Exhibition dates: 9th November 2018 – 28th April 2019
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Lord Balgonie
1855
Albumen print
17.7 x 11.7cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500273
This portrait (above) shows Captain Alexander Leslie-Melville (1831-1857), known as Lord Balgonie. He was the eldest son of the 8th Earl of Leven, a Scottish peer. Lord Balgonie served in the Grenadier Guards during the war, and died only a couple of years after returning to Britain. At the time, his death was attributed to the hardships of the war. Fenton has photographed him standing in front of a sheet, which serves as a make-shift studio and he looks unkempt and shaken, as if he has recently stepped off the battlefield. In recent years, this photograph has been described as the first photographic portrait of shell-shock. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
The Crimean photographs of Roger Fenton represent the beginning of war photography. These staged photographs, documented for the edification of a viewing public back home in England and for the purpose of making money for the photographer, set the trend for the genre for the next 80 years. Staging photographs of war, and altering reality to suit the commercial, political or moral aspirations of photographer or institution, continues to this day.
For most of the images, “research for the exhibition has revealed that Fenton’s portraits and topographical views were principally intended as source material for the artist Thomas J Barker, who had been commissioned by Agnews to produce an oil painting of the senior officers of the allied forces. Barker used over 50 of Fenton’s images to create the monumental work The Allied Generals with the officers of their respective staffs before Sebastopol (private collection).” Fenton was fulfilling his commission and earning a living by taking photographs for a painter. But Fenton’s photographs are most successful when he has a personal connection to the subject matter, whether it be portrait or landscape. In other words, when he is not constructing or documenting as representation, but attempting to capture the spirit of person/place.
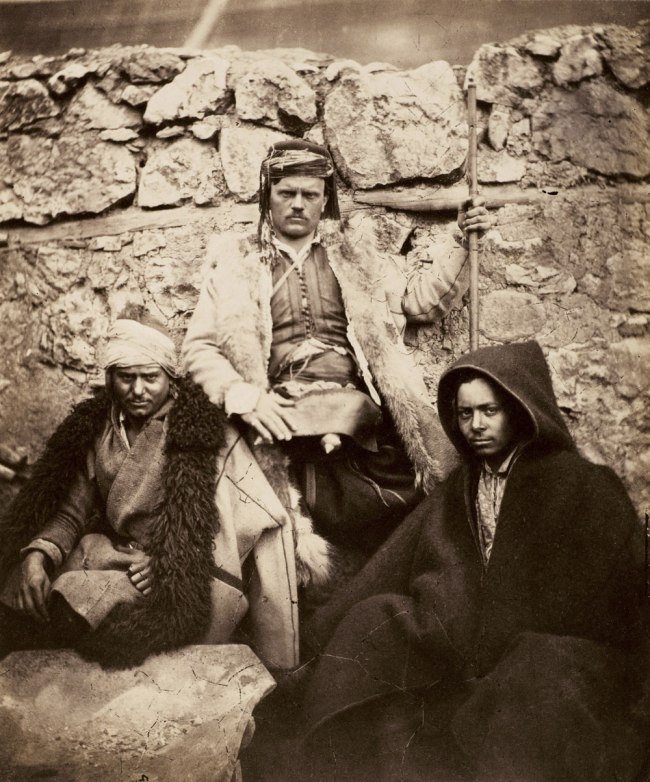
In portraiture, this personal connection can be seen in the photographs, Lord Balgonie (1855, above), Fitzroy James Henry Somerset, Baron Raglan (1788-1855) (4 Jun 1855, below), Omar Pacha (1806-1871) (1855, below) and General James Bucknall Estcourt (1802-1855) (1855, below), a man deep in thought or, perhaps, melancholy. These are psychological portraits that attempt to get under the skin of the sitter, not mere representations for use as a template for painting.
The portraits of Baron Raglan and Omar Pacha are taken in the same location, probably at the same sitting. In the portrait of Baron Raglan, this man (soon to die) is relatively small in proportion to the overall framing of the photograph, his dark shadow falling on the wall behind, his hat and white plume pulled forward and out of focus in the image, incredibly large in comparison with the size of the body. In three-quarter profile he gazes out of the image, while the right and top of the image falls into soft, velvet darkness. By comparison, the portrait of Omar Pacha presents to us a much more self possessed and confident man. Fenton has moved the camera closer to his subject. No shadow falls on the wall behind and the light frames the head of the sitter perfectly. His bearing is upright but relaxed; his hands gently rest in his lap; and his gaze stares directly out of the image but not directly into the camera lens as though her is in deep thought somewhere beyond the photographer’s left shoulder. Both are magnificent portraits.
