Exhibition dates: 16th October 2021 – 27th March 2022
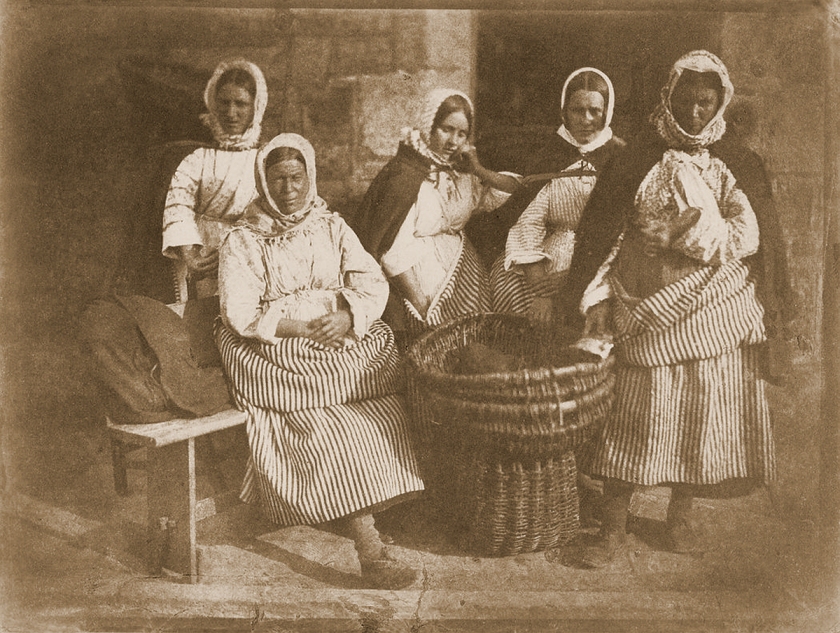
Installation view of the exhibition Clandestine – The Human Body in Focus at the Cobra Museum of Modern Art, Amstelveen showing from left to right, Armando Cristeto (Mexico, b. 1957) Apolo urbano, c. 1981; Antonio Reynoso, La Gorda, c. 1960; Herb Ritts, Wrestling Torsos, Hollywood, c. 1987
I’m working from my iPad at the moment as my computer has gone down, so this will be short and sweet.
It’s disappointing, to say the least, that in this day and age a museum provides so few media images on such an important theme that I had to spend many hours digging around trying to find images for this posting. I examined the labels on the installation photographs, and then looked at the museum’s Instagram account where there was much more information, before searching for large enough images online for the posting. Some artists are little known so this proved very difficult.
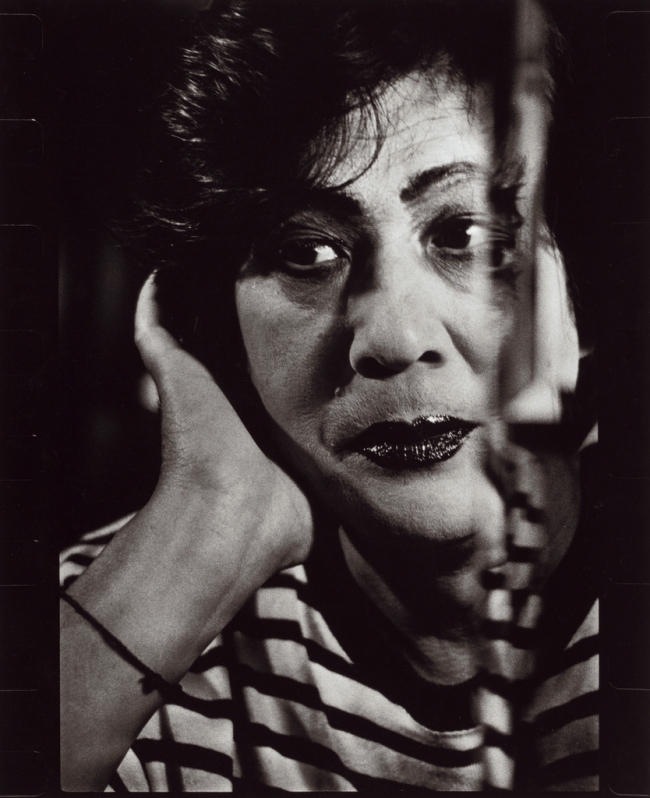
It’s good to see Arlene Gottfried’s strong, brash, direct photographs of gay icons, Jewish bodybuilders and street urchins but they are standard clubbing / street fare and there is little subtlety in her work.
While Gottfried may have survived to tell her story her own way the work only documents. For a photograph is that ever enough? Here the photographs in no way provide a fresh perspective on a clubbing street aesthetic grounded in the milieu of the mid 70s to early 80s Studio 54, pre-AIDS, groovy, disco party vibe. Nostalgia, history and memory are their appeal today.
