Visited October 2019 posted May 2020
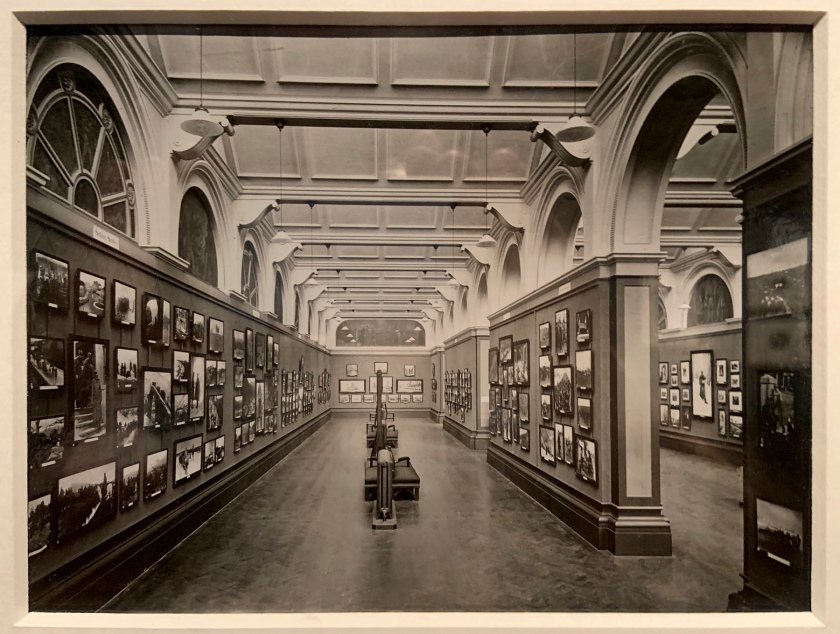
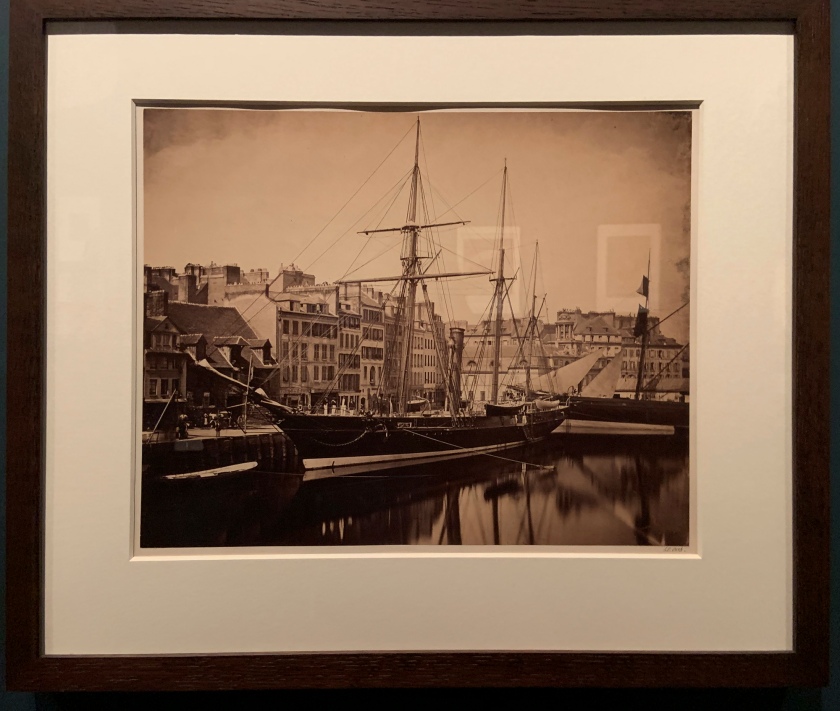
Unknown photographer
Photograph of Allied War exhibition, Serbian Section, V&A (installation view)
1917
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The older I grow, the more exponentially I appreciate and love these early photographs. Imagine having a collection like this!
Wonderful to see Edward Steichen’s Portrait – Lady H (1908, below) as I have a copy of Camera Work 22 in my collection.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
All iPhone images © Dr Marcus Bunyan. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
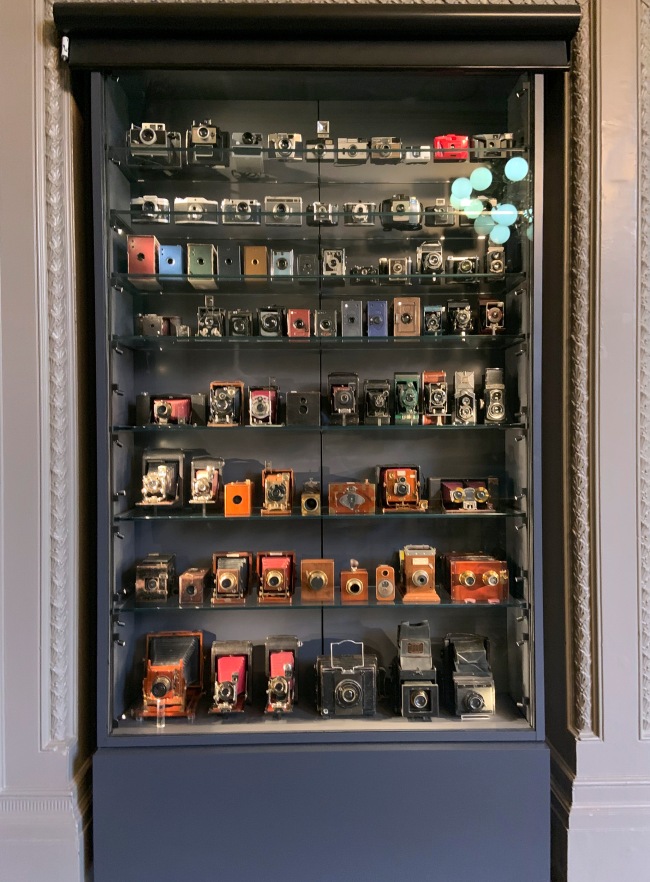
The V&A has been collecting photographs since 1856, the year the Museum was founded, and it was one of the first museums to present photography exhibitions. Since then the collection has grown to be one of the largest and most important in the world, comprising around 500,000 images. The V&A is now honoured to have added the Royal Photographic Society (RPS) collection to its holdings, which contains around 270,000 photographs, an extensive library, and 6,000 cameras and pieces of equipment associated with leading artists and photographic pioneers.
Take a behind-the-scenes look at our world class photography collection following the transfer of the Royal Photographic Society (RPS) Collection, which has enabled a dramatic reimagining of the way photography is presented at the V&A. The photographs curators introduce a series of five highlights that are on display in the new Photography Centre, which opened on 12th October 2018. The first phase of the centre will more than double the space dedicated to photography at the Museum.
Text from the V&A and YouTube websites
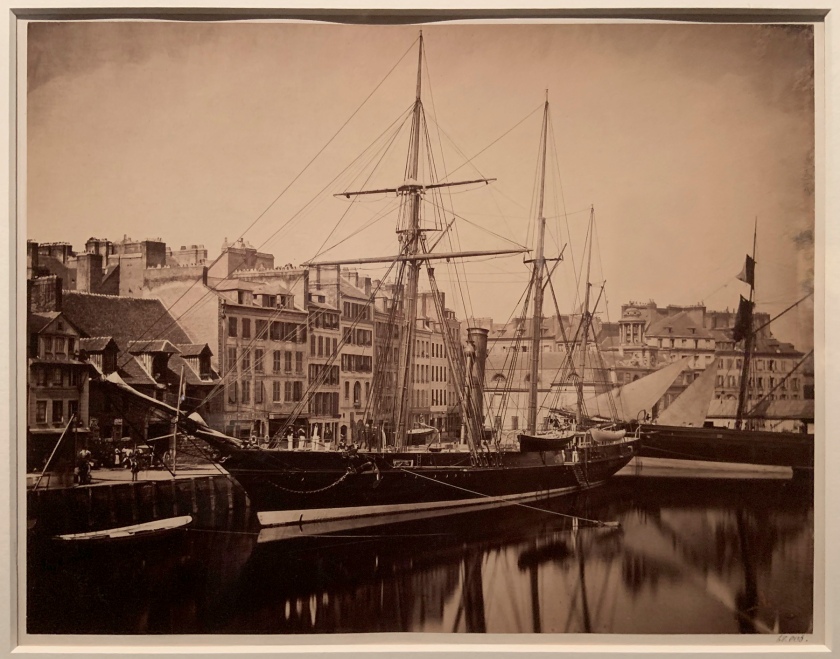
Unknown photographer
Photograph of Allied War exhibition, Serbian Section, V&A (installation view)
1917
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The V&A has been collecting and exhibiting photographs since the 1850s. This image shows part o a photographic exhibition held over 100 years ago in the same galleries you are standing in today. The exhibition presented a densely packed display of images depicting the Allied Powers during the First World War.
Installation views of the V&A Photography Centre, London
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
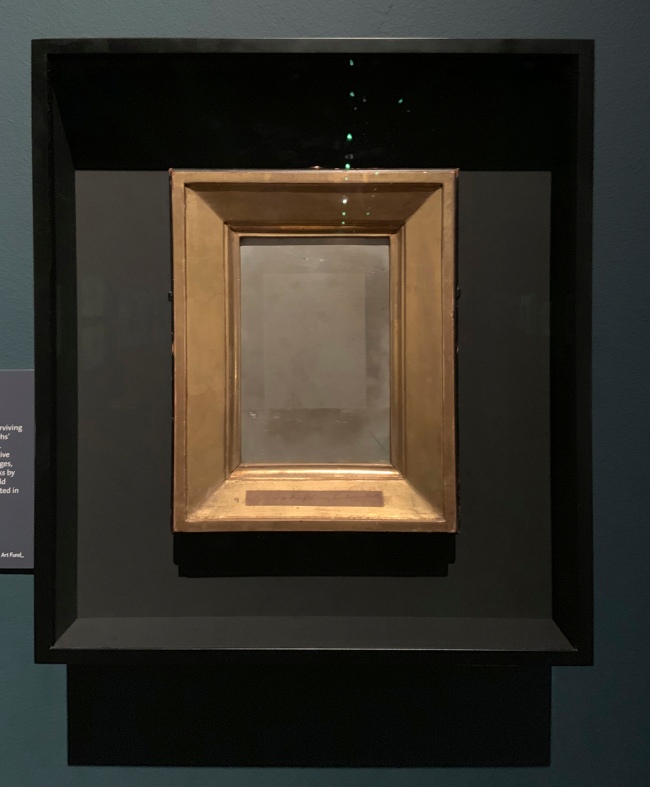
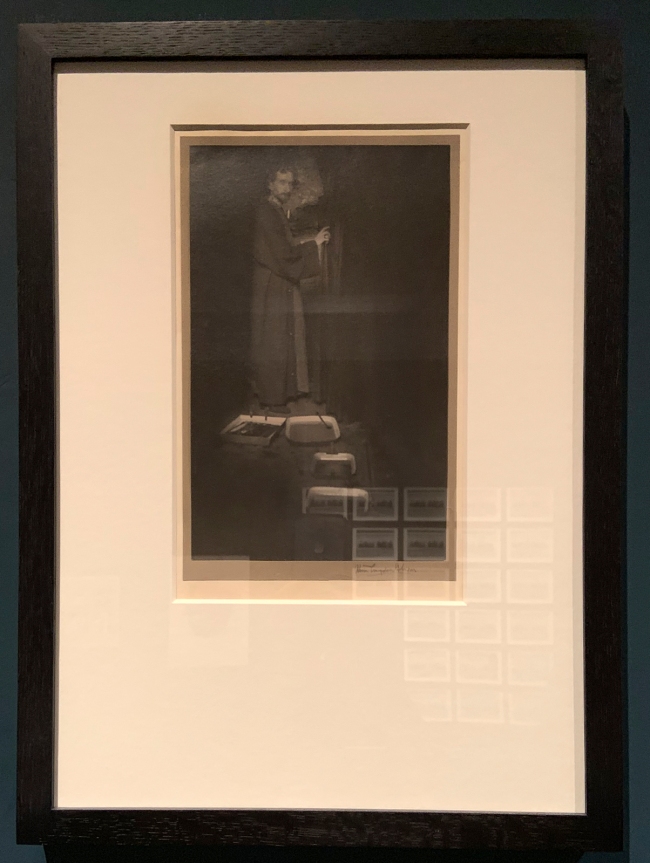
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce (French, 1765-1833)
Christ Carrying his Cross (installation views)
1827
Heliograph on pewter plate
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
The French inventor Niépce made the earliest surviving photographic images, which he called ‘heliographs’ or ‘sun-writing’. Only 16 are thought to still exist. Although Niépce experimented with light-sensitive plates inside a camera, he made most of his images, including this one, by placing engravings of works by other artists directly onto a metal plate. He would probably have had the resulting heliographs coated in ink and printed.
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce (French, 1765-1833)
Christ Carrying his Cross (installation view)
1827
Heliograph on pewter plate
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
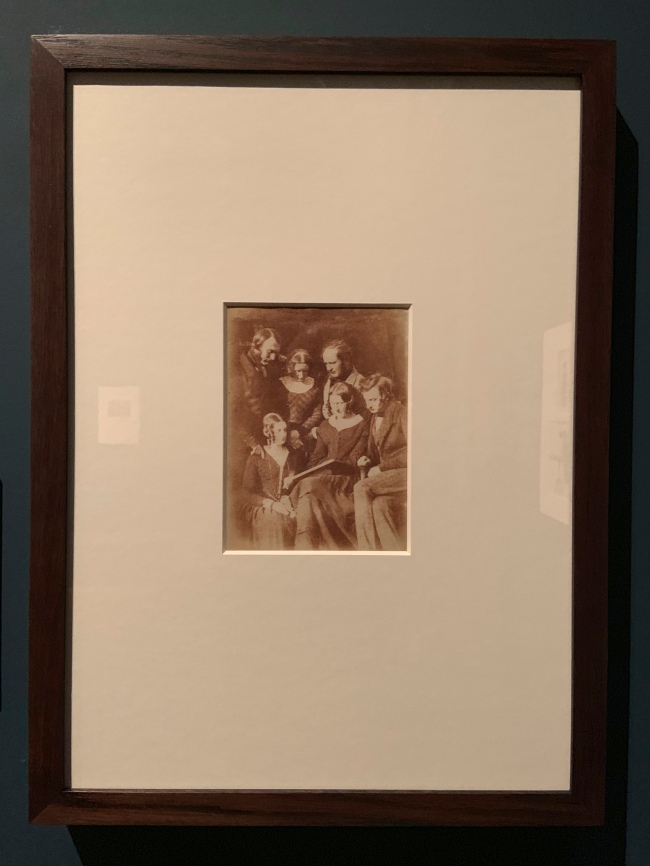
David Octavius Hill (Scottish, 1802-1870) and Robert Adamson (Scottish, 1821-1848)
The Adamson Family (installation view)
1843-1845
Salted paper print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The partnership between Scottish painter Hill and chemist Adamson merged the art and science of photography. The pair initially intended to create preliminary studies for Hill’s paintings, but soon recognised photography’s artistic potential. With Hill’s knowledge of composition and lighting, and Adamson’s considerable sensitivity and dexterity in handling the camera, together they produced some of the most accomplished photographic portraits of their time.
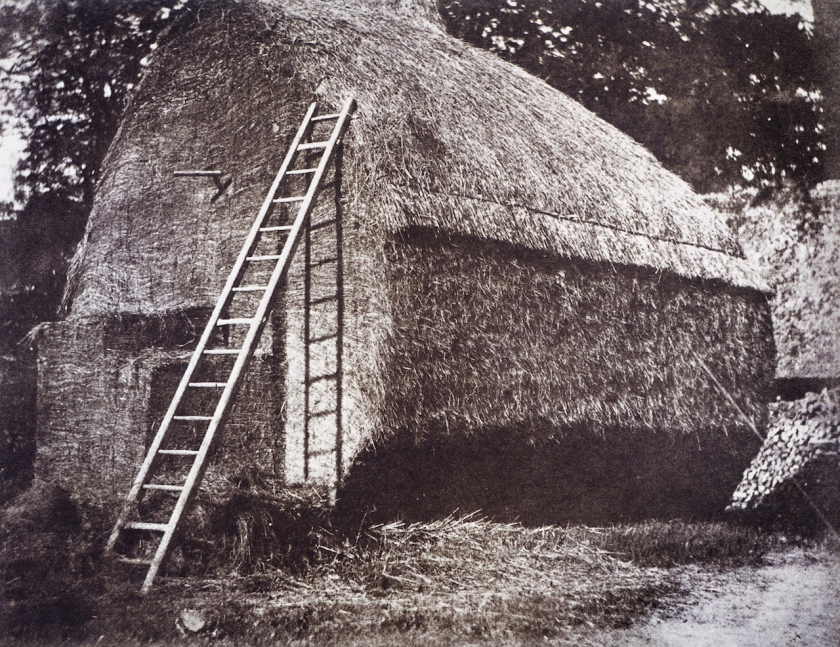
William Henry Fox Talbot (British, 1800-1877)
The Haystack
1844
From The Pencil of Nature
Salted paper print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
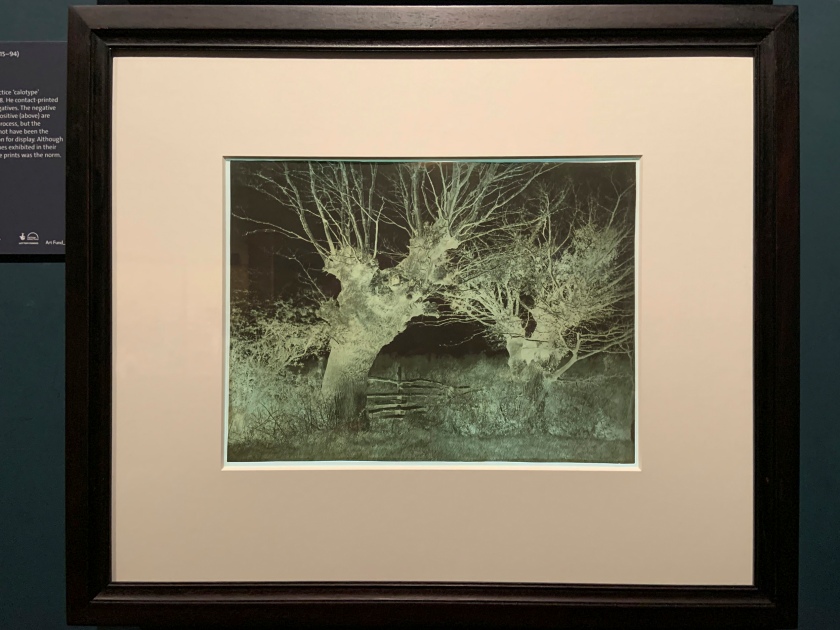
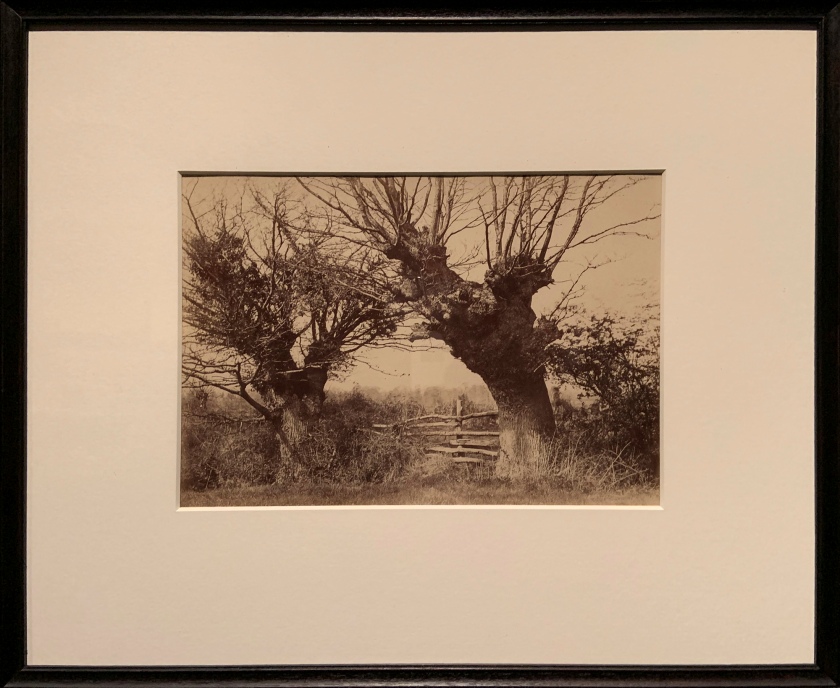
Benjamin Brecknell Turner (British, 1815-1894)
Hedgerow Trees, Clerkenleap (installation views)
1852-1854
Albumen print; Calotype negative
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Turner took out a licence to practice ‘calotype’ photography from Talbot in 1848. He contact-printed positive images from paper negatives. The negative (below) and its corresponding positive (above) are reunited here to illustrate this process, but the pairing as you see them would not have been the photographer’s original intention for display. Although unique negatives were sometimes exhibited in their own right, only showing positive prints was the norm.
