Exhibition dates: 27th March – 9th September 2012
Many thankx to the Metropolitan Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
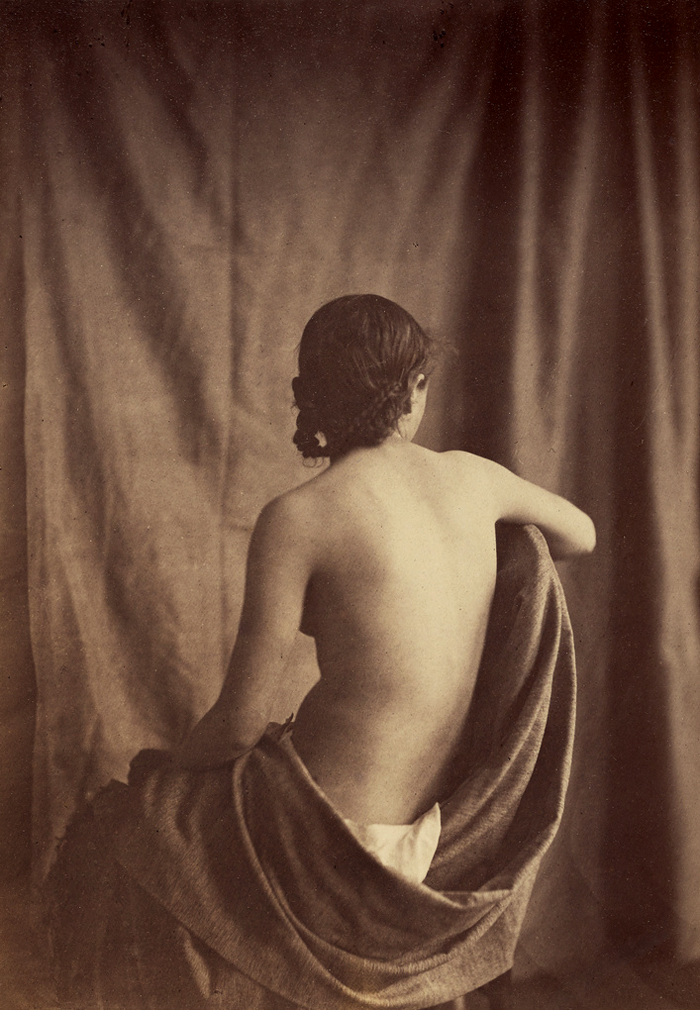
Franck-François-Genès Chauvassaignes (French, 1831 – after 1900)
Untitled [Female Nude in Studio]
1856-1859
Salted paper print from glass negative
19.1 x 15.2cm (7.5 x 6 in.)
Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1998
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Public domain
This corner of a painter’s atelier somewhere in France in the middle of the nineteenth century is scarcely tethered to time or place; it could as easily be a loft in New York today or, had photography existed four centuries earlier, a studio in the Italian Renaissance. What is surprising here is the absence of even the thinnest disguise – no swags of drapery, elaborate coiffure, or skeins of beads as are commonly found in the work of other purveyors of “studies for artists.” Here, the model is utterly naked. With her intelligent head and dirty feet, this young woman helped found the matter-of-fact modelling sorority joined a decade later by Édouard Manet’s Olympia.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Eugène Durieu (French, 1800-1874)
Untitled [Seated Female Nude]
1853-54
Albumen silver print from glass negative
6 13/16 × 4 11/16 in. (17.3 × 11.9cm)
Gilman Collection, Purchase, Mr. and Mrs. Henry R. Kravis Gift, 2005
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Public domain
Durieu was a lawyer and early advocate and practitioner of photography in France who, in 1853-1854, made a series of photographic studies of nude and costumed figures as models for artists. The French Romantic painter Eugène Delacroix helped him pose the figures and later praised the prints, from which he sketched, as “palpable demonstrations of the free design of nature.” While the painter saw the accurate transcription of reality as a virtue of photography, Durieu knew that a good photograph was not simply the result of the correct use of the medium but, more significantly, an expression of the photographer’s temperament and vision. In an important article he emphasised the interpretative nature of the complex manipulations in photography and explained that the photographer must previsualise his results so as to make a “picture,” not just a “copy.”
