March 2023

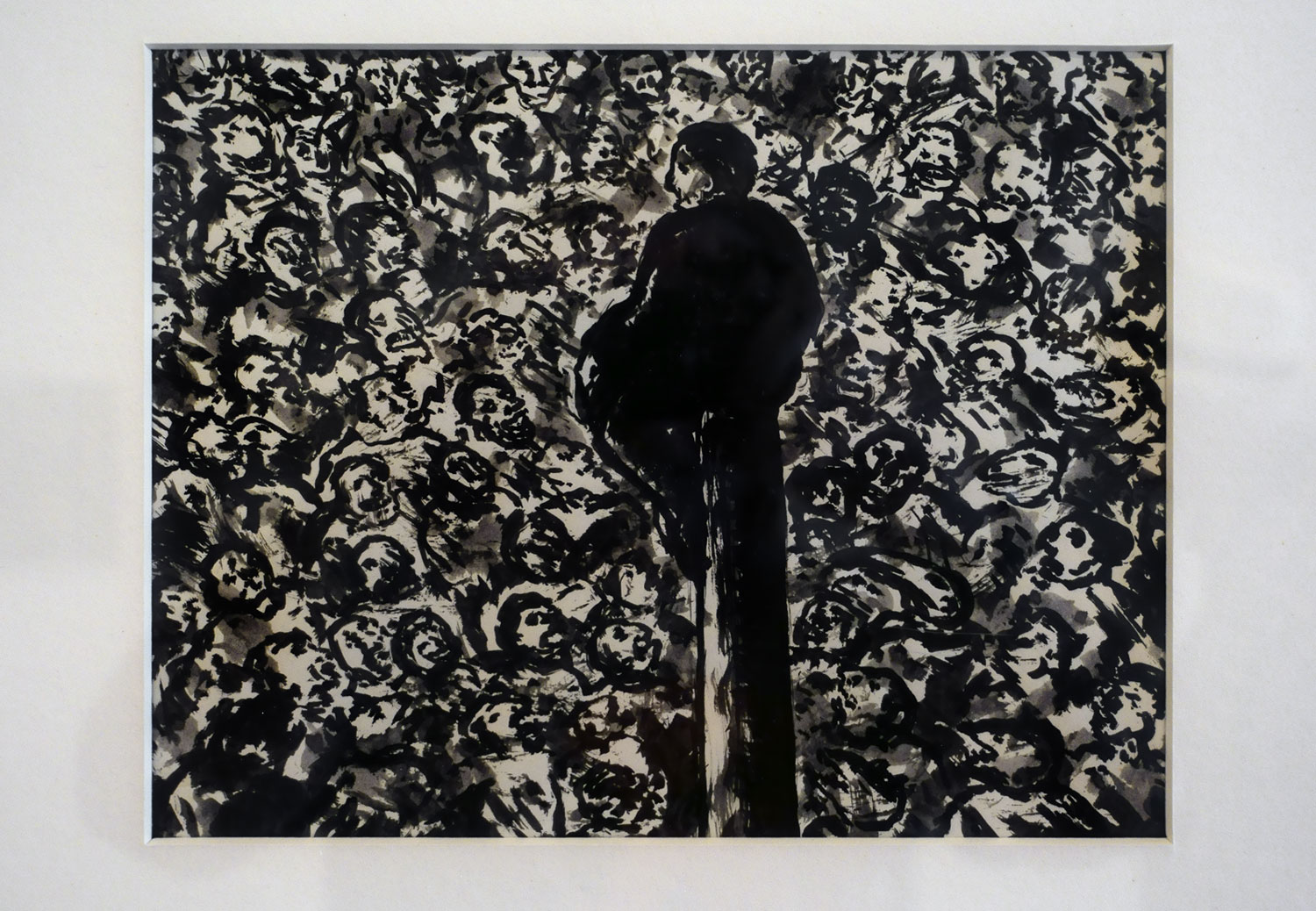
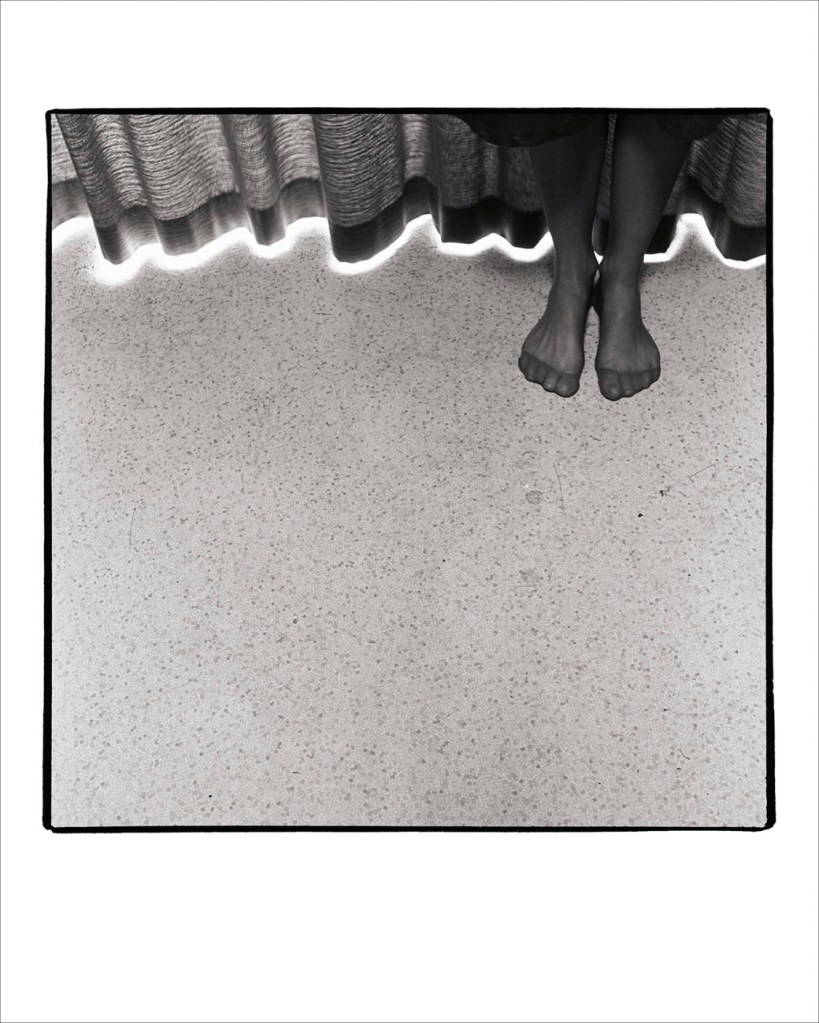
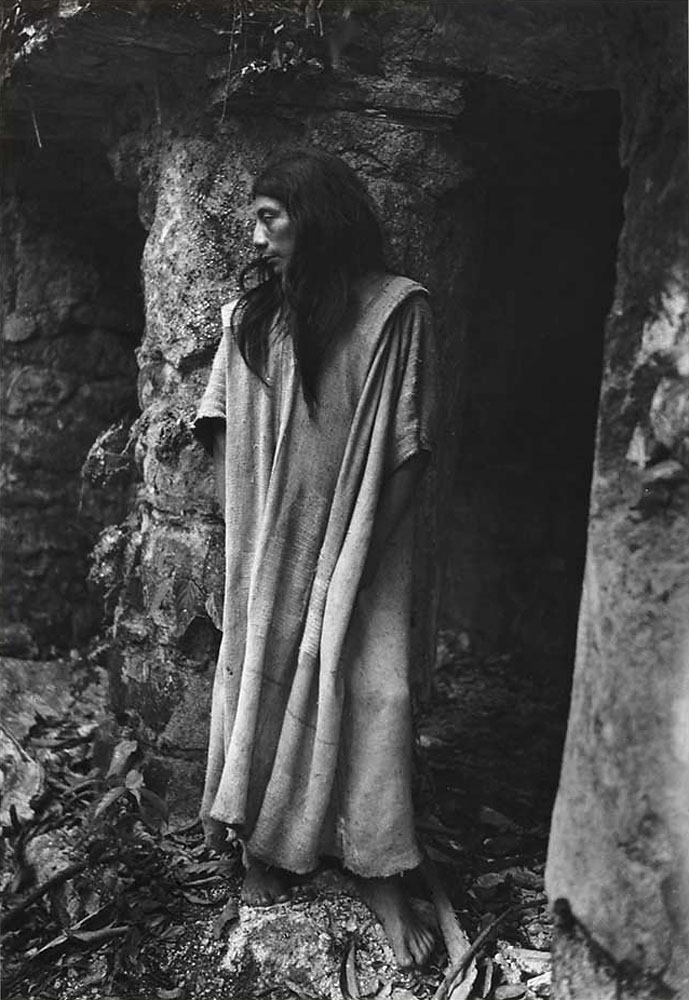
Diane Arbus (American, 1923-1971)
Seated man in a bra and stockings, N.Y.C.
1967
Gelatin silver print
Since the demise of my old website, my PhD research Pressing the Flesh: Sex, Body Image and the Gay Male (RMIT University, Melbourne, 2001) has no longer been available online.
I have now republished the third of twelve chapters, “In Press”, so that it is available to read. More chapters will be added as I get time. I hope the text is of some interest. Other chapters include Historical Pressings which examines the history of photographic images of the male body; Bench Press which investigates the development of gym culture, its ‘masculinity’, ‘lifestyle’, and the images used to represent it; and Re-pressentation which alternative investigates ways of imag(in)ing the male body and the issues surrounding the re-pressentation of different body images for gay men.
Dr Marcus Bunyan March 2023
“In Press” chapter from Marcus Bunyan’s PhD research Pressing the Flesh: Sex, Body Image and the Gay Male RMIT University, Melbourne, 2001
Through plain language English (not academic speak) the text of this chapter investigates the photographic representation of the muscular male body in the (sometimes gay) media and gay male pornography. In the title of the chapter I use the word ‘press’ to infer a link to the media.
Keywords
photography, muscular male body, muscular male body in the media, appearance, lifestyle, narcissism, advertising, media, appearance, consumer capitalism, visible bodies, gay male, gay male pornography
Sections
1/ Consuming the Appearance
2/ Consumer Capitalism and Narcissism
3/ Visible Bodies
4/ Gay Male Pornography
5/ Alternatives to American gay male pornography
6/ Alternative bodies
Word count: 6,884
In Press
“Not only do the media shape our vision of the contemporary world, determining what most people can and cannot see and hear, but the very images of our own body, our own selves, our own personal self worth (or lack of it) is mediated by the omnipresent images of mass culture…”
Douglas Kellner1
From the fervent explosion that saw the birth of the gay liberation movement in the late 1960s and early 1970s there emerged a period of amazing freedom and growth for many gay people. Sexualities that were previously hidden behind a veil of secrecy were now being expressed and fought for out on the streets. Sex, especially the desire of gay men for casual sex, was now out in the open. A new body image emerged from this revolution, one that was neither male nor female, but androgynous. This new androgynous body image can be seen as a reflection of societal changes that were happening during the swinging Sixties, the era of “free love.” You could swing, i.e., move both ways sexually. The joining together of male and female, gay men and lesbians was a very positive force in the formation and acceptance of new identities.
But the honeymoon was soon over.
