Exhibition dates: 7th October, 2017 – 7th January, 2018
Curator: Anne McCauley
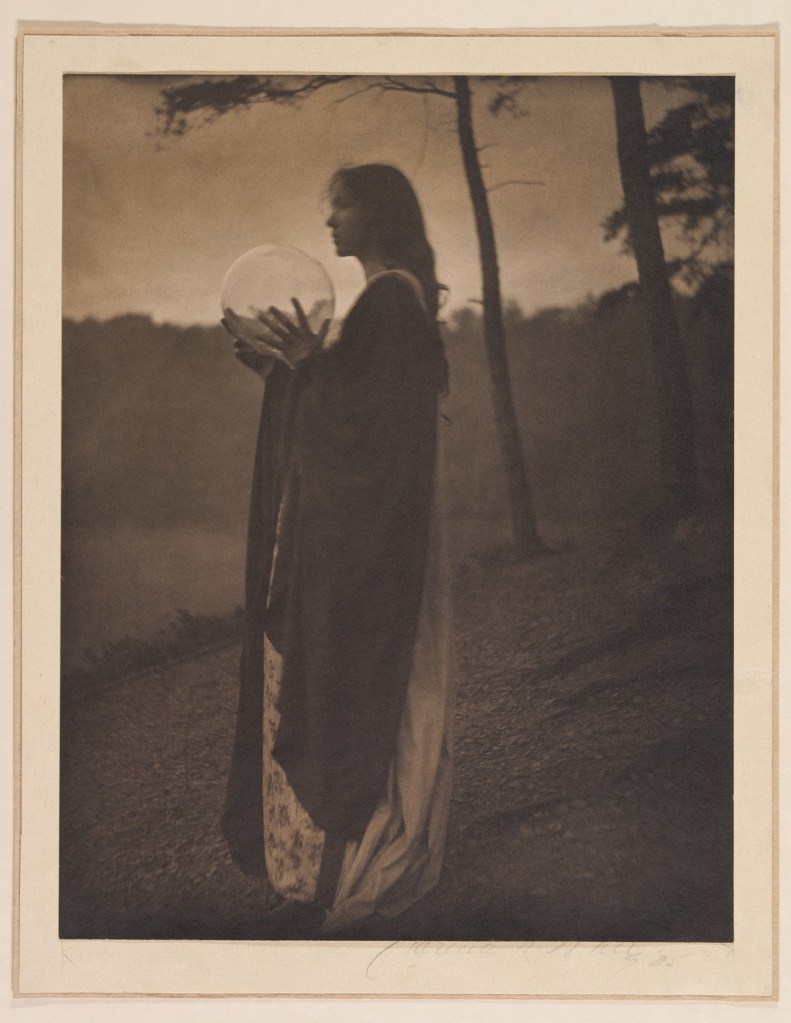

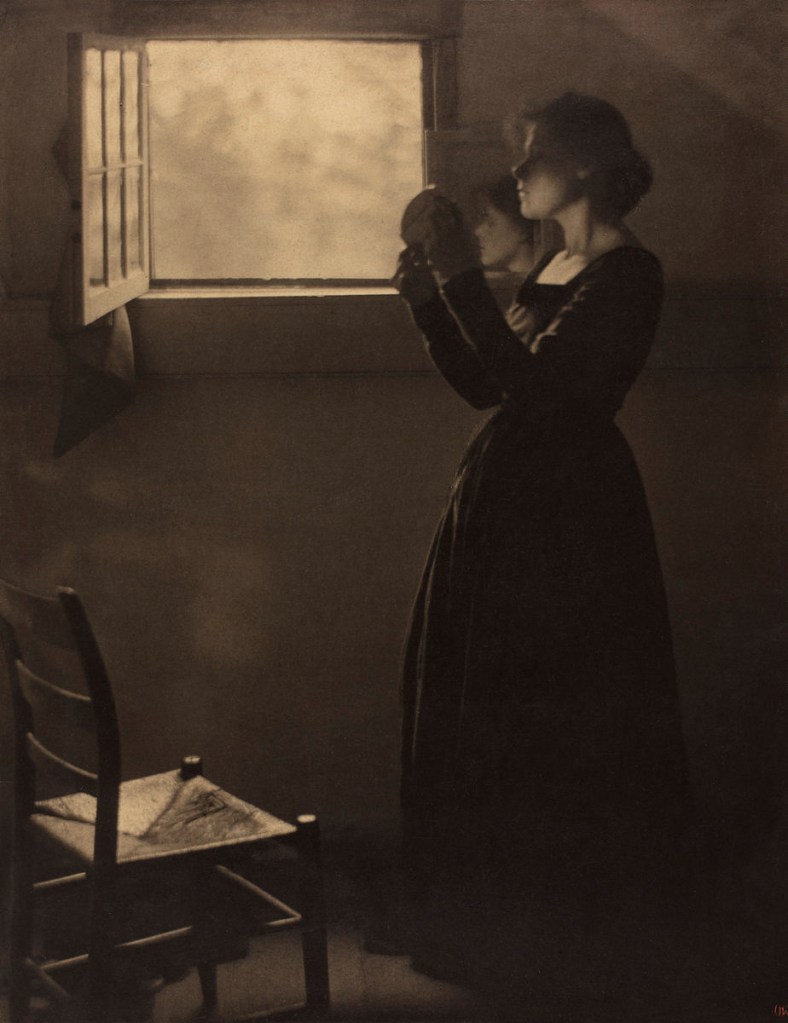
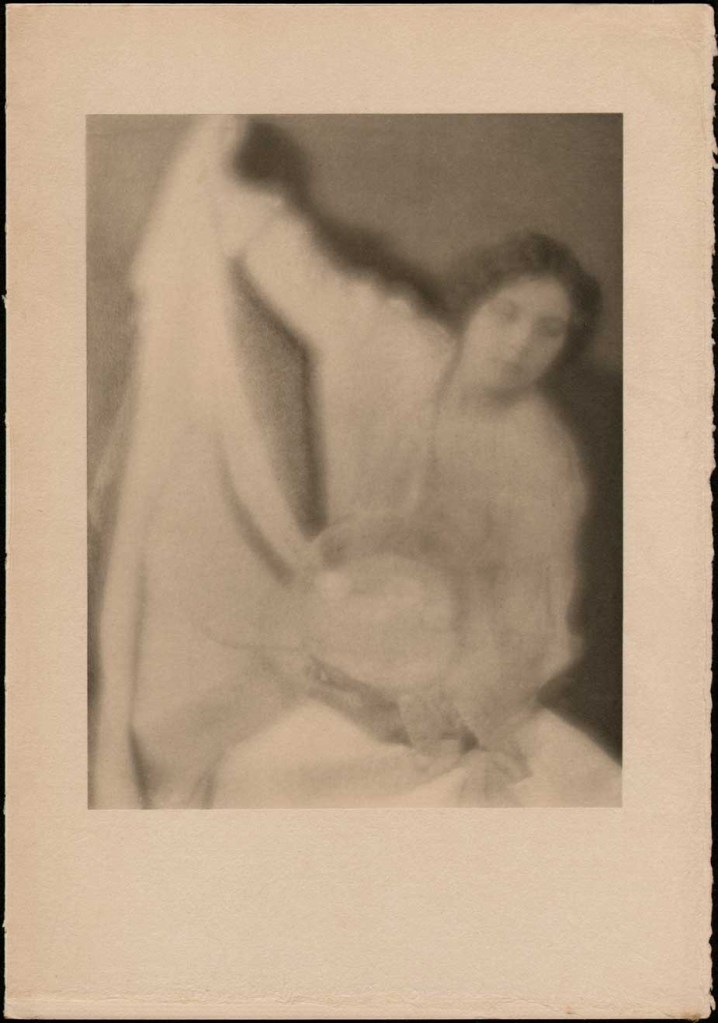
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Bubble
1898, printed 1905
Platinum print
24.2 x 19.3cm (9 1/2 x 7 5/8 in.)
Alfred Stieglitz Collection, 1933
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
A sense of the beyond
I have waited over nine years to be able to do a posting on this artist. This is the first retrospective of Clarence H. White’s photographs in a generation… and my first posting for 2018. What a beauty the posting is, and what beauty is contained within, his photographs.
White was born in Newark, Ohio (see map below) in 1871. Just to put that into perspective, of the big three Alfred Stieglitz was born in 1871, Edward Steichen in 1879 and Paul Strand in 1890. Soon after marrying his wife in 1893 White took up photography, applying some of his artistic vision, developed earlier through filling sketchbooks with pencil sketches, pen-and-ink drawings and watercolours, to the craft of photography. “He learned how to use light, or the lack of it, to draw attention to his subject. He also learned how to visualise his subjects in his mind.” He was completely self-taught, “in part because he had no money to pay for training or courses at the time when he was developing his own vision in the medium. Many of his friends, students and biographers believe his lack of any formal training was one of his greatest strengths… It is important to note that at that time there were no formal schools of photography in the U.S. or even acknowledged leaders with whom White might have studied.”1
In 1895, he exhibited his first photos in public, at the Camera Club of Fostoria, Ohio, and by 1898 he had met Fred Holland Day and Alfred Stieglitz. His star continued to rise, White having solo exhibitions in 1899 at the Camera Club of New York and at the Boston Camera Club, and he also exhibited in the London Photographic Salon organised by The Linked Ring. In 1900 White was elected to membership in The Linked Ring and in 1901 White and 10 others to become “charter members” of the Photo-Secession, a group founded by Alfred Stieglitz to promote Pictorialism and fine art photography. Due to financial constraints during this time, White was only able to create about 8 photographs each month, and he had to photograph either very early in the morning, after he finished work as a bookkeeper, or at the weekend. Some of his most memorable images were created at this time, before his move to New York in 1906. As Cathleen A. Branciaroli and William Inness Homer observe in “The Artistry of Clarence H. White”, “White is most significant in the history of photography because, in his early years, he redefined the nature of picture-making, creating a distinctly modern idiom for his own time…. He reduced his compositions to very simple elements of form, and by experimenting with principles of design derived largely from Whistler and Japanese prints, he created a personal style that was unique for photography.”2
If the photograph consumes light, then Clarence H. White was consumed by photography. Informed by the widespread Japonisme of the period, especially ukiyo-e prints (the term ukiyo-e translates as “picture[s] of the floating world”) with their flat perspective, unmodulated colours and outlined forms – his photographs “sought to capture either the geometry of perceived pattern or the gorgeous effect of shimmering light… qualities of image that the camera, conjoining realism and poetic perception, could render with compelling effect.”3 We now group these kind of photographs under the label “pictorialism,” soft-focus photographs that were more than purely representational, that project “an emotional intent into the viewer’s realm of imagination.”4 Here, an “atmosphere” (formulated, created, conceptualised, captured) is the key to conveying an expressive mood and an emotional response to the viewer “through an emphasis on the atmospheric elements in the picture and by the use of “vague shapes and subdued tonalities … [to convey] a sense of elegiac melancholy.””5
After his move to New York in 1906, White and Stieglitz “jointly created a series of photographs of two models, Mabel Cramer and another known only as Miss Thompson,” in 1907. This was the only time that Stieglitz ever worked with another photographer. “In 1908 Stieglitz continued to show his admiration for White by devoting an entire issue of Camera Work to him and 16 of his photographs. It was only the third time Stieglitz had singled out an individual photographer for this honor (the others were Steichen and Coburn).”6 In 1910, White set up the Seguinland School of Photography, the first independent school of photography in America, while in 1912 he had a terminal falling out with the excessive ego of Stieglitz. “First Käsebier, then White and finally Steichen broke off their relationship with Stieglitz, each citing Stieglitz’s overbearing ego, his refusal to consider other’s viewpoints and his repeated actions on behalf of the Photo-Secession without consulting any of the so-called “members” of the group.”7
Encouraged by his newfound freedom to act outside of the shadow of Stieglitz, White founded the Clarence H. White School of Photography in 1914… an influential school which, over the next decade, “attracted many students who went on to become notable photographers, including Margaret Bourke-White, Anton Bruehl, Dorothea Lange, Paul Outerbridge, Laura Gilpin, Ralph Steiner, Karl Struss, Margaret Watkins and Doris Ulmann.”8 In his class “The Art of Photography” White stressed that the primary thing his students had to learn was “the capacity to see.” White became one of the most important teachers of photography of the age. White died suddenly of a heart attack while on a trip to Mexico with students to take his first photographs in years. He was 54 years old.
After Alfred Stieglitz died in 1946 numerous photographs by White were found in his personal collection. Despite their differences, it is obvious that Stieglitz held White in very high regard, “one of the very few who understand what the Photo-Session means & is.”9 “Although White and Stieglitz had tried to reconcile their differences before White died, Stieglitz never forgave White for breaking from him in 1912. Upon hearing about White’s untimely death, Stieglitz wrote to Kuehn, “Poor White. Cares and vexation. When I last saw him he told me he was not able to cope with [life as well as he was] twenty years ago. I reminded him that I warned him to stay in business in Ohio – New York would be too much for him. But the Photo-Session beckoned. Vanity and ambitions. His photography went to the devil.” In spite of these words, Stieglitz had 49 of White’s photographs, including 18 created jointly with Stieglitz, in his personal collection when he died.”10
There is something undeniable in what Stieglitz says. White’s greatest photographs emerge from the Stygian dusk, a dash of melancholy, a lot of beauty, mostly before he moved to New York. It says a lot that Stieglitz still thought that much of him as an artist, a man, and as an emasculated friend, that he kept nearly 50 of his photographs in his personal collection until he died. Stieglitz knew the nature of (his) genius.
The value of self-expression and direct engagement with experience
Clarence H. White’s artistic achievements may have been overshadowed by the likes of Stieglitz, Steichen and Strand’s later modernist photographs, but there is no doubt in my mind that he is a colossus, a monster in the history of art photography. Simply put, there is no one else like him in the history of photography, for you can always recognise the “signature” of a White photograph.
Peter Bunnell notes, “[White] celebrated elemental things, the time spent playing in the fields or woods, the simple pleasure of unhurried living, the playing of games in interior spaces…. White, growing up within an extended family, knowing nothing else, had no real sense of other societies and his pictures thus had a kind of fortification against the outside. They were his private epic.”12 His private epic was a personal mythology which expressed his personality and distinctive sentiments through his photographs of imagined worlds. This is the critical thing that makes him so different from other photographers of the period: he was beholden to no movement, no school, teacher or narrative – but only to himself. In his best photographs it was this private world writ large in light that made him famous.
His “masterful reinterpretation of the possibilities of light and the photographic medium done with artistic intent”11 allowed him to develop this personal mythology. White learned how to visualise his subjects in his imagination, before rendering them by drawing in light. His unique prints, made in a variety of processes (platinum, gum-platinum, palladium, gum-palladium, gum, glycerin developed platinum, cyanotype and hand-coated platinum) with the same image sometimes printed using different processes,13 celebrate “pure photography”, a cerebral, ethereal emanation of pure light and form. They seem not of this earth. Indeed, I would argue that White steps outside strict Pictorialism into this “other”, private realm.
There may be, as Peter Bunnell suggests, a luminosity of tone in his prints rarely achieved in the history of photography, but there was also a luminosity in his thinking, in the way he approaches the medium itself. I look at the photograph The Deluge (c. 1902-1903, below) and I think of William Blake. I look at the three versions of the photograph Spring – A Triptych [Letitia Felix] (1898, below) and observe how each iteration is different (in colour, tone and inflection), but how they are just as valid as each other. There are personal, domestic quotidian scenes (Blindmans’ Bluff, 1898 or Mother was living in the old home alone, 1902); mythic scenes, such as the glorious photograph The Bubble (1898, above) where the figure seems to hover above the ground (“pictures of the floating world”); and early Modernist inclinations such as Drops of Rain (1903, below) and Newport the Maligned (1907, below). But above all, there is the light which shines from within.
Further, his was a whole art aligned perhaps subconsciously, perhaps not, to that German Art Nouveau movement named after the Munich periodical Die Jugend (‘Youth’) – Jugendstijl. “A decorative art with the mid-century idea of the gesamtkunstwerk; the ‘total work of art’ applied in Wagner’s opera and in Dülfer’s architecture, Jugendstil before 1900 favoured floral motifs and ukiyo-e prints of Japanese art.” Evidence of this ‘total work of art’ (an expression of folk legend as universal humanist fable), can be seen in the few Pictorialist works from the late 1890s that survive in their original exhibition frames (see below). The plain dark wood frames with their curved tops serve to further isolate and flatten the pictorial space of the photograph; the dark colour of the wood pushing against the luminosity, line, form and reddish brown colour of the prints. The last version of Spring – A Triptych (Letitia Felix) (1898, below) is particularly illuminating in this respect, the dark wood framing the individual panels fragmenting the field upon which the young woman stands, so that we are no longer in a fairytale landscape (as in the first iteration) but surrounded by writhing tree trunks of sombre hue with a ghost-like presence walking amongst them. And then we see how these photographs were originally exhibited!
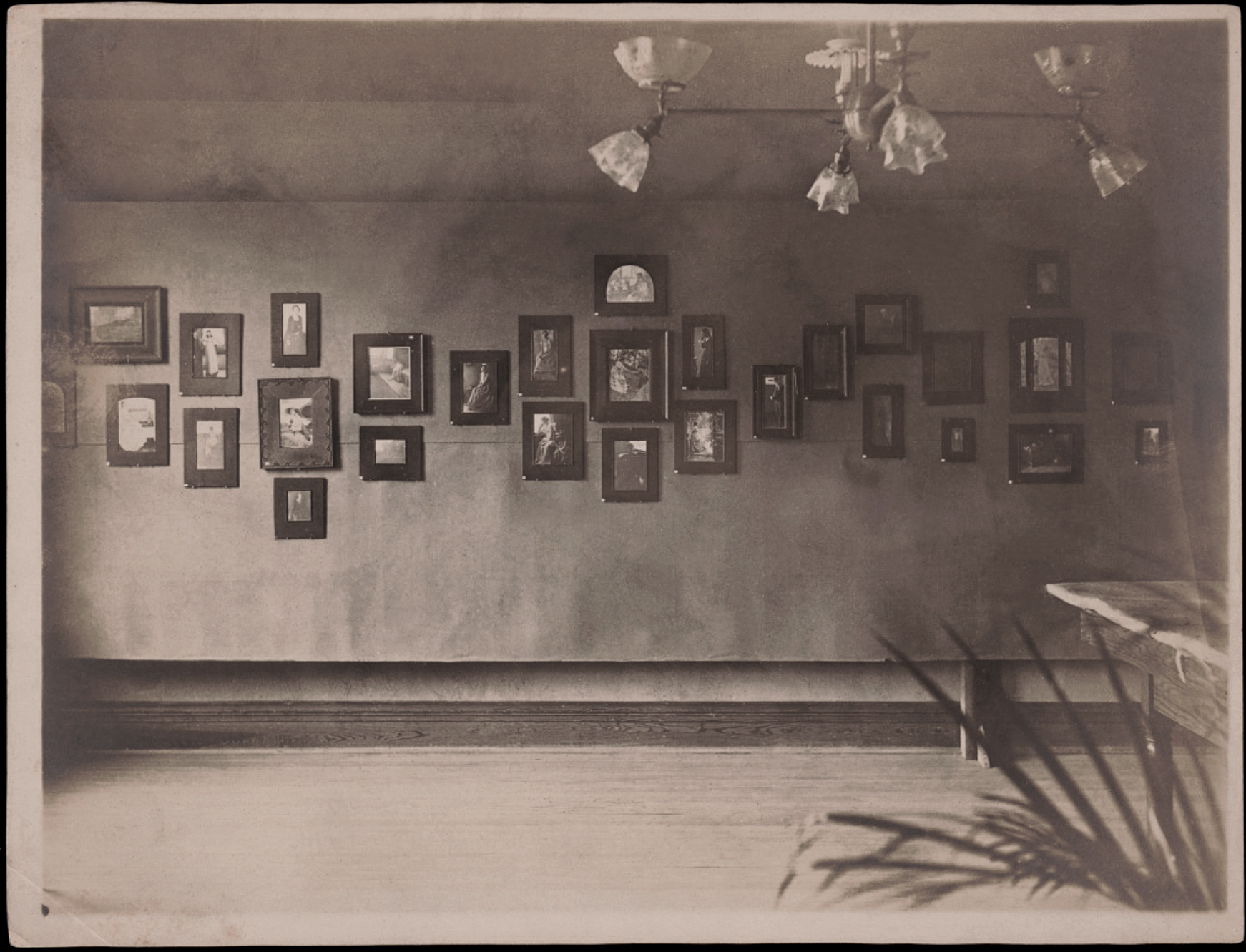
In Display of Clarence H. White photographs in Newark Camera Club exhibition, Young Men’s Christian Association building, Newark, Ohio, 1899 (below) we observe, we are witness to, a flow of energy from one side of the wall to the other – none of this staid singular hanging “on the line” – but a dynamic narrative that moves the viewer both physically and mentally. How wondrous is this display! An then in William Herman Rau’s photograph Untitled [Clarence H. White works in Second Philadelphia Photographic Salon installation (1899, below) we see a networked display, almost a cross-like shape, with portraits surrounding what looks like a central landscape image (although it is difficult to make out exactly what the image is). This is an almost contemporary sequencing of photographic work, still used by the likes of Annette Messager today… a perfect example of gesamtkunstwerk, where White has fully understood concept, narrative, form, function, the physicality of the photograph, it’s frame, and the context and environment of the image display.
To me, the early prints of Clarence H. White give the sense that he has found a metaphor, but he is not sure what that metaphor relates to: a cosmology? / man creating something of wonder (when viewed with imagination)?
He is still working it out… and then he goes to New York.
Does it matter that he didn’t find the answer? A thing that is done as a reaction to a situation.
Not at all. It’s the journey that matters.
The sense of ethereal beauty and the beyond that he captured on his glass plates are enough to make him a genius in my eyes. “Images arising from dreams are the well spring of all our efforts to give enduring form and meaning to the urgencies within,” states Douglas Fowler.14 White’s oneiric photographs, and our prior experiences with dreaming and imagination, help to create a sense of oneness with his photographs. Ultimately, his private epic, his personal mythology brought these aspects of art into photography.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Princeton University Art Museum for allowing me to publish the art work in the posting. Please click on the art work for a larger version of the image.
Footnotes
1/ Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
2/ Cathleen A. Branciaroli and William Inness Homer. “The Artistry of Clarence H. White,” in Homer, William Innes (ed.). Symbolism of Light: The Photographs of Clarence H. White. Wilmington, DE: Delaware Art Museum, 1977, p. 34
3/ Richard K. Kent. “Early Twentieth-Century Art Photography in China: Adopting, Domesticating, and Embracing the Foreign,” in Local Culture / Global Photography, Trans Asia Photography Review Vol. 3, Issue 2, Spring 2013 [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
4/ “Pictorialism is the name given to an international style and aesthetic movement that dominated photography during the later 19th and early 20th centuries. There is no standard definition of the term, but in general it refers to a style in which the photographer has somehow manipulated what would otherwise be a straightforward photograph as a means of “creating” an image rather than simply recording it. Typically, a pictorial photograph appears to lack a sharp focus (some more so than others), is printed in one or more colours other than black-and-white (ranging from warm brown to deep blue) and may have visible brush strokes or other manipulation of the surface. For the pictorialist, a photograph, like a painting, drawing or engraving, was a way of projecting an emotional intent into the viewer’s realm of imagination.”
Anonymous. “Pictorialism,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
5/ Naomi Rosenblum. A World History of Photography. New York: Abbeville Press, 1989, p. 297 quoted in Anonymous. “Pictorialism,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
6/ Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
7/ Maynard Pressley White Jr. Clarence H. White: A Personal Portrait. Wilmington, Delaware: University of Delaware, PhD dissertation, 1975 quoted in Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
8/ Lucinda Barnes (ed.) with Constance W. Glenn and Jane L. Bledsoe. A Collective Vision: Clarence H. White and His Students. Long Beach, CA: University Art Museum, 1985 in Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
9/ Maynard Pressley White Jr. Clarence H. White: A Personal Portrait. Wilmington, Delaware: University of Delaware, PhD dissertation, 1975, p. 175 quoted in Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
10/ Weston J. Naef. The Collection of Alfred Stieglitz, Fifty Pioneers of Modern Photography. NY: Viking Press, 1978, pp. 482-493 quoted in Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
11/ Peter Bunnell. Clarence H. White: The Reverence for Beauty. Athens, Ohio: Ohio University Gallery of Fine Arts, 1986, p. 17 quoted in Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
12/ Anonymous. “A Reevaluation: Clarence H. White,” on the Photoseed blog [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
13/ “White sometimes printed the same image using different processes, and as a result there are significant variations in how some of his prints appear. His platinum prints have a deep magenta-brown tone, for example, whereas his gum prints have a distinct reddish hue. Photogravures of his images in Camera Work, which he considered to be true prints, were more neutral, tending toward warm black-and-white tones.”
Maynard Pressley White Jr. Clarence H. White: A Personal Portrait. Wilmington, Delaware: University of Delaware, PhD dissertation, 1975, p. 68 quoted in Anonymous. “Clarence Hudson White,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 02/01/2018
14/ Douglas Fowler. The Kingdom of Dreams in Literature and Film: Selected Papers from the Tenth Annual Florida State University Conference on Literature and Film. Tallahassee: University Presses of Florida, 1986, p. 10 quoted in Anonymous. “Oneiric (film theory),” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 03/01/2018
Newark, Ohio – where Clarence H. White was born and taught himself photography
Lecture Clarence H White and His World
Anne McCauley, curator of the exhibition and David Hunter McAlpin Professor of the History of Photography and Modern Art, explores the legacy of one of the early twentieth century’s most gifted photographers and influential teachers. Program took place on Saturday, October 14, 2017.
Clarence H. White Analysis and Collaborative Discovery
Collaboration with Yale Reveals Late Nineteenth and Early Twentieth-Century Photographic Processes
Preparations for the first retrospective exhibition in a generation of pioneer photographer Clarence Hudson White (1871-1925) have inspired an unexpected collaboration between the Princeton University Art Museum and the Yale Institute for the Preservation of Cultural Heritage. Immersed in the real-life setting of the Princeton University Art Museum, the project drew students, researchers, and curators from across two universities and from numerous disciplines to analyse the experimental techniques that took place during the “Pictorialism” period of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Unknown photographer
Display of Clarence H. White photographs in Newark Camera Club exhibition, Young Men’s Christian Association building, Newark, Ohio, 1899
1899
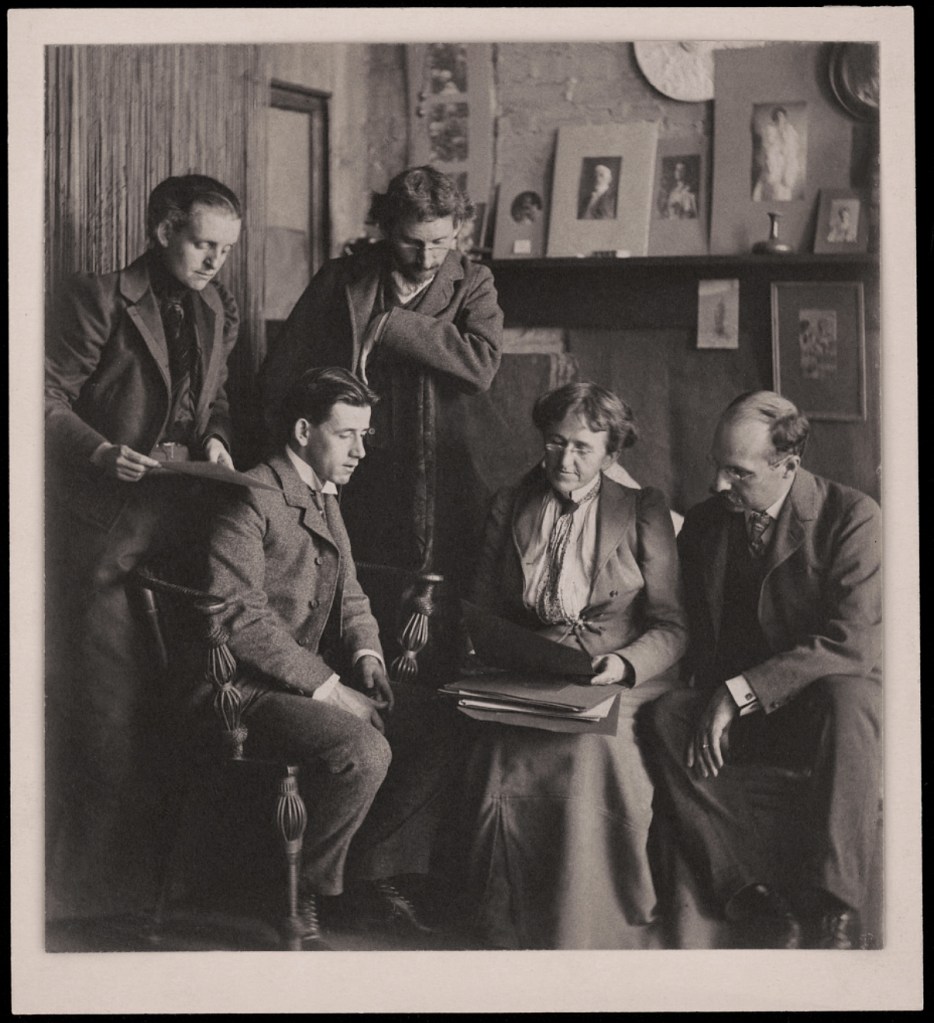

