Exhibition dates: 14th March – 16th June 2013

Alexander Alland (Ukranian-American, 1902-1989, born Sevastopol, Ukraine)
Untitled (Brooklyn Bridge)
1938
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: William and Jane Schloss Family Foundation Fund
Conscience of the brave
Bradley Manning.
A slight, bespectacled, intelligent gay man.
A man who has the courage of his convictions.
He revealed truth at the heart of the world’s largest “democracy.”
There is something insidious about the American nation. Not its citizens, not its place, but its government. This government has perpetrated evil in the name of its people. Think of Iraq and Afghanistan, invasions in the name of freedom, the support of puppet governments, the assassinations, the military advisors on the ground, the profits made.
The torture. The deaths.
Bradley Manning revealed all of this because he has a mighty moral compass. He knows right from wrong. He was not afraid to expose the hypocrisy that for many years has beaten, unfettered, in the breast of a nation. The home of the brave and the free is sadly under attack from within. In the name of its people.
And why is this text relevant to this posting?
So often in the history of America, dissension is shut down because of some imagined menace, from within or without. Here another group of people (photographers documenting American social conditions) were persecuted for standing up for social causes, for the freedom to expose injustice where it lives. The paranoia of patriotism.
As Harold Pinter has so pithily observed,
“The crimes of the United States have been systematic, constant, vicious, remorseless, but very few people have actually talked about them. You have to hand it to America. It has exercised a quite clinical manipulation of power worldwide while masquerading as a force for universal good. It’s a brilliant, even witty, highly successful act of hypnosis.”
Except the hypnotist is a deranged psychopath, a divided split personality arraigning god, greed and guns. Out of one, many sins.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to The Norton Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“When the persecution of an individual who has exposed an evil is pursued so ruthlessly and yet the evil itself is studiedly ignored, all of us know that there is something very wrong with the way that our society is conducting itself. And if we do not protest in the strongest terms about what is being done in our name, then we become complicit.”
Alan Moore
“The US has shown remarkable energy in its pursuit of alleged whistleblowers. Has it investigated the deaths of those innocent civilians with the same vigour? With any vigour whatsoever? And which would you consider a crime? To conceal the deaths of innocent civilians, or to reveal them? I know what my answer would be.”
Les Barker
“To suggest that lives were put in danger by the release of the WikiLeaks documents is the most cynical of statements. Lives were put in danger the night we invaded the sovereign nation of Iraq, an act that had nothing to do with what the Bradley Mannings of this country signed up for: to defend our people from attack. It was a war based on a complete lie and lives were not only put in danger, hundreds of thousands of them were exterminated. For those who organised this massacre to point a finger at Bradley Manning is the ultimate example of Orwellian hypocrisy.”
Michael Moore
“Private Manning is the world’s pre-eminent prisoner of conscience, having remained true to the Nuremberg principle that every soldier has the right to ‘a moral choice.’ His suffering mocks the notion of the land of the free.”
John Pilger

Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016)
Coming to America
c. 1951
Gelatin silver print The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Photography Acquisitions Committee Fund
Louis Stettner
Louis Stettner (November 7, 1922 – October 13, 2016) was an American photographer of the 20th century whose work included streetscapes, portraits and architectural images of New York and Paris. His work has been highly regarded because of its humanity and capturing the life and reality of the people and streets. Starting in 1947, Stettner photographed the changes in the people, culture, and architecture of both cities. He continued to photograph New York and Paris up until his death. …
Back from the war Stettner joined the Photo League in New York. Stettner visited Paris in 1946 and in 1947 moved there. From 1947 to 1949 he studied at the “Institut des Hautes Études Cinématographiques” in Paris and received a Bachelor of Arts in Photography & Cinema. He went back and forth between New York and Paris for almost two decades and finally settled permanently in Saint-Ouen, near Paris, in 1990. Stettner still frequently returned to New York.
Stettner’s professional work in Paris began with capturing life in the post-war recovery. He captured the everyday lives of his subjects. In the tradition of the Photo League, he wanted to investigate the bonds that connect people to one another. In 1947 he was asked by the same Photo League to organise an exhibition of French photographers in New York. He gathered the works of some of the greatest photographers of the era, including Doisneau, Brassaï, Boubat, Izis, and Ronis. The show was a big success and was largely reviewed in the annual issue of U.S. Camera. Stettner had begun a series of regular meetings with Brassaï who was a great mentor and had significant influence on his work. In 1949, Stettner had his first exhibition at the “Salon des Indépendants” at the Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris.
In 1951 his work was included in the famous Subjektive Fotografie exhibition in Germany. During the 1950s he free-lanced for Time, Life, Fortune, and Du (Germany). While in Paris he reconnected with Paul Strand, who had also left New York because of the political intolerance of the McCarthy era – Strand had been a founder of the Photo League that would be blacklisted and then banned during those years.
In the 1970s Stettner spent more time in New York City, where he taught at Brooklyn College, Queens College, and Cooper Union.
Text from the Wikipedia website
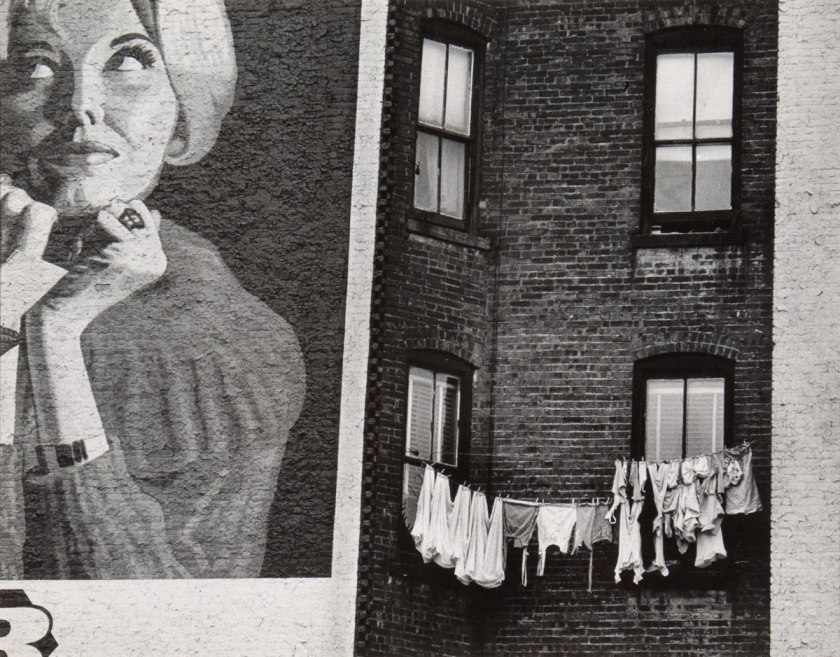

Erika Stone (German, b. 1924)
Lower Eastside Facade
1947
Gelatin silver print
Columbus Museum of Art, Ohio, Photo League Collection
Museum purchase with funds provided by Elizabeth M. Ross, the Derby Fund,
John S. and Catherine Chapin Kobacker, and the Friends of the Photo League
Stone’s adroit cropping of this image emphasises the coy upward gaze of the woman in the advertisement, away from the laundry line (emblem of poverty), and suggests the social mobility of the postwar era.
Erika Stone’s documentary photographs reflect her long, active career as a photo journalist and magazine photographer. In the 40’s, Stone was a member of the legendary Photo League, an organisation of photo documentarians which she feels most influenced her approach to her personal photographic work. It was during the years as a League member that she developed her interest in documenting people and at the age of seventeen, produced her Bowery series.
Although she considers herself mostly self-taught, she studied at the New School of Social Research with Bereniece Abbott and George Tice.
Stone was a stringer for both Time and Der Spiegel magazines and worked as a general photojournalist until 1960. After the birth of her two sons, she made photographing children and family her specialty. Her photographs have been and are widely published in magazines and textbooks around the world.
Anonymous. “Erika Stone,” on the American Photography Archives Group website Nd [Online] Cited 13/07/2024

