Exhibition dates: 25th February – 13th August 2023
Curator: Teresa Gruber at Fotostiftung Schweiz
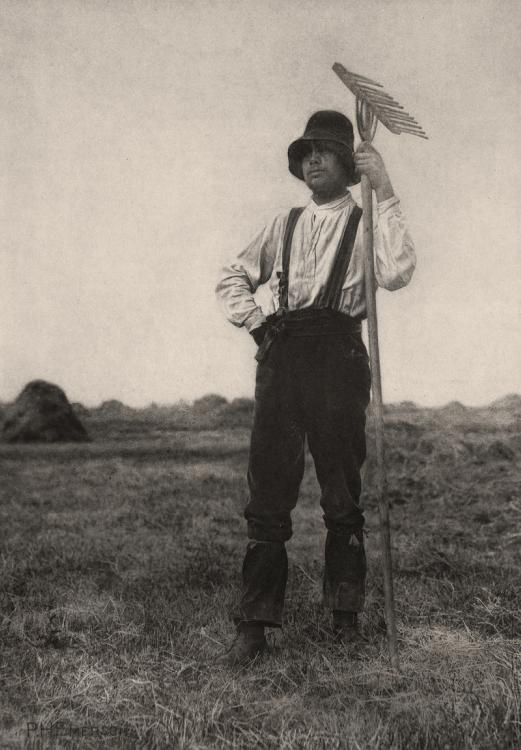
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
In the children’s room
1978
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
A short text this week because I’m suffering from sinusitis and headache.
Annelies Štrba’s “intimate family scenes… breaking away from the rules of perfect photographic reproduction” are the antithesis – or anti-thesis – of last weeks posting were the curators conceptualised 1930s American documentary photography as a sort of reality-dream.
Here there is no need to conceptualise such a response to the photographs for Štrba’s unconventional, poetic photographs really are a mixture of dream and reality. At the limits of visibility Štrba’s glances, glimpses, clefts, over / under exposures, double exposures, colour disfigurations and ingressions – the process by which a potentiality enters into actuality – offer to the viewer a “no place” of becoming, where “recognition” is the trigger of exposure.
Like the sudden gust of wind drops the ripe apple. (Minor White)
It is difficult in a posting to leave an “impression” of an artists body of work in so few photographs, especially an artist who works in series of images. Therefore, I heartily recommend viewing the familial architectural Shades of Time series (1970-1997) on Annelies Štrba’s website.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Fotostiftung Schweiz for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
The exhibition Annelies Štrba – “My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds” focuses on Annelies Štrba’s early works. Black-and-white photo canvases, colour photographs and the projection Shades of Time show images from the years 1974 to 1997. These works are framed by her later expressionist video stills, a newly conceived projection with photographs from the years up to 2015 and staged scenes of fairy-tale princesses sleeping in enchanted landscapes. All the pictures revolve around the theme of family. Their juxtaposition enables an understanding of how this artist’s personal and artistic development over time is reflected in her view of children and grandchildren.
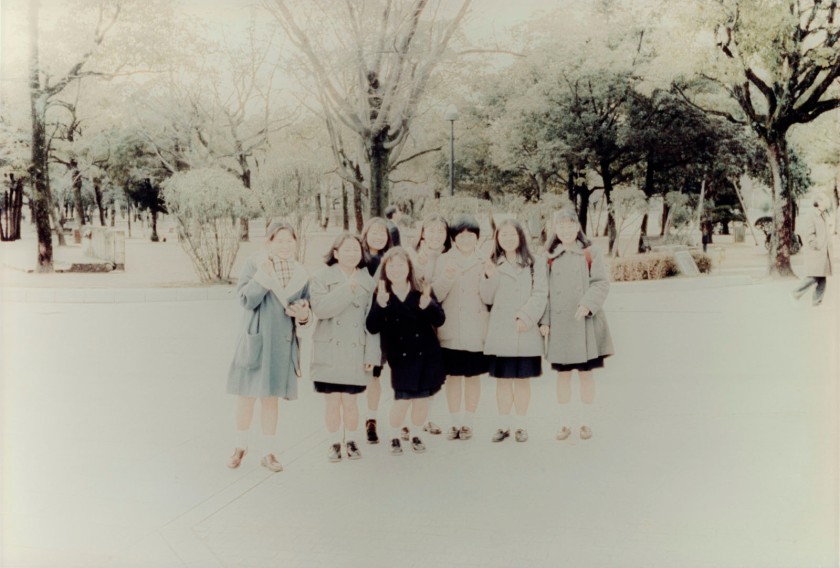
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Drying cherries
1979
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Linda with Teddybear
1981
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
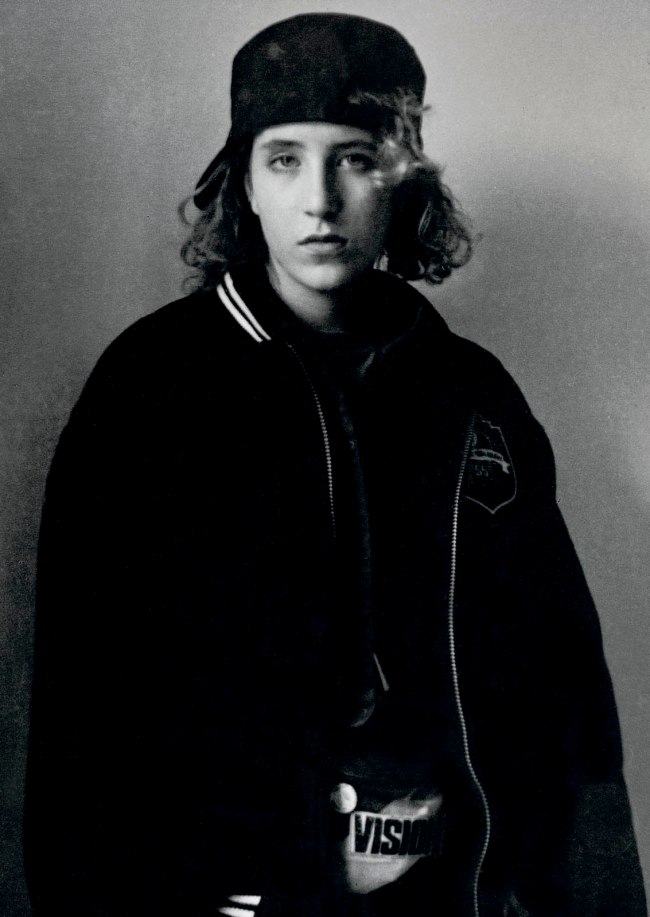
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Linda Vision
1980
