s world – as a wife and mother in her case – to live within the parameters of the social construct that is a patriarchal society. At the time (in the 1960s) she said she felt less than human… for there was no help and little opportunity for women to escape their situation. Her one salvation was music and the one way she found to subvert the dominant structures was to teach piano. Now ninety years old, she has taught piano for the rest of her life. She found her voice and her independence. She found her integrity.
Earlier generations
In earlier generations, before the “New Woman”, women had to conform (to society’s expectations) and submit (to men) … unless they were notorious, celebrities or geniuses. Otherwise they were mainly disenfranchised and disempowered.
Women had to write under men’s names to be accepted, to sell and make a living. The novelist Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin initially collaborated with the male writer Jules Sandeau and they published under the name Jules Sand before Dupin took up the pen name that was to make her famous and a celebrity across Europe: George Sand (French, 1804-1876). “Sand’s writing was immensely popular during her lifetime and she was highly respected by the literary and cultural elite in France.”1 She chose to wear male attire in public without a permit (which “enabled her to circulate more freely in Paris than most of her female contemporaries, and gave her increased access to venues from which women were often barred, even women of her social standing”1), and she smoked “tobacco in public; neither peerage nor gentry had yet sanctioned the free indulgence of women in such a habit, especially in public… While there were many contemporary critics of her comportment, many people accepted her behaviour until they became shocked with the subversive tone of her novels.”1 Sand was also politically active and “sided with the poor and working class as well as women’s rights. When the 1848 Revolution began, she was an ardent republican. Sand started her own newspaper, published in a workers’ co-operative.”1
![Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) 'George Sand (Amandine-Aurore-Lucile Dupin), Writer' c. 1865 Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) 'George Sand (Amandine-Aurore-Lucile Dupin), Writer' c. 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/10/realideal5-web.jpg?w=650&h=854)
Nadar (Gaspard Félix Tournachon) (French, 1820-1910)
George Sand (Amandine-Aurore-Lucile Dupin), Writer
c. 1865
Albumen silver print from a glass negative
24.1 x 18.3 cm (9 1/2 x 7 1/4 in.)
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
In other words because of her visibility, celebrity, social standing, writing, intellect and revolutionary fervour she was acknowledged as a great woman. Men consulted with her and took her advice. Upon her death under the heading “Emancipated Woman,” in The Saturday Review, Victor Hugo commented: “George Sand was an idea. She has a unique place in our age. Others are great men … she was a great woman.” All well and good, but then he continues, “In this country, whose law is to complete the French Revolution, and begin that of the equality of the sexes, being a part of the equality of men, a great woman was needed. It was necessary to prove that a woman could have all the manly gifts without losing any of her angelic qualities; be strong without ceasing to be tender. George Sand proved it.”2 In other words to be the equal of a man, a woman must act like a man but also keep her womanly qualities (tenderness, femininity). She couldn’t really be herself because she had to measure up to the ideals of men. What a slap in the face, a kind of pseudo-equality – if you played your cards right and obeyed the rules of the game.
An incredibly sad example of female disenfranchisement in the arts is that of August Rodin’s assistant Camille Claudel (French, 1864-1943) who became his model, his confidante, and his lover. Claudel started working in Rodin’s workshop in 1883 and became a source of inspiration for him.

César (French)
Portrait de Camille Claudel
before 1883
Musée Camille Claudel
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
“The exact nature of the tasks with which she was entrusted remains uncertain, but she apparently spent most of her time on difficult pieces, such as the hands and feet of figures for monumental sculptures (notably The Gates of Hell). For Claudel, this was an intensive period of training under Rodin’s supervision: she learned about his profiles method and the importance of expression. In tandem, she pursued her own investigations, accepted her first commissions and sought recognition as an independent artist at the Salon. Between 1882 and 1889, Claudel regularly exhibited busts and portraits of people close to her at the Salon des Artistes Français. Largely thanks to Léon Gauchez, Rodin’s friend the Belgian art dealer and critic, several of her works were purchased by French museums in the 1890s.”3
But women working under the “master” were not often acknowledged.
“Le Cornec and Pollock state that after the sculptors’ physical relationship ended [with Rodin in 1892 after an abortion], she was not able to get the funding to realise many of her daring ideas – because of sex-based censorship and the sexual element of her work. Claudel thus had to either depend on Rodin, or to collaborate with him and see him get the credit as the lionised figure of French sculpture. She also depended on him financially, especially after her loving and wealthy father’s death, which allowed her mother and brother, who disapproved of her lifestyle, to maintain control of the family fortune and leave her to wander the streets dressed in beggars’ clothing.
Claudel’s reputation survived not because of her once notorious association with Rodin, but because of her work. The novelist and art critic Octave Mirbeau described her as “A revolt against nature: a woman genius.”” …
Ayral-Clause says that even though Rodin clearly signed some of her works, he was not treating her as different because of her gender; artists at this time generally signed their apprentices’ work. Others also criticise Rodin for not giving her the acknowledgment or support she deserved. …
Other authors write that it is still unclear how much Rodin influenced Claudel – and vice versa, how much credit has been taken away from her, or how much he was responsible for her woes. Most modern authors agree that she was an outstanding genius who, starting with wealth, beauty, iron will and a brilliant future even before meeting Rodin, was never rewarded and died in loneliness, poverty, and obscurity. Others like Elsen, Matthews and Flemming suggest it was not Rodin, but her brother Paul who was jealous of her genius, and that he conspired with her mother, who never forgave her for her supposed immorality, to later ruin her and keep her confined to a mental hospital.”4
This “sculptor of genius” was eventually “voluntarily” committed by her family to a psychiatric hospital in 1913 where she lived the remaining 30 years of her life, unable to practice her art. Her remains were buried in a communal grave at the asylum, her bones mixed with the bones of the most destitute. Her brother Paul Claudel could not be bothered with a grave for her, while he specified the exact place of his internment… the ultimate irony being that, Rodin had decided to include an exhibition space reserved exclusively for Camille Claudel’s works in the future museum that would house the collections he bequeathed to the French state on his death (at the Rodin Museum) – a request that could not be honoured until 1952, when Paul Claudel donated four major works by his sister to the museum.5 Bitter irony.

Ruth Orkin (American, 1921-1985)
American Girl in Italy
1951
Gelatin silver print
© Ruth Orkin
Courtesy of Howard Greenberg Collection
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
The female flâneuse and a period of transition
During the 19th century women could not stroll alone in the city.
“In Baudelaire’s essays and poems, women appear very often. Modernity breeds, or makes visible, a number of categories of female city-dwellers. Among the most prominent in these texts are: the prostitute, the widow, the old lady, the lesbian, the murder victim, and the passing unknown woman… But none of these women meet the poet as his equal. They are subjects of his gaze, objects of his ‘botanising’. The nearest he comes to a direct encounter, with a woman who is not either marginal or debased, is in the poem, À Une Passante (Even here, it is worth noting that the woman in question is in mourning – en grand deuil). The tall, majestic woman passes him in the busy street; their eyes meet for a moment before she continues her journey, and the poet remains to ask whether they will only meet again in eternity… (But if this is the rare exception of a woman sharing the urban experience, we may also ask whether a ‘respectable’ woman, in the 1850s would have met the gaze of a strange man).”6
But as Janet Wolff observes, women clearly were active and visible in other ways in the public arena, especially when it came to the construction of women’s dress as a sign of their husbands’ position: in effect, the less they worked and the more they evidenced the performance of conspicuous leisure and consumption, the more this was to the credit of their master rather than to their own credit. Wolff further notes, “The establishment of the department store in the 1850s and the 1860s provided an important new arena for the legitimate public appearance of middle-class women…” but denies this has anything to do with women being a female flâneur – a flâneuse – because the fleeting, anonymous encounters and purposeless strolling she has been considering “do not apply to shopping, or to women’s activities either as public signs of their husband’s wealth or as consumers.”7 Wolff rejects the notion of a female flâneuse as “such a character was rendered impossible by the sexual divisions of the nineteenth century.”8
Others disagree with this interpretation. In a paper titled “Gender Differences in the Urban Environment: The flâneur and flâneuse of the 21st Century”, Akkelies van Nes and Tra My Nguyen offer the following history of the flâneur9 and the flâneuse concepts (apologies for the long quotation but it necessary):
“The term flâneur originated from the 18th century. It was described by Charles Baudelaire as ‘gentleman stroller of city streets’ (van Godsendthoven, 2005). …
‘The flâneur was an idle stroller with an inquisitive mind and an aesthetic eye, a mixture of the watchful detective, the aesthetic dandy and the gaping consumer, the badaud. A solitary character, he avoided serious political, familial or sexual relationships, and was only keen on the aesthetics of city life. He read the city as a book, finding beauty in the obsolete objects of other people, but in a distanced, superior way’ (van Godsendthoven, 2005).
The flâneur is a product of modern life and the industrial revolution, parallel to the references of the tourist in contemporary times. The arrival of department stores and the ‘Haussmannization’ of Paris’ streets in the second half of the nineteenth century swept away large parts of the historical city and also the domain of the flâneur. The archetype of the flâneur disappeared with its surroundings, in favour of the women- oriented department stores. ‘The department store may have been, as Benjamin put it, the flâneur’s last coup, but it was the flâneuse’s first’ (Friedberg, 1993).
The flâneuse is not a female flâneur, but she is a version of the flâneur. She does not experience the city in the same way as he does. It is hard to define the archetype of the flâneuse, because the flâneur himself consists of paradoxes and many subcategories. Key concepts for flâneur and flâneuse are the amount of spare time, the aesthetic detachment towards objects, crowd and sceneries they see and their ambiguity about it.
The department stores were a starting point for the existence of the flâneuse, but this also marked her as a consumer, a ‘badaud’. The difference between badauds and flâneuses are the distance they create between themselves and the activities in the city. A characteristic of flânerie is an aesthetic distance between the subject and the object of attention. The badaud-flâneuse lacks this distance. The city is not being experienced, but is reduced to a place to consume.
As implied, the badaud-flâneuse did not have the full ability to flânerie. However, she has many qualities, which are at least some first initiatives to stroll around. Her domain moved from the interior of her home to the interior of the department store and sometimes even to the streets (Parsons, 2000). Shopping, art and day trips contribute to develop a certain view in that period of society, which was at the end of 19th century. Friedberg was very well aware that this new freedom was not the same as the freedom of the flâneur (Friedberg, 1993).
The flâneuse concept developed throughout the years expanded somehow further than being a badaud. She was discovering domains like art forms, like for example the cinema and the theatre at the beginning of the 20th century. But she was still objectified by men and patriarchic institutes. However, women became independent, without taking over the absent look and gaze of the flâneur. They changed their lives into art forms and had an opinion about the society they lived in. To gain respect as artists, the image of women as muses had to disappear. She had to claim an active role and to develop her own personality.
Through the literature, the life of the flâneuse and the female characters in the city, like passersby, artists, dandies and badauds [gawkers, bystanders] are often interlaced with each other, and difficulties they experienced are alike. The flâneuse often shifted between these roles, but distinguished herself by her independency and distanced. She became a symbol for post-modern urban life: a wanderer in many shapes.”10
Nes and Nguyen further argue that the emancipation of women over the last two decades “has brought the flâneuse to a more equal position with the flâneur in the invisible right to be in public urban space. However, aspects like safety and when and where women are spending time in urban space still have effect on how women use public spaces and affect the public spheres.”11 Indeed, with the despicable murder of too many women in Melbourne in recent years by predatory men (Aiia Maasarwe, Mersina Halvagis, Masa Vukotic, Eurydice Dixon, Tracey Connelly, Sarah Cafferkey, Renea Lau and Jill Meagher to name just a few…), women still fear walking the streets alone. “Even when grief enveloped his family, Bill Halvagis can recall the wider sense of public outrage that followed the murder of his older sister Mersina. The shock that someone could do such a thing in a public place was as brutal as the crime itself.”12

Unknown photographer (Australian)
People march through Brunswick in Melbourne after the murder of Jill Meagher in 2012
2012
Australian Associated Press (AAP)
Republished under Creative Commons from The Conversation website
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
Looking back a century later, one of the key points of female emancipation in the early twentieth century is that women gained their independence “and had an opinion about the society they lived in… She had to claim an active role and to develop her own personality” while present and visible in the community, present in a public place. The world-wide suffragette movement was at the forefront of this early twentieth-century revolution.
“A suffragette was a member of an activist women’s organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner “Votes for Women”, fought for the right to vote in public elections. The term refers in particular to members of the British Women’s Social and Political Union (WSPU), a women-only movement founded in 1903 by Emmeline Pankhurst, which engaged in direct action and civil disobedience.” During the First World War “the suffragette movement in Britain moved away from suffrage activities and focused on the war effort… Women eagerly volunteered to take on many traditional male roles – leading to a new view of what women were capable of.”13 However, this new found capability and visibility in society “cast women as passive, erotic objects, subjecting them to a kind of voyeuristic control” by men, embodying the gaze of modernity which is both covetous and erotic – public sites (of interaction) producing “meanings and positions from which those meanings are consumed.”14 Women were “playing” in a man’s world subject to their approval, their gaze and their desire to possess and control the female both physically and sexually.
But, as Griselda Pollock observes, “modernity was not represented as taking place in exclusively masculine, because public, domains: rather, the spaces of modernity were in fact marginal spaces, those in which the city’s “new subjective experiences of exhilaration and alienation, pleasure and fear, mobility and confinement, expansiveness and fragmentation,” were most intense. These spaces of intersection happened to be sites in which bourgeois men came into contact with women…”15
Here comes the “New Woman” taking on traditional male roles, socialising in marginalised spaces, boldly going where few women had gone before, sampling new subjective experiences, becoming who they wanted to be… all under the munificent gaze of the (bourgeois) male.
Two women and two men
The “New Woman”, mainly middle class females, took their courage in their hands to become professional photographers and artists: photojournalists, fashion photographers, war photographers, magazine and picture photographers, working with successful men and women in fashion, interior design, news, graphics and art. At the Bauhaus female students pushed the boundaries in fields such as textiles, lighting, ceramics and costume, the “New Woman” putting her femininity under the spotlight.
By pushing boundaries, female artists and photographers broke ground becoming female in a male world… within the framework of modernity and aesthetics, to form the modern divine. In a youthful culture of commercial and technological changes they gained their independence through hard work and talent via the stereotype of the “New Woman” – a constructed image portrayed in the magazines (bobbed hair beauty, flapper, speed, fast cars, cigarette smoking) which played into the male system of the recognition of the feminine subject. By playing the system they became successful and visible, self conscious of their undeniable abilities. But at what cost? Many women, excited by the world of men, where chewed up and spat out, dumped, and sometimes met a terrible end.

Unknown photographer (German)
Leni Riefenstahl with Heinrich Himmler (left) during the 1934 Nuremberg Nazi Party Rally in the Luitpold Arena while recording her film “Triumph of the Will”
September 9, 1934
German Federal Archives / Wikipedia (public domain)
The epito/me of this new self consciousness and will to power was the Nazi film director Leni Reifenstahl (German, 1902-2003). Reifenstahl began as an interpretive dancer who often made almost 700 Reichsmarks for each performance. “Her dancing revealed her childlike quality, her surrender to the moment, and this natural, naïve quality made her the perfect heroine for his [Arnold Fanck’s] Alpine love stories. Riefenstahl was involved in a love triangle involving Fanck and her leading man [in director Fanck’s 1920s “mountain films”], Luis Trenker, demonstrating, in Mr. Bach’s words, “Leni’s skill at dominating the exclusive male society in which she found herself now and for almost all the rest of her professional life.””16 Reifenstahl used her beauty, voracious sexual prowess (with both women and men) and talent to infiltrate the world of film and learn acting and film editing techniques. Hitler saw her films and thought Riefenstahl epitomised the perfect German female.
“Riefenstahl heard Nazi Party (NSDAP) leader Adolf Hitler speak at a rally in 1932 and was mesmerised by his talent as a public speaker… Hitler was immediately captivated by Riefenstahl’s work. She is described as fitting in with Hitler’s ideal of Aryan womanhood, a feature he had noted when he saw her starring performance in Das Blaue Licht. After meeting Hitler, Riefenstahl was offered the opportunity to direct Der Sieg des Glaubens (“The Victory of Faith”), an hour-long propaganda film about the fifth Nuremberg Rally in 1933… Still impressed with Riefenstahl’s work, Hitler asked her to film Triumph des Willens (“Triumph of the Will”), a new propaganda film about the 1934 party rally in Nuremberg. More than one million Germans participated in the rally. The film is sometimes considered the greatest propaganda film ever made… In February 1937, Riefenstahl enthusiastically told a reporter for the Detroit News, “To me, Hitler is the greatest man who ever lived. He truly is without fault, so simple and at the same time possessed of masculine strength”.”17
After the Second World War Riefenstahl was tried four times by postwar authorities for denazification and eventually found to be a “fellow traveller” (Mitläufer) who sympathised with the Nazis but she won more than fifty libel cases against people accusing her of having previous knowledge regarding the Nazi party.18 Research in the first decade of the twenty-first century (Jürgen Trimborn Leni Riefenstahl: A Life Faber & Faber, 2007 and Steven Bach Leni – The Life and Work of Leni Riefenstahl Knopf, 2007) dismantle Riefenstahl’s myth that she was an artist innocent of political motivations. She hitched her wagon to National Socialism, taking money to make her film Tiefland (Lowlands) and then bringing in extras from a concentration camp, keeping them in rags and starving them. After filming some were executed in the gas chambers. “Bach shows that the contract she entered into with the camp commandant makes clear the terms on which she had access to these ‘extras’ and that she knew they were going back to (at the very least) an uncertain future ‘in the east’.”19 Riefenstahl would later claim that all of the Romani extras – 53 Roma and Sinti from Maxglan, and a further 78 from a camp in eastern Berlin – had survived the war. In fact, almost 100 of them are known or believed to have been gassed in Auschwitz.20
Riefenstahl’s image of wholesome “New Woman” – a “version of an ideal presence, a kind of imperishable beauty” – never faded and she never wavered in her belief in herself and her innocence. The hubris of her egotistical narcissism denied any other version of history was possible, jealousy protecting her self-believed legacy like a protective tigress guarding her cubs, all the while denying her servitude and slavery to Nazi propaganda. Of course, all of it is a lie. There is Riefenstahl after the invasion of Poland filming away dressed as a uniformed army war correspondent replete with revolver around her waist.

Oswald Burmeister (German)
Visit of Leni Riefenstahl with a pistol at the XIV Army Corps, conversation with soldiers, on the left a film camera
Poland, September, 1939
German Federal Archives / Wikipedia (public domain)
“Four of the six feature films she directed are documentaries, made for and financed by the Nazi government… [they] celebrate the rebirth of the body and of community, mediated through the worship of an irresistible leader.”21 Susan Sontag saw Riefenstahl’s aesthetics as entirely inseparable from Nazi ideology, “consistent with some of the larger themes of Nazi ideology: the contrast between the clean and the impure, the incorruptible and the defiled, the physical and the mental, the joyful and the critical.”22
Naturally, and I use the word advisedly, the leader was male. While Riefenstahl could wish all she liked that she had power as a “New Woman”, “dominating the exclusive male society” of Nazi Germany, she was in reality just a pawn of their largesse. Women in Nazi Germany were seen mainly as baby producing machines, representing the fundamental ideologies of the role of the mother (the role of women under National Socialism). To that end the Cross of Honour of the German Mother (Mutterkreuz – Mother’s Cross) conferred by the government of the German Reich to honour a Reichsdeutsche German mother for exceptional merit to the German nation – 1st class, Gold Cross: eligible mothers with eight or more children; 2nd class, Silver Cross: eligible mothers with six or seven children; 3rd class, Bronze Cross: eligible mothers with four or five children – reinforced traditional feminine and family values, and “traditional” lifestyle patterns.23 The New Woman in Germany thus became a pure woman of German blood-heredity and genetically fit, the mother worthy of the decoration. In Nazi Germany the New Woman became “decoration” herself, the ideal protected as Sontag puts it as, “the family of man (under the parenthood of leaders).”24

Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946)
Georgia O’Keeffe
1920
Platinum print
Wikiart (Public domain)
One of the greatest artists of the twentieth-century was the painter Georgia O’Keeffe (American, 1887-1986). O’Keeffe, born in a small town named Sun Prairie in Dane County, Wisconsin grew up on the family farm south of the city. “As a child she received art lessons and her abilities were recognised and encouraged by local teaches and family throughout her school years. After O’Keeffe left Sun Prairie she pursued studies at the Art Institute of Chicago (1905-1906) and at the Arts Students League, New York (1907-9108).”25 She took a job as a commercial artist and then began teaching art, taking summer at classes at the University of Virginia for several years before becoming chair of an art department beginning the fall of 1916. A friend sent some of O’Keeffe’s charcoal drawings to the photographer, gallerist and impresario Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) who exhibited them at his 291 gallery in April 1916. Stieglitz found them to be the “purest, finest, sincerest things that had entered 291 in a long while,” and in the spring of 1917 he sponsored her first one-artist exhibition at 291 – the last show held at the galleries before they closed in July of that year.
At this time, “O’Keeffe painted to express her most private sensations and feelings. Rather than sketching out a design before painting, she freely created designs. O’Keeffe continued to experiment until she believed she truly captured her feelings [in watercolour] … After her relationship with Alfred Stieglitz started, her watercolour paintings ended quickly. Stieglitz heavily encouraged her to quit because the use of watercolour was associated with amateur women artists. … Stieglitz, twenty-four years older than O’Keeffe, provided financial support and arranged for a residence and place for her to paint in New York in 1918. They developed a close personal relationship while he promoted her work. She came to know the many early American modernists who were part of Stieglitz’s circle of artists, including painters Charles Demuth, Arthur Dove, Marsden Hartley, John Marin, and photographers Paul Strand and Edward Steichen. Strand’s photography, as well as that of Stieglitz and his many photographer friends, inspired O’Keeffe’s work.”26 Stieglitz and O’Keeffe were married in 1924. Between 1918 and 1928 O’Keeffe worked primarily in New York City and at the Stieglitz family’s summer home at Lake George.
Working creatively side by side with that egotistical beomoth of American art that was Stieglitz could not have been easy. While Stieglitz promoted his wife’s art, provided financial support, directed the medium of her continued development, he also controlled her “purest” form (a symbol of the ideal) – that of her image. O’Keeffe became Stieglitz’s muse (a goddess, a person or personified force who is the source of inspiration for a creative artist), between 1918-1920 the photographer “making more than 140 photographs of O’Keeffe that, unlike his earlier analytic work, resonated with emotion and personal meaning… conjoining her art and her body, suggesting they were one.”27
“Stieglitz conceived of his portraits of O’Keeffe as a single work – a composite portrait. Each photograph stands on its own, revealing a certain innate quality at a given moment. But because change is a constant, only a series of photographs can evoke a subject’s entire being over time. To underscore the composite nature of his project, in 1921 Stieglitz exhibited more than forty photographs of O’Keeffe – many clustered by body part – under the title “Demonstration of Portraiture.”
Stieglitz and O’Keeffe married in 1924, and he continued to photograph her through the 1930s – his composite portrait eventually numbering 331 works. But his pictures of her changed markedly over the years. In 1923 when he became entranced with photographing clouds, he made smaller, more casual pictures of her at work or holding the subjects of her paintings. Many of his portraits of her from the 1930s lack the feverish intensity of those he made from 1918 to 1920 and reveal instead the distance in their relationship.”28
Stieglitz’s early photographs of O’Keeffe capture her in intimate encounters with the camera, portraying her through the gaze of male passion. “Extreme close-ups evoke an intimate sense of touch,” “different body parts were expressive of O’Keeffe’s individuality,” while in other photographs “she looks directly and longingly at the camera…”.29 O’Keeffe’s supposed independent New Woman was tied to the coat tails of an older man, her place in the cult of beauty (the ideal of life as art) an ideal eroticism. Her image was presented not as a temptation, not as a repression of the sexual impulse … but as its ultimate revelation in the seduction of the physicality of the photograph. Stieglitz’s composite “portrait in time,” “reflects his ideals of modern womanhood and is evocative of their close relationship.”30 Under the control of the man.

Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946)
Georgia O’Keeffe
1918
Wikipedia (Public domain)
O’Keeffe of course realised the power that Stieglitz had over her and she started to remove herself from his field of vision, from his power of influence. To truly gain her independence. As Akkelies van Nes and Tra My Nguyen observed earlier, “To gain respect as artists, the image of women as muses had to disappear” as so this is what O’Keeffe did: she stopped becoming Stieglitz’s muse. After first visiting New Mexico in 1917 O’Keeffe returned to what was her spiritual home in 1929 when she travelled to Mexico with her friend Rebecca Strand and stayed in Taos with Mabel Dodge Luhan, who provided the women with studios,31 from then on spending part of nearly every year working in New Mexico. “Upon returning to the place that touched her heart so deeply, O’Keeffe’s mental health did indeed improve. Her life and her artwork would never be the same again. “I felt as if something was ending and another was beginning,” O’Keeffe once said. She began to feel more like her true self, integrated with parts of her personality that had been submerged in New York City.”32
The distance in the relationship between O’Keeffe and Stieglitz (both physical, he in New York and she in New Mexico, and spiritual with her attenuation to the Cerro Pedernal landscape) was exacerbated by his long-term relationship with Dorothy Norman which started in 1928, leading to O’Keeffe’s mental breakdown and hospitalisation in 1933. She returned to New Mexico and in August 1934 moved to Ghost Ranch, north of Abiquiú. Literally, her place in Mexico was faraway, an isolated landscape which she called the Faraway: “She often talked about her fondness for Ghost Ranch and Northern New Mexico, as in 1943, when she explained, “Such a beautiful, untouched lonely feeling place, such a fine part of what I call the ‘Faraway’. It is a place I have painted before … even now I must do it again.””33 Metaphorically, it was faraway from the life she led with Stieglitz, far away from her wifely concerns. “Shortly after O’Keeffe arrived for the summer in New Mexico in 1946, Stieglitz suffered a cerebral thrombosis. She immediately flew to New York to be with him. He died on July 13, 1946. She buried his ashes at Lake George. She spent the next three years mostly in New York settling his estate, and moved permanently to New Mexico in 1949, spending time at both Ghost Ranch and the Abiquiú house that she made into her studio.”34
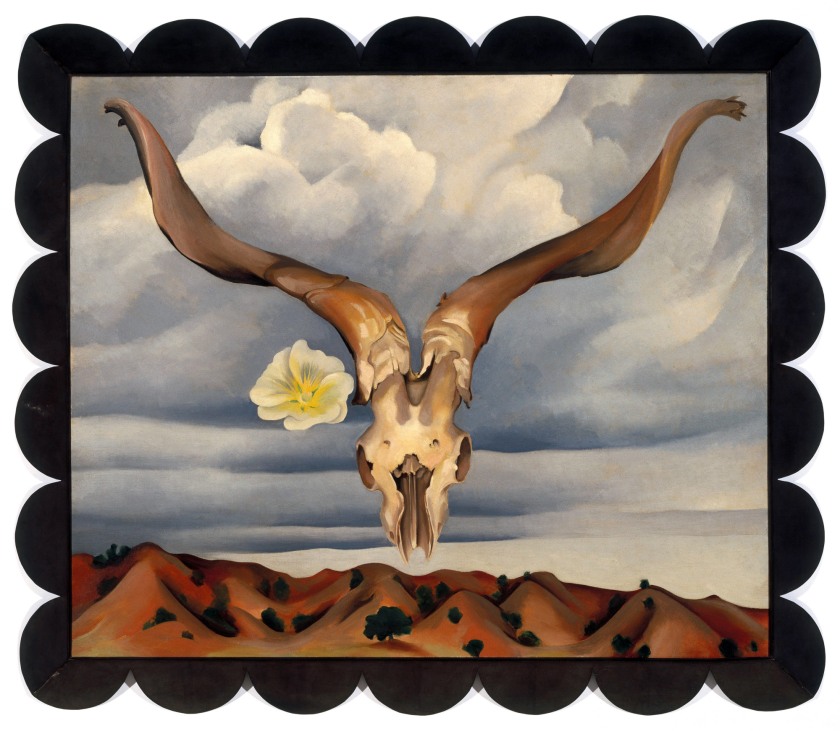

