Exhibition dates: 14th September 2021 – 13th February 2022
Curated by Sarah Meister, former Curator, Department of Photography, The Museum of Modern Art, New York and Quentin Bajac, Director, Jeu de Paume, with Jane Pierce, Carl Jacobs Foundation Research Assistant, The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Organised by the Museum of Modern Art, New York
Max Burchartz (German, 1887-1961)
Lotte (Eye)
1928
Gelatin silver print
30.2 × 40cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Acquired through the generosity of Peter Norton © 2021 Max Burchartz/Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York/VG Bild-Kunst, Germany
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
A huge posting today that took hours to compile and all I can think of to say is – wow, I want them all in my collection!
If I had to specify one era of photography that is my favourite it would be the experimental, avant-garde photographs from the interwar period. There was such freedom, revolution and danger in the air which encouraged artists to produce radical art that defined a generation (and which ideological others found offensive and degenerate).
The tremendous diversity of “modern” photography is on show in the different sections of the exhibition – from portraiture to perspective, from science to magic realism, from interiority and surrealist dreams to new objective visions of self and the landscape – the works investigating how photographs transcend their conventional function of documentation through their social, psychological, and metaphysical implications.
I have added relevant biographical details and salient book covers and pages from the exhibition catalogue to enhance the viewing experience. My particular favourites in the posting are Willi Ruge’s vertiginous Seconds before Landing (1931, below); Stanisław Ignacy Witkiewicz’s unforgettable portrait of Anna Oderfeld, Zakopane (1911-1912, below); Lyonel Feininger’s almost-there, atmos/sphere Bauhaus (February 26, 1929 below); and Gertrud Arndt’s masterpiece, At the Masters’ Houses (1929-1930, below).
I hope you enjoy your Sunday looking at these stunning images.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Jeu de Paume for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Kate Steinitz (American born Poland, 1889-1975)
Backstroke
1930
Gelatin silver print
26.6 × 34.1cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
Reprinted with permission of the Steinitz Family Art Collection
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Runner in the City (Experiment for a Fresco for a Sports-Club)
1926
Gelatin silver print
26.7 × 22.4cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Lotte (Charlotte) Beese (German-Dutch, 1903-1988)
Untitled (Bauhaus Weavers)
1928
Gelatin silver print
8.4cm (diam.)
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Maurice Tabard (French, 1897-1984)
Test for the Film “Culte Vaudou,” Exposition 1937
1936
Gelatin silver print with cellophane sheet
29.3 × 23cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Maurice Tabard (French, 1897–1984)
Untitled (Self-Portrait with Roger Parry)
c. 1936
Gelatin silver print
9 1/4 × 6 5/8″ (23.5 × 16.8cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
Roger M. Parry (French, 1905-1977)
Born and educated in Paris, Roger Parry was originally interested in painting and worked as a draftsman after graduation. In 1928 he met Maurice Tabard, who taught him photography and for whom Parry worked as a darkroom assistant. Parry published his photographs in Art et Métiers Graphiques, a photographic annual, and Banalités, a book of poems. These publications gained the attention of André Malraux, with whom Parry became associated around 1930.
Parry worked for Malraux and the Gallimard publishers for more than forty years. In 1934 Gallimard published Parry’s photographs of Tahiti. During World War II Parry was a photography war correspondent for the news agency L’Express. He eventually became head of photography and art director for the Gallimard publication Nouvelle Revue Française.
Text from the J. Paul Getty website [Online] Cited 25/01/2022
Lotte Jacobi (American, 1896-1990)
Franz Lederer
c. 1929
Gelatin silver print
21.3 × 15.5cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Grace M. Mayer Fund
© Lotte Jacobi Collection, University of New Hampshire
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Francis Lederer (November 6, 1899 Prague – May 25, 2000) was a Czech-born American film and stage actor with a successful career, first in Europe, then in the United States. His original name was Franz (Czech František) Lederer.
Unknown photographer / Press-Photo G.M.B.H.
Untitled (Cover illustration from Here Comes the New Photographer)
c. 1928-1929
Gelatin silver print
21.9 × 16.2cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Edward Steichen, by exchange
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Masterworks of MoMA
Introduction
In 2001 and 2017, The Museum of Modern Art in New York acquired more than 350 photographs from the collector Thomas Walther. This collection, which is now one of the pillars of MoMA’s modern collection, is presented for the first time in France in an exhibition of some 230 images.
Comprising iconic works from the first half of the twentieth century, the exhibition provides a history of the European and American photographic avant-gardes. Through the works of a hundred or so photographers, from Berenice Abbott to Karl Blossfeldt, from Claude Cahun to El Lissitzky, from Edward Weston to André Kertész, this fusion of masterpieces and lesser-known images traces the history of modernity in photography. Mixing genres and approaches – architecture and urban landscapes, portraits and nudes, reportage, photomontage, experimentation, etc. – the exhibition delves deep into the artistic networks of the inter-war period, from the Bauhaus to Surrealist Paris, via Moscow and New York.
In their visually radical inventiveness, these images capture perfectly the utopian spirit of those who wanted to change images in order to change the world; now we fully understand the words of the photographer and theoretician Lázló Moholy-Nagy who, a century ago, stated that “the illiterate of the future will be ignorant of the camera and the pen alike.”
The Exhibition
Life as an artist
While it is true that throughout the 20th century photographers took great pleasure in portraiture, the Thomas Walther Collection also illustrates the spirit of freedom that characterised the lives of these artists and the circles they moved in.
Marcel Duchamp once described the Paris of the 1920s as home to the first truly international community of artists. The body of photographs by André Kertész assembled by Thomas Walther offers a fine summary of the photographer’s affinities, empathies and networking during his Parisian years, while also reflecting his interest in abstract and post-Cubist art and the play of light on highly geometric volumes.
The period between the two World Wars saw the affirmation of a collective artistic adventure most strikingly evidenced by the Bauhaus – one of the main axes of the Thomas Walther collection. From Florence Henri to Lotte Beese and Umbo, many of the artists represented in the collection spent time there; and all of them practiced photography without necessarily being photographers. Thus the works relating to the Bauhaus here are essentially snapshots of documentary interest. Lázsló Moholy-Nagy and Lucia Moholy were both very active photographers, but while Lázsló’s work attracted considerable critical attention, this is less true of his wife, who, although not an official member of the school, took numerous photographs of architecture and portraits.
Similarly, Lyonel Feininger, a trained painter and head of the engraving workshop, and Gertrud Arndt and Lotte Beese, students in the weaving workshop, acquired skills through an intense photographic activity that went far beyond the official teaching.
Experiments with night photography, high- and low-angle shots, multiple exposures, distorting reflections: a large part of the vocabulary of the avant-gardes can be found at the Bauhaus.
The third body of work in this section documents these artistic networks and communities in a different way. The self-portrait plays a predominant role here, revealing the shaping of a new identity for the photographer via an emphasis on the camera that underscored photography’s mechanical character – an aspect often skirted by the art photographers of the previous generation.
Now, whether on a tripod or in the hand, the camera was omnipresent, to the point where it merged completely with the user as an artificial extension of the eye.
El Lissitzky redefined photography as a mental activity and the photographer as a “constructor”, a producer of images who must unify the work of eye and hand, in a context of photography become inseparable from graphics.
Here comes the new photographer!
Photography was the ideal medium for catching the feel of modern life in the aftermath of the First World War: looking both up and down – from planes, bridges and skyscrapers – photographers discovered unparalleled views and a new, dynamic visual language, free of convention.
A new thirst for photographic images took hold of the illustrated press between the wars, a period that saw the advent of reports and magazines built entirely around the photographic image. Another feature of this period was its passion for sport and speed. Advances in the sensitivity of photographic film and paper and the development of more manageable cameras allowed artists to capture movement as never before.
Totally unexpected points of view were thus created. One of the most famous is doubtless the aerial view, where the aviator embodies this new sporting modernity, as does the racing driver.
A sense of weightlessness and lightness is found in the images of Kate Steinitz and John Gutmann, both influenced by Dada and European Surrealism. Alexander Rodchenko’s images of divers emphasise the space that the body travels through as well as the athlete himself.
Their out-of-kilter framing, pushing the bodies into the corners of the image, attempts to summarise a rapid, complex movement in a single still image. While using an overtly avant-garde photographic grammar – high-angle, low angle – the themes of these photographs seem to be fully in line with the political context of the Soviet Union in the 1930s. Lissitzky too was fascinated by the figure of the athlete: his photomontage Rekord (Record), a model of a project for the photographic decoration of a sports club in Moscow, offers a modernist yet dreamlike vision in which the entire illuminated metropolis mutates into a sports arena.
Finally, this exaltation of a new humanity underlies in a much more literal way Leni Riefenstahl’s images of the 1936 Berlin Olympic Games. Armed with impressive technical and financial resources, photographer / filmmaker Riefenstahl directed Olympia, commissioned by the Hitler regime to hymn the new Aryan type. In images markedly avant-garde in style, one finds many features of the aesthetics of the Third Reich, from the references to antiquity to the celebration of the athlete-hero and the geometrisation and perfect synchronisation of figures in movement.
Discovering photography
In 1925, László Moholy-Nagy asserted that although photography had been invented a hundred years earlier, its true aesthetic potential had only just been discovered when he and other members of avant-garde circles adopted the medium. With their brief history and no connection to traditional fine arts disciplines, photography and film became true modernist instruments.
Moving away from the efforts of the art photographers of the previous generation, out to obscure the mechanical nature of the photographic print through various subterfuges – timeless subjects, use of blur, etc. – the photographic avant-gardes of the early 20th century drew on images from non-art spheres: X-rays, astronomy, medicine and science provided them with representations of the invisible; photojournalism revealed forms in motion, improbably frozen by the snapshot; amateur photography offered a repertoire of strange viewpoints and aberrations of perspective. See differently, that was the maxim.
They experimented every which way, playfully and undeterred by reversion to archaic forms and processes. The photogram is probably the best illustration of this new language. This camera-less technique, which simply prints images of objects directly onto sensitised paper that has been exposed to light, is the origin of photography. It was practiced by all of photography’s pioneers before falling into disuse except as a mere laboratory exercise. It was only after the First World War that it was rediscovered by a few enthusiasts and became a major avant-garde gambit.
Appreciated for its simplicity, playfulness, and undeniable visual impact, it also became a much appreciated tool in the field of applied photography. Moreover, in addition to the photogram as such, advertising, Industry, and publishing were becoming broadly receptive to the new avant-garde photographic language, just as photography was gradually beginning to oust graphic techniques in their respective fields.
At the same time the laboratory began to function as a venue for exploration of both the negative and the print. The stretching of exposure times, with the resultant blurring of movement, allows the representation of time to be modified by embedding duration and movement in the still image. In some cases – think Albert Renger-Patzsch and Jean Painlevé – the precision of a simple close-up framing a particular being or thing as closely as possible, sufficed to imbue the subject with fresh presence and reality.
Last but not least, the avant-gardes revelled in the construction of composite images, notably through collage and photomontage, using all the resources made available to them by the illustrated press and publishing of the time. To these image games we should add the multiple exposure, long considered as no more than a photographer’s failure. In this sense, this generation was the first to practice borrowing and reusing images and forms on such a scale, attesting to the – already – rapid circulation of images within the European avant-garde.
Magic Realisms
In the mid-1920s, members of European art movements ranging from Surrealism to New Objectivity moved away from a realist approach, seeking instead to highlight the strangeness of everyday life or to bring together dreams and unusual states of consciousness. Echoes of these preoccupations, centred on the human figure, can be found throughout the Thomas Walther collection.
The images in this section hijack two traditional photographic genres, the portrait and the nude, with the aid of various processes: close-ups, inversion of negative-positive values through solarisation, photograms, overprints. Many of the techniques employed by photographers close to Surrealism aimed to transform reality by pushing technique to the point of destroying the human form. The diffuse influence of Surrealism is of course particularly evident among Parisian photographers, as can be seen in the numerous, often virtuoso laboratory games of commercial, advertising or fashion photographers like Maurice Tabard or Aurel Bauh, and even André Kertész in the early 1930s. The “distortions” Kertész produced, using the countless optical possibilities offered by deforming mirrors, are part of a photographic tradition that goes back to the 19th century, but also remind us of the representation and deformation of the human body undertaken by Picasso and Dalí in the same years.
The press of the 1920s was fond of optical visual games, transforming the human body in line with a certain objectification: loss of scale and reference points, oddness induced by a detail or the texture of skin. Of all the parts of the body, it was undoubtedly the eye, the organ of sight, that attracted the attention of distinction between the real and the fantastic – and created interplay between the animate and the inanimate by approaching the human body through substitutes such as dolls, mannequins, or masks.
Symphony of a Great City
Like the cinema, photography in the first half of the 20th century achieved a fragmentation and recomposition of an increasingly insistent urban reality. In an era of rapidly advancing urbanisation, the big city was the stamping ground par excellence for photographers and filmmakers.
The period saw the emergence of a large number of films that treated the city as a living organism: Paul Strand’s Manhattan, Charles Sheeler on New York and Berlin, Walther Ruttmann’s Symphony of a Great City. Often consisting of short, rapidly edited shots, these films have obvious links with the photography of the time: the German photographer Umbo was involved in the making of Ruttmann’s film. The four images on display here play on some of the optical games dear to the avant-garde: the derealisation effected by the bird’s-eye view and cast shadows, the simultaneous transparency and reflection of store windows, and the repetitive geometry of certain urban spaces.
The advent of an architecture of mobility was exactly contemporary with that of the first Kodak-type cameras, which allowed the operator a hitherto unknown freedom and mobility. Photographers would take full advantage of all the new possibilities open to them by favouring symbols and places emblematic of the contemporary: factory chimneys and industry at work; the iron architecture of buildings like the Eiffel Tower in Paris or the Brooklyn Bridge in New York; subjects and objects in movement, such as cyclists caught in urban traffic; newly pullulating public spaces; and, of course, the omnipresent street. The city was indeed this dynamic organism, the locus of human encounters, of incongruous objects and visual signs, captured at random in its streets. Constantly on the lookout, the pedestrian-photographer of the inter-war period appears as a modern version of the Baudelairean flâneur of the preceding century. With its unprecedented vertical extension, the modern city offers a multitude of new points of view, high-angle or low-angle, magnifying the impression of vertigo or crushing weight.
The city allowed for all kinds of new visual and optical experiments. Iron architecture, by erasing the boundaries between interior and exterior, offered countless possibilities for framing, as in the work of Germaine Krull, a photographer particularly attentive to these exercises in “framing within the frame”. Night shots, which gave pride of place to lighting effects, renewed the experience of nocturnal vision to a point of near-abstraction, simple luminous inscriptions of objects in movement.
But the fragmenting dear to Walter Benjamin is probably nowhere more perceptible than in photomontage, with its fantasised, idealised or monstrous version of the urban and industrial universe. The visual chaos of Paul Citroën’s Metropolis, composed of some two hundred images pasted together, is a perfect example. Citroën evokes a city not in ruins but in pieces, a cacophonous space, all the elements piled up in an incoherent spirit close to Dada.
High fidelity
At a time when, in Europe, experimentation was being put forward as a core concept by the photographic avant-gardes, the Americans seem to have put more emphasis on a search for a truth of the world through exact representation. “High fidelity”, a term borrowed from the world of acoustics, was used to designate this approach and its taste for a clear and faithful image.
Pure photography is a discipline in search of perfection and technical mastery at all stages of the production of the image. It is in this near-contradictory tension between the “highly detailed” and the “abstract”, between the use of a large format camera combining an almost hyper-realistic rendering with simplified shooting strategies, that lies one of the main characteristics of a certain American modernist approach. It seems logical, then, that this aesthetic of attention to object, texture and form, quickly pervaded various spheres of American commercial photography of the time.
At Film und Foto, the flagship exhibition of the international photographic avant-garde, some people remarked on the extent to which the American section, with its “refined technique that can rightly be described as cultivated”, contrasted with the more raw work of the Europeans.
However, while straight photography remained a very American movement, it also had ramifications in Europe. In Germany, in the late 1920s and early 1930s, voices began to be raised in photographic circles against the expressive experiments of the previous decade, urging respect for reality and greater objectivity. Karl Blossfeldt’s direct and unmanipulated approach to plants, produced for documentary purposes as part of his teaching at the Berlin School of Applied Arts, was praised. At the same time, it was the sweeping aerial views of Germany taken by balloonist Robert Petschow that aroused the enthusiasm of avant-garde circles, which exhibited them and celebrated both their quasi-abstract singularity and their informative content, blended in the manner of a topographical survey.
Umbo (Otto Umbehr) (German, 1902-1980)
View of Berlin’s Department Store Karstadt
1929
Gelatin silver print
23.7 × 15.5cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
© ADAGP, Paris, 2021
© 2021 Umbo/ Gallery Kicken Berlin/ Phyllis Umbehr/VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Cover study for America: The Development of Style in New Buildings in the United States (New Ways of Building in the World)
1929-1930
Gelatin silver print
10 1/4 × 7 5/8″ (26 × 19.4cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Henri Cartier-Bresson, by exchange
© 2022 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Fifth Avenue, Nos. 4, 6, 8, Manhattan
March 20, 1936
Gelatin silver print
38.6 × 49.5cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Mr. Robert C. Weinberg, by exchange
© 2021 Estate of Berenice Abbott
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Pitmen’s houses in Essen, Stoppenberg
1929
Gelatin silver print
10 3/4 × 14 13/16″ (27.3 × 37.6cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of James Thrall Soby, by exchange
© 2022 / Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Germany
Aenne Biermann (German, 1898-1933)
Summer Swimming
1925-1930
Gelatin silver print
17.8 × 20cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Bequest of Ilse Bing, by exchange
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Aurel Bauh (Romanian, 1900-1964)
Untitled
1929-1932
Gelatin silver print
29.4 × 23.3cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Karl Blossfeldt (German, 1865-1932)
Acanthus mollis (Soft Acanthus, Bear’s Breeches. Bracteoles with the Flowers Removed, Enlarged 4 Times)
1898-1928
Gelatin silver print
29.8 × 23.8cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Aenne Biermann (German, 1898-1933)
Ficus elastica
1926
Gelatin silver print
14 3/4 × 11 1/8″ (37.5 × 28.2cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
John Gutmann (American born Germany, 1905-1998)
Classe (Marjorie Gestring, championne olympique 1936 de plongeon de haut vol)
Class (Marjorie Gestring, 1936 Olympic champion in high diving)
1935
Gelatin silver print
22.3 x 19.2cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
© 2020 The Museum of Modern Art, New York/Scala, Florence
Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Girl with a Leica
1932-1933
Gelatin silver print
30 x 20.3cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Collection Thomas Walther
Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
© ADAGP, Paris 2021
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Wanda Wulz (Italian, 1903-1984)
Exercise
1932
Gelatin silver print
11 1/2 × 8 5/8″ (29.2 × 21.9cm)
Thomas Walther Collection
Abbott-Levy Collection funds, by exchange
© Fratelli Alinari Museum Collections-Studio Wulz Archive, Florence
George Hoyningen-Huene (American born Russia, 1900-1968)
Henri Cartier-Bresson
1935
Gelatin silver print
9 11/16 × 7 11/16″ (24.6 × 19.5cm)
Thomas Walther Collection
Abbott-Levy Collection funds, by exchange
© George Hoyningen-Huene Estate Archives
El Lissitzky (Russian, 1890-1941)
Self-Portrait
1924
Gelatin silver print
5 1/2 × 3 1/2″ (13.9 × 8.9cm)
Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
© 2022 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
The essence of New Vision photography is pointedly expressed in this picture, commonly known as The Constructor, which puts the act of seeing at center stage. Lissitzky’s hand, holding a compass, is superimposed on a shot of his head that explicitly highlights his eye: insight, it expresses, is passed through the eye and transmitted to the hand, and through it to the tools of production. Devised from six different exposures, the picture merges Lissitzky’s personae as photographer (eye) and constructor of images (hand) into a single likeness. Contesting the idea that straight photography provides a single, unmediated truth, Lissitzky held instead that montage, with its layering of one meaning over another, impels the viewer to reconsider the world. It thus marks a conceptual shift in the understanding of what a picture can be.