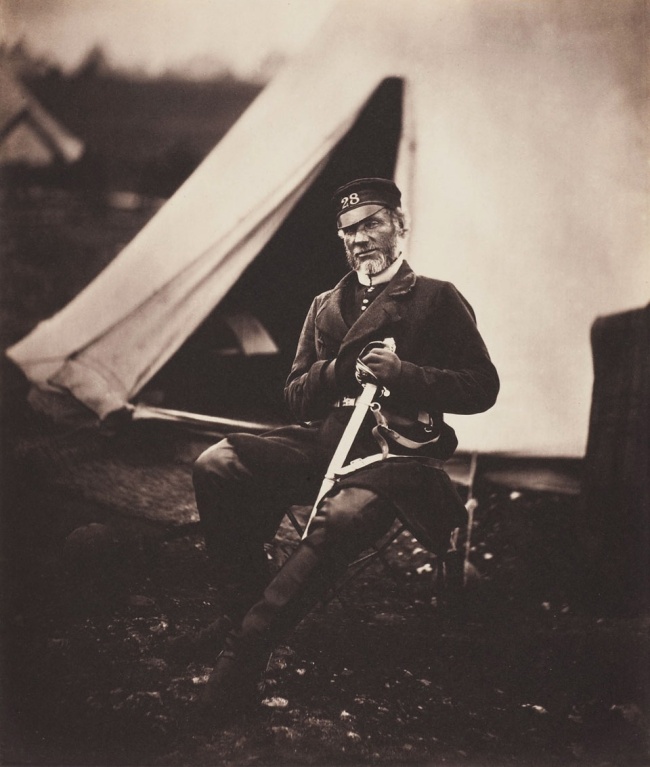
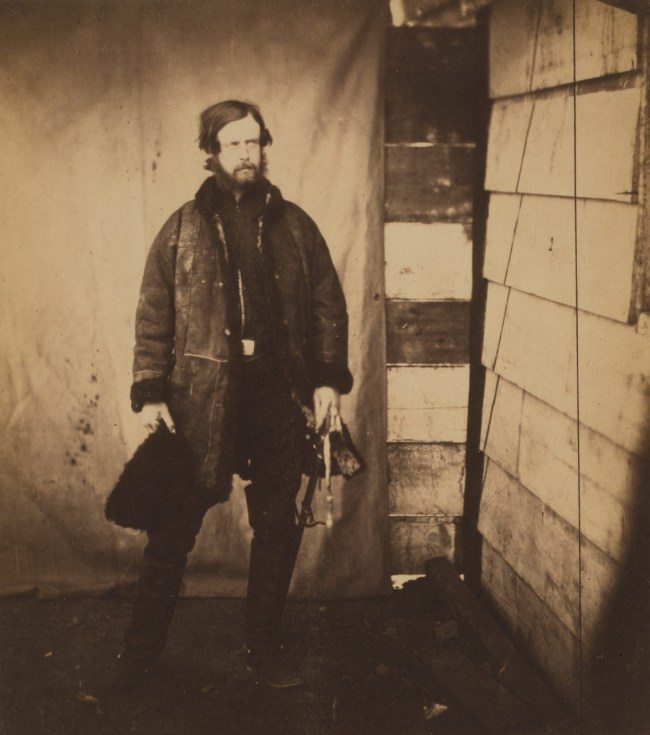
With regard to his landscapes of the Crimea the same feelings can be observed. One is the representational urge, the other the artistic. The first problem is the barrenness of the landscape and what to do with the inevitable horizon line. When photographing people in the landscape Fenton makes use of low depth of field either pulling the figures towards the front of the image (Sir John Miller Adye (1819-1900) 1855, and General Scarlett and Colonel Low Apr 1855, below) or the mid-distance (such as Captain and Mrs Duberly Apr 1855 and Colonel Doherty and the Officers of the 13th Light Dragoons 1855, below) whilst allowing the horizon line to float in the distance, either placed through the figures or floating above them. This low depth of field allows the horizon line to soften and the solid space around the figures to become ambiguous and fluid. It also allows the light in this vast expanse of country to do its duty, to illuminate the isolation of these figures “in the field.” A similar technique was used by Edward S. Curtis when photographing the Native American Indians against the vastness of country – low depth of field, letting the light and composition do the work as subject is located – or vanishes – into the landscape.
For the shear complexity of their visualisation, Fenton’s photographs of Balaklava are among my favourites. The placement of camera, the line of composition (ship masts, hills, horizon line, stacking of cannonball), the flattening of perspective (The Ordnance Wharf at Balaklava Mar 1855, below) and the tonality of the images are exemplary.
Taken a mere 15 years after the birth year of practical photography, Fenton’s “subtle and poetic interpretations” still resonate today. That he captured such acclaimed images using a heavy land camera, the photographs taken sometimes under fire, the glass plates prepared and developed in a ‘travelling darkroom’ – his horse drawn photographic van – make Fenton’s achievement all the more remarkable. The shadow of war that he captured, the presence of the men, women and landscapes of that time and place, are made alive to us today.
Note this
There is the date a photograph is made, and the date it is viewed. There is something about the different way a photograph exists in time, different from the date a poem is written and the date it is read, different from the date a painting is finished and the date it is viewed.
And then
Photographs remind us
of people, passing
They distill an essence
which
in turn
Instills in us
memory of time, place, spirit
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to The Queen’s Gallery for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
This is the first exhibition to focus exclusively on Roger Fenton’s pioneering photographs of the Crimean War, taken in 1855. Fenton was already an accomplished and respected photographer when he was sent by the publishers Agnew’s to photograph a war that pitched Britain, France and Turkey as allies against Russia. Arriving several months after the major battles were fought in 1854, Fenton focused on creating moving portraits of the troops, as well as capturing the stark, empty battlefields on which so many lost their lives.
Published in contemporary newspaper reports, Fenton’s photographs showed the impact of war to the general public for the first time. Through his often subtle and poetic interpretations Fenton created the genre of war photography, showing his extraordinary genius in capturing the futility of war.
Half a league,
half a league,
Half a league onward,
All in the valley of Death
Rode the six hundred.
Lord Tennyson. The Charge of the Light Brigade
John Gilbert (British, 1817-1897)
The Queen Inspecting wounded Coldstream Guards in the Hall of Buckingham Palace, 22 February 1855
1856
Watercolour
138 x 214.5 x 13cm
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 451958
This painting depicts the second meeting with Guardsmen which took place at Buckingham Palace. The first meeting had been with the Grenadier Guards on 20 February 1855. The artist John Gilbert prepared a sketch of the event for the newspaper the Illustrated London News, published on 10 March 1855. He went on to create this painting using photographs of the soldiers for accuracy. Prince Albert supplied photographs of himself and the royal children. Gilbert was also given permission by the Queen to visit the Marble Hall in Buckingham Palace to recreate the scene. The scale of the watercolour caused a sensation when it was exhibited in 1856. Probably acquired by the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Queen Victoria and Prince Albert
1854
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
A Zouave (Self-portrait as a Zouave)
1855
Salted paper print
18.2 x 14.1cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500562
The title of this work gives no indication that this is a self-portrait. Fenton has dressed himself in the uniform of a Zouave, a type of Algerian soldier who fought with the French army during the Crimean War. The Zouaves were admired both for their bravery and for their colourful dress. In 1855, when this photograph was exhibited for the first time, Fenton was Britain’s leading photographer but only a handful of fellow artists would have known that this was Fenton and not a Zouave soldier from the war. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Sir John Miller Adye (1819-1900)
1855
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017
The exhibition
Roger Fenton (1819-69) was the first photographer to document a war for public consumption. From March 1855, Fenton spent four months photographing the people and the terrain affected by the Crimean War, fought between the allied nations of Britain, France and the Ottoman Empire against Russia.
