Exhibition dates: 18th October, 2016 – 15th January, 2017
Curator: Georges Didi-Huberman, philosopher and art historian
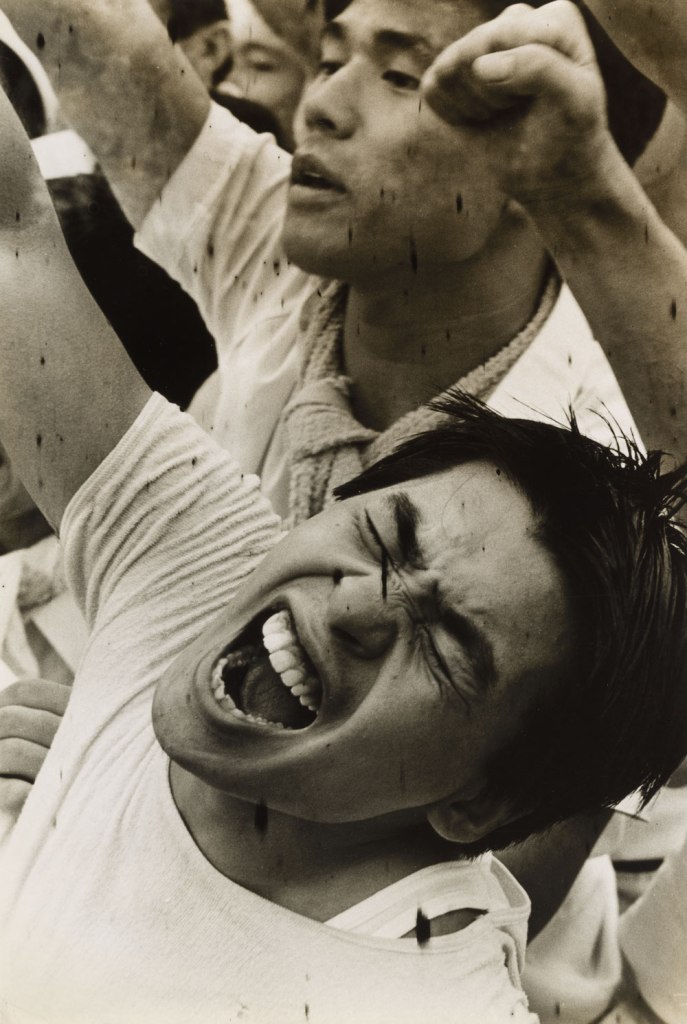
Hiroji Kubota (Japanese, b. 1939)
Black Panthers in Chicago, Illinois
1969
Gelatin silver print
© Hiroji Kubota/Magnum Photos
soulèvement m (plural soulèvements)
1/ the act of raising, the act of lifting up
2/ revolt, uprising
I believe this to be one of the most complex, original and important exhibitions of 2016. Conceptually, intellectually, ethically and artistically, the exhibition “Soulèvements / Uprisings” seems to stand head and shoulders above most others I posted on during 2016.
Through the profound curatorship of philosopher and art historian Georges Didi-Huberman (a man whose writing I admire), Soulèvements e/merges as a “trans-disciplinary exhibition on the theme of human gestures that raise up the world or rise up against it: collective or individual gestures, actions or passions, works or thoughts” actioned through five themes: Elements (Unleashed); Gestures (Intense); Words (Exclaimed); Conflicts (Flared up); and Desires (Indestructibles), evidenced across mediums: paintings, drawings, prints, video installations, photographs, fiction films, documentary images, writers’ manuscripts, tracts, posters, etc., without hierarchies. Unlike the earlier posting, Intersections: Photographs and Videos from the National Gallery of Art and the Corcoran Gallery of Art at the National Gallery of Art, Washington, where I noted that the self-contained themes of that exhibition seemed purely illusory, here the themes are active and engaging, fluid in meaning and representation (the choice of laterally aligned art works to the themes – dust breeding, waves, sea concertos, banners and capes, red tape, montages, posters etc…), which emphasis resistance, the raising up, the uprising as a desirous and joyful act, one that is performative (hence the wonderful video elements in the exhibition) and transgressive.
As one of the most important mediums of the twentieth century in terms of documenting, promoting, obscuring and forgetting “uprisings” – gestures of resistance and joy of any kind – photography is capable of concealing, denying and sustaining the social context in which we are living … obscuring the ethics and morals of dubious political positions; reinforcing or obscuring the issues behind revolution, rebellion, and revolt; or, through collective amnesia and inertia, through the millions of forgettable images produced each day, overwhelming the authenticity of living that leads to “uprisings” in the first place. Photographs, as people do, cross borders: they are transnational and multidisciplinary. They are global thought patterns that can, in skilled hands, document and sustain alternative ways of seeing the world through a “rising up” of feeling – the “soul” of soulèvement – the act of raising up, the act of lifting ones eyes and one’s spirit from the dire circumstances of oblivion to the hope of a future redemption.
Through photographs, we witness Insurgents killed during bloody week of the Commune (1871, below), where “the exposure of these bodies is transformed by the photographic act. The latter confers on the rebels a particular aura, passing thus from figures of guilty to those of martyrs.” The political act, although a failure in reality in this case, is sustained through time and space by the performance of the documentary image. Their monstration [the act of demonstrating; proof] – the insurgents act of demonstrating; the photograph as an act of demonstrating their death for judicial purposes; and also a certain monstration (proof) that these mostly young, skinny men died for a belief in a better world – is an evidentiary act of transubstantiation. Is the camera looking down on these bodies in cheap coffins from above, or are the coffins propped up against a wall? How do we feel about these people we do not know, who existed in past time now made present, without being that person who tucked a wreath into the hands of the man at bottom right, someone’s brother, father or son.
In “uprisings” (as the hands raise the camera to the face), there is also an acknowledgment of a certain despair at the death of an innocent. In Manuel Álvarez Bravo’s Striking worker, assassinated (1934, below) the young, handsome youth has been killed with a blow to the head. He lies prostrate on the ground, arm outstretched, hand curled, his body and clothes spattered with his own blood his eyes, open, staring at the now invisible sky. A flow of dried blood has discharged from his mouth and nose, coating and matting his thick long hair and running away in rivulets, soaking into the parched d/earth. Bits of dust and earth are still stuck to his arm through the viscosity of his blood. Earlier, he had dressed for the day in a white singlet, put on his trousers and fastened them with an embossed belt, then put on a crisp, stripped shirt and neatly rolled up the sleeves to his elbows. He might have had breakfast before heading of to a meeting outside where he worked. This day he died, protesting his rights – striking worker, assassinated! Assassinated – executed, eliminated, liquidated (to which the congealing blood attests) … slaughtered. For his right to strike, to protest, the conditions of his being. Any human “being”.
And, mortally, I comment on that one photograph, that one evidence of human beings transcending their own lives (knowing they were going to die) for the greater good – the anonymous photograph taken by members of the Sonderkommando of Auschwitz-Birkenau death camp that documents AS PROOF of the reality of the Final Solution: Women pushed towards the gas chamber of crematorium V of Birkenau (1944, below). The risks that these people took to capture this photograph speaks to the power of photography to transcend even the most barbaric of circumstances, to prove to the world what was happening in this place. As Georges Didi-Huberman affirms, “in the depths of this fundamental despair, the “solicitation to resist” has probably detached itself from the beings themselves, who have been promised to disappear, to fix themselves on signals to be emitted beyond the boundaries of the camp.” Among others, the image, this “eye of history”, is then invested with the only hope still possible: to make the hell of Auschwitz visible and therefore imaginable.”
In other words, the solicitation to resist is not singular or human, but collective and eternal, embodied and embedded in cultural thoughts and actions. Even though they knew they were going to die (almost none of the 2,000 prisoners placed in these Sonderkommando units survived to the camp’s liberation), because they have been “promised to disappear”, their spirit flowed beyond the boundaries of the camp into the ether of history, into the elemental upper air, the raising up of spirits: as an observation and representation of the difference between right and wrong. As the world enters a renewed period of right wing promulgation we must resist the rump of bigotry and oppression. Not just for ourselves but for all those that have passed before.
This is why this exhibition is so important. It speaks to the need for vigilance and protest against discrimination and dictatorship, against the persecution of the less fortunate in society. It also speaks to our desire as human beings that our actions and the actions of others be held to account. Intrinsically uprisings are all about desire, the desire to be stand up and be counted, to put your reputation (as Oscar Wilde did) or your life on the line for what you believe in. The courage of your convictions. As Edmund Burke said, “The only thing necessary for the triumph of evil is for good men to do nothing.”
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Addendum
Thank goodness for Google translate because otherwise I would have had no text to put under most of these images. This becomes problematic for weak images such as Dennis Adams’ Patriot (2002, below). Without text to support the image you would have absolutely no idea what this image is about… it’s just a plastic bag floating in the air against the azure sky.
The text states: “… considering the serenity that emanates from the photographs of this series, to imagine that they refer to a dramatic event: the attack of the World Trade Center. Located in Lower Manhattan, Dennis Adams’ studio is very close to the twin towers that were destroyed on September 11, 2001. However, rather than rushing to witness the catastrophe, Dennis Adams photographed for three months the roof of his building, the newspapers and the rubbish that fly away from the ruins.”
Who would have thunk it! From a plastic bag floating in the sky!
Such insight proffered months after the event by any plastic bag floating in the air. The image does not invite reverie and meditation because there is nothing to meditate on. It is an example of contemporary photography as graphic art THAT MEANS ABSOLUTELY NOTHING! If an image cannot stand on its own two feet, without the help of reams of text to support its substance, its contention, then no wonder there are millions of vacillating images in this world. Including contemporary art.
Out, damned spot! the stain of thy blood cannot be exacted from your feeble representation.
Word count: 1,451
Translations of soulèvement
noun
uprising – soulèvement, révolte
rising – soulèvement, hausse (rise), insurrection, montant, lever, élévation
insurrection – insurrection, soulèvement, émeute (riot), rébellion
uplift – soulèvement
upheaval – bouleversement, soulèvement, agitation, perturbation, séisme, renversement
Many thankx to Jeu de Paume for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Uprisings at Jeu de Paume – Concorde, Paris / Teaser
Uprisings is a trans-disciplinary exhibition on the theme of human gestures that raise up the world or rise up against it: collective or individual gestures, actions or passions, works or thoughts. They are gestures which say no to a state of history that is considered too “heavy” and that therefore needs to be “lifted” or even sent packing. They are also gestures that say yes to something else: to a desired better world, an imagined or adumbrated world, a world that could be inhabited and conceived differently.
Foreword
“For almost a decade, the Jeu de Paume’s exhibition program has been conceived with the conviction that twenty-first century museums and cultural institutions cannot be detached from the social and political challenges of the society of which they are part. To us, this approach is a matter of simple common sense.
The program it has shaped does not monitor market trends or seek complacent legitimacy within the field of contemporary art. Rather, we have chosen to work with artists whose poetic and political concerns are attuned to the need to critically explore the models of governance and practices of power that mold much of our perceptual and emotional experience, and thus, the social and political world we live in.
Because the Jeu de Paume is a centre for images, we are aware of the urgent necessity – in line with our societal responsibilities – to revise the analysis of the historical conditions in which photography and the moving image developed in modernity and, subsequently, in postmodernity, with all its alternatives, provocations, and challenges.
Thankfully, the history of images and our ways of seeing and understanding the world through them is neither linear nor unidirectional. These are the sources of our fascination with images that don’t tell everything they show and with images affected by the vicissitudes of the human condition.
Photography, and images in general, represent not only reality, but things that the human eye cannot see; like us, photography is capable of concealing, denying and sustaining. It is only waiting for someone to listen to its joys and its sorrows.
The Jeu de Paume’s programming sites its oblique look at history and contemporaneity in this oscillation between the visible and the invisible in the life of images, creating a space for encounter and the clashing of ideas, emotions, and knowledge, accepting that the coexistence of conflict and antagonism are an essential part of community building.
For these reasons, and from this position, in the superb proposal by the philosopher and art historian Georges Didi-Huberman to form an exhibition from his research on the theme of “uprisings,” we found the ideal intellectual, artistic, and museological challenge.
While the notion of revolution, rebellion, and revolt isn’t alien in contemporary society’s vocabulary, the object of its action is replete with collective amnesia and inertia. That is why analysing the representations of “uprisings” – from the etchings Goya, to contemporary installations, paintings photographs, documents, videos, and films – demonstrates an unequivocal relevance to the social context in which we are living in 2016. […]
Marta Gili, “Foreword,” in Uprisings, catalogue of the exhibition, p. 7-10.
Enrique Ramirez (Chile, b. 1979)
Cruzar un muro [Franchir un mur] (Crossing a wall)
2013
Vidéo HD couleur, son, 5’15”
Courtesy de l’artiste et galerie Michel Rein, Paris/Brussels
A series of images of people in a waiting room is in an unusual place, perhaps in our imagination, or perhaps anywhere. The short by Enrique Ramirez addresses article number 13 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights: “Everyone has the right to leave any country, including his own, and to return to his country”.
Gilles Caron (French, 1939-1970)
Manifestations anticatholiques à Londonderry
Anticatholic protests, Londonderry, Northern Ireland
August 1969
© Gilles Caron / Fondation Gilles Caron / Gamma Rapho
Known for his wartime photo-reports, fascinated by liberating acts and the figure of the insurgent, photographer Gilles Caron carried throughout the 1960s an interest in the social conflicts that marked his time. At first he is led to cover is a peasant revolt which takes place in Redon in 1967. Anxious to produce an image which appears to him as a formal translation of the anger of these peasants, he seizes the gesture of a demonstrator sending a projectile in the direction of the forces of order. Photogenic, this suspended gesture gives the insurrections a choreographic dimension and testifies to the violence of the social demands that animate the demonstrators. The “figure of the pitcher” then reappears on the occasion of the events of May 1968 and then of the conflicts that took place in Northern Ireland in 1969. This archetype is part of the tradition of the representation of David against Goliath: the symbol of the power carried by the faith of one who is thought weak in the face of brute force. If there is no question of faith in the images of Caron, it is nonetheless an irrepressible form of desire that animates those bodies which revolt: no matter the imbalance of forces, the insurgents are carried by a feeling of invulnerability and of power in the face of the forces of order objectively much more armed.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Man Ray (American, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 1890-1976 Paris)
Dust Breeding (Duchamp’s Large Glass with Dust Motes)
1920
Gelatin silver print
23.9 x 30.4cm (9 7/16 x 12 in.)
© 2016 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York
One of Duchamp’s close friends and a member of the New York Dada scene, the American photographer and painter Man Ray (1890-1976) was also one of Duchamp’s collaborators. His photograph Dust Breeding (Duchamp’s Large Glass with Dust Motes) from 1920 is a document of The Large Glass after it had collected a year’s worth of dust while Duchamp was in New York. The photograph was taken with a two-hour-long exposure that beautifully captures the complex texture and diversity of materials that lay atop the glass surface. Dust Breeding marks a pivotal phase in the development of Duchamp’s masterpiece. After the photograph was taken, Duchamp wiped The Large Glass almost entirely clean, leaving a section of the cones covered with dust, which he permanently affixed to the glass plate with a diluted cement.
Text from The Met website
Introduction
by Georges Didi-Huberman, curator of the exhibition
What makes us rise up? It is forces: mental, physical, and social forces. Through these forces we transform immobility into movement, burden into energy, submission into revolt, renunciation into expansive joy. Uprisings occur as gestures: arms rise up, hearts beat more strongly, bodies unfold, mouths are unbound. Uprisings are never without thoughts, which often become sentences: we think, express ourselves, discuss, sing, scribble a message, create a poster, distribute a tract, or write a work of resistance.
It is also forms: forms through which all of this will be able to appear and become visible in the public space. Images, therefore; images to which this exhibition is devoted. Images of all times, from Goya to today, and of all kinds: paintings, drawings, sculptures, films, photographs, videos, installations, documents, etc. They interact in dialogue beyond the differences of their times. They are presented according to a narrative in which there will appear, in succession, unleashed elements, when the energy of the refusal makes an entire space rise up; intense gestures, when bodies can say “No!”; exclaimed words, when barricades are erected and when violence becomes inevitable; and indestructible desires, when the power of uprisings manages to survive beyond their repression or their disappearance.
In any case, whenever a wall is erected, there will always be “people arisen” to “jump the wall”, that is, to cross over borders. If only by imagining. As though inventing images contributed – a little here, powerfully there – to reinventing our political hopes.
The exhibition
“Soulèvements / Uprisings” is a trans-disciplinary exhibition on the theme of human gestures that raise up the world or rise up against it: collective or individual gestures, actions or passions, works or thoughts.
They are gestures which say no to a state of history that is considered too “heavy” and that therefore needs to be “lifted” or even sent packing. They are also gestures that say yes to something else: to a desired better world, an imagined or adumbrated world, a world that could be inhabited and conceived differently.
These figures of uprising and up-raising will range freely across mediums: paintings, drawings, prints, video installations, photographs, fiction films, documentary images, writers’ manuscripts, tracts, posters, etc., without hierarchies.
The exhibition sequence will follow a sensitive, intuitive path along which the gaze can focus on exemplary “cases” treated with a precision that prevents any kind of generalisation. We will be mindful not to conclude, not to dogmatically foreclose anything. The sequence will comprise five main parts:
ELEMENTS (UNLEASHED)
GESTURES (INTENSE)
WORDS (EXCLAIMED)
CONFLICTS (FLARED UP)
DESIRES (INDESTRUCTIBLES)
“All the uprisings failed, but taken together, they succeeded.”
“They rise, but they do not simply stand up – they rise up.”
Judith Butler, “Uprisings” catalogue of the exhibition Uprisings
ELEMENTS (UNLEASHED)
The elements become unleashed, time falls out of joint. – And if the imagination made mountains rise up?
To rise up, as when we say “a storm is rising.” To reverse the weight that nailed us to the ground. So it is the laws of the atmosphere itself that will be contradicted. Surfaces – sheets, draperies, flags – fly in the wind. Lights that explode into fireworks. Dust that rises up from nooks and crannies. Time that falls out of joint. The world upside down. From Victor Hugo to Eisenstein and beyond, uprisings are often compared to hurricanes or to great, surging waves. Because then the elements (of history) become unleashed.
We rise up first of all by exercising our imagination, albeit through our “caprichos” (whims or fantasies) or “disparates” (follies) as Goya said. The imagination makes mountains rise up. And when we rise up from a real “disaster,” it means that we meet what oppresses us, and those who seek to make it impossible for us to move, with the resistance of forces that are desires and imaginations first of all, that is to say psychical forces of unleashing and of reopening possibilities.
Dennis Adams, Francis Alÿs, Léon Cogniet, Marcel Duchamp, Francisco de Goya, William Hogarth, Victor Hugo, Leandro Katz, Eustachy Kossakowski, Man Ray, Jasmina Metwaly, Henri Michaux, Tina Modotti, Robert Morris, Saburô Murakami, Hélio Oiticica, Roman Signer, Tsubasa Kato, Jean Veber, French anonymous.
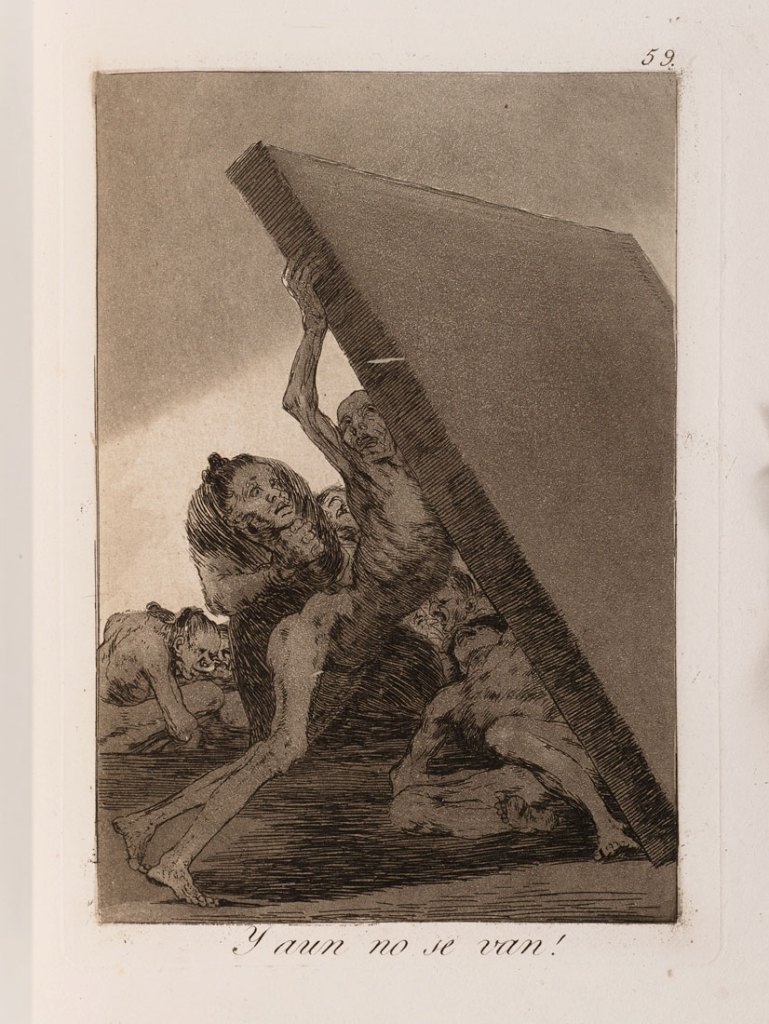

Francisco de Goya (Spanish, 1746-1828)
Los Caprichos
1799
Eau-forte, aquatinte et burin, 2e édition de 1855.
Collection Sylvie et Georges Helft
Photo: Jean de Calan
Between 1797 and 1799, Francisco de Goya composed a collection of engravings, Los Caprichos [Les Caprices], in which he portrayed in a satirical way the behaviour of his Spanish fellow citizens. “Y aun no se van!” (“And yet they do not go away!”) is the 59th engraving of a set of 80. Each time the title constitutes an ironic commentary on the image. This one refers to the group of people represented on the engraving, with the bodies emaciated, folded on themselves, praying, looking scared. One of them tries to prevent the tombstone from falling on them, but all seem helpless, destitute of strength, unable to resist this final ordeal. The use of chiaroscuro, which produces a dramatic effect, as well as the thick slice of the slab that forms the diagonal of the composition, accentuates the desperate character of the scene. Finally, the massive aspect and the weight of the stone, opposed to fragile and denuded bodies, complete their inexorable destiny. This engraving thus seems to illustrate the absolute dejection felt by individuals under certain circumstances. For Georges Didi-Huberman, degradation is one of the conditions conducive to the uprising. The imagination and the critical eye of the artist – a fervent supporter of the Enlightenment – can constitute a force of resistance and struggle for the oppressed.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Léon Cogniet (French, 1794-1880)
Les Drapeaux (The flags)
1830
Huile sur toile
Musée des Beaux-Arts, Orléans
Photo: François Lauginie
The Revolution of 1830 led to the overthrow of the government of King Charles X. After the publication of several ordinances, including a restriction on freedom of the press, this episode, which failed to restore the Republic, The tricolour flag, abandoned by the Restoration for the benefit of the white flag, symbol of royalty. This is evidenced by Leon Cogniet’s study of a painting that will never see the light of day.
These revolutionary days, also called the Three Glorious Days, are symbolically represented by three flags caught in the turmoil. The first, white, overhung by a menacing sky, is hoisted on a mast adorned with a fleur-de-lis. The second tears apart and reveals the blue sky as a promise of freedom. Finally, the third, torn and covered with blood, allows the reconstruction of the tricolour emblem created during the Revolution of 1789. Thus the blood poured during these days allows the people to reconnect with the revolutionary ideals. The unleashing of elements, a metaphor for the tempestuous popular revolt, accompanies the transformation of the banished flag of royalty to the national flag. This sketch is repeated and widely circulated at the time, accompanied by an anonymous poem: “To the darkness finally succeeds the clarity / And pale shreds of the flag of the slaves / And of the azure sky and the blood of our brave / The brilliant standard of our freedom is born.”
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Victor Hugo (French, 1802-1885)
La vague ou Ma destinée (The wave or My destiny)
1857
Plume et lavis d’encre brune, gouache, papier vélin
Maison de Victor Hugo
© Maisons de Victor Hugo / Roger-Viollet
This drawing is the witness of Victor Hugo’s fascination with the sea. His pen marries the movements of the ocean, which then becomes the symbol of his exile: “It is the image of my current destiny stranded in abandonment and solitude,” he says. On the drawing he calls ‘My destiny’, it is not known whether the ship, alone in front of the monster of the sea, enveloped by its foam, is carried or precipitated by the immense wave. It is a figure of his destiny, but also of the human condition.
Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
“Sculpture mouvante” ou “La France” (“Moving Sculpture” or “La France”)
1920
Musée national d’Art moderne, Centre Pompidou, Paris, dation en 1994
Negative gelatin-silver on glass plate
9 x 12cm
Photo: © Centre Pompidou, MNAM-CCI, Dist. RMN-Grand Palais / image Centre Pompidou, MNAM-CCI
Image obtenue par inversion des valeurs du scan du négatif
© Man Ray Trust / ADAGP, Paris, 2016
An active member of the Dada group in New York with Marcel Duchamp, Man Ray joined the surrealists in Paris in 1921. He was interested in questioning the conventions of the world of art and considered photography as a means of expression. It explores all potentialities: experiments, diversions, portraits, advertising applications … The fixation of an element in movement constitutes one of the specificities of photography that fascinates the surrealists because the object thus grasped by the apparatus appears in an unexpected light: the linen which dries, inflated under the effect of the wind, becomes a moving sculpture as the title of the work suggests. This way the title can guide the reception of the passionate photography of Man Ray. This image is also published on the cover of the sixth issue of La Révolution Surréaliste in 1926, accompanied by the legend “La France”. This enigmatic title, rather than helping to understand photography, multiplies the possible interpretations and attests to Man Ray’s desire to subvert the use and meaning of the images. Thus this wind which “transforms” linen into sculpture, appears as a metaphor for the surrealist project, which makes the photographic medium the operator of a true conversion of the gaze. By this image of the “uprising”, Man Ray thus gives a visual form to the aesthetic and political revolution that the members of the Surrealist group called for.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Eustachy Kossakowski (Polish, 1925-2001)
Le “Panoramic Sea Happening – Sea Concerto, Osieki” de Tadeusz Kantor (extrait d’une série)
The “Panoramic Sea Happening – Sea Concerto, Osieki” by Tadeusz Kantor (from a series)
1967
Inkjet pigment print
Owner of negatives and slides: Musée d’Art Moderne de Varsovie
© Collection Anka Ptaszkowska
In 1967 Tadeusz Kantor with a group of other Polish avant-garde artists delivered Panoramic Sea Happening. They were working in frames of artistic plain-air in Osieki (near Koszalin) organised there every year since 1963. This complex action was in a way a preface to Kantor’s theatre. But it was also parallel to actions of Western artists, which led to the birth of performance art. In this important moment Kantor formulated a category of impossible. It derived from the night dream but as this one was compromised Kantor wanted to use a new word: ‘impossible’. At the same time the very essence of the happening, as he was saying, was to make impossible real. How did he do it? By reenactment, repetition and documentation.
Dorota Sosnowska. From the abstract for “Impossible is Real: Tadeusz Kantor at the seashore” 2016
Hélio Oiticica (Brazilian, 1937-1980) and Leandro Katz (Argentinian, b. 1938)
Parangolé – Encuentros de Pamplona (Parangolé – Encounters of Pamplona)
1972
Impression chromogène (sur papier et carton)
Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid
Photo: Archives Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía
© Projeto Hélio Oiticica / © Leandro Katz
“At the time when he was producing his first Penetrables, Oticica started to design Parangolés, banners and capes printed in a great variety of colors and designs, and occasionally inscribed with mottoes, advertisement lines, or found phrases. Oiticica premiered his (anti)fashion statements in 1965 in what he called a Parangolé Coletivo, in which he distributed his creations among friends and members of the Mangueira samba school – he had joined in 1964 – who paraded wearing them while dancing to samba… He would continue making Parangolés and staging Parangolé events throughout the rest of his life, at times through friends who acted as intermediaries, as in the Pamplona encounters of 1972 in Spain when Argentinean artist Leandro Katz ran a Parangolé event on Oiticica’s behalf.”
Juan A. Suárez. “Jack Smith, Hélio Oiticica, Tropicalism,” in Criticism Vol. 56, No. 2, Jack Smith: Beyond the Rented World (Spring 2014) pp. 310-311.
Henri Michaux (French born Belgium, 1899-1984)
Untitled
1975
Acrylic on paper
Private collection
© ADAGP, Paris, 2016
Photo: Jean-Louis Losi
Dennis Adams (American, b. 1948)
Patriot
2002
From the series Airborne
C-Print contrecollé sur aluminium.
Prêt du Centre national des Arts Plastiques, Paris, inv. FNAC 03.241.
© Dennis Adams / CNAP / Courtesy Galerie Gabrielle Maubrie
A plastic bag stands out on the azure sky and floats in the air. Difficult, considering the serenity that emanates from the photographs of this series, to imagine that they refer to a dramatic event: the attack of the World Trade Center. Located in Lower Manhattan, Dennis Adams’ studio is very close to the twin towers that were destroyed on September 11, 2001. However, rather than rushing to witness the catastrophe, Dennis Adams photographed for three months the roof of his building, the newspapers and the rubbish that fly away from the ruins. These images, although directly related to this highly publicised event have nothing of the “shock” images that then invade the press.
They carry neither sensationalism nor exaggerated patriotism, but rather invite reverie and meditation. By adopting this attitude to the antipodes of the media and political enthusiasm that follows September 11, Dennis Adams questions the relationship to temporality in the face of this type of event. He denounces the “greed of politicians and military men who have a definite opinion on moments of history”* and questions the imperative of hyper-reactivity not conducive to the analysis and the constitution of a historical consciousness.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
*Dennis Adams quoted by Michel Guerrin, “In Madrid, photographers face history”, in Le Monde, June 15, 2004, p. 30.
Roman Signer (Swiss, b. 1938)
Rotes Band / Red Tape
2005
Vidéo couleur, son, 2’07′”
Caméra: Aleksandra Signer
Courtesy de l’artiste et d’Art: Concept, Paris
Tsubasa Kato (Japanese, b. 1984)
Break it before it’s broken
2015
Video: colour, sound, 4:49 min
© Tsubasa Kato / caméraman: Taro Aoishi
On March 11, 2011, a tsunami struck the Japanese coast and caused a nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi plant. The disastrous environmental and social consequences are still impossible to evaluate and the inhabitants, partly neglected by the public authorities, have to face an unprecedented crisis. Many of them have been displaced and most of their income from fishing is reduced to nothing because of the contamination of the ocean. Tsubasa Kato then decides to get involved with them by accompanying them daily in this difficult period. In addition to this support, he decided on November 3rd (03/11) – the day of the celebration of culture in Japan (Bunka no Hi) and date whose numerical writing is the inverse of that of the tsunami (11/03) – to achieve a strongly symbolic performance.
Entitled Break it before it’s broken, the video of this action shows residents of the region invited to overthrow the structure of a house washed away by the tsunami and destroy it definitively. Becoming actors of destruction and no longer passive observers, participants can then transform the event undergone into action. This festival of culture, for Tsubasa Kato, is an opportunity to initiate a unifying artistic moment that testifies to the strength of collective movements and the mobilisation necessary to reverse the course of events. He will then reiterate this performance in other parts of the world, which are often subject to delicate social situations.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Mari Kourkouta (Greek, b. 1982)
Remontages
2016
16 mm sur vidéo (en boucle), noir et blanc, silencieux, 4’ 10.
© Maria Kourkouta. Production : Jeu de Paume, Paris
“Body, mind and soul are uplifted by the divine energy of desire”
Marie-José Mondzain, “To those who sail the sea…” catalogue of the exhibition Uprisings
“To make the world rise up we need gestures, desires, and depths.”
Georges Didi-Huberman, “By the desires (Fragments on What Makes Us Rise Up)” catalogue of the exhibition Uprisings
GESTURES (INTENSE)
From burden to uprising. – With hammer blows. – Arms rise up. – The pasión. – When bodies say no. – Mouths for exclaiming.
Rising up is a gesture. Before even attempting to carry out a voluntary and shared “action,” we rise up with a simple gesture that suddenly overturns the burden that submission had, until then, placed on us (be it through cowardice, cynicism, or despair). To rise up means to throw off the burden weighing down on our shoulders, keeping us from moving. It is to break a certain present – be it with hammer blows as Friedrich Nietzsche and Antonin Artaud sought to do – and to raise your arms towards the future that is opening up. It is a sign of hope and of resistance.
It is a gesture and it is an emotion. The Spanish Republicans – whose visual culture was shaped by Goya and Picasso, but also by all the photographers on the field who collected, the gestures of freed prisoners, of voluntary combatants, of children and of the famous La Pasionaria, Dolores Ibárruri – fully assumed this. In the gesture of rising up, each body protests with all of its limbs, each mouth opens and exclaims its no-refusal and its yes-desire.
Paulo Abreu, Art & Language, Antonin Artaud, Taysir Batniji, Joseph Beuys, Désiré-Magloire Bourneville, Gilles Caron, Claude Cattelain, Agustí Centelles, Chim, Pascal Convert, Gustave Courbet, Élie Faure, Michel Foucault, Leonard Freed, Gisèle Freund, Marcel Gautherot, Agnès Geoffray, Jochen Gerz, Jack Goldstein, Käthe Kollwitz, Alberto Korda, Germaine Krull, Hiroji Kubota, Annette Messager, Lisette Model, Tina Modotti, Friedric Nietzsche, Willy Römer, Willy Ronis, Graciela Sacco, Lorna Simpson, Wolf Vostell, anonymes catalans, français, italiens.
Gustave Courbet (French, 1819-1877)
Home en blouse debout sur une barricade (projet de frontispice pour Le Salut public)
Man in a smock standing on a barricade (frontispiece for Le Salut public project)
1848
Fusain sur papier
Musée Carnavalet – Histoire de Paris
© Musée Carnavalet / Roger-Viollet