Gallery label from The Shaping of New Visions: Photography, Film, Photobook, April 16, 2012 – April 29, 2013
Aleksandr Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Demonstration
1932
Gelatin silver print
11 5/8 × 9″ (29.6 × 22.8cm)
Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
Alvin Langdon Coburn (American, 1882-1966)
The Octopus
1909
Gelatin silver print
22 1/8 × 16 3/4″ (56.2 × 42.6cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© George Eastman House
Franz Roh (German, 1890-1965)
Lightbulb
1928-1933
Gelatin silver print
7 3/16 × 9 7/16″ (18.2 × 23.9cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Willys P. Wagner and Mrs. Gerald F. Warburg, by exchange
© Estate Franz Roh, Munich
Hans Finsler (Swiss, 1891-1972)
Incandescent Lamp
1928
Gelatin silver print
14 1/2 × 9 3/4″ (36.9 × 24.7cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© Stiftung Moritzburg, Kunstmuseum des Landes. Sachsen-Anhalt
Jaroslav Rössler (Czech, 1902-1990)
Untitled
1923-1925
Gelatin silver print
8 11/16 × 8 9/16″ (22.1 × 21.8cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Horace W. Goldsmith Fund through Robert B. Menschel
© 2022 Sylva Vitove-Rösslerova
André Kertész (Hungarian, 1894-1985)
Les Lunettes et la Pipe de Mondrian, Paris (Glasses and Pipe of Mondrian, Paris)
1926
Gelatin silver print
3 1/8 × 3 11/16″ (7.9 × 9.3cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Grace M. Mayer Fund
© 2022 Estate of André Kertész
André Kertész (American, born Hungary. 1894–1985)
Chez Mondrian
1926
Gelatin silver print
4 1/4 × 3 1/16″ (10.8 × 7.8cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Grace M. Mayer Fund and gift of the artist, by exchange
© 2022 Estate of André Kertész
Gertrud Arndt (German, 1903-2000)
At the Masters’ Houses
1929-1930
Gelatin silver print
8 7/8 × 6 1/4″ (22.6 × 15.8cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2022 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
Germaine Krull (Dutch born Germany, 1897-1985)
Untitled
1927-1928
Gelatin silver print
9 × 6 1/4″ (22.9 × 15.9cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© Estate Germaine Krull, Museum Folkwang, Essen
Germaine Krull (Dutch born Germany, 1897-1985)
Germaine Krull was a pioneer in the fields of avant-garde photomontage, the photographic book, and photojournalism, and she embraced both commercial and artistic loyalties. Born in Wilda-Poznań, East Prussia, in 1897, Krull lived an extraordinary life lasting nine decades on four continents – she was the prototype of the edgy, sexually liberated Neue Frau (New Woman), considered an icon of modernity and a close cousin of the French garçonne and the American flapper. She had a peripatetic childhood before her family settled in Munich in 1912. She studied photography from 1916 to 1918 at Bayerische Staatslehranstalt für Lichtbildwesen (Instructional and Research Institute for Photography), and in 1919 opened her own portrait studio. Her early engagement with left-wing political activism led to her expulsion from Munich. Then, on a visit to Russia in 1921, she was incarcerated for her counterrevolutionary support of the Free French cause against Hitler. In 1926, she settled in Paris, where she became friends with artists Sonia and Robert Delaunay and intellectuals André Malraux, Jean Cocteau, Colette, and André Gide, who were also subjects of her photographic portraits.
Krull’s artistic breakthrough began in 1928, when she was hired by the nascent VU magazine,the first major French illustrated weekly. Along with photographers André Kertész and Éli Lotar, she developed a new form of reportage rooted in a freedom of expression and closeness to her subjects that resulted in intimate close-ups, all facilitated by her small-format Icarette, a portable, folding bed camera. During this period, she published the portfolio, Metal (Métal) (1928), a collection of 64 pictures of modernist iron giants, including cranes, railways, power generators, the Rotterdam transporter bridge, and the Eiffel Tower, shot in muscular close-ups and from vertiginous angles. Krull participated in the influential Film und Foto, or Fifo, exhibition (1929-1930), which was accompanied by two books, Franz Roh’s and Jan Tschichold’s Foto-Auge (Photo-Eye) and Werner Gräff’s Es kommt der neue Fotograf! (Here Comes the New Photographer!). Fifo marked the emergence of a new critical theory of photography that placed Krull at the forefront of Neues Sehen or Neue Optik (New Vision) photography, a new direction rooted in exploring fully the technical possibilities of the photographic medium through a profusion of unconventional lens-based and darkroom techniques. After the end of World War II, she traveled to Southeast Asia, and then moved to India, where, after a lifetime dedicated to recording some of the major upheavals of the twentieth century, she decided to live as a recluse among Tibetan monks.
Introduction by Roxana Marcoci, Senior Curator, Department of Photography, 2016, text from the MoMA website [Online] Cited 01/02/2022
Paul Citroen (Dutch born Germany, 1896-1983)
Metropolis (City of My Birth) (Weltstadt (Meine Geburtsstadt))
1923
Gelatin silver print
8 × 6″ (20.3 × 15.3cm)
Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2022 Paul Citroen/Artist Rights Society (ARS), New York/Pictoright, Amsterdam
César Domela-Nieuwenhuis (Dutch, 1900-1992)
Hamburg, Germany’s Gateway to the World
1930
Gelatin silver print
Dimensions
15 7/8 × 16 1/2″ (40.3 × 41.9cm)
Thomas Walther Collection
Abbott-Levy Collection funds, by exchange
© 2022 César Domela/ Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris
Masterworks of Modern Photography 1900-1940 book
The creative possibilities explored through photography were never richer or more varied than in the years between the two world wars, when photographers tested the medium with unmatched imaginative fervor. This moment of inventive approaches to documentary, abstract, and architectural subjects is dramatically captured in the more than three hundred and fifty photographs that constitute the Thomas Walther Collection at The Museum of Modern Art. The Museum acquired these photographs from Thomas Walther’s private collection, which includes exceptionally striking prints by towering figures in the field alongside lesser known treasures by more than one hundred other practitioners. This exhibition also highlights the artists whose work Walther collected in depth, including André Kertész, Germaine Krull, Franz Roh, Willi Ruge, Maurice Tabard, Umbo, and Edward Weston. Made on the street and in the studio, intended for avant-garde exhibitions and the printed page, these photographs provide unique insight into the radical objectives of their creators. The transatlantic circulation of ideas, images, objects, and people stimulated vibrant dialogues concerning the transformation of vision, and the varied uses and capacities of photography. Organised to explore thematic connections between the works, the exhibition testifies to the dynamic experience of modernity through genres such as portraiture, expressions of the urban experience, and techniques of estrangement and experimentation, including unfamiliar points of view and distortions.
Purisms
Beginning in the 1890s, in an attempt to distinguish their efforts from those of the growing ranks of professionals and the new hordes of Kodak-wielding amateurs, “artistic” photographers referred to themselves as Pictorialists. They embraced soft focus and painstakingly wrought prints to encourage an awareness of the preciousness of their photographs as objects, often emulating strategies from contemporary fine-art prints and drawings and choosing subjects that underscored the ethereal effects of their methods. Before long, however, some avant-garde photographers came to celebrate precise and distinctly photographic qualities as virtues, and by the early twentieth century, photographers on both sides of the Atlantic were transitioning from Pictorialism to Modernism – and occasionally blurring the distinction. Modernist photographers made exhibition prints using precious platinum or palladium, or, particularly after World War I, matte surfaces that mimicked those materials. These techniques are in evidence in the work of Edward Weston, whose suite of prints in the Walther Collection suggests the range of appearances achievable with unadulterated contact prints from large-format negatives.
Edward Weston (United States, 1886-1958)
In 1922, en route from his home in Los Angeles to New York City, where he planned to meet Alfred Stieglitz, Weston stopped to visit his sister in Ohio. There he made a series of pictures of the Armco Steel factory that signalled a break from the ethereal portrait practice that characterised his early professional work and an embrace of pure, industrial form. The following year Weston relocated to Mexico City, where he expanded his modernist vocabulary in the company of his apprentice, lover, and muse, the photographer Tina Modotti. In 1926, Weston returned to the United States, where he received increasingly international recognition for the formal rigour of his distilled subjects and the expressive luminosity of his prints.
Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
Shells
1927
Gelatin silver print
9 1/2 × 7 1/2″ (24.1 × 19cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Purchase
© 1981 Center for Creative Photography, Arizona Board of Regents
Books and Magazines
The extraordinary fecundity of the photographic medium between the First and Second World Wars can be persuasively attributed to the dynamic circulation of people, ideas and images that was a hallmark of that era in Europe and the United States. Migration, a profusion of publications distributed and read on both sides of the Atlantic, and landmark exhibitions that brought artistic achievements into dialogue with one another all contributed to a period of innovation that was a creative peak both in the history of photography and in the field of arts and letters. Overall, only a small number of European photobooks made their way to the United States, but their significance was evidently appreciated by those Americans who encountered them. These publications signalled a recognition of the artistic potential of photography while also cementing its centrality in the popular imagination, as well as providing the opportunity to discover photographic works no matter the artist’s place of origin. Photographs also circulated in Europe and America through various types of publications such as avant-garde magazines and more widely circulated periodicals. The vast majority of magazines and reviews founded in the 1910s and 1920s did not survive the economic crisis of the end of the decade. This is not to say that the era of photographs in magazines was over – far from it. Life was founded in 1936, and its extraordinary success was followed, if not matched, by dozens of other magazines in the United States and Europe. These, however, did not embrace the experimental artistic and literary practices that had flourished on the pages of magazines and journals in the first quarter of the twentieth century.
Cover of László Moholy-Nagy (Hungarian, 1895-1946)
Painting, Photography, Film (Malerei, Fotografie, Film)
Munich: Albert Langen Verlag, 1925
Malerei Photographie Film (Painting Photography Film) marked the beginning of an explosively creative and influential decade of photography books. The book features the work of Walther Collection artists Paul Citroen, Georg Muche, and István Kerny in addition to Moholy-Nagy, and was the eighth in the Bauhausbücher (Bauhaus Books) publications series, which was edited by Moholy-Nagy and Walter Gropius, the German art school’s founding director. Although photography was central to the thinking of Moholy-Nagy and his fellow Bauhaus teacher Josef Albers, and each incorporated it into the school’s preliminary course, the medium was not formally made a part of the curriculum until 1929, when the Bauhaus hired photographer Walter Peterhans. Peterhans balanced a rigorous attention to technical detail with the reputational benefits of having his work circulate in publications and exhibitions, and he was responsible for teaching a significant number of Walther Collection photographers – from the Argentine Horacio Coppola to the German Umbo.
In 1922, Laszlo Moholy-Nagy published the short article “Produktion-Reproduktion” in the Dutch journal De Stijl, identifying the potential for the relatively new mediums of photography and film to transcend their conventional function of documentation. He advocated for their creative application – through multiple exposures, typographic interventions, montage, and oblique perspectives – to produce “new, as yet unfamiliar relationships” in the visual field. In the first half of the twentieth century, publications featuring photography were one of the primary outlets for expressing these new ways of seeing. Viewing these books and journals today provides a richer understanding of modernist photography and its impact on other mediums.
Text from the MoMA website
Cover of Werner Gräff (German, 1901-1978)
Es kommt der neue Fotograf! (Here comes the new photographer!)
Berlin: H. Reckendorf, 1929
Es kommt der neue Fotograf! (Here Comes the New Photographer!) features eleven artists (and four artworks) of the Walther Collection, and was likewise designed as a primer for those interested in but unfamiliar with the experimental front lines of its medium. “The purpose of this book is to break down barriers, not create them,” wrote the author of the book Werner Gräff. He declared his bias in favour of “unconventional photographs,” including photomontage, which is featured in a dedicated section.
Cover of Franz Roh (German, 1890-1965) and Jan Tschichold (German, 1902-1974)
Foto-Auge: 76 Fotos der Zeit (Photo-eye: 76 photos of the time)
Stuttgart: F. Wedekind, 1929
The Museum of Modern Art Library, New York
© 2014 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York/VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
Foto-Auge (Photo-Eye) features on its cover El Lissitzky’s work Self-Portrait (The Constructor), a complex photomontage that collapses pictorial and graphic space, merging image with text, geometry with human form, and the act of seeing with, as the title suggests, constructing. In 1931, just two years after it appeared, Foto-Auge was recognised as a vital publication by the American photographer Walker Evans. Evans wrote, “Photo-Eye is a nervous and important book. Its editors call the world not only beautiful but exciting, cruel, and weird. In intention social and didactic, this is an anthology of the ‘new’ photography; yet its editors knew where to look for their material, and print examples of the news photo, aerial photography, microphotography, astronomical photography, photomontage and the photogram, multiple-exposure and the negative print.”
Cover from August Sander (German, 1876-1964) and Alfred Döblin (German, 1878-1957)
Antlitz der Zeit. Sechzig Aufnahmen Deutscher Menschen Des 20. Jahrhunderts (Face of our time: Sixty portraits of twentieth-century Germans)
Munich: Transmare Verlag, 1929
By the mid-1920s, August Sander had fixed on a wildly ambitious (if not intentionally impossible) goal of publishing a synthetic portrait – Menschen des 20. Jahrhunderts (People of the Twentieth Century) – comprising hundreds of individual portraits of his fellow Germans. Although this project of capturing “an absolutely faithful historical picture of our time” would remain unrealised in his lifetime, Antlitz der Zeit (Face of Our Time), published in Munich in 1929, distilled his vision into a suite of sixty photographs accompanied by an essay by novelist Alfred Doblin.
Cover of Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Die Welt ist schön
1928
Munich: Kurt Wolff Verlag, 1928
Pages from Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Die Welt ist schön. Einhundert photographische Aufnahmen (The world is beautiful: One hundred photographic images)
Munich: Kurt Wolff Verlag, 1928
The Museum of Modern Art Library, New York
© 2014/Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York/VG Bild-Kunst, Germany
Left: Albert Renger-Patzsch. Kauper, von unten gesehen. Hochofenwerk. Herrenwyk (Cowper, Seen from below. Blast furnace plant. Herrenwyk).
Right: Albert Renger-Patzsch. Bügeleisen für Schuhfabrikation (Iron shoe for fabrication).
Cover from Karl Blossfeldt (German, 1865-1932)
Urformen der Kunst (Art forms in nature) with original dust jacket
Berlin: Ernst Wasmuth, 1928
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. Ford Motor Company Collection. Gift of Ford Motor Company and John C. Waddell
© 2014 Karl Blossfeldt/Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York
Pages from Karl Blossfeldt (German, 1865-1932)
Urformen der Kunst (Art forms in nature)
Berlin: Ernst Wasmuth, 1928
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. Ford Motor Company Collection. Gift of Ford Motor Company and John C. Waddell
© 2014 Karl Blossfeldt/Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York
Left: Adiantum pedatum. Haarfarn
Right: Acanthus mollis. Akanthus. Bärenklau
Albert Renger-Patzsch’s Die Welt ist schön (The World Is Beautiful) and Karl Blossfeldt’s Urformen der Kunst (Art Forms in Nature) both appeared in 1928, published in Munich and Berlin, respectively. Renger-Patzsch and Blossfeldt represented two threads of the New Vision: the former was committed to unadulterated photographic depiction as the essence of a modern way of seeing, while the latter explored the intersection of mechanical processes and natural form. Neither chose the path of experimentation that Moholy-Nagy had defined earlier in the decade with Malerei Photographie Film, but in their embrace of the camera’s mechanical capacity, their work resonated with avant-garde practices.
Albert Renger-Patzsch was one of the most important promoters of modern photography in Weimar Germany. Die Welt ist Schön (The World is Beautiful) is his most well-known book, and the one that has come to define his career. It contains 100 closeup photographs of natural and man-made objects which are sequenced in progression from plants, animals, people, and the natural landscape, to turbines, girders, and other elements of industry before ending with a pair of hands clasped in prayer. The book was hugely popular at the time but received some criticism, particularly over the title which has contributed to a possible misreading of the work. In A Short History of Photography, Walter Benjamin wrote: ‘Therein is unmasked a photography which is able to relate a tin of canned food to the universe, yet cannot grasp a single one of the human connections in which that tin exists.’ Renger-Patzsch himself maintains that he would have preferred to have used the title Die Dinge (Things), which is more in keeping with his straight documentary approach. He maintained that his aesthetic arose from an interest in the precise nature of scientific photography and an interest in the composition of visual structures of the outside world, rather than from a desire to create a harmonic universal design. In a 1930 letter to Franz Roh he expressed his concern that Die Welt ist Schön was being interpreted philosophically, holding it up instead as his declared belief in optimism. To the end of his life Renger-Patzsch rejected any attempts to push photography toward total abstraction. He maintained his belief that photography was not an art but a means of documenting and recording, and that any attempt to compete with the graphic arts would cause photography to lose it own inherent characteristics of nuance and detail.
Text from the Oliver Wood Books website [Online] Cited 26/01/2022
Artist’s Life
Photography is particularly well suited to capture the distinctive nuances of the human face, and photographers delighted in portraiture throughout the twentieth century. In the Thomas Walther Collection, portraits and self-portraits of artists – as varied as the individuals portrayed – are complemented by works that convey a free-spirited sense of artists’ lives and communities, generously represented here through photographs made by André Kertész in Paris, and by students and faculty at the Bauhaus. When the Hungarian-born Kertész moved to the French capital in 1925, large sheets of photographic paper were a luxury he couldn’t afford. Choosing less expensive postcard stock instead, he made intimate prints that function as miniature windows into the lives of his bohemian circle of friends. The group of photographs made at the Bauhaus in the mid-1920s, before the medium was formally integrated into the school’s curriculum, includes playful and spontaneous snapshot-like pictures, as well as more considered compositions in which students explore their relationship to the architecture of the school and other aspects of their coursework.
Lucia Moholy (European, 1894-1989)
Florence Henri
1927
Gelatin silver print
37.2 × 27.9cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2021 Lucia Moholy Estate/Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York/VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn.
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
Between 1924 and 1930, Moholy photographed dozens of Bauhaus students, masters, and their families, creating often startlingly close views with her large-format camera. Within very narrow parameters, Moholy conveys her sensitivity to her sitters. Having printed many enlargements for her husband, László Moholy-Nagy, she was well aware of the visual impact afforded by large prints, and she had the experience and talent required to produce them.
The glass plate negative from which this image was made is the largest Moholy used, exposed in a large wooden camera on a tripod. The advantage to working with these fragile and cumbersome glass plates is their exceptionally high resolution, as well as the possibility that one could retouch directly on the negative. Indeed, this print reveals extensive retouching, both in the negative and on the print.
Lyonel Feininger (German-American, 1871-1956)
Bauhaus
February 26, 1929; print 1929-1932
Gelatin silver print
7 × 8 1/2″ (17.8 × 21.6cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2022 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
At the Bauhaus in Dessau, all members of the Feininger family (Lyonel, his wife, Julia, and their sons, Andreas, Laurence, and Theodore Lux) were active photographers. In 1927, Andreas built a darkroom in the Feininger basement. The year after, his father also took up photography, initially as an activity to enliven his long, solitary evening walks. Bauhaus is a view of the workshop wing of the school, carefully trimmed, retouched, and inscribed on the verso with the time and place it was taken. Feininger chose a matte paper that invites the eye to sink into the velvety blacks and allows the gradual discrimination of degrees of darkness within this nocturne.
In 1926, Lyonel Feininger, accompanied by his wife, Julia, and their adolescent sons, Andreas, Laurence, and Theodore Lux, moved into one of the double Masters’ Houses at the Dessau Bauhaus. In the other half of the house – designed by Walter Gropius, the director of the school – lived the photographer Lázsló Moholy-Nagy with his wife, Lucia Moholy, a skilled professional photographer. Moholy-Nagy enthusiastically advocated photography as the essential modern language, a message he broadcast in his influential book Malerei, Fotographie, Film (Painting, Photography, Film), which was published by the school in 1925 and reprinted in 1927. Feininger initially considered Moholy’s vigorous embrace of camera optics, new perspectives, and recombinant techniques to be outside the realm of art, but after a few years of living in the same house he changed his views: Moholy’s ideas and vitality had proved irresistible not only to the painter but to his three sons as well.
From the Feininger basement, where Andreas built a darkroom in 1927, emerged lively photographs of Bauhaus theatre productions, of the Bauhaus jazz band in which T. Lux and other students played, and of their friends involved in all manner of events. To enlarge their images, the young Feiningers fabricated a projector from a wood box, four lightbulbs, and a camera lens. They secured a glass negative to the front of the device and projected the negative’s image onto sheets of unexposed photographic paper pinned to an easel. The only signs of this procedure in the prints are the tiny white lines of shadow cast by the pins, which blocked the paper’s exposure to the light.
Prior to his arrival at the Bauhaus, in 1919, Feininger had shown his paintings with the artist group Blaue Reiter (Blue Rider), at the Galerie der Sturm and at the Galerie Dada. Because of these and other accomplishments, Gropius deferred to the somewhat older master and let him give up teaching and devote himself entirely to painting. In 1928 Feininger also took up photography, initially as an activity to enliven his long, solitary evening walks. Bauhaus is a view of the workshop wing of the school printed from a 4.5 by 6 centimeter (1 3/4 by 2 3/8 inch) glass-plate negative using the projection technique worked out by his sons. Feininger carefully trimmed, retouched, and inscribed this large print on the verso with the time and place it was taken.
In making his prints Feininger drew from his experience as a printmaker who knew the critical role of craft and materials – of inks and papers – and Lucia Moholy’s fine printing may also have made him especially attentive to print quality. Feininger chose a thin matte paper with a high rag content, which instead of reflecting light, as glossy papers do, absorbs it. This invites the viewer’s eye to sink into the velvety blacks and allows the gradual discrimination of degrees of darkness within these meditative nocturnes.
Lee Ann Daffner, Maria Morris Hambourg on the Object: Photo MoMA website [Online] Cited 26/01/202
Hajo Rose (German, 1910-1989)
Untitled (Self-Portrait)
1931
Gelatin silver print
9 7/16 × 7 1/16″ (23.9 × 17.9cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2022 Hajo Rose/ Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Germany
Trained first as a graphic artist and introduced to photography only upon enrolling at the Bauhaus in 1930, Rose applied his talents with both disciplines to generate this superimposition made from two different negatives: the distinctive facade of the Bauhaus in Dessau circumscribed by a self-portrait. Photography was formally integrated into the Bauhaus curriculum with the appointment of Walter Peterhans to the faculty in 1929, and this image may have been Rose’s response to a Peterhans assignment. Like the school’s curriculum, the picture weaves together photography, graphic design, and architecture into a unique, instructive whole, suggesting the collective nature of the school and the inculcation of Constructivist ideals in the individuals that made up the student body.