Fenton’s time in the Crimea was relatively short given the war lasted over two years (October 1853 – March 1856) but his photographs captured, for the first time, the chaos and disorder of a war zone, and showed the Victorian public portraits of soldiers in the field, directly affected by battle. Although Fenton was fulfilling a commercial commission, he allowed himself to respond emotionally in his work and this is perhaps why his photographs continue to represent the Crimean War more effectively than any other visual record of the conflict.
This exhibition presents Fenton’s work within the wider context of the war, alongside other contemporary artists, photographers and writers also in the Crimea at that time. We begin with two sections which, through Fenton’s portraits, introduce some of the key individuals and events that occurred prior to Fenton’s arrival in the Crimea.
Subsequently we examine Fenton’s work in more detail, before considering the significant role played by the royal family in focusing the attention of the British public on the impact of war and the returning wounded veterans.
The Crimean War, 1853-1856
The Crimean War, also known as the Russian War, pitched the allied nations of Britain, France, the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Sardinia against the Russian Empire. At its simplest, the war was fought to prevent Russia gaining territorial control of various regions in eastern Europe, then under Ottoman control, and of routes into British India. These regions included the Black Sea, the Mediterranean, the Caucasus region and the Danubian provinces of modern-day Romania. Other more complex reasons included disputes over the control of religious sites and the protection of Christians in the Middle East, as well as concern over the declining influence of the Ottoman Empire and the growth of nationalism in various regions.
War with Russia had been publicly discussed for several years before Russian incursions into Romania, then under Ottoman control, led to a declaration of war from Constantinople in October 1853. Britain and France, fearing the collapse of the Ottoman Empire and the growth of Russian power, followed with their support for the Ottomans by declaring war on Russia at the end of March 1854.
The conflict began in Europe and could have ended there in July 1854 when Russia began to withdraw but the European allies decided to confront Russia directly by besieging the Russian port of Sevastopol, an important naval base on the Crimean peninsula. The allies landed in the Crimea on 14 September 1854 and made their way towards Sevastopol, encountering the Russians in several major battles en route including Alma (20 September), Balaklava (25 October) and Inkerman (5 November). On 9 September 1855, after numerous other battles and skirmishes, Sevastopol fell to the allies.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Fitzroy James Henry Somerset, Baron Raglan (1788-1855)
4 Jun 1855
Albumen print
18.3 x 14.5cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500229
Lord Raglan (1788-1855) was a veteran of the Napoleonic Wars. He lost his right arm during the Battle of Waterloo in 1815, whilst he was an aide to the Duke of Wellington. Despite having never commanded in the field, he was named as the expedition Commander-in-Chief in early 1854 when war seemed inevitable. He was to become the focus of heavy public criticism over the apparent poor organisation and logistics during the campaign. This criticism contributed to his declining health, and he died in the Crimea on 28 June 1855. He was succeeded as Commander-in-Chief by General James Simpson. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Lieutenant-General Burgoyne and his aide-de-camp Lieutenant Stopford
1855
Salted paper print
21.9 x 17.6cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500553
John Burgoyne (1782-1871) was a key member of the senior command during the war. After the Battle of Alma on 20 September 1854, Burgoyne proposed that the army march south of Sevastopol and besiege the city, rather than attacking the city from the north. This decision ultimately committed the allies to a siege of almost a year. Burgoyne returned to Britain in the winter of 1854-1855 before Fenton arrived in the Crimea. As Fenton sought to photograph all the senior commanders from the war, he arranged this session in his London studio sometime after he returned to Britain in mid-July 1855. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
General Scarlett and Colonel Low
April 1855
Albumen print
19.5 x 16.0cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500250
Sir James York Scarlett (1799-1871), here seated on a horse, played a key role in the Battle of Balaklava on 25 October 1854. The Charge of the Heavy Brigade, under Scarlett’s command, was a highly successful attack on the Russian army which has become overshadowed by the infamous Charge of the Light Brigade which occurred later during the same battle. Alexander Low (1817-1904) held the rank of Captain in the 4th Light Dragoons at the time of this photograph. He was a highly skilled cavalryman and served with distinction during the Charge of the Light Brigade. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Officers of the 8th Hussars
Apr 1855
Albumen print
16.7 x 16.3cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500355
Fenton made a number of group portraits of men from the five Light Cavalry regiments that charged on 25 October. News of the action had caught the public imagination, and the names of the regiments became well-known. Fenton would probably have seen photographs of men who may have fought in the battle as having greater commercial potential. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
The Battle of Inkerman 5 November 1854
After Balaklava, the allied armies continued to besiege Sevastopol. The Russian army occupied a strong position between the city and the allies, and on 5 November 1854 they attempted to end the siege. The Battle of Inkerman saw fierce fighting hampered by thick fog, resulting in poor communication between the troops. Casualties were disproportionately high. The battle was a victory for the allies but it also committed the troops to a long winter in the Crimea.
Most of the injured soldiers were shipped to Scutari hospitals, near Constantinople. As the Inkerman wounded arrived, so too did Florence Nightingale and her nurses. During October, reports in The Times sent by William Howard Russell had described the poor care for the wounded and the lack of nurses. This led Sidney Herbert, Secretary of State for War, to ask Nightingale to lead a nursing party to Scutari. They arrived on 4 November 1854.
