Exhibition dates: 5th April – 1st October, 2017
Curators: Clare Barlow, Assistant Curator, Tate Britain with Amy Concannon, Assistant Curator, Tate Britain

Queer British Art 1861-1967 book cover
Very Pauline
Queer British Art 1861-1967 at Tate Britain examines the “historical reality of same-sex relationships and non-normative sexual identities” from 1861, the year for the end of the death penalty for sodomy in Great Britain, through to 1967 which is when sex between consenting adults in private, obviously male homosexuality is partially decriminalised in England and Wales. The timescale of the exhibition encompasses the beginning of a more considered understanding of gender and sexual identity through to the beginnings of a limited freedom: from repression to liberation.
For a man who came out in London in 1975, only 8 short years after the decriminalisation of homosexuality, this exhibition should have been more engaging than it was. While there were some outstanding art works and artefacts presented in the eight rooms of the exhibition, chronologically laid out in the posting below – such as the prison door from Oscar Wilde’s cell at Reading Gaol, Joe Orton and Kenneth Halliwell’s book covers, the paintings of Henry Scott Tuke and the photography of Angus McBean – there was little of the passion of being gay in evidence in much of the objects, or how they were presented. It all seemed so very academic, and not in a good way. Other than some stunning erotic drawings by Aubrey Beardsley, Duncan Grant and Keith Vaughan (see below) there was little to suggest that being gay had anything to do with sex, the exhibition living up to that very British of axiom’s, “No sex please, we’re British!” The curators may have thought that sex would be a distraction, for it was all ‘very Pauline’.
The exhibition is full of innuendo, supposition, obfuscation, abstinence, hints, traces, clouded desires and supposed longings – in both the art work and the wall texts which accompanied the work. Of course, this is how artists had to hide their sexuality, same-sex desires and relationships during much of this period for fear of ostracisation from society and possible prosecution, but the presentation came across as little more than “au fait”, so much matter of fact. The exhibition was not helped by illuminating texts such as this: “The exact nature of Thomas and Philpot’s relationship is unknown. Many of Philpot’s depictions of Thomas carry a homoerotic charge and some are exoticising. What Thomas felt about his years with Philpot from 1929 to the artist’s death in 1937 is unknown.” Ugh!
You might as well have said nothing, and let the art work speak for itself.
Other commentaries could have done with a more insightful enunciation of the circumstances of the particular artist, in addition to text on the specific art work. A perceptive anointing of their life would have added invaluably to the frisson of the exhibition. For example, I wanted to know why the painter Christopher Wood died at the young age of 29 as well as the specifics of his painting Nude Boy in a Bedroom (1930, below). According to Wikipedia, Wood – bisexual, addicted to opium and painting frenetically in preparation for his Wertheim exhibition in London – became psychotic and jumped under a train at Salisbury railway station. These are the things that you need to know if you are to fully appreciate the gravitas of a life and a person’s relationship to their art, don’t you think?
Further, no pictures were allowed in the gallery spaces. Whereas I could take photographs of the Rachel Whiteread exhibition at the same venue to my heart’s content (even after being confronted by a guard who said I couldn’t, who was then corrected by a colleague with no apology for his attitude to me), I had to play a Machiavellian game of cunning hide and seek with guards and attendants to get the installation photographs of this exhibition. Why was this so? It almost seemed to be a case of the gallery being ashamed of the art they were exhibiting, as though the attitudes of the past towards art that explores same-sex relationships was being replicated by the duplicity of the gallery itself: the art could be seen but not heard, hidden away in the bowls of an academic institution. I also noted that one of 19 collages that Kenneth Halliwell exhibited at the Anno Domino gallery in 1967 (see below) was purchased by the Tate in 2016. Considering “the exhibition was a failure and Halliwell’s professional frustration contributed to the breakdown of his relationship with Orton,” eventuating the murder of the playwright and his own suicide… for some of those very same works to now reside at the Tate is the ultimate irony. I doubt Halliwell would have been laughing in his grave.
The stand out works in this exhibition were by Duncan Grant and Keith Vaughan. Their work explores the strength and beauty of the male form with a vitality of purpose and harmony of composition that was succinct and illuminating for this viewer. Grant’s Bathing (1911, below) ascribes anthropomorphic qualities to distorted figures whose elongated arms, distended chests and exposed buttocks would have been shocking to the people of Belle Epoque Britain. His erotic drawings (below) were the most beautiful, sensitive and sensual art works in the whole exhibition. Vaughan’s simplification of the figuration of the male form into abstract shapes, whilst still retaining the enigma of sensuality, narrative and context, are the triumph of this inverts painting. Their patterning and displacement of time and space onto an intimate other – a copious, coital realm of existence full of feeling, information and matter – were a revelation to me.
While the exhibition enunciates a remarkable range of identities and stories, from the playful to the political and from the erotic to the domestic, it was a deflating experience. I came away thankful that I had seen the work, that the artist’s had been able to express themselves however surreptitiously, but angry that so much of the world still sees LGBTQI people as second class citizens whose art work has to be examined through the prism of sexuality, rather than on the quality of the work itself.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
PS. How you can classify Claude Cahun as a British artist I will never know: she lived on the Channel Islands for a few years, but she was the very epitome of a French artist!
Many thankx to Tate Britain for allowing me to publish the art work in the posting. All installation images are © Dr Marcus Bunyan. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Much more fucking and they’ll be screaming hysterics in next to no time.”
Joe Orton
“For me, to use the word ‘queer’ is a liberation; it was a word that frightened me, but no longer.”
Derek Jarman
“It’s really interesting as to whether or not we should be concerned with the sexuality of an artist when we consider the merits of his artwork, because really what he does behind closed doors – or she does – has nothing to do, or shouldn’t have anything to do with the impact of the artwork as we see it. But what is important is the artist can use that material of their personal life and create a work that is almost a personal diary but visually.”
Estelle Lovatt
Featuring works from 1861-1967 relating to lesbian, gay, bisexual, trans and queer (LGBTQ) identities, the show marks the 50th anniversary of the partial decriminalisation of male homosexuality in England. Queer British Art explores how artists expressed themselves in a time when established assumptions about gender and sexuality were being questioned and transformed.
Deeply personal and intimate works are presented alongside pieces aimed at a wider public, which helped to forge a sense of community when modern terminology of ‘lesbian’, ‘gay’, ‘bisexual’ and ‘trans’ were unrecognised. Together, they reveal a remarkable range of identities and stories, from the playful to the political and from the erotic to the domestic. With paintings, drawings, personal photographs and film from artists such as John Singer Sargent, Dora Carrington, Duncan Grant and David Hockney the diversity of queer British art is celebrated as never before.
Text from the Tate Britain website
100 years of gay art history, from repression to liberation
On the 50th anniversary of the partial decriminalisation of homosexuality in England and Wales, the Tate Britain gallery is launching a major exhibition exploring Queer British Art. The new exhibition showcases 100 years of art and artists from the repression of the Victorian era through to the love and lust of 1960s Soho.
Room 1: Coded Desires
In spite of the Victorian era’s prudish reputation, there are many possible traces of transgressive desire in its art – in Frederic Leighton’s sensuous male nudes, for instance, or Evelyn De Morgan’s depictions of Jane Hales. Simeon Solomon attracted sustained criticisms of ‘unwholesomeness’ or ‘effeminacy’ – terms which suggest disapproval of alternative forms of masculinity as much as same sex desire. Yet other works which might look queer to us passed without comment.
The death penalty for sodomy was abolished in 1861 but it was still punishable with imprisonment. Sex between women was not illegal and society sometimes tolerated such relationships. Yet for most people, there seems to have been little sense that certain sexual practices or forms of gender expression reflected a core aspect of the self. Instead, this was a world of fluid possibilities.
These ambiguities offered scope for artists to produce work that was open to homoerotic interpretation. Queer subcultures developed: new scholarship on same-sex desire in Renaissance Italy and ancient Greece allowed artists to use these civilisations as reference points, while the beautiful youths in Wilhelm von Gloeden’s photographs attracted communities of collectors. As long as there was no public suggestion that artists had acted on their desires, there was much that could be explored and expressed.
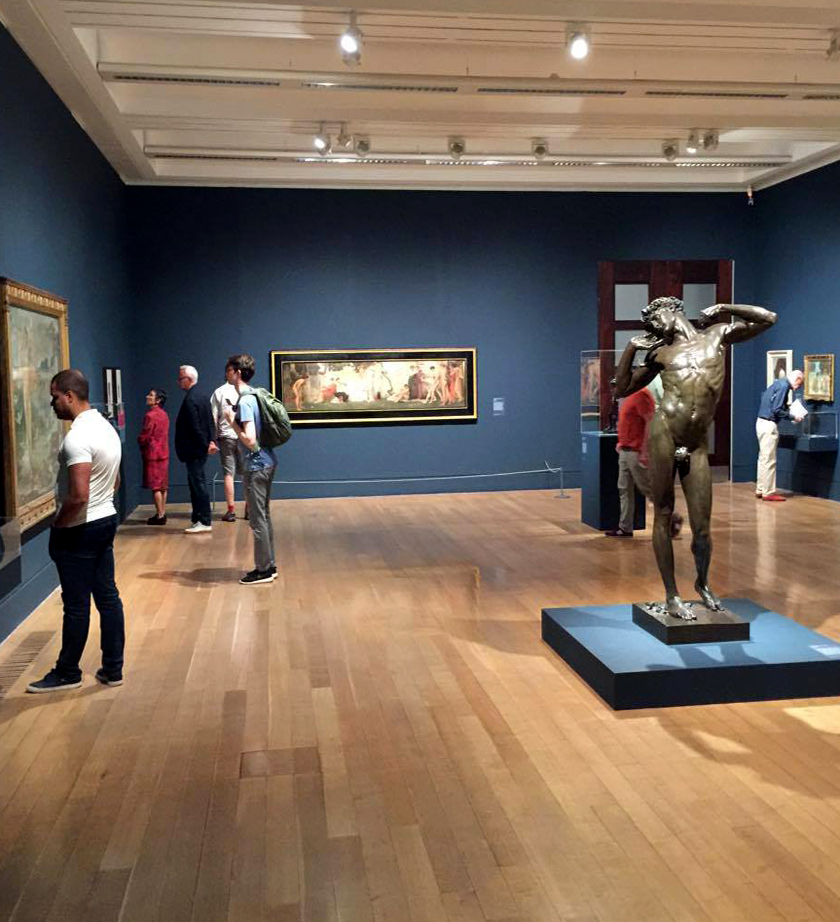


Installation views of Room 1 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain with Frederic Leighton’s The Sluggard (1885, bronze) in the middle of the room
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
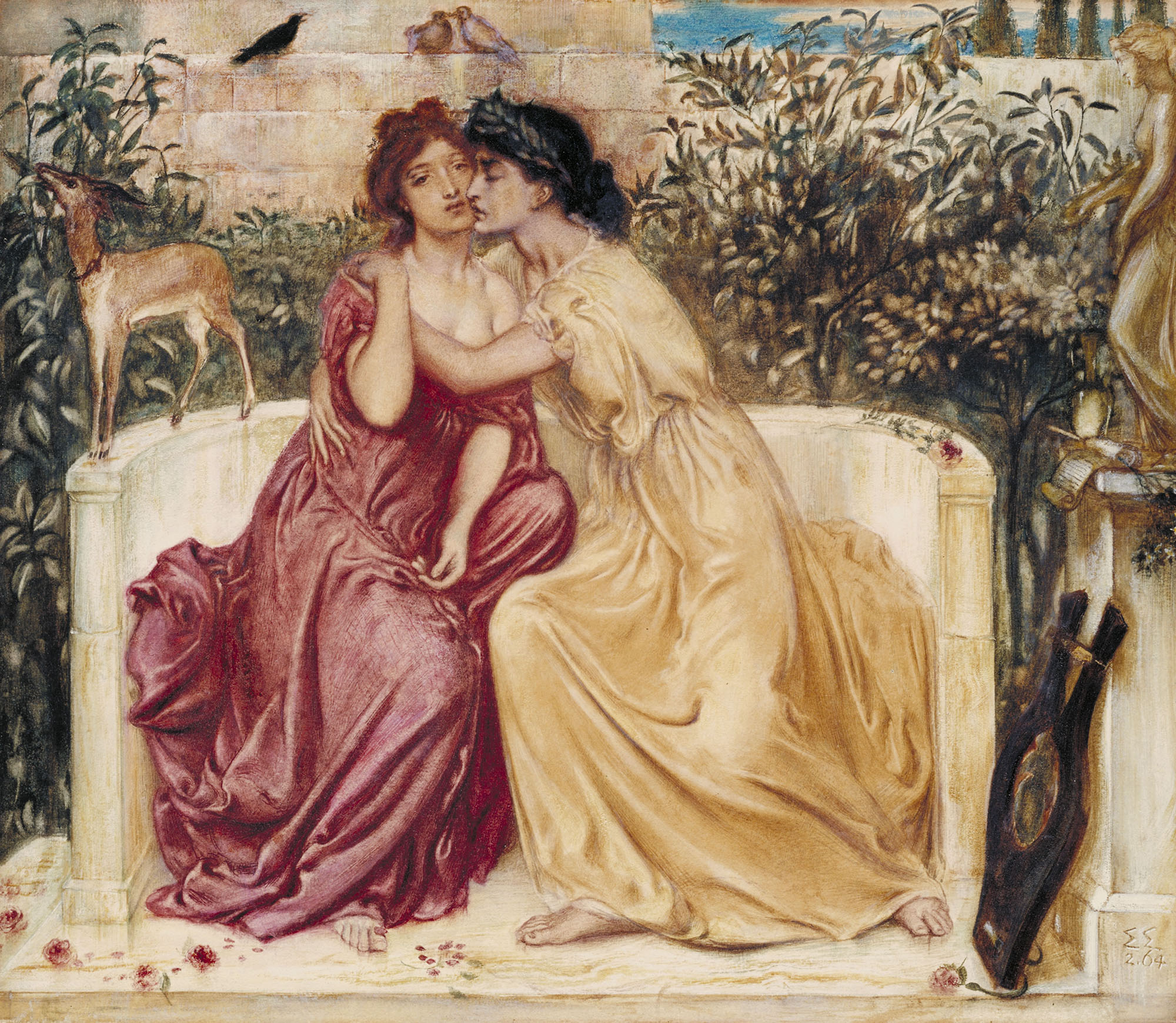

Simeon Solomon (British, 1840-1905)
Sappho and Erinna in a Garden at Mytilene
1864
Watercolour on paper
330 x 381mm
Tate. Purchased 1980
Sappho and Erinna in a Garden at Mytilene is a touching image of female love. The piece is inspired by fragmented poems written by a woman named Sappho in the 4th century BC, in which she pleads that Aphrodite help her in her same-sex relationship. The term ‘lesbian’ derives directly from this poet, as her homeland was the Greek Island of Lesbos. Sappho’s story points to a longer history of same-sex desire. It’s perhaps for this reason that Simeon Solomon, a man who was attracted to men in defiance of the law, painted her. While a depiction of two men kissing would have been completely taboo, this is a passionate depiction of same-sex desire.
Solomon’s own sexual preferences eventually lead to his incarceration. When he was released from prison he was rejected by many of his acquaintances, struggled to find work and soon became homeless; a painful reminder of our repressive past.
Text from the Tate website
This strikingly frank image shows the ancient Greek poet Sappho in a passionate embrace with her fellow poet Erinna. Sappho is associated with the Island of Lesbos and her story gives us the word ‘lesbian’. There was a surge of interest in Sappho’s achievements and desires from the 1840s onwards. Solomon may be responding to his friend Algernon Charles Swinburne’s poem Anactoria which includes Erinna amongst Sappho’s lovers. While female same-sex desire was considered more acceptable than its male equivalent, Solomon’s depiction of Sappho’s fervent kiss and Erinna’s swooning response is unusually explicit and the image was not publicly exhibited.
Wall text from the exhibition

Simeon Solomon (British, 1840-1905)
The Bride, Bridegroom and Sad Love
1865
Ink on paper
Victoria and Albert Museum
This work was inspired by a passage from the Gospel of St John which tells how ‘the friend of the bridegroom… rejoices greatly at the bridegroom’s voice’. In Solomon’s drawing, the friend of the bridegroom has the wings of love but his downcast expression identifies him as ‘sad love’, forever excluded. The positioning of his and the bridegroom’s hands hints at the reason for his grief, implying that that they are former sexual partners. He is forced to look on as his lover enters a heterosexual marriage: a fate shared by many men in same-sex relationships in this period.
Wall text from the exhibition

Simeon Solomon (British, 1840-1905)
Bacchus
1867
Oil paint on paper on canvas
Lent by Birmingham Museums Trust on behalf of Birmingham City Council
The classical god of wine, Bacchus also embodies sexual ambiguity and gender fluidity. While grapes and vine leaves identify the god in Solomon’s painting, Bacchus’s full lips, luxuriant hair and enigmatic gaze hint at his elusive sexuality. When it was exhibited at the Royal Academy in 1867, the critic of The Art Journal thought the figure looked effeminate, commenting ‘Bacchus is a sentimentalist of rather weak constitution; he drinks mead, possibly sugar and water, certainly not wine’. Solomon’s friend, critic Walter Pater wrote a favourable essay about the painting and poet Algernon Charles Swinburne said he found in Solomon and Bacchus alike, ‘the stamp of sorrow; of perplexities unsolved and desires unsatisfied’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Simeon Solomon (British, 1840-1905)
The Moon and Sleep
1894
Oil paint on canvas
Tate. Presented by Miss Margery Abrahams in memory of Dr Bertram L. Abrahams and Jane Abrahams 1973
Made a few years after Solomon’s arrest and social ostracisation, this painting depicts the love of the moon goddess Selene for Endymion, who, in one version of the myth, is given eternal youth and eternal sleep by Zeus. While it ostensibly depicts a heterosexual pairing, the striking similarity of the profiles of the figures in Solomon’s painting gives them both an air of androgyny. This painting was given to Tate by a descendent of Rachel Simmons, Solomon’s first cousin, who helped to support him after his fall from public favour by regularly buying his works for small sums of money.
Wall text from the exhibition

Photographer unknown
John Addington Symonds (installation view)
c. 1850s
Photograph, tinted collodion on paper
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
John Addington Symonds was a writer, critic and an early campaigner for greater tolerance of same-sex desire. This photograph probably dates from Symonds’s time at Oxford University (1858-1863). His studies informed his later essay, A Problem in Greek Ethics 1873, one of the earliest attempts at a history of male same-sex desire. Symonds frankly discussed his desires in his diaries and unpublished writings, which he believed would be ‘useful to society’. However, when his friend Edmund Gosse inherited Symonds’s papers in 1926, he burned them all apart from Symonds’s autobiography. This destruction nauseated Symonds’s granddaughter Janet Vaughan. It was not until 1984 that Symonds’s autobiography was finally published.
Wall text from the exhibition
Sidney Harold Meteyard (English, 1868-1947)
Hope Comforting Love in Bondage
Exhibited 1901
Oil paint on canvas
Lent by Birmingham Museums Trust on behalf of Birmingham City Council
Hope is depicted as a respectably fully-clothed matron, whereas Love’s only costume is his elaborate cloth bindings and the rose briars that are delicately threaded through the feathers of his wings. The flowers and thorns of the roses hint at pleasures and pains combined. Love’s pensive expression and androgynous beauty is reminiscent of the work of Simeon Solomon and, while Hope stretches out her hand to comfort him, his gaze is fixed elsewhere, leaving the object of his affections undefined.
Wall text from the exhibition
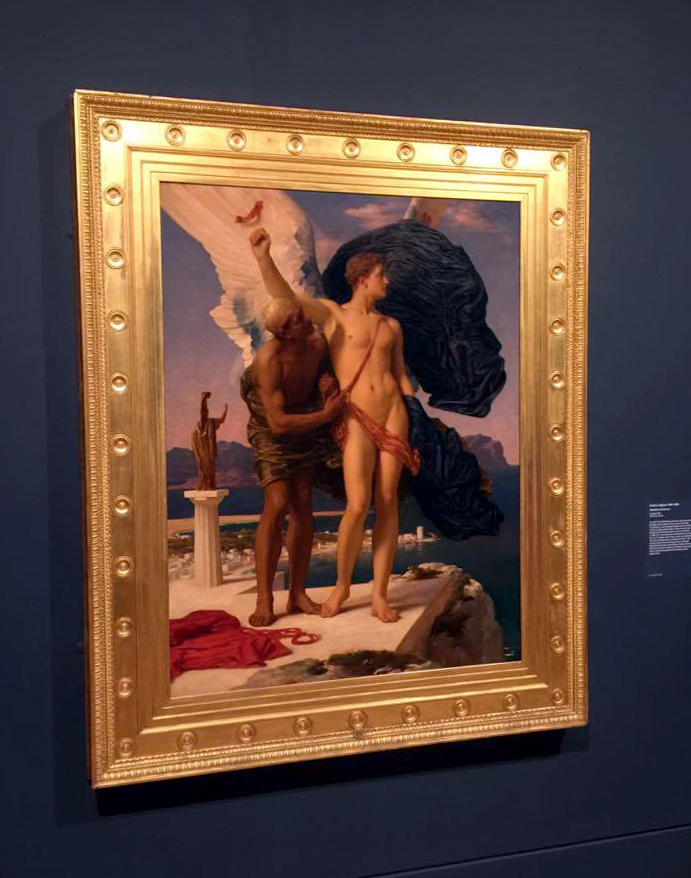

Installation view of Frederic Leighton’s Daedalus and Icarus 1896 from the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
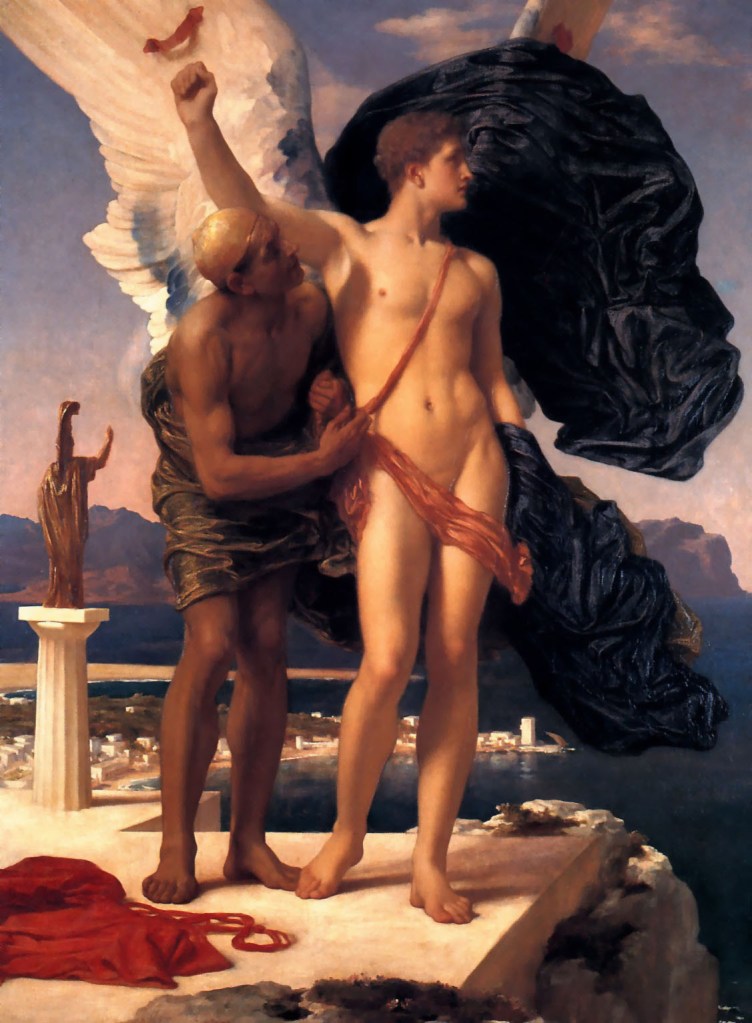

Frederic Leighton (British, 1830-1896)
Daedalus and Icarus
Exhibited 1869
Oil paint on canvas
Private collection
In a story from the Roman poet Ovid’s Metamorphoses, Daedalus made wings for his son Icarus to escape from Rhodes. Icarus’s golden beauty is here contrasted with his weather-beaten father. When the work was exhibited at the Royal Academy Summer Exhibition in 1869, The Times anxiously remarked that Icarus had the air of ‘a maiden rather than a youth’ and exhibited ‘the soft rounded contour of a feminine breast’. This response may reflect increasing concern amongst educated circles about the pairings of older men and adolescent youths in books such as Plato’s Symposium, as new scholarship explored the eroticism of the original texts.
Wall text from the exhibition

Installation view of Henry Scott Tuke’s A Bathing Group 1914 from the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
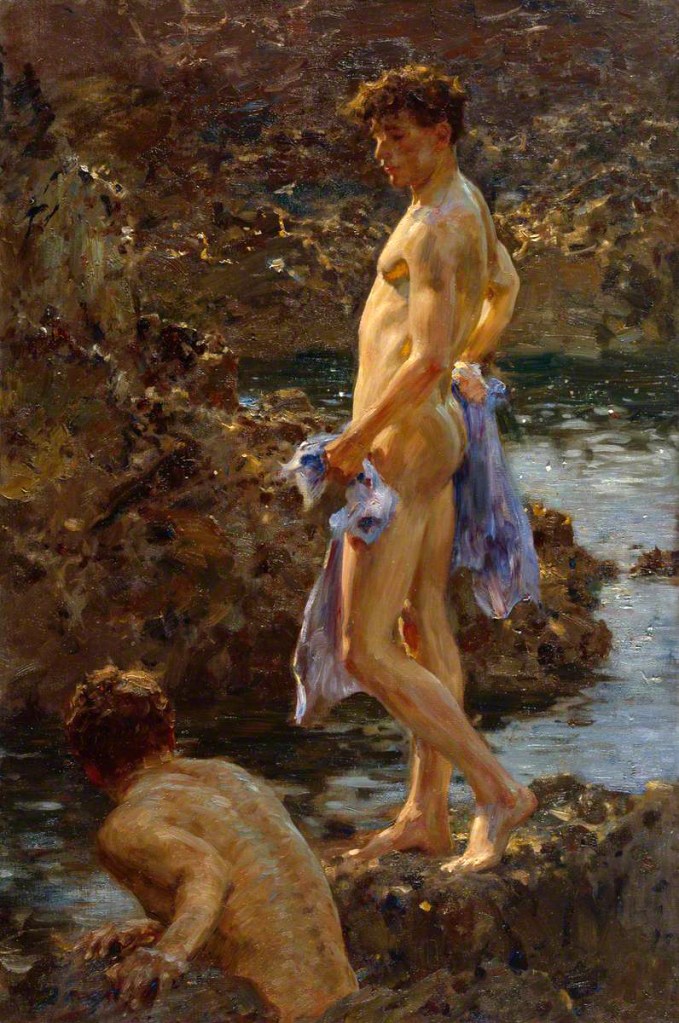

Henry Scott Tuke (English, 1858-1929)
A Bathing Group
1914
Oil paint on canvas
Lent by the Royal Academy of Arts, London
While Henry Scott Tuke used the professional model Nicola Lucciani for this painting, it is similar to his images of Cornish youths in its frank appreciation of the male nude. Lucciani’s torso is illuminated by a shaft of sunlight and he looks towards the second figure, who crouches as if in awe of his godlike beauty. Tuke presented the painting to the Royal Academy on his election as a member. Tuke used professional models when he first moved to Cornwall, but he soon befriended some of the local fishermen and swimmers in Falmouth who modelled for him in many paintings.
Wall text from the exhibition
Henry Scott Tuke (English, 1858-1929)
The Critics
1927
Oil paint on board
Courtesy of Leamington Spa Art Gallery & Museum (Warwick District Council)
Made just two years before Tuke’s death, The Critics is one of a number of works by Henry Scott Tuke depicting young men bathing off the Cornish coast. There has been much speculation about his relationships with his Cornish models although nothing has been substantiated. It is, however, not difficult to find a homoerotic undercurrent in this painting, as the two men on the shore appraise the swimming technique – and possibly the physique – of the youth in the water. Writer John Addington Symonds was a frequent visitor and he encouraged Tuke in his painting of male nudes in a natural outdoor setting.
Wall text from the exhibition
Room 2: Public Indecency
This room looks at ways in which sexuality and gender identity did – and did not – go public, from the 1880s to the 1920s. Public debate over sexuality and gender identity was stirred up by scandals, campaigns and scientific studies. The trials of Oscar Wilde in 1895 for gross indecency and Radclyffe Hall’s novel The Well of Loneliness in 1928 for supposed obscenity put a spotlight on same-sex desire. In the field of science, the project of classifying sexual practices and forms of gender presentation into distinct identities, which had been begun by German psychiatrists such as Richard von Krafft-Ebing, reached Britain through the work of Havelock Ellis who co-authored his book Sexual Inversion 1896 with John Addington Symonds. However, change was slow, and many people remained unaware of new terminologies and approaches to the self that this new science offered.

Installation view of Henry Bishop’s Henry Havelock Ellis from the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan

Henry Bishop (British, 1868-1939)
Henry Havelock Ellis
1890s
Oil paint on canvas
National Portrait Gallery, London. Bequeathed by François Lafitte, 2003
The sexologist Henry Havelock Ellis’s great work Sexual Inversion, co-authored with John Addington Symonds, defined queer sexualities in Britain for a generation. Published in English in 1897, it drew on the experiences of people such as Edward Carpenter (whose portrait hangs nearby). It was effectively banned in Britain after the prosecution of a bookseller, George Bedborough. This informal portrait was probably made around the time of Bedborough’s trial. It depicts Ellis sitting in a deckchair in Henry Bishop’s studio in St Ives. There is some evidence Bishop was attracted to men and Ellis’s non-judgemental attitudes may have encouraged Bishop to make his acquaintance. He became a lifelong friend.
Wall text from the exhibition
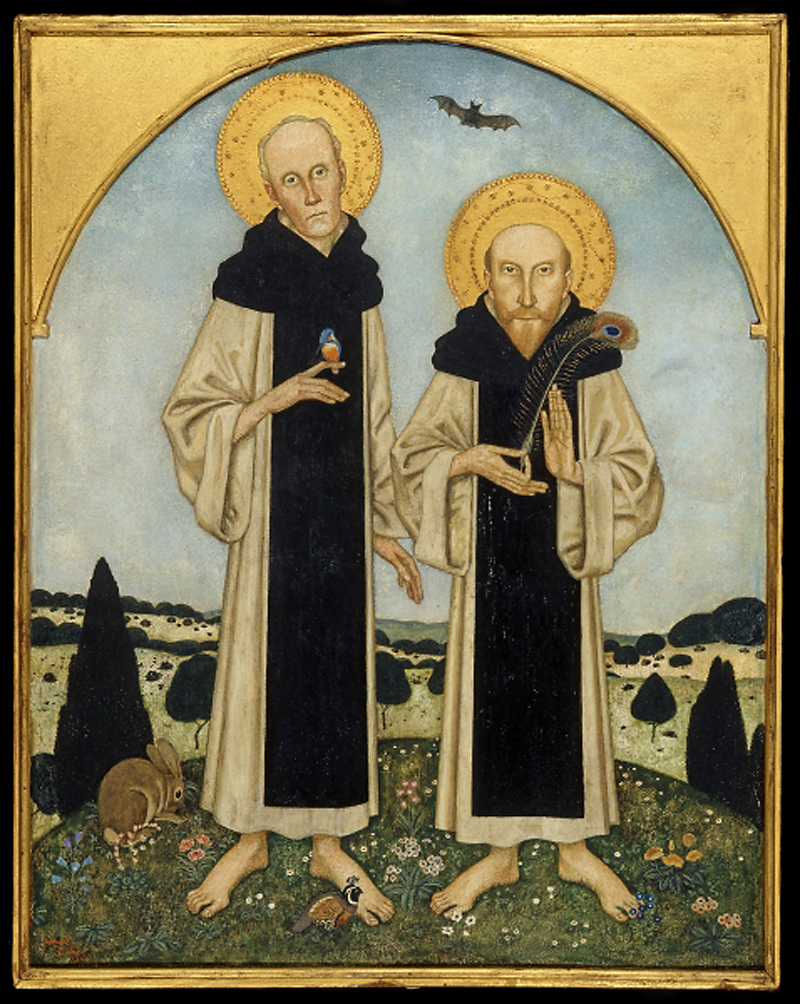

Edmund Dulac (British born France, 1882-1953)
Charles Ricketts and Charles Shannon as Medieval Saints
1920
Tempera on linen over board
The Syndics of the Fitzwilliam Museum, University of Cambridge
Oscar Wilde described the home of the artist and designer Charles Ricketts and his lifelong partner the painter Charles Shannon as ‘the one house in London where you will never be bored’. Here, the couple are playfully depicted by their friend Edmund Dulac in the robes of Dominican friars. These robes possibly hint at the permanence of their bond: monastic vows were, after all, intended to mark entry for life into an all-male community. The peacock feather in Rickett’s hand signals their devotion to aestheticism, an art movement dedicated to beauty and ‘art for art’s sake’. By the 1920s, this was an emblem of a previous era.
Wall text from the exhibition

Charles Buchel (British, 1872-1950)
Radclyffe Hall (installation view)
1918
Oil paint on canvas
National Portrait Gallery, London. Bequeathed by Una Elena Vincenzo (née Taylor), Lady Troubridge, 1963
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Born ‘Marguerite’ Radclyffe Hall and known as ‘John’ to close friends, Radclyffe Hall was a key figure in provoking debate on female same-sex desire. This portrait was made ten years before Hall found fame as the author of The Well of Loneliness 1928. Despite the pleas of literary figures, including Virginia Woolf, this novel was effectively banned on the grounds of obscenity for its frank depiction of female same-sex desire. It was semi-autobiographical and was influenced by Havelock Ellis’s Sexual Inversion. Hall’s sober jacket, skirt, cravat and monocle in this image reflected contemporary female fashions for a more masculine style of dress. After the trial, Hall’s clothes and cropped hair became associated with lesbianism and this portrait has become a queer icon. It was given to the National Portrait Gallery by Hall’s lover, Una Troubridge.
Wall text from the exhibition
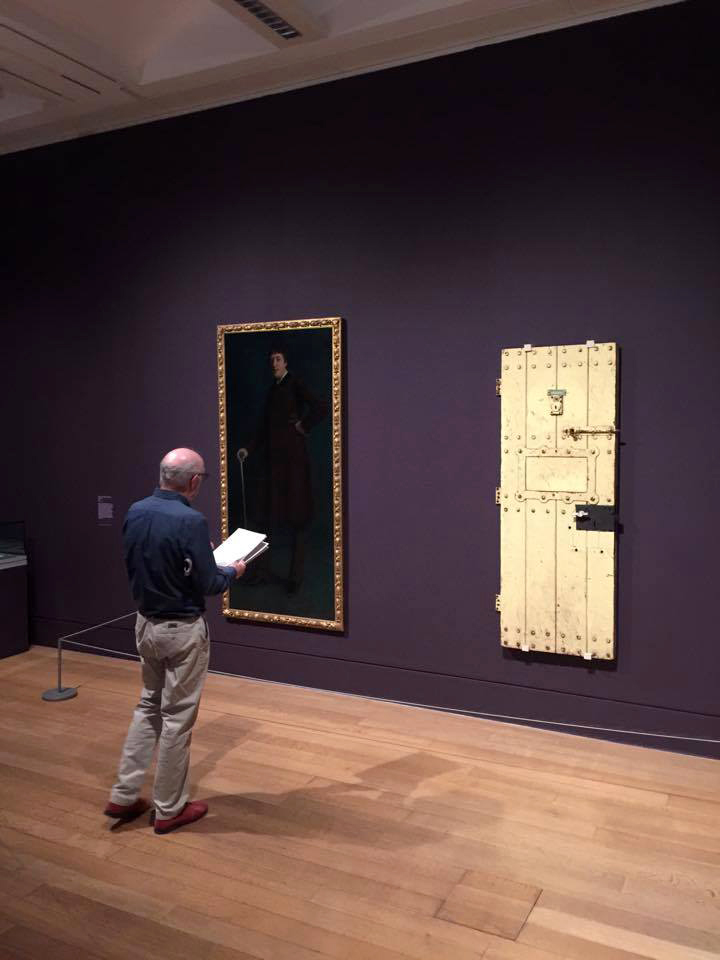
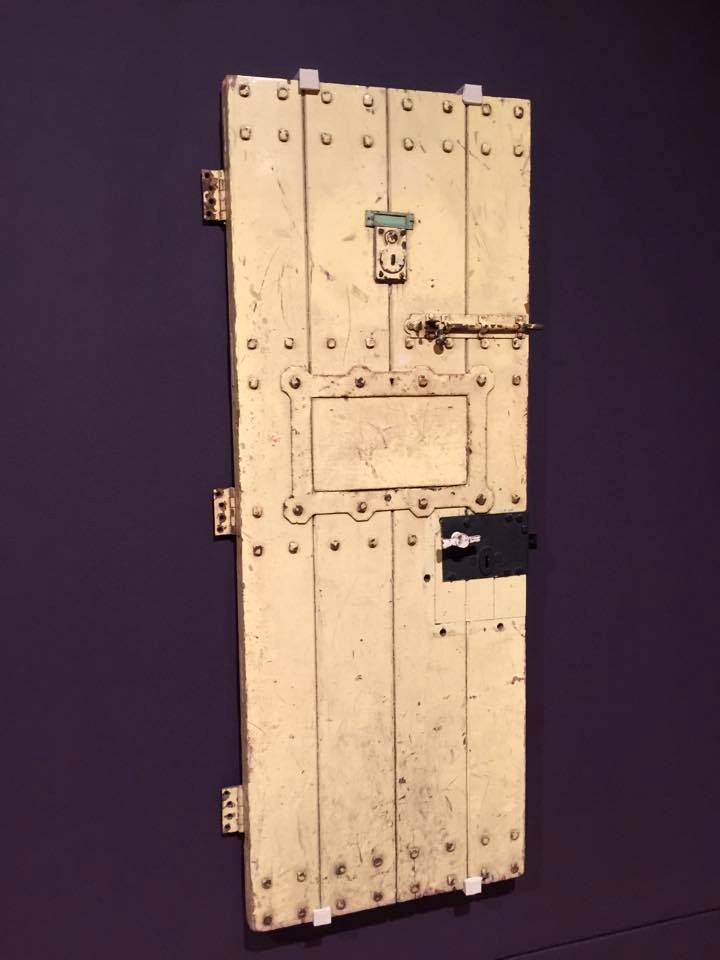


Installation views of Room 2 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain with Oscar Wilde’s Prison Door c. 1883
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
This is the door of Oscar Wilde’s prison cell at Reading Gaol. Wilde spent three months of his incarceration writing a tortured letter to his lover Lord Alfred Douglas. This was later published as De Profundis (‘from the depths’). Wilde was not allowed to send the letter, although the manuscript was given back to him when he left prison. He told his friend Robert Ross, ‘I know that on the day of my release I will merely be moving from one prison into another, and there are times when the whole world seems to be no larger than my cell, and as full of terror for me’.
Wall text from the exhibition
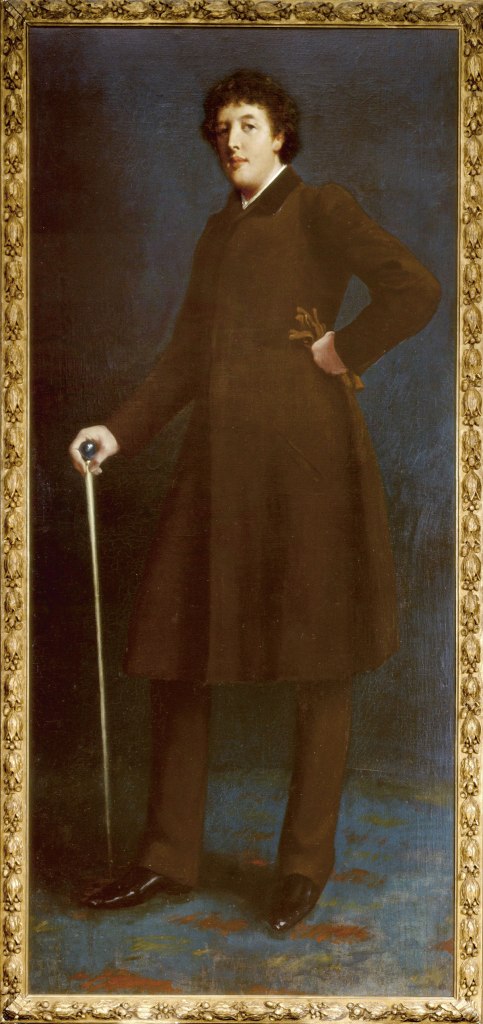

Robert Goodloe Harper Pennington (American, 1854-1920)
Oscar Wilde (installation view)
c. 1881
William Andrews Clark Memorial Library, Los Angeles, California
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
The American artist Harper Pennington gave this portrait to Wilde and his wife Constance as a wedding present in 1884. It captures Wilde as a young man aged 27, on the cusp of success and it hung in Wilde’s home in Tite Street, Chelsea, London. While awaiting trial, Wilde was declared bankrupt and all his possessions, including this portrait, were sold at public auction to pay his debts. Few objects from his extensive collection have been traced. This painting was bought by Wilde’s friend Ada Leverson and it was kept in storage. Wilde told a friend that Ada’s husband ‘could not have it in his drawing-room as it was obviously, on account of its subject, demoralising to young men, and possibly to young women of advanced views’.
Wall text from the exhibition

Aubrey Beardsley (English, 1872-1898)
Enter Herodias from ‘Salome’ by Oscar Wilde
1890s
Photo-process print on paper
Victoria and Albert Museum
Here Herodias, Salome’s mother makes a dramatic entrance, bare-breasted and positioned at the centre of the composition. The grotesque figure on the left plucks at her cloak, his robe barely concealing his giant phallus, while the slender page appears notably unmoved. They seem to epitomise two forms of masculinity: the grotesquely heterosexual and the elegantly ambiguous. Oscar Wilde is satirised as the showman-like jester in the foreground.
Wall text from the exhibition
Cecil Beaton (British, 1904-1980)
Cecil Beaton and his Friends
1927
Photograph, bromide print on paper
National Portrait Gallery, London. Accepted in lieu of tax by H.M. Government and allocated to the Gallery, 1991
This photograph was taken at Wilsford Manor in Wiltshire, Stephen Tennant’s childhood home. The party depicted here includes Tennant, artist Rex Whistler, society hostess Zita Jungman and Beaton himself, although their elaborate fancy dress and make-up makes it hard to tell them apart. The poet Siegfried Sassoon, Tennant’s lover at this time, wrote in his diary, ‘It was very amusing, and they were painted up to the eyes, but I didn’t quite like it’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Room 3: Theatrical Types
The use of ‘theatrical’ as a euphemism for queer hints at the rich culture on the late nineteenth and early twentieth century stage. The extent to which audiences were aware of this varied. Music hall male and female ‘impersonation acts’ were wildly popular but were mostly seen as innocent ‘family fun’. In the formal theatre, plays for public production had to be passed by the Lord Chamberlain’s office. While some directors found ways to avoid censorship, there were few positive and explicit depictions of queer lives and experience. Many celebrities who were in same-sex relationships understandably tried to keep their lives from public view, although their desires were often open secrets. Nevertheless, whether as the subject of a moralistic ‘problem’ play or an innuendo in a saucy song, queer perspectives could find public expression on the stage.