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (b. 1947) is an observer and magician: She captures fleeting moments and creates dream images; life and art intertwine. When her children were small, the camera was part of everyday family life; at night, the mother would develop her prints in the darkroom. Again and again, she adopted new techniques and forms of presentation, for instance when she began working with video in the 1990s and when she eventually started to paint over photographs printed on canvas. While her earlier analogue works play with snapshot aesthetics, her video stills and edited digital photographs achieve the intensity of expressionist paintings.
The Fotostiftung Schweiz collection contains a big group of Štrba’s early black-and-white photo canvases and colour photographs – intimate family scenes, but also bleak facades of large-panel-system buildings and high-rises.
This retrospective exhibition, whose title quotes a poem by Emmy Hennings, presents these works for the first time. They are positioned around two newly conceived projections of the work cycles with which Annelies Štrba translated her view of the family into images: Shades of Time brings together photographs taken between 1974 and 1997, showing the children Sonja, Samuel and Linda as they grow up. Noonday is dedicated to her children’s children. When these series are seen together, the interweaving of eras becomes tangible. The visual worlds, characterised by subjectivity and intuition, merge to form one comprehensive cosmos.
Text from the Fotostiftung Schweiz website
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Zeitz
1983
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
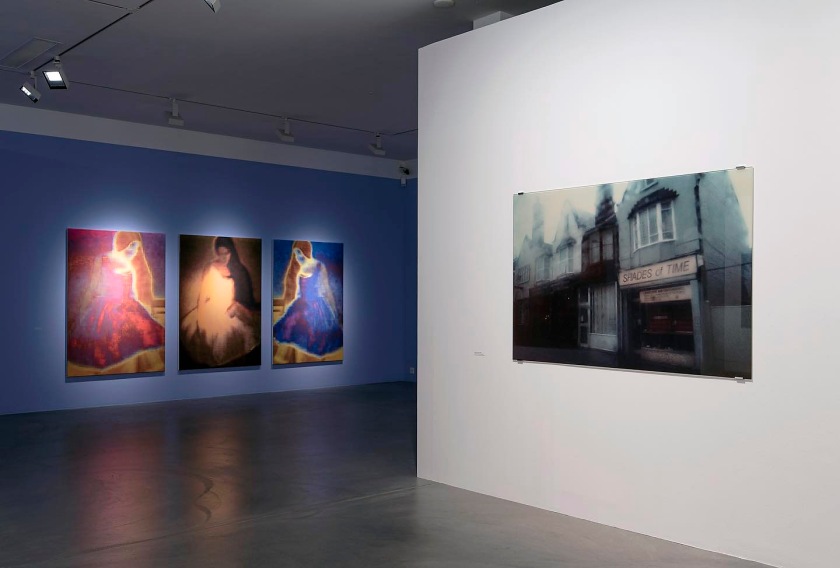
Installation view of the exhibition Annelies Štrba – “My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds” at the Fotostiftung Schweiz, Winterthur, Zurich
Annelies Štrba (b. 1947) is one of Switzerland’s most internationally renowned contemporary artists using photography. In her works, she captures fleeting moments and creates dream images; life and art intertwine. This exhibition at Fotostiftung Schweiz presents, for the first time, large-format photo canvases from the collection and a projection specially conceived for Fotostiftung Schweiz.
The exhibition Annelies Štrba – “My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds” focuses on Annelies Štrba’s early works. Black-and-white photo canvases, colour photographs and the projection Shades of Time show images from the years 1974 to 1997. These works are framed by her later expressionist video stills, a newly conceived projection with photographs from the years up to 2015 and staged scenes of fairy-tale princesses sleeping in enchanted landscapes. All the pictures revolve around the theme of family. Their juxtaposition enables an understanding of how this artist’s personal and artistic development over time is reflected in her view of children and grandchildren.
