Exhibition dates: 14th October – 3rd December, 2017
Curator: Richard Perram OAM
Warning: this posting contains male nudity. If you don’t want to see please do not look.
Todd Fuller (Australian, b. 1988) and Amy Hill (Australian, b. 1988)
They’re Only Words (video still)
2009
Film, sound duration: 2:42 mins
Courtesy the artists and May Space, Sydney
I must congratulate curator and gallery Director, Richard Perram OAM and the Bathurst Regional Art Gallery for putting on such a fine exhibition, worthy of many a large gallery in a capital city. An incredible achievement, coming at the same time as Latrobe Regional Art Gallery put on the recent René Magritte exhibition. All power to these regional galleries. Now on with the show…
Show and tell
The male body. The female body. The trans body. The gay body. Etc. etc. etc. …
The male gaze. The female gaze. The trans gaze. The gay gaze. Etc. etc. etc. …
I did my Doctor of Philosophy, all four and a half years of it, on the history of photography and its depiction of the male body so I know this subject intimately. It is such a complicated subject that after all of time, nothing is ever certain, everything is changeable and fluid.
To start, the definition of masculinity that I used as a determination for the term in my PhD is included as the first quotation below. The quotation is followed by others – on the optic experience and the creation of body image; on body image and our relation to other people; on the anxiety caused by the crisis of looking as it intersects with the crisis of the body; and how we can overcome the passivity of objective truth (accepting dominant images in this case, as they are presented to us) through an active struggle for subjective truth, or an acceptance of difference. A further, longer quote in the posting by Chris Schilling examines Ernst Goffman’s theories of body, image and society in which Goffman states that the body is characterised by three main features: firstly, that the body as material property of individuals; secondly, that meanings attributed to the body are determined by ‘shared vocabularies of body idiom’ such as dress, bearing, movements and position, sound level, physical gestures such as waving and saluting, facial decorations, and broad emotional expressions; and thirdly; that the body plays an important role in mediating the relationship between people’s self-identity and their social identity. These quotations just start to scratch the surface of this very complicated, negotiated social area.
What we can say is this: that masculinity is always and forever a construct; that male body image is always and forever a further construct built on the first construct; and that photo media images of the male body are a construct, in fact a double or triple construct as they seek to capture the surface representation of the previous two conditions.
What strikes me with most of the photographs in this posting is that they are about a constructed “performance” of masculinity, performances that challenge cultural signifiers of mainstream and marginalised aspects of Western patriarchal culture. In most the masculine subject position is challenged through complex projections of masculinity, doubled through the construction of images. In fact, spectatorship is no longer male and controlling but polymorphous and not organised along normative gender lines.
Thus, these artists respond to four defined action problems in terms of representation of body usage: “… control (involving the predicability of performance); desire (whether the body is lacking or producing desire); the body’s relation to others (whether the body is monadic and closed in on itself or dyadic and constituted through either communicative or dominating relations with others); and the self-relatedness of the body (whether the body associates and ‘feels at home’ in itself, or dissociates itself from its corporeality).”1 Further, four ideal types of body usage can be defined in terms of these action problems: the disciplined body where the medium is regimentation, the model of which is the rationalisation of the monastic order; the mirroring body where the medium is consumption, the model of which is the department store; the dominating body where the medium is force, the model of which is war; and the communicative body where the medium is recognition, the model of which could be shared narratives, communal rituals (such as sex) and caring relationships.2
As Chris Schilling observes, “The boundaries of the body have shifted away from the natural and on to the social, and the body now has ‘a thoroughly permeable “outer layer” through which the reflexive project of the self and externally formed abstract systems enter.” In other words, masculinity and male figure can be anything to any body and any time in any context. The male body can be prefigured by social conditions. But the paradox is, the more we know masculinity and the male body, the more knowledge we have, the more we can alter and shape these terms, the less certain we are as to what masculinity and the male body is, and how or if it should be controlled. Taking this a step further, Schilling notes that the photographic image of the body itself has become an abstract system/symbolic token which is traded without question, much as money is, without the author or participants being present.3 You only have to look into some of the gay chats rooms to know this to be true!
The most difficult question I had to ask myself in relation to this exhibition was, what is it to be male? Such a question is almost impossible to answer…
Is being male about sex, a penis, homosociality, homosexuality, heterosexuality, friendship, braveness, dominance, perversity, fantasy, love, attraction, desire, pleasure, Ockerism, respect, loyality, spirituality, joy, happiness etc. etc. It is all of these and more besides. And this is where I find some most of these images to be just surface representations of deeper feelings: I just like dressing in drag; I like pulling a gun on someone; I like holding a knife next to my penis to make my phallus and my armoured body look “butch”. It’s as though the “other”, our difference from ourselves (and others), has been normalised and found wanting. I want to strip them away from this performative, normalising aspect. Most of these photographs are male figures dressed up to the nines, projecting an image, a surface, to the outside world (even though the performative tells us a great deal about the peculiarities of the human imagination). I want them to be more essential, not just a large penis dressed up for show. Only in the image Untitled (Auschwitz victim) (Nd, below), where the performance for the camera and the clothing the man is wearing is controlled by others – does some sense of an inner strength of a male come through. In times of unknown horror and dire circumstances, this man stares you straight in the eye with a calm presence and inner composure.
For me personally, being male is about a spiritual connection – to myself, to the earth and to the cosmos. I hope it is about respect for myself and others. Of course I use the systems above as a projection of myself into the world, as to who I am and who I want people to see through my image. But there is so much more to being male than these defined, representational personas. This is not some appeal to, as David Smail puts it, “a simple relativity of ‘truths'” (anything to anybody at anytime in any context), nor a essentialist reductionism to a “single truth” about our sense of being, but an appeal for a ‘non-finality’ of truth, neither fixed nor certain, that changes according to our values and what we understand of ourselves, what it is to be male. This understanding requires intense, ongoing inner work, something many males have no desire to undertake…
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Word count: 1,230
Footnotes
1/ Chris Schilling, The Body and Social Theory, Sage Publications, London, 1993, p.95.