Claude Cahun (Lucy Schwob) (French, 1894-1954), Marcel Moore (Suzanne Malherbe) (French, 1892-1972)
Untitled
1921-1922
Gelatin silver print
9 5/16 × 5 7/8″ (23.7 × 15cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Mrs. Leon Dabo, by exchange
© 2022 Estate of Claude Cahun
Lucy Schwob was a writer, actress, and outspoken member of the lesbian community of Paris between the two world wars. She and her half-sister, Suzanne Malherbe, became partners in life, love, and art, and took the ambiguously gendered pseudonyms Claude Cahun and Marcel Moore for their theatrical and photographic works. These mostly depict Cahun, and sometimes Moore, in a variety of masculine, androgynous, and feminine personas in minimally staged scenes in their home. This cropped image shows just Cahun’s head. In the full negative she appears full-length as a dandy in a man’s evening suit, her stance brazen, with hand on hip and improper cigarette in hand.
Lucy Schwob was a writer, actress, and outspoken member of the Parisian lesbian community between the two world wars. She and Suzanne Malherbe, her stepsister, became partners in life, love, and art, and took the ambiguously gendered pseudonyms Claude Cahun and Marcel Moore for their collaborative theatrical and photographic works. The images they made mostly depict Cahun, and sometimes Moore, in a variety of masculine, androgynous, and feminine personas set in minimally staged scenes in their home.
This print is an enlargement from a negative that was cropped to frame Cahun’s face and torso; the full-length image reveals a dandy in a men’s evening suit, her stance brazen, with hand on hip and cigarette in hand. Cahun erased the visible traces of her femininity by shaving her head, wearing masculine clothes, and avoiding jewellery and makeup. Through her wide variety of self-portrayals, she undercut the notion of a fixed identity and challenged the concept of a strict gender binary. Cahun and Moore’s writings – particularly their 1930 book Aveux non avenus (Disavowals), where this photograph was reproduced – also explored a shifting, malleable concept of personhood. Cahun considered their self-imaging project to be never-ending, explaining, “Under this mask another mask. I will never finish removing all these faces.”
Publication excerpt from MoMA Highlights: 375 Works from The Museum of Modern Art, New York. New York: The Museum of Modern Art, 2019
Cover of Claude Cahun (Lucy Schwob) (French, 1894-1954)
Aveux Non Avenus
Paris- Éditions du Carrefour, 1930
Pages of Claude Cahun (Lucy Schwob) (French, 1894-1954)
Aveux Non Avenus
Paris- Éditions du Carrefour, 1930
Man Ray (Emmanuel Radnitzky) (American, 1890-1976)
Three Heads – Joseph Stella and Marcel Duchamp
1920
Gelatin silver print
8 1/8 × 6 3/16″ (20.7 × 15.7cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2022 Man Ray Trust / Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris
In 1920, collector-philanthropist Katherine Dreier and Marcel Duchamp cofounded the Société Anonyme, an organisation intended to promote and exhibit modern European and American art in New York. Various other artists assisted in this enterprise, including Man Ray, who photographed the art and artists for publicity and postcards, and the Italian Futurist Joseph Stella, who helped to select and hang the early exhibitions.
The presence of Stella and Duchamp together on the couch in this image reflects their close association with Dreier at this moment. Stella contrasts in joviality and girth with the monkish intensity of Duchamp; combined with the photograph of the woman smoking on the wall (an image also taken by Man Ray) this incidental pairing was just the sort of delicious, lightly barbed nonsense that delighted Man Ray. He referred to portrait photography, with which he would earn his living in Paris, as “taking heads”; that he considered the picture of the woman an essential part of this image is indicated by his title, Three Heads.
August Sander (German, 1876-1964)
High School Student
1926
Gelatin silver print
10 3/16 × 7 3/8″ (25.8 × 18.7cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Edward Steichen, by exchange
© 2022 Die Photographische Sammlung / SK Stiftung Kultur – August Sander Archiv, Cologne / ARS, NY
Around 1910 Sander began producing his monumental project, Menschen des 20. Jahrhunderts (People of the Twentieth Century): a photographic catalogue of the German people that traces the country’s transformation from agrarian society into modern industrialised nation, organised in seven categories: farmers, workers, women, professionals, artists, urbanites, and the “last people,” or those individuals on the fringe of society. In 1929, he published Antlitz der Zeit (Face of Our Time), a group of sixty of these photographs that outlined his ideas about the existing social order, but the project’s incompatibility with Nazi ideology eventually caught the attention of Third Reich censors, who destroyed the printing plates in 1936. This portrait appeared in Antlitz der Zeit, and was classified in Menschen des 20. Jahrhunderts as a representative image of a modern high school student.
Atelier Stone. Sasha Stone (Russian, 1895-1940) and Cami Stone (born Wilhelmine Schammelhout, Belgian 1892-1975)
Woman Smoking
1928
Gelatin silver print
23 1/16 × 16 5/16″ (58.6 × 41.4cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Committee on Photography Fund
Atelier Stone was a photography studio founded in Berlin by Sasha and Cami Stone, a married couple who collaborated professionally. Their pictures were disseminated in German magazines throughout the 1920s, and in 1929 their photographs were included in the exhibition Film und Foto. This large-scale print was almost certainly made for display, rather than reproduction. Oozing cool confidence, the figure portrayed here is emblematic of the Weimar-era “neue Frau,” or “new woman,” a social type whose independence, feminist outlook, and daring style challenged traditional gender expectations.
Magic Realisms
In the mid-1920s, members of European artistic movements ranging from Surrealism to New Objectivity shifted away from a realist approach, instead seeking to highlight the strangeness of everyday life or to mingle dreams and conscious states. Echoes of these concerns, centred on the human figure, can be found throughout the Walther Collection. Some photographers used anti-naturalistic methods – capturing hyperreal, close-up details, playing with scale, or rendering the body as landscape – to challenge the viewer’s perception. Others, in line with Sigmund Freud’s definition of “the uncanny” in 1919 as an effect resulting from the blurring of distinctions between the real and the fantastic, offered plays on life and the lifeless, the animate and the inanimate, engaging the human body through surrogates in the form of dolls, mannequins, and masks. Photographers influenced by Surrealism, such as Maurice Tabard, subjected the human figure to distortions and transformations by experimenting with photographic techniques while capturing the image or developing prints in the darkroom.
Maurice Tabard (France, 1897-1984)
Although he started out as a more conventional portrait photographer in the United States, Tabard made his name internationally as a magician of solarisation – a method that creates a hybrid image (part negative, part positive) by interrupting the development process to expose the image to an additional flash of light – and other darkroom manipulations. From 1928 to 1931 he was director of the photography lab at the Parisian type foundry Deberny & Peignot, which was at the forefront of the printing, advertising, and magazine trades, bringing him into contact with leading writers and artists of the day.
Herbert Bayer (American born Austria, 1900-1985)
Humanly Impossible (Self-Portrait)
1932
Gelatin silver print
38.9 × 29.3cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Acquired through the generosity of Howard Stein
© ADAGP, Paris, 2021
© 2021 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York/VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
In the case of the Germans Herbert Bayer and John Guttman, it is the photographer’s own body that is the object of this doubling. In his Humanly Impossible – part of a series of photomontages titled Man and Dream – Bayer calls up the themes of the double and the ancient. Mingling disbelief and horror, the photographer watches himself performing his own amputation. The reflection in the mirror shows him his own body turned into a statue, his own flesh transformed into marble, and the present reverting to antiquity.
From 1925 to 1928 Bayer led the workshop in printing and advertising at the Bauhaus. In 1928, he relocated to Berlin, where he became the art director of the German edition of Vogue magazine and of Dorland Studio, an international advertising agency. It is at that time that he started creating dramatic montages, including this one, in which Bayer observes his reflected double in a mirror. A slice of his arm is severed from his torso. Although the picture is playful, reflecting both Dada humour and Surrealist dream states, the horror on Bayer’s face could reflect something darker, perhaps the physical and psychological traumas of World War I and the growing fears that such a cataclysmic nightmare might recur.
Raoul Hausmann (Austrian, 1886-1971)
Untitled
February 1931; print 1931-1933
Gelatin silver print
5 3/8 × 4 7/16″ (13.7 × 11.3cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2015 Raoul Hausmann / Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Pari
A key Berlin-based Dadaist, Hausmann exhibited assemblage sculptures, collages, and photomontages made with magazines and newspaper clippings between 1918 and 1922. By the late 1920s he had taken up photography in earnest, making straight camera-based images of landscapes and plants before turning to more experimental works on light and optics. Hausmann made this untitled image during these years of intense focus on photography. The model is his second wife, Hedwig Mankiewitz-Hausmann. The reflection in the shaving mirror magnifies the organ of vision, the eye, a strategy popular in avant-garde photography of that period. The round mirror becomes a metaphor for the camera’s mechanical lens, which enables the operator to see the world literally larger than life.
Jindřich Štyrský (Czech, 1899-1942)
Untitled
1934-1935
From Na jehlách těchto dní. On the Needles of These Days
Gelatin silver print
3 9/16 × 3 3/8″ (9 × 8.5cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Abbott-Levy Collection funds, by exchange
Štyrský – an avant-garde poet, photographer, editor, painter, and collagist – was among the many avant-garde artists between the two world wars who were interested in the mannequin motif. Like the Surrealists in France, he was drawn to the bizarre, erotic, and morbid, and to the symbolic forms in which they appeared in popular culture. Štyrský trawled the streets of Paris and Prague, looking for such subjects. In 1941, in occupied Czechoslovakia, he published a clandestine edition of On the Needles of These Days, a book of photographs accompanied by Jindřich Heisler’s poems. This print of a mannequin in the window of a Prague shop comes from a maquette for the book.
“Na Jehlach Techto Dni (On the Needles of These Days)” published by Fr. Borovy v Praze, Prague in 1945 was preceded by the extremely scarce clandestine self-published edition of 1941 with original tipped-in silver gelatin prints. In “The Photobook: A History”, Parr and Badger write, “This remains a haunting photobook, 50 years after the war. It is a prime example of one of the photobook’s great truths – it’s not necessarily the individual pictures that count, but what you do with them”. Commenting in the book, “The Book of 101 Books: Seminal Photographic Books of the Twentieth Century”, Vince Aletti states, “On the Needles of These Days” is a Surrealist meditation on war and resistance the book’s aura of alienation, repression, and anxiety not only captured the war’s home front theatre of the absurd, it anticipated the depth of postwar pessimism.” Cited in all three reference books on photobooks: “The Book of 101 Books: Seminal Photographic Books of the Twentieth Century” by Andrew Roth and “The Photobook: A History”, by Parr and Badger, and “The Open Book” by Andrew Roth.
Text from the Abebooks website
Raoul Ubac (Belgian born Germany, 1910-1985)
The Secret Gathering
1938
Gelatin silver print
15 5/8 × 11 11/16″ (39.7 × 29.7cm)
Thomas Walther Collection
Abbott-Levy Collection funds, by exchange
© 2022 / Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris
At the time of his association with Surrealism in the 1930s, Ubac distinguished himself with deft darkroom manipulations, creating complex photographs through multiple experimental techniques. This image is from a series that has come to be associated with the legend of Penthesilea, the mythical queen of the Amazons. To construct this picture, Ubac carefully lit and posed his wife, Agui, and a friend in the studio. The resulting images were collaged into a new composition, which he rephotographed and solarised (exposed to an additional flash of light) to partially annihilate their forms. Recalling the transformative rituals of secret societies, the tangled mass of naked flesh and hair evokes unconscious sexual and aggressive drives, while the title suggests secret societies and subterfuge.
Stanisław Ignacy Witkiewicz (Polish, 1885-1939)
Anna Oderfeld, Zakopane
1911-1912
Gelatin silver print
6 11/16 × 4 3/4″ (17 × 12.1 cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Mrs. Willard Helburn, by exchange
Writer, painter, and philosopher, Witkiewicz made extraordinary close-up portraits of himself, his parents, and his friends, including this elusive portrait of his lover, Anna Oderfeld. This photograph is an intimate record of a young man’s romantic obsession, yet the blurred image and extremely tight cropping look nothing like a traditional portrait of a sweetheart. As evidenced by the dark oval left by a negative clip in the top right corner, this is a contact print, and the light source – a paned window – is reflected in the dark of the subject’s eyes. Witkiewicz’s embrace of these technical “flaws” was not merely a signal of creative license; he was keenly attuned to their social, psychological, and metaphysical implications.
Iwao Yamawaki (Japanese, 1898-1987)
Articulated Mannequin
1931
Gelatin silver print
9 1/16 × 6 13/16″ (23 × 17.3cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Thomas Walther
© 2022 Makoto Yamawaki
Trained in architecture at the Tokyo School of Arts but disenchanted with architectural practice in his native country, Yamawaki applied to study architecture and interior design at the Bauhaus in Dessau. Once in Germany, however, he turned to photography, creating images of architecture, people, furniture, and objects. This image is a prime example of the exquisite sculptural quality Yamawaki could achieve in his photographs. Involved in designing and producing theatre and dance at the school, Yamawaki employed theatrical lighting to emphasise the voluminous forms of a commonly available artist’s mannequin.
Experiments in Form
In 1925 László Moholy-Nagy asserted that although photography had been invented one hundred years earlier, its true aesthetic possibilities were only then being discovered, as he and others in his avant-garde circles adopted the medium. As products of technological culture, with short histories and no connection to the old fine-art disciplines, photography and cinema were truly modern instruments with the greatest potential for transforming visual habits – a key goal of the New Vision, the movement of young photographers synthesised through Moholy’s writing. These ideas were distilled in widely circulated publications by Moholy-Nagy, Franz Roh, and others who deployed innovative combinations of text and image. From the photogram to solarisation, from negative prints to double exposures, New Vision photographers explored the medium in countless ways, rediscovering older techniques and inventing new ones. Echoing the cinematic experiments of the same period, their emerging photographic vocabulary was adopted by the advertising industry, which was quick to exploit the visual efficiency of its bold graphic simplicity.
Franz Roh (Germany, 1890-1965)
Roh was an art historian and a pioneering critic of the twentieth-century avant-garde, with a special interest in photography. In 1927, encouraged by his friend László Moholy-Nagy, whom he had visited at the Bauhaus in Dessau the year before, he started making his own experimental photos. Some of Roh’s favourite techniques were photomontage, which he often used to combine shots of nudes and of architecture in nonsensical compositions; negative printing; and sequenced contact prints that suggest a film-like narrative. He coauthored the seminal photography book Foto-Auge with the Dutch graphic designer Jan Tschichold in 1929 and launched Fotothek (Photo Library), a short-lived series of small books about new photographers, in 1930.
Florence Henri (European born America, 1893-1982)
Composition No.19
1928-1930
10 5/16 × 14 3/8″ (26.2 × 36.5cm)
Thomas Walther Collection. Gift of Shirley C. Burden, by exchange
© 2022 Florence Henri, Galleria Martini e Ronchetti, Genova, Italy
Henri arrived at the Bauhaus in Dessau in 1927 as a painter and left a few short months later as a photographer. Back in Paris in 1928 and influenced by Lucia Moholy’s ideas about photography, Henri started a series of still lifes with mirrors, playing with photography’s usual perspective. Every adjustment of mirrors and objects yielded fascinating new perceptions in this elastic environment. These images circulated in avant-garde magazines and major photography exhibitions of the day, including the 1929 exhibition Film und Foto.
“With photography, what I really want to do is compose the image, as I do in painting,” the artist Florence Henri has said about her artistic approach. “The volumes, lines, shadows and light should submit to my will and say what I would like them to say. All of this under the strict control of the composition, because I do not claim to be able to explain the world or to explain my own thoughts.” …
Henri turned to photography after spending a semester at the Bauhaus in Dessau, Germany, in 1927. Even though photography wasn’t introduced into the curriculum until 1929, it had already been used on campus for documentary, publicity, and experimental purposes for years. Henri’s professor, László Maholy-Nagy said, “With Florence Henri’s photos, photographic practice enters a new phase, the scope of which would have been unimaginable before today… Reflections and spatial relationships, superposition and intersections are just some of the areas explored from a totally new perspective and viewpoint.”
Though photography is a medium that uses light to capture the surfaces of physical objects, she manipulated light and manipulated objects to create a dialogue between realism and abstraction. Henri frequently experimented with mirror, angling them to create surreal still lives and self-portraits marked by spatial ambiguity. She also manipulated her images via photomontage, multiple exposures, and negative printing. This experimental work exemplified the New Vision movement (a term coined by Moholy-Nagy), and it earned its place on the walls of the prominent international photography exhibitions of the time, including Fotografie der Gegenwart (1929), Film und Foto (1929), and Das Lichtbild (1930).
In 1929, Henri established her own successful studio in Paris, and she taught photography to artists such as Gisèle Freund and Lisette Model. During the Nazi occupation, photographic supplies became difficult to acquire, and Henri’s experimental style was in danger of being deemed “degenerate” by the regime. Henri returned to painting, but it was her photographs, taken mainly between 1927 and 1940, that left lasting impressions on her contemporaries and later generations alike.
Jane Pierce, Carl Jacobs Foundation Research Assistant, Department of Photography. “Florence Henri,” on the MoMA website Nd [Online’ Cited 292/01/2022
The Modern World
Even before the introduction of the handheld Leica camera in 1925, photographers were avidly exploring the unique experience of capturing the world through a camera’s lens. Photography was ideally suited to express the tenor of modern life in the wake of World War I: looking both up and down (from airplanes, bridges, and skyscrapers), photographers found unfamiliar points of view and a new dynamic visual language, freed from convention. Improvements in the light sensitivity of photographic films and papers meant that photographers could capture motion as never before. At the same time, technological advances in printing resulted in an explosion of opportunities for photographers to present their work to ever-widening audiences. From inexpensive weekly magazines to extravagantly produced journals, periodicals exploited the potential of photographs and imaginative layouts to tell a story. It wasn’t just photojournalists like Willi Ruge whose work appeared in magazines and newspapers; the illustrated press was a primary means of distribution and circulation for most photographers of this era.
Leni Riefenstahl (German, 1902-2003)
Schönheit im Olympischen Kampf
Berlin: Deutschen Verlag 1937
Having enjoyed success as a dancer and actress, Riefenstahl pivoted to directing films in the 1930s. Although never a formal member of the Nazi Party, she infamously made propaganda films for the Nazi Party and cultivated a close personal and professional relationship with Hitler. With the assistance of various cameramen Riefenstahl extensively documented the 1936 Olympics in Berlin in both still photography and film, using her technical virtuosity to craft an image of German triumph for an international audience. The resultant 1938 film Olympia broke ground with its innovative cinematography, and many photographs of the games taken by her and her team, including this one, were compiled in the 1936 multilingual publication Schönheit im Olympischen Kampf (Beauty in the Olympic Games) [above]. During post-war denazification proceedings, Riefenstahl was classified as a Nazi sympathiser.
Willi Ruge (German, 1892-1961)
Seconds before Landing
1931
From the series I Photograph Myself during a Parachute Jump
Gelatin silver print
20.4 × 14.1cm
The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Thomas Walther Collection
Gift of Thomas Walther
Digital Image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York
In 1931, the photojournalist Willi Ruge took a series of photographs during a parachute jump over Berlin, using a camera attached to his waist. The reportage was backed up by a number of more conventional shots from another plane and from the ground. The story was published in the Berliner Illustrierte Zeitung, at the time Germany’s leading magazine using photography. Such was the success of the story that it was subsequently picked up by other magazines ranging from England to the United States.
Oscillating between documentation and entertainment stunt, this series depicts a parachute jump made by press photographer Ruge in 1931 from the Staaken airfield, near Berlin. In addition to the photographs Ruge made during his descent using a camera strapped to his belt, published accounts included pictures made from a second plane, and by at least one other photographer on the ground before and after the jump. The images Ruge produced while jumping echo many of the concerns and qualities put forward by New Vision photographers, including taking a more personal and almost amateur approach; unusual, dynamic vantage points; unexpected cropping; fractured, collage-like images; and the exaltation of modern sporting heroism. Distributed by the Berlin-based press agency Fotoaktuell, the pictures were published in a variety of magazines, first in Germany and then in Great Britain.