Germaine Krull (European, 1897-1985)
The Dancer Jo Mihaly, danse “Révolution”
1925
Gelatin silver print
Museum Folkwang, Essen
© Estate Germaine Krull, Folkwang Museum, Essen
Pioneer and adventurous, Germaine Krull is one of those women photographers of the inter-war period who contributed largely to the emergence of a nervous and dynamic photographic approach, in step with a modern world in constant acceleration. In photographing Jo Mihaly, she portrays a dancer who shares this avant-garde sensibility. Indeed, a pupil of Mary Wigman, this singular figure of dance participates in the German expressionist movement and contributes to the development of a modern choreographic art: the unconstrained body emancipates itself from the conventions of classical dance, the gesture of the dancer is released and regains its vitality. The movement then becomes the result of the personal expression of the dancer whose photographer has the burden of seizing the fulgurance [dazzling speed]. Stretched arm, smoky eyes and feverish eyes, Jo Mihaly – who has always claimed her commitment to the Communist Party – realises a gesture that resonates with her time but also with the youth of Germaine Krull, marked by its proximity to the Republic of the Soviets of Berlin in 1919. Thus, it is as much for these artists to participate in an aesthetic revolution in their respective artistic fields as to echo the social and political uprisings that have taken place throughout Europe since the the advent of the industrial era.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate

Alberto Korda (Cuban, 1928-2001)
El Quijote de la Farola, Plaza de la Revolución, La Habana, Cuba
Don Quixote of the streetlamp, Plaza de la Revolución, Havana, Cuba
1959
Vintage gelatin silver print on baryta paper
Leticia et Stanislas Poniatowski collection
© ADAGP, Paris, 2016
Kitai Kazuo (Japanese, b. 1944)
Resistance (book)
1965
BAL
© Kitai Kazuo/ Collection privée
With a manifesto both aesthetic and philosophical, the Japanese publication Provoke proposed a radical break in only three issues, published in 1968 and 1969. Provoke (photographers Takuma Nakahira, Yutaka Takanashi and Daidō Moriyama, critic Kōji Taki and poet Takahiko Okada) proposes a new visual language – rough, grainy and blurred – that captures the complexity of the experience and the paradoxes of modernity suffered by all.
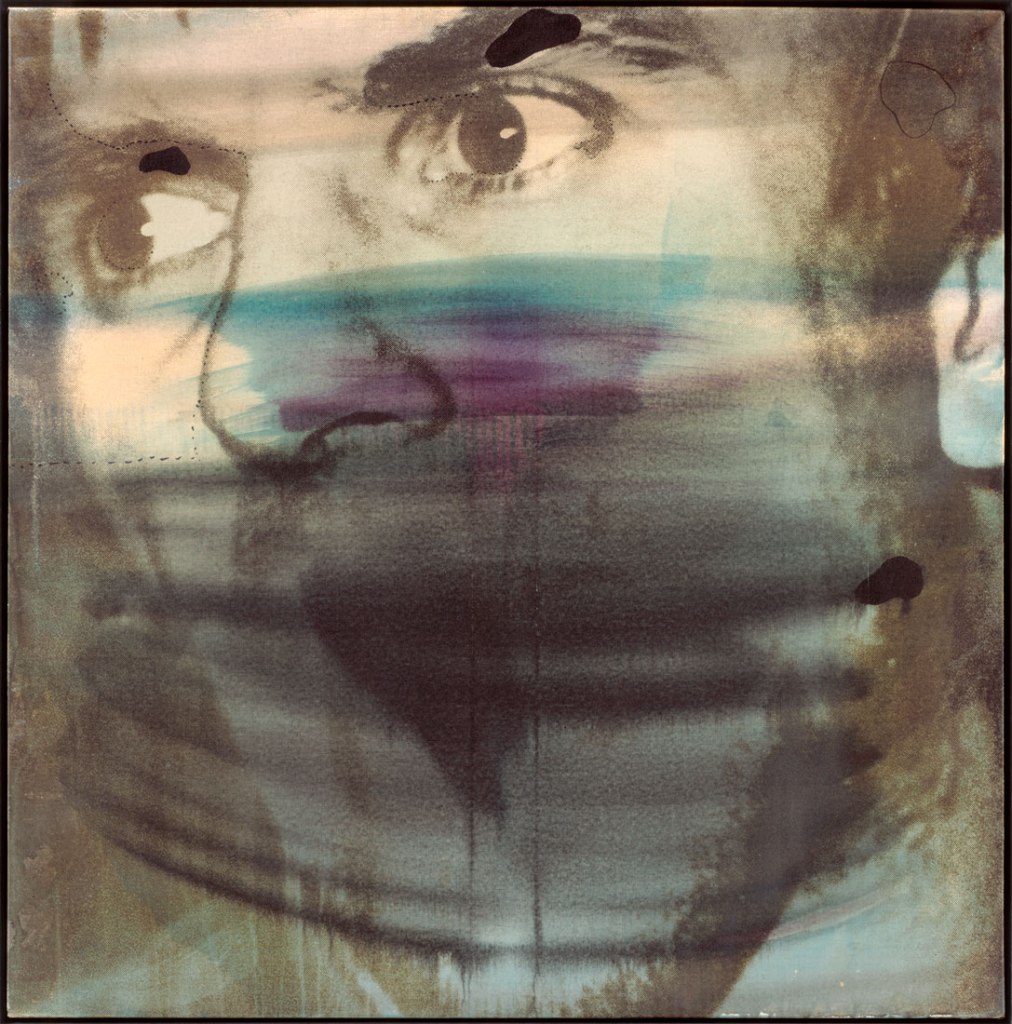

Wolf Vostell (German, 1932-1998)
Dutschke
1968
Polymer painting on canvas
Haus der Geschichte der Bundensrepublik Deutschland, Bonn
© ADAGP, Paris, 2016



Art and Language (collective created late 1960s)
Shouting Men (details)
1975
Screenprint and felt pen on paper
Museu d’Art Contemporani de Barcelona collection
Photo: Àngela Gallego
© Art and Language
Patrick Zachmann (French, b. 1955)
L’armée bloquée par la foule aux portes de la capitale
The army blocked by the crowd at the gates of the capital
1989
Gelatin-silver bromide print on baryta paper
50.4 x 60.9cm
Musée du quai Branly – Jacques Chirac
© Patrick Zachmann
From the early 1980s, Patrick Zachmann carried out an in-depth investigation into the Chinese diaspora. Present in China at the time of the events in Tiananmen Square, he photographed particularly symbolic episodes. This picture, taken on 20 May, is located just after the beginning of the hunger strikes, and before the massive repression known as the Tiananmen massacre. The nocturnal atmosphere and the gestures of the orator confer on this “moment before” a dramatic theatricality.
Annette Messager (French, b. 1943)
47 Piques (47 Pikes)
1992
Soft toys, coloured pencils on paper, various materials, and 47 metal pikes
270 x 570 x 70cm
Annette Messager and Marin Karmitz collection/Marian Goodman Gallery, Paris
© ADAGP, Paris, 2016
Graciela Sacco (Argentinian, 1956-2017)
from the “Bocanada” (A breath of fresh air) series
1992-1993
Posters in the streets of Rosario, Argentina
© Graciela Sacco
This series of photographs of open mouths was immediately considered by Graciela Sacco as being intended to circulate in the public space on various supports (stamps, spoons, stickers, posters …). It is however in the form of a wild display that the artist has most often given to see this set. The first of these displays took place in 1993, during a strike, in public school canteens in the town of Rosario. It was then a question of questioning the impossibility of the municipal staff to make their claims heard and the consequences of this movement knowing that for the majority of the children, this meal was the only one of the day. Graciela Sacco then continues to post these posters in cities like Buenos Aires, São Paulo or New York, often during election campaigns or close to advertising images. Are they hungry mouths? Cries of claims? Of suffering? Or even breathing as the title suggests? Be that as it may, this repeated but inaudible message tends to become oppressive. By exposing them in public space, the artist seems to give visibility to those anonymous calls that we do not want or can not hear.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
WORDS (EXCLAIMED)
Poetic insurrections. – The message of the butterflies. – Newspapers. – Making a book of resistance. – The walls speak up.
Arms have been raised, mouths have exclaimed. Now, what are needed are words, sentences to say, sing, think, discuss, print, transmit. That is why poets place themselves “at the forefront” of the action itself, as Rimbaud said at the time of the Paris Commune. Upstream the Romantics, downstream the Dadaists, Surrealists, Lettrists, Situationists, etc., all undertook poetic insurrections.
“Poetic” does not mean “far from history,” quite the contrary. There is a poetry of tracts, from the protest leaflet written by Georg Büchner in 1834 to the digital resistance of today, through René Char in 1943 and the “cine-tracts,” from 1968. There is a poetry particular to the use of newspapers and social networks. There is a particular intelligence – attentive to the form – inherent in the books of resistance or of uprising. Until the walls themselves begin to speak and occupy the public space, the sensible space in its entirety.
Antonin Artaud, Ever Astudillo, Ismaïl Bahri, Artur Barrio, Georges Bataille, Charles Baudelaire, Joseph Beuys, Enrique Bostelmann, André Breton, Marcel Broodthaers, Cornelius Castoriadis, Champfleury, Dada, Armand Dayot, Guy Debord, Carl Einstein, Jean-Luc Fromanger, Federico García Lorca, Jean-Luc Godard, Groupe Dziga Vertov, Raymond Hains, Raoul Hausmann, John Heartfield, Bernard Heidsieck, Victor Hugo, Asger Jorn, Jérôme Lindon, Rosa Luxemburg, Man Ray, Germán Marín, Chris Marker, Cildo Meireles, Henri Michaux, Tina Modotti, Pier Paolo Pasolini, Pablo Picasso, Sigmar Polke, Jacques Rancière, Alain Resnais, Armando Salgado, Álvaro Sarmiento, Philippe Soupault, Félix Vallotton, Gil Joseph Wolman, German, Chilean, Cuban, Spanish, French, Italian, Mexican, Russian unknowns.

Raoul Hausman (Austrian, 1886-1971)
Portrait of Herwarth Walden at Bonset
1921
Postcard sent by Raoul Hausmann to Theo van Doesburg
Archives Theo and Nelly van Doesburg
Photo: collection RKD – Netherlands Institute for Art History
© ADAGP, Paris, 2016
Herwarth Walden (German, 1879-1941)
Herwarth Walden (actual name Georg Lewin, 16 September 1879 in Berlin – 31 October 1941 in Saratov, Russia) was a German Expressionist artist and art expert in many disciplines. He is broadly acknowledged as one of the most important discoverers and promoters of German avant-garde art in the early twentieth century (Expressionism, Futurism, Dadaism, Magic Realism).
From 1901 to 1911 Walden was married to Else Lasker-Schüler, the leading female representative of German Expressionist poetry. She invented for him the pseudonym “Herwarth Walden”, inspired by Henry Thoreau’s novel Walden, or Life in the Woods (1854). In 1912 he married Swedish painter Nell Roslund. In 1919 he became a member of the Communist Party. In 1924 he was divorced from his second wife.
With the economic depression of the 1930s and the subsequent rise of National Socialism, his activities were compromised. In 1932 he married again and left Germany shortly later because of the threat of the Gestapo. He went to Moscow, where he worked as a teacher and publisher. His sympathies for the avant-garde soon aroused the suspicion of the Stalinist Soviet government, and he had to repeatedly defend against the equation of avant-garde and fascism. Walden died in October 1941 in a Soviet prison in Saratov.
Text from the Wikipedia website

John Heartfield (German, 1891-1968)
Benütze Foto als Waffe!
Utilise la photo comme une arme !
Use photography as a weapon !
AIZ, année VIII, no 37, Berlin, 1929, p. 17
Revue
37.8 x 27.5cm
Akademie der Künste, Berlin, Kunstsammlung, Inv.-Nr.: JH 2265
© The Heartfield Community of Heirs/ADAGP, Paris, 2016
In the late 1910s, members of the Dada movement practiced the first collages using images from cheap publications. The iconoclastic dimension of these heterogeneous juxtapositions allows them to open up the critical potential of images. Then, in the 1920s in Berlin, the Dada movement became politicised and the idea that the affiliated artists of the Communist Party were to serve the proletarian cause was strengthened. Few artists felt as committed to this mission as John Heartfield (his real name was Helmut Herzfeld). From the end of the 1920s, he developed a practice of satirical photomontage for the press, and in particular of the Communist journal AIZ (Arbeiter Illustrierte Zeitung) for which he worked until 1938. He then produced 237 photomontages denouncing Fascist ideology, the financing of the Nazi party by the industrialists and the extreme violence of the national socialist program. Invited to the Film und Foto exhibition in 1929 in Stuttgart, he had inscribed above the section devoted to him the slogan found in AIZ the same year: “Use photography as a weapon!”. Through the massive dissemination of his photomontages, he wants to mobilise public opinion and incite him to rise up against the rise of the fascisms that threaten Europe.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Heartfield lived in Berlin until April 1933, when the National Socialists took power. On Good Friday, the SS broke into his apartment, and the 5’2″ Heartfield escaped by jumping from his balcony and hiding in a trash bin. He left Germany by walking over the Sudeten Mountains to Czechoslovakia. In Czechoslovakia, John Heartfield rose to number-five on the Gestapo’s most-wanted list.
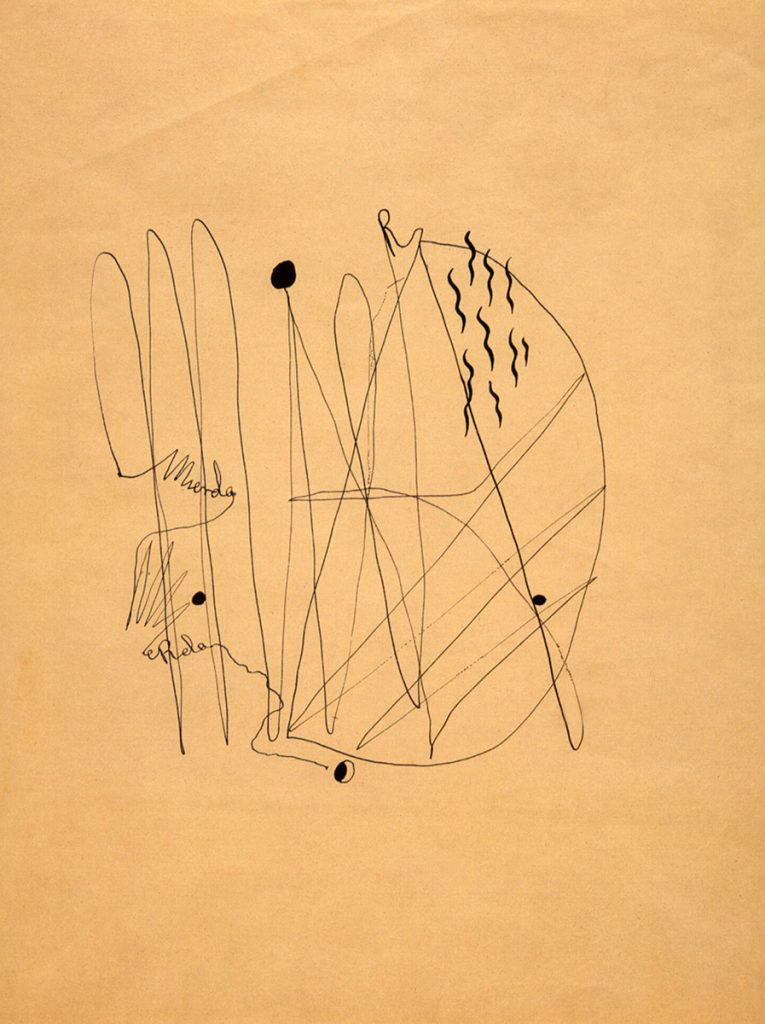

Federico García Lorca (Spanish, 1898-1936)
Mierda (Shit)
1934
Calligram, Indian ink
Federico García Lorca foundation, Madrid
© Federico García Lorca foundation, Madrid / VEGAP
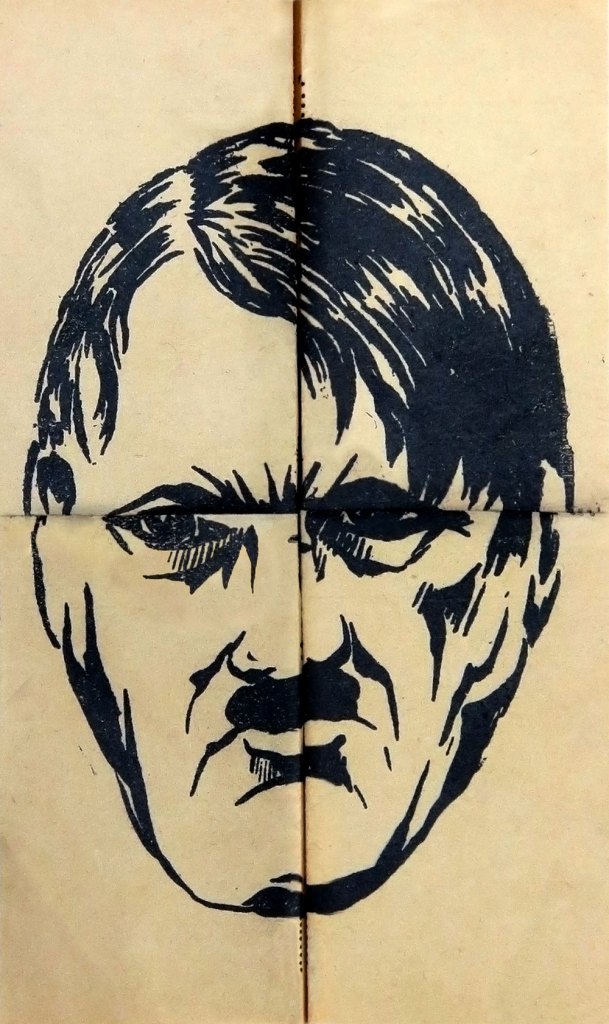