Tastes have changed. Personally I find more power and sensitivity in Kike Arnal’s Untitled (Emmanuel, trans man and tattoo artist) (2018, below) than most of Gottfried’s graphic photographs – her subjects caught as if the lights had come up in the club at 6am (believe me this has happened many times, all of us looking like startled rabbits). Strike a pose!
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Cobra Museum of Modern Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
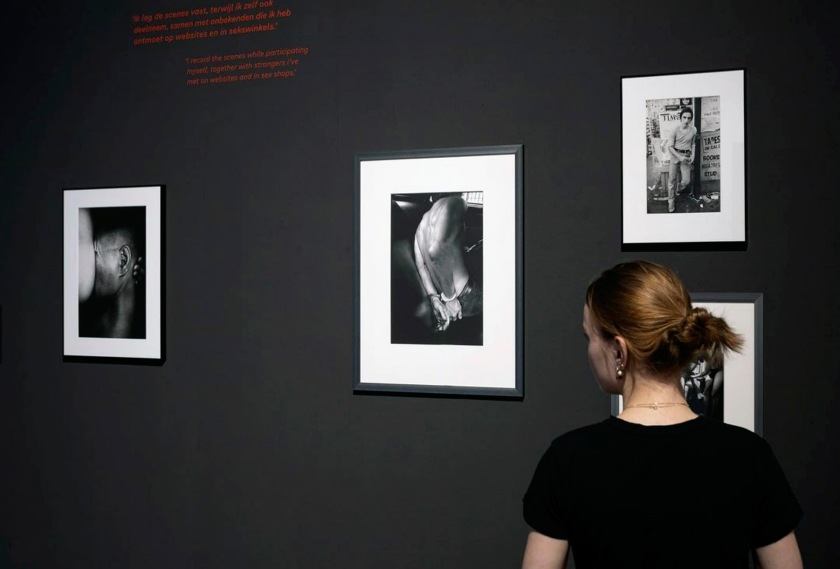
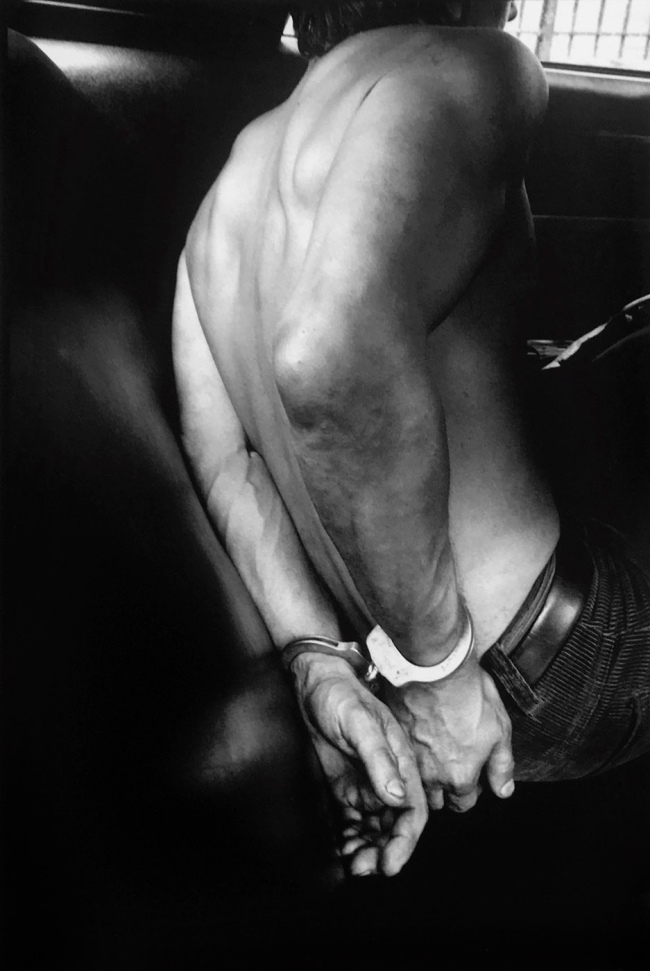
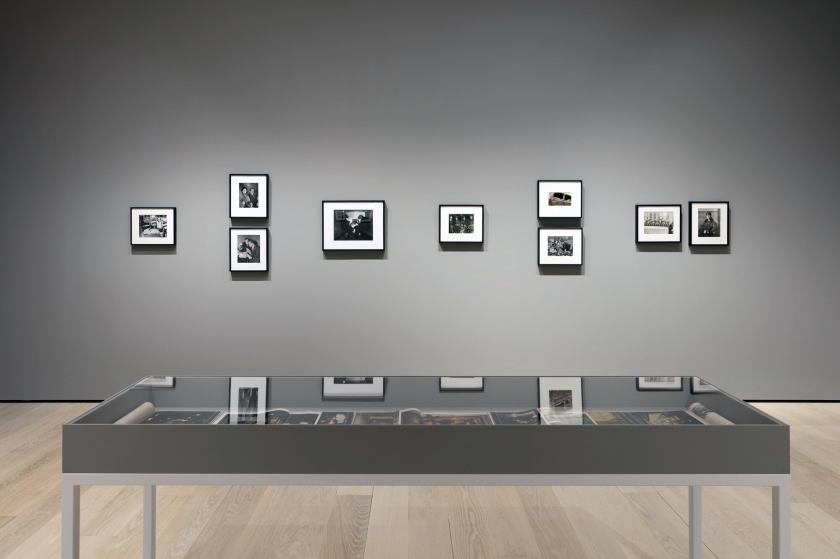
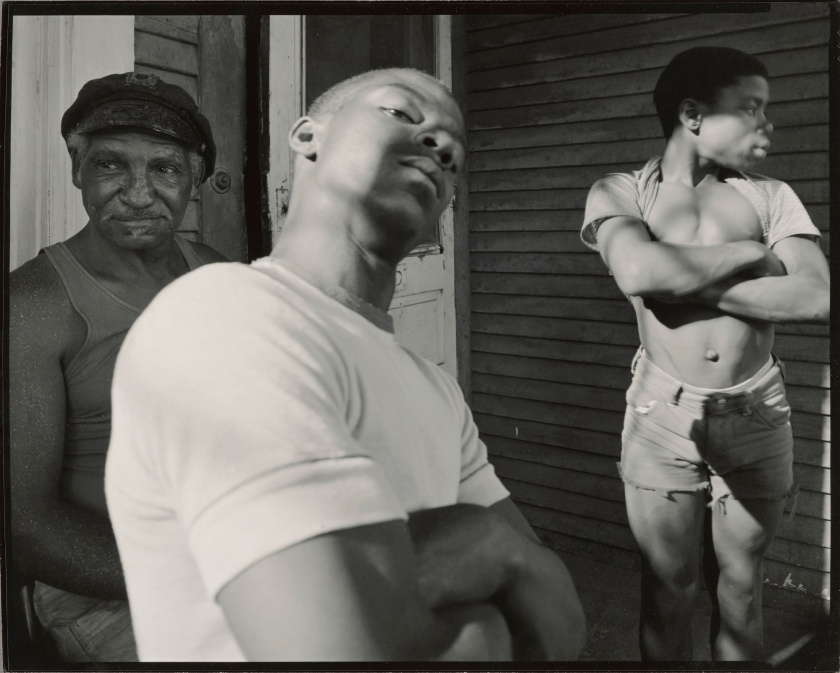
Installation view of the exhibition Clandestine – The Human Body in Focus at the Cobra Museum of Modern Art, Amstelveen showing from left to right, Shohei Miyachi, Untitled, c. 2018; Leonard Freed, Handcuffed, New York City, from Police Work series, c. 1978; Larry Clark, Chuck, c. 1981
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Angel and Woman on Boardwalk, Brighton Beach
1976
Vintage gelatin silver print
Framework: 59.5 x 46.5cm
Photo: 27.9 x 35.5cm
Pedro Slim Collection
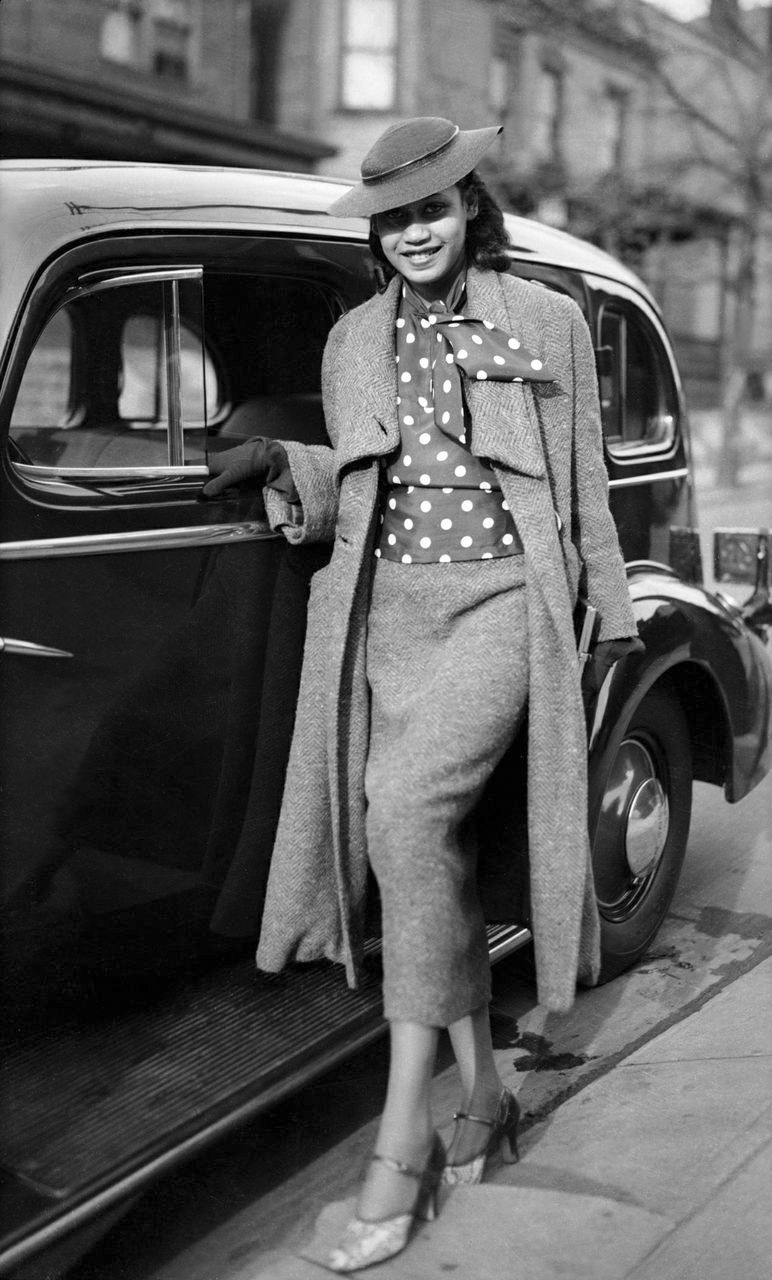
How does your gender impact your work as an artist? The candid photographs of Arlene Gottfried have become everlasting memories of New York’s fast-evolving culture(s). For over 40 years, Gottfried photographed the intimate stories of the American domestic life, as well intrepid snapshots of the Puerto Rican community or the wild nights inside Studio 54.