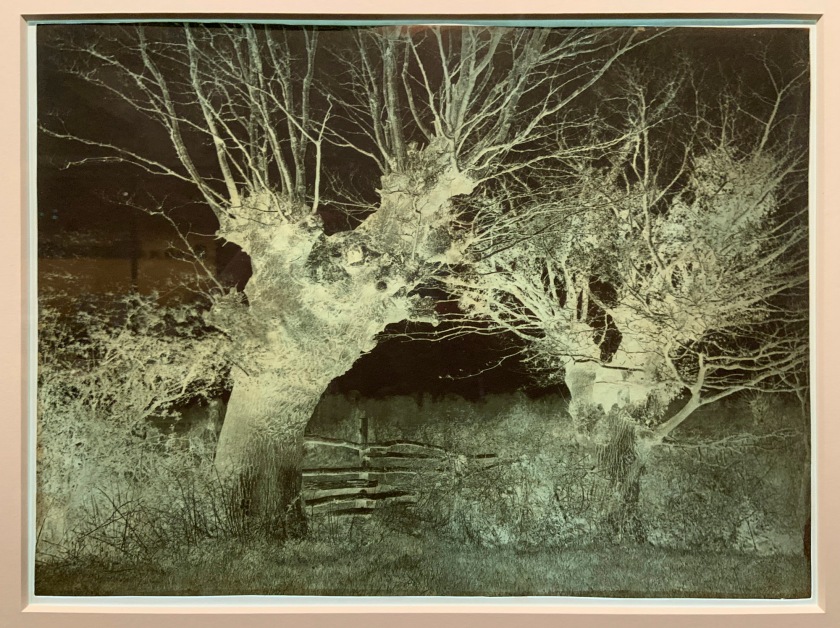
Benjamin Brecknell Turner (British, 1815-1894)
Hedgerow Trees, Clerkenleap (installation view)
1852-1854
Albumen print; Calotype negative
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
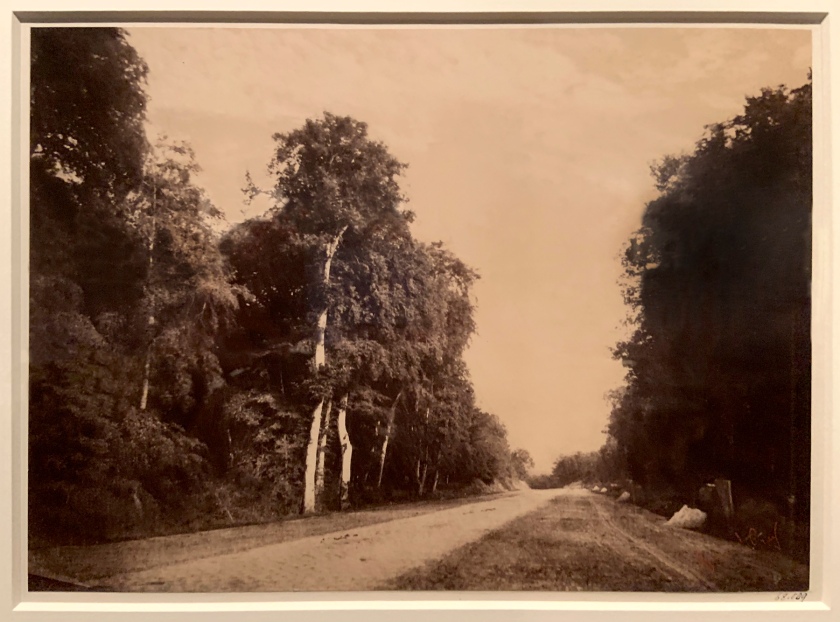
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
The Road to Chailly, Forest of Fontainebleau (installation view)
1852
Albumen print from a collodion glass negative
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Installation views of the V&A Photography Centre, London
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
The Marseillaise (The Departure of the Volunteers of 1792), by Francois Rude, 1833-35, Arc de Triomphe de l’Etoile, Paris (installation view)
1852
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
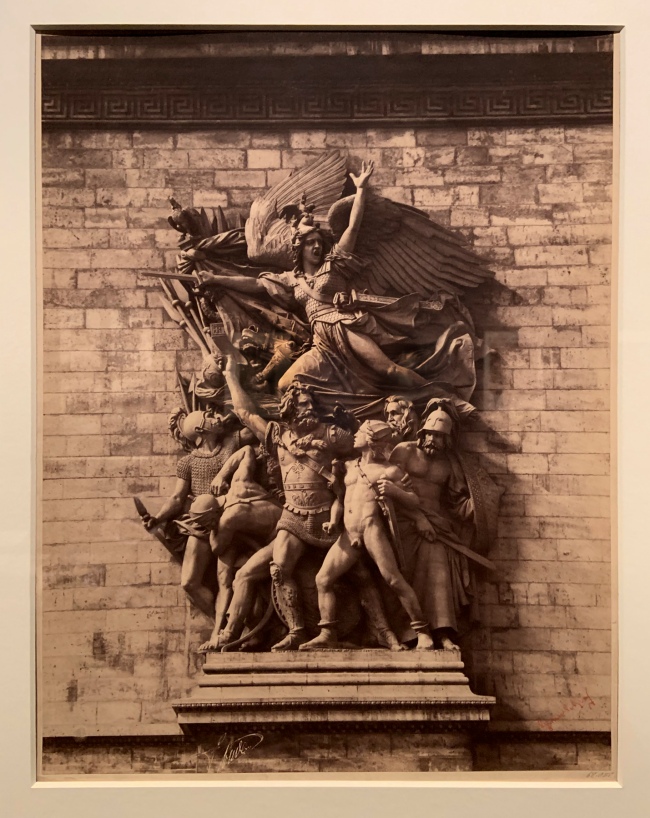
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
The Marseillaise (The Departure of the Volunteers of 1792), by Francois Rude, 1833-35, Arc de Triomphe de l’Etoile, Paris (installation view)
1852
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
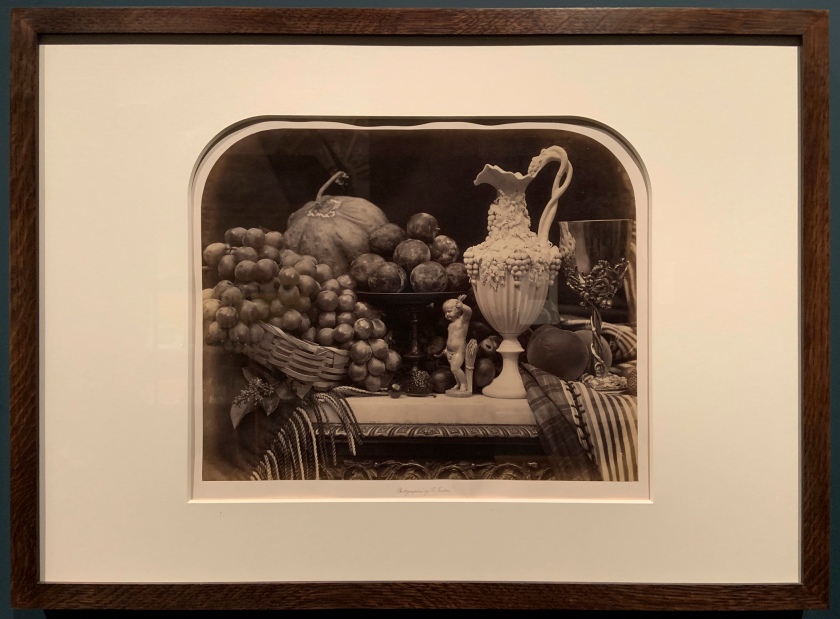
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Parian Vase, Grapes and Silver Cup (installation view)
1860
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
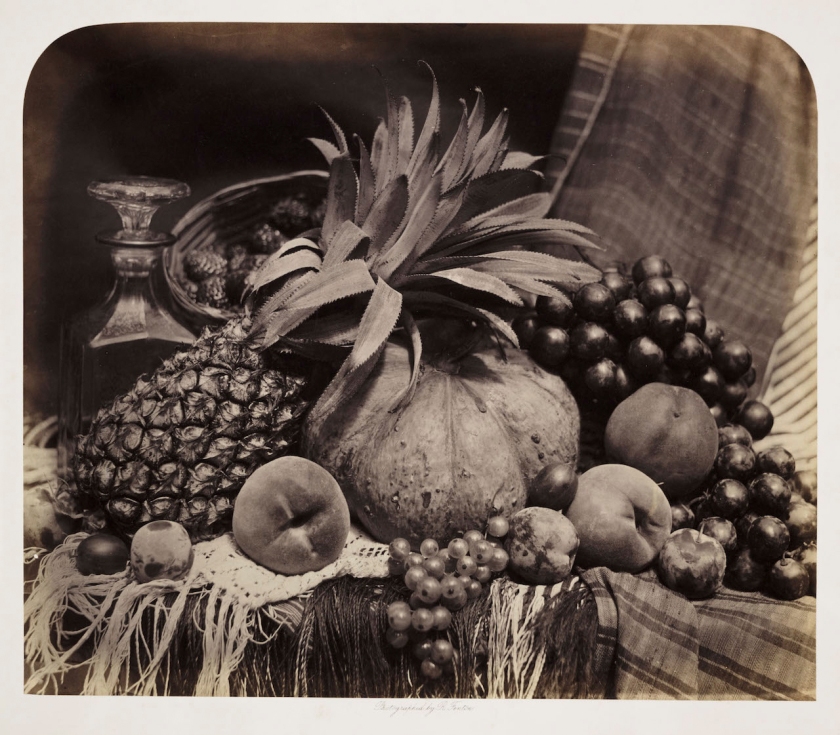
Fenton was one of the most versatile and technically brilliant photographers of the 19th century. He excelled at many subjects, including war photography, portraiture, architecture and landscape. He also made a series of lush still lives. Here, grapes, plums and peaches are rendered in exquisite detail, and the silver cup on the right reflects a camera tripod.
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Parian Vase, Grapes and Silver Cup (installation view)
1860
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
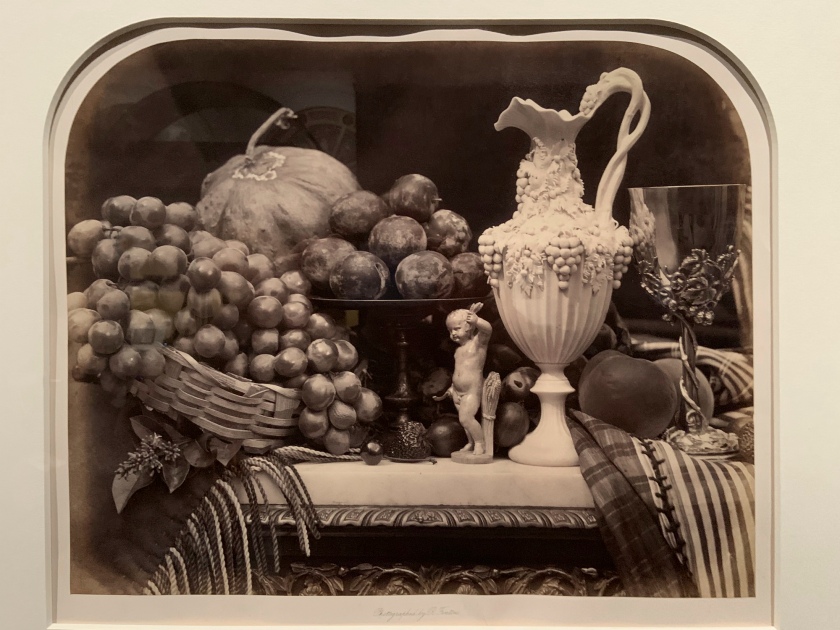
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Parian Vase, Grapes and Silver Cup (installation view)
1860
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
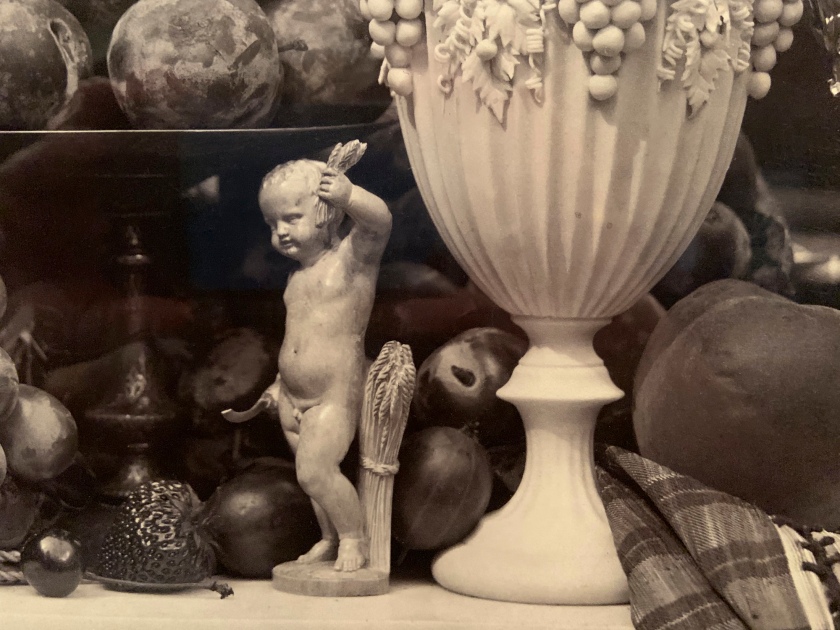
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Parian Vase, Grapes and Silver Cup (installation view detail)
1860
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Still Life with Fruit and Decanter
1860
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
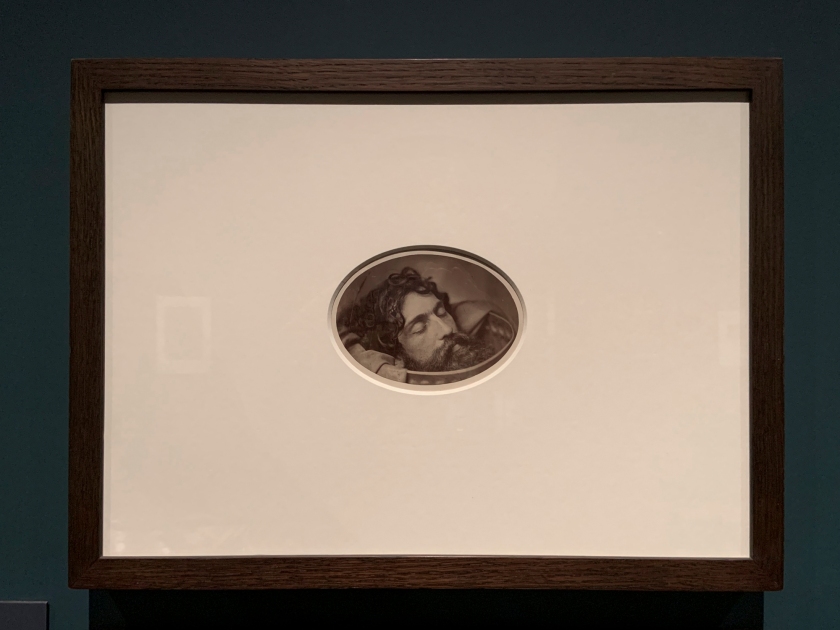
Oscar Gustaf Rejlander (British born Sweden, 1813-1875)
Head of St John the Baptist on a Charger (installation view)
c. 1856
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
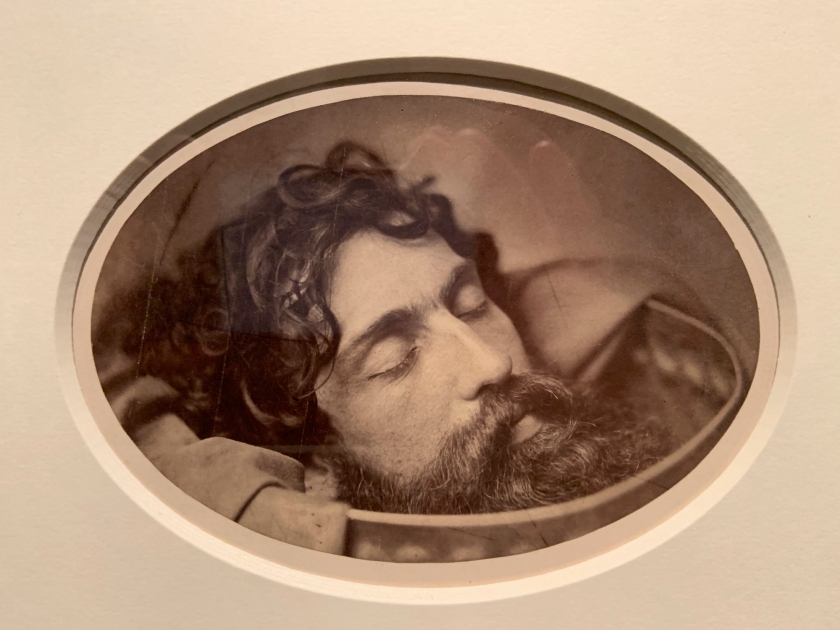
Rejlander probably intended this photograph to be part of a larger composition telling the biblical story of Salome, in which the severed head of John the Baptist was presented to her on a plate. Rejlander never made the full picture, however, and instead produced multiple prints of the head alone.