From Scutari, Nightingale made three visits to the Crimea, the first in May 1855 when she caught a serious illness that was to affect her for the rest of her life. By this time, Nightingale was already well-known to the British public and had been depicted in the press as the ‘Lady with the Lamp’. She returned to Britain in July 1856 and devoted much of the rest of her life to hospital and healthcare reform.
Inkerman
Roger Fenton produced this panoramic view of the Inkerman Valley, the scene of a fierce battle on 5 November 1854 that pitched the British and French allies against the Russian army. The battle took place in thick fog, resulting in troops becoming cut off from their commanders and a high number of casualties. Although the battle was an allied success, its impact was such that it extended the war by months, condemning the troops to the harsh winter of 1854-1855 in the Crimea. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
The Ruins of Inkerman
May 1855
20.2 x 25.8cm (image)
Albumen print
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
The Quarries and Aqueduct in the Valley of Inkerman
May 1855
18.5 x 25.4cm (image)
Albumen print
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Hardships in the Crimea
1855
Albumen print
17.6 x 16.2cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500388
Fenton took a number of staged photographs of camp life, including this group of the 4th Dragoon Guards. Generally, the titles of his portraits are the name of the sitter or regiment photographed, but this is one of a small number which have been given a more emotive title. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Haunting images that brought the stark reality of war into public consciousness for the first time have gone on display in a new exhibition Shadows of War: Roger Fenton’s Photographs of the Crimea, 1855 at The Queen’s Gallery, Buckingham Palace, London. Roger Fenton (1819-1869) was the first photographer to document conflict in such a substantial way at a time when the medium of photography was still in its infancy and there was no expectation of what ‘war photography’ should be.
Drawn entirely from the Royal Collection, the exhibition explores the impact and legacy of Fenton’s Crimean work, which is shown in Scotland for the first time since 1856. It also tells the story of the historically close relationship between the Royal Family and those who have served their country in battle, with contributions to the exhibition’s multimedia guide by Prince Harry, photojournalist Sir Don McCullin and exhibition curator Sophie Gordon.
One of the leading photographers of the 19th century, Roger Fenton was commissioned by the art dealer and publisher Thomas Agnew & Sons to photograph the officers and other people of interest during the Crimean conflict. On 20 February 1855 Fenton set sail for the Crimea on board HMS Hecla, accompanied by 36 chests of cameras, glass plates, chemicals, a stove and other pieces of equipment, and a wine merchant’s van converted into a travelling darkroom and accommodation for the photographer and his two assistants.
Research for the exhibition has revealed that Fenton’s portraits and topographical views were principally intended as source material for the artist Thomas J Barker, who had been commissioned by Agnews to produce an oil painting of the senior officers of the allied forces. Barker used over 50 of Fenton’s images to create the monumental work The Allied Generals with the officers of their respective staffs before Sebastopol (private collection). The painting reproduces some of Fenton’s portraits directly, including those of the Scottish General Sir Colin Campbell and The Times reporter William Howard Russell, as well as his photographs of camp life, such as 8th Hussars Cooking Hut.
Other figures within the painting, such as Barker’s depiction of Florence Nightingale, are clearly inspired by Fenton’s photographs. Although Nightingale was in the Crimea in 1855, she was a reluctant sitter for the camera and appears not to have been photographed by Fenton. Instead Barker’s portrait of her on horseback seems to be inspired by Fenton’s photograph Mr and Mrs Duberly.
In the 19th century there was a thriving market for prints of popular paintings. An engraving of Barker’s work was published in 1859 with a key to help the public identify the figures. The reproduction of the painting in newspapers and exhibitions of Fenton’s photographs raised awareness of the conditions endured by soldiers at a time when the wounded began to arrive home.
The concern and admiration for the veterans displayed by Queen Victoria and members of the royal family helped to highlight the plight of those returning from war. The Queen met groups of soldiers, visited military hospitals and inspected troops of veterans at Buckingham Palace. One such occasion was recorded by John Gilbert in The Queen inspecting wounded Coldstream Guardsmen in the Hall of Buckingham Palace, 22 February 1855. This large watercolour, which has hung at Sandringham House since it was acquired by Queen Victoria’s eldest son, the future King Edward VII, is exhibited for the first time.
Queen Victoria was the first British monarch to meet and support wounded soldiers in public. Today Prince Harry’s work with veterans promotes a wider understanding and respect for those who serve their country. On the exhibition’s multimedia guide His Royal Highness speaks about a number of Fenton’s images and how they helped change attitudes towards those affected by their experiences on the battlefield.
Speaking about Fenton’s image Lord Balgonie, the first visual record of someone suffering from ‘shell shock’ Prince Harry says in the multimedia guide: ‘There has always been a fascination about people returning from war, what they’ve been through and what they’ve seen. The psychological impact of being on the battlefield is something that servicemen and women have had to deal with, but have often found it hard to talk about. As a result of photographers like Roger Fenton and those who have followed him, the public have gained a better appreciation of these experiences and consequently, over the years this fascination has turned to appreciation and respect.’
Press release from The Queen’s Gallery
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Photographic Van
1855
Albumen print
17.4 x 15.9cm
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500439
Fenton’s ‘travelling darkroom’ was the only space he had in which to prepare his glass plates before they were exposed in the camera, and afterwards, to develop the negative image. Beyond a few test prints, however, Fenton would not have done any significant printing of photographs in the Crimea. All the negatives were transported back to Britain and printed there. This photograph was probably taken shortly before Fenton went into the ‘Valley of the Shadow of Death’. He later wrote in a letter, perhaps half-jokingly, that he feared the van being destroyed by enemy fire in the valley so he felt he should preserve its memory in a photograph. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Fenton’s Crimean Commission: 8 March – June 1855
Fenton was commissioned to go to the Crimean War by the Manchester-based publishers Thomas Agnew & Sons. Agnew’s was one of the leading publishers, print sellers and dealers at the time, and the firm saw the war as an opportunity to sell new images to a public hungry for information. The war coincided with an increased number of public art exhibitions as the middle classes in particular had more time and money to spend on leisure activities.