Jeu de Paume
1, Place de la Concorde
75008 Paris
métro Concorde
Phone: 01 47 03 12 50
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Sunday 11am – 7pm
Closed Mondays
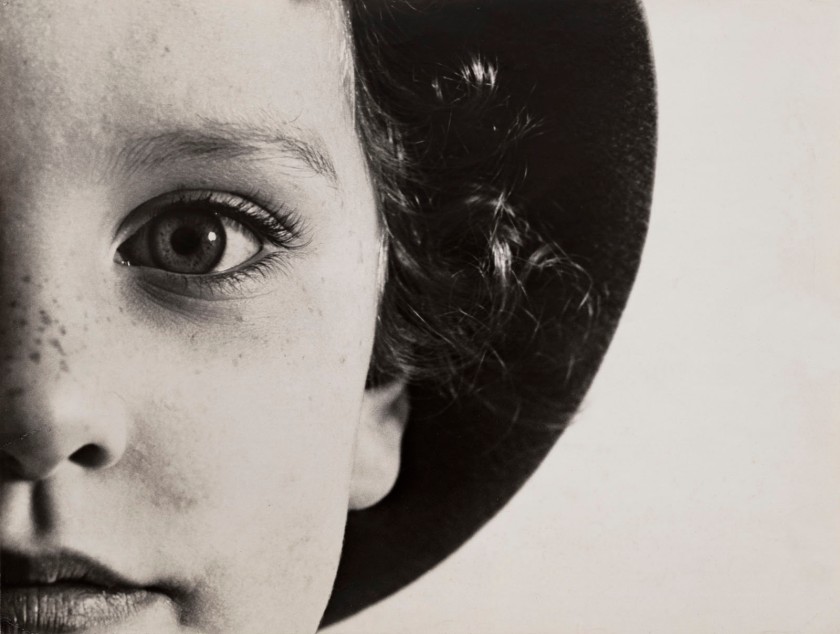
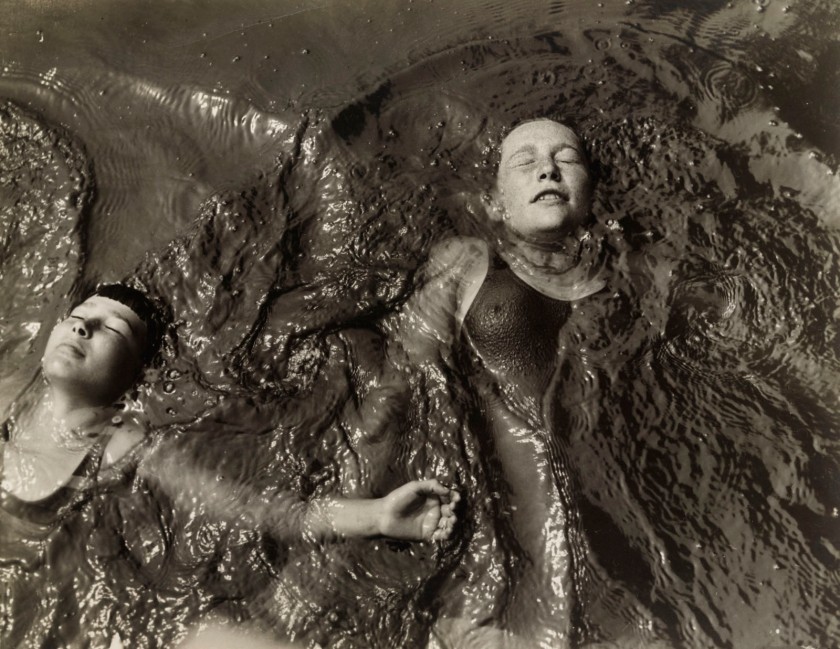
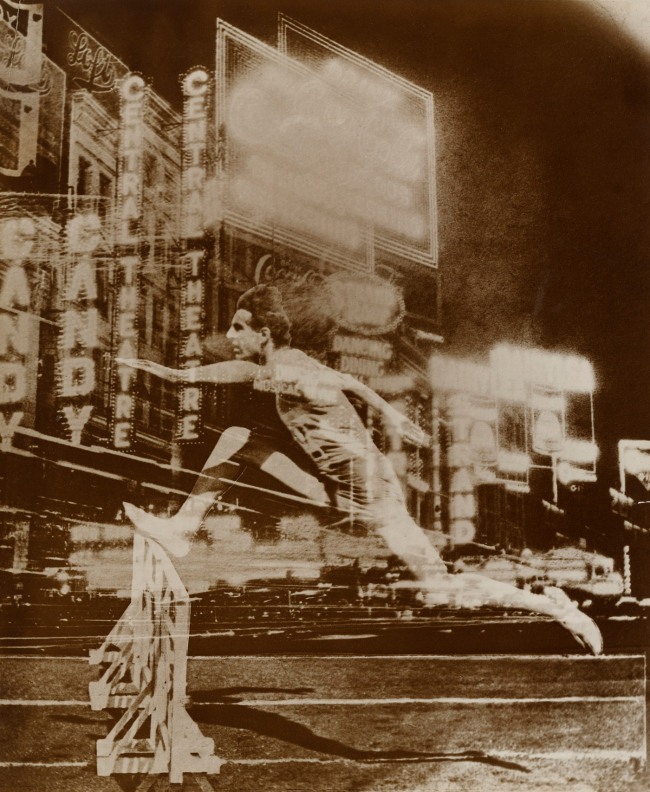
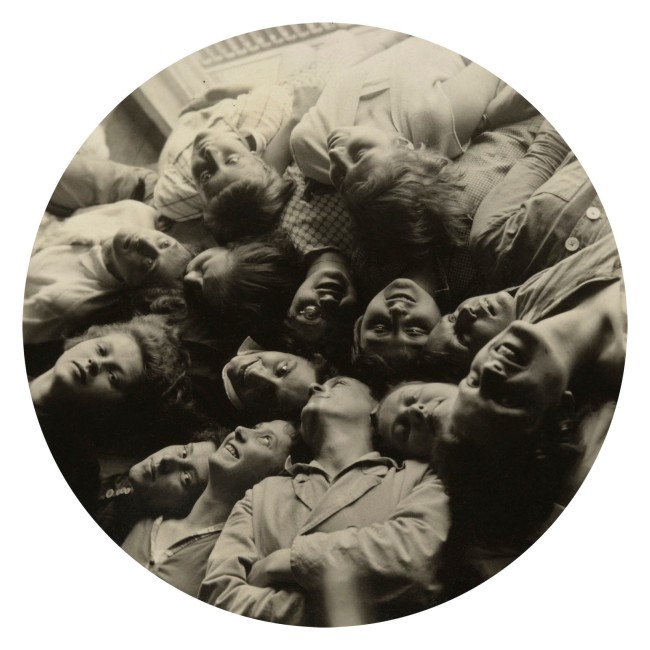
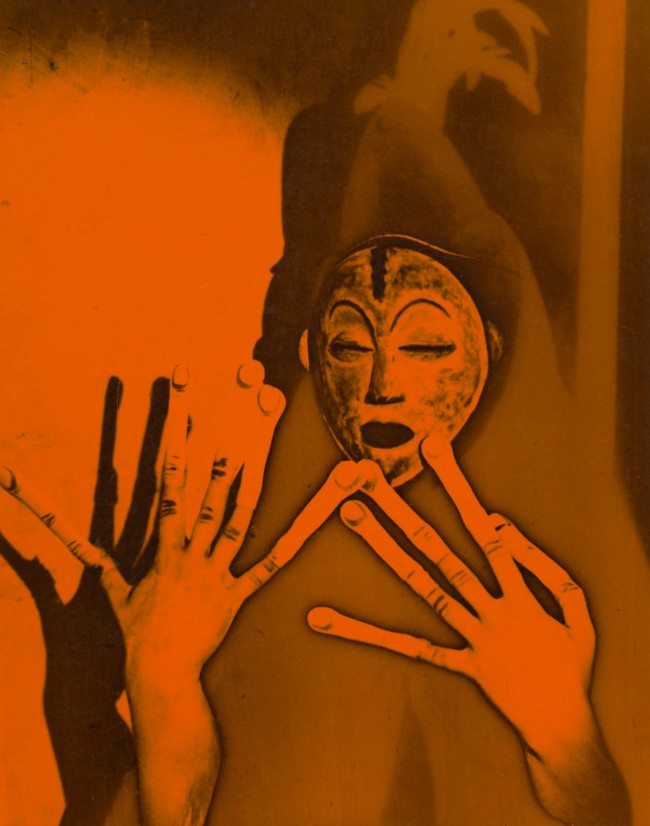
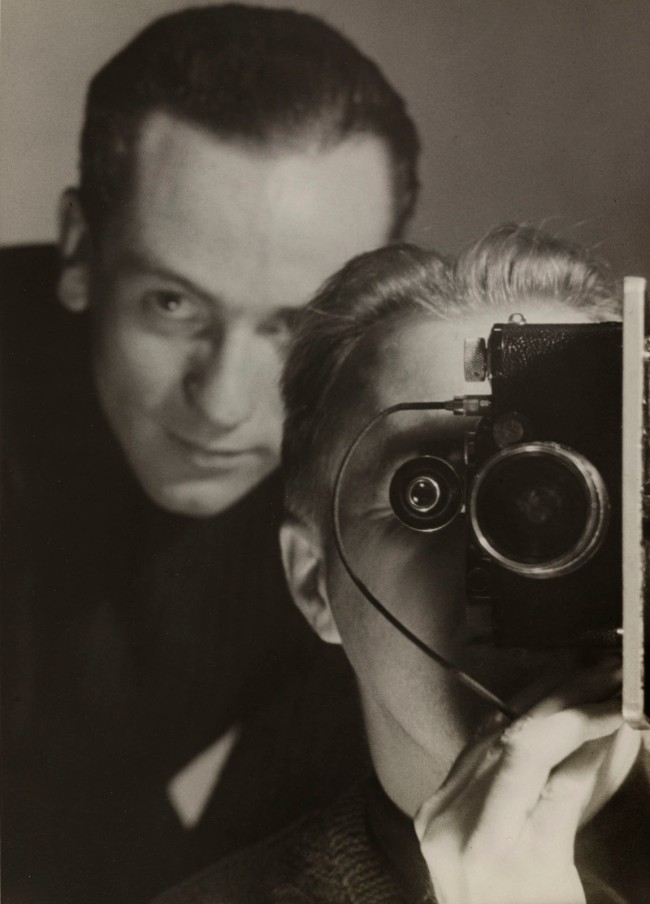
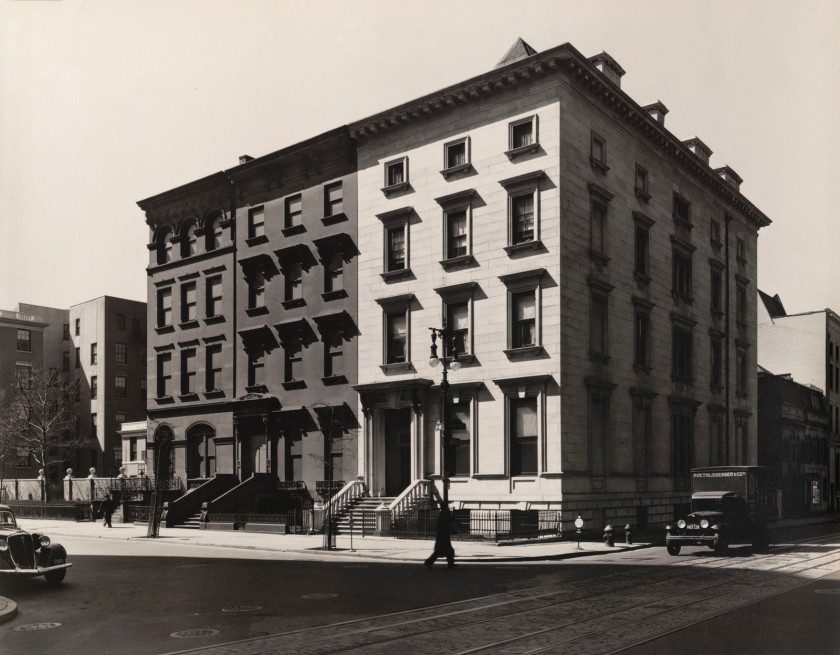
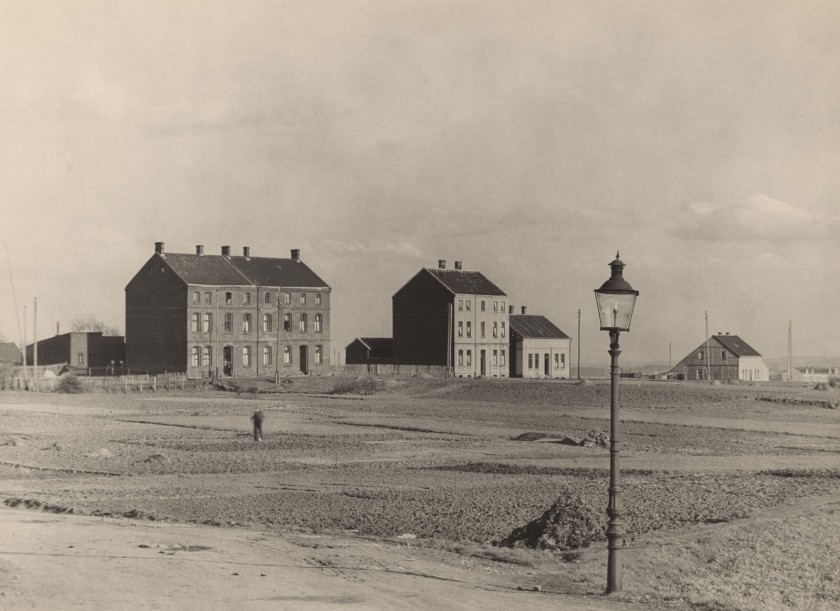
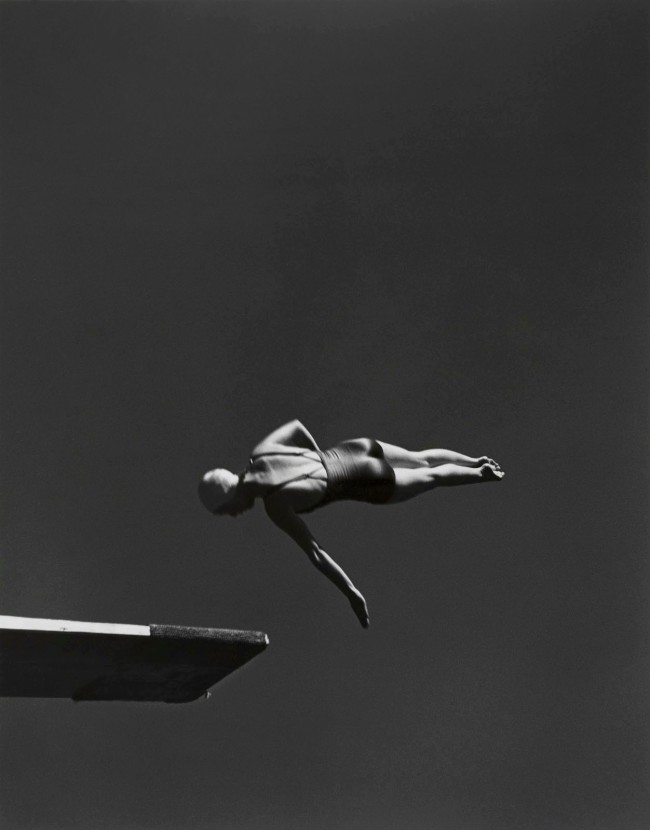
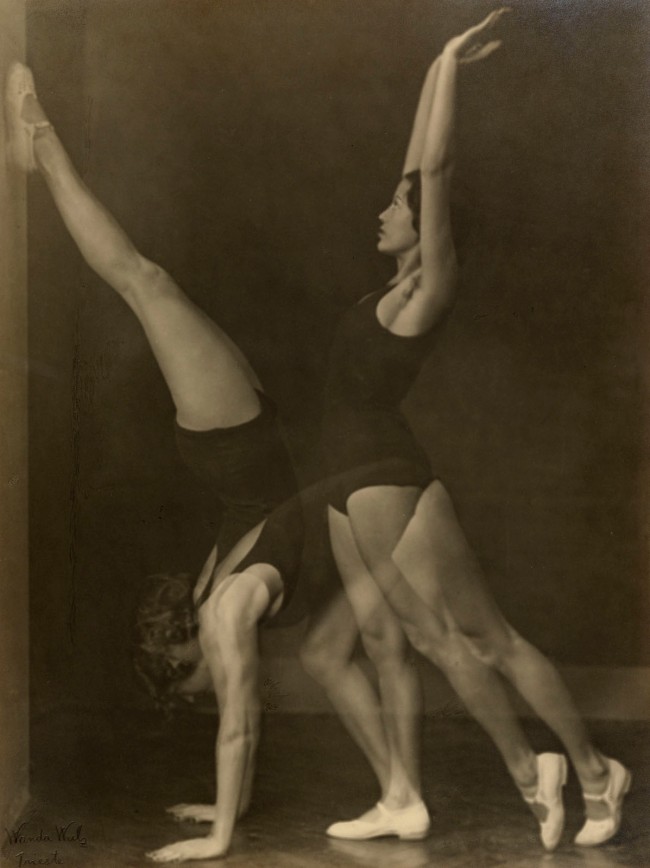
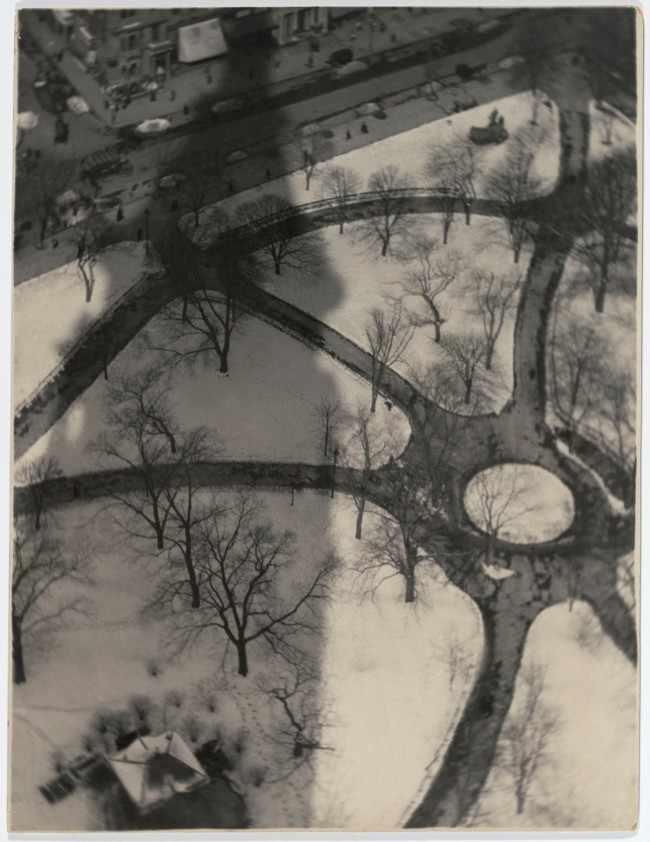
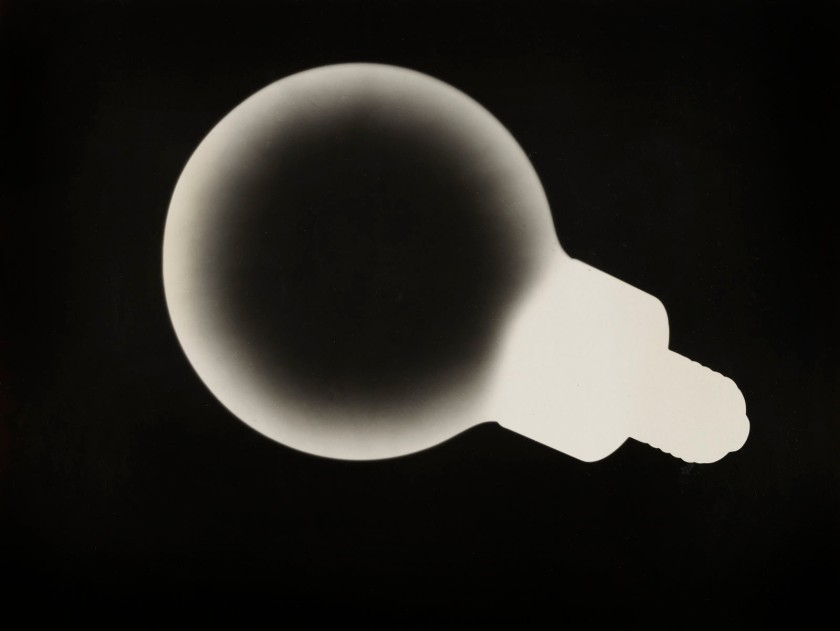
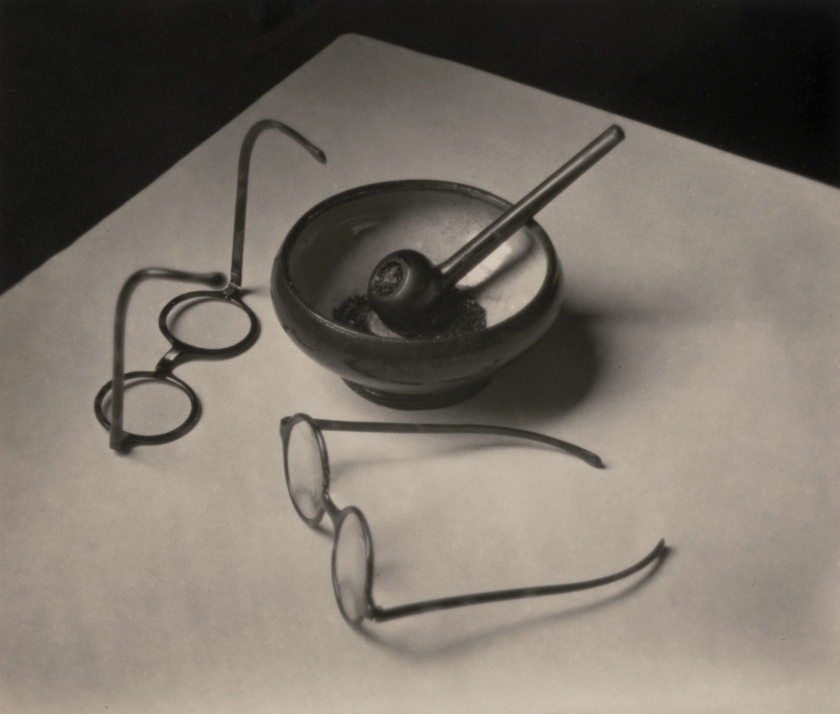