The idealism of the early gay liberation movement did not last long. Gay men, long persecuted for their camp and feminine ways sought images to combat the long held stereotype of the limp-wristed pansy who had abdicated his male power to others through his effeminacy. Manliness came out of the closet of the physique magazines to express the longed for power of patriarchy that gay men sought. There was an enormous surge in the production of homoerotic imagery and gay men responded by imitating heterosexual masculinity in an ironic way; the ‘clone’ image was born: boots, tight fitting jeans, check shirts, short hair and usually a moustache to top off the image. Anybody could go out and purchase such an outfit. It did not discriminate along class or social boundary lines and the ‘look’ was relatively ageless. This clone image extended to other identities that included the leather man, the sailor, the construction worker & the cowboy. But the image was still ‘butch’; skinny or fat guys really need not apply.
The pop group ‘The Village People’ are a perfect example of the camp irony that infused the gay scene at this time. Their song “Macho Man” echoes the desire for gay men to be seen as butch: “I wanna be a macho, macho man – I wanna be, a macho man,” they sing parading around in their tight fitting and revealing outfits. By making their stereotypical cloned images of the cowboy, construction worker, cop, etc., … incredibly camp they undermined the credibility of traditional masculinity. But soon this camp ironic comment was devoured by the dichotomy of existing sex and gender differences. As Dennis Altman has said,
“In the early days of the movement, both women and men saw the process of gay liberation as intimately related to the blurring of sexual and gender boundaries, a move toward androgyny … Our biggest failure was an inability to foresee the extent to which the opposite would happen and a new gay culture / identity would emerge that would build on existing male / female differences.”2
The body and its visibility became increasingly important as a site of construction that was and is crucial to a persons identity and self-esteem. Appearance is critical to this construction.
I suggest that in contemporary gay culture the muscular body of the gay male has stopped being a ‘camp’ ironic comment on ‘normal’ masculinity and instead the body and photographic images of it have become a marketable asset, a commodity3 in a selling and surveillance exercise. Men advertise for sex by displaying their muscular body for admiration and desire by others and observe themselves and others reactions to it. Identity is now mediated by acceptance of their image and by ‘measuring up’ to a perceived image ideal. Media started to make use of this new availability of the male body as an objectified image of desire as it opened up new markets to companies. It encouraged men to undertake face lifts, tummy tucks, pectoral implants and hair removal, to purchase underwear, toiletries, clothes and all manner of goods so that they too could approach the archetypal ‘ideal’ of the masculine male.