Réseau Buckmaster (Buckmaster Network)
Tract clandestin (Clandestine Tract)
1942
Papier
17 x 25cm
Collection particulière
Courtesy des éditions de L’échappée
This satirical tract was realised and distributed in 1942 by the network of the Resistance Buckmaster, during the German occupation in France. The flying leaflet, given from hand to hand or slipped into a mailbox, the leaflet or the butterfly (smaller) is at the same time the expression of a refusal – that of yielding – and of an imperious desire to act and call for a start. Intended to mark the minds and to attract adhesion, they can be formed of short and poetic texts, slogans or images. Open, it presents a caricature drawing of four pigs and, in the centre, an inscription in capital letters which apostrophes the reader and invites him to look for the fifth … Indeed, if the recipient folds the sheet according to the dotted lines, he makes Hitler’s acrimonious face! Thus, like any clandestine message, the meaning of the leaflet is not given immediately. The system of folding conceals and intrigues before revealing, but also accentuates the critical and percussive nature of the subject. Opening and closing like two wings, this butterfly is an anonymous, ephemeral and fragile missive ready to fly in the air to carry its message of rising. Like a firefly gleaming in the night of war, “an indication of a desire that flies, goes where it wants, insists, persists, resists in spite of everything”*, in the words of Georges Didi-Huberman, this image constitutes a weapon at the same time frail and powerful.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
*Georges Didi-Huberman, “Through desires (fragments on what raises us)”, in Soulèvements, Paris, Jeu de Paume, 2016, p. 372.
Raymond Hains (French, 1926-2005)
OAS. Fusillez les plastiqueurs (OAS. Shoot the bombers)
1961
Torn poster on canvas backing
Private collection
© ADAGP, Paris, 2016
Photo: Michel Marcuzzi
By the end of the 1940s, Raymond Hains paced the streets of Paris and sought out surprising agglomerates of torn posters that he picked up before painting them on canvas. The artist, flâneur, is the catalyst of a new form of urban poetry that gives rise to impromptu entanglements of words and images. This practice of hijacking posters largely echoed the world of art and French society after the Second World War. These torn posters formally evoke the canvases of “action painting” in vogue at the time, which Hains enjoys by calling himself “inaction painter”. The proliferation of these posters accompanies the rise of consumption but also the many political debates that agitate France. Thus futile advertisements co-exist promoting an eternally joyful world and political posters whose subjects are sometimes dramatic. In 1961, Raymond Hains realised an exhibition entitled “La déchirée France” [The Torn France] which presents itself as a sounding board of contemporary French history, marked by the decomposition of the Fourth Republic and what is not yet called the war of Algeria. The work OAS. Shoot the bombers testifies to the violence of the positions taken with regard to this organisation favourable to the maintenance of French Algeria, but also to the reality of the attacks they commit.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Sigmar Polke (German, 1941-2010)
Gegen die zwei Supermächte – für eine rote Schweiz (1e version)
(Against the two superpowers – for a red Switzerland) (1st version)
1976
Spray paint and stencil on paper
Ludwig Forum für internationale Kunst, Aachen
© The Estate of Sigmar Polke, Cologne /ADAGP, Paris, 2016
Henri Michaux (French born Belgium, 1899-1984)
Untitled
1975
Indian ink, acrylic on paper
50 x 65cm
Private collection
© ADAGP, Paris, 2016 / Photo : Jean-Louis Losi
The poet Henri Michaux has endeavoured to combine writing and drawing. Already in his invention of a new graphic alphabet in 1927, and then in his hallucinogenic experiments by absorption of mescaline from 1955, Henri Michaux sought to liberate, unbind language and drawing and thus to explore “the space within”. This ink on paper presents an entanglement of disorderly spots more or less energetic or impregnated. Just as his poems try to lift the tongue, this drawing seems to express what he calls “trembling in images”. Traces of liberating gestures, this expressive “new language”, noisy, made of floods of forms and collisions of signs, becomes the image of the disorderly world and the claimed insubordination of its author. In 1971, Michaux always seems to be looking for what he calls in the turbulent infinity “a confidence of a child, a confidence that goes ahead, hopes, raises you, confidence which, entering into the tumultuous universe … becomes a greater upheaval, a prodigiously great uprising, an extraordinary uprising, an uprising never known, a rising above itself, above all, a miraculous uprising which is at the same time an acquiescence, an unbounded, calming and exciting acquiescence, an overflow and a liberation.” Thus Michaux considered drawing as a movement, the very rise of thought and bodies.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
“Uprising transforms consciousness and in this movement it reconstitutes it. It gathers needs together and turns them into demands, it turns affects into desires and wills, it positions them in a tension towards liberty.”
Antonio Negri, “Uprisings” catalogue of the exhibition Uprisings
CONFLICTS (FLARED UP)
To go on strike is not to do nothing. – Demonstrating, showing oneself. – Vandal joys. – Building barricades. – Dying from injustice.
And so everything flares up. Some see only pure chaos. Others witness the sudden appearance of the forms of a desire to be free. During strikes, ways of living together are invented. To say that we “demonstrate,” is to affirm – albeit to be surprised by it or even not to understand it – that something appeared that was decisive. But this demanded a conflict. Conflict: an important motif of modern historical painting (from Manet to Polke), and of the visual arts in general (photography, cinema, video, digital arts).
It happens sometimes that uprisings produce merely the image of broken images: vandalism, those kinds of celebrations in negative format. But on these ruins will be built the temporary architecture of uprisings: paradoxical, moving, makeshift things that are barricades. Then, the police suppress the demonstration, when those who rise up had only the potency of their desire (potency: not power). And this is why there are so many people in history who have died from having risen up.
Manuel Álvarez Bravo, Hugo Aveta, Ruth Berlau, Malcolm Browne, Henri Cartier-Bresson, Agustí Centelles, Chen Chieh-Jen, Armand Dayot, Honoré Daumier, Adolphe-Eugène Disdéri, Robert Filliou, Jules Girardet, Arpad Hazafi, John Heartfield, Dmitri Kessel, Herbert Kirchhorff, Héctor López, Édouard Manet, Ernesto Molina, Jean-Luc Moulène, Voula Papaioannou, Sigmar Polke, Willy Römer, Pedro G. Romero, Jésus Ruiz Durand, Armando Salgado, Allan Sekula, Thibault, Félix Vallotton, Jean Veber, German, Catalan, French, Mexican, South African unknowns.
Charles-François Thibault (French)
La Barricade de la rue Saint-Maur-Popincourt avant l’attaque par les troupes du général Lamoricière
The Barricade of the Rue Saint-Maur-Popincourt before the attack by the troops of General Lamoriciere
Sunday, June 25, 1848
Daguerréotype
11.7 x 15cm
Musée d’Orsay, Paris
Photo © RMN-Grand Palais (musée d’Orsay) / Hervé Lewandowski
This daguerreotype is part of a series of two exceptional views of the barricades taken during the popular insurrection of June 1848. Disseminated in the form of woodcuts in the newspaper L’Illustration at the beginning of the following July, these photographs were realised by an amateur named Thibault, from a point of view overlooking the Rue Saint-Maur-Popincourt, June 25 and 26, before and after the assault. The first photographs reproduced in the press, they show the value of proof given to the medium in the processing of information since the middle of the nineteenth century, well before the development of photomechanical reproduction techniques. The inaccuracies and ghostly traces caused by a long exposure time limit the accuracy lent to the medium. Also the engraver allowed himself to “rectify” the views for the newspaper, adding clouds here and there and specifying the posture or the detail of the silhouettes. The remarkable interest of these daguerreotypes, however, resides in their indeterminate aspect. In fact, they reveal the singular temporality of these events: both short (since each second counts during the confrontations) and at the same time extended (in the moments of preparation and waiting). The temporalities proper to events and photography are thus combined in order to offer the perennial image of an invisible uprising and therefore always in potentiality.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
The first photo of an insurrectionary barricade
This photo was taken by a young photographer, by the name of Charles-François Thibault, at the level of no. 92 of the current rue du Faubourg-du-Temple on the morning of Sunday June 25, 1848. The insurrection is coming to an end, and only the last defences of the working-class districts of eastern Paris resist.
Thibault used twice, probably between 7 am and 8 am, his daguerreotype, a primitive process of photography which fixed the image on a metal plate. These two pictures are visible in Parisian museums, the first at the Carnavalet museum, the second (featured image) at the Musée d’Orsay. One distinguishes there in particular a flag planted in the axle of a wheel on the first barricade (which according to the researches of Olivier Ilh [La Barricade reversed, history of a photograph, Paris 1848, Editions du Croquant, 2016] carried the inscription “Democratic and social Republic”) as well as silhouettes of back.
Anonymous text. “The first photo of a barricade,” on the Un Jour de Plus a Paris website [Online] Cited 11/11/2021.
Édouard Manet (French, 1832-1883)
Guerre civile (Civil war)
1871
Two-tone lithograph on thick paper
Musée Carnavalet – Histoire de Paris
© Musée Carnavalet / Roger-Viollet
André Adolphe Eugène Disdéri (French, 1819-1889) (attributed to)
Insurgés tués pendant la Semaine sanglante de la Commune
Insurgents killed during bloody week of the Commune
1871
Albumen photograph
21 x 27cm
Musée Carnavalet – Histoire de Paris, Paris
© André A.E. Disdéri / Musée Carnavalet / Roger-Viollet
This photograph was taken at the end of the tragic Bloody Week which concluded the Commune of Paris in May 1871. It shows the corpses of Communards shot by the Versailles troops, presented in their coffins at the public exhibition of their bodies. This image is imprinted with brutality: that of the authors of the massacre of these young men struggling for the independence of Paris, that of the monstration [The act of demonstrating; proof] and, that of photography, in its realisation, its frontality and its precision. Why did one of the most famous portraitists of the Second Empire record the image of these inanimate bodies? We know today that photography has played an important role in anti-communard propaganda, the aim of which was to show the “exactions” of the insurgents (barricades, vandalism, assassinations …) and to present this event not as a revolution but as a civil war. It was also used for identification purposes, used for judicial proceedings and repression. The value of this image, however, is due to the fact that the exposure of these bodies is transformed by the photographic act. The latter confers on the rebels a particular aura, passing thus from figures of guilty to those of martyrs. Gathered for the occasion and set up facing us, they form, through photography, the image of an inseparable community. Even if the revolution has failed and power has failed, its power remains and continues to nourish the memory of political uprisings.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Allan Hughan (British, 1834-1883)
Installations de la colonie pénitentiaire (Installations of the penal colony)
May 1874
Albumen print
14.7 x 19.6cm
Musée du quai Branly – Jacques Chirac
The legend of the image, written in the thirties, states: “In the foreground the tribe of rebels of 1878”, while that handwritten on the original negative says “tribe of Atai revolted.” These elements drag the meaning of this image realised by the first photographer present in New Caledonia. The photographs he takes of kanaks, villages, but also of the prison and mining facilities in 1874, take on a new retrospective significance after the great Kanak revolt of 1878.
Félix Vallotton (Swiss-French, 1865-1925)
La Charge (The Charge)
1893
Proof, woodcut on paper
Musée national d’Art moderne, Centre Pompidou, Paris
Gift of Adèle et Georges Besson en 1963. On loan to Musée des Beaux-Arts et d’Archéologie de Besançon
© Centre Pompidou / MNAM / Cliché Pierre Guenat, Besançon, Musée des Beaux-Arts et d’Archéologie
Felix Vallotton made this engraving on wood in 1893 as part of his critical contributions to social violence for newspapers and magazines of his time. Composed with great economy of means, La Charge represents the brutal repression of a demonstration by the forces of the order. The diving point of view testifies to the influence of photography on his work and reinforces the voyeur character of the viewer as well as his feeling of helplessness. The formal repetition of the uniform of the “guardians of the peace” and the resemblance of their faces, all wedged between their moustache and their kepi, translates well the impression of mechanical unleashing of a blind violence. By contrasting black and white, Vallotton refers to the physical confrontation between civilians and policemen. The centrifugal force which animates the composition gives the impression that the wounded bodies shatter like an explosion. By distorting the characteristic perspective of the Nabi aesthetic, the victims’ bodies seem to be abandoned. Through the eyes of man in the foreground, the artist denounces the abuse of force but also takes the spectator to witness and invites him to rise up against this injustice. The artist, known for his anarchist positions, broke as much with the traditional principles of composition as with the established order. At the charge against the protesters, he responds by his own charge against the authorities.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Joseph Marie Ernest Prud’Homme
Submission of Rabezavana and Rainibetsimisaraka
1897
Print on aristotype paper
12 x 17 cm
Musée du quai Branly – Jacques Chirac
On July 29, 1897, Rabezavana and Rainibetsimisaraka, two of the greatest leaders of the Menalamba insurrection, which began after the abdication of Queen Ranavalona III and the establishment of the protectorate in October 1895, publicly knelt before Governor General Joseph Gallieni to signify their submission. This ceremony is the theatrical acme of the policy of “pacification” carried out in Madagascar by Gallieni, since his arrival in September 1896.
Anonymous photographer
Les Habés envoient un parlementaire pour faire leur soumission au commandant Pognio
The Habés send a parliamentarian to make their submission to Major Pognio
17 March 1910
Print on baryta paper
10.9 x 16.7cm
Musée du quai Branly – Jacques Chirac
The French colonial conquest of West Africa, begun in 1854, stops with the unification of its possessions within French West Africa in 1895. It was mainly carried out by the infantry which had to face populations hostile to colonization. The Habés (Dogons) of the Bandiagara region (present-day Mali) resisted the French soldiers from 1894 to 1910.
José Clemente Orozco (Mexican, 1883-1949)
Les Femmes des soldats (The Women Soldiers)
1926
Oil on canvas
México, INBA, Collection Museo de Arte Moderno
Photo © Francisco Kochen
© Adagp, Paris 2016
Tina Modotti (Italian American, 1896-1942)
Guitare, cartouchière et faucille (Guitar, cartridge belt and sickle)
1st June 1929
Illustration de l’annonce pour la chanteuse communiste Concha Michel, publiée dans el machete, no 168, 1
Illustration of the announcement for the communist singer Concha Michel, published in El Machete, no 168, 1
Gelatin silver print
México, INBA, Museo Nacional de Arte
Donation de la famille Maples Arce, 2015
© Francisco Kochen
The Mexican Revolution profoundly changed the structure of society: since men had gone to war or to search for work and livelihoods, women took on new tasks, first in armed struggle and then in rebuilding culture and education within society. Thus, the image of the soldiaderas, those women who followed the revolutionary troops, acquired a special significance and was symbolically compared to the “strong women” of the Bible. In the artistic field, women also played a decisive role, sometimes called “proto-feminism”: patrons of valuable artists or artists themselves, they participated in the quest for an aesthetic language capable of expressing their doubts and questioning.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Concha Michel (1899-1990) was a singer-songwriter, political activist, playwright, and a researcher who published several projects on the culture of Indigenous communities. She was one of the few women who performed in the corrido style. She created the Institute of Folklore in Michoacan and was one of the first collectors of folklore and preservers of the traditions of the Mexican people. She was a cultural icon having relationships with two presidents, and a broad range of Mexico’s most prominent artists including Diego Rivera, Frida Kahlo, Guadalupe Marín, Tina Modotti, Elena Poniatowska, Anita Brenner and others.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Ruth Berlau (Danish, 1906-1974)
Grévistes américains (American warriors)
1941
Gelatin silver print
10 x 15cm
Akademie der Künste, Berlin, Bertolt Brecht Archiv
© by R. Berlau/Hoffmann
Ruth Berlau, actress, director and photographer of Danish origin realises this photograph shortly after his arrival in the United States. She fled Nazi Germany with the writer and playwright Bertolt Brecht and accompanied him during much of his exile. In line with her commitment to the Spanish war and her communist ideas, she photographed American social movements and showed the actors of the struggle and the victims of oppression. This series on strikes highlights the workforce of the workers, with the desire to get their faces out of anonymity. It is in keeping with the documentary use of photography undertaken by social programs such as the New Deal and in particular the path traced by Walker Evans, initiator of the “documentary style”. It chooses a frontal point of view, apt to reveal with precision and clarity the faces of the strikers. In doing so, it applies itself to restoring their dignity while producing the documents of a social history. The counter-drive gives the strikers a particular scope and strength, just as the framing, which ostensibly divides the group, suggests that they belong to a powerful and determined group. The photographic practice of Ruth Berlau seems to embody a democratic ideal, revealing both the unity and the singularity of each and a common political commitment, which is reflected here through the exchange of views.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Manuel Álvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1902-2002)
Ouvrier en grève, assassiné (Striking worker, assassinated)
1934
Gelatin silver print
Musée d’Art moderne de la Ville de Paris
© Musée d’Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris / Roger Viollet
© Estate Manuel Álvarez Bravo


Unknown photographer
Contestation autour de la construction de l’aéroport de Narita
Contestation around the construction of Narita airport
1969
Gelatin silver prints
© Collection Art Institute of Chicago
In parallel with the dazzling rise of a consumer society on the Western model, for ten years (from 1960 to 1970) Japan went through a major identity crisis that unfolded on multiple fronts: American military bases in Okinawa, construction of Narita airport, occupation of universities by students …
Chieh-Jen Chen (Taiwanese, b. 1960)
The Route
2006
35 mm film transferred onto DVD: color and black and white, silent, 16:45 min.
© Chieh-Jen Chen, courtesy galerie Lily Robert
“To rise up is to break a history that everyone believed to have been heard. It is to break the foreseeability of history, to refute the rule that presided, as we thought, over its development or its preservation.”
Georges Didi-Huberman, “By the desires (Fragments of What Makes Us Rise Up)” catalogue of the exhibition Uprisings
DESIRES (INDESTRUCTIBLES)
The hope of one condemned to death. – Mothers rise up. – They are your own children. – They who go through walls.
But potency outlives power. Freud said that desire was indestructible. Even those who knew they were condemned – in the camps, in the prisons – seek every means to transmit a testimony or call out. As Joan Miró evoked in a series of works titled “The Hope of a Condemned Man,” in homage to the student anarchist Salvador Puig i Antich, executed by Franco’s regime in 1974.
An uprising can end with mothers’ tears over the bodies of their dead children. But these tears are merely a burden: they can still provide the potencies of uprising, like in the “resistance marches” of mothers and grandmothers in Buenos Aires. It is our own children who rise up: “Zero for Conduct!” was Antigone not almost a child herself? Whether in the Chiapas forests or on the Greece – Macedonia border, somewhere in China, in Egypt, in Gaza, or in the jungle of computerised networks considered as a vox populi, there will always be children to jump the wall.
Francisca Benitez, Ruth Berlau, Bruno Boudjelal, Agustí Centelles, Eduardo Gil, Mat Jacob, Ken Hamblin, Maria Kourkouta, Joan Miró, Pedro Motta, Voula Papaioannou, Estefania Peñafiel Loaiza, Enrique Ramirez, Argentinian, Greek, Mexican unknowns.
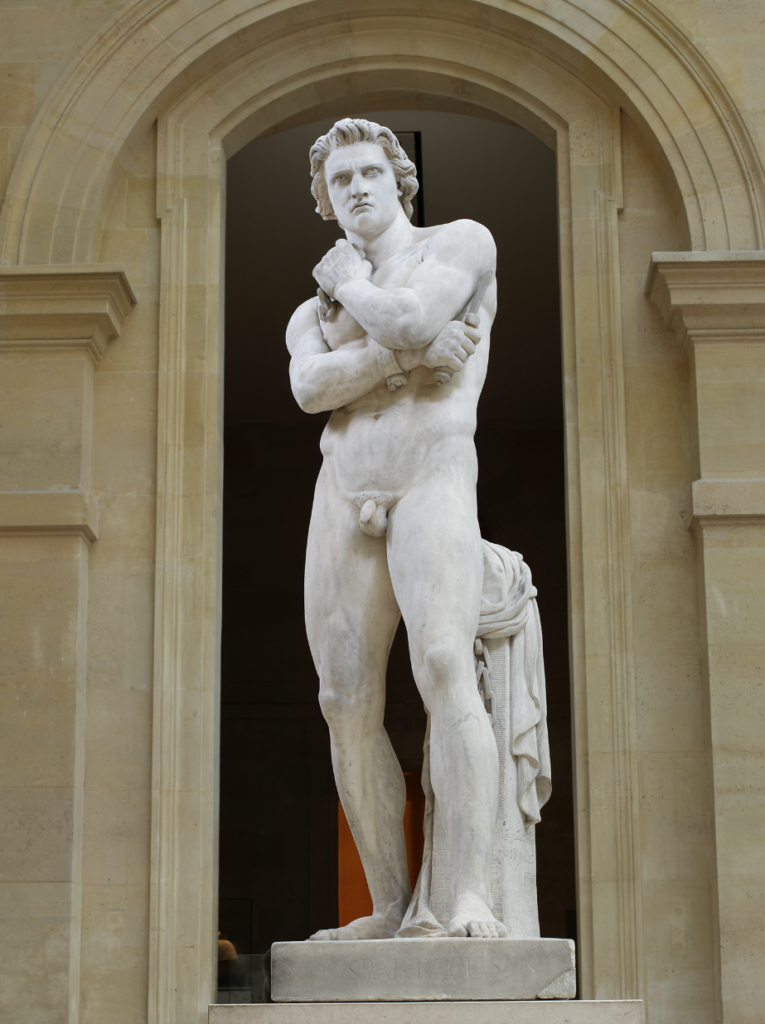

Denis Foyatier (French, 1793-1863)
Spartacus
1830
Marble
Commande de Charles X, 1828
Département des Sculptures
© 2011 Musée du Louvre, dist. RMN – Grand Palais / Thierry Ollivier

Victor Hugo (French, 1802-1885)
Le Pendu (The hanged man)
1854
Pen and brown ink wash, black ink, charcoal, black chalk, gouache on paper
Paris, Maison de Victor Hugo
© Maisons de Victor Hugo / Roger-Viollet
While in exile in Jersey, Victor Hugo is deeply moved by the death sentence in Guernsey of John Charles Tapner, a condemnation against which he protests and asks for a pardon that he will not get. Hugo then makes four drawings depicting a gaunt hanged man at his gallows. The museum preserves two (Ecce and Ecce Lex). Hugo had hung them in his room in Marine Terrace in Jersey, and in his study under the roof of Hauteville House in Guernsey.
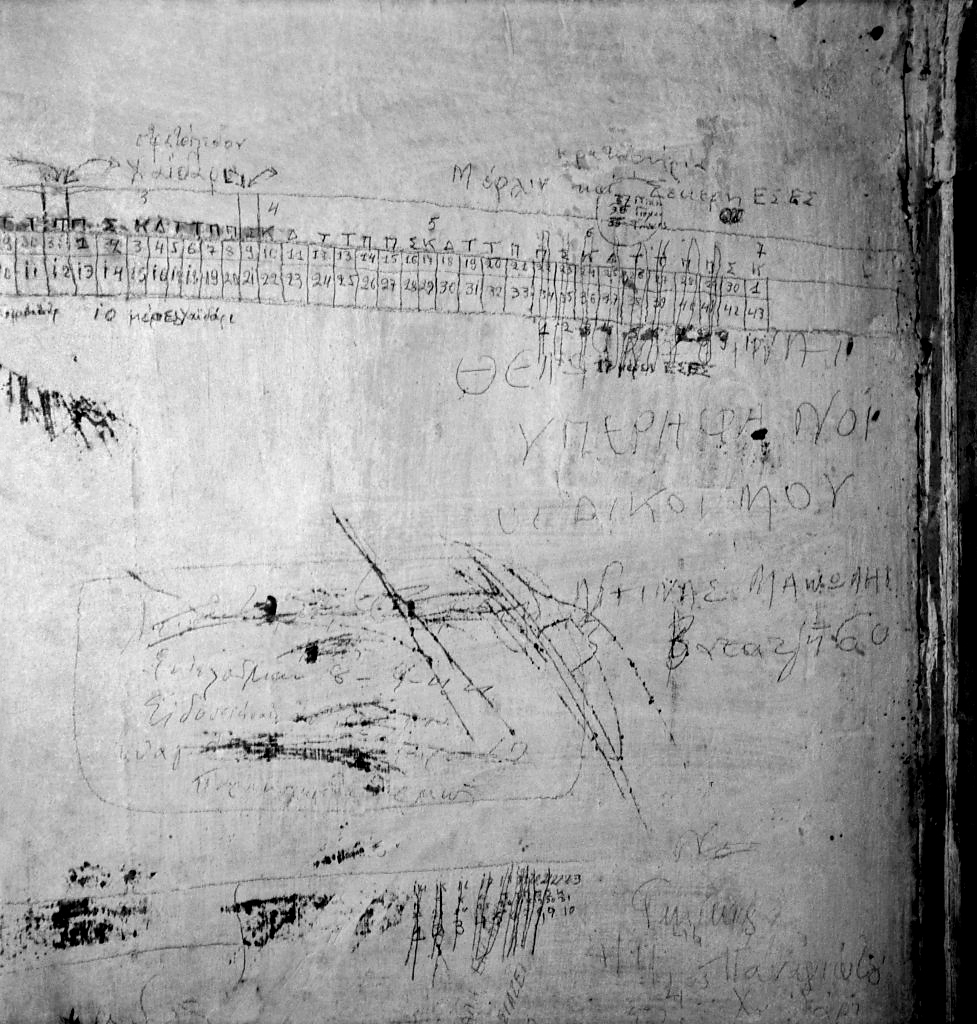

Voula Papaioannou (Greek, 1898-1990)
Graffitis de prisonniers sur les murs de la prison allemande de la rue Merlin à Athènes
Graffiti of prisoners on the walls of the German prison in Merlin Street, Athens
1944
Gelatin-silver print, modern print
24 x 30cm
Benaki Museum Photographic Archive, Athènes
Voula Papaioannou is a major figure in Greek documentary photography. Born in 1898, she made numerous photographs of landscapes, monuments and archaeological sites in the 1930s. The Second World War led her to wonder about her practice and she was committed to covering the realities of the conflict. Her apparatus then becomes a tool to testify and publicise the misery and suffering of the Greek population during the German occupation. It reflects the difficulties of everyday life, the departure of the military in combat and the famines that strike civilians. During the liberation, she made a few shots of street fights as well as these images of the walls of the prison of Athens held until then by the Germans. It shows the graffiti (inscriptions and drawings) left by the detainees, most of them awaiting execution. Many say their names and send a message to their families (“I want my relatives to be proud of me”) or claim their political convictions (“Vive le KKE”, Greek Communist Party) for the sake of transmitting until the day before their deaths the reasons for their struggle and the conditions of their disappearance. These photographic recordings are similar to archaeological documents bearing the traces of the imprisonment of the Greek Resistance fighters and their hope that these messages will one day be read in a Greece freed from the Nazi occupation.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Photographe Anonyme (membre du Sonderkommando d’Auschwitz-Birkenau)
Anonymous photographer (member of the Auschwitz-Birkenau Sonderkommando)
Femmes poussées vers la chambre à gaz du crématoire V de Birkenau
Women pushed towards the gas chamber of crematorium V of Birkenau
1944
Contact plate with two images
12 x 6cm
Archival collection of the State Museum Auschwitz-Birkrenau, Oświęcim
Photo: Archival collection of the State Museum Auschwitz-Birkrenau, Oświęcim
This photograph was taken by a member of the Sonderkommando Auschwitz-Birkenau, a special unit of Jewish inmates commissioned by the SS to carry out the final solution. It belongs to a set of four photographs carried out clandestinely on a piece of film, using a photographic camera infiltrated in the camp and then concealed at the bottom of a bucket. Hidden near crematory furnace V, the author of these photographs was assisted by other members of the Sonderkommando. To do such an act was indeed extremely dangerous. The sloping framing and the blur reflect the perilous conditions in which the photographer was then placed. This picture, however, clearly shows a convoy of naked women pushed by the special unit to the gas chamber, located off-field. The film was then filtered from the camp into a tube of toothpaste to join the Polish Resistance, accompanied by an explanatory letter. These photographs therefore have an informative aim and constitute the only photographic documents on the gas chambers. As Georges Didi-Huberman affirms, “in the depths of this fundamental despair, the “solicitation to resist” has probably detached itself from the beings themselves, who have been promised to disappear, to fix themselves on signals to be emitted beyond the boundaries of the camp.*” Among others, the image, this “eye of history”, is then invested with the only hope still possible: to make the hell of Auschwitz visible and therefore imaginable.
*Georges Didi-Huberman, Images malgré tout, (Images despite everything), Paris, Les Editions de Minuit, 2003, p. 14.
Sonderkommandos were work units made up of German Nazi death camp prisoners. They were composed of prisoners, usually Jews, who were forced, on threat of their own deaths, to aid with the disposal of gas chamber victims during the Holocaust. The death-camp Sonderkommandos, who were always inmates, should not be confused with the SS-Sonderkommandos which were ad hoc units formed from various SS offices between 1938 and 1945. The term itself in German means “special unit”, and was part of the vague and euphemistic language which the Nazis used to refer to aspects of the Final Solution (cf. Einsatzkommando units of the Einsatzgruppen death squads).
About 120 SS personnel were assigned to the gas chambers and lived on site at the crematoria. Several SS personnel oversaw the killings at each gas chamber, while the bulk of the work was done by the mostly Jewish prisoners known as Sonderkommandos (special squads) Sonderkommando responsibilities included guiding victims to the gas chambers and removing, looting, and cremating the corpses.
The Sonderkommado were housed separately from other prisoners, in somewhat better conditions. Their quality of life was further improved by access to the goods taken from murdered prisoners, which Sonderkommandos were sometimes able to steal for themselves and to trade on Auschwitz’s black market. Hungarian doctor Miklós Nyiszli reported that the Sonderkommando numbered around 860 prisoners when the Hungarian Jews were being killed in 1944. Many Sonderkommandos committed suicide due to the horrors of their work; those who did not generally were shot by the SS in a matter of weeks, and new Sonderkommando units were then formed from incoming transports. Almost none of the 2,000 prisoners placed in these units survived to the camp’s liberation.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Ken Hamblin (American, b. 1940)
Beaubien Street
1971
Modern gelatin silver print
Fifth Estate photo
Joseph A. Labadie Collection, Special Collections Library, University of Michigan
Joan Miró (Spanish, 1893-1983)
L’Espoir du prisonnier, dessin préparatoire pour L’Espoir du condamné à mort I, II et III
Prisoner’s Hope, Preparatory Drawing for The Hope of the Dead Man I, II and III
1973
Colored pencils and pen on paper (notepad)
7.7 x 12.5cm
Fundació Joan Miró, Barcelone
© Successió Miró / ADAGP, Paris, 2016
Photo: Fundació Miró, Barcelone
This sketch is part of a series of preparatory studies for a triptych entitled The Hope of the Condemned to Death, completed in March 1974. It is already possible to guess the overall design (three horizontal compositions of primary colours formed of sinuous lines) and the title seems to be clarified with the addition of these words: “the hope of the prisoner”. Sensitive to the death sentence of the anarchist and anti-fascist militant Salvador Puig i Antich, a member of the Movimiento Ibérico de Liberación, Joan Miró claims that he completed his triptych on the day of his execution on 2 March 1974. Thus the artwork – initially imagined in an abstract and metaphorical way – then encounters history. This triptych executed in very large format so as to address the greatest number, as Miró wished that the painting would be, thus constitutes a real monument to the memory of one of the last victims of Francoism. Judged “prophetic” by the artist, he presents a series of black lines that he interpreted as an image of the tourniquet used for execution. Struggling or playing as much with the void as with the spots of vivid colours, these dark lines on a light background also seem to be distended and open like a permitted hope. From his first studies, Joan Miró managed to preserve intact, by the energy of the gesture and the vivacity of the keys, the “indestructible desire” to hope and resist, which culminated the following year in the fall of the Franco regime.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Eduardo Gil (Argentinian, b. 1948)
Niños desaparecidos. Secunda Marcha de la Resistancia (Murdered children. Second Resistance March)
December 9-10 1982
Modern gelatin silver print
Eduardo Gil collection
© Eduardo Gil
Eduardo Gil was born in 1948 in Buenos Aires, Argentina. After studying sociology, he became a photographer. Self-taught and sensitive to social struggles, his commitment was linked to the establishment of the military dictatorship following the coup d’état of 24 March 1976. Working for the press and as an independent author, he made a series of reports on the political situation and social life of his country. He photographed in particular the second March for the Resistance in Buenos Aires on 9 and 10 December 1982. Organised at the call of the Mothers of the Place de Mai in tribute to the missing children during the dictatorship, the First march of the Resistance in 1981 ‘Is then reproduced every year until 2006, involving the entire society, including after the end of the dictatorship. Faced with the march, Eduardo Gil records the determined faces of the women, mothers and grandmothers of the children of Argentina, demonstrating to obtain answers on the fate of the disappeared. The use of black and white flattened the composition and accentuated the juxtaposition of the women’s faces with the banners and placards. The photographs of the children brandished by the demonstrators thus seem to merge in the procession. All appear in this sense more united than ever, stretched out towards us, as towards politics. Eduardo Gil seems to prove here that by recording the image of the missing among the living, photography itself is a force of uprising.
Text from the Jeu de Paume website translated by Google translate
Francisca Benítez (Chilean, b. 1974)
Garde l’Est
2005
Still frame
Francisca Benitez collection
© Francisca Benítez
Gohar Dashti (Iranian, b. 1980)
From the series Today’s Life and War
2008
Institut des Cultures d’Islam
The photographs of the Iranian artist Gohar Dashti’s Today’s Life and War show the daily life of a young couple against a background of war. Surrounded by tanks, bunkers and armed soldiers, the spouses live in the middle of the fields of ruins and continue to go about their occupations. Between impassivity and disillusionment, their attitudes show perseverance and unwavering determination to simply continue living. With these surreal scenes, the artist is witnessing a generation caught between the memories of ten years of war against Iraq and the permanent threat of conflict.