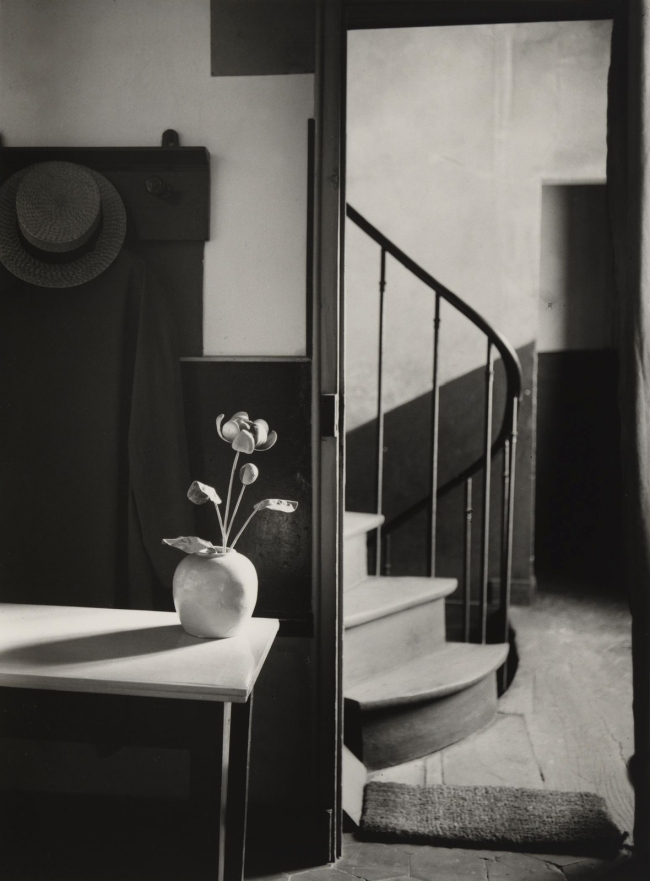
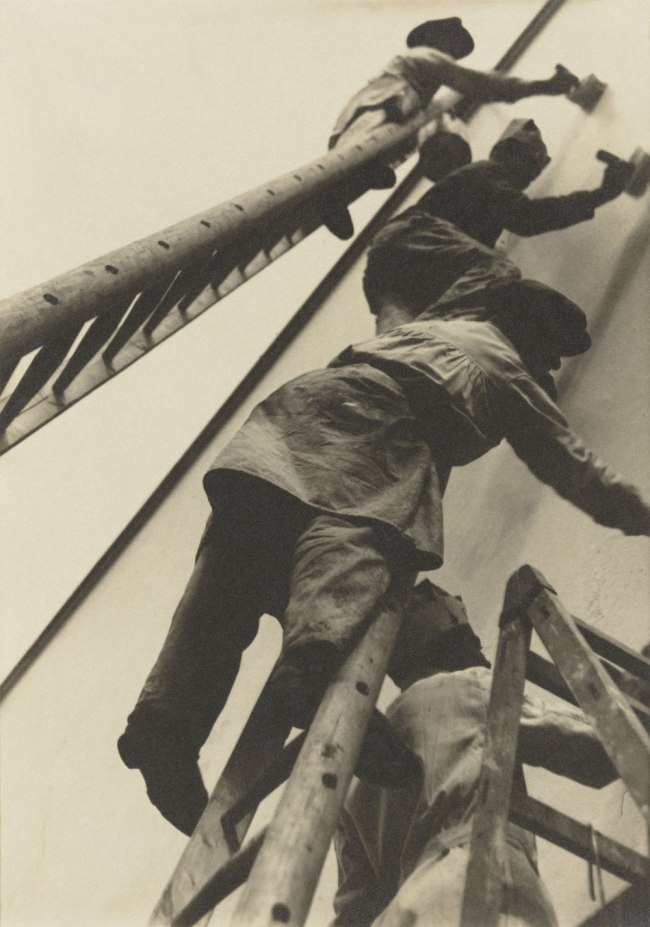
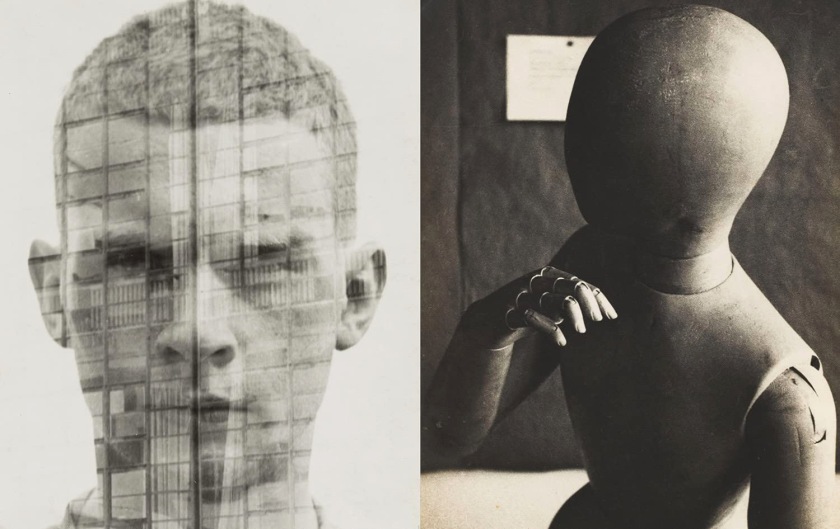
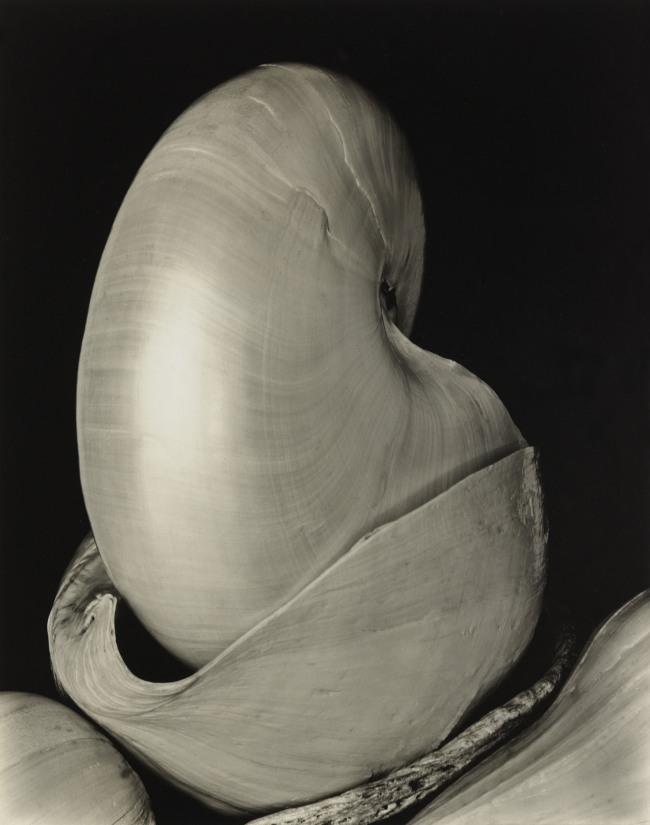
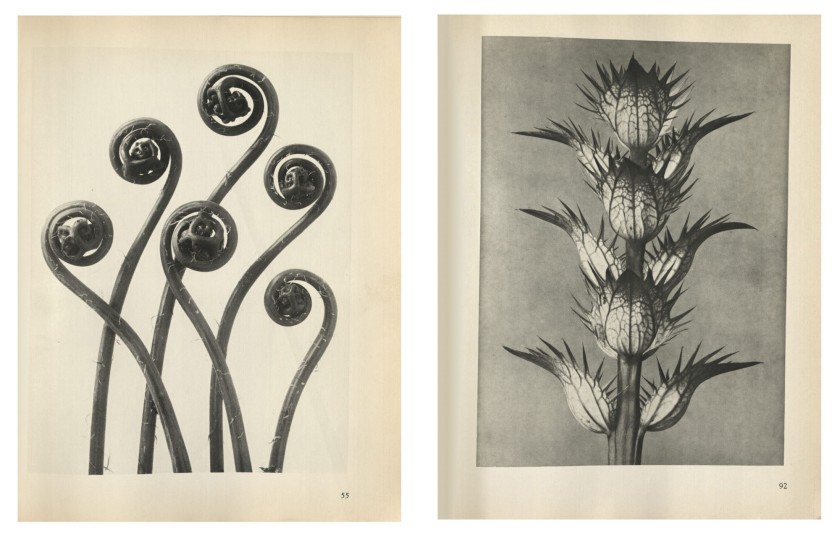
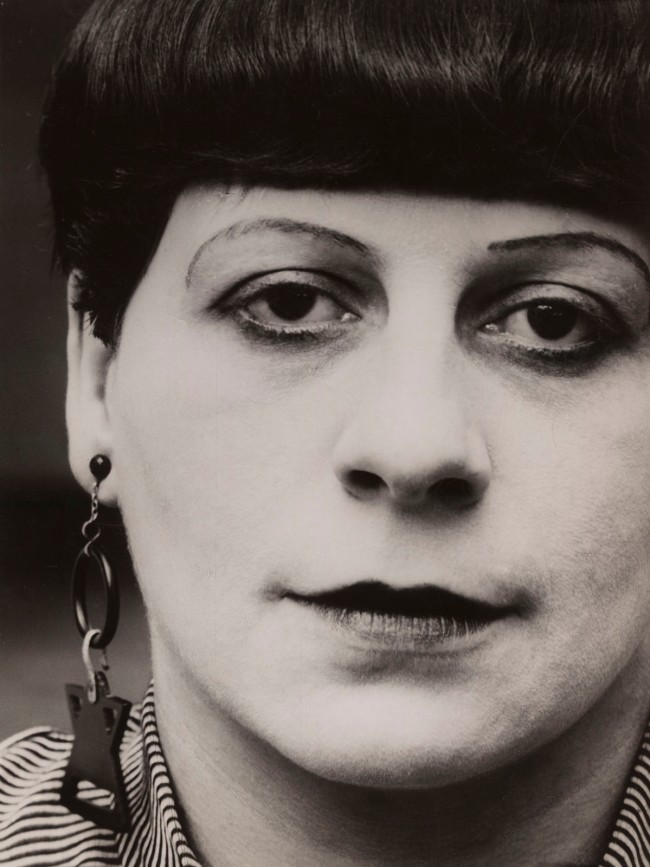
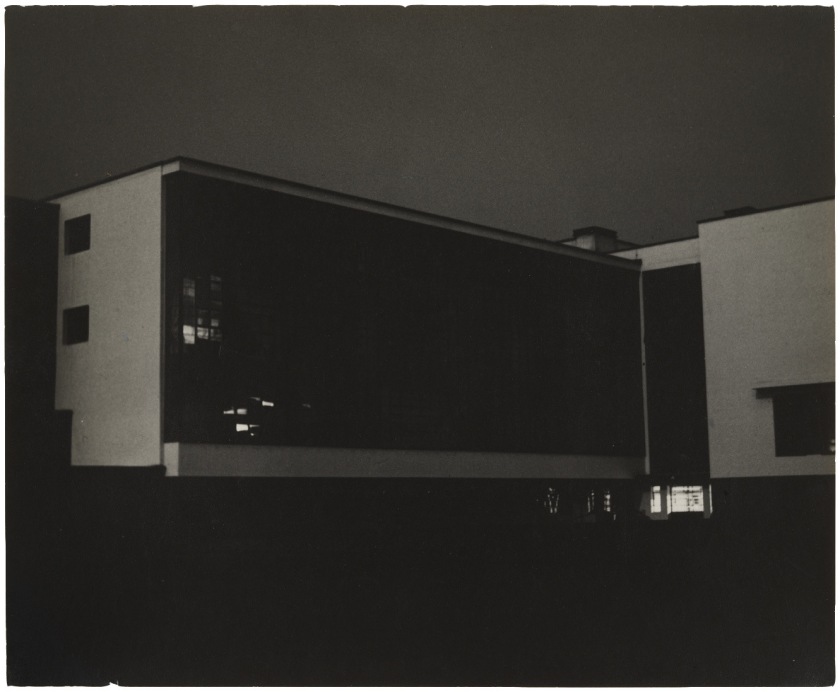
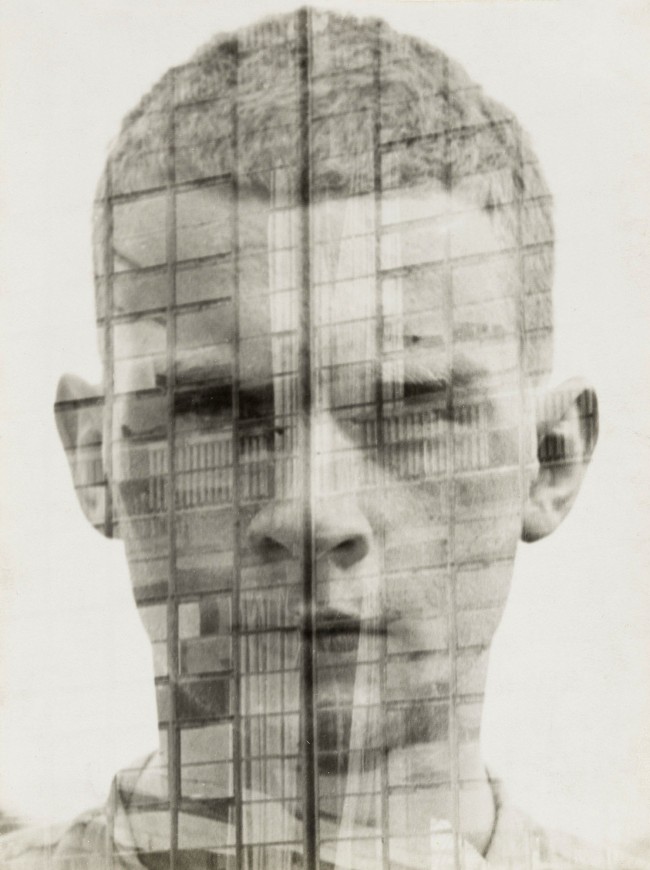
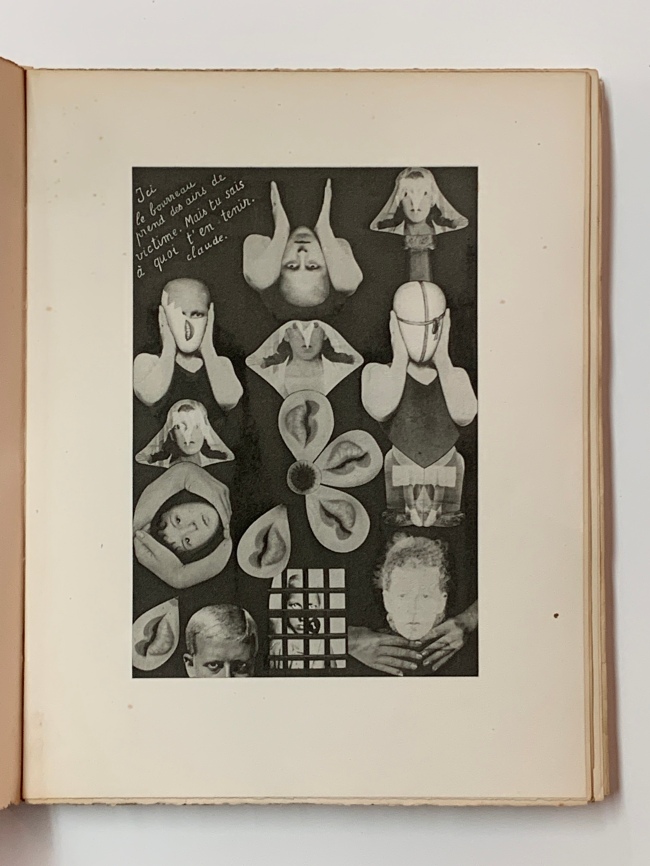
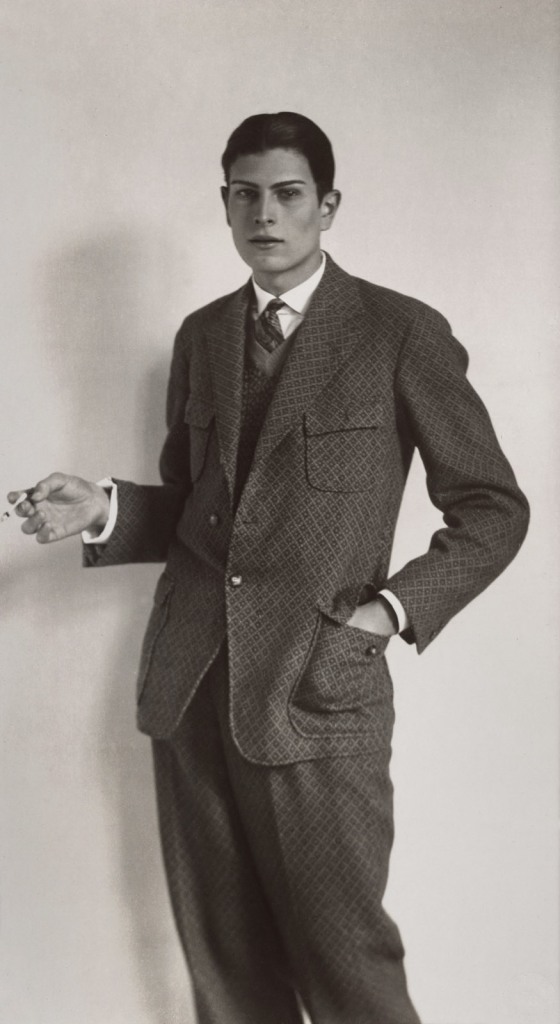
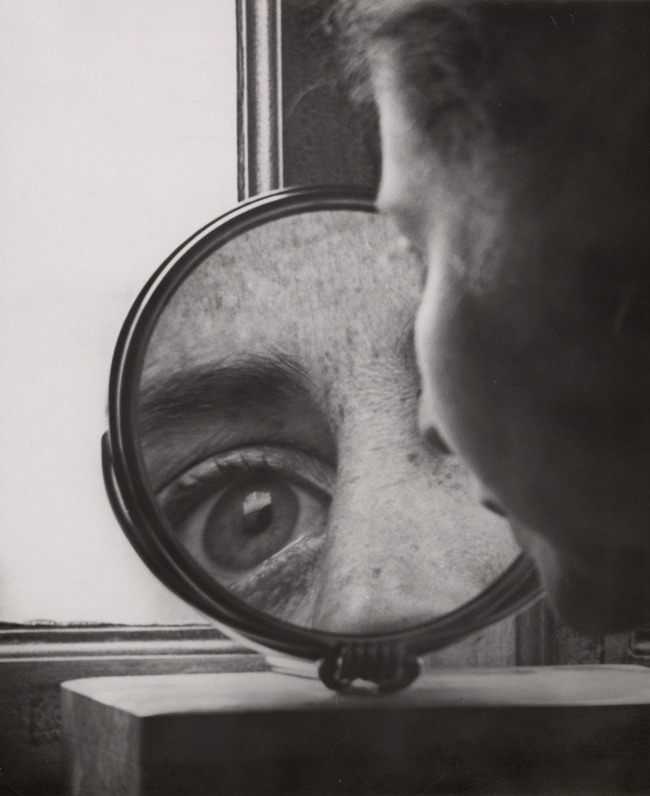
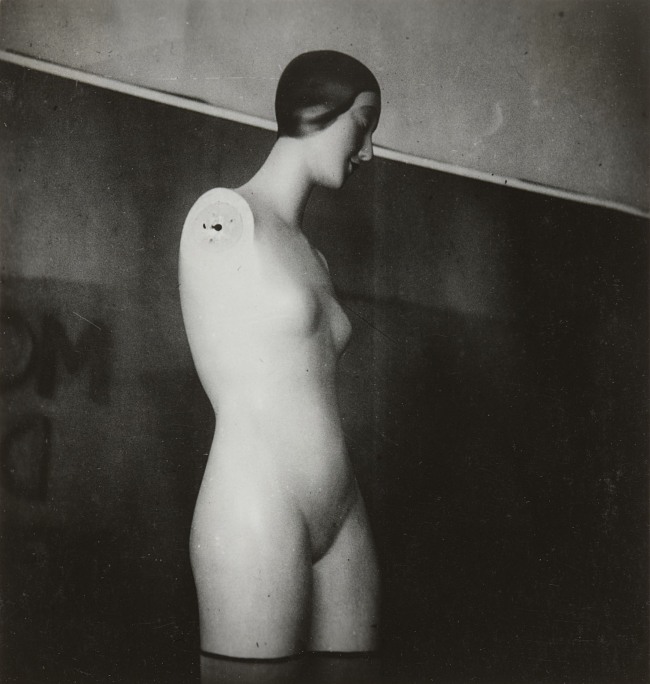
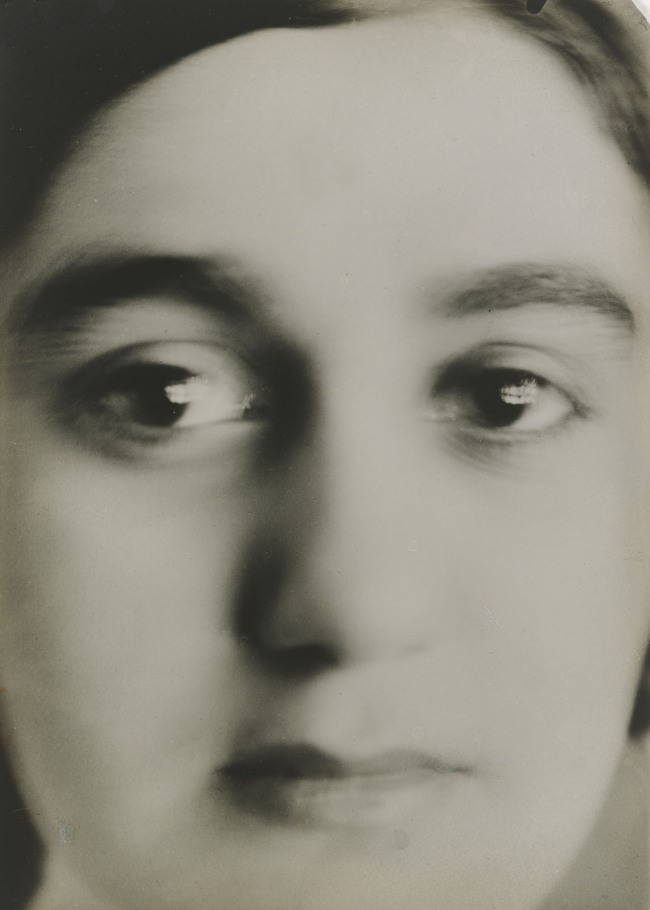
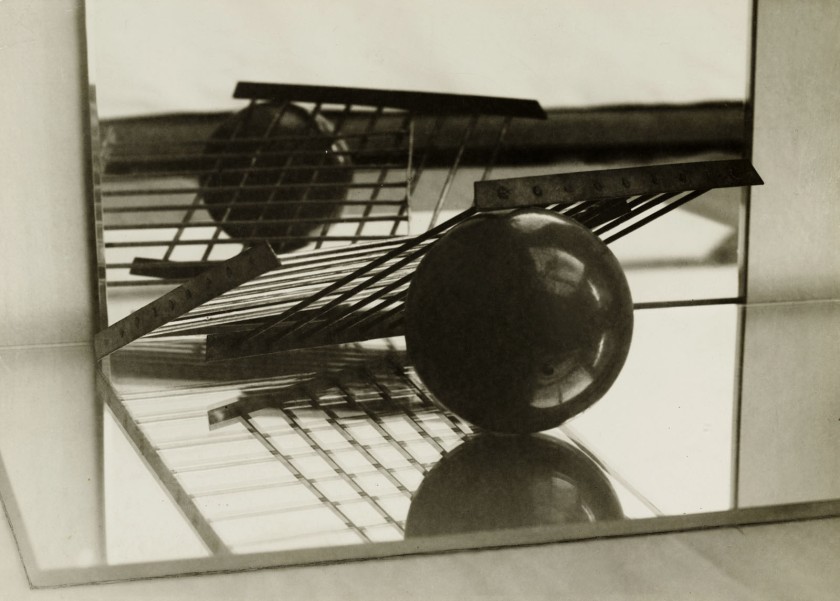















































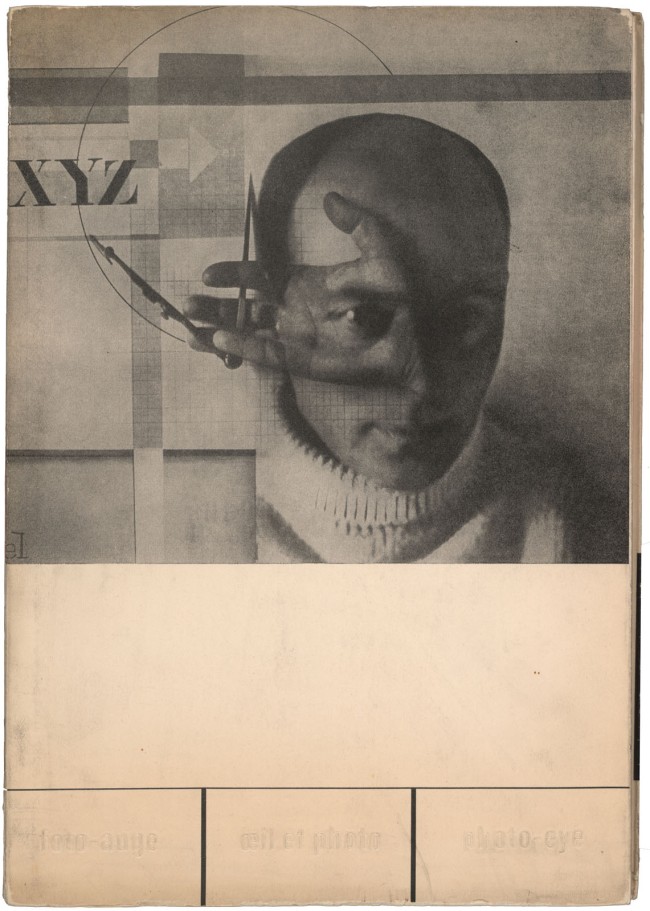


























![Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) 'George Sand (Amandine-Aurore-Lucile Dupin), Writer' c. 1865 Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) 'George Sand (Amandine-Aurore-Lucile Dupin), Writer' c. 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/10/realideal5-web.jpg?w=650&h=854)
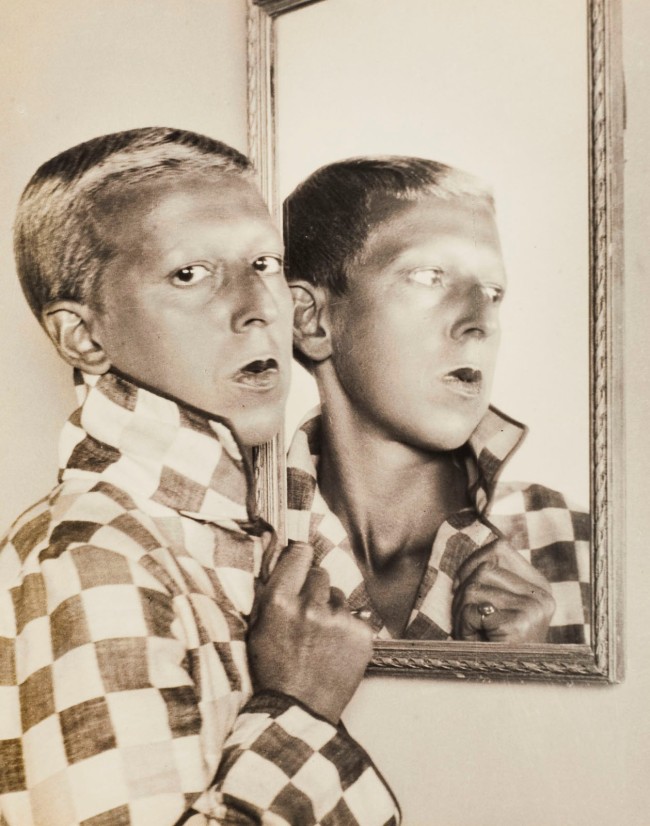
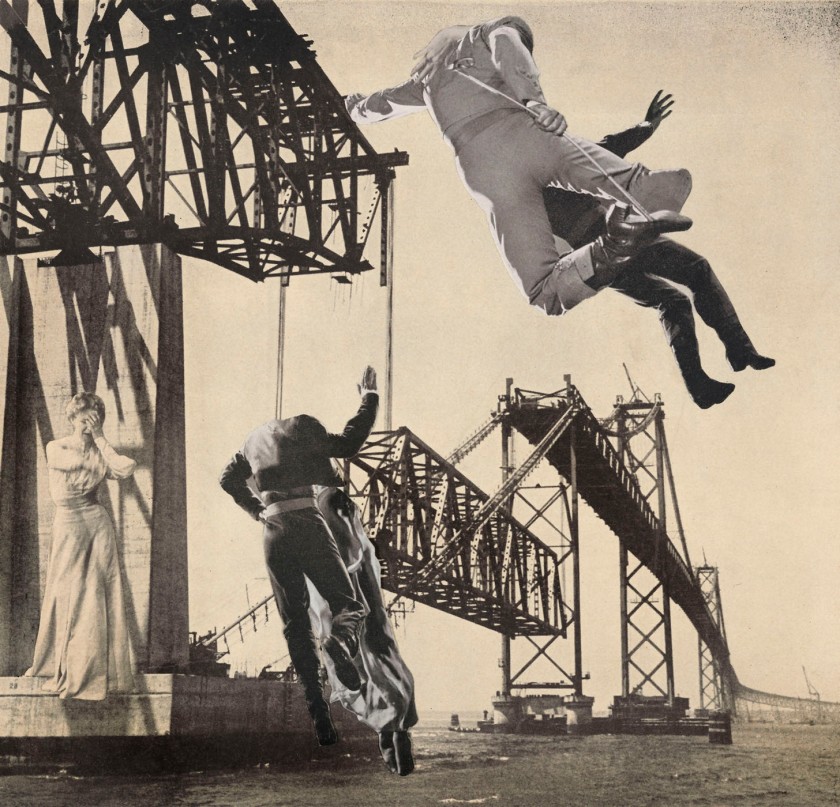
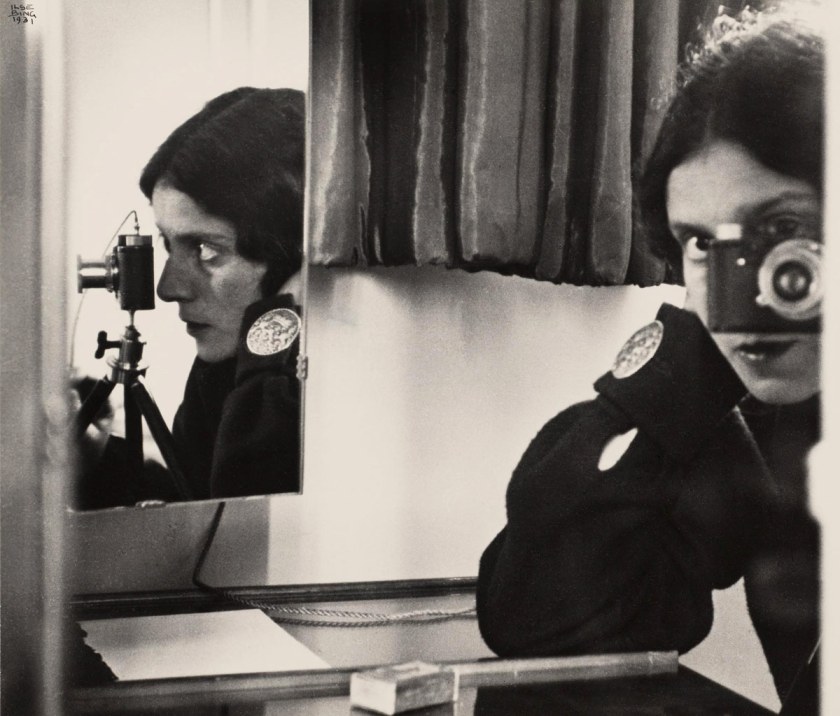
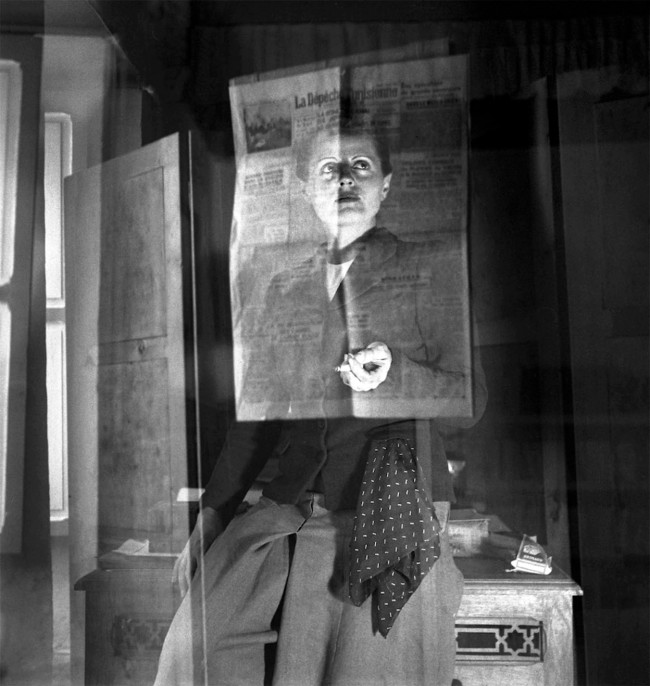
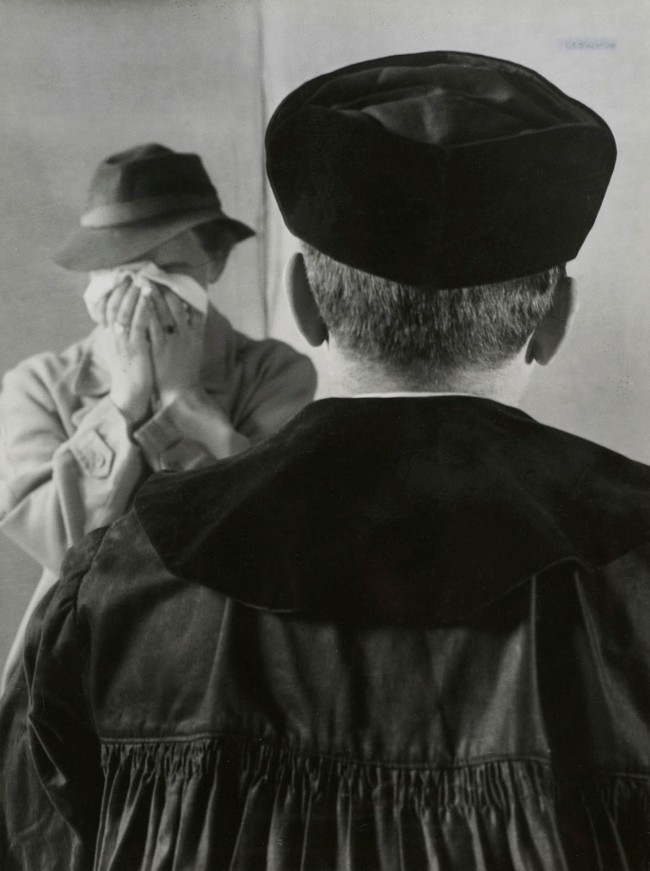
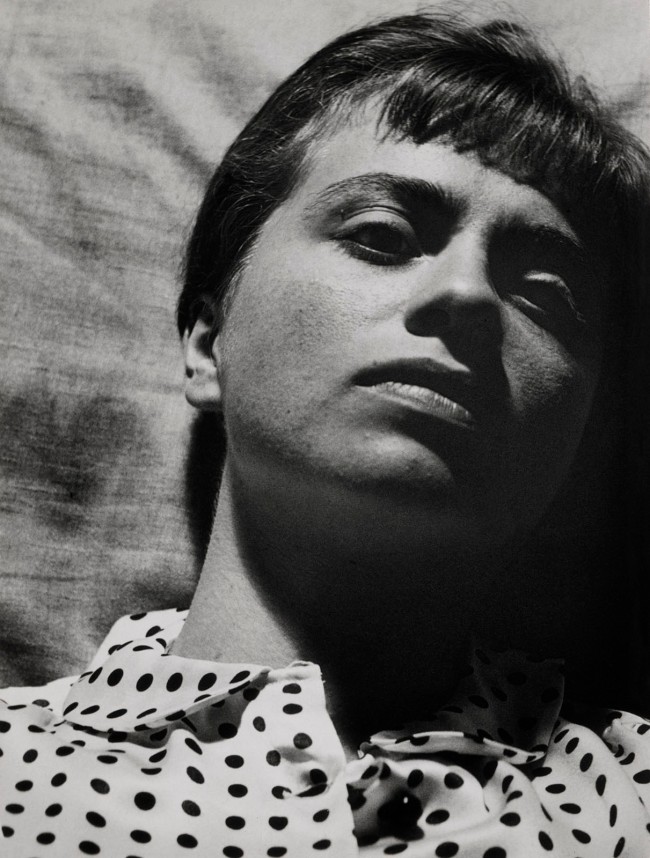
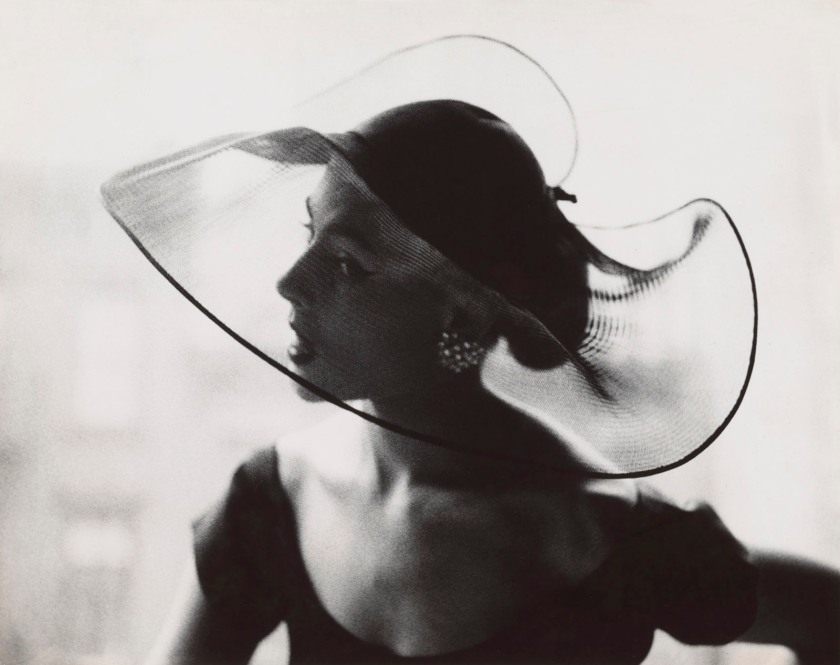
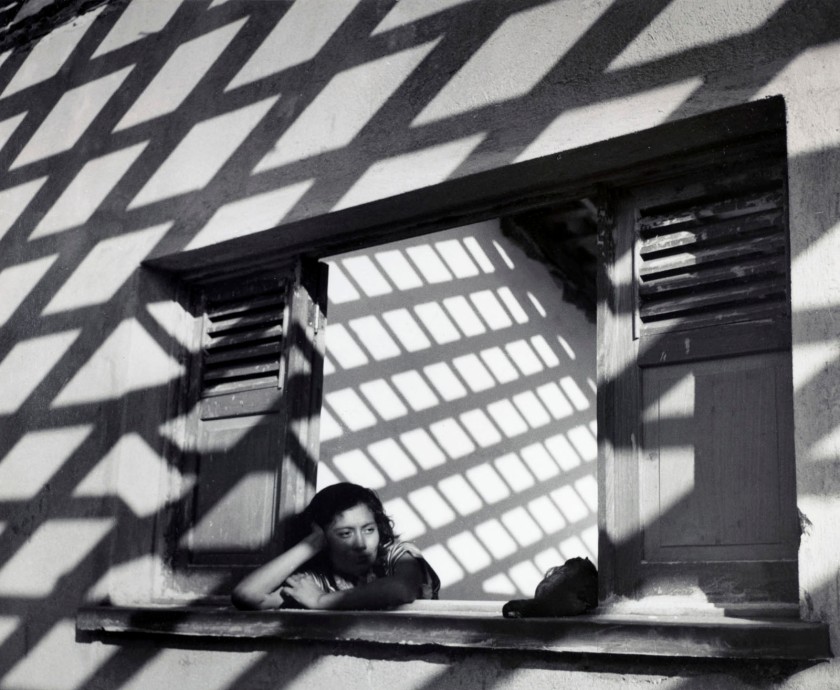
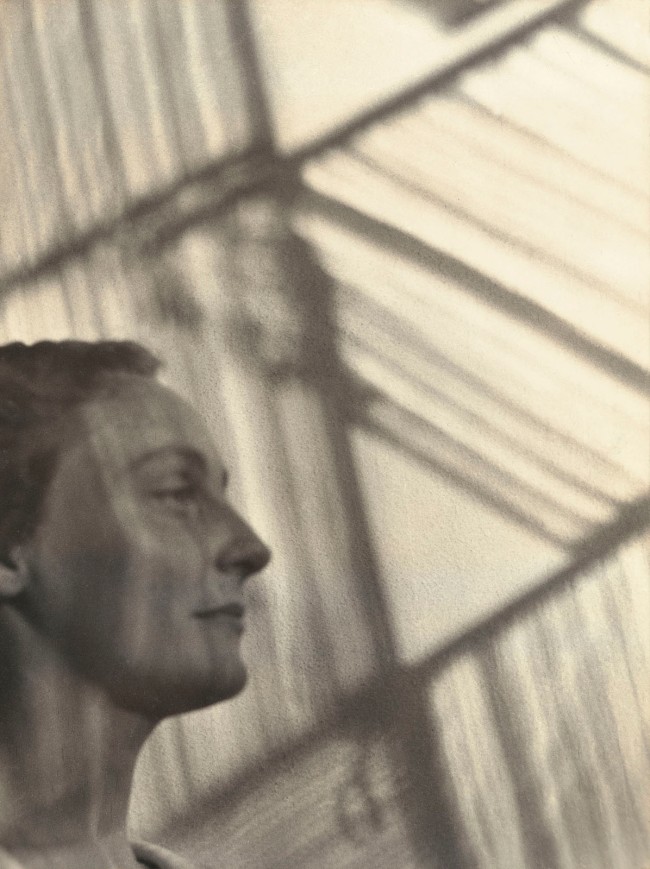
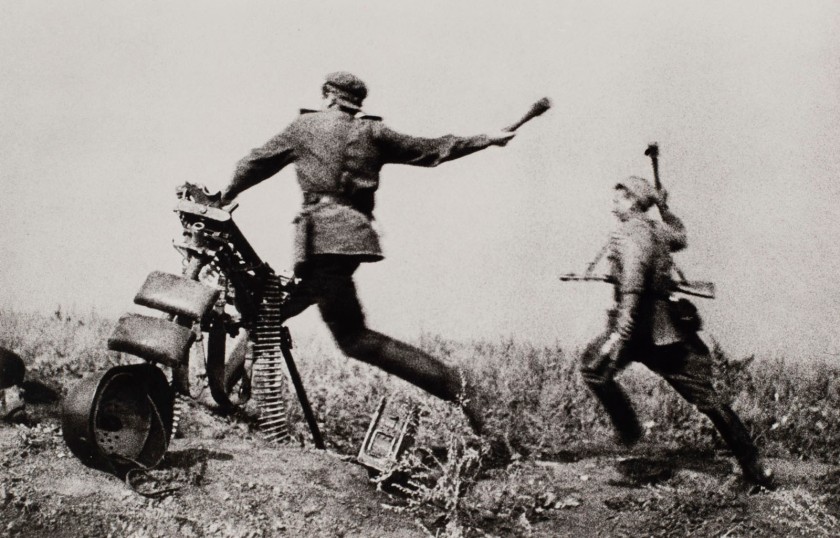