Georgia O’Keeffe (American, 1887-1986)
Rams Head and White Hollyhock, New Mexico
1935
Oil on canvas
Brooklyn Museum
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
Stieglitz never came to New Mexico. It was her space. Here she found her integrity, her own voice, far from the madding crowd, far from the gallery openings – a voice full of songs of the world. “She painted Taos Pueblo, San Francisco de Asís Catholic Church, a tree on the D.H. Lawrence ranch (that still stands), Mexican paper flowers, wood carvings, wild flowers, hills and sky around Taos.”35 She painted her “flowers of the desert”, bleached animal bones that were alive to her; and “she hoped people could see the music that she painted.” In New Mexico she truly became a “New Woman”: independent, intelligent, talented and famous … and her own woman – untamed by men, full of fierce self-protection and formidable work ethic, a woman adept at embracing the unknown and appreciative of the art of solitude.
Pushing the boundaries, finding themselves
While the physical presence of women photographers and their work in the “Roaring Twenties” or “golden 1920s” – “which saw young women breaking with traditional “mores” or likewise step aside from “traditional” lifestyle patterns”36 – was apsirational for young and independent women in order to achieve social prestige and material success, for most women photographers it was all about having a job and making a living.
Paradoxically, while the “New Woman” behind the camera “embraced photography as a mode of professional and personal expression”, promoting female empowerment based on real women making revolutionary changes in life and art they also bought into a capitalist system of male dominance in a patriarchal society where the “feminine” – that is a feminine perspective – underwent a process of sublimation through the sequestering (hiding away) of gender. As women photographers “sought to redefine their positions in society and expand their rights”, their independence, so women were still outsiders in the male system of the recognition of the feminine subject – both of the female body as subject and that of the female photographers’ body (although the latter less so, with the numerous self-portraits of the “New Woman” and their cameras captured in mirrors). Indeed, most “New Woman” photographers never seem to have had the desire, or the eroticism, to virtually put gender in the image. They were still in servitude to the dominant status quo.
The story of the two mites is apposite here. In the story (see below) many rich people put money into the treasury, while a poor widow puts in two mites (two small coins worth a few cents) which is all she has. “The same religious leaders who would reduce widows to poverty also encourage them to make pious donations beyond their means. In [Adison] Wright’s opinion, rather than commending the widow’s generosity, Jesus is condemning both the social system that renders her poor, and “… the value system that motivates her action, and he condemns the people who conditioned her to do it.””37 In other words, the widow (in our case the New Woman) contributes her whole livelihood to maintaining the social system (patriarchal society) that oppresses her by supporting the value system that motivates her action… a system, controlled by men, that keeps her in servitude.
Many “New Woman” photographers behind the camera had to operate in such a value system in order have a job and make a living. Variously, they had to build a career as a fashion photographer, advertising and graphic photographer, magazine photographer, studio photographer, photojournalist, war photographer, social documentary photographer, street photographer and ethnographic photographic … and usually had be proficient at most styles of photography in order to obtain sufficient work for survive. For example, Sabine Weiss bridled at being labelled a humanist, “because she considered her street photography to be just one part of her oeuvre. Most of her career was spent as a fashion photographer and a photojournalist, shooting celebrities like Brigitte Bardot and musicians like Benjamin Britten. “From the start I had to make a living from photography; it wasn’t something artistic,” Weiss told Agence France-Presse in 2014. “It was a craft, I was a craftswoman of photography.”38
I suspect for most women photographers of the era this was the truth: taking photographs wasn’t something artistic it was a craft from which they earned a living. While part of the profound shaping of the medium during a time of tremendous social and political change they did not initiate the “modernisation” of photography but were undoubtedly an important part of that movement. But, and here is the key point, they were still producing “mainstream” images and, as Annette Kuhn notes, “‘Mainstream’ images in our culture bear the traces of the capitalist and patriarchal social relations in which they are produced, exchanged and consumed.”39 They bought into the value system.
Among others (such as Dora Maar, Tina Modotti, Lucia Moholy, Aenne Biermann, Eva Besnyö and Florence Henri to name just a few of my favourites) … two women photographers who did push the boundaries of the art of photography and, in their case, what was acceptable in terms of the representation of gender identity were the temporarily bisexual, pan-world Germaine Krull (1897-1985) and the “neuter” (neither) photographer Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954).
Krull published her seminal book Métal in 1928 in Paris, and began to receive attention alongside other practitioners of new, assertively modern photographic styles such as Man Ray and André Kertész.
“With Métal, Krull turned her lens on the soaring structures of industrial Europe: Rotterdam’s railroad bridge De Hef, Marseille’s Pont Transbordeur, a number of nameless industrial cranes, factory machinery, and, most recognizably, the Eiffel Tower. The portfolio bore the subtitle “métaux nus” (bare metals), and critics have often likened these metallic bodies to the nude photographs she made around the same time. In both cases, Krull got close to her subjects, dislocating them from their environments. In Métal, Krull rendered the familiar form of the Eiffel Tower nearly unrecognizable…
In an untitled nude photograph from 1928 or ’29, she deployed a similar approach, keeping the camera fixed on an unclothed torso twisting off toward the edge of the frame with upturned face cut off at mid-cheek. The dramatic play of shadow and light renders the figure’s gender indistinct. Whether focused on a living subject or an architectural one, Krull’s camera resists the viewer’s urge to name and categorize.”40

Germaine Krull (1897-1985, photographer)
Cover design by M. Tchimoukow (Louis Bonin)
MÉTAL cover
1928
Librairie des Arts décoratifs A. Calavas, Editeur.
Portfolio comprising a title page, a preface by Florent Fels and sixty four (64) loose photogravures, each mentioning the photographer’s name, titled ‘MÉTAL’, plate number and publisher’s name. Original dust jacket. Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
Folio 30 x 23.5cm; 11 3/4 x 9 1/4 in.
Plate 29.2 x 22.5cm; 11 1/2 x 8 3/4 in.
Image 23.6 x 17.1cm; 9 1/4 x 6 1/2 in.
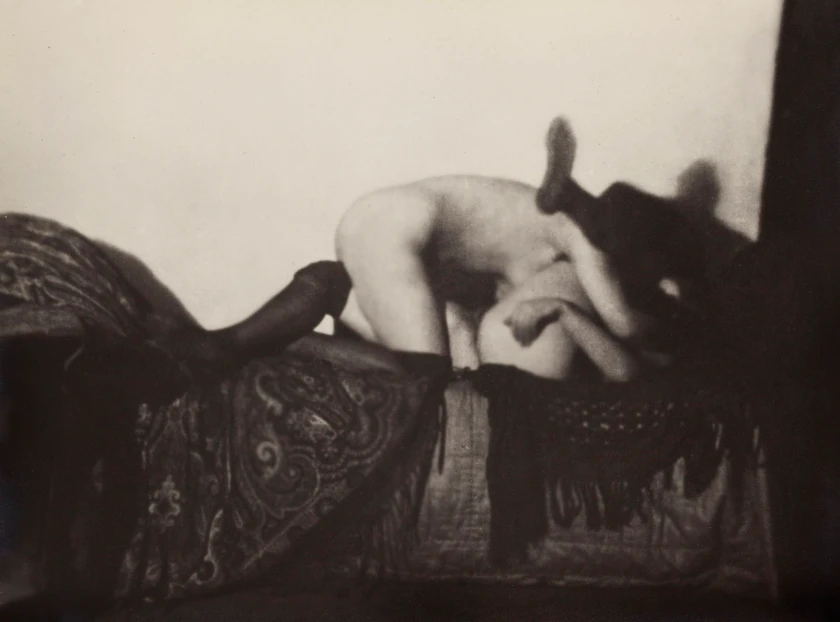

Germaine Krull (1897-1985, photographer)
From the portfolio Les amies
c. 1924
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
In 1924, in an earlier portfolio of eleven photographs titled Les amies (French for “the friends,” specifically denoting female friends), Krull depicts “a pair of women in stages of gradual undress, eventually left only in their stockings, the rest of their flesh laid bare.” In a tangle of insouciant bodies that hid breasts and eyes, in which none of the models stares at the camera, Krull presents an eroticism that “is contained between the two women, with no imaginary space for a third, presumably male, viewer to enter…,” Krull dismissing “”the male gaze of Weimar culture in favor of a female gaze” and her emphasis on the gazes within the images as the female models view each other. In Les Amies, there is no space for a third party: the only possibility is to become one of the women.”41
“By photographing erotic scenes, Krull not only constructed the desiring gaze but also placed herself in the position of that gaze, taking on privileges previously permitted only to male photographers…”42 whilst at the same time transgressing the definition of middle-class respectability – all the while emphasising the fluidity of female sexual identity in the 1920s, especially for the adventurous “New Woman”.
While these images received little attention during her lifetime (much like the gender bending images of Claude Cahun) they are representations of queer desire which picture the dissolution of the controlling male gaze. Using the mirror of her / Self and her camera, Krull’s staged (erotic) encounters in Les Amies and Métal undermine the male space of control through spatial disorientation – her “reforming mirror” performing a tangle of limbs, the fragmentation of the female body in which gender becomes neutral coupled with the dismantling of the phallocentrism of the (Eiffel) tower until its form becomes an unrecognisable and different “other”. “Armed with her camera, she had the power not only to depict reality but to transform it.”43
The French surrealist photographer, sculptor, and writer Lucy Renee Mathilde Schwob adopted the pseudonym Claude Cahun in 1914.
“In Disavowals, she writes: “Masculine? Feminine? It depends on the situation. Neuter is the only gender that always suits me.” … [She] is most remembered for her highly staged self-portraits and tableaux that incorporated the visual aesthetics of Surrealism. During the 1920s, Cahun produced an astonishing number of self-portraits in various guises such as aviator, dandy, doll, body builder, vamp and vampire, angel, and Japanese puppet.
Some of Cahun’s portraits feature the artist looking directly at the viewer, head shaved, often revealing only head and shoulders (eliminating body from the view), and a blurring of gender indicators and behaviours which serve to undermine the patriarchal gaze. Scholar Miranda Welby-Everard has written about the importance of theatre, performance, and costume that underlies Cahun’s work, suggesting how this may have informed the artist’s varying gender presentations.”44
Cahun’s self-portraiture over a period of 27 years (in collaboration with her lover Marcel Moore) was a unique investigation into the multiplicity of sexuality and gender identity. “By 1930, Cahun had amassed a considerable image bank of photographic self-portraits; that year, she publicly disseminated a handful of those images for the first and only time.”45 In her photographs she explored the mutable definitions of gender through multiple ‘masked’ personas – using photomontage, the doubling of the image (asserting another conception of gender identity that of a “third sex” or an “Androgyne”), the various ways photographs can be produced and viewed (meant to unsettle the audience’s understanding of photography as a documentation of reality), and the dissolution of the self in the space between the body and the mirror to aid her investigation. Self-reflection was not her objective in the use of the mirror but Cahun did use the mirror as a source of reflection in a contemplative, interrogatory mode in her photographs; and these were private photographs never intended for public display. “It has been proposed that these personal photographs allowed for Cahun to experiment with gender presentation and the role of the viewer to a greater degree.”46
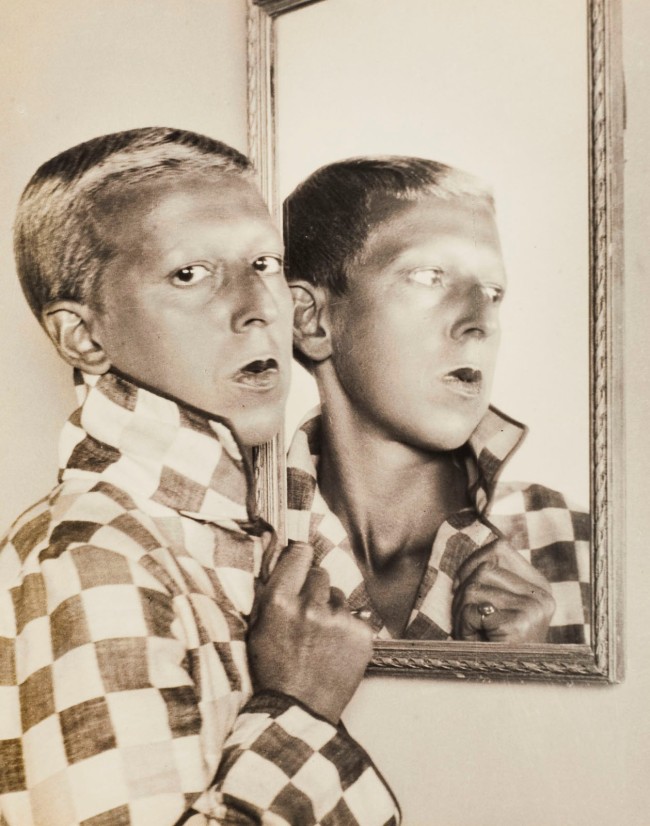

Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait (Self-Portrait)
c. 1927
Gelatin silver print
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education

Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Self-Portrait
1927
Gelatin silver print
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
In Cahun’s gender non-conforming self-portraits “identity and gender is played out through performance and masquerade in a constructive way, a deep, probing interrogation of the self in front of the camera. While Cahun engages with Surrealist ideas – wearing masks and costumes and changing her appearance, often challenging traditional notions of gender representation – she does so in a direct and powerful way. As Laura Cumming observes, “She is not trying to become someone else, not trying to escape. Cahun is always and emphatically herself. Dressed as a man, she never appears masculine, nor like a woman in drag. Dressed as a woman, she never looks feminine. She is what we refer to as non-binary47 these days, though Cahun called it something else: “Neuter is the only gender that always suits me.””
Cahun had a gift for the indelible image but more than that, she possesses the propensity for humility and openness in these portraits, as though she is opening her soul for interrogation, even as she explores what it is to be Cahun, what it is to be human. This is a human being in full control of the balance between the ego and the self, of dream-state and reality. The photographs, little shown in Cahun’s lifetime, are her process of coming to terms with the external world, on the one hand, and with one’s own unique psychological characteristics on the other. They are her adaption48 to the world.”49
These were private manifestations of her inner self for the benevolence of her own spirit. She made art for herself, willing enough to face uncertainty and take the untrodden path of inner discovery. She was a “New Woman” where the term “woman” is fluid and fragmentary, open to adaptation and interpretation.
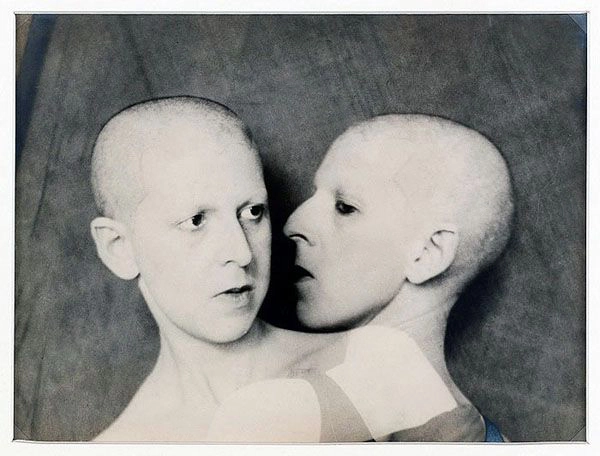
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Que me veux tu? (What do you want from me?)
1929
Gelatin silver print
Used under fair use conditions for the purposes of academic research and education
A proposition and, the particular becomes universal
So the question becomes – when is a photographer a photographer a photographer. Does it matter who is behind the lens?
On the evidence of almost 200 photographs in the postings on this exhibition, if the photographs were labelled “unknown photographer”, many of these images could as easily have been made by men as by women. So in one sense it does not matter. What matters is the quality of the work.
But from other perspectives of course it matters, it matters a great deal. These women photographers have been whitewashed from the history of photography as though they never existed. Their challenge to the dominant narrative of male supremacy in society and the continuation of the struggle for female visibility and emancipation, requires a recognition of their courage and sacrifices. These were talented, strong and creative human beings and their work demands the recognition it deserves.
And then we ask, why has it taken a hundred years to shift the institutionally constructed history of photography, which has been perpetuated from generation to generation, where only male photographers were to be looked at, collected, admired and displayed? And the simple answer is that one word: “men”. Although things are changing slowly, too slowly, it was and still is a patriarchal society, a system of society controlled by men, and in the time period we are talking about (1920s-1950s), it was a world where institutions and their collecting practices were controlled by men; where photography was not being collected by many museums; and where the photographs of the “New Woman” behind the camera was not seen as collectible because it was what they did to make a living… it wasn’t art.
Further, we might postulate a proposition with regard to the practice of “New Woman” photographers, a form of Zen kōan if you like:
It doesn’t matter that I am a woman / I am a woman
In relation to this in/sight, I muse on a quotation about the work of Imogen Cunningham: “I keep coming back to this duality: Don’t pigeonhole her for being a woman. But don’t forget she’s a woman!” says Dunn Marsh. “She photographed flowers, which people sort of treated as a feminine subject matter. But Edward Weston was photographing peppers, and nobody considered that to be an exclusively masculine subject matter.”50
If we unpack this quotation, it reads as ‘it doesn’t matter that Cunningham was a woman… but don’t forget she’s a woman!’. Weston made images of peppers and nobody commented on his masculinity or the masculine “nature” of his subject matter and the same should go for Cunningham. Just because she is a women why comment on the femininity of flowers – but don’t forget Imogen is a women! It’s about the quality of the work, not the gender of the artist and then maybe it’s about being female but only if the artist chooses it to be … (Georgia O’Keeffe got very annoyed by the reading of her close-up flower paintings which many interpreted as representing female genitalia, insisting that the paintings has nothing to do with female sexuality).
Finally we can say, it’s doesn’t matter what gender you are when you look through the camera lens (as a machine it’s impartial), it is about the reality of yourself as a human being and your relationship to the camera. The actions of the photographer are a personal engagement with the camera (in other words, in relation to the women behind the camera, the camera in relation to her/Self) but through direct action – an engagement with time and light – their can be a shift in consciousness from the personal (the particular) to the universal.
It shouldn’t (that is the key word) matter whether you are male or female … it’s about the quality of the work and it’s about following the light. The light of self recognition of the path that you are on. As Maria Popova insightfully observes,
“And so the best we can do is walk step by next intuitively right step until one day, pausing to catch our breath, we turn around and gasp at a path. If we have been lucky enough, if we have been willing enough to face the uncertainty, it is our own singular path, unplotted by our anxious younger selves, untrodden by anyone else.”51
The “New Woman” broke new ground by challenging the (in)visibility of women in a male dominated world. She placed herself in a man’s world but she still had to fit into that man’s world and conform to his image of her. But she followed her path of uncertainty with conviction and motivation, a path until then untrodden by anyone else, until she turned around and found that she had forged her own singular path, had looked within and had found her own voice. Looking back from a contemporary perspective we can finally recognise the struggle of the “New Woman” behind the camera, we can see their singular paths and recognise their achievements. What we can learn from the “New Woman” today, is that we all have a choice… to accept the status quo or offer determined defiance to prejudiced social conventions.
All human beings have to live within the parameters of social constructs but as human beings what we can do is push against the limits society imposes on us, push against the barriers of economic, political and sexual freedom. We can transgress the taboo. We can struggle that great and mighty struggle on the path of life, to push at the boundaries of being. What we all need to do, both women and men, is to find our integrity in relation to the reality of the world and to our own spirit. Through the efforts of those that came before us, we all now have a choice as to the path we follow and how we fit into this multifarious society.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
January 2021
Word count: 8,590
Footnotes
1/ Anonymous text. “George Sand,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 14/12/2021
2/ Victor Hugo. Les funérailles de George Sand quoted “Emancipated Woman,” in the Saturday Review: Politics, Literature, Science and Art, Volume 41, June 17, 1876, pp. 771 [Online] Cited 14/12/2021
3/ Anonymous text. “Camille Claudel,” on the Musée Rodin website [Online] Cited 14/12/2021
4/ Anonymous text. “Camille Claudel,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 14/12/2021
5/ Musée Rodin op cit.,
6/ Janet Wolff. “The Invisible Flaneuse. Women and the Literature of Modernity” in Theory, Culture and Society Volume 2, Number 3, Sage, 1985, p. 42
7/ Ibid., p. 44
8/ Ibid.,
“When flanerie moves into the private realm of the department store, feminization alters this urban practice almost beyond recognition … By abolishing the distance between the individual and the commodity, the feminization of flanerie redefines it out of existence. The flaneur‘s dispassionate gaze dissipates under pressure from the shoppers’ passionate engagement in the world of things to be purchase and possessed. The flaneur ends up going shopping after all. … The department store cannot be the scene of urban strolling, not only because it is an enclosed and circumscribed space, but, more importantly, because shopping is a pre-defined and purposeful activity.”
Janet Wolff. “Gender and the haunting of cities (or, the retirement of the flâneur),” in Aruna D’Souza and Tom McDonough (eds.,) The Invisible Flâneuse? Gender, Public Space, and Visual Culture in Nineteenth-Century Paris. London, UK: Manchester UP, 2006, p. 21
9/ Flaneur – “The flaneur symbolises the privilege or freedom to move about the public arenas of the city observing but never interacting, consuming the sights through a controlling but rarely-acknowledged gaze… The flaneur embodies the gaze of modernity which is both covetous and erotic. … The site of pleasurable looking, this look actively cast women as passive, erotic objects, subjecting them to a kind of voyeuristic control; it was in this sense that the visual purview of the bourgeois stroller – now the representative of middle-class masculinity in its entirety – became thoroughly implicated in issues of gender.”
Griselda Pollock. Vision and Difference: Femininity, Feminism and the Histories of Art. London, UK: Routledge, 1988.
10/ Akkelies van Nes and Tra My Nguyen. “Gender Differences in the Urban Environment: The flâneur and flâneuse of the 21st Century,” in Daniel Koch, Lars Marcus and Jesper Steen (eds.,). Proceedings of the 7th International Space Syntax Symposium. Stockholm: KTH, 2009
11/ Ibid.,
“Prostitution was indeed the female version of flânerie, which serves only to emphasise the inequality of gender differences in this era. The male flâneur was simply a man who loitered on the streets; but women who loitered risked being seen as prostitutes, streetwalkers, or les grandes horizontales as they were known in nineteenth-century Paris.”
Bobby Seal. “From Streetwalker to Street Walker: The Rise of the Flâneuse,” on the Psychogeographic Review website 24/12/20212 [Online] Cited 20/01/2022
12/ Bianca Hall and Adam Cooper. “From Jill Meagher to Aiia Maasarwe: The murders that changed Melbourne over the past decade,” on The Age website December 30, 2019 [Online] Cited 15/12/2021.
13/ “Suffragette,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 14/12/2021
14/ Aruna D’Souza and Tom McDonough (eds.,) The Invisible Flâneuse? Gender, Public Space, and Visual Culture in Nineteenth-Century Paris. London, UK: Manchester UP, 2006, p. 8
15/ Ibid., p. 6
16/ Steven Bach quoted in Carl Rollyson. “Leni Riefenstahl on Trial,” on The New York Sun website March 7, 2007 [Online] Cited 04/01/2022
17/ Anonymous. “Leni Riefenstahl,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2021
18/ Ibid.,
19/ Taylor Downing. “Leni: fully exposed,” on The Observer website Sun 29 April 2007 [Online] Cited 12/01/2022
20/ Kate Connolly. “Burying Leni Riefenstahl: one woman’s lifelong crusade against Hitler’s favourite film-maker,” on The Guardian website Thursday 9 December 2021 [Online] Cited 12/01/2022
21/ Susan Sontag. “Fascinating Fascism,” in The New York Review February 6, 1975 issue [Online] Cited 12/02/2022
22/ Ibid.,
23/ See “Cross of Honour of the German Mother” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 12/01/2022
24/ Sontag, op. cit.,
25/ Text from a sign commemorating birth of Georgia O’Keeffe, located next to Sun Prairie City Hall, 300 E, Main Street
26/ Anonymous. “Georgia O’Keeffe,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2022
27/ Mark Levitch. “Stieglitz Career Overview: Georgia O’Keeffe, 1918-1920,” on the National Gallery of Art website Nd [Online] Cited 12/02/2022
28/ Ibid.,
29/ Ibid.,
30/ John Black. “Alfred Stieglitz and Modern America,” on the Boston Event Guide website Wednesday, 23 August 2017 [Online] Cited 12/02/2022. No longer available online
31/ Anonymous. “Georgia O’Keeffe,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 12/02/2022
32/ Roberta Courtney Meyers. “O’Keeffe in Taos,” on the Taos News website May 21, 2019 [Online] Cited 12/02/2022
33/ Anonymous. “Georgia O’Keeffe,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 12/02/2022
34/ Ibid.,
35/ Meyers, op. cit.,
36/ Anonymous. “Cross of Honour of the German Mother” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 12/01/2022
37/ Anonymous. “Lesson of the widow’s mite,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 15/02/2022
38/ Clay Risen. “Sabine Weiss, Last of the ‘Humanist’ Street Photographers, Dies at 97,” on The New York Times website Jan 4, 2022 [Online] Cited 06/01/2022
39/ Annette Kuhn. The Power of the Image: Essays on Representation and Sexuality. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1985, p. 10.
40/ Marina Molarsky-Beck. “Germaine Krull’s Queer Vision,” on The Met website August 17 2021 [Online] Cited 15/12/2021
41/ Anonymous. “Germaine Krull, From Séries les Amies, 1924,” on the La Petite Mélancolie website 19/06/2012 [Online] Cited 15/01/2022
42/ Ibid.,
43/ Ibid.,
44/ Anonymous. “Claude Cahun,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 16/01/2022
45/ Jennifer Josten. “Reconsidering Self-Portraits by Women Surrealists: A Case Study of Claude Cahun and Frida Kahlo,” in the Atlantis Journal Vol. 30, No. 2, 30/02/2006 p. 24
46/ Anonymous. “Claude Cahun,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 16/01/2022
47/ Those with non-binary genders can feel that they: Have an androgynous (both masculine and feminine) gender identity, such as androgyne. Have an identity between male and female, such as intergender. Have a neutral or unrecognised gender identity, such as agender, neutrois, or most xenogenders.
48/ “The constant flow of life again and again demands fresh adaptation. Adaptation is never achieved once and for all.” Carl Jung. “The Transcendent Function,” CW 8, par. 143.
49/ Marcus Bunyan. “Gillian Wearing and Claude Cahun: Behind the mask, another mask” on the Art Blart website 24th May 2017 [Online] Cited 16/01/2022
50/ Dunn Marsh quoted in Margo Vansynghel. “How Seattle’s Imogen Cunningham changed photography forever,” on the Crosscut website November 16, 2021 [Online] Cited 08/01/2022
51/ Maria Popova. “Carl Jung on How to Live and the Origin of “Do the Next Right Thing”,” on The Marginalian website 12th July 2021 [Online] Cited 13/12/2021
Many thankx to the National Gallery of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Uncertainty is the price of beauty, and integrity the only compass for the territory of uncertainty that constitutes the landmass of any given life.
And so the best we can do is walk step by next intuitively right step until one day, pausing to catch our breath, we turn around and gasp at a path. If we have been lucky enough, if we have been willing enough to face the uncertainty, it is our own singular path, unplotted by our anxious younger selves, untrodden by anyone else.
Maria Popova. “Carl Jung on How to Live and the Origin of “Do the Next Right Thing”,” on The Marginalian website 12th July 2021 [Online] Cited 13/12/2021
The beautiful woman will continue to serve as a symbol of feminine mystery to the man who desires her and of potency and success to the man who can claim her. And to the women around her, she will remain a symbol of the ideal against which they will be judged. This can only change when beauty loses its distorted power in the evaluation of a “woman’s worth”; that is, when the dependent relationship between women and men has been dismantled. Thus are the politics of appearance inextricably bound up with the structures of social, political and economic inequality … Fighting pressure to conform, attempting to hold one’s own against the commercial and cultural images of the acceptable is a crucial first act of resistance. The attempt to pass and blend in actually hides us from those we most resemble. We end up robbing each other of authentic reflections of ourselves. Instead, imperfectibly visible behind a fashion of conformity, we fear to meet each others’ eyes …
Real diversity can only become a source of strength if we learn to acknowledge it rather than disguise it. Only then can we recognize each other as different and therefore exciting, imperfect and as such enough.
Wendy Chapkis. Beauty Secrets: Women and the Politics of Appearance. Boston: South End Press, 1986, p. 175.
… in practice, images are always seen in context: they always have a specific use value in the particular time and place of their consumption. This, together with their formal characteristics, conditions and limits the meanings available from them at any on moment. But if representations always have use value, then more often than not they also have exchange value: they circulate as commodities in a social / economic system. This further conditions, or overdetermines, the meanings available from representations. Meanings do not reside in images, then: they are circulated between representation, spectator and social function.
Kuhn, Annette. The Power of the Image: Essays on Representation and Sexuality. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1985, p. 6.
Meanings readable from photographs … are at all points connected with the status they occupy as products, with the contexts of reception and the discourses of authorship, aesthetics, criticism and marketing which surround them. ‘Mainstream’ images in our culture bear the traces of the capitalist and patriarchal social relations in which they are produced, exchanged and consumed.
Kuhn, Annette. The Power of the Image: Essays on Representation and Sexuality. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1985, p. 10.