Pedro Motta (Brazilian, b. 1977)
Natureza das coisas #024, (The nature of things #024)
From the “Natureza das coisas” series
2013
Mineral print on cotton paper
Private collection
Courtesy of the artist and gallery Bendana Pinel
Maria Kourkouta (Greek, b. 1982)
Idomeni, 14 mars 2016. Frontière gréco-macédonienne, (Idomeni, March 14, 2016. Greek-Macedonian border)
2016
HD video loop: colour, sound, 36:00 min.
© Maria Kourkouta. Production: Jeu de Paume, Paris
Jeu de Paume
1, Place de la Concorde
75008 Paris
métro Concorde
Phone: 01 47 03 12 50
Opening hours:
Tuesday: 11.00 – 21.00
Wednesday – Sunday: 11.00 – 19.00
Closed Monday
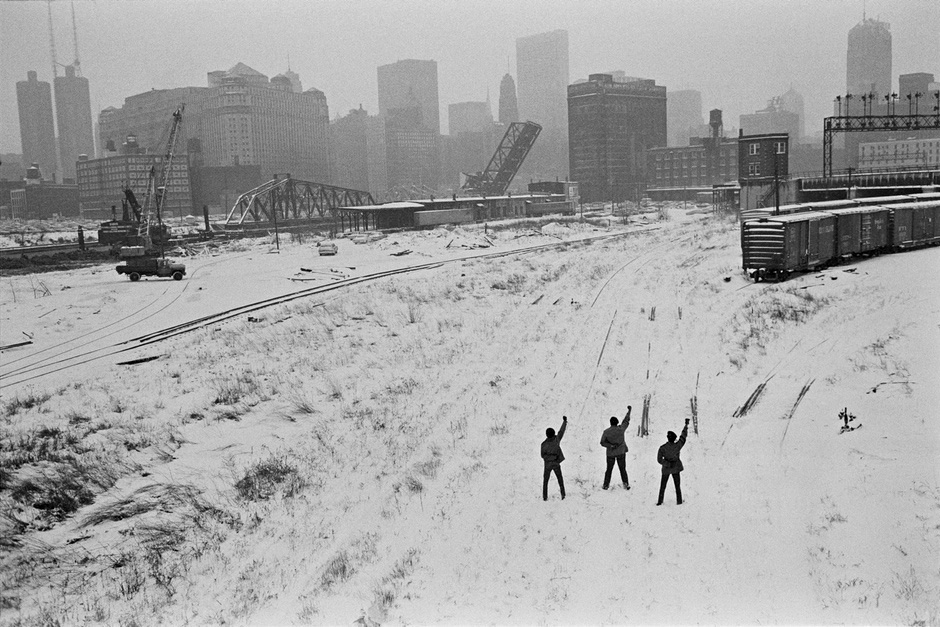