Marvin E. Newman (American, 1927-2023)
Halloween, South Side
1951
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Photography Acquisitions Committee Fund
Marvin Newman
Born in New York; Newman attended Brooklyn College, where he studied sculpture with Burgoyne Diller and photography with Walter Rosenblum. Following Rosenblum’s suggestion, he joined the Photo League in 1948, taking classes with John Ebstel. The Photo League, founded in 1936, blazed a trail for serious photographers for 15 years, providing a forum for ideas, cheap darkroom space, and the vision of using the art of picture taking to change the world. Newman then attended the Institute of Design, Chicago (1949-52), where, after studying with Harry Callahan and Aaron Siskind, he received one of the first MS degrees in photography (1952).
During this time, Newman won national contests, including one sponsored by American Photography (1950) and another by Time, Inc. (1951). His work appeared in the Always a Young Stranger exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art, New York, and in a one-man show at Roy De Carava’s A Photographer’s Gallery (1956). Well-known as a photojournalist, Newman has been a major contributor to Sports Illustrated since its inception (1953), as well as to Life, Look, Newsweek, and Smithsonian magazines. In addition, he has been the national president of the American Society of Magazine Photographers, authored or coauthored eight books on photography, and received the Art Director’s Gold Medal for Editorial Photography.

Ida Wyman (American, 1926-2019)
Spaghetti 25 Cents, New York
1945
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Photography Acquisitions Committee Fund
This Italian restaurant was near the offices of Acme Newspictures, where Wyman became the company’s first female photo printer in 1943. After the war she lost her job at the agency. The “Ladies Invited” sign on the window is a reminder of a time when unescorted women were not always welcome in public dining establishments.
Ida Wyman
When I began working in the 1940s, few women were doing magazine photography in a field that was almost exclusively male. As I progressed from box camera to Speed Graphic (my first professional camera), and then to a Rolleiflex, I stopped thinking about the mechanics of film speed, f-stops, shutter speed, and began focusing on subject matter that interested me. What interested me so much were ordinary people and their everyday activities. Early on, I had documented children’s games and unusual architectural details in my Bronx neighbourhood. I decided to expand, to go elsewhere, taking the subway to Harlem, Chinatown, and lower Manhattan, exploring those neighbourhoods and looking for photos.
I became a member of the Photo League in 1946. I considered myself a documentary photographer and the League’s philosophy of honest photography appealed to me. I also began to understand the power of photos to help improve the social order by showing the conditions under which many people lived and worked. Even after leaving the League the following year, I continued to emphasise visual and social realities in my straightforward photographs.
Beginning with my earliest photos seeing New York City with my feet, and in whatever part of the country I was in, I continued my own walkabout, learning the area, engaging my subject, listening, and respecting their dignity. This continued to be my approach when taking photos. My photographs depicted daily life in America’s modern metropolitan centres, including Chicago and Los Angeles as well as New York.

Aaron Siskind (American, 1903-1991)
The Wishing Tree
1937, printed later
from Harlem Document, 1936-40
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Lillian Gordon Bequest
Harlem’s legendary Wishing Tree, bringer of good fortune, was once a tall elm that stood outside a theatre at 132nd Street and Seventh Avenue. When it was cut down in 1934 Bill “Bojangles” Robinson, the celebrated tap dancer, moved the stump to a nearby block and planted a new Tree of Hope beside it to assume wish granting duties. A piece of the original trunk is preserved in the Apollo Theatre on 125th Street, where performers still touch it for luck before going onstage.