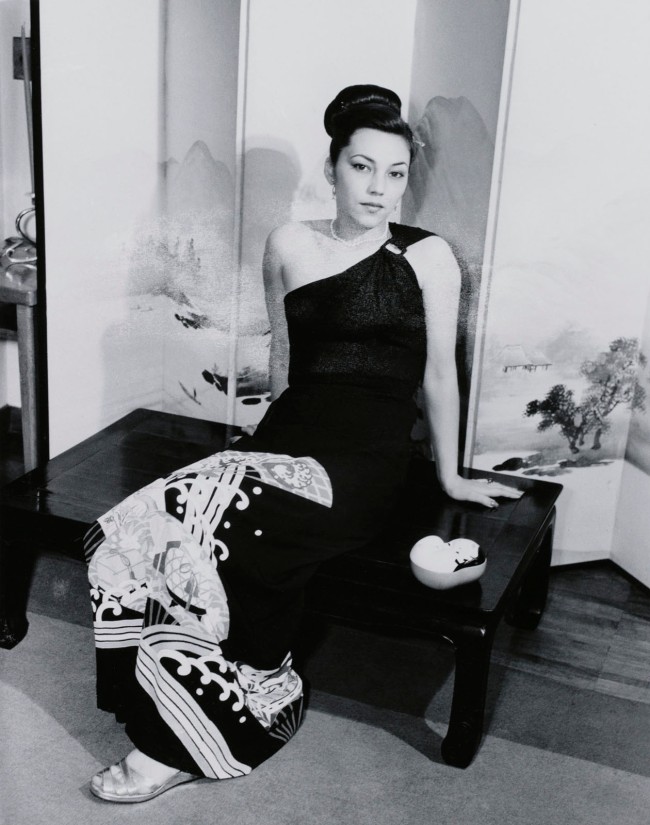
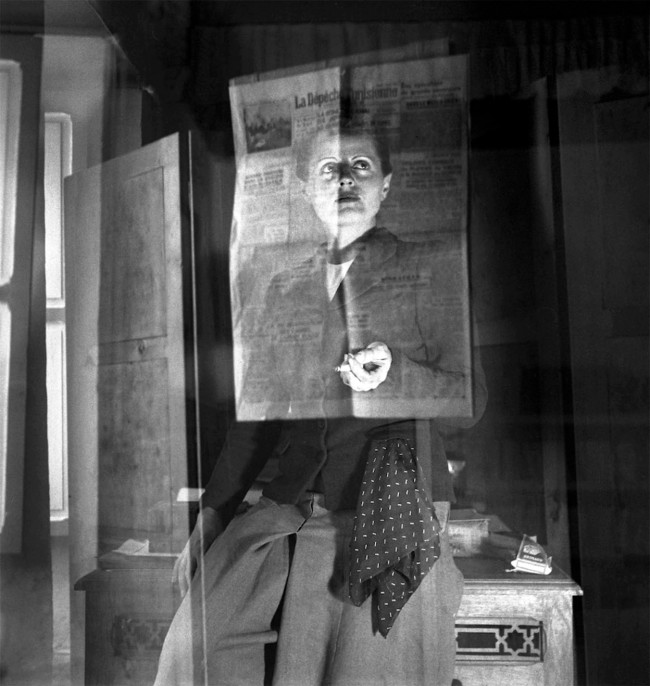
Tsuneko Sasamoto (Japanese, b. 1914)
Woman Selling Her and Her Husband’s Poetry Books (Street Snapshot in Tokyo)
c. 1950-1953, printed 1993
Gelatin silver print
Image: 29.6 x 29.6cm (11 5/8 x 11 5/8 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 41 x 51.2 x 2.5cm (16 1/8 x 20 3/16 x 1 in.)
Collection of Tokyo Photographic Art Museum
Lesson of the widow’s mite
The lesson of the widow’s mite or the widow’s offering is presented in the Synoptic Gospels (Mark 12:41-44, Luke 21:1-4), in which Jesus is teaching at the Temple in Jerusalem. The Gospel of Mark specifies that two mites (Greek lepta) are together worth a quadrans, the smallest Roman coin. A lepton was the smallest and least valuable coin in circulation in Judea, worth about six minutes of an average daily wage.
Biblical narrative
“He sat down opposite the treasury and observed how the crowd put money into the treasury. Many rich people put in large sums. A poor widow also came and put in two small coins worth a few cents. Calling his disciples to himself, he said to them, ‘Amen, I say to you, this poor widow put in more than all the other contributors to the treasury. For they have all contributed from their surplus wealth, but she, from her poverty, has contributed all she had, her whole livelihood.'”
Commentary
… In the passage immediately prior to Jesus taking a seat opposite the Temple treasury, he is portrayed as condemning religious leaders who feign piety, accept honour from people, and steal from widows. “Beware of the scribes, who like to go around in long robes and accept greetings in the marketplaces, seats of honour in synagogues, and places of honour at banquets. They devour the houses of widows and, as a pretext, recite lengthy prayers. They will receive a very severe condemnation.”
The same religious leaders who would reduce widows to poverty also encourage them to make pious donations beyond their means. In [Adison] Wright’s opinion, rather than commending the widow’s generosity, Jesus is condemning both the social system that renders her poor, and “… the value system that motivates her action, and he condemns the people who conditioned her to do it.”
Text from the Wikipedia website

Tsuneko Sasamoto (Japanese, b. 1914)
The Labor Offensive Heats Up
1946, printed 1993
Gelatin silver print
Image: 24.9 x 37.2cm (9 13/16 x 14 5/8 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 41 x 51.2 x 2.5cm (16 1/8 x 20 3/16 x 1 in.)
Collection of Tokyo Photographic Art Museum

Tsuneko Sasamoto (Japanese, b. 1914)
“Living New Look” Photography Exhibitionkru
1950, printed 1993
Gelatin silver print
Image: 37.6 x 29.5cm (14 13/16 x 11 5/8 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8 cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 41 x 51.2 x 2.5 cm (16 1/8 x 20 3/16 x 1 in.)
Collection of Tokyo Photographic Art Museum

Photographer unknown
Tsuneko Sasamoto, Tokyo
1940, printed 2020
Inkjet print
Image: 18.2 x 18.2cm (7 3/16 x 7 3/16 in.)
Frame: 45.72 x 35.56cm (18 x 14 in.)
Frame (outer): 46.99 x 36.83cm (18 1/2 x 14 1/2 in.)
Tsuneko Sasamoto / Japan Professional Photographers Society

Tsuneko Sasamoto (Japanese, 1914-2022)
Hiroshima Peace Memorial
1953, printed 2020
Inkjet print
Image: 37.4 x 37.3cm (14 3/4 x 14 11/16 in.)
Frame: 55.88 x 50.8cm (22 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 57.15 x 52.07cm (22 1/2 x 20 1/2 in.)
Tsuneko Sasamoto / Japan Professional Photographers Society

Tsuneko Sasamoto (Japanese, 1914-2022)
Untitled
1940, printed 2020
Inkjet print image: 47.5 x 33.8cm (18 11/16 x 13 5/16 in.)
Frame: 60.96 x 45.72cm (24 x 18 in.)
Tsuneko Sasamoto / Japan Professional Photographers Society
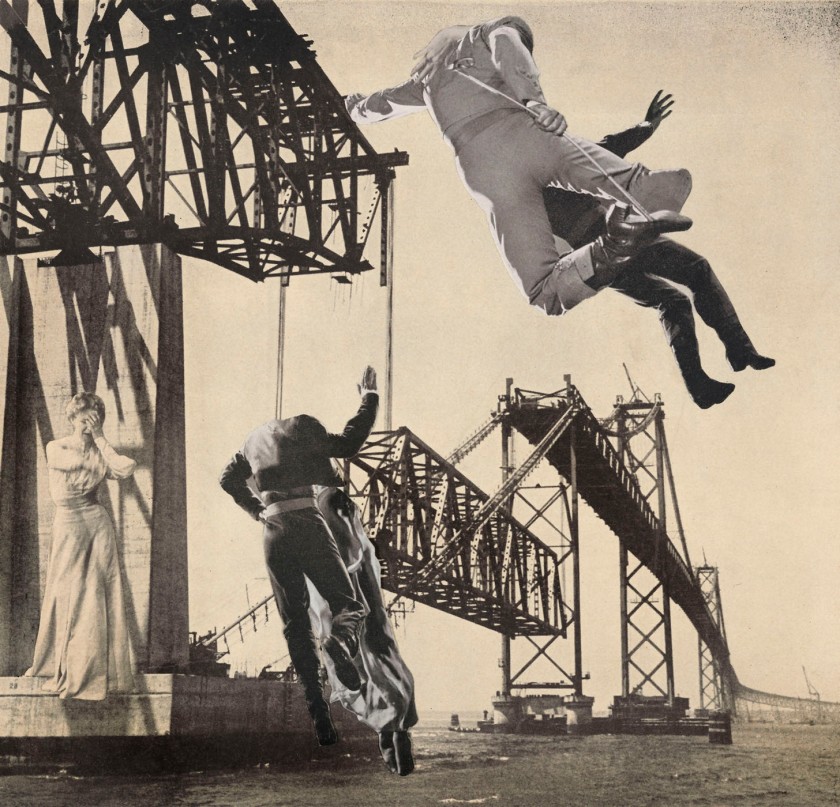

Toshiko Okanoue (Japanese, b. 1928)
Full of Life
1954
Collage on paper
Image/sheet: 23.8 x 24.9cm (9 3/8 x 9 13/16 in.)
Frame: 50.8 x 40.64cm (20 x 16 in.)
Frame (outer): 53.34 x 43.18cm (21 x 17 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, Alfred H. Moses and Fern M. Schad Fund
© Okanoue Toshiko
Toshiko Okanoue (Japanese, b. 1928)
Toshiko Okanoue (岡上 淑子, Okanoue Toshiko, born 3 January 1928) is a Japanese artist associated with the Japanese avant-garde art world of the 1950s and best known for her Surrealist photo collages. …
Early career
Born in Kochi and raised in Tokyo, Okanoue began to make photo collages while studying fashion and drawing at the Bunka Gakuin in Tokyo in the early 1950s. The young Okanoue, initially knew little of art history or the Surrealist movement.
In 1952, a classmate from Keisen Girls’ High School introduced Okanoue to poet and art critic Shuzo Takiguichi, a leading figure in the Japanese Surrealist movement, who would help introduce her to the wider art world, including the work of European Surrealists, such as German artist Max Ernst, who was an influence on her subsequent work.
Over the next six years she would produce over 100 works. She exhibited in two exhibits including, solo shows at the Takemiya Gallery in Tokyo, In the second show at Takemiya, over fifty pieces of Okanoue’s monochrome photographs were hung on display. Also exhibited at the “Abstract and Illusion” exhibition at the National Museum of Modern Art, Tokyo between 1 December 1953 and 20 January 1954, which attracted total of 16,657 audiences appreciating 91 artworks by 91 artists.
Artistic style
In post-war Japan, shortages of goods meant that foreign goods filled the market and fashion and lifestyle magazines such as Vogue, Harpers Bazaar and Life magazine provided the raw materials for Okanoue’s collages. Her black and white photo collages mix images of places, objects and people, often fashionable European women, in dynamic and often unsettling compositions whose subjects explored themes of war, femininity and the relations between the sexes.
Text from the Wikipedia website
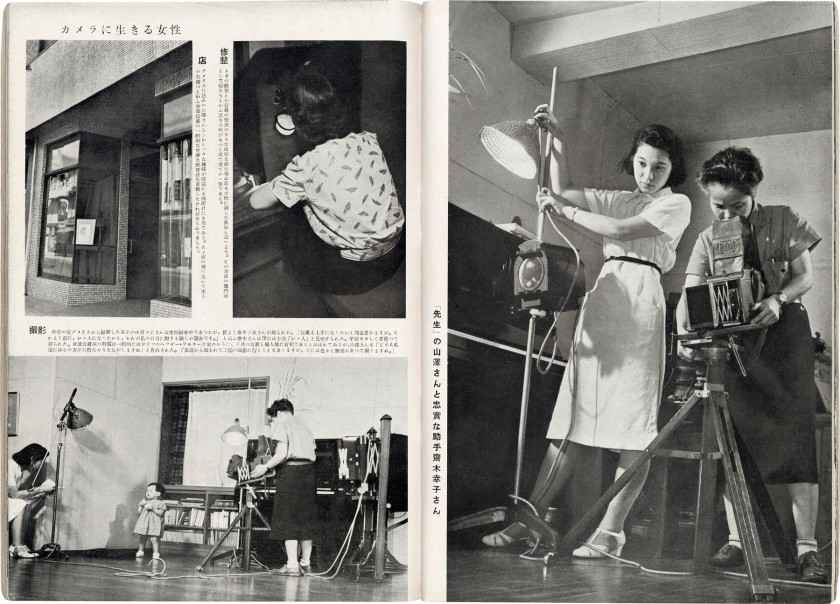

Photographer unknown
Page spread featuring Eiko Yamazawa and her assistant, from the “Photo Times”
October 1940
Magazine
Open: 25.4 x 30.48cm (10 x 12 in.)
Cradle: 8.89 x 33.02 x 26.35 cm (3 1/2 x 13 x 10 3/8 in.)
National Gallery of Art Library, Gift of the Department of Photographs

American, 20th Century
“Photo-Fighter,” in “True Comics”
July 1944
Comic book
Open: 25.4 x 35.56cm (10 x 14 in.)
National Gallery of Art Library, Gift of the Department of Photographs
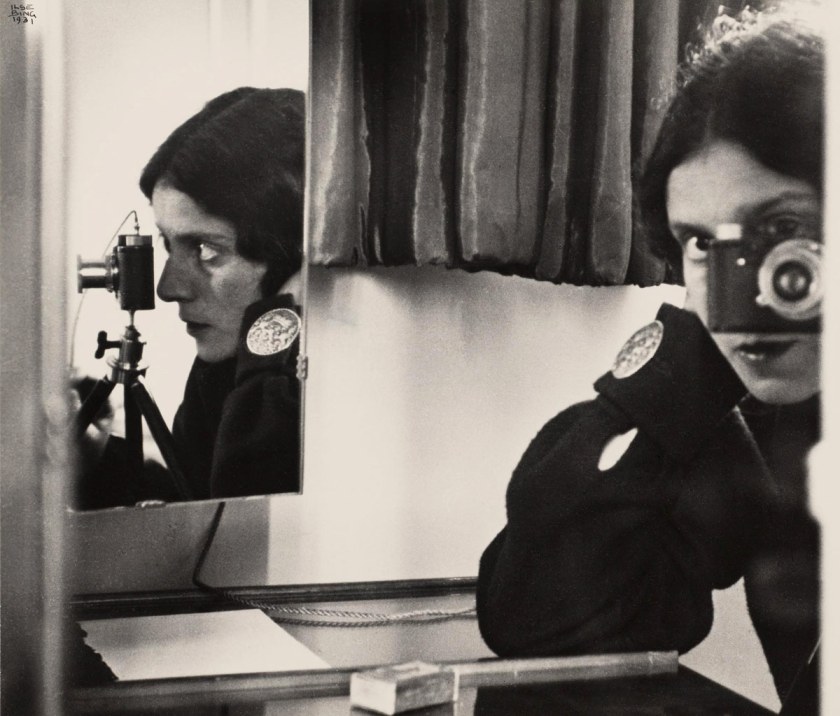

Ilse Bing (United States of America, Germany 1899-1998)
Self-Portrait With Leica
1931
Gelatin silver print
Collection of Michael Mattis and Judith Hochberg/Ilse Bing Estate

Ré Soupault (German, 1901–1996)
Self-Portrait, Tunis
1939
Gelatin silver print
Artists Rights Society, New York
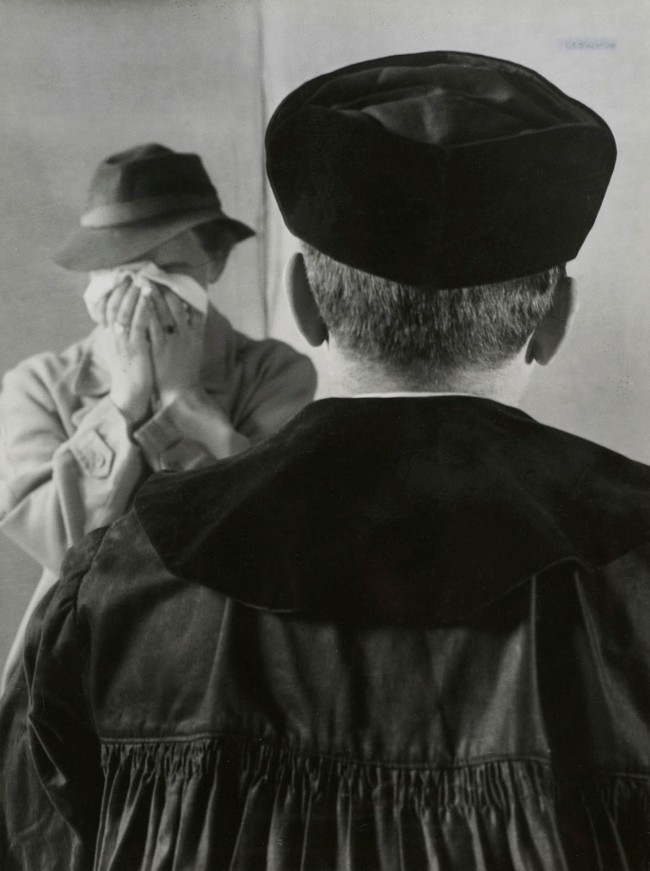

Elisabeth Hase (German, 1905-1991)
Ohne Titel (Weinende Frau) (Untitled (Crying woman))
c. 1934
Gelatin silver print
Image/sheet: 22.8 x 17.1cm (9 x 6 3/4 in.)
Frame (outer): 44.5 x 36.8cm (17 1/2 x 14 1/2 in.)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Twentieth-Century Photography Fund, 2016
Image © The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Art Resource, NY
Elisabeth Hase (German, 1905-1991)
Elisabeth Hase (December 16, 1905 – October 9, 1991) was a German commercial and documentary photographer active in Frankfurt from 1932 until her death in 1991, at the age of 85.
Hase was born in Döhlen bei Leipzig, Germany. She studied typography and commercial art from 1924 to 1929 at the School of Applied Arts, and later at the Städelschule, under, among other teachers, Paul Renner and Willi Baumeister. Hase was active as a photographer during the time of the transition from the Weimar Republic to the Third Reich and through post-WWII Germany. She was able to avoid government oversight of her work by establishing her own photographic studio in 1933.
Hase’s work included surreal photography, such as close-up photographs of dolls.
She received several awards, several for paper designs and collages. During a two-year collaboration in the studio of Paul Wolff and Alfred Tritschler, Hase took architectural photographs in New Objectivity style for the magazine Das Neue Frankfurt (The New Frankfurt) and documentary photographs of modern housing projects, including those of Ferdinand Kramer.
In 1932, Hase started her own business. It focused on timeless designs like still life, structures, plants, dolls, people, especially self-portraits. Often she used herself as a model in her photographic “picture stories.” Cooperation with agencies like Holland Press Service and the Agency Schostal enabled her to publish her photographs internationally.
Despite the bombing of Frankfurt in 1944 by the Allies, Hare’s photographic archive survived the war without major damage. Many of those works are now part of the collections held by the Folkwang Museum in Essen, Germany, in the Albertina (Vienna) in Vienna, and in the Walter Gropius estate in the Bauhaus Archive in Berlin, as well as in private collections in Germany and abroad.
Despite loss of her cameras and other technical equipment in the chaos of war, Hase was able to resume taking photographs in 1946 by the help of emigre friends who provided her with film and cameras to use. Among other subjects Hase documented was the reconstruction of St. Paul’s Church in Frankfurt.
From 1949, her work focused on advertising, consisting mostly of plant portraits.
Hase died at the age of 85 in 1991 in Frankfurt am Main.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Erna Lendvai-Dircksen (German, 1883-1962)
Mädchen aus dem Guttachtal, Schwarzwald (Young Woman from the Guttach Valley, Black Forest)
Before 1934
Gelatin silver print
Image: 17.1 x 13.2cm (6 3/4 x 5 3/16 in.)
Mount: 26 x 18.4cm (10 1/4 x 7 1/4 in.)
Frame (outer): 52.07 x 39.37cm (20 1/2 x 15 1/2 in.)
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Erna Lendvai-Dircksen (German, 1883-1962)
Erna Lendvai-Dircksen (born Erna Katherina Wilhelmine Dircksen, 31 May 1883 – 8 May 1962) was a German photographer known for a series of volumes of portraits of rural individuals from throughout Germany. During the Third Reich, she also photographed for eugenicist publications and was commissioned to document the new autobahn and the workers constructing it. …
Critical reception
Lendvai-Dircksen’s portraits of farmers suited the Nazi ethos except that in her initial publication, almost all her subjects were old, and indeed she clearly portrayed the damage to their bodies as a sign of authenticity. She later widened her focus to include children. She never, however, photographed sport, whether for technical reasons or because of her personal philosophy.
Although Lendvai-Dircksen has been referred to as “brown Erna” for the promotion of Nazi ideals in her work under the Third Reich, her portrait photography can be compared to the work of Dorothea Lange or Walker Evans as documentation of impoverished people, and Margaret Bourke-White also photographed labourers in a heroic light. As pointed out by Berlin photographic curator Janos Frecot in the catalogue of an exhibition at the Albertina which included her work, her portraits and those of others at the time can be seen as applications of the same ethnographic principle as portraits of people in faraway cultures; similarly, Leesa Rittelmann has shown that the same principle of characterising a country by the physiognomies of its people, although a throwback to 19th-century theories, was shared by Weimar-era photographers such as the progressive August Sander, in his Antlitz der Zeit (Face of Our Time).
Text from the Wikipedia website

Annemarie Heinrich (Argentinian born Germany, 1912-2005)
Serge Lifar, “El espectro de la rosa” (Serge Lifar, “The Spirit of the Rose”)
1935
Gelatin silver print
Image: 28.4 x 20.7cm (11 3/16 x 8 1/8 in.)
Frame: 45.72 x 35.56cm (18 x 14 in.)
Frame (outer): 49.53 x 39.37cm (19 1/2 x 15 1/2 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, Pepita Milmore Memorial Fund
Annemarie Heinrich (Argentinian born Germany, 1912-2005)
Annemarie Heinrich (9 January 1912 – 22 September 2005) was a German-born naturalised Argentine photographer, who specialised in portraits and nude photographs. Heinrich is considered one of Argentina’s most important photographers.
She is known for having photographed various celebrities of Argentine cinema, such as Tita Merello, Carmen Miranda, Zully Moreno and Mirtha Legrand; as well as other cultural personalities like Jorge Luis Borges, Pablo Neruda and Eva Perón. She also photographed landscapes, city scenes, animals, and abstracts. Her photographs of South America hold significant ethnographic value, showing changes to the area through the 20th century.
Career
In 1930, she opened her first studio in Villa Ballester, Buenos Aires. She also married Ricardo Sanguinetti, a writer under the name Alvaro Sol, in the same year. Two years later she moved to a larger studio and began photographing actors from the Teatro Colón.
Heinrich co-founded Foto Club Argentino and was a founding member of Consejo Argentino de Fotografía (Argentine Council on Photography) and the Consejo Latinoamericano de Fotografía (Latin American Council on Photography). Her photos were also the cover of magazines such as El Hogar, Sintonía, Alta Sociedad, Radiolandia and Antena for forty years.
In Argentina during the Second World War, Heinrich was part of the anti-war movement, Consejo Argentino por la Paz (Argentinian Council for Peace). She was also in the Junta de la Victoria (Victory Board), a women’s group advocating against fascism and for the Allies. After the war, Heinrich travelled across Europe, exhibiting her work in Rome, Milan, Paris, and Zürich. In the 1950s Heinrich was part of a modernist group calling themselves Carpeta de los diez (Group of Ten).
Heinrich was brought to court in 1991 for displaying one of her nude photographs in the Avenida Callao studio window. National and international outcry in support of Heinrich and the aesthetic value of the photograph led to the case being dropped.
In 2015, the Museo de Arte Latinoamericano de Buenos Aires held a retrospective of her work. Heinrich’s work was shown in New York for the first time in 2016 at Nailya Alexander Gallery in the show “Annemarie Heinrich: Glamour and Modernity in Buenos Aires.”
Heinrich’s archive has been digitised in a project between the British Library Endangered Archives Programme and the Institute for Research in Art and Culture, Universidad Nacional de Tres de Febrero, in 2016. The collection is available online at the Endangered Archives Programme website.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Germaine Krull (German, French, and Dutch, Brazil, Republic of the Congo, Thailand and India, 1897-1985)
Ohne Titel (Studie für “Der Akt”) (Untitled (Study for “The Nude”))
1924
Gelatin silver print
Image: 22.23 x 16.51cm (8 3/4 x 6 1/2 in.)
Frame: 50.8 x 40.64cm (20 x 16 in.)
Frame (outer): 53.34 x 43.18cm (21 x 17 in.)
Trish and Jan de Bont
Germaine Krull’s Queer Vision
The photographer Germaine Krull is little known outside of specialist circles today, but in 1928 she was the toast of Paris. Her avant-garde photographs of the city filled the pages of VU, a magazine known for its dynamic spreads and modern, bold aesthetic. Krull was one of its signature photographers. She shot sailors on the docks, piles of curios at the flea market, dancers at the Moulin Rouge. As both photojournalist and art photographer, Krull was one of the leading lights of the Parisian photography scene. Her pictures hung in the Salon de l’Escalier, a major exhibition of modernist photography, and over the next few years, her work featured in exhibitions across Europe. By 1931, the cultural critic Walter Benjamin used Krull as an example of photography’s potential in his celebrated essay “Little History of Photography.”1
Krull, born in Posen (then Germany, now Poznán, Poland), wound up in Paris after an itinerant childhood, a few years’ study of photography in Munich, and a series of political embroilments that sound like the stuff of fiction. Banned from Bavaria for aiding a Bolshevik emissary’s attempted escape through the Alps, she was later deported from the Soviet Union as a supposed counterrevolutionary.
After a stint in Berlin, where she ran her own photography studio, she made her way to Paris. There, she published her photo book Métal in 1928 and began to receive attention alongside other practitioners of new, assertively modern photographic styles such as Man Ray and André Kertész.
With Métal, Krull turned her lens on the soaring structures of industrial Europe: Rotterdam’s railroad bridge De Hef, Marseille’s Pont Transbordeur, a number of nameless industrial cranes, factory machinery, and, most recognizably, the Eiffel Tower.2 The portfolio bore the subtitle “métaux nus” (bare metals), and critics have often likened these metallic bodies to the nude photographs she made around the same time. In both cases, Krull got close to her subjects, dislocating them from their environments. In Métal, Krull rendered the familiar form of the Eiffel Tower nearly unrecognizable. She tended to shoot the tower from beneath, its iron lattices stretching vertiginously upward, such that the monument’s iconic shape is lost.
In an untitled nude photograph from 1928 or ’29, she deployed a similar approach, keeping the camera fixed on an unclothed torso twisting off toward the edge of the frame with upturned face cut off at mid-cheek. The dramatic play of shadow and light renders the figure’s gender indistinct. Whether focused on a living subject or an architectural one, Krull’s camera resists the viewer’s urge to name and categorize.
Before Krull became a famous Parisian photojournalist, she made a series of enigmatic pictures of female couples. In 1924, while living in Berlin, Krull shot a portfolio of eleven photographs entitled Les amies (French for “the friends,” specifically denoting female friends). The photographs depict a pair of women in stages of gradual undress, eventually left only in their stockings, the rest of their flesh laid bare. In the narrative that unfolds from image to image, the two women move between sofa and floor: the shape of their union shifts but their bodies remain interlocked. The images were risqué enough that they received little attention during Krull’s lifetime – perhaps a bit too lewd for fine art display, and yet not quite pornographic either. Certainly though, these photographs are representations of queer desire; they were made by an artist who desired women herself.
In her memoirs, Krull describes the relationship she had with a woman (perhaps pseudonymously) referred to as “Elsa,” noting, “We would have laughed if someone had labeled us lesbians.” At the time, Krull and Elsa were both married to men, and Krull frames the affair as an exception. She calls Elsa “the only woman I have loved and who has loved me.” In another passage, she seems to contradict herself, stating, “I never loved a woman.” But she does not altogether dismiss this relationship: “With Elsa, the joy of feeling united was so great. … She was so much mine that the physical question did not count.”3
One of the Les amies photographs in The Met collection shows two women wrapped in an amorous knot, so engaged in their pursuit of pleasure that their faces remain almost entirely obscured. This elision of the models’ faces is, perhaps, an effect of modesty or concealing their identity, but it also produces a sense of intense absorption in the sexual act – despite performing for a camera, the two women seem concerned only with each other. The photographs offer a vision of queer feminine sexuality in its most visible form.
Krull’s straightforward depiction of these female lovers is all the more striking given that she took these photographs at a time when lesbians were often imagined to be invisible – or at the very least, imperceptible. In the interwar years of the 1920s and ’30s, and especially in France, anxieties ran high about precisely this problem. If lesbians could not be identified on sight, how could they be apprehended? How could the dangers of rampant female sexuality be curtailed with lesbians walking around Paris in plain sight, undetected? These worries occupied novelists, social scientists, and sexologists alike, as Carolyn J. Dean describes in her book, The Frail Social Body.4
Krull, unlike her (largely male) contemporaries, seems to have had no trouble locating queer female sexuality, or representing it. On the contrary, the Les amies photographs adopt a direct, frontal view of the two lovers. Krull’s models become almost indistinguishable over the course of the series. This compositional strategy suggests a particularly queer eroticization of sameness, very different from the conception of a butch-femme dyad imaged by Krull’s contemporary Brassaï in his photographs of the Parisian lesbian bar Le Monocle. But the representation of queerness as a kind of doubling accords with popular French conceptions of the so-called sapphist as a “female Narcissus,” as Nicole Albert puts it in her 2005 study of the lesbian phantasm at the fin-de-siècle, Lesbian Decadence.5
Just as Narcissus gazed upon his own likeness, the lesbian often appeared in popular representations gazing upon another woman as a kind of mirror image of herself. Mirrors, long linked with feminine vanity, became a convenient shorthand for the idea that lesbian desire is the ultimate narcissism. This allowed for artists and writers to simultaneously denounce sexual immorality and the eroticization of that sin. Contemporary illustrations in magazines and advertisements, for instance, offered up sensuous sights of women embracing through, near, or against mirrors. The mirror’s reflection plays up the autoeroticism of self-regard, and supposedly of sapphism itself. Meanwhile, literary accounts of lesbianism in the interwar period frequently staged scenes of erotic encounters in mirrored rooms.6 Such spaces – be they brothels, nightclubs, or private bedrooms – facilitated both voyeurism and spatial disorientation.
Nor was sapphism the mirror’s only resonance in the 1920s. Contemporary critics frequently compared photography to a mirror. The poet and polymath Jean Cocteau, for instance, told Krull of her art: “You are a reforming mirror. You and the darkroom [chambre noire] obtain a new world, a world that has passed through [the camera’s] workings and a soul.”7 Here, he plays upon the double meaning present in the French “chambre noire,” which refers at once to the literal darkroom where photographs are developed and to the camera obscura, which we might think of as a stand-in for the enterprise of photography itself. As Cocteau would have it, Krull herself was the mirror, not photography. Armed with her camera, she had the power not only to depict reality but to transform it.”
Marina Molarsky-Beck. “Germaine Krull’s Queer Vision,” on The Met website August 17 2021 [Online] Cited 15/12/2021
Footnotes
1/ Walter W. Benjamin, “Little History of Photography,” in Selected Writings: 1927-1934, ed. Howard Eiland, Michael W. Jennings, and Gary Smith, trans. Rodney Livingstone (Cambridge, M.A.: Harvard University Press, 1996), 507-528
2/ Kim Sichel, Making Strange: The Modernist Photobook in France (New Haven: Yale University Press, 2020), 19
3/ Germaine Krull, La vie mène la danse, ed. Françoise Denoyelle (Textuel, 2015), 179-180
4/ Carolyn J. Dean, The Frail Social Body: Pornography, Homosexuality, and Other Fantasies in Interwar France (Berkeley, C.A.: University of California Press, 2000)
5/ Nicole G. Albert, Lesbian Decadence: Representations in Art and Literature of Fin-de-Siècle France, trans. Nancy Erber and William A. Peniston (New York: Columbia University Press, 2016), 241-242. Originally published as Albert, Saphisme et décadence dans Paris fin-de-siècle (Paris: Martinière, 2005)
6/ Dean, The Frail Social Body, 193
7/ “Vous êtes un miroir reformant. Vous et la chambre noire obtenez un monde neuf, un monde qui a traversé des mécanismes et une âme.” Jean Cocteau, Jean Cocteau to Germaine Krull, April 1930. Quoted in Pierre MacOrlan, Germaine Krull (Paris: Librairie Gallimard, 1931), 16