2/ Ibid., p. 95.
3/ Ibid., p. 183.
Many thankx to Director Richard Perram, Assistant Curator Julian Woods and the Bathurst Regional Art Gallery for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“The category of “masculinity” should be seen as always ambivalent, always complicated, always dependent on the exigencies (necessary conditions and requirements) of personal and institutional power … [masculinity is] an interplay of emotional and intellectual factors – an interplay that directly implicates women as well as men, and is mediated by other social factors, including race, sexuality, nationality, and class … Far from being just about men, the idea of masculinity engages, inflects, and shapes everyone.”
Berger, Maurice; Wallis, Brian and Watson, Simon. Constructing Masculinity. Introduction. New York: Routledge, 1995, pp. 3-7.
“We choose and reject by action … Nietzsche calls the body ‘Herrschaftsgebilde’ (creation of the dominating will). We may say the same about body-image. Since optic experience plays such an enormous part in our relation to the world, it will also play a dominating role in the creation of the body-image. But optic experience is also experience by action. By actions and determinations we give the final shape to our bodily self. It is a process of continual active development.” (My underline)
Schilder, Paul. The Image and Appearance of The Human Body. New York: International Universities Press, 1950, pp. 104-105.
“Body images should not exist in isolation. We desire the relation of our body-images to the body-images of all other persons, and we want it especially concerning all sexual activities and their expression in the body-image. Masturbation is specifically social. It is an act by which we attempt to draw the body-images of others, especially in their genital region, nearer to us.”
Schilder, Paul. The Image and Appearance of The Human Body. New York: International Universities Press, 1950, p. 237.
“As the French critic Maurice Blanchot wrote, “The image has nothing to do with signification, meaning, as implied by the existence of the world, the effort of truth, the law and the brightness of the day. Not only is the image of an object not the meaning of that object and of no help in comprehending it, but it tends to withdraw it from its meaning by maintaining it in the immobility of a resemblance that it has nothing to resemble” … It is this severance of meaning and its object, this resemblance of nothing, that the crisis of looking intersects with the crisis of the body. In contemporary culture we promote the body as infinitely extendable and manageable. Indeed, we mediate this concept through the permeation of the photographic image in popular culture – through advertising and dominant discourse that place the young, beautiful, erotic body as the desirable object of social attention. This is a body apparently conditioned by personal control (moral concern). But the splitting apart of image and meaning pointed to by Blanchot suggests that such control is illusory. There is no single truth; there are only competing narratives and interpretations of a world that cannot be wholly, accurately described.” (My underline)
Blanchot, Maurice. The Gaze of Orpheus. New York: Barrytown, 1981, p. 85, quoted in Townsend, Chris. Vile Bodies: Photography and the Crisis of Looking. Munich: Prestel, 1998, p. 10.
“Where objective knowing is passive, subjective knowing is active – rather than giving allegiance to a set of methodological rules which are designed to deliver up truth through some kind of automatic process [in this case the construction of the male figure through the image], the subjective knower takes a personal risk in entering into the meaning of the phenomena to be known … Those who have some time for the validity of subjective experience but intellectual qualms about any kind of ‘truth’ which is not ‘objective’, are apt to solve their problem by appealing to some kind of relativity. For example, it might be felt that we all have our own versions of the truth about which we must tolerantly agree to differ. While in some ways this kind of approach represents an advance on the brute domination of ‘objective truth’, it in fact undercuts and betrays the reality of the world given to our subjectivity. Subjective truth has to be actively struggled for: we need the courage to differ until we can agree. Though the truth is not just a matter of personal perspective, neither is it fixed and certain, objectively ‘out there’ and independent of human knowing. ‘The truth’ changes according to, among other things, developments and alterations in our values and understandings … the ‘non-finality’ of truth is not to be confused with a simple relativity of ‘truths’.” (My underline).
Smail, David. Illusion and Reality: The Meaning of Anxiety. London: J.M. Dent & Sons, 1984, pp. 152-153.
The Unflinching Gaze: photo media & the male figure
The Unflinching Gaze: photo media & the male figure surveys how the male figure has been depicted by Australian and international artists in photo media over the last 140 years. It includes historic and contemporary fine art photography and film, fashion photography, pop videos and homoerotic art. Images range from the beautiful to the banal to the confounding.
The Unflinching Gaze: photo media & the male figure is a Bathurst Regional Art Gallery exhibition in partnership with Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay and Lesbian Art, New York. Curated by Richard Perram OAM. This exhibition is supported by the Dobell Exhibition Grant, funded by the Sir William Dobell Art Foundation and managed by Museums & Galleries of NSW.