Oscar Gustaf Rejlander (British born Sweden, 1813-1875)
Head of St John the Baptist on a Charger (installation view)
c. 1856
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
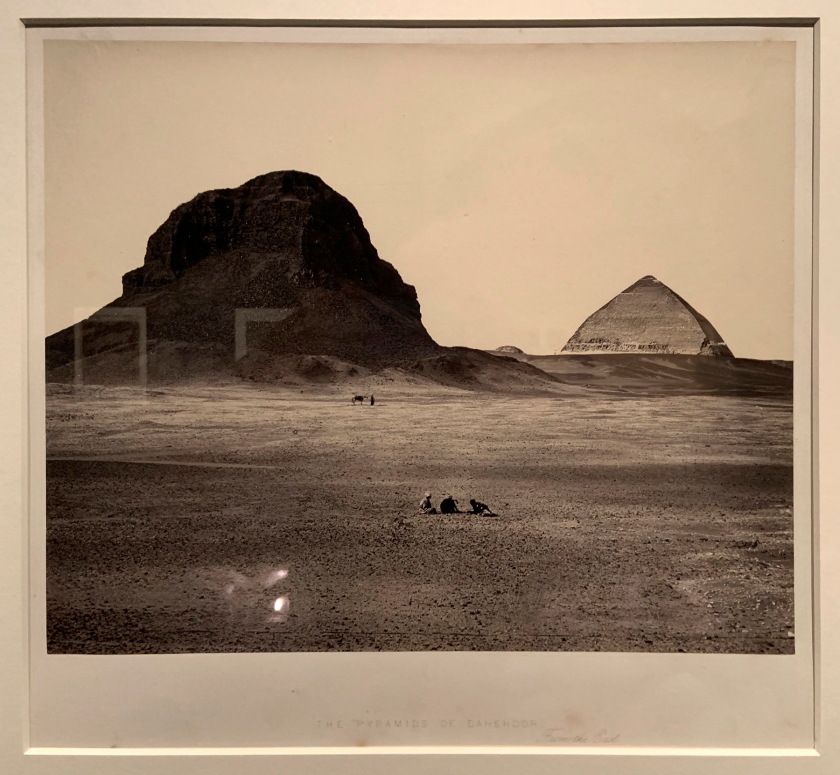
Francis Frith (British, 1822-1898)
The Pyramids of Dahshoor [Dahshur], from the East, from Egypt, Sinai, and Jerusalem: A Series of Twenty Photographic Views by Francis Frith (installation view)
1858 (published 1860 or 1862)
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Frith’s photographs were popular and circulated widely, both because of their architectural interest and because they often featured sites mentioned in the Bible. Photographs of places described in biblical stories brought a new level of realism to a Christian Victorian audience, previously only available through the interpretations of a painter or illustrator.
Francis Frith (British, 1822-1898)
The Pyramids of Dahshoor [Dahshur], from the East, from Egypt, Sinai, and Jerusalem: A Series of Twenty Photographic Views by Francis Frith (installation view)
1858 (published 1860 or 1862)
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Francis Frith (British, 1822-1898)
The Pyramids of Dahshoor [Dahshur], from the East, from Egypt, Sinai, and Jerusalem: A Series of Twenty Photographic Views by Francis Frith
1858 (published 1860 or 1862)
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Installation view of the V&A Photography Centre, London
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
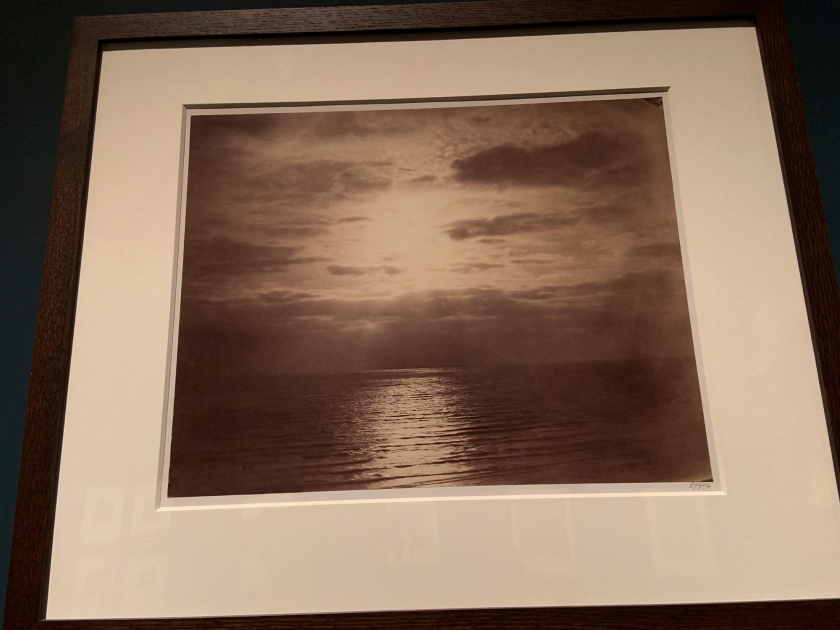
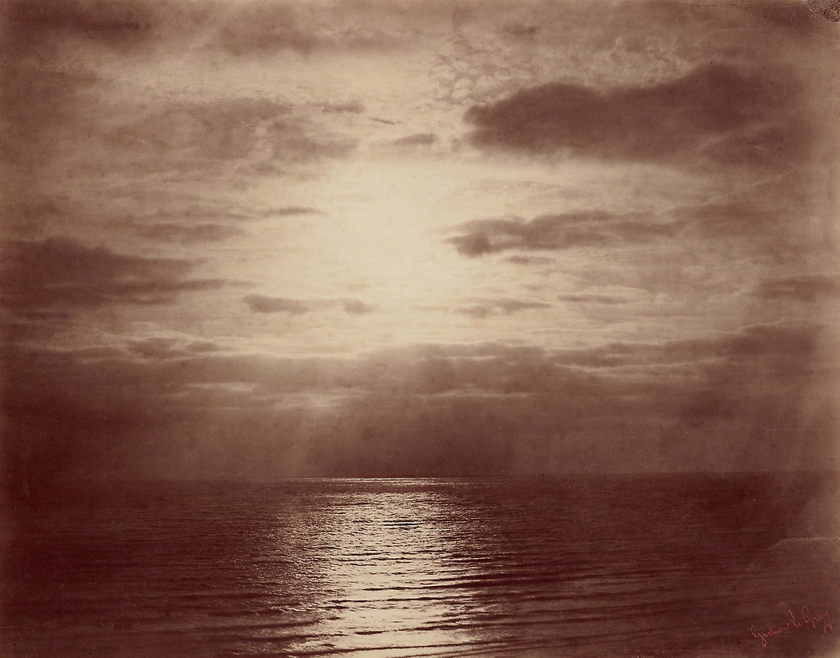
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
Solar Effect in the Clouds – Ocean (installation view)
1856-1859
Albumen Print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
Solar Effect in the Clouds – Ocean
1856-1859
Albumen Print
Art Institute of Chicago
Creative Commons Zero (CC0)
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
The Imperial Yacht, La Reine Hortense, Le Havre (installation view)
1856-1857
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
The Imperial Yacht, La Reine Hortense, Le Havre (installation view)
1856-1857
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
The Imperial Yacht, La Reine Hortense, Le Havre
1856-1857
Albumen print
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Public domain
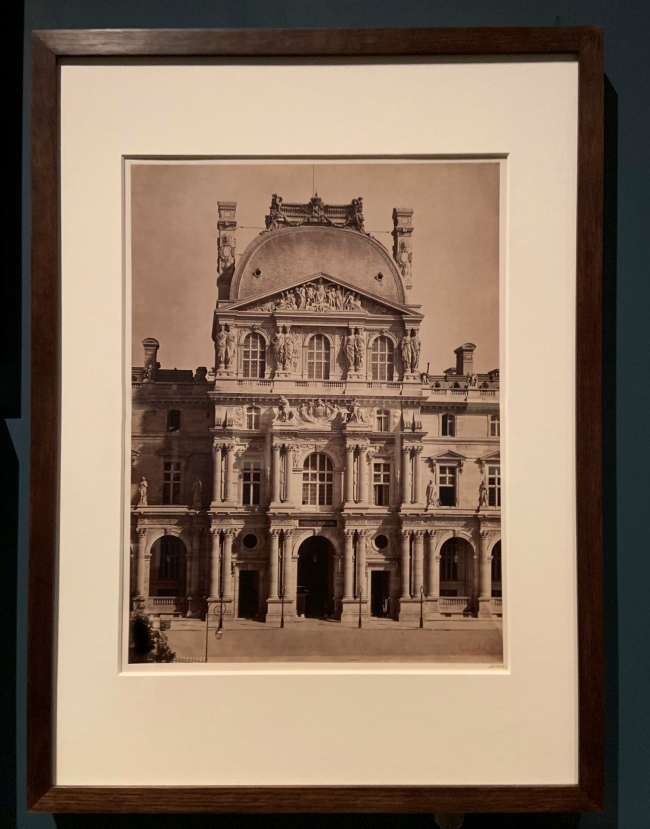
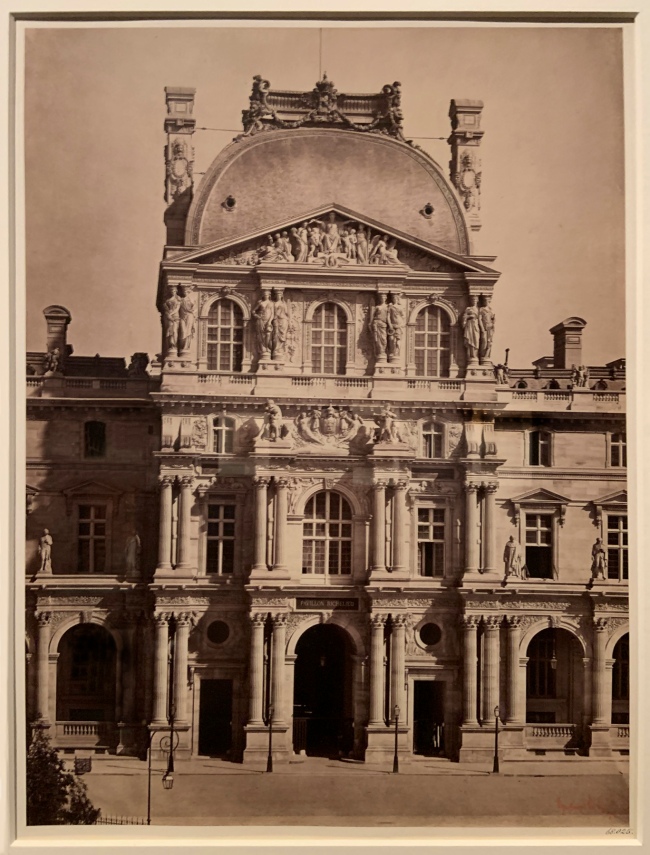
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
Pavilion Richelieu, Louvre, Paris (installation view)
1857-1859
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gustave Le Gray (French, 1820-1884)
Pavilion Richelieu, Louvre, Paris (installation view)
1857-1859
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
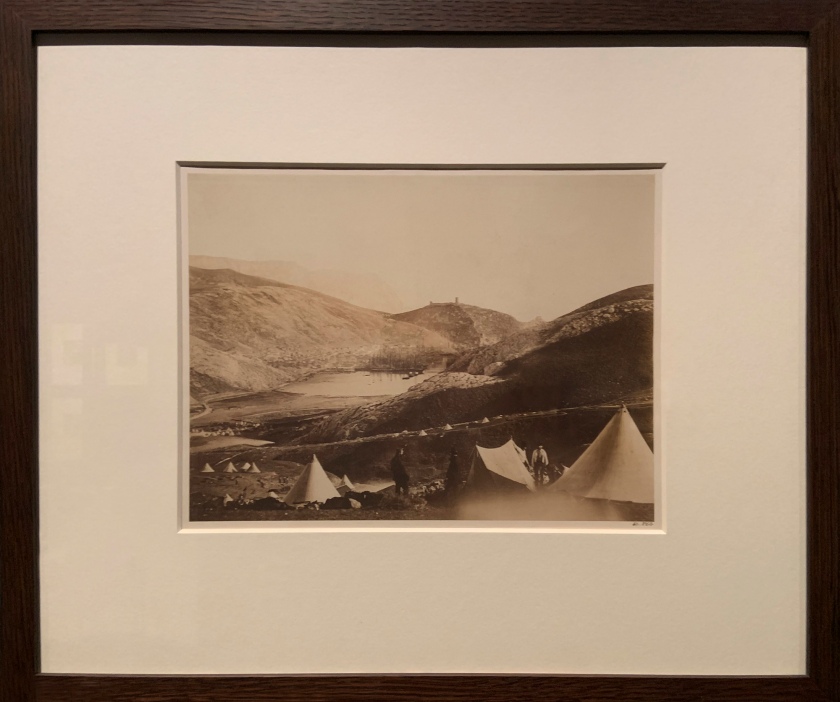
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-1869)
Balaclava from Guard’s Hill, the Crimea (installation view)
1855
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
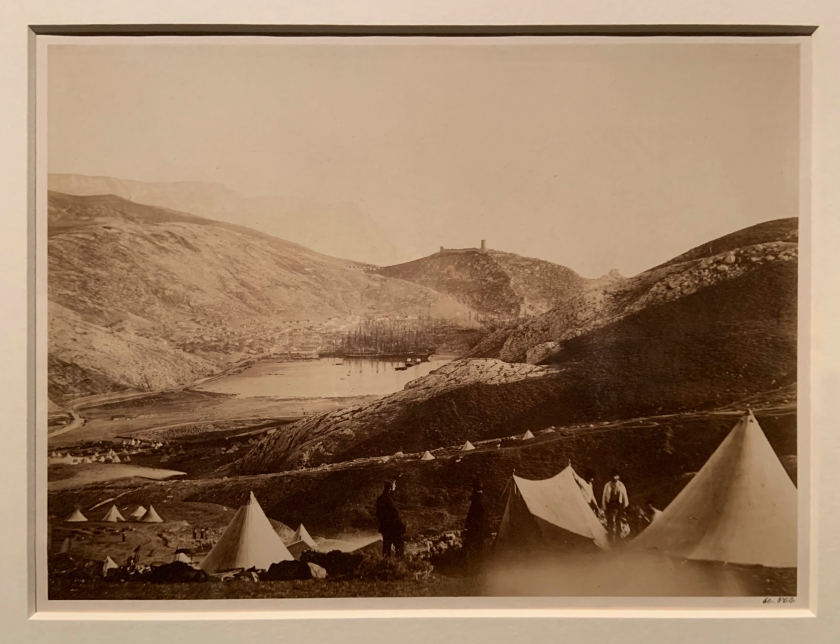
Roger Fenton (British, 1819-69)
Balaclava from Guard’s Hill, the Crimea (installation view)
1855
Albumen print
Bequeathed to the V&A by Chauncey Hare Townshend
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
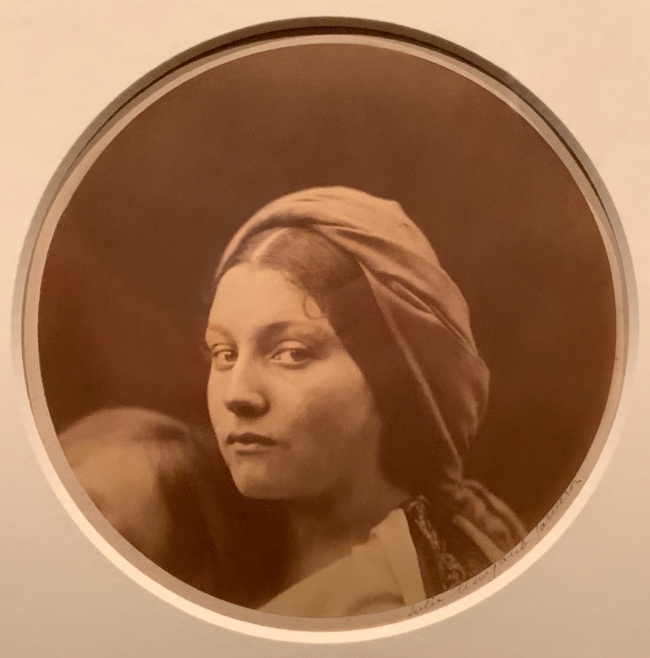
Julia Margaret Cameron (British, born India, 1815-1879)
Lucia (installation view)
1864-1865
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
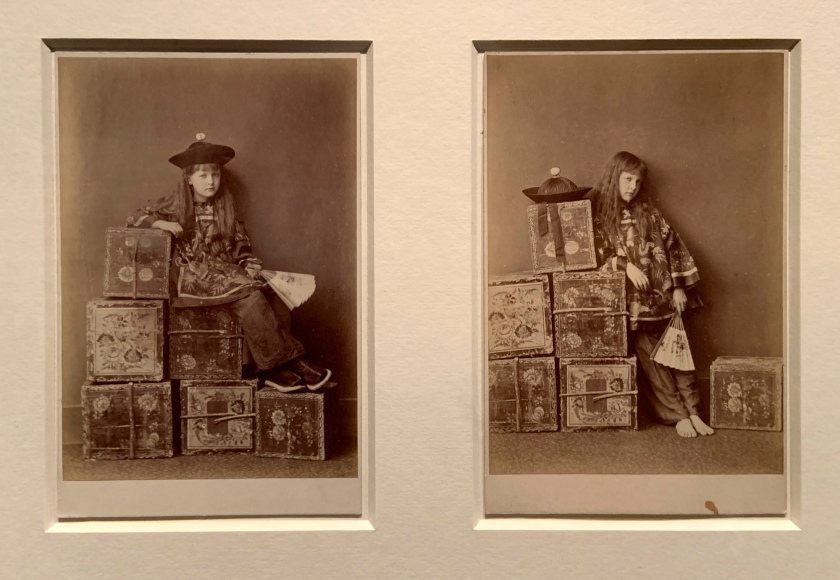
Charles Lutwide Dodgson (also known as Lewis Carroll)(British, 1832-1898)
Tea Merchant (On Duty) and Tea Merchant (Off Duty) (installation view)
1873
Albumen prints
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
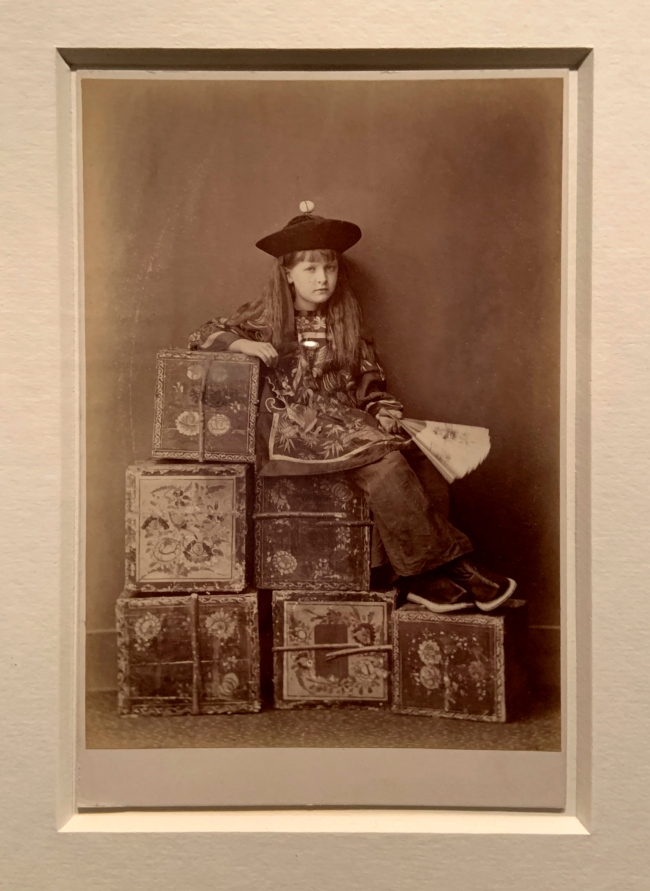
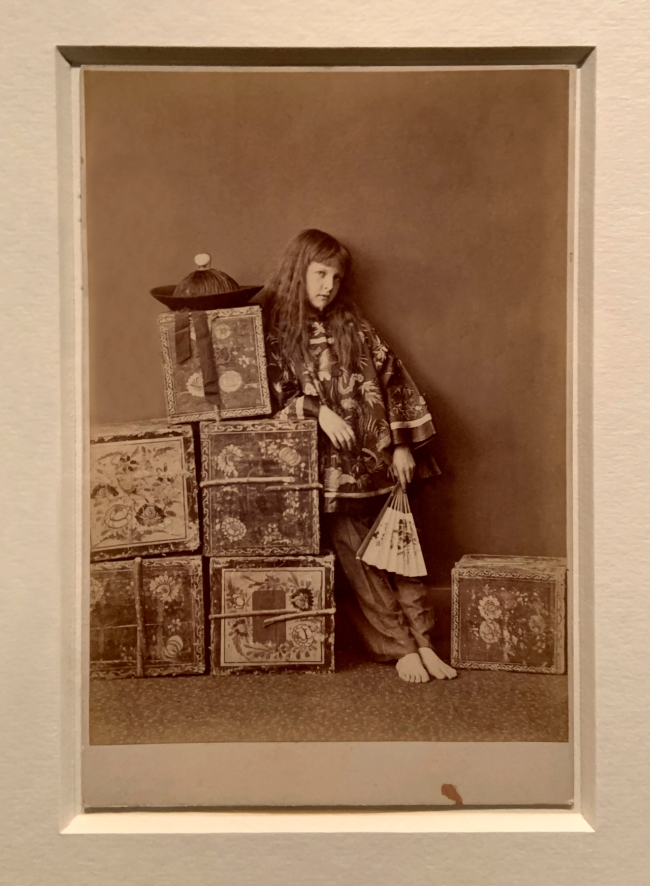
Lewis Carroll is best known as the author of Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland, but he was also an accomplished amateur photographer. Approximately half of his photographs are portraits of children, sometimes wearing foreign costumes or acting out scenes. Here, Alexandra ‘Xie’ Kitchen, his most frequent child sitter, poses in Chinese dress on a stack of tea chests.