From the attic to Kunsthalle Zurich
Despite her photographic apprenticeship, which she commenced at the age of 16, Annelies Štrba is a self-taught artist, as she never attended an art school. In 1969, she married Bernhard Schobinger, whom she accompanied and assisted in his work as a goldsmith and artist. Štrba came into contact with the art scene in her husband’s gallery for contemporary art, which he opened in Richterswil, where the pair lived. Mostly though, she took care of their three children: Sonja, Samuel and Linda. With the little ones in tow, she sold selected clothes and shoes for the punk and new wave scene at the Bürkliplatz flea market in Zurich to support their modest household. Meanwhile, without any ambition at first, she documented family life with her camera, developing her prints at night in the attic and storing them in boxes.
It was in Bernhard Schobinger’s 1987 publication Devon-Karbon-Perm that Štrba’s photographs first attracted attention. Her presentation of Schobinger’s jewellery in photographs that look raw and unmediated, and reproductions of handmade prints with scratches and streaks, bear witness to a confident photographic language, vehemently rejecting any smoothness, perfection or conformity. However, it was not until 1990, at the age of 43, that Annelies Štrba first appeared as an artist in her own right. Bernhard Mendes Bürgi, who was Kunsthalle Zurich’s curator at the time, offered her an exhibition. Against all expectations and advice (from the men involved), Annelies Štrba decided to enlarge her intimate sketchy pictures on photo canvases, in formats of up to 100 by 150 centimetres. From the very start, she emphasised the difference between a mother’s snapshots hoarded in a photo album and the visual works that were now revealed to the public. The formats and the rough unprotected surface of the canvases gave the photographs the presence of paintings. Štrba abstracted and thereby intensified the peculiar mood of the everyday scenes. She superimposed a heaviness, a seriousness, on the photographs of the children playing, sleeping or sitting together in the kitchen, which turned them into symbolic images of the human condition: loneliness in togetherness, eeriness in the familiar, the depths of the family.
Shades of Time: changes in the visual language
As the children grew older and the artist became more successful, her radius of movement increased: In the 1990s, Annelies Štrba received a studio scholarship from Landis+Gyr. She travelled to England, Scotland, Ireland and Japan, and exhibited in Berlin, London, New York, Paris and Tokyo. In 1997, Lars Müller Publishers released her extensive monograph Shades of Time (which has long since been out of print). In this book’s series of images, a change can be seen in her visual language and attitude to life over the years: landscapes passing by the car window, house facades, gardens, but above all Sonja and Linda as young women continuing the game with the camera, on equal footing, and obviously enjoying it. The birth of the first grandchild, Samuel-Maria, brings a Madonna-like depiction of maternal love and care into Štrba’s visual cosmos – a motif that had been absent until then, not least because the mother had remained hidden behind the camera.
First video works and video stills
Also in 1997, Štrba produced her first video, because a filmed portrait of the artist was required for the Whitechapel Gallery in London and she did not want to leave the making of it to anyone else. Enthused by the possibilities for manipulation offered by this technique, which was new to her, she put the still camera aside and concentrated on video works, in addition to video stills produced as stand-alone images. By adjusting or saturating the colours and using visual distortion, she created special aesthetics that looked painterly and technical at the same time. The motifs also liberated themselves more and more radically from the domesticity of the previous years. Landscapes, cityscapes and flowers served as visual composition elements, as did the silhouettes of her adult daughters.
However, still photography and children did come back to dominate Annelies Štrba’s imagery once again. From countless photographs of her grandchildren, especially Linda’s daughter Shereen, a new cycle of works emerged, culminating in the 2015 publication Noonday: Colourful scenes, many of which were taken at the artist’s home in Amden, show a children’s paradise comprising brightly coloured fabrics, cushions, blankets and a trove of princess dresses.
“My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds”
The photo canvases that were purchased in 2015 and 2021 with support from the Förderverein Fotostiftung Schweiz, among others, and supplemented by generous donations from the artist, are presented for the first time in this exhibition, whose title quotes a poem by Emmy Hennings, The motifs also appear in a digital interpretation of the Shades of Time slide show, newly conceived in 2020. In addition, Štrba has composed a projection from the Noonday picture series specifically for this exhibition in Winterthur, with a soundtrack produced by her son, Samuel Schobinger. The Shades of Time and Noonday projections run alternately in the exhibition, one after the other, uniting their eras in a never-ending flow of images. The inclusion of selected video stills, mounted behind glass in a large format, also visualises the themes of the artist’s life and her tireless pursuit of image forms for her cosmos.
With the exhibition Annelies Štrba – “My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds”, Fotostiftung Schweiz continues its commitment to honouring female photographers. Like previous presentations of female artists, such as Pia Zanetti and Manon, this show offers a focused retrospective on an oeuvre that shaped the history of photography in Switzerland. The exhibition was curated by Teresa Gruber, curator at Fotostiftung Schweiz.