Sonia Handelman Meyer (American, 1920-2022)
Hebrew Immigration Aid Society
c. 1946
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Mimi and Barry J. Alperin in memory of Max Alperin
The efforts of the New York based Hebrew Immigration Aid Society (HIAS) to rescue European Jews during the war were severely hampered by US immigration laws. After the war it aided in the resettlement of some 150,000 displaced persons, including, presumably, these three, whom Handelman Meyer has chosen to photograph in close-up. She conveys both their common suffering and their individuality, emphasising differences in body language and dress.
Sonia Handelman Meyer
I first heard of the Photo League from Lou Stoumen in Puerto Rico in 1942. I was working for the U.S. Army Signal Corps and Lou was preparing to join Yank Magazine. When I returned to New York City, I walked up the rickety stairs to League Headquarters and took a beginners class with Johnny Ebstel. I bought a used Rolleicord for a precious $100, and dared to go out on the city streets to photograph the life around me. Soon the guys began to come back from the war and the heady life of Photo League workshops, exhibits, lectures, photo hunts, and committee assignments intensified. I took eye-heart-soul opening workshops with Sid Grossman, worked as the paid (!) secretary for a year or so, and worked on the Lewis Hine Committee under Marynn Ausubel.
I photographed in Spanish Harlem, Greenwich Village, midtown Manhattan, at the Hebrew Immigration Aid Society, at an anti-lynching rally in Madison Square Park, at a Jehovah’s Witness convention in Yankee Stadium, and on Coney Island. Mostly, I photographed children and reflections of my city – rough-edged, tender, and very beautiful in its diversity. Some of this work was shown in the major 1949 exhibition, This is the Photo League.
The heartbreaking end of the League coincided with a huge change in my personal life. I got married and my husband began to go to college and we were out of NY for a while. And then the biggest change: our own family arrived and the joys of our son, and later our daughter, absorbed my time. Prints and negatives were stashed away in boxes and I lost track of all the old friends at the League. After so many years of being in the shadows, you can imagine my pleasure, at 90+ years of age, to have my photographs out of their boxes and onto walls where they can be seen, thought about, and enjoyed – and perhaps again take their place in the history of the Photo League.

Arthur Leipzig (American, 1918-2014)
Chalk Games, Prospect Place, Brooklyn
1950
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Rictavia Schiff Bequest

Arnold Eagle (Hungarian-American, 1909-1992)
Chatham Square Platform, New York City
c. 1939
Silver gelatin print

Joe Schwartz (American, 1913-2013)
Slums Must Go! May Day Parade, New York
c. 1936
Gelatin silver print
Columbus Museum of Art, Ohio, Photo League Collection
Museum Purchase with funds provided by Elizabeth M. Ross, the Derby Fund, John S. and Catherine Chapin Kobacker, and the Friends of the Photo League