Germaine Krull (German, French, and Dutch, Brazil, Republic of the Congo, Thailand and India, 1897-1985)
André Malraux
1930
Gelatin silver print
Image: 22.5 x 16cm (8 7/8 x 6 5/16 in.)
Mount: 29.1 x 22.8cm (11 7/16 x 9 in.)
Frame: 45.72 x 35.56cm (18 x 14 in.)
Frame (outer): 49.53 x 39.37cm (19 1/2 x 15 1/2 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, R. K. Mellon Family Foundation
© Estate Germaine Krull, Museum Folkwang, Essen

Germaine Krull (German, French, and Dutch, Brazil, Republic of the Congo, Thailand and India, 1897-1985)
Selbstporträt mit Icarette (Self-Portrait with Icarette)
c. 1925, printed 1978
Gelatin silver print sheet: 30.8 x 24.3cm (12 1/8 x 9 9/16 in.)
Image: 23.3 x 17.3cm (9 3/16 x 6 13/16 in.)
Frame: 50.8 x 40.64cm (20 x 16 in.)
Frame (outer): 53.34 x 43.18cm (21 x 17 in.)
Department of Image Collections, National Gallery of Art Library © Estate Germaine Krull, Museum Folkwang, Essen
During the 1920s, the iconic New Woman was splashed across the pages of magazines and projected on the silver screen. As a global phenomenon, she embodied an ideal of female empowerment based on real women making revolutionary changes in life and art. Featuring more than 120 photographers from over 20 countries, the groundbreaking exhibition, The New Woman Behind the Camera, explores the diverse “new” women who embraced photography as a mode of professional and personal expression from the 1920s to the 1950s. The first exhibition to take an international approach to the subject, it examines how women brought their own perspectives to artistic experimentation, studio portraiture, fashion and advertising work, scenes of urban life, ethnography, and photojournalism, profoundly shaping the medium during a time of tremendous social and political change. Accompanied by a fully illustrated catalogue, this landmark exhibition will be on view from October 31, 2021 through January 30, 2022, in the West Building of the National Gallery of Art, Washington. It was previously on view at The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, from July 2 through October 3, 2021.
In an era when traditional definitions of womanhood were being questioned, women’s lives were a mix of emancipating and confining experiences that varied by country. Many women around the world found the camera to be a means of independence as they sought to redefine their positions in society and expand their rights. This exhibition presents a geographically, culturally, and artistically diverse range of practitioners to advance new conversations about the history of modern photography and the continual struggle of women to gain creative agency and self-representation.
“This innovative exhibition reevaluates the history of modern photography through the lens of the New Woman, a feminist ideal that emerged at the end of the 19th century and spread globally during the first half of the 20th century,” said Kaywin Feldman, director, National Gallery of Art. “The transnational realities of modernism visualised in photography by women such as Lola Álvarez Bravo, Berenice Abbott, Claude Cahun, Germaine Krull, Dorothea Lange, Niu Weiyu, Tsuneko Sasamoto, and Homai Vyarawalla offer us an opportunity to better understand the present by becoming more fully informed of the past.”
About the exhibition
This landmark exhibition critically examines the extraordinary impact women had on the practice of photography worldwide from the 1920s to the 1950s. It presents the work of over 120 international photographers who took part in a dramatic expansion of the medium propelled by artistic creativity, technological innovation, and the rise of the printed press. Photographers such as Berenice Abbott, Ilse Bing, Lola Álvarez Bravo, Madame d’Ora, Florence Henri, Elizaveta Ignatovich, Germaine Krull, Dorothea Lange, Dora Maar, Niu Weiyu, Eslanda Goode Robeson, Tsuneko Sasamoto, Gerda Taro, and Homai Vyarawalla, among many others, emerged at a tumultuous moment in history that was profoundly shaped by two world wars, a global economic depression, struggles for decolonisation, and the rise of fascism and communism. Against the odds, these women were at the forefront of experimentation with the camera and produced invaluable visual testimony that reflects both their personal experiences and the extraordinary social and political transformations of the era.
Organised thematically in eight galleries, The New Woman Behind the Camera illustrates women’s groundbreaking work in modern photography, exploring their innovations in the fields of social documentary, avant-garde experimentation, commercial studio practice, photojournalism, ethnography, and the recording of sports, dance, and fashion. By evoking the global phenomenon of the New Woman, the exhibition seeks to reevaluate the history of photography and advance new and more inclusive conversations on the contributions of female photographers.
Known by different names, from nouvelle femme and neue Frau to modan gāru and xin nüxing, the New Woman was easy to recognise but hard to define. Fashionably dressed with her hair bobbed, the self-assured cosmopolitan New Woman was arguably more than a marketable image. She was a contested symbol of liberation from traditional gender roles. Revealing how women photographers from around the world gave rise to and embodied the quintessential New Woman even as they critiqued the popular construction of the role, the exhibition opens with a group of compelling portraits and self-portraits. In these works, women defined their positions as professionals and artists during a time when they were seeking greater personal rights and freedoms.
For many women, the camera became an effective tool for self-determination as well as a source of income. With better access to education and a newfound independence, female photographers emerged as a major force in studio photography. From running successful businesses in Berlin, Buenos Aires, London, and Vienna, to earning recognition as one of the first professional female photographers in their home country, women around the world, including Karimeh Abbud, Steffi Brandl, Trude Fleischmann, Annemarie Heinrich, Eiko Yamazawa, and Madame Yevonde, reinvigorated studio practice. A collaborative space where both sitters and photographers negotiated gender, race, and cultural difference, the portrait studio was also vitally important to African American communities which sought to represent and define themselves within a society that continued to be plagued by racism. Photography studios run by Black women, such as Florestine Perrault Collins and Winifred Hall Allen, thrived throughout the United States, and not only preserved likenesses and memories, but also constructed a counter narrative to the stereotyping images that circulated in the mass media.
With the invention of smaller lightweight cameras, a growing number of women photographers found that the camera’s portability created new avenues of discovery outside the studio. In stunning photographs of the city, photographers such as Alice Brill, Rebecca Lepkoff, Helen Levitt, Lisette Model, Genevieve Naylor, and Tazue Satō Matsunaga used their artistic vision to capture the exhilarating modern world around them. They depicted everyday life, spontaneous encounters on the street, and soaring architectural views in places like Bombay (now Mumbai), New York, Paris, São Paulo, and Tokyo, revealing the multiplicity of urban experience. Many incorporated the newest photographic techniques to convey the energy of the city, and the exhibition continues with a gallery focused on those radical formal approaches that came to define modern photography. Through techniques like photomontage, photograms, sharp contrasts of light and shadow, extreme cropping, and dizzying camera angles, women including Aenne Biermann, Imogen Cunningham, Dora Maar, Tina Modotti, Lucia Moholy, and Cami Stone pushed the boundaries of the medium.
Women also produced dynamic pictures of the modern body, including innovative nude studies as well as sport and dance photography. Around the world, participation in spectator and team sports increased along with membership in fitness and hygiene reform movements. New concepts concerning health and sexuality along with new attitudes in movement and dress emphasised the body as a central site of experiencing modernity. On view are luminous works by photographers Laure Albin Guillot, Yvonne Chevalier, Florence Henri, and Jeanne Mandello who reimagined the traditional genre of the nude. Photographs by Irene Bayer-Hecht and Liselotte Grschebina highlight joyous play and gymnastic exercise, while Charlotte Rudolph, Ilse Bing, Trude Fleischmann, and Lotte Jacobi made breathtaking images of dancers in motion, revealing the body as artistic medium.
During the modern period, a growing number of women pursued professional photographic careers and traveled widely for the first time. Many took photographs that documented their experiences abroad and interactions with other cultures as they engaged in formal and informal ethnographic projects. The exhibition continues with a selection of photographs and photobooks by women, mainly from Europe and the United States, that reveal a diversity of perspectives and approaches. Gender provided some of these photographers with unusual access and the drive to challenge discriminatory practices, while others were not exempt from portraying stereotypical views. Publications by Jette Bang, Hélène Hoppenot, Ella Maillart, Anna Riwkin, Eslanda Goode Robeson, and Ellen Thorbecke exemplify how photographically illustrated books and magazines were an influential form of communication about travel and ethnography during the modern period. Other works on display include those by Denise Bellon and Ré Soupault, who traveled to foreign countries on assignment for magazines and photo agencies seeking ethnographic and newsworthy photographs, and those by Marjorie Content and Laura Gilpin, who worked on their own in the southwestern United States.
The New Woman – both as a mass-circulating image and as a social phenomenon – was confirmed by the explosion of photographs found in popular fashion and lifestyle magazines. Fashion and advertising photography allowed many women to gain unprecedented access to the public sphere, establish relative economic independence, and attain autonomous professional success. Producing a rich visual language where events and ideas were expressed directly in pictures, illustrated fashion magazines such as Die Dame, Harper’s Bazaar, and Vogue became an important venue for photographic experimentation by women for a female readership. Photographers producing original views of women’s modernity include Lillian Bassman, Ilse Bing, Louise Dahl-Wolfe, Toni Frissell, Toni von Horn, Frances McLaughlin-Gill, ringl + pit, Margaret Watkins, Caroline Whiting Fellows, and Yva.
The rise of the picture press also established photojournalism and social documentary as dominant forms of visual expression during the modern period. Ignited by the effects of a global economic crisis and growing political and social unrest, numerous women photographers including Lucy Ashjian, Margaret Bourke-White, Kati Horna, Elizaveta Ignatovich, Kata Kálmán, Dorothea Lange, and Hansel Mieth engaged a wide public with gripping images. So-called soft topics such as “women and children,” “the family,” and “the home front” were more often assigned to female photojournalists than to their male counterparts. The exhibition asks viewers to question the effect of having women behind the camera in these settings. Pictures produced during the war, from combat photography by Galina Sanko and Gerda Taro to images of the Blitz in London by Thérèse Bonney and the Tuskegee airmen by Toni Frissell, are also featured. At the war’s end, haunting images by Lee Miller of the opening of Nazi concentration camps and celebratory images of the victory parade of Allied Forces in New Delhi by Homai Vyarawalla made way for the transition to the complexities of the postwar era, including images of daily life in US-occupied Japan by Tsuneko Sasamoto and the newly formed People’s Republic of China by Hou Bo and Niu Weiyu.
The New Woman Behind the Camera acknowledges that women are a diverse group whose identities are defined not exclusively by gender but rather by a host of variable factors. It contends that gender is an important aspect in understanding their lives and work and provides a useful framework for analysis to reveal how photography by women has powerfully shaped our understanding of modern life.
Exhibition catalog
Published by the National Gallery of Art, Washington and distributed by DelMonico Books | D.A.P., this groundbreaking, richly illustrated 288-page catalog examines the diverse women whose work profoundly marked the medium of photography from the 1920s to the 1950s. The book – featuring over 120 international photographers, including Lola Álvarez Bravo, Elizaveta Ignatovich, Germaine Krull, Dorothea Lange, Tsuneko Sasamoto, and Homai Vyarawalla – reevaluates the history of modern photography through the lens of the iconic New Woman. Inclusive scholarly essays introduce readers to these important photographers and question the past assumptions about gender in the history of photography. Contributors include Andrea Nelson, associate curator in the department of photographs, National Gallery of Art; Elizabeth Cronin, assistant curator of photography in the Miriam and Ira D. Wallach Division of Art, Prints, and Photographs, New York Public Library; Mia Fineman, curator in the department of photographs, Metropolitan Museum of Art; Mila Ganeva, professor of German in the department of German, Russian, Asian, and Middle Eastern languages and cultures, Miami University, Ohio; Kristen Gresh, Estrellita and Yousuf Karsh Senior Curator of Photographs, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston; Elizabeth Otto, professor of modern and contemporary art history, University at Buffalo (The State University of New York); and Kim Sichel, associate professor in the department of the history of art and architecture at Boston University; biographies of the photographers by Kara Felt, Andrew W. Mellon postdoctoral fellow in the department of photographs, National Gallery of Art.
Press release from the National Gallery of Art

Dora Maar (French, 1907-1997)
Père Ubu (Portrait of Ubu)
1936
Gelatin silver print
Image: 24.13 x 17.78cm (9 1/2 x 7 in.)
Framed (outer): 40.01 x 33.66 x 2.86cm (15 3/4 x 13 1/4 x 1 1/8 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, Gift of J. Patrick and Patricia A. Kennedy
© 2020 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris
Portrait of Ubu (1936; also called Père Ubu), a monstrous close-up image by Maar of what may be an armadillo fetus (she would never confirm), became an icon of the movement.
Dora Maar (French, 1907-1997)
Henriette Theodora Markovitch (22 November 1907 – 16 July 1997), known as Dora Maar, was a French photographer, painter, and poet. A love partner of Pablo Picasso, Maar was depicted in a number of Picasso’s paintings, including his Portrait of Dora Maar and Dora Maar au Chat. …
Dora Maar the photographer
Maar’s earliest surviving photographs were taken in the early 1920s with a Rolleiflex camera while on a cargo ship going to the Cape Verde Islands.
At the beginning of 1930, she set up a photography studio on rue Campagne-Première (14th arrondissement of Paris) with Pierre Kéfer, photographer, and decorator for Jean Epstein’s 1928 film, The Fall of the House of Usher. In the studio, Maar and Kefer worked together mostly on commercial photography for advertisements and fashion magazines. Her father assisted with her finances in this period of her life as she was establishing herself while trying to earn a living. The studio displayed fashion, advertising and nudes, and it became very successful.
She met the photographer Brassaï with whom she shared the darkroom in the studio. Brassai once said that she had “bright eyes and an attentive gaze, a disturbing stare at times”.
During this time working in advertising and fashion photography, the influence of Surrealism could be seen in her work through her heavy use of mirrors and contrasting shadows. She felt that art should represent the content of reality through links with intuitions or ideas, rather than visually reproduce the natural. Maar also met Louis-Victor Emmanuel Sougez, a photographer working for advertising, archeology and artistic director of the newspaper L’Illustration, whom she considered a mentor.
In 1932, she had an affair with the filmmaker Louis Chavance. Maar frequented the “October group”, formed around Jacques Prévert and Max Morise after their break from surrealism. She had her first publication in the magazine Art et Métiers Graphiques in 1932. Her first solo exhibition was held at the Galerie Vanderberg in Paris.
It is the gelatin silver works of the surrealist period that remain the most sought after by admirers: Portrait of Ubu (1936), 29 rue d’Astorg, black and white, collages, photomontages or superimpositions. The photograph represents the central character in a popular series of plays by Alfred Jarry called Ubu Roi. The work was first shown at the Exposition Surréaliste d’objets at the Galerie Charles Ratton in Paris and at the International Surrealist Exhibition in London in 1936. She also participated in Participates in Fantastic Art, Dada, Surrealism, at the MoMA in New York the same year.
Surrealist concepts and interests often aligned with the ideas of the political left of the time and so Maar became very politically active at this point in her life. After the fascist demonstrations of 6 February 1934, in Paris along with René Lefeuvre, Jacques Soustelle, supported by Simone Weil and Georges Bataille, she signed the tract “Appeal to the Struggle” written at the initiative of André Breton. Much of her work is highly influenced by leftist politics of the time, often depicting those who had been thrown into poverty by the Depression. She was part of an ultra-leftist association called “Masses”, where she first met Georges Bataille, an anti-fascist organisation called the Union of Intellectuals Against Fascism, and a radical collective of left-wing actors and writers called October.
She also was involved in many Surrealist groups and often participated in demonstrations, convocations, and cafe conversations. She signed many manifestos, including one titled “When Surrealists were Right” in August 1935 which concerned the Congress of Paris, which had been held in March of that year.
In 1935, she took a photo of fashion illustrator and designer Christian Berard that was described by writer and critic Michael Kimmelman as “wry and mischievous with only his head perceived above the fountain as if he were John the Baptist on a silver platter”.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Arthur Rothstein (American, 1915-1985)
Untitled (Marion Post Wolcott on assignment, Montgomery County, Maryland)
1940
Gelatin silver print
Image: 22.86 x 17.4cm (9 x 6 7/8 in.)
Sheet: 25.2 x 20.2cm (9 15/16 x 7 15/16 in.)
Frame (outer): 50.48 x 37.78cm (19 7/8 x 14 7/8 in.)
The J. Paul Getty Museum, Los Angeles
Marion Post Wolcott with Rolleiflex and Speed Graphic in hand in Montgomery County, Maryland
Marion Post (June 7, 1910 – November 24, 1990)
Marion Post (June 7, 1910 – November 24, 1990), later Marion Post Wolcott, was a noted American photographer who worked for the Farm Security Administration during the Great Depression documenting poverty and deprivation. …
Life
Marion Post was born in New Jersey on June 7, 1910. Her parents split up and she was sent to boarding school, spending time at home with her mother in Greenwich Village when not at school. Here she met many artists and musicians and became interested in dance. She studied at The New School.
Post trained as a teacher, and went to work in a small town in Massachusetts. Here she saw the reality of the Depression and the problems of the poor. When the school closed she went to Europe to study with her sister Helen. Helen was studying with Trude Fleischmann, a Viennese photographer. Marion Post showed Fleischmann some of her photographs and was told to stick to photography.
While in Vienna she saw some of the Nazi attacks on the Jewish population and was horrified. Soon she and her sister had to return to America for safety. She went back to teaching but also continued her photography and became involved in the anti-fascist movement. At the New York Photo League she met Ralph Steiner and Paul Strand who encouraged her. When she found that the Philadelphia Evening Bulletin kept sending her to do “ladies’ stories”, Ralph Steiner took her portfolio to show Roy Stryker, head of the Farm Security Administration, and Paul Strand wrote a letter of recommendation. Stryker was impressed by her work and hired her immediately.
Post’s photographs for the FSA often explore the political aspects of poverty and deprivation. They also often find humour in the situations she encountered.
In 1941 she met Leon Oliver Wolcott, deputy director of war relations for the U. S. Department of Agriculture under Franklin Roosevelt. They married, and Marion Post Wolcott continued her assignments for the FSA, but resigned shortly thereafter in February 1942. Wolcott found it difficult to fit in her photography around raising a family and a great deal of traveling and living overseas.
In the 1970s, a renewed interest in Wolcott’s images among scholars rekindled her own interest in photography. In 1978, Wolcott mounted her first solo exhibition in California, and by the 1980s the Smithsonian and the Metropolitan Museum of Art began to collect her photographs. The first monograph on Marion Post Wolcott’s work was published in 1983. Wolcott was an advocate for women’s rights; in 1986, Wolcott said: “Women have come a long way, but not far enough. … Speak with your images from your heart and soul” (Women in Photography Conference, Syracuse, N.Y.).
Marion Post Wolcott’s work is archived at the Center for Creative Photography at the University of Arizona in Tucson, Arizona.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Arthur Rothstein (July 17, 1915 – November 11, 1985) was an American photographer. Rothstein is recognised as one of America’s premier photojournalists. During a career that spanned five decades, he provoked, entertained and informed the American people. His photographs ranged from a hometown baseball game to the drama of war, from struggling rural farmers to US Presidents.

Genevieve Naylor (American, 1915-1989)
A Café, Brazil
Early 1940s
Gelatin silver print
Image/sheet: 16.51 x 17.78cm (6 1/2 x 7 in.)
Frame: 35.56 x 45.72cm (14 x 18 in.)
Frame (outer): 38.1 x 48.26 cm (15 x 19 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, Alfred H. Moses and Fern M. Schad Fund
Genevieve Naylor (American, 1915-1989)
Genevieve Naylor (February 2, 1915 – July 21, 1989) was an American photographer and photojournalist, best known for her photographs of Brazil and as Eleanor Roosevelt’s personal photographer. …
Career
At the age of 22, in 1937, Naylor was chosen by Holger Cahill of the Works Progress Administration (WPA) as a photographer for the Harlem Arts Center. She also worked for the WPA in New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, Washington D.C., and New York. She then worked for the Associated Press and was one of the first women photojournalists to be hired by any American news wire services.
In 1940, Genevieve Naylor was assigned by the U.S. State department as part of a team to travel to Brazil. In an effort to further and strengthen the anti-Nazi relationship between the United States and Brazil and to promote mutual cultural awareness, the U.S. Office of Inter-American Affairs, under the leadership of Nelson Rockefeller, created a team of notable Americans that included Orson Welles, Errol Flynn, and Walt Disney. Genevieve Naylor and her partner (and later husband) Misha Reznikoff arrived in Brazil in October, 1940, where he showed his paintings while Miss Naylor took photographs. Naylor’s assignment was to document Brazil’s progress toward becoming a modern nation, capture images that would boost war-time morale, foster cultural interchange, and promote the Allied cause. But Naylor, with her energetic and outgoing personality, soon ventured into other milieus, taking photographs of Brazilian workers jammed into trams, school children, religious and street festivals, and various aspects of everyday lives. Because it was war time, film was rationed, and Naylor’s equipment was modest. She had neither flash nor studio lights and had to carefully choose her shots, balancing spontaneity with careful composition. Of her work, nearly 1,350 photos survived and were preserved. After her return to the states in 1943, Naylor become only the second woman photographer to be given a one-woman show when her work was exhibited by New York’s Museum of Modern Art.
Naylor later spent 15 years as a photographer with Harper’s Bazaar and from 1944 to 1980 was a freelance photographer for Vogue, McCall’s, Town and Country, Life, Look, Saturday Evening Post, Women’s Home Companion, Cosmopolitan, Fortune, Collier’s, Glamour, Good Housekeeping, Vanity Fair, Elle, Ladies’ Home Journal, Redbook, House Beautiful, Holiday, Mademoiselle, American Home, Seventeen, Better Homes and Gardens, Charm, Bride’s, amongst others. She was a war time photographer, covering parts of the Korean War for Look magazine.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Genevieve Naylor (American, 1915-1989)
São Januário Trolley
Early 1940s
Gelatin silver print
Image: 19.05 x 19.05cm (7 1/2 x 7 1/2 in.)
Sheet: 20.32 x 25.4cm (8 x 10 in.)
Frame: 35.56 x 45.72cm (14 x 18 in.)
Frame (outer): 38.1 x 48.26cm (15 x 19 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, Alfred H. Moses and Fern M. Schad Fund
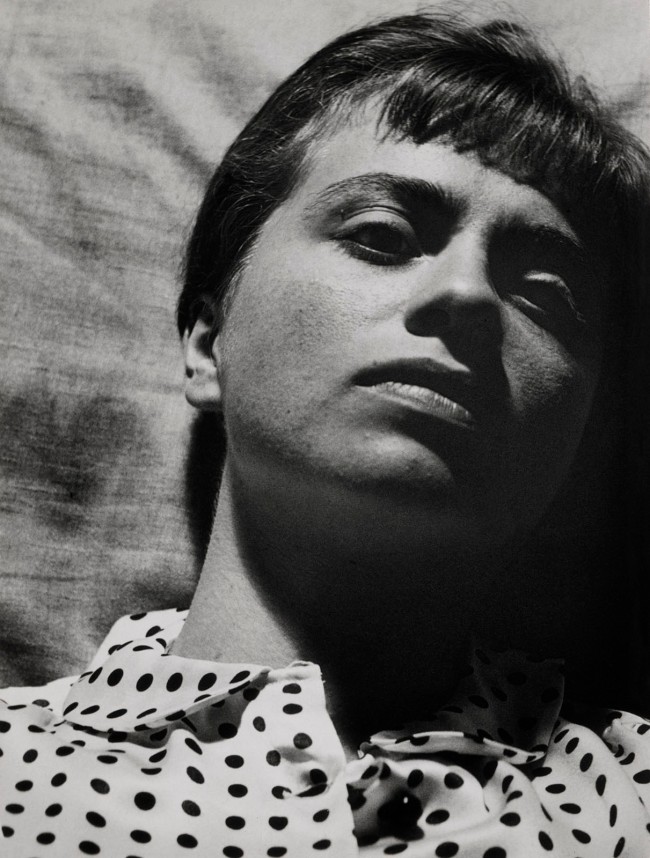