At the same time, Agnew’s also commissioned the British historical painter Thomas Barker (1815-1882) to produce a large oil painting depicting the expected allied victory at Sevastopol. Fenton’s photographs were to be used as source material by Barker. This enabled the artist to claim absolute truthfulness and accuracy in his portraits.
Barker incorporated versions of at least 50 of Fenton’s photographs into his painting. Some photographs have been copied almost exactly; others have been reversed or combined with other images, with elements from some photographs appearing alongside people from other works. The painting was completed in 1856 and the associated engraving was published by Agnew’s in 1859. A key was also produced, identifying each individual in the work, in which Fenton’s role was explicitly acknowledged.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Valley of the Shadow of Death
23 Apr 1855
Albumen print
25.7 x 35.0cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500514
Perhaps Fenton’s most well-known photograph, ‘The Valley of the Shadow of Death’, is not in fact the location of the charge of the Light Brigade. When Fenton reached the ravine seen in this photograph, he found himself the target of enemy fire. Even so, Fenton managed to make at least two distinct views: the version seen here, and another in which far fewer cannon balls lie on the ground, indicating that he re-arranged one of the scenes. This photograph, which has become one of Fenton’s most famous compositions, demonstrates the power of the camera at war. The scene is still and almost barren, but the power of the imagination draws the viewer into the landscape and the title, with its reference to Psalm 23, suggests that we walk between the realms of life and sudden death. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
James Robertson (English, 1813-1888)
Valley of the Shadow of Death
1855-1856
Salted paper print
22.3 x 29.2cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500723
Neither Robertson’s photograph nor Simpson’s lithograph show the same location as Fenton’s image, despite all three works having the same title. The full phrase from Psalm 23 from which the title comes is ‘Yea, though I walk through the valley of the shadow of death, I will fear no evil’. It is reported that the British soldiers gave the ravine its name. The emotive pull of Fenton’s composition is all the more apparent when compared with Robertson’s photograph and Simpson’s lithograph, although the round shot in Simpson’s work links it visually to Fenton’s photograph.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Omar Pacha (1806-1871)
1855
Salted paper print
17.6 x 14.2cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500341
Omar Pacha (1806-1871) was the commander of the Ottoman army at the beginning of the war, when the Russian incursions into the Balkan regions began. He was later to win a significant victory against the Russians at the Battle of Evpatoria on 17 February 1855 in the Crimea. Omar Pasha was photographed several times by Fenton, both seated and on horseback. A number of commanding officers were photographed in this way. It was probably to give the artist Thomas Barker a variety of poses which could be incorporated into his painting. Omar Pasha does appear on a horse in the final painting, but his head is a copy of this seated portrait. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Colonel Brownrigg and the two Russian boys Alma and Inkerman
1855
Salted paper print
16.8 x 15.5cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500375
This portrait shows Colonel Brownrigg of the Grenadier Guards, with two Russian boys who were apparently taken prisoner by the British. In a letter from 29 April 1855 to his wife, Fenton described what happened, ‘Tell Annie [Fenton’s daughter] there are two Russian boys here who both would like to come to England which will she have Alma or Inkermann, such are their new names. One is an orphen [sic] the other has or had his parents in the town. They went out nutting last autumn & were taken, cried sadly but now would cry to go back’. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Cooking house, 8th Hussars
1855
Albumen print
15.3 x 19.6cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500384
This beautifully composed group was incorporated almost entirely into Barker’s painting, although the woman standing at the back of the group was omitted. It is easily identifiable on the left-hand side of the painting. Fenton made a handful of photographs which try to capture the camp life of the ordinary soldier. The 8th Hussars were one of the regiments involved in the Charge of the Light Brigade and this association would give the photograph greater interest to the Victorian public. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Maréchal Pélissier, Duke of Malakoff (1794-1864)
Jun 1855
Albumen print
17.9 x 15.5cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500327
Fenton made several portraits of General Pélissier (1794-1864), on horseback and seated. Barker probably used this particular photograph to paint the general, who as the French Commander-in-Chief at the time of the final assault on Sevastopol in Summer 1855, features prominently in his painting. Pélissier had taken command of the French army on 16 May 1855, replacing General François Canrobert. He brought with him the energy and determination required to bring the siege of Sevastopol to a conclusion. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
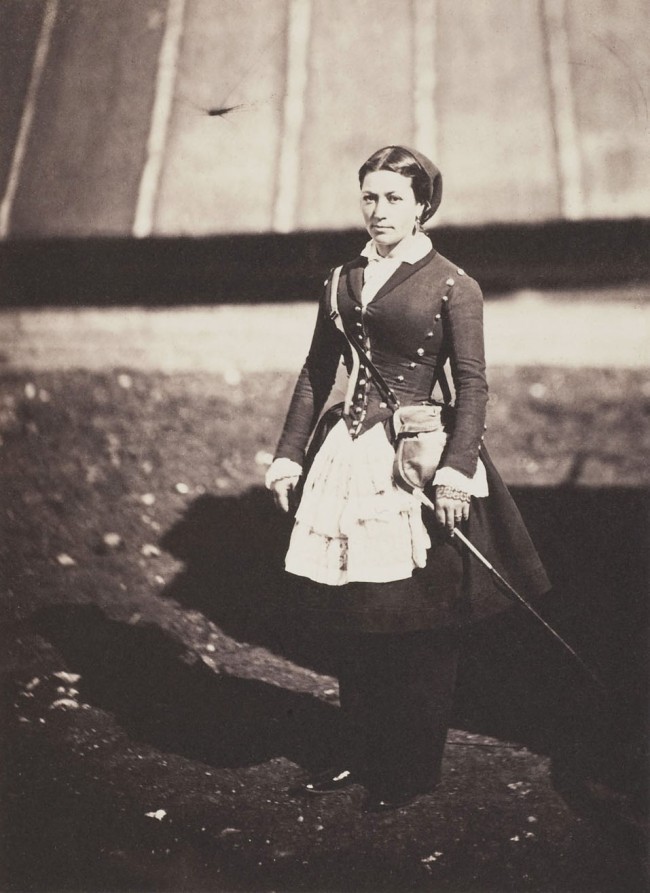
Captain and Mrs Duberly
Apr 1855
Albumen print
15.2 x 16.0 cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust / © Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500314