Morris Huberland (Polish-American, 1909-2003 born Warsaw, Poland)
Union Square, New York
c. 1942
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Mimi and Barry J. Alperin Fund
The Norton Museum of Art’s newest special exhibition, The Radical Camera: New York’s Photo League, 1936-1951, is a formidable survey of the League’s history, and its artistic, cultural, social, and political significance. Opening March 14 and on view through June 16, 2013, this striking exhibition includes nearly 150 vintage photographs from Photo League collections at the Columbus Museum of Art, Ohio, and The Jewish Museum in New York City.
The exhibition is organised by Mason Klein, Curator of Fine Arts at The Jewish Museum and Catherine Evans, the William and Sarah Ross Soter Curator of Photography of the Columbus Museum of Art. It premiered in at The Jewish Museum in 2011 to rave reviews. The New York Times called The Radical Camera a “stirring show,” and the New York Photo Review hailed it as “nothing short of splendid.” The New Yorker named the exhibition one of the top 10 photography exhibitions of 2011. The Norton is the final venue on the exhibition’s tour.
The exhibition explores the fascinating blend of aesthetics and social activism at the heart of the Photo League. League members were known for capturing sharply revealing, compelling moments from everyday life. The League focused on New York City and its vibrant streets – a shoeshine boy, a brass band on a bustling corner, a crowded beach at Coney Island. Many of the images are beautiful, yet harbour strong social commentary on issues of class, race, and opportunity. The organisation’s members included some of the most noted photographers of the mid-20th century – W. Eugene Smith, Weegee (Arthur Fellig), Lisette Model, Berenice Abbott and Aaron Siskind, to name a few.
In 1936, a group of young, idealistic photographers, most of them Jewish, first-generation Americans, formed an organisation in Manhattan called the Photo League. Their solidarity centred on a belief in the expressive power of the documentary photograph, and on a progressive alliance in the 1930s of socialist ideas and art. (The Photo League also helped validate photography as a fine art, presenting student work and guest exhibitions by established photographers.) The Radical Camera presents the development of the documentary photograph during a tumultuous period that spanned the New Deal reforms of the Depression, World War II, and the Cold War. Offering classes, mounting exhibitions, and fostering community, members of the Photo League focused on social reform and the power of the photograph to motivate change. At the height of their influence, their membership included the most important photographers of their day including Berenice Abbot, Aaron Siskind, Barbara Morgan, Sid Grossman, Weegee (Arthur Fellig), and Lisette Model. Featuring more than 175 works by these artists as well as many more Photo League members, The Radical Camera traces the organisation’s interests, attitudes toward photography, and impact during its 15-year lifespan.
The innovative contributions of the Photo League during its 15-year existence (1936-1951) were significant. As it grew, the League mirrored monumental shifts in the world starting with the Depression, through World War II, and ending with the Red Scare. Born of the worker’s movement, the Photo League was an organisation of young, idealistic, first-generation American photographers, most of them Jewish, who believed in documentary photography as an expressive medium and powerful tool for exposing social problems. It was also a school with teachers such as Sid Grossman, who encouraged students to take their cameras to the streets and discover the meaning of their work as well as their relationship to it. The League had a darkroom for printing, published an acclaimed newsletter called Photo Notes, offered exhibition space, and was a place to socialise.
The Photo League helped validate photography as a fine art, presenting student work and guest exhibitions by established photographers such as Eugène Atget, Henri Cartier-Bresson, and Edward Weston, among others. These affecting black and white photographs show life as it was lived mostly on the streets, sidewalks and subways of New York. Joy and playfulness as well as poverty and hardship are in evidence. In addition to their urban focus, “Leaguers” photographed rural America, and during World War II, took their cameras to Latin America and Europe. The exhibition also addresses the active participation of women who found rare access and recognition at the League. The Radical Camera presents the League within a critical, historical context. Developments in photojournalism were catalysing a new information era in which photo essays were appearing for the first time in magazines such as Life and Look. As time went on, its social documentary roots evolved toward a more experimental approach, laying the foundation for the next generation of street photographers.
In 1947, the League came under the pall of McCarthyism and was blacklisted for its alleged involvement with the Communist Party. Ironically, the Photo League had just begun a national campaign to broaden its base as a “Center for American Photography.” Despite the support of Ansel Adams, Beaumont and Nancy Newhall, Paul Strand, and many other national figures, this vision of a national photography centre could not overcome the Red Scare. As paranoia and fear spread, the Photo League was forced to disband in 1951. The Radical Camera: New York’s Photo League, 1936-1951 has been organised by The Jewish Museum, New York, and the Columbus Museum of Art, Ohio. Major support was provided by the Phillip and Edith Leonian Foundation, the National Endowment for the Arts, and Limited Brands Foundation.”
Press release from The Norton Museum of Art website

Sy Kattelson (American, 1923-2018)
Untitled (Subway Car)
1949
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: The Paul Strand Trust for the benefit of Virginia Stevens Gift

Jerome Liebling (American, 1924-2011)
Butterfly Boy, New York
1949
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York, Purchase: Mimi and Barry J. Alperin Fund
© Estate of Jerome Liebling

Lee Sievan (American, 1907-1990)
Salvation Army Lassie in Front of a Woolworth Store
c. 1940
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Fund
This is a classic photograph. Look at the triangle that forms the central part of the image, from the girl at left looking with disdain at the matriarch singing then down to the look on the organ players face. Notice the girl at right covering her ears so she cannot hear the racket. Imagine the legs of the organ player going up and down, pumping air into the organ; and finally observe the shadow of a man’s face captured by reflection in the shop window as he walks past the scene. Magic.