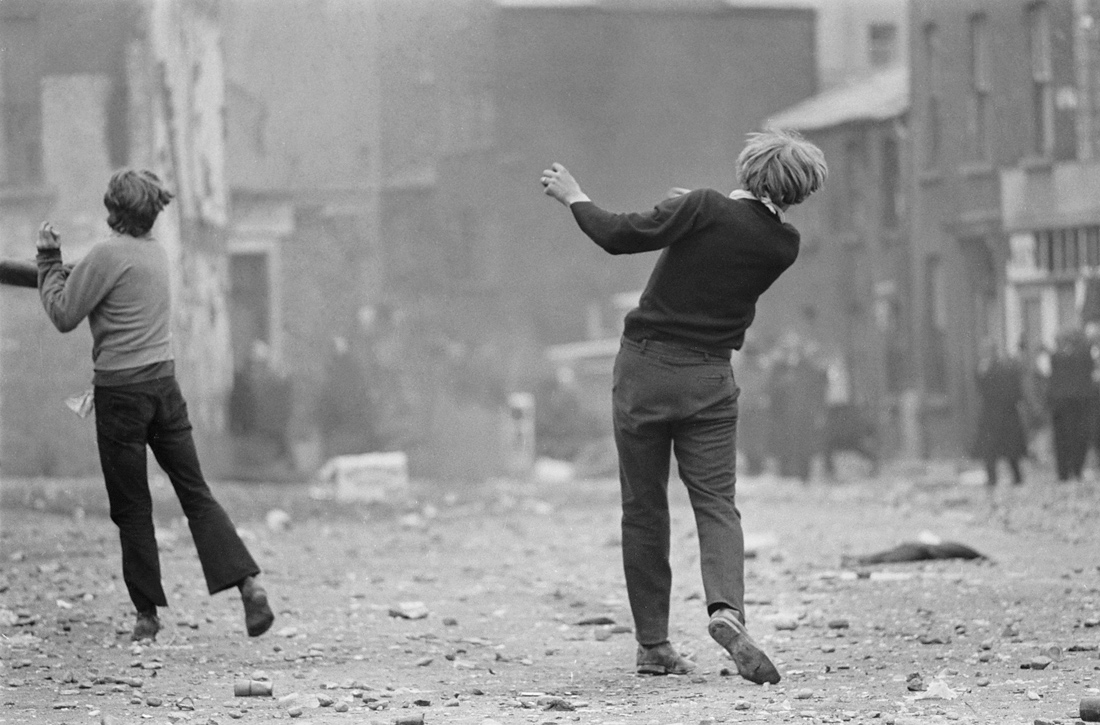
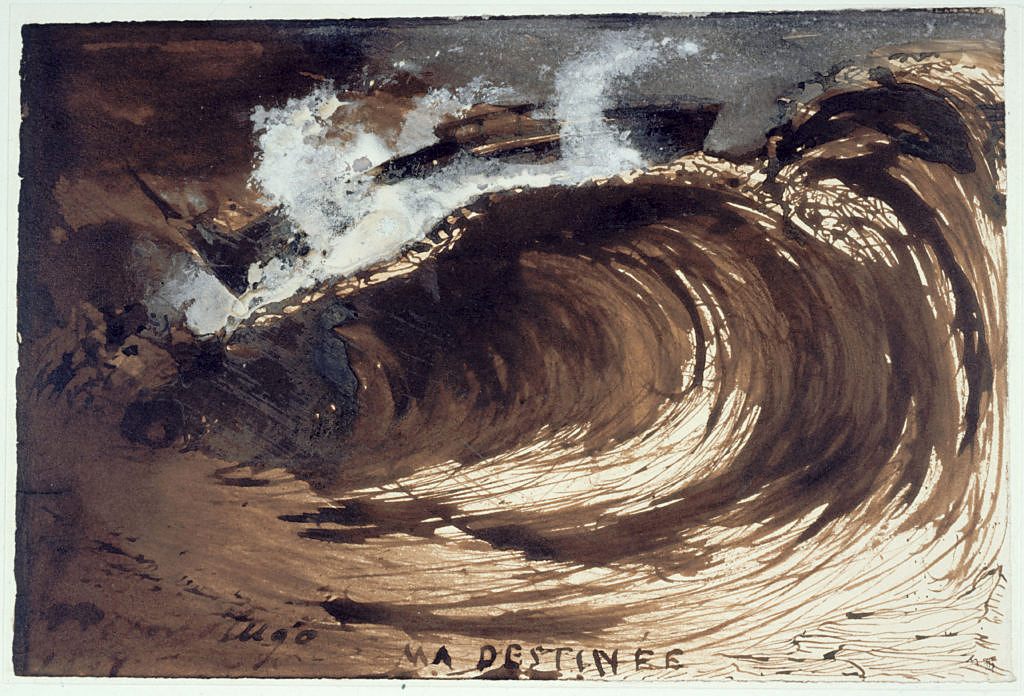
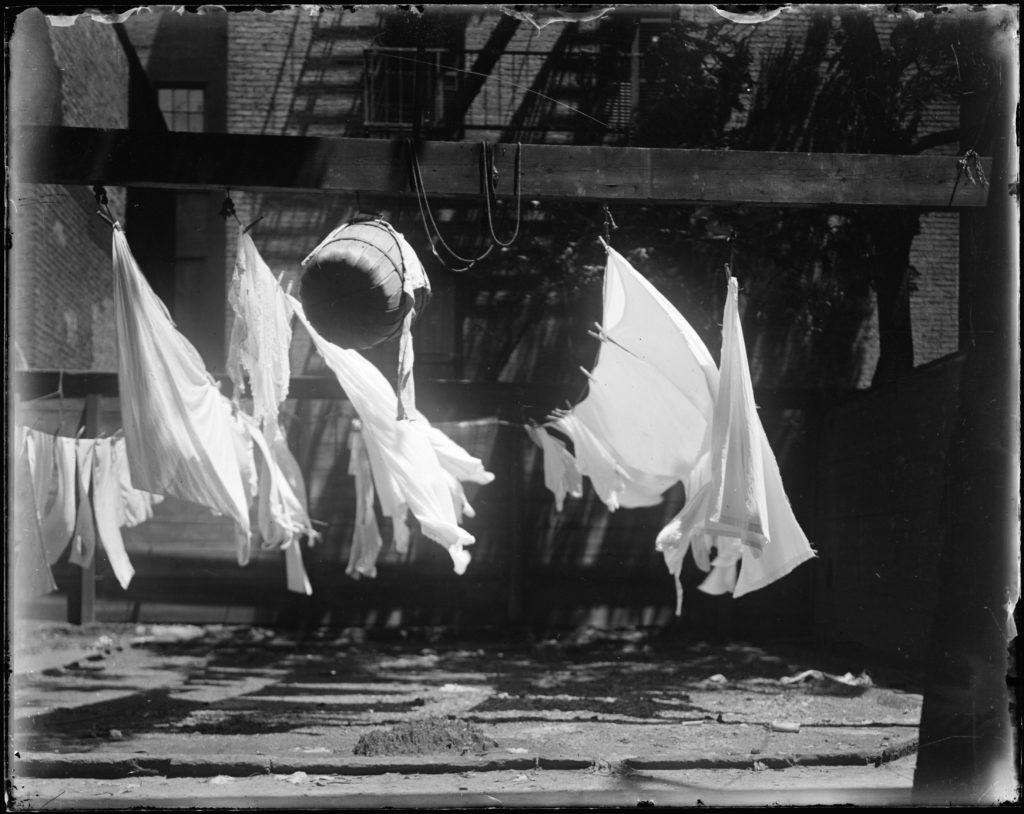
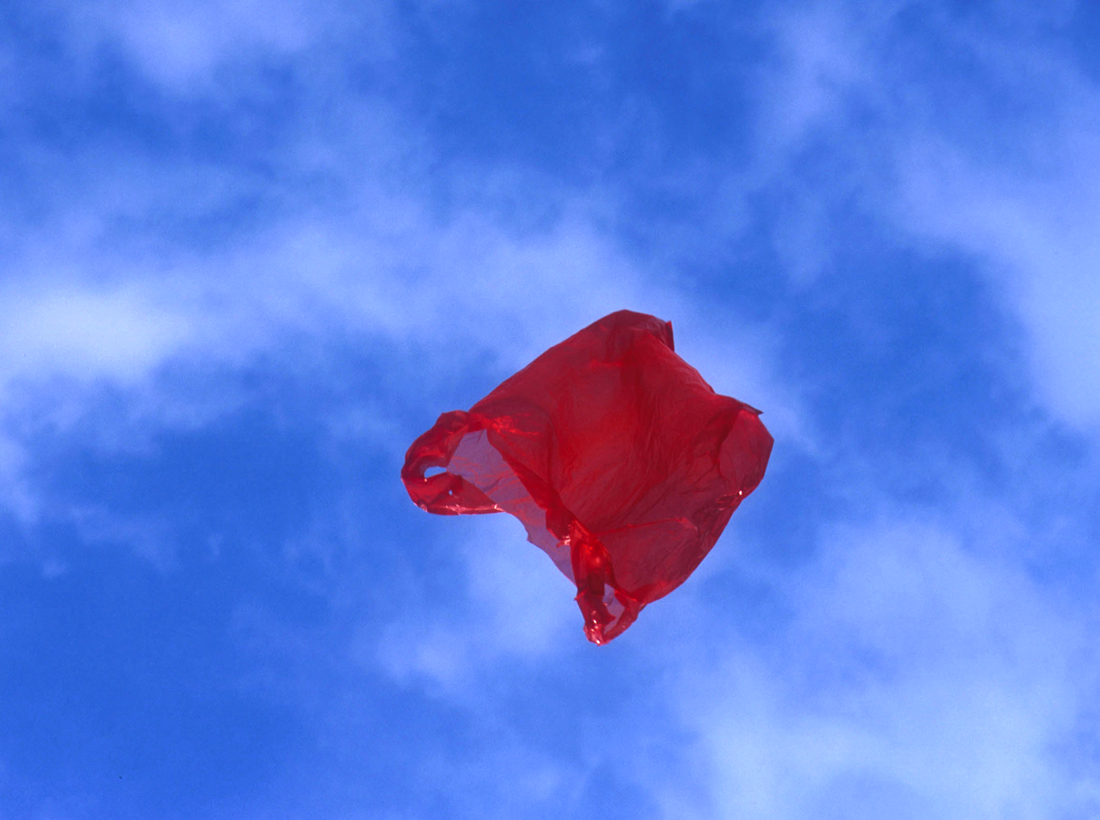
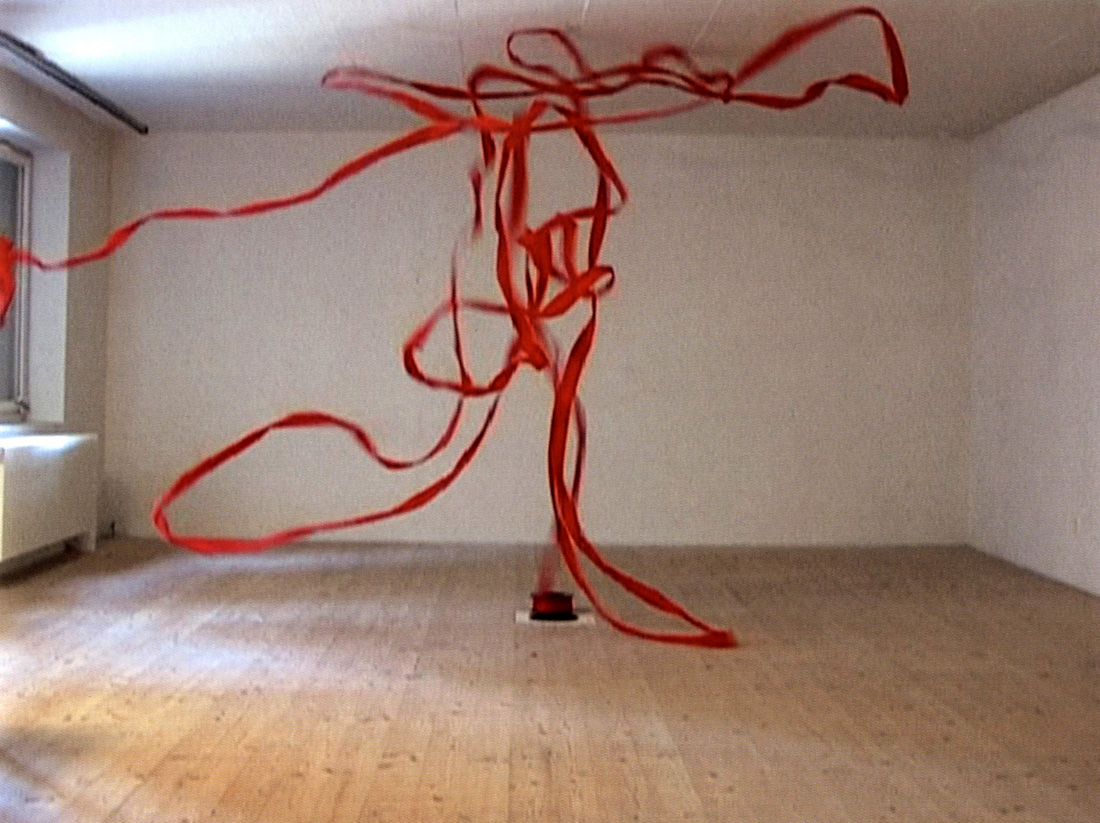
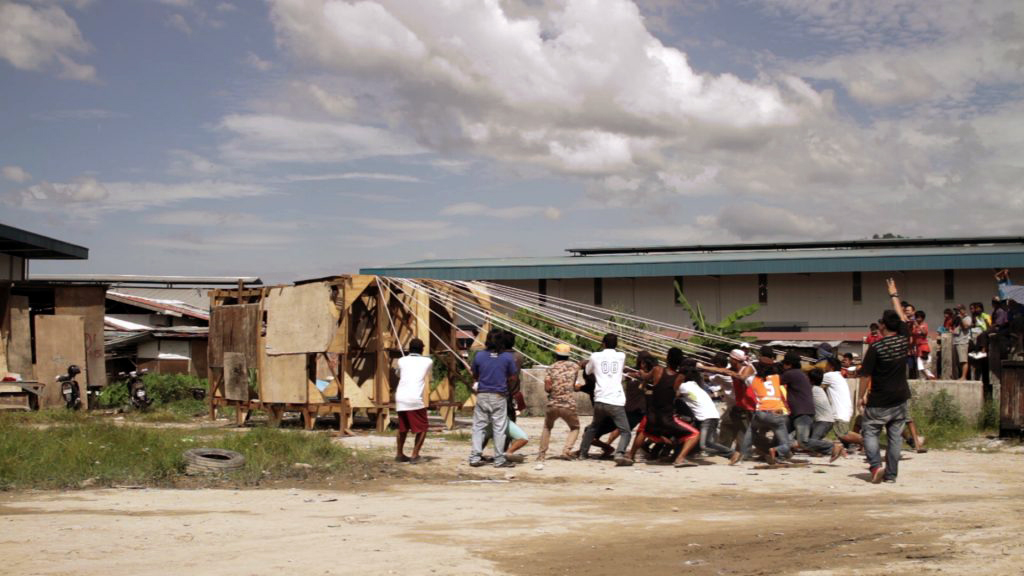
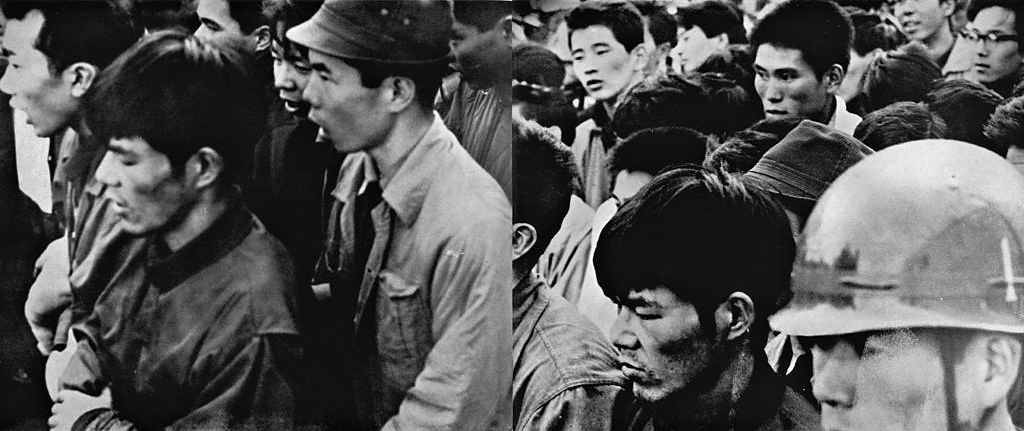
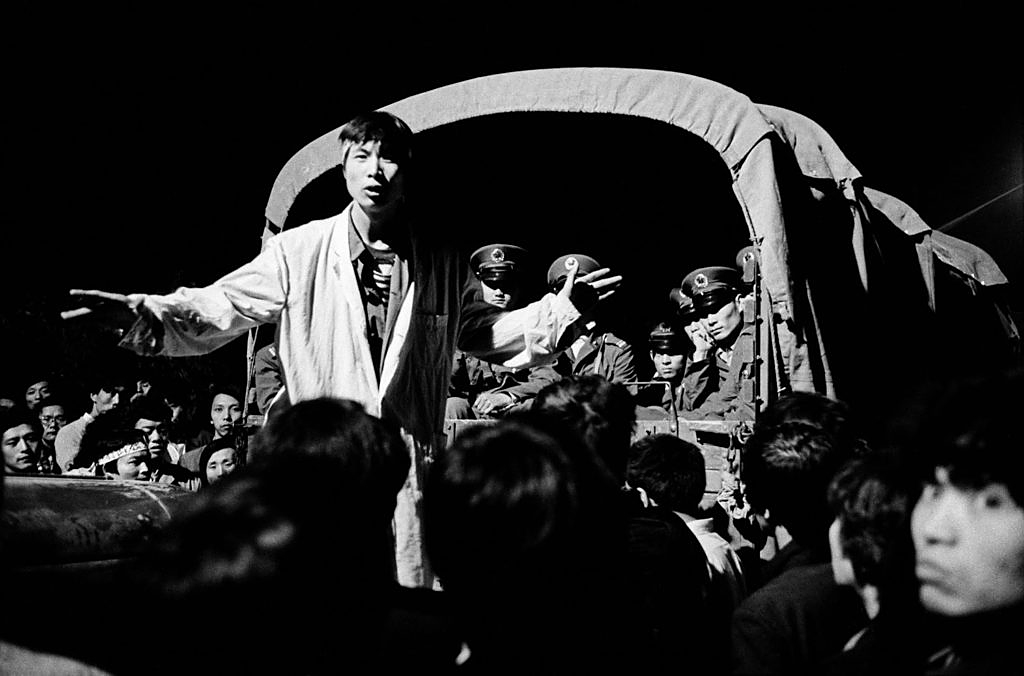
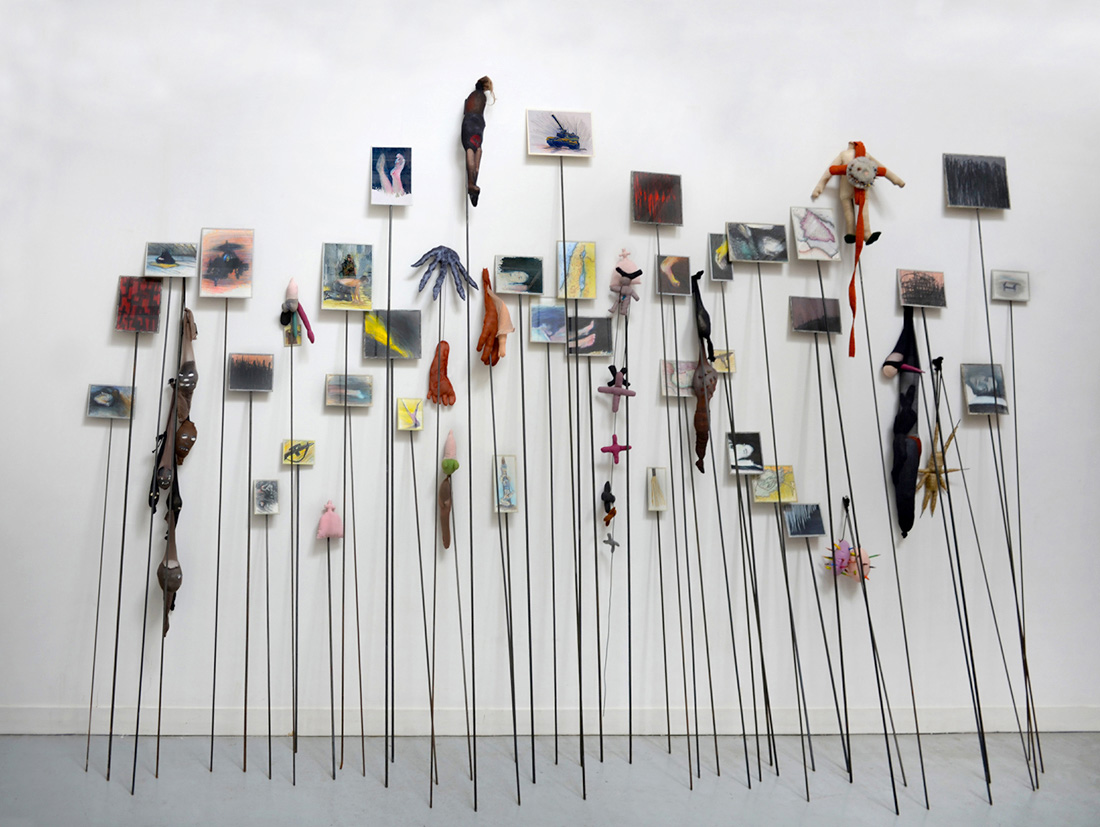
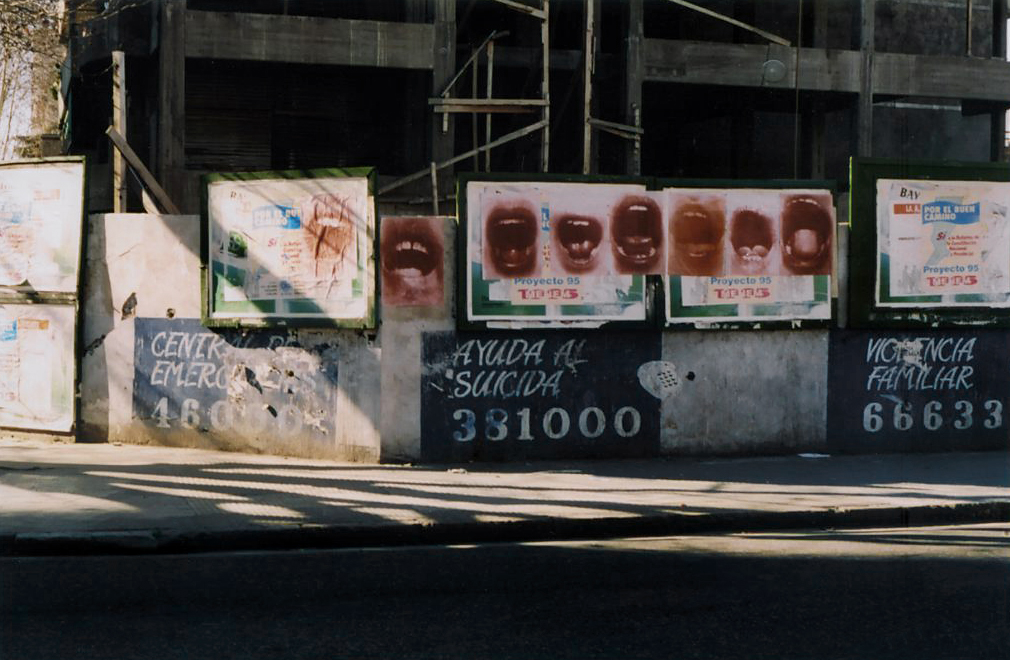
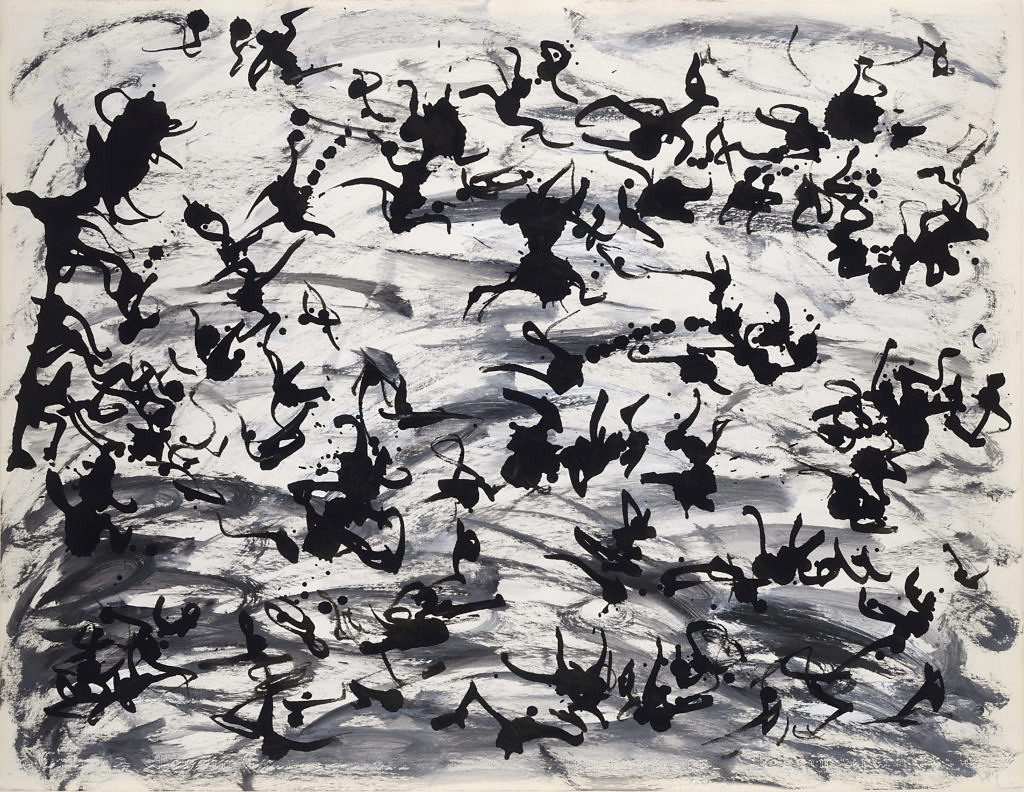
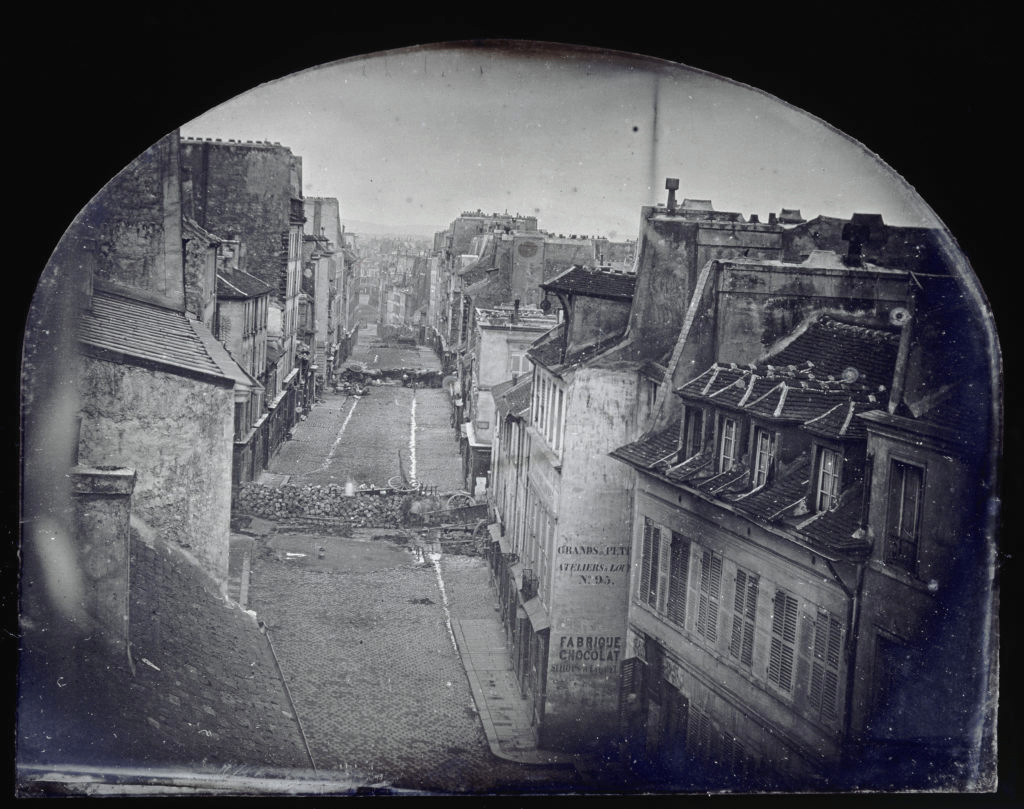
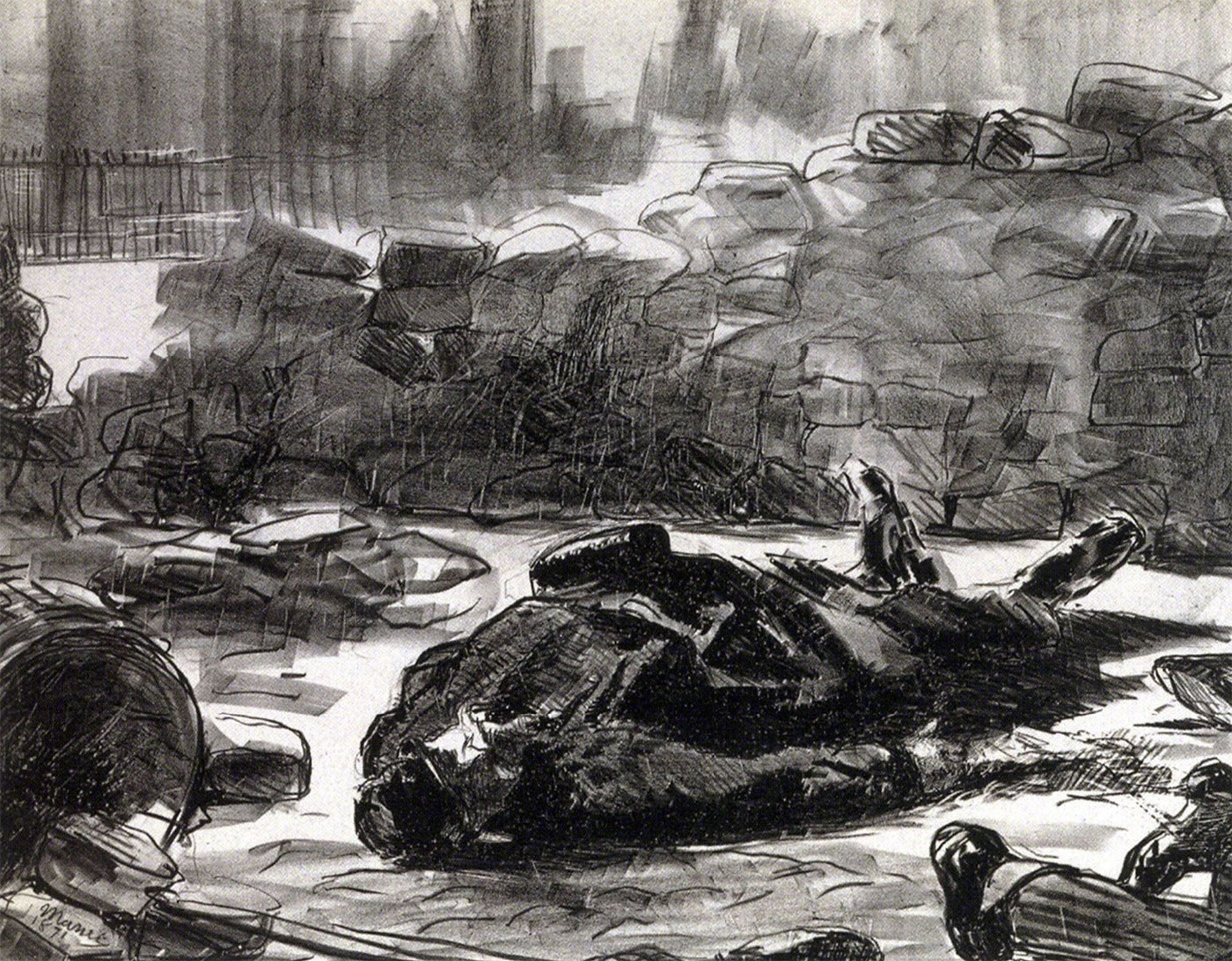
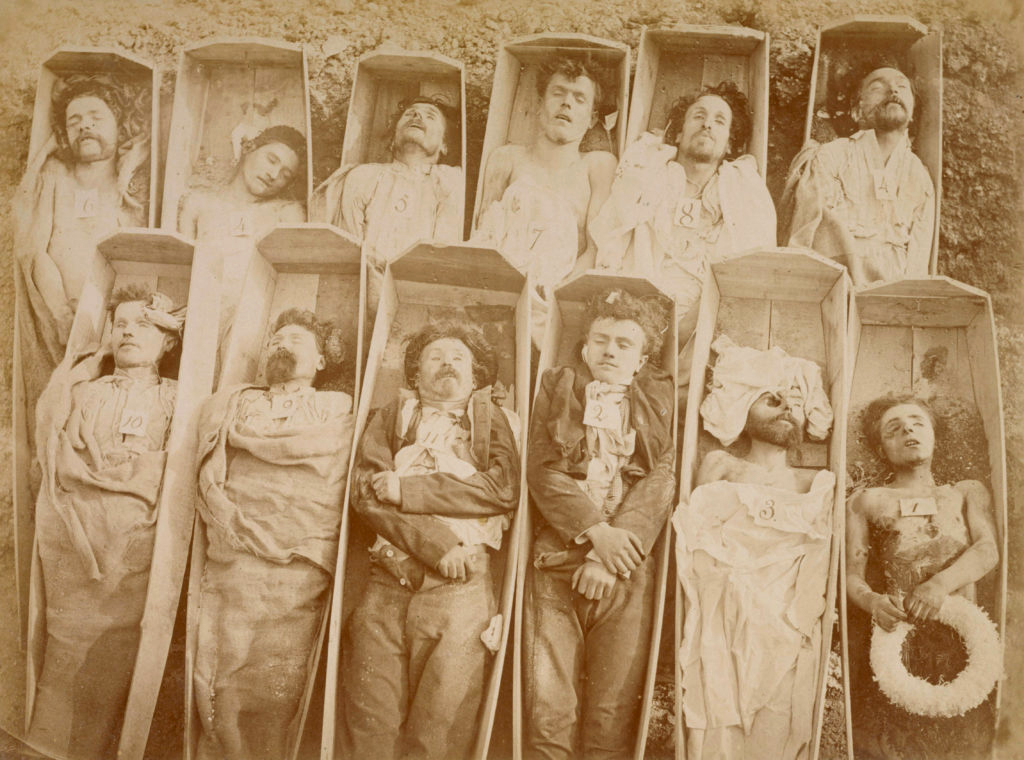
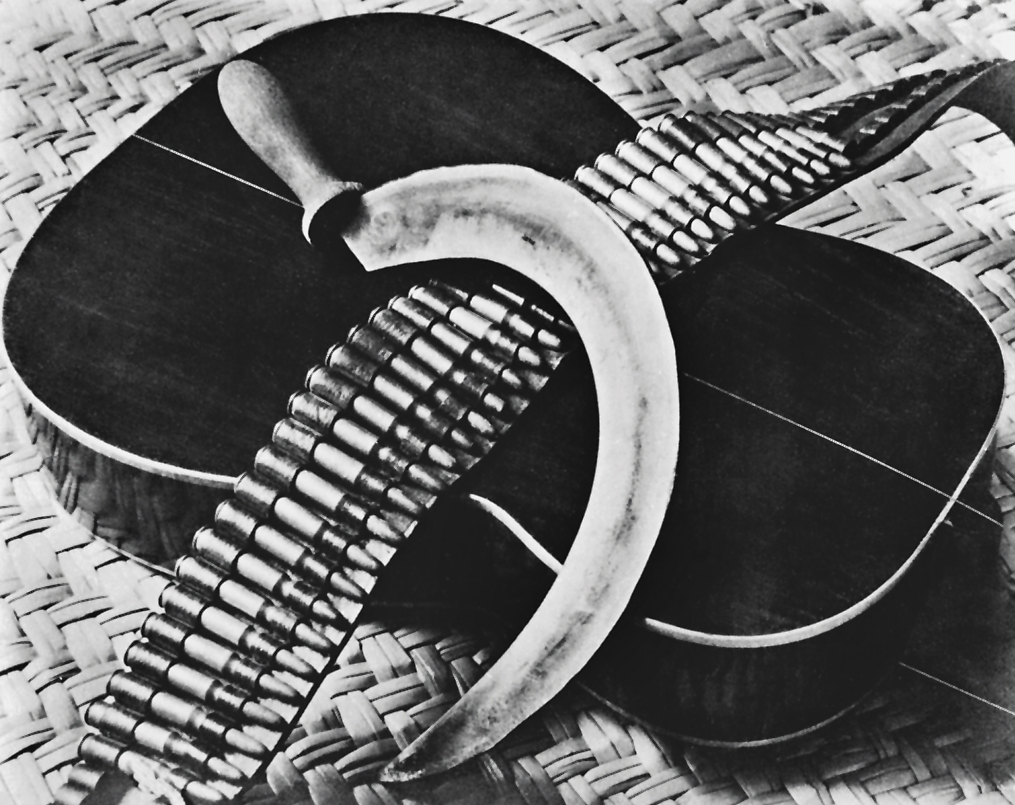
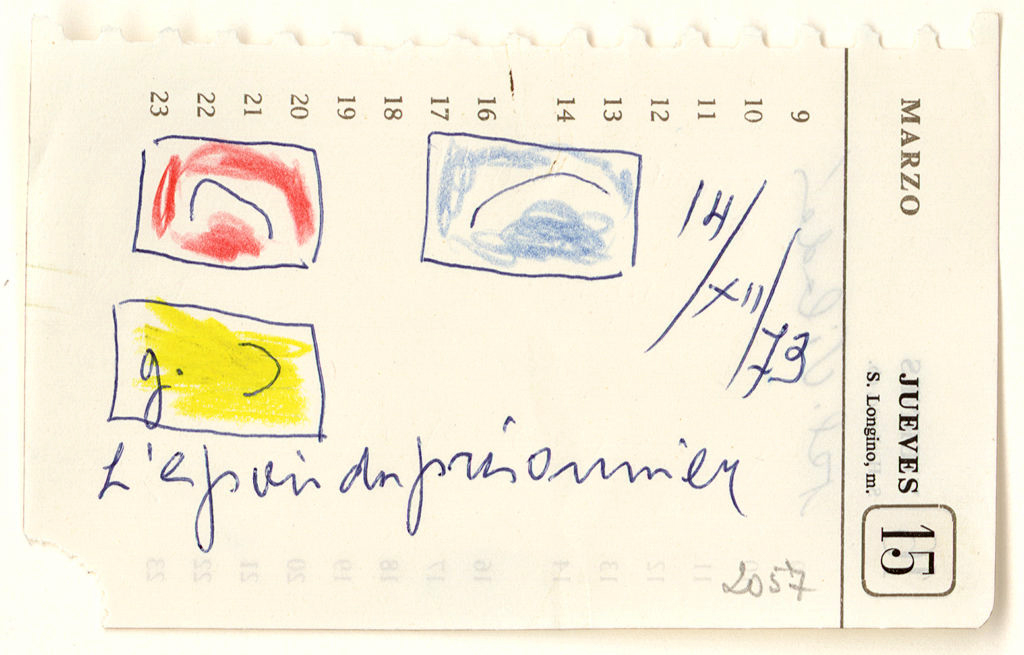
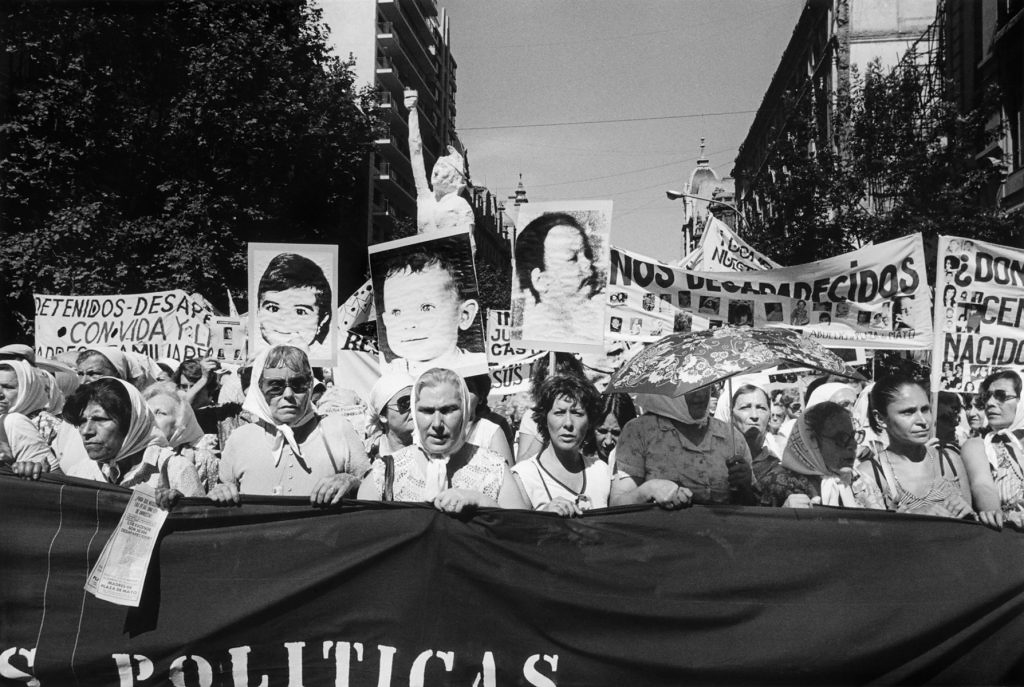