Installation view of Room 3 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
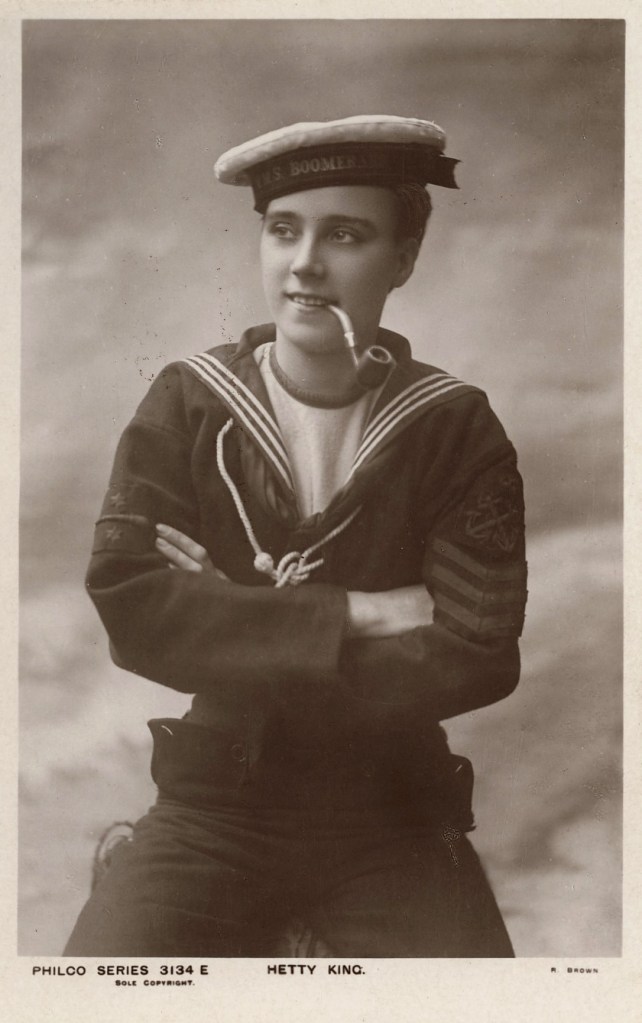

Unknown photographer, published by The Philco Publishing Company
Hetty King (Winifred Ems)
1910s
National Portrait Gallery
Angus McBean (Welsh, 1904-1990)
Angus McBean’s career was forged in the theatre. Success came in 1936 with his photographs of Max Beerbohm’s The Happy Hypocrite 1896, starring Ivor Novello. In a break with convention, McBean’s close-up images were well lit with studio lights and staged as intimate tableaux. Inspired by the International Surrealist exhibitions of 1936 and 1937, he began to make playful ‘surrealised portraits’, which were initially published in The Sketch. These used complex props and staging to create fantastical scenes and to give the illusion of distorted scale.
The images here all depict sitters who were in same-sex relationships. McBean’s own relationships with men led to a police raid on his house and his arrest in 1942 for criminal acts of homosexuality. He was convicted and sentenced to four years in jail but was released in 1944 and quickly reestablished his reputation as a photographer.

Angus McBean (Welsh, 1904-1990)
Sir Robert Murray Helpmann
1950
Photograph, bromide print on paper
© Estate of Angus McBean / National Portrait Gallery, London
McBean’s portrait of Robert Helpmann, published in The Tatler and Bystander on 28 April 1948, shows him in the role of Hamlet, which he was then playing at Stratford-upon-Avon. The production was designed to be Victorian gothic: an Elsinore of guttering candles and chiaroscuro lighting effects. There is perhaps some suggestion of this in the heavy shadows of McBean’s photograph, while Helpmann’s dramatic make-up emphasises his melancholic expression. The backdrop was created from a blown-up photograph of text from the First Folio of the play. In defiance of the law, Helpmann lived comparatively openly with his partner, the theatre director Michael Benthall. Their relationship lasted from 1938 until Benthall’s death, in 1974.
Wall text from the exhibition

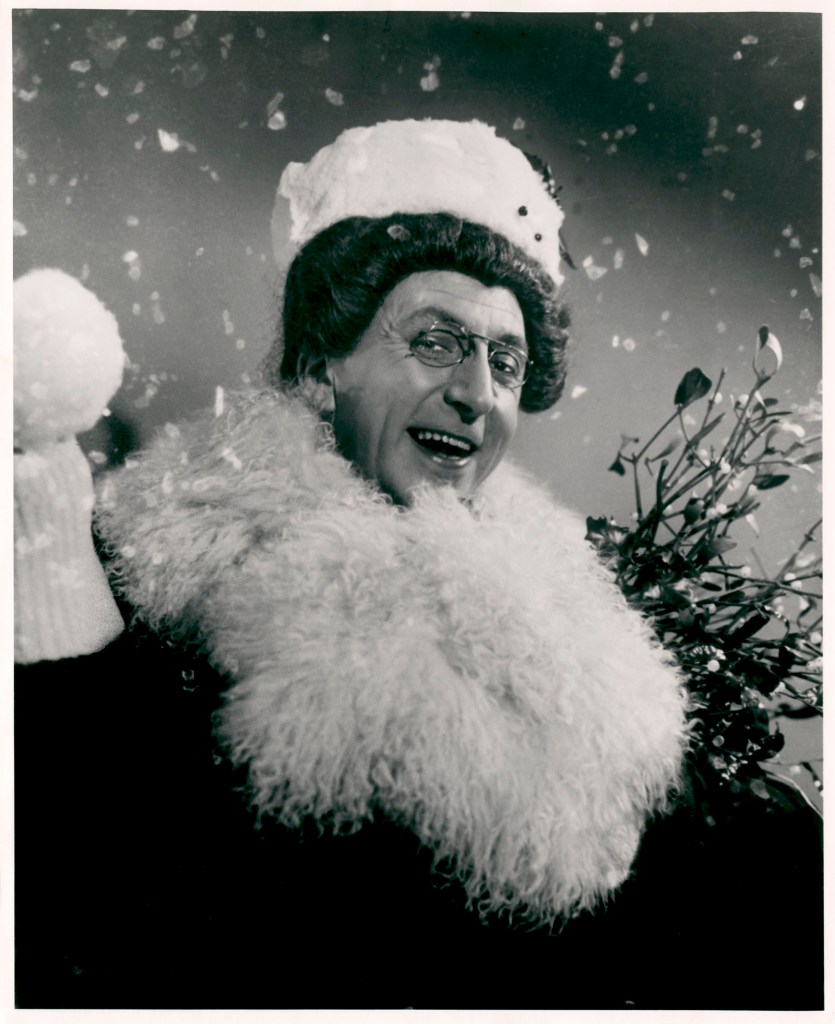
Angus McBean (Welsh, 1904-1990)
Danny La Rue
1968
Photograph, bromide print on paper
National Portrait Gallery, London
Born Danny Carroll, Danny La Rue was one of the greatest stars in female impersonation. La Rue first performed while in the navy during the Second World War and later toured with all male revues such as Forces in Petticoats before becoming a cabaret star. La Rue’s glamorous appearance on stage, captured here, was undercut by the gruff ‘wotcher mates’, with which he opened his set. La Rue preferred the term ‘comic in a frock’ to ‘female impersonator’ and described his act as ‘playing a woman knowing that everyone knows it’s a fella’.
Wall text from the exhibition
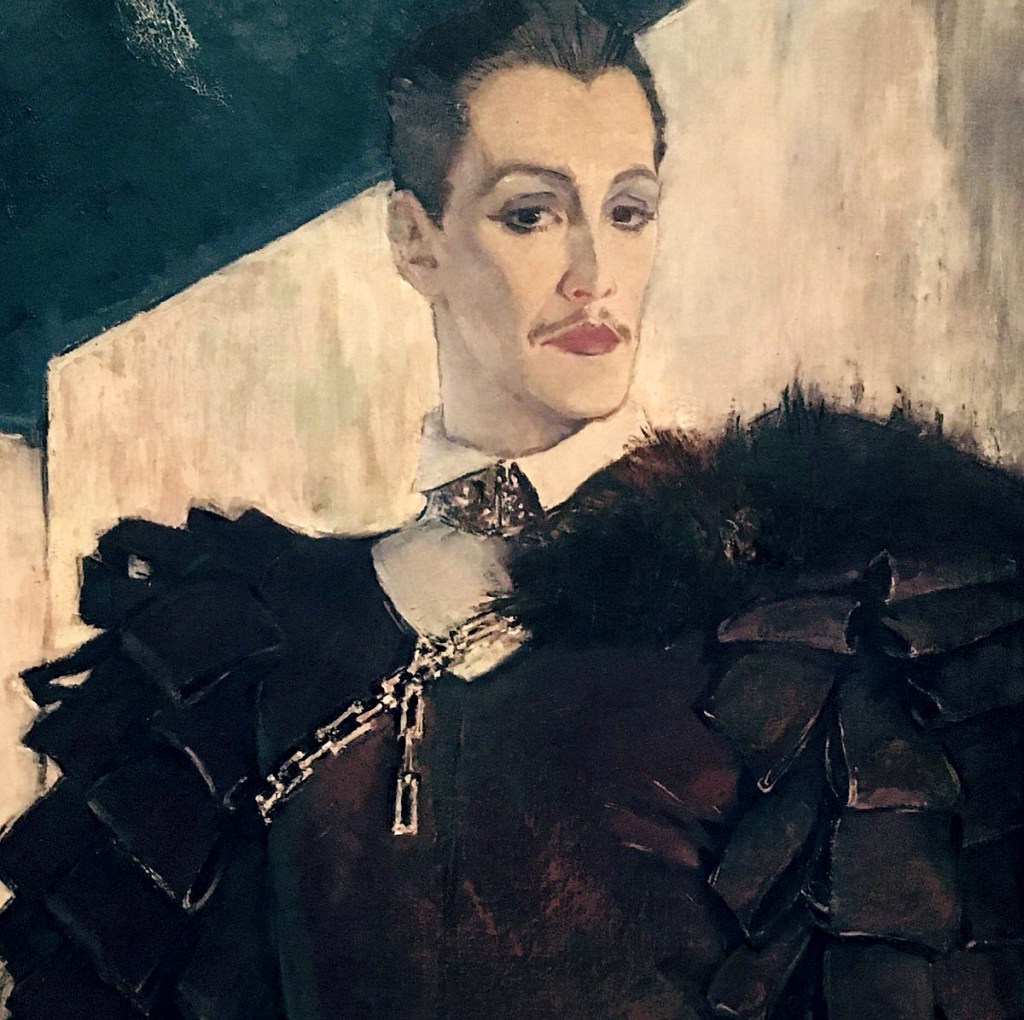

Glyn Warren Philpot (British, 1884-1937)
Glen Byam Shaw as ‘Laertes’
1934-1935
Oil paint on canvas
Kindly lent by the sitter’s grandson, Charles Hart
The actor Glen Byam Shaw is depicted here as Laertes in John Gielgud’s 1934 critically acclaimed production of Hamlet in a costume designed by Motley: Elizabeth Montgomery, Margaret Percy and Sophie Harris. Glyn Philpot cut down the original three-quarter length portrait after it was exhibited at the Royal Academy in 1935. This reduction puts even greater focus on Byam Shaw’s face and heavy stage make-up. While the image is typical of productions of the period, the medium of the portrait removes it from its original theatrical context. Coupled with Byam Shaw’s arch expression, the overriding impression is one of high camp. Byam Shaw had almost certainly been the lover of the poet Siegfried Sassoon (1886-1967) and may have met Philpot through Sassoon.
Wall text from the exhibition
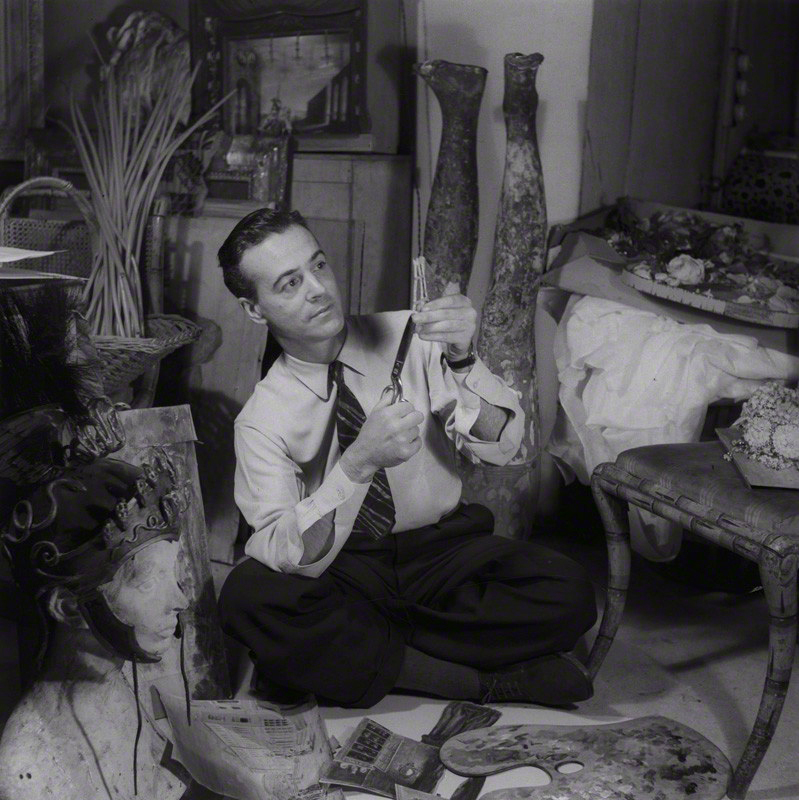

Francis Goodman (English, 1913-1989)
Oliver Messel
1945
Photograph, silver gelatin print on paper
National Portrait Gallery, London
Bequeathed by the estate of Francis Goodman, 1989
Francis Goodman’s carefully posed photograph depicts Oliver Messel, the foremost British stage designer from the 1920s to the 1950s, surrounded by eclectic props. The producer Charles Cochran recalled how Messel ‘would pull something new out of his pocket – usually something used for domestic work – which he proposed to employ to give the illusion of some other fabric’. Messel was attracted to men and his fascination with dandyish excess, pastiche and artifice has been interpreted as a queer aesthetic.
Wall text from the exhibition

Paul Tanqueray (English, 1905-1991)
Douglas Byng
1934
Photograph, bromide print on paper
National Portrait Gallery. Given by Paul Tanqueray, 1974
Gay performer Douglas Byng gained the title ‘The Highest Priest of Camp’ with songs such as ‘Doris the Goddess of Wind’, ‘I’m a Mummy (An Old Egyptian Queen)’ and ‘Cabaret Boys’, which he performed with Lance Lester. Coward described him as ‘The most refined vulgarity in London, mais quel artiste!’ Byng’s costume in Paul Tanqueray’s photograph was probably the one he wore for his song ‘Wintertime’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Room 4: Bloomsbury and Beyond
The Bloomsbury Group of artists and writers famously ‘lived in squares and loved in triangles’. Dora Carrington had relationships with men and women but loved and was loved by Lytton Strachey, who was attracted to men. Duncan Grant and Vanessa Bell lived together in Charleston Farmhouse in East Sussex. A chosen few of Duncan Grant’s male lovers made visits but Paul Roche was forced to camp on the South Downs as he did not meet with Bell’s approval. Bell’s husband Clive lived apart from her but they remained happily married. While sexual intimacy was valued by the Group, it was not the most important bond tying the members together. Their network was a profoundly queer experiment in modern living founded on radical honesty and mutual support.
Bloomsbury’s matter-of-fact acceptance of same-sex desire was unusual but not unique. The objects in this room show a variety of different perspectives, from the quiet homeliness of Ethel Sands’s Tea with Sickert, to Gluck’s defiant self-portrait. Together, they reveal a generation of artists and sitters exploring, confronting and coming to terms with themselves and their desires.
Installation view of Room 4 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain featuring Ethel Walker’s Decoration: The Excursion of Nausicaa 1920
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Ethel Walker (Scottish, 1861-1951)
Decoration: The Excursion of Nausicaa
1920
Oil paint on canvas
The composition of this painting reveals Ethel Walker’s fascination with Greco-Roman friezes, as well as the artistic possibilities of the female nude. The painting is inspired by Book IV of Homer’s Odyssey, in which the princess Nausicaa bathes with her maidens. In 1900, Walker became the first woman member of the New English Arts Club, whose select committee reacted to this painting with ‘spontaneous and enthusiastic applause’. There has been some speculation about the nature of Walker’s relationship with painter Clara Christian, with whom she lived and worked in the 1880s, although little evidence survives. This image offers a utopian vision of an all-female community.
Wall text from the exhibition
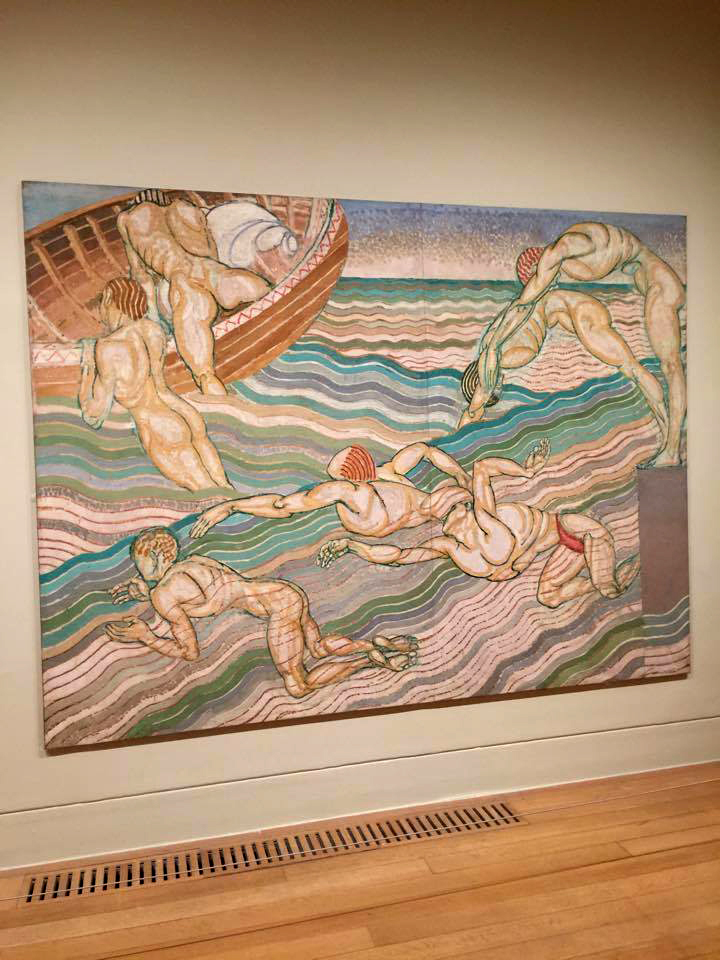

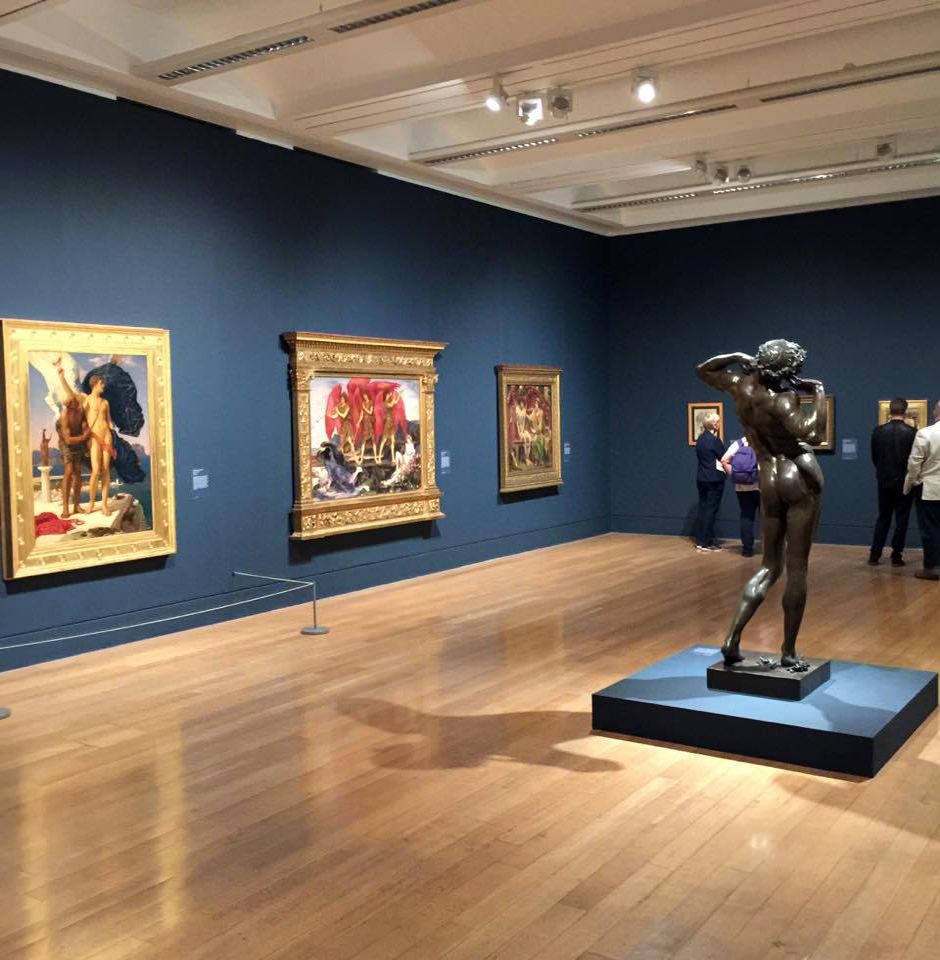
Installation views of Room 4 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain featuring Duncan Grant’s Bathing 1911 (at left in the bottom image)
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Duncan Grant (British, 1885-1978)
Bathing
1911
Oil paint on canvas
2286 x 3061mm
© Tate. Purchased 1931
Bathing was conceived as part of a decorative scheme for the dining room at Borough Polytechnic, and it was Duncan Grant’s first painting to receive widespread public attention. Grant’s design takes inspiration from summers spent around the Serpentine in Hyde Park, which was one of a number of sites associated with London’s queer culture. The painting celebrates the strength and beauty of the male form, and its homoerotic implications were not lost on Grant’s contemporaries: the National Review described the dining room as a ‘nightmare’ which would have a ‘degenerative’ effect on the polytechnic’s working-class students.
Wall text from the exhibition
Duncan Grant (British, 1885-1978)
Bathers by the Pond (installation view)
1920-1921
Oil paint on canvas
Pallant House Gallery, Chichester (Hussey Bequest, Chichester District Council 1985)
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
This painting shows a scene filled with homoerotic possibilities. The setting is possibly Charleston Farmhouse in East Sussex, where Duncan Grant lived with Vanessa Bell, her children and his lover David (Bunny) Garnett. Grant’s use of dots of colour shows the influences of the pointillist technique pioneered by Georges Seurat. The nude figure in the foreground basks in the sun while the seated figures behind him exchange appreciative glances. Swimming ponds often served as cruising grounds and it is perhaps unsurprising that this work was not exhibited in Grant’s lifetime.
Wall text from the exhibition

Duncan Grant (British, 1885-1978)
Paul Roche Reclining (installation view)
c. 1946
Oil paint on canvas
The Charleston Trust
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
This painting depicts Duncan Grant’s close friend and possible lover Paul Roche, lying as if asleep. He is depicted against a patterned background reminiscent of colours and fabrics produced by the Omega Workshop, the design collective founded in 1913 by Roger Fry. These soft textures contrast with Roche’s bare torso, which is further emphasised by his briefs, socks and open shirt. Grant and Roche met by chance in July 1946: after making eye contact crossing the road at Piccadilly Circus, the two struck up a conversation. Their friendship lasted until Grant’s death in 1978.
Wall text from the exhibition
Duncan Grant (British, 1885-1978)
Duncan Grant produced erotic works on paper prolifically throughout his life. These objects were created in private and for personal consumption only. Racially diverse figures are presented in various states of sexual play, and Grant’s range of representation moves from explicit passion to tender post-coital repose. Overlapping bodies are depicted in impossible contortions, and the works reveal Grant’s fascination with the artistic possibilities of the male form as well as the importance of harmonious composition. The objects also demonstrate a characteristically witty approach to sexuality, with some copulating figures playfully masquerading as ballet dancers and wrestlers. As his daughter Angelica Garnett recalled, one of Grant’s favourite maxims was to ‘never be ashamed’, and his private erotica offers an unapologetic celebration of gay male sex and love.
Installation views of erotic drawings by Duncan Grant
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan

Installation view of Ethel Sands’ Tea with Sickert c. 1911-1912 from Room 4 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan

Ethel Sands (English born America, 1873-1962)
Tea with Sickert
c. 1911-1912
Oil paint on canvas
Tate. Bequeathed by Colonel Christopher Sands 2000, accessioned 2001
The scene of this painting is the sitting room Nan Hudson and Sands’s home. Although it features two figures – the artist Walter Sickert and Hudson – the table is set for afternoon tea for three. The composition of the painting is arranged as if the artist was standing behind Nan, and this perspective highlights their position as a couple. In 1912, the work was exhibited as part of Sands and Hudson’s joint exhibition at the Carfax Gallery and it drew mixed reactions: Westminster Gazette called it ‘a daring picture’ but ‘a somewhat overwhelming indulgence in pure orange vermilion’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Clare Atwood (British, 1866-1962)
John Gielgud’s Room
1933
Oil paint on canvas
Tate. Presented by Mrs E.L. Shute 1937
This picture was painted in Sir John Gielgud’s flat at the time he was playing Richard II in Gordon Daviot’s Richard of Bordeaux at the New Theatre. Rather than emphasising his life in the public eye, this work draws attention to Gieglud’s domestic life. In this way, Clare ‘Tony’ Atwood gently subverts traditional associations of the feminine with private space. Atwood lived in a menage a trois with Gielgud’s second-cousin, Edith (Edy) Craig and the feminist playwright Christopher St John, who had previously lived together as an openly lesbian couple. St John later stated that ‘the bond between Edy and me was strengthened not weakened by Tony’s association with us’.
Wall text from the exhibition

Installation view of Gluck’s Self-Portrait 1942 from Room 4 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan

Gluck (Hannah Gluckstein) (British, 1895-1978)
Self-Portrait
1942
Oil paint on canvas
National Portrait Gallery, London
Given by the sitter and artist, ‘Gluck’ (Hannah Gluckstein), 1973
Gluck locks gazes with the viewer in this unflinching self-portrait. Born Hannah Gluckstein, Gluck requested that the name Gluck be reproduced with ‘no prefix, suffix or quotes’. Gluck exhibited to great acclaim at the ‘The Gluck Room’ of The Fine Art Society, where visitors included Queen Mary. This painting was painted in 1942, in a difficult period in Gluck’s relationship with Nesta Obermer, Gluck’s ‘darling wife’. Obermer was frequently away, sometimes with her husband Seymour Obermer. In 1944, their relationship broke down and Gluck went to live with Edith Shackleton Herald. Their relationship lasted until Gluck’s death.
Wall text from the exhibition

Gluck (Hannah Gluckstein) (British, 1895-1978)
Lilac and Guelder Rose
1932-1937
Oil paint on canvas
Manchester Art Gallery
This was one of a number of flower paintings that Gluck made during and immediately after her relationship with society florist and author Constance Spry, who she met in 1932. Spry was a leading figure in cultivating a fashion for white flowers, and often used Gluck’s paintings to illustrate her articles. Many of Spry’s customers also commissioned flower paintings from Gluck. When Lilac and Guelder Rose was exhibited at Gluck’s 1937 exhibition at the Fine Art Society, it was much admired by Lord Villiers, who remarked ‘It’s gorgeous, I feel I could bury my face in it’.
Wall text from the exhibition

Glyn Warren Philpot (British, 1884-1937)
Henry Thomas (installation view)
1934-1935
Oil paint on canvas
Pallant House Gallery, Chichester (Bequeathed by Mrs Rosemary Newgas, the neice of the artist 2004)
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Henry Thomas was Glyn Philpot’s servant and one of his favourite models. The high-cheekboned angularity of Thomas’s face is echoed in the diagonal lines of the abstracted background, perhaps an allusion to the batik fabric behind. The exact nature of Thomas and Philpot’s relationship is unknown. Many of Philpot’s depictions of Thomas carry a homoerotic charge and some are exoticising. What Thomas felt about his years with Philpot from 1929 to the artist’s death in 1937 is unknown. The words he wrote on Philpot’s funeral wreath, ‘For memory to my dear master as well as my father and brother to me’, hints at the imbalance between them, while also suggesting many complex layers of relationship.
Wall text from the exhibition

Edward Wolfe (British, 1897-1982)
Portrait of Pat Nelson (installation view)
1930s
Oil paint on canvas
James O’Connor
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Patrick Nelson emigrated from Jamaica to North Wales in 1937, before settling in London to study law the following year. While living in Bloomsbury, Nelson worked as an artists’ model and soon became acquainted with Edward Wolfe. Nelson would also meet other prominent gay artists at this time, including his sometime boyfriend and lifelong friend Duncan Grant. Wolfe’s depiction of Nelson against the rich green background is exoticising and his pose invites the viewer to admire his body. Such objectification was typical of many depictions of black men from this time and reflects an uneven power dynamic, although Nelson’s friendship with members of the Bloomsbury group adds a level of complexity to the relationship between artist and sitter.
Wall text from the exhibition
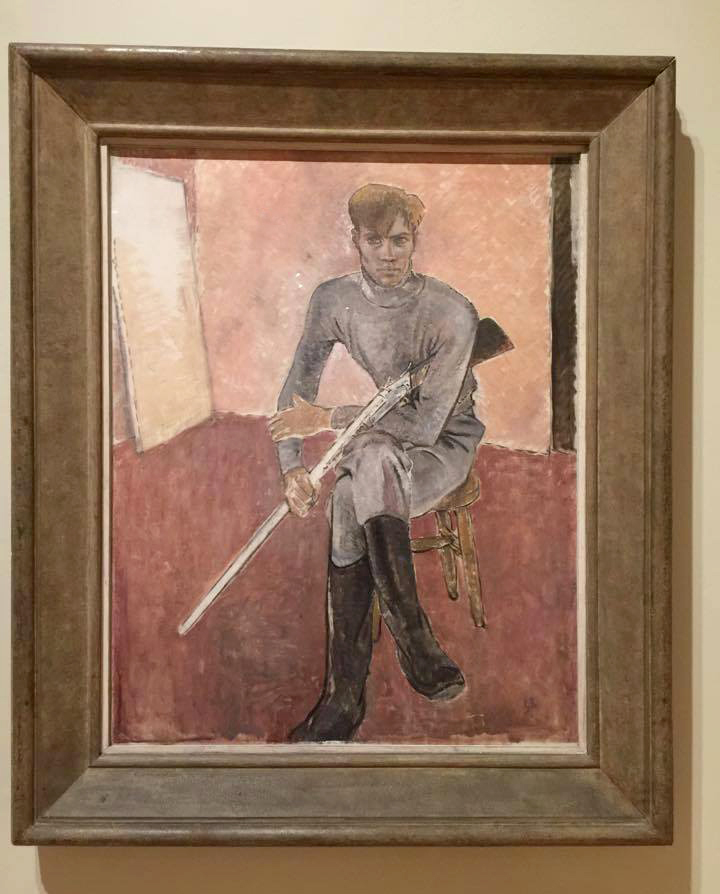

Glyn Warren Philpot (British, 1884-1937)
Man with a Gun (installation view)
1933
Oil paint on canvas
The Ashmolean Museum, Oxford. Bequeathed by Jeffrey Daniels, 1986
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Glyn Philpot developed a strong reputation as a society portraitist until the 1930s, at which point he began to explore modernist forms, as well as express his sexuality more openly. This work depicts Philpot’s friend Jan Erland, who was the subject of a series of paintings by Philpot on the theme of sports and leisure. Erland is depicted cradling a gun which, he recalled, had been specifically borrowed for the occasion. Erland’s firm grip on the gun’s phallic barrel seems suggestive. Writing to his sister Daisy, Philpot described ‘every moment with this dear Jan’ as filled with ‘inspiration and beauty’.
Wall text from the exhibition
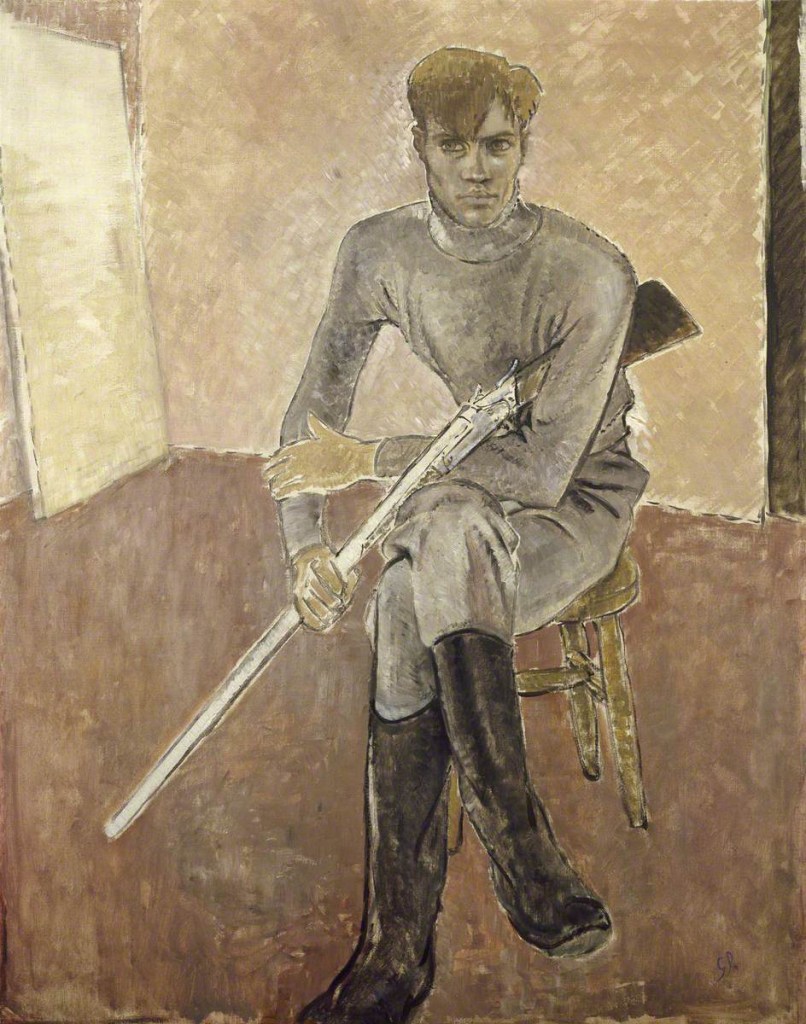

Glyn Warren Philpot (British, 1884-1937)
Man with a Gun
1933
Oil paint on canvas
The Ashmolean Museum, Oxford. Bequeathed by Jeffrey Daniels, 1986
Tate Britain today opens the first exhibition dedicated to queer British art. Unveiling material that relates to lesbian, gay, bisexual, trans and queer (LGBTQ+) identities, the show marks the 50th anniversary of the partial decriminalisation of male homosexuality in England and Wales. It presents work from the abolition of the death penalty for sodomy in 1861 to the passing of the Sexual Offences Act in 1967 – a time of seismic shifts in gender and sexuality that found expression in the arts as artists and viewers explored their desires, experiences and sense of self.
Spanning the playful to the political, the explicit to the domestic, Queer British Art 1861-1967 showcases the rich diversity of queer visual art and its role in society. Themes explored in the exhibition include coded desires amongst the Pre-Raphaelites, representations of and by women who defied convention (including Virginia Woolf), and love and lust in sixties Soho. It features works by major artists such as Francis Bacon, Keith Vaughan, Evelyn de Morgan, Gluck, Glyn Philpot, Claude Cahun and Cecil Beaton alongside queer ephemera, personal photographs, film and magazines.
Work from 1861 to 1967 by artists with diverse sexualities and gender identities is showcased, ranging from covert images of same-sex desire such as Simeon Solomon’s Sappho and Erinna in a Garden at Mytilene 1864 through to the open appreciation of queer culture in David Hockney’s Going to be a Queen for Tonight 1960. A highlight of the exhibition is a section focusing on the Bloomsbury set and their contemporaries – an artistic group famous for their bohemian attitude towards sexuality. The room includes intimate paintings of lovers, scenes of the homes artists shared with their partners and large commissions by artists such as Duncan Grant and Ethel Walker.
Many of the works on display were produced in a time when the terms ‘lesbian’, ‘gay’, ‘bisexual’ and ‘trans’ had little public recognition. The exhibition illustrates the ways in which sexuality became publicly defined through the work of sexologists such as Henry Havelock Ellis and campaigners such as Edward Carpenter. It also looks at the high profile trials of Oscar Wilde and Radclyffe Hall. Objects on display include the door from Wilde’s prison cell, Charles Buchel’s portrait of Radclyffe Hall and erotic drawings by Aubrey Beardsley.
In contrast to the bleak outlook from the courtroom prior to 1967, queer culture was embraced by the British public in the form of theatre. From music hall acts to costume design, the theatre provided a forum in which sexuality and gender expression could be openly explored. Striking examples on display include photographs of performers such as Beatrix Lehmann, Berto Pasuka and Robert Helpmann by Angus McBean, who was jailed for his sexuality in 1942, alongside stage designs by Oliver Messel and Edward Burra. Theatrical cards of music hall performers such as Vesta Tilley (whose act as ‘Burlington Bertie’ had a large lesbian following) are featured, as well as a pink wig worn in Jimmy Slater’s act ‘A Perfect Lady’ from the 1920s.
Queer British Art 1861-1967 shows how artists and audiences challenged the established views of sexuality and gender identity between two legal landmarks. Some of the works in the show were intensely personal while others spoke to a wider public, helping to forge a sense of community. Alongside the exhibition is a room showing six films co-commissioned by Tate and Channel 4 Random Acts. Created in response to Queer British Art 1861-1967 and featuring figures in the LGBTQ+ community, including Sir Ian McKellen and Shon Faye, they present personal stories prompted by the themes in the show, and invite visitors to relate their own experiences.
Queer British Art 1861-1967 is curated by Clare Barlow, Assistant Curator, Tate Britain with Amy Concannon, Assistant Curator, Tate Britain. The exhibition is accompanied by a fully illustrated catalogue from Tate Publishing and a programme of talks and events in the gallery.
Press release from Tate Britain
Why is the word ‘queer’ used in the exhibition title?
Queer has a mixed history – from the 19th century onwards it has been used both as a term of abuse and as a term by LGBT people to refer to themselves. Our inspiration for using it came from Derek Jarman who said that it used to frighten him but now ‘for me to use the word queer is a liberation’. More recently, of course, it has become reclaimed as a fluid term for people of different sexualities and gender identities. Historians of sexuality have also argued that it is preferable to other terms for sexualities in the past as these often don’t map onto modern sexual identities. In addition to carrying out audience research, we took advice from Stonewall and other LGBT charities and held focus groups with LGBT people. The advice from all of these sources was overwhelmingly that we should use it. While we tried other titles, no other option captured the full diversity of sexualities and gender identities that are represented in the show.
Text provided by Clare Barlow, curator of Queer British Art.
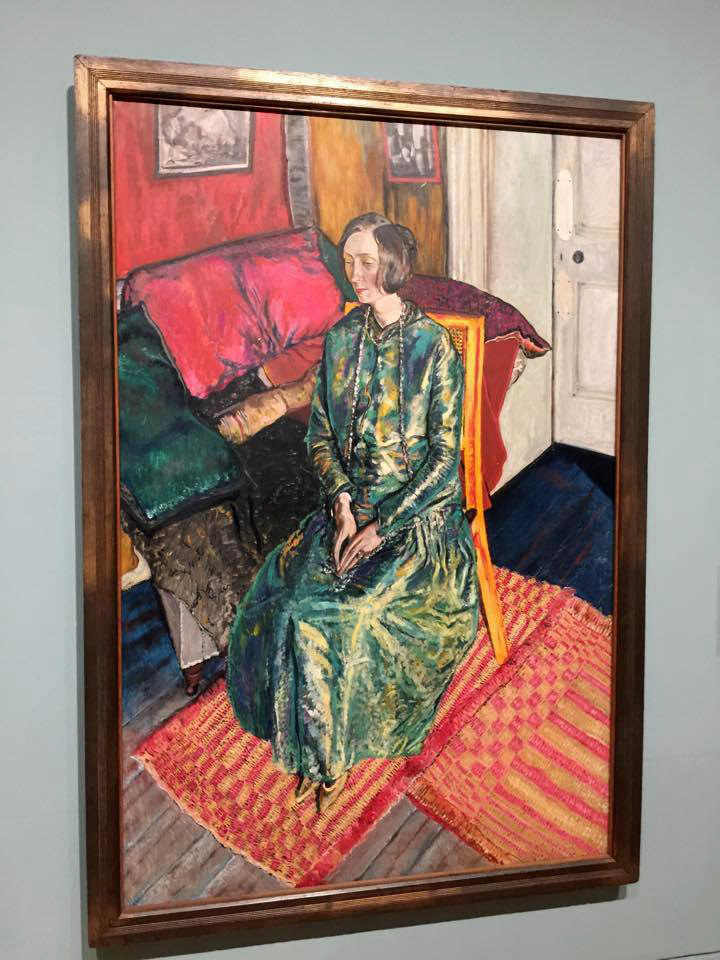

Installation view of Alvaro Guevara’s Dame Edith Sitwell 1916 from Room 5 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
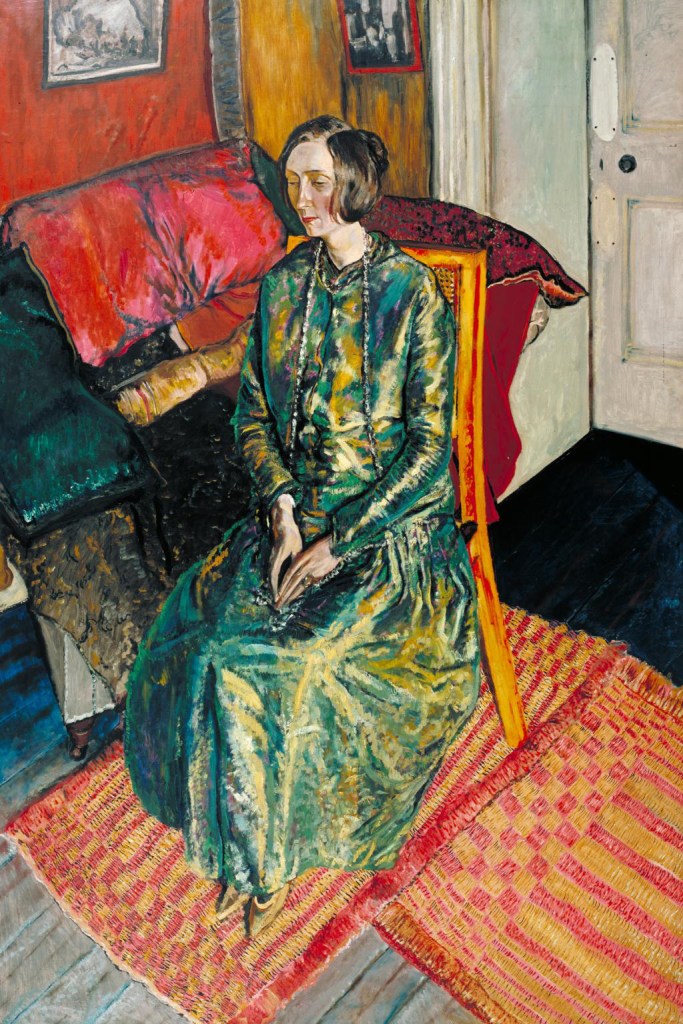