Elfriede Stegemeyer (German, 1908-1988)
Selbstporträt (Self-Portrait)
1933
Gelatin silver print
Image: 23.81 x 17.94cm (9 3/8 x 7 1/16 in.)
Support: 23.81 x 17.94cm (9 3/8 x 7 1/16 in.)
Mat: 50.8 x 40.64cm (20 x 16 in.)
Frame: 50.8 x 40.64cm (20 x 16 in.)
Frame (outer): 51.44 x 41.28 x 3.33cm (20 1/4 x 16 1/4 x 1 5/16 in.)
Los Angeles County Museum of Art, The Audrey and Sydney Irmas Collection
Elfriede Stegemeyer (1908-1988); German photographer, painter and film artist. In a bombing raid on Berlin in 1943, much of her work was destroyed. After the war, she dedicated herself under the pseudonym Elde Steeg increasingly to painting and drawing, and experimented with Surrealist and Constructivist expression. From 1945 she lived and worked under the name Elde Steeg. In 1974 she moved to Innsbruck and worked there until her death.
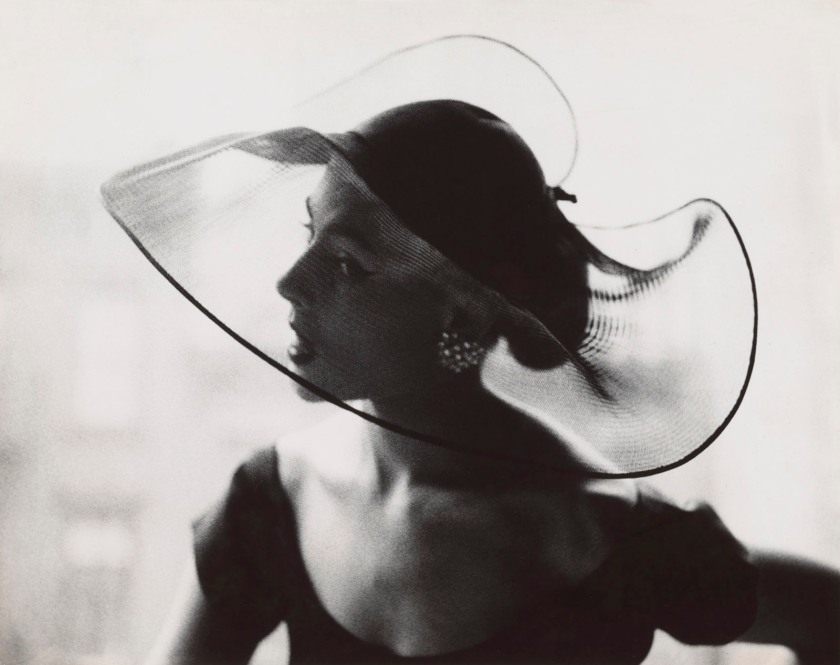

Lillian Bassman (American, 1917-2012)
Translucent Hat
c. 1950
Gelatin silver print
Image/sheet: 26.99 x 34.29cm (10 5/8 x 13 1/2 in.)
Frame: 50.8 x 60.96cm (20 x 24 in.)
Frame (outer): 53.34 x 63.5cm (21 x 25 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, Renee Harbers Liddell Fund and Alfred H. Moses and Fern M. Schad Fund
© Estate of Lilian Bassman
Lillian Bassman (American, 1917-2012)
Lillian Bassman (June 15, 1917 – February 13, 2012) was an American photographer and painter.
Career
From the 1940s until the 1960s Bassman worked as a fashion photographer for Junior Bazaar and later at Harper’s Bazaar where she promoted the careers of photographers such as Richard Avedon, Robert Frank, Louis Faurer and Arnold Newman. Under the guidance of the Russian emigrant, Alexey Brodovitch, she began to photograph her model subjects primarily in black and white. Her work was published for the most part in Harper’s Bazaar from 1950 to 1965.
By the 1970s Bassman’s interest in pure form in her fashion photography was out of vogue. She turned to her own photo projects and abandoned fashion photography. In doing so she tossed out 40 years of negatives and prints – her life’s work. A forgotten bag filled with hundreds of images was discovered over 20 years later. Bassman’s fashion photographic work began to be re-appreciated in the 1990s.
She worked with digital technology and abstract colour photography into her nineties to create a new series of work. She used Photoshop for her image manipulation.
The most notable qualities about her photographic work are the high contrasts between light and dark, the graininess of the finished photos, and the geometric placement and camera angles of the subjects. Bassman became one of the last great woman photographers in the world of fashion. A generation later, Bassman’s pioneering photography and her mentor Alexey Brodovitch’s bold cropping and layout innovations were a seminal influence on Sam Haskins and his black and white work of the sixties.
Bassman died on February 13, 2012, at age 94.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Edith Tudor-Hart (British born Austria, 1908-1973)
Untitled (Street, London)
1940s, printed later
Gelatin silver print
Image: 21 x 28cm (8 1/4 x 11 in.)
Frame: 35.56 x 45.72cm (14 x 18 in.)
Frame (outer): 38.1 x 48.26cm (15 x 19 in.)
Peter Suschitzky, Julia Donat, and Misha Donat
Edith Tudor-Hart (British born Austria, 1908-1973)
Edith Tudor-Hart (née Suschitzky; 28 August 1908 – 12 May 1973) was an Austrian-British photographer and spy for the Soviet Union. Brought up in a family of socialists, she trained in photography at Walter Gropius’s Bauhaus in Dessau, and carried her political ideals through her art. Through her connections with Arnold Deutsch, Tudor-Hart was instrumental in the recruiting of the Cambridge Spy ring which damaged British intelligence from World War II until the security services discovered all their identities by the mid-1960s. She recommended Litzi Friedmann and Kim Philby for recruitment by the KGB and acted as an intermediary for Anthony Blunt and Bob Stewart when the rezidentura at the Soviet Embassy in London suspended its operations in February 1940.
Read a fuller biography on the Wikipedia website
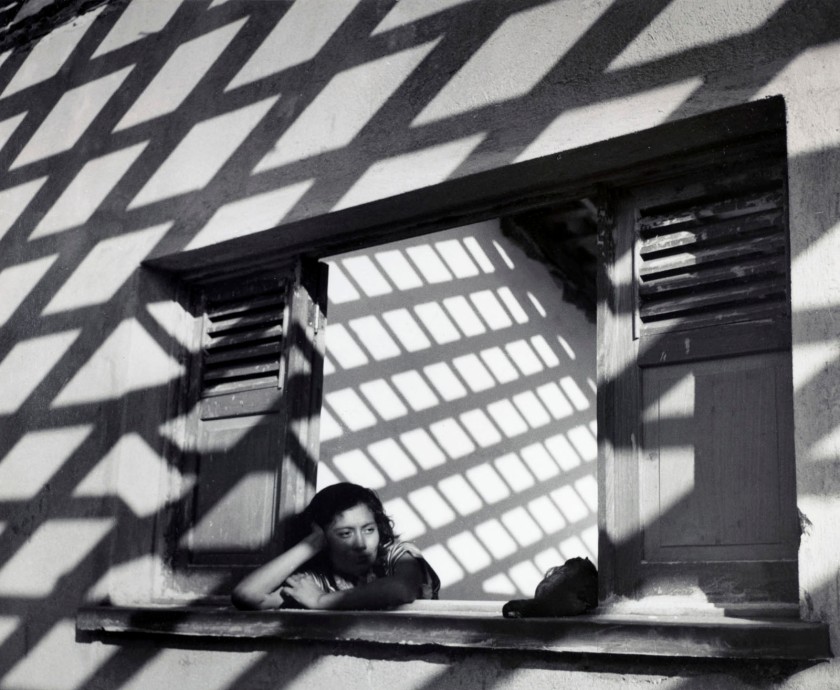

Lola Álvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1903-1993)
En su propia cárcel (In Her Own Prison)
c. 1950
Gelatin silver print
Image: 18.42 x 21.27cm (7 1/4 x 8 3/8 in.)
Frame: 50.8 x 45.72cm (20 x 18 in.)
Frame (outer): 53.34 x 48.26cm (21 x 19 in.)
Daniel Greenberg and Susan Steinhauser
© Center for Creative Photography, The University of Arizona Foundation
Lola Álvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1903-1993)
Lola Álvarez Bravo (3 April 1903 – 31 July 1993) was the first Mexican female photographer and a key figure in the post-revolution Mexican renaissance. Known for her high level of skill in composition, her works were seen by her peers as fine art. She was recognised in 1964 with the Premio José Clemente Orozco (José Clemente Orozco Prize), by the State of Jalisco, for her contributions to photography and her efforts to preserve the culture of Mexico. Her works are included in the permanent collections of international museums, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York City.
Álvarez was born in a small town in Jalisco, but moved to Mexico City with her father when her parents separated around 1906. For a decade, she lived with her father in a large mansion, but upon his death was taken in by her older half-brother, who sent her to boarding school. After completing a traditional education, in 1922 she enrolled in the Escuela Nacional Preparatoria, where she met her lifelong friend, Frida Kahlo. A friendship with another of her childhood friends, Manuel Álvarez Bravo, blossomed into romance around the same time and the two married in 1925. Her husband taught her photography, as well as development techniques, and for nearly a decade, she acted as his assistant. As she sought to explore her own creativity and was unhappy in the marriage, the couple separated in 1934.
Beginning her career as a teacher, Álvarez took photographic assignments for magazines and newspapers, developing a reputation as one of the only women photojournalists working in Mexico City. She chose to portray subjects candidly, revealing the deeper meaning of culture and social significance, rather than seeking newsworthy work. In 1935, she began cataloging photographs in the Department of Education and two years later was hired to run the photography workshops of the National Autonomous University of Mexico, where she remained until her retirement in 1971.
In addition to her contributions to advertising and photojournalism, Álvarez took many photographs of her artistic friends, and in 1951 opened the Galeria de Arte Contemporáneo (Gallery of Contemporary Art) to promote their work. In 1953 at the Galeria, she hosted the only exhibition of Frida Kahlo’s works held in Mexico during the artist’s life. From the late 1970s until her death in 1993, she gained international recognition for her body of work. Her photo archive is located at the Center for Creative Photography in Tucson, Arizona, United States.
Read a fuller biography on the Wikipedia website

Jette Bang (Danish, 1914-1964)
Grønland
1940
Bound volume
Open: 26.04 x 44.45cm (10 1/4 x 17 1/2 in.)
Closed: 26.04 x 22.86cm (10 1/4 x 9 in.)
Cradle: 6 1/8 (maximum height at left) x 15 1/2 (width) x 10 1/2 (depth) x 3 3/8 in. (maximum height at right)
National Gallery of Art Library, Gift of the Department of Photographs
Jette Bang (Danish, 1914-1964)
Jette Bang (February 4, 1914 – February 16, 1964) was a Danish photographer and film maker who is remembered for the large collection of photographs and films she took in Greenland, depicting the country and the way of life of its inhabitants before their old culture disappeared. …
Career
In 1936, Bang arrived in Greenland for the first time and spent eight months taking photographs of the traditional lifestyle of the Greenlandic Inuit, which was beginning to die out as a result of European influence. She travelled around on dog sleds and lived with the natives, sharing their way of life. The result was 400 photographs which were exhibited at the Danish Museum of Art & Design in 1937. Some were published in her book Grønland (1940) with a foreword by Minister of State Thorvald Stauning. The book was an eyeopener for the Danes.
Her next expedition in the winter of 1938-1939 was supported by Denmark’s Greenland Administration, who provided a motorboat, lighting and helpers. Under harsh and primitive conditions, she lived closely together with the Greenlanders, spending most of the winter in a hole in the ground with floor space of just four square metres. Joining the Thule postal sleds, she travelled across Melville Bay up to Cape York in the district of Thule. Her trip resulted in a revealing colour film, Inuit, seen as a work of art when it was shown in Denmark in 1938. The film was in two parts, depicting the old and the new Greenland. The reels on Melville Bay were lost in a fire while she was in Thule but there was still enough material for a four-hour production.
For a time, Jette Bang hoped to go back and take some additional shots but her plans were brought to a standstill by the outbreak of the Second World War. Only after the liberation in 1945 was she able to continue her project.
Many stills taken from the film were published in her book 30.000 Kilometer med Sneglefart (30,000 kilometers at a snail’s pace) (1941). Bang, a good storyteller, was able to provide an excellent account of her experiences. With the photo book Grønlænderbørn (Greenlandic Children) (1944) she continued to report on her travels, now addressing Danish schoolchildren.
She travelled to Greenland five more times. Disappointed with modern developments there, she republished her book Grønland in 1961. In 1962, she travelled to Greenland for the last time, trying to rework her 1938 colour film; but illness prevented any more trips.
In 1959, she took part in Peter Glob’s archaeological expedition to Bahrain, which led to her film Beduiner (1962).
Assessment
Jette Bang was the first photographer to take close-up portraits of the Greenlanders. While earlier photographers had been more interested in their clothing and surroundings, she was more concerned with their behaviour, creating more lasting and universal impressions.
Jette Bang’s photographs from Greenland are the only remaining material documenting the old Greelandic way of life which has now almost disappeared. Her dedication to the country and its people was legendary. She was also a talented author: “The full moon’s twisted face tripped up over the tops of the pointed peaks in the north west like a fakir trying to walk on a bed of nails,” she wrote in 30.000 Kilometer med Sneglefart.
Many of her photographs are in the National Museum of Greenland in Nuuk. The main collection of 12,000 photographs is with the Arktisk Institut in Copenhagen, which has made them available on the Internet.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Gerda Leo (German, 1909-1993)
Korbgeflecht (Wicker Basket)
c. 1928
Gelatin silver print
Image: 36.3 x 29.2cm (14 5/16 x 11 1/2 in.)
Frame (outer): 51.3 x 41.3 x 2.7cm (20 3/16 x 16 1/4 x 1 1/16 in.)
Galerie Berinson, Berlin
Gerda Leo (born February 1, 1909 in Hagen, Westphalia , died September 28, 1993 in Amsterdam, Netherlands) was a German photographer in the field of New Vision and New Objectivity. She studied at the Burg Giebichenstein State School of Applied Arts in Halle (Saale) with Hans Finsler and worked as an assistant to Albert Renger-Patzsch. Her photographic estate is in the Moritzburg Art Museum Halle (Saale).
Read a fuller biography on the Wikipedia website
Behind the Camera
Women actively participated in the development of photography soon after its inception in the 19th century. Yet it was in the 1920s, after the seismic disruptions of World War I, that women entered the field of photography in force. Aided by advances in technology and mass communications, along with growing access to training and acceptance of their presence in the workplace, women around the world made an indelible mark on the growth and diversification of the medium. They brought innovation to a range of photographic disciplines, from avant-garde experimentation and commercial studio practice to social documentary, photojournalism, ethnography, and the recording of sports, dance, and fashion.
The New Woman
A global phenomenon, the New Woman of the 1920s embodied an ideal of female empowerment based on real women making revolutionary changes in life and art. Her image – a woman with bobbed hair, stylish dress, and a confident stride – was a staple of newspapers and magazines first in Europe and the United States and soon in China, Japan, India, Australia, and elsewhere. A symbol of the pursuit of liberation from traditional gender roles, the New Woman in her many guises represented women who faced a mix of opportunities and obstacles that varied from country to country. The camera became a powerful means for female photographers to assert their self-determination and redefine their position in society. Producing compelling portraits, including self-portraits featuring the artist with her camera, they established their roles as professionals and artists.
The Studio
Commercial studio photography was an important pathway for many women to forge a professional career and to earn their own income. Running successful businesses in small towns and major cities from Buenos Aires to Berlin and Istanbul, women reinvigorated the genre of portraiture. In the studio, both sitters and photographers navigated gender, race, and cultural difference; those run by women presented a different dynamic. For example, Black women operated studios in Chicago, New Orleans, and elsewhere in the United States, where they not only preserved likenesses and memories, but also constructed a counter narrative to racist images then circulating in the mass media.
The City
The availability of smaller, lightweight cameras and the increasing freedom to move about cities on their own spurred a number of women photographers to explore the diversity of the urban experience beyond the studio walls. Using their creative vision to capture the vibrant modern world around them, women living and working in Bombay (now Mumbai), London, New York, Paris, São Paulo, Tokyo, and beyond photographed soaring architecture and spontaneous encounters on the street.
Avant-Garde Experiments
Creative formal approaches – photomontage, photograms, sharp contrasts of light and shadow, unconventional cropping, extreme close-ups, and dizzying camera angles – came to define photography during this period. Women incorporated these cutting-edge techniques to produce works that conveyed the movement and energy of modern life. Although often overshadowed by their male partners and colleagues, women photographers were integral in shaping an avant-garde visual language that promoted new ways of seeing and experiencing the world.
Modern Bodies
Beginning in the 1920s, new concepts concerning health and sexuality, along with changing attitudes about movement and dress, emphasised the human body as a central site of experiencing modernity. Women photographers produced incisive visions of liberated modern bodies, from pioneering photographs of the nude to exuberant pictures of sport and dance. Photographs of joyous play and gymnastic exercise, as well as images of dancers in motion, celebrate the body as artistic medium.
Ethnographic Approaches
During this modern period, numerous women pursued professional photographic careers and traveled extensively for the first time. Many took photographs that documented their experiences abroad in Africa, China, Afghanistan, and elsewhere, while others engaged in more formal ethnographic projects. Some women with access to domains that were off limits to their male counterparts produced intimate portraits of female subjects. While gender may have afforded these photographers special connections to certain communities, it did not exempt some, especially those from Europe and the United States, from producing stereotypical views that reinforced hierarchical concepts of race and ethnocentrism.
Fashion and Advertising
Images splashed across the pages of popular fashion and lifestyle magazines vividly defined the New Woman. The unprecedented demand for fashion and advertising photographs between the world wars provided exceptional employment opportunities for fashion reporters, models, and photographers alike, allowing women to emerge as active agents in the profession. Cultivating the tastes of newly empowered female consumers, fashion and advertising photography provided a space where women could experiment with pictures intended for a predominantly female readership.
Social Documentary
Galvanised by the effects of a global economic crisis and the growing political and social unrest that began in the 1930s, numerous women photographers produced arresting images of the human condition. Whether working for government agencies or independently, women contributed to the visual record of the Depression and the events leading up to World War II. From images of breadlines and worker demonstrations to forced migration and internment, women photographers helped to expose dire conditions and shaped what would become known as social documentary photography.
Reportage
The rise of the picture press established photojournalism as a dominant form of visual expression during a period shaped by two world wars. Women photographers conveyed an inclusive view of worldwide economic depression, struggles for decolonisation in Africa, and the rise of fascism and communism in Europe and the Soviet Union. They often received the “soft assignments” of photographing women and children, families, and the home front, but some women risked their lives close to the front lines. Images of concentration camps and victory parades made way for the complexities of the postwar era, as seen in pictures of daily life in US-occupied Japan and the newly formed People’s Republic of China.
The photographers whose works are in The New Woman Behind the Camera represent just some of the many women around the world who were at the forefront of experimenting with the camera. They produced invaluable visual testimony that reflected both their personal experiences and the extraordinary social and political transformations of the early 20th century. Together, they changed the history of modern photography.
Text from the National Gallery of Art website

Dulce Carneiro (Brazilian, 1929-2018)
Mulher (Woman)
c. 1957
Gelatin silver print
Image: 37.94 x 28.58cm (14 15/16 x 11 1/4 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 43.18 x 53.34cm (17 x 21 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington, Robert B. Menschel and the Vital Projects Fund

Galina Sanko (Russian, 1904-1981)
During an Attack
1943, printed c. 1960s
Gelatin silver print
Image: 15.72 x 24.29cm (6 3/16 x 9 9/16 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 43.18 x 53.34cm (17 x 21 in.)
Robert Koch Gallery
Galina Sanko (Russian, 1904-1981)
Galina Sanko (Russian: Галина Захаровна Санько and also Galina Sankova or Galina Sankowa) (1904-1981) was a Russian photographer who worked as a photojournalist and was one of only five women who served as a war photographer during World War II. She was one of the most noted Soviet photographers and known in the West, winning awards both at home and abroad. …
After the persecution of her husband in 1938, Sanko dedicated her life to photography. When the war broke out, she asked to go to the front as a war correspondent. Initially, Sanko trained as a nurse and then studied driving and auto mechanics. She bandaged the wounded and once she had proved her fitness for battle was allowed as one of only five women who served as war photographers. She worked for the magazine Frontline Illustration (Russian: Фронтовая иллюстрация) and took photographs of battles in Kursk, Moscow and Stalingrad, taking pictures at Bryansk and the Don Campaign near Stallingrad. In 1944, during the northern offensive, she took photographs of the siege of Leningrad. Near the end of the war, she took photographs of the fighting against Japan. She was seriously injured twice during the war. In the movie Wild Honey (Russian: Дикий мед) (1967) based on the novel by Leonid Pervomaisky, there is a scene based upon a real-life event in which Sanko escaped in the nick of time from being fired upon by a German tank.
At the end of the war, Sanko worked for the magazine Spark (Russian: Огонек) but until the 1960s, her work was banned and hidden in an archive. Accused of distorting the truth, with her photographs of the liberation of the Petrozavodsk camp, Sanko was exonerated when 20 years after the war, she returned to the Republic of Karelia and found one of the children she had photographed in the camp. After publishing “Claudia 20 years later”, her archive was opened in 1966 and Sanko participated in many photographic exhibitions at home and abroad. She was awarded the Order of the Red Star. Sanko died in Moscow in 1981.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Galina Sanko (Russian, 1904-1981)
Prisoners, Stalingrad
1943, printed c. 1960s
Gelatin silver print
Image: 20.32 x 29.53cm (8 x 11 5/8 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 43.18 x 53.34cm (17 x 21 in.)
Robert Koch Gallery

Galina Sanko (Russian, 1904-1981)
Behind the front lines, workers at a factory evacuated from Ukraine to a town on the Volga
1942, printed c. 1960s
Gelatin silver print
Image/sheet: 24.13 x 16.67cm (9 1/2 x 6 9/16 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 43.18 x 53.34cm (17 x 21 in.)
Robert Koch Gallery

Galina Sanko (Russian, 1904-1981)
Observation Post, the Fight for Hill N
1942
Gelatin silver print
Image/sheet: 29.21 x 20.96cm (11 1/2 x 8 1/4 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 43.18 x 53.34cm (17 x 21 in.)
Robert Koch Gallery

G. Herbert Taylor
My Best Photograph and Why
1937
Photography book
Closed: 29.53 x 23.18cm (11 5/8 x 9 1/8 in.)
Open: 29.53 x 44.77cm (11 5/8 x 17 5/8 in.)
Mount: 1.43 x 44.93 x 29.69cm (9/16 x 17 11/16 x 11 11/16 in.)
National Gallery of Art Library, David K.E. Bruce Fund

Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait (Self-Portrait)
c. 1927
Gelatin silver print
Image: 25.5 x 20.1cm (10 1/16 x 7 15/16 in.)
Frame: 53 x 42cm (20 7/8 x 16 9/16 in.)
Wilson Centre for Photography
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Claude Cahun (born Lucy Renee Mathilde Schwob, 25 October 1894 – 8 December 1954) was a French surrealist photographer, sculptor, and writer. Schwob adopted the pseudonym Claude Cahun in 1914. Cahun is best known as a writer and self-portraitist, who assumed a variety of performative personae. Cahun’s work is both political and personal. In Disavowals, she writes: “Masculine? Feminine? It depends on the situation. Neuter is the only gender that always suits me.” During World War II, Cahun was also active as a resistance worker and propagandist. …
Cahun’s works encompassed writing, photography, and theatre. She is most remembered for her highly staged self-portraits and tableaux that incorporated the visual aesthetics of Surrealism. During the 1920s, Cahun produced an astonishing number of self-portraits in various guises such as aviator, dandy, doll, body builder, vamp and vampire, angel, and Japanese puppet.
Some of Cahun’s portraits feature the artist looking directly at the viewer, head shaved, often revealing only head and shoulders (eliminating body from the view), and a blurring of gender indicators and behaviours which serve to undermine the patriarchal gaze. Scholar Miranda Welby-Everard has written about the importance of theatre, performance, and costume that underlies Cahun’s work, suggesting how this may have informed the artist’s varying gender presentations. …
Cahun’s work was often a collaboration with Marcel Moore. Cahun and Moore collaborated frequently, though this often goes unrecognised. It is believed that Moore was often the person standing behind the camera during Cahun’s portrait shoots and was an equal partner in Cahun’s collages.
With the majority of the photographs attributed to Cahun coming from a personal collection, not one meant for public display, it has been proposed that these personal photographs allowed for Cahun to experiment with gender presentation and the role of the viewer to a greater degree.
One of my favourite artists – a hero of mine!
Read a fuller biography on the Wikipedia website

Toni von Horn (American born Germany, 1899-1970)
Untitled
1932
Gelatin silver print
Image/sheet: 23 x 19cm (9 1/16 x 7 1/2 in.)
Frame: 40.64 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Frame (outer): 45.09 x 55.25cm (17 3/4 x 21 3/4 in.)
National Gallery of Art, Washington
Gift of Charles van Horne on behalf of the family of Toni von Horn
Toni von Horn (American born Germany, 1899-1970)
Baroness Antonie “Toni” von Horn was born to a prominent family in Germany in 1899. Around 1920, she opened a photography studio in Heidelberg. While in New York on an assignment, she met the editor of Vanity Fair who recommended she pursue a career in New York.
She did, and soon became a leading fashion and advertising photographer in the 1920s and 30s, working for Vanity Fair, Vogue, and Harper’s Bazaar and at her own studio. She was one of the first woman photographers to gain a national and international reputation, Her many celebrity portraits included Greta Garbo, Eleanor Roosevelt, Ginger Rogers, Cole Porter, Clark Gable, Claudette Colbert, and Jean Harlow. Her photograph of Albert Einstein has been called the best ever made of him.
Toni von Horn was among the first woman professional photographers and was the first to join the stable of Conde Nast’s Vogue and Vanity Fair, and Harper’s Bazaar during those magazines’ glorious years of the early 1930s. Active as Tony von Horn, her images were regular features, along with such luminaries as Edward Steichen, Adolf de Meyer and George Hoyningen-Heune among others, in the magazines from the end of 1930 to 1935.