This photograph proves Durieu’s point: through the elegant contours of the drapery, the smooth modelling of the flesh, and the grace and restraint of the pose, the picture attains an artistic poise that combines Delacroix’s sensuality with Ingres’s classicism, and rivals both.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
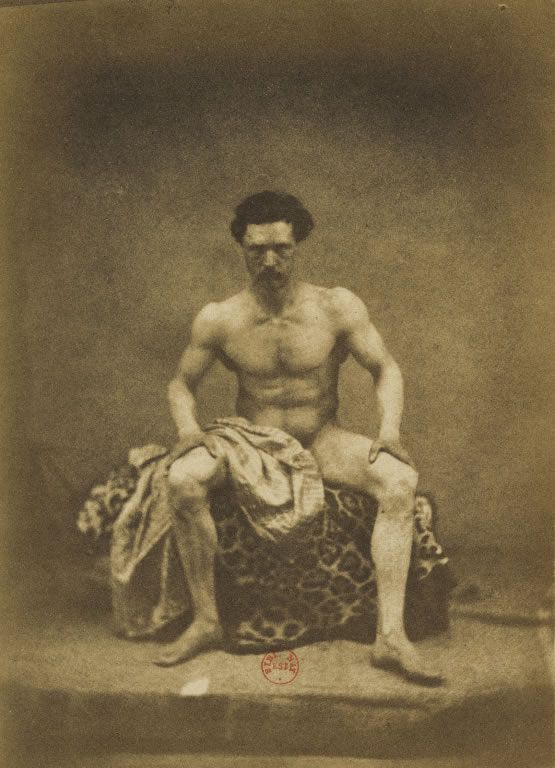
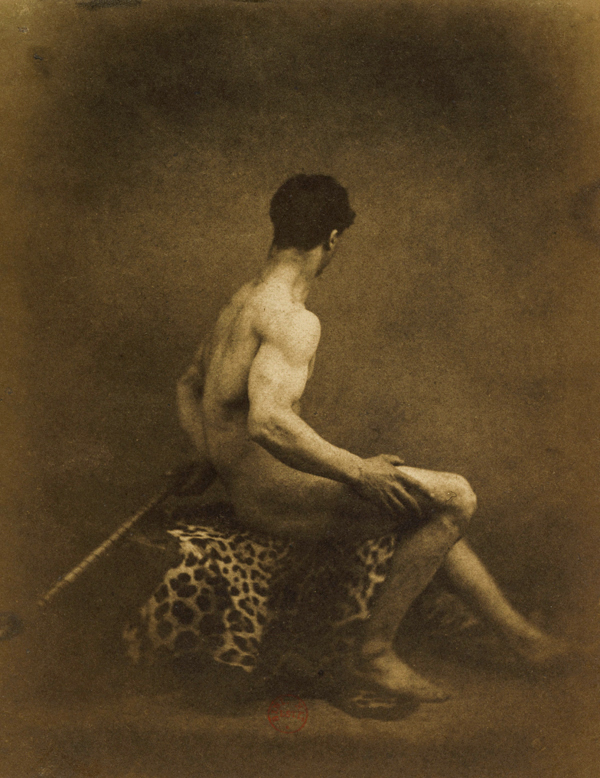
Charles Alphonse Marlé (French, 1821 – after 1867)
Untitled [Standing Male Nude]
c. 1855
Salted paper print from paper negative
25.7 x 17.6cm (10 1/8 x 6 15/16 in.)
Purchase, Ezra Mack Gift and The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1991
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Marlé’s photograph was probably intended as an aid for painters and sculptors. The jury-rigged arrangement of podium, books, and potted tree, as well as the painting held in the background by a studio assistant, may strike the modern viewer as an incongruous contrast to the heroic gesture of the model. Marlé and those who bought his photograph, however, would have been absorbed by the grand academic pose and likely would have thought the awkward accoutrements of little consequence.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Félix-Jacques-Antoine Moulin (French, 1800 – after 1875)
Untitled [Two Standing Female Nudes]
c. 1850
Daguerreotype
Visible: 14.5 x 11.1cm (5 11/16 x 4 3/8 in.)