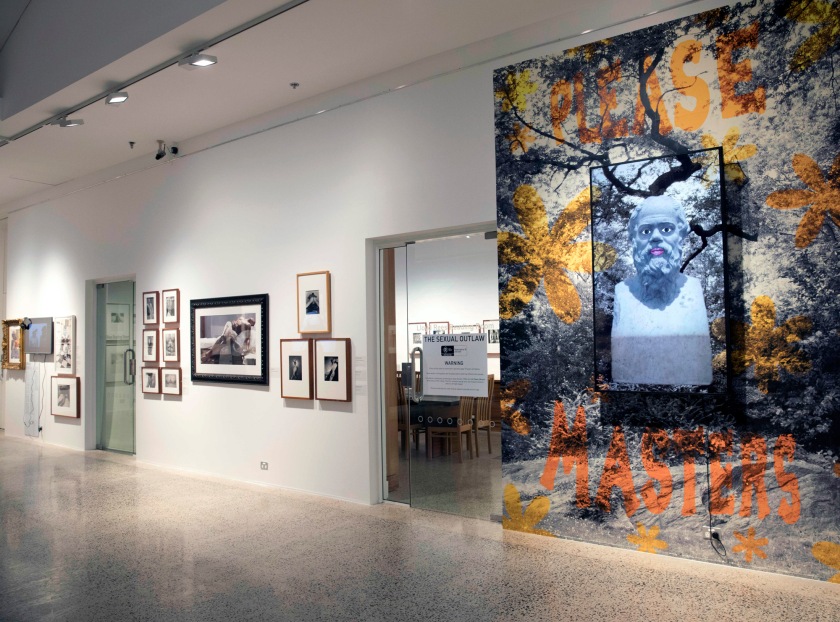
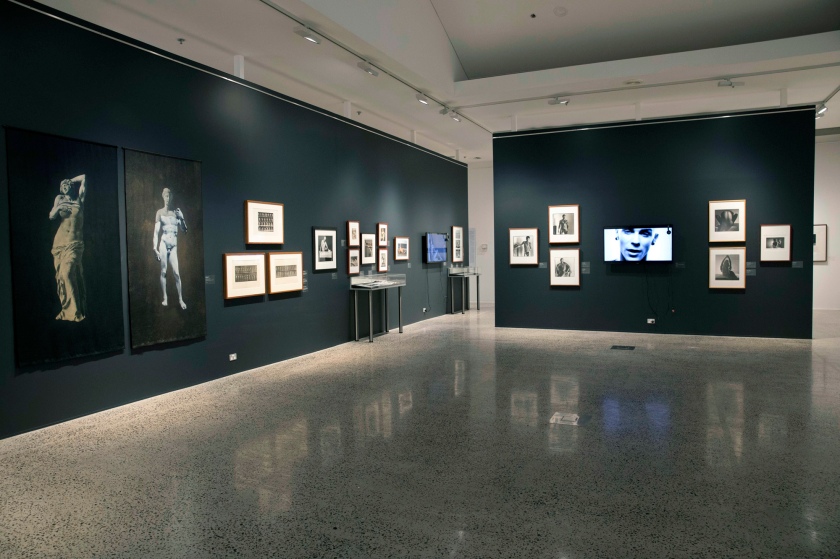
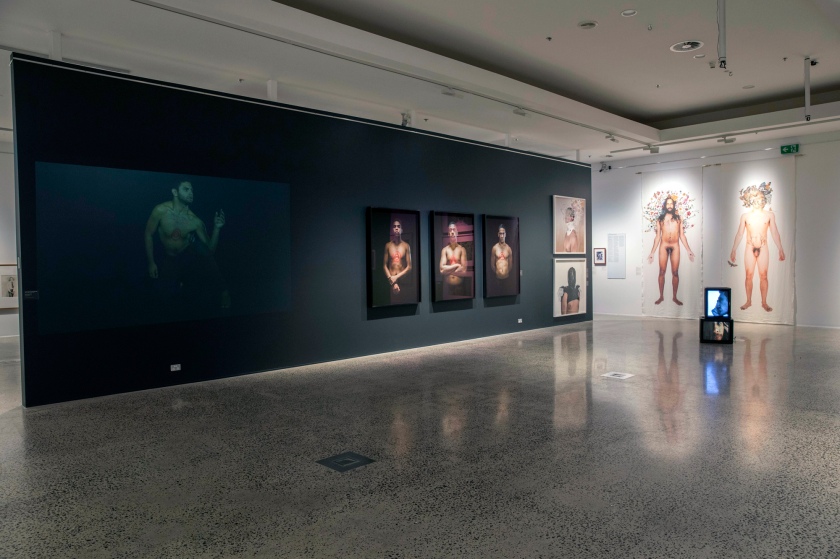
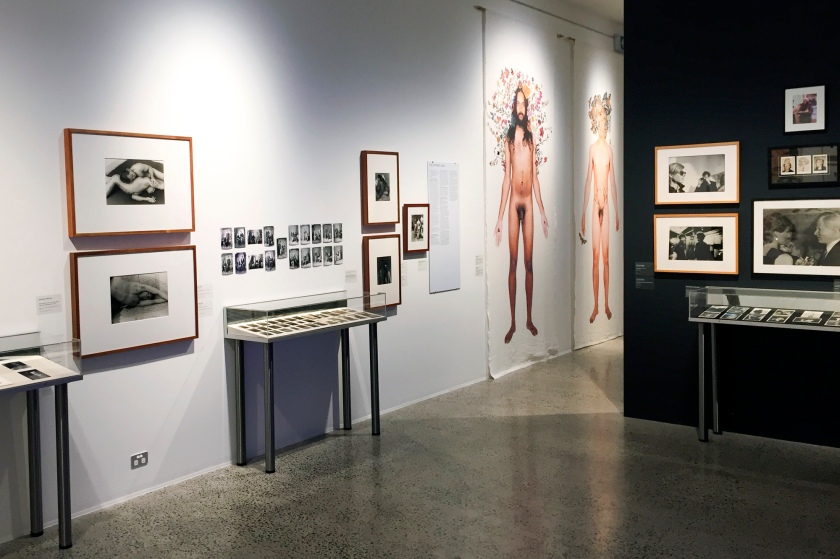
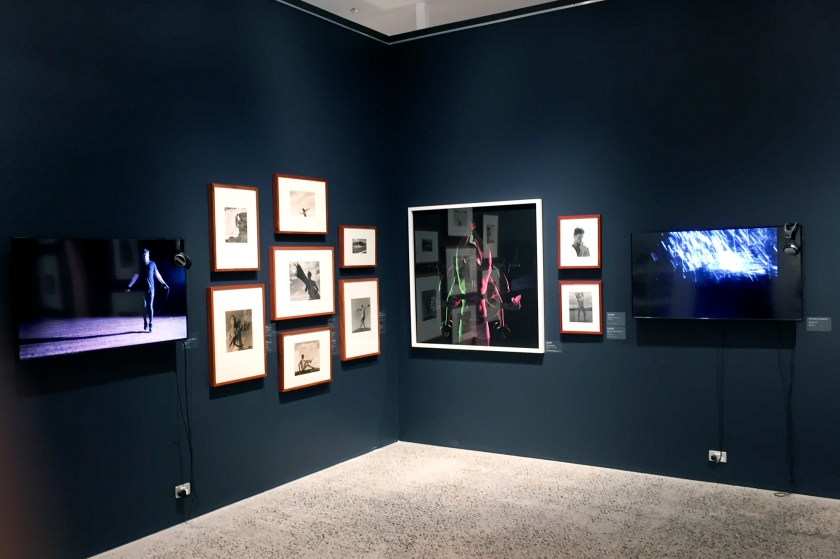
Installation views of the exhibition The Unflinching Gaze: photo media and the male figure at the Bathurst Regional Art Gallery, New South Wales
Photos: Sharon Hickey Photography
In line with current thinking the exhibition posits masculinity, and gender itself, as a kind of performance – a social construct that is acquired rather than biologically determined.