Frances Isabella Duberly (1829-1902), known as Fanny, accompanied her husband Captain Henry Duberly (1822-1891), Paymaster of the 8th Hussars, to the war against the orders of Lord Raglan. She kept a journal of her experience, which included witnessing the Battle of Balaklava. She was also one of the first civilians to enter Sevastopol after it fell to the allies. Mrs Duberly attempted to dedicate the published version of her journal to Queen Victoria, titled Journal Kept During the Russian War, but this was refused. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Wounded Zouave and Vivandiere
5 May 1855
Salted paper print
17.4 x 15.8cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500401
The vivandières, also known as cantinières, were attached to French regiments to supply the troops with food and drink beyond the standard rations. In a letter to his wife, Fenton described how he photographed this group on 5 May, ‘In the afternoon a Cantiniere was brought up I made first a picture of her by herself & then a group in which she is giving assistance to a wounded soldier. It was great fun the soldiers enjoyed it so much & entered so completely into the spirit of the thing’. This group was incorporated into Barker’s painting, although the composition was reversed. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Vivandière
5 May 1855
Albumen print
17.4 x 13.1cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500338
This striking portrait was taken at the same time as the earlier group photograph with the ‘wounded soldier’. The vivandières usually dressed in a feminised version of the uniform of the regiment to which they were attached. There were women attached to the British regiments, known as sutlers, who helped with food, drink and domestic duties. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Colonel Doherty and the Officers of the 13th Light Dragoons
1855
Salted paper print
14.6 x 19.0cm
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500354
Lieutenant Colonel Charles Doherty (d. 1866) was the commanding officer of the 13th Light Dragoons on the day of the Battle of Balaklava. His regiment was part of the Light Brigade, and his men participated in the famous charge. However, due to illness, Doherty did not join the battle. Doherty’s replacement that day, Captain John Oldham, was killed in the battle. Fenton probably photographed this group in anticipation of the interest in regiments who formed the Charge of the Light Brigade. Some of the men included in the group were amongst the chargers. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Ismael Pacha receiving his chibouque
27 Apr 1855
Albumen print
17.2 x 16.1cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500427
Ismael Pacha (1813-1865), also known as György Kmety, fought against the Russians in the 1848 Hungarian Revolution. After its failure and the harsh Russian reprisals, he joined the Ottoman army. Fenton took a series of photographs of Ismael Pacha receiving a pipe from his servants. Both Ismael Pacha and his Nubian servant, seen to the right of this photograph, appear in Barker’s painting The Allied Generals. Presumably acquired by Queen Victoria.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Ismael Pacha receiving his chibouque (detail)
27 Apr 1855
Albumen print
17.2 x 16.1cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500427
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
View from Cathcart’s Hill
1855
Albumen print
24.1 x 33.7cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500534
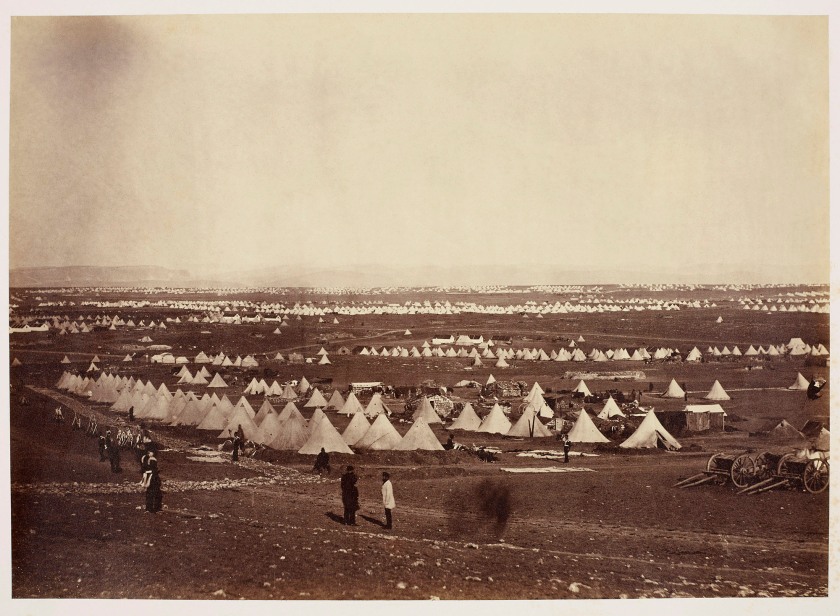
This photograph shows the British camps as seen from Cathcart’s Hill, the main British cemetery in the Crimea. The cemetery took its name from the grave of Sir George Cathcart, a senior military officer who was killed during the Battle of Inkerman. The hill was also used as an observation point as from it commanders could view the progress of the Siege of Sevastopol. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
General James Bucknall Estcourt (1802-1855)
1855
Albumen print
20.5 x 15.2cm
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500239
General Estcourt was a chief staff officer during the difficult first winter in the Crimea. He was among those most strongly criticised by the public and the press for the suffering of the army, although he was defended by his close friend Lord Raglan. He died of cholera in the Crimea in June 1855. The photograph is hard to interpret. It can be seen as someone taking a break from military concerns but it could also be a portrait of illness and exhaustion. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Sir William Howard Russell (1820-1907)
Jun 1855
Albumen print
18.1 x 15.3cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500306
William Howard Russell was a reporter for The Times who rose to fame during the Crimean War for his vivid descriptions of major battles and the conditions faced by British troops. The Crimean War was the first conflict where advances in technology allowed newspapers to quickly print reports from their correspondents in the field. These reports attracted great public interest and influenced both official and public attitudes to the war. Russell’s emotive account of the Charge of the Light Brigade, published in The Times on 13 November 1854, inspired the poem of the same name by Alfred, Lord Tennyson. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Sir Colin Campbell
1855
Albumen print
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017
Balaklava – the British base
When the British and French armies moved south to besiege Sevastopol, they had to choose a location in which to base themselves. The armies needed to be able to receive both men and supplies without hindrance for what might be many months. The French based themselves at Kamiesch, whilst the British chose Balaklava. The army took over the town, setting up its own infrastructure including a Post Office and constructing a military railway to transport the supplies as close as possible to the front lines.