Unknown photographer
Jury of the Second Philadelphia Photographic Salon
1899
Photograph shows, from left: Frances Benjamin Johnston, Clarence H. White, F. Holland Day, Gertrude Käsebier, and Henry Troth
![William Herman Rau (1855-1920) 'Untitled [Clarence H. White works in Second Philadelphia Photographic Salon installation]' 1899 William Herman Rau (1855-1920) 'Untitled [Clarence H. White works in Second Philadelphia Photographic Salon installation]' 1899](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-works-in-second-philadelphia-photographic-salon-installation-1899-web.jpg?w=932)
William Herman Rau (1855-1920)
Untitled [Clarence H. White works in Second Philadelphia Photographic Salon installation]
1899
Photograph shows a wall installation of photographs by Clarence H. White at the second exhibition of the Philadelphia Photographic Salon; according to the catalog for the exhibition, the works shown are “Fear”, “Morning”, “A Puritan”, “The Bubble”, “Lady in Black”, “Evening : An Interior”, “On the Old Stair”, “At the Old Canal Lock”, and “Lady with the Venus.” Also includes a portrait, presumably of White, half-length, facing right.
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
A Rift in the Clouds
1896
Platinum print
Image (window): 10.3 x 13.9cm (4 1/16 x 5 1/2 in.)
Frame: 28.6 × 36.2cm (11 1/4 × 14 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
A Rift in the Clouds
1896
Platinum print
Image (window): 10.3 x 13.9cm (4 1/16 x 5 1/2 in.)
Frame: 28.6 × 36.2cm (11 1/4 × 14 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
White was completely self-taught throughout his career, in part because he had no money to pay for training or courses at the time when he was developing his own vision in the medium. Many of his friends, students and biographers believe his lack of any formal training was one of his greatest strengths. When a one-man exhibition of his work was held in Newark in 1899, fellow Newark photographer Ema Spencer wrote, “He has been remote from artistic influences and is absolutely untrained in the art of the schools. In consequence, traditional lines have unconsciously been ignored and he has followed his own personal bent because he has been impelled by that elusive and inscrutable force commonly known as genius.” It is also important to note that at that time there were no formal schools of photography in the U.S. or even acknowledged leaders with whom White might have studied. The most common way a new photographer learned the trade was by working with an experienced photographer, and, other than a few portraitists, there was no one to learn from in Newark.
Text from the Wikipedia website
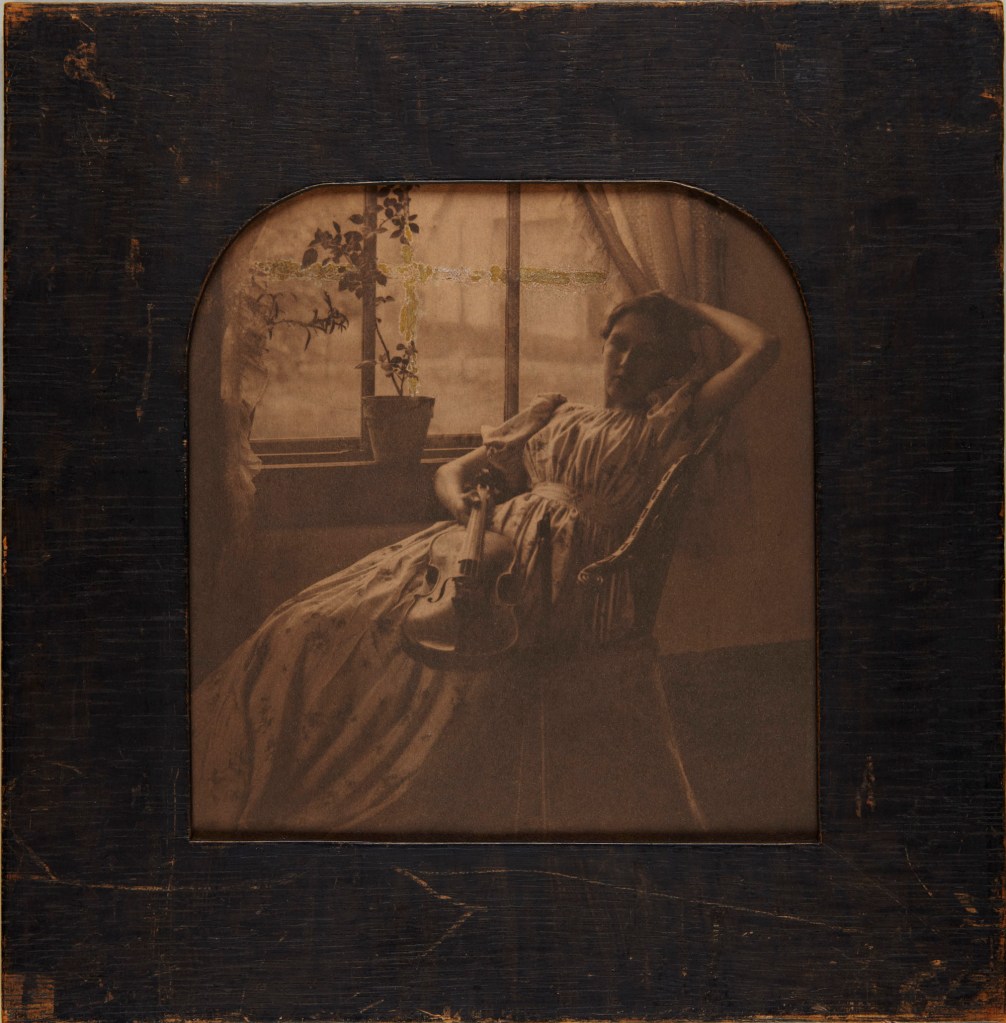