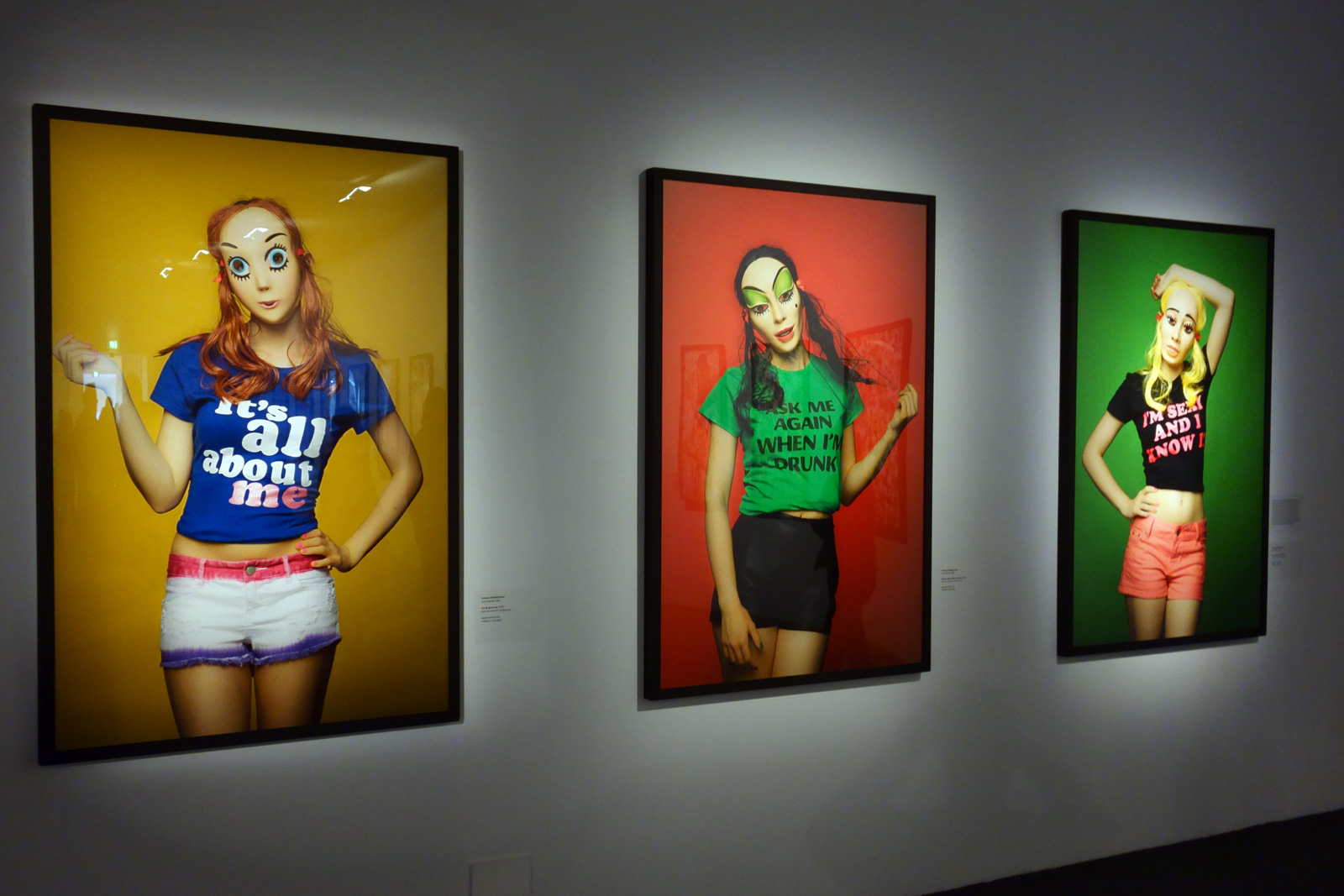
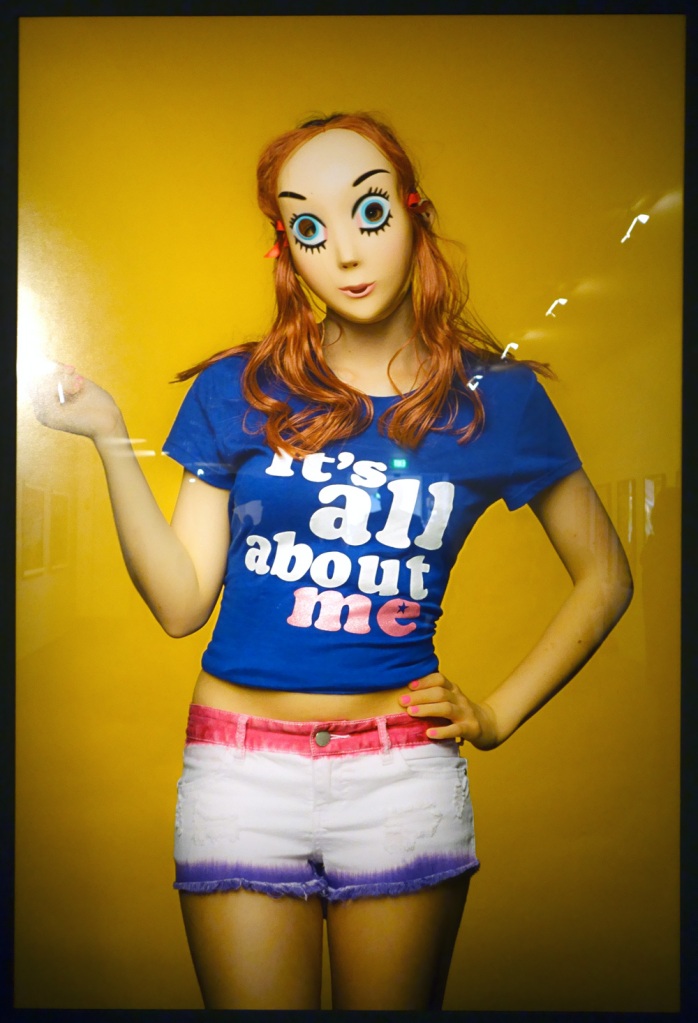
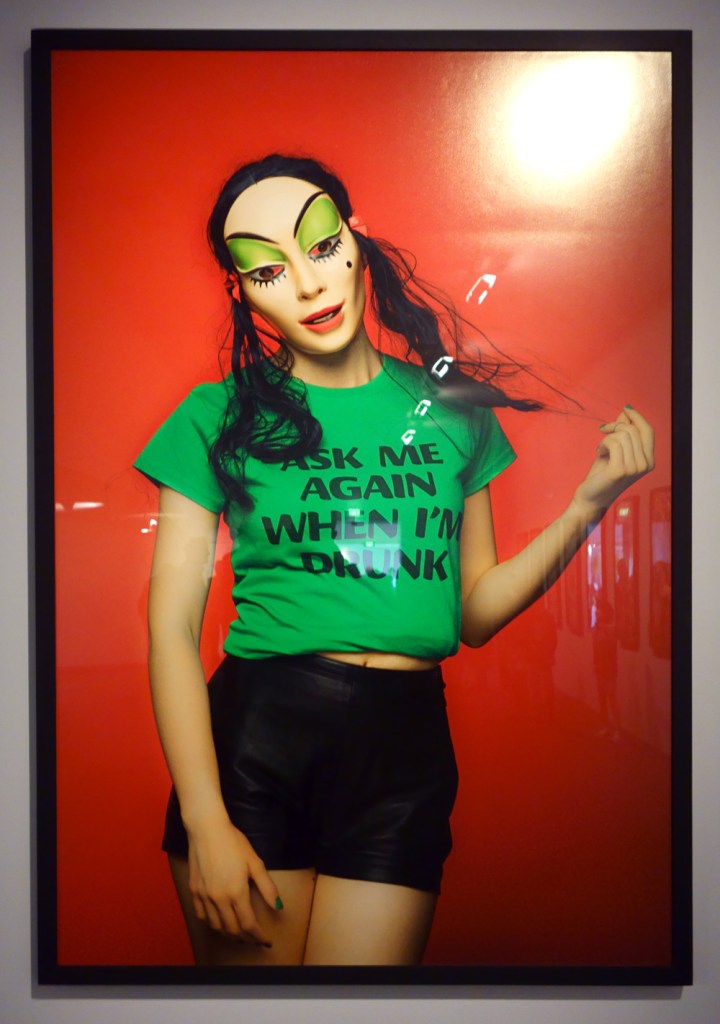
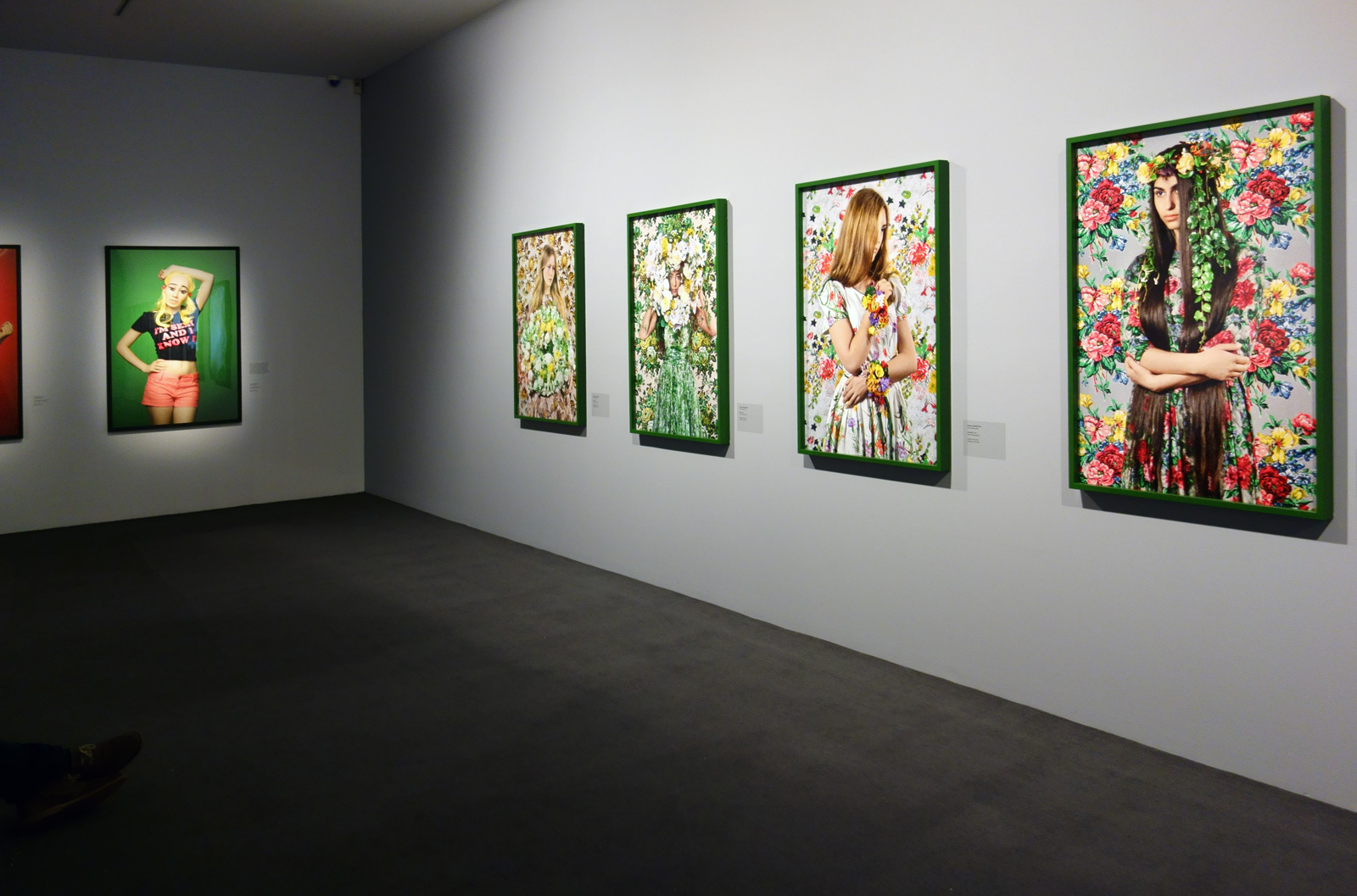
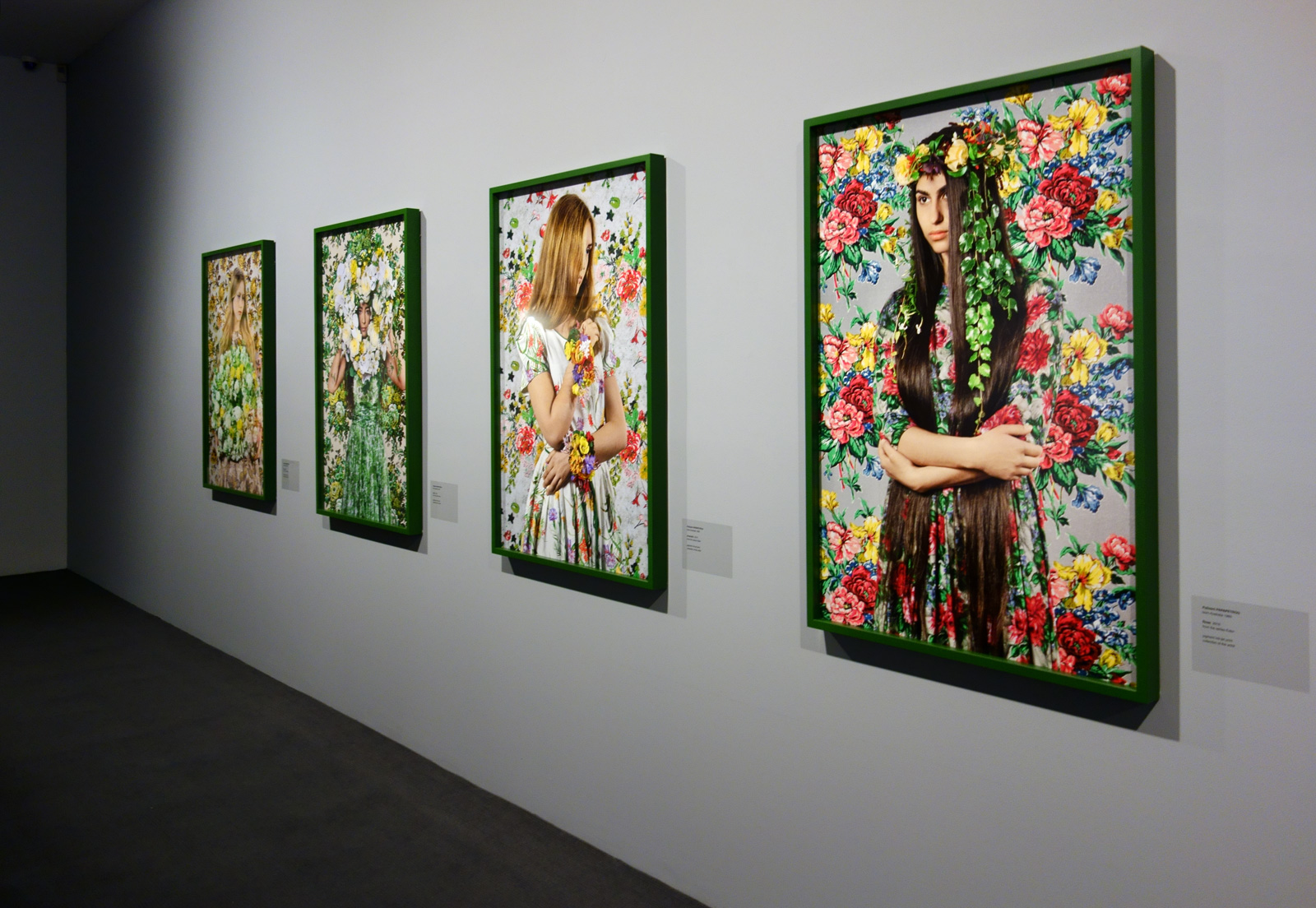
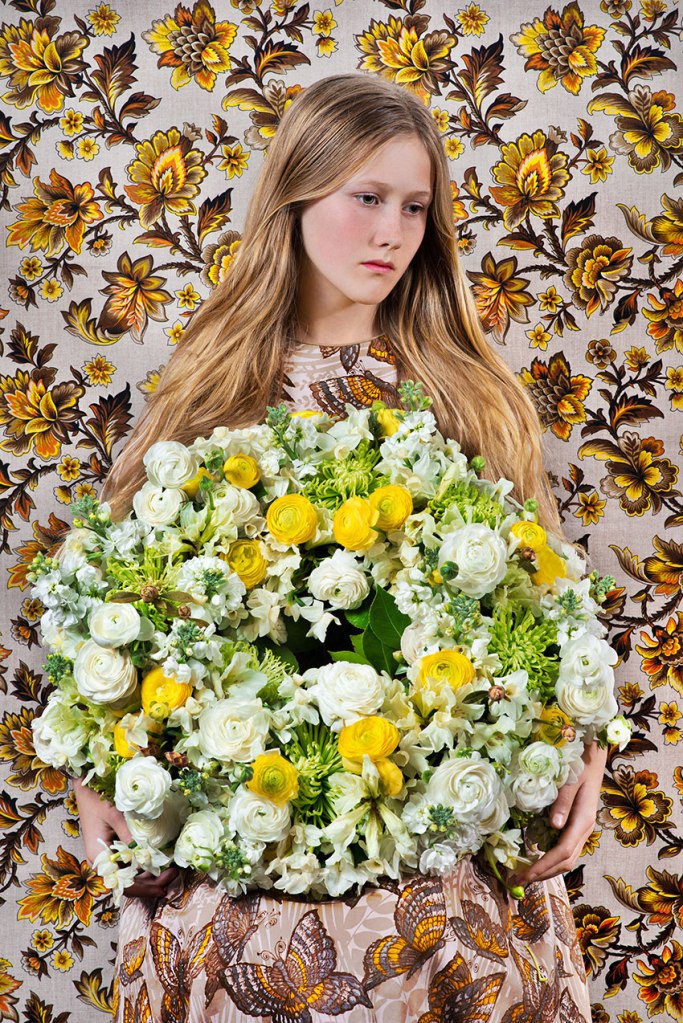
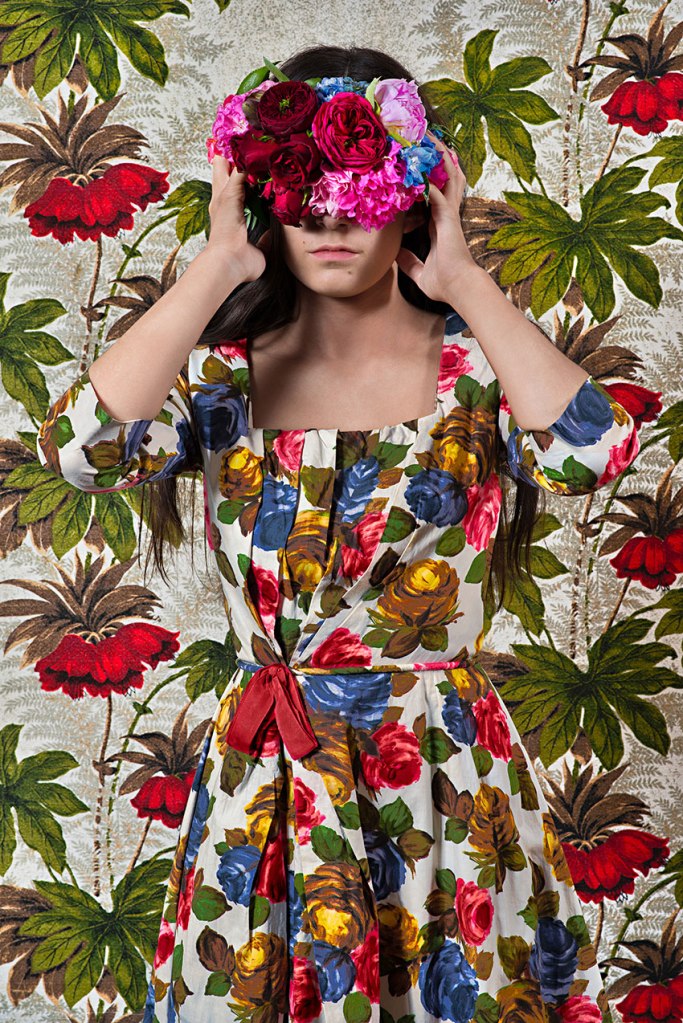
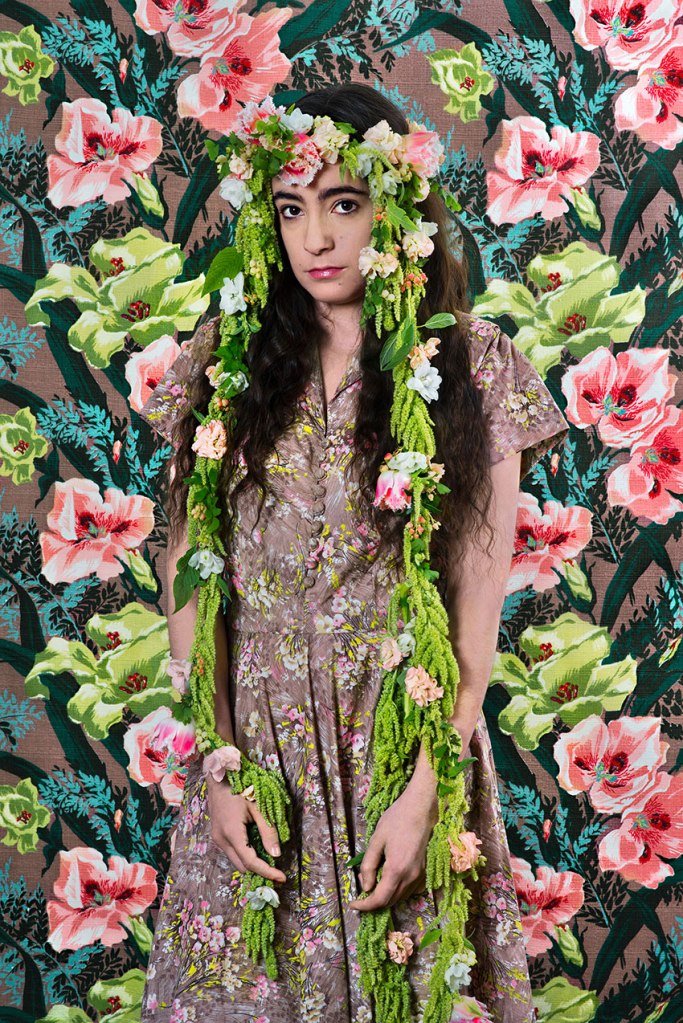
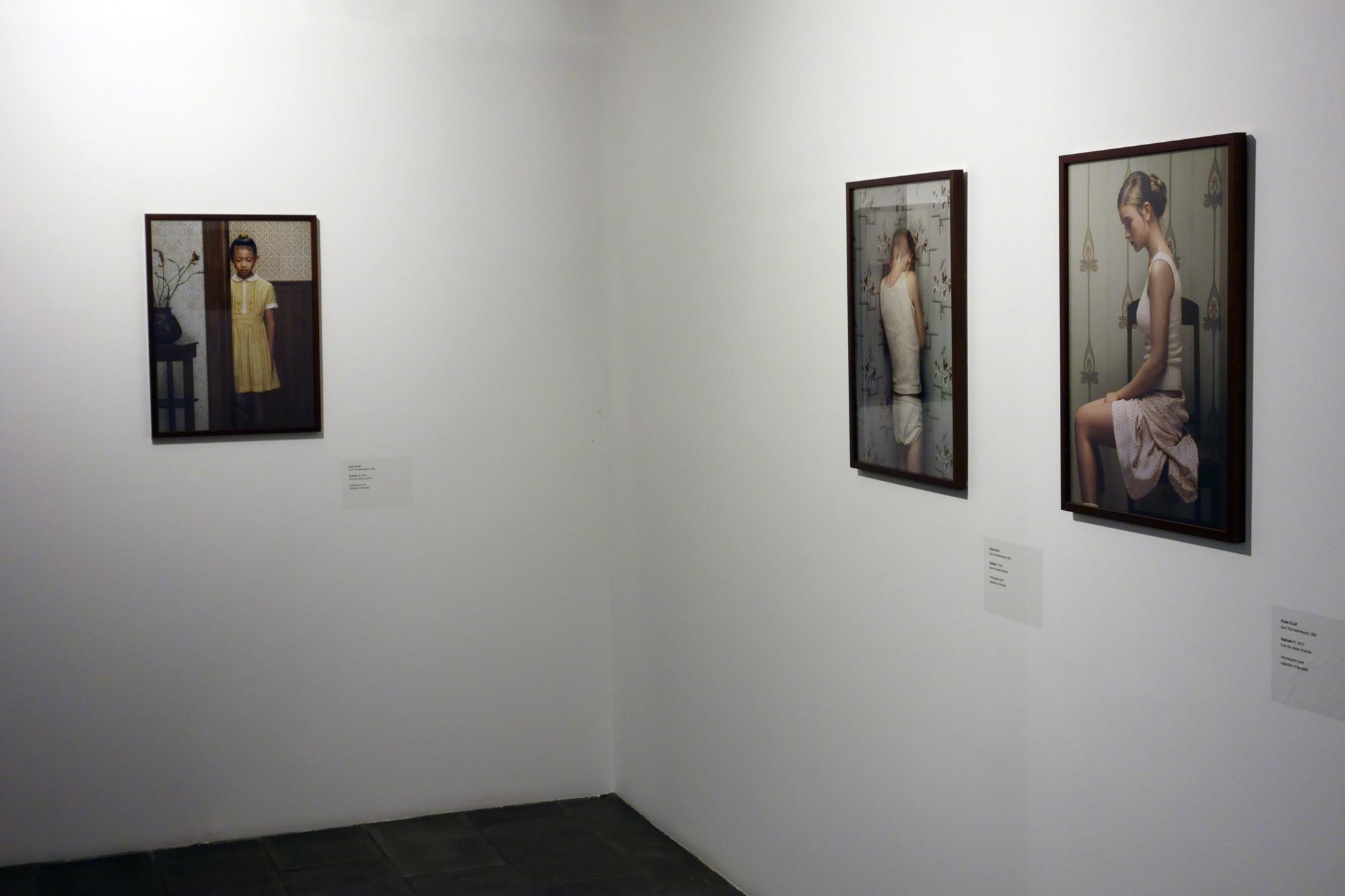
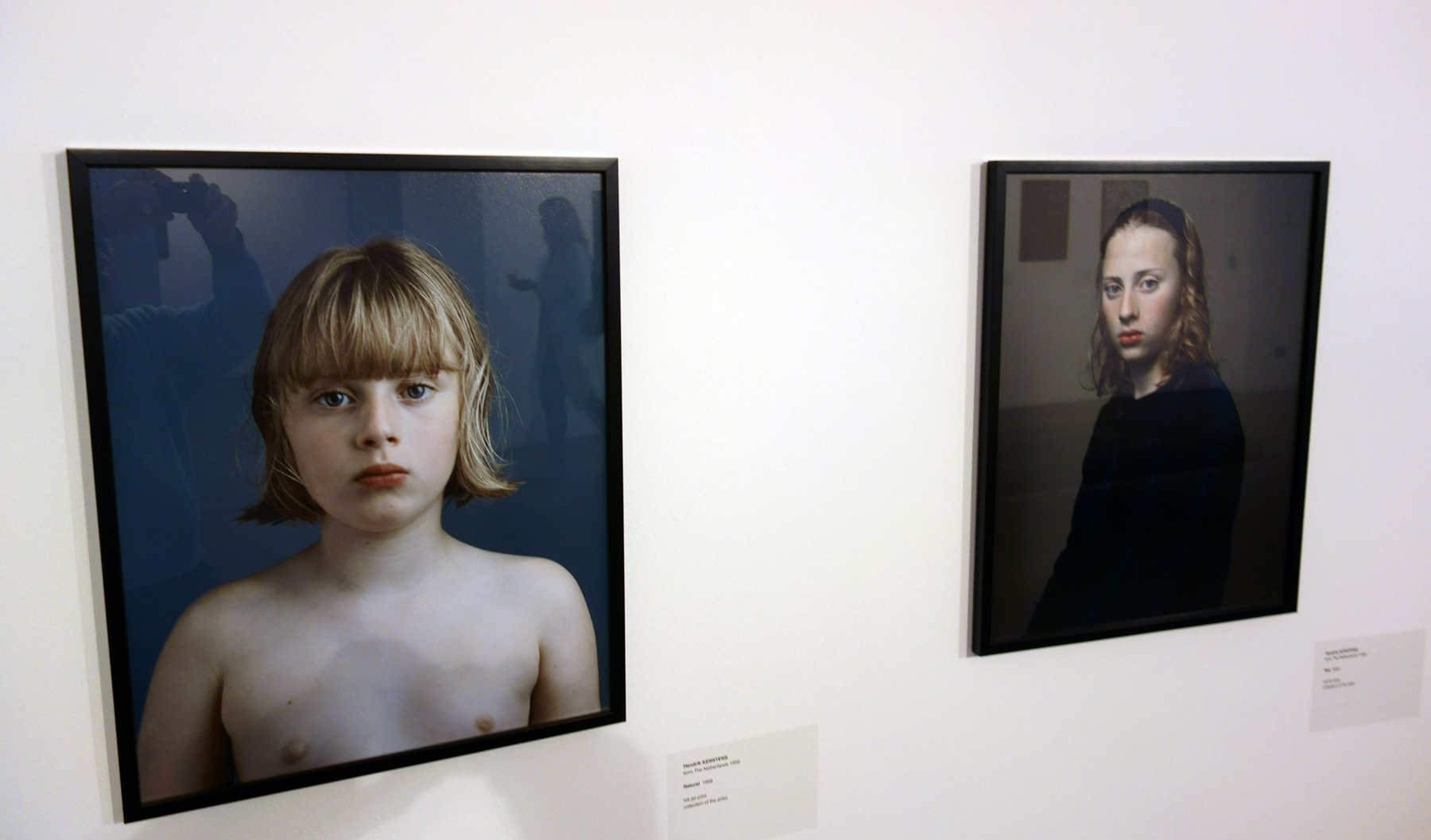
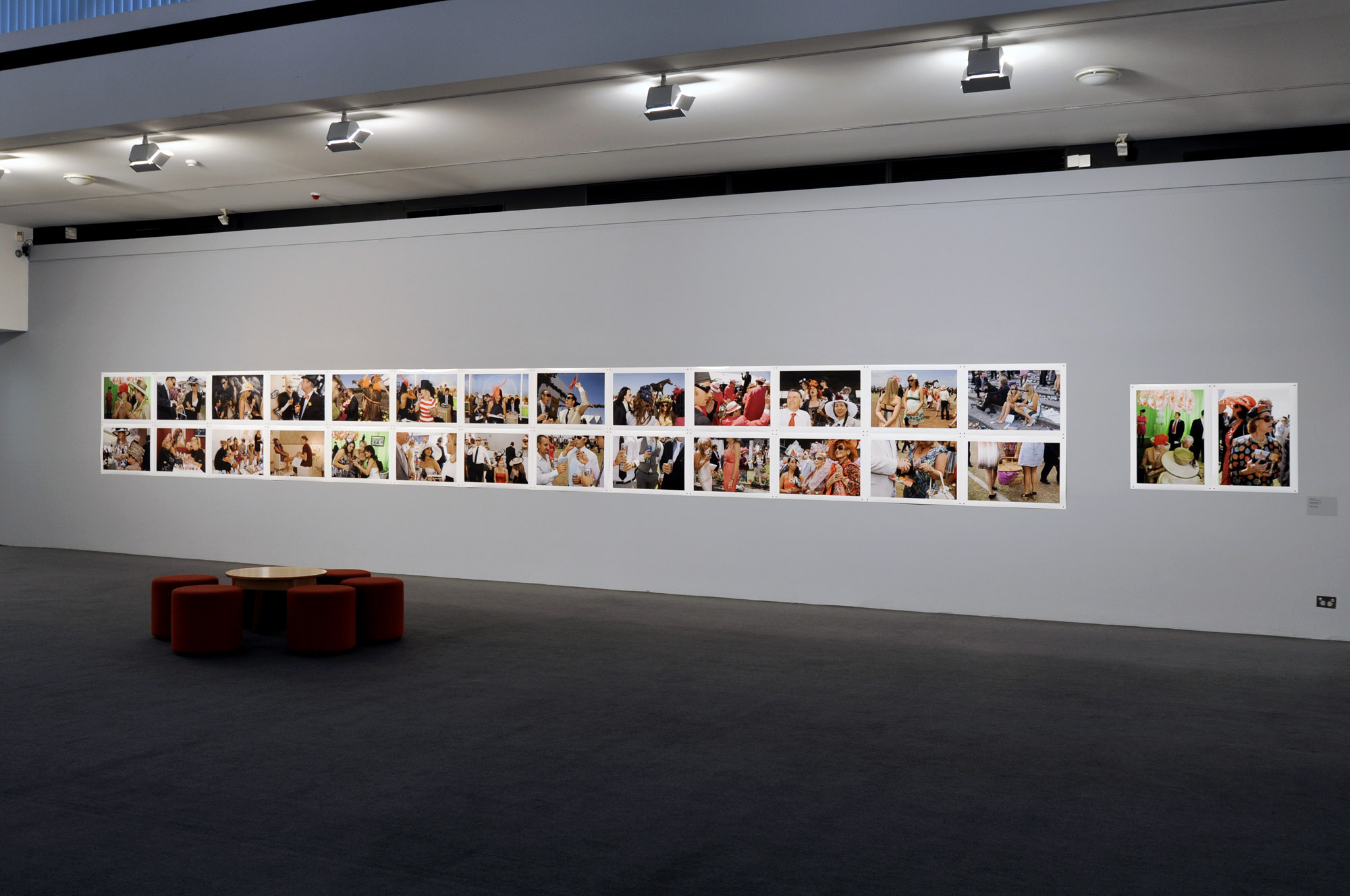
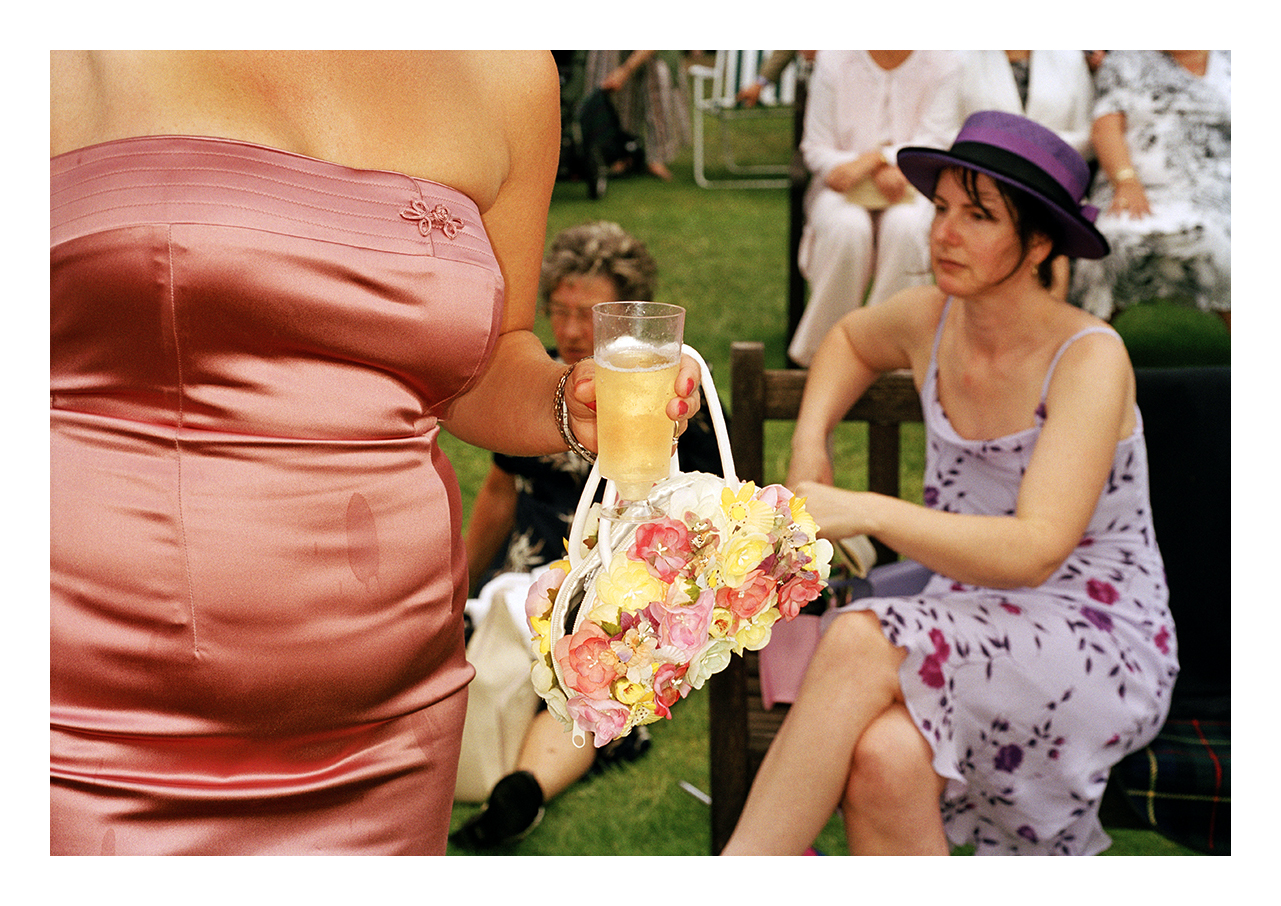
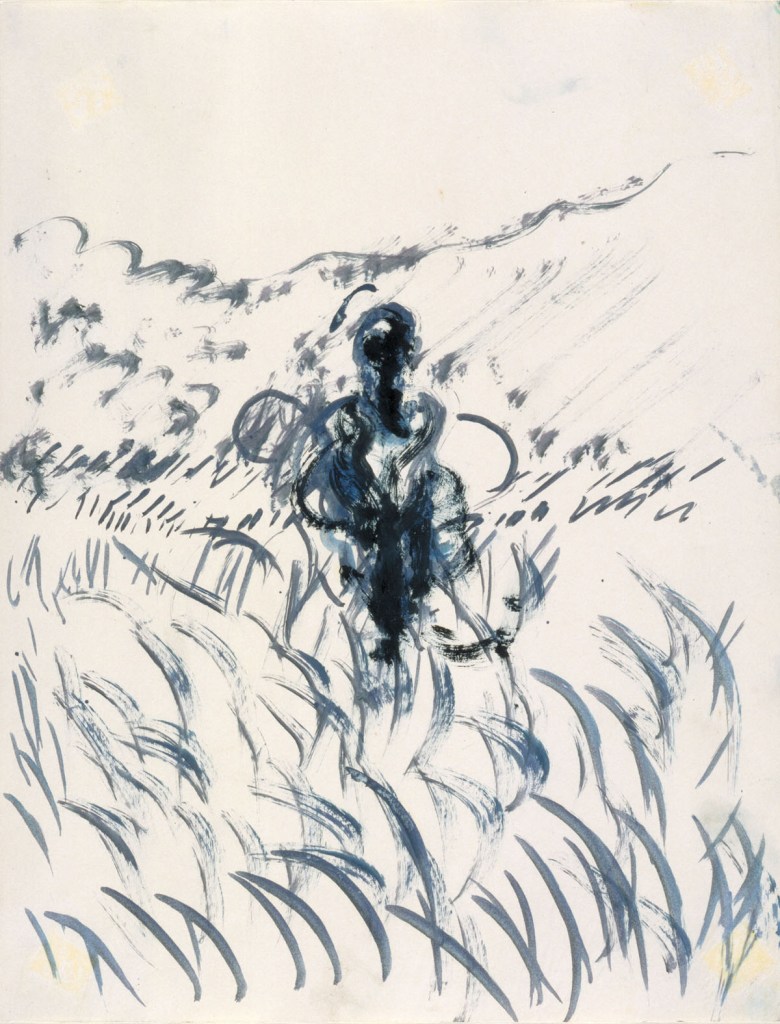
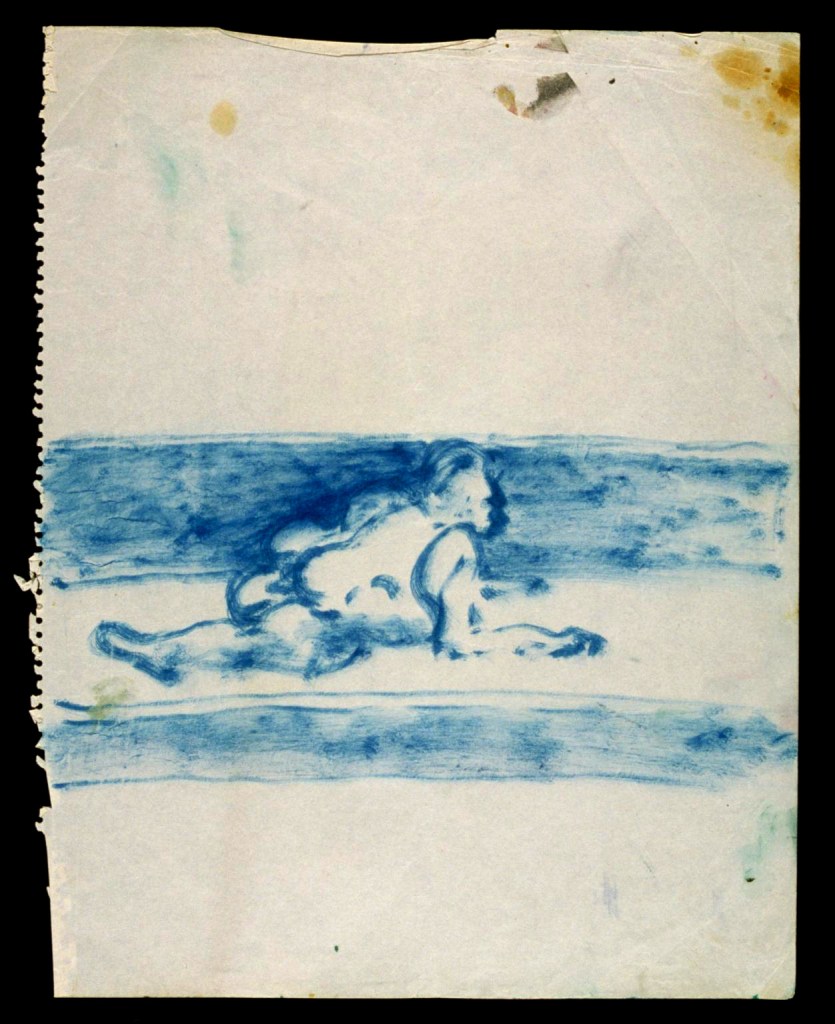
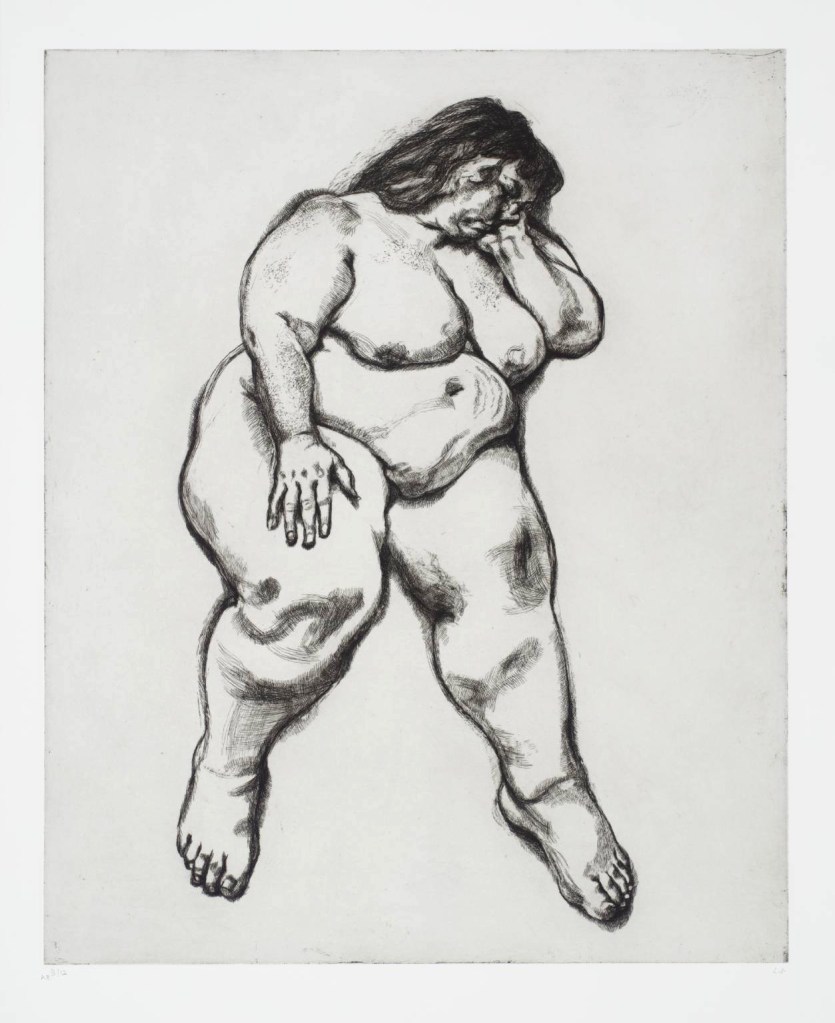
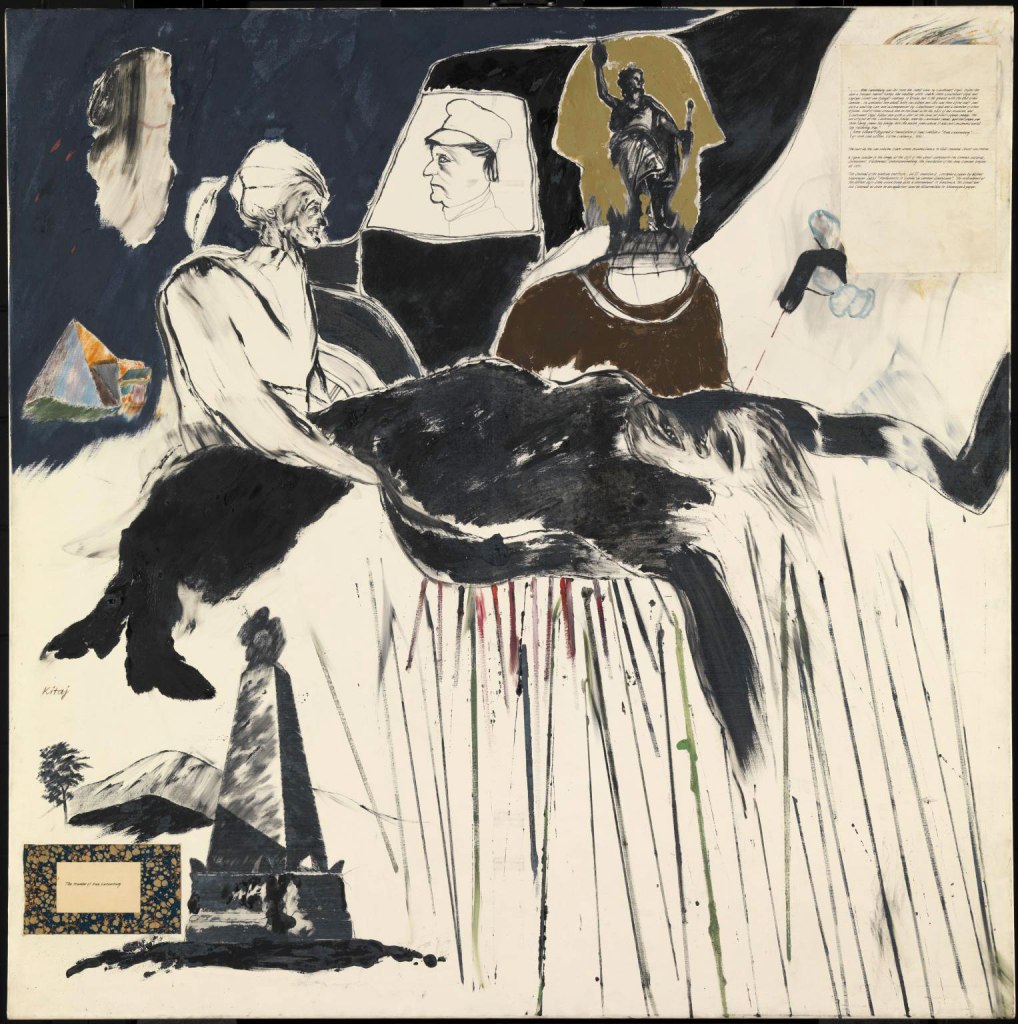