She emphasised that being a female photographer back in the 70s was very different than now:
‘A lot of the male photographers [in the past] felt threatened and didn’t like it. […] It’s changed so much with women working. They’re more visible now. I don’t know the statistics on museums and how many are being collected. But on an everyday level, you see women in jobs that used to be male – bus driver, train conductor – typically male jobs that now have female employees and photography was the same. It used to be only guys, really. And actually, in my first photography class, I was the only young woman in the class and I had a lump in my throat, like I wanted to cry, only guys there. But it wound up being a very supportive environment and I learned a lot.
Unless you’re doing something that’s a very feminine kind of a topic, I don’t think gender is really all that visible.’
Anonymous text from the Cobra Museum of Modern Art Instagram page
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Guy With Radio, East 7th Street
1977
Vintage gelatin silver print
Framework: 59.5 x 46.5cm
Photo: 35.5 x 27.9cm
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Pituka at Bethesda Fountain, Central Park
1977
Vintage gelatin silver print
Framework: 59.5 x 46.5cm
Photo: 35.5 x 27.9cm
Pedro Slim Collection
The legendary street photographer who captured more than neutral subjects, but also the living faces and bodies of people along with their memories. Arlene Harriet Gottfried photographs preserve cultural heritage of the urban atmosphere.
One of the most quintessential projects Gottfried produced was a black-and-white series of street photography from the 1970s and 80s in New York. Her work will form part of our exhibition Clandestine. This is a photo exhibition about the human body. One of the most dominant themes in the exhibition is the constant dialogue between culture and bodies. This is something Arlene Gottfried captures particularly well. Arlene Gottfried documented scenes of ordinary daily life. The everyday life from the past that still lives vividly in her photographs. Her work embodied stories and memories of people who although you will never get to know, you can easily feel familiarised.
Anonymous text from the Cobra Museum of Modern Art Instagram page
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Disco Sally at Studio 54
1979
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Pose
Early 1980s
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Le Clique
Early 1980s
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Installation view of the exhibition Clandestine – The Human Body in Focus at the Cobra Museum of Modern Art, Amstelveen showing Arlene Gottfried’s portrait Marsha P. Johnson c. 1983
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Marsha P. Johnson
c. 1983
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Marsha P. Johnson was an African-American trans woman who lived in New York and is celebrated for her contribution to the LGBTQI+ movement. She was often referred to as ‘Saint Marsha’ for serving as a “drag mother” aiding and welcoming homeless people as well as young members of the LGBTQ movement.
Marsha P. Johnson was the Rosa Parks of the LGBT+ movement. She was a devoted activist, drag performer, sex worker and at some point she even modelled for Andy Warhol. She established safe spaces for transgender people and was thoroughly dedicated to defending the rights of trans people, sex workers, people with HIV/AIDS and prisoners.
‘You never completely have your rights, one person, until you all have your rights.’ ~ Marsha P. Johnson
Our exhibition, Clandestine – The Human Body in Focus presents stories in black and white photographs about people who have not been recognised yet for their bravery. Today, Marsha lives in the hearts of brave activists as well as many transgender people.
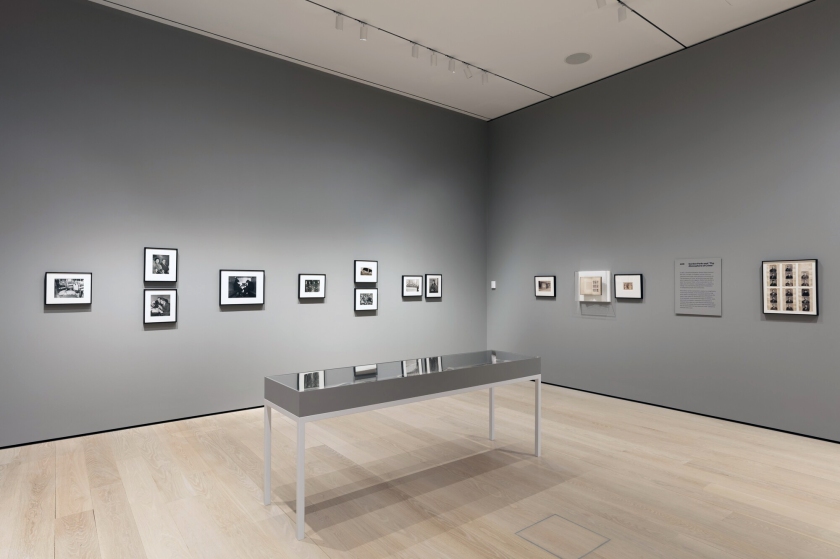
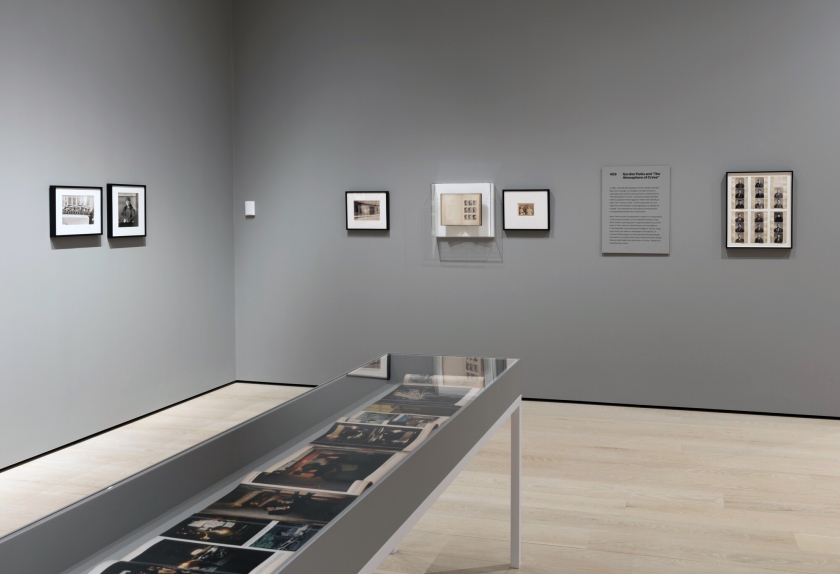
The human body is the central theme of the Clandestine photo exhibition. About a hundred black-and-white photographs express an unreserved love of the body in all its manifestations: perfect, imperfect, elegant, erotic, proud or, on the contrary, very vulnerable. The works come from the extensive collection of photographer and collector Pedro Slim (Beirut, Lebanon, 1950) and are shown in the Netherlands for the first time.