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Girl with the Violin
1897
Platinum print with gouache in original frame
Image: 14.7 x 14cm (5 13/16 x 5 1/2 in.)
Frame: 22.9 x 22.4cm (9 x 8 13/16 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
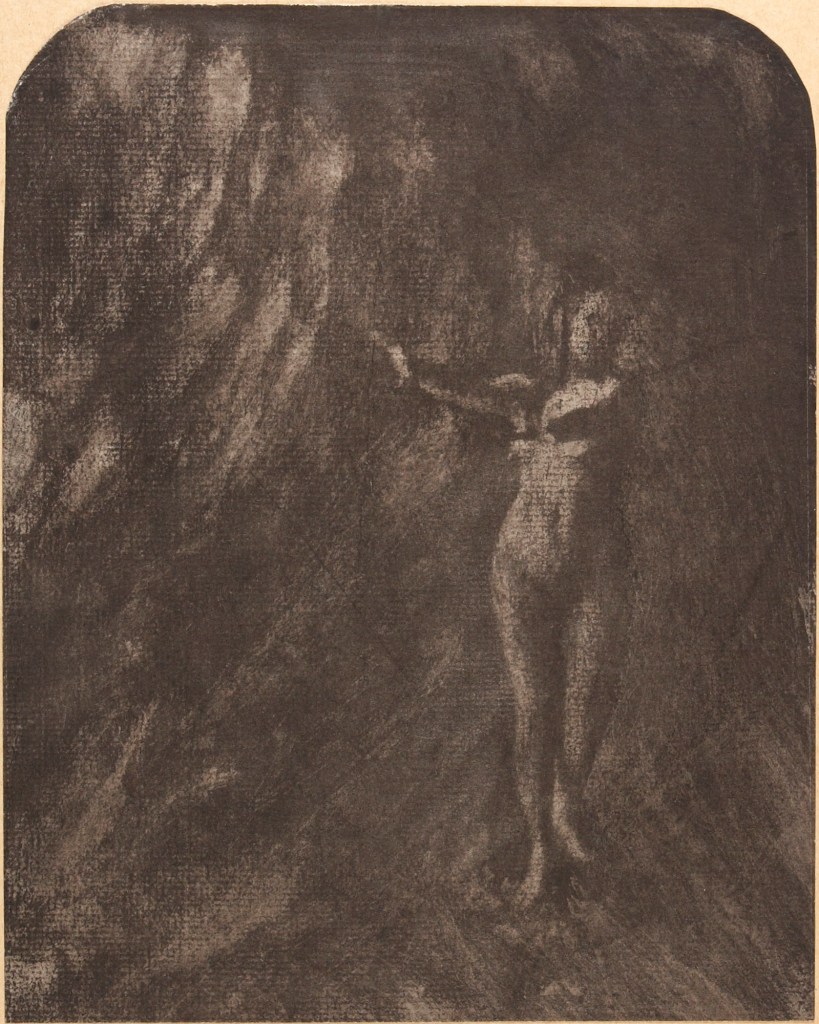

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Deluge
c. 1902-1903
Gum bichromate print
Image (arched top): 20.2 x 16.2cm (7 15/16 x 6 3/8 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
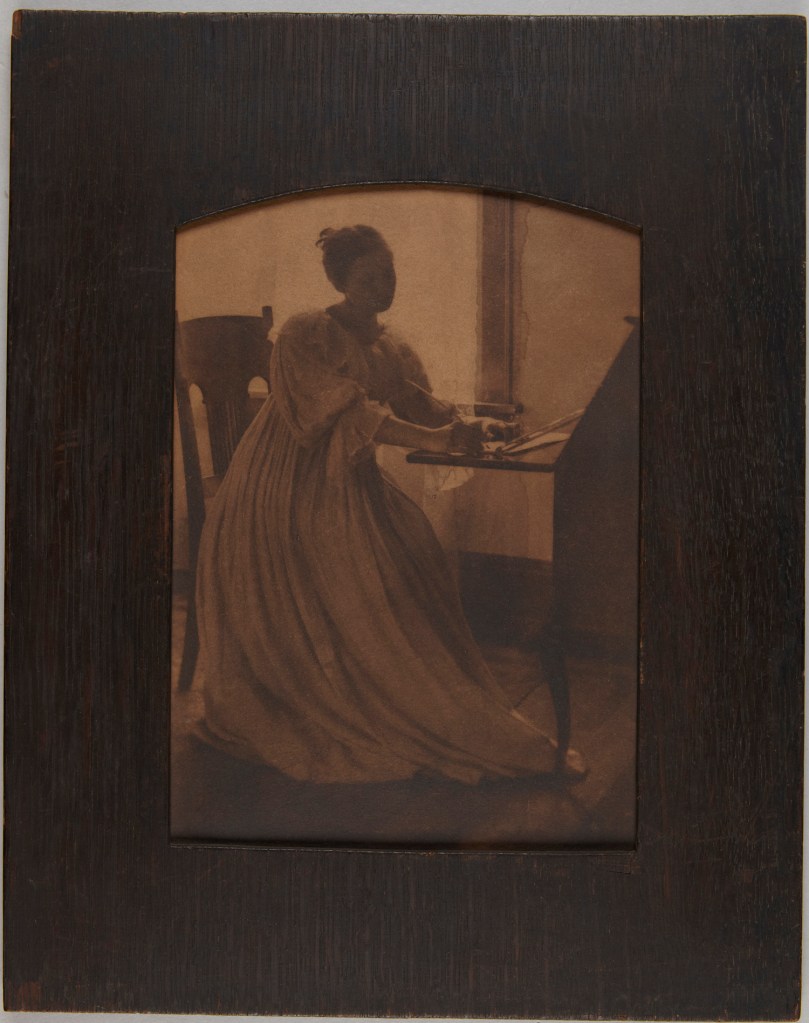

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Just a Line
1897
Platinum print in original frame
Image: 19.2 x 13.3cm (7 9/16 x 5 1/4 in.)
Frame: 28.8 x 22.9cm (11 5/16 x 9 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
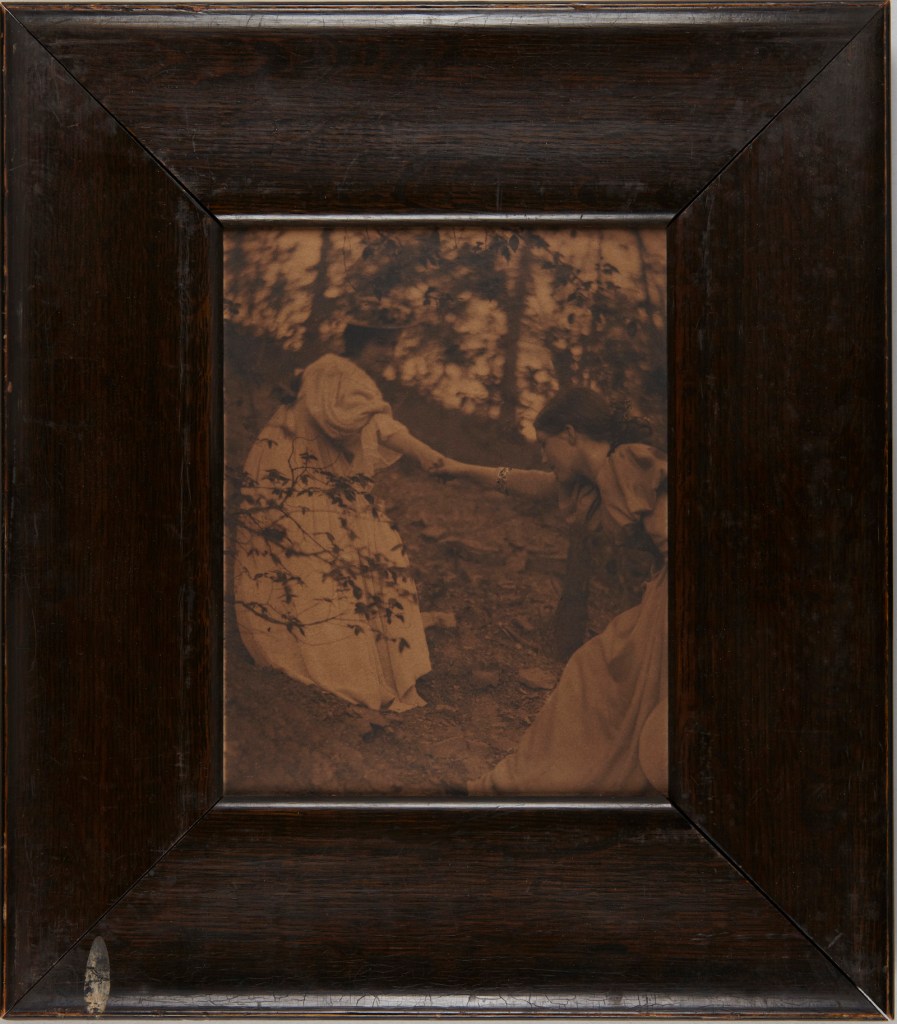

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Climbing the Hill
1897
Platinum print with gouache in original frame
Image: 20 x 16cm (7 7/8 x 6 5/16 in.)
Frame: 34.5 x 30.5cm (13 9/16 x 12 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
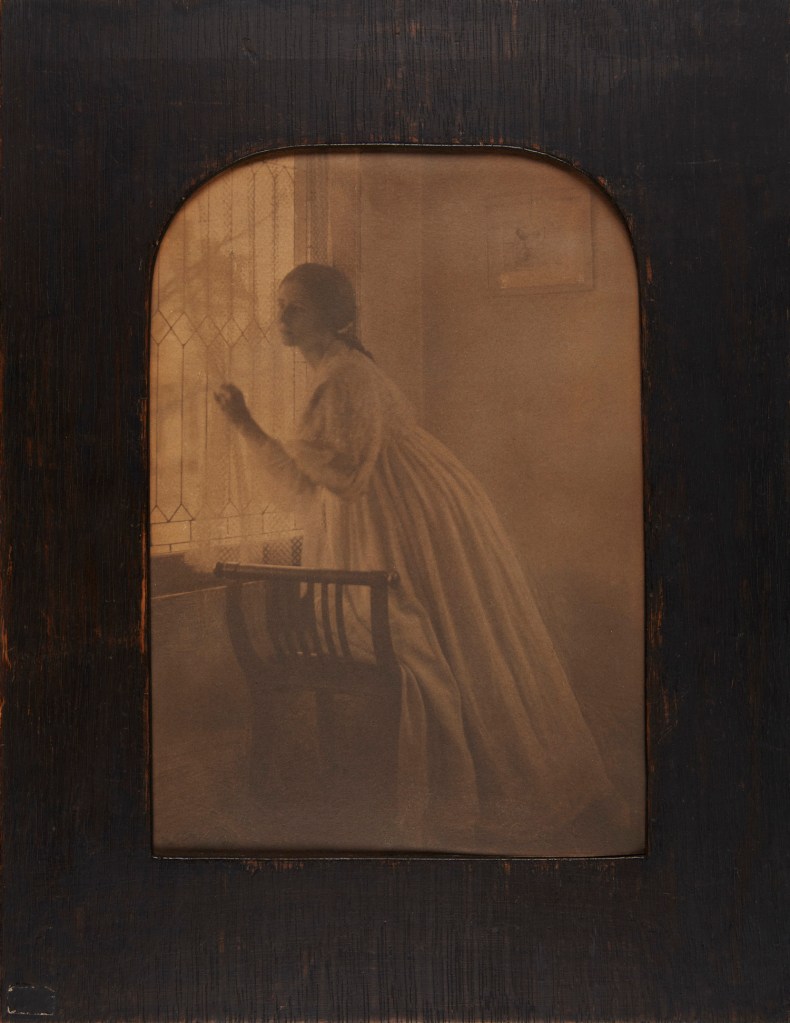