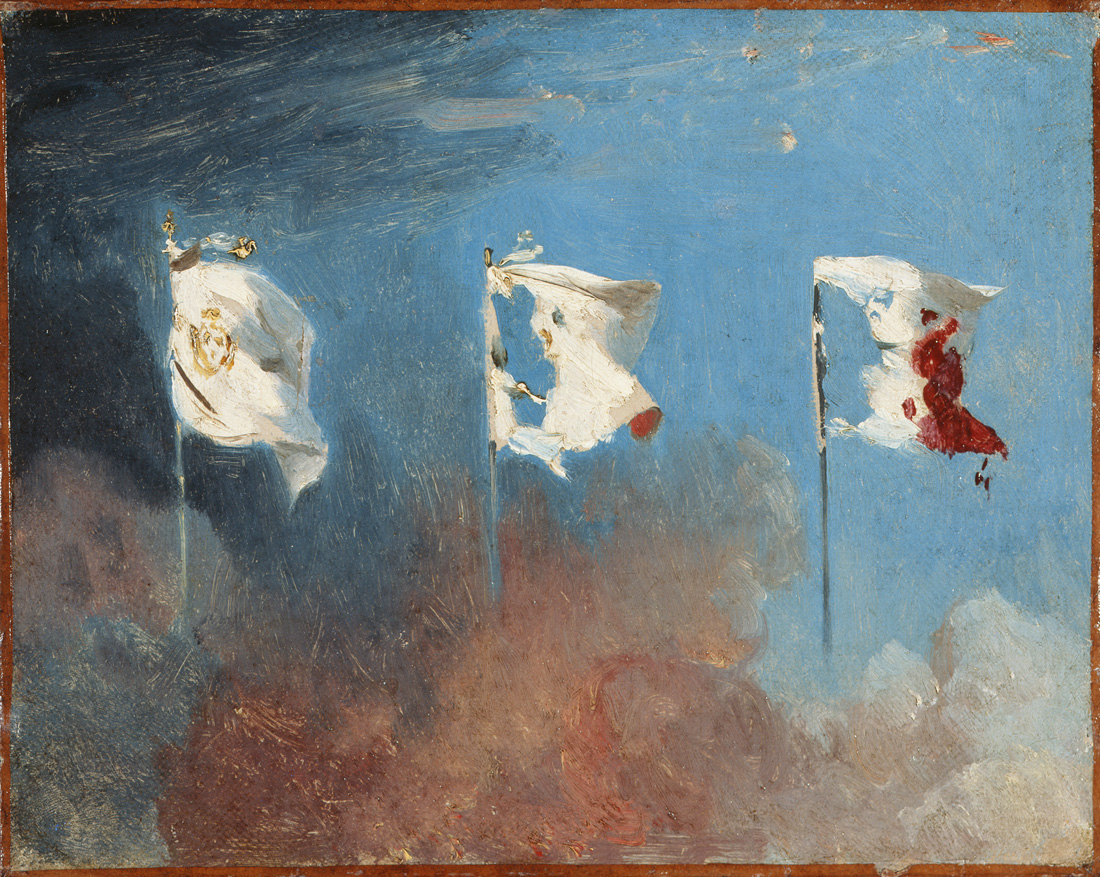


























































































































![Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) 'Untitled [O'Keeffe with sketchpad and watercolors]' 1918 from the exhibition 'Georgia O'Keeffe' at Tate Modern, London, July - Oct, 2016 Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) 'Untitled [O'Keeffe with sketchpad and watercolors]' 1918 from the exhibition 'Georgia O'Keeffe' at Tate Modern, London, July - Oct, 2016](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/georgia_okeeffe_by_stieglitz_1918-web.jpg)
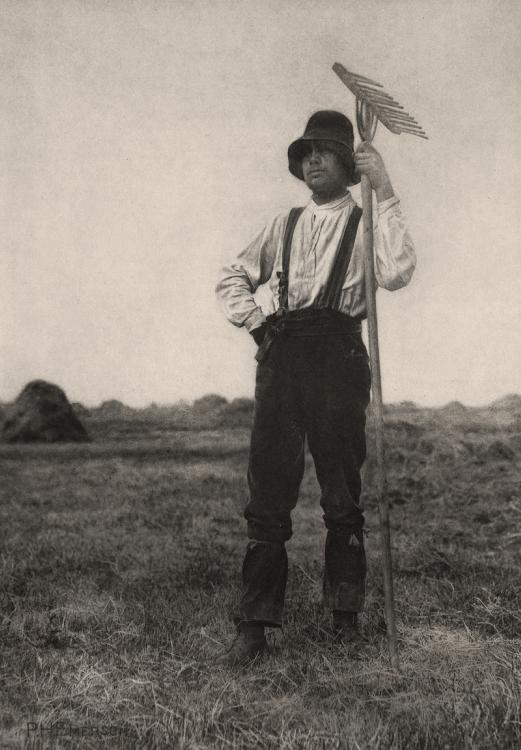
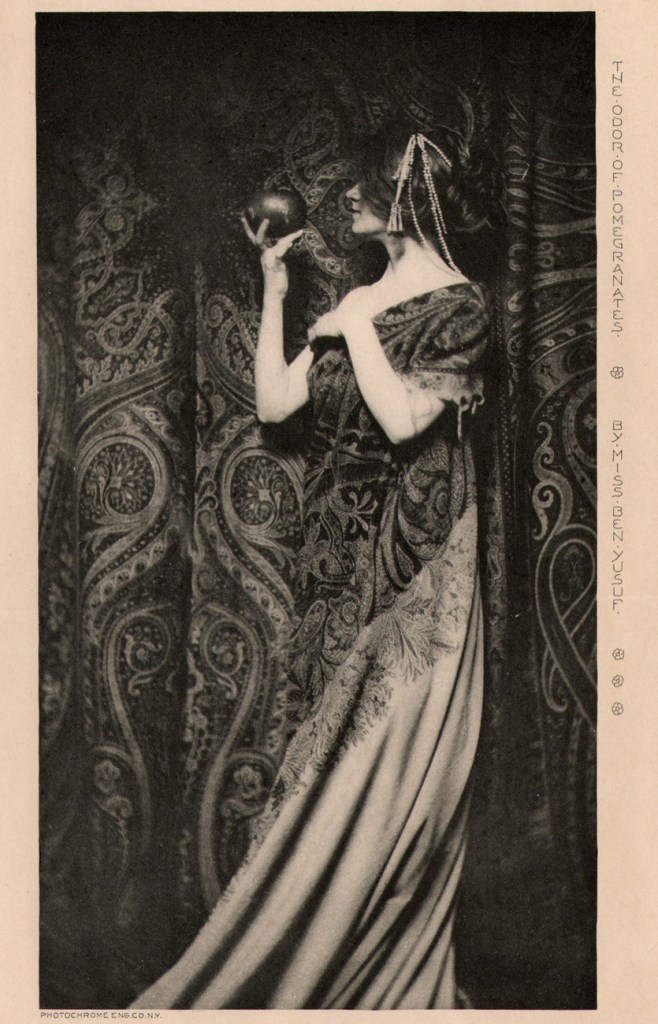
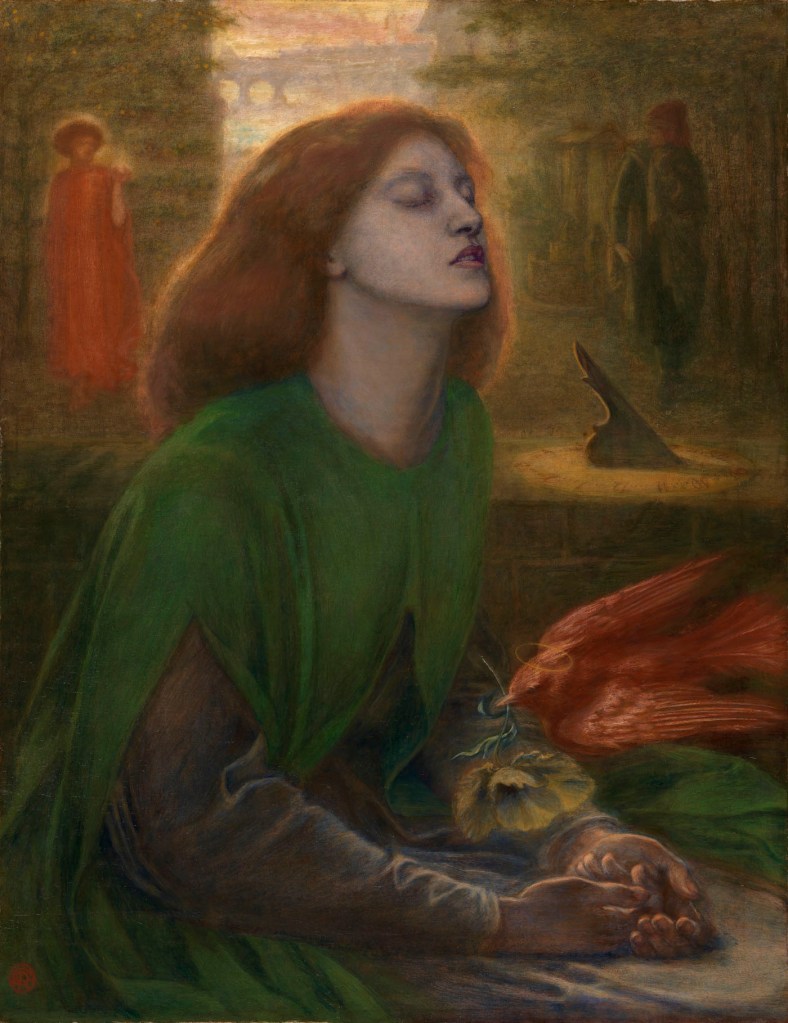
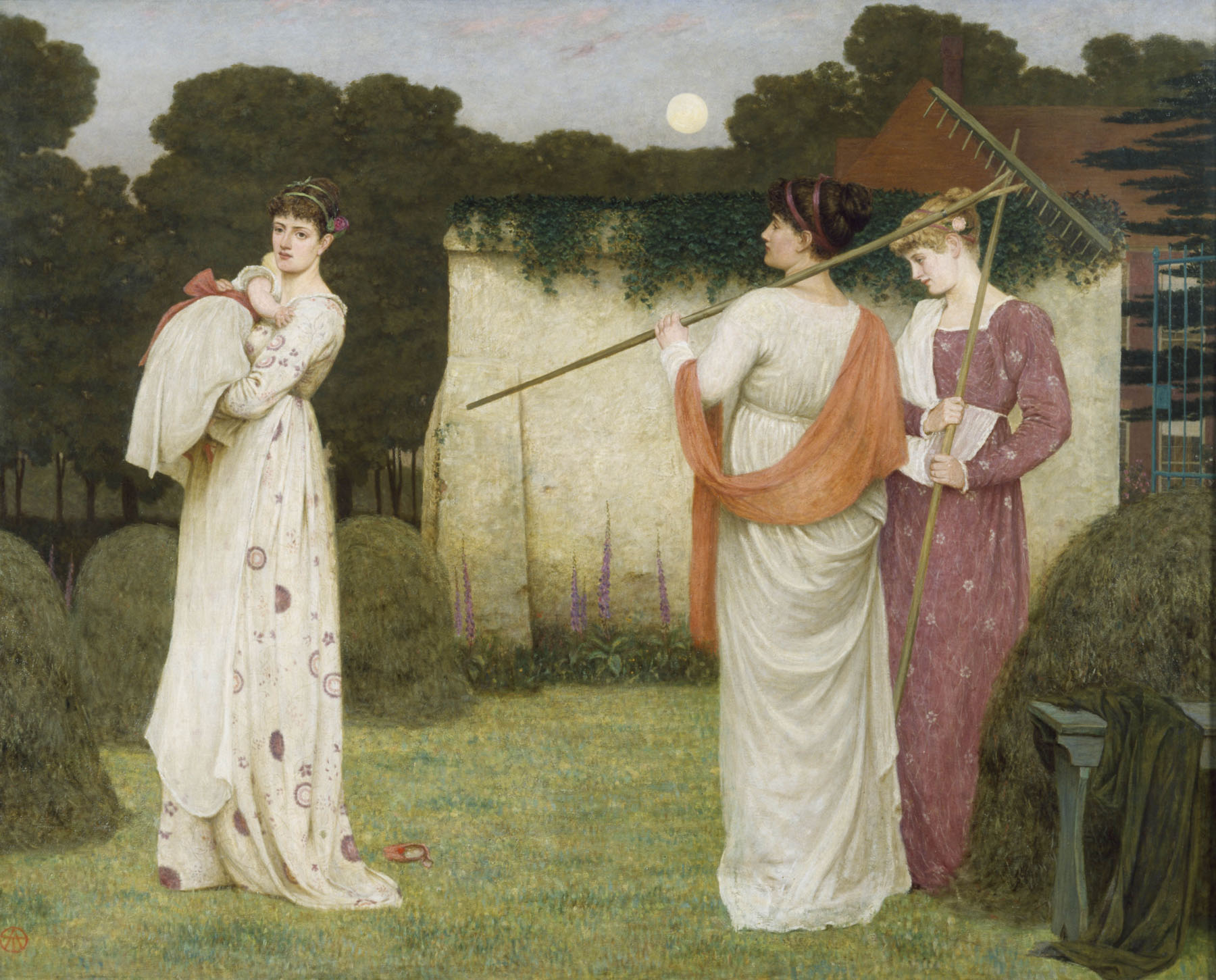
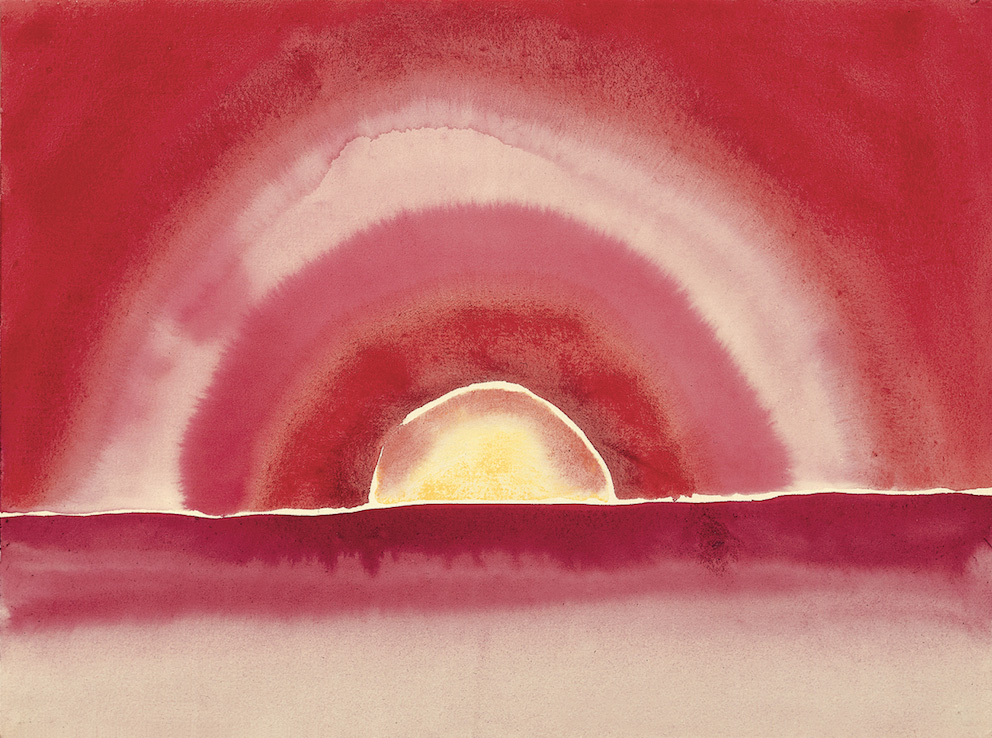














































































![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Danseuses, éventail [Dancers (Fan, design)]' 1879 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Danseuses, éventail [Dancers (Fan, design)]' 1879 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-al.jpg)

![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917 'La Loge [Theatre box]' 1885 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917 'La Loge [Theatre box]' 1885 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-am.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'La Loge [Theatre box]' 1880 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'La Loge [Theatre box]' 1880 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-an.jpg)
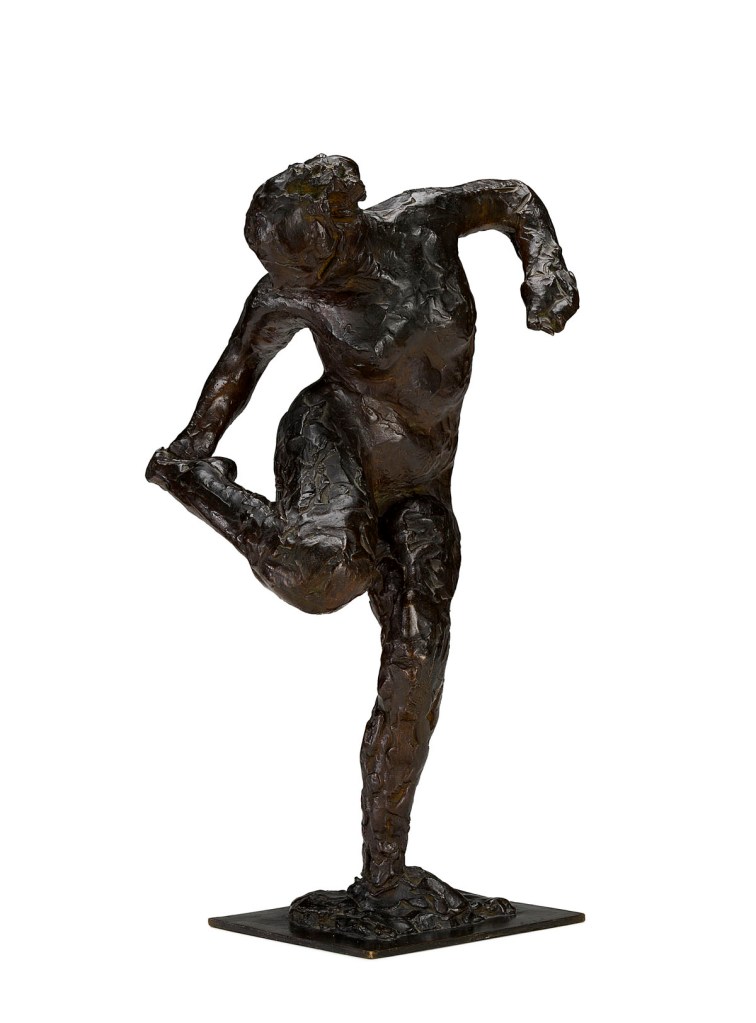
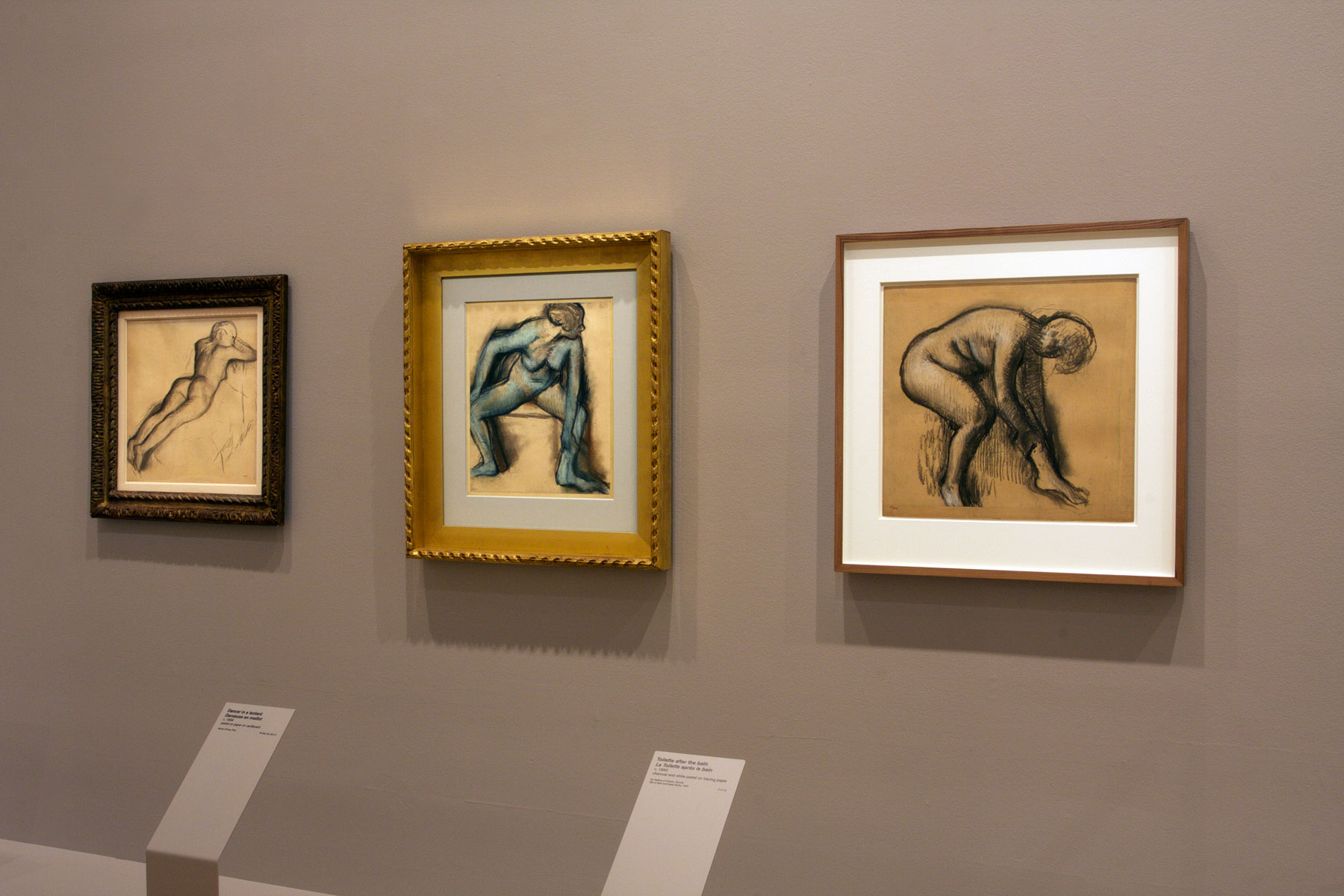



































![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'La Baigneuse [The bather]' c. 1895 Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'La Baigneuse [The bather]' c. 1895](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-bp.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Femme a la toilette [Woman at he toilette] c. 1895-1900 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Femme a la toilette [Woman at he toilette] c. 1895-1900 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-bd.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Femme a la toilette [Woman at her toilette] c. 1894 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Femme a la toilette [Woman at her toilette] c. 1894 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-be.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Femme a la toilette [Woman at her toilette] c. 1894 Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Femme a la toilette [Woman at her toilette] c. 1894](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/exhi036044-web.jpg)




![Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at right, 'Femme au Tub' [Nude woman drying herself] c. 1884-1886 Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at right, 'Femme au Tub' [Nude woman drying herself] c. 1884-1886](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-bh.jpg)
![Edgar Degas. 'Femme au Tub [Nude woman drying herself]' c. 1884-1886 (installation view) Edgar Degas. 'Femme au Tub [Nude woman drying herself]' c. 1884-1886 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-bi.jpg)

![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Chevaux de courses [Racehorses]' c. 1895-1899 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Chevaux de courses [Racehorses]' c. 1895-1899 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/installation-bf.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Chevaux de courses [Racehorses]' c. 1895-1899 Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Chevaux de courses [Racehorses]' c. 1895-1899](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/exhi039831_web.jpg)
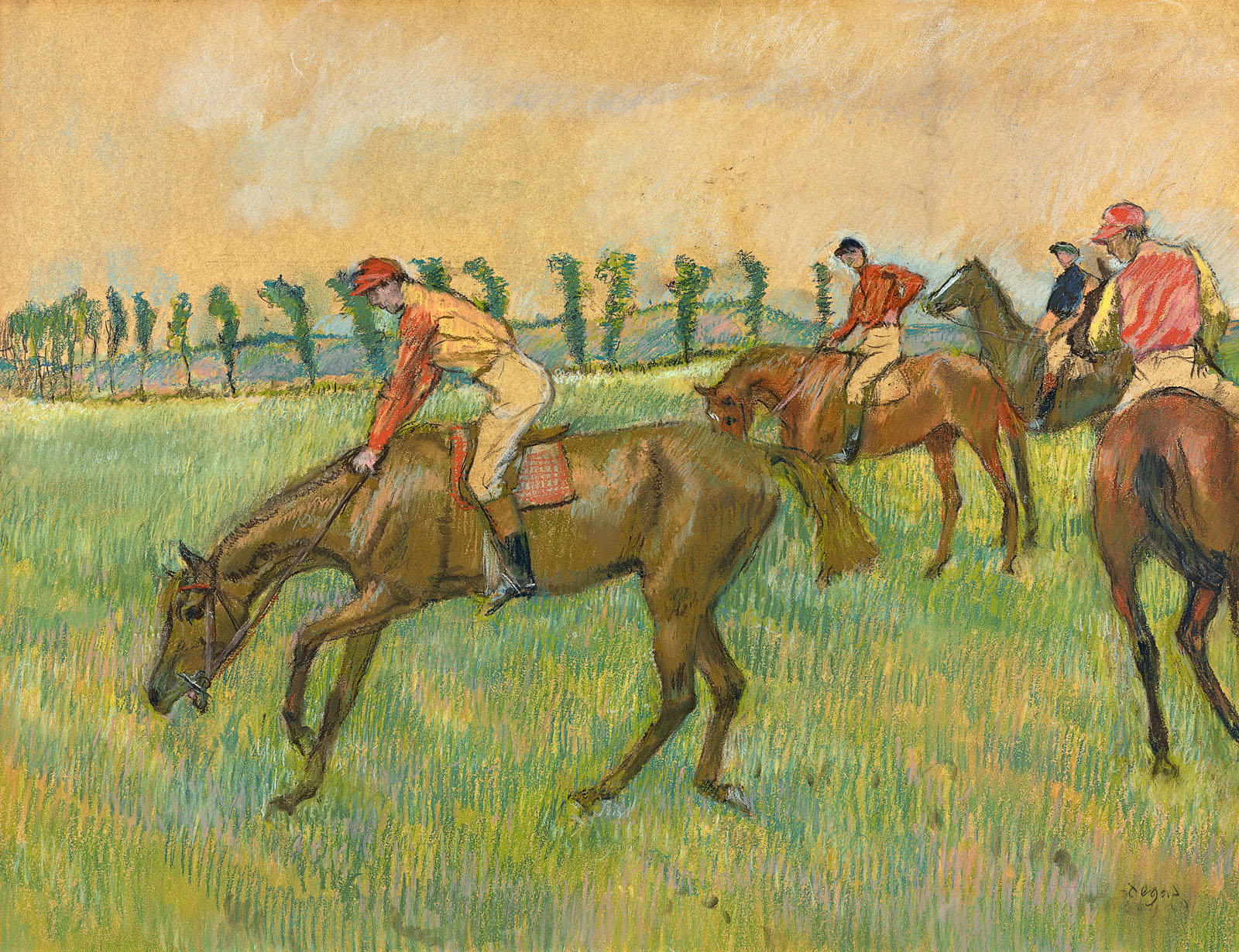
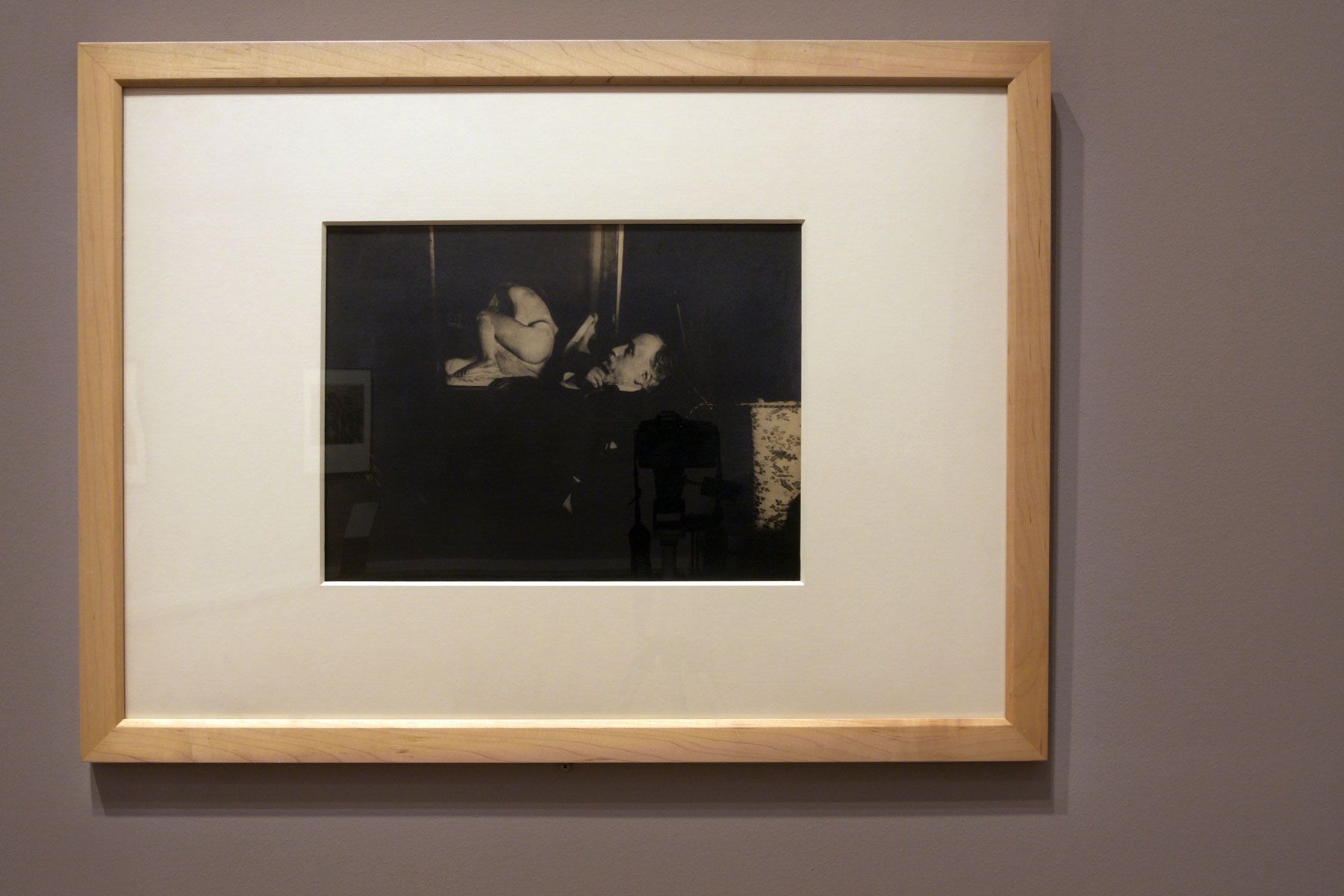
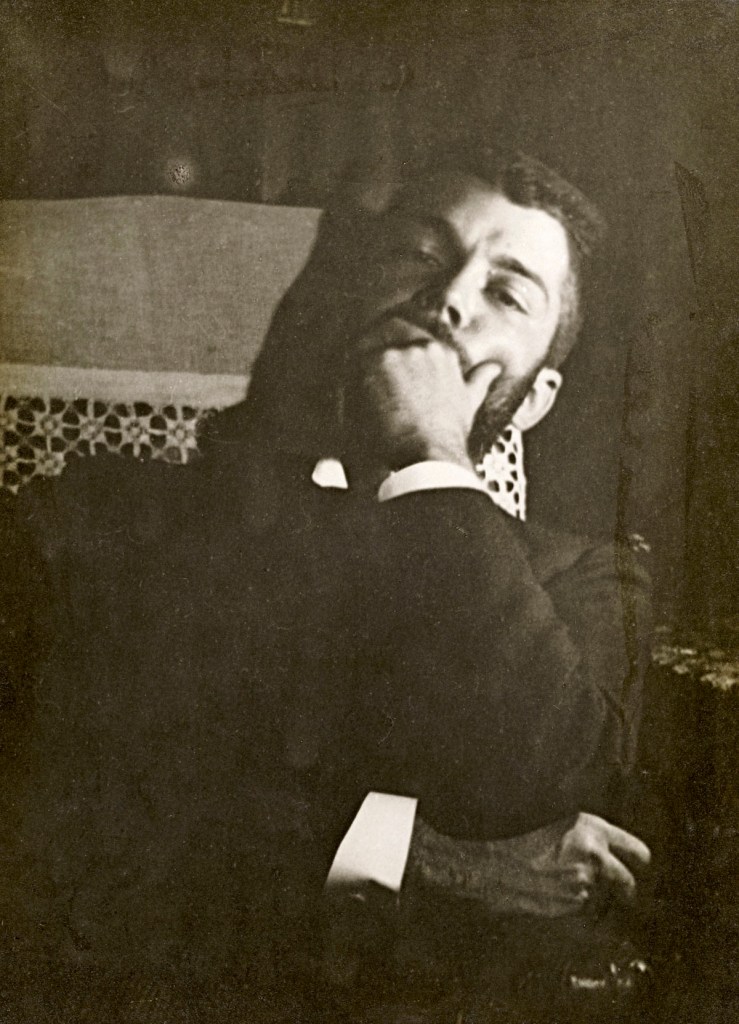