Clandestine showcases photography by some 60 artists, including Diane Arbus, Horst P. Horst, Arlene Gottfried, Graciela Iturbide, Robert Mapplethorpe, Diana Blok, Helmut Newton and Man Ray. The exhibition presents original and contemporary prints (including silver on gelatine, photogravure), collages and photomontages. These photographs are placed in the context of New York in the 1970s and 1980s, where many were taken. Pedro Slim’s photo collection holds a unique place in the field of photography. In 1985, Slim started collecting photographs in which the human body plays a central role. With his collection, Slim highlights the power of images and seeks to transform and break open the paradigm that dictates what is feminine, masculine, non-binary or trans. Pedro Slim’s collection consists of more than 300 vintage prints and has rarely been exhibited.
The beauty of the photographs lies especially in the personal expression of those portrayed. The artists seek to go beyond the prevailing standards and ideals of beauty, and make a plea to appreciate the body in all its manifestations. The photographs are thus an ode to diversity and are still very relevant today.
Three themes
The exhibition revolves around three themes. The first part of the exhibition focuses on past and present ideals of beauty. The photographs show a diversity of body types and invite us to transcend judgements such as ‘beautiful’ and ‘ugly’. The photographs within the second theme show people living on the fringes of society, many of the recorded scenes are raw, everyday situations. The visitor sees sex work, drug use and indecency. There are painful stories behind the provocative looks and poses.
The third part of the exhibition is entirely devoted to the work of Arlene Gottfried (1915-2017). Gottfried specialised in the genre known as street photography, recording life in the less well-to-do neighbourhoods of New York. Her themes included gospel, schizophrenia, the Puerto Rican community, and the women in her family. Pedro Slim owns more than twenty original prints by Gottfried. This makes him the most important collector of her work.
About the collector
Photographer and collector Pedro Slim was born in Beirut, Lebanon, in 1950. He studied architecture and photography in Mexico and New York. Since the early 1990s, he has exhibited in various museums and galleries. His most recent exhibition was in 2017 at the Museo de Arte Moderno in Mexico City. His passion for photography led him to start a collection.
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Brothers with their Vines, Coney Island, NY
1976
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Third Avenue Shopping, El Barrio
1978
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
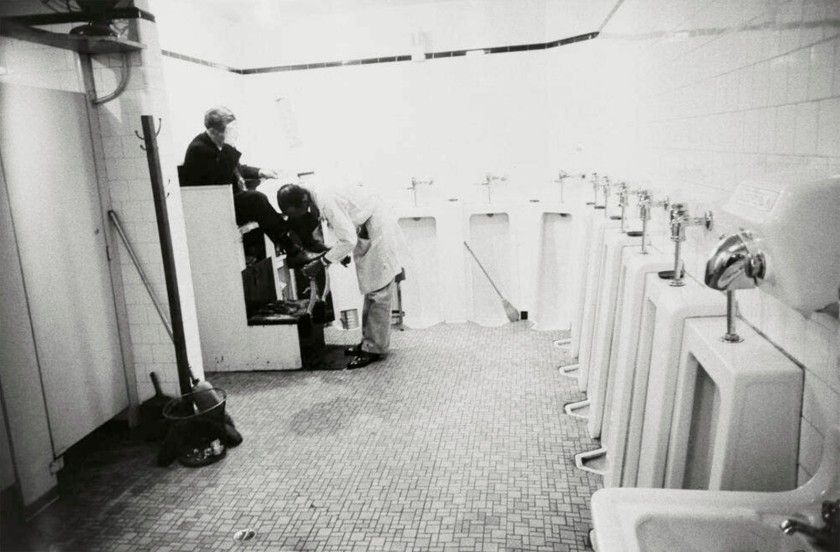
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Men’s Room at Disco
1978
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Doorway in Soho, NY
1980
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Savage Riders at The Puertican Day Parade
1980
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
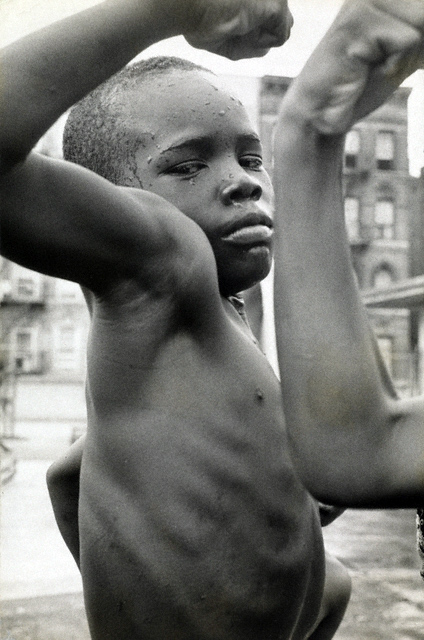
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Hassid and Jewish Bodybuilder
1980
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Riis, Nude Bay, Queens
1980
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
After completing a two-year photography program at FIT, Arlene moved to Greenwich Village in 1972, when the community was still an affordable outpost for artists, musicians and bohemians. She took a job as an assistant with an advertising agency. “I did everything: printing, processing, lighting, studio work, on location, a lot of it was for comps and sometimes it was for the ad itself, for sales promotion and point of purchase,” Arlene revealed in her final book, Mommie. “I didn’t always love what it was about but I always took photographs on the weekend and used their fantastic darkroom.”
“It’s nice to be young and be able to run across the beach like wild and be able to meet people and take their picture,” she continued. “That’s what I remember about it: Having a great time, and having a job so I could pay for things, and having a darkroom where I could print everything. You couldn’t ask for anything better. It was like a little grant at a little job, you know, a moderate income but just enough.”
Arlene made “just enough” to carry her through the next 45 years of her life, transforming her home in the West Village’s famed Westbeth Artists Housing into a bohemian palace. Above her kitchen table, she hung her photographs in a plastic carousel designed to air-dry intimate apparel. She entertained visitors, serving cherries and chocolate-covered espresso beans with a bottle of seltzer at the ready. When her cancer treatments stole her brunette curls in the years before her death, Arlene donned a burgundy velvet turban for her nights out.
Although she disliked hustle culture before it was named as such, Arlene maintained resolute faith in the importance of her work and the vitality of her gifts. Where other photographers sought to be a fly on the wall, Arlene was a butterfly in the mix, always aligned with the energy so that her presence only added to the beauty of the images she made. She loved to laugh, to sing, to dance and to celebrate the extraordinary stars in her orbit. In Mommie, Arlene remembers, “The clubs were very provocative then: People putting on these shows, taking their clothes off, acting things out. There’d be a theme and they’d be doing all kinds of crazy things like giving birth to dolls, simulating sex in public. I went in with my camera, took photographs and it was great.”