This idea has its limits, with most people happy to accept anatomy as destiny. Nevertheless, there is much we view as ‘natural’ that might be more accurately described as ‘cultural’. In an exceptional catalogue essay, Peter McNeil refers to Jonathan Ned Katz’s book, The Invention of Heterosexuality, which notes that the term “heterosexual” was first published in the United States in 1892. This is a remarkably late entry for a concept often viewed as a cornerstone of social orthodoxy.
A condition doesn’t require a word to make it a reality but it sure helps. Wittgenstein’s famous dictum: “The limits of my language are the limits of my world,” reminds us of the power of naming and categorisation.
To establish anything as an unquestionable norm is to stigmatise other views as abnormal. From the perception of abnormality comes the fear and hatred that surfaced during a same-sex marriage postal survey that revealed more about political cowardice than it did about Australian social attitudes. Although Perram has no qualms about celebrating gay sexuality his chief concern is to encourage a broader, more inclusive understanding of masculinity. …
One of the most striking moments in Perram’s show is a juxtaposition of Mapplethorpe’s 1983 portrait of gay porn star, Roger Koch, aka Frank Vickers, wearing a wig, bra and fishnets, his hands clasped demurely over his groin. The feminine coyness is at odds with Vickers’s musclebound torso and biceps which are fully on display in his self-portrait of the same year, along with his semi-erect penis.
The photos may be two versions of camp but the comparison shows how an individual’s sexual identity can be reconfigured with the appropriate props and body language. In the case of performance artist, Leigh Bowery, captured in a series of photos by Fergus Greer, the play of fantasy transcended the simple binary opposition of male and female, to create monstrous hybrids that question the limits of what it is to be human.”
John McDonald. “The Unflinching Gaze,” November 24, 2017
Tony Albert (Australian, b. 1981)
Brother (Our Past) 2013
Brother (Our Present) 2013
Brother (Our Future) 2013
Pigment on paper, edition of 3 150 x 100cm each
Courtesy UTS Art, Corrigan Collection
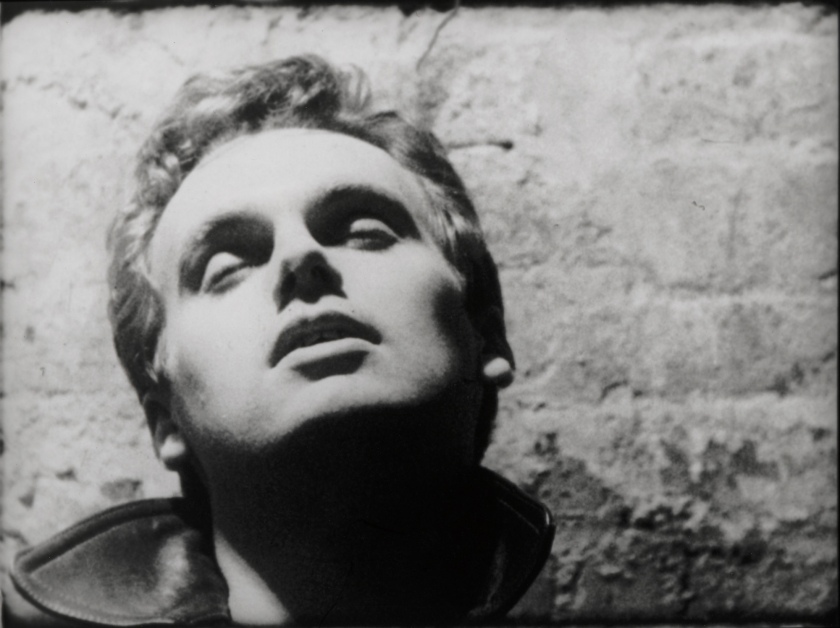
Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Blow Job [still]
1964
16mm film, black and white, silent duration: 41 min at 16 frames per second
© 2017 The Andy Warhol Museum, Pittsburgh, PA, a museum of Caregie Institute. All rights reserved
Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Blowjob
1964
Robert Wilson (American, b. 1941)
Brad Pitt
2004
Video portrait, looped
Dimensions variable
Courtesy the artist and the Byrd Hoffman Water Mill Foundation, New York
Robert Wilson (American, b. 1941)
Brad Pitt video portrait
2004
Peter Elfes (Australian, b. 1961)
Brenton (Heath-Kerr) as Tom of Finland
1992
Cibachrome print
51 x 40.6cm
Courtesy the artist
© Peter Elfes
Casa Susanna
Attributed to Andrea Susan
(Lee in white dress)
1961
Digital copy from colour photographs
Collection of Art Gallery of Ontario, purchased with funds generously donated by Martha LA McCain 2015
© Art Gallery of Ontario
Photo: Ian Lefebvre
Nikki Johnson (American, b. 1972)
David Amputation Fetishist
2007
Digital print (from a set of images)
Courtesy the artist
Luke Parker (Australian, b. 1975)
Double hanging
2005
Photograph, cotton thread, pins
15 x 40cm
Courtesy the artist and 55 Sydenham Rd
Gregory Collection
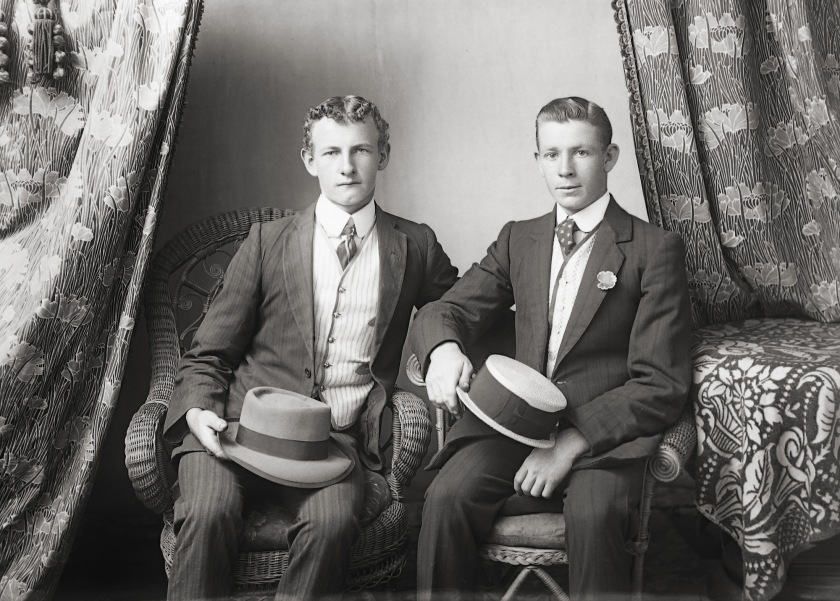
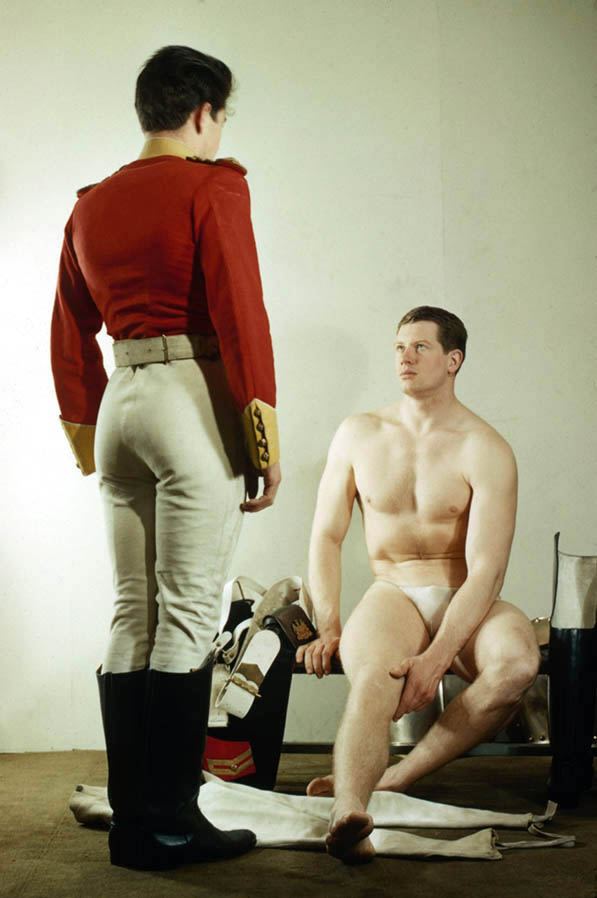
Mr Cullen & Mr Gornall
Date unknown
Digital copy from scanned negative
Courtesy the Bathurst Historical Society
Two hundred photos and videos by sixty two leading artists (twenty four Australian and thirty eight international) will be exhibited at Bathurst Regional Art Gallery (BRAG) from Saturday 14 October until Sunday 3 December 2017.
Curated by BRAG Director Richard Perram OAM, an openly gay man, The Unflinching Gaze: photo media and the male figure surveys how the male figure has been depicted by Australian and international artists in photo media over the last 140 years. It includes historic and contemporary fine art photography and film, fashion photography, pop videos and homoerotic art. Images range from the beautiful to the banal to the confounding.
Key artists in the exhibition include iconic American artists Robert Mapplethorpe, Andy Warhol, and avant-garde theatre director Robert Wilson with a video portrait of Brad Pitt; European artists such as Eadweard Muybridge, and Baron Wilhelm Von Gloeden; and historic and contemporary Australian artists including Beaufoy Merlin and Charles Bayliss, Max Dupain, Deborah Kelly, William Yang, Gary Carsley, Owen Leong and Liam Benson. Works have been sourced from Australian and international collections, including a major loan of 60 works from the Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay and Lesbian Art, New York.