Ruth Orkin (American, 1921-1985)
Ethel Waters, Carson McCullers, and Julie Harris at the Opening Night Party for “The Member of the Wedding,” New York City
1950
Gelatin silver print
Image/sheet: 39.7 x 49.5cm (15 5/8 x 19 1/2 in.)
Frame (outer): 57.6 x 67.8cm (22 11/16 x 26 11/16 in.)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Purchase, Dorothy Levitt Beskind Gift, 1980
© Ruth Orkin
Image: © The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Image source: Art Resource, NY
Ruth Orkin (American, 1921-1985)
Ruth Orkin (September 3, 1921 – January 16, 1985) was an American photographer, photojournalist, and filmmaker, with ties to New York City and Hollywood. Best known for her photograph An American Girl in Italy (1951), she photographed many celebrities and personalities including Lauren Bacall, Doris Day, Ava Gardner, Tennessee Williams, Marlon Brando, and Alfred Hitchcock.
Life
Ruth Orkin was born on September 3, 1921 in Boston, Massachusetts to Mary Ruby and Samuel Orkin. Ruth grew up in Hollywood, due to her mother’s career as a silent film actress. In 1931, she received her first camera, a 39-cent Univex, and soon began experimenting by taking photographs of her friends and teachers at school. At the age of 17, she decided to bike across America, beginning in Los Angeles, and ending in New York City for the 1939 World’s Fair. She completed the trip in three weeks’ time, taking photographs along the way.
She briefly attended Los Angeles City College for photojournalism in 1940, prior to becoming the first messenger girl at MGM Studios in 1941, citing a desire to become a cinematographer. She left the position after discovering the union’s discriminatory practices that did not allow female members. She joined the Women’s Auxiliary Army Corps during World War II, in 1941 in an attempt to gain filmmaking skills, as advertisements promoting the group promised. The attempt was not fruitful, however, and she was discharged in 1943 without any filmmaking training.
In 1943, Orkin moved to New York City in pursuit of a career as a freelance photojournalist. She began working as a nightclub photographer, and received her first assignment in 1945 from The New York Times to shoot Leonard Bernstein. Shortly after, her freelance career grew as she traveled internationally on assignments and contributed photographs to Life, Look, Ladies’ Home Journal, and others. Orkin is credited with breaking into a heavily male field.
Orkin’s most celebrated image is An American Girl in Italy (1951). The subject of the now-iconic photograph was the 23-year-old Ninalee Craig (known at that time as Jinx Allen). The photograph was part of a series originally titled “Don’t Be Afraid to Travel Alone.” The image depicted Craig as a young woman confidently walking past a group of ogling Italian men in Florence. In recent articles written about the pair, Craig claims that the image was not staged, and was one of many taken throughout the day, aiming to show the fun of traveling alone.
In 1952 Orkin married photographer, filmmaker and fellow Photo League member Morris Engel. Orkin and Engel collaborated on two major independent feature films, “Little Fugitive” (1953) and “Lovers and Lollipops” (1955). After the success of the two films, Orkin returned to photography, taking colour shots of Central Park as seen through her apartment window. The resulting photographs were collected in two books, “A World Through My Window” (1978) and “More Pictures from My Window” (1983).
Orkin taught photography at the School of Visual Arts in the late 1970s, and at the International Center of Photography in 1980. After a long, private battle with cancer, Orkin died of the disease at her New York City apartment on January 16, 1985.
Text from the Wikipedia website
National Gallery of Art
National Mall between 3rd and 7th Streets
Constitution Avenue NW, Washington
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm
National Gallery of Art website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top
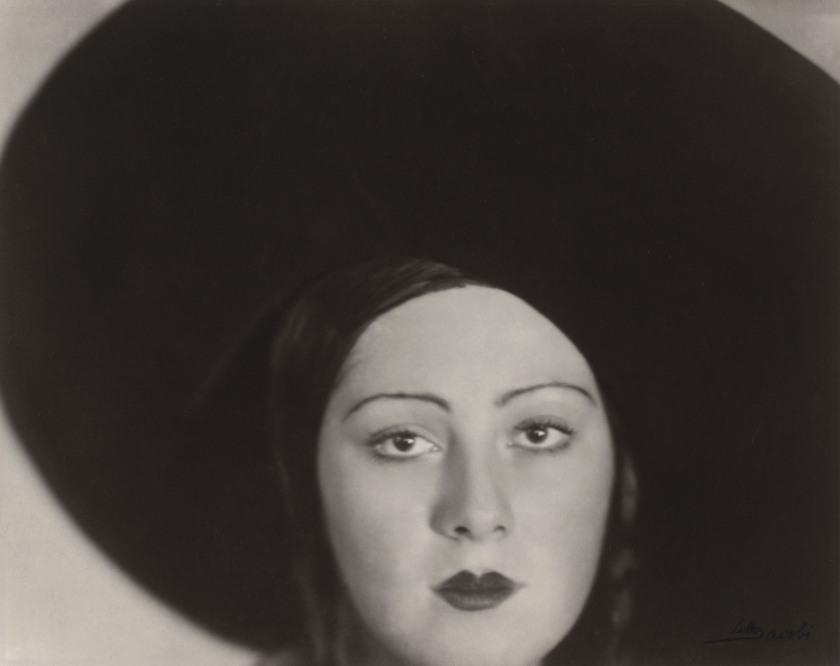
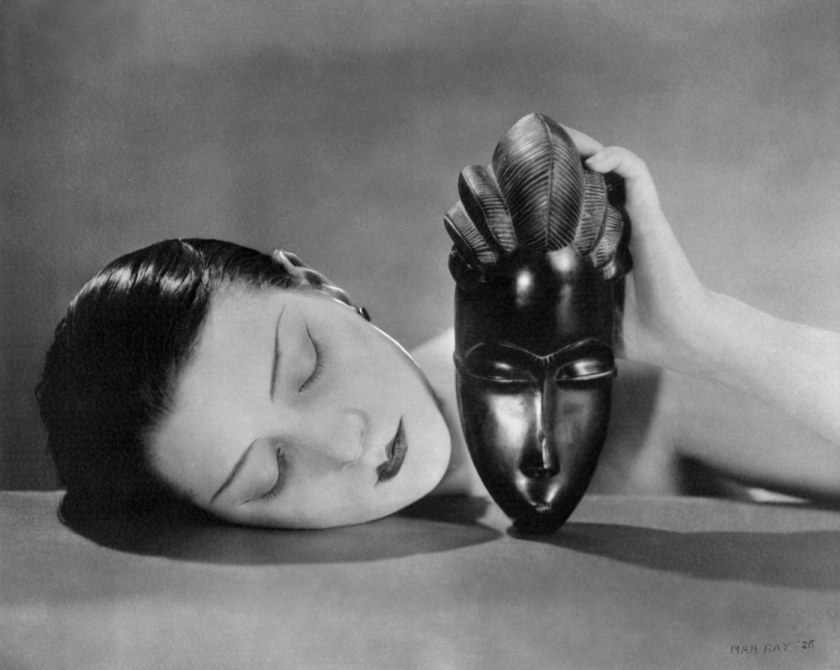
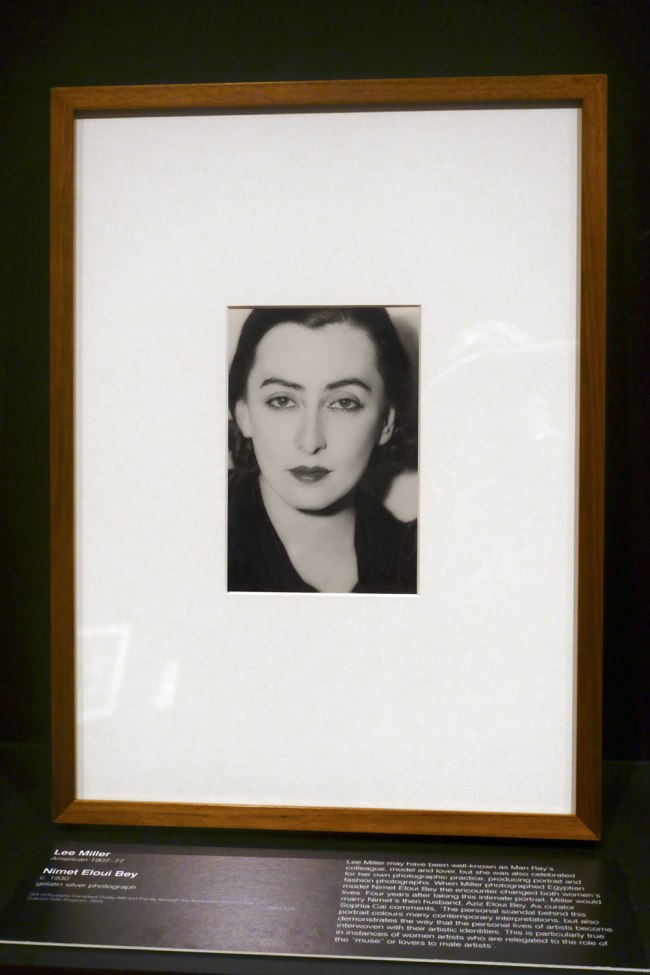
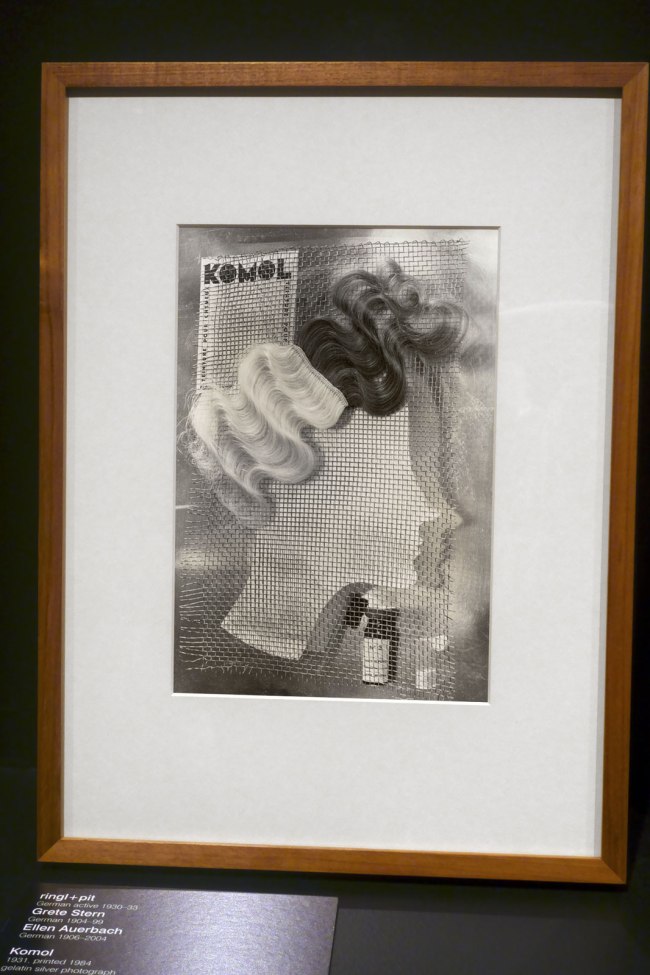
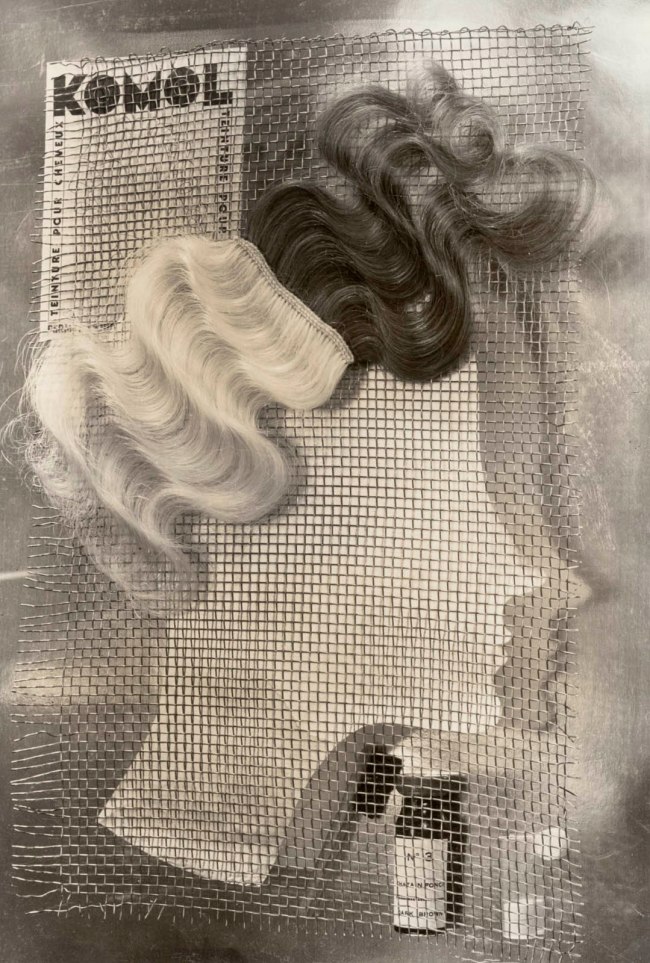
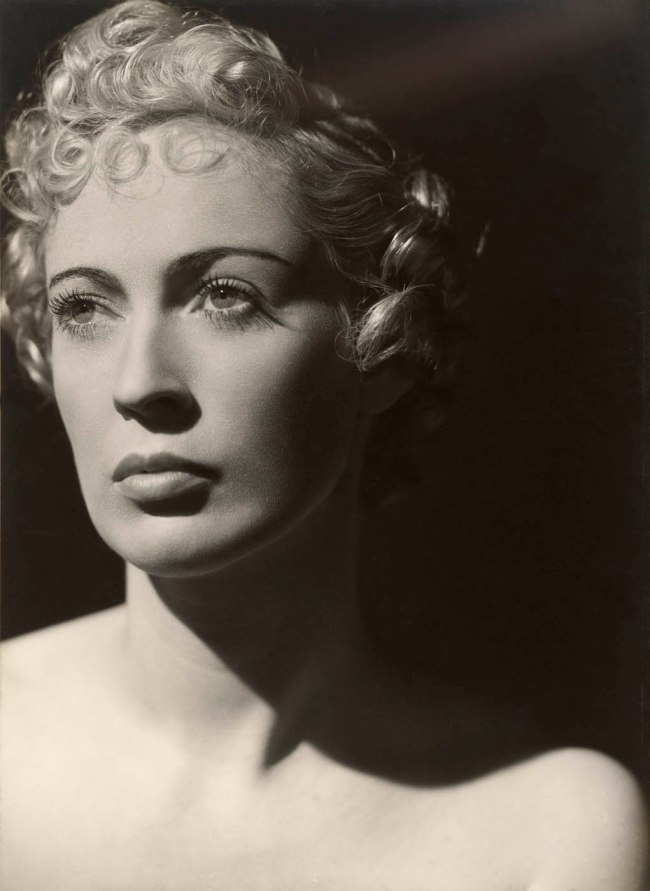
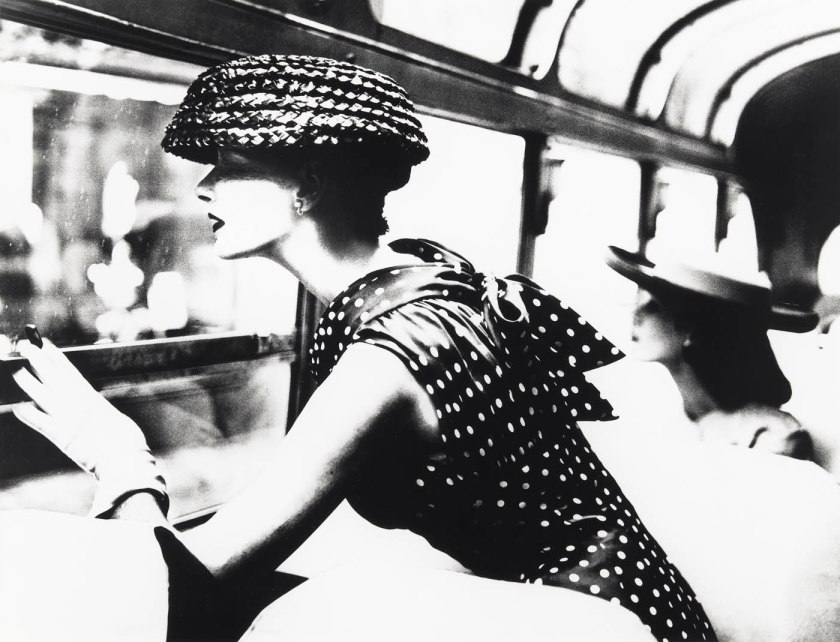
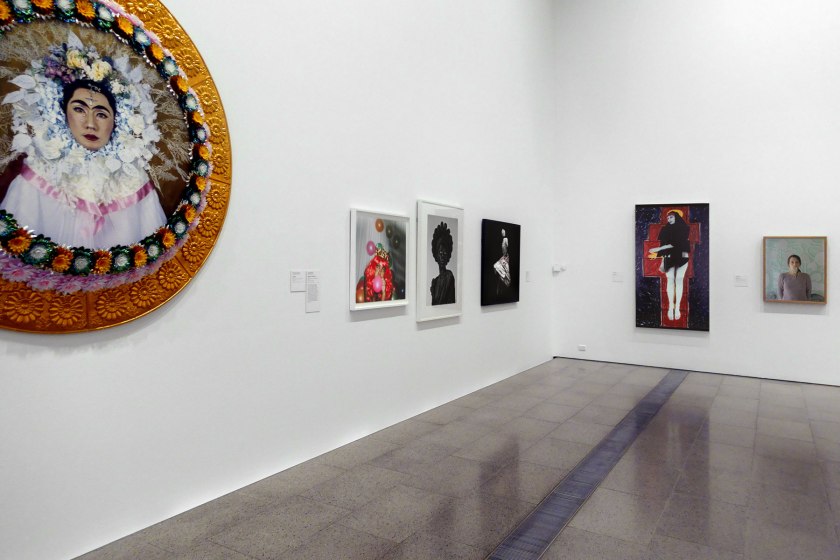
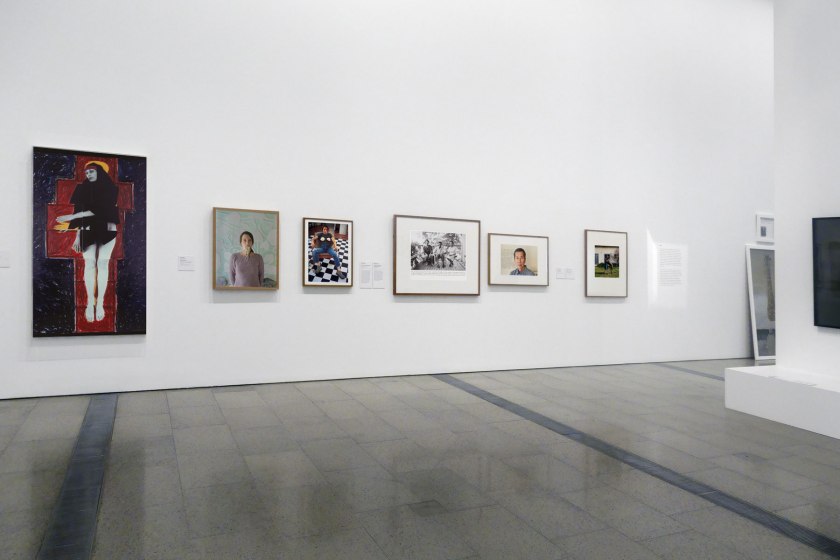
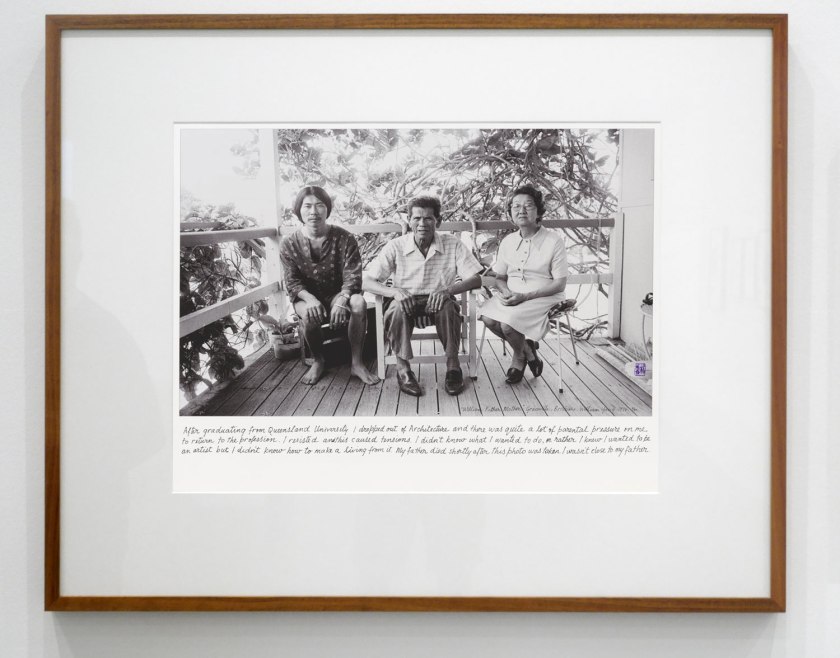
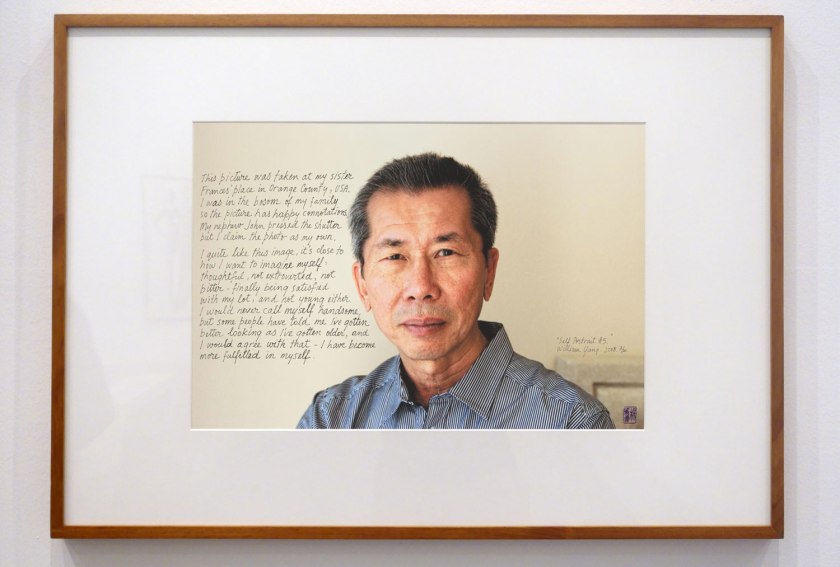
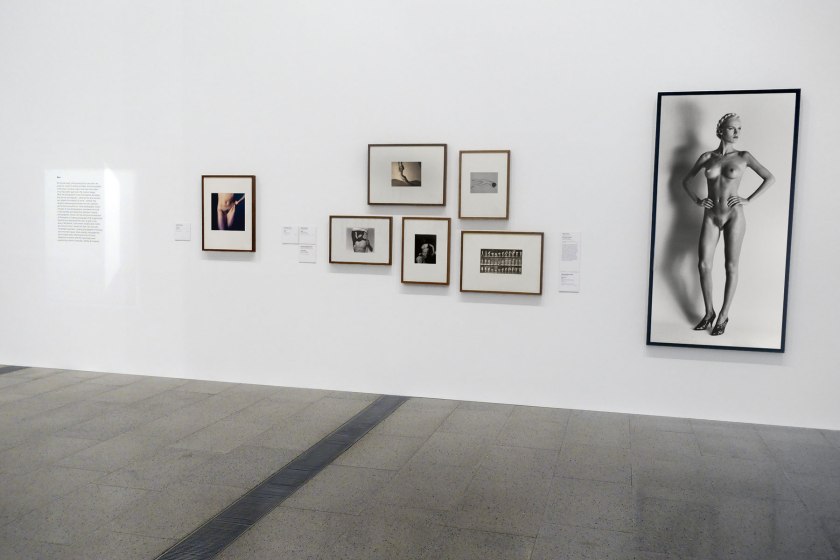
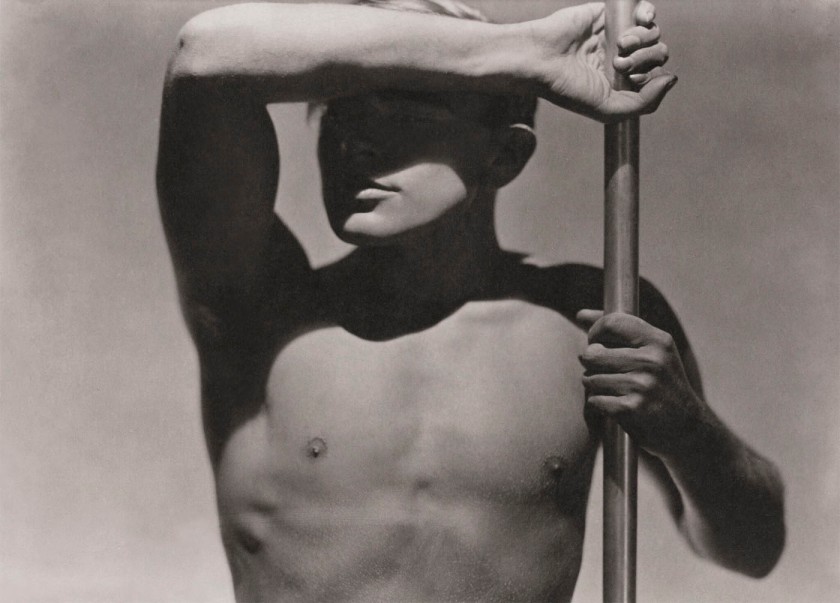
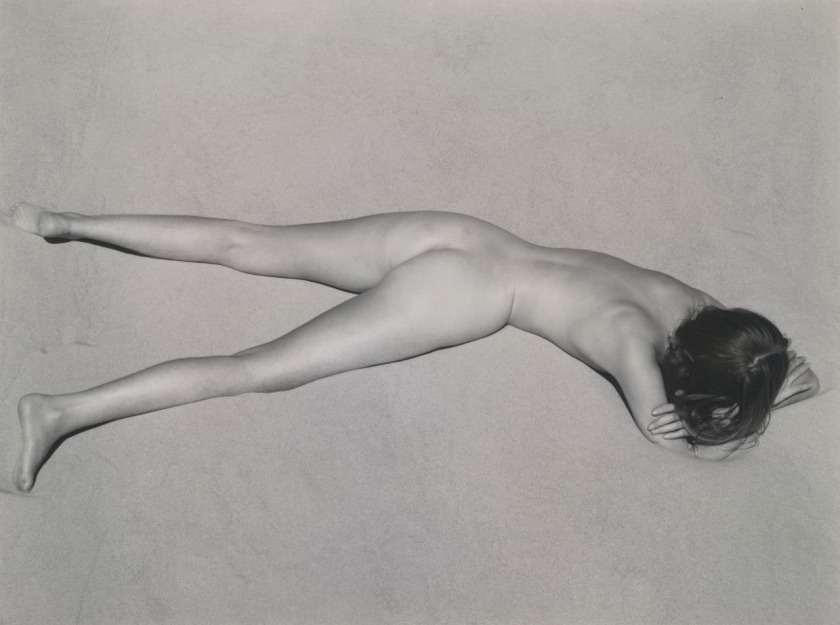
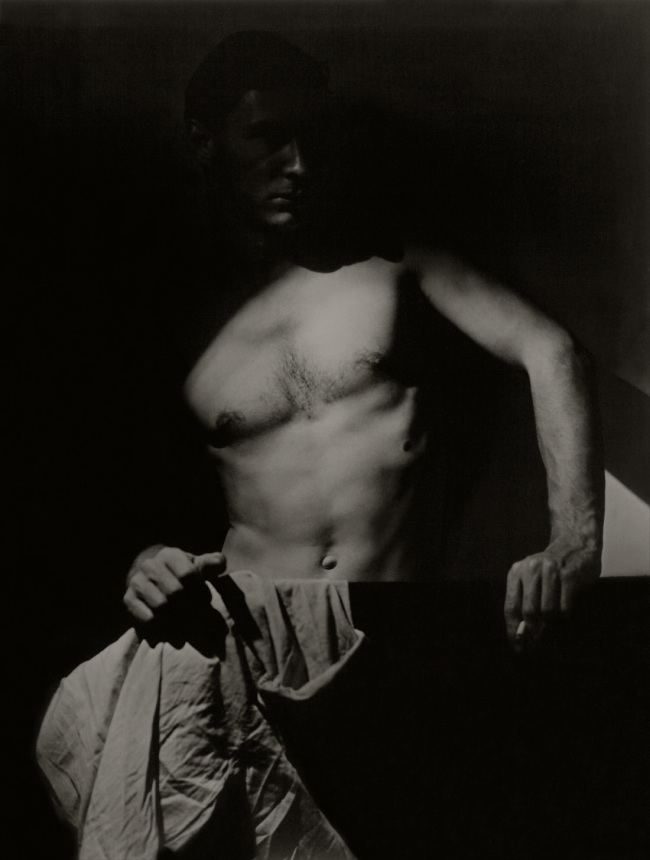
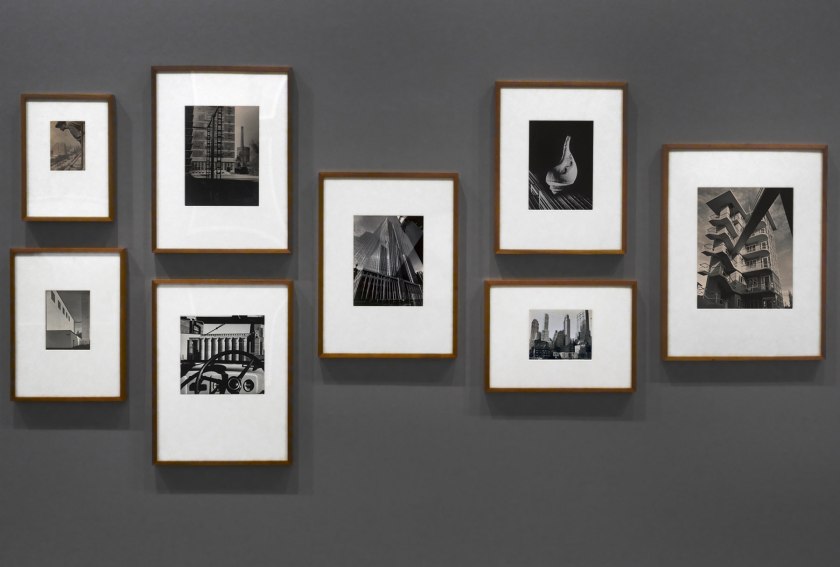
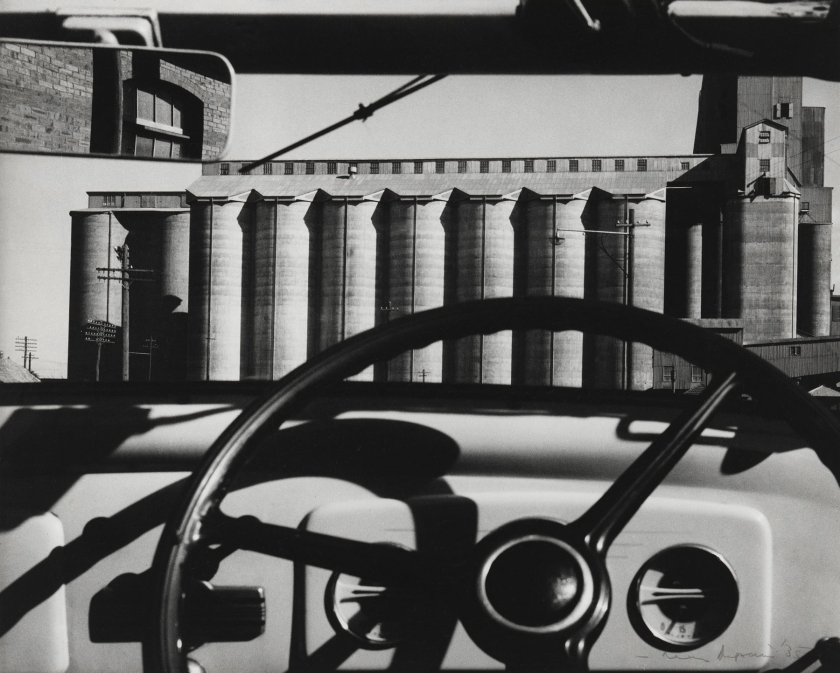
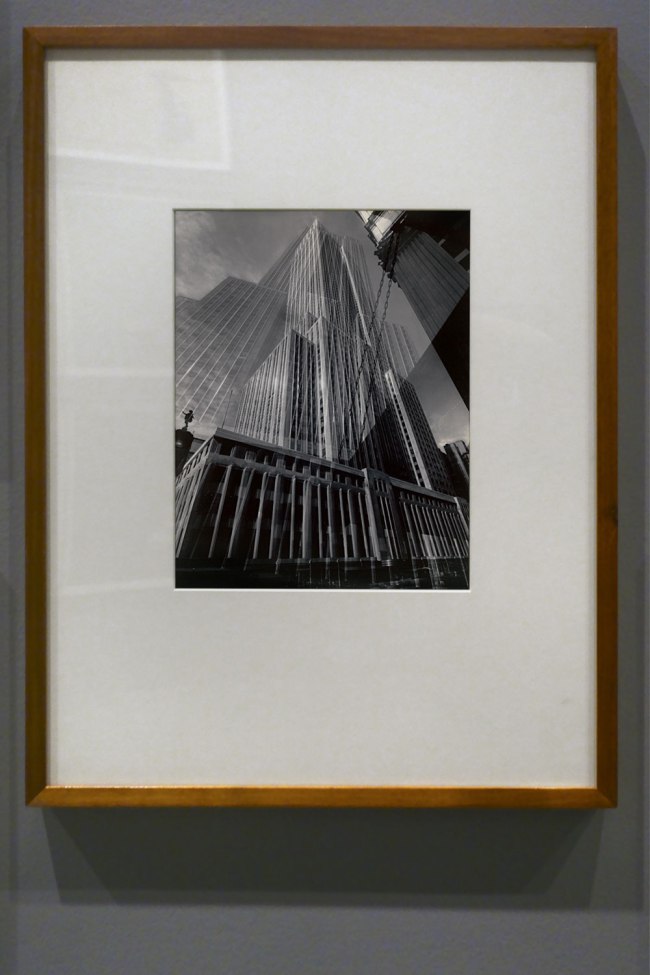
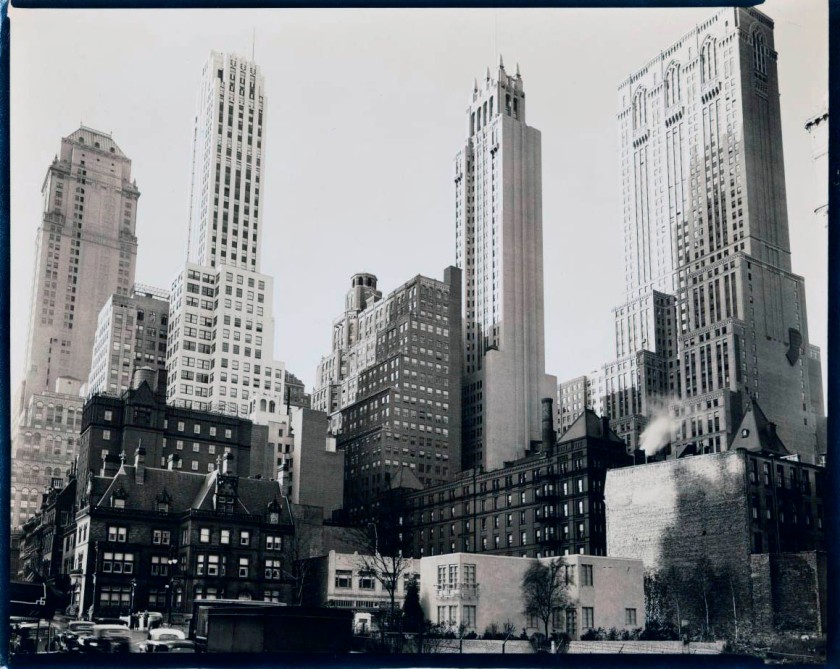
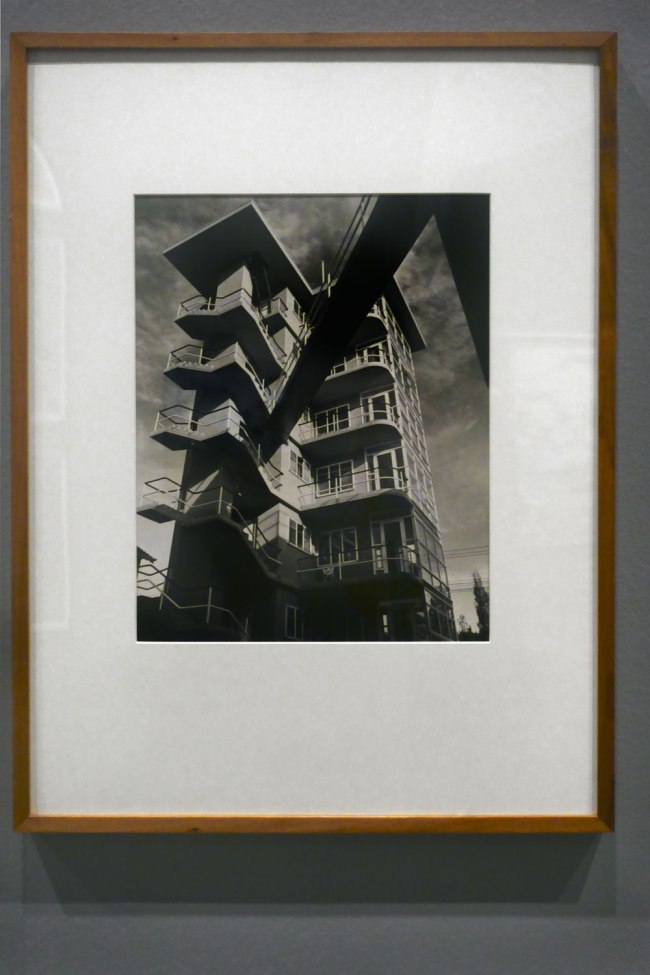
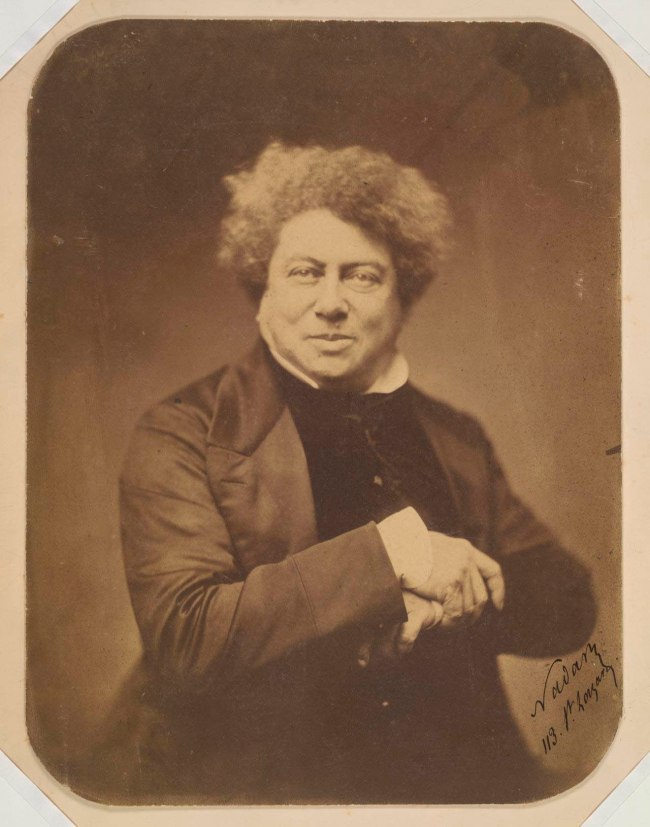
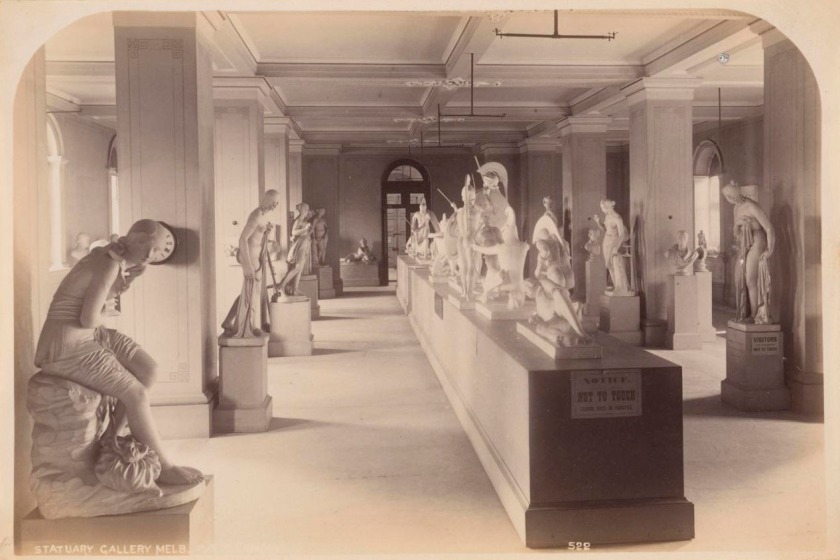
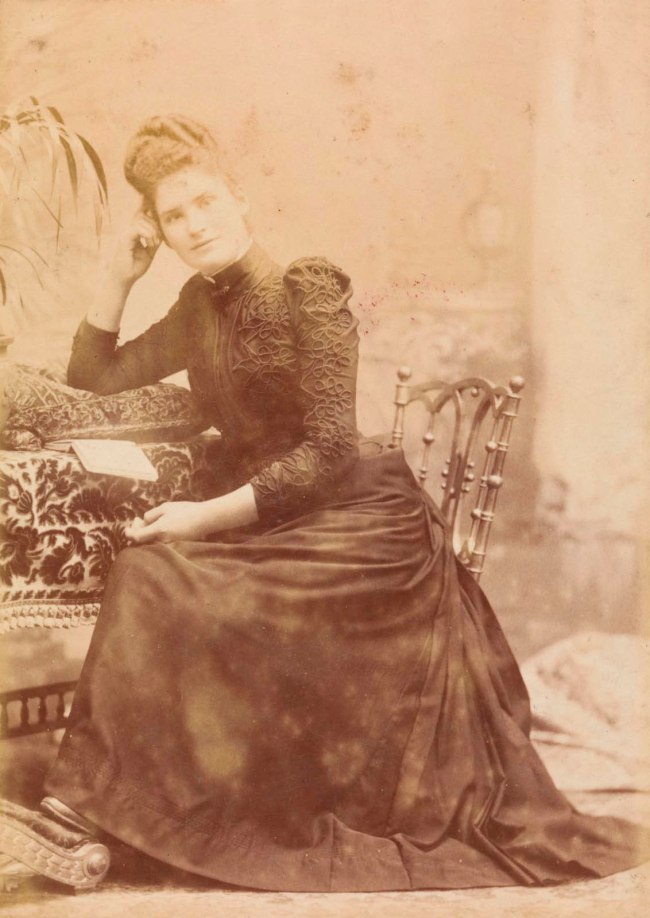
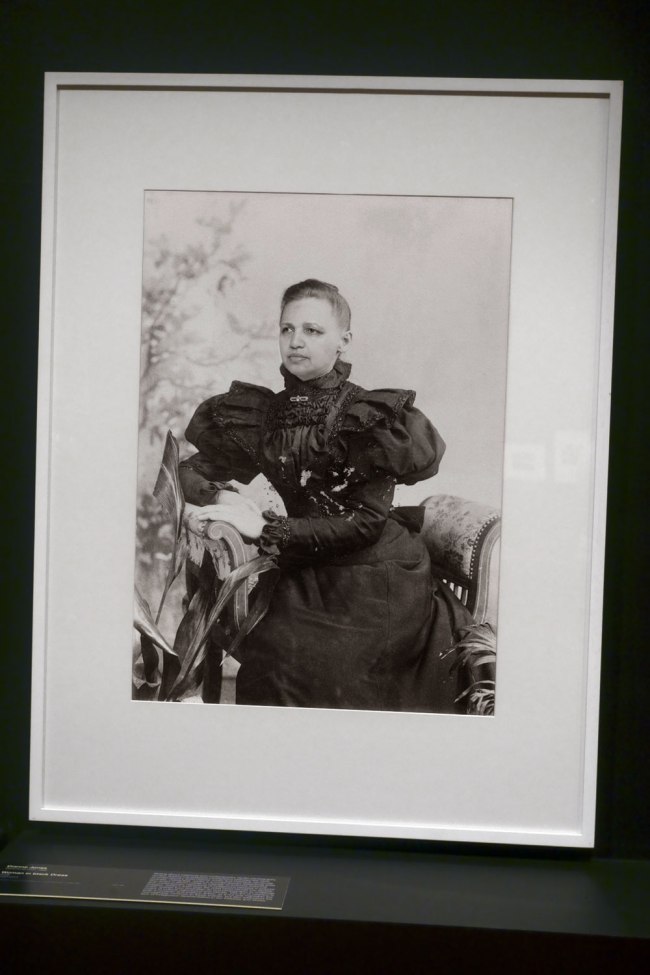
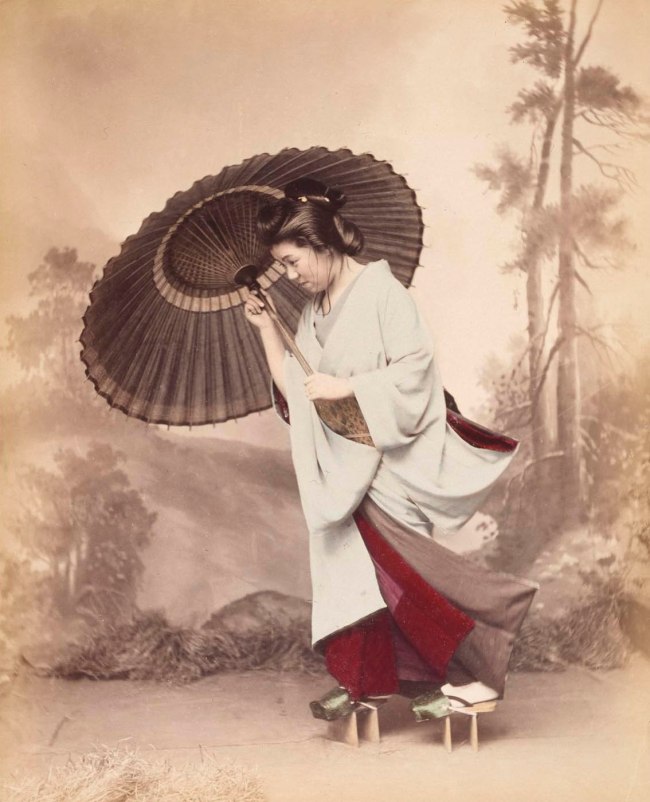


























































































