After the party, Arlene described the feeling of a glorious high that comes from a night on the town, surrounded by people doing what they love. She walked out of the club into the crisp winter air as snowflakes floated down from the sky like confetti in a parade. She then began strolling down Fifth Avenue, heading home, like the final scene of a Hollywood film.
Extract from Miss Rosen. “Sex clubs, Studio 54, Central Park: A portrait of NYC in the 70s & 80s,” on the i-D website 15 October 2021 [Online] Cited 16/10/2021
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Giant Dildo, Les Mouches Party, NY
1979
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arlene Gottfried (American, 1950-2017)
Miguel Pinero and Friend
1980
Vintage gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
As an insider, Gottfried was able to tell the story on her own terms, capturing a slice of life that has vanished forevermore. “Now the only way to know what New York was like is from fleeting glimpses in movies made years ago like Taxi Driver, Death Wish, or Midnight Cowboy,” Gilbert Gottfried observes. “I remember there were neighbourhoods you didn’t want to be in and we lived in a few of those. Arlene had already been living on her own when me, my mother, and my other sister Karen moved to Avenue A. People were saying, ‘You’re nuts.'”
Arlene Gottfried flourished amongst her own, whether palling around with poet Miguel Piñero at the Nuyorican Poets Café, kicking it at Brooklyn’s famed Empire Roller Skating Center, or trooping uptown to the streets of El Barrio. Wherever she went, there she was, ready for whatever would come her way.
“I met Miguel Piñero at the Poet’s Café. I loved to dance and you could really dance over there!” she told me in 2014, roaring with laughter at the memory of her youth. “Salsa. R&B. There was a lot of good energy there. It was rough and raw. Not trendy. And that’s an amazing thing – that the Poet’s Café has lasted so long. I loved it. I stayed there until the sun came up, literally. That doesn’t last forever, these moments in time.”
Though Gottfried and many she photographed have passed, their legacies live on in her warm and loving photographs. Gottfried followed her heart and went with the flow, documenting everything from her years singing gospel with the Eternal Light Community Singers to her long-standing relationship with Midnight, a man suffering from paranoid schizophrenia.
For Gottfried, the camera was her diary and confidant. “I don’t know exactly when Arlene started taking pictures, but I know she got into it and then it was all the time,” her brother says with a laugh. “Sometimes we were both on the bus with my mother. I would be helping my mother off and Arlene was taking pictures. I was thinking, ‘Put down the camera and help me help her out of the bus!'”
Gottfried’s archive holds vast treasures of New York at a time when everyone was a character yet no one would stare because that would suggest you were a tourist, unfit to make it here. Her photographs are a tribute to Old New York, to a city of myth, magic, and madness that many did not survive. Yet in her pictures, their lives are restored to the pantheon of grit, glamour, and glory.
It is a city the lingers like wafts of weed smoke on a warm summer day, a city that still exists if you look for it. Gilbert Gottfried remembers, “A year or two ago I was walking with my wife and we saw these two homeless men. One was fixing the other guy’s hair with his hand, and my wife said, ‘Ahh. That’s an Arlene picture.'”
Extract from Miss Rosen. “Arlene Gottfried photographed the magic and madness of Old New York,” on the Document Journal website June 28, 2019 [Online] Cited 16/10/2021
George Hoyningen-Huene (American-Russian, 1900-1968)
A.E. Sudan
c. 1935
Gelatin silver print
George Hoyningen-Huene Estate Archives
Let’s talk about representation. A Russian man takes a photo of a Sudanese man. Superficially, this might seem problematic, but why?
In our exhibition, Clandestine – The Human Body in Focus, the portrait by the Russian photographer George Hoyningen-Huene, titled A.E. Sudan presents a naked Sudanese.
In a traditional setting, material items like clothes and jewellery help people express their values and beliefs. In this photo, the Sudanese man is alien from any form of expression. In addition, presented in front of a white wall strips the subject away from his situational contexts – such as time and place. This photo shows a person in a blank state, disconnected from any form of cultural or individual expression.
Despite these characteristics (or lack of characteristics), the photographer still opted to include the nationality of the subject in the title – Sudanese. We do not know if the artist understood the semantic power of the title, but by giving us some context, we know this person is not simply a naked model detached from his culture, but rather a ‘Sudanese’ man.
Here is where the questions that concerns representation starts gaining weight. Artists, including photographers, carry tremendous responsibility. Through their medium, they have the power to frame a subject as they please. In the creative process, it is possible that the view of the artist becomes the dominant perception understood by the audience.
For instance, in this case the Sudanese man has no voice concerning how the viewer perceives any of the characteristics that represent his identity, such as his skin colour, nationality, gender or age. It is virtually impossible to discuss all the concerns linked to cultural representation in a post, hence this conversations is far from over. Also, we do not intend to shame the way the artist framed the Sudanese man, but rather our whole aim, inspired by the Cobra movement, is to present new ways to think critically about art, ourselves and society.
Anonymous text from the Cobra Museum of Modern Art Instagram page
Edmund Teske (Chicago, Illinois, 1911 – Los Angeles, California, USA, 1996)
Male Nude, Davenport Iowa
1942
Vintage gelatin silver print
Framework: 59.2 x 48.9cm
Photo: 33 x 23.5cm
Pedro Slim Collection
© Estate of Edmund Teske, Courtesy Gitterman Gallery
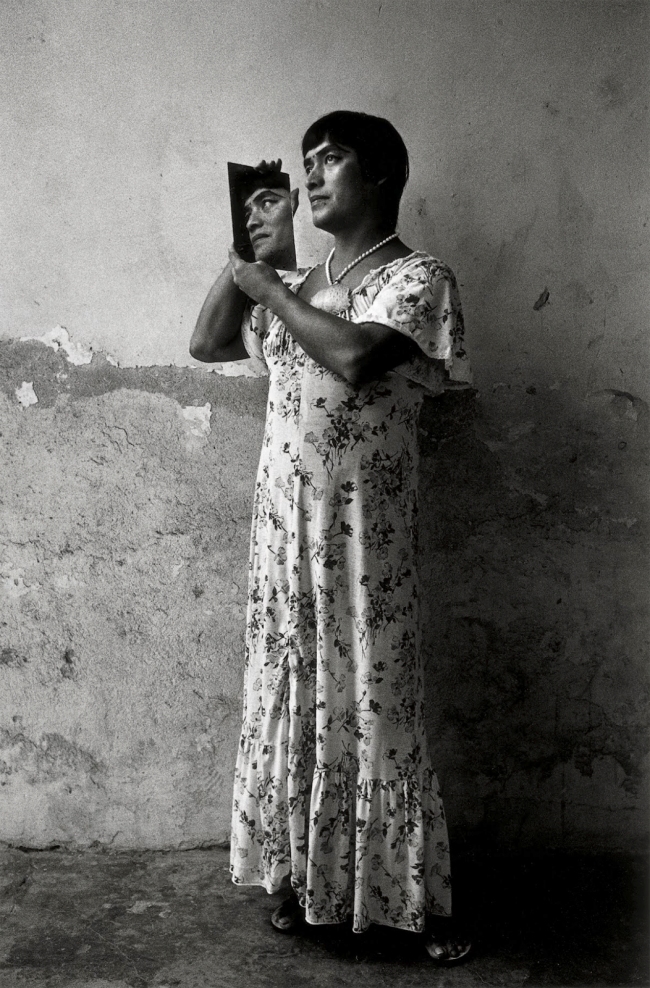
Installation view of the exhibition Clandestine – The Human Body in Focus at the Cobra Museum of Modern Art, Amstelveen showing from left to right, Nan Goldin’s Ivy wearing a fall Boston 1973 and Antonio Reynoso’s La Gorda (The Fat Woman) c. 1960
Antonio Reynoso (Mexican, 1919-1996)
La Gorda (The Fat Woman)
c. 1960
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Beauty lies in the eye of the beholder. This phrase stresses that beauty is thoroughly subjective and only limited by social constructs.