Charles Lutwide Dodgson (also known as Lewis Carroll)(British, 1832-1898)
Tea Merchant (On Duty) (installation view)
1873
Albumen prints
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Charles Lutwide Dodgson (also known as Lewis Carroll)(British, 1832-1898)
Tea Merchant (Off Duty) (installation view)
1873
Albumen prints
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
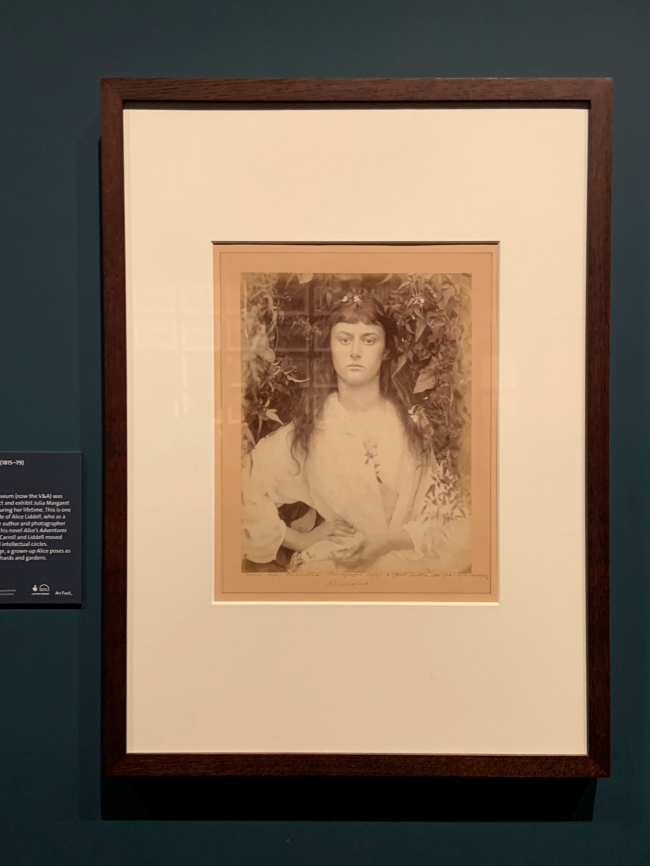
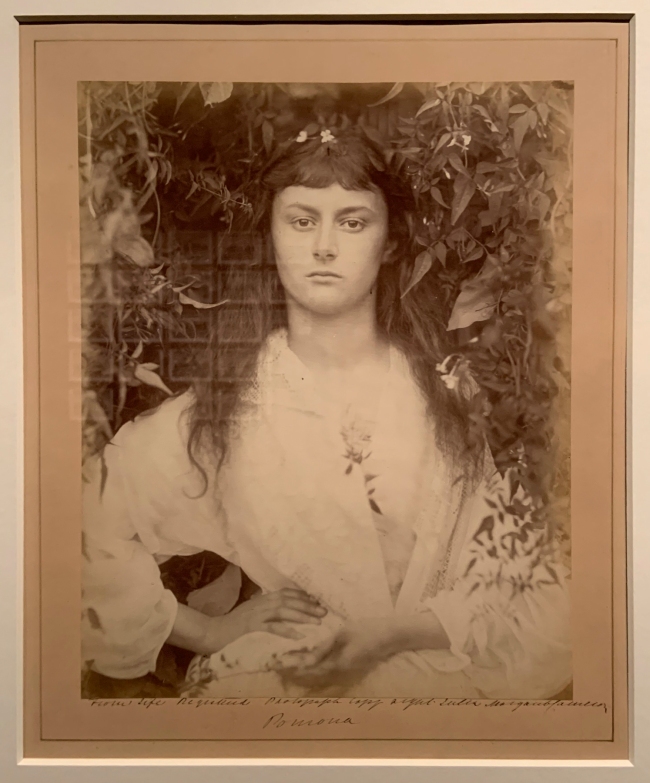
Julia Margaret Cameron (British, born India, 1815-1879)
Pomona (installation view)
1887
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The South Kensington museum (now the V&A) was the only museum to collect and exhibit Julia Margaret Cameron’s during her lifetime. This is one of several studies she made of Alice Liddell, who as a child had modelled for the author and photographer Lewis Carroll and inspired his novel Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland. Cameron, Carroll and Liddell moved in overlapping artistic and intellectual circles. Here, surrounded by foliage, a grown-up Alice poses as the Roman goddess of orchards and gardens.
Julia Margaret Cameron (British, born India, 1815-1879)
Pomona (installation view)
1887
Albumen print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Installation view of the V&A Photography Centre, London
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
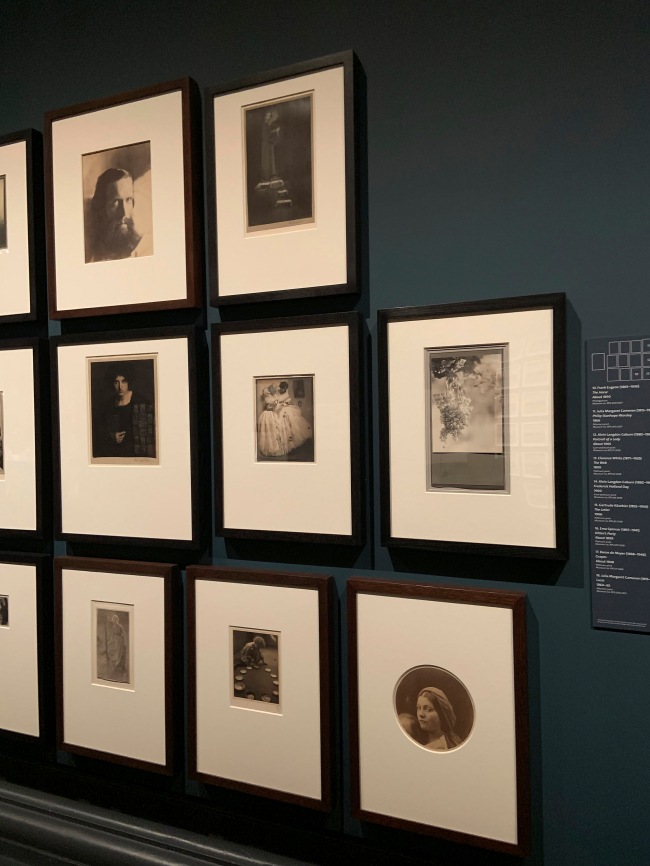
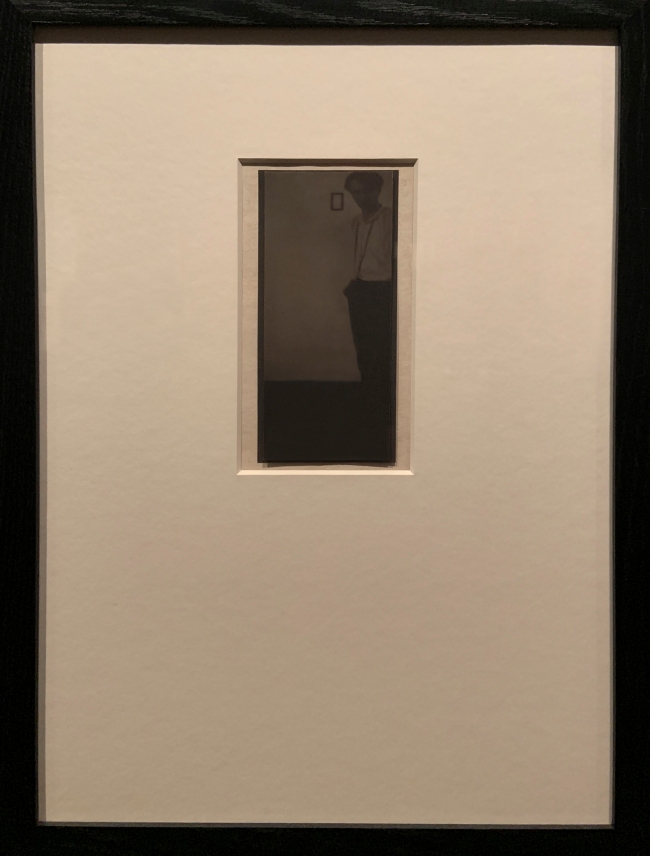
Alvin Langdon Coburn (American 1882-1966)
Frederick Holland Day (installation view)
1900
Gum platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The British-American photographer Alvin Langdon Coburn enjoyed success on both sides of the Atlantic. Active in the early 20th century, he gained recognition from a young age as a talented photographer. His style ranged from the painterly softness of Pictorialism to the unusual vantage points and abstraction of Modernism. As well as being a practising photographer, Coburn was an avid collector. In 1930 he donated over 600 photographs to the Royal Photographic Society. The gift included examples of Coburn’s own work alongside that of his contemporaries, many of whom are now considered to be the most influential of their generation. Coburn also collected historic photographs, and was among the first in his time to rediscover and appreciate the work of 19th-century masters like Julia Margaret Cameron and Hill and Adamson.
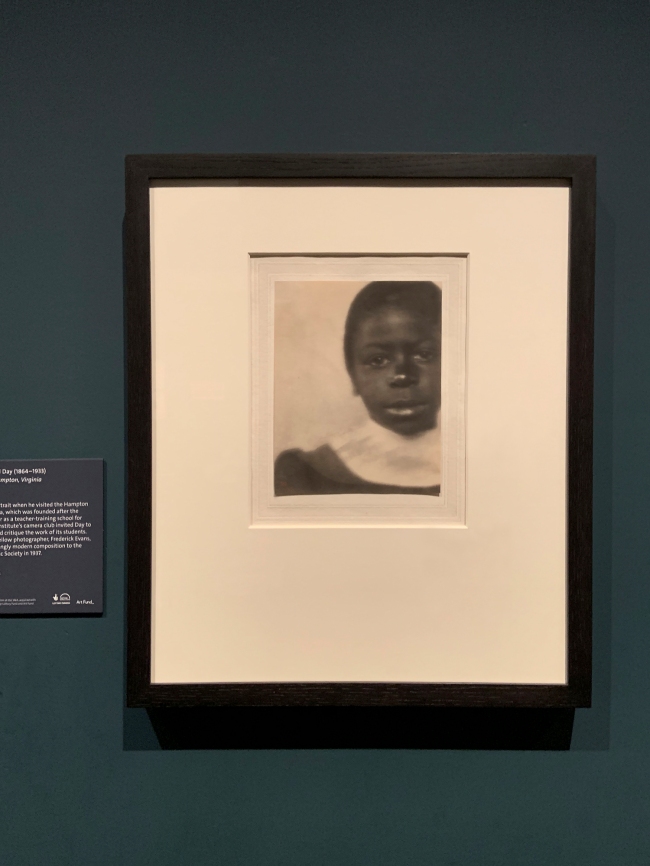
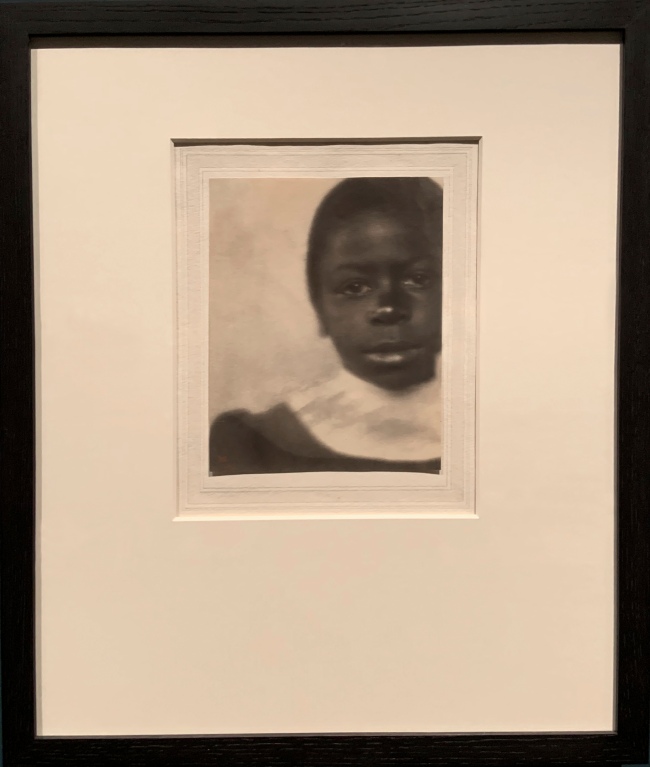
Fredrick Holland Day (American, 1864-1933)
Head of a Girl, Hampton, Virginia (installation view)
1905
Gum platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
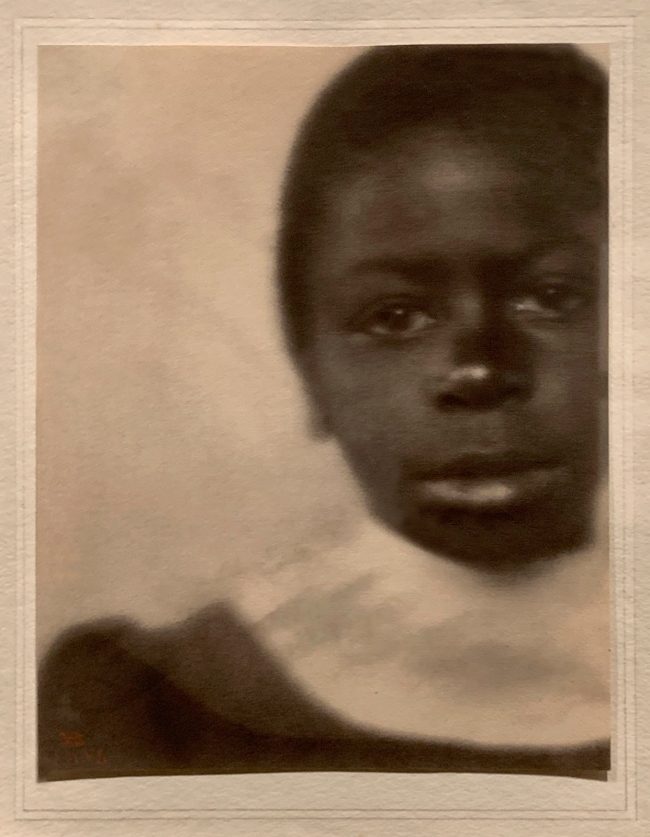
Day made this portrait when he visited the Hampton Institute in Virginia, which was founded after the American Civil War as a teacher-training school for freed slaves. The institute’s camera club invited Day to visit the school and critique the work of its students. Day’s friend and fellow photographer, Frederick Evans, donated this strikingly modern composition to the Royal Photographic Society in 1937.