David Lloyd
Untitled
Nd
Cover of Naked Men of San Diego calendar
Santa Monica: The Phenomenon Factory, 1998
Today images of the smooth, muscular, white male body are everywhere in advertising, encouraging us to purchase more, to help us get closer to the ideal. As David Kellner has said in the quotation at the beginning of the chapter, the images of mass culture have become omnipresent. Naked men now adorn calendars containing full frontal nudity of smooth muscular white bodies all sporting the latest in designer erections! You can have your man any time of the day, any time of the year, when you get poked in the eye with this calendar.
The muscular Billy Doll, complete with huge anatomically correct penis, (read ‘scientifically’ or how big a gay man’s penis should be) is the contemporary idealisation of earlier stereotypical gay fantasy images, a kind of male Barbie doll on steroids for gay men. I believe that in today’s incarnation of the gay male body the camp ironic comment present in the fantasy images of an earlier generation has disappeared.

Behavior Saviour
Untitled
‘Billy postcard’
1998
“Born to love you!! Billy is an anatomically correct adult doll standing 32 cm tall, weighing 320g. Choose from – Master Billy, Sailor Billy, Cowboy Billy and San Francisco Billy! Billy, the world’s first out and proud gay doll, comes beautifully packaged in a high quality presentation case with photographic backdrop.”
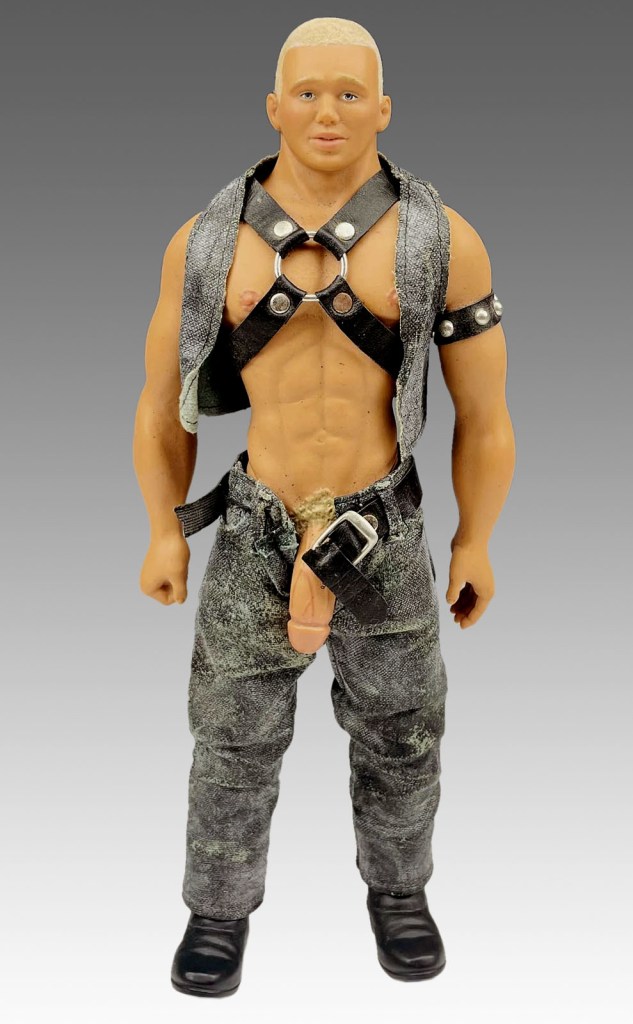

Billy Doll
c. 1997
It has been replaced by a desiring consumerism, in this case the desire for a muscular form complete with jaw dropping penis, the envy of every gay man. And after all, consumerism is a form of self-obsession. Makes you feel a little insecure, eh? Billy doesn’t have an inch of fat or any body hair, is perfectly proportioned (particularly his huge endowment) and is made of plastic. No fear of infection here! Women have been fighting this kind of body stereotyping with the Barbie Doll for years and now the gay male has his own equivalent.
Oh but Billy – he’s born to love you!!
Consuming the Appearance
Sex sells. The appearance and image of hard bodies sells. They are consumed by individuals and societies eager to attain what they offer; individuality, success, popularity and ‘lifestyle’. But these images are not individual, they are ‘the same’, to be consumed by every-body. Below are three examples of the current genre of male body photography; all bodies are of the same homogenised type. Only the photographers are different, but they might as well have been the same.
Michael Childers
Untitled
Nd
Blue Magazine
Sydney: Studio Magazines, February 1999, p. 68
Jason Lee
Untitled
Nd
Blue Magazine
Sydney: Studio Magazines, April 1997, p. 108
Rob Lang
Untitled
Nd
Blue Magazine
Sydney: Studio Magazines, February 1999, p. 93
Apparently, “Jason Lee’s brooding male nudes plumb the shadowy depths of Mystery, Sensuality and Despair … Figures possess an aura of subdued eroticism … Faces and identities are almost inconsequential, the subject reduced to a study of line and texture.”4 He says that he doesn’t want to use clichés that tend to occur when photographing women and to establish an identity and style all of his own. Michael Childers images are supposedly, “Dynamic, sensual and glamorous,”5 while Rob Lang’s desert studies of the male nude, “Document his search for the man within … and [are] essentially about unearthing an emotional bond.”6
These “types” of photographer (ie. ones who take generic photographs of the muscular male body) and many more like them feature heavily in Blue Magazine, a glossy publication aimed at the gay ‘lifestyle’ demographic. Of course most photographers would like to think that their work contains a deep revealing: mystery, sensuality, emotional bonds, etc., … but speaking as a photographer myself, I believe that this type of body photography (with its self-absorption and narcissism), isolates the body from communication with others. The bodies are complete(d) within their own sensual gratification. The construction of these images is formulaic, the body forming a masturbatory landscape endlessly repeated by different photographers in slightly different poses that appeal to a gay erotic consumerism. There is no individual identity present in photographer or subject contrary to what Jason Lee would like to think.
Identities of the models and photographers are inconsequential. These images are used by advertisers, fashion photographers, media and “artists” alike to sell product and fall into clichés that have developed in the photography of the male body over the last 60 years.

Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
Yves Saint Laurent advertisement
Blue Magazine
Sydney: Studio Magazines, February 1999, p. 9
1999
I suggest that these images are no longer just a fashion, but that they are here to stay. I believe that the problems associated with the idealisation of these male images (for example steroid abuse, low self-esteem, body dysmorphia), can be compared to the eating disorders that women have succumbed to in their attempts to attain the waif like super-model look of many contemporary women fashion models.
Some social commentators have argued that the multiplicity of images available to the public (in consumer culture) open up new identities and new areas of becoming, deconstructing the hierarchy of what is seen as valuable in body image types. Central to this hierarchy is the ability of dominant groups (such as supermodels or muscular mesomorphs) to prove that their lifestyle7 and body type are desirable, are superior and worthy of emulation. Chris Schilling has observed that,
“The rapid internationalization and circulation of consumer and ‘lifestyle’ goods threatens the readability of those signs used by the dominant to signify their elite physical capital. These issues raise doubts about the continuing management and control by the dominant class of those fields in which physical capital is recognized and valorized. If fields become saturated with increasing body images and social practices which are presented as constituting valuable forms of physical capital, then their structure may change. Unless dominant sections of society are able to classify these styles into existing hierarchies, and have these classifications recognized as valid, then the logic of differences in which taste in cultural and consumer goods and lifestyle activities are held to be oppositionally structured is threatened. In contemporary consumer society, then, we may be witnessing processes which will make it extremely difficult for any one group to impose as hegemonic, as worthy of respect and deference across society, a single classificatory scheme of ‘valuable bodies’.”8
I disagree with this argument.
It is still all too easy for the dominant group within a subculture or society to impose and identify a ‘valuable’ body. This can be seen in any of the above images and the way they are used by all types of artists, media & advertisers to attract ‘value’ status. The body of the muscular mesomorph attracts a projected desire that media and advertisers rely on. It is still very difficult to put forward alternate body images that can be seen as fantasies, both desirable & ‘valuable’. Since most males would like to have a muscular mesomorphic body shape this body type does have social status. Covers of gay magazines such as Outrage (below) sell far more copies when they have an attractive, muscular smooth young man on the front of them.

Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
2(x)ist underwear advertisement
in Blue Magazine. Sydney: Studio Magazines, February 1999, p.15

Darren Tieste
Geoff
Nd
Outrage Magazine cover, “Making Porn” play and underwear feature
in Outrage Magazine No. 189. Melbourne: Bluestone Press, February 1999. Front cover / p. 63
Here Outrage kills three birds with one stone. Firstly, they have their attractive semi-naked cover model to help sell the mag. Secondly, there is an article on the play in which the model / actor is acting (different photographs). This promotes both the play and fills the magazine. Thirdly, the image is repeated inside the magazine with other models / actors in designer underwear as part of a photographic feature. Nice one Outrage!
This and other contemporary images of muscular male bodies are unlike the clone image of an earlier generation because the ‘look’ is now ageist, elitist and requires great sacrifices in order to come close to possessing the ‘ideal’. Great value is put on appearance, youth, beauty, and lifestyle to the possible detriment of everything else.
Consumer Capitalism and Narcissism
Consumer capitalism encourages the consumption of items that promote a socially valued model. This encourages narcissism9 in the individual as each seeks to tailor their appearance through the consumption of such items. The individual reflexively watches how they ‘measure up’ to the model of a socially valued self and modulates what they consume so that they can be seen as popular, attractive & possessing a good ‘lifestyle’. Anthony Giddens notes,
“Consumption addresses the alienated qualities of modern social life and claims to be their solution: it promises the very things the narcissist desires – attractiveness, beauty and personal popularity – through the consumption of the ‘right’ kinds of goods and services. Hence all of us, in modern social conditions, live as though surrounded by mirrors; in these we search for the appearance of an unblemished, socially valued self.”10
I suggest that looking at the self in a mirror may not be the same as seeking the truth of the Self in reality; after all, a mirror image is only a reflected surface, seen in reverse. This reflection, this appearance, dominates your social ‘value’ in contemporary society. Appearances are marketable, and the more unblemished a product you have the better. Across the many spectrums of life it is a buyers and sellers market, whether it is the body, the underwear or the aftershave. They have what you want; you might have what they want. What price a sale? Maybe it’s all an illusion with mirrors?
(Please see the Eye-Pressure chapter for more information on the gaze).
Anonymous photographer
Fresh, Pure, Cool – It’s milk
Nd
Style Council milk advertisement
in Large Magazine Issue No.8. Melbourne: Large Publications Pty Ltd., 21st March 1997, back cover
Anonymous photographer
Fresh, Pure, Cool – It’s milk
Nd
Style Council milk advertisement
in Large Magazine Issue No.8. Melbourne: Large Publications Pty Ltd., 21st March 1997, pp. 1-2
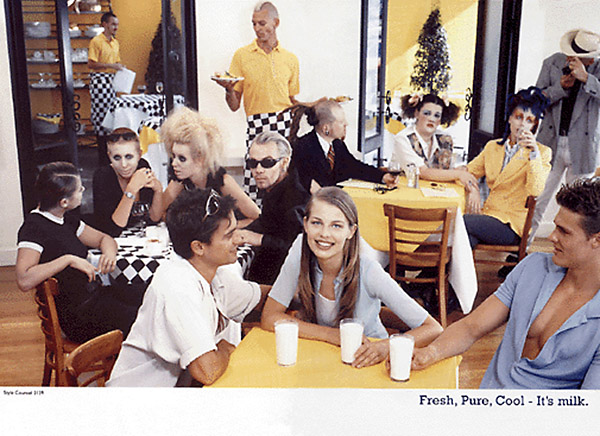
The surface of such an identity construction hides the cost of its production. Seemingly, no effort is required to possess such a socially valuable body and ‘lifestyle’. Advertising promotes these socially valued bodies and lifestyles; this can be seen in the imagery and advertising message of the two milk advertisements. In the above advert the (phallic) glass of milk is linked to the smooth muscular body of the man holding it, who is the only person dressed in white. The milk and the man who is about to drink it are both, by association, fresh, pure, cool. The surrounding crowd is not staring at the milk, they are staring at, and desiring, him. On the left well-heeled matrons eye him with open desire and behind a group of (gay) men, all of a similar smooth, muscular body-type stare with open mouths and obviously lust after his sculptured torso. This tableaux reinforces the message that such a body is fresh, pure and cool, and is seen as a ‘valuable’ status symbol by society. It’s possible that by drinking milk you too can acquire such a possession!.
In the second advert a women and two men are again surrounded by ‘others’, people that could be regarded as freaks, with most of them having strange hair, over the top make-up and wearing dark clothes. They are not ‘normal’. When the advertising agency was casting for this campaign in Melbourne I went along – they wanted the weirdest looking people they could find. In contrast the male model at right reveals his smooth sculptured torso to the desiring gaze of an admiring viewer, much as in the first advertisement above.
This is the desirable body and the desirable ‘lifestyle’ to which we should all aspire!
Visible Bodies
“Visible bodies are caught in webs of communication irrespective of individual intentions and these systems can exert a considerable influence on the behaviour of those involved.”
Tom Burns11
Media advertising makes use of these webs of communication to reinforce it’s system of consumer control. Sometimes advertisers do not openly deploy these lines of communication. In the example below Sheridan sheets has, perhaps subconsciously perhaps deliberately, targeted the gay ‘lifestyle’ demographic without making it too obvious. In the first photograph a beautiful, smooth, tanned young man lies in bed happily smiling at the camera …

Anonymous photographer
‘Sheer Poetry’ by Sheridan
Nd
in Sheridan Australia brochure. Mordialloc: DDI Adworks, 1998, pp. 17-20
On turning the page we find that this image is followed by a double page spread of towels in assorted colours. On the next page we find another gorgeous smooth, tanned young man reclining in bed smiling at the camera. Funny isn’t it that the sheets on both beds are identical, that one boy is photographed from one side of the bed and the other boy from the opposite side. They couldn’t be in the same bed could they, heaven forbid!
Instead of showing the boys in bed together which would not appeal to the wider heterosexual male or female purchaser, the designer of the brochure has cleverly suggested the possibility of homosexuality through the use of visible bodies in a disguised web of communication. The symbolic representation of such photographs (with their implicit language of sexual contact) can be recognised by gay men without the overt nature of homosexuality being thrust in the face of the general public. It took me some time to realise what the designers had done. I wonder how many gay men have consciously realised this association? I think most would only perceive and understand this message projection, this web of communication on a subconscious level. Still this subconscious recognition only serves to reinforce societal values of what is seen as worthy of esteem, what is desirable in a lifestyle, through visible bodies, possessions and in this case, sheets. It is the insidious nature of media advertising that it evens out the bumps of difference, that is, it standardises and shapes levels of diversity, style and taste into what is socially acceptable and desirable.
The advertising media that targets consumers are not the only one’s guilty of promoting a limiting desirability of ‘ideals’ through photographic imagery, the representation of valuable male bodies. Equally to blame are some well known health organisations, both gay and straight, that use ‘the same’ stereotypical muscular mesomorphic bodies to illustrate their health campaigns.