One would argue that beauty is different from sciences like physics or chemistry since it is not quantifiable or measurable. Nonetheless, through non-scientific agreement people still know how to distinguish what is pretty from what is not. For instance, a swampy pond is less pretty than a turquoise ocean. This is the shared opinion, of at least the majority, but is this a view shared by everyone? Even more importantly, is this our view or was it simply bestowed upon us without our prior consent?
Being critical when looking at a work of art, or more frankly when looking at anything, is an exercise to strengthen our own individuality and potential to envision a new beauty. This does not mean one should automatically discredit beauty from something or someone that is socially considered beautiful but to question it. This is a call to acknowledge that the notion of beauty can be challenged, abstracted or even reconstructed.
This is a portrait by Mexican photographer Antonio Reynoso La Gorda (The Fat Woman). It invites us to reconsider the meanings of several attributes including, beauty, sensuality and femininity.
Anonymous text from the Cobra Museum of Modern Art Instagram page
Nan Goldin (American, b. 1953)
Ivy wearing a fall
Boston 1973
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Allen Frame (American, b. 1951)
Young Man, New York
1974
Gelatin silver print
Framework: 40.5 x 50.5cm
Photo: 27.9 x 35.5cm
Pedro Slim Collection
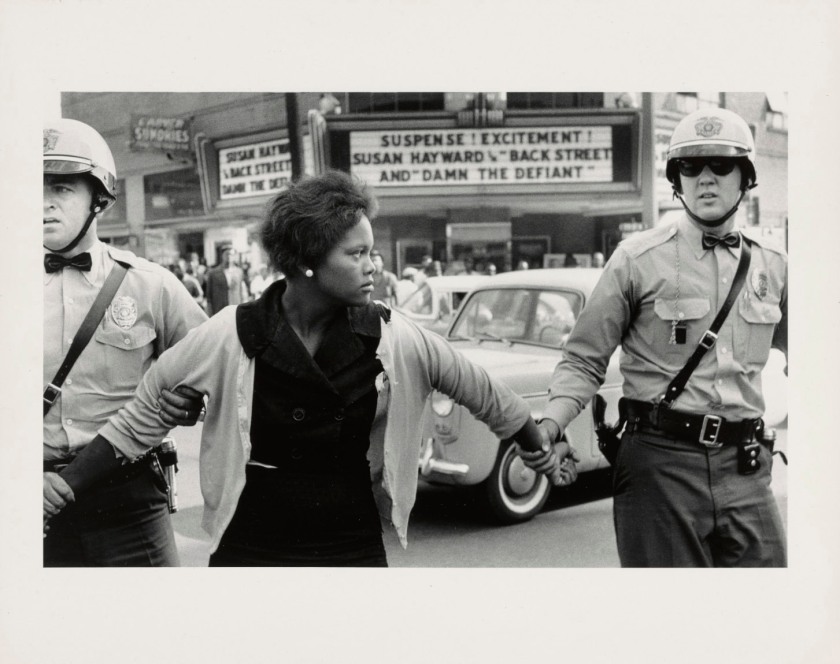
Leonard Freed (American, 1929-2006)
Handcuffed, New York City
c. 1978
From Police Work series
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
David Wojnarowicz (American, 1954-1992)
Arthur Rimbaud in New York
1978-1979
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Arthur Rimbaud in New York, one of David Wojnarowicz’s few incursions into photography, is the articulation of a testimony to urban, social and political change in New York.
Wojnarowicz, using the figure of the accursed poet as the only way for an artist to intervene in reality, chronicles his own life and his emotional relationship with New York City in the late 1970s. The artista portrays a number of friends with a life-size mask of the French poet Arthur Rimbaud, thereby taking on his identity and highlighting the parallels in their lives: the violence suffered in their youths, the feeling of being denied freedom, the desire to live far away from the bourgeois environment and the fact of their homosexuality. Wojnarowicz is juxtaposing the historical time of the symbolist poet with the artist’s present.
The series, taken in places that the artist used to frequent with photographer Peter Hujar, represents the emergence of identity politics and queer visibility in contemporary art, and the debates surrounding the public sphere as a space for individual non-conformity that were to shape the 1980s. The series also represents a contemplation of the end of the experimental artists’ collectives on the Lower East Side, as gentrification and urban speculation transformed the neighbourhood, and AIDS had begun to decimate the gay community, also causing the early death of the artist in 1992.
Salvador Nadales. “Arthur Rimbaud in New York,” on the Museo Reina Sofía website Nd [Online] Cited 23/02/2022
George Dureau (American, 1930-2014)
B.J. Robinson
c. 1980
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
What happens when people become labelled as objects of inspiration?
Popular culture often exotifies or objectifies a group of people who are slightly different from the majority. Sayings such as ‘you cannot fail if you have not tried’ accompanied by a photo of a person with a disability, portrays the subject as a source of exceptional inspiration for the viewer. This may objectify the subject in the photo.
This is something that happens in the art world too. For instance, the monumental achievements of artists with a disability, such as Frida Kahlo or Vincent van Gogh, are sometimes phrased as a direct outcome of their condition. By doing so the condition of the artist becomes bigger than the persona. This undermines the different elements that constitute the artist as a whole.
For the photographer George Dureau, whose work is displayed in our exhibition Clandestine, photography is a medium with the potential to empower people with disabilities by simply representing them, without objectifying them. By photographing people with disabilities the same way traditional photographers captured images of models, Dureau reconceptualised the standards of beauty.
The conversation revolving around objectification is far from over. Dureau’s views present an interesting way to think about the topic, but we still need more critical and engaged dialogue and we want to hear your opinion. Where is the boundary between admiration and objectification?