Alvaro Guevara (Chilean, 1894-1951)
Dame Edith Sitwell
1916
Oil paint on canvas
Tate. Presented by Lord Duveen, Walter Taylor and George Eumorfopoulos through the Art Fund 1920
The poet Edith Sitwell does not seem to have had sexual relationships but was viciously satirised by the artist and writer Wyndham Lewis as a lesbian. Sitwell described the life of the artist as ‘very Pauline’, referring to the letters of St Paul, which may suggest she thought sex would be a distraction. She was close friends with Alvaro Guevara, the artist of this portrait, who had relationships with men and women. Diana Holman Hunt in her 1974 biography of Guevara suggested that Sitwell and Guevara shared a love that was ‘not physical but certainly romantic and spiritual.’ The bright colours reflect the designs of Roger Fry and Vanessa Bell’s Omega Workshops and Sitwell is sitting on a dining chair designed by Fry.
Wall text from the exhibition
Room 5: Defying Conventions
This room shows how artists and writers in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century challenged gender norms. Some, such as Laura Knight, laid claim to traditionally masculine sources of artistic authority by depicting themselves in the act of painting nude female models. Others, such as Vita Sackville-West, had open marriages and same-sex relationships, or, like Claude Cahun, questioned the very concept of gender binaries. This was a period of radical social change. Women took on new roles during the First and Second World Wars, and gained the vote in 1918. Sackville-West worked with the Land Girls. Cahun resisted the Nazis on Jersey and was sentenced to death, imprisoned for a year and only freed by the end of the war. New fashions developed. For women, wearing trousers in public became stylishly avant-garde. Expectations were changing. Public discussion about female same-sex desire offered ways of viewing the self, but it also brought problems. Lives that had previously passed without comment might now be labelled transgressive. But for some, this was a time of liberating possibilities.
Installation view of Room 5 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain featuring with at left, Laura Knight’s Self-portrait 1913; second right, William Strang’s Lady with a Red Hat 1918, and at right Alvaro Guevara’s Dame Edith Sitwell 1916
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
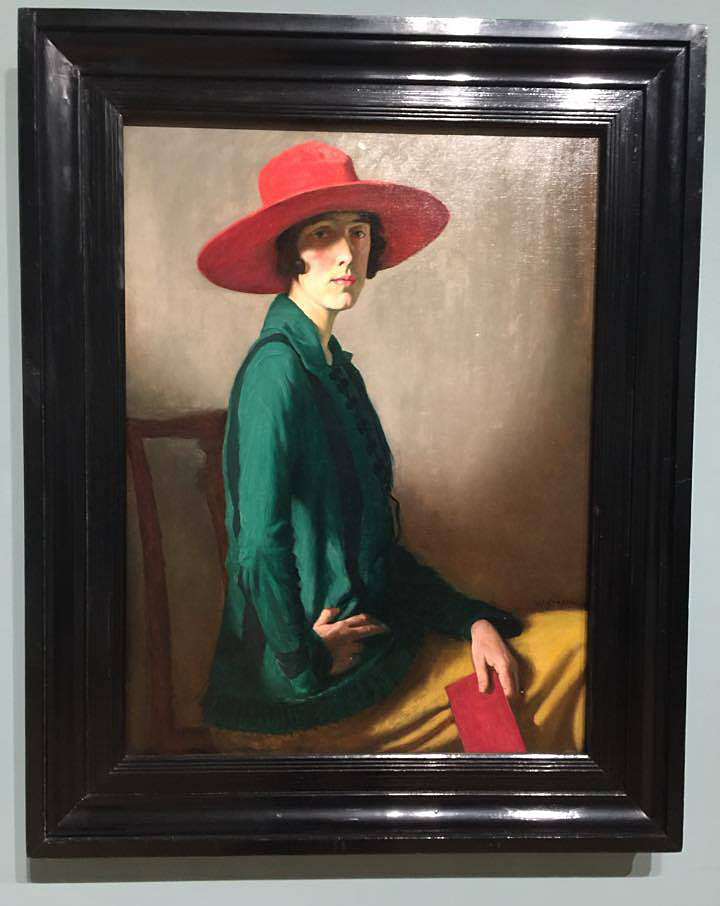

Installation view of William Strang’s Lady with a Red Hat 1918 from Room 5 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan

William Strang (Scottish, 1859-1921)
Lady with a Red Hat
1918
Oil paint on canvas
Lent by Glasgow Life (Glasgow Museums) on behalf of Glasgow City Council
Purchased 1919
This portrait is of writer Vita Sackville-West. According to her son, Nigel Nicolson, she attended sittings with her lover Violet Trefusis. Sackville-West adopted a male persona, ‘Julian’, at some points in this relationship, allowing her and Trefusis to pose as a married couple so they could stay together at a boarding-house. Her fashionable dress in this image, however, gives no sign of such androgynous role-playing. The book in Sackville-West’s hand may refer to her book Poems of East and West 1917. At the time this was painted she was writing Challenge, a novel about her relationship with Trefusis, but this was not published until 1974.
Wall text from the exhibition

Laura Knight (English, 1877-1970)
Self-portrait
1913
Oil paint on canvas
National Portrait Gallery, London
When this painting was exhibited at the Grosvenor Gallery in 1913, the reviewer Claude Phillips wrote ‘it repels, not by any special inconvenience – for it is harmless enough and with an element of sensuous attraction – but by dullness and something dangerously close to vulgarity’. His strong reaction hints at anxieties over women painting the female nude, which subverted the hierarchy of male artist and female model. When Laura Knight was at art school women were not been allowed to attend life classes. Her sensuous depiction of herself painting Ella Naper, a friend, lays claim to a professional artistic identity. In 1936, Knight was the first woman to become an Academician since its foundation.
Wall text from the exhibition
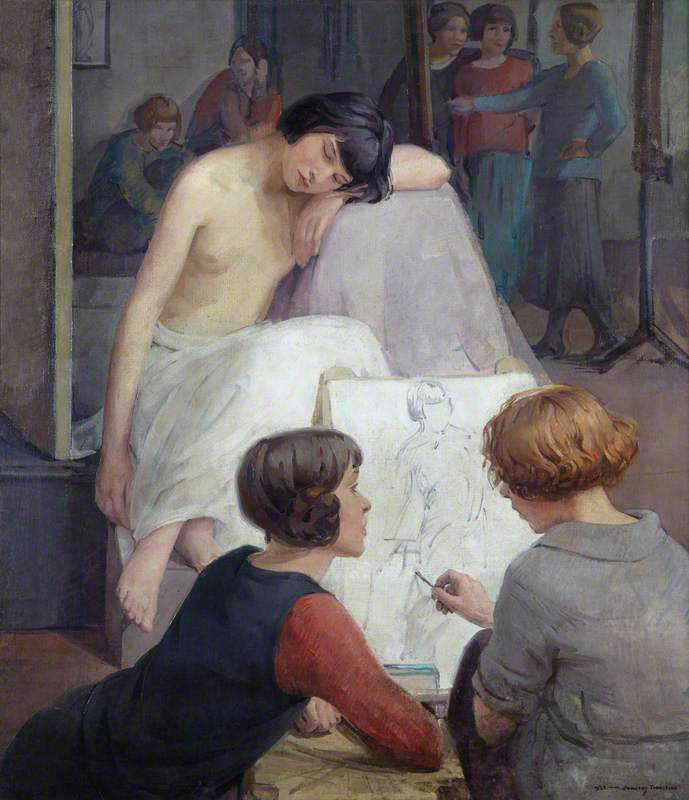

Dorothy Johnstone (Scottish, 1892-1980)
Rest Time in the Life Class
1923
Oil paint on canvas
City Art Centre, City of Edinburgh Museums and Galleries
This image depicts the life-class Johnstone taught for women at Edinburgh College of Art, which Johnstone presents as a space of friendship and collaboration. In the foreground, one woman comments on another’s drawing while in the background, Johnstone depicts herself gesturing towards the canvas. Johnstone had an intense relationship with Cecile Walton and Walton’s husband Eric Robertson, who were also part of the Edinburgh Group of artists. She later married fellow artist David Macbeth Sutherland.
Wall text from the exhibition


Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Untitled
1936
2 photographs, gelatin silver print on paper
These images (to the left and right of I Extend My Arms), from a larger group of photographs, hint at different narrative possibilities for the sexless manikin. In one, the doll seems to take on a feminine air, posed as if delighting in the long hair that trails round its body. The other is less overtly gendered, wearing a hat made from an upright feather and holding aloft a tiny plant. The porcelain dolls’ heads outside the jar in one image are reminiscent of the masks that repeated occur in Cahun’s work and these images seem to hint at the themes of role-playing that Cahun explored in earlier self-portraits.
Wall text from the exhibition
Room 6: Arcadia and Soho
London was a magnet for queer artists. In the 1950s and 1960s, Soho was the epicentre of queer culture, described by Francis Bacon as ‘the sexual gymnasium of the city’. Many of the artists shown in this room were friends, often living in London, sometimes sharing studios. Several were encouraged by the patron and collector Peter Watson, founder of the influential literary magazine Horizon and co-founder of the Institute of Contemporary Arts. Their work was often inspired by travel: to the Mediterranean, to costal Brittany, or to the seedy American bars that inspired works such as Edward Burra’s Izzy Orts.
John Craxton, John Minton and Keith Vaughan have been described as ‘neo-romantics’. Craxton, however, preferred the term ‘Arcadian’, referencing a classical utopian vision of a harmonious wilderness, populated by innocent shepherds. Yet, while it is idealised, depictions of Arcadia still sometimes include references to death and its peace can be disrupted by undercurrents of desire.
Installation view of Christopher Wood’s Nude Boy in a Bedroom 1930 from Room 6 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Christopher Wood (English, 1901-1930)
Nude Boy in a Bedroom
1930
Oil paint on hardboard laid on plywood
Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, Edinburgh
Christopher Wood’s Nude Boy in a Bedroom depicts the artist’s friend and sometime lover Francis Rose, in a hotel room in Brittany where they stayed with a group of friends in 1930. The group was later joined by Wood’s mistress, Frosca Munster. According to Rose, the work ‘is a nude painting of me washing at a basin’ in which Wood ‘scattered playing cards on the bed’. The cards are tarot cards and the top card shows the Page of Cups reversed, symbolising anxiety about a deception that will be soon discovered, or referring to someone incapable of making commitments. Wood may have included these cards as an oblique reference to his ongoing relationships with his male lover and female mistress.
Wall text from the exhibition
Edward Burra (English, 1905-1976)
Soldiers at Rye
1941
Tate
© Tate. Presented by Studio 1942
Edward Burra based Soldiers at Rye on sketches of troops around his home town of Rye between September and October 1940. His macabre sensibility was informed by his experiences in the Spanish Civil War. In the final stages of painting, he added red and yellow Venetian carnival masks, giving the figures the air of predatory birds – a regular symbol in Burra’s work from the 1930s. Seen from behind, the soldiers’ close-fitting uniforms and bulbous physiques led one critic to comment that they had the ‘bulging husky leathery shape’ of ‘military ruffians’. There is an ominous atmosphere to the painting, conveying a dangerous homoeroticism.
Wall text from the exhibition

John Craxton (English, 1922-2009)
Head of a Cretan Sailor
1946
Oil paint on board
On loan from the London Borough of Camden Art Collection
© Estate of John Craxton. All rights reserved, DACS 2016
Photo credit: London Borough of Camden
The sitter in this portrait was on national service in the Greek Navy when he first met John Craxton in a taverna in Poros. He caught Craxton’s eye with his performance of the Greek dance the zeibékiko, with ‘splendidly controlled steps, clicking his thumbs and forefingers and circling round and round in his white uniform like a seagull’. Craxton followed him to Crete in 1947, where the sailor was now working as a butcher in Herákleion. The island was a revelation and Craxton returned often, eventually partly settling there in 1960.
Wall text from the exhibition
Installation views of Room 6 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain with Robert Medley’s Summer Eclogue No. 1: Cyclists 1950 at left in the bottom image, Keith Vaughan’s Kouros 1960 second left, Keith Vaughan’s Three Figures 1960-1961 second right, and his Bather: August 4th 1961 1961 at right
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Robert Medley (English, 1905-1994)
Summer Eclogue No. 1: Cyclists
1950
Oil paint on canvas
Tate. Purchased 1992
Exhibited at the Hanover Gallery in February 1950, Robert Medley’s painting of racing cyclists on a summer’s evening in a Gravesend public park underscores his attraction to cross-class sociability. The river esplanade offers a permissible space for observing the muscular bodies and taut limbs of the youths and their admirers. The title refers to Virgil’s Eclogues, in which pastoral tranquillity is disrupted by erotic forces and revolutionary change. Medley wrote in his autobiography that the eclogue theme provided for ‘a more contemporary subject matter’. One of the cyclists was modelled on fellow artist Keith Vaughan’s lover, Ramsay McClure.
Wall text from the exhibition
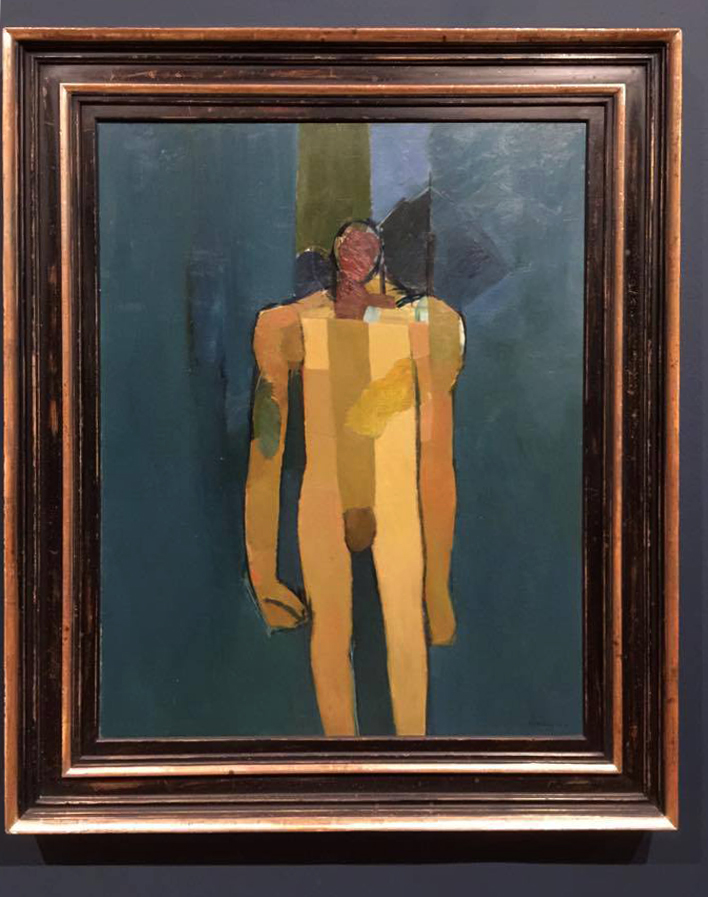

Installation view of Keith Vaughan’s Kouros 1960 from Room 6 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
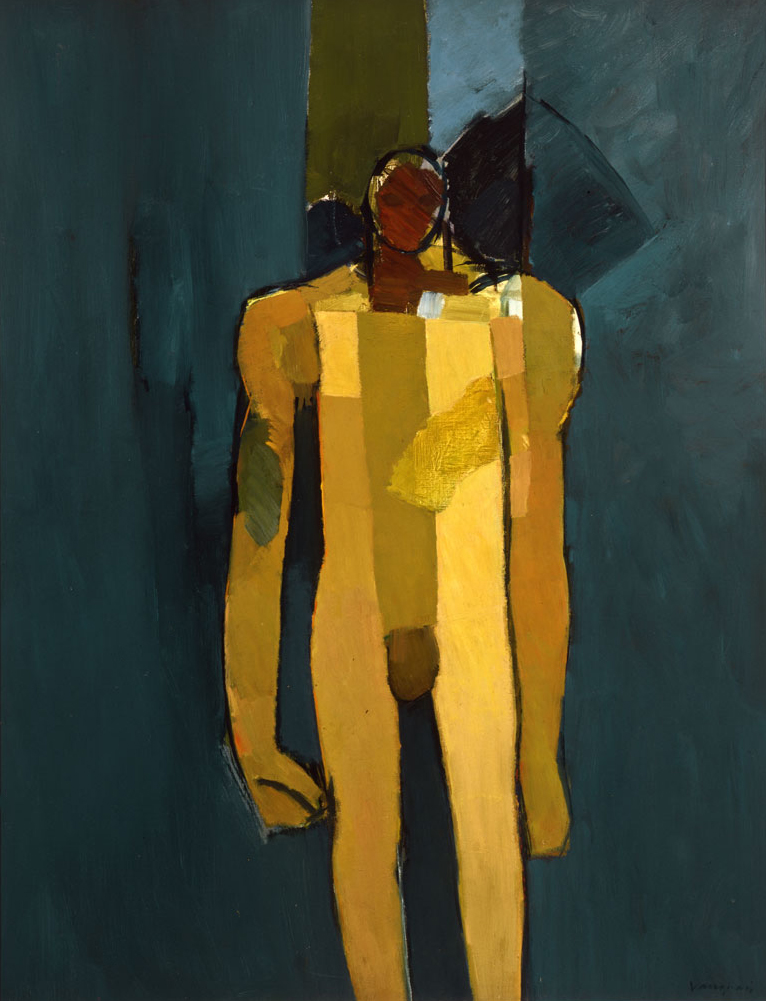

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Kouros
1960
Oil paint on canvas
Private collection
In a diary entry for 1956, Keith Vaughan wrote of ‘A silver bromide image of Johnny standing naked in my studio, aloof, slightly tense, withdrawn like a Greek Kouros, gazing apprehensively at himself in the mirror, lithe, beautiful… it lies tormenting me on my table’. This was a photograph of Vaughan’s lover Johnny Walsh who is also represented in this painting. A ‘Kouros’ was a free-standing ancient Greek sculpture of a male youth and the image may also have been inspired by a visit Vaughan made to Greece in 1960.
Wall text from the exhibition
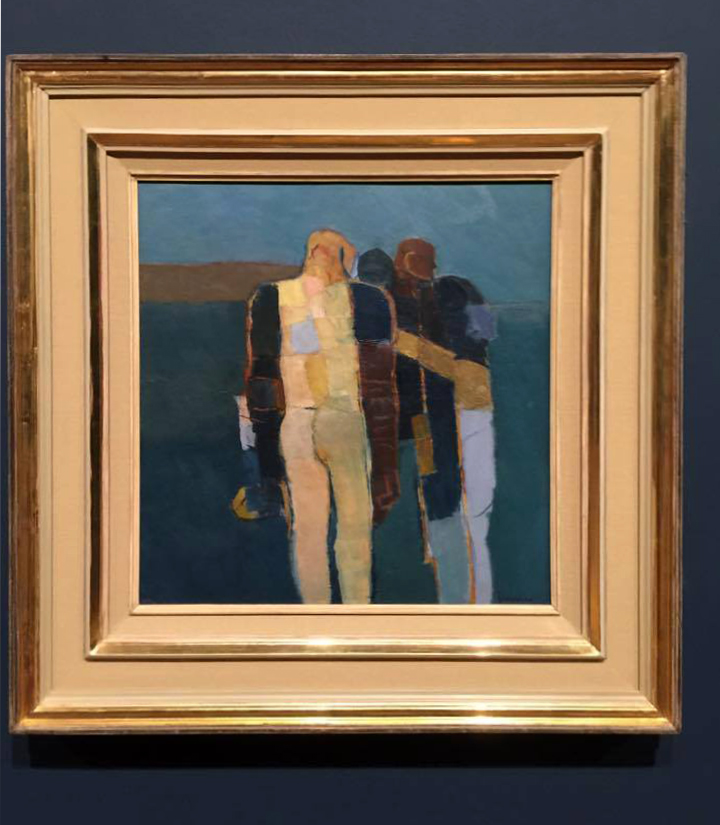

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Three Figures (installation view)
1960-1961
Oil paint on board
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Three Figures is typical of Keith Vaughan’s approach to group figure painting. The subjects are depicted in indeterminate locations and the lack of details a makes it to impossible to identify them or guess at their social class or profession. The close proximity of the figures in this image and the contrast between the nudity of the man with his back towards us and the other two men might suggest that this is an erotic encounter. Yet the composition remains intentionally enigmatic.
Wall text from the exhibition
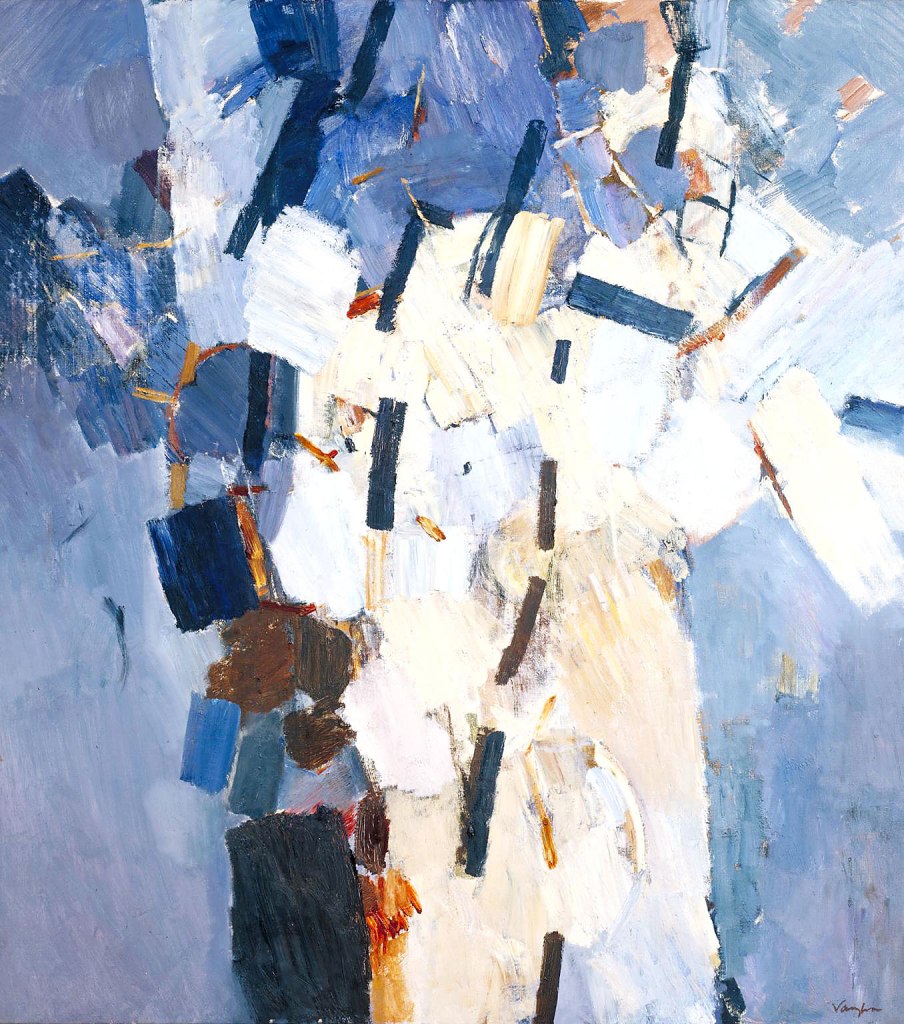

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Bather: August 4th 1961
1961
Oil paint on canvas
Tate. Purchased 1962
Keith Vaughan wrote in his journal, ‘The continual use of the male figure…retains always the stain of a homosexual conception… “K.V. paints nude young men”. Perfectly true, but I feel I must hide my head in shame. Inescapable, I suppose – social guilt of the invert’. He wrestled with the competing impulses of figuration and abstraction in his work, describing how: ‘I wanted to go beyond the specific, identifiable image – yet I did not want to do an “abstract” painting. Bather: August 4th 1961 was the first break through. Every attempt up to then had finally resolved itself into another figure painting or an “abstract”.’
Wall text from the exhibition
Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
In contrast over his concerns whether his desires would be shown in his paintings, Keith Vaughan’s private drawings are explicitly erotic. Across them he depicts a range of different encounters, from sadomasochistic fantasies through to moments of tender intimacy. This is perhaps a hint of these fluctuating desires in his descriptions of relationship with his lover Jonny Walsh, of which Vaughan said, ‘I can move from tenderness to sadism in the same harmonic key’.
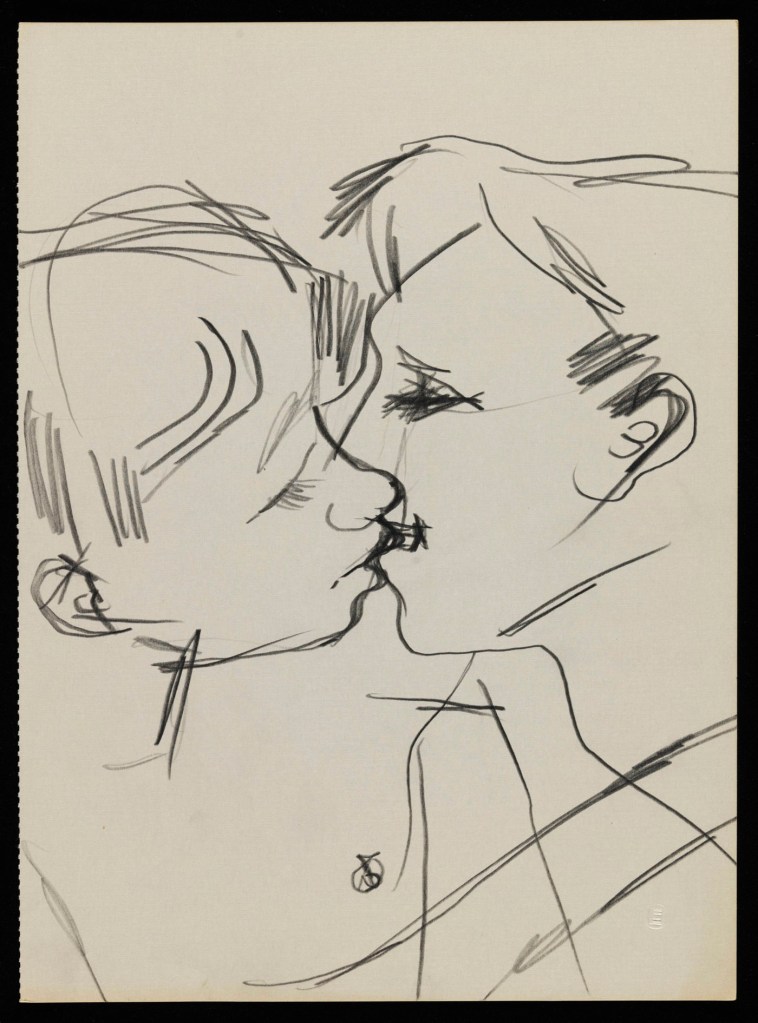

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Drawing of two men kissing
1958-1973
Tate Archive © DACS, The Estate of Keith Vaughan
Room 7: Public / Private Lives
This room explores the contradictions of queer life in the 1950s and 1960s. Before the partial decriminalisation of sex between men in 1967, the boundaries between public and private were acutely important to couples in same-sex relationships. Joe Orton and Kenneth Halliwell had separate beds in their tiny flat to maintain the pretence that they weren’t a couple. Such caution was justified. Peter Wildeblood, Lord Montagu of Beaulieu and Michael Pitt-Rivers were sent to jail in a case that became a rallying point for calls to change the law, which was increasingly attacked as a ‘blackmailer’s charter’. Lesbianism was not illegal, but women faced prejudice. Avant-garde photographer Barbara Ker-Seymer was thrown out of her room after she left a copy of Radclyffe Hall’s banned book The Well of Loneliness out in plain sight.
Yet despite the threat of exposure, couples lived happily together, community flourished, and a few even became queer celebrities.

Stephen Tennant (British, 1906-1986)
Lascar, a story of the Maritime Boulevard
Nd
Ink, watercolour and collage on paper
The Viktor Wynd Museum of Curiosities, Fine Art & Natural History, London
In this illustration for Stephen Tennant’s novel Lascar a riotous collage of burly sailors, bright flowers, letters and visiting cards seem to burst forth from the page. Some of Tennant’s initial sketches of sailors were made on visits to the Old Port of Marseilles in the 1930s, but he constantly reworked the illustrations and text, never completing it. In the last two decades of his life, visitors to Wilsford Manor in Wiltshire where Tennant lived in virtual seclusion, found pages of the novel strewn across the decaying interiors.
Wall text from the exhibition
Because We’re Queers
Between 1959 and 1962, couple Joe Orton and Kenneth Halliwell borrowed and stole books from libraries around Islington. They cut out some of the illustrations, which they used to paper the walls of their flat and to create new collaged covers for the books. They then returned the volumes to the shelves of the libraries and waited to watch reactions.
The covers they created are full of jokes and references to queer culture. The addition of wrestling men turns Queen’s Favourite into an innuendo. Acting family the Lunts become kitsch glass figurines, while The Secret of Chimneys is depicted as a pair of giant cats. Others were more explicit: The World of Paul Slickey gains not only a phallic budgerigar but also a cut out shape of an erect penis. The plays of Emlyn Williams are retitled Knickers must fall and Fucked by Monty.
Orton and Halliwell were eventually caught and jailed for six months for ‘malicious damage’, which Orton claimed was ‘because we’re queers’. Prison destroyed Halliwell. While Orton became a successful playwright, Halliwell became an alcoholic. In 1967, he killed Orton and took his own life. Yet while their lives ended in tragedy, the book covers give insight into a playful and subversive relationship.

Joe Orton (British, 1933-1967) and Kenneth Halliwell (British, 1951-1967)
The Secret Chimneys by Agatha Christie
Islington Local History Centre

Joe Orton (British, 1933-1967) and Kenneth Halliwell (British, 1951-1967)
Queen’s Favourite
Islington Local History Centre
Interior of the flat at 25 Noel Rd showing the extent of the collages
Image courtesy of Islington Council

Kenneth Halliwell (British, 1951-1967)
Untitled (installation view)
1967
Printed papers on hardboard
Tate. Purchased 2016
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
This is one of 19 collages that Halliwell exhibited at the Anno Domino gallery in 1967. Unlike the earlier book-covers, these were made by Halliwell alone, yet they are similarly kaleidoscopic in their use of images. An archeological artefact here sits alongside fashion photography, sea-shells, insects and words from newspapers and magazines. Some of these juxtapositions are playful: ‘Eye’ appears where an eye would be. Others are more obscure and the phrases ‘Blackmail’ and ‘dirty word’ perhaps hint at oppression. The exhibition was a failure and Halliwell’s professional frustration contributed to the breakdown of his relationship with Orton, who was now established as a playwright.
Wall text from the exhibition
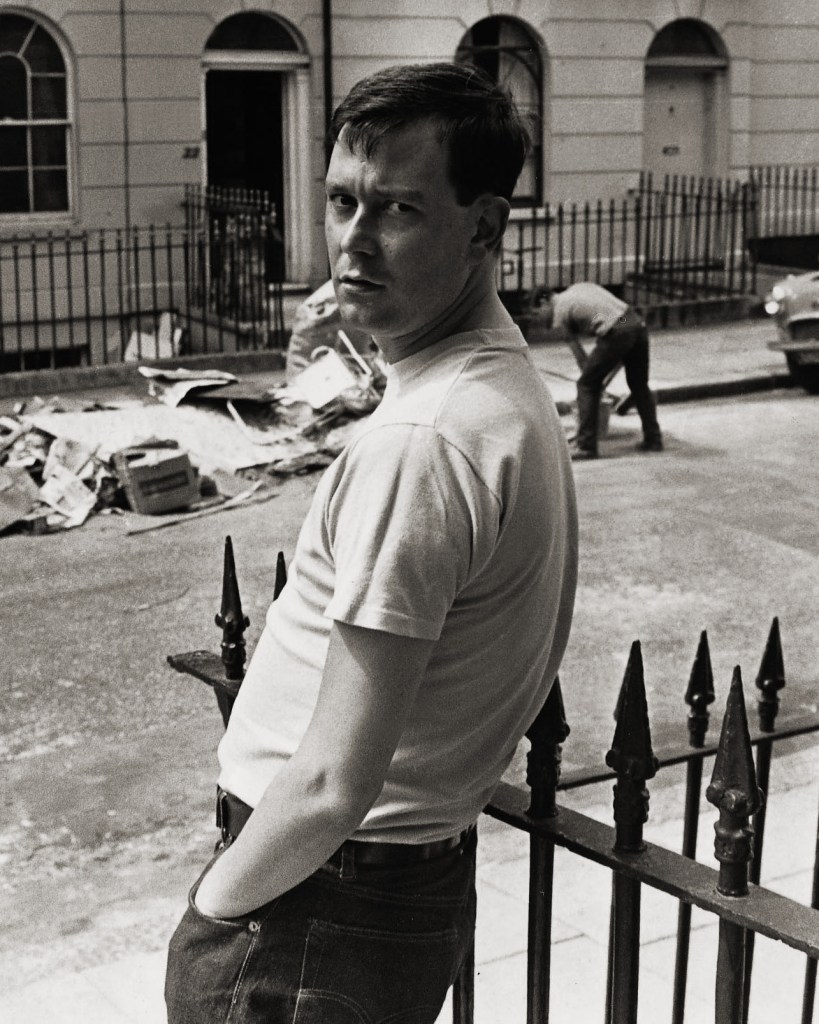

George Elam
Joe Orton in Islington, London
1967
George Elam/Daily Mail/REX
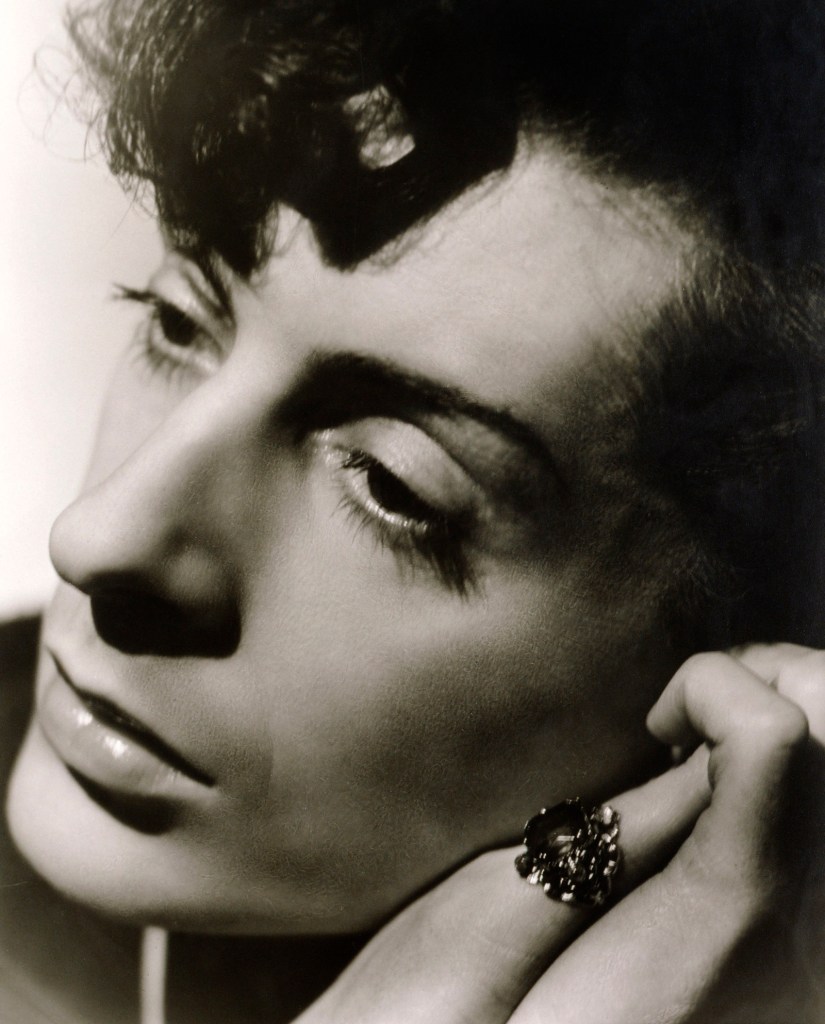

Angus McBean (Welsh, 1904-1990)
Quentin Crisp
1941
Photograph, bromide print on paper
National Portrait Gallery, London
Angus McBean met the writer and raconteur Quentin Crisp while walking in the blackout in 1941 and the two became lovers. McBean later said of Crisp, ‘He was really one of the most beautiful people I have ever photographed. It was a completely androgynous beauty and under different circumstances it would have been difficult to know what sex he was’. This ambiguity is captured in McBean’s photograph, which is posed to emphasise Crisp’s long lashes, glossy lips and elaborate ring, the position of which is suggestive of an earring. Crisp’s refusal to conform to traditional masculine appearance was courageous and unswerving.
Wall text from the exhibition

John Deakin (English, 1912-1972)
Colin (installation view)
c. 1950s
Photograph, gelatin silver print on paper
John Deakin Archive / James Moores Collection
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
We don’t know anything about the sitter in this portrait. Deakin’s friend Bruce Bernard, who catalogued John Deakin’s negatives, likely gave it the label ‘Colin’, perhaps from memory, perhaps from an original sleeve note by Deakin. It is therefore not clear whether it depicts a drag performance or whether the glamorous outfit reflects the sitter’s true identity. It is, however, shot in a domestic setting rather than on the stage, leaving open the possibility that it depicts the sitter’s lived experience.
Wall text from the exhibition
John Deakin (English, 1912-1972)
John Deakin seems almost to embody queer Soho of the 1950s. A close friend and drinking companion of Francis Bacon, his portrait photographs include many artists, actors, poets and celebrities. His style was often startlingly unflattering, capturing his sitters as they truly were. He said of his work, ‘Being fatally drawn to the human race, what I want to do when I take a photograph is make a revelation about it. So my sitters turn into my victims’. Deakin admitted to a drink problem which led to a chequered career and was twice sacked from Vogue. After his death, many of his photographic negatives were found in a box under his bed and were saved by his friend, writer and picture editor Bruce Bernard.
John Deakin (Englsih, 1912-1972)
The Two Roberts Asleep – Colquhoun and MacBryde
c. 1953
Photograph, gelatin silver print on paper
John Deakin Archive / James Moores Collection
Robert Colquhoun and Robert MacBryde are here shown asleep on each other shoulders in a moment of tender intimacy. They had met on their first day at Glasgow School of Art and became lovers and lifelong partners. This photograph was probably taken at Tilty Mill, the home of the writer Elizabeth Smart, who invited Colquhoun and MacBryde to live with her and her partner the poet George Barker, when they’d been evicted from their studio in London. They spent the next four years there, combining painting with helping to raise Smart and Barker’s four children. The edges of the image show evidence of fire damage from some forgotten occasion.
Wall text from the exhibition
Barbara Ker-Seymer (British, 1905-1993)
Barbara Ker-Seymer was a photographer active in the interwar years. After studying at the Chelsea School of Art, she worked for the society portrait photographer Olivia Wyndham. When Wyndham moved to New York to be with her lover, the African-American actress Edna Lloyd-Thomas, Ker-Seymer was left in charge of her studio. She established her own studio on New Bond Street in 1931, and began a successful career as a fashion photographer for Harper’s Bazaar. She pursued relationships with both men and women, and was associated with the queer subculture known as the Bright Young Things. After the Second World War, she ceased to work as a photographer, opening a laundrette in 1951. Her papers, in Tate Archive, are full of playful images of her friends.
Barbara Ker-Seymer (British, 1905-1993)
Photograph album (installation view)
Nd
Tate Archive
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
This creatively arranged spread in one of Ker-Seymer’s photograph albums shows images of a number of her friends, including Marty Mann, an American who was for a time Ker-Seymer’s business partner and lover. Mann’s drinking was increasingly a problem and their relationship floundered. She later became an important advocate for the newly formed ‘Alcoholics Anonymous’.
Wall text from the exhibition
Room 8: Francis Bacon and David Hockney
The most fearless depictions of male same-sex desire in the years before 1967 are in the work of Francis Bacon and David Hockney. Bacon told how as a teenager his parents threw him out of their home for trying on his mother’s underwear. He gravitated to London, where he began his visceral exploration of the human figure. Hockney arrived in London in 1959 to study at the Royal College of Art. He was deeply impressed by Bacon’s 1960 exhibition at the Marlborough Gallery, commenting ‘you can smell the balls’, but his own style was more playful, experimenting with abstraction and graffiti.
Hockney and Bacon both drew heavily on the visual culture that surrounded them, from well-established artistic sources such as Eadweard Muybridge’s innovative photographs of wrestlers to cheap bodybuilding magazines. They were not alone in spotting the homoerotic potential of this material – artists such as Christopher Wood had already used the trope of wrestlers to hint at queer intimacy. Yet Hockney and Bacon went further, fearlessly stripping away ambiguities.
Their work was controversial. Bacon’s 1955 exhibition at the Institute of Contemporary Arts was investigated by the police for obscenity while Hockney once described his early paintings as ‘homosexual propaganda’. They both continued to push the boundaries of what could be depicted in art, breaking new ground.