Press release from the Fotostiftung Schweiz
Installation view of the exhibition Annelies Štrba – “My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds” at the Fotostiftung Schweiz, Winterthur, Zurich showing at left, Linda (1991, below); Hiroshima (1994, below); and Linda and Sonja with Samuel-Maria (1995, below)
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Linda
1991
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Hiroshima
1994
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Linda and Sonja with Samuel-Maria
1995
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
From Shades of Time
1970-1997
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
In the kitchen
1995
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (b. 1947) is a keen observer, but also a magician: She intuitively captures fleeting moments, then transforms them into images that come across as symbolic. Today, she is one of Switzerland’s most internationally renowned artists working with photography. Her first solo exhibition though, in 1990 at Kunsthalle Zurich, was provocative. An unknown at the time, she appeared in public with her intimate family scenes, defying all expectations and breaking away from the rules of perfect photographic reproduction. Shortly afterwards, Annelies Štrba’s works were exhibited in Berlin, London and New York. She has continued to amaze ever since. Always open to new stylistic devices, techniques and modes of presentation, she translates her view of the world into unconventional poetry.
In this exhibition at Fotostiftung Schweiz, her early work comes to the fore: Black-and-white photo canvases, colour photographs and (in a reconceived digital interpretation from 2020) the slide show Shades of Time present images from the 1970s through to 1997. They show Štrba’s children Sonja, Samuel and Linda growing up. There are also indications of an initial shift in the visual language here, towards more movement and a playful handling of motifs, in which the daughters participate as young women. These almost traditional works are framed by the video stills created later. By means of manipulation carried out on the monitor, colours are remixed and stills dissolve into shimmering structures.
Annelies Štrba’s grandchildren then brought her back to photography. With a mobile phone camera and digital photography, she accompanied her heroines and heroes through everyday life, opening up a new colourful cosmos, which she encapsulated under the title Noonday in 2015. From that group of works, Štrba has also composed a projection, specifically for this exhibition in Winterthur. The Shades of Time and Noonday projections run alternately in the exhibition, one after the other, uniting their eras in a never-ending flow of images. Finally, princesses sleeping in fairy-tale landscapes (usually granddaughter Shereen is the performer) whisk the observer away to the land of dreams: The artist had begun to work on the picture surfaces with brush and paint. Štrba made reference to art history and her own images, reproducing, defamiliarising and creating objects, into which the marks of time are, in turn, inscribed.
In 2015 and 2021, Fotostiftung Schweiz was able to purchase a group of Annelies Štrba’s canvases, with support from the society Friends of Fotostiftung Schweiz, among others. These works were supplemented by generous donations from the artist. Representing various phases of her early work, they are now being exhibited together for the first time – and confronted with later works.
Biography
Annelies Štrba was born in 1947 in Zug. After training as a photographer and completing her first professional assignments, she married Bernhard Schobinger in 1969, whom she accompanied and assisted in his work as a goldsmith and artist. Štrba came into contact with the art scene in her husband’s gallery for contemporary art, which he opened in Richterswil. Mostly though, she took care of their three children: Sonja, Samuel and Linda. With the little ones in tow, she sold selected clothes and shoes for the punk and new wave scene at the Bürkliplatz flea market in Zurich to support their modest household. Meanwhile, without any ambition at first, she documented family life with her camera, developing her prints at night in the attic and storing them in boxes. It was in Bernhard Schobinger’s 1987 publication Devon-Karbon-Perm that Štrba’s photographs first attracted attention. Her presentation of Schobinger’s jewellery in pictures that look raw and unmediated, and reproductions of handmade prints with scratches and streaks, bear witness to a confident photographic language, vehemently rejecting any smoothness, perfection or conformity. However, it was not until 1990, at the age of 43, that Štrba first appeared as an artist in her own right. Bernhard Mendes Bürgi, who was Kunsthalle Zurich’s curator at the time, offered her an exhibition.
Triptych
The first room of the exhibition introduces Annelies Štrba’s various spheres by means of a brightly coloured triptych – a group of three, albeit constituting one female figure. By extracting two stills from a video work and mirroring one of them, the artist has created a ‘community’ and arranged it as a psychedelic altarpiece: Shown frontally and immersed in golden brown, the internally calm queen is bowed to by her brightly dressed servants on the left and right – one in blue, the other in magenta, with glowing contours. Due to the coarse resolution of the video images, the surface and figure disintegrate into pixel-like patches of colour, bringing to mind the structure of paintings. The pictures’ saturated defamiliarised colouring makes reference to expressionist works.
Canvases
For her first exhibition, at Kunsthalle Zurich in 1990, Annelies Štrba enlarged her photographs on canvases in formats of up to 100 by 150 centimetres. From the very start, she emphasised the difference between a mother’s snapshots hoarded in a photo album and these visual works that were now revealed to the public. The formats and the rough unprotected surface of the canvases gave the photographs the presence of paintings. At the same time, they came across like washed-out yellowed pictures from a bygone era. Štrba abstracted and thereby intensified the peculiar mood of the everyday scenes. She superimposed a heaviness, a seriousness, on the photographs of the children playing, sleeping or sitting together in the kitchen, which turned them into symbolic images of the human condition: loneliness in togetherness, eeriness in the familiar, the depths of the family.