The exhibition brings an unflinching gaze to how concepts of humanity and the male figure are intertwined and challenged. Themes include the Pink Triangle, which deals with the persecution, torture and genocide of homosexuals in concentration camps during World War II to those in Chechyna today; and the AIDS crisis in the 1980s.
The Unflinching Gaze exhibition is a unique opportunity for audiences in the Bathurst Region to access a world class photo-media exhibition, says Richard Perram OAM. The Unflinching Gaze not only deals with aesthetic concerns but also engages the community in a discussion around social issues. BRAG is working with local Bathurst LGBTI community groups to ensure that one of the most important outcomes of the exhibition will be to inform and educate the general Bathurst community and support and affirm the Bathurst LGBTI community.
The Unflinching Gaze: photo media and the male figure is a Bathurst Regional Art Gallery exhibition in partnership with Leslie Lohman Museum of Gay and Lesbian Art, New York. Curated by Richard Perram OAM. This exhibition is supported by the Dobell Exhibition Grant, funded by the Sir William Dobell Art Foundation and managed by Museums & Galleries of NSW.
Press release from the Bathurst Regional Art Gallery (BRAG)
American & Australian Photographic Company
(Beaufoy Merlin and Charles Bayliss)
Mssrs. Bushley & Young
Nd
Digital reproductions from glass photo negatives, quarter plate
From the Collections of the State Library of NSW
Horst P. Horst (Germany; United States, 1906-1996)
Male Nude I NY
1952
Silver gelatin print
25.4 x 20.3cm
Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay & Lesbian Art, gift of Ricky Horst
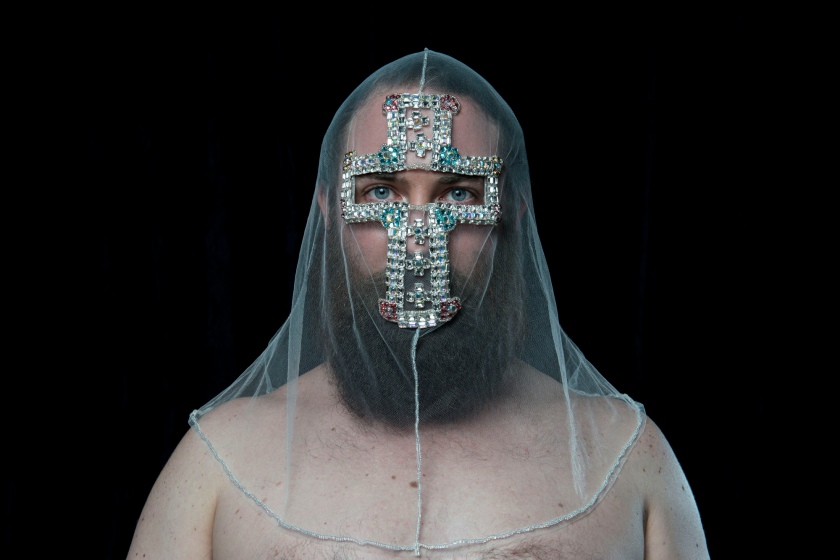
Liam Benson (Australian, b. 1980)
The Crusader 2015
The Executioner 2015
The Terrorist 2015
Inkjet print on cotton rag paper, edition of 5 90 x 134cm
Photograph by Alex Wisser
Courtesy of the artist and Artereal Gallery
George Platt Lynes (American, 1907-1955)
Blanchard Kennedy
1936
Gelatin silver photograph
23 x 18.2cm
National Gallery of Australia, Canberra. Purchased 1981
Christopher Makos (American, b. 1948)
Altered Image: One Photograph of Andy Warhol
1982
Gelatin silver photograph
50.6 x 40.8cm each
National Gallery of Australia, Canberra. Purchased 1982
Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Helmut, N.Y.C. (from X Portfolio)
1978
Selenium toned silver gelatin print
19.7 x 19.7cm
Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay & Lesbian Art, Foundation Purchase
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation. Used by permission
Robert Mapplethorpe (American, 1946-1989)
Roger Koch aka Frank Vickers: From the “Roger” Series
1983
Gelatin silver photo
48.9 x 38.1cm
Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay & Lesbian Art, Founders Gift
© Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation. Used by permission
Body, image and society
Goffman’s approach to the body is characterised by three main features. First, there is a view of the body as material property of individuals. In contrast to naturalistic views … Goffman argues that individuals usually have the ability to control and monitor their bodily performances in order to facilitate social interaction. Here, the body is associated with the exercise of human agency, and it appears in Goffman’s work as a resource which both requires and enables people to manage their movements and appearances.
Second, while the body is not actually produced by social forces, as in Foucault’s work, the meanings attributed to it are determined by ‘shared vocabularies of body idiom’ which are not under the immediate control of individuals (E. Goffman, Behaviour In Public Places: Notes on the Social Organisation of Gatherings, The Free Press, New York, 1963, p.35). Body idiom is a conventionalized form of non-verbal communication which is by far the most important component of behaviour in public. It is used by Goffman in a general sense to refer to ‘dress, bearing, movements and position, sound level, physical gestures such as waving and saluting, facial decorations, and broad emotional expressions’ (Goffman, 1963:33). As well as allowing us to classify information given off by bodies, shared vocabularies of body idiom provide categories which label and grade hierarchically people according to this information. Consequently, these classifications exert a profound influence over ways in which individuals seek to manage and present their bodies.
The first two features of Goffman’s approach suggest that human bodies have a dual location. Bodies are the property of individuals, yet are defined as significant and meaningful by society. This formulation lies at the core of the third main feature of Goffman’s approach to the body. In Goffman’s work, the body plays an important role in mediating the relationship between people’s self-identity and their social identity. The social meanings which are attached to particular bodily forms and performances tend to become internalized and exert a powerful influence on an individuals sense of self and feelings of inner worth.