The Rubel Collection, Purchase, Anonymous Gift and Lila Acheson Wallace Gift, 1997
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Public domain
Although Moulin was sentenced in 1851 to a month in jail for producing images that, according to court papers, were “so obscene that even to pronounce the titles… would be to commit an indecency,” this daguerreotype seems more allied to art than to erotica. Instead of the boudoir props and provocative poses typical of hand-coloured pornographic daguerreotypes, Moulin depicted these two young women utterly at ease, as unselfconscious in their nudity as Botticelli’s Venus.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Depicting the human body has been among the greatest challenges, preoccupations, and supreme achievements of artists for centuries. The nude – even in generalised or idealised renderings – has triggered impassioned discussions about sin, sexuality, cultural identity, and canons of beauty, especially when the chosen medium is photography, with its inherent accuracy and specificity. Through September 9, 2012, Naked before the Camera, an exhibition of more than 60 photographs selected from the renowned holdings of The Metropolitan Museum of Art, surveys the history of this subject and explores some of the motivations and meanings that underlie photographers’ fascination with the nude.
“In every culture and across time, artists have been captivated by the human figure,” commented Thomas P. Campbell, Director of the Metropolitan. “In Naked before the Camera, we see how photographers have used their medium to explore this age-old subject and create compelling new images.”
The exhibition begins in the 19th century, when photographs often served artists as substitutes for live models. Such “studies for artists” were known to have been used by the French painter Gustave Courbet, whose Woman with a Parrot (1866), for instance, is strikingly similar to photographer Julien Vallou de Villeneuve’s Female Nude of 1853. Even when their stated purpose was to aid artists, however, the best of these 19th-century photographs of the nude were also intended as works of art in their own right. Two recently acquired photographs, made in the mid-1850s by an unknown French artist, are striking examples. Not only are they larger than all other photographic nudes from the time, they stand out due to an extraordinary surface pattern that interrupts the images and suggests a view through gossamer or a photograph printed on finely pleated silk rather than paper. The elegant Female Nude harkens back to an Eve or Venus and is vignetted by the camera lens as if seen through a peephole, while her male counterpart is shown in strict profile in a pose that recalls precedents from antiquity. Each figure draws from the past while being presented in a strikingly modern way, without any equivalent among other 19th-century studies for artists.
Not all photographers of the nude were motivated by artistic desire. The second section of Naked before the Camera includes photographs made for medical and forensic purposes, as ethnographic studies, as tools to analyse anatomy and movement, and – not surprisingly – as erotica. The lines between such categories were not always clearly drawn; some photographers called their images “studies for artists” merely to evade the censors, while viewers of the G. W. Wilson Studio’s Zulu Girls (1892-93) or Paul Wirz’s ethnographic photographs of scantily clad Indonesians from the 1910s and 1920s were undoubtedly titillated by the blending of exoticism and eroticism.
Beginning in the fertile period of modernist experimentation that followed on the heels of World War I, photographers such as Brassaï, Man Ray, Hans Bellmer, André Kertész, and Bill Brandt found in the human body a perfect vehicle for both visual play and psycho-sexual exploration. In Distortion #6 (1932) by André Kertész, a woman’s body is stretched and pulled in the reflections of a fun-house mirror – a figure from a Surrealist dream that stands in stark contrast to the images of perfect feminine beauty by earlier photographers.
In mid-20th-century America, photographers more often communicated an intimate connection with their subjects. Following the example of Alfred Stieglitz’s famed portraits of Georgia O’Keeffe, photographers such as Edward Weston, Harry Callahan, and Emmet Gowin made many nude studies of their wives. Callahan’s photograph of his wife and daughter, Eleanor and Barbara, Chicago (1954), for instance, gives the viewer access to a private, tender moment of intimacy.
In the wake of the sexual revolution of the 1960s and the AIDS crisis that began in the 1980s, artists began to think of the body as a politicised terrain and explored issues of identity, sexuality, and gender. Diane Arbus’s Retired man and his wife at home in a nudist camp one morning, N.J. (1963) and A naked man being a woman, N.Y.C. (1968), Larry Clark’s untitled image (1972-1973) from the series Teenage Lust, and Hannah Wilke’s Snatch Shot with Ray Gun (1978) are among the works featured in the concluding section of the exhibition.