Kitchen pictures
The kitchen was the heart of the Richterswil house in which Annelies Štrba and Bernhard Schobinger raised their three children Sonja, Samuel and Linda together. Here, they did not merely cook and eat, but also received visitors, discussed and pondered. In this room, which looks cramped and humble, cosiness and chaos merge. Years pass, and suddenly adult daughters are sitting at the same table. The video Max, Annelies Štrba’s first video piece, marks a turning point in her oeuvre and shows a bizarre kitchen spectacle. Although all movements are in slow motion, the activeness of Sonja and Linda setting and clearing the table contrasts with the rather passive attitude that they exhibit in many photographs. In flowing dresses, they make preparations, but these do not lead to anything and instead seem to represent an inherently strange ritualistic process. Annelies Štrba produced this video when a filmed portrait of the artist was required for a 1997 exhibition at the Whitechapel Gallery in London and she did not want to leave the making of it to anyone else. Enthused by the possibilities for manipulation offered by the technology, which was new to her, she put the still camera aside and concentrated on video works, in addition to video stills produced as stand-alone images.
Shades of Time projection
Also in 1997, Lars Müller Publishers released an extensive monograph that encompassed Annelies Štrba’s photographic oeuvre. Its title, Shades of Time, was provided by a sign on a shop front, photographed from a moving car during a trip to England. Years and impressions pass by in an associative and only roughly chronological sequence. The shots of sleeping and playing children are