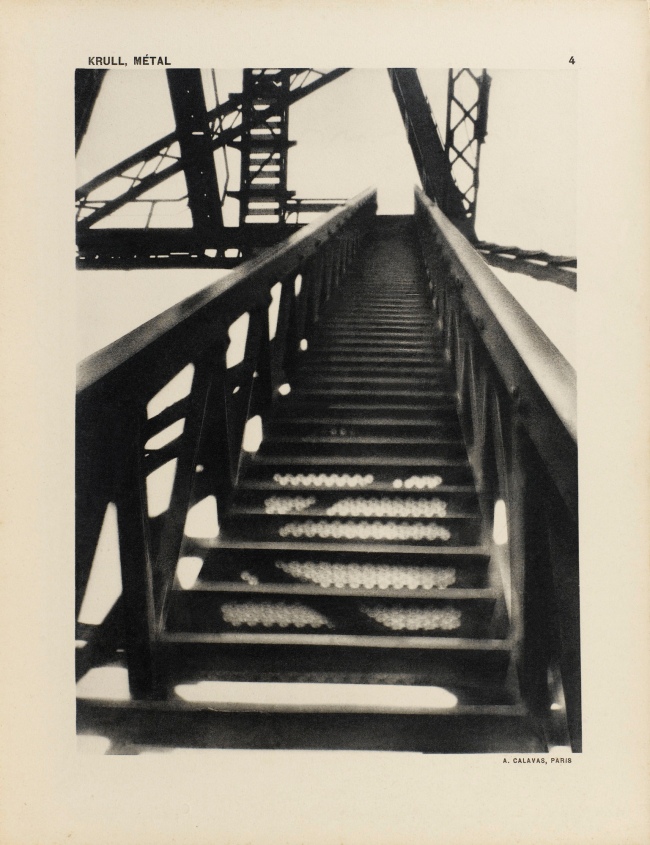
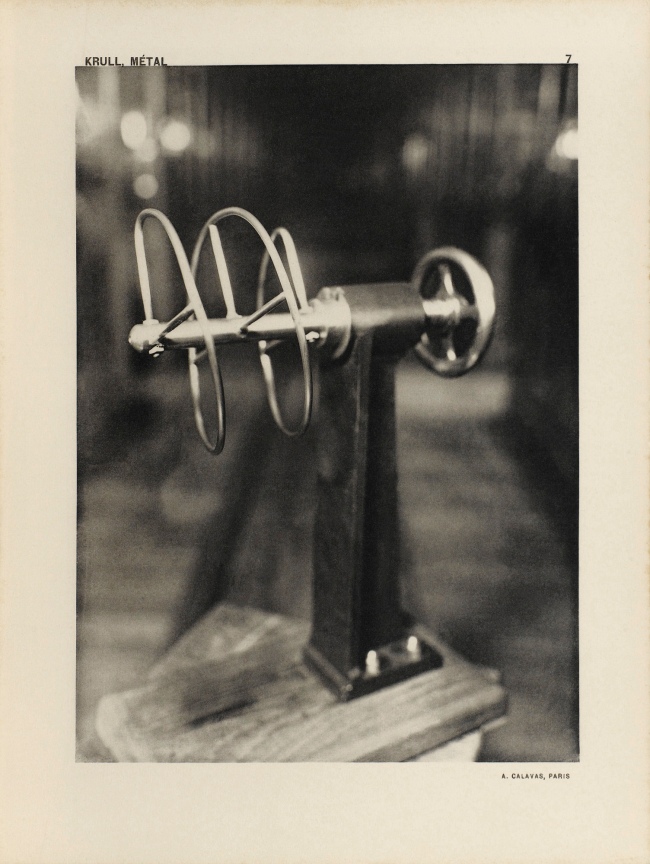
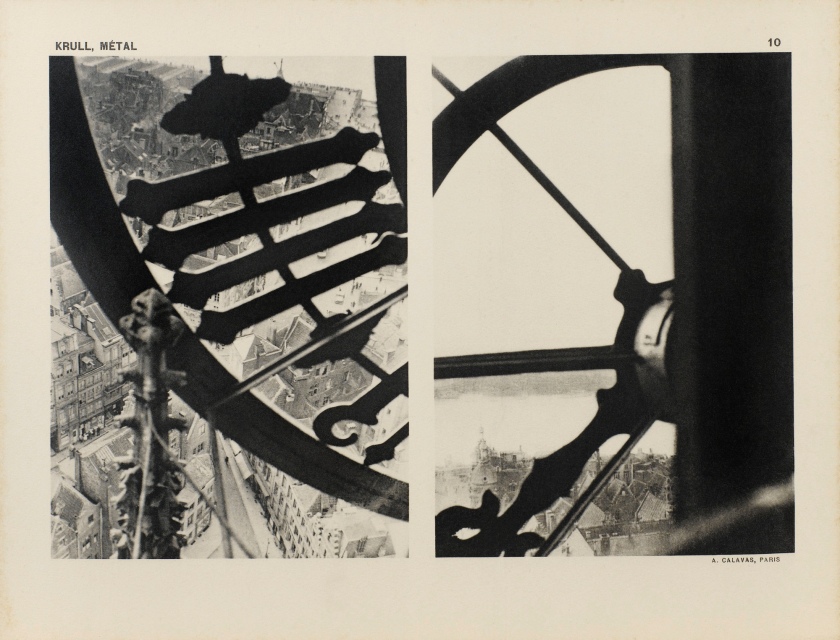
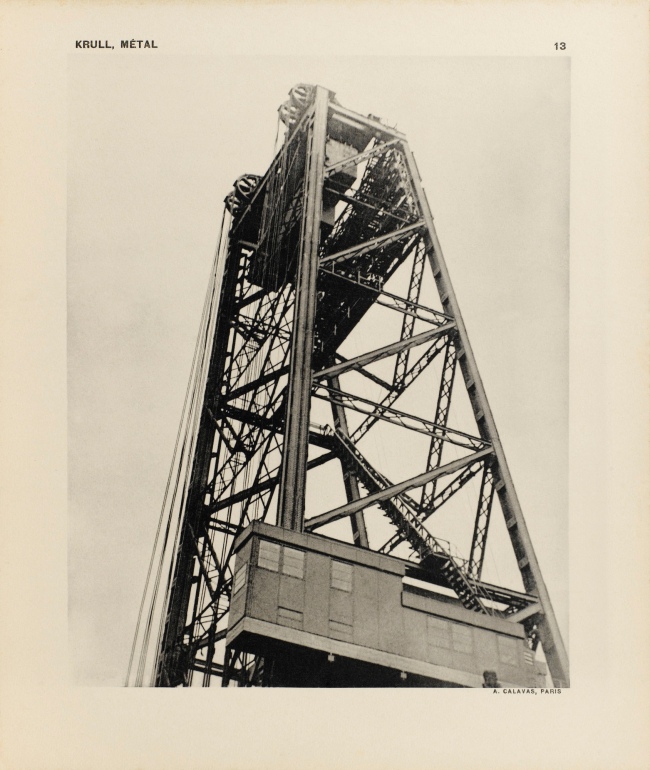
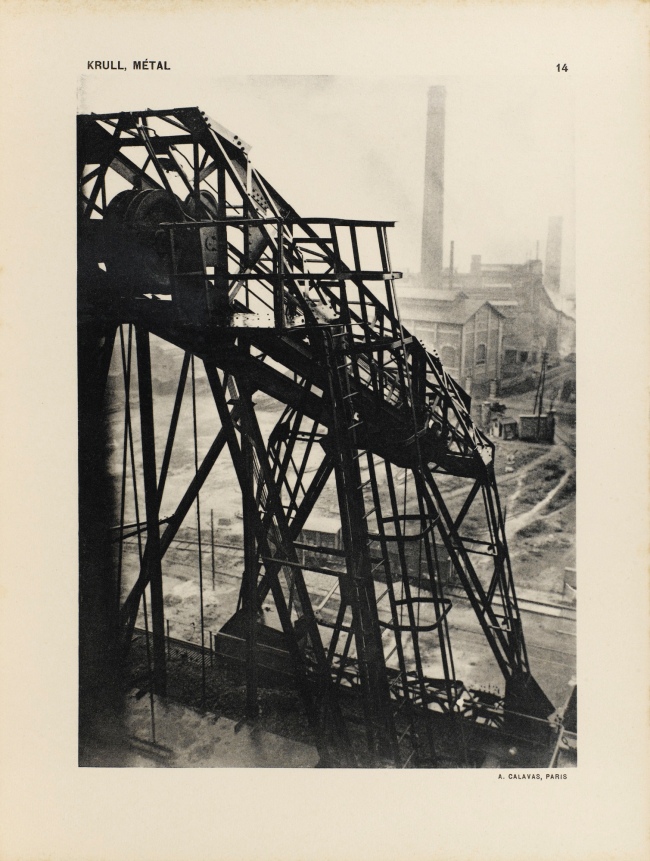
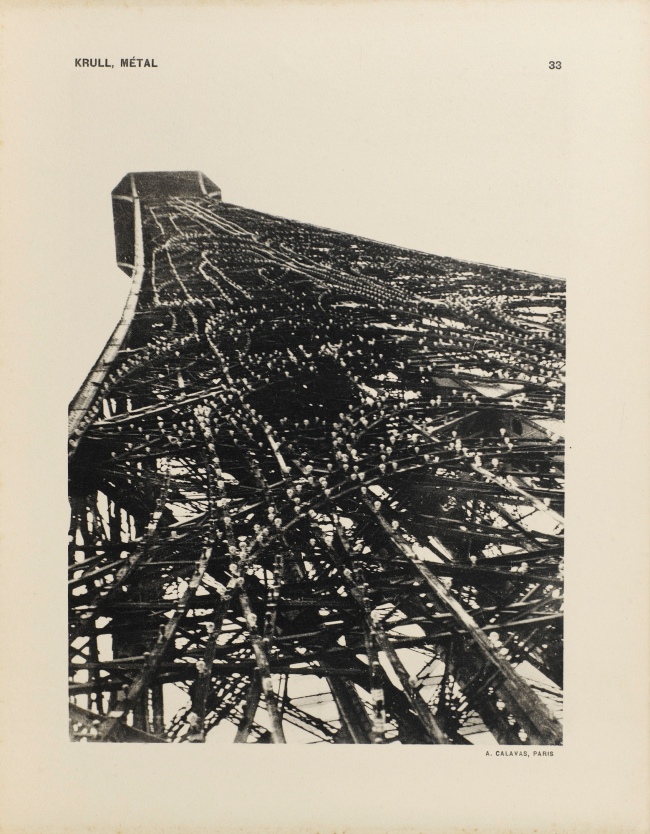
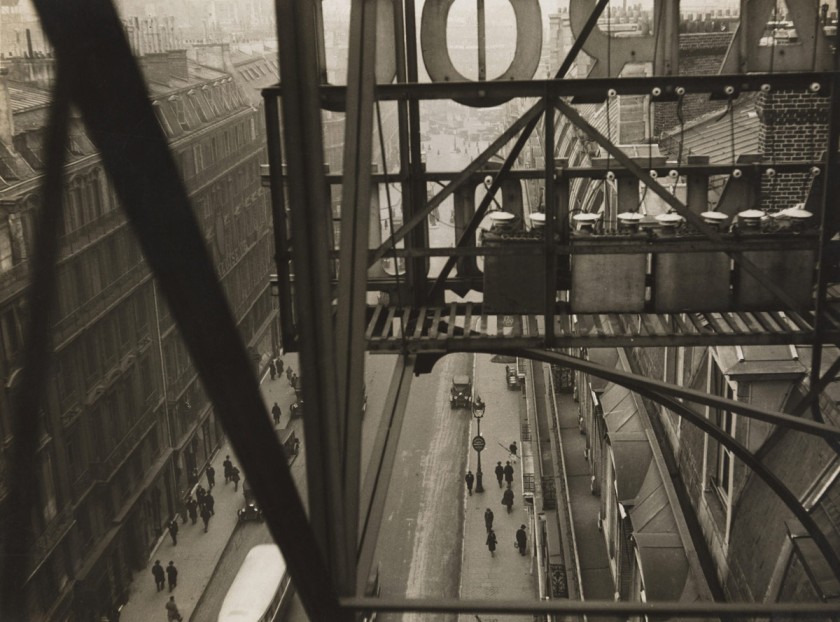












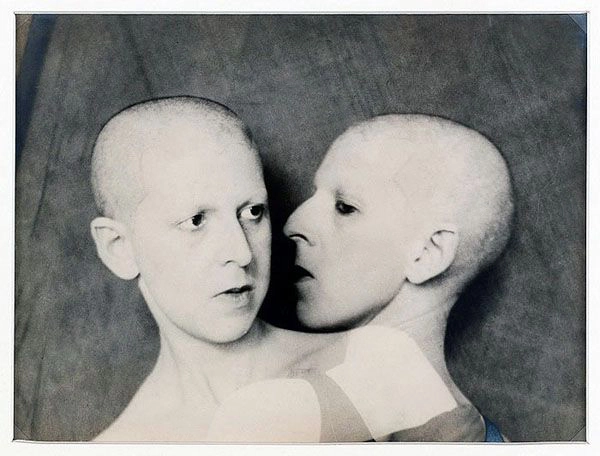









































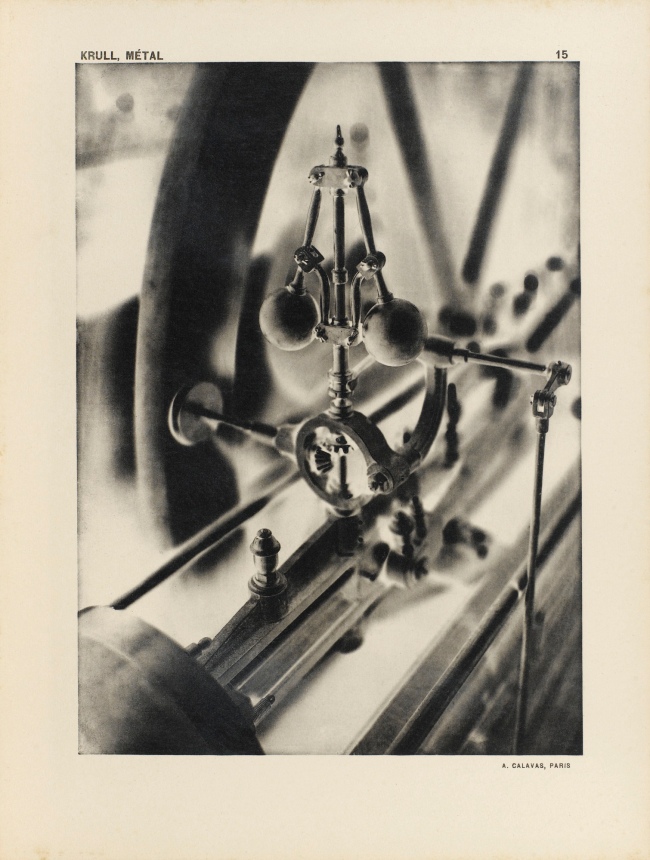
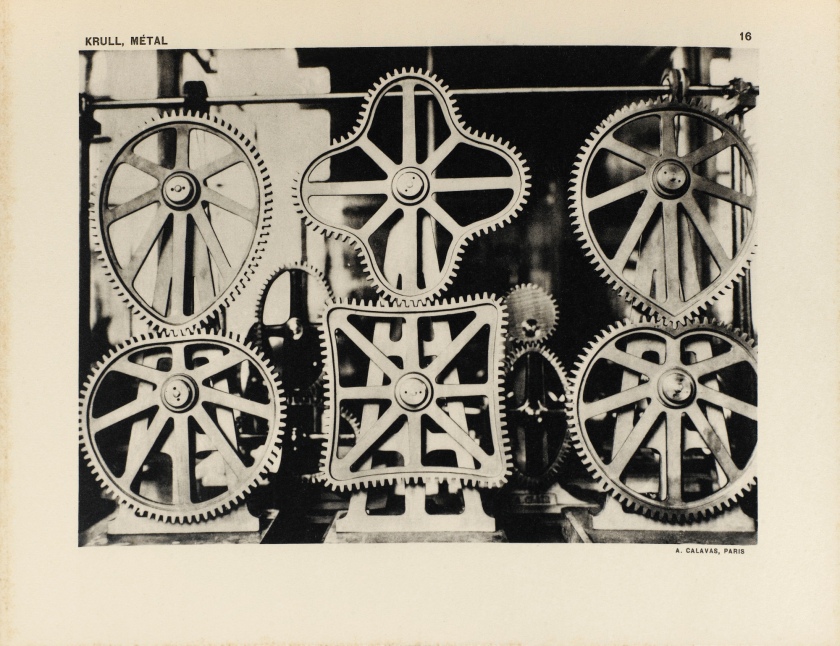
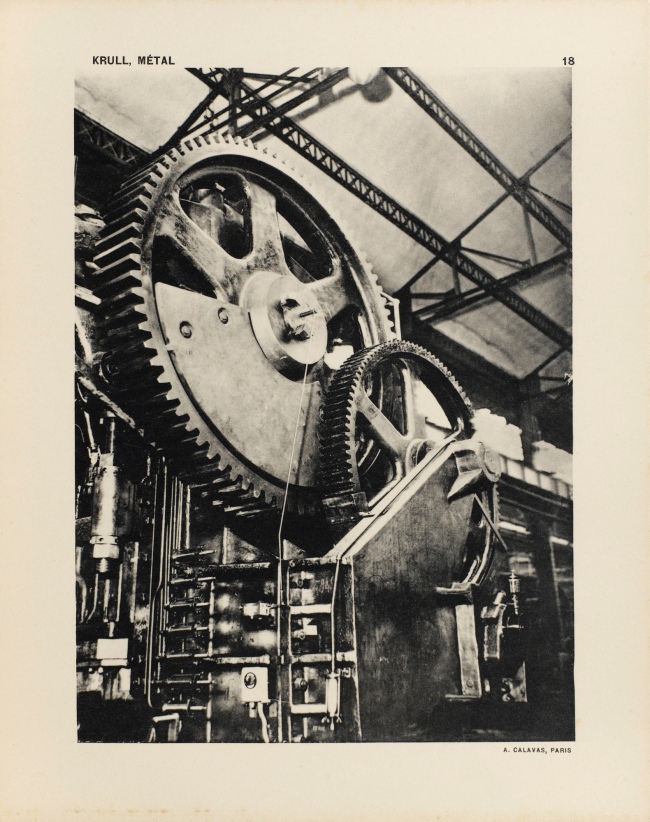






![Germaine Krull. 'Étalage: les mannequins [Display: mannequins]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/gkrull_09-web.jpg?w=840)
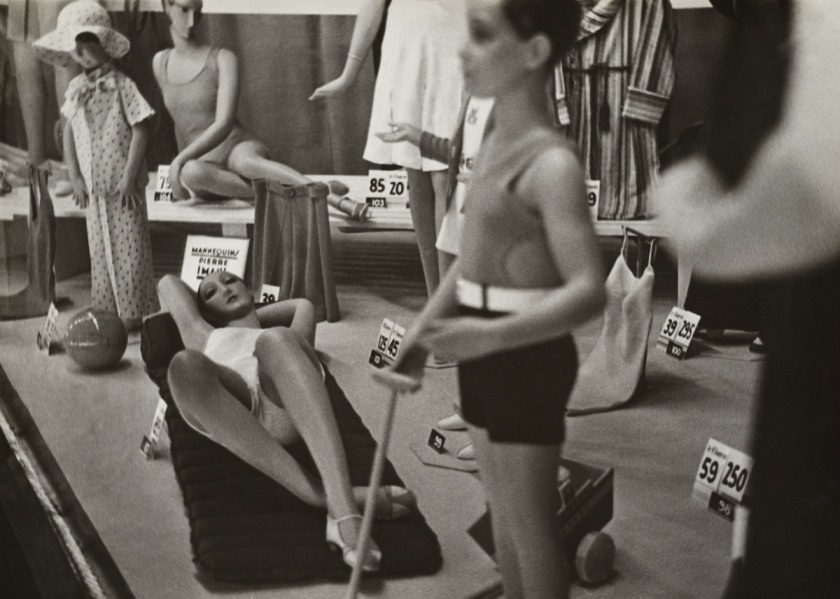
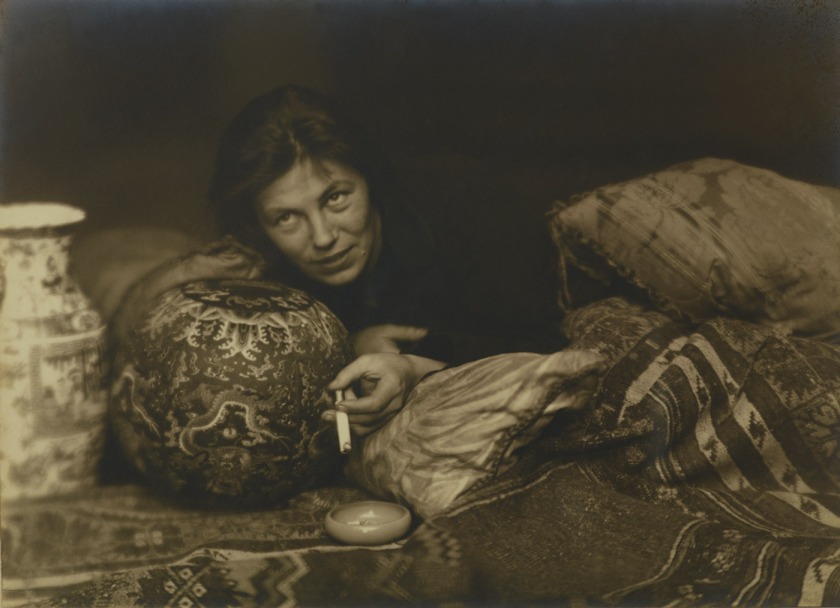