Stephen Paul
Are Men from Mars?
c. 1998
‘Momentum’ Postcard
Bristow and Prentice Response Advertising
Melbourne: Victorian AIDS Council/Gay Mens Health Centre Inc. c. 1998

Stephen Paul
Loves me, Loves me not
c. 1998
‘Momentum’ Postcard
Bristow and Prentice Response Advertising
Melbourne: Victorian AIDS Council/Gay Mens Health Centre Inc. c. 1998

Anonymous photographer
Now I’m immune!
Nd
‘Get Vaccinated’ Postcard
Australian College of Sexual Health Physicians 1997
To be fair, there is an awareness amongst quite a few people at The Victorian AIDS Council / Gay Mens Health Centre in Melbourne, Australia, of the need for the imaging of a broader cross section of body-types in health promotions. Still, this does not stop the images on postcards such as the two above (designed by an advertising company), appearing with regular monotony. The back of “Are Men from Mars?” asks you to discover for your yourself what makes men tick by joining one of the many VAC courses. From the card image it would seem that what makes men tick is a muscular well defined body, clenched hands (symbol of phallic masculinity)12 and beer!
Once introduced to the VAC young gay men may attend the ‘Young and Gay’, ‘Boyant’ or ’18 and under’ courses. In an interview with Jim Sotiropolous13 I asked him about the courses, media advertising and body image commodification:
MAB: OK, so one example I heard about as that you looked at people’s underwear to see whether they were wearing Calvin Klein.
JS: The only thing I can relate that too is that in the first week we use autograph sheets as an icebreaker. A sheet has 6 questions on it and one of these questions is who owns a pair of CK underwear.
MAB: Why is that there? This is interesting to me because of the commodification of the body and consumer culture – if you can’t have the body you can buy the underwear!
JS: Because people talk about it. It is something that we know will get people saying “Well, yeah I do.” So they will sign it. Its no use asking very vague questions and you won’t get a response, so you have to ask very specific questions because we just know they will respond. They know about it. I think it is stronger than a gay focused strategy. You can’t miss the billboards and the advertising.
MAB: So they have been attracted by those images of men and gone out and bought this underwear pre-knowing about the gay community and what’s expected of a gay image?
JS: Yes – the images are very erotic in the CK ads. I was in New York recently and there is a billboard that stretches 2 blocks with the range of CK underwear, its amazing!
MAB: Is this self-reflective narcissism good for how people feel about their own bodies?
JS: No – I think that there a lot of people who know they will never achieve that ideal but I’m not sure …
MAB: … whether that’s a bad thing
JS: Up to a point, yeah.
MAB: I’m not positing it as a totally bad thing.”
I suggest that the very presence of this kind of question (whether it elicits a response or not), still smacks of a certain elitism and the promotion of a particular ‘lifestyle’ as desirable. Calvin Klein models are, after all, the epitome of the clean cut, well groomed, tanned, successful visible male body promoted by an advertising web of communication. This is how bodies unintentionally get caught up in webs of communication which affects the behaviour of all bodies, in this case through the proposition of such a question. This enmeshment causes problems not only for the gay male but also for the heterosexual male; increased levels of body dissatisfaction, eating disorders and steroid abuse have been noted by researchers.14 This may be due in part to the desirability and valued social status of muscular mesomorphic body images such as those used in the Calvin Klein advertisements.
I believe that the search for self-identity through consumption is, in the end, a self defeating exercise. It is like looking into a thousand mirrors at an image of infinite regress never able to find the original image, that essence of inner Self that is ours only in the most insightful of moments. WE are the ones that create the images in the media, the mirror images of how we would like to be. As Lakoff and Scherr have said,
“Who, in the first place, are these faceless hordes? Who is ‘society’ but you and me? And the ‘media’ are not active, it is well known, but reactive; what they discern that their viewers / hearers / readers want, they provide. If we, the viewing public, are not stimulated to buy by the blandishments dangled before us, the media will be instantly responsive – there will be a whole new set of blandishments dangled faster than the eye can blink. So if the same tired messages, the same recycled pictures, pass across our weary retinas year after year, we cannot in all honesty blame the media.”15
We can only blame ourselves.
Gay Male Pornography
“If one were to write the ultimate cliched Australian coming out story, it would be about a boy born in a hick town who has the lithe body of a ballet dancer. Engaged to be married, he instead becomes a flight steward. The scales of heterosexuality drop from his eyes and he moves to Sydney to reinvent himself via the Yellow Brick Road of pumping at the City Gym, over-tanning at Tamarama, pulling beers at the Albury, and joining that bare-chested Roman garrison who shoulder their way across dance party floors. There is only one thing for him left to do: preserve the dream forever by becoming an American (which means the world) video sex icon.”
Peter Jordaan16
Following on from the previous text we might be able to say that we have only ourselves to blame if the media reinforce images of traditional ‘virile’ masculinity in a consumer society. It is we who have created these erotic male fantasy images, images that express our desires, not the media. But it is also true that capitalism and consumerism rely on the sale of product and constantly enlarge and amplify product appeal by advertising, thrusting these fantasy images into our faces until they become an overpowering omnipotent archetype. The male body in the contemporary gay porn industry is a prime example of such an archetype, the (re)enforcement of masculine power in the desirable image of the muscular mesomorphic body. How did this (re)enforcement of masculine power in the body image of gay porn stars come about?