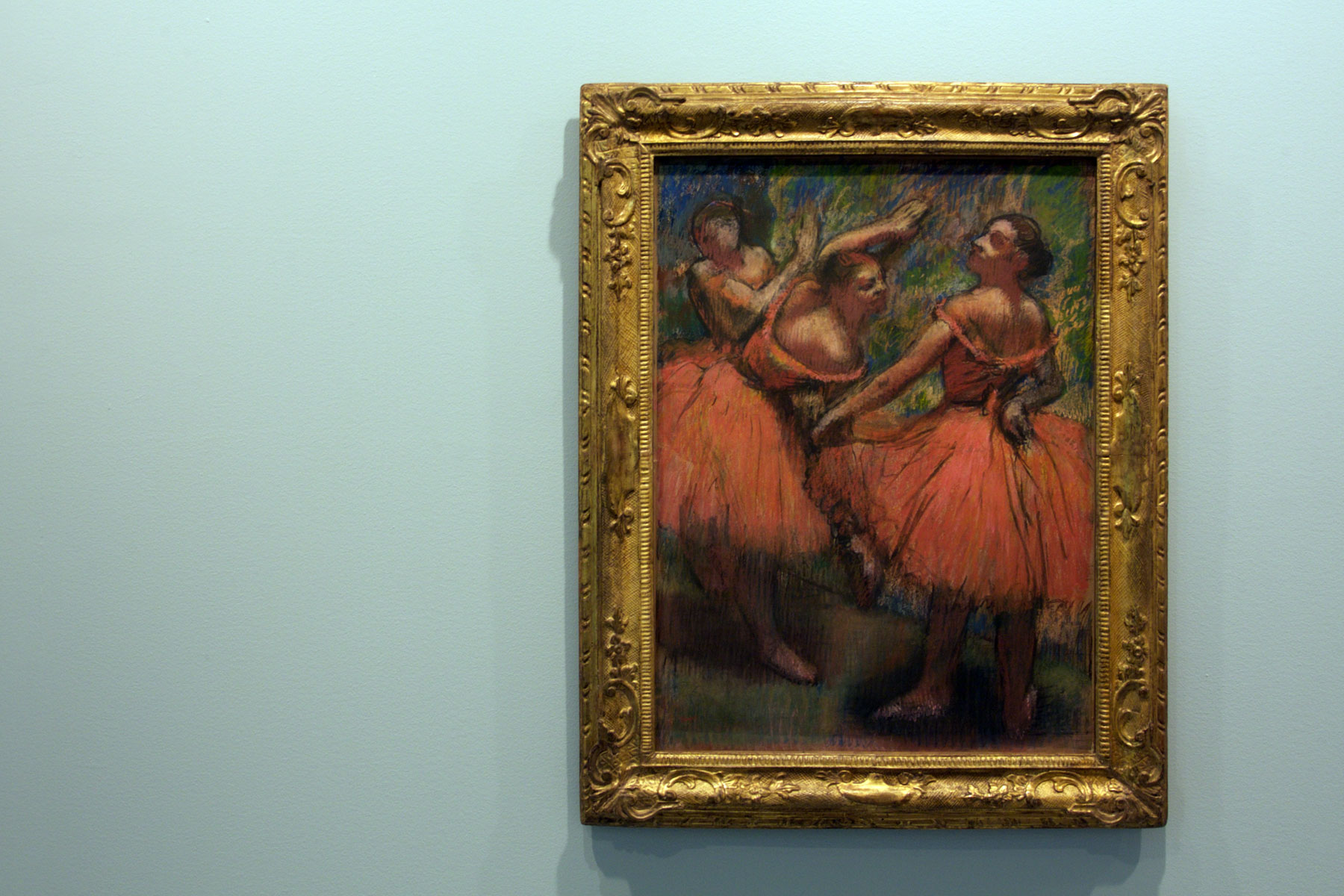






![Joan Miró (Spanish, 1893-1983) 'Tête de Paysan Catalan' [Head of a Catalan Peasant] 1925 from the Collections of Roland Penrose, Edward James, Gabrielle Keiller and Ulla and Heiner Pietzsch' at the Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, Edinburgh, June- Sept, 2016 Joan Miró (Spanish, 1893-1983) 'Tête de Paysan Catalan' [Head of a Catalan Peasant] 1925 from the exhibition 'Surreal Encounters: Collecting the Marvellous: Works from the Collections of Roland Penrose, Edward James, Gabrielle Keiller and Ulla and Heiner Pietzsch' at the Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, Edinburgh, June- Sept, 2016](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/joan-mirc3b3-tc3aate-de-paysan-catalan-web.jpg?w=795)
![Francis Picabia (French, 1879-1953) 'Fille née sans mère' [Girl Born without a Mother] c. 1916-1917 from the Collections of Roland Penrose, Edward James, Gabrielle Keiller and Ulla and Heiner Pietzsch' at the Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, Edinburgh, June- Sept, 2016 Francis Picabia (French, 1879-1953) 'Fille née sans mère' [Girl Born without a Mother] c. 1916-1917 from the Collections of Roland Penrose, Edward James, Gabrielle Keiller and Ulla and Heiner Pietzsch' at the Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art, Edinburgh, June- Sept, 2016](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/francis-picabia-fille-nc3a9e-sans-mc3a8re-web.jpg)


![Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'La Joie de vivre' [The Joy of Life] 1936 Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'La Joie de vivre' [The Joy of Life] 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/max-ernst-la-joie-de-vivre-1936-web.jpg)

![Dorothea Tanning (American, 1910-2012) 'Eine Kleine Nachtmusik' [A Little Night Music] 1943 Dorothea Tanning (American, 1910-2012) 'Eine Kleine Nachtmusik' [A Little Night Music] 1943](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/dorothea-tanning-eine-kleine-nachtmusik-1943-web.jpg)





![Salvador Dalí (Spanish, 1904-1989) 'Couple aux têtes pleines de nuages' [Couple with their Heads Full of Clouds] 1936 Salvador Dalí (Spanish, 1904-1989) 'Couple aux têtes pleines de nuages' [Couple with their Heads Full of Clouds] 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/salvador-dalc3ad-couple-aux-tc3aates-pleines-de-nuages-web.jpg)


![Pablo Picasso (Spanish, 1881-1973) 'Tête' [Head] 1913 Pablo Picasso (Spanish, 1881-1973) 'Tête' [Head] 1913](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/tc3aate-head-1913-by-pablo-picasso-web.jpg?w=763)




![Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'Jeune homme intrigué par le vol d’une mouche non-euclidienne' [Young Man Intrigued by the Flight of a Non-Euclidean Fly] 1942–1947 Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'Jeune homme intrigué par le vol d’une mouche non-euclidienne' [Young Man Intrigued by the Flight of a Non-Euclidean Fly] 1942–1947](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/32_ernst-max_jeune-homme-intriguc3a9-1942-47-web.jpg?w=817)
![Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'Une semaine de bonté' [A Week of Kindness] 1934 Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'Une semaine de bonté' [A Week of Kindness] 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/ernst-une-semaine-de-bontc3a9-web.jpg?w=761)
![Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'Une semaine de bonté' [A Week of Kindness] 1934 Max Ernst (German, 1891-1976) 'Une semaine de bonté' [A Week of Kindness] 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/ernst-une-semaine-de-bontc3a9-web2.jpg?w=755)


![Alberto Giacometti (Italian, 1901-1966) 'Objet désagréable, à jeter' [Disagreeable Object, to be Thrown away] 1931 Alberto Giacometti (Italian, 1901-1966) 'Objet désagréable, à jeter' [Disagreeable Object, to be Thrown away] 1931](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/alberto-giacometti-objet-dc3a9sagrc3a9able-web.jpg)
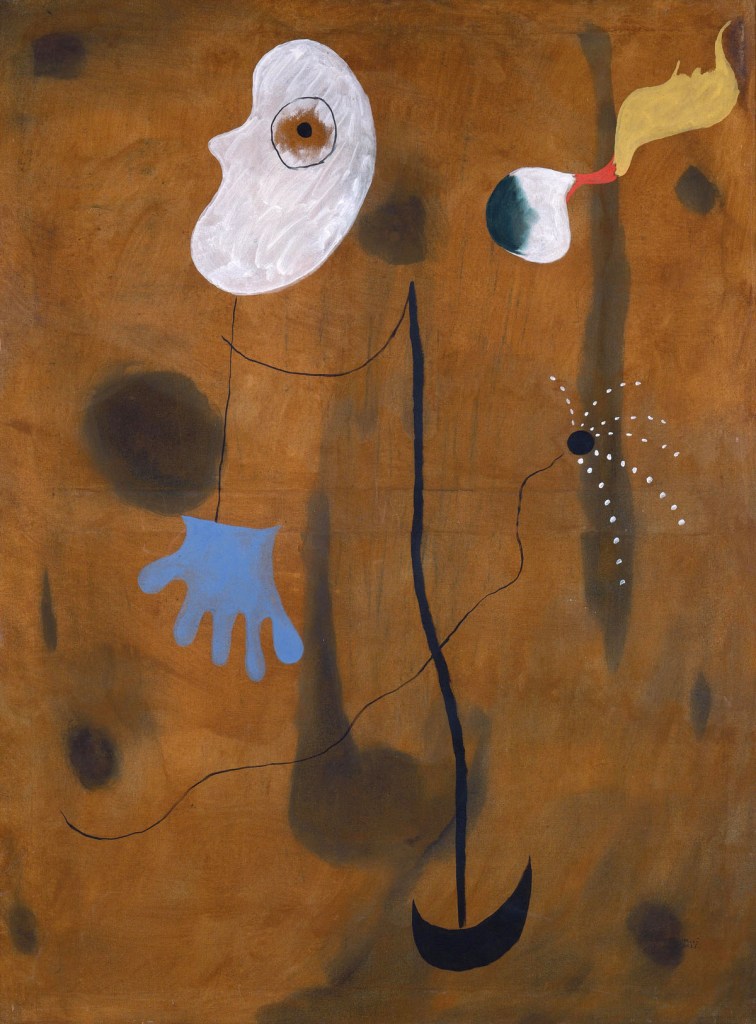
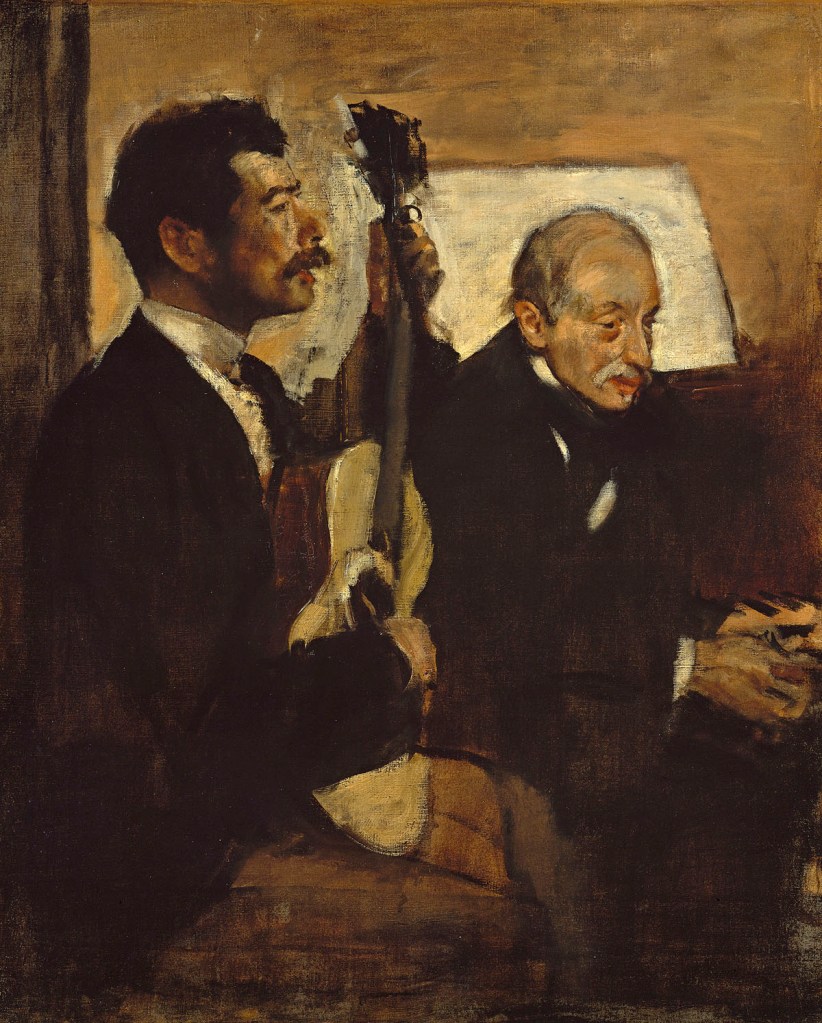


















![Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Mendiante romaine' [Roman beggar women] (1857) Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Mendiante romaine' [Roman beggar women] (1857)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-l.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Mendiante romaine' [Roman beggar women] 1857 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Mendiante romaine' [Roman beggar women] 1857 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-m.jpg)
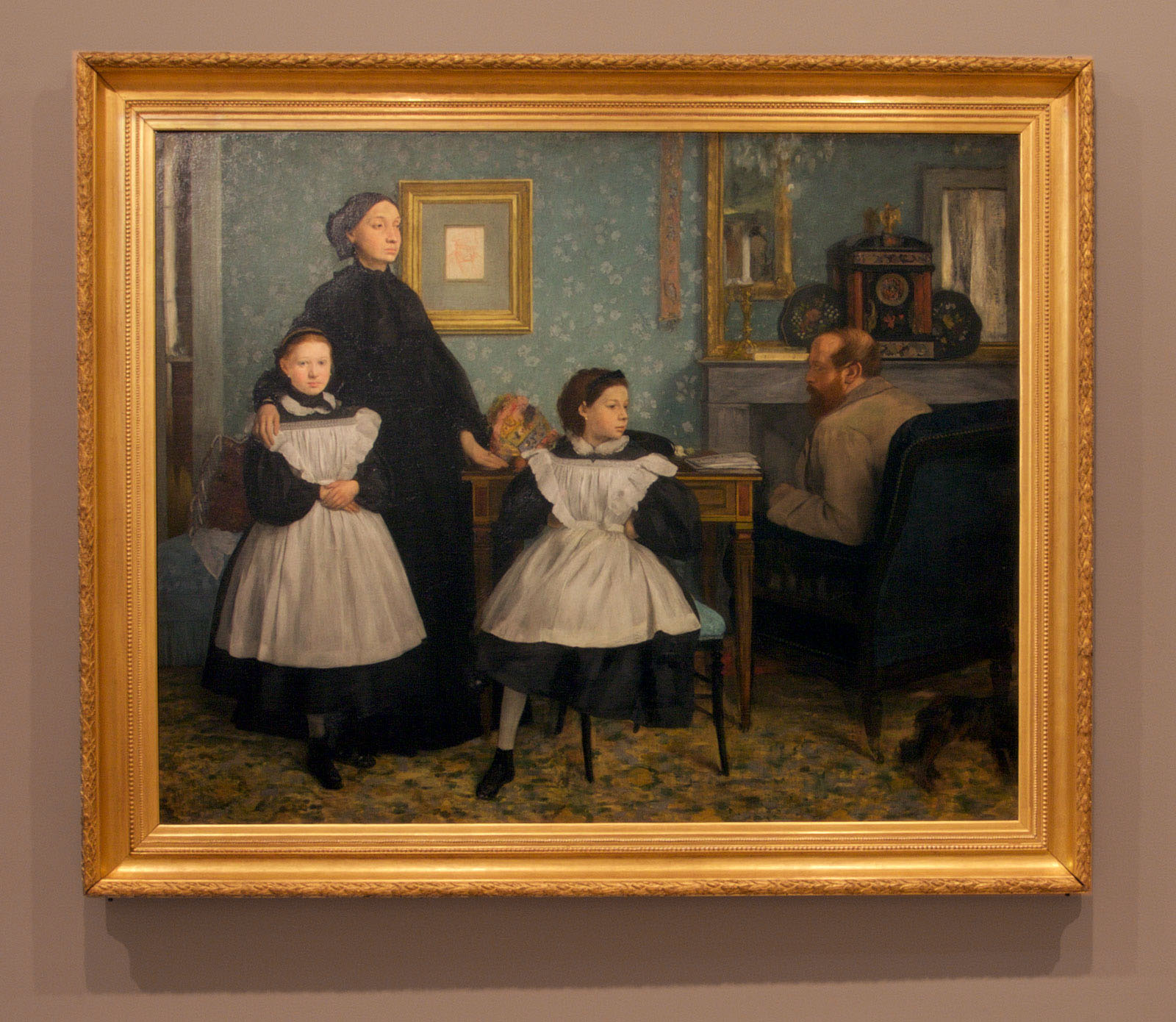



![Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Monsieur Reulle' (1861); and at right, 'Portrait de jeune femme' [Portrait of a young woman] (1867) Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Monsieur Reulle' (1861); and at right, 'Portrait de jeune femme' [Portrait of a young woman] (1867)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-q.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Étude pour Jeunes Spartiates s'exerçant à la lutte' [Study for The young Spartans exercising] c. 1860-1861 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Étude pour Jeunes Spartiates s'exerçant à la lutte' [Study for The young Spartans exercising] c. 1860-1861 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-o.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Petites filles spartiates provoquant des garçons' [Young Spartan girls challenging boys] c. 1860 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Petites filles spartiates provoquant des garçons' [Young Spartan girls challenging boys] c. 1860 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-n.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Petites filles spartiates provoquant des garçons' [Young Spartan girls challenging boys] c. 1860 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Petites filles spartiates provoquant des garçons' [Young Spartan girls challenging boys] c. 1860 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-p.jpg)



![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Etude de nus: Mlle Fiocre dans le ballet La Source' [Nude study: Mademoiselle Fiocre in the ballet 'The Spring'] 1867-1868 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Etude de nus: Mlle Fiocre dans le ballet La Source' [Nude study: Mademoiselle Fiocre in the ballet 'The Spring'] 1867-1868 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-aa.jpg)
![Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Portrait d'homme' [Portrait of a man] (c. 1866) and at right, 'Victoria Dubourg' (1868-1869) Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Portrait d'homme' [Portrait of a man] (c. 1866) and at right, 'Victoria Dubourg' (1868-1869)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-z.jpg)
![Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Portrait d'homme' [Portrait of a man] (c. 1866) and at right, 'Victoria Dubourg' (1868-1869) Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne Installation view of the exhibition 'Degas: A New Vision' at the National Gallery of Victoria International, Melbourne showing at left, 'Portrait d'homme' [Portrait of a man] (c. 1866) and at right, 'Victoria Dubourg' (1868-1869)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-v.jpg)

![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Mme Jeantaud sur sa chaise longue, avec deux chiens' [Madame Jeantaud on her chaise longue, with two dogs] 1877 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Mme Jeantaud sur sa chaise longue, avec deux chiens' [Madame Jeantaud on her chaise longue, with two dogs] 1877 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-x.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Mme Jeantaud sur sa chaise longue, avec deux chiens' [Madame Jeantaud on her chaise longue, with two dogs] 1877 (installation view detail) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Mme Jeantaud sur sa chaise longue, avec deux chiens' [Madame Jeantaud on her chaise longue, with two dogs] 1877 (installation view detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-x-detail.jpg)










![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Un bureau de coton à la Nouvelle-Orléans' [A cotton office in New Orleans] 1873 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Un bureau de coton à la Nouvelle-Orléans' [A cotton office in New Orleans] 1873 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/installation-af.jpg)
![Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Un bureau de coton à la Nouvelle-Orléans' [A cotton office in New Orleans] 1873 (installation view) Edgar Degas (French, 1834-1917) 'Un bureau de coton à la Nouvelle-Orléans' [A cotton office in New Orleans] 1873 (installation view)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/exhi040021_web.jpg)
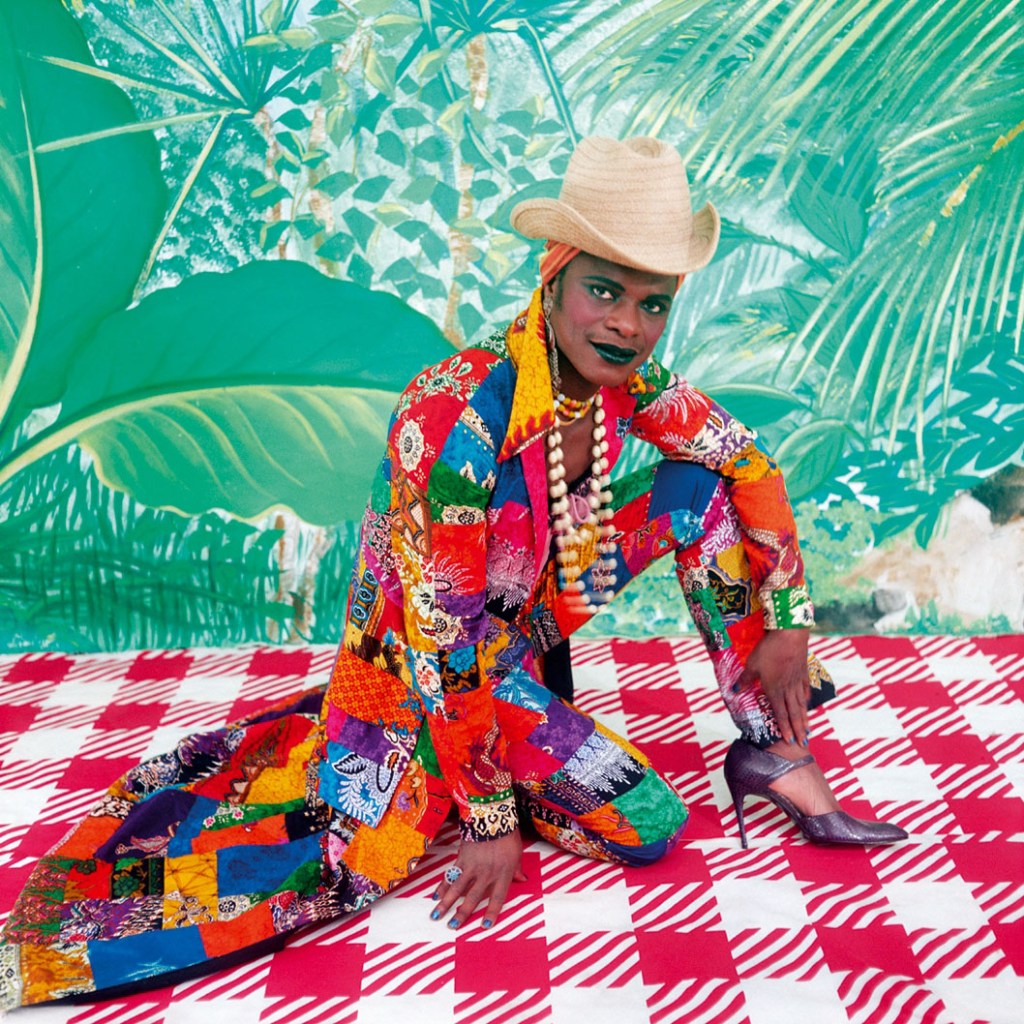
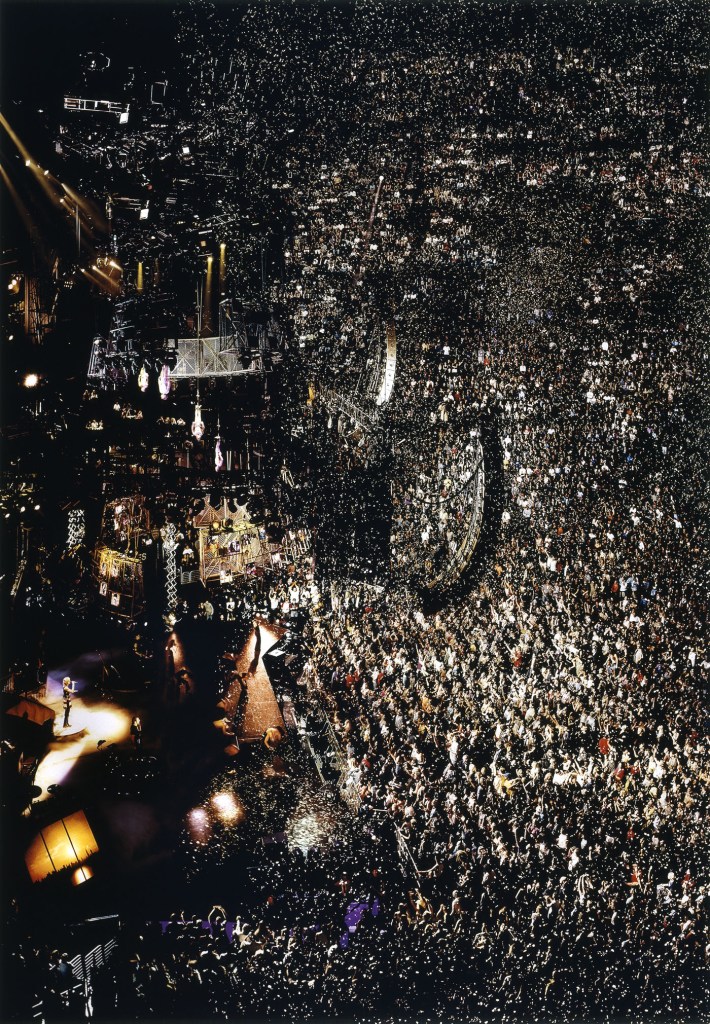
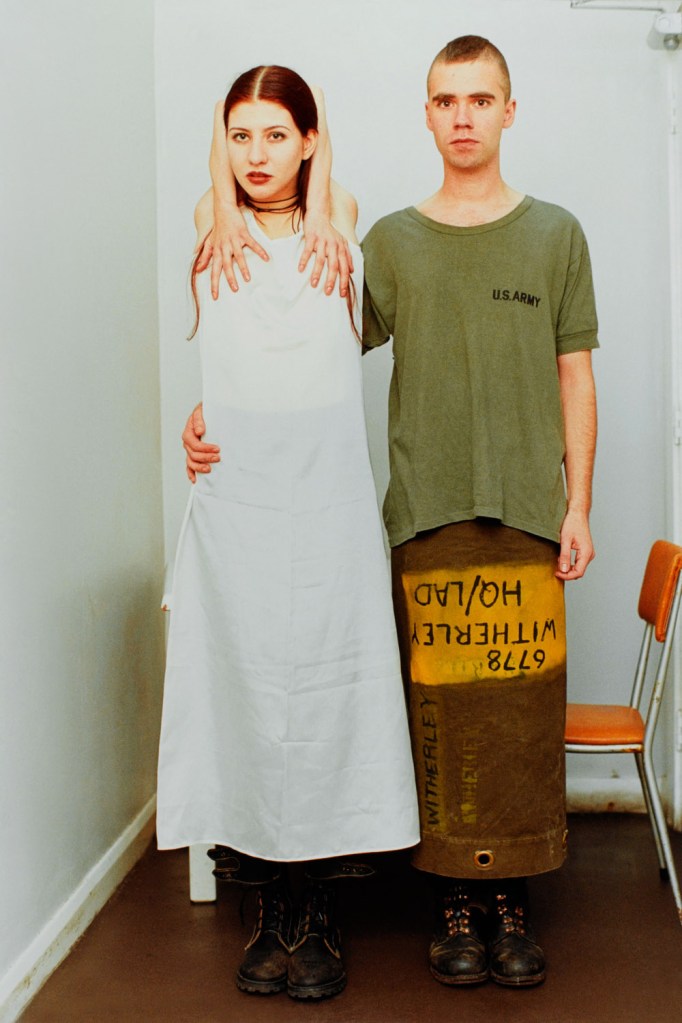



































You must be logged in to post a comment.