Fredrick Holland Day (American, 1864-1933)
Head of a Girl, Hampton, Virginia (installation view)
1905
Gum platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Fredrick Holland Day (American, 1864-1933)
Head of a Girl, Hampton, Virginia (installation view)
1905
Gum platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Fredrick Holland Day (American, 1864-1933)
Head of a Girl, Hampton, Virginia
1905
Gum platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
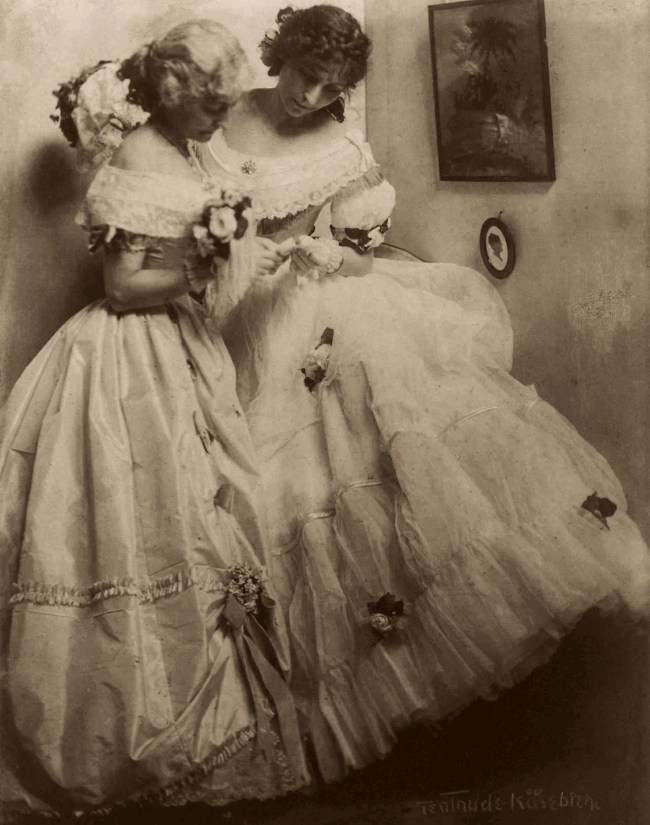
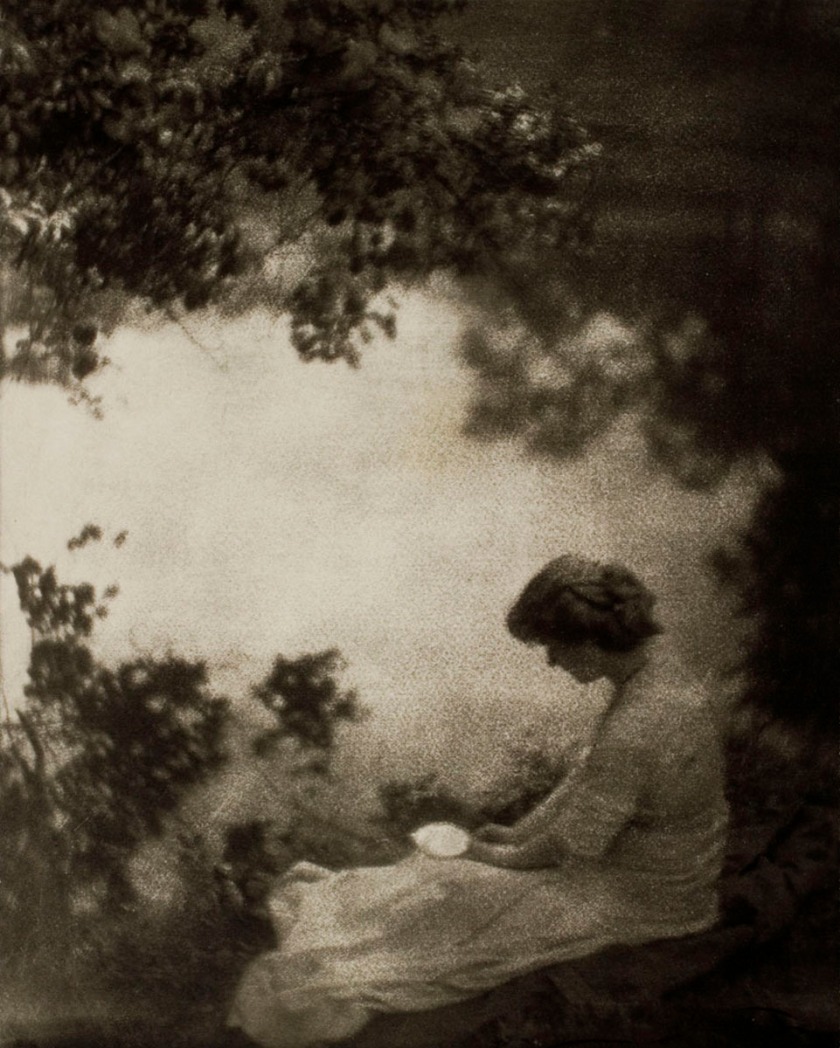
Gertrude Käsebier (American, 1852-1934)
The Letter
1906
Platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Käsebier studied painting before opening a photography studio in New York. Her Pictorialist photographs often combine soft focus with experimental printing techniques. These sisters were dressed in historic costume for a ball, but their pose transforms a society portrait into a narrative picture. In a variant image, they turn to look at the framed silhouette on the wall.
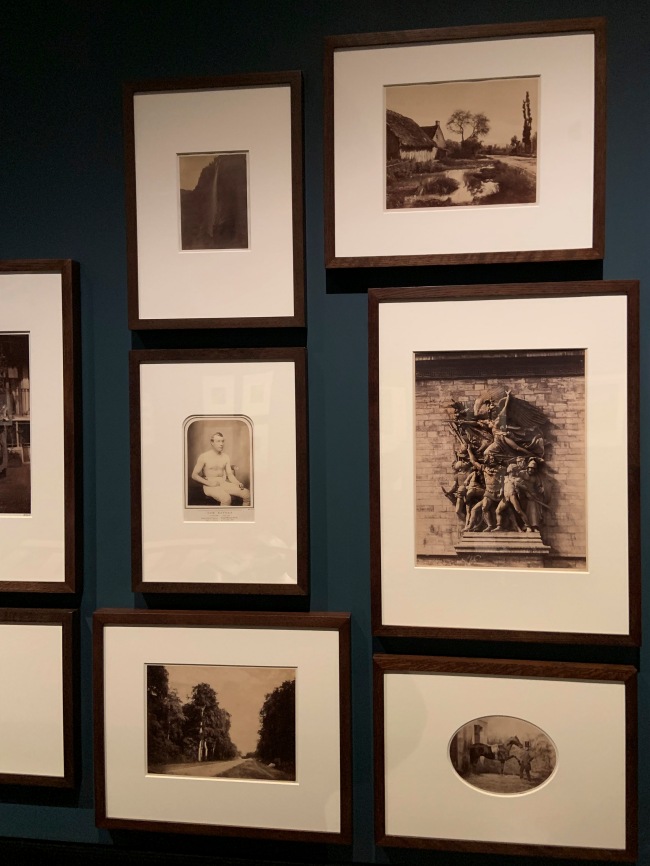
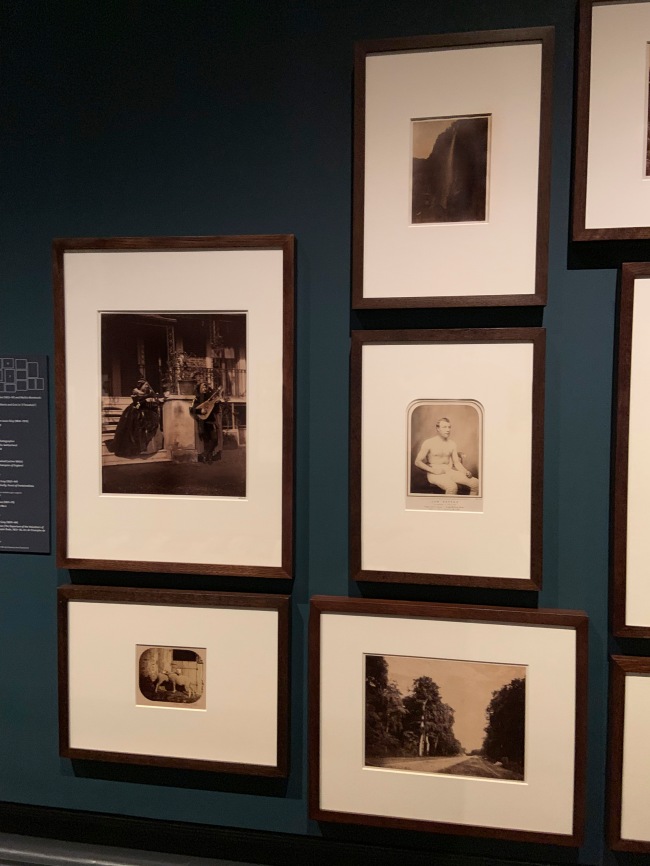
Installation views of the V&A Photography Centre, London
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Francis James Mortimer (British, 1874-1944)
Alvin Langdon Coburn at the Opening of His One-Man Exhibition the Royal Photographic Society, London (installation view)
1906
Carbon print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
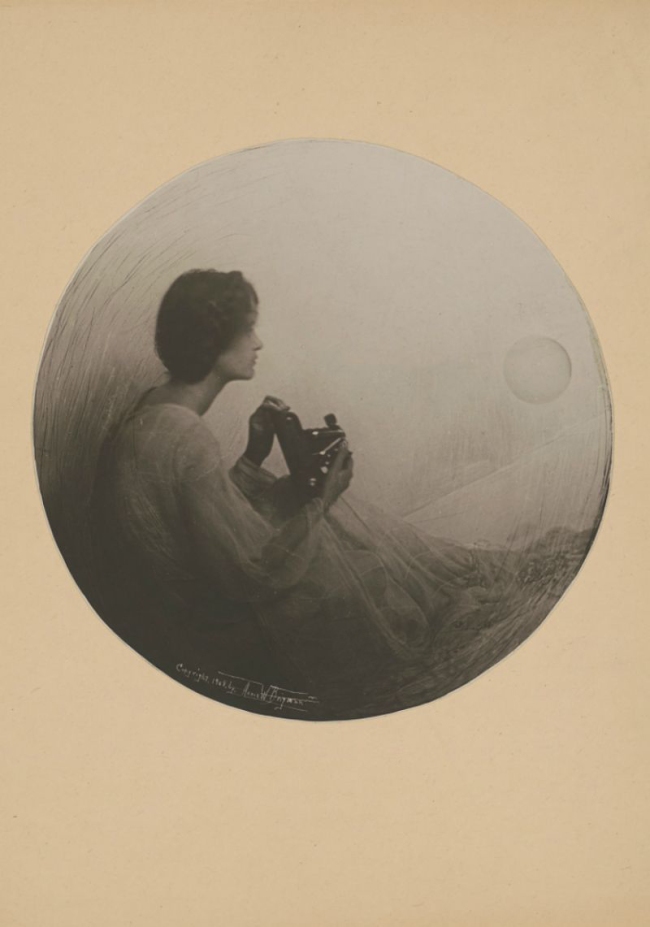
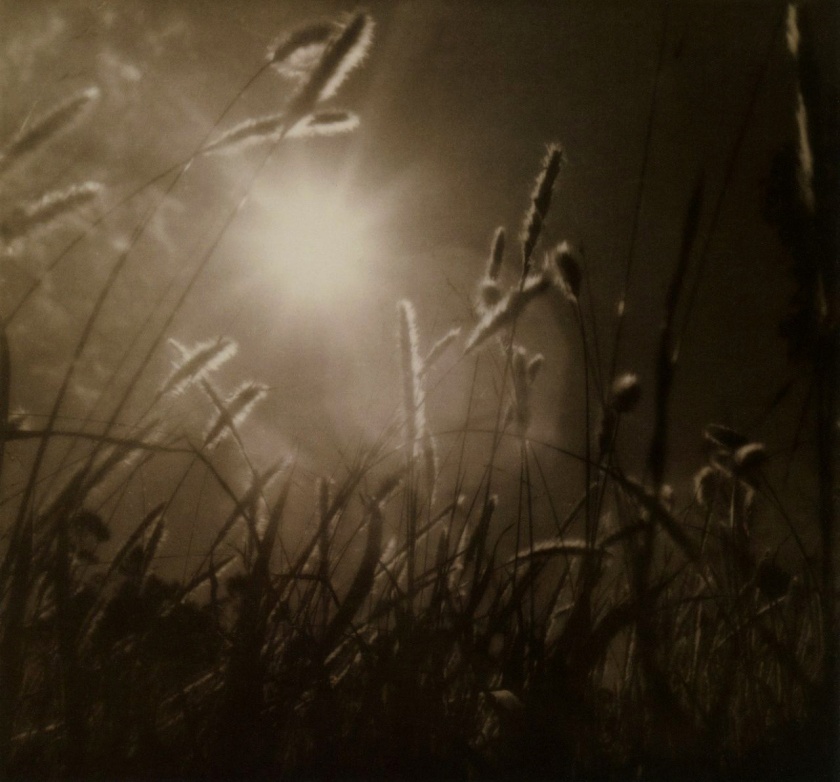
Annie Wardrope Brigman (American, 1869-1950)
The Spirit of Photography
c. 1908
Platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
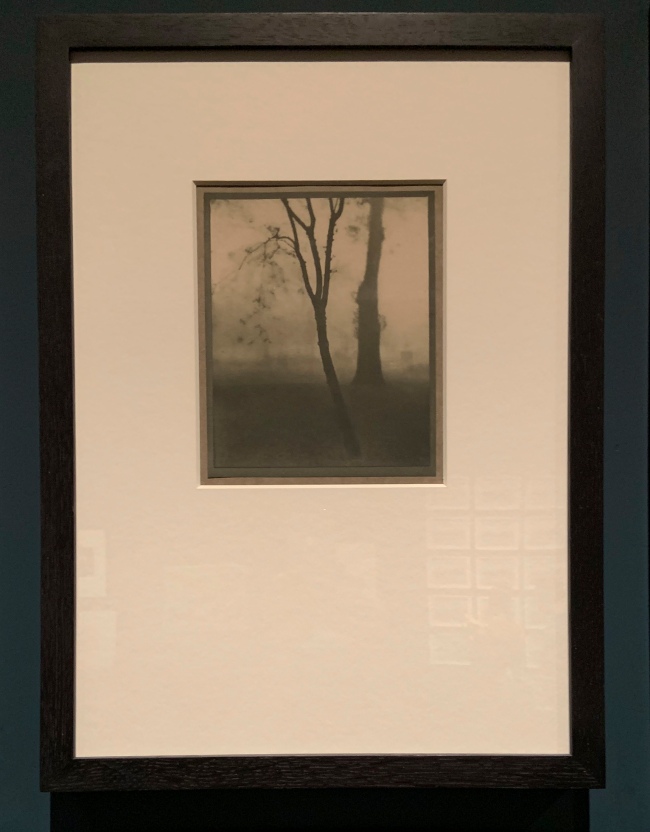
Alvin Langdon Coburn (American 1882-1966)
Kensington Gardens (installation view)
1910
Platinum print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Cover of Camera Work Number XXVI (installation view)
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
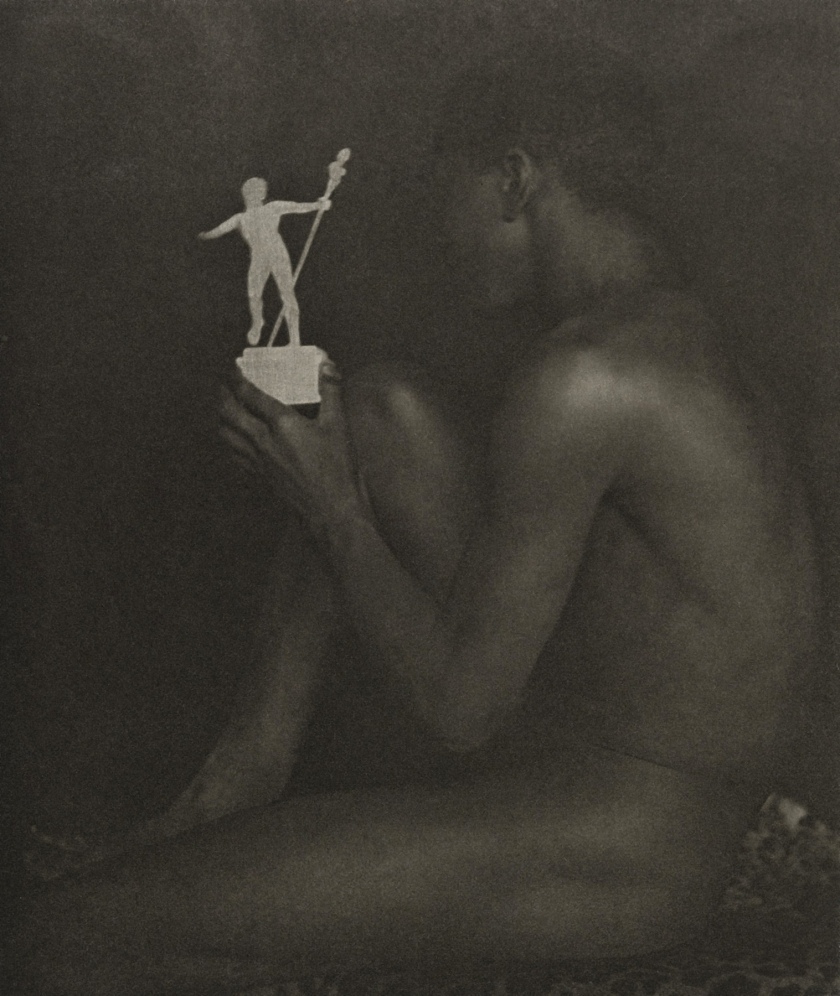
Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973)
Portrait – Lady H (installation view)
1908
Camera Work 22
1908
Photogravure
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973)
Portrait – Lady H
1908
Camera Work 22
1908
Photogravure
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Paul Strand (American, 1890-1976)
New York (installation view)
1916
Camera Work 48
1916
Photogravure
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) was an American photographer, publisher, writer and gallery owner. From 1903-1917, he published the quarterly journal Camera Work, which featured portfolios of exquisitely printed photogravures (a type of photograph printed in ink), alongside essays and reviews. Camera Work promoted photography as an art form, publishing the work of Pictorialist photographers who drew inspiration from painting, and reproducing 19th-century photographs. It also helped to introduce modern art to American audiences, including works by radical European painters such as Matisse and Picasso.