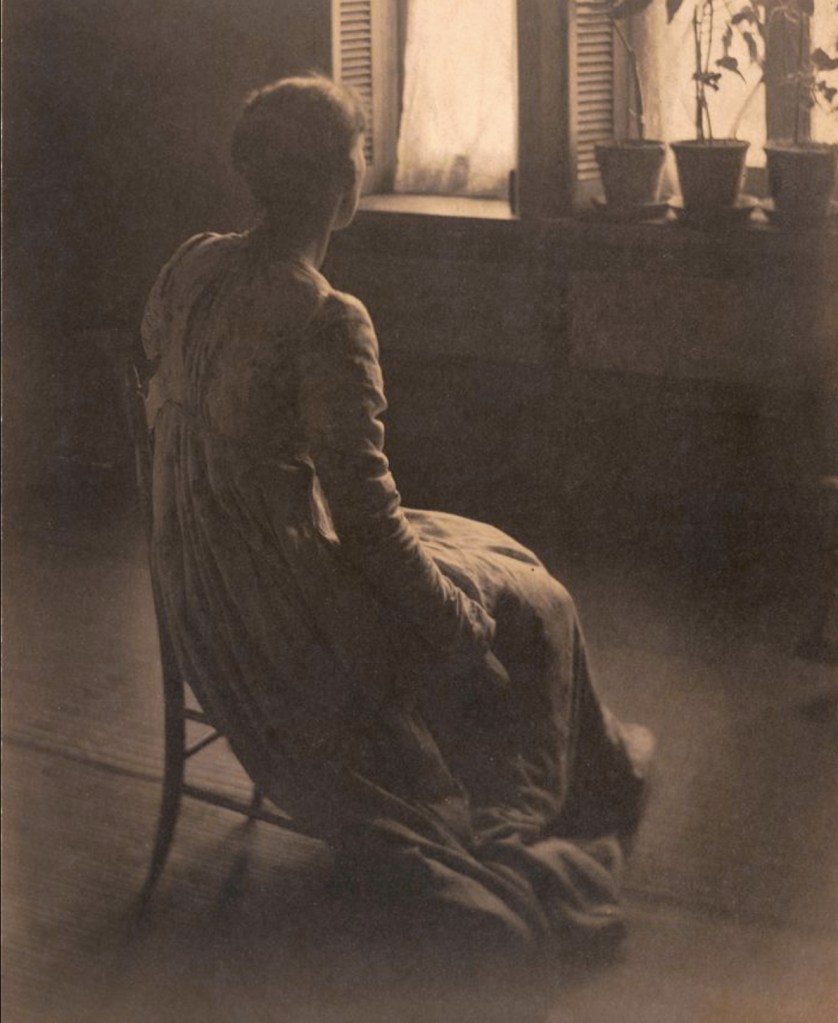
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
At the Window
1896, printed 1897
Platinum print in original frame
Image: 20.4 x 14.2cm (8 1/16 x 5 9/16 in.)
Frame: 29.8 x 22.9cm (11 3/4 x 9 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
“These photographs [above] are among the few Pictorialist works from the late 1890s that survive in their original exhibition frames.”
Wall text from the exhibition
Gertrude L. Brown (approximately 1870-1934)
Clarence H. White (seated center), Gertrude Käsebier (seated right), and students, Summer School of Photography, Five Islands, Maine
c. 1913
Clarence H. White School of Photography
“My photographs were less sharp than others and I do not think it was because of the lens so much as the conditions under which the photographs were made – never in the studio, always in the home or in the open, and when out of doors at a time of day very rarely selected for photography.”
Clarence H. White
“I think that if I were asked to name the most subtle and refined master photography has produced, that I would name him… To be a true artist in photography one must also be an artist in life, and Clarence H. White was such an artist.”
Alvin Langdon Coburn
“What he brought to photography was an extraordinary sense of light. ‘The Orchard’ is bathed in light. ‘The Edge of the Woods’ is a tour de force of the absence of light.”
Beaumont Newhall
“Clarence White’s poetic vision and sensitive intuition produced images that insinuate themselves deeply into one’s consciousness.”
Edward Steichen
“[White] celebrated elemental things, the time spent playing in the fields or woods, the simple pleasure of unhurried living, the playing of games in interior spaces… White, growing up within an extended family, knowing nothing else, had no real sense of other societies and his pictures thus had a kind of fortification against the outside. They were his private epic.”
“The qualities that make White’s photographs memorable have to do with both form and content. In his finest pictures the disposition of every element, of each line and shape, is elevated to an expressive intensity few photographers managed to attain. … White was able to transform the sensory perception of light into an exposition of the most fundamental aspect of photography – the literal materialisation of form through light itself. His prints, mostly in the platinum medium, display a richness, a subtlety, and a luminosity of tone rarely achieved in the history of photography.”
Peter Bunnell
Innovative American Photographer Clarence H. White Receives First Retrospective in a Generation
The vision and legacy of photographer Clarence H. White (1871-1925), a leader in the early twentieth-century effort to position photography as an art, will be the focus of a major traveling exhibition organised by the Princeton University Art Museum. The first retrospective devoted to the photographer in over a generation, Clarence H. White and His World: The Art and Craft of Photography, 1895-1925 will survey White’s career from his beginnings in 1895 in Ohio to his death in Mexico in 1925.
On view at the Princeton University Art Museum from October 7, 2017, through January 7, 2018, the exhibition will draw on the Clarence H. White Collection at the Museum and the deep holdings at the Library of Congress as well as loans from other public and private collections. Clarence H. White and His World reasserts White’s place in the American canon and, in the process, reshapes and expands our understanding of early twentieth-century American photography.
White’s career spans the radical shifts in photographic styles and status from the Kodak era of the 1890s; the corresponding fight for art photography primarily associated with his friend and fellow photographer Alfred Stieglitz; and the postwar rise of advertising and fashion photography. While living in a small town in Ohio, White received international recognition for his beautiful scenes of quiet domesticity and his sensitivity to harmonious, two-dimensional composition. With his move to New York in 1906, he became renowned as a teacher, first at Teachers College with Arthur Wesley Dow, then in the summer school he established in Maine, and finally with the Clarence H. White School of Photography, founded in 1914. Among his students were some of the most influential artistic and commercial photographers of the early twentieth century: Laura Gilpin, Doris Ulmann, Paul Outerbridge, Ralph Steiner, Margaret Watkins, Dorothea Lange, Karl Struss, Anton Bruehl and hundreds more who did not become professional photographers but were shaped by White’s belief that art could enrich the lives of everyday Americans.
“The goal of the exhibition is to locate White’s own diverse and rich body of work within a period of great social and aesthetic change, from the Gilded Age to the Roaring Twenties,” said Anne McCauley, exhibition curator and David Hunter McAlpin Professor of the History of Photography and Modern Art at Princeton. “Far from staying stuck in the nineteenth century, White embraced new media like cinema and new commercial uses for photography, including fashion and advertising.”
The exhibition will feature photographs by White’s fellow Photo-Secessionists and his students as well as a selection of paintings and prints by other artists whom he knew and admired, and was influenced by or whose work he shaped, including William Merritt Chase, Thomas Dewing, Max Weber, Edmund Tarbell and John Alexander.
Also explored within the exhibition are White’s links to the American Arts and Crafts movement, his embrace of socialism, his radically modern representations of childhood, and his complicated printing and framing processes. Of particular note is his lifelong investment in photographing the nude model, culminating in series that he made with Alfred Stieglitz in 1907 and with Paul Haviland in 1909, brought together here for the first time.
“As an artist and a teacher, White emerges as one of the essential American innovators of the early twentieth century, dedicated to the creation of beauty,” notes James Steward, Nancy A. Nasher – David J. Haemisegger, Class of 1976, Director. “Through significant new archival research and bringing together works not seen in one setting since the artist’s lifetime, this exhibition and publication aim to reaffirm White’s astonishing accomplishments.”
After premiering at the Princeton University Art Museum, the exhibition travels to the Davis Museum, Wellesley College (February 7-June 3, 2018), the Portland Museum of Art, Maine (June 30-September 16, 2018) and the Cleveland Museum of Art (October 21, 2018-January 21, 2019). The exhibition is accompanied by a sumptuous 400-page catalogue by Anne McCauley, published by the Princeton University Art Museum and distributed by Yale University Press, with contributions by Peter C. Bunnell, Verna Posever Curtis, Perrin Lathrop, Adrienne Lundgren, Barbara L. Michaels, Ying Sze Pek and Caitlin Ryan.
Press release from the Princeton University Art Museum
The Clarence H. White School of Photography
In 1910, to augment his courses in New York City and bring in extra income, White opened a summer school for photography. Named the Seguinland School of Photography, it was housed in a hotel, which was to be part of the new “Seguinland” resort on the mid-coast of Maine near Georgetown and Seguin Island. Pictorialist photographer F. Holland Day, who summered nearby, had earlier invited White and his family to the area for a respite from the city and the opportunity to explore creative photography outdoors. The fellowship between the two photographers and their families was an important factor in White’s decision to start the summer school. Students wore sailor suits, a practice begun by Day and his summer guests, and boarded at the Seguinland Hotel. Day regularly conducted critiques for White’s students, as on occasion did New York photographer Gertrude Käsebier. After 1912, the Pilot House adjacent to the hotel served as the school’s studio and darkroom. Among the students attracted to the idyllic coastal setting was the Pictorialist Anne W. Brigman from Northern California, who made the pilgrimage to Maine during an eight-month visit to the East Coast. White’s summer school in Maine lasted until 1915, when White relocated to northwestern Connecticut’s Berkshire Hills for summers. He reintroduced a summer school there, first in East Canaan, and then in Canaan that lasted until his death.
In the fall of 1914, the Clarence H. White School of Photography opened its doors at 230 E. 11th St. in New York City. This was the first of four locations for the school in the burgeoning art and publishing capital. White’s first instructor for art appreciation and design between 1914 and 1918 was avant-garde painter Max Weber, who often posed for the students. When Weber left, White hired one of his Columbia students, Charles J. Martin.
In 1917 the school occupied the “Washington Irving House” at 122 E. 17th St. at the corner of Irving Place near Union Square and Gramercy Park. Three years later, when that location was no longer available, the Clarence H. White Realty Corp. was formed in order to purchase a building for the school, and the White School resettled again, at 460 W. 144th St., where it remained until 1940. The uptown location provided a meeting place for White’s Columbia classes. From the 1920s on, photographer Edward Steichen was among those who served regularly as guest lecturers. White students paid $150 per semester, a fee that held constant until the school’s closing.
After Clarence White’s unexpected death in 1925, friends urged his widow to carry on despite the fact that his personality had been crucial to the advancement of the school. Though Jane Felix White was not a photographer herself, she took on the challenge and remained the school’s director until her retirement in 1940, when her youngest son, Clarence H. White Jr., took over. Jane and Clarence Jr. recruited more students, raising the enrolment to 106 by 1939. With greater numbers came significant changes: twice as many men as women (a reversal of the previous 2-to-1 ratio of women to men) and new classes. Art integrated with technique – the school’s previous hallmark – was no longer central to the curriculum. Nonetheless, the school continued to prosper, and its reputation surpassed other competitors, such as the New York Institute of Photography, a commercial school established in 1910, and the Studio School of Art Photography, which began in 1920 and continued a strict orientation toward the soft-focus, Pictorialist style. A poorly timed and costly move to larger, more centrally located quarters at 32 West 74th Street in 1940, however, soon helped bring about its closure. The mobilisation for World War II dealt the White School its final blow. After surviving for three decades, it closed its doors in 1942.
Vern Posever Curtis. “Photos from the Clarence H. White School,” on the Library of Congress website December 2001 [Online] Cited 03/01/2018
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Spring - A Triptych [Letitia Felix]' 1898 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Spring - A Triptych [Letitia Felix]' 1898](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-spring-web.jpg)
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Spring - A Triptych [Letitia Felix]' 1898 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Spring - A Triptych [Letitia Felix]' 1898](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-spring-a-triptych-1898-web.jpg?w=939)
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Spring - A Triptych [Letitia Felix]' 1898 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Spring - A Triptych [Letitia Felix]' 1898](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-spring-a-triptych-1898-b-web.jpg?w=866)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Spring – A Triptych (Letitia Felix)
1898
Gum bichromate prints with graphite
Image (1): 16.8 x 2.7cm (6 5/8 x 1 1/16 in.)
Image (2): 20.7 x 9.8cm (8 1/8 x 3 7/8 in.)
Image (3): 16.8 x 2.7cm (6 5/8 x 1 1/16 in.)
Frame: 34 x 28.5 x .5cm (13 3/8 x 11 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White

Arthur Wesley Dow (American, 1857-1922)
Spring Landscape
1892
Oil on canvas
University of Michigan Museum of Art
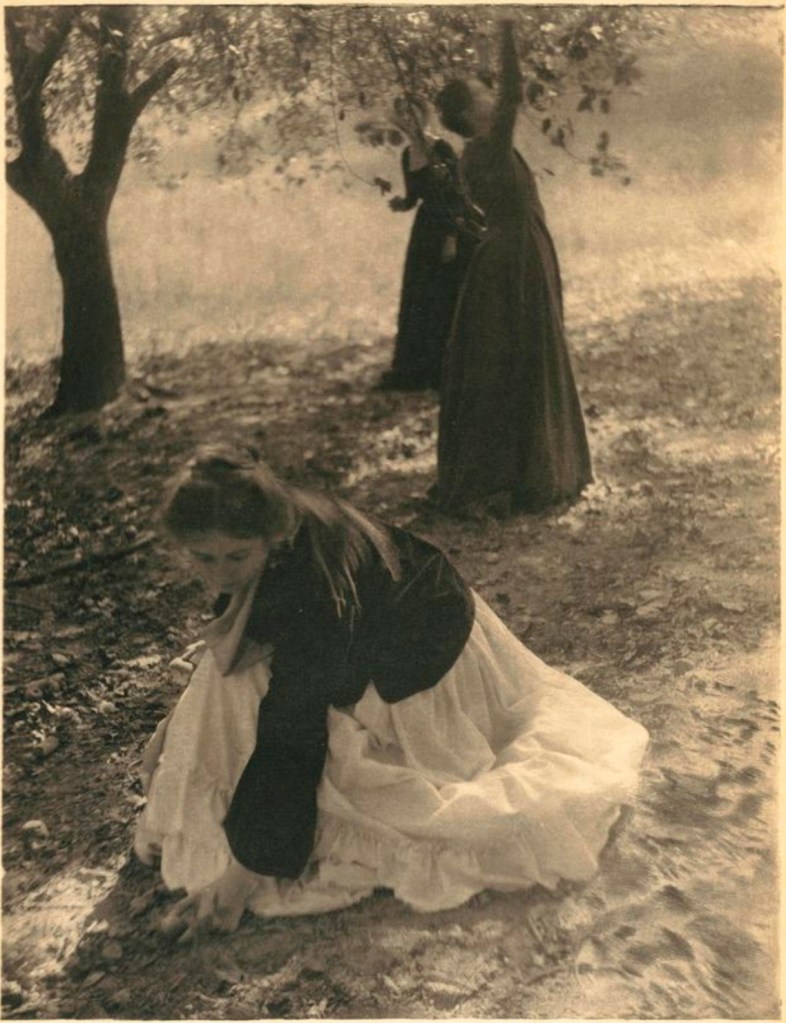

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Orchard
1902
Palladium print
24.3 x 19.1cm (9 9/16 x 7 1/2 in.)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
What shall I say?
1896, printed after 1917
Palladium print
Image: 14.8 × 17.3cm (5 13/16 × 6 13/16 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Girl with Mirror
1898
Varnished palladium print
George Eastman Museum, purchase

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Evening Interior
c. 1899
Platinum print
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Male academic nude]' c. 1900 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Male academic nude]' c. 1900](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-untitled-male-academic-nude-c-1900-web.jpg?w=663)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Untitled [Male academic nude]
c. 1900
Waxed platinum print
Image: 22.7 x 14.7cm (8 15/16 x 5 13/16 in.)
Frame: 51.4 × 41.3 × 3.2cm (20 1/4 × 16 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Ring Toss
1899
Palladium print
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Portrait of F. Holland Day with Male Nude]' 1902 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Portrait of F. Holland Day with Male Nude]' 1902](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-portrait-of-f-holland-day-with-male-nude-1902-platinum-print-web.jpg?w=796)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Untitled [Portrait of F. Holland Day with Male Nude]
1902
Platinum print
24.2 x 18.8cm (9 1/2 x 7 3/8 in.)
Gilman Collection, Purchase, Harriette and Noel Levine Gift, 2005
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [F. Holland Day lighting a cigarette]' 1902 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [F. Holland Day lighting a cigarette]' 1902](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-untitled-f-holland-day-lighting-a-cigarette-1902-web.jpg?w=809)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Untitled [F. Holland Day lighting a cigarette]
1902
Cyanotype
Image: 24.2 x 19.2cm (9 1/2 x 7 9/16 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'The Boy with His Wagon [1/3]' 1898 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'The Boy with His Wagon [1/3]' 1898](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-boy-web.jpg?w=891)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Boy with His Wagon [1/3]
1898
Platinum print
Sheet: 17.7 x 15.5cm (6 15/16 x 6 1/8 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
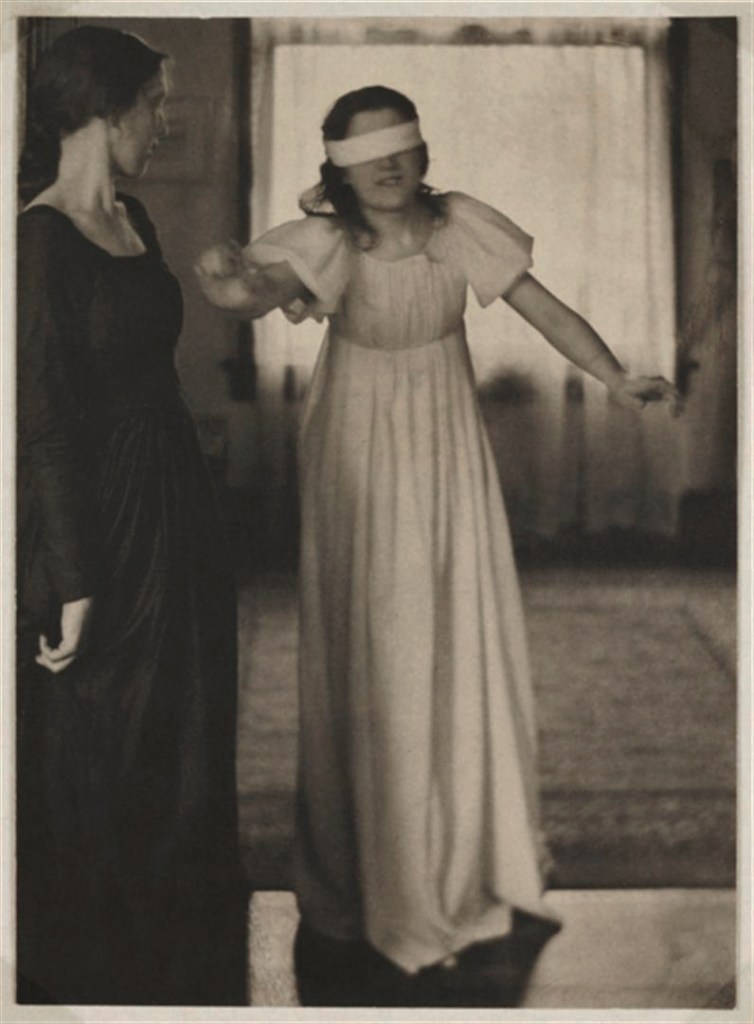