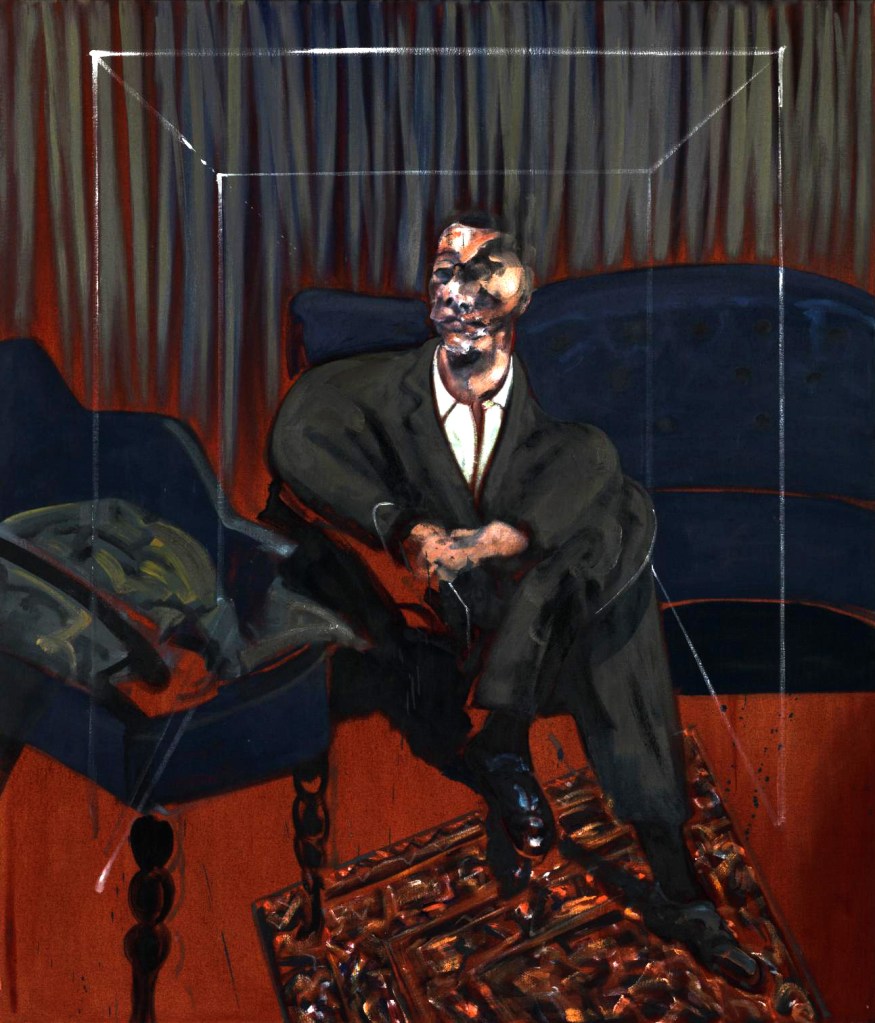
Francis Bacon (British, 1909-1992)
Two Figures in a Landscape (installation view)
1956
Oil paint on canvas
Lent by Birmingham Museums Trust on behalf of Birmingham City Council
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Two Figures in a Landscape combines the homoerotic themes of the ‘crouching nude’ and ‘figures in the grass’ that Francis Bacon explored in multiple paintings throughout the 1950s. He was inspired by Eadweard Muybridge’s photographs of wrestlers and athletes, along with Michelangelo’s drawings and sculpture. Bacon adapted these to explore his homosexuality with varying degrees of ambiguity. He later explained ‘Michelangelo and Muybridge are mixed up in my mind together’ and ‘I manipulate the Muybridge bodies into the form of the bodies I have known’.
Wall text from the exhibition

Francis Bacon (British, 1909-1992)
Seated Figure
1961
Tate. Presented by J. Sainsbury Ltd 1961
© Estate of Francis Bacon
This image probably depicts Francis Bacon’s former lover Peter Lacy. Bacon was a masochist and Lacy once told him ‘you could live in a corner of my cottage on straw. You could sleep and shit there’. Lacy’s suit and the inclusion of domestic details such as the exotic rug and chair contrast with the tempestuous abstract backdrop, giving the image an air of suppressed violence. Bacon spoke of his treatment of sitters in his portraits as an ‘injury’ and once said ‘I hate a homely atmosphere… I want to isolate the image and take it away from the interior and the home’.
Wall text from the exhibition

Installation view of David Hockney’s Life Painting for a Diploma 1962 from Room 8 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
David Hockney (British, b. 1937)
Life Painting for a Diploma
1962
Oil paint, charcoal and collage on canvas
Yageo Foundation Collection, Taiwan
Life Painting for a Diploma formed part of David Hockney’s final submission at the Royal College of Art. The hanging skeleton displays Hockney’s skills as a draftsman but it is the well-toned bodybuilder who catches the viewer’s attention. Hockney’s gay American friend Mark Berger introduced him to ‘beefcake’ magazines such as Physique Pictorial. Here, the stereotypical model and inscription PHYSIQUE references this material. Hockney claimed he painted this image to satisfy the RCA’s requirement that students produce a number of life-drawings. The work’s title and its contrast between the arid skeleton and lively model (clearly not painted from life) subtly mocks his instructors.
Wall text from the exhibition

David Hockney (British, b. 1937)
Going to be a Queen for Tonight
1960
Oil paint on canvas
Royal College of Art
The words ‘queer’ and ‘queen’, both terms for gay men at this time, are scrawled across the surface of this image. Hockney was fascinated with the graffiti in the public toilets at Earls Court Underground station. Here, messages about opportunities for casual sex were mixed with other slogans. The title playfully hints at these possibilities – ‘queen’ but only for the night. It was one of a number of paintings made by Hockney at the Royal College Of Art which reference queer urban life. Hockney described his early works as ‘a kind of mixture of Alan Davie cum Jackson Pollock cum Roger Hilton’.
Wall text from the exhibition