Anonymous text from the Cobra Museum of Modern Art Instagram page
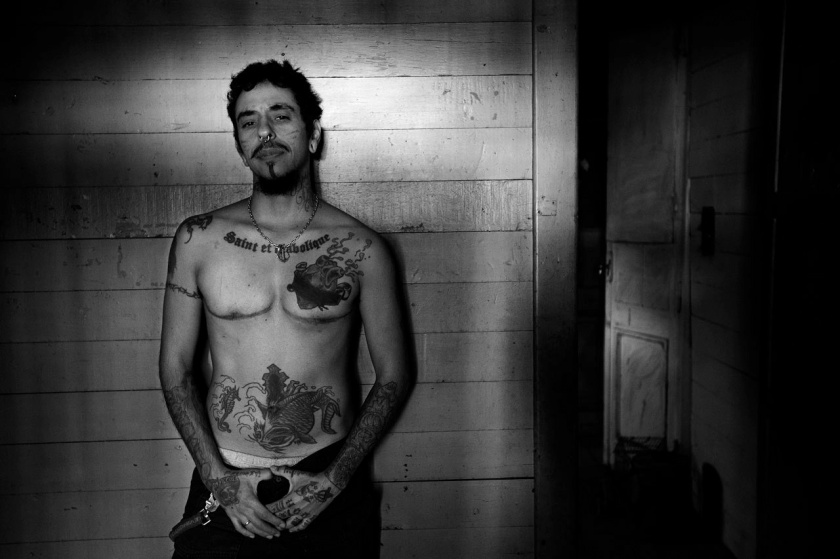
Larry Clark (American, b. 1943)
Chuck
c. 1981
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Armando Cristeto (Mexican, b. 1957)
Apolo Urbano (Urban Apollo)
Mexico City, 1981
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
© Armando Cristeto
Born in 1957 in Mexico City, photographer and historian Armando Cristeto began to study photography in 1977 at the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Mexico. He was a member of the photography collective known as the Grupo de Fotografos Independientes, one of the numerous cooperatives of artists known as ‘Los Grupos’ proliferating during the late 1970s in Mexico.
Founded by Amando Cristeto’s brother Adolfo Patino, the Fotografos Independientes sought to reach new audiences by taking their exhibitions out onto the street, where their works could interact with the urban context and be appreciated by new classes of people. Their exhibitions were installed along the sidewalks of Mexico City, employing clothesline to hang their photographic prints, or were even paraded through the streets on wheeled carts.
Anonymous text. “Armando Cristeto,” on the ultrawolvesunderthefullmoon website June 9, 2020 [Online] Cited 23/03/2022
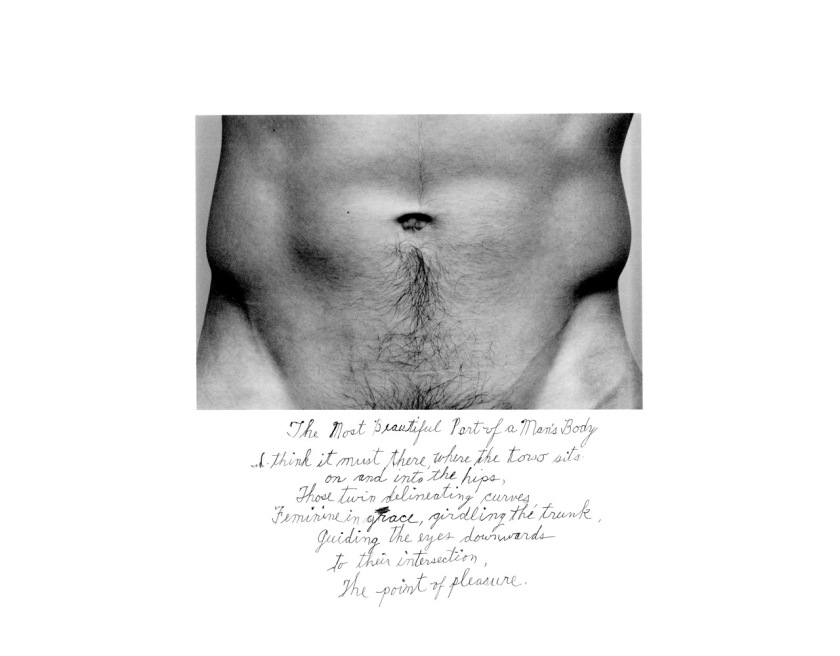
Duane Michals (American, b. 1932)
The Most Beautiful Part of a Woman’s Body
c. 1986
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Duane Michals (American, b. 1932)
The Most Beautiful Part of a Man’s Body
c. 1986
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Graciela Iturbide (Mexican, b. 1942)
Magnolia, Juchitán, México
1986
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Is symmetry more beautiful than asymmetry?
The notion of symmetry is occasionally interchanged with the one of beauty as if these would be synonyms. Artists and philosophers from different cultures and times have championed equilibrium and positioned symmetry on an untouchable pedestal, but culturally speaking, asymmetry might be more valuable.
The mathematical notion of symmetry suggests that if an object is changed – say a cube or a sphere is rotated – it stays the same as before it was moved. Aiming for symmetrical forms seems reasonable from the functional standpoint of an architect or a mathematician, but why do our cultures dismiss or shame asymmetry?
Asymmetry presupposes that something, or someone, changes after its circumstances changed. Transforming when situations demand it, is necessary to evolve. One symmetric thought or body would entail that it does not change when it is moved. That said, maybe it is time to reevaluate the way we perceive notions of beauty and reformulate our societal desires. Asymmetric bodies might be much more sexy and beautiful after all.
The exhibition, Clandestine – The Human Body in Focus, presents black and white photographs of the human body. The photographs render asymmetric human bodies.
Anonymous text from the Cobra Museum of Modern Art Instagram page
Herb Ritts (American, 1952-2002)
Wrestling Torsos, Hollywood
c. 1987
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Merry Alpern (American, b. 1955)
Dirty Windows #16
1994
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Merry Alpern (American, b. 1955)
Untitled from the series Dirty Windows
1994
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
How to take dramatic photos of strangers? Wait, should you ask for their consent before photographing them?
In most countries, it is legal to take photos of people, including children in public. The question of whether it is morally right or wrong to take photos of strangers remains problematic. Some would say that it depends on the purpose of the photo. Judging a body of work that is intended to be used for profit, such as to promote a product, is different from photojournalism or a photo exhibition.
When seeing the photos exhibited in our exhibition Clandestine- The Human Body in Focus, one wonders if every single body was aware it would end up framed in the museum, or in the Instagram account of the museum itself.
To give this situation a context, consider Merry Alpern’s Dirty Windows series from 1994. Rather than posing her subjects, Alpern captured women (and men) crowded into the tiny bathroom of a sex club in the Wall Street district of Manhattan. Her photos were taken at night, in dim light, from a friend’s apartment, one story higher and about five meters away from the bathroom window. Her obsessive, voyeuristic, and even paranoic project as well as her overtly sexual scenes, caused a national controversy at the time.
With these images, Alpern encapsulated and reduced the identity of her subjects as ‘sex workers’. By taking a single shot of a person and framing it as the complete one, the photo runs the risk of stripping the full identity away from the subject. The women in the Dirty Windows series could be mothers, daughters, great sports players, activists and so on, but not everyone gets to see that part of the story.
Let this be a reminder that when taking a photo of a person, you should make sure the person is aware of the photo’s purpose as well as what part of the story- of their identity – is framed.