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
“Blindman’s Bluff”
1898
Platinum print
Library of Congress
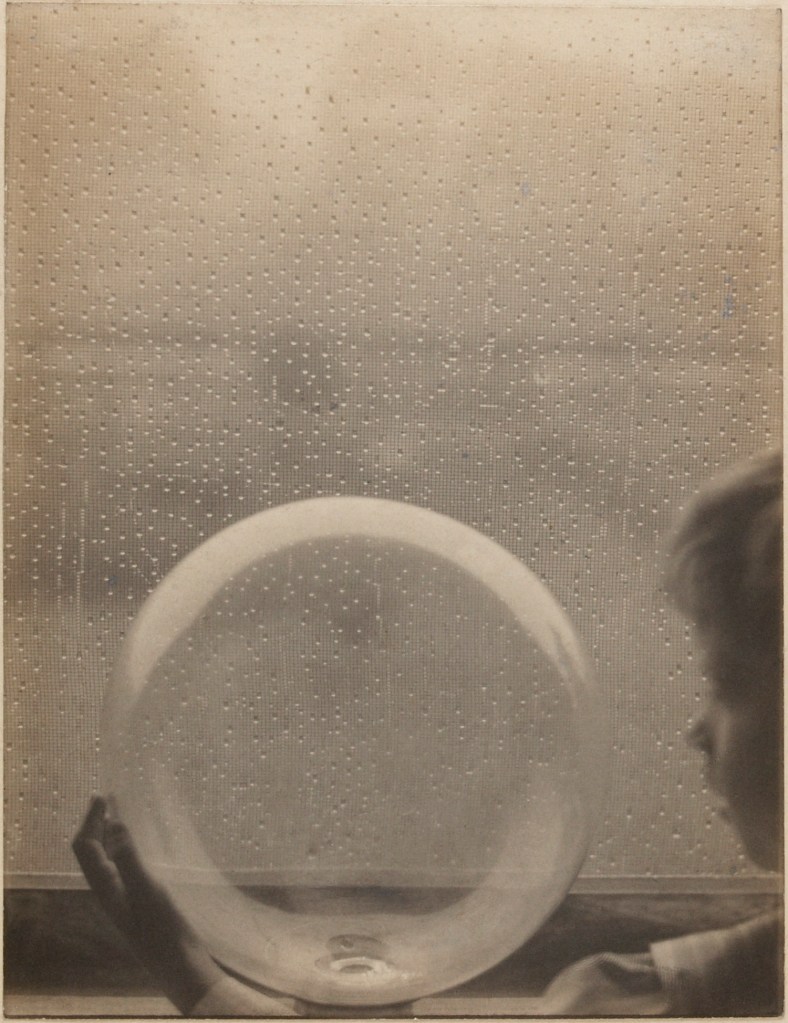

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Drops of Rain
1903
Platinum print
Image: 21.1 × 16.2cm (8 5/16 × 6 3/8 in.)
Frame: 51.4 × 41.3 × 3.2cm (20 1/4 × 16 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Winter Landscape
1903
Photogravure
Léon Dabo (American born France, 1868-1960)
Rondout, New York
c. 1907
Oil on canvas
68.6 x 91.4cm
Indianapolis Museum of Art, Gift of S. O. Buckner
© Estate of Léon Dabo
Leon Dabo (July 9, 1864 – November 7, 1960) was an American tonalist landscape artist best known for his paintings of New York, particularly the Hudson Valley. His paintings were known for their feeling of spaciousness, with large areas of the canvas that had little but land, sea, or clouds. During his peak, he was considered a master of his art, earning praise from such luminaries as John Spargo, Bliss Carman, Benjamin De Casseres, Edwin Markham, and Anatole Le Braz. His brother, Scott Dabo, was also a noted painter.
Text from the Wikipedia website
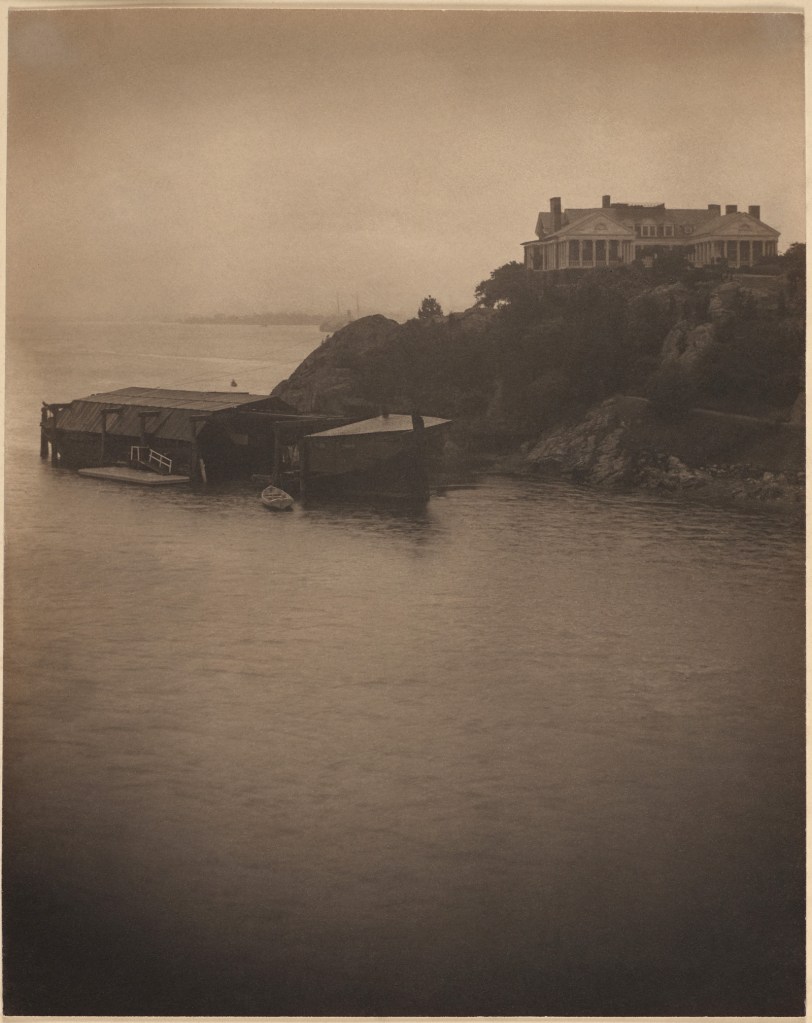

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Unpublished illustration [Beacon Rock with home of E. D. Morgan III] for Gouverneur Morris, “Newport the Maligned”
1907
Platinum print
Image: 23.9 x 19.2cm (9 7/16 x 7 9/16 in.)
Frame: 51.4 × 41.3 × 3.2cm (20 1/4 × 16 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
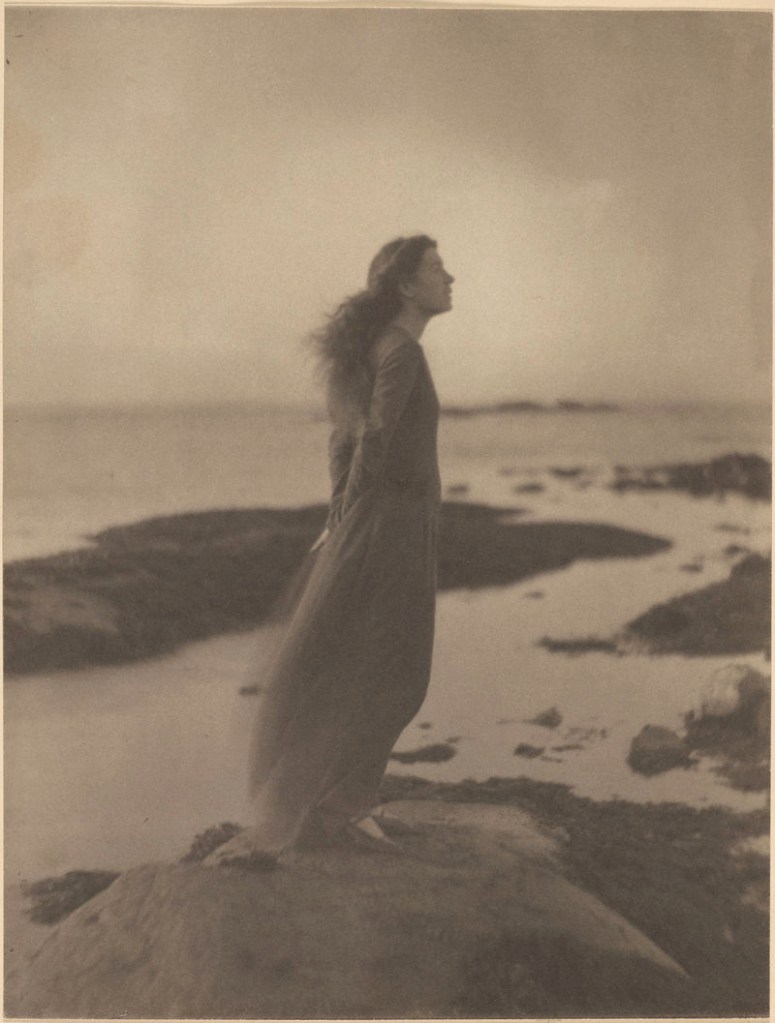

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Sea (Rose Pastor Stokes, Caritas Island, Connecticut)
1909
Platinum print
The Clarence H. White Collection, Princeton University Art Museum
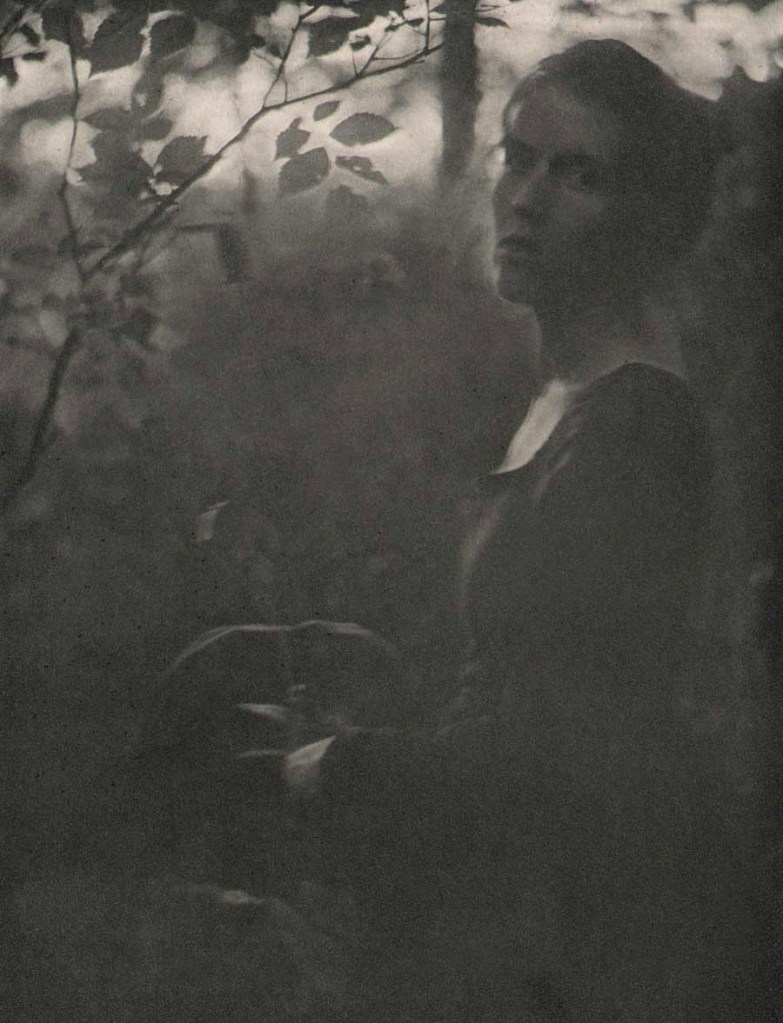
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
“At the Edge of the Woods – Evening” [Letitia Felix]
1901
Chine-collé photogravure
14.4 x 10.1cm
28.6 x 19.6cm uncut
Camera Notes, Vol. IV, April 1901
![Clarence H. White (1871-1925) 'Untitled [Jean Reynolds in Newark, Ohio]' c. 1905 Clarence H. White (1871-1925) 'Untitled [Jean Reynolds in Newark, Ohio]' c. 1905](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-untitled-jean-reynolds-in-newark-ohio-c-1905-web.jpg?w=817)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Untitled [Jean Reynolds in Newark, Ohio]
c. 1905
Gum bichromate print
Image: 24.1 x 19cm (9 1/2 x 7 1/2 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Mother was living in the old home alone
1902
Photogravure
From the book Eben Holden, John Andrew & Son (Boston) 1903
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Untitled [Interior of Weiant house, Newark, Ohio]
1904
Platinum print
Image: 15.6 x 19.6cm (6 1/8 x 7 11/16 in.)
Frame: 36.2 × 43.8 × 3.2cm (14 1/4 × 17 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
Gift of Edmund T. Weiant
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) and Paul Burty Haviland (French, 1880-1950) 'Untitled [Florence Peterson]' 1909, printed after 1917 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) and Paul Burty Haviland (French, 1880-1950) 'Untitled [Florence Peterson]' 1909, printed after 1917](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/white-haviland-untitled-florence-peterson-1909-printed-after-1917-web.jpg?w=820)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) and Paul Burty Haviland (French, 1880-1950)
Untitled [Florence Peterson]
1909, printed after 1917
Palladium print
Image: 25.6 x 19.6cm (10 1/16 x 7 11/16 in.)
Frame: 51.4 × 41.3 × 3.2cm (20 1/4 × 16 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
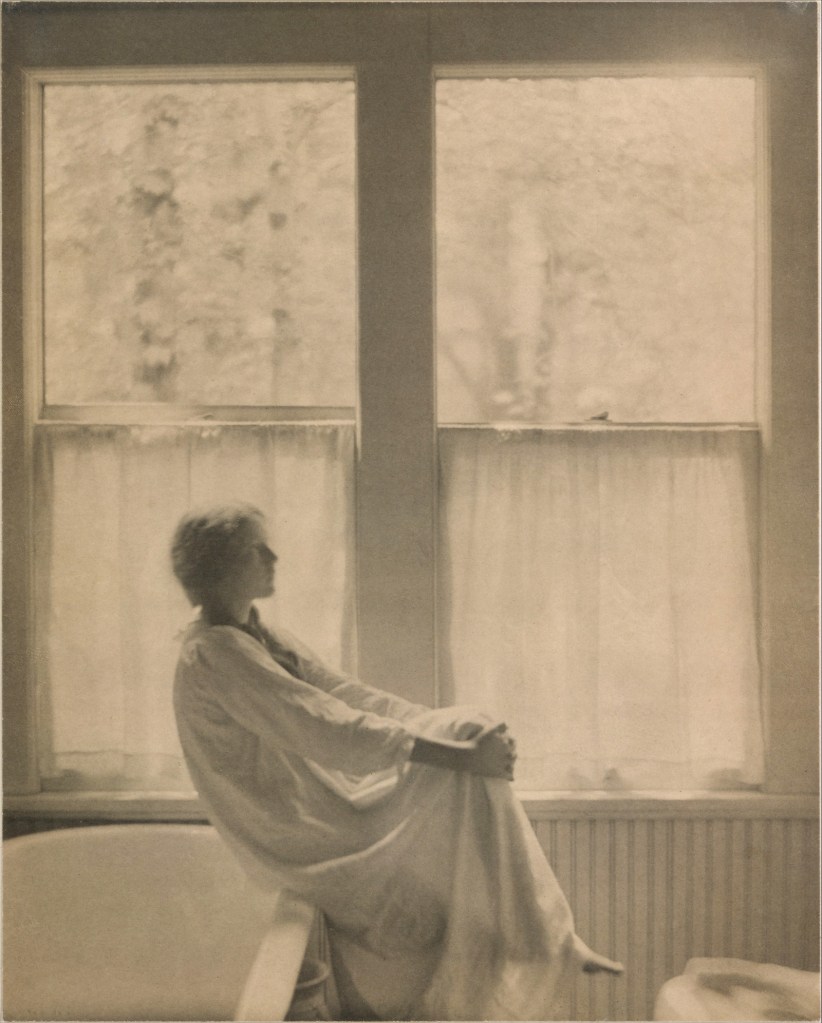

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Morning – The Bathroom
1906
Platinum print
22.3 x 18.0cm (8 3/4 x 7 1/16 in.)
Alfred Stieglitz Collection, 1933
The Metropolitan Museum of Art

Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) and Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
“Experiment 28”
1907
Vintage japanese tissue photogravure
20.6 x 15.9cm
30.2 x 21.1cm uncut
Published in Camera Work XXVII, 1909
In 1907, the year after Clarence White arrived in New York City, he collaborated with Photo-Secession founder Alfred Stieglitz on a series of portraits featuring two models. Shown here holding a glass globe, California model Mabel Cramer poses in a portrait later reproduced as a plate in Camera Work. Said to be a friend of the German American photographer Arnold Genthe and possessing a face worthy of Cleopatra, Cramer and a woman known only as a Miss Thompson, posed for a series of photographs intended to promote photography as an equivalent medium to painting. It was the only time Stieglitz would ever work in tandem with another photographer and shows the extent to which the photographers were allied aesthetically and technically.
![Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) and Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Miss Thompson]' 1907 Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) and Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Miss Thompson]' 1907](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/stieglitz-and-white-untitled-miss-thompson-1907-web.jpg?w=794)
Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) and Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Untitled [Miss Thompson]
1907
Platinum print
Image: 23.7 x 18.4cm (9 5/16 x 7 1/4 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
Also in 1910, Stieglitz led an effort to create a major exhibition of the Photo-Secession artists at what was then called the Albright Gallery in Buffalo, New York (now known as the Albright-Knox Art Gallery). While this effort was announced as a group activity of the Photo-Secession, Stieglitz refused to allow any others to have input or make decision about who would be included in the exhibition and how it would be displayed. Stieglitz, who was already known for his domineering ways and dogmatic approach to photography, took his self-assigned, unilateral authority even beyond his past actions; in this case he proved to have gone too far for several people who had been closely aligned with him. First Käsebier, then White and finally Steichen broke off their relationship with Stieglitz, each citing Stieglitz’s overbearing ego, his refusal to consider other’s viewpoints and his repeated actions on behalf of the Photo-Secession without consulting any of the so-called “members” of the group.
Stieglitz reacted to these claims and White’s departure in particular with his usual antagonistic manner. Within a short while, he delivered to White most of the negatives and prints he had jointly produced with White in 1907. The split between the two was so deep that Stieglitz wrote to White “One thing I do demand… is that my name not be mentioned by you in connection with either the prints or the negatives… Unfortunately I cannot wipe out the past…” …
Although White and Stieglitz had tried to reconcile their differences before White died, Stieglitz never forgave White for breaking from him in 1912. Upon hearing about White’s untimely death, Stieglitz wrote to Kuehn, “Poor White. Cares and vexation. When I last saw him he told me he was not able to cope with [life as well as he was] twenty years ago. I reminded him that I warned him to stay in business in Ohio – New York would be too much for him. But the Photo-Session beckoned. Vanity and ambitions. His photography went to the devil.” In spite of these words, Stieglitz had 49 of White’s photographs, including 18 created jointly with Stieglitz, in his personal collection when he died.
Text from the Wikipedia website
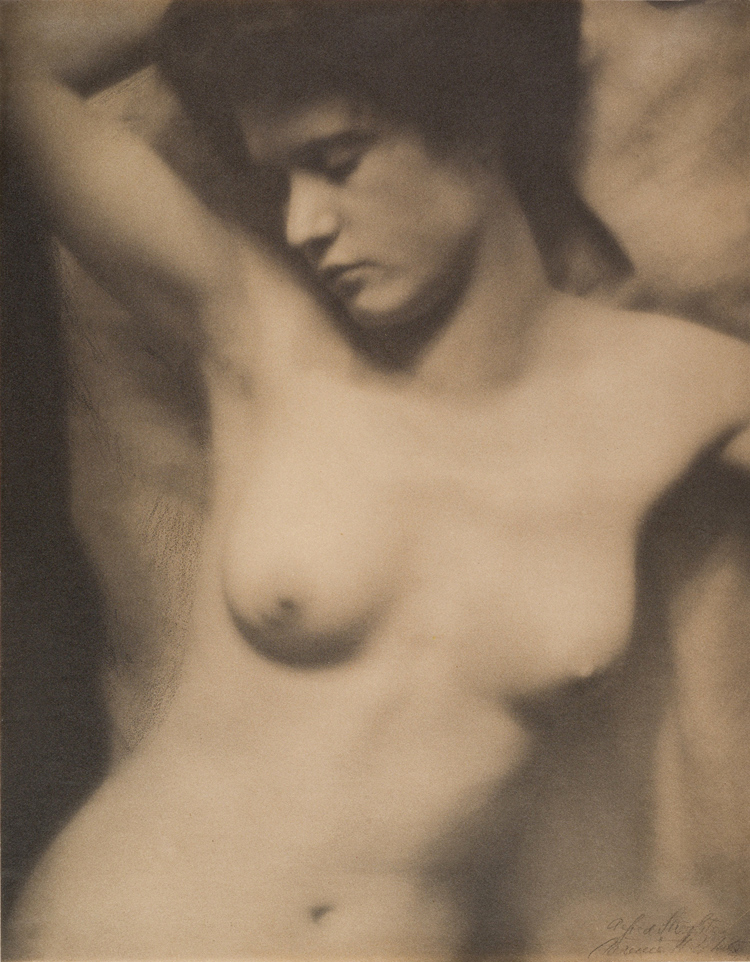

Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946) and Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Torso
1907
Platinum print
22.1 x 18.7cm (8 11/16 x 7 3/8 in.)
Alfred Stieglitz Collection, 1933
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
In 1907 White and Stieglitz collaborated on a series of nude studies in which they planned to experiment with various lenses and papers. Stieglitz placed the camera and choreographed the poses, much as he would later do in his extensive portrait of Georgia O’Keeffe, while White focused the camera and developed the negatives. These three photographs illustrate the range of the imagery and its progression from the most formal and demure image in which the draped Miss Thompson assumes a cool classical pose to the second image which is surprisingly intimate and unaffected. Combining the compositional strength and naturalism of the first two photographs, but exchanging props and interior surroundings for tight framing and expressive chiaroscuro, the third and most accomplished photograph is both modern and sensual.
Text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art website
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Florence Peterson]' c. 1909 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Florence Peterson]' c. 1909](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-untitled-florence-peterson-c-1909-web.jpg?w=754)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Untitled [Florence Peterson]
c. 1909
Platinum print
Image (arched top): 22.5 x 16.5cm (8 7/8 x 6 1/2 in.)
Frame: 51.4 × 41.3 × 3.2cm (20 1/4 × 16 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
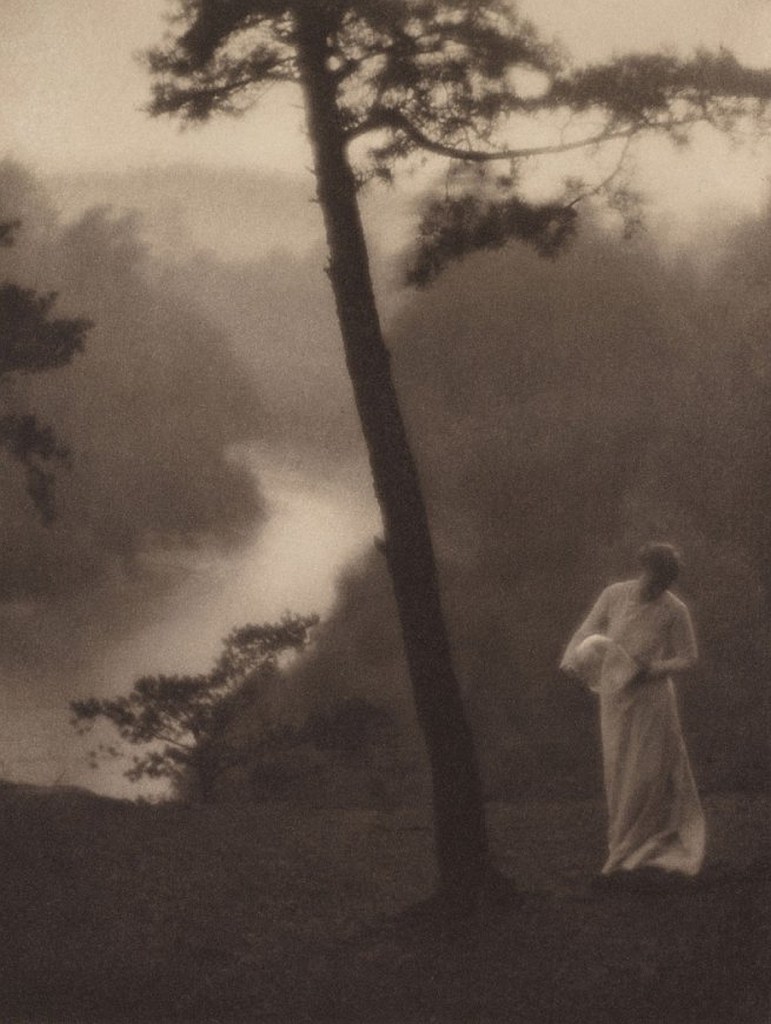

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Morning
1905
Platinum print
From Camera Work (No. 23, July 1908)
Morning perfectly embodies the tenets of Pictorialism: expressive, rather than narrative or documentary, content; craftsmanship in the execution of the print; and a carefully constructed composition allied to Impressionist and American Tonalist painting and to popular Japanese prints. His photographs from the period before he moved to New York in 1906 signalled a remove from the modern urban world. Neither genre scene nor narrative tableau, this photograph is a retreat into domesticised nature.
Text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art website
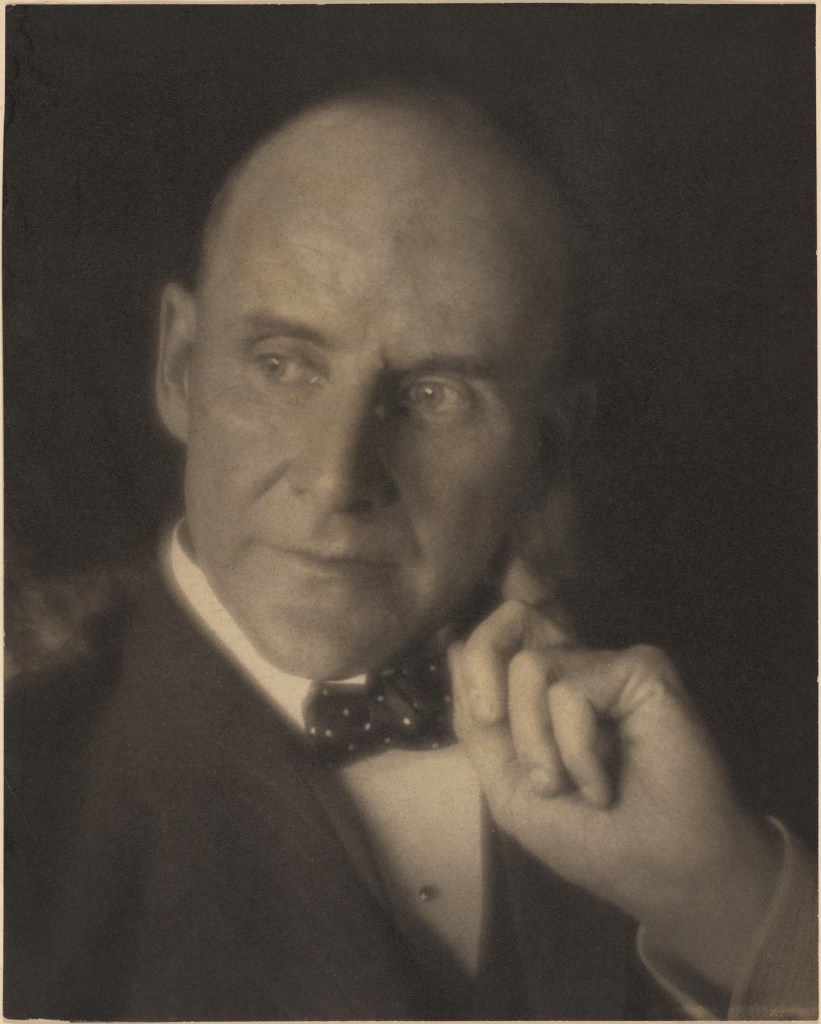

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Eugene Debs
c. 1906-1908
Platinum print
Image: 22.2 x 17.8cm (8 3/4 x 7 in.)
Frame: 51.4 × 41.3 × 3.2cm (20 1/4 × 16 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
Eugene Debs (American, 1855-1926)
Eugene Victor Debs (November 5, 1855 – October 20, 1926) was an American union leader, one of the founding members of the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW or the Wobblies), and five times the candidate of the Socialist Party of America for President of the United States. Through his presidential candidacies, as well as his work with labor movements, Debs eventually became one of the best-known socialists living in the United States. …
Debs ran as a Socialist candidate for President of the United States five times, including 1900 (earning 0.63% of the popular vote), 1904 (2.98%), 1908 (2.83%), 1912 (5.99%), and 1920 (3.41%), the last time from a prison cell. He was also a candidate for United States Congress from his native state Indiana in 1916.
Debs was noted for his oratory, and his speech denouncing American participation in World War I led to his second arrest in 1918. He was convicted under the Sedition Act of 1918 and sentenced to a term of 10 years. President Warren G. Harding commuted his sentence in December 1921. Debs died in 1926, not long after being admitted to a sanatorium due to cardiovascular problems that developed during his time in prison. He has since been cited as the inspiration for numerous politicians.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Alfred Stieglitz
1907
Cyanotype
Image: 24.2 x 19.2cm (9 1/2 x 7 9/16 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
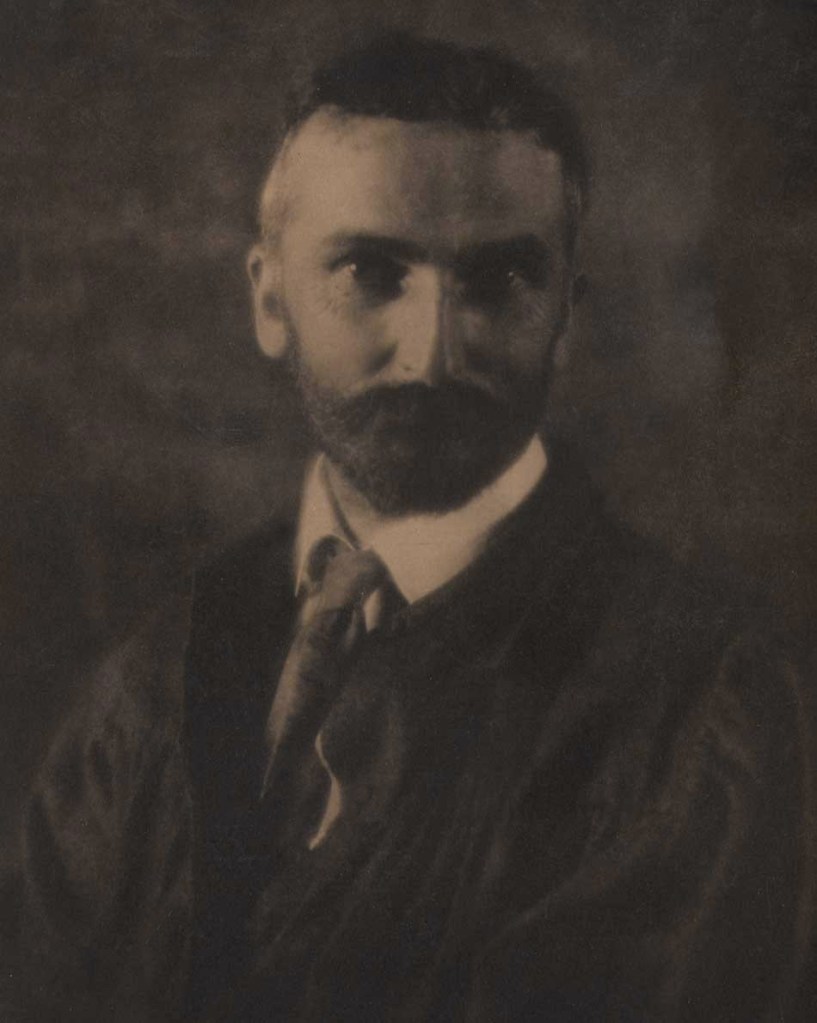

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Portrait of Arthur Wesley Dow
1908
Vintage waxed platinum print
22.1 x 16.6cm
“White was hired by Arthur Wesley Dow at Teachers College in 1907 and shared Dow’s philosophy that students of the fine and the applied arts should have the same fundamental training based on design principles (anticipating the approach of the Bauhaus in the 1920s).”
Arthur Wesley Dow (American, 1857-1922)
Arthur Wesley Dow (April 6, 1857 – December 13, 1922) was an American painter, printmaker, photographer and influential arts educator.
Dow taught at three major American arts training institutions over the course of his career beginning with the Pratt Institute from 1896-1903 and the New York Art Students League from 1898-1903; then, in 1900, he founded and served as the director of the Ipswich Summer School of Art in Ipswich, Massachusetts, and from 1904 to 1922, he was a professor of fine arts at Columbia University Teachers College.
His ideas were quite revolutionary for the period; he taught that rather than copying nature, art should be created by elements of the composition, like line, mass and colour. He wanted leaders of the public to see art is a living force in everyday life for all, not a sort of traditional ornament for the few. Dow suggested this lack of interest would improve if the way art was presented would permit self-expression and include personal experience in creating art.
Text from the Wikipedia website
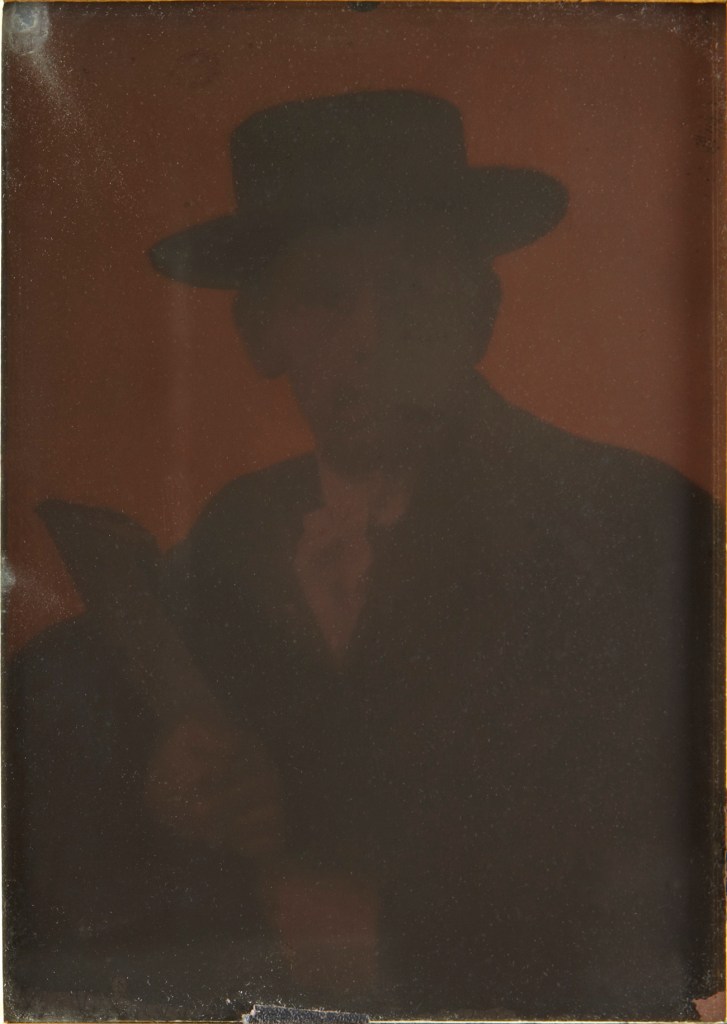