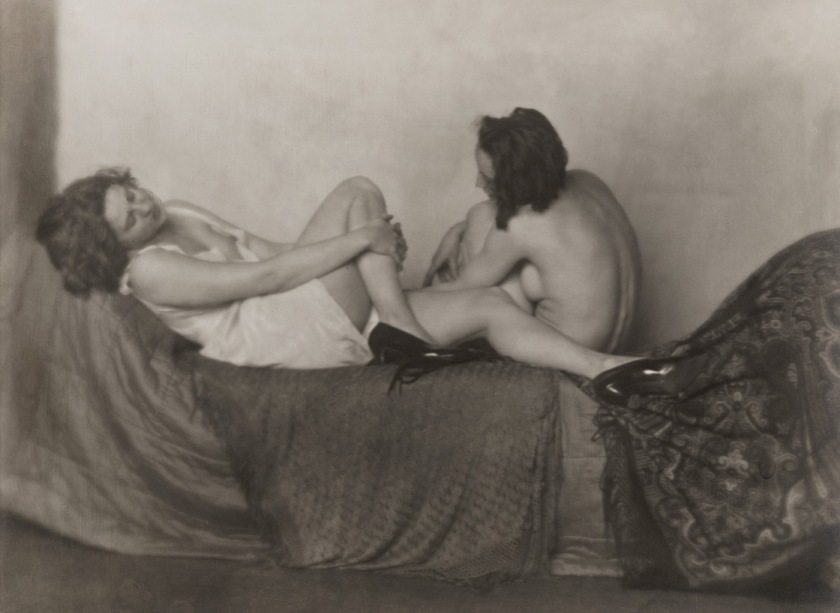
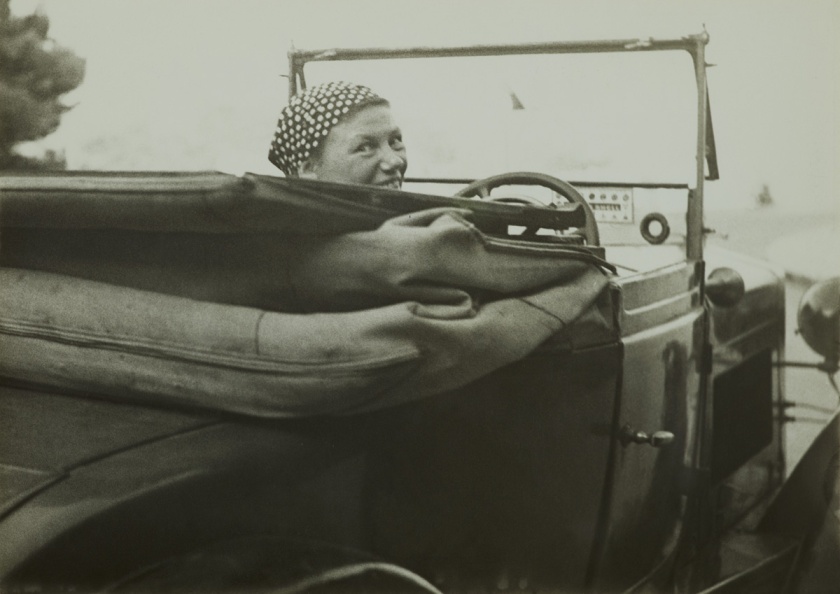
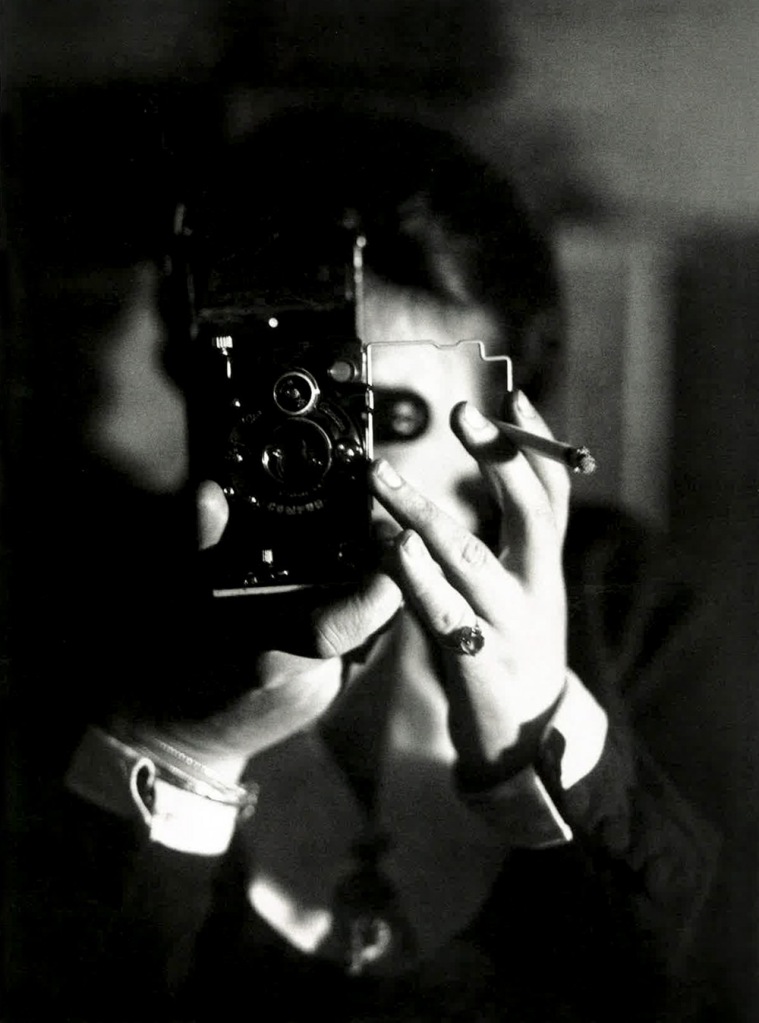
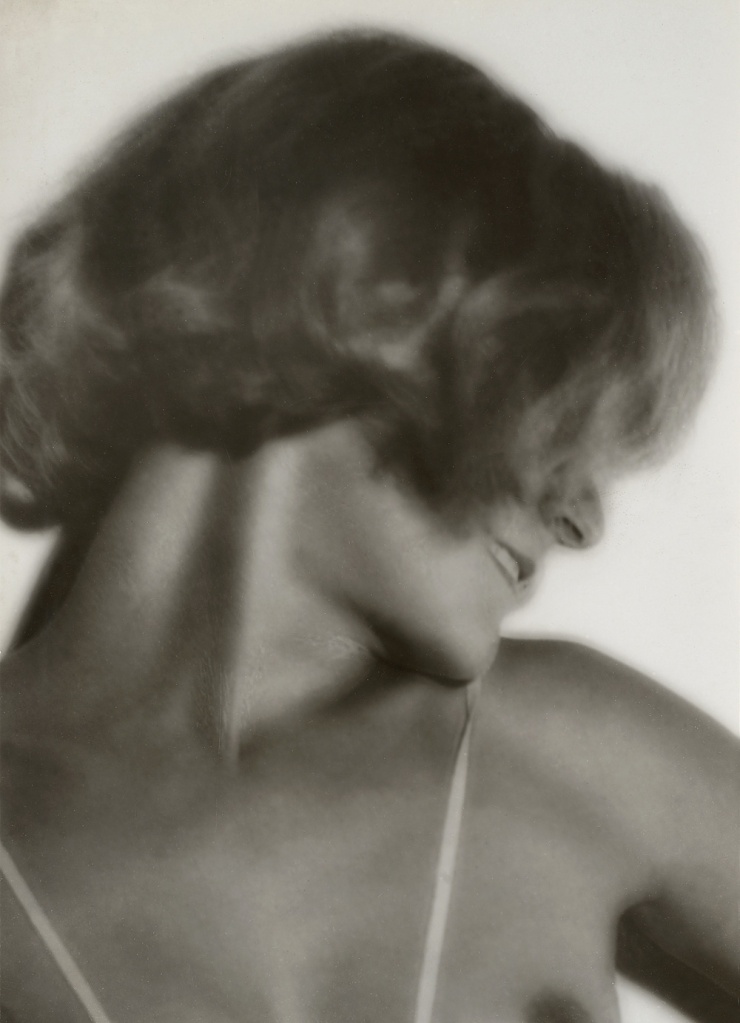







![Germaine Krull. 'Étude pour La Folle d’Itteville [Study for The Madwoman of Itteville]' 1931 Germaine Krull. 'Étude pour La Folle d’Itteville [Study for The Madwoman of Itteville]' 1931](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/gkrull_14-web.jpg?w=767&h=1024)
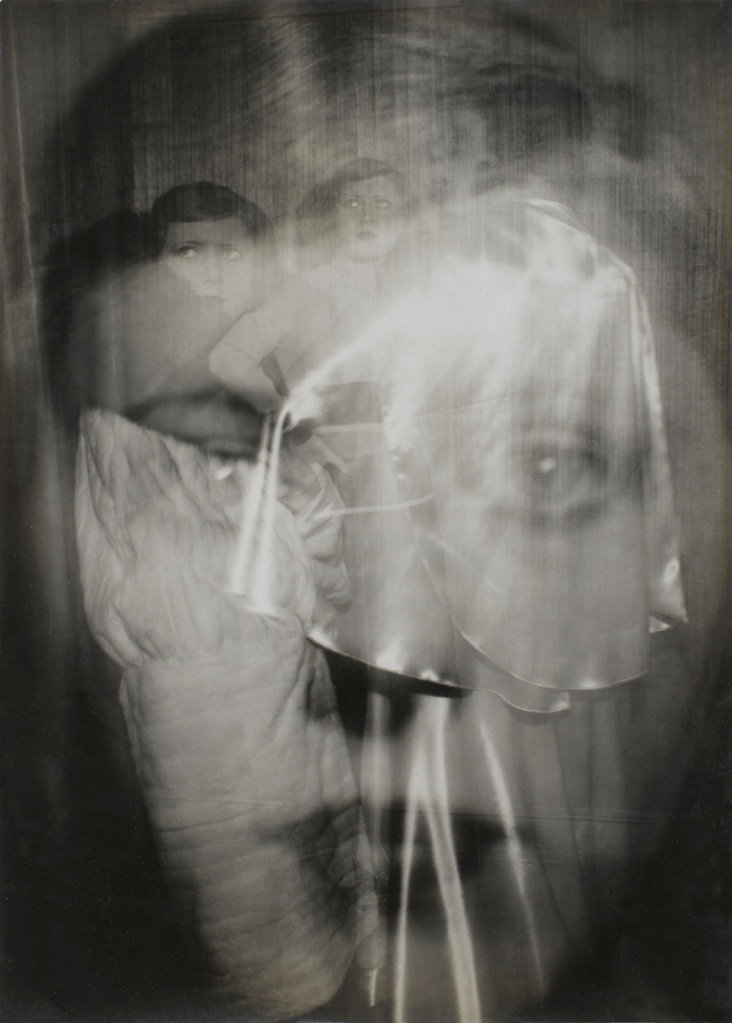
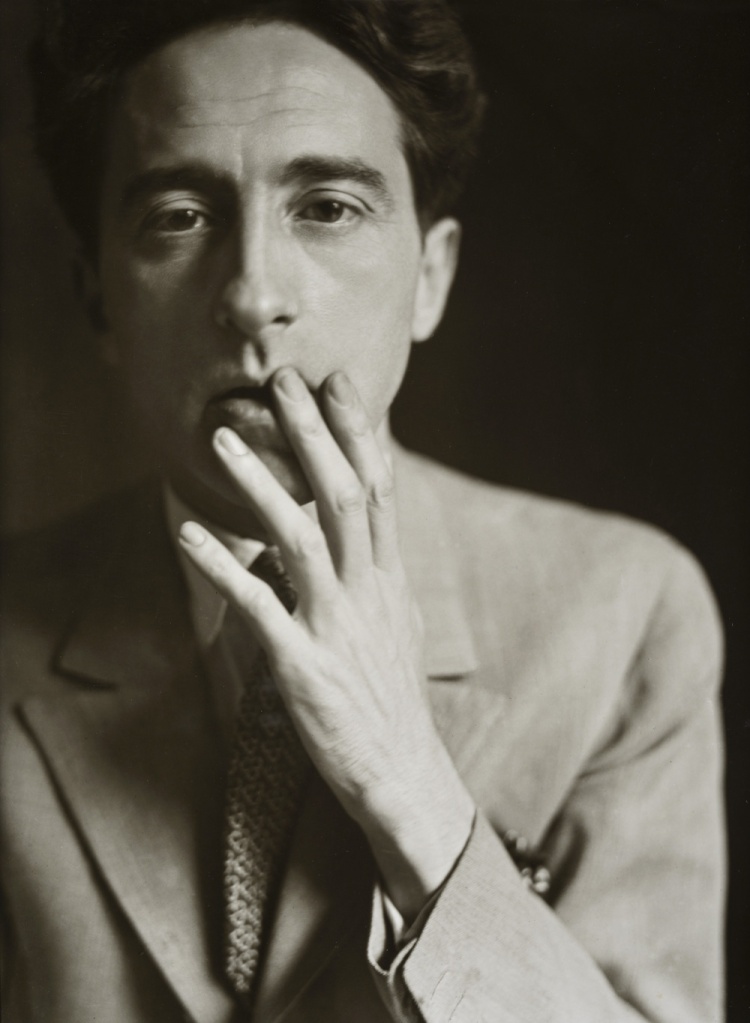
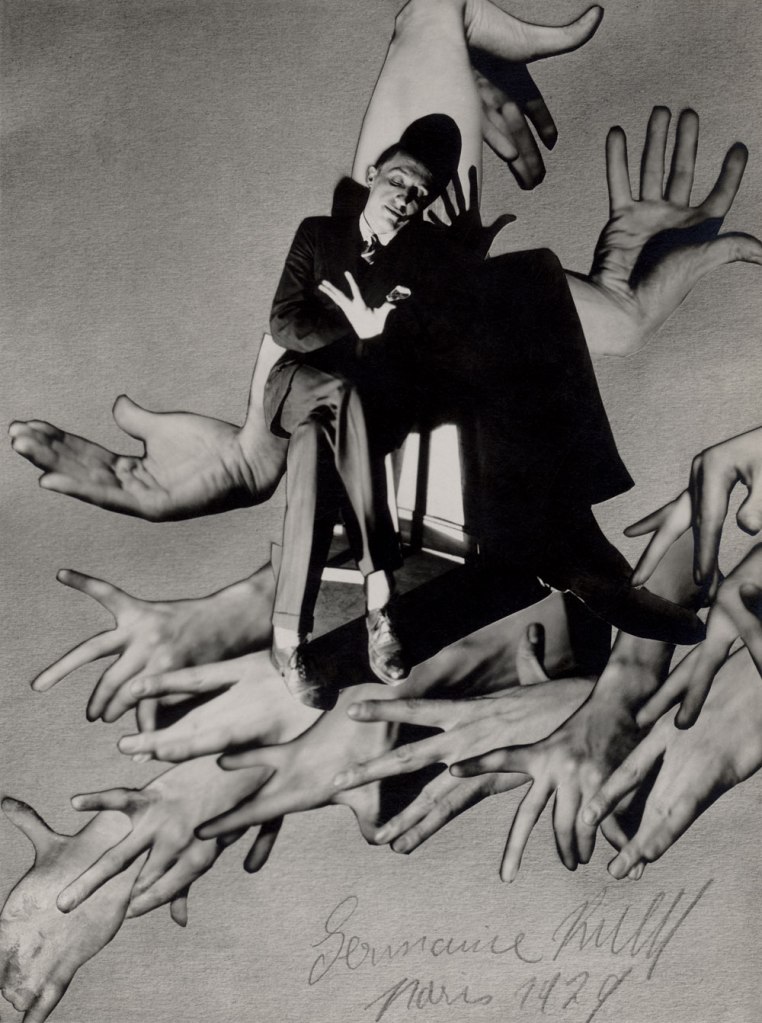
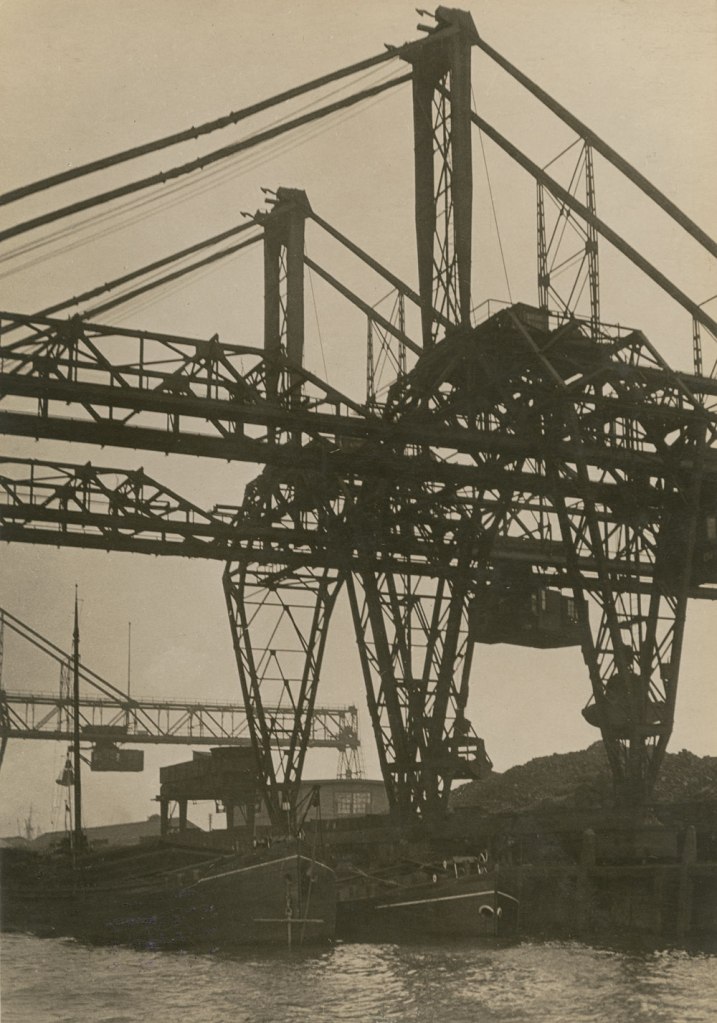

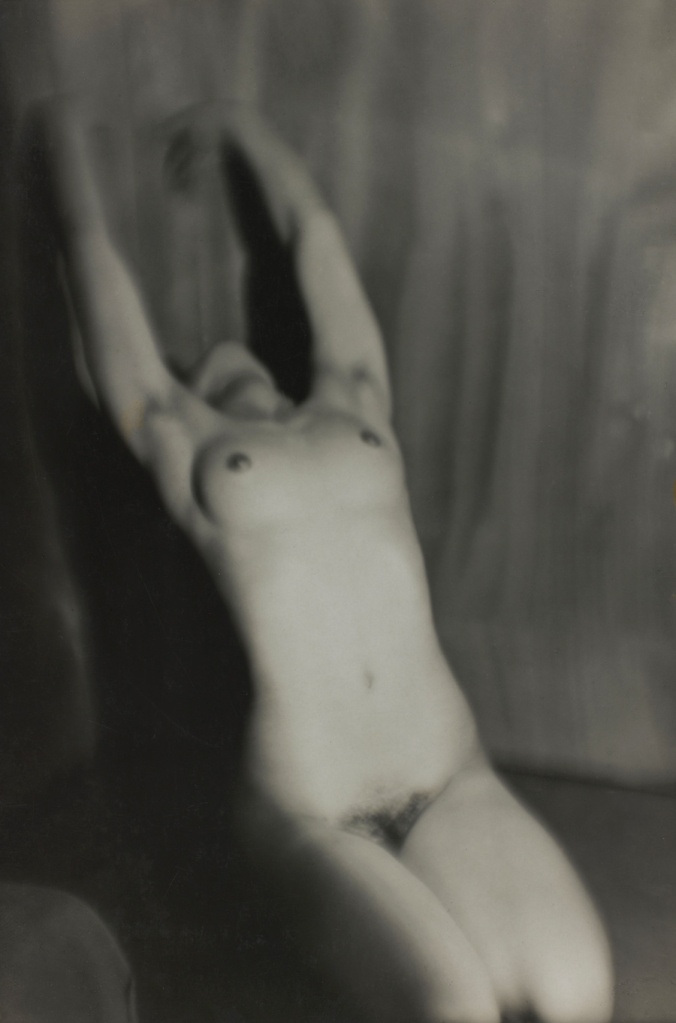













You must be logged in to post a comment.