Rosalie Gwathmey (American, 1908-2001)
Shout Freedom, Charlotte, North Carolina
c. 1948
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Gay Block and Malka Drucker Fund of the Houston Jewish Community Foundation

Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American born Ukraine, 1899-1968)
Max Is Rushing in the Bagels to a Restaurant on Second Avenue for the Morning Trade
c. 1940
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Joan B. and Richard L. Barovick Family Foundation and Bunny and Jim Weinberg Gifts

Bernard Cole (English, 1911-1992, born London, England)
Shoemaker’s Lunch
1944
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York,
Purchase: The Paul Strand Trust for the benefit of Virginia Stevens Gift
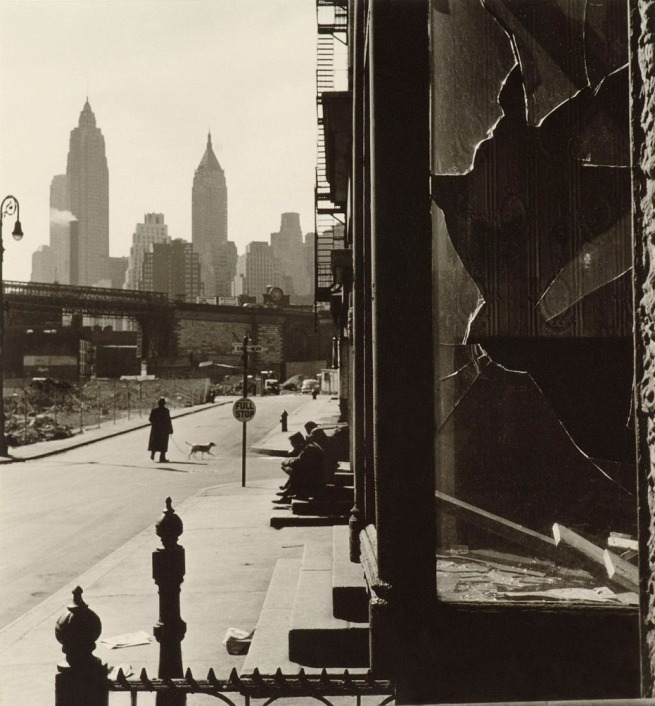

Rebecca Lepkoff (American, 1916-2014)
Broken Window on South Street, New York
1948
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Esther Leah Ritz Bequest

Arthur Leipzig (American, 1918-2014)
Ideal Laundry
1946
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Esther Leah Ritz Bequest

Consuelo Kanaga (American, 1894-1978)
Untitled (Tenements, New York)
c. 1937
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: The Paul Strand Trust for the benefit of Virginia Stevens Gift
Leftist political activism was a strong element in Kanaga’s work, beginning with her photographs of a labor strike in San Francisco in 1934. She provided photographs for progressive publications such as New Masses, Labor Defender, and Sunday Worker. Underlying this formal study of tenement laundry lines (a common motif in League imagery) is Kanaga’s empathy for the living conditions of the working class.

Ruth Orkin (American, 1921-1985)
Boy Jumping into Hudson River
1948
Gelatin silver print The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Fund

Sol Prom (Solomon Fabricant) (American, 1906-1989)
Untitled (Dancing School)
1938
from Harlem Document, 1936-40
Gelatin silver print
The Jewish Museum, New York
Purchase: Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Fund
Mary Bruce opened a dancing school in Harlem in 1937. For fifty years she taught ballet and tap, giving free lessons to those who could not afford them. Her illustrious pupils included Katherine Dunham, Nat King Cole, Ruby Dee, and Marlon Brando.
The Norton Museum of Art
1451 S. Olive Avenue
West Palm Beach, FL 33401
Phone: (561) 832-5196
Opening hours:
Thursday – Tuesday 10am – 5pm
Closed Wednesdays
Norton Museum of Art website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top


















































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.