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Clarence H. White
c. 1908-1910
Autochrome
17.5 x 12.5cm
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
In the decade after the invention of the Kodak point-and-shoot camera in 1888, thousands of men and women began taking their own amateur photographs. Some of them, generally from educated backgrounds and interested in the fine arts, aspired to make aesthetically pleasing images that rivalled paintings and prints in their compositions and tonal effects. These serious photographers, favouring large-format view cameras on tripods, called themselves pictorialists, which merely meant that they were concerned with making artistic “picture” rather than documents.
One of the most successful and influential of these self-taught amateurs was Clarence H. White (1871-1925), who rose from modest origins in Newark, Ohio, to become an internationally known art photographer and teacher. Clarence H. White and His World: The Art and Craft of Photography, 1895-1925 celebrates the short-lived career of this dedicated visionary, which spans the turbulent era from the Gilded Age through the 1913 Armory Show to the Roaring Twenties.
Drawing primarily on the vast collection of prints and archival material acquired by former curator Peter C. Bunnell for the Princeton University Art Museum and from the Library of Congress’s White Family Collection, the exhibition also includes photographs by White’s friends – such as Alvin Langdon Coburn, F. Holland Day, and Gertrude Käsebier – and works by a sampling of the hundreds of students who White trained at Columbia Teachers College, the Brooklyn Institute of Arts and Sciences, and the schools he founded in New York, Maine, and Connecticut. Complementing more than 140 rare photographic prints, illustrated books, and albums are paintings and drawings by John White Alexander, Léon Dabo, Thomas Wilmer Dewing, Arthur Wesley Dow, Alice Barber Stephens, Edmund Charles Tarbell, Max Weber, and Marius de Zayas that illuminate the artistic milieu in which White’s style evolved.
White’s early career centers on his Midwestern hometown, where he took up the camera in 1894. Squeezing photographic sittings into the spare time he had from his job as a bookkeeper for a wholesale grocer, he dressed his wife, her sisters, and his friends in costumes evocative of the colonial or antebellum era and posed them in penumbral interiors or the twilit hills outside Newark. White’s knack for setting up tableaux that were at once naturalistic and yet formally striking won him prizes in regional exhibitions, followed by his acceptance in 1898 in the exclusive group show of art photographs held at the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts. His meeting there with Alfred Stieglitz, F. Holland Day, Gertrude Käsebier, and others led to his participation in international exhibitions and his eventual inclusion as a founding member of the group that Stieglitz in 1902 dubbed the “Photo-Secession.” White stood out from his contemporaries for his assimilation of the radical cropping and flattened planes of Japanese prints, his melancholy, introspective women, and his frank, unromanticised portrayals of children.
White’s decision in 1904 to become a full-time photographer and his move in 1906 to New York transformed his life and his subjects. While in Newark, he had already earned extra income from commercial jobs illustrating fiction, primarily stories set in frontier America, such as the bestselling novel by Irving Bacheller, Eben Holden: A Tale of the North Country. A section of the exhibition reveals the extent to which White, like many Photo-Secessionists, sold portraits, landscapes, and narrative illustrations to magazines – a practice that has received little attention as a result of Alfred Stieglitz’s renowned dismissal of commercial photography.
Another discovery explored in the exhibition is the importance of socialism for White’s aesthetic vision. White’s selection of handmade printing techniques – such as gum prints in which a pigmented gum emulsion is hand applied to drawing paper – and his transformation of each platinum print (made in contact with a negative) into a unique object are indebted to the ideals of William Morris and the Arts and Crafts movement, which valued hand labor over standardised machine production. White’s deep friendship with the family of Stephen M. Reynolds, Eugene Debs’s campaign manager and a leading Indiana socialist, resulted in idealised portraits of a family that embraced the simple life, racial and social equality, and the philosophy that every object in the home should be harmonious. White also went on to celebrate Rose Pastor Stokes and her husband, Graham Stokes, a socialist power couple in the years prior to the American entry into World War I.
Consistent with many socialists’ embrace of Morris and Walt Whitman, White also accepted the undressed human form as natural and free of sin. Throughout his career he made photographs of nude figures, primarily his sons outdoors and young women posed in the studio or in secluded glens. Drawing upon his greater experience with indoor lighting, White joined with Stieglitz in 1907 for a series of soft-focus studies of female models. A sampling of these prints is reunited here for the first time since 1912, when Stieglitz split with White and disavowed this collaborative venture.
The latter part of the exhibition is devoted to White’s innovations as a teacher, which form a major part of his legacy. White was hired by Arthur Wesley Dow at Teachers College in 1907 and shared Dow’s philosophy that students of the fine and the applied arts should have the same fundamental training based on design principles (anticipating the approach of the Bauhaus in the 1920s). At a time when the few American schools that existed to teach photography focused solely on processes and technique, White assigned more open-ended compositional and exposure problems followed by group critiques. Later, at the Clarence H. White School that he founded in New York in 1914, he hired a series of artists (starting with Max Weber) to teach art history and composition. White’s students – represented here by Anton Bruehl, Laura Gilpin, Paul Burty Haviland, Paul Outerbridge, Karl Struss, Doris Ulmann, and Margaret Watkins, among others – mastered abstract principles of framing, cropping, and lighting that prepared them for a wide array of professional careers, including the growing arenas of advertising and fashion photography.
White’s late works include portraits of famous, but now forgotten, actresses and silent film stars, such as Alla Nazimova and Mae Murray, as well as the painter Abbott Thayer and the art director for Condé Nast, Heyworth Campbell. White also tried his hand at fashion photography and welcomed filmmaking into the White School in the months before he led a summer class to Mexico City, where he tragically succumbed to a heart attack at the age of fifty-four.
Far from rejecting modern styles, White accommodated them in his school, although he maintained his preference for matte printing papers and a degree of soft focus for his personal salon prints. What unites his career, and allows his work to speak to us today, is his belief in the transformative power of art and the potential of every individual to craft objects of lasting beauty.
Anne McCauley
David Hunter McAlpin Professor of the History of Photography and Modern Art
Margaret Watkins (Canadian, 1884-1969)
Untitled [Kitchen still life]
c. 1919-1920
Gelatin silver print
16 x 18.7cm
Los Angeles County Museum of Art, The Marjorie and Leonard Vernon Collection, gift of the Annenberg Foundation, acquired from Carol Vernon and Robert Turbin
© The Estate of Margaret Watkins, courtesy of Robert Mann Gallery, New York
Digital image © Museum Associates / LACMA
Margaret Watkins (Canadian, 1884-1969)
Margaret Watkins (1884-1969) was a Canadian photographer who is remembered for her innovative contributions to advertising photography. She lived a life of rebellion, rejection of tradition, and individual heroism; she never married, she was a successful career woman in a time when women stayed at home, and she exhibited eroticism and feminism in her art and writing. …
Watkins opened a studio in Greenwich Village, New York City, and in 1920 became editor of the annual publication Pictorial Photography in America. She worked successfully as an advertising photographer for Macy’s and the J. Walter Thompson Company and Fairfax, becoming one of the first women photographers to contribute to advertising agencies. She also produced landscapes, portraits, nudes and still lifes. While teaching at the Clarence White school from 1916 to 1928, her students included Margaret Bourke-White, Laura Gilpin, Paul Outerbridge, Ralph Steiner and Doris Ulmann.
One of the earliest art photographers in advertising, her images of everyday objects set new standards of acceptability. From 1928, when she was based in Glasgow, she embarked on street photography in Russia, Germany and France, specialising in store fronts and displays. Watkins died in Glasgow, Scotland in 1969, largely forgotten as a photographer.
Watkins legacy exists in her exemplary work left behind, but also her example as a single, successful woman. According to Queen’s Quarterly, her life is an inspiration for single women, who are fulfilled by their careers, rather than the traditional gender roles women face of fulfilment through marrying and having children.
Before she died, Watkins handed over a sealed box of all her work to her neighbour and executor of her will, Joseph Mulholland. She gave him strict instructions to not open it until after she died. As a result, several solo exhibitions were subsequently held in Britain and North America. When she died in November 1969, she left most of her estate to music charities.
In October 2012, a retrospective exhibition of Margaret Watkins’ work titled “Domestic Symphonies” opened at the National Gallery of Canada. This exhibition showcased 95 of her photographs dating from 1914-1939. Of these photos were portraits and landscapes, modern still life, street scenes, advertising work, and commercial designs. Music was a vital inspiration for Watkins, and that can be seen just from the title of this exhibition.
Text from the Wikipedia website
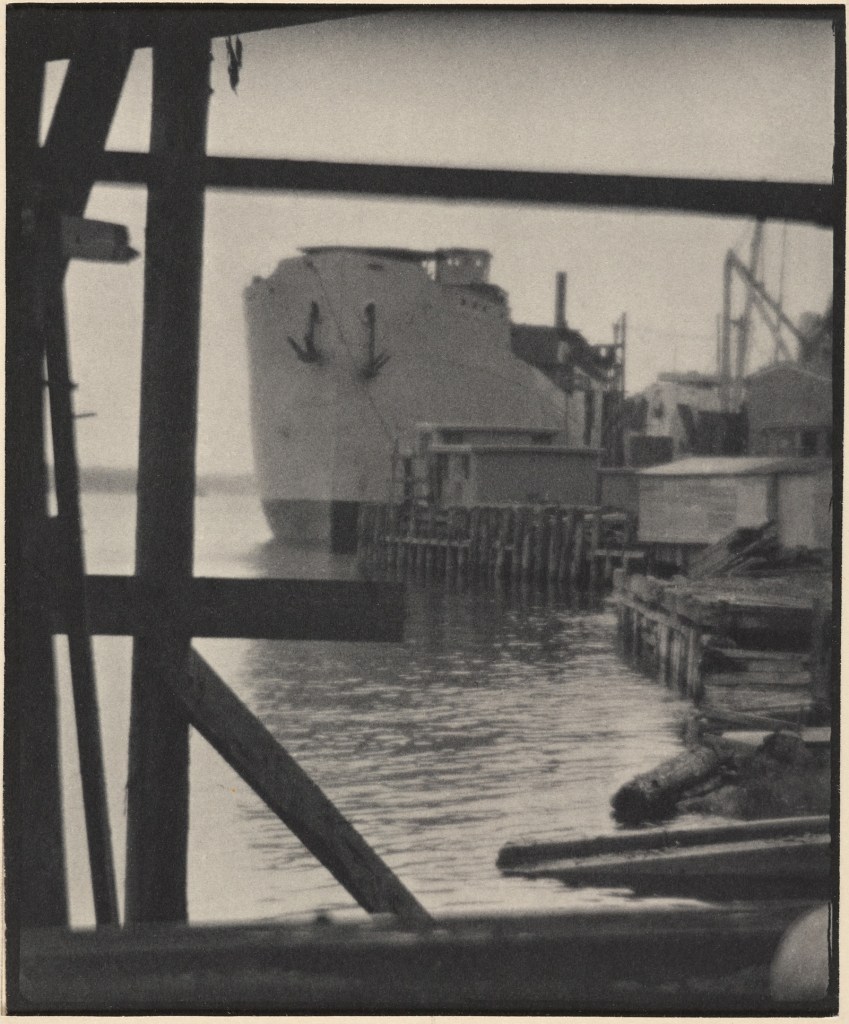

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Shipbuilding, Bath, Maine
1917
Hand-applied platinum print
Image: 12.1 x 9.8cm (4 3/4 x 3 7/8 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Dome of the Church of Our Lady of Carmen, San Ángel, Mexico]' 1925 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Dome of the Church of Our Lady of Carmen, San Ángel, Mexico]' 1925](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-dome-of-the-church-of-our-lady-of-carmen-1925-web.jpg?w=803)
Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Printed by Clarence H. White Jr., American, 1907-1978
Untitled [Dome of the Church of Our Lady of Carmen, San Ángel, Mexico]
1925
Palladium print by Clarence H. White Jr.
Image: 21.9 x 17.1cm (8 5/8 x 6 3/4 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Mae Murray
c. 1919-20
Platinum print with graphite
Image: 24.3 x 14.8cm (9 9/16 x 5 13/16 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
Mae Murray (May 10, 1885 – March 23, 1965) was an American actress, dancer, film producer, and screenwriter. Murray rose to fame during the silent film era and was known as “The Girl with the Bee-Stung Lips” and “The Gardenia of the Screen”.

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Alla Nazimova
1919
Photogravure
Library of Congress
All Nazimova (Russian, 1879-1945)
Alla Nazimova (Russian: Алла Назимова; born Marem-Ides Leventon; June 3 [O.S. May 22], 1879 – July 13, 1945) was a Russian actress who immigrated to the United States in 1905. On Broadway, she was noted for her work in the classic plays of Ibsen, Chekhov and Turgenev. Her efforts at silent film production were less successful, but a few sound-film performances survive as a record of her art. Nazimova openly conducted relationships with women, and her mansion on Hollywood’s Sunset Boulevard was believed to be the scene of outlandish parties. She is credited with having originated the phrase “sewing circle” as a discreet code for lesbian or bisexual actresses.
Text from the Wikipedia website
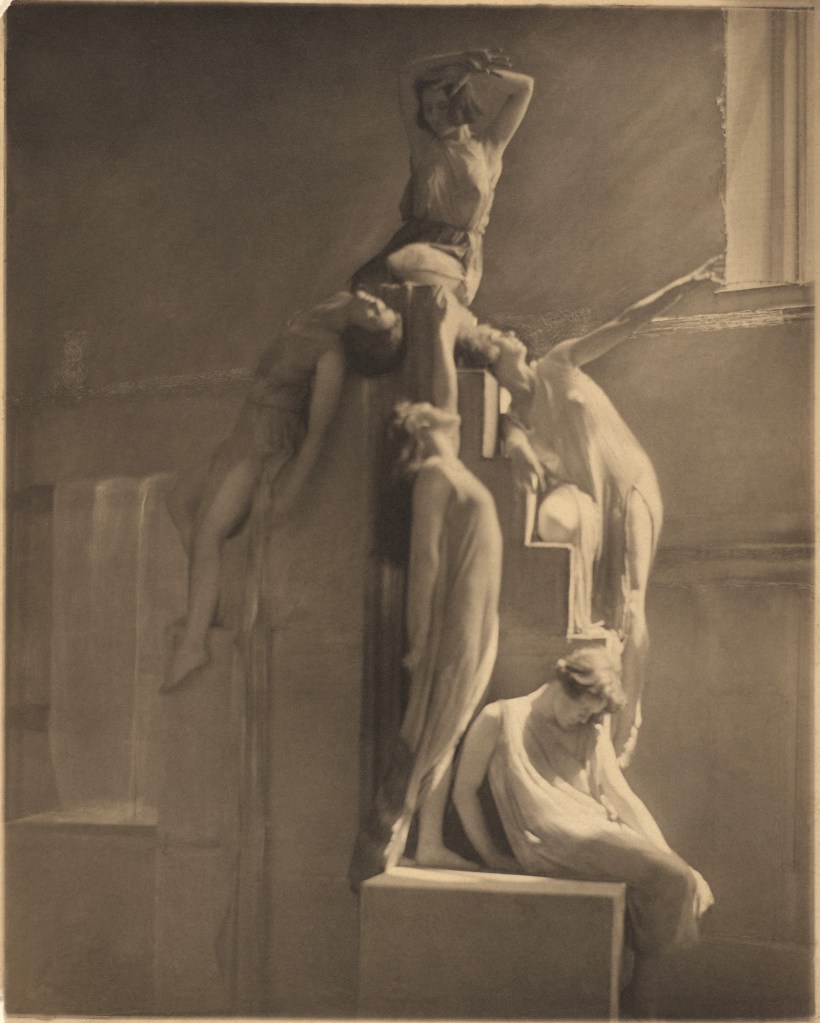