When Fenton arrived in the Crimea on 8 March 1855, he disembarked at Balaklava. He took his first photographs on 15 March and spent the next two weeks exploring the port. He described the place in a letter as ‘one great pigsty’, noting the chaos and confusion which he managed to convey in his photographs.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Railway sheds and workshops at Balaklava
15 Mar 1855
Albumen print
20.9 x 26.1cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500463
This photograph clearly shows the scale of activity in Balaklava. There are ships in the harbour, and supplies (probably flour bags) are piled high on the water’s edge. In the foreground in ‘Railway Yard’ the new military railway is being constructed. It was paid for by Samuel Morton Peto (1809-1889) who had also provided Fenton’s passage to the Crimea. Construction of the railway began in February 1855 and part of the line was in use within weeks, probably around the same time that Fenton arrived at Balaklava. The railway was dismantled in 1856 after the end of the war. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Guards Hill Church Parade Balaklava in the distance
1855
Salted paper print
26.1 x 35.3cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500530
Towards the end of March, Fenton made a number of views from ‘Guards Hill’ looking down towards the harbour of Balaklava. The ‘church parade’ referred to in the title is the parade of Scots Fusilier Guards seen to the right of the image. Although the group is indistinct, the bearskin hats of the Guards can be clearly distinguished. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Cossack Bay Balaklava
Mar 1855
Albumen print
26.8 x 35.6cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500498
Despite the title, Cossack Bay is only slightly visible in the middle distance of this photograph. The main view with the ships, including one bearing the number ’69’, centres around Cattle Pier. The ship with the transport number 69 is the Albatross, which at the time of this photograph had recently arrived from Constantinople after a four-day journey bringing Mary Seacole (1805-1881). Mrs Seacole set up a store and ‘hotel’ for British servicemen, supplying food, drink and medical supplies. In 1857 Mrs Seacole published an autobiographical account of her life and experiences in the Crimea, titled Wonderful Adventures of Mrs Seacole in Many Lands. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
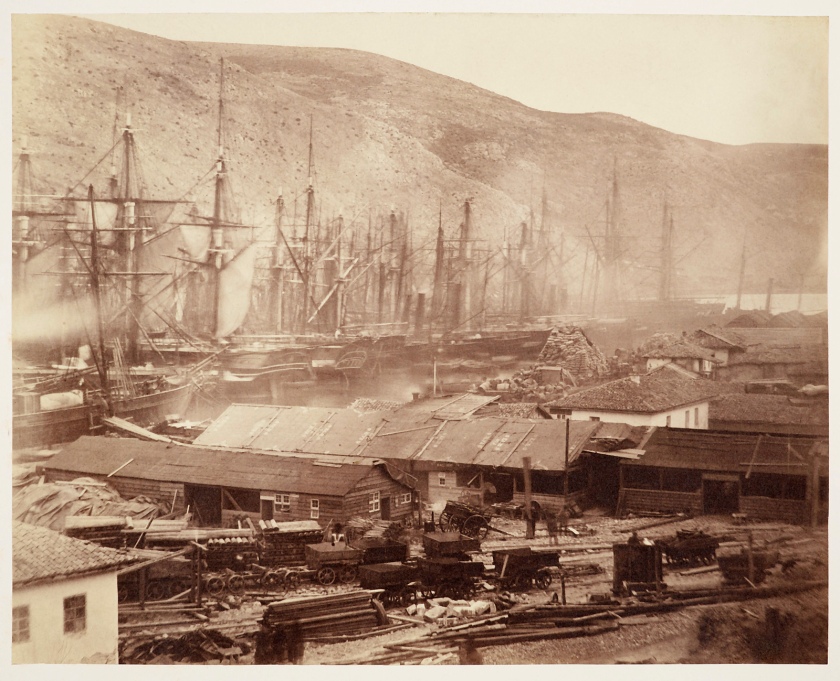
The Ordnance Wharf at Balaklava
Mar 1855
Albumen print
20.5 x 25.2cm (image)
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017 RCIN 2500461
The Ordnance Wharf was the place where military supplies arrived – the British army’s Board of Ordnance was responsible for supplying weapons and ammunition, which can be clearly seen in the foreground of this photograph. The round shot is stacked awaiting transportation on the railway to reach the army camps besieging Sevastopol. The performance of the Board of Ordnance came under heavy criticism during the Crimean War, particularly during the 1854-1855 winter. As a result, after a 400 year existence, the Board was abolished and its responsibilities were transferred to the War Office. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Balaklava from the Russian Church, Upper Harbour, and Church of Kadikoi in the distance
1855
Albumen print
Royal Collection Trust
© Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2017
After the war
Fenton left the Crimea on 22 June 1855, so missed the fall of Sevastopol. He arrived back in Britain on 11 July. Queen Victoria saw a selection of his work in August, whilst she was at Osborne House, and Fenton visited France in early September to show his photographs to the Emperor.