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Wrestlers (installation view)
1965
Watercolour and ink on paper
York Museums Trust (York Art Gallery)
Gifted through the Contemporary Art Society, as a bequest from Dr Ronald Lande, in memory of his life partner Walter Urech, 2012
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Physique Photography In Britain
British Physique photography flourished after the Second World War. Body-building magazines such as Health and Strength or Man’s World could be purchased quite innocently in newsagents. For many gay men, however, these publications were an important first step towards finding a community.
Bodybuilding shots, wrestlers and ‘art studies’ offered a pretext for gay photographers such as Vince, Basil Clavery (alias ‘Royale’ and ‘Hussar’), Lon of London and John Barrington to produce homoerotic imagery. Their work often included references to classical civilisation, an established shorthand for queer culture. Some dropped the pretence of bodybuilding altogether and sold more explicit material directly to a burgeoning private market.
This was a risky business: selling or sending such images through the post could land both photographer and purchaser in jail. Yet for many gay men, the easy availability of physique imagery gave reassurance that they were not alone. Somebody out there understood and shared their desires.
Installation views of physique album pages from Room 8 of the exhibition Queer British Art at Tate Britain
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan
Tate Britain
Millbank, London SW1P 4RG
United Kingdom
Phone: +44 20 7887 8888
Opening hours:
10.00am – 18.00pm daily
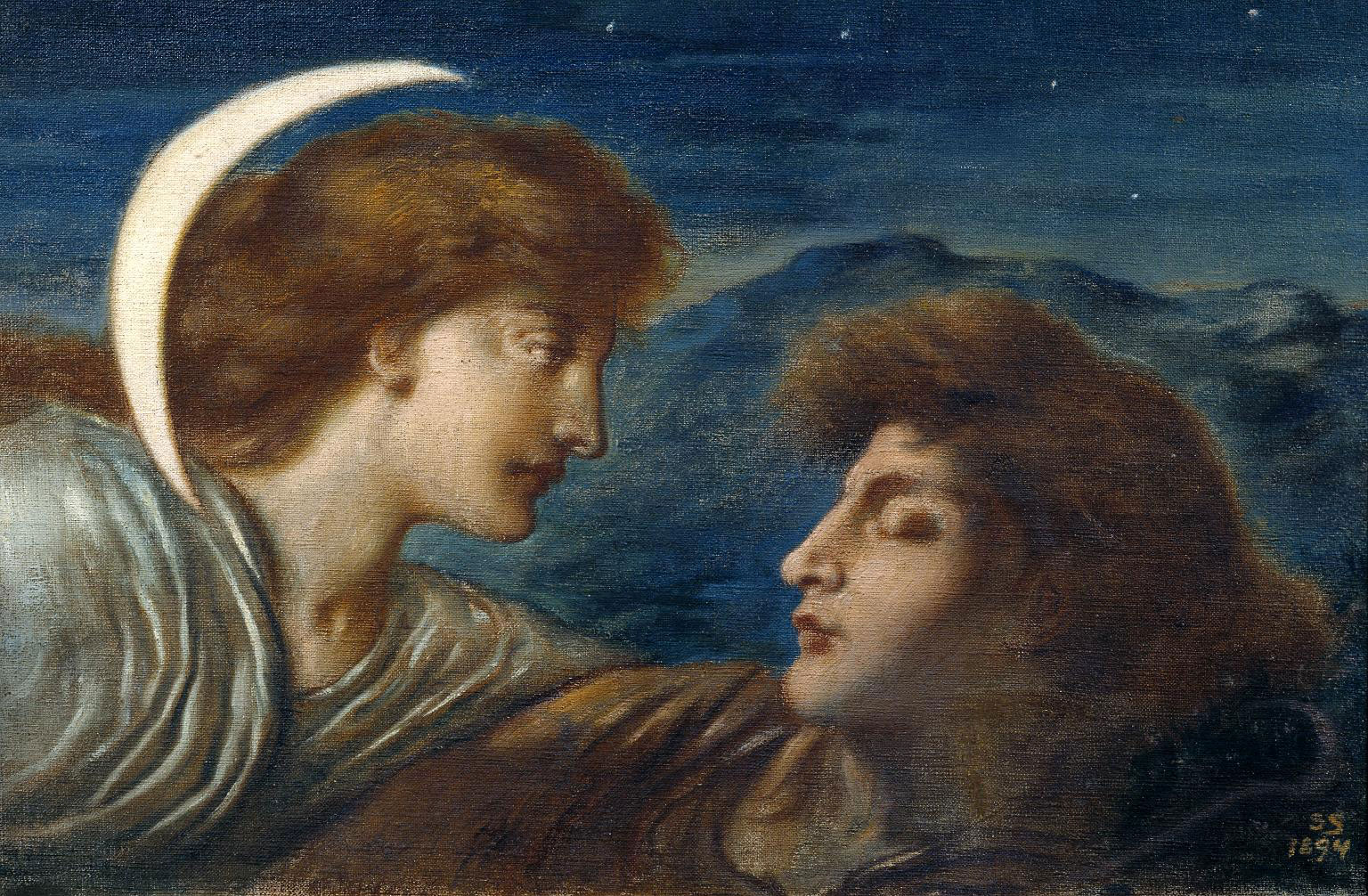
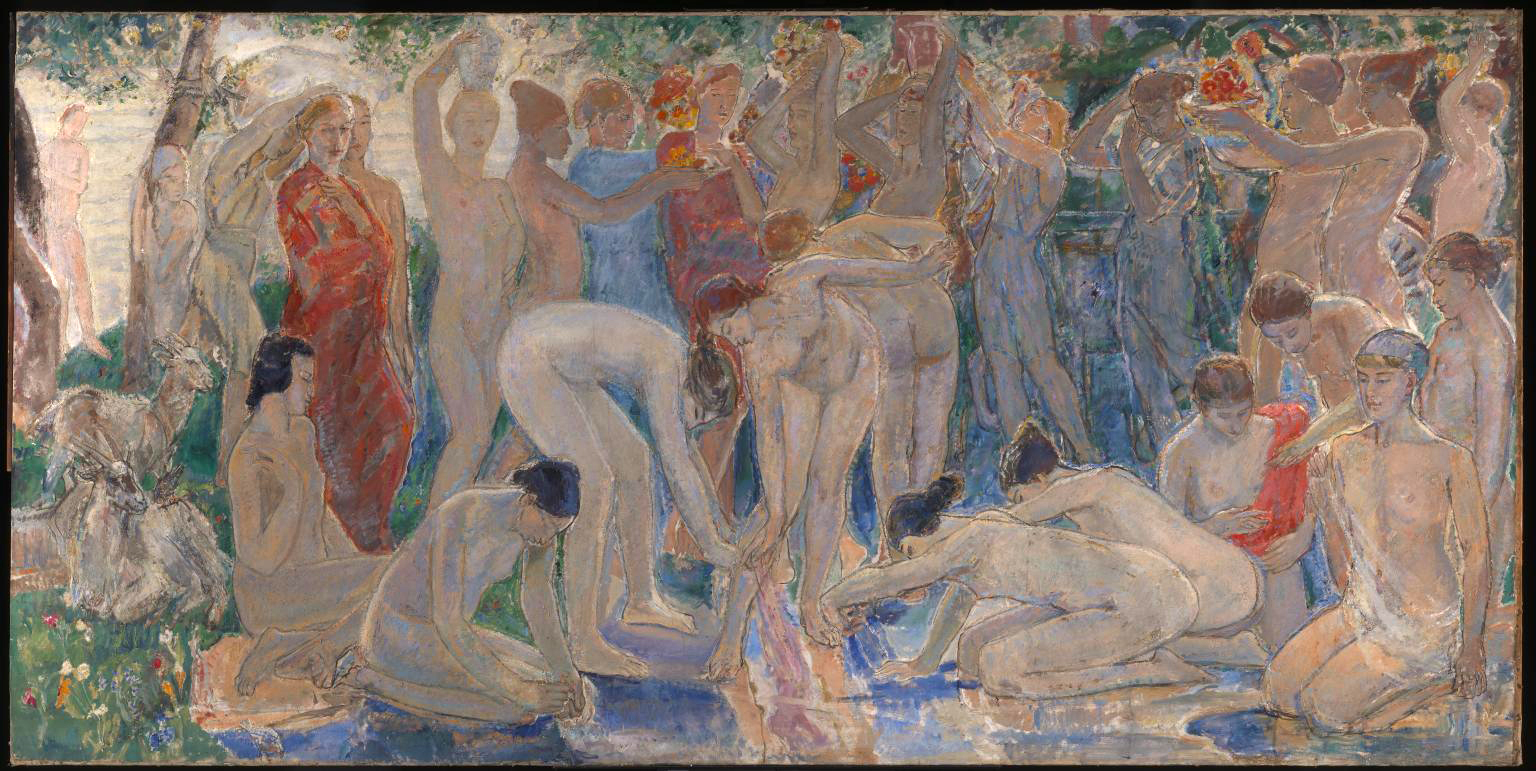
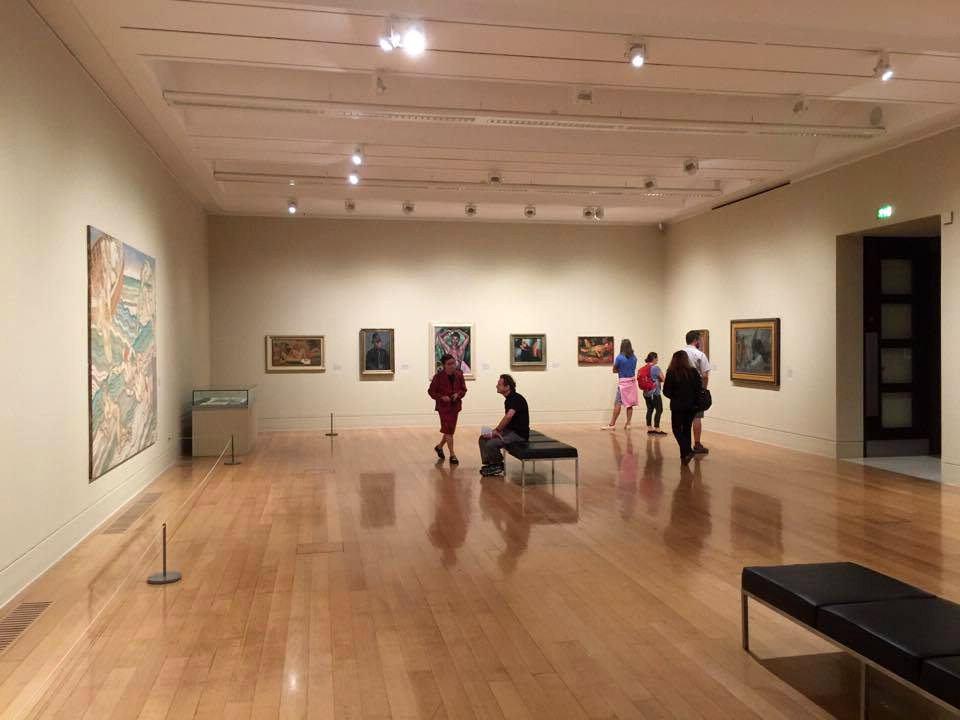
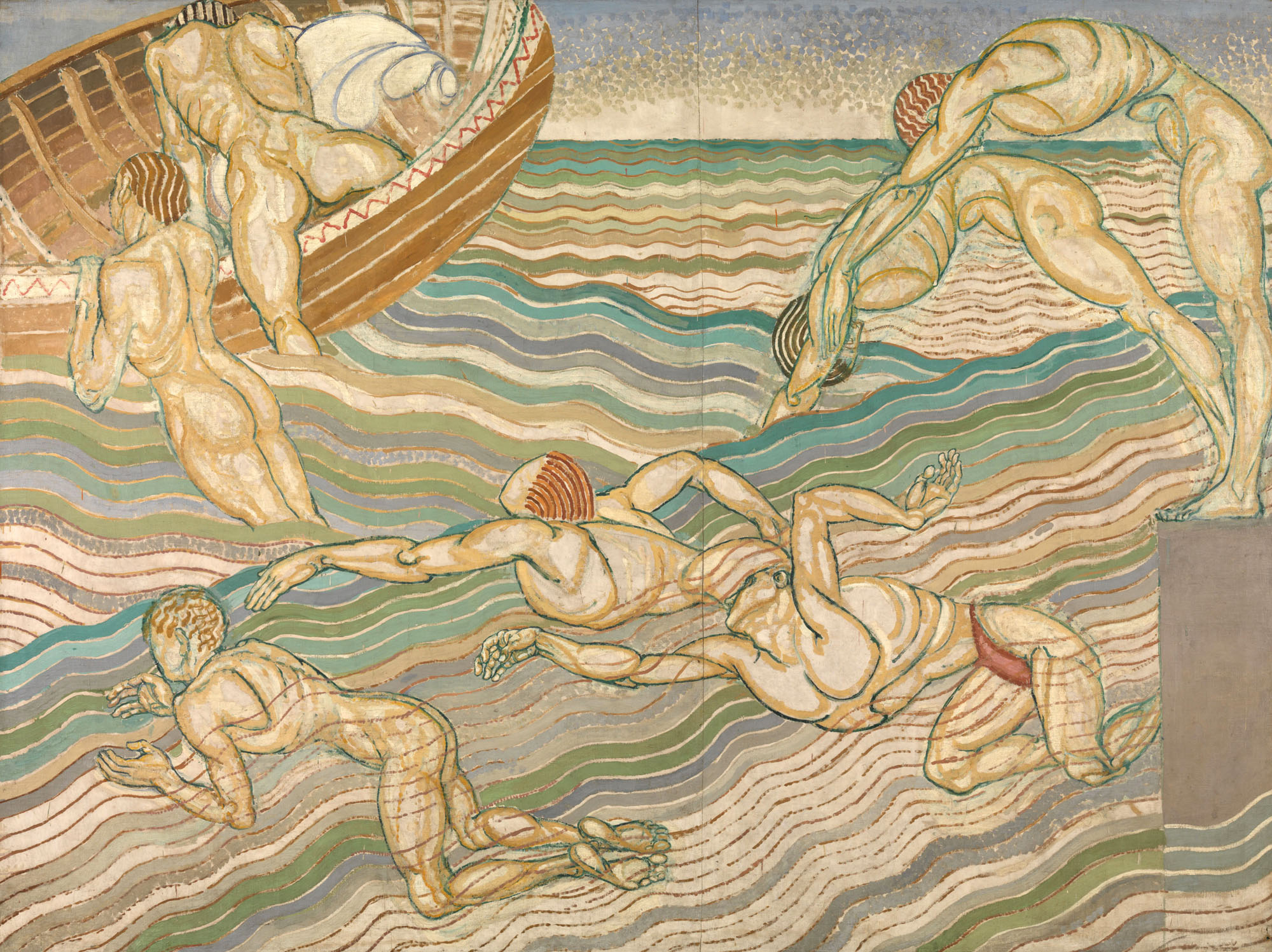
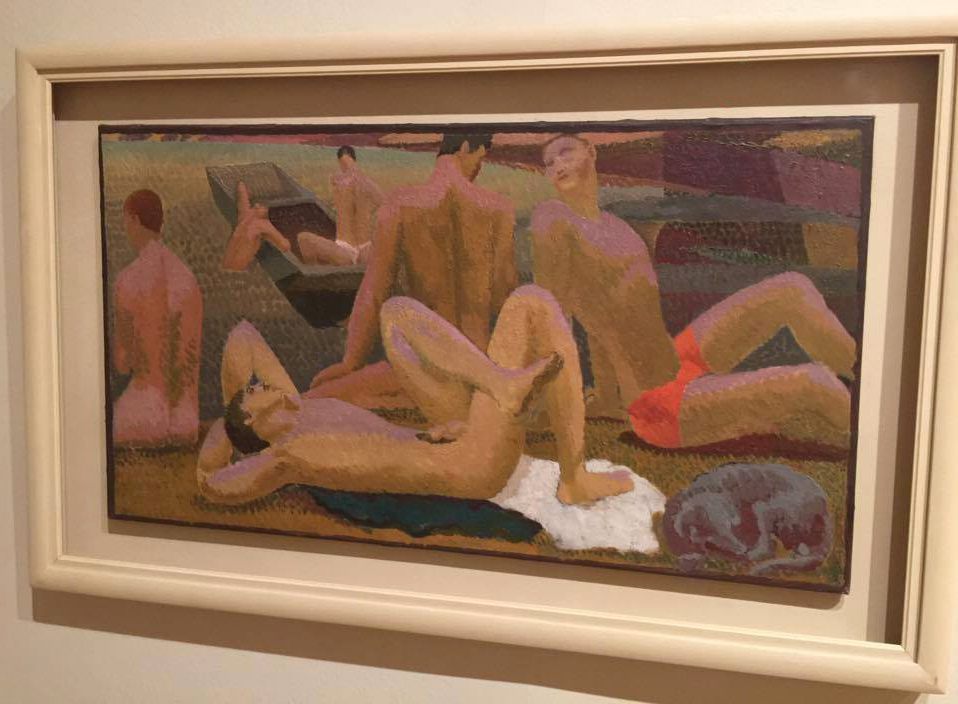
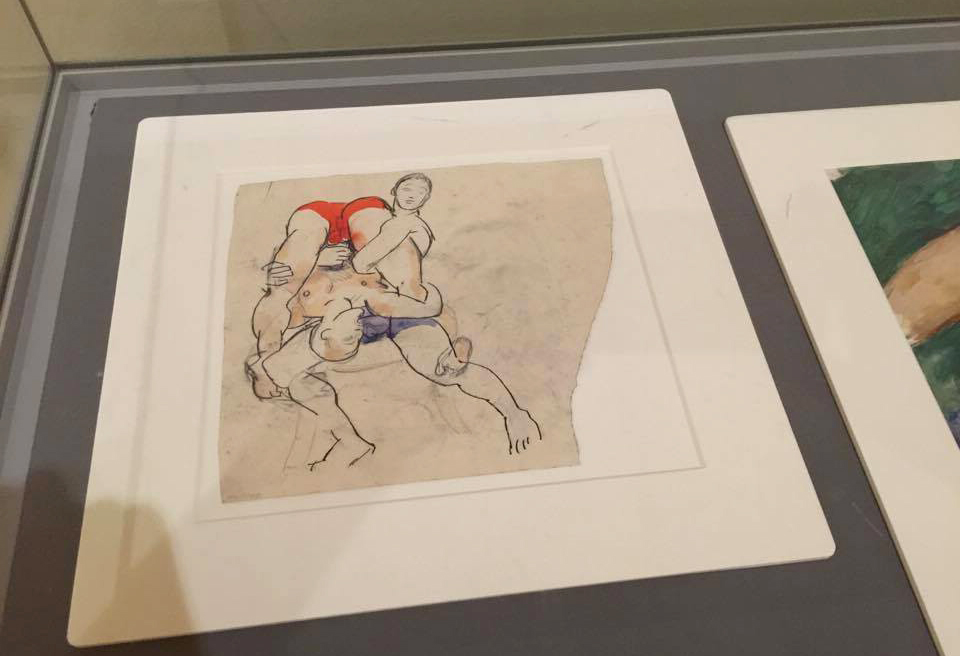
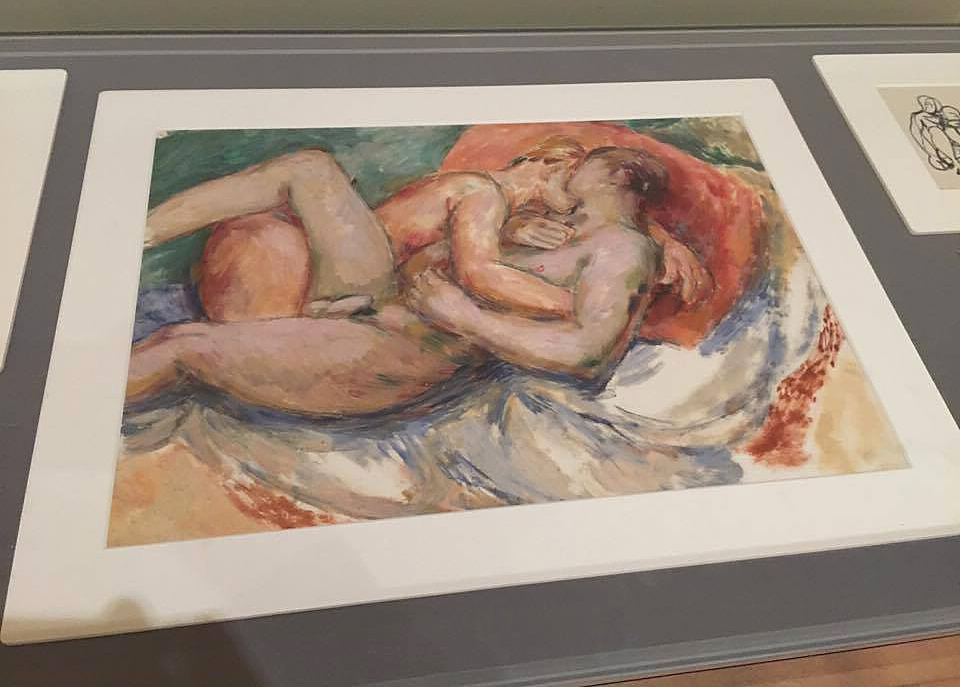
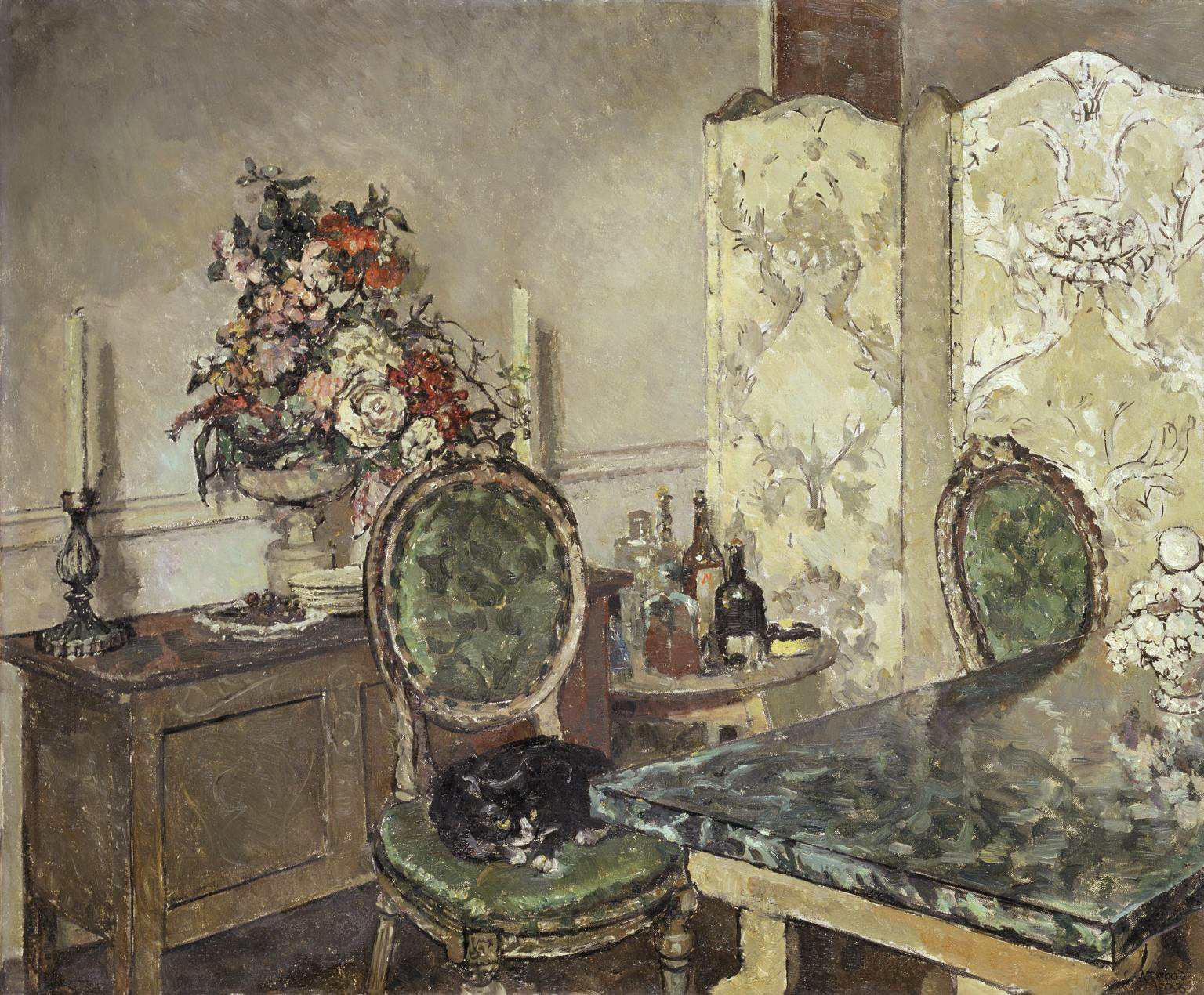
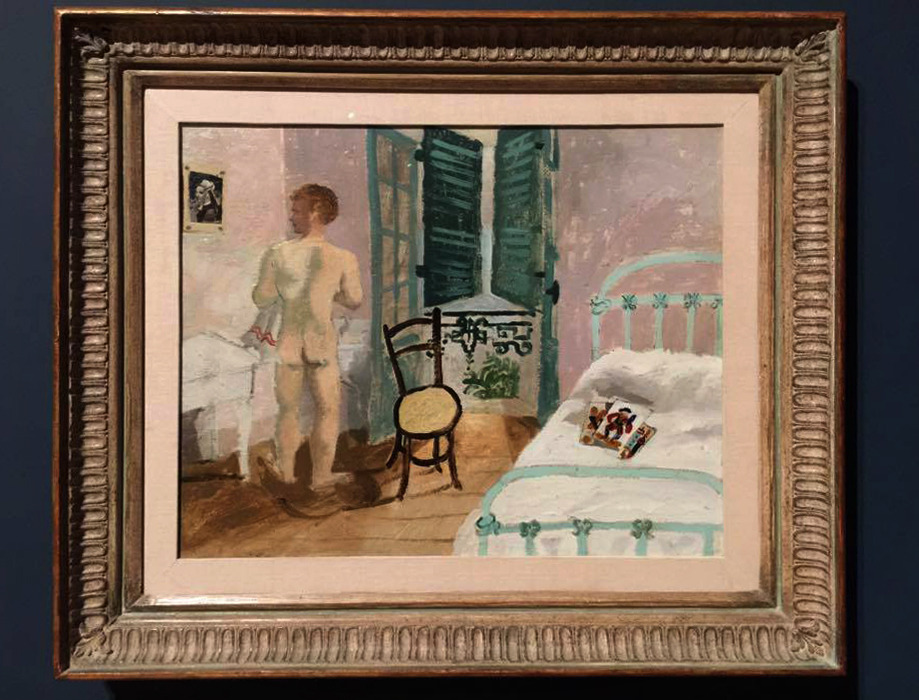
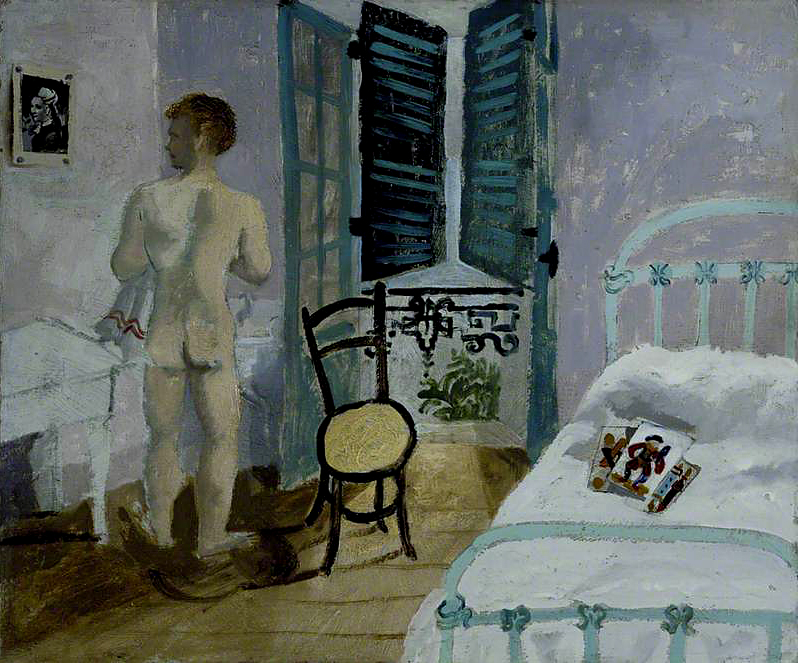
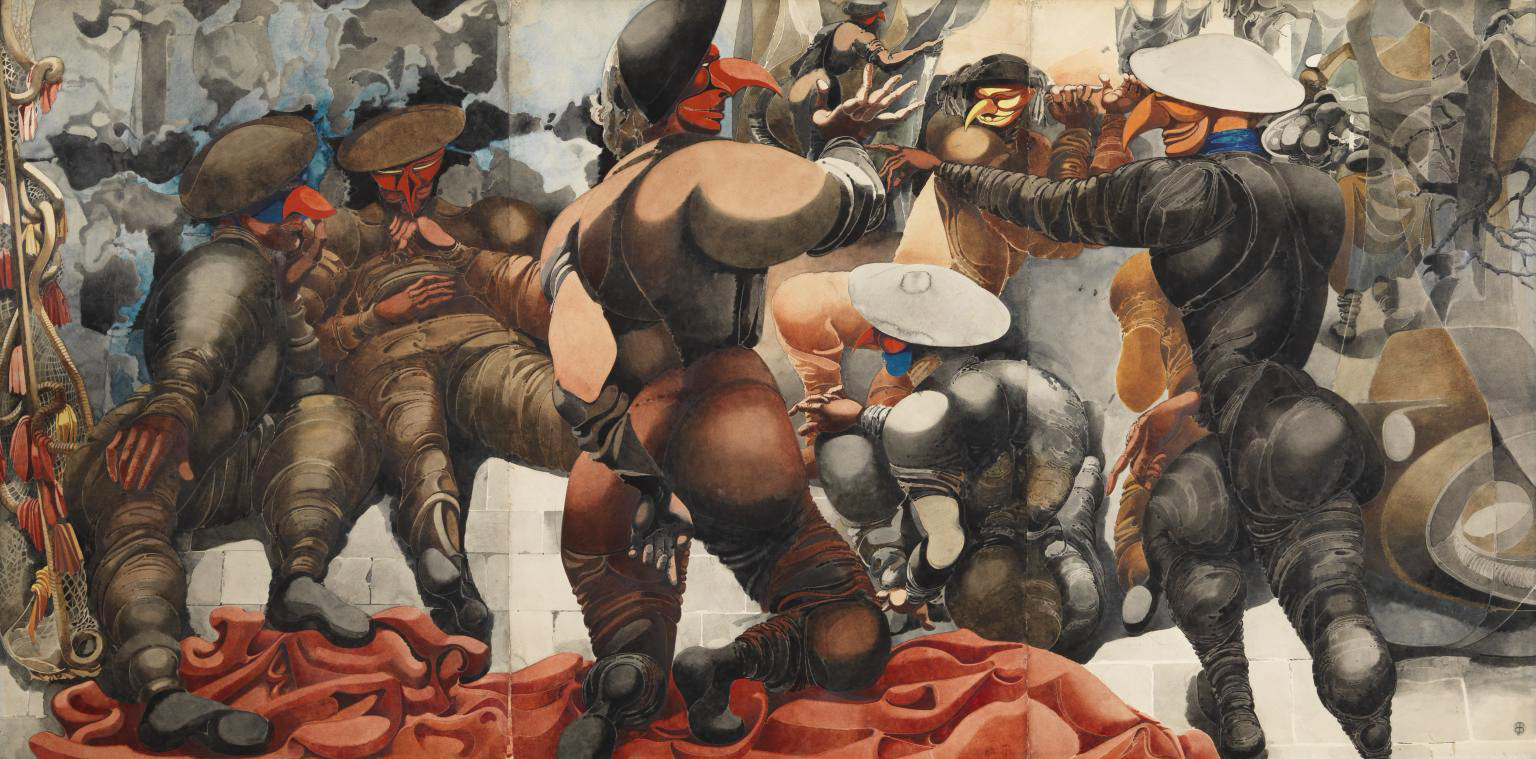
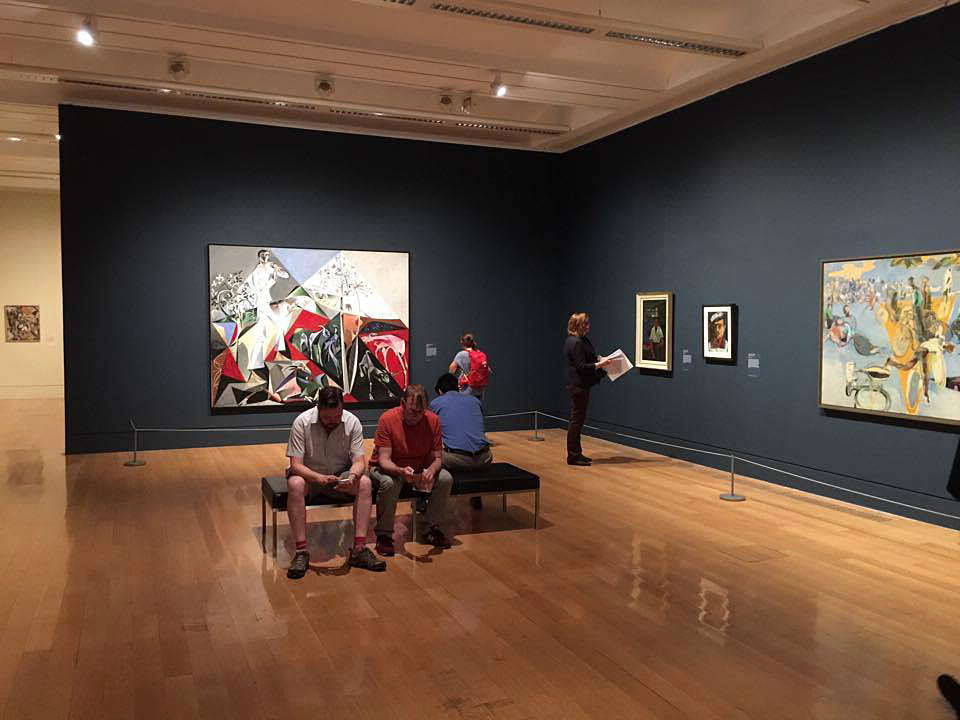
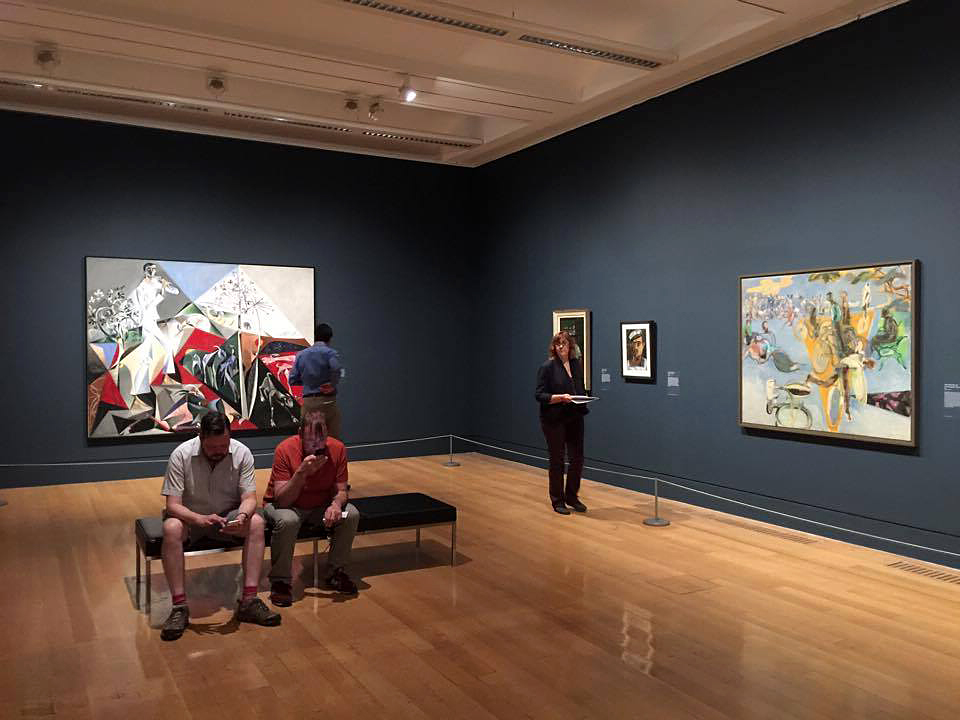
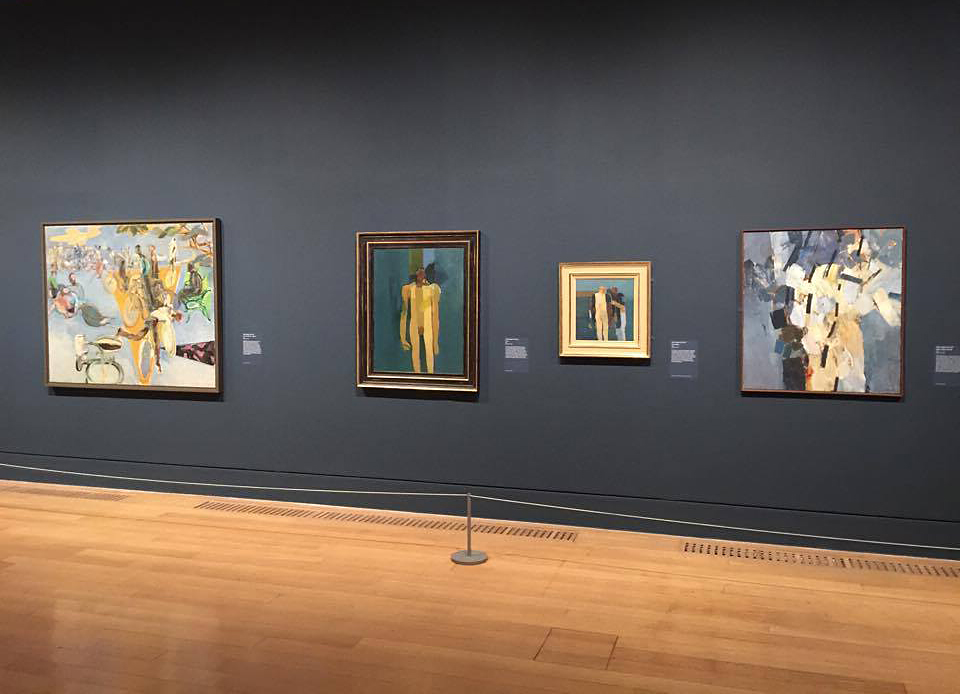
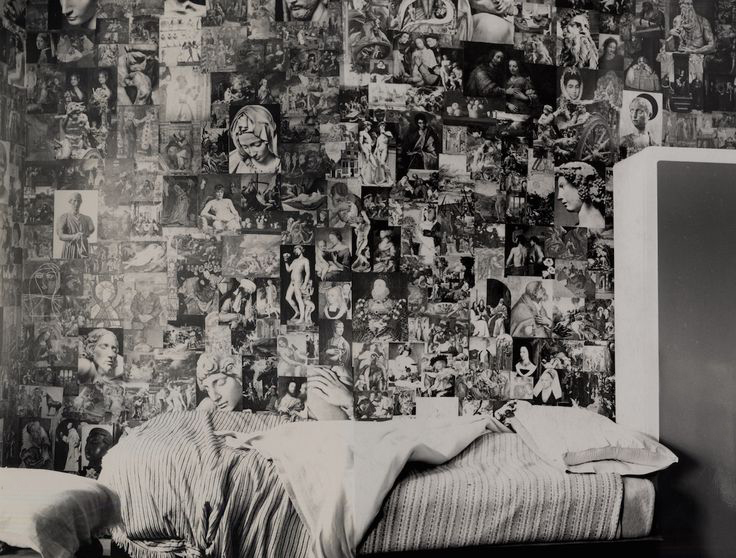
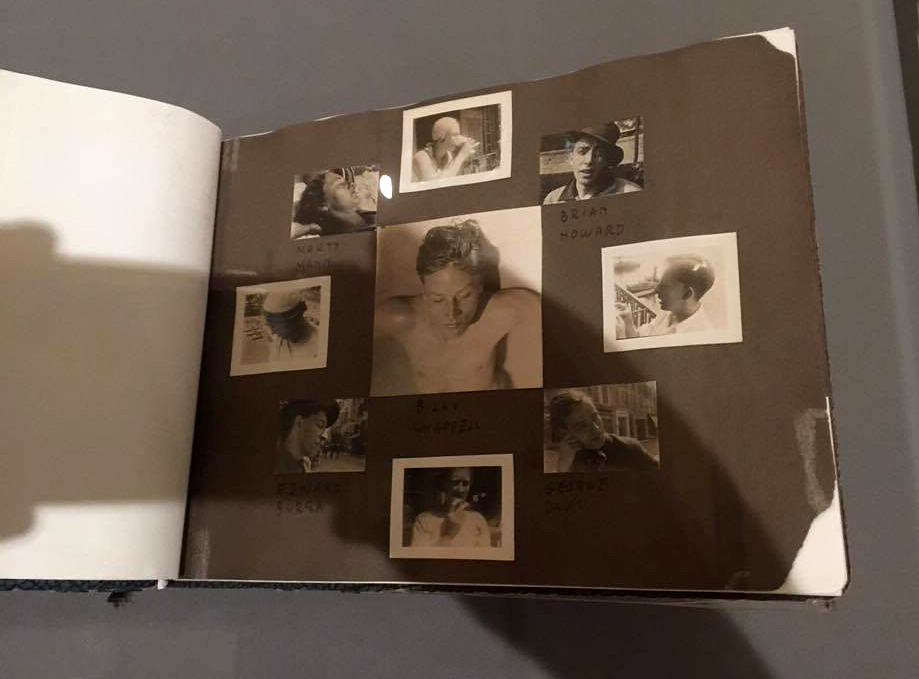
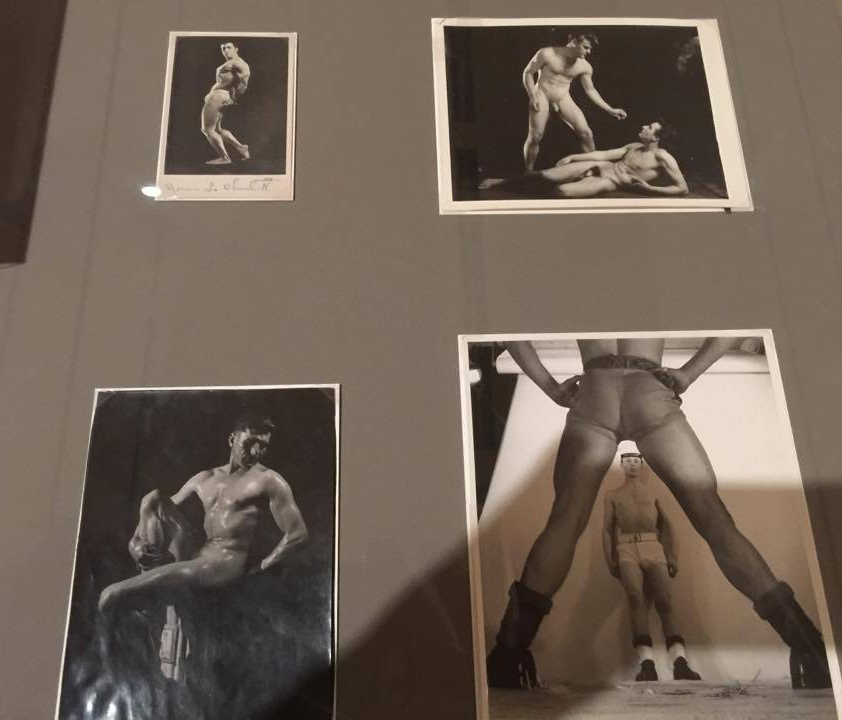
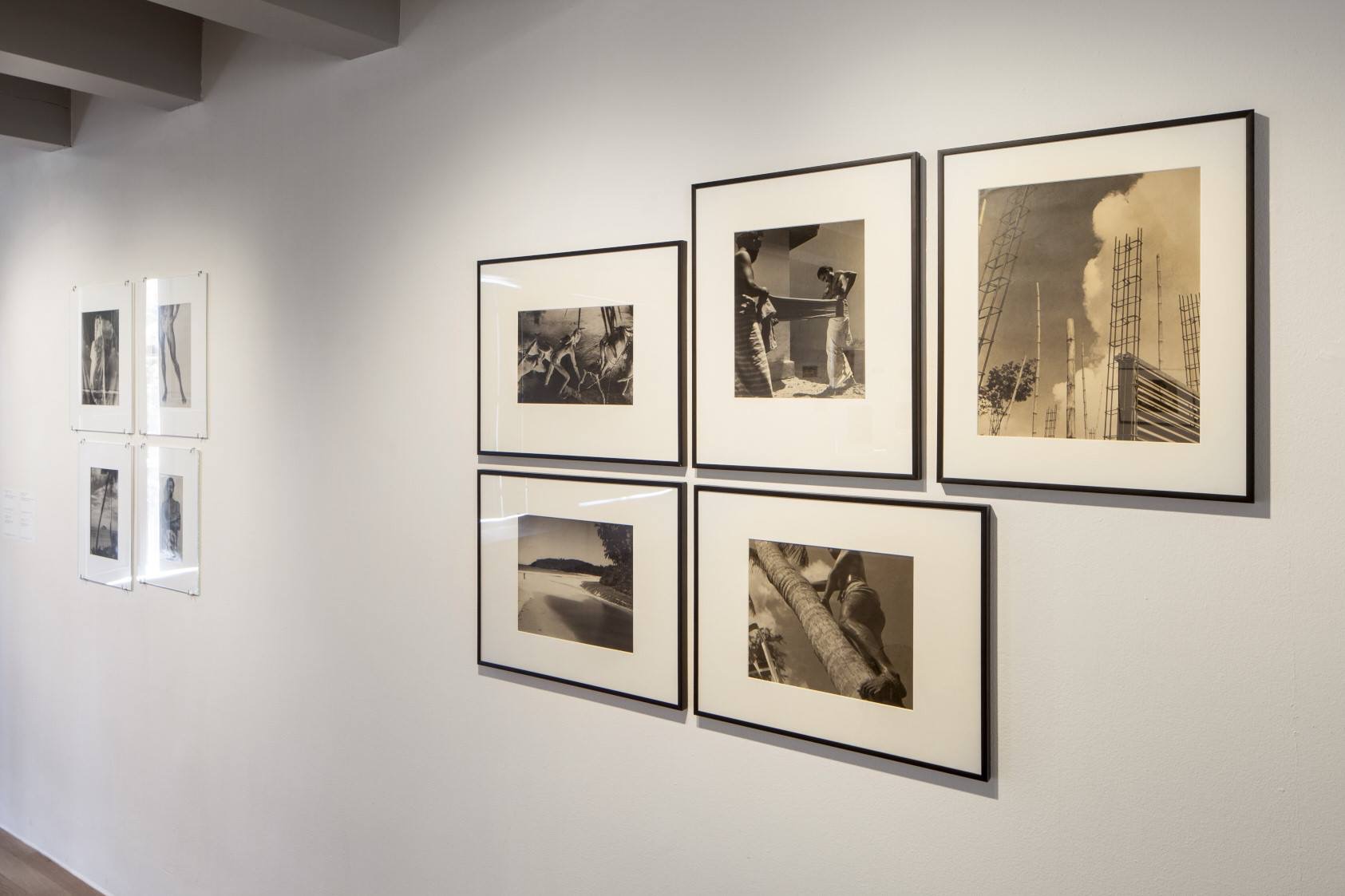
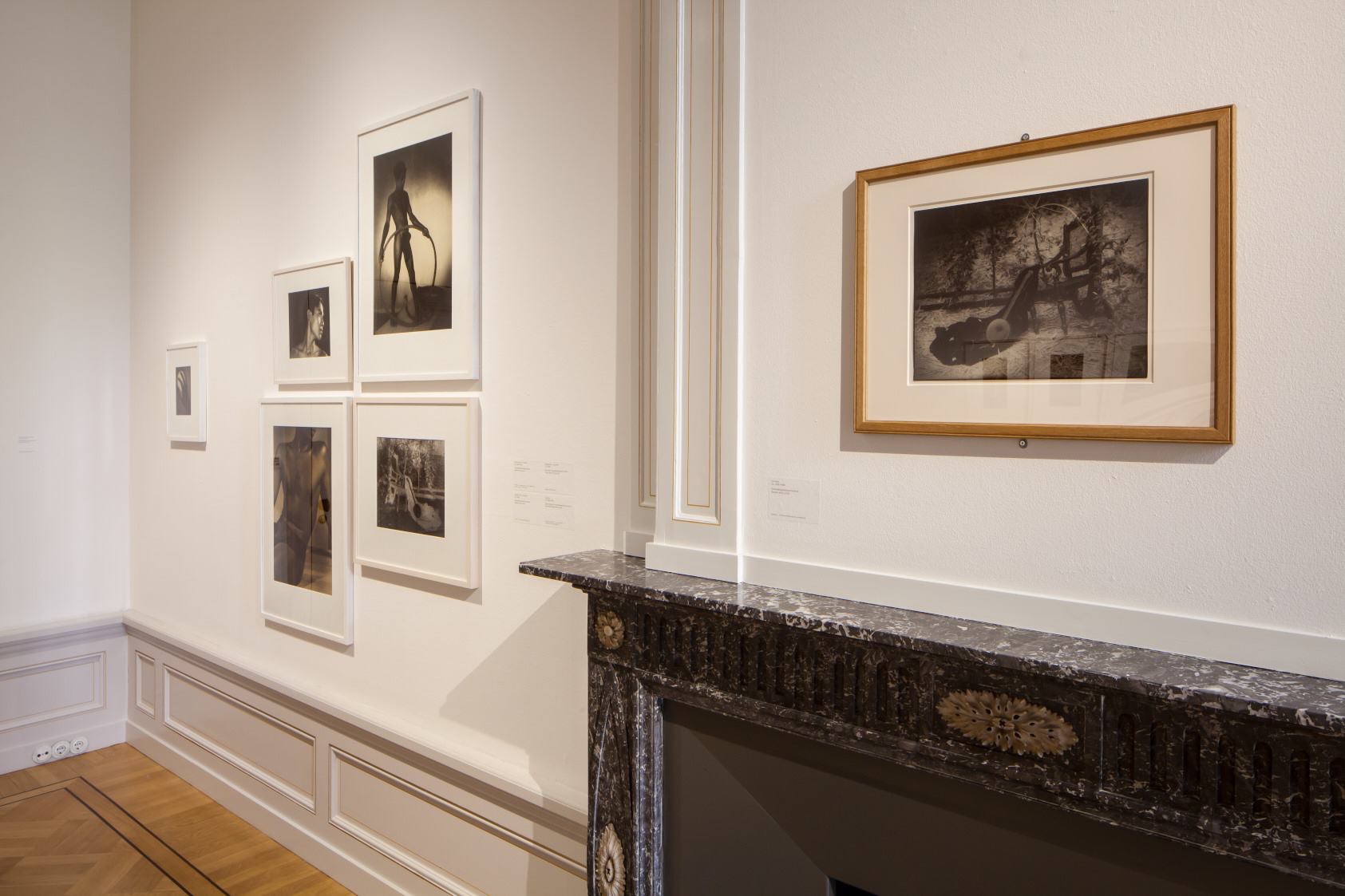
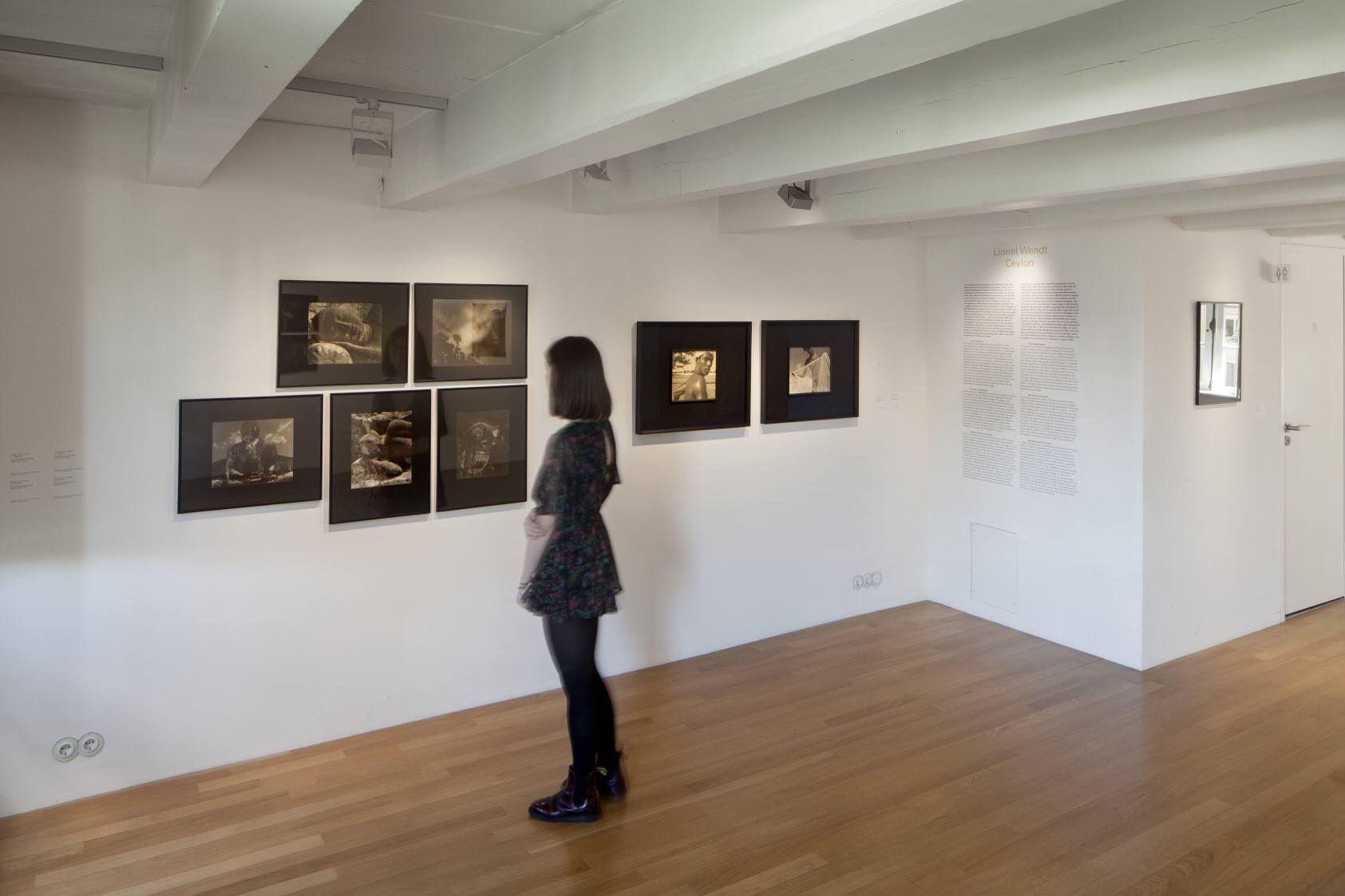
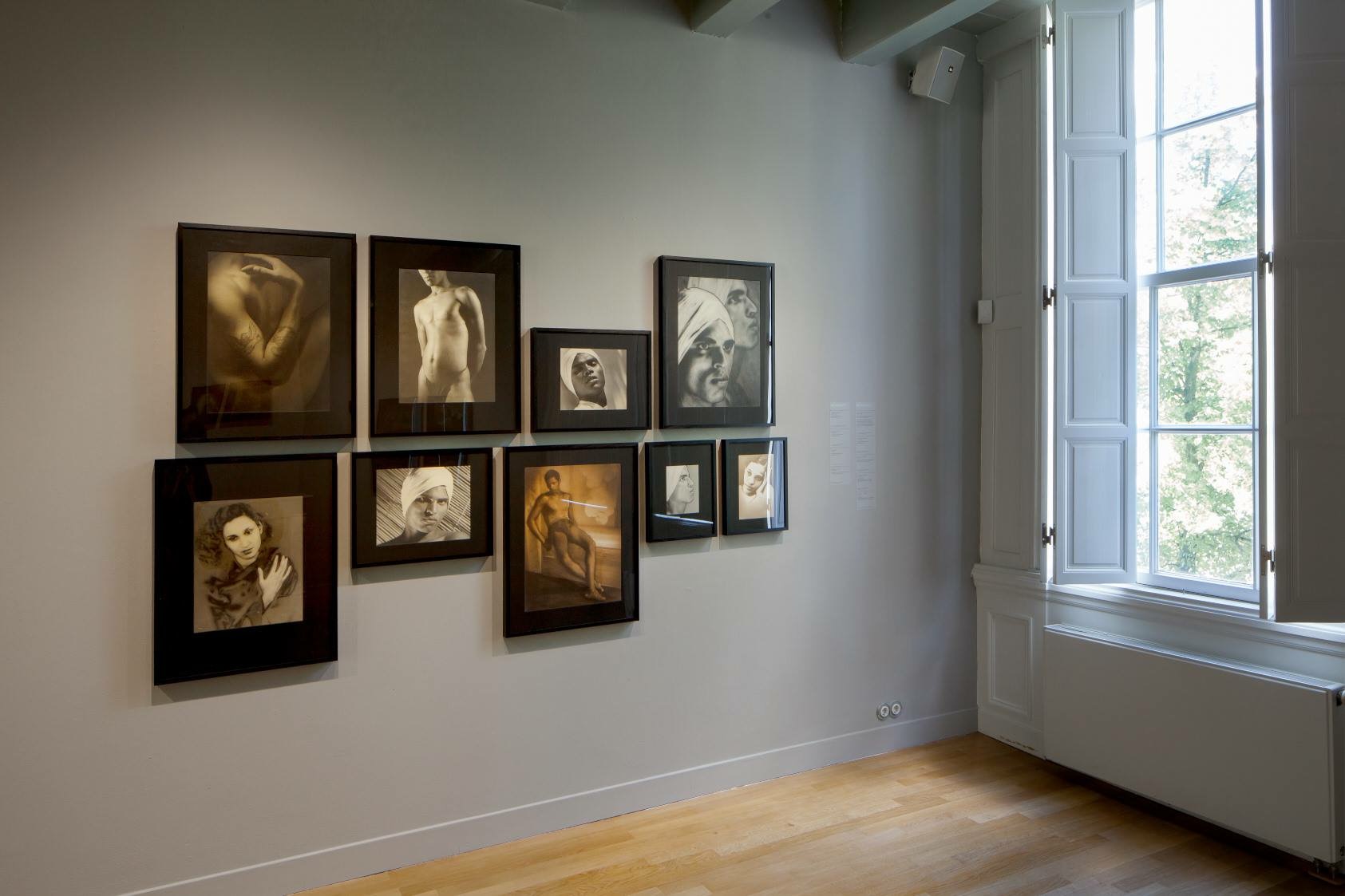
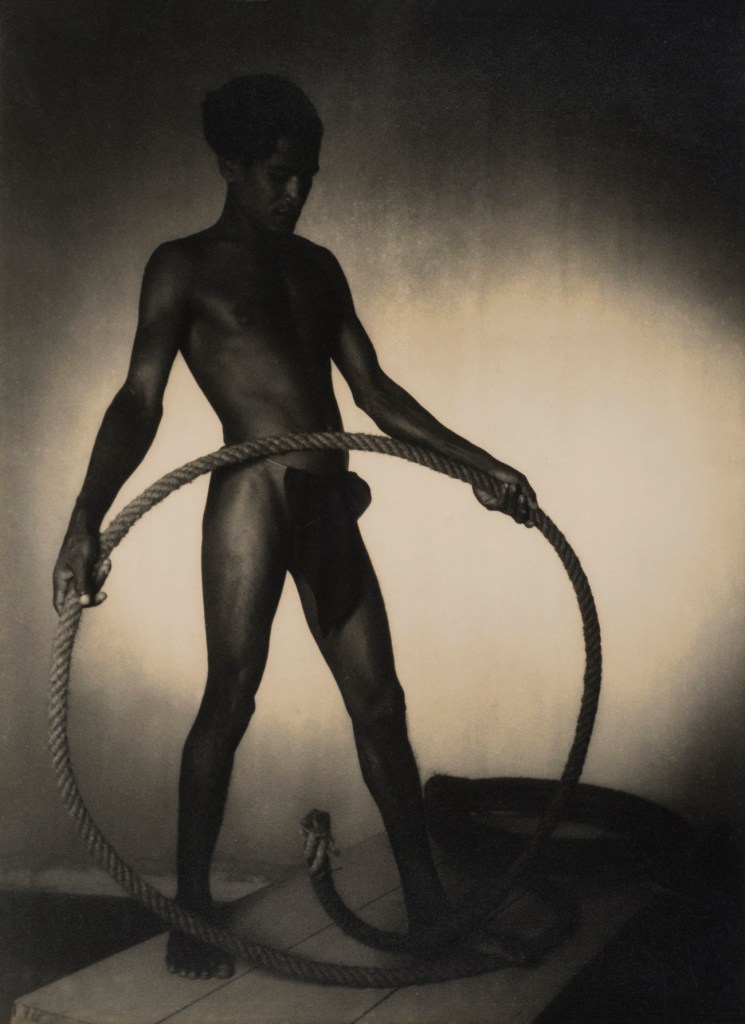
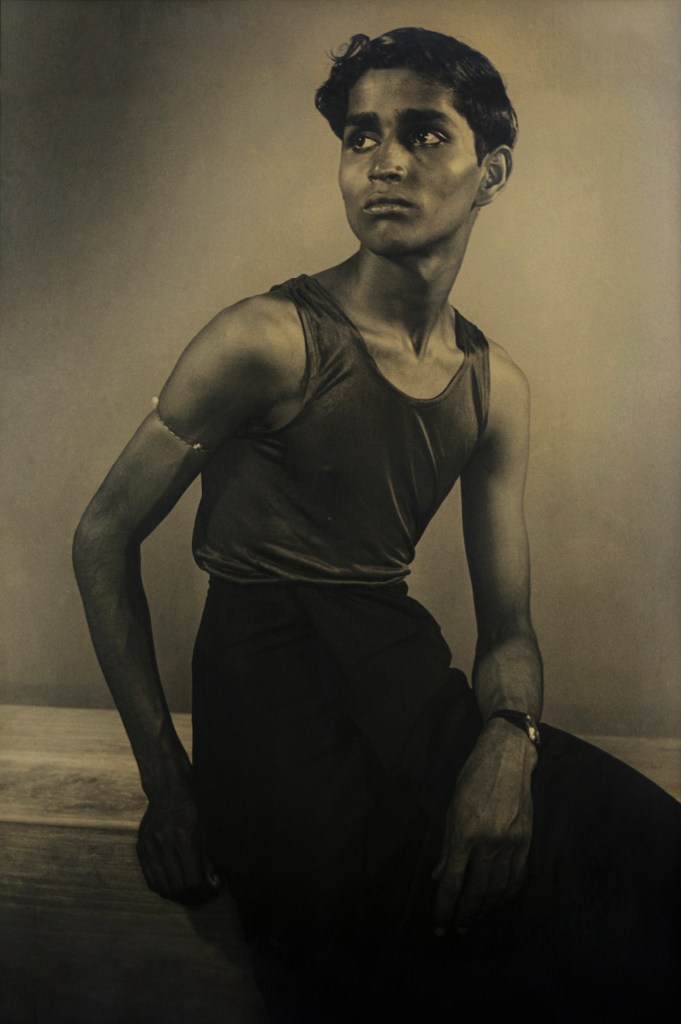
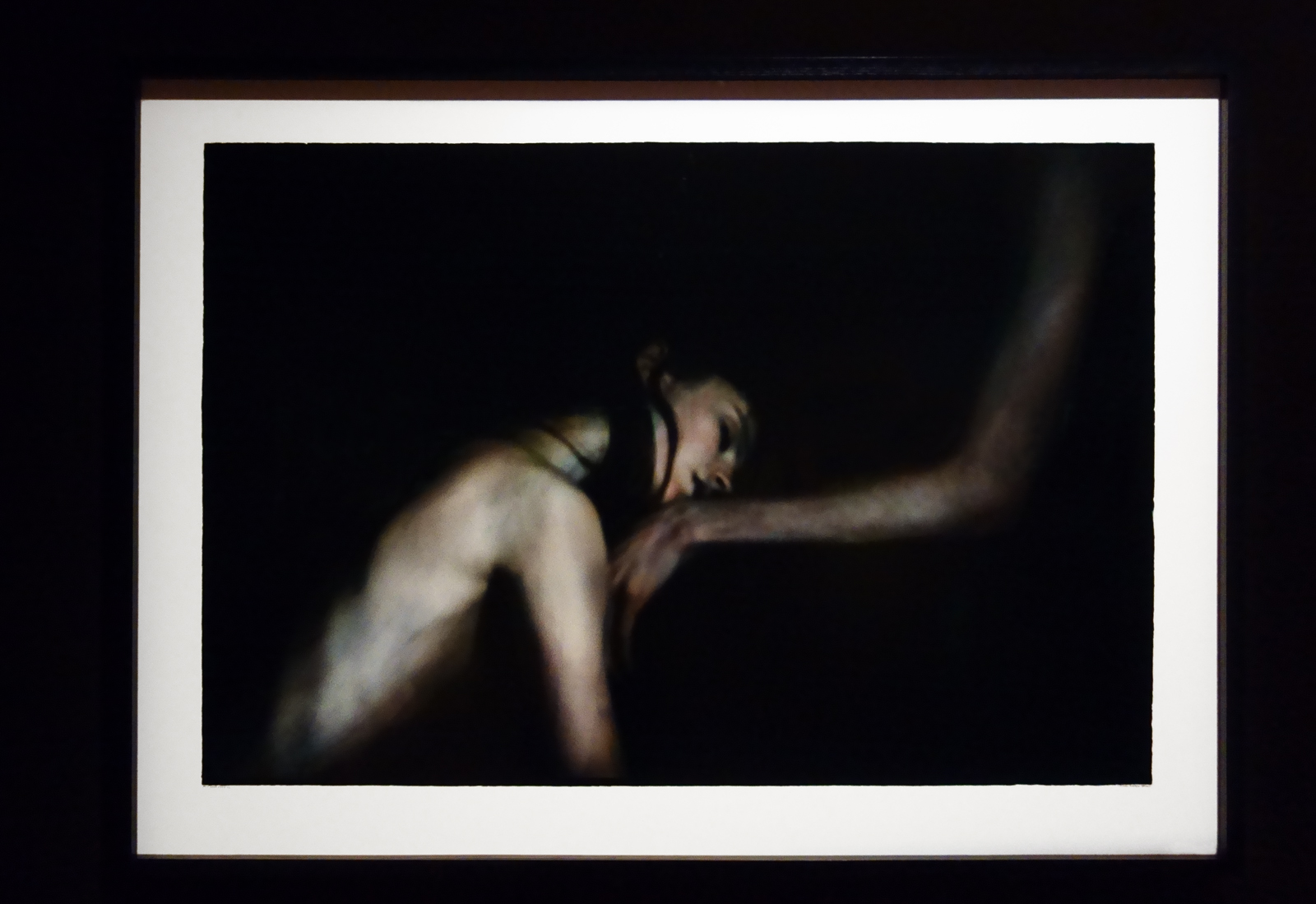
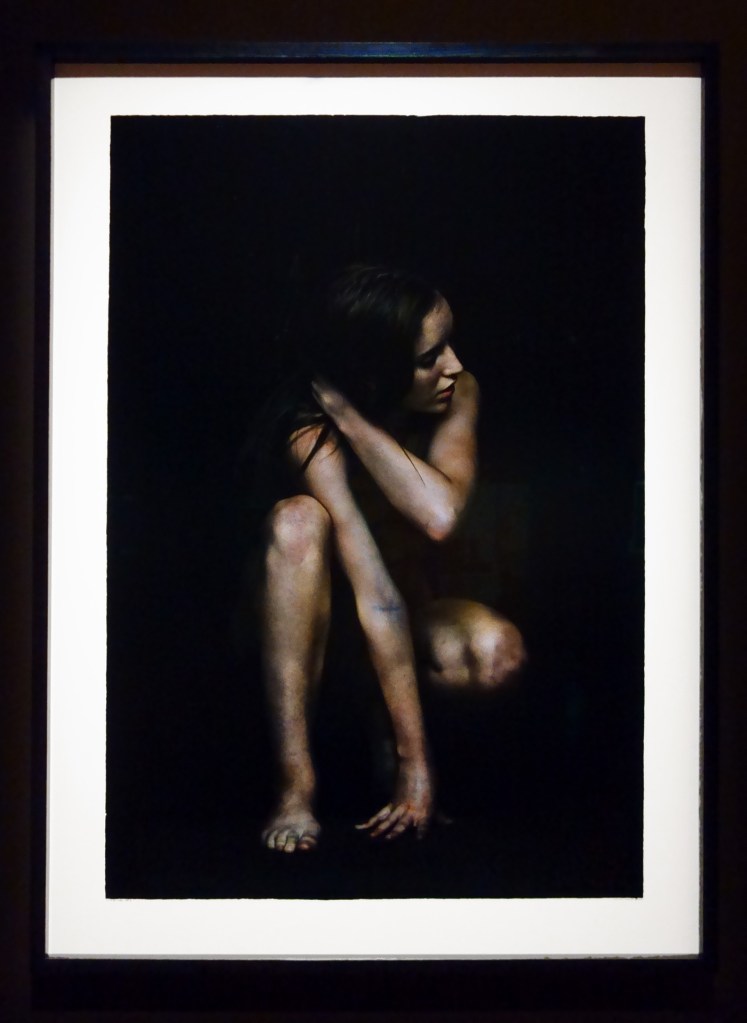
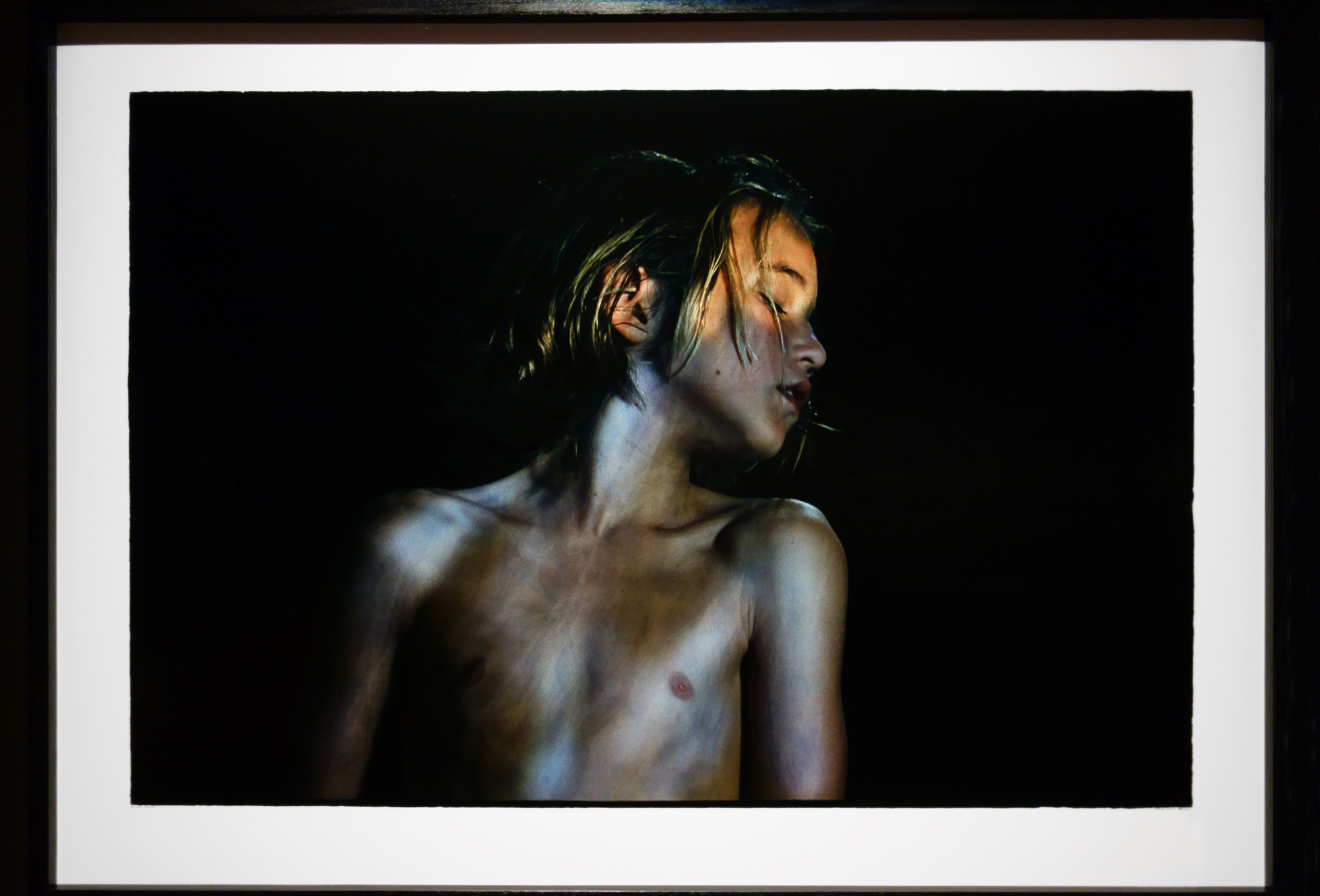
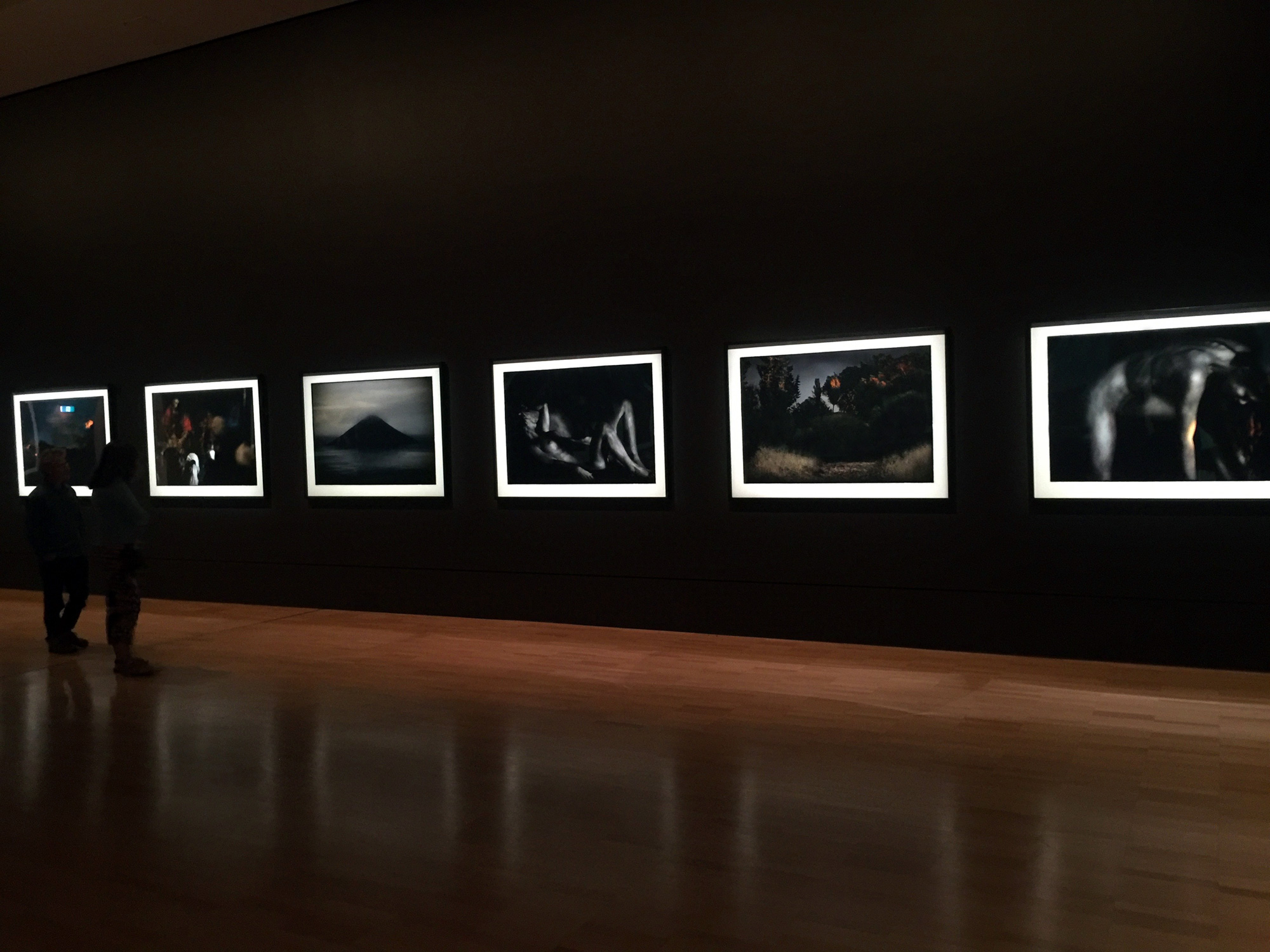
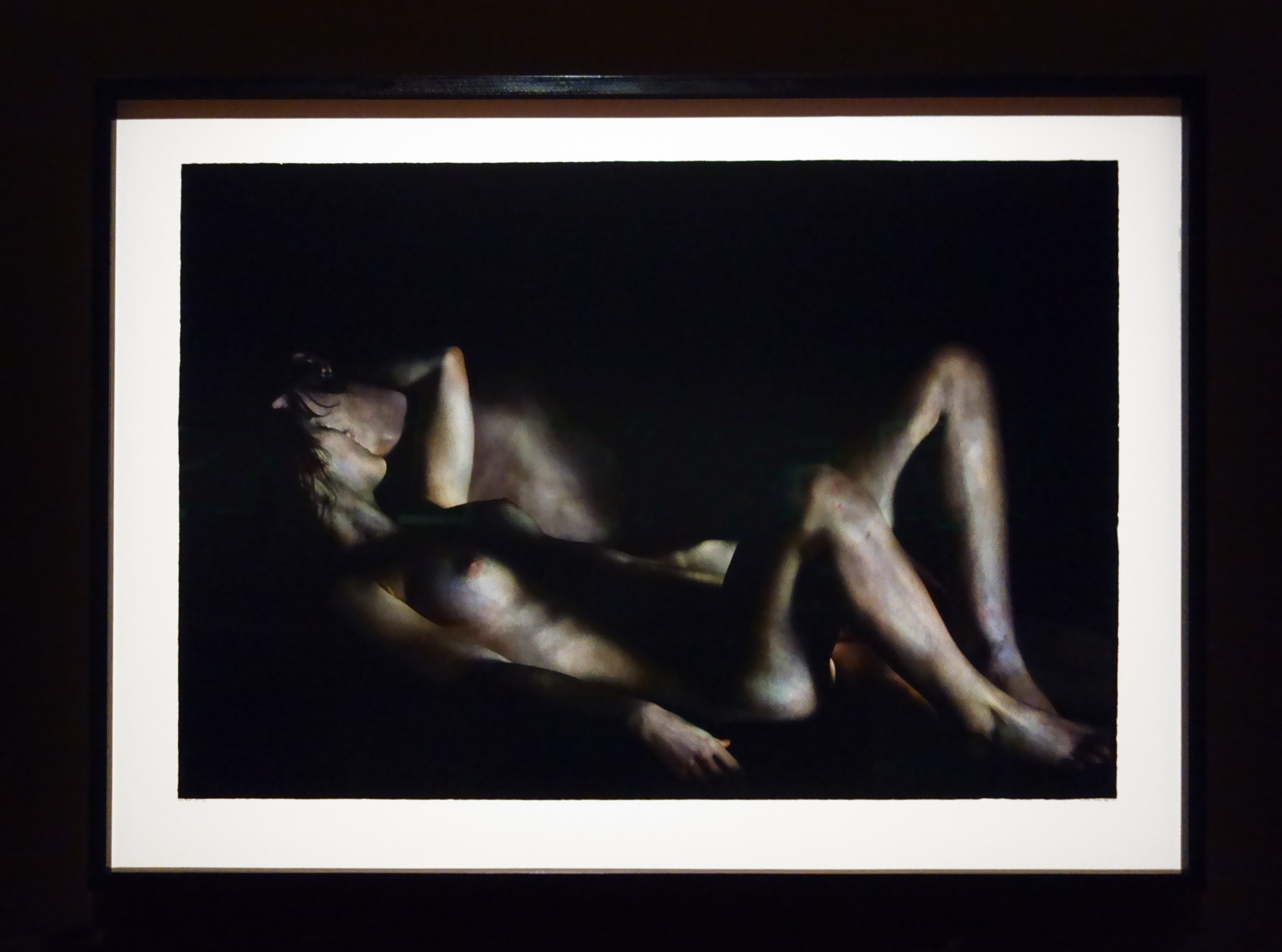
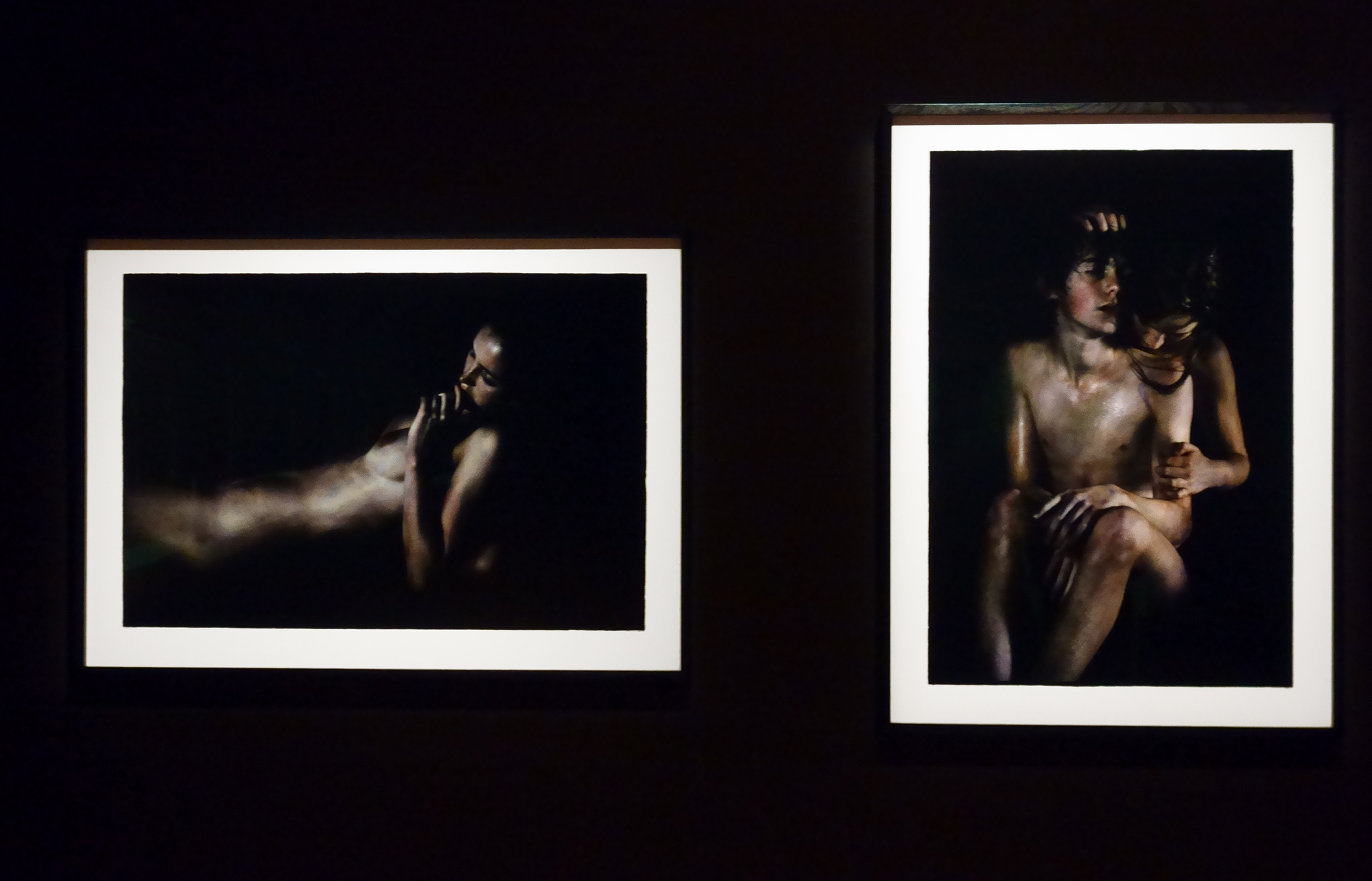
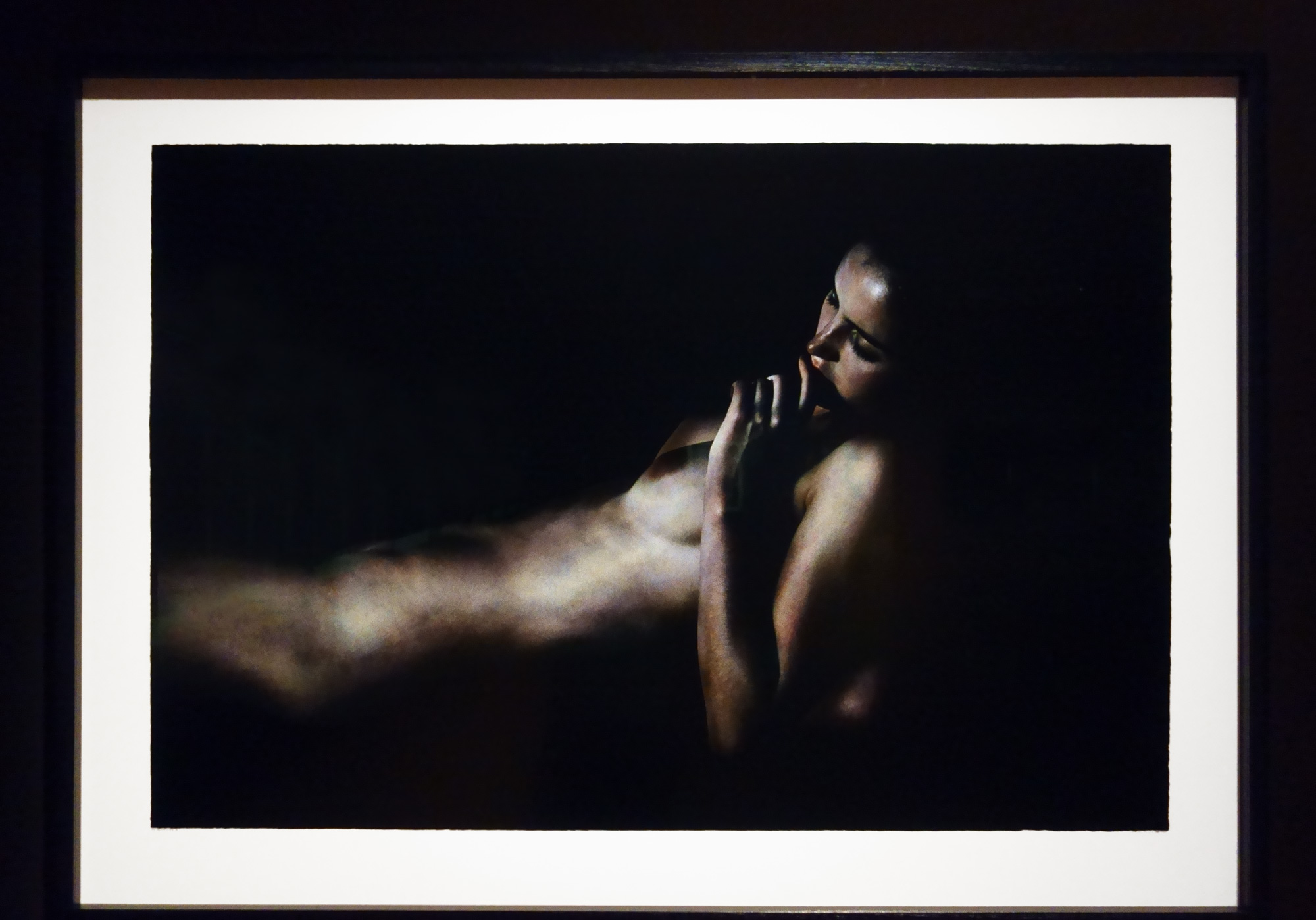
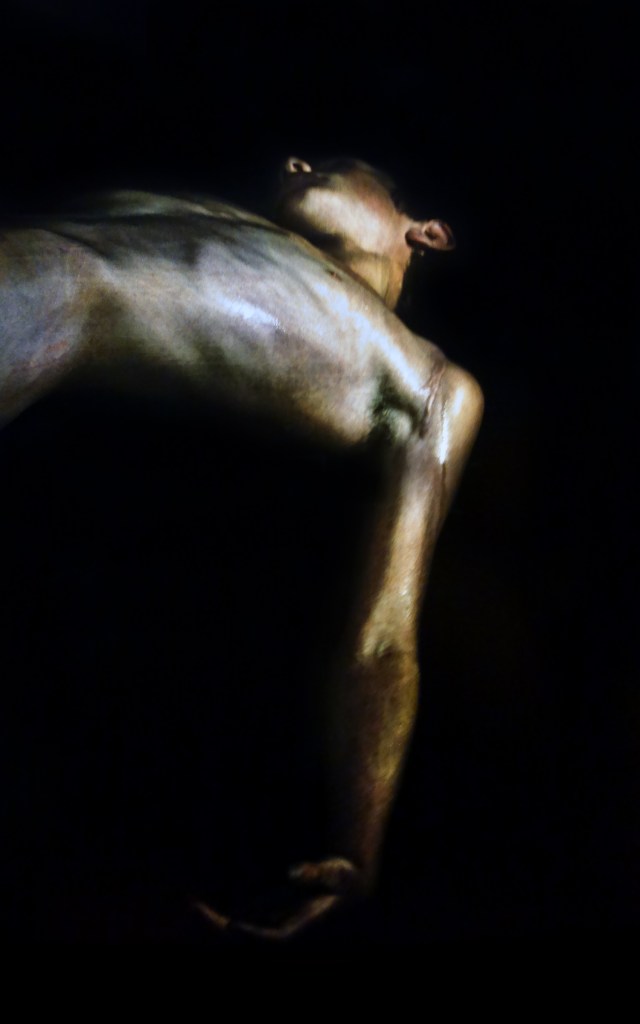
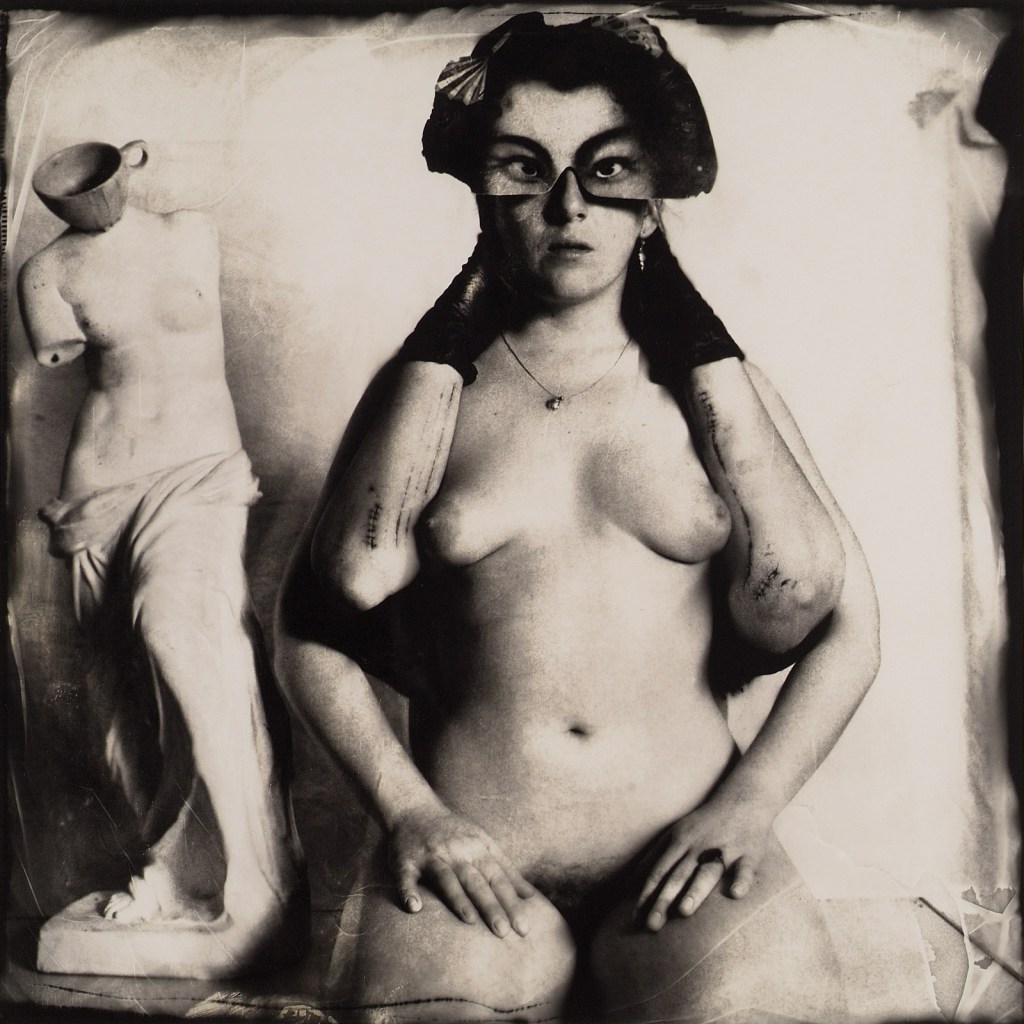
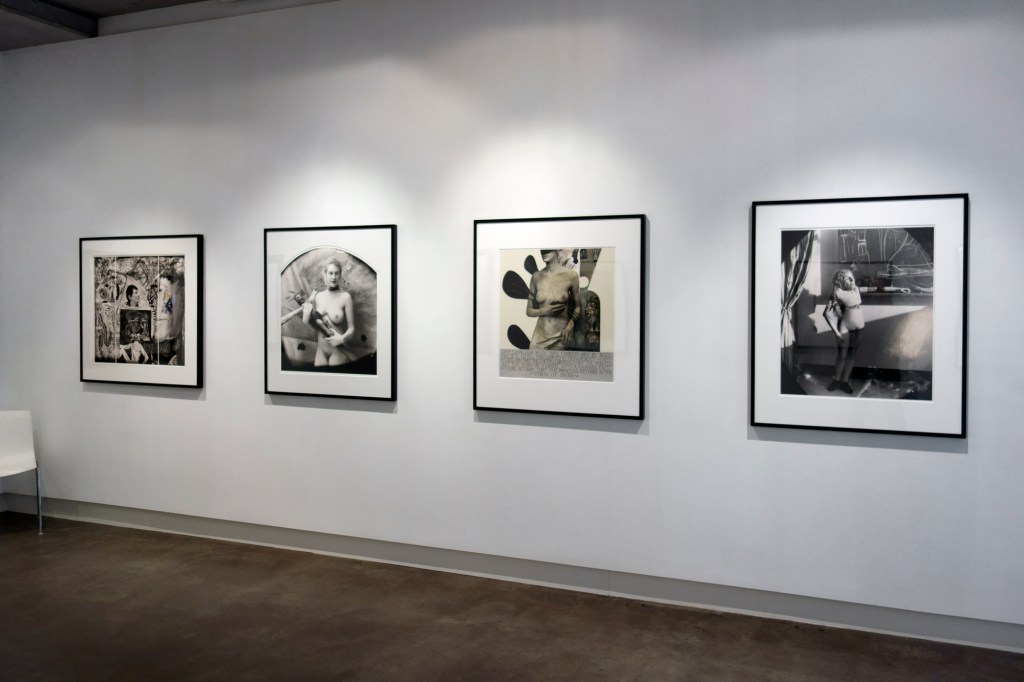
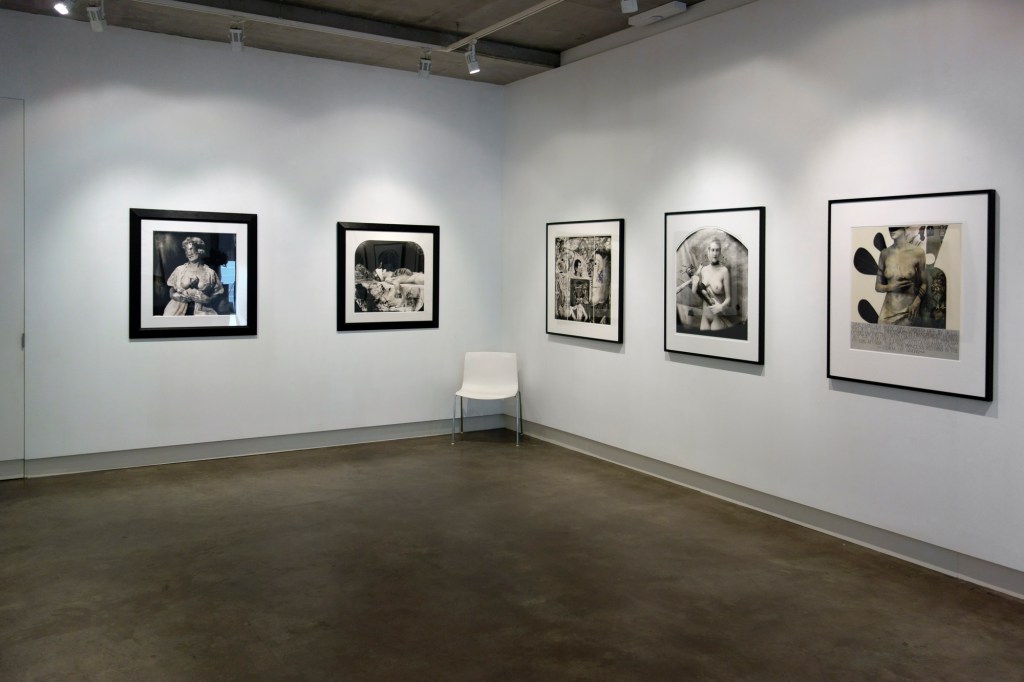
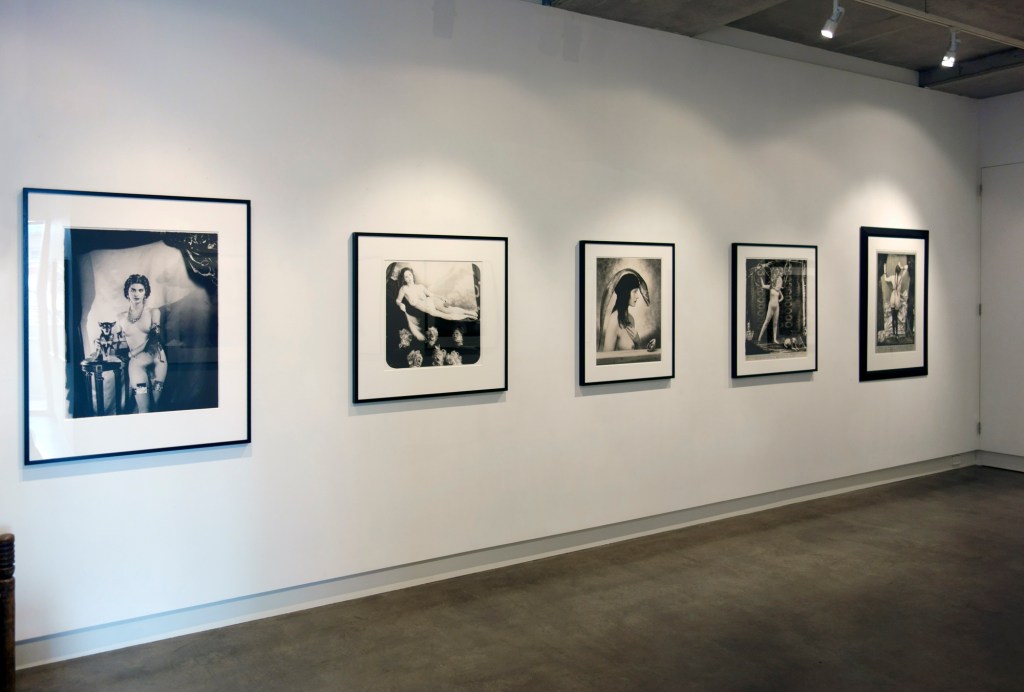
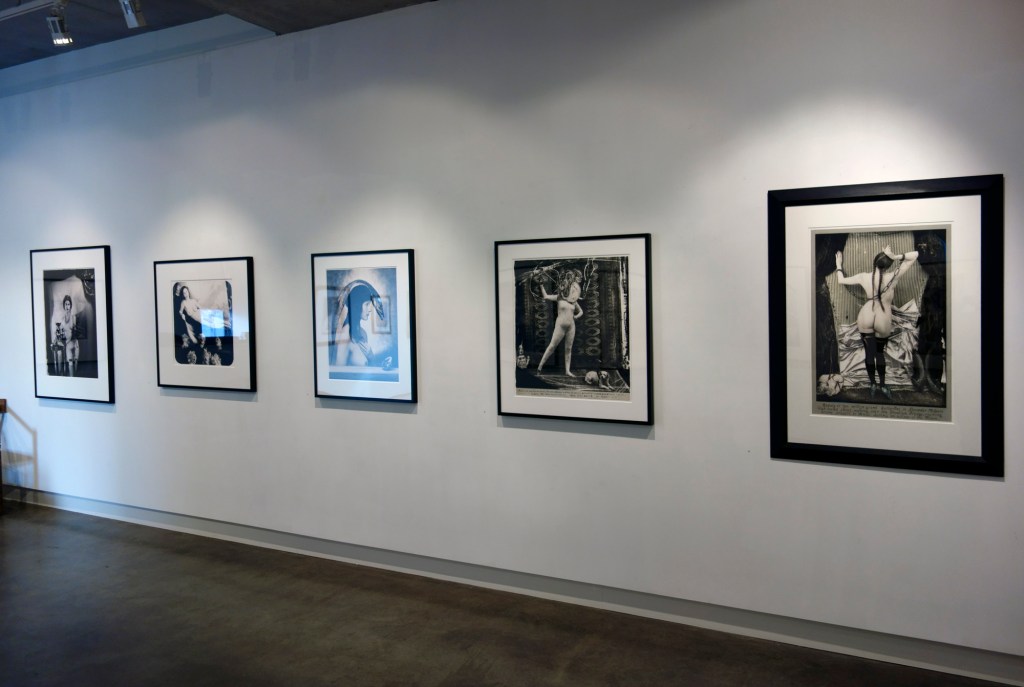
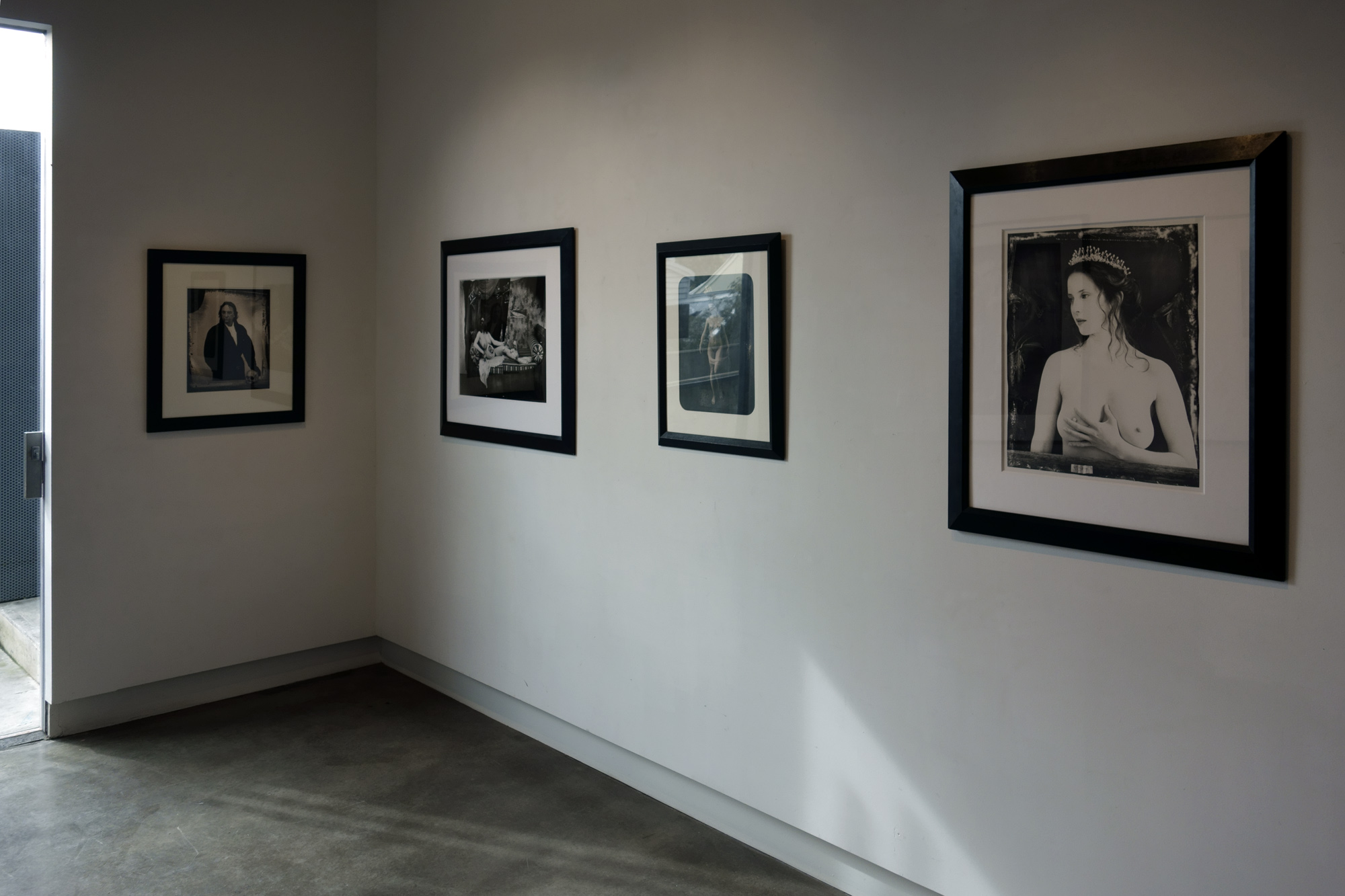
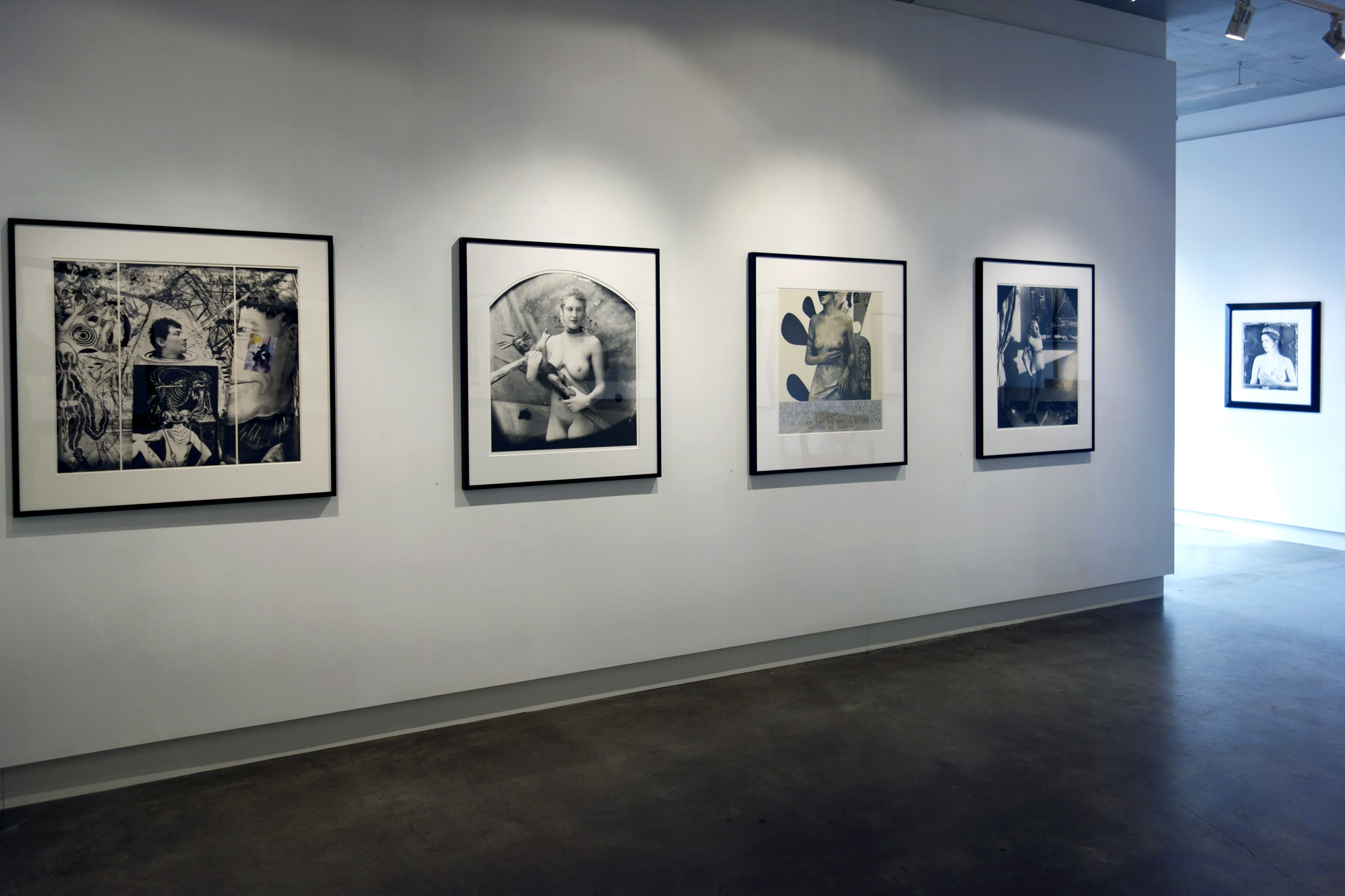
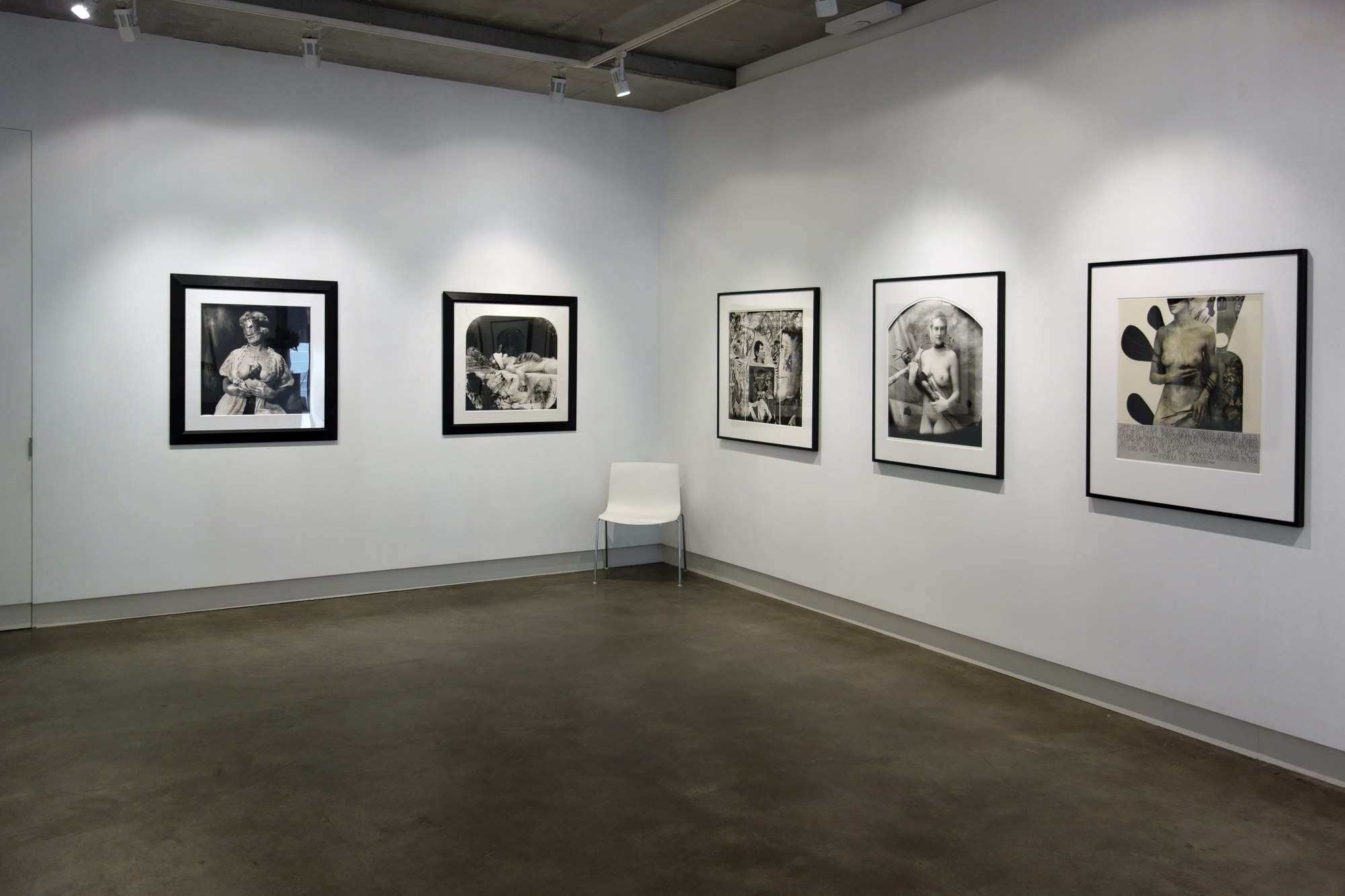