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
The Dancers – Barnard Greek Games
1922
Palladium print
Image: 24.5 x 19.6cm (9 5/8 x 7 11/16 in.)
Frame: 43.8 × 36.2 × 3.2cm (17 1/4 × 14 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White
The Barnard Greek Games were a tradition at Barnard College pitting the freshman and sophomore classes against one another in a series of competitions. They began in 1903 when the Class of 1905 challenged the Class of 1906 to an informal athletic contest. In later years upperclass students would cheer on their juniors, “odds” cheering for “odds” and “evens” for “evens.” Signature events included a chariot race, with chariots pulled by teams of 4 students, and a torch race. The torch race is captured in the “Spirit of the Greek Games” statue outside Barnard Hall that was given by the Class of 1905 as a gift on the 25th anniversary of the games in 1928. The games, a central part of Barnard campus life, were held annually until 1968, when upheaval on campus caused their cancellation, snuffing out this tradition along with such longstanding features of campus life as the Varsity Show.
After a 22 year absence, the Games were revived in 1989 as part of Barnard’s Centennial celebrations. The games were revived again in 2000, and have been held sporadically since.
Text from the Wikicu website
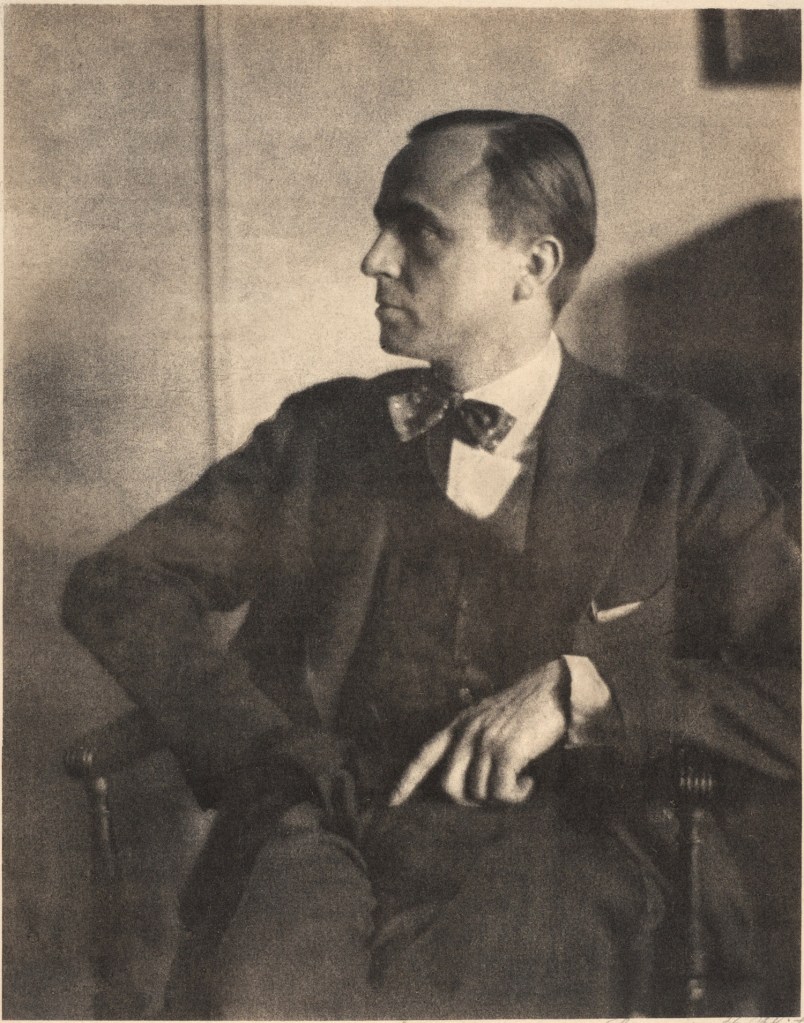

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Heyworth Campbell
c. 1921
Hand-applied platinum print
Image: 24 x 18.9cm (9 7/16 x 7 7/16 in.)
Frame: 51.4 × 41.3 × 3.2cm (20 1/4 × 16 1/4 × 1 1/4 in.)
The Clarence H. White Collection, assembled and organised by Professor Clarence H. White Jr., and given in memory of Lewis F. White, Dr. Maynard P. White Sr., and Clarence H. White Jr., the sons of Clarence H. White Sr. and Jane Felix White

Gertrude Käsebier (1852 – 1934)
Portrait of Clarence H. White
c. 1910
Silver gelatin print
Library of Congress
Note: Digital clean and print balance by Dr Marcus Bunyan
Princeton University Art Museum
McCormick Hall, Princeton, NJ
Phone: (609) 258-3788
The main Museum building is closed for construction of our new Museum, designed by architect Sir David Adjaye and anticipated to open in late 2024.








![Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Interior of Weiant house, Newark, Ohio]' 1904 Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925) 'Untitled [Interior of Weiant house, Newark, Ohio]' 1904](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/clarence-h-white-untitled-interior-of-weiant-house-newark-ohio-1904-web.jpg)
![Margaret Watkins (Canadian, 1884-1969) 'Untitled [Kitchen still life]' c. 1919-1920 Margaret Watkins (Canadian, 1884-1969) 'Untitled [Kitchen still life]' c. 1919-1920](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/margaret-watkins-untitled-kitchen-still-life-c-1919-20-web.jpg)








![Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal ceremony]' c. 1892 Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal ceremony]' c. 1892](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/a-collection-of-five-photographs-nicholas-caire-and-unknown-photographers-king-billy-maloga-aboriginal-native-group-aboriginals-lake-tyers-aborignal-ceremony-d-web.jpg)


![J. W. Lindt. 'Untitled [Two men in rural Victoria]' c. 1880s J. W. Lindt. 'Untitled [Two men in rural Victoria]' c. 1880s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/a-collection-of-18-photographs-depicting-rural-scenes-in-victoria-circa-1880s-men-web.jpg?w=730)

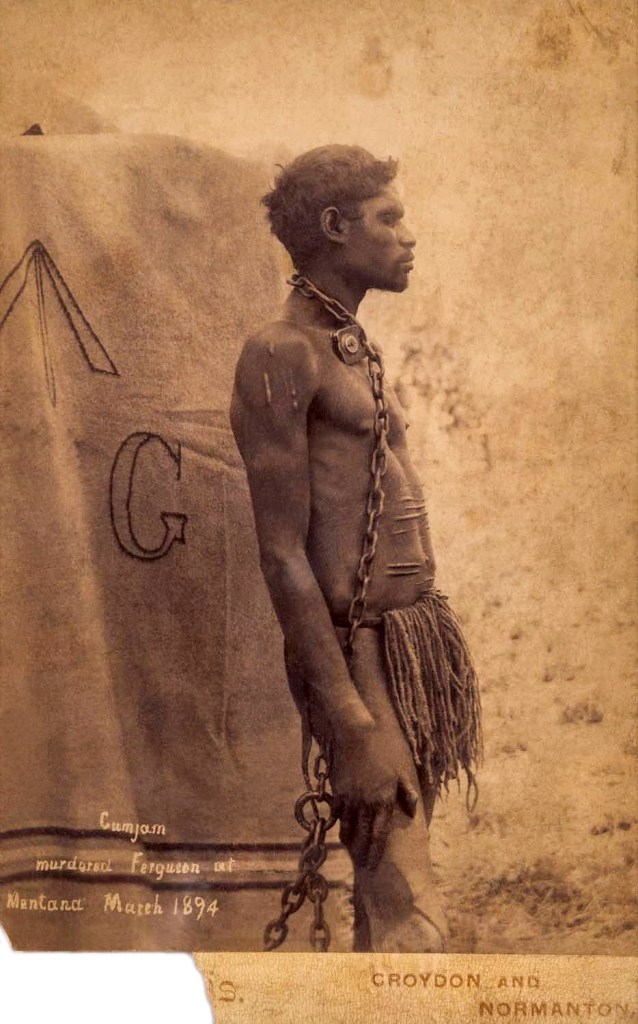
![Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Australian Aborigines in chains]' Nd Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Australian Aborigines in chains]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/australian-aborigines-c-web.jpg)


![Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal man smoking a pipe]' Nd Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal man smoking a pipe]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/artist-unknown-aboriginal-man-smoking-a-pipe-web.jpg?w=627)
![Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal making fire]' Nd Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal making fire]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/anonymous-photographer-aboriginal-making-fire-nd-web.jpg?w=637)
![Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal with spear]' Nd Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal with spear]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/anonymous-photographer-aboriginal-with-spear-nd-web.jpg?w=699)

![Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal with scars]' Nd Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal with scars]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/anonymous-photographer-aboriginal-with-scars-nd-web.jpg?w=752)

![Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal group]' Nd Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal group]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/anonymous-photographer-aboriginal-group-nd-web.jpg)
![Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal family group]' Nd Anonymous photographer. 'Untitled [Aboriginal family group]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/anonymous-photographer-aboriginal-family-group-nd-web.jpg?w=781)


![Hermann and Marianne Aubel (authors) Karl Robert Langewiesche (publisher) 'Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time]' 1928 Hermann and Marianne Aubel (authors) Karl Robert Langewiesche (publisher) 'Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time]' 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/book-cover-web.jpg?w=757)
![Elvira (Munich) 'Isadora Duncan' from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 1 Published 1928 Elvira (Munich) 'Isadora Duncan' from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 1 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/isadora-duncan-p1-web11.jpg?w=680)
![Rudolf Jobst (Austrian, 1872-1952) 'Schwestern Wiesenthal [Wiesenthal sisters]' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 4 Published 1928 Rudolf Jobst (Austrian, 1872-1952) 'Schwestern Wiesenthal [Wiesenthal sisters]' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 4 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/schwestern-wiesenthal-p4-web2.jpg?w=1024)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Schwestern Wiesenthal [Wiesenthal sisters]' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 5 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Schwestern Wiesenthal [Wiesenthal sisters]' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 5 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/schwestern-wiesenthal-p5-web2.jpg?w=1024)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Grete Wiesenthal' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 6 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Grete Wiesenthal' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 6 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/grete-wiesenthal-p6-web2.jpg?w=712)
![Rudolf Jobst (Vienna) 'Else Wiesenthal' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 7 Published 1928 Rudolf Jobst (Vienna) 'Else Wiesenthal' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 7 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/else-wiesenthal-p7-web2.jpg?w=739)
![Hanns Holdt (German, 1887-1944) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 10 Published 1928 Hanns Holdt (German, 1887-1944) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 10 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p10-web1.jpg?w=770)
![Franz Löwy (Austrian, 1883-1949) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 11 Published 1928 Franz Löwy (Austrian, 1883-1949) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 11 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p11-web1.jpg?w=686)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 12 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 12 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p12-web1.jpg?w=739)
![d'Ora (Arthur Benda) (Vienna) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 13 Published 1928 d'Ora (Arthur Benda) (Vienna) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 13 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p13-web1.jpg?w=456)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 14 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 14 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p14-web1.jpg?w=785)
![Hanns Holdt (Munich) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 15 Published 1928 Hanns Holdt (Munich) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 15 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p15-web1.jpg)
![Hanns Holdt (German, 1887-1944) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 16 Published 1928 Hanns Holdt (German, 1887-1944) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 16 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p16-web1.jpg?w=701)
![Franz Löwy (Austrian, 1883-1949) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 17 Published 1928 Franz Löwy (Austrian, 1883-1949) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 17 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p17-web1.jpg?w=656)
![Hanns Holdt (German, 1887-1944) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 18 Published 1928 Hanns Holdt (German, 1887-1944) 'Sent M'Ahesa' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 18 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/sent-m-ahesa-p18-web1.jpg?w=708)
![Minya Diez-Dührkoop (German, 1873-1929) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 19 Published 1928 Minya Diez-Dührkoop (German, 1873-1929) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 19 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/clotilde-von-derp-sacharoff-p19-web1.jpg?w=760)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 20 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 20 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/clotilde-von-derp-sacharoff-p20-web1.jpg?w=769)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 21 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 21 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/clotilde-von-derp-sacharoff-p21-web1.jpg?w=691)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 23 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 23 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/clotilde-von-derp-sacharoff-p23-web2.jpg?w=710)
![Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 26 Published 1928 Hugo Erfurth (German, 1874-1948) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 26 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/clotilde-von-derp-sacharoff-p26-web2.jpg?w=710)
![Atelier Veritas (Munich) (Stephanie Held-Ludwig) (German born Schaulen, Russia now Lithuania, 1871-1943) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 27 Published 1928 Atelier Veritas (Munich) (Stephanie Held-Ludwig) (German born Schaulen, Russia now Lithuania, 1871-1943) 'Clotilde von Derp-Sacharoff' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 27 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/clotilde-von-derp-sacharoff-p27-web1.jpg?w=659)
!['Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 28 Published 1928 'Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 28 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/nijinski-p28-web1.jpg?w=709)
!['Nijinski' Portrait cards Verlag Leiser, Berlin - Wilmersdorf c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 29 Published 1928 'Nijinski' Portrait cards Verlag Leiser, Berlin - Wilmersdorf c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 29 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/nijinski-p29-web2.jpg?w=714)
![E. O. Hoppé (British, 1878-1972) 'Nijinski' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 30 Published 1928 E. O. Hoppé (British, 1878-1972) 'Nijinski' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 30 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/nijinski-p30-web2.jpg?w=590)
!['Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 31 Published 1928 'Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 31 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/nijinski-p31-web2.jpg?w=710)
!['Nijinski' Portrait cards Verlag Leiser, Berlin - Wilmersdorf c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 32 Published 1928 'Nijinski' Portrait cards Verlag Leiser, Berlin - Wilmersdorf c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 32 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/nijinski-p32-web1.jpg?w=686)
!['Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 33 Published 1928 'Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 33 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/nijinski-p33-web1.jpg?w=800)
!['Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 35 Published 1928 'Nijinski' From the works "The Russian Theater", Amalthea-Verlag, Vienna c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 35 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/nijinski-p35-web2.jpg)
![d'Ora (Arthur Benda) (Vienna) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 36 Published 1928 d'Ora (Arthur Benda) (Vienna) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 36 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-36-web1.jpg?w=767)
![Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 37 Published 1928 Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 37 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-37-web1.jpg?w=737)
![Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 38 Published 1928 Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 38 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-38-web1.jpg?w=780)
![Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 39 Published 1928 Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 39 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-39-web1.jpg?w=750)
![Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 40 Published 1928 Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 40 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-40-web3.jpg?w=728)
![Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 41 Published 1928 Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 41 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-41-web3.jpg?w=801)
![Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 42 Published 1928 Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 42 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-42-web1.jpg?w=689)
![Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 43 Published 1928 Hänse Herrmann (German, 1864-1932) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 43 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-43-web2.jpg?w=793)
![Ernst Schneider (German, 1881-1959) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 44 Published 1928 Ernst Schneider (German, 1881-1959) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 44 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-44-web1.jpg?w=687)
![E. O. Hoppé (British, 1878-1972) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 45 Published 1928 E. O. Hoppé (British, 1878-1972) 'Anna Pavlova' c. 1928 from Der Kunstlerische Tanz Unserer Zeit [The Artistic Dance of Our Time] p. 45 Published 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/anna-pavlova-p-45-web1.jpg?w=730)




![Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Wilde Schlussszene des Opfertanzes [Wild final scene of the sacrificial dance]' 1926-1927 Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Wilde Schlussszene des Opfertanzes [Wild final scene of the sacrificial dance]' 1926-1927](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/lbs_mh02-03-0084-a-web.jpg)



![Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Fremdenverkehr vor der Sphinx [Tourism in front of the Sphinx]' 1929 Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Fremdenverkehr vor der Sphinx [Tourism in front of the Sphinx]' 1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/lbs_mh02-07-0161-web.jpg)










![Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Itu-Mann vom Südosten Abessiniens [Itu man from southeastern Abyssinia]' c. 1934 Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Itu-Mann vom Südosten Abessiniens [Itu man from southeastern Abyssinia]' c. 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/lbs_mh02-22-0756-web.jpg?w=971)
![Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Dankali-Mädchen [Dankali girl]' c. 1934 Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Dankali-Mädchen [Dankali girl]' c. 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/lbs_mh02-22-0775-web.jpg?w=969)
![Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Flugplatz in Addis Abeba [Airfield in Addis Ababa]' c. 1934 Walter Mittelholzer (Swiss, 1894-1937) 'Flugplatz in Addis Abeba [Airfield in Addis Ababa]' c. 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/lbs_mh02-22-0778-web.jpg?w=966)

































![Peter Elfes (Australia, b. 1961) 'Brenton [Heath-Kerr] as Tom of Finland' 1992 Peter Elfes (Australia, b. 1961) 'Brenton [Heath-Kerr] as Tom of Finland' 1992](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/elfes-brenton-heath-kerr-web.jpg?w=686)

























![Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Auschwitz victim]' N Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Auschwitz victim]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/unknown-photographer-untitled-auschwitz-victim-nd-web.jpg)






































































![René Magritte (Belgium 1898-1967) 'Les Amants [The lovers]' 1928 René Magritte (Belgium 1898-1967) 'Les Amants [The lovers]' 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/magritte-the-lovers-web.jpg)



































You must be logged in to post a comment.