Press release from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Julien Vallou de Villeneuve (French, 1795-1866)
[Reclining Female Nude]
c. 1853
Salted paper print from paper negative
11.8 x 16.0cm (4 5/8 x 6 5/16 in.)
Purchase, Lila Acheson Wallace Gift, 1993
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Public domain
A student of the painter Jean François Millet and a lithographer of scenes of daily life, costume, and erotica in the 1820s and 1830s, Vallou reportedly took up photography in the early 1840s, but his early photographs have not been identified. Perhaps they depicted naked women, a subject for which it was improper to acknowledge authorship.
Between 1851 and 1855, however, Vallou made a series of photographs of female nudes that he marketed (and legally registered) as models for artists. Vallou’s nudes have long been associated with those of Gustave Courbet, who is known to have used photographs in his painting process. Although no absolute one-to-one correspondence can be pointed to, the heavy soporific quality of Vallou’s models is very close to Courbet’s concept of the nude, and the reclining figure displayed here is strikingly similar in pose to the painter’s Woman with a Parrot (1866), on view in the galleries for nineteenth-century painting.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Brassaï (French born Romania, Brasov 1899 – 1984 Côte d’Azur)
Nude
1931-1934
Gelatin silver print
14.1 x 23.5cm (5 9/16 x 9 1/4 in.)
Twentieth-Century Photography Fund, 2007
© The Estate of Brassai
Metropolitan Museum of Art
One of the most radically abstract of Brassaï’s nudes, this image was published in 1933 in the inaugural issue of the avant-garde magazine Minotaure. With the figure’s head and legs cut off by the picture’s edges, the twisting, truncated torso seems to float in space like an apparition – an ambiguous, organic form with an uncanny resemblance to a phallus. This transformation of the female figure into a fetish object is a hallmark of Surrealism that reflects the important influence of Freud’s psychoanalytic theory on European art of the early twentieth century.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Man Ray (American, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 1890 – 1976 Paris)
Arm
c. 1935
Gelatin silver print
29.7 x 23.0cm (11 11/16 x 9 1/16 in.)
Ford Motor Company Collection, Gift of Ford Motor Company and John C. Waddell, 1987
© 2012 Man Ray Trust / Artists Rights Society (ARS), NY / ADAGP, Paris
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Man Ray’s photograph of an arm is cropped so abstractly that it seems to metamorphose into other body parts – a knee, a calf, a thigh – or into some utterly unidentifiable yet heroic form. This image appeared on the cover of Formes Nues (1935), which also included the work of Brassaï, László Moholy-Nagy, Franz Roh, and George Platt Lynes, among others.
In the magazine’s introduction, Man Ray wrote, “were it not for the fact that photography permits me to seize and to possess the human body and face in more than a temporary manner, I should quickly have tired of this medium.”
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
André Kertész (American born Hungary, Budapest 1894 – 1985 New York City)
Distortion #6
1932
Gelatin silver print
23.4 x 17.3cm (9 3/16 x 6 13/16 in.)
Ford Motor Company Collection, Gift of Ford Motor Company and John C. Waddell, 1987
© The Estate of André Kertész / Higher Pictures
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Although Kertesz had long been interested in mirrors, reflections, and the idea of distorting the human figure, he did not seriously investigate their photographic possibilities until 1933, when the risqué French magazine Le Sourire commissioned him to make a series of figure studies. Using a funhouse mirror from a Parisian amusement park, Kertesz, who had never photographed nudes before, spent four weeks making about two hundred negatives.
Kertész accentuated the narrow ribcage and long waist of the ideal contemporary woman by photographing his model in a carnival mirror. If the top half of this beautiful nude resembles those Modigliani painted, the swell of the haunch recalls Mannerist nudes and their nineteenth-century revivals, especially Ingres’ grande odalisque.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Irving Penn (American, Plainfield, New Jersey 1917 – 2009 New York City)
Nude No. 57
1949-1950
Gelatin silver print
39.4 x 37.5cm (15 1/2 x 14 3/4 in.)