Goffman’s general approach to the body is revealed through his more specific analyses of the procedures involved in what he terms the ‘interaction order’. Goffman conceptualises the interaction order as somehow autonomous sphere of social life (others include the economic sphere) which should not be seen as ‘somehow prior, fundamental, or constitutive of the shape of macroscopic phenomena’ (Goffman, 1983:4). His analysis of this sphere of life demonstrates that intervening successfully in daily life, and maintaining a single definition in the face of possible disruptions, requires a high degree of competence in controlling the expressions, movements and communications of the body.” (Goffman, 1969).
Schilling, Chris. The Body and Social Theory. London: Sage Publications, 1993, pp. 82-83.
Owen Leong (Australian, b. 1979)
Resistance Training
2017
Archival pigment print on cotton paper, edition of 5 + 2 AP
120 x 120cm
Courtesy the artist and Artereal Gallery, Sydney Commissioned by BRAG for The Unflinching Gaze: photo media & the male figure with funds from BRAGS Inc. (Bathurst Regional Art Gallery Society Inc.)
Owen Leong (Australian, b. 1979)
Milk Teeth
2014
Archival pigment print on cotton paper, edition of 5 + 2Ap
120 x 120cm
Courtesy of the artists and Artereal Gallery Sydney
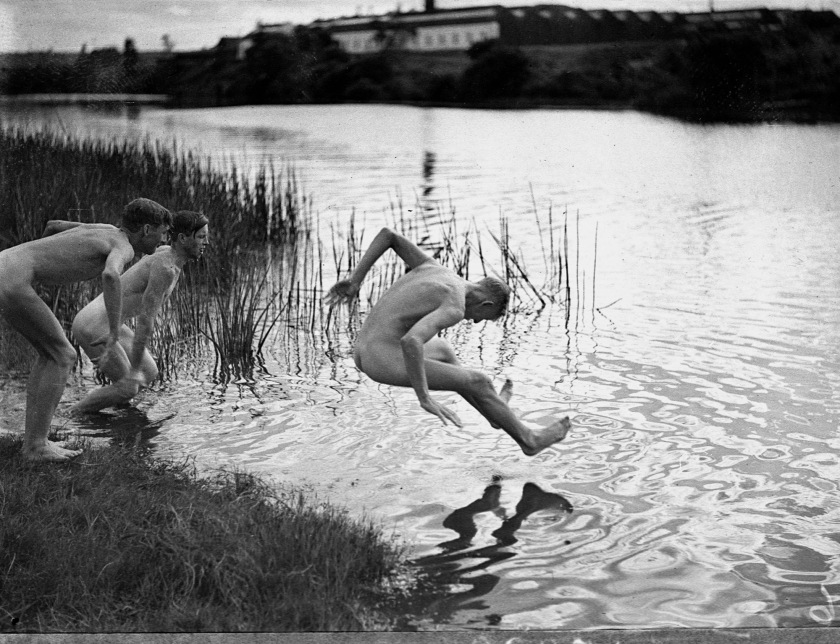
Samuel J Hood (Australian, 1872-1953)
The 9th Field Brigade (four images)
24/2/1938 (Liverpool, NSW)
Photo negative (copied from original nitrate photograph) 35mm
From the Collections of the State Library of NSW
Anthony Sansone (Italy; United States, 1905-1987)
Untitled
1935
Bromide print
24.1 x 18.9cm
Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay & Lesbian Art, gift of David Aden Gallery
Fergus Greer (United Kingdom, 1961-1994)
Leigh Bowery, Session V
Look 27 February 1992
Digital reproduction
Courtesy Fergus Greer
Fergus Greer (United Kingdom, 1961-1994)
Leigh Bowery, Session VII
Look 34, June 1994
Digital reproduction
Courtesy Fergus Greer
Fergus Greer (United Kingdom, 1961-1994)
Leigh Bowery, Session VII, Look 34
June 1994
Silver gelatin print
60.7 × 50.5cm
Unknown American
Vintage photograph from the Closeted History/Wunderkamera
Nd
Tintypes, paper photographs
Collection of Luke Roberts
Frank Vickers (American, 1948-1991)
Untitled (self-portrait)
1983
Silver gelatin print
17.8 x 12.4cm
Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay & Lesbian Art, Founders’ gift
Baron Wilhelm von Gloeden (Germany; Italy, 1856-1931)
Untitled
c. 1910
Albumen silver print
20.3 x 15.2cm
Leslie-Lohman Museum of Gay and Lesbian Art, Founders’ gift
Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Untitled (Victor Hugo’s Penis)
Date unknown
Polaroid
8.5 x 10.5cm
Collection of Byrd Hoffman Water Mill Foundation
Gary Carsley (Australian, b. 1957)
YOWL [still]
2017
Single Channel HD Video on Layered A3 Photocopy substrate
360 x 247cm
Duration 4.32 min
Videography Ysia Song, Soundscape Tarun Suresh, Art Direction Shahmen Suku
Royale Hussar (Basil Clavering and John Parkhurst)
Queens Guard 3
1959-1960
Digital print from original negative
William Yang (Australian-Chinese, b. 1943)
‘Allan’ from the monologue ‘Sadness’
1992
19 gelatin silver photographs in the monologue
51.0 x 41.0cm each sheet
Photograph: William Yang/Bathurst Regional Art Gallery
A photograph from the Sadness series, which depicts the slow death of his sometime lover, Allan Booth.
Unknown photographer
Untitled [Auschwitz victim]
Nd
Photograph: Bathurst Regional Art Gallery
This prisoner was sent to Auschwitz under Section 175 of the German Criminal Code, which criminalised homosexuality.