replaced by house fronts and landscapes. The heaviness of the early domestic scenes dissolves into increasing movement and colourfulness. This shift in photographic language can also be interpreted autobiographically. In 2001, Annelies Štrba conceived a slide show in which the images were projected in groups of three, with a techno audio accompaniment by Peter Ford. The duplication and mirroring of some individual motifs give rise to arrangements that sometimes appear ornamental or even sacral. The digital version of this projection was made in 2020, in collaboration with video company in Zofingen.
Noonday projection
While growing up, Annelies Štrba’s grandchildren presented her with a new world of images: a chaotic clarity, a banal colourfulness, in which there is also room for laughter and group photos. Annelies Štrba cleverly combined the children’s joy in dressing up and acting with spontaneous photo shoots. Mostly though, she reacted impartially to life as it happened, proudly taking part in the daily routine and marvelling at it. Štrba herself remains invisible, but her backdrop, her colourfully designed nest, as if made for her little protagonists, frames the action. In 2015, the book Noonday, comprising over three hundred pages, was released by Lars Müller Publishers. In 2023, the artist has collaborated with video company to compose a Noonday projection, adding new motion to the captured moments, with the accompaniment of a soundtrack by her son Samuel Schobinger.
Buildings
Already in her first exhibitions, Annelies Štrba placed architectural photographs between the pictures of her children. The bleak facades of residential blocks and high-rise buildings that she photographed on her travels through Silesia contrast with the depictions of cosiness at home. Often, the photographer seems to just glance at these buildings in passing. People also live in most of them, including families. On the other hand, the ruins of Einstürzende Neubauten (collapsing new buildings) captured in the Polish city of Sosnowiec recall Soviet planning and memorialise the Berlin band of the same name, founded in 1980. Štrba’s interest in experimental and electronic music is also incorporated into her video works and projections.
Fairy-tale pictures
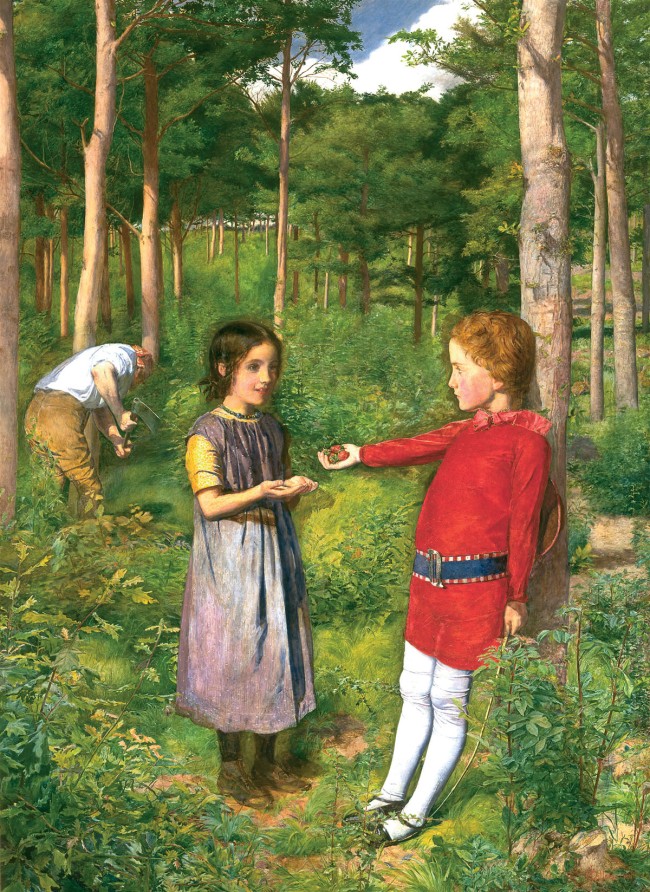
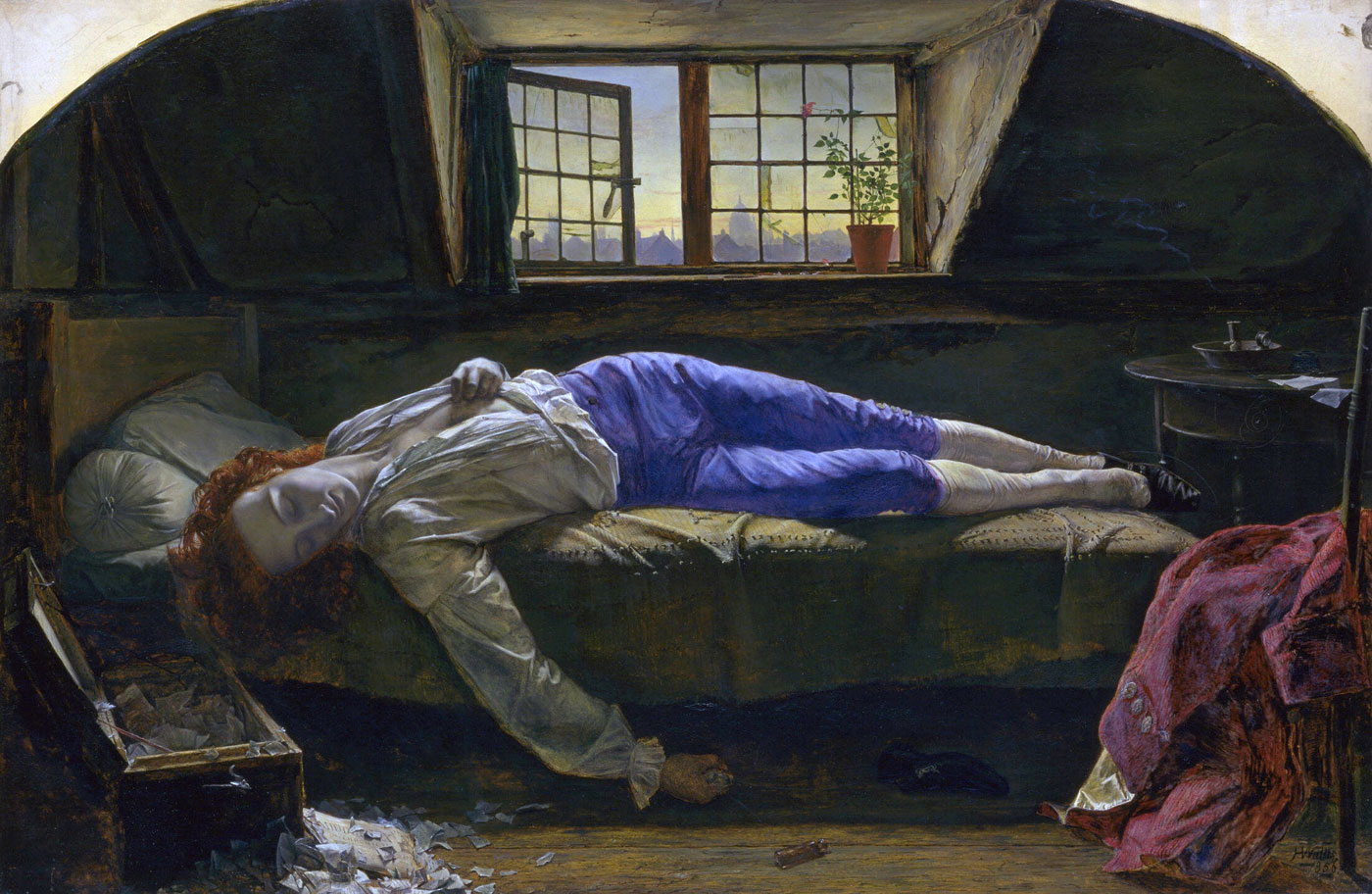
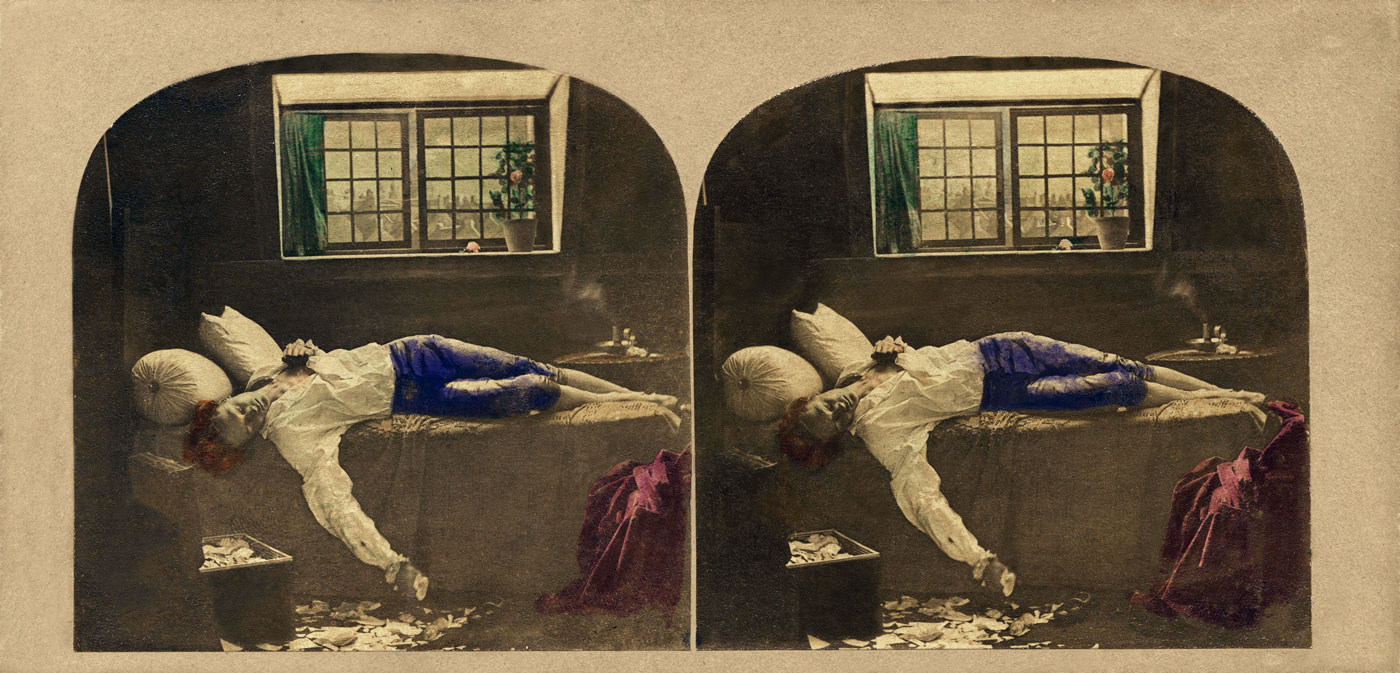
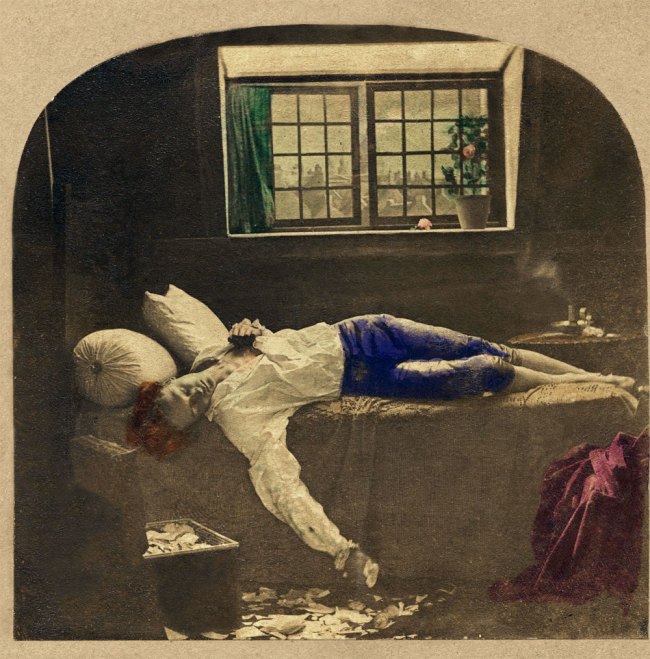
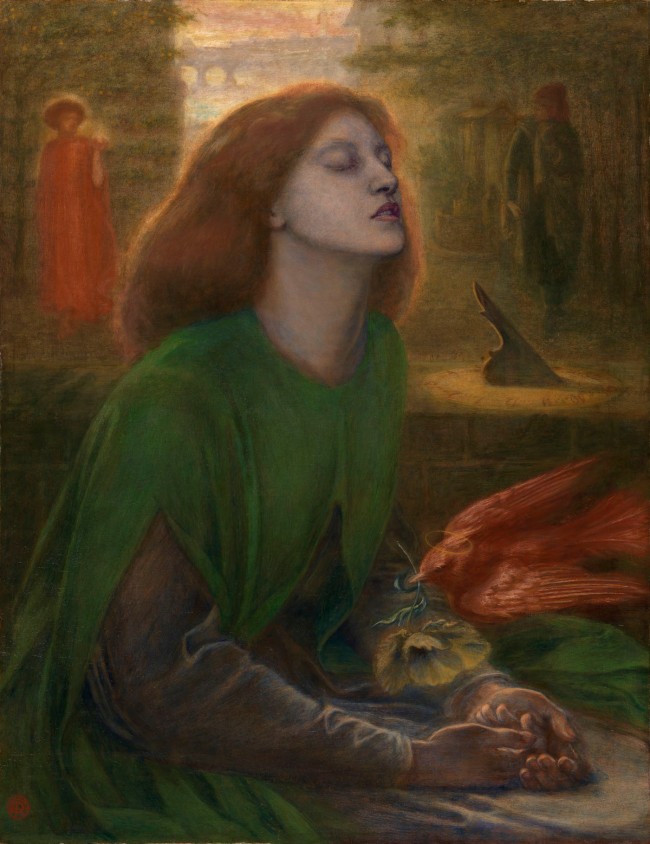
The motif of sleeping children connects the Shades of Time and Noonday groups of works with NYIMA and Momoka. For the latter, Annelies Štrba edited digital photographs, some of which were taken in the context of Noonday, but also took new photographs: staged scenes, mostly featuring her granddaughter Shereen. All of them show resting girls – in forests, in meadows or on sofas, seemingly immersed in deep sleep. In their princess dresses, they appear to be from another time. Defamiliarisation of colours and superimposition of multiple exposures transform the photographs into visualisations of these dainty figures’ dreams. Aesthetically and compositionally, they resemble the famous painting by the Pre-Raphaelite John Everett Millais, which depicts the drowned Ophelia lying in a stream, surrounded by plants, flowers and her magnificent gown. The romantic beauty of Štrba’s pictures can also evoke associations with the relationship between sleep and death.