Gift of the artist, 2002
© 1950-2002 Irving Penn
Diane Arbus (American, 1923-1971)
Retired man and his wife at home in a nudist camp one morning, N.J.
1963
Gelatin silver print
39.9 × 37.9cm (15 11/16 × 14 15/16 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Arbus’s interest in the tension between revelation and concealment comes into starkest focus in the portraits she made at Sunshine Park, a family nudist camp in New Jersey. While nudism might be considered the ultimate form of exposure, it often required a different kind of cover-up. As the artist remarked in an unpublished article written for Esquire magazine in 1966: “For many of these people, their presence here is the darkest secret of their lives, unsuspected by relatives, friends, and employers in the outside world, the disclosure of which might bring disgrace.”
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Diane Arbus (American, 1923-1971)
A naked man being a woman, N.Y.C.
1968
Gelatin silver print
38.2 x 36.2cm
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Mark Morrisroe (American, 1959 – 1989)
Untitled [Two Men in Silhouette]
c. 1987
Gelatin silver print
28.4 x 20.8cm (11 3/16 x 8 3/16 in.)
Twentieth-Century Photography Fund, 2009
© The Estate of Mark Morrisroe (Ringier Collection) at Fotomuseum Winterthur
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Sexuality and mortality – which many would say are central preoccupations of humankind – are key to Morrisroe’s biography and art. The son of a drug-addicted mother, a teenage hustler, and a precocious punk queer, Morrisroe carried a bullet (shot by a disgruntled john) in his chest from the age of eighteen and consequently walked with a limp that added one more element to his outsider self-image. Sex and death were persistent themes in his work, with pronounced poignancy after his 1986 AIDS diagnosis. In this work, Morrisroe has taken a page from a gay S&M magazine, cut out the shapes of two naked men, and used the sheet as a negative to print a unique image in which the figures – literally absent – appear as dark silhouettes against a netherworld of sexual activity.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
1000 Fifth Avenue at 82nd Street
New York, New York 10028-0198
Phone: 212-535-7710
Opening hours:
Thursday – Tuesday 10am – 5pm
Closed Wednesday

![Franck-François-Genès Chauvassaignes (French, 1831 - after 1900) 'Untitled [Female Nude in Studio]' 1856-59 Franck-François-Genès Chauvassaignes (French, 1831 - after 1900) 'Untitled [Female Nude in Studio]' 1856-59](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/chauvassaignes_seated-nude-web.jpg?w=838&h=1024)
![Eugène Durieu (French, 1800-1874) 'Untitled [Seated Female Nude]' 1853-54 Eugène Durieu (French, 1800-1874) 'Untitled [Seated Female Nude]' 1853-54](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/durieu_nude_ph8976-web.jpg?w=704&h=1024)
![Charles Alphonse Marlé (French, 1821 - after 1867) 'Untitled [Standing Male Nude]' c. 1855 Charles Alphonse Marlé (French, 1821 - after 1867) 'Untitled [Standing Male Nude]' c. 1855](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/marle_standing-male-nude-web.jpg?w=701&h=1024)
![Félix-Jacques-Antoine Moulin (French, 1800 - after 1875) 'Untitled [Two Standing Female Nudes]' c. 1850 Félix-Jacques-Antoine Moulin (French, 1800 - after 1875) 'Untitled [Two Standing Female Nudes]' c. 1850](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/moulin_two-nudes-standing-web.jpg?w=811&h=1024)
![Julien Vallou de Villeneuve (French, 1795-1866) '[Reclining Female Nude]' c. 1853](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/julien-vallou-de-villeneuve-reclining-female-nude.jpg?w=840)






![Mark Morrisroe (American, 1959 - 1989) 'Untitled [Two Men in Silhouette]' c. 1987 Mark Morrisroe (American, 1959 - 1989) 'Untitled [Two Men in Silhouette]' c. 1987](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/16_morrisroe_untitled-web.jpg?w=740&h=1024)














You must be logged in to post a comment.