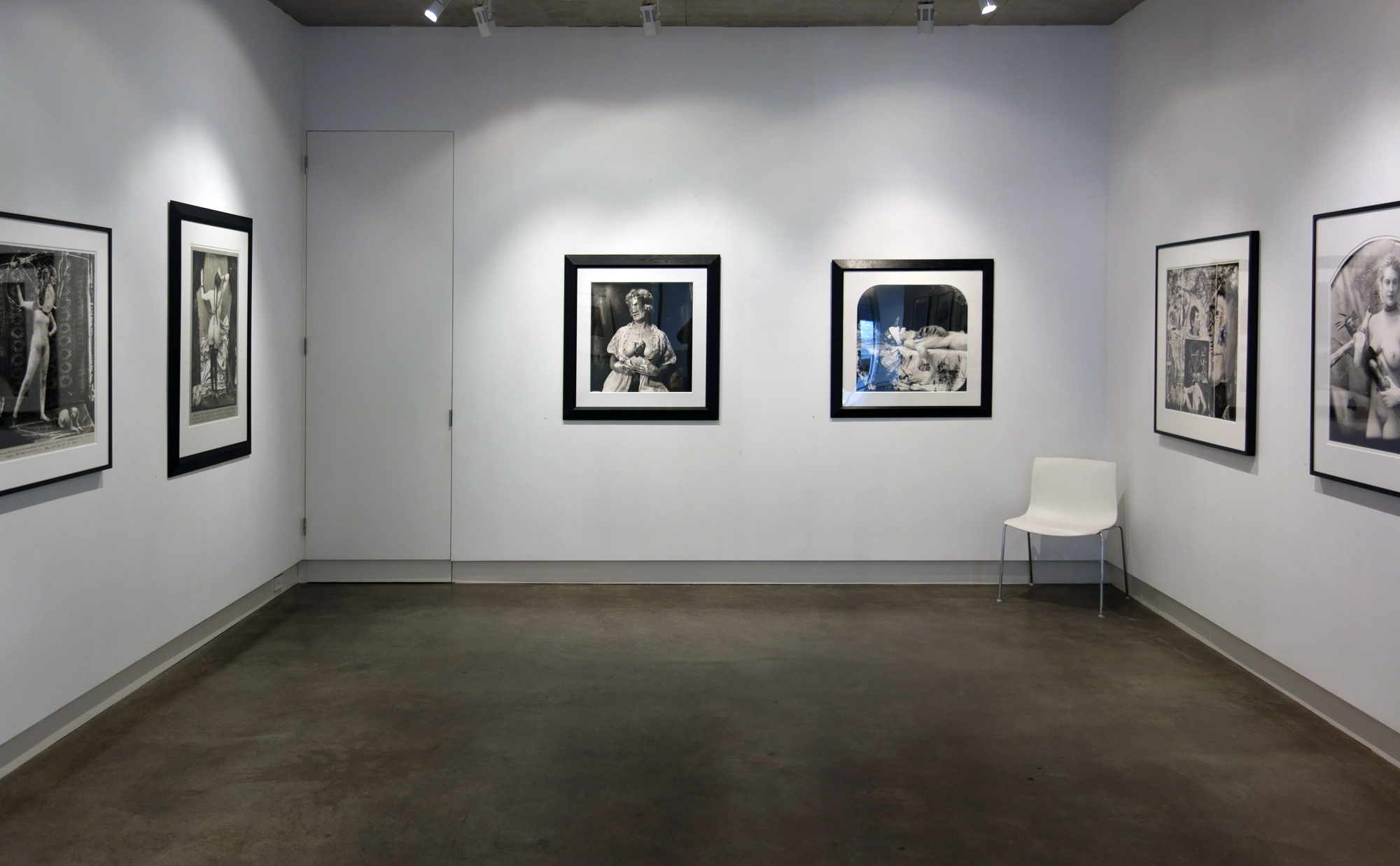
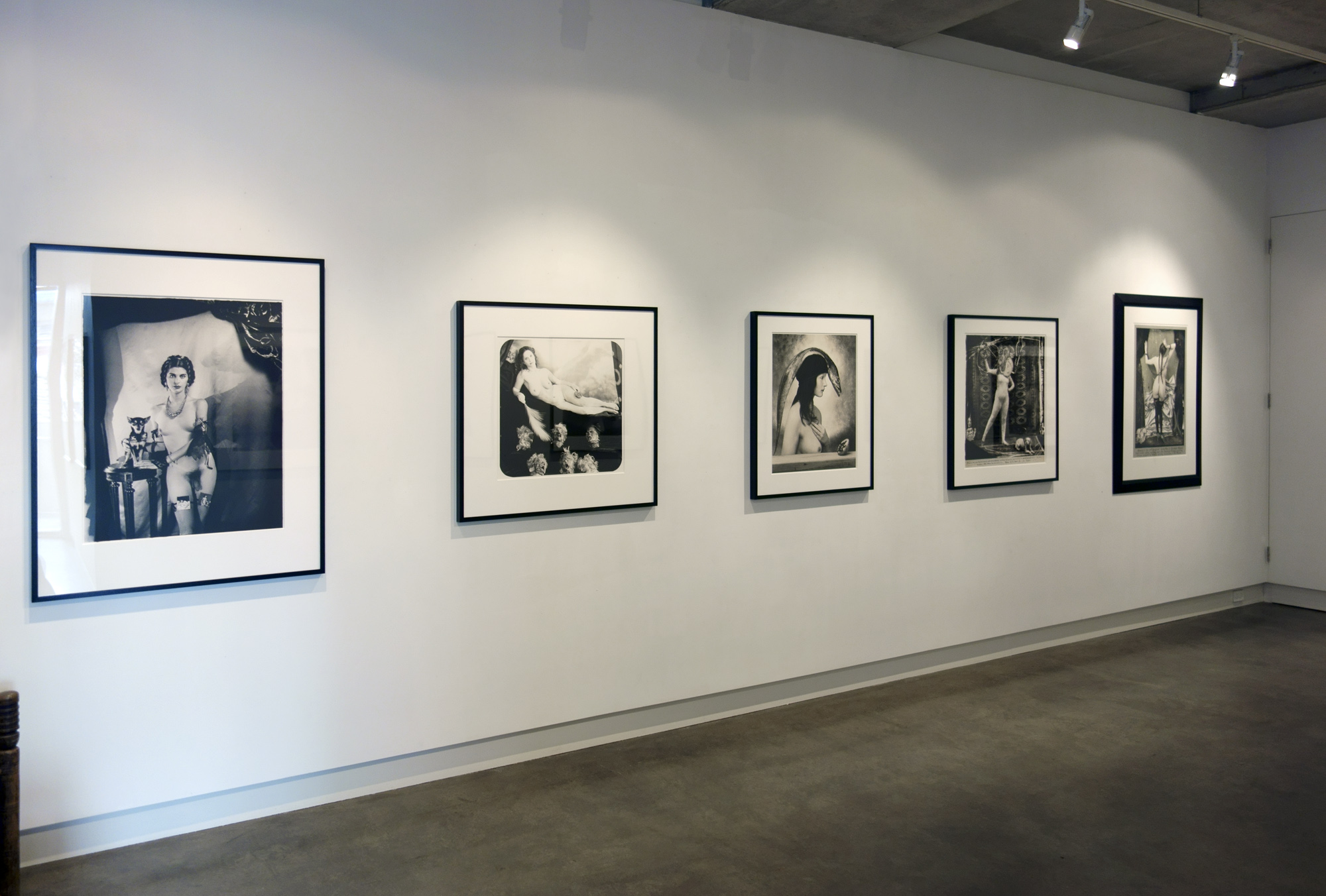
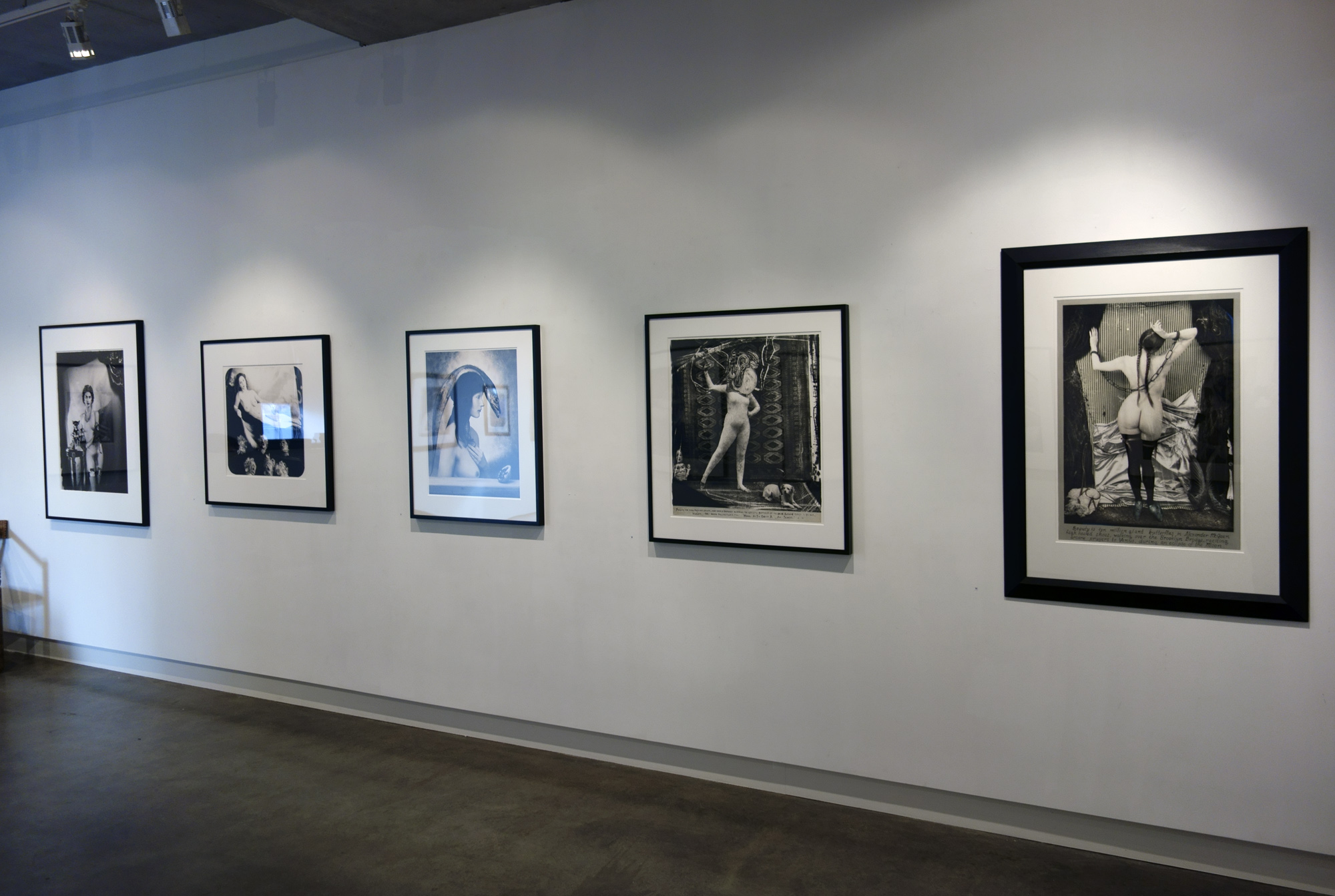
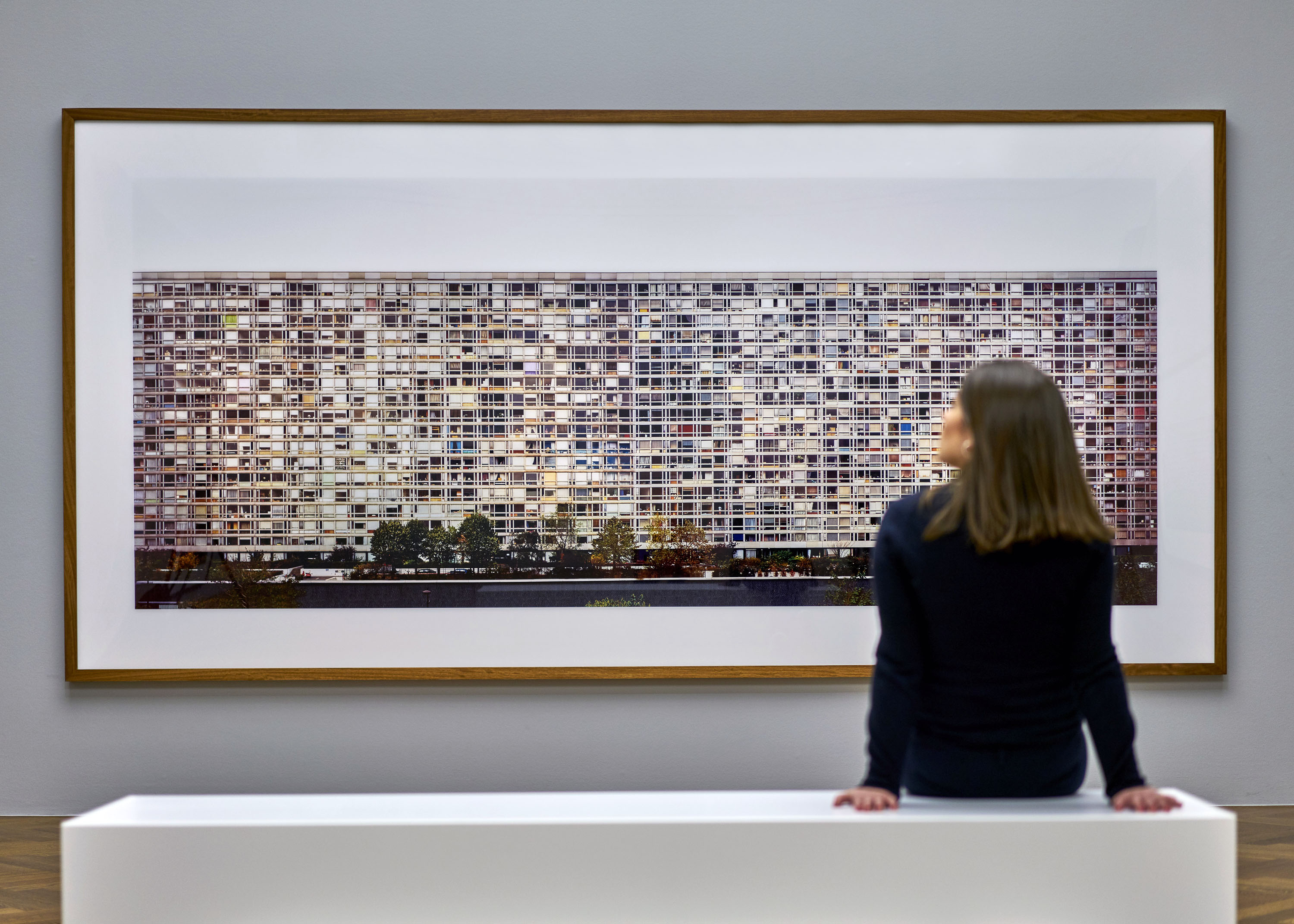
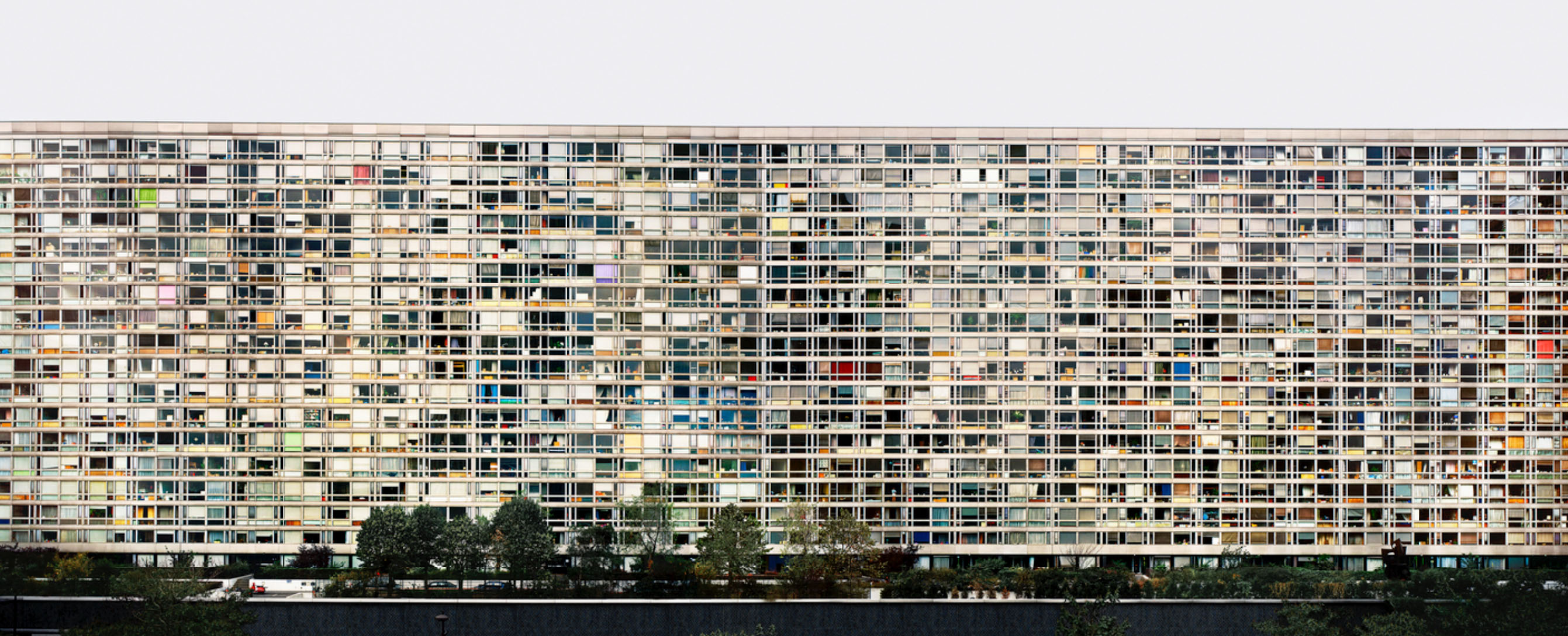
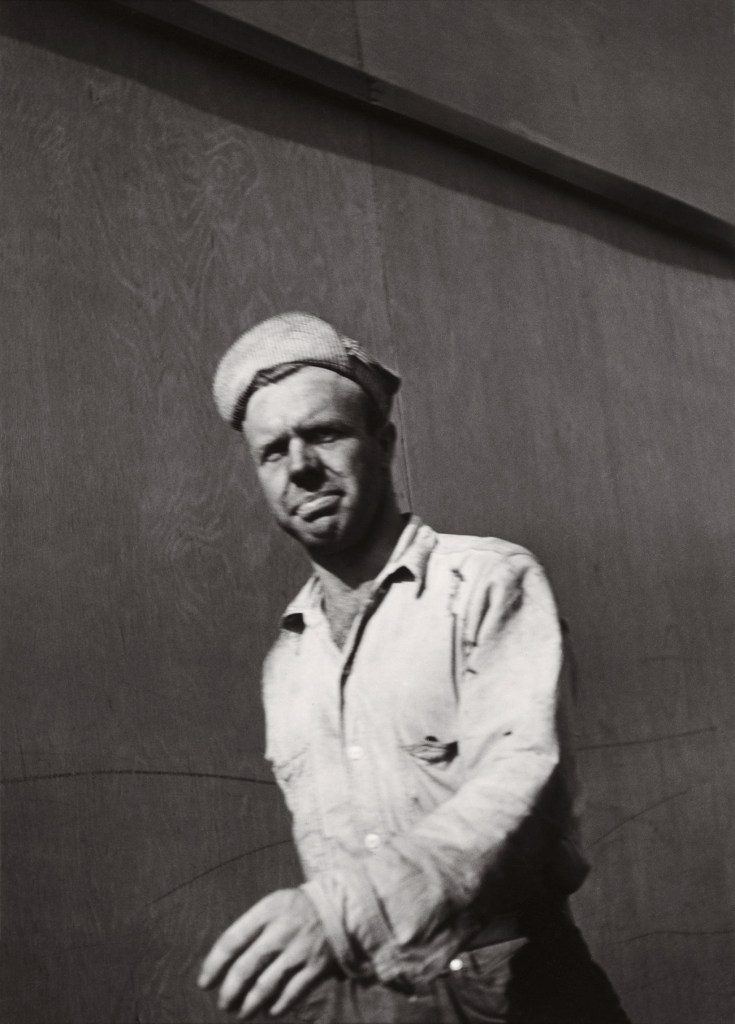
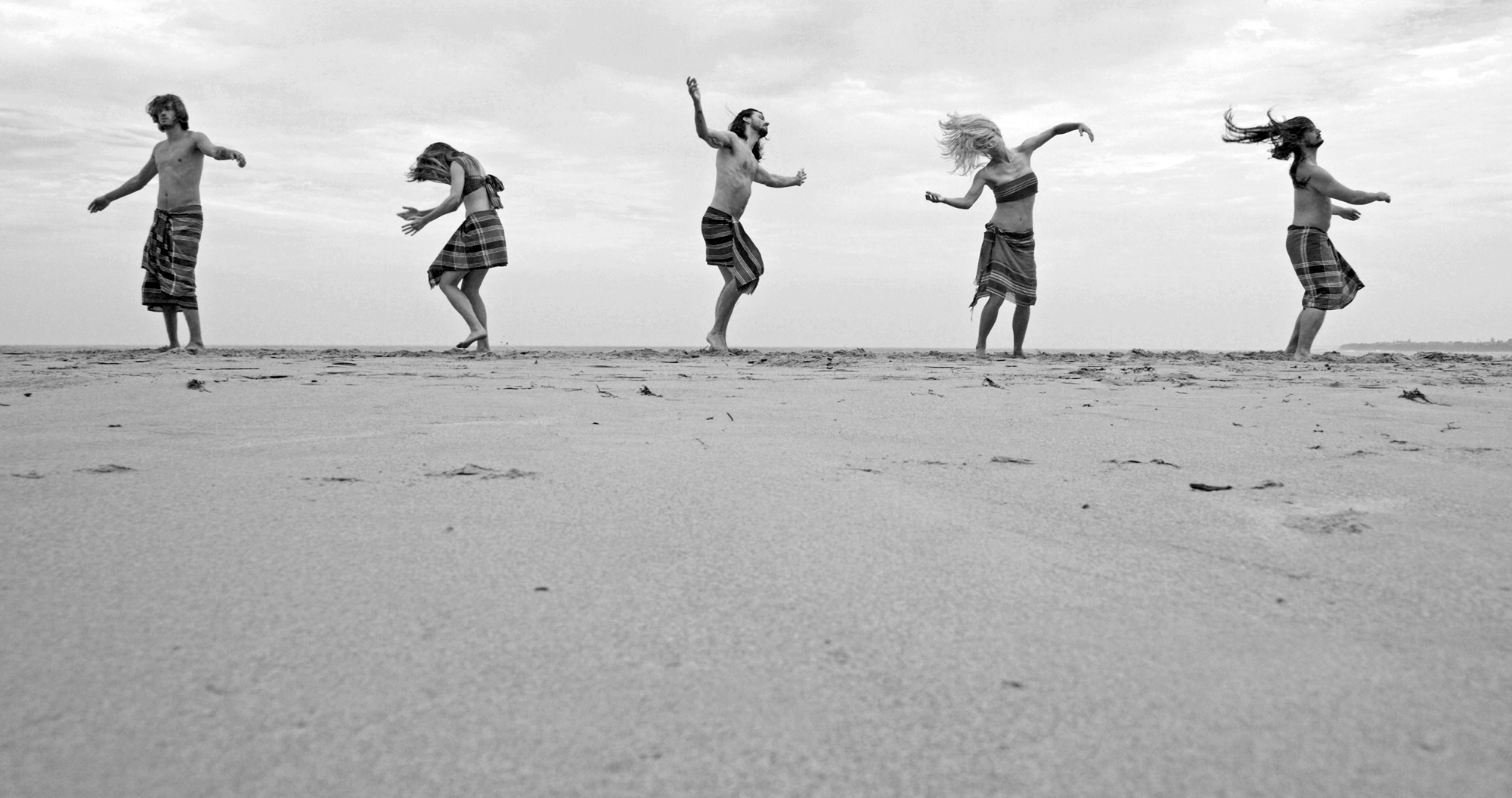
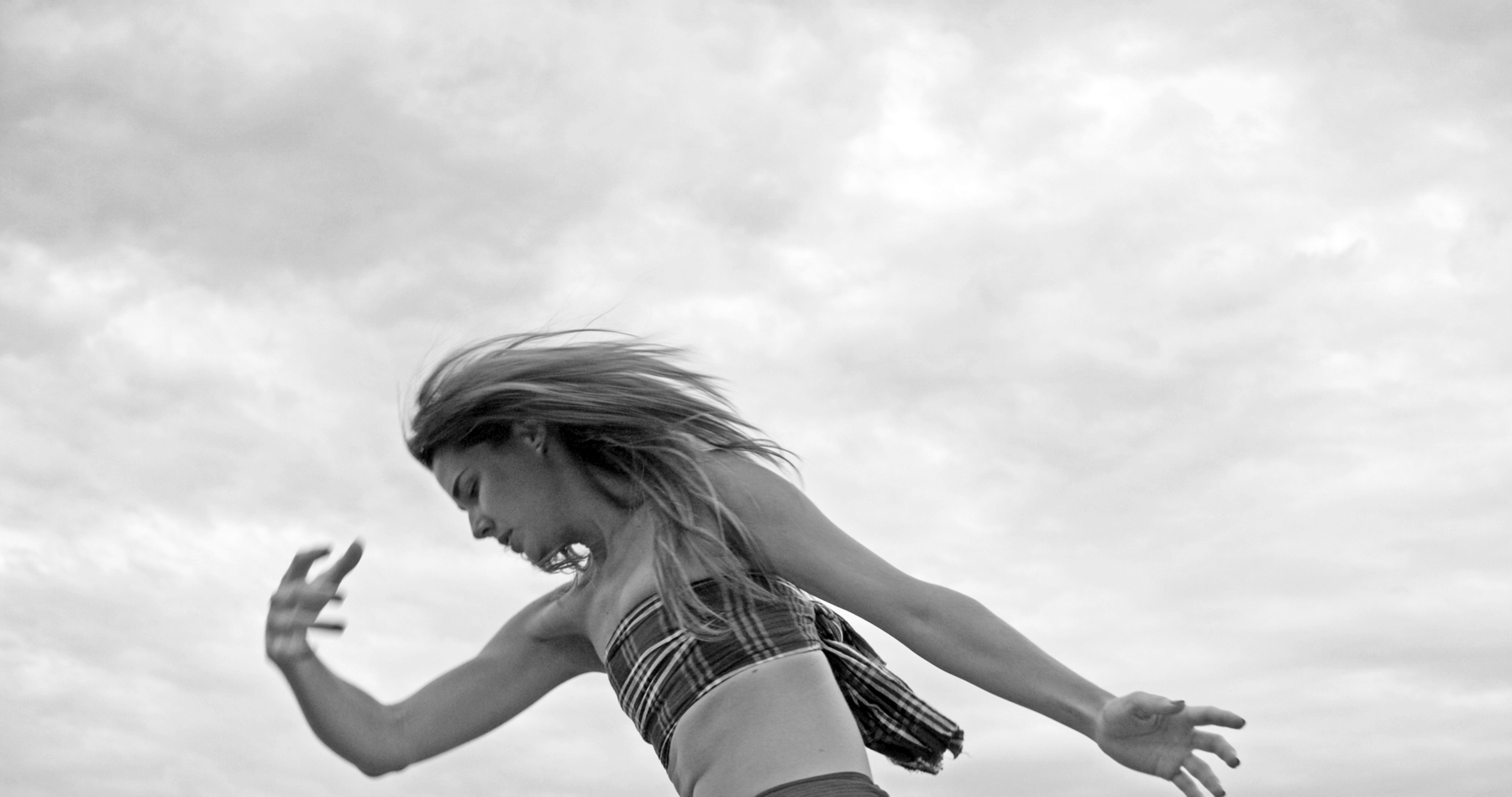
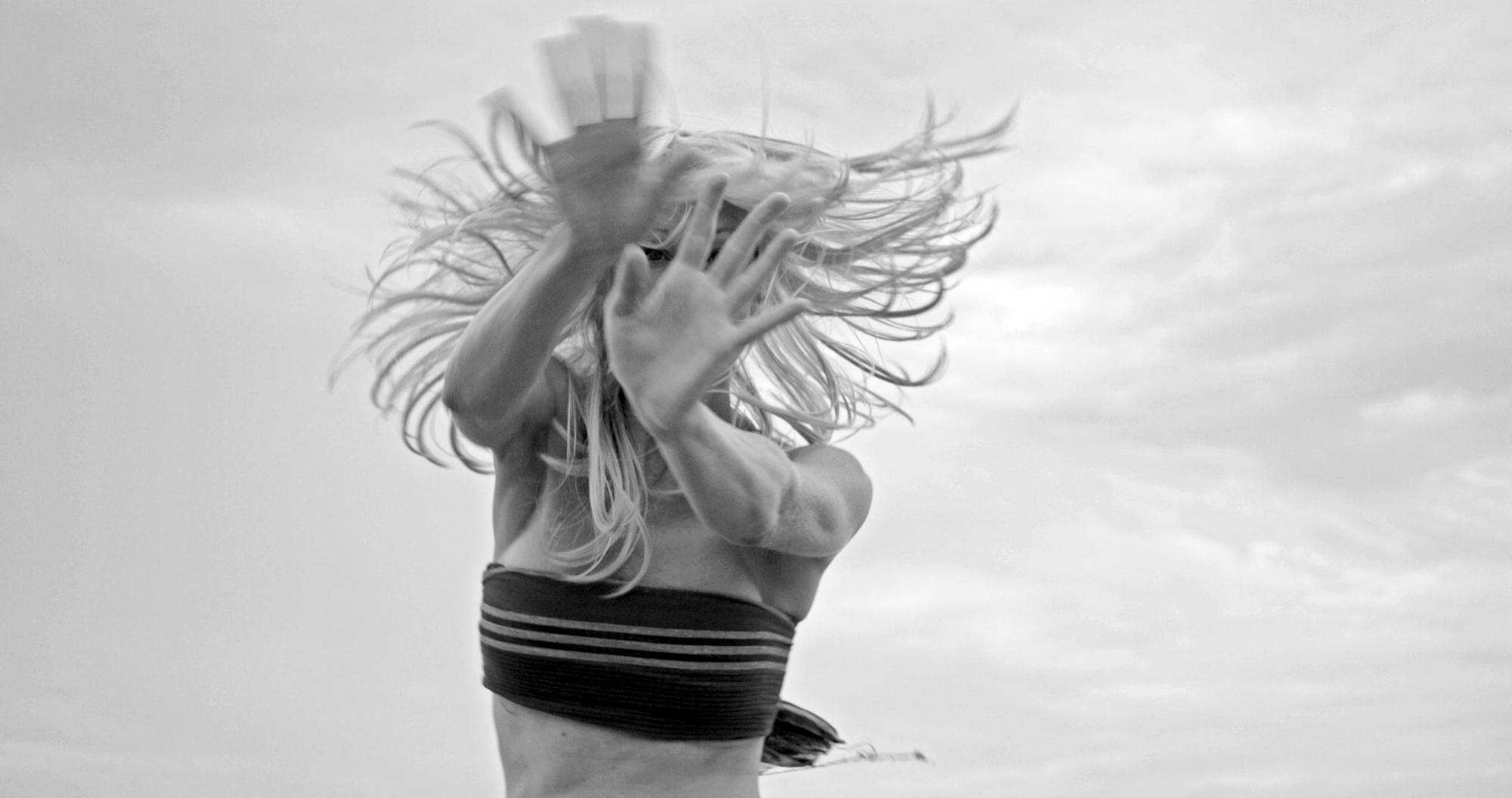
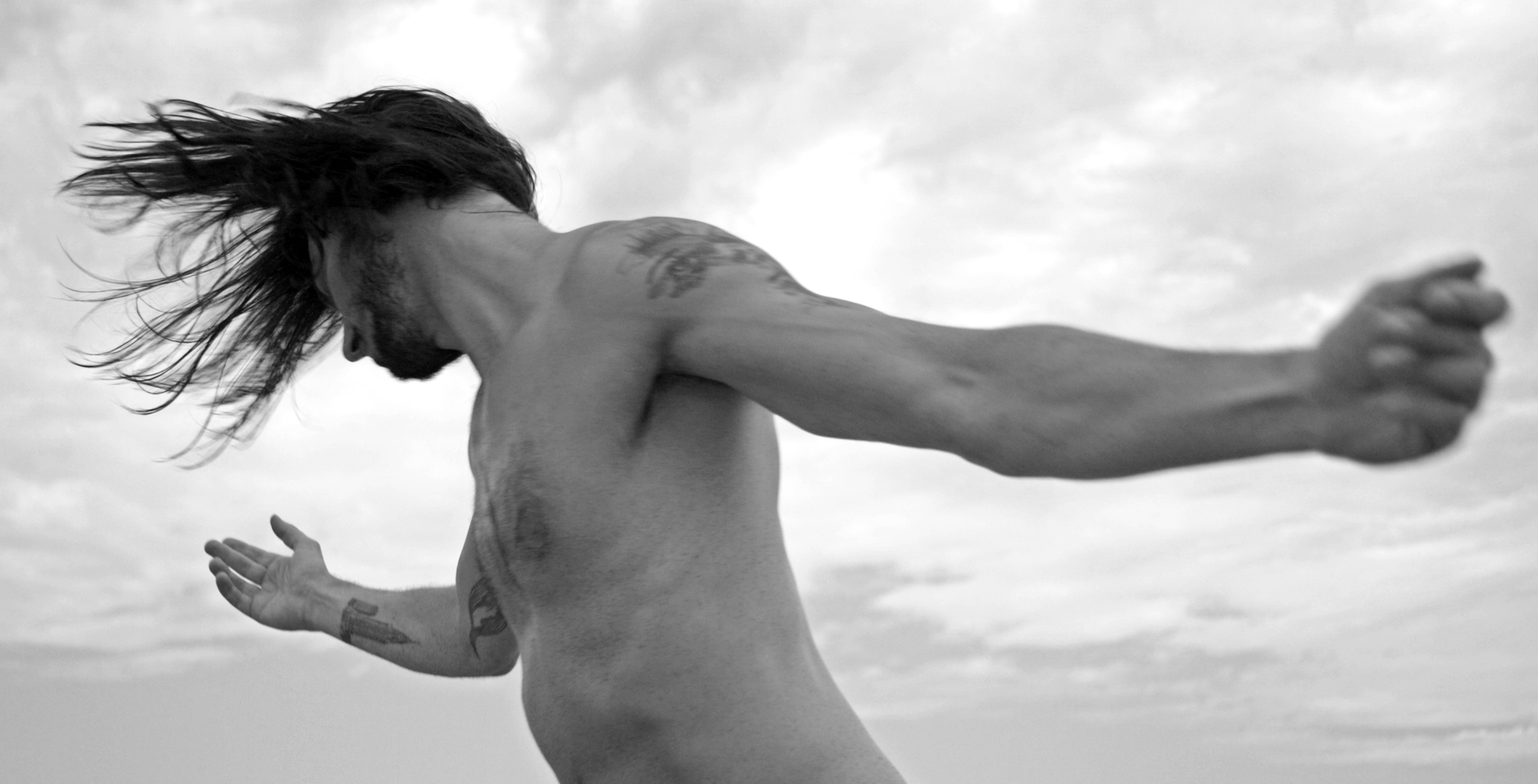
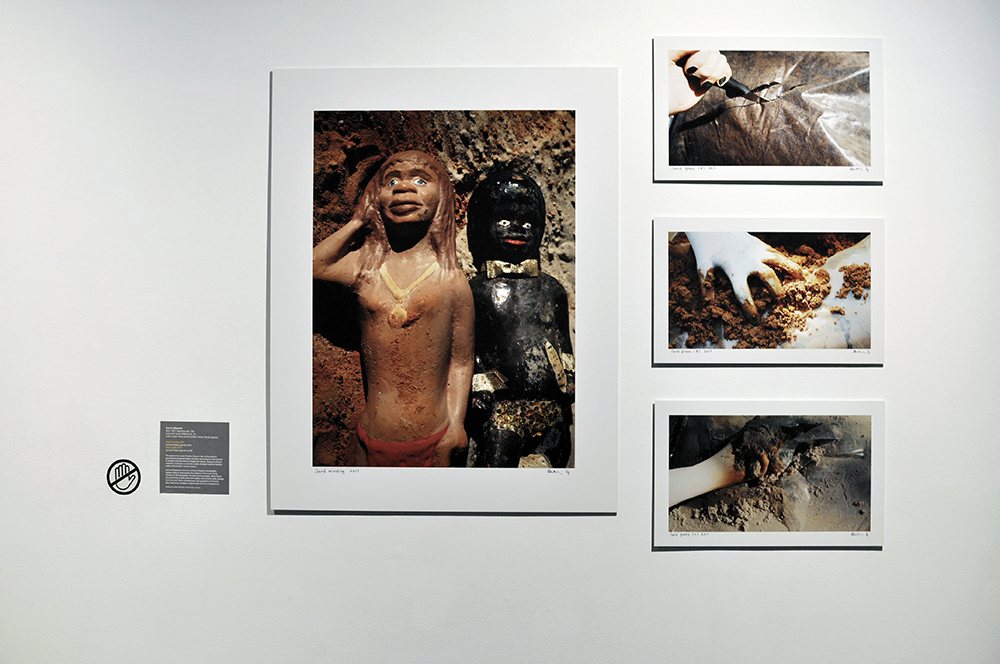
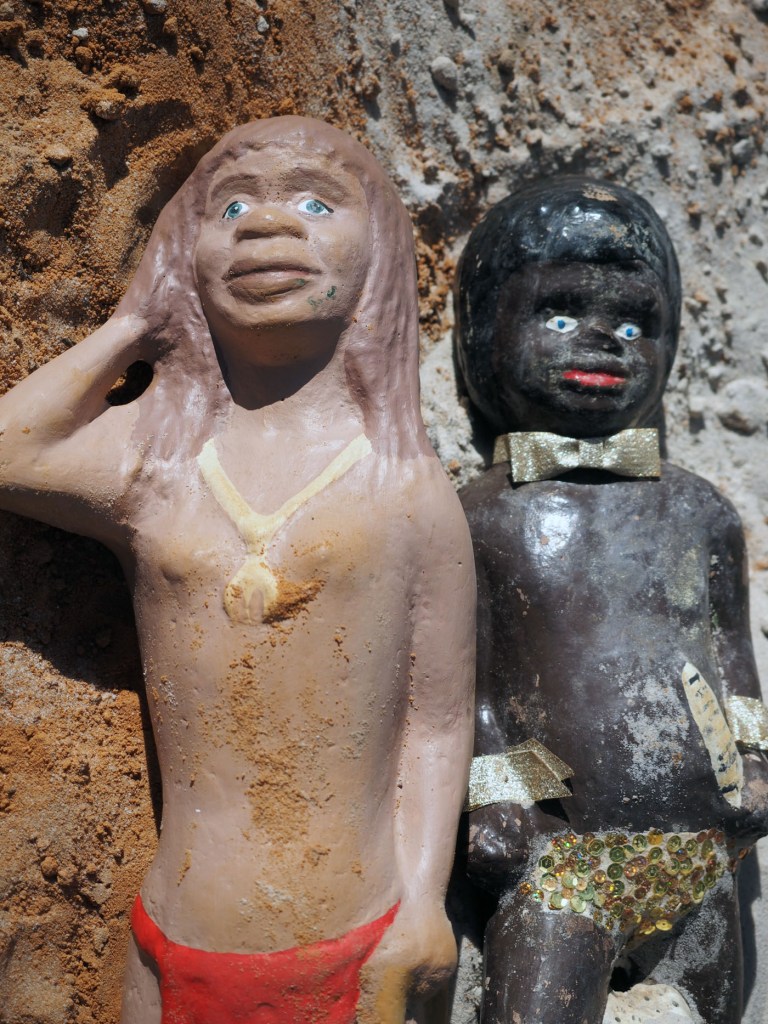
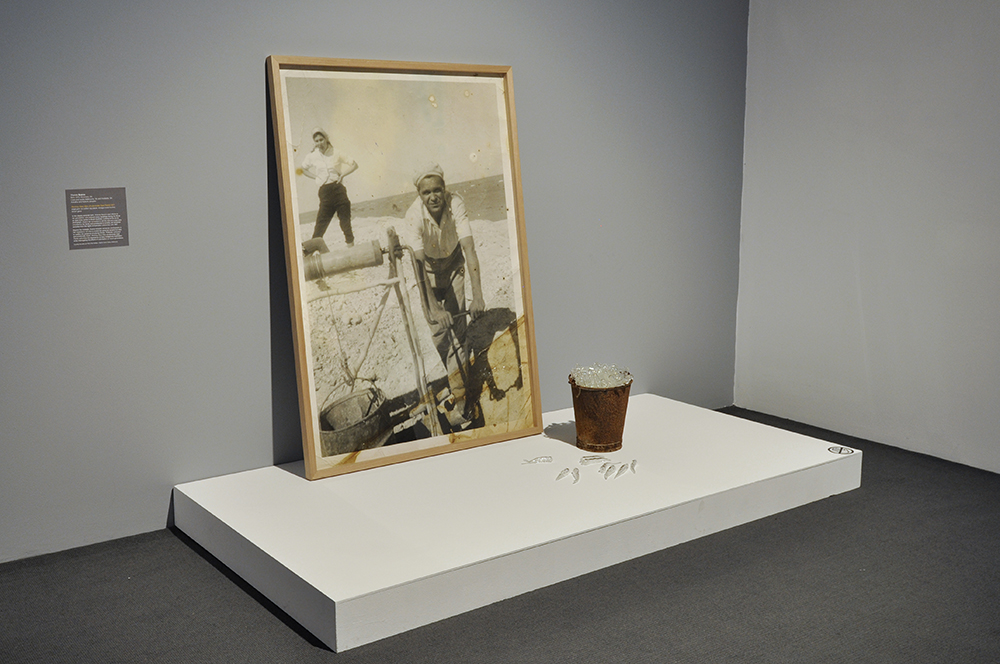
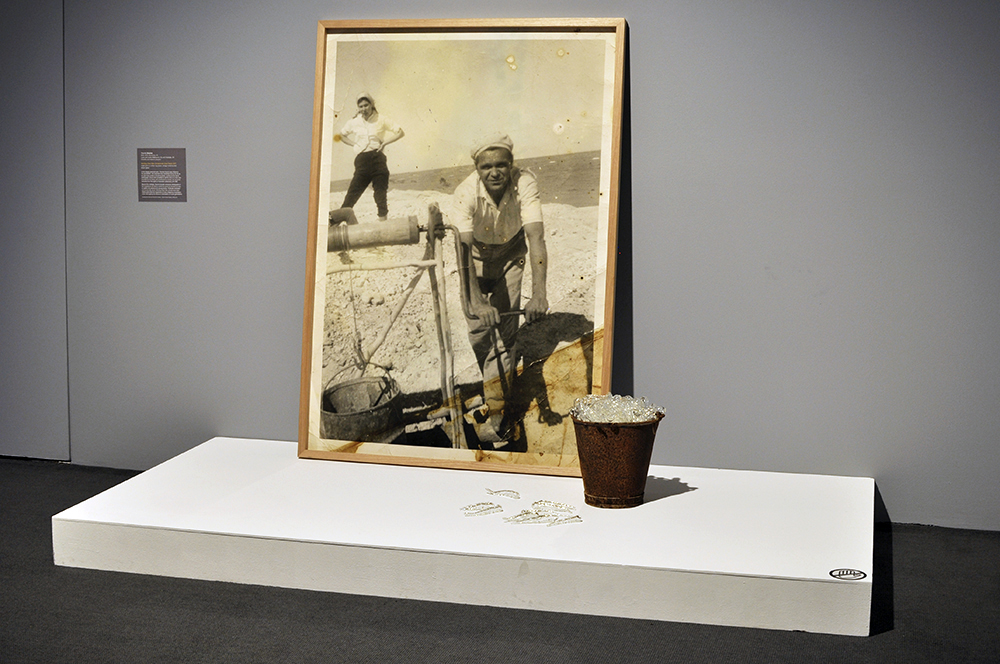
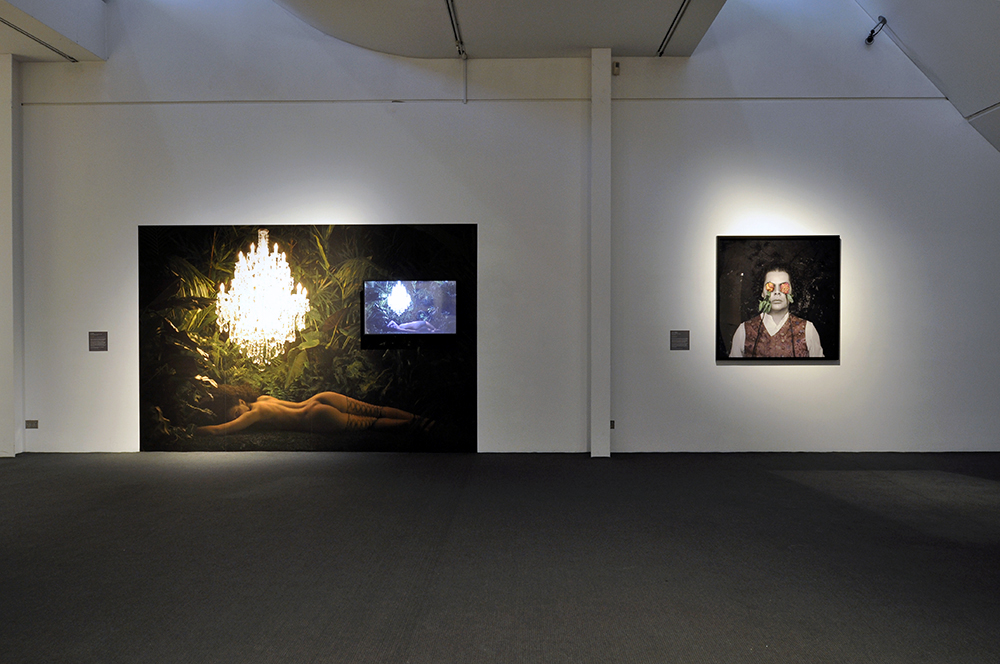
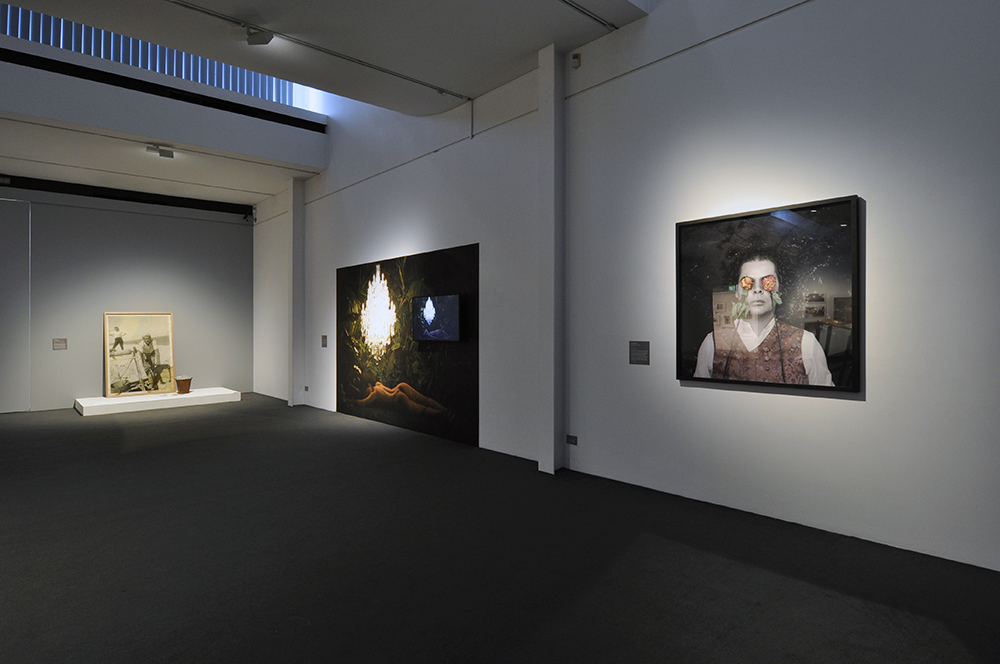
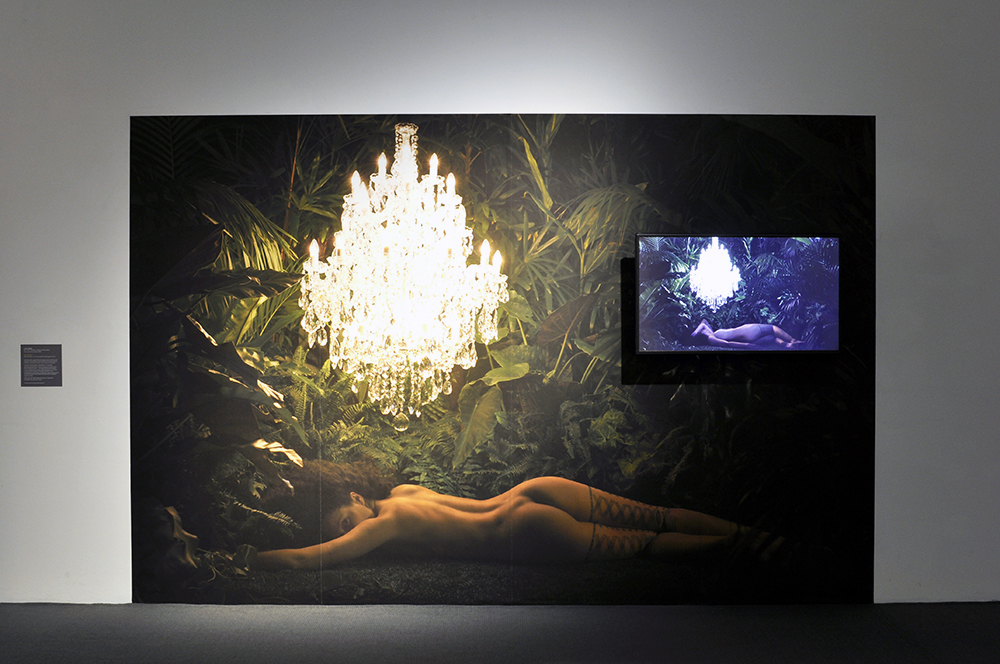
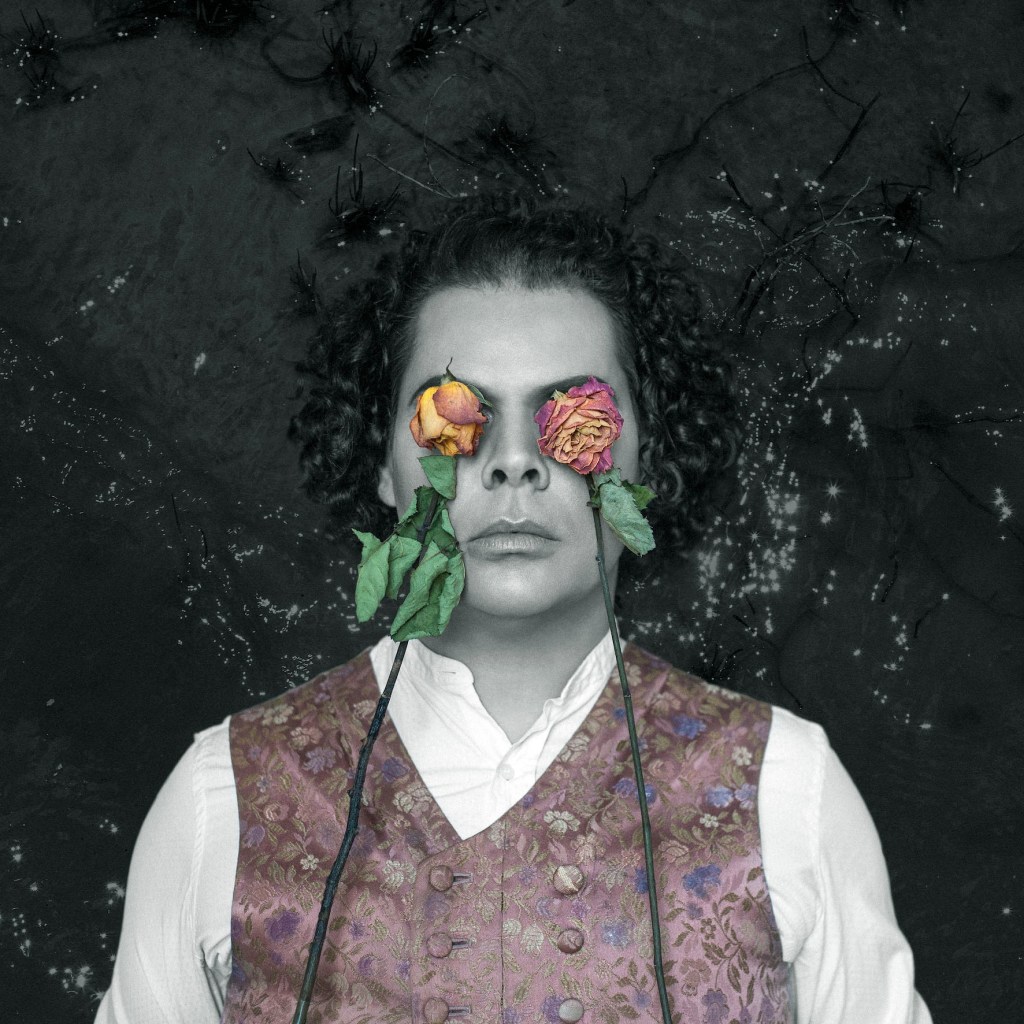
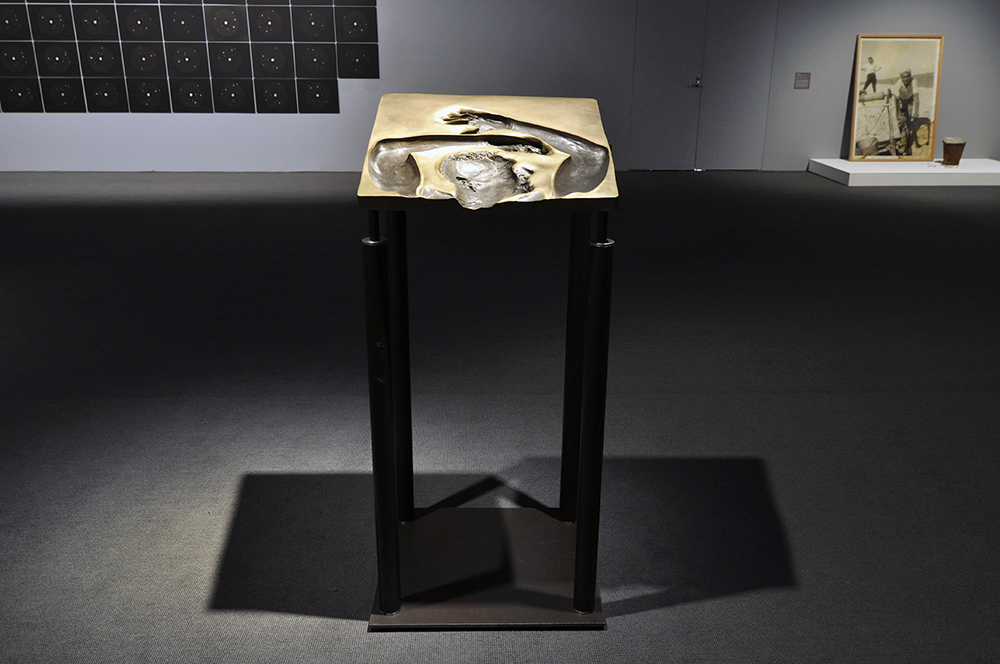
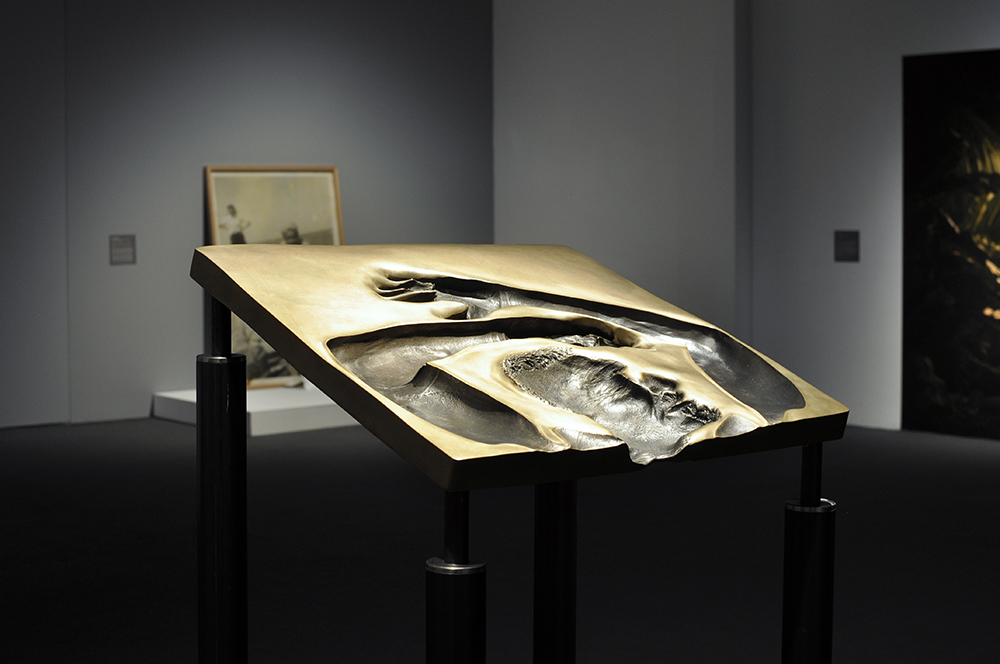
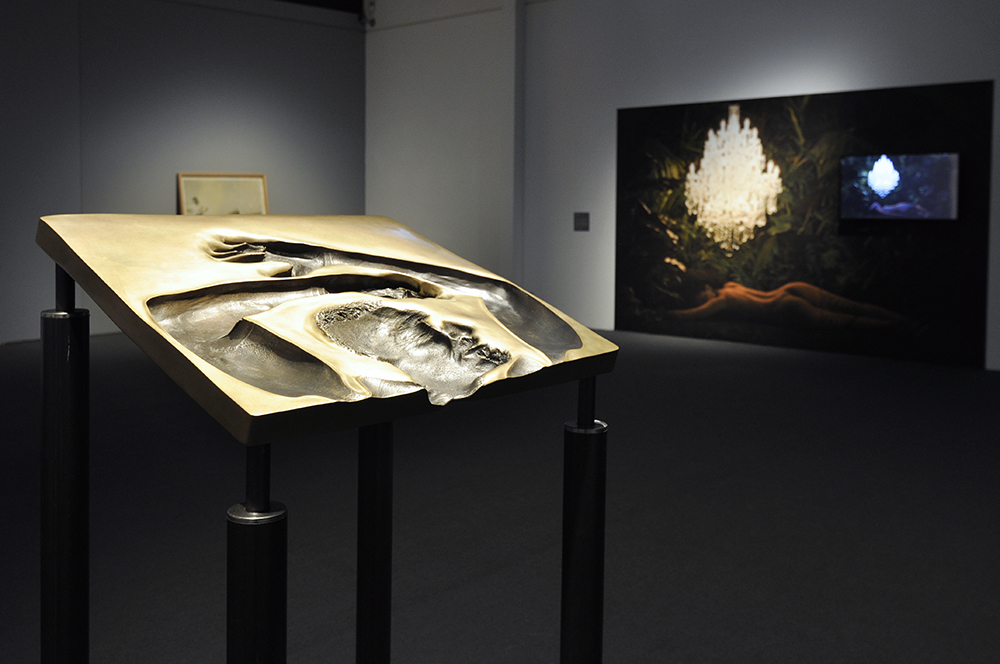
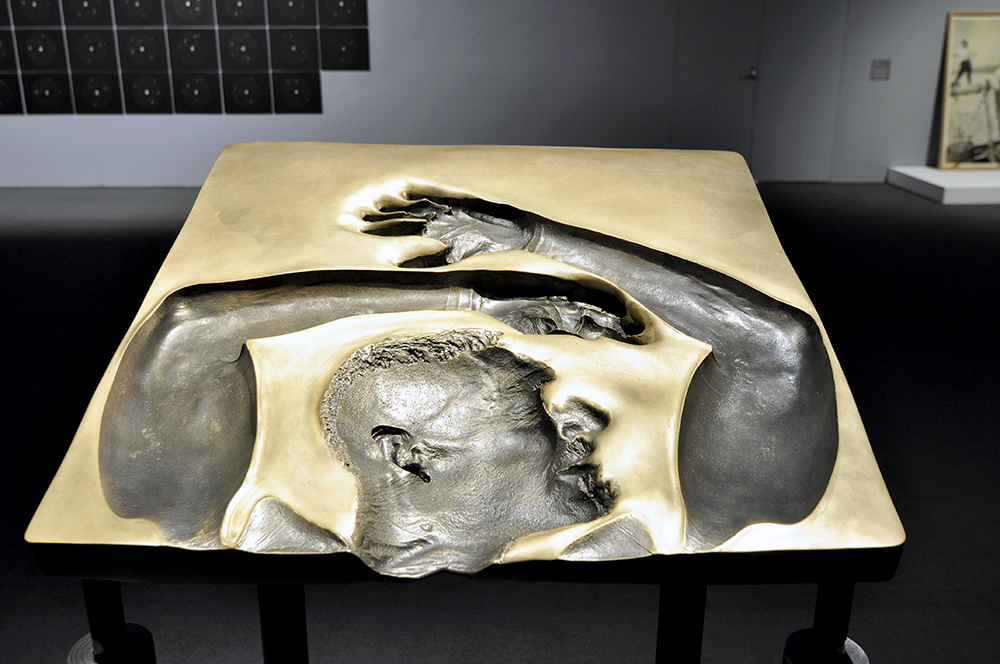
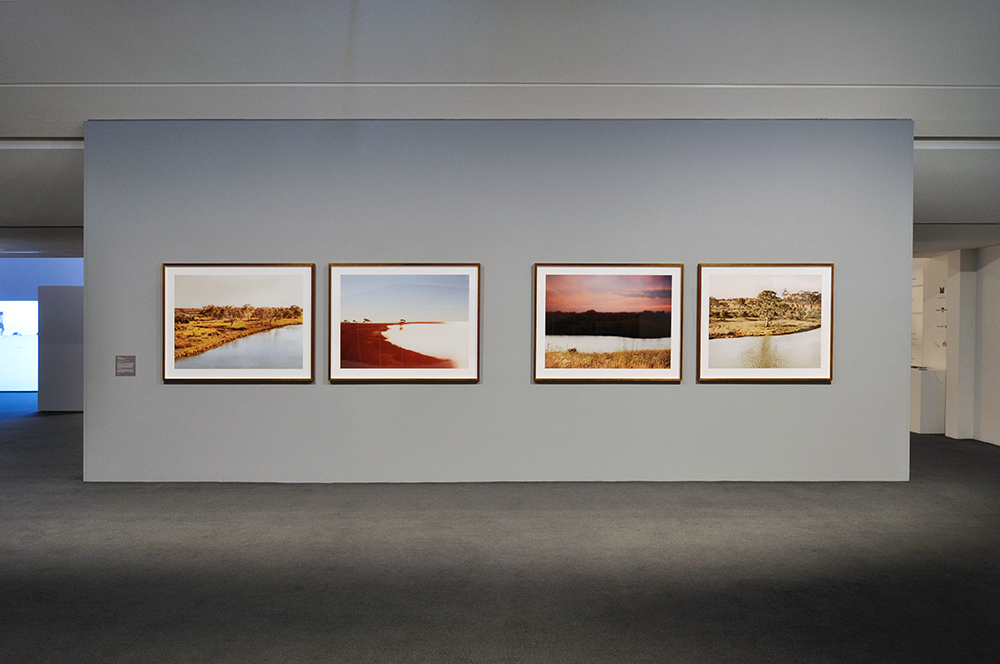
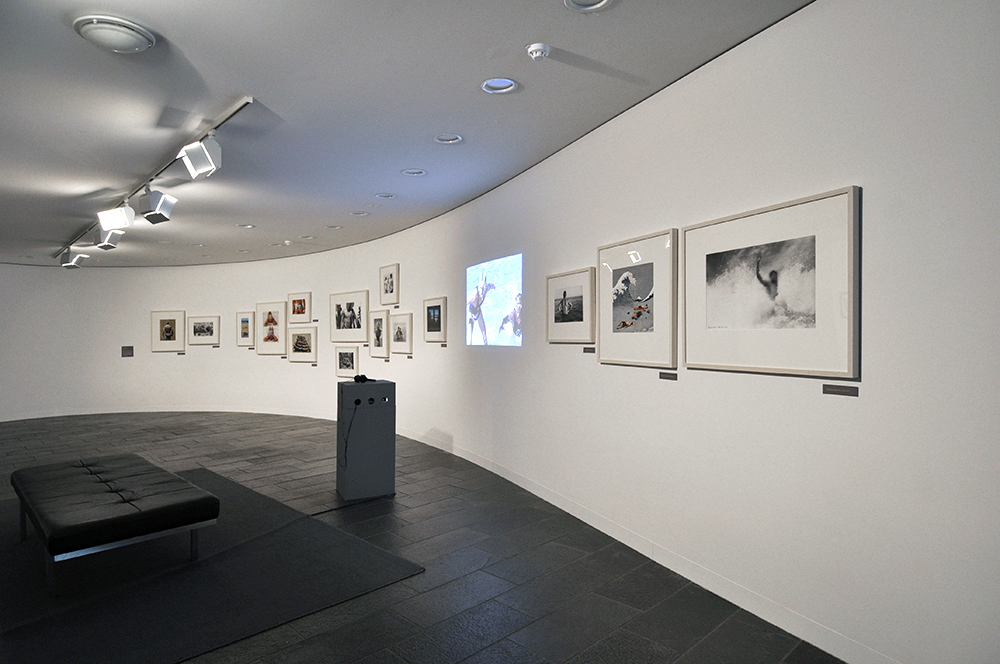
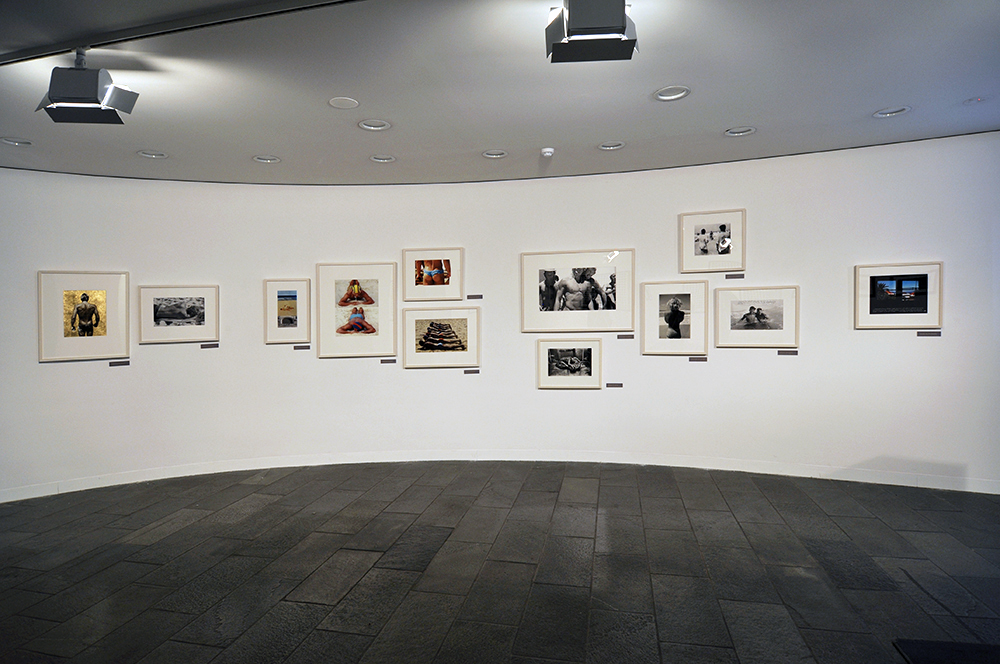
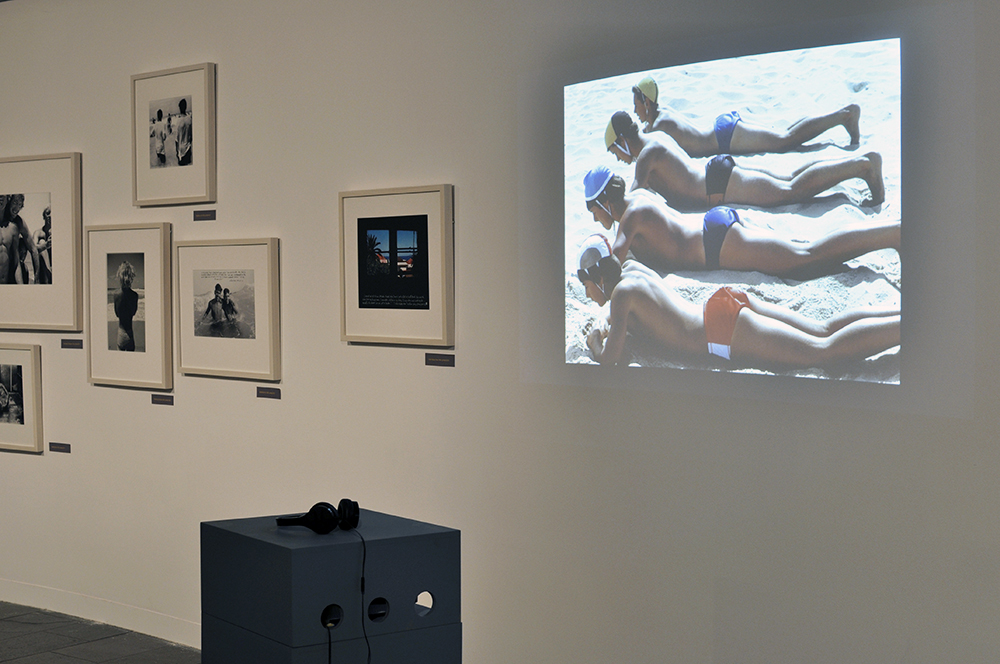
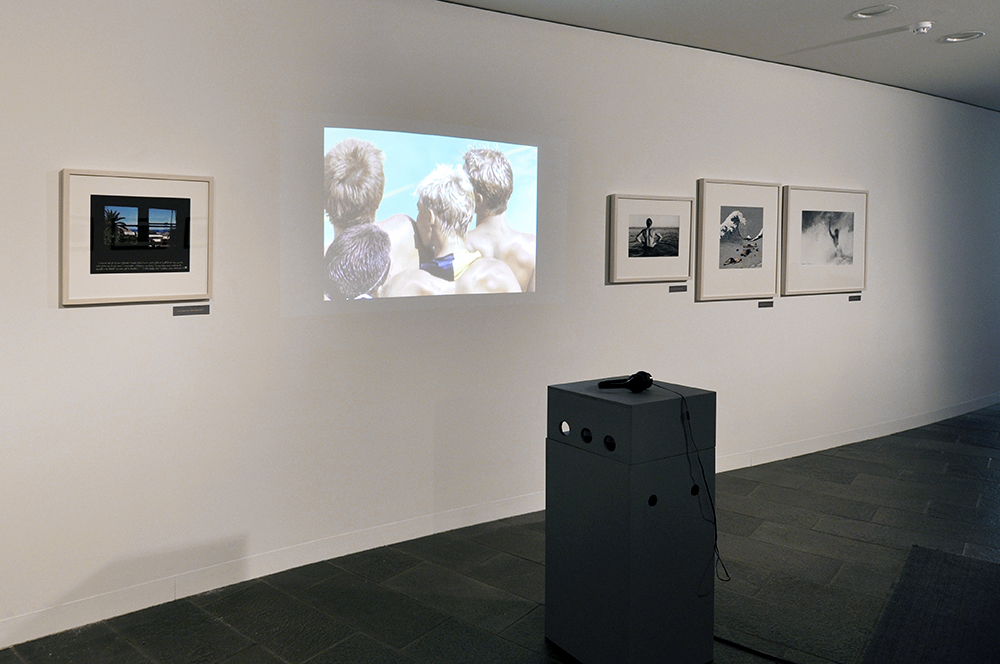
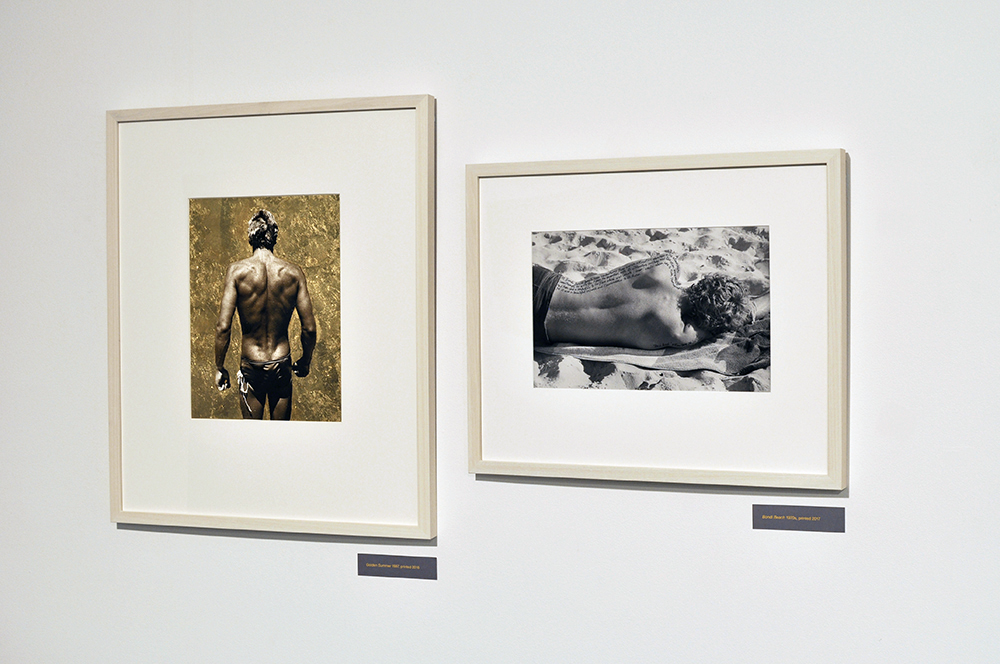
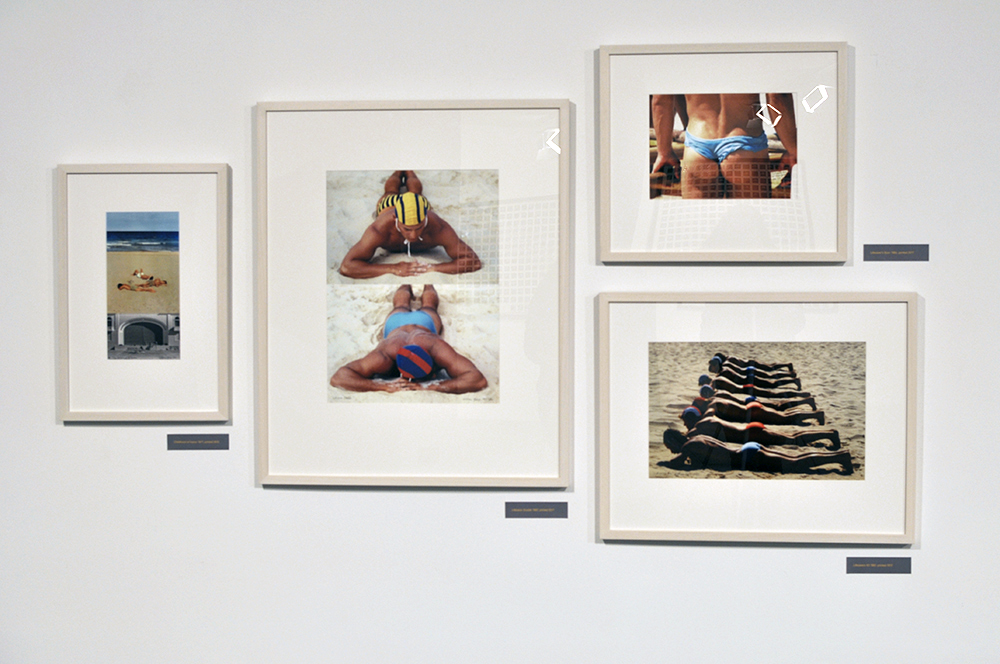
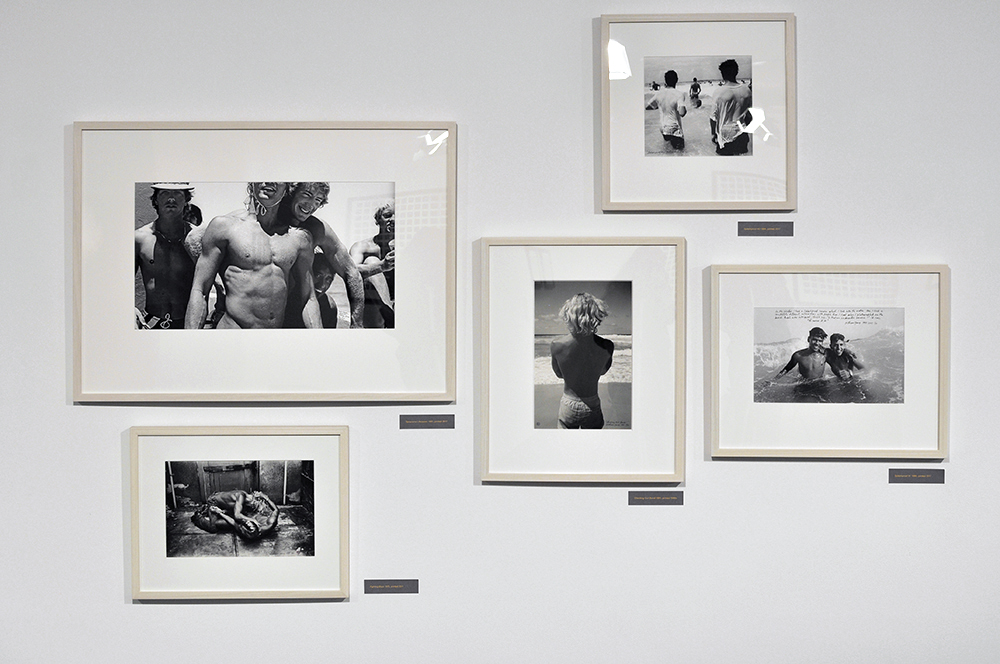
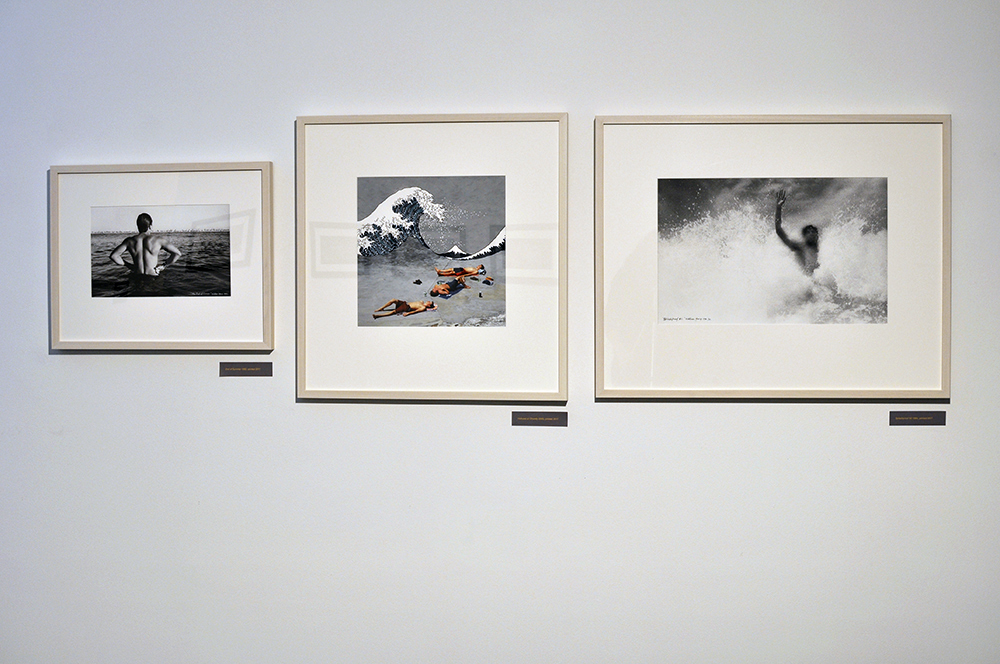
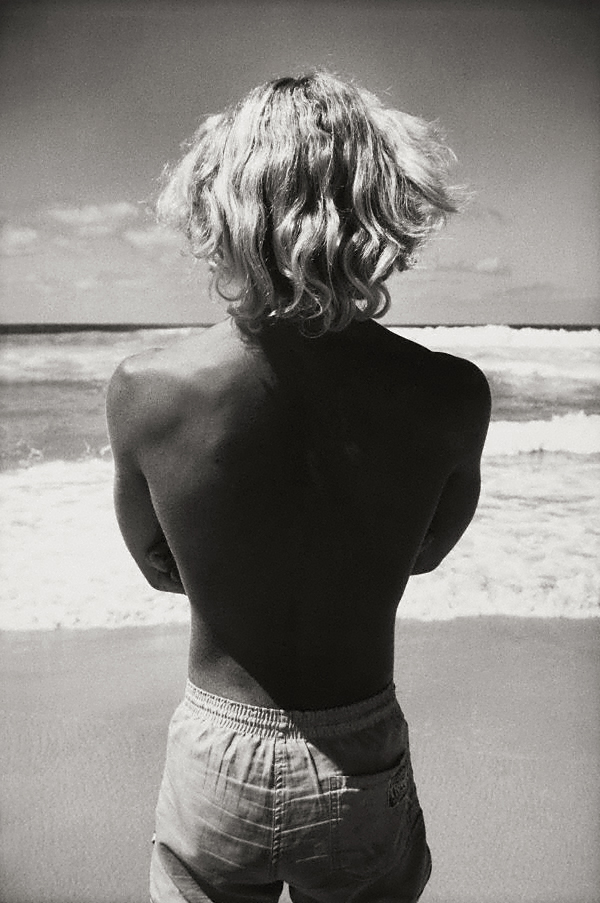
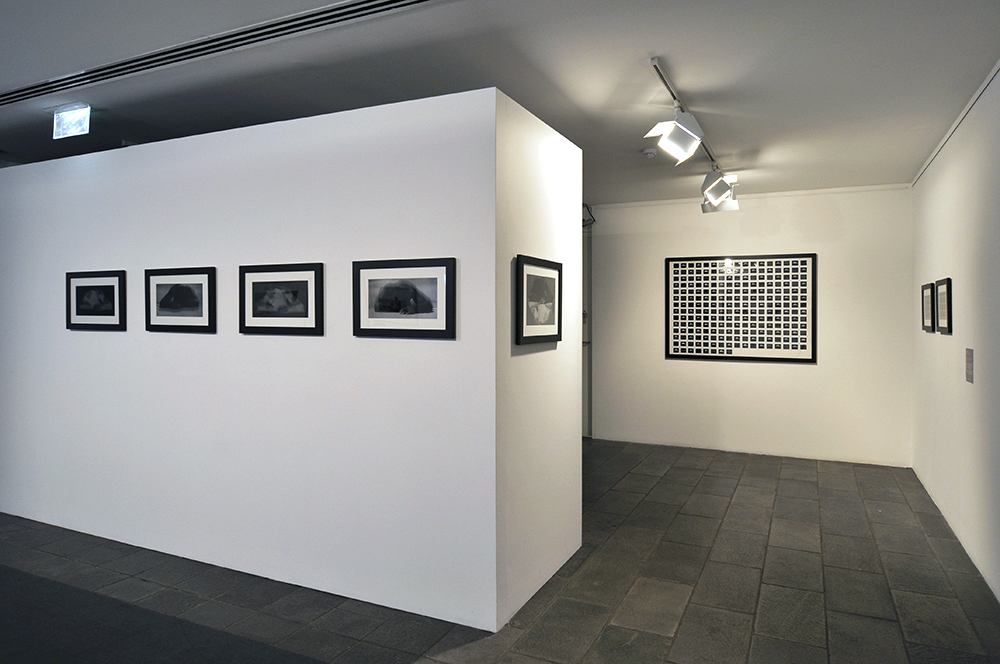
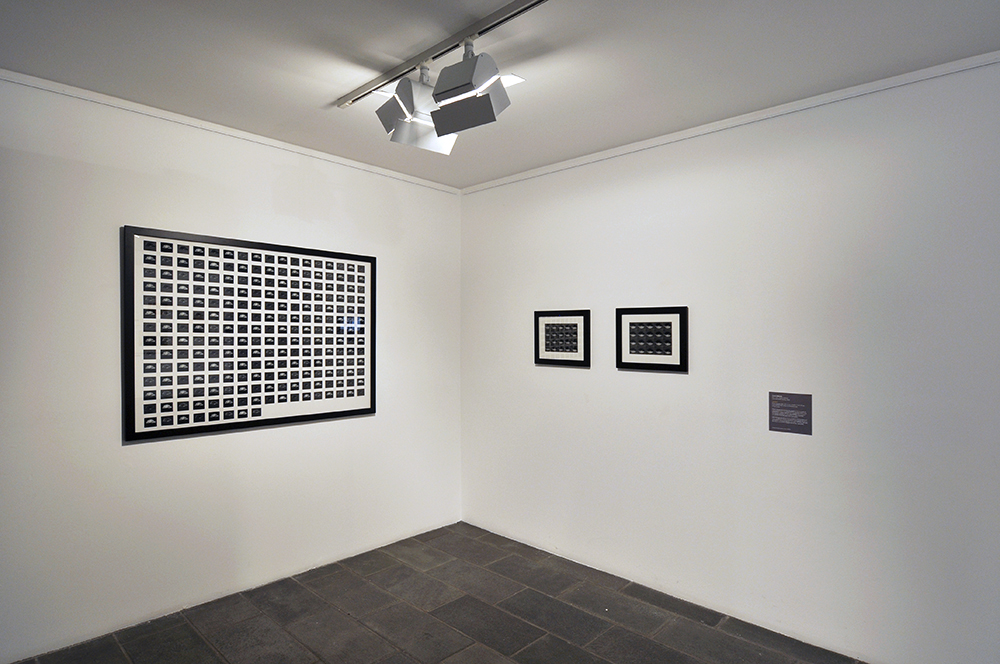
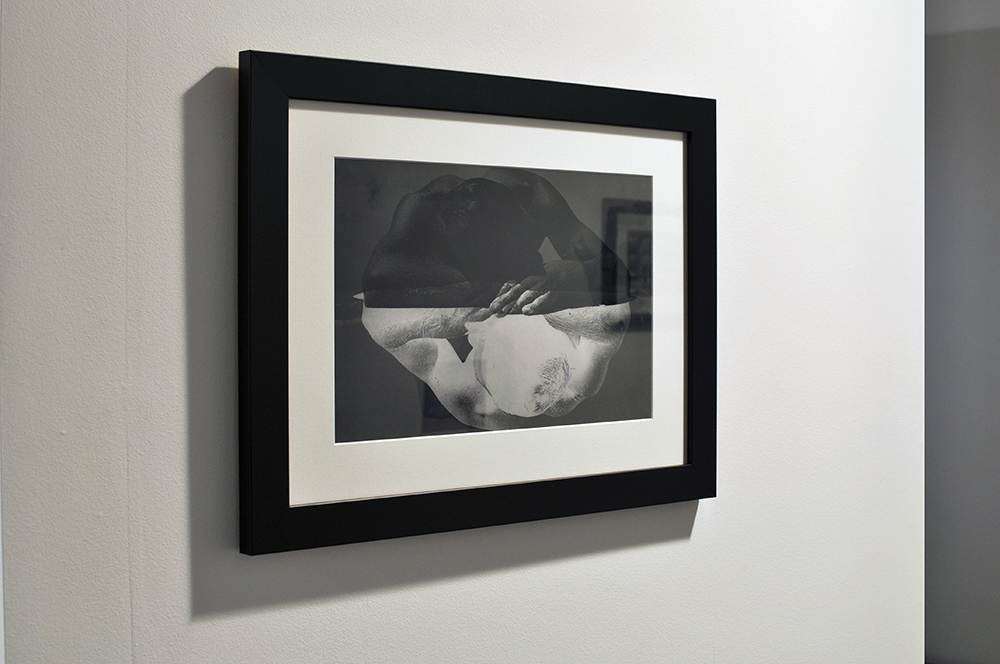
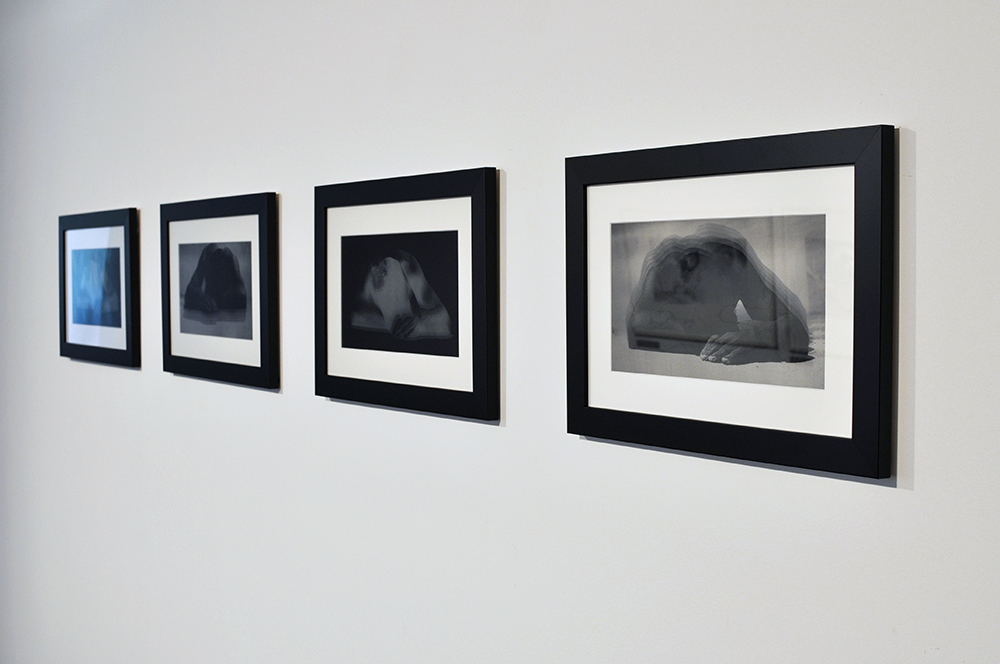
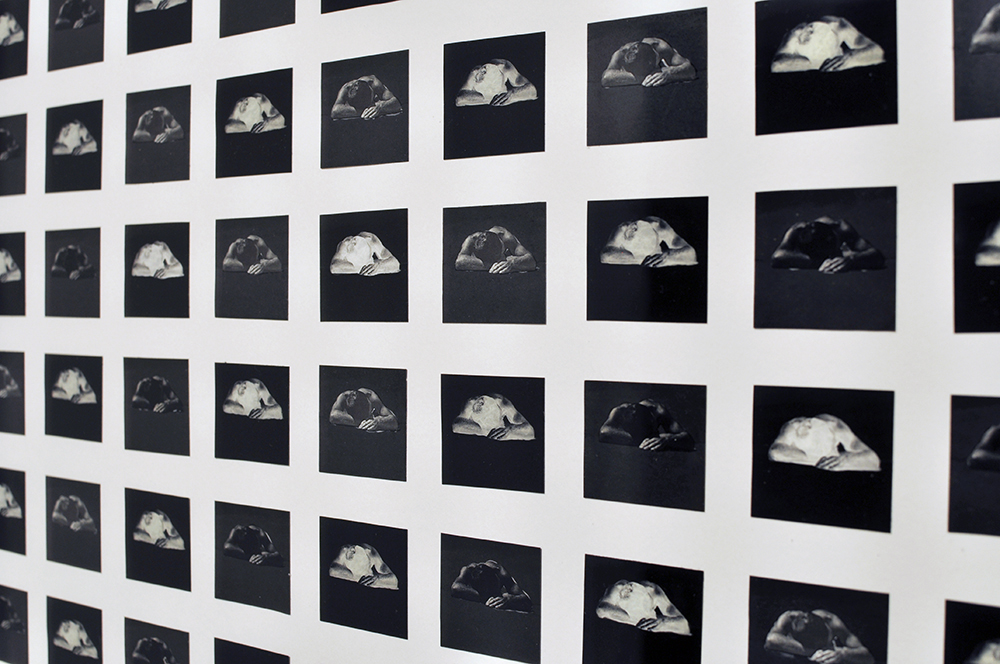
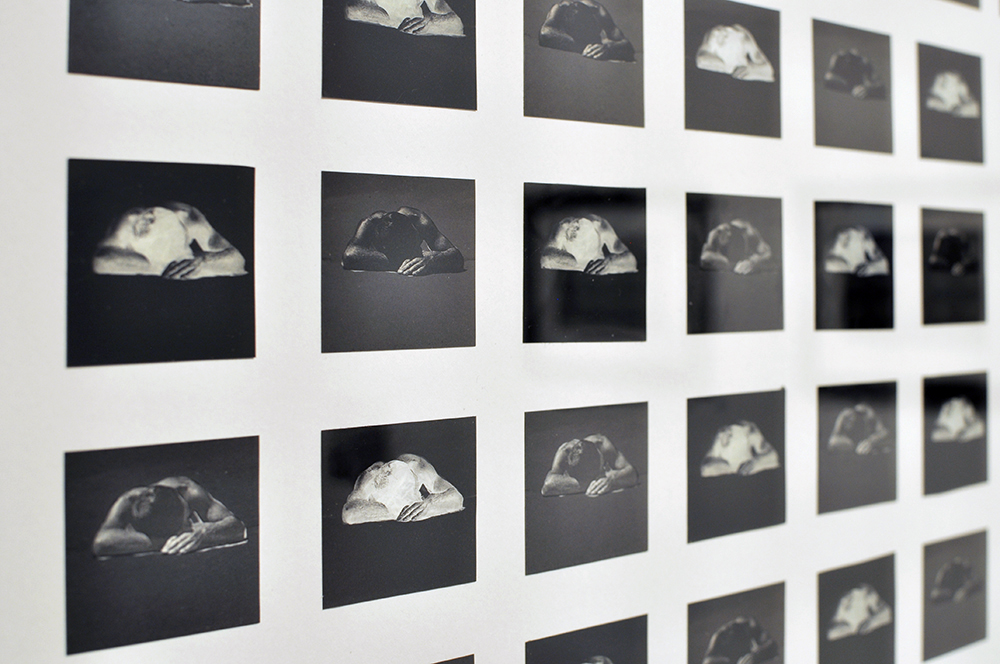
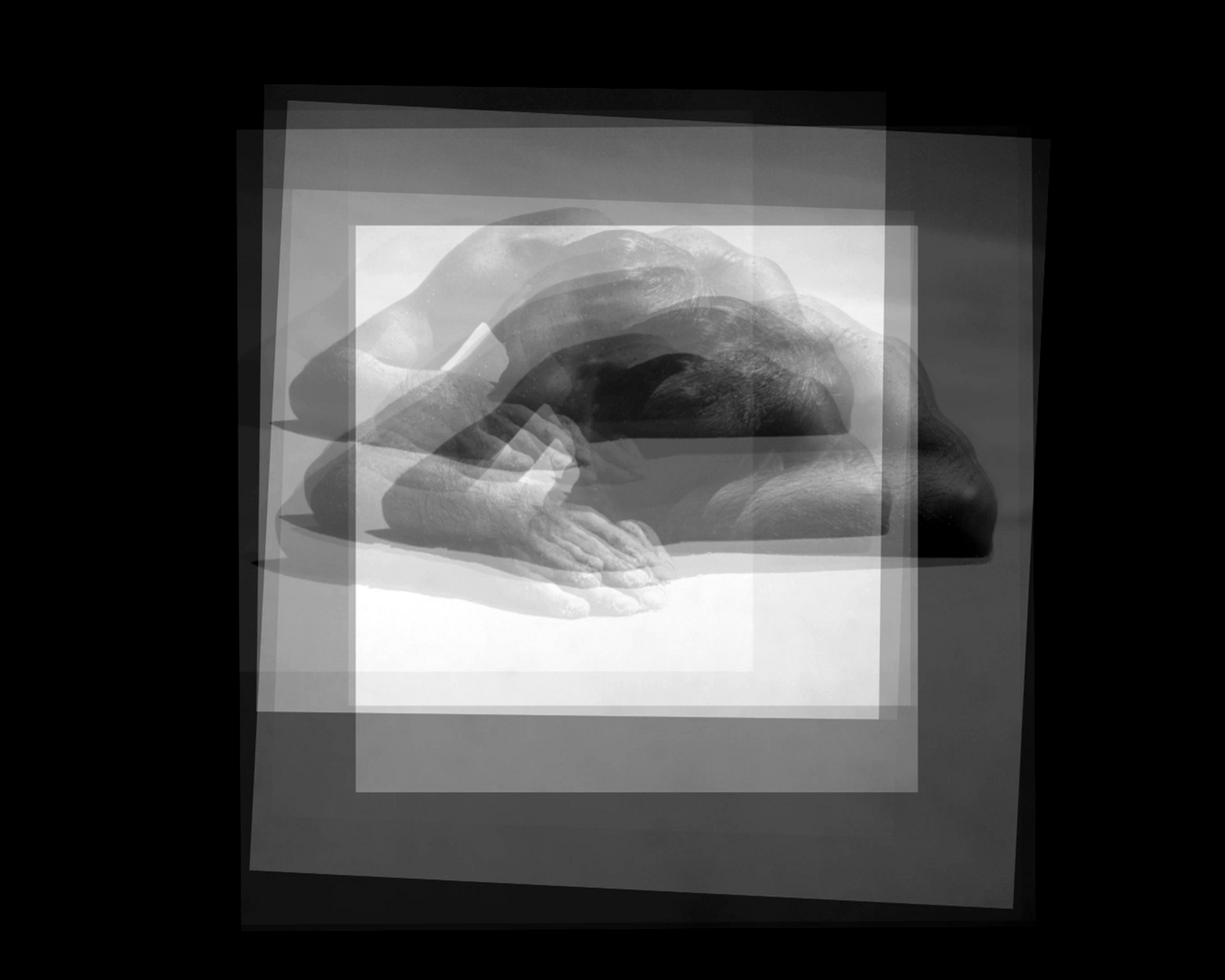
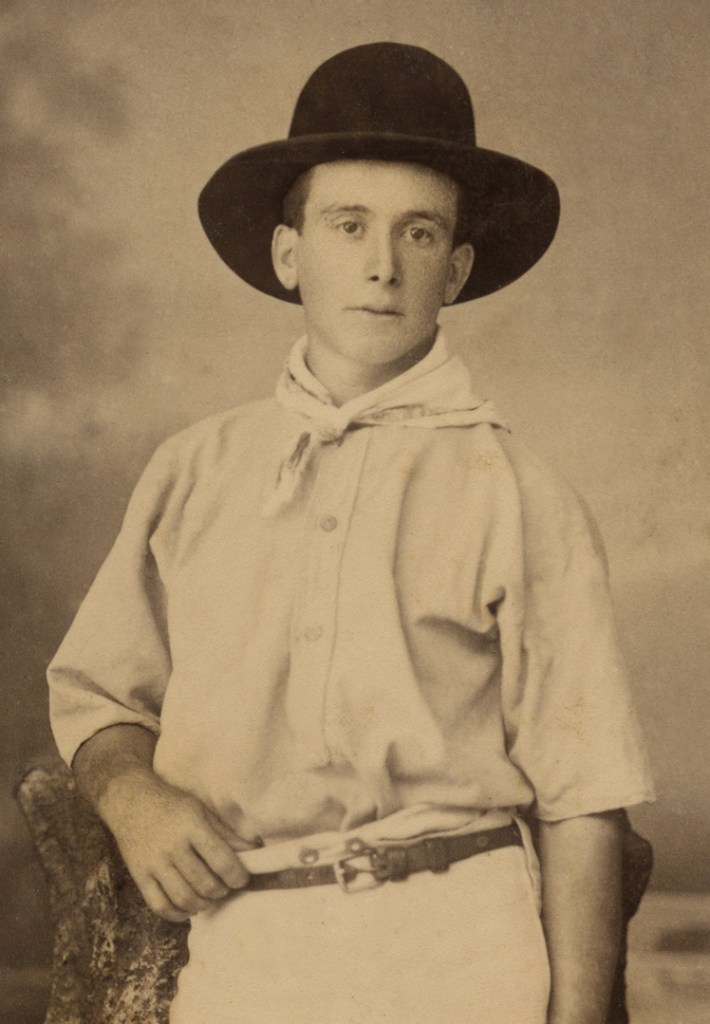