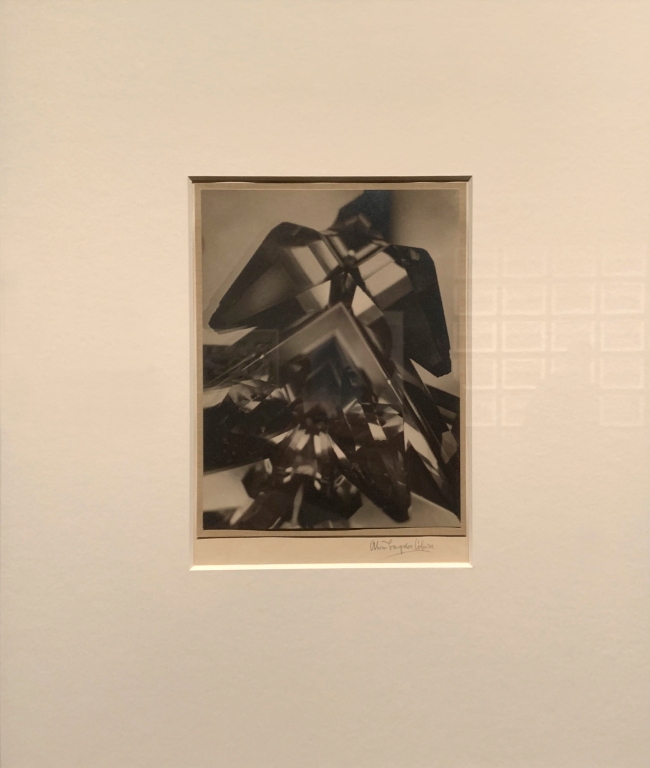
Alvin Langdon Coburn (American 1882-1966)
Vortograph (installation view)
1917
Bromide print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
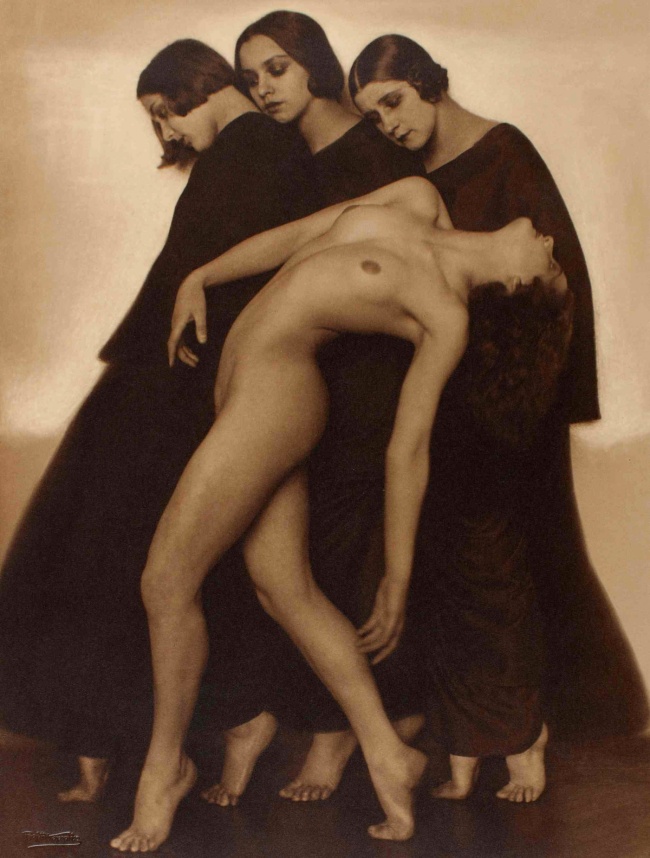
Rudolph Koppitz (American, 1884-1936)
Bewegungsstudie (Movement Study)
1926
Carbon print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Koppitz was a leading art photographer in Vienna between the two World Wars, as well as a master of complex printing processes, including the pigment, gum and broccoli process of transfer printing. Tis dynamic and sensual composition captures dancers from the Vienna State Opera Ballet frozen mid-movement.
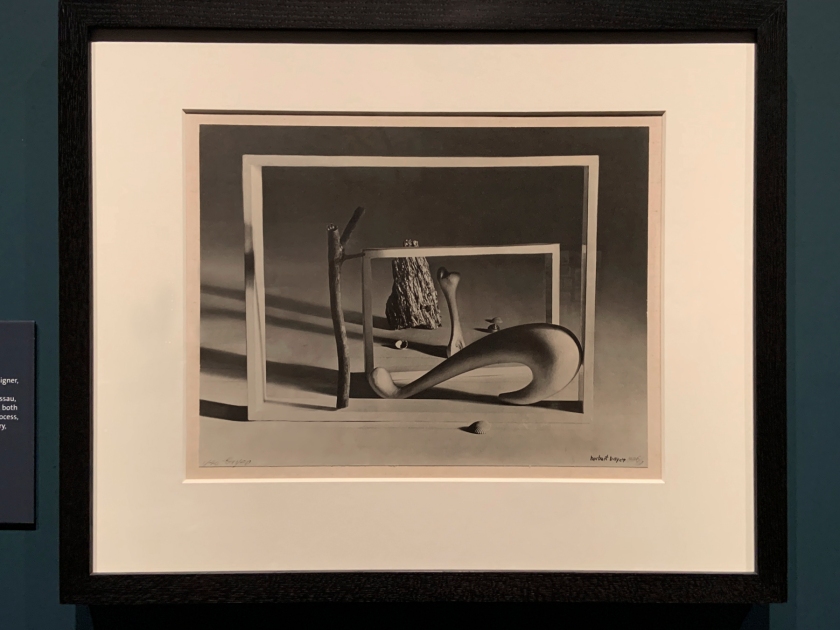
Herbert Bayer (Austrian American, 1900-85)
Shortly Before Dawn (installation view)
1932-39
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Bayer had a varied and influential career as a designer, painter, photographer, sculptor, art director and architect. He taught at the Bauhaus school in Dessau, Germany, and later began to use photomontage, both in his artistic and advertising work. Using this process, he combined his photographs with found imagery, producing surreal or dreamlike pictures.
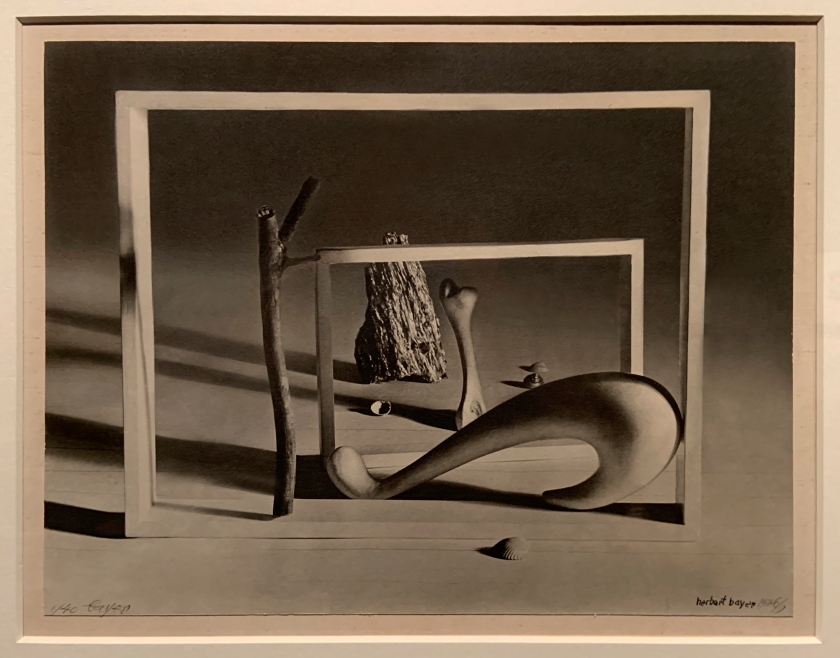
Herbert Bayer (Austrian American, 1900-85)
Shortly Before Dawn (installation view)
1932-39
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
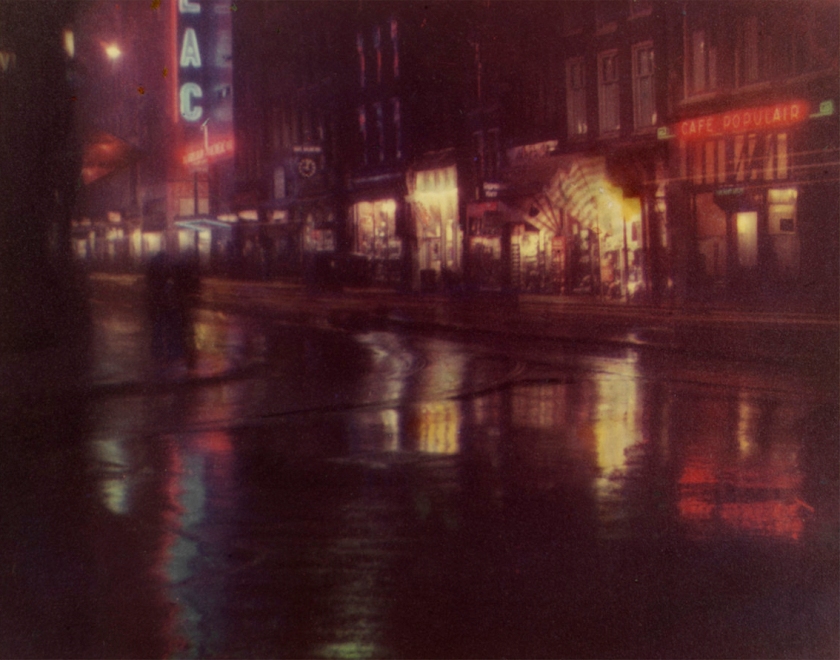
Bernard Eilers (Dutch, 1878-1951)
Reguliersbreestraat, Amsterdam (installation view)
1934
Foto-choma Eilers
Given by Joan Luckhurst Eilers
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
In the 1930s, the Dutch photographer Bernard Eilers developed an experimental new photographic colour separation process known as ‘Foto-chroma Eilers’. Although the process was short-lived, Eilers successfully used this technique to produce prints like this of great intensity and depth of colour. Here, the misty reflections and neon lights create an atmospheric but modern view of a rain-soaked Amsterdam at night.
Bernard Eilers (Dutch, 1878-1951)
Reguliersbreestraat, Amsterdam (installation view)
1934
Foto-choma Eilers
Given by Joan Luckhurst Eilers
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
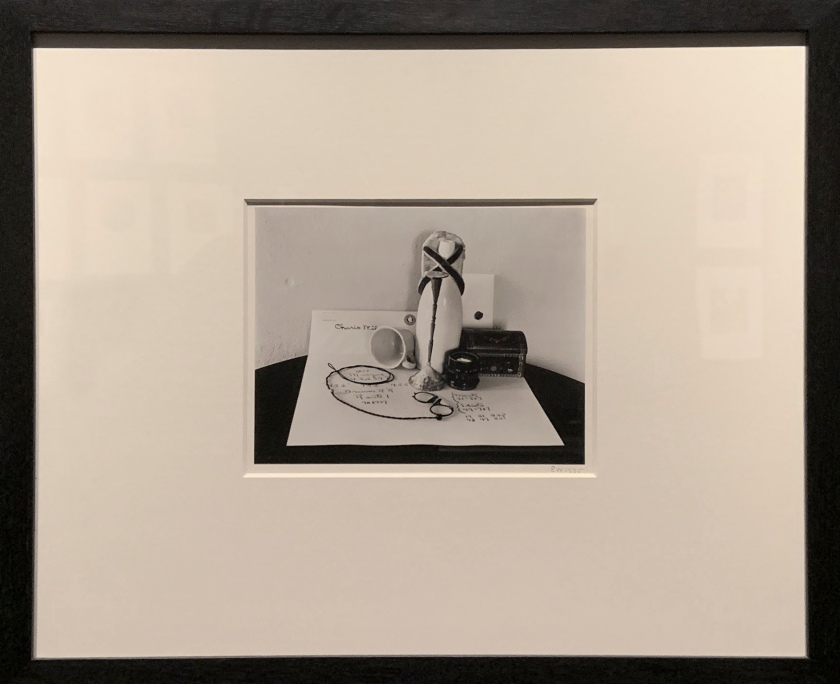
Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
Valentine to Charis (installation view)
1935
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
When Weston met the model and writer Charis Wilson in 1934, he was immediately besotted. This valentine to her contains a cluster of objects arranged as a still life, including the photographer’s camera lens and spectacles. Some of the objects seem to hold a special significance that only the lovers could understand. The numbers on the right possibly refer to their ages – there were almost thirty years between them.