The picture may have been taken by Wilhelm Brasse who was born on this date, 3 December in 1917, who became known as the “photographer of Auschwitz concentration camp”, though he was one of several, including Alfred Woycicki , Tadeusz Myszkowski, Józef Pysz, Józef Światłoch, Eugeniusz Dembek, Bronisław Jureczek, Tadeusz Krzysica, Stanisław Trałka, and Zdzisław Pazio whom the Camp Gestapo kept alive for the job of recording thousands of photographs of their fellow prisoners, supervised by Bernhard Walter, the head of Erkenundienst.
The photographs themselves present a transgression of the subject’s own self-image. The carte-de-visite format forces a confrontation of the victim (which in this situation, they are) with themselves in a visual interrogation, by placing a profile and a three-quarter view either side of a frontal mug shot. The final image seems to depict the subject beholden to a higher authority.
Brasse had been arrested in 1940, at age 23, for trying to leave German-occupied Poland and sent to KL Auschwitz-Birkenau where because he had been a Polish professional photographer in his aunt’s studio his skills were useful. Brasse has estimated that he took 40,000 to 50,000 “identity pictures” from 1940 until 1945.
Brasse and another prisoner Bronisław Jureczek preserved the photographs when in January 1945, during the evacuation of the camp, they were ordered to burn all of the photographs. They put wet photo paper in the furnace first and followed by such a great number of photos and negatives that the fire was suffocated. When the SS-Hauptscharfürer Walter left the laboratory, Brasse and Jureczek swept undestroyed photographs from the furnace, scattering them in the rooms of the laboratory and boarding up the door to the laboratory. 38,916 photographs were saved.
James McCardle. “Ghosts,” on the On This Day in Photography website 03/12/2017
M. P. Rice (American)
American poet Walt Whitman and his ‘rebel soldier friend’, Pete Doyle
Walt Whitman and Peter Doyle, Washington DC.
c. 1865
Charles E. Feinberg Collection, Library of Congress
Photograph: Library of Congress/Library of Congress/Bathurst Regional Art Gallery
The first extant photo of Whitman with anyone else, here Peter Doyle, Whitman’s close friend and companion in Washington. Doyle was a horsecar driver and met Whitman one stormy night in 1865 when Whitman, looking (as Doyle said) “like an old sea-captain,” remained the only passenger on Doyle’s car. They were inseparable for the next eight years.
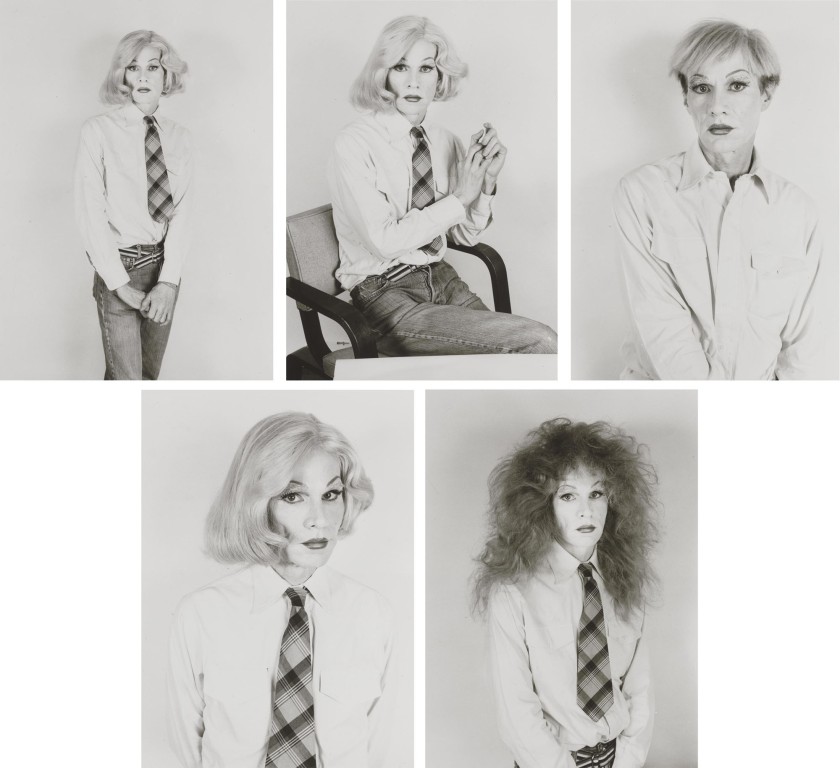
Christopher Makos (American, b. 1982)
Altered Image: Five Photographs of Andy Warhol
1982
Portfolio of five gelatin silver prints
Each sheet: 20 x 16 in. (50.8 x 40.6cm)
Each image: 18 x 12 ¾ in. (45.7 x 32.3cm)
Bathurst Regional Art Gallery (BRAG)
70 -78 Keppel St
Bathurst NSW 2795
Opening hours:
Tues to Sat 10am – 5pm
Sundays 11am – 2pm












![Peter Elfes (Australia, 1961-) 'Brenton [Heath-Kerr] as Tom of Finland' 1992 Peter Elfes (Australia, 1961-) 'Brenton [Heath-Kerr] as Tom of Finland' 1992](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/elfes-brenton-heath-kerr-web.jpg?w=650&h=970)


























![Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Auschwitz victim]' N Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Auschwitz victim]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/unknown-photographer-untitled-auschwitz-victim-nd-web.jpg?w=840)


















You must be logged in to post a comment.