Fenton also began preparations for the display of his work at numerous venues across Britain. Hundreds of prints would have been required for the 26 venues identified so far, including Edinburgh, Glasgow, Exeter, Cardiff, Belfast and Dublin. Fenton also managed to photograph some of the significant individuals he had been unable to capture in the Crimea, in order to complete his commission for Agnew’s.
The photographs were extraordinarily popular with the public. One publication stated that two million visitors had seen the photographs by the end of March 1856. It is unlikely that this translated into financial success for Fenton, however. At the end of 1856 Agnew’s sold the negatives and remaining prints to a rival print seller, who continued to sell the work at a much lower price. Fenton continued his association with the royal family, travelling to Balmoral in September 1856 where he photographed the royal children.
Felice Beato (Italian-British, 1832-1909)
The Docks after the Explosion
1856
Salted paper print
23.7 x 28.7cm (image)
RCIN 2500683
James Robertson’s business partner and brother-in-law, Felice Beato, returned to Sevastopol in March or April 1856 to make a further set of photographs. By then the docks had been destroyed. Viewed together, these photographs provide a record of the changing landscape of the city in the aftermath of the war. From the collection of the Prince of Wales, later King Edward VII.
Fenton’s photographic process
Fenton made his photographs by printing from glass negatives, using a process called the wet collodion process. The negatives were then shipped back to Britain where they were used to make prints in two different ways – the salted paper print and the albumen print.
The wet collodion process used a prepared piece of glass which, in the darkroom, would be coated with collodion and then made light-sensitive with further chemicals. Before the plate could dry, it would be placed in the camera and exposed. Then the plate would be returned to the darkroom and developed, rinsed, fixed, washed, dried and varnished. It was then ready for printing.
The salted paper print used paper which had been prepared by coating it in a salted solution. After drying, it would be made light-sensitive in the darkroom and then placed in a frame in contact with the glass negative to be exposed to sunlight. Once the image had appeared satisfactorily on the paper, the print would be processed, washed, fixed and toned.
The Queen’s Gallery
Buckingham Palace,
London, SW1A 1AA
Opening hours:
Open daily 09.30 – 16.15























































































![David Hill and Robert Adamson. 'The Gowan [Margaret and Mary Cavendish]' c. 1843-1848 David Hill and Robert Adamson. 'The Gowan [Margaret and Mary Cavendish]' c. 1843-1848](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/david-hill-and-robert-adamson-the-gowan-margaret-and-mary-cavendish-c-1843-1848-web.jpg?w=840)
























![John S. Johnston. 'One of Dr Kane’s Men [possibly William Morton]' c. 1857 John S. Johnston. 'One of Dr Kane’s Men [possibly William Morton]' c. 1857](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/john-s-johnston-one-of-dr-kanes-men-possibly-william-morton-c-1857-web.jpg?w=650&h=930)
































































![Andrea Bruce. 'Untitled [A father home on leave reading the newspaper with his son, who wears his dad’s helmet]' 2006 Andrea Bruce. 'Untitled [A father home on leave reading the newspaper with his son, who wears his dad’s helmet]' 2006](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/12/andrea-bruce.jpg?w=840)






















![Harry Callahan (American, 1912-1999) [Detroit] 1941](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/10/harry-callahan-detroit.jpg?w=840)







![Franck-François-Genès Chauvassaignes (French, 1831 - after 1900) 'Untitled [Female Nude in Studio]' 1856-59 Franck-François-Genès Chauvassaignes (French, 1831 - after 1900) 'Untitled [Female Nude in Studio]' 1856-59](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/chauvassaignes_seated-nude-web.jpg?w=838&h=1024)
![Eugène Durieu (French, 1800-1874) 'Untitled [Seated Female Nude]' 1853-54 Eugène Durieu (French, 1800-1874) 'Untitled [Seated Female Nude]' 1853-54](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/durieu_nude_ph8976-web.jpg?w=704&h=1024)
![Charles Alphonse Marlé (French, 1821 - after 1867) 'Untitled [Standing Male Nude]' c. 1855 Charles Alphonse Marlé (French, 1821 - after 1867) 'Untitled [Standing Male Nude]' c. 1855](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/marle_standing-male-nude-web.jpg?w=701&h=1024)
![Félix-Jacques-Antoine Moulin (French, 1800 - after 1875) 'Untitled [Two Standing Female Nudes]' c. 1850 Félix-Jacques-Antoine Moulin (French, 1800 - after 1875) 'Untitled [Two Standing Female Nudes]' c. 1850](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/moulin_two-nudes-standing-web.jpg?w=811&h=1024)
![Julien Vallou de Villeneuve (French, 1795-1866) '[Reclining Female Nude]' c. 1853](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/09/julien-vallou-de-villeneuve-reclining-female-nude.jpg?w=840)






![Mark Morrisroe (American, 1959 - 1989) 'Untitled [Two Men in Silhouette]' c. 1987 Mark Morrisroe (American, 1959 - 1989) 'Untitled [Two Men in Silhouette]' c. 1987](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/16_morrisroe_untitled-web.jpg?w=740&h=1024)
You must be logged in to post a comment.