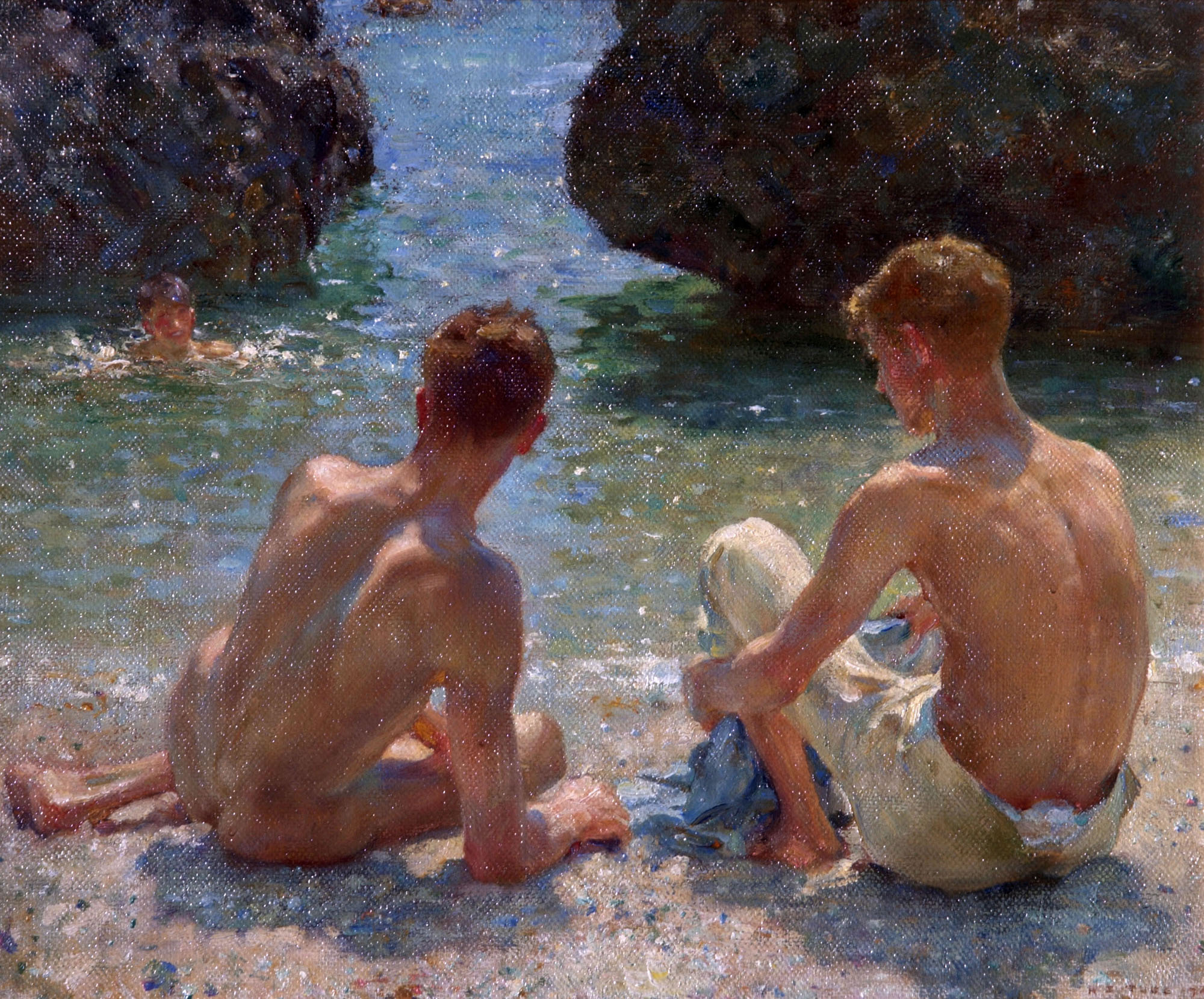











































































































































































































































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.