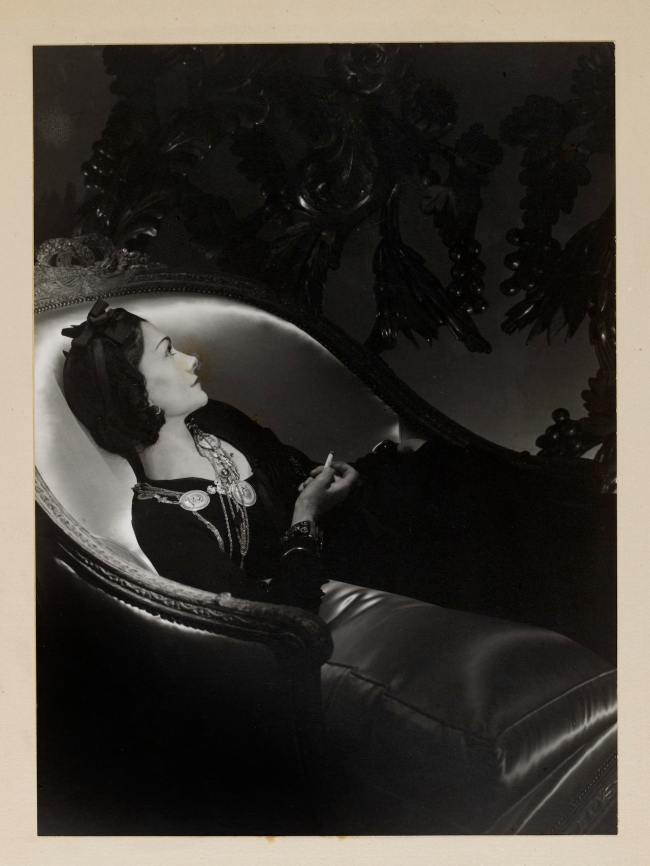
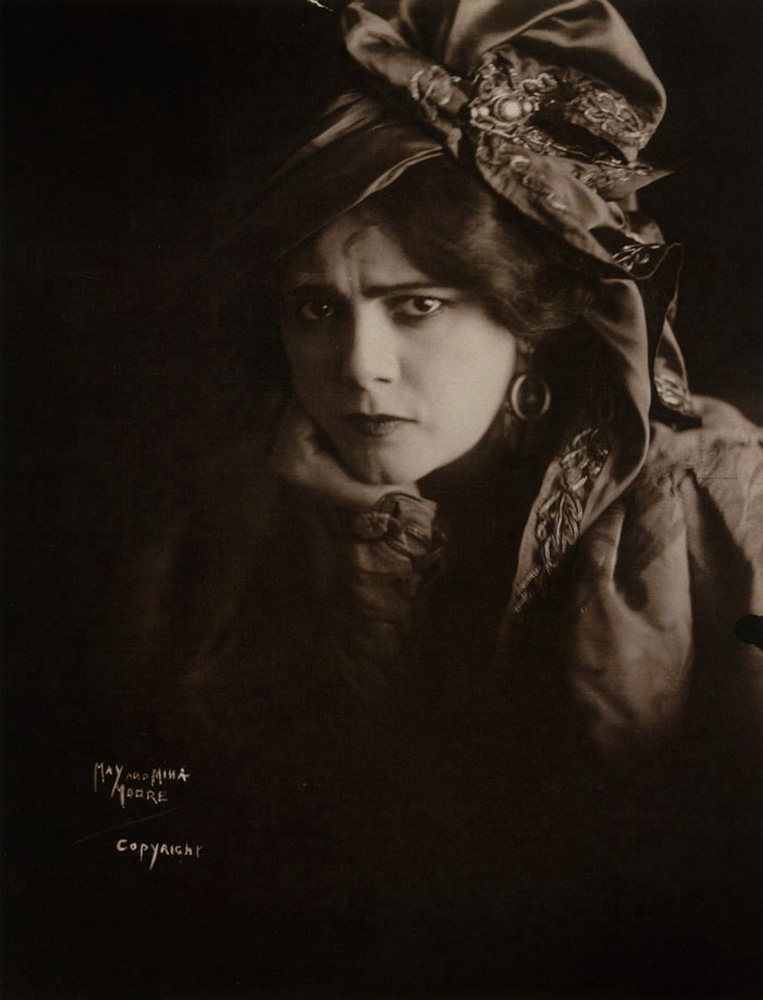
Horst P. Horst (German-American, 1906-1999)
Portrait of Gabrielle (‘Coco’) Chanel
1937
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Variant, American Vogue, 1 December 1937, p. 86: ‘Fashion: Mid-Season Prophecies’
Caption reads: Chanel in her fitted, three-quarters coat / Mademoiselle Chanel, in one of her new coats that are making the news – a three quarters coat buttoned tightly and trimmed with astrakham like her cap. 01/12/1937
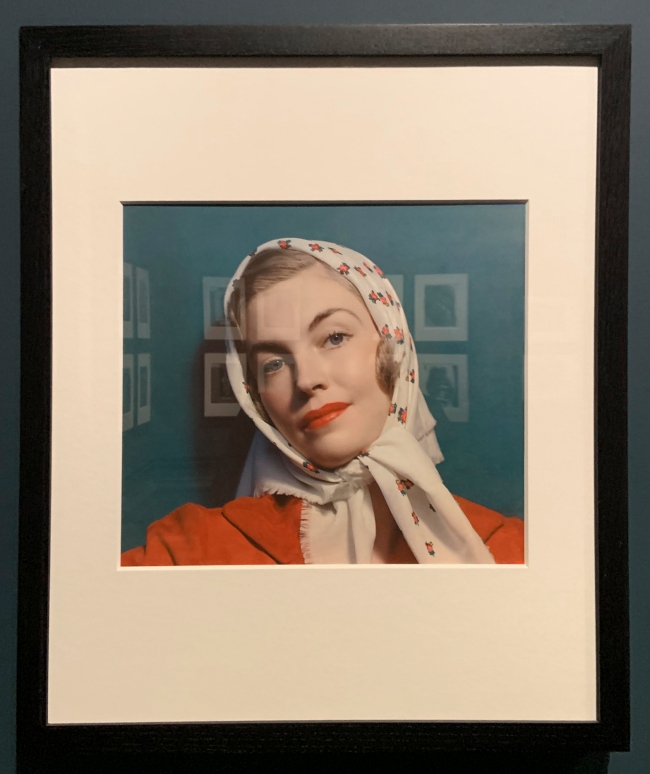
Nickolas Muray (American, 1892-1965)
Women with headscarf, McCall’s Cover, July 1938 (installation view)
1938
Tricolour carbro print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
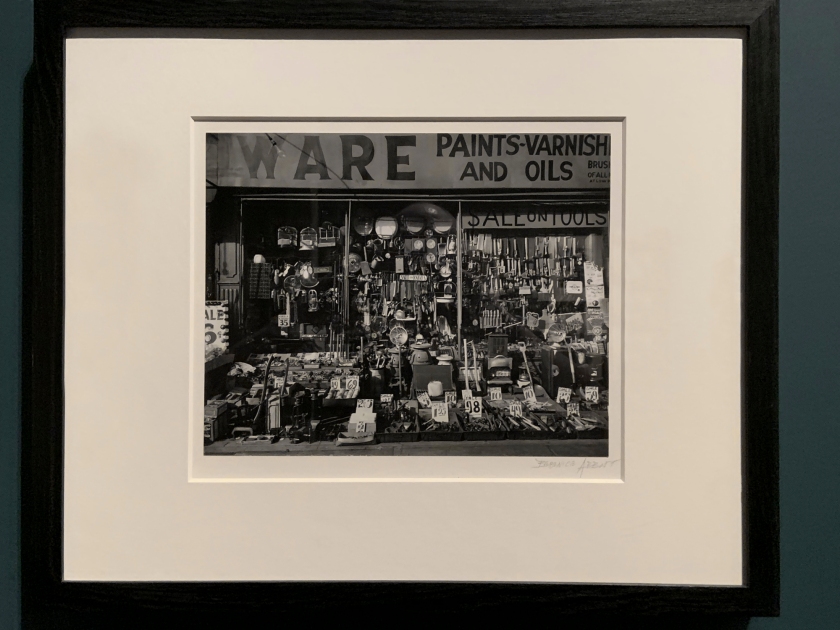
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Hardware Store (installation view)
1938
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Between 1935 and 1939, the Federal Art Project emptied Abbott to make a series of photographs entitled Changing New York, documenting the rapid development and urban transformation of the city. This picture shows the facade of a downtown hardware store, its wares arranged in a densely-packed window display with extend onto the pavement.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Hardware Store (installation view)
1938
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Hardware Store
1938
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
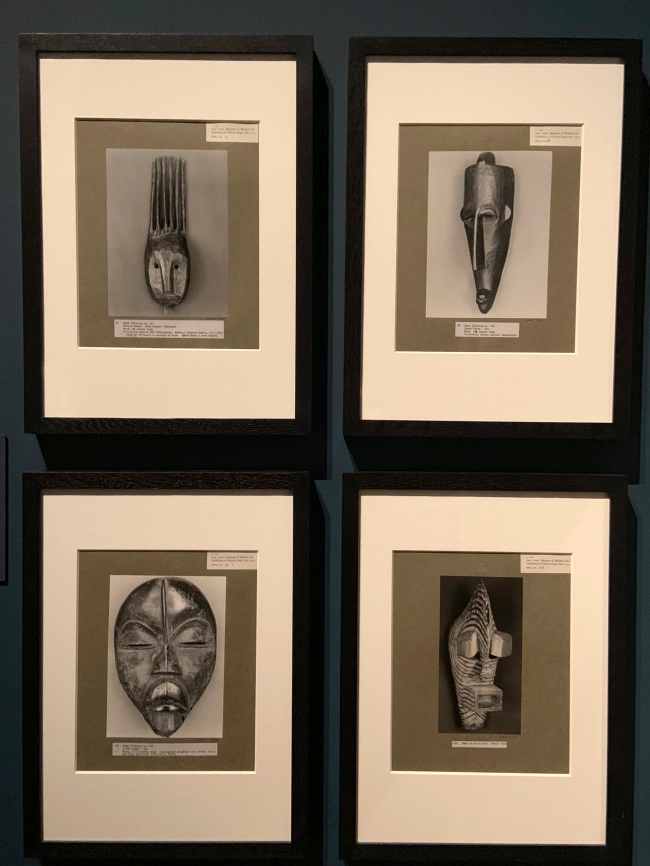
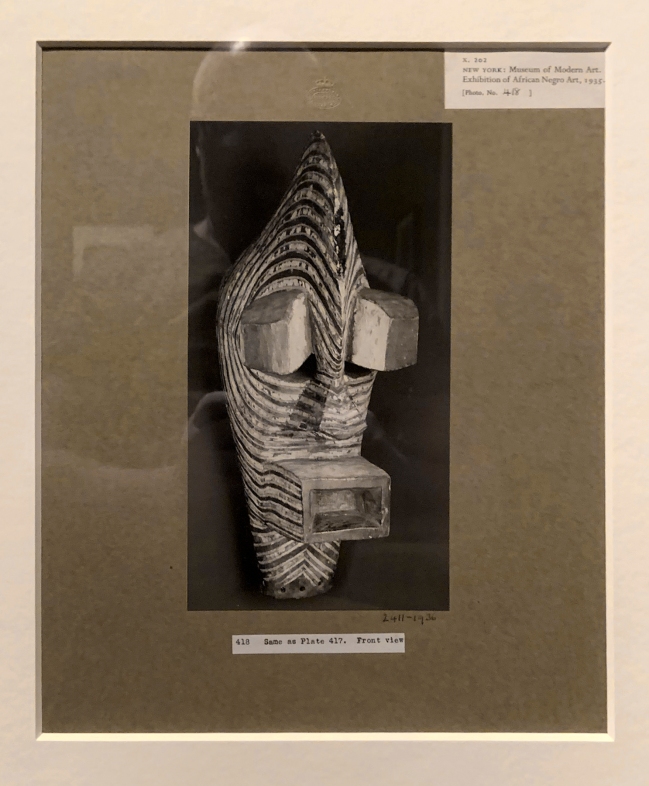
Walker Evans (American, 1903-75)
Photographs of African masks, from an exhibition entitled African Negro Art at the Museum of Modern Art, New York (installation view)
1935
Gelatin silver prints
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
In 1935, the Museum of Modern Art commissioned Evans to photograph objects in its major exhibition of African art. Using his 8 x 10 inch view camera, he highlighted the artistry and detail of the objects, alternating between front, side and rear views. In total, Evans produced 477 images, and 17 complete sets of them were printed. Several of these sets were donated to colleges and libraries in America, and the V&A bought one set in 1936 to better represent African art in its collection.
The term ‘negro’ is given here in its original historical context.
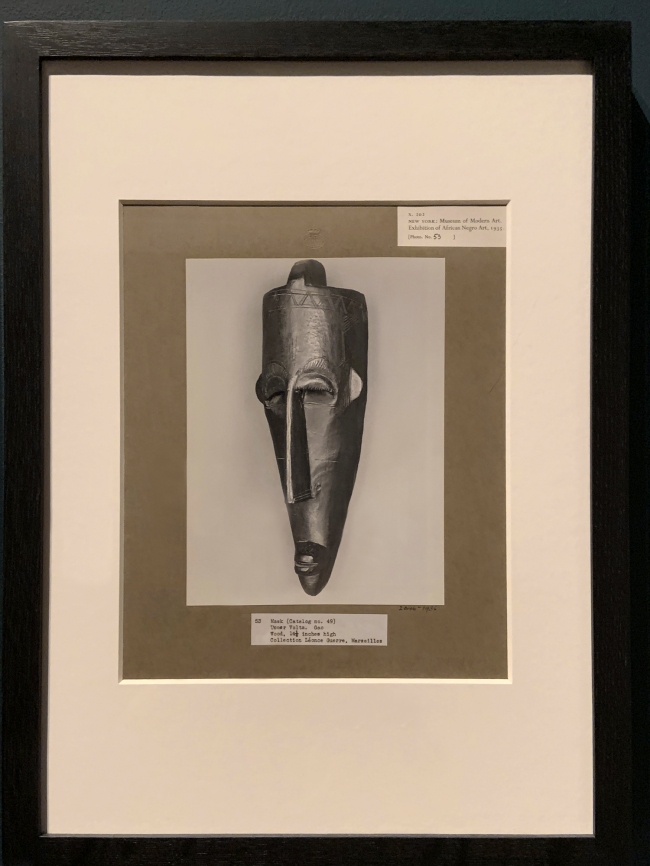
Walker Evans (American, 1903-75)
Photograph of African mask, from an exhibition entitled African Negro Art at the Museum of Modern Art, New York (installation view)
1935
Gelatin silver prints
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Walker Evans (American, 1903-75)
Photograph of African mask, from an exhibition entitled African Negro Art at the Museum of Modern Art, New York (installation view)
1935
Gelatin silver prints
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Walker Evans (American, 1903-75)
Photograph of African mask, from an exhibition entitled African Negro Art at the Museum of Modern Art, New York (installation view)
1935
Gelatin silver prints
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
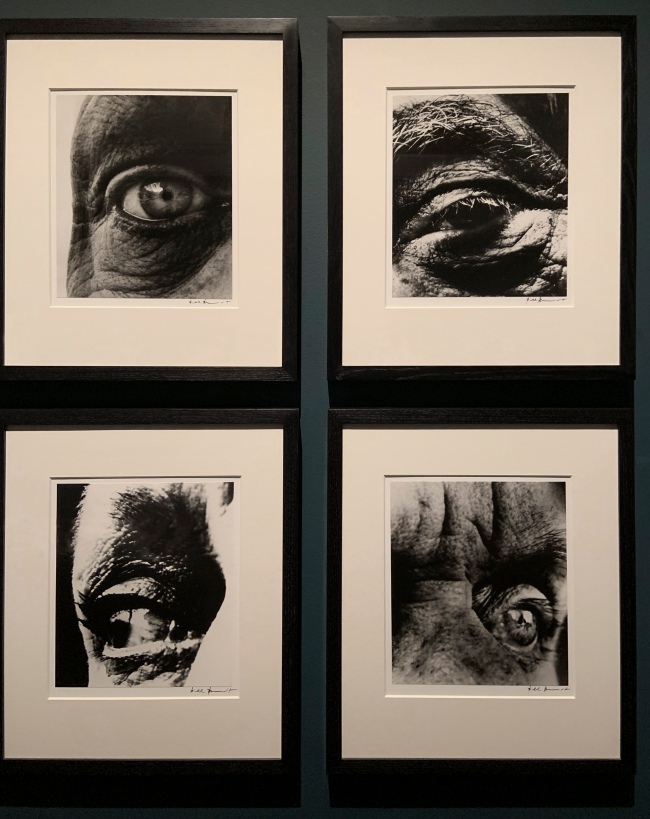
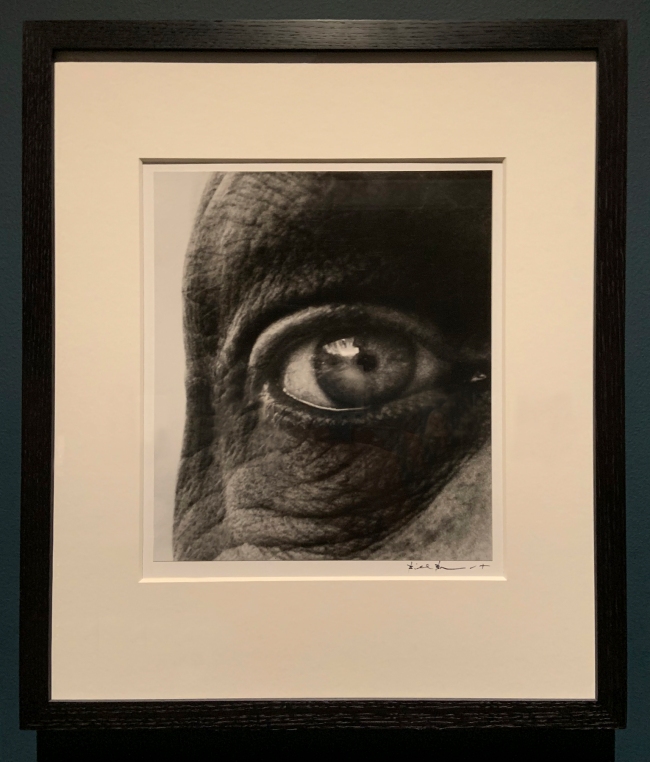
Bill Brandt (British, 1904-1983)
Dubuffet’s Right Eye
Alberto Giacometti’s Left Eye
Louise Nevelson’s Eye
Max Ernst’s Left Eye (installation view)
1960-1963
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Bill Brandt (British, 1904-83)
Dubuffet’s Right Eye (installation view)
1960-1963
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
German-born Brandt moved to London in the 1930s. In his long and varied career, he made many compelling portraits of people including Ezra Pound, Dylan Thomas, the Sitwell family, Robert Graves and E.M. Forster. For this series he photographed the eyes of well-known artists over several years, creating a substantial collection of intense and unique portraits. The pictures play upon ideas of artistic vision and the camera lens, which acts as a photographer’s ‘mechanical eye’.
Josef Sudek (Czech, 1896-1976)
Simple Still Life, Egg (installation view)
1950
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Throughout his career, Sudek used various photographic styles but always conveyed an intensely lyrical vision of the world. Here, his formal approach to a simple still life presents a poetic statement, and evokes an atmosphere of contemplation. Sudek’s motto and advice to his students – ‘hurry slowly’ – encapsulates his legendary patience and the sense of meditative stillness in his photographs.