Sleeping children
The exhibition’s final room completes the circle and leads back to the beginnings of Annelies Štrba’s photographic oeuvre. While the kitchen has already been examined as an important motif, we now look into the bedroom or children’s room. The artist remembers how, after long evenings in the darkroom, she used to find her children asleep. She would often feel an urge to photograph them like this, cosy in their nests, or surrounded by evidence of play. However, the bed is also a platform on which the state of being awake can be presented: Time and time again, the artist produced portraits of her children sitting on beds.
Text from the exhibition leaflet
Installation view of the exhibition Annelies Štrba – “My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds” at the Fotostiftung Schweiz, Winterthur, Zurich showing at right, Linda with Shereen (2000, below)
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Linda with Shereen
2000
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Aya 026
2002
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Installation view of the exhibition Annelies Štrba – “My Otherness Colourfully Unfolds” at the Fotostiftung Schweiz, Winterthur, Zurich showing at left, Nyima 410, Nyima 409, Nyima 408 (2009, below); and on the right a photograph from the series Shades of Time (1970-1997)
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
From Shades of Time
1970-1997
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Nyima 408
2009
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
In Tibetan Nima (also spelled as “Nyima”) is also a female or male given name which means ‘the sun’, also the one with radiance of the Sun. And in Hebrew as a female given name it means ‘grace, mercy’.
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Nyima 409
2009
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Nyima 410
2009
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Nyima 438
2010
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Annelies Štrba (Swiss, b. 1947)
Nyima 445
2010
© Annelies Štrba / Pro Litteris
Fotostiftung Schweiz
Grüzenstrasse 45
CH-8400 Winterthur (Zürich)
Phone: +41 52 234 10 30
Opening hours:
Tuesday to Sunday 11am – 6pm
Wednesday 11am – 8pm (with free admission from 5 pm!)
Closed on Mondays







































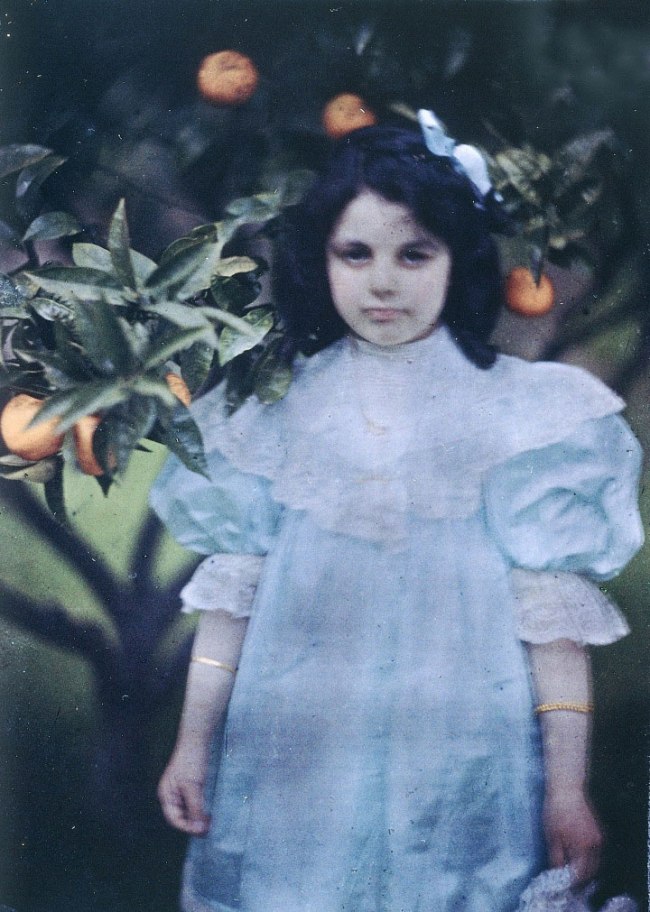














You must be logged in to post a comment.