![Garry Winogrand (American, 1928-1984) 'Untitled [Liberace with his mother]' New York, 1954 Garry Winogrand (American, 1928-1984) 'Untitled [Liberace with his mother]' New York, 1954](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2023/09/83204a.jpg?w=840)


![Max Yavno (American, 1911-1985) 'Untitled [Opening Night at the San Francisco Opera]' 1947 Max Yavno (American, 1911-1985) 'Untitled [Opening Night at the San Francisco Opera]' 1947](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2023/09/92143117.jpg?w=650&h=547)
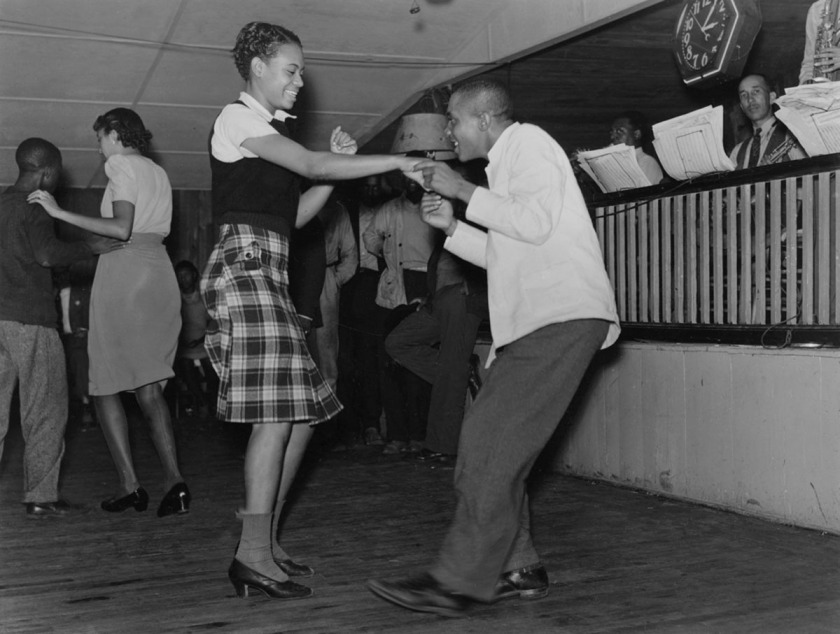
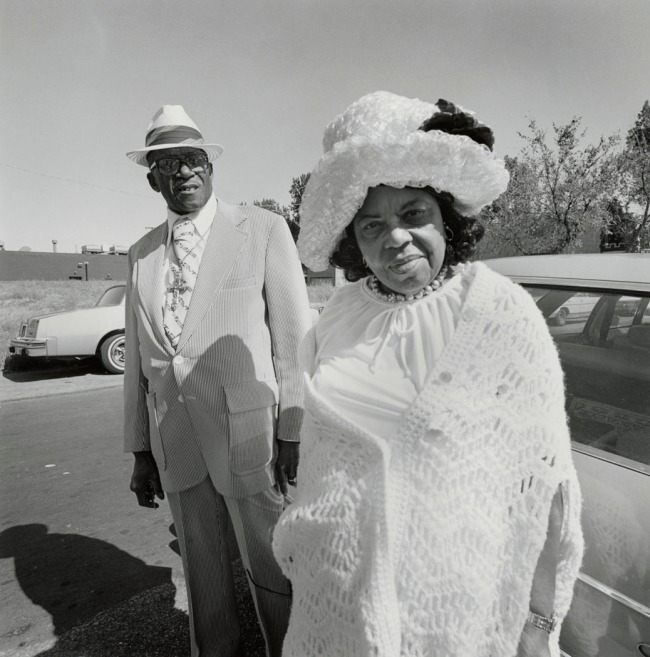
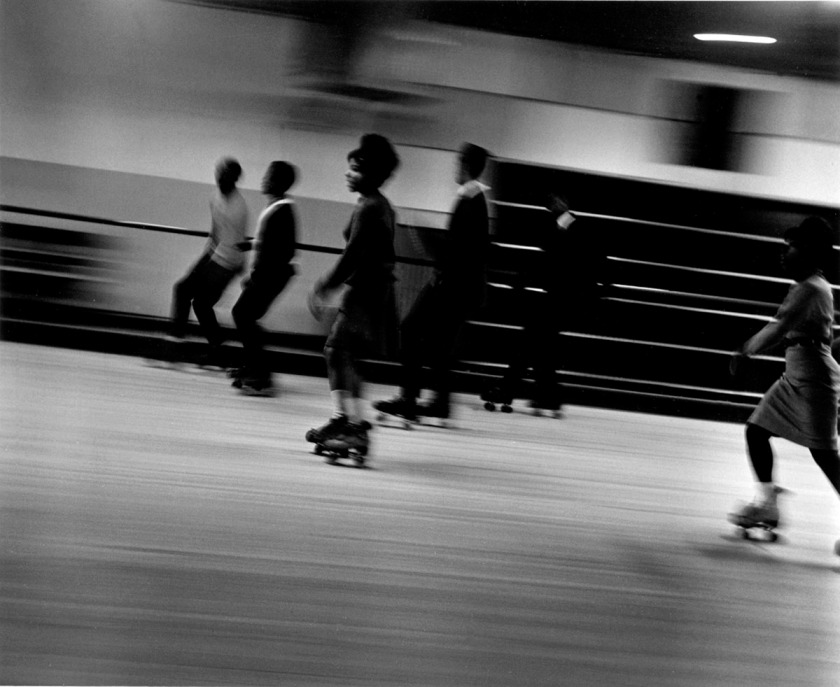
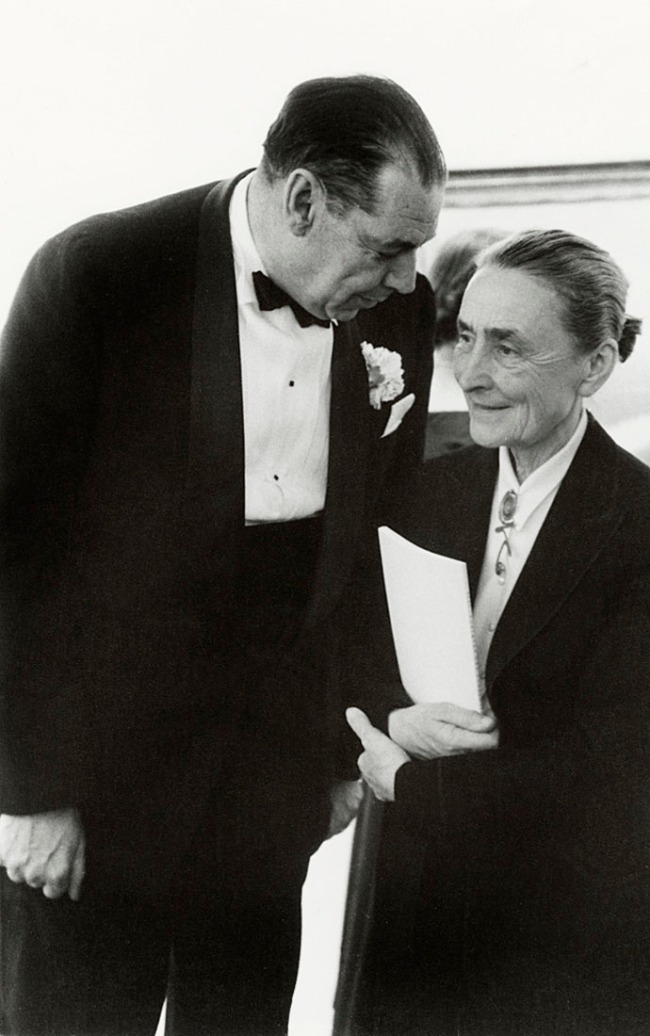
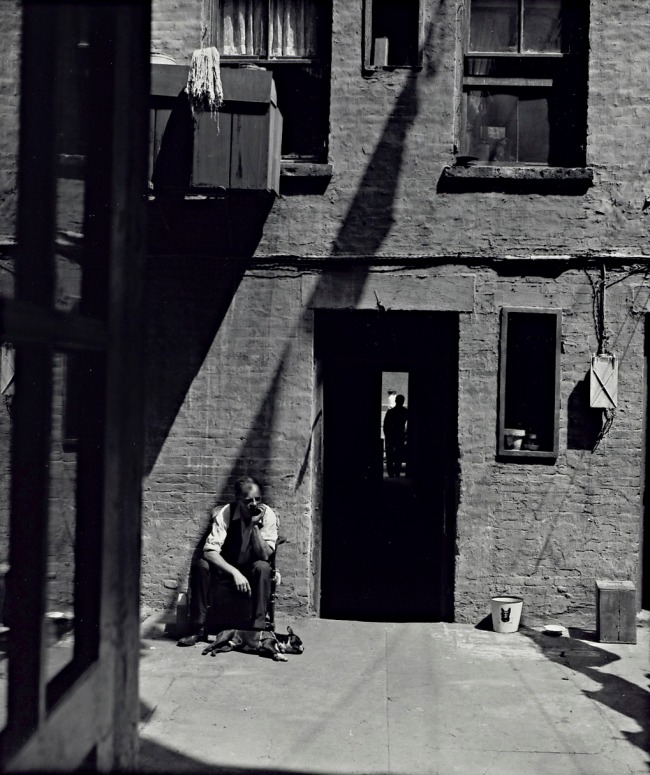
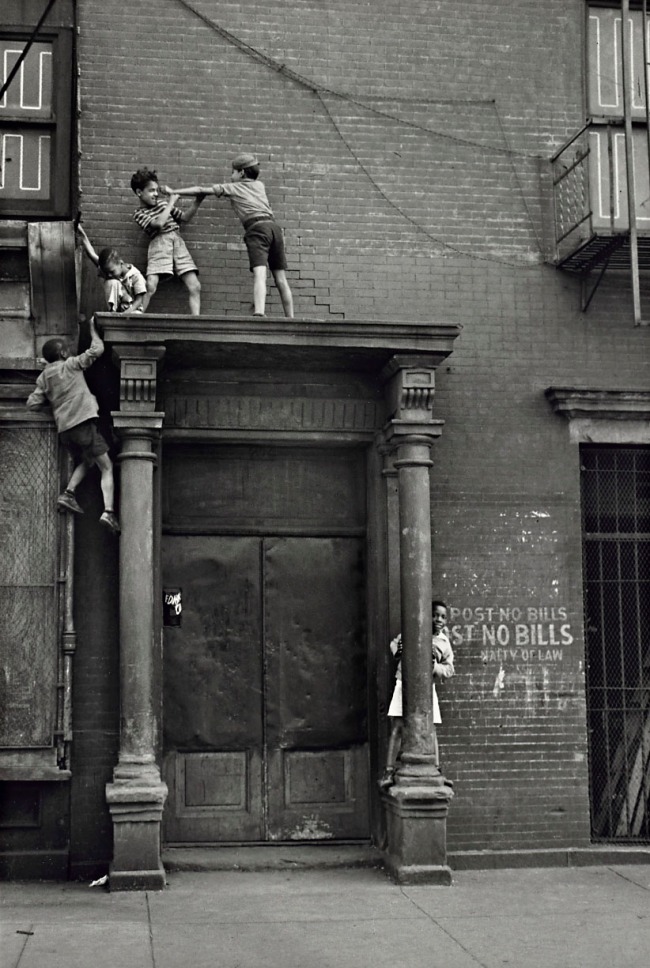
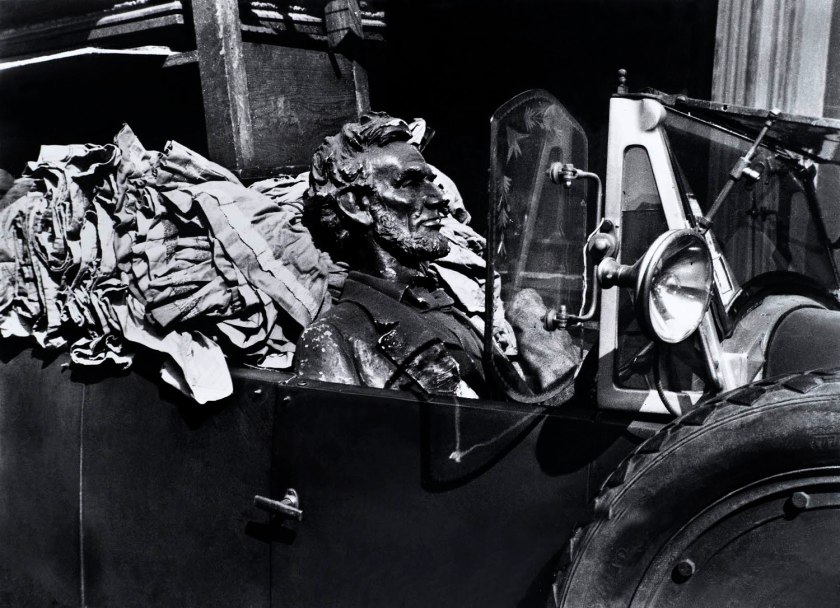
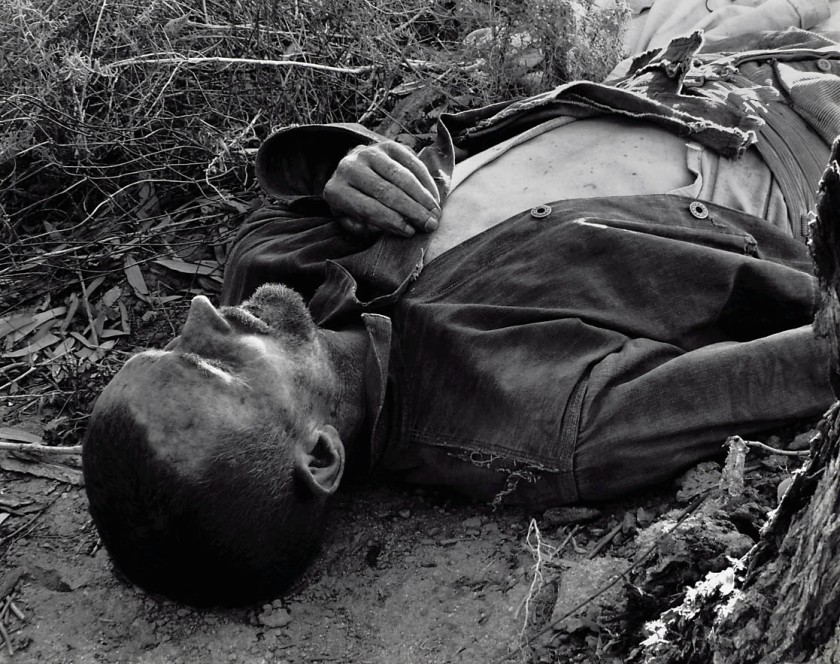























































































![Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) 'George Sand (Amandine-Aurore-Lucile Dupin), Writer' c. 1865 Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) 'George Sand (Amandine-Aurore-Lucile Dupin), Writer' c. 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/10/realideal5-web.jpg?w=650&h=854)
















































![Marion Post Wolcott (American, 1910-1990) '[Haircutting in Front of General Store and Post Office on Marcella Plantation, Mileston, Mississippi]' 1939 Marion Post Wolcott (American, 1910-1990) '[Haircutting in Front of General Store and Post Office on Marcella Plantation, Mileston, Mississippi]' 1939](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/07/wolcott-haircutting.jpg?w=840)
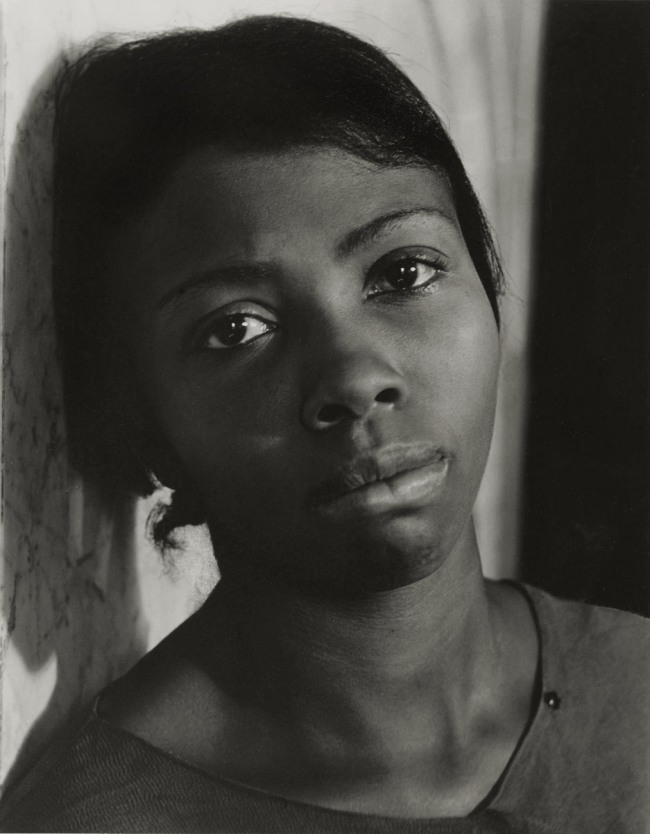
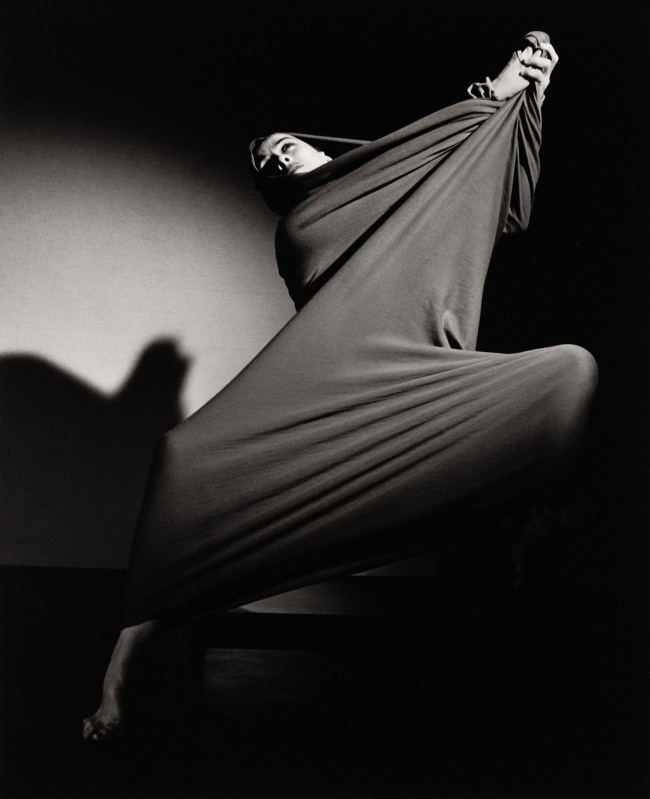
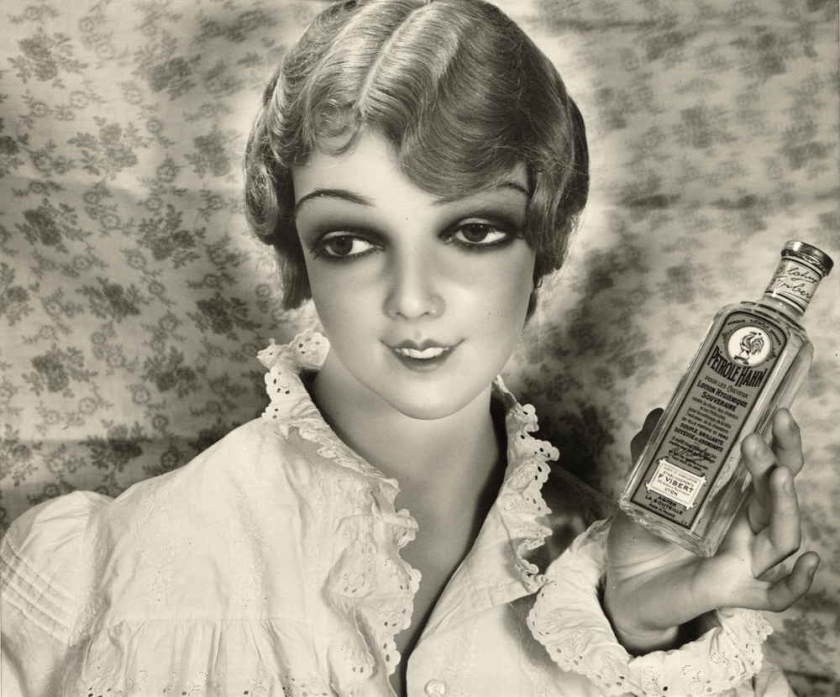





![Lucy Ashjian (American, 1907-1993) '[Savoy Dancers]' 1935-1943 Lucy Ashjian (American, 1907-1993) '[Savoy Dancers]' 1935-1943](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/07/lucy-ashjian-savoy-dancers.jpg?w=650&h=788)
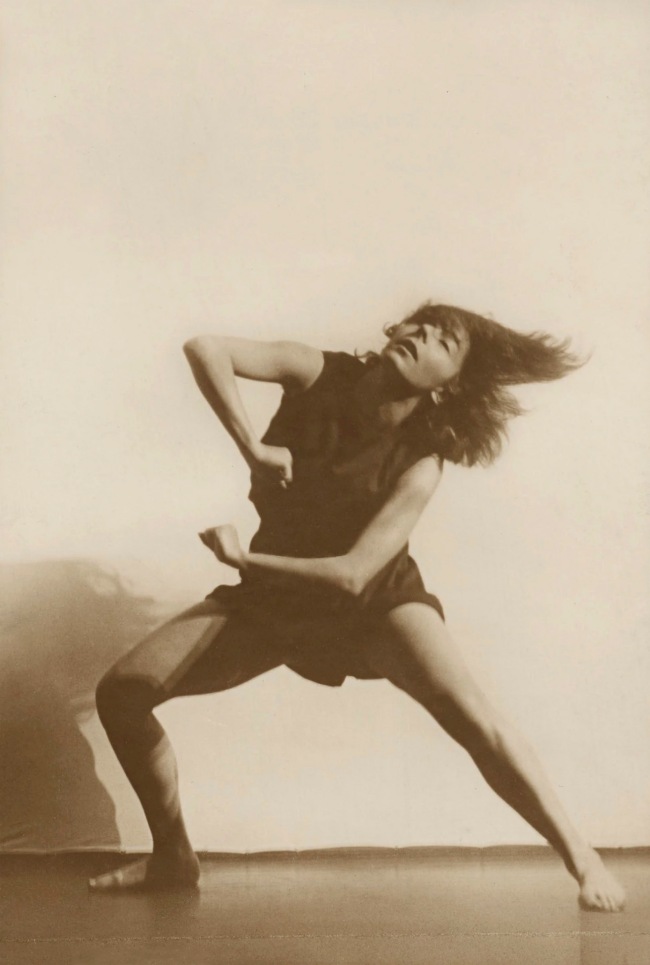
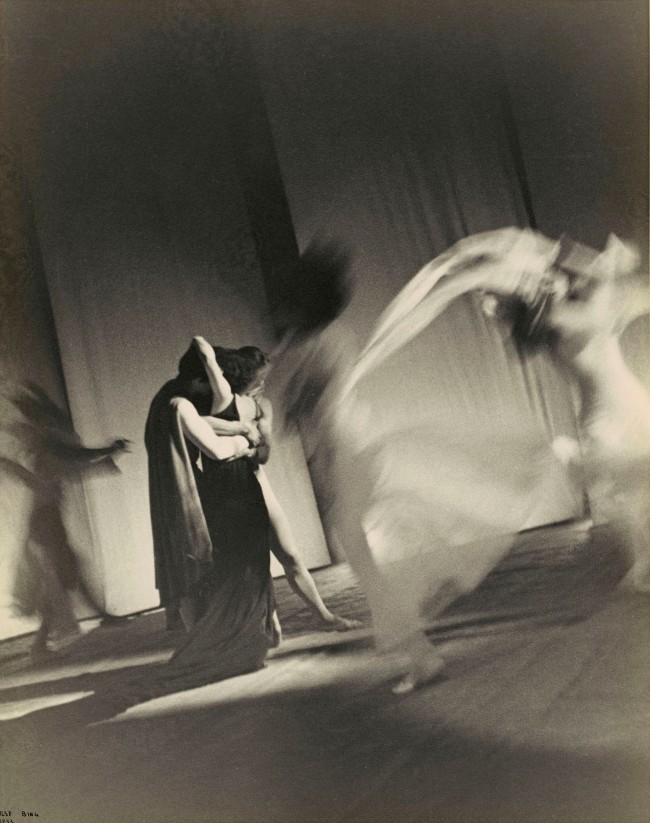
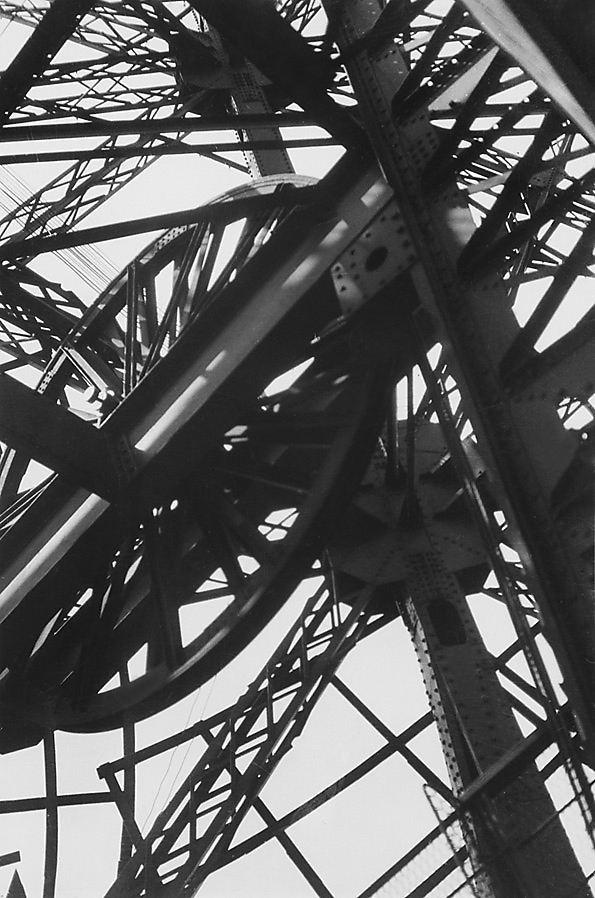









![Dora Maar (French, 1907-1997) '[Boy with a Cat]' 1934 Dora Maar (French, 1907-1997) '[Boy with a Cat]' 1934](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/07/dora-maar-boy-with-a-cat.jpg?w=650&h=864)
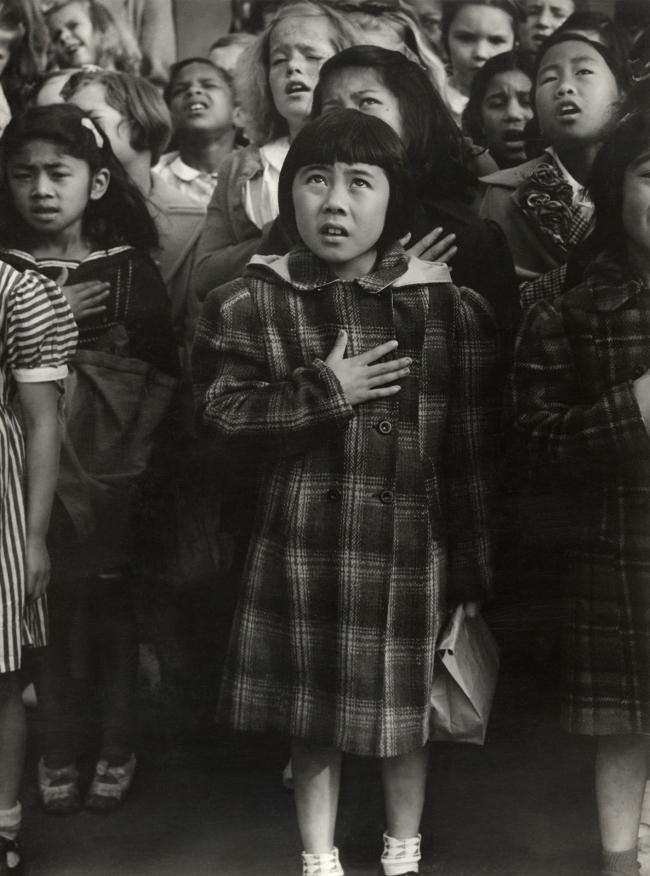
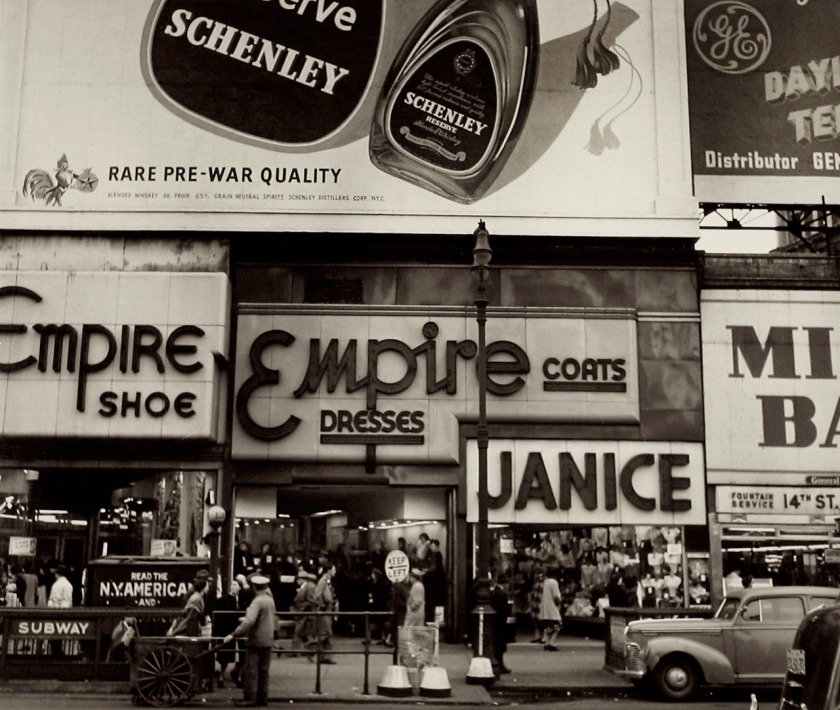
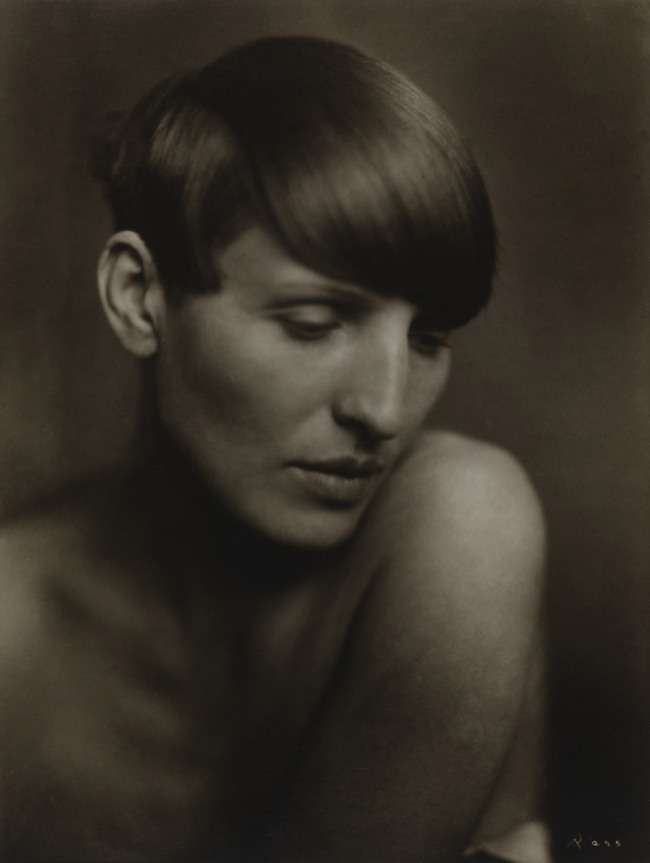



















![Tina Modotti (Italian, 1896-1942) 'La técnica [or, Mella's Typewriter]' 1928 Tina Modotti (Italian, 1896-1942) 'La técnica [or, Mella's Typewriter]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/07/tina-modotti-la-technica.jpg?w=650&h=811)
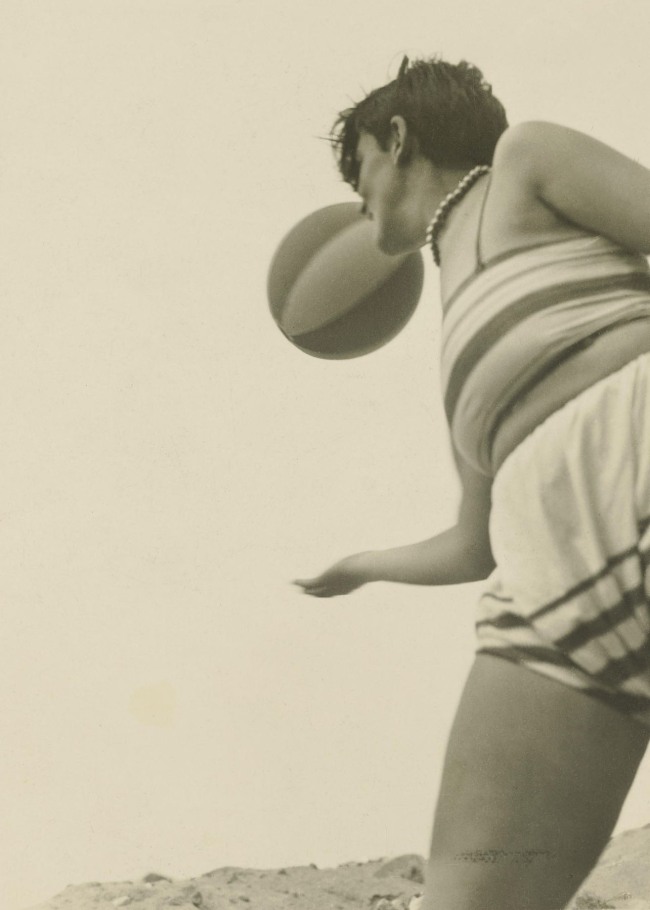
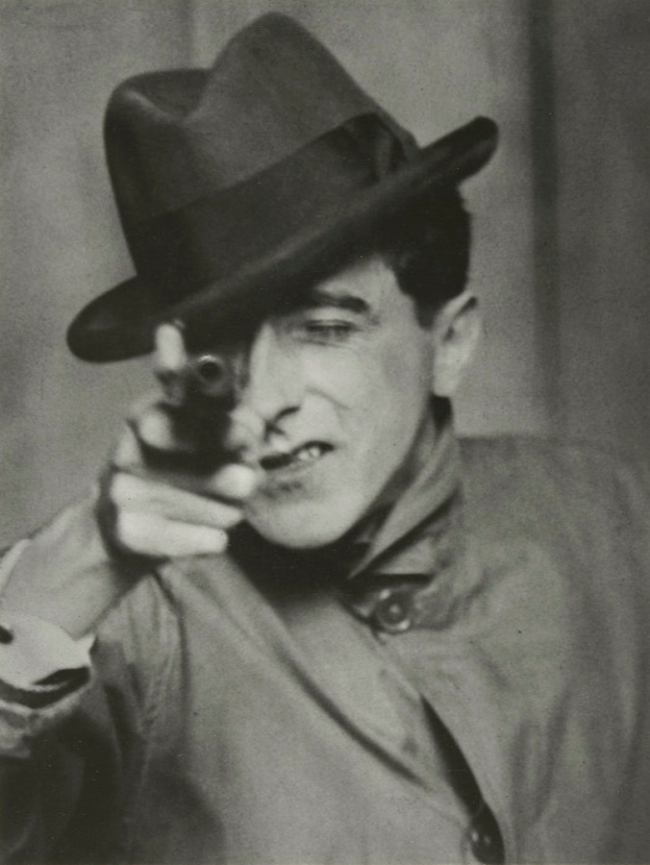
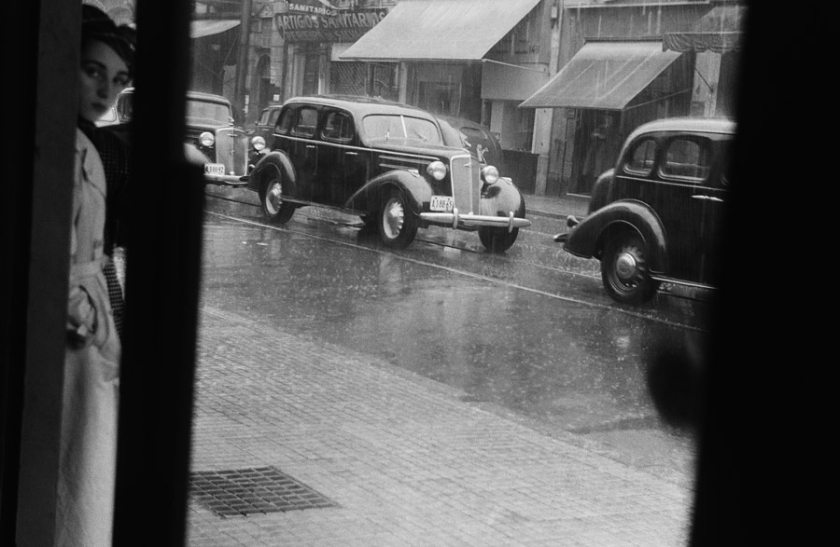
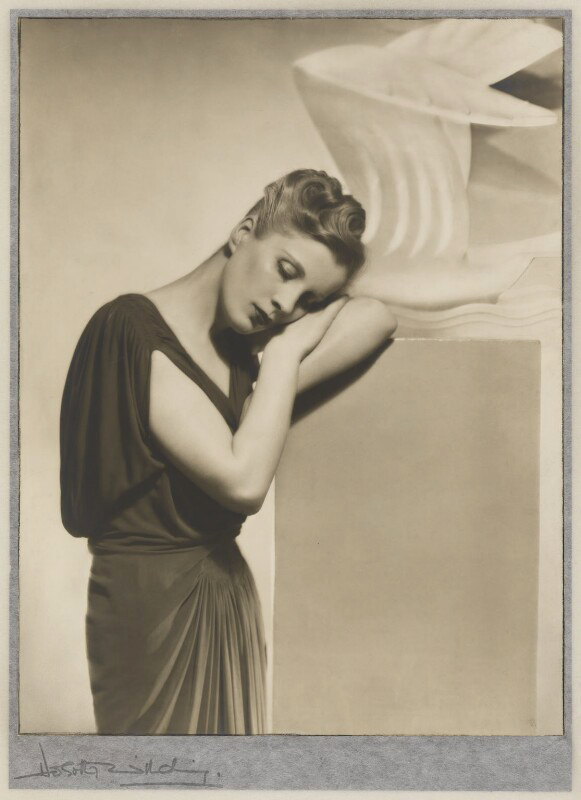




























You must be logged in to post a comment.