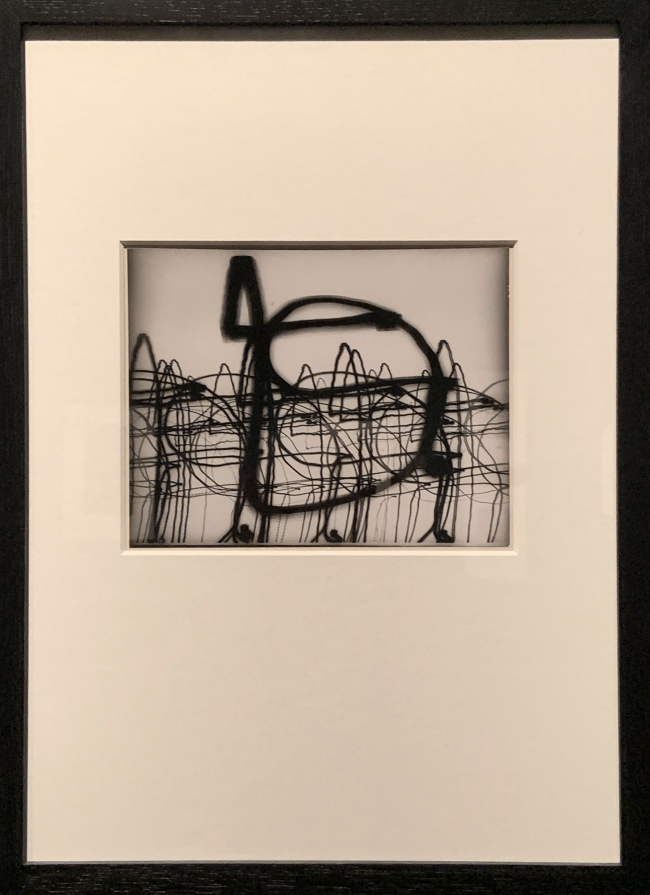
Otto Steiner (German, 1915-1978)
Luminogram (installation view)
1952
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Otto Steiner (German, 1915-1978)
Luminogram (installation view)
1952
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
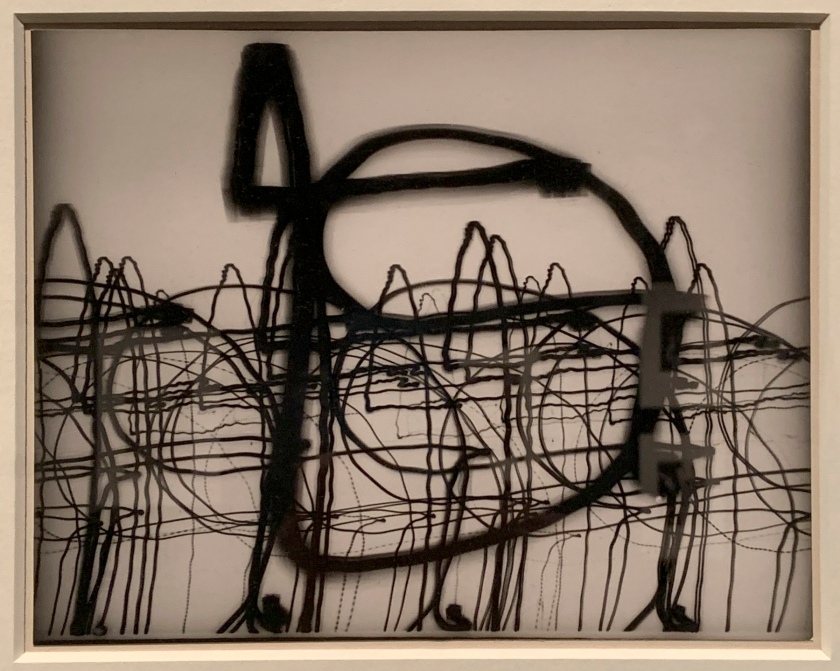
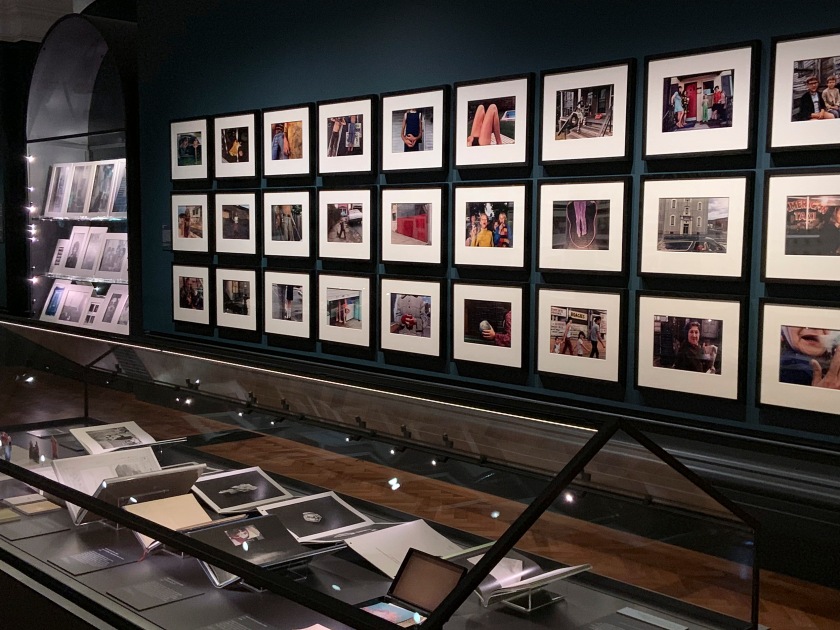
Mark Cohen (American, b. 1943)
True Color (installation views)
1974-1987
Portfolio of thirty dye transfer prints, printed in 2007
American Friends of the V&A through the generosity of The Michael G. and C. Jane Wilson 2007 Trust
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
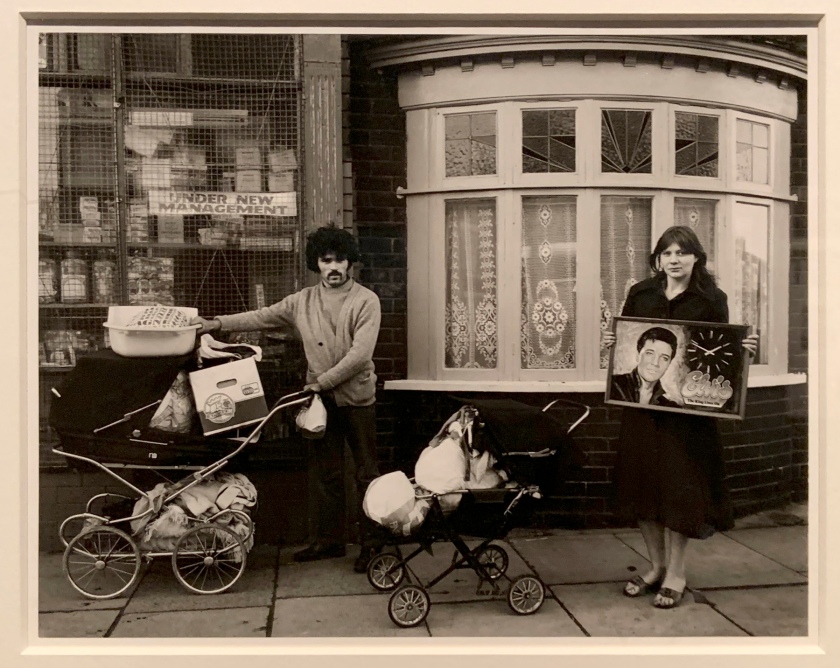
Known for his dynamic street photography, Cohen’s work presents a fragmented, sensory image of his hometown of Wiles-Barre, Pennsylvania. This set of pictures was taken at a time when colour photography was just beginning to be recognised as a fine art. Until the 1970s, colour had largely been associated with other advertising or family snapshots, and was not thought of as a legitimate medium for artists. Cohen and other photographers like William Eggleston transferred this perception using the dye-transfer printing process. Although complicated and time-consuming, the technique results in vibrant and high quality colour prints.
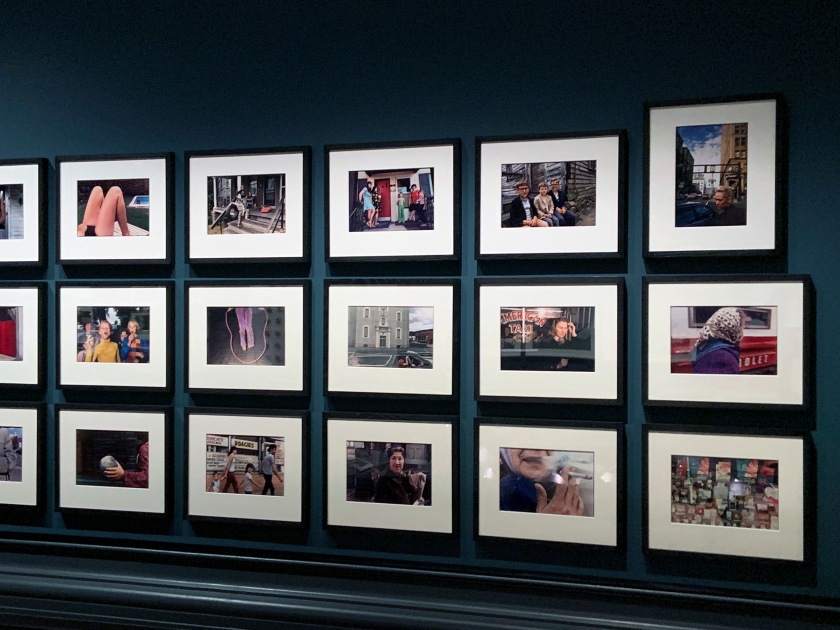
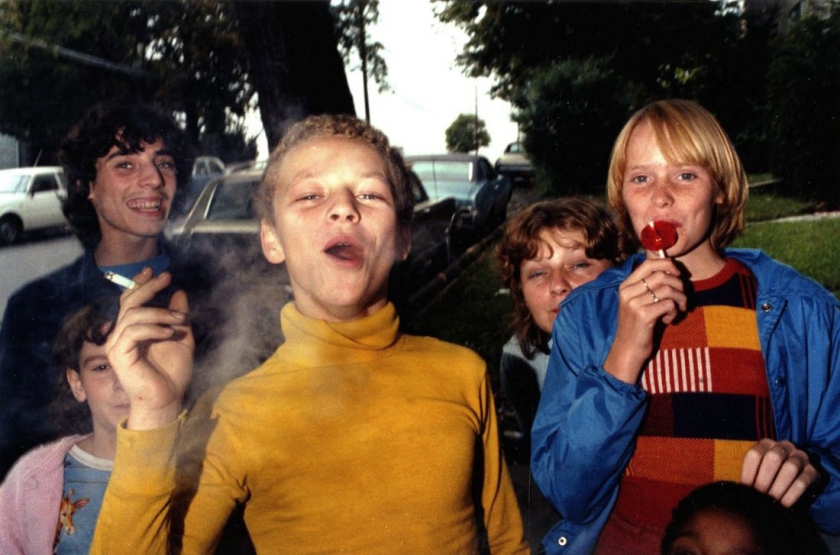
Mark Cohen (American, b. 1943)
True Color (installation view detail)
1974-1987
Portfolio of thirty dye transfer prints, printed in 2007
American Friends of the V&A through the generosity of The Michael G. and C. Jane Wilson 2007 Trust
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Mark Cohen (American, b. 1943)
True Color (installation view detail)
1974-1987
Portfolio of thirty dye transfer prints, printed in 2007
American Friends of the V&A through the generosity of The Michael G. and C. Jane Wilson 2007 Trust
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
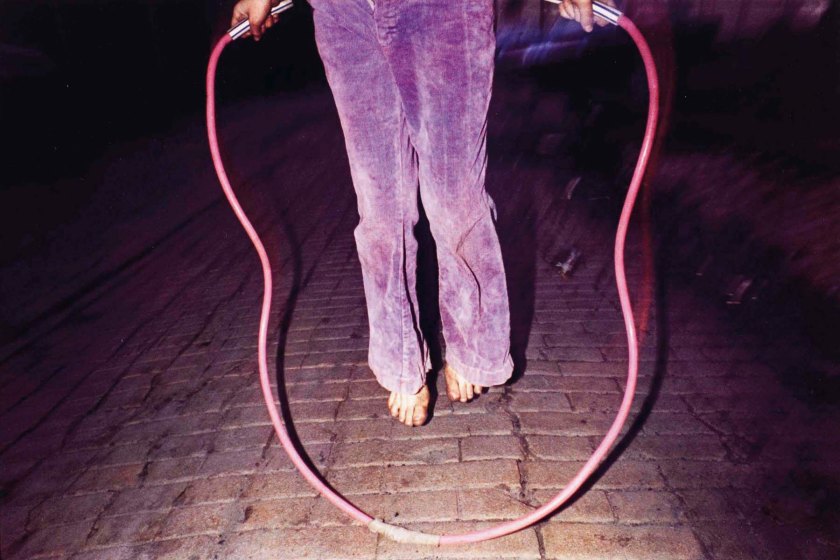
Graham Smith (British, b. 1947)
What she wanted & who she got (installation view)
1982
Gelatin silver print
The Royal Photographic Society Collection at the V&A Museum
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Since the 1980s, Graham Smith has been photographing his hometown of South Bank near Middlesbrough. His images convey his deep sensitivity towards the effects of changing working conditions on the former industrial north-east. In this photograph, despite the suggested humour of the title, we are left wondering who the couple are and what the nature of their relationship might be.
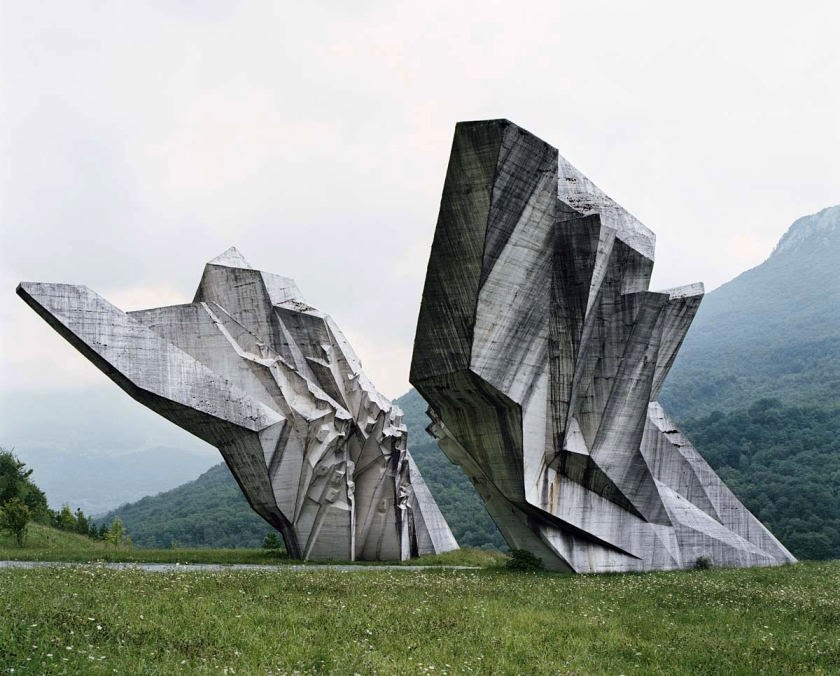
Jan Kempenaers (Belgian, b. 1968)
Spomenik #3
2006
C-type print
The Kosmaj monument in Serbia is dedicated to soldiers of the Kosmaj Partisan detachment from World War II.
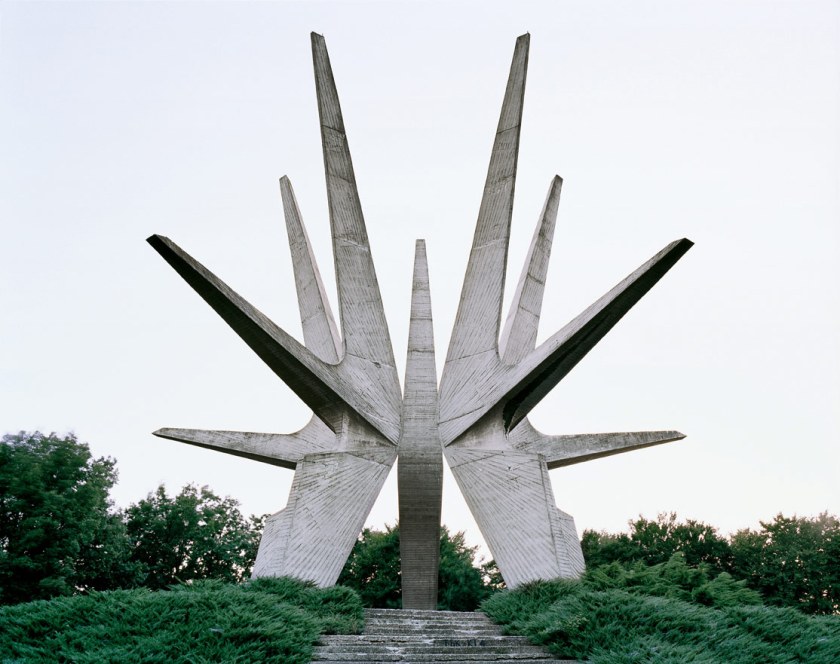
Jan Kempenaers (Belgian, b. 1968)
Spomenik #4
2007
C-type print
This monument, authored by sculptor Miodrag Živković, commemorates the Battle of Sutjeska, one of the bloodiest battles of World War II in the former Yugoslavia.
Kempenaers toured the balkans photographing ‘Spomeniks’ – monuments built in former Yugoslavia in the 1960s and ’70s on the sites of Second World War battles and concentration camps. Some have been vandalised in outpourings of anger against the former regime, while others are well maintained. In Kempenaers’ photographs, the monuments appear otherworldly, as if dropped from outer space into a pristine landscape.
Installation view of the V&A Photography Centre, London
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Victoria and Albert Museum
Cromwell Road
London
SW7 2RL
Phone: +44 (0)20 7942 2000
Opening hours:
Daily 10.00 – 17.45
Friday 10.00 – 22.00
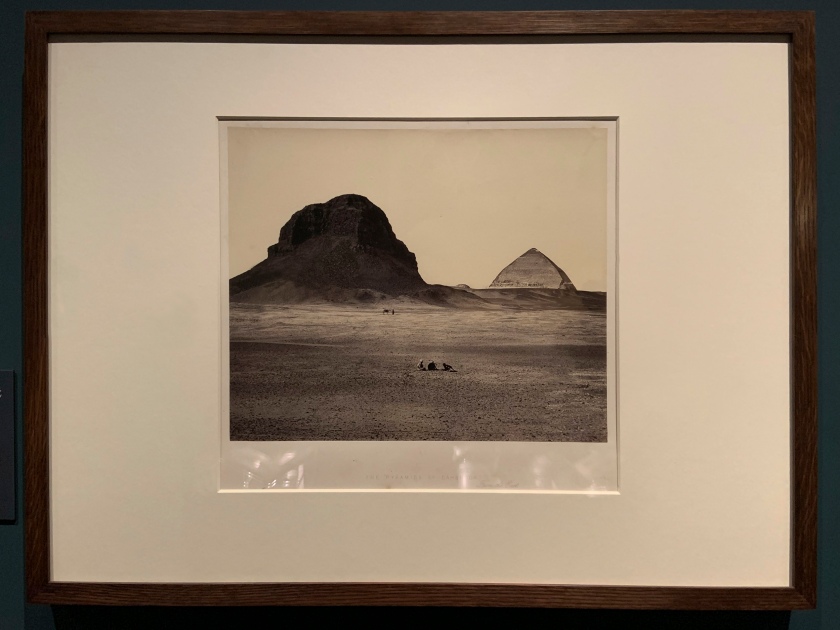






























![Francis Frith (British, 1822-98) 'The Pyramids of Dahshoor [Dahshur], from the East, from Egypt, Sinai, and Jerusalem: A Series of Twenty Photographic Views by Francis Frith' 1858 (published 1860 or 1862) Francis Frith (British, 1822-98) 'The Pyramids of Dahshoor [Dahshur], from the East, from Egypt, Sinai, and Jerusalem: A Series of Twenty Photographic Views by Francis Frith' 1858 (published 1860 or 1862)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2020/05/frith-the-pyramids-of-dahshoor-web.jpg?w=840)





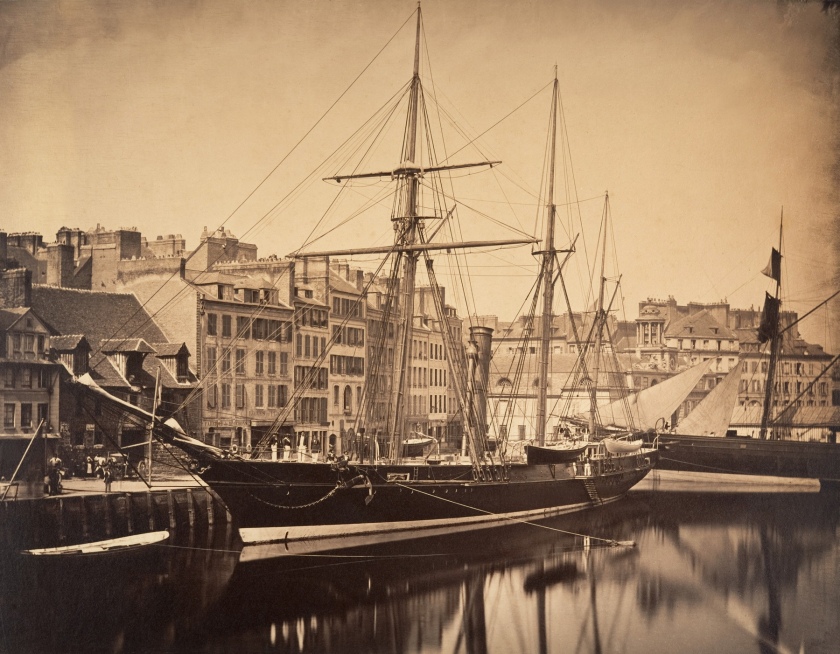
































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.