Anonymous text from the Cobra Museum of Modern Art Instagram page
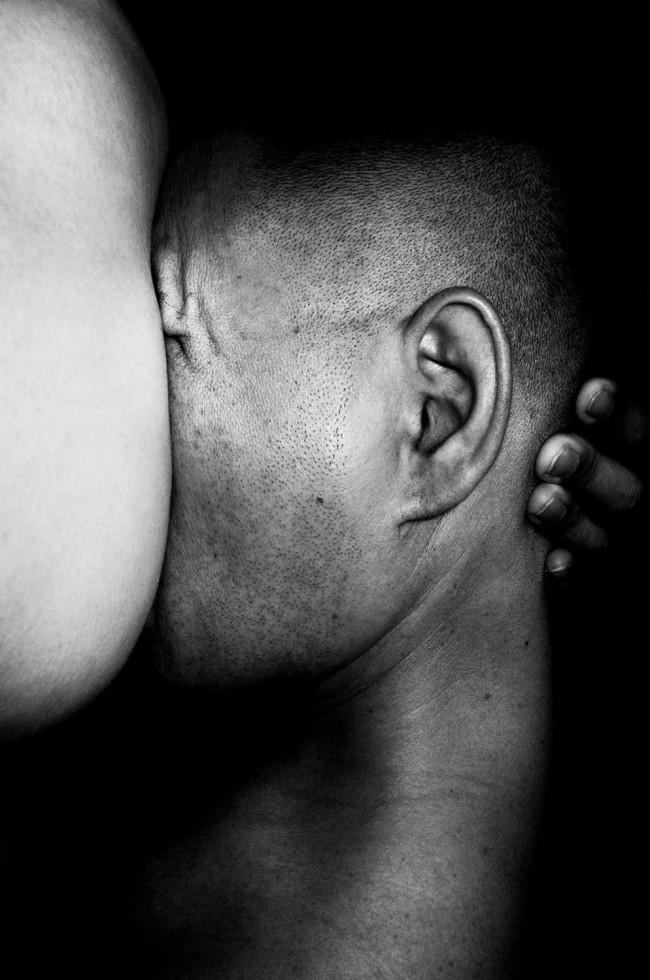
Shohei Miyachi (Japanese, b. 1989)
Untitled
c. 2018
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
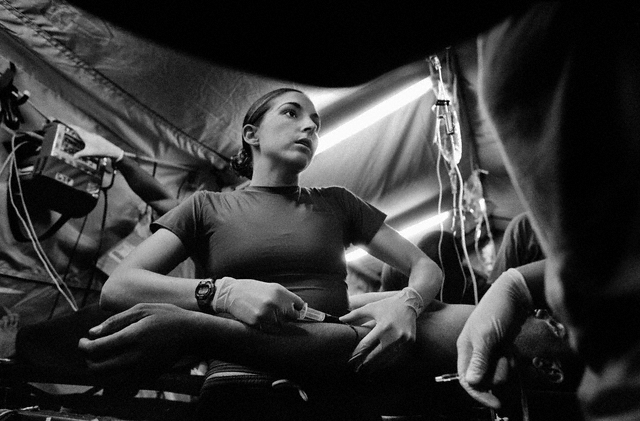
Kike Arnal (Venezuelan)
Untitled (Emmanuel, trans man and tattoo artist)
2018
From the series Revealing Selves – Transgender Portraits from Argentina
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
When it comes to transgender rights, Argentina is a country rife with contradictions. After being subject to widespread medicalization and incarceration throughout the 20th century, Argentina’s transgender community began to see a number of windfall legal and political wins in the early 21st century that would secure them progress once only dreamed of. These included the Gender Identity Law of 2012, landmark legislation which guarantees transgender Argentinians the right to change their sex in the public record, access free gender reassignment surgery and hormone therapy that doesn’t require medical or psychological diagnoses, and enshrines transgender discrimination protections in law.
But the gulf between legislative gains and reality can be wide in many countries, and Argentina is no exception. Despite these rights, 88 percent of Argentinian trans women have never had a formal job; their average life expectancy is 35, whereas the national average is 77; and only 40 percent graduate from high school. Transgender Argentinians still face massive cultural and social stigma, which can lead to family rejection and poverty.
In Revealing Selves: Transgender Portraits from Argentina … documentary photographer Kike Arnal provides a window into the homes and lives of Argentina’s transgender community, one that captures these contradictions.
Anonymous text. “Revealing Portraits from Argentina’s Transgender Community,” on the Them website April 10, 2018 [Online] Cited 23/02/2022
Kike Arnal (Venezuelan)
Untitled (Emmanuel, trans man and tattoo artist)
2018
From the series Revealing Selves – Transgender Portraits from Argentina
Gelatin silver print
Pedro Slim Collection
Cobra Museum of Modern Art
Sandbergplein 1, 1181 ZX Amstelveen
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Sunday 10am – 5pm
Closed Monday






































![Underwood & Underwood (American, founded 1881, dissolved 1940s) '[Women's Campaign Train for Hughes]' 1916 Underwood & Underwood (American, founded 1881, dissolved 1940s) '[Women's Campaign Train for Hughes]' 1916](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2021/09/underwood-underwood-womens-campaign-train-for-hughes.jpg?w=840)


















































































![Erich Salomon (German, 1886-1944) '[Portrait of Madame Vacarescu, Romanian Author and Deputy to the League of Nations, Geneva]' 1928 Erich Salomon (German, 1886-1944) '[Portrait of Madame Vacarescu, Romanian Author and Deputy to the League of Nations, Geneva]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/in-focus-expressions-1-web.jpg?w=840)





![Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) '[Mme Ernestine Nadar]' 1880-1883 Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) '[Mme Ernestine Nadar]' 1880-1883](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/in-focus-expressions-4-web.jpg?w=840)
![Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) '[Mme Ernestine Nadar]' 1880-1883 (detail) Nadar [Gaspard Félix Tournachon] (French, 1820-1910) '[Mme Ernestine Nadar]' 1880-1883 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/in-focus-expressions-4-detail.jpg?w=650&h=873)











![Lisette Model (American born Austria, 1901-1983) '[War Rally]' 1942 Lisette Model (American born Austria, 1901-1983) '[War Rally]' 1942](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/in-focus-expressions-2-web.jpg?w=650&h=805)

![Unknown maker (American) '[Smiling Man]' 1860 Unknown maker (American) '[Smiling Man]' 1860](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/unknown-maker-smiling-man-1860-web.jpg?w=650&h=794)
![Baron Adolf de Meyer (American born France, 1868-1946) '[Ruth St. Denis]' c. 1918 Baron Adolf de Meyer (American born France, 1868-1946) '[Ruth St. Denis]' c. 1918](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/baron-adolf-de-meyer-ruth-st-denis-c-1918-web.jpg?w=650&h=956)
![Woodbury & Page (British, active 1857-1908) '[Javanese woman seated with legs crossed, basket at side]' c. 1870 Woodbury & Page (British, active 1857-1908) '[Javanese woman seated with legs crossed, basket at side]' c. 1870](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/woodbury-and-page-javanese-woman-web.jpg?w=650&h=1104)





![Camille Silvy (French, 1834-1910) '[Madame Camille Silvy]' c. 1863 Camille Silvy (French, 1834-1910) '[Madame Camille Silvy]' c. 1863](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/camille-silvy-web.jpg?w=650&h=960)
![Mikiko Hara (Japanese, b. 1967) '[Untitled (Making a Void)]' Negative 2001; print about 2007 Mikiko Hara (Japanese, b. 1967) '[Untitled (Making a Void)]' Negative 2001; print about 2007](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/06/mikiko-hara-untitled-web.jpg?w=650&h=650)



























You must be logged in to post a comment.