Anonymous photographers
Solo Man
Nd
Super 8mm pornography films advertisement in Super Star Studs No. 2. New York: No publisher, Nd (early 1970s) Back cover
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
During my research at The One Institute in Los Angeles I investigated the type of body images that appeared in the transitional phase from physique magazines of the mid-late 1960s into the early gay pornography magazines of 1969-1970 in America which occurred after the Supreme Court ruling on obscenity. I wanted to find whether there had been a crossover, a continuation of the muscular mesomorphic body image that was a favourite of the physique photographers into the early pornography magazines. From the evidence of the images in the magazines I would have to say that there was a limited crossover of the bigger muscular bodies but most bodies that appeared in the early gay porn mags were of the youthful, smooth, muscular ephebe-type body image.
As can be seen from the images (above) most of the men featured in the early gay pornography magazines and films have bodies that appear to be quite ‘natural’ in their form. Models are mostly young, smooth, quite solid with toned physiques, not as ‘built’ as in the earlier physique magazines but still well put together. Examining the magazines at the One Institute I found that the bodies of older muscular/hairy men were not well represented. Perhaps this was due to the unavailability of the bigger and older bodybuilders to participate in such activity? In the male bodies of the c. early-1970s Super 8 mm pornography films (above) we can observe the desirable image of the smooth youthful ephebe (males between boy and man) being presented for our erotic pleasure.
We can also observe in the bodies of Mark Hammer, Mike Powers and Bob Noll the presence of a bigger more muscular body. These bodies are an early indication of the later development that was to take place in the body images of men in gay pornography – a shift to older more ‘masculine’ bodies, probably as a reaction to the stereotype of the effeminate limp-wristed pansy and also the fear of being seen as a pederast, that is a person who has sex with underage boys.
In the late 1970s another revolution started to take place; towards the end of the decade porn films became more widely available on videocassette. This made porn much more accessible to the gay consumer and allowed the expansion of the gay pornography industry. Instead of having to buy Super 8 movies and use home projectors that took an age to set up gay men could now have their ‘hit’ of pornography in a quick, convenient package.

Anonymous photographer
Perfect Room Service
c. 1976
Homo Action 14 Color-Climax Corporation
Copenhagen: Peter Theander, 1976
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
Not all male bodies (especially those that appeared in the early European pornography films and magazines), conformed to the ‘ideal’ of the hairless muscular ephebe, as can be seen in this magazine ‘still’ photograph taken from a Danish Super 8 mm gay pornography film. Curiously the magazine is printed in Australia.
Early gay male pornographic films have a distinctly ‘underground’ flavour but some managed to capture the frenzied passion that drives such erotic encounters where the people really want to have sex with each other. In the early 1980s the amateurism of the early films was replaced by the professionalism (and money making power) of such directors as Steve Scott, Matt Sterling, John Travis and William Higgins who still managed to capture this sexual frenzy. Gone are the really youthful body types of the earlier magazines and films – smooth, white, older muscular bodies now dominate.
William Higgins is one of my favourite directors for his unique shooting style. He makes use of oblique angles, incredible distorted close-ups of blood engorged penises (Sailor in the Wild, 1983), slow motion repeats of cum shots from many angles, and jump cuts from one carnal scene to another without a break (Class Reunion, 1982). This surreal celluloid confusion adds to the mystery and excitement of the scenes and the participants really seem to enjoy their sex; they wince as the cock goes up their arse and there is a certain ‘reality’ about the whole sex thing.
Even in these early 1980s films the star has numerous sexual partners and fucks his way through the whole video having multiple ejaculations within the space of a few minutes running time. At the drop of a hat muscular men drop their pants and their loads all over the place and some of the scenes are really horny!
As with any pornography though, you have to trawl through heaps of dross before you find the gems that get you going. Multiple orgasms by the stars of pornographic videos help reinforce compulsive sexual behaviour17 that is learnt by gay men to be a societal performance ‘norm’.18 Withdrawing before cumming enabled the director to capture the ‘money shot’ (ejaculation) for the viewer; gay male sex on video became not a passionate intimate union between two men but a performance, a display of shooting skills (both physical and pictorial) which presents the body to best advantage. Later in his career William Higgins also pioneered the shaved bum which epitomises the pumped up, perfectly groomed young white male available for plumbing lessons.

Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
Cover image from The Devil and Danny Webster pornography video
Champions Video of Australia catalogue Issue 31. Canberra: No publisher, 1997, p. 12
“Unable to compete with the ‘sun-bronzed gym gods’, Danny spends his nights alone watching old movies – hoping for a miracle … “

Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
in Take it All! They Ate the Whole Thing! Vol. 1 No. 1. American: No place or publisher, Nd
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
Rare image of thin bodies in gay male pornography.
Gay men wanted to be seen as virile ‘real’ men in reaction to the stereotype of the effeminate pansy. This emphasis on the possession and display of a muscular body became even more prevalent in pornography with the onset of the HIV / AIDS crisis in the mid-1980s.
Driven by the fear of disease and the anxiety, insecurity and dis-ease of being thin and being seen as possibly infected gay men started going to the gym and ‘pumping’ up in ever increasing numbers. A big, healthy, muscular body couldn’t possibly be infected with the virus! Body hair was out as it was a sign of experience and maturity and therefore of disease according to Michelangelo Signorile.19
Healthiness was in. Gay men with thin bodies (such as those above) or bodies like that of Danny Webster (above), hoped for a miracle otherwise they would be left on the shelf, never having any sex! Either that or they went to the gym and capitulated to the emerging stereotype. There was apparently no hope if you didn’t ‘fit’ the ideal. But this is not the real world, this is a fantasy! Many gay men gave in to this fantasy becoming ‘simulations’, carbon copies if you like, of their porn star heroes. Lots take illegal steroids to get close to their ‘ideal’.
Other gay men have carried on as they have always done; living their lives as positively as they can; incorporating their sexuality as part of their identity; coping with feelings of inadequacy that such bodily facades can generate. Perhaps if these bodies were seen as ‘unnatural’ gay men would get over some of their attraction towards them. Perhaps if they accepted them as an artifice, a deception; that the material (steroid abuse20 and possible HIV virus contraction to name two) and psychological (high / low self-esteem leading to depression and anxiety) cost of their production is hidden behind the rose coloured lens of the camera or the surface of the body, then their erotic power would be lessened. I suggest that gay men DO realise that these images are fantasies but still strive to attain the fantasy in themselves and in the bodies of their partners.

Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
Image from The Big Thrill pornography video Nd
Cover of Champions Video of Australia catalogue Issue 46, 1998
“… when a dozen handsome young college guys arrive at the Kingsley Institute, the first thing they do is have a big pillow-fight, get incredibly horny, take their clothes off and have an all-in jerk off. After that, things get increasingly out of hand. All the young men are exceedingly cute and built like young gods, so they can link up in any combination they care to and make a very handsome couple. And they do care to. The viewer soon loses track of who’s doing what with who, or indeed of who is who, but it doesn’t really matter. These boys fit together like parts of a well-lubricated machine. They appear to have been selected for something more than their writing skills, then waxed and polished till they glow.” (My italics)
~ Rod Pounder21
In the above quotation we can see how the bodies in contemporary male pornography have become interchangeable, replaceable one with another. The image above is also a good example of the phenomenon of the homogenised body stamped out of the same mould. I believe that in contemporary gay male erotica it is not so much the sex that matters but the display of the body for admiration. There is a certain stiffness (pardon the pun) of performance now. The frenzied passion of sex has gone replaced by the surface, the positioning of the body for the benefit of the camera. It’s all to a formula. Big pricks have become even more important and stars have their dicks cast in rubber so the viewer at home can purchase and enjoy the satisfaction of taking their heroes prick (or a ‘simulation’ of it) up his own arse whilst watching the video at the same time.
Gay pornography depicts gay sex as ‘manly’ because gay men want to see themselves that way even though one man is fucking another man, supposedly queering ‘normal’ heterosexual masculinity. I believe this is not gay men ironically challenging traditional masculinity but the confirmation it’s power over them. As noted earlier, the body becomes a phallus – hard as granite and as tough as steel – signifying and embodying a mythological power. These bodies are built ‘tough’ despite the fact that you could probably drive a semi-trailer up their rear end and they probably wouldn’t feel a thing! Now, in contemporary male pornography, the range of body types is much narrower. Of course there are still specialist videos catering to the leather subculture, shaving fetishists, young men fantasies (mainly videos from Germany), wrestling, hairy men, toys, black men, etc., … but these form a small specialist minority group of the video market. In the main the videos that fill the Champions catalogue, for example, feature models that are constructed of smooth, prime white beef.

John Travis
Untitled
Nd
Cover image from Billy 2000: Billy Goes to Hollywood pornography video
Studio 2000, 1999
Recently I watched a video called Billy 2000: Billy Goes to Hollywood, directed by John Travis. The video features 4 couples and one solo performance. The story, as far as it goes, is that gay men go into a shop and sees the Billy doll (discussed earlier) and starts fantasising about meeting a man who looks exactly like the doll, including having his large ‘anatomically correct penis’. Low and behold we fade out into dream sex scenes between different men and different versions of the doll which has now come to life, wearing exactly the same clothes as the doll does. What follows are, I think, four of the most boring gay sex scenes I have ever seen. There is no passion in the sex and all four couples copy exactly (deliberately?) the same positions by rote: man sucks dolls dick, man sits on dolls dick, man gets fucked from behind by dolls dick, doll ejaculates all over mans back. This is formulaic sex. As we can see in the above image the muscular male body is now simulating the ‘ideal’ embodied in a doll! Great marketing ploy to link the sale of the doll and the video together…
As Peter Jordaan has observed,
“There is a desperate need for more gay romance. A video like 1992’s Matt Sterling effort ‘Scorcher’ stands out simply because one of the couples in it actually look with pleasure into each other’s eyes while they are fucking … dick-tugging videos which also tug at the heart remain rare delights indeed.”22
I most certainly agree.
Alternatives to American gay male pornography
As an alternative to American videos three names stand out in the pantheon of porn directors. The first is Kristen Bjorn was has made a reputation for himself and his videos by photographing men from all over the world in apparently natural, spontaneous sexual situations. His videos feature large casts of men from different ethnic backgrounds but all his actors are power- fully built, masculine men. The second is Jean-Paul Cadinot. His videos, usually set in reform schools, school dormitories, scout troops and army barracks feature young ephebes having their way with each other with a lusty abandon not usually present in American videos. Lastly there is George Duroy, pioneer of EuroAmerican videos such as Accidental Lovers (1993) and Sauna Paradiso (1994) that have been shot (using American money) in Eastern Europe after the fall of the Iron Curtain using East European men.
His videos include a combination of athletic, young performers who are all smooth; from the slim and toned ephebe to the more muscular built lad. And well built they are. The images below are a good examples of both body types. The boys, for they are not men in the American sense of the porn video word, really do seem to enjoy having sex and ‘making it’ with each other in a loving and intimate way. Which is great!

George Duroy
Untitled
Nd
Image from Sauna Paradiso pornography video
Falcon International Collection 1994
in Douglas, Jerry (ed.,). Manshots: The Firsthand Video Guide Vol. 7 No. 2. Teaneck, N.J.: FirstHand Ltd., December, 1994, p. 46.
Milan Demko, Victor Gravek, Pavol Zurek and Thomas Novak compare stiff dicks

Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
Image from Lucky Lukas pornography video
Blue Diamond Video Services advertisement in ‘Meetmarket’ section in Outrage Magazine No. 189. Melbourne: Bluestone Press, February 1999, p. 1
Dean Durber, in an article for Blue Magazine called “New Wood” observes,
“Even if the innocence of much cuter and younger faces is forced off the shelves, the recent interest in intimacy and tenderness cannot be ignored. We might yet see older men on screen who actually appear to enjoy what they do. Especially if there’s money to be made and pleasure to be had.”
Why forced off the shelves? Apparently because of concerns over pederasty (love of young boys) and the perceived age of the ephebes involved. But here’s the rub – it’s all in the name of money in the end. It’s all about selling product even if you do have a good time. The fantasy scenarios are just that – idealised fantasies. They are set up to sell product and use body image to do so. These EuroAmerican videos just use the fresh new faces and bodies of muscular young men to appeal to a different market demographic.
Let me comment on just one more thing that happens in a lot of porn videos. I have noticed that it is usually the bigger guy (either dick or body size) that fucks the smaller guy therefore marking him as the man – no matter who is making the video. Commenting, unwittingly, on this disparity in body size Stan Ward in his review of Sauna Paradiso says that when the boys in the above photograph have a fourway, “Soon enough the boys are separated from the men. Novak and Demko continue the oral action while Gravec gives Zurek a royal screw up the arse … For the money shots, the boys and men come together …”23
Does that mean that if you have a smaller body that you are not a man? Does it mean that to be a gay man you have to partake in anal sex? It would seem that a big cock or its substitute, a big body, will always classify you as a man and not a boy and to participate in anal sex will make you a man not a boy. But whether its boys or men, gay pornography is there for one major reason – to make money within a media driven, image conscious consumer society.
Alternative bodies
There are, however, one group of photographs that have appeared in some porn mags that do not represent the ideal of the perfect muscular mesomorph or the smooth, young ephebe. These are photographs that accompany the messages of ordinary gay men wanting to meet other men for sex and companionship. These are the images of themselves they want to show to the general public. How they perceive themselves. How they are posed reveals small contexts of identity, even though their actual identity is hidden because of the masking of the face (No. 3 is ingenious in this regard; it uses the flash of the camera in the mirror to obliterate the facial features). The backgrounds and attire (when present) can tell a lot about a person.
(left to right)
Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
in ‘Get In Touch’ section in Gay No. 104. Enmore: No publisher, 1984, p. 48.
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
in ‘Get In Touch’ section in Gay No.100. Enmore: No publisher, 1984, p. 46.
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
in ‘Get In Touch’ section in Gay No.121. Enmore: No publisher, 1985, p. 48.
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
in ‘Get In Touch’ section in Gay No. 101. Enmore: No publisher, 1984, p. 47.
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
Anonymous photographer
Untitled
Nd
in ‘Get In Touch’ section in Gay No. 118. Enmore: No publisher, 1985, p. 47.
Courtesy: Marcus Bunyan
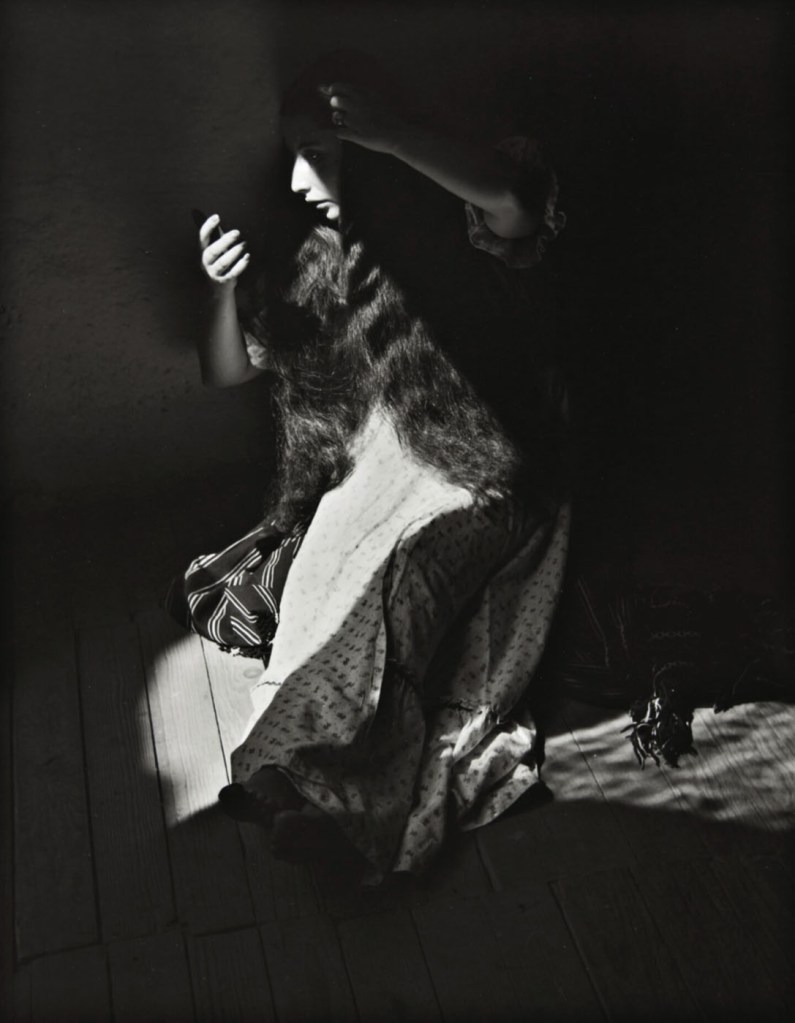
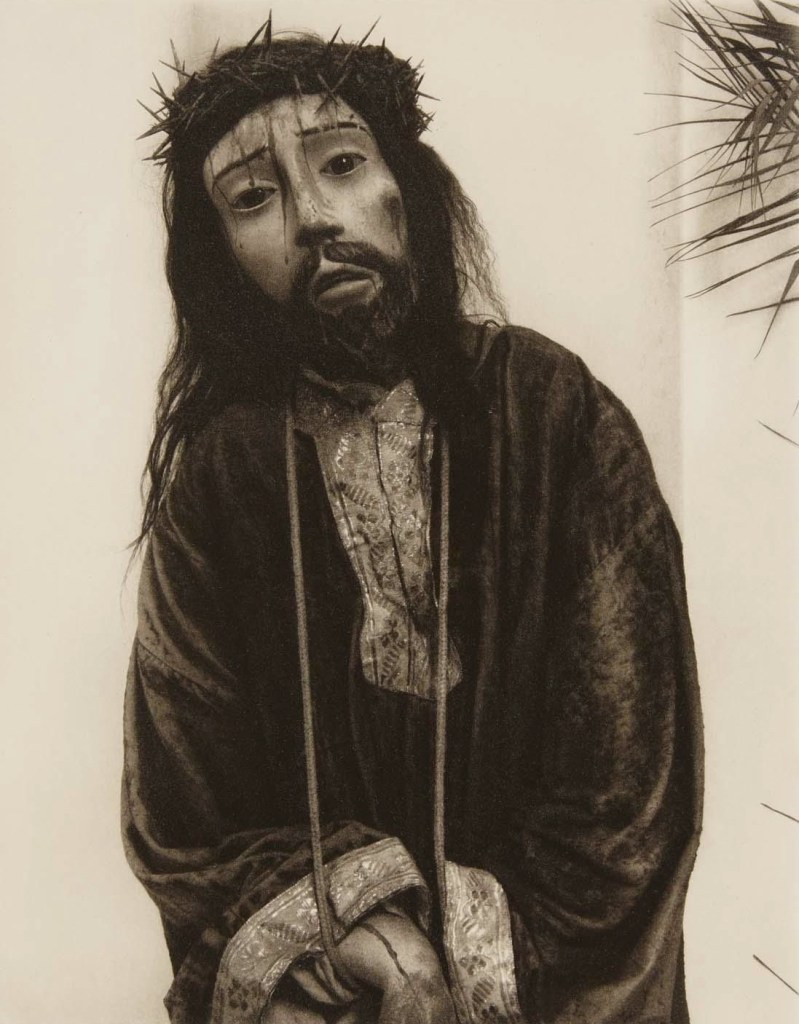
Numbers 1 and 3 remind me of the photographs of Diane Arbus, shot in that person’s lounge room and bedroom respectively (see the photograph at the beginning of the chapter and below). In the background of No.3 we can see an ironing board, a wooden bed head and the bed itself. In the foreground we can see a full cup of tea or coffee sitting on the dressing table to which the mirror is attached.
No.’s 2, 4, and 5 feature men who are obviously into leather, cock rings, boots and whips; a poster of a man stares over the shoulder of the figure in No. 2 adding to the menacing air – I’m watching you! Note in all the images the bodies are of an everyday, ‘natural’ type. Types that we can see down the beach or at the sauna that are not toned and tanned but older, plumper, taller or skinnier, and for this reason they have an attractiveness which is solely their own.
These bodies have been lived in, they have earnt every wrinkle and crease, have survived their life experiences and are still sexually valuable in their own individuality and difference. These bodies are not fantasy material in the ‘normal’ understanding of what a contemporary male fantasy body should look like. This is because in the buyers and sellers market of contemporary gay society big, buff, and beautiful is the perfect dish of the last two decades and will continue to be so as long as gay men continue to desire this ‘ideal’.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
2001
Bodies are unstable … and how frightening, that can be, and how those two emotions comprise desire.”
Jesse Dorris. “Jimmy DeSana’s Transgressive Vision of Life and Desire,” on the Aperture website December 14, 2022 [Online] Cited 19/12/2022

Diane Arbus (American, 1923-1971)
A naked man being a woman, N.Y.C.
1968
Gelatin silver print
Footnotes
1/ Kellner, D. “Critical Theory, Commodities and the Consumer Society,” in Theory, Culture and Society 1, 3: 1983, p. 66, quoted in Evans, David. Sexual Citizenship: The Material Construction of Sexualities. London: Routledge, 1993, p. 48.
2/ Altman, Denis. The Homosexualisation of America. Boston: Beacon Press, 1982, p. 211, quoted in Chapkis, Wendy. Beauty Secrets: Women and the Politics of Appearance. Boston: South End Press, 1986, p. 136.
3/ This is not a new concept and the lament that the gay body is used as a commodity and marketable sexual tool and not exclusively joined in affection and love has been around since well before Stonewall within the gay community. Of course sex and love are NOT mutually exclusive but some people seem to think that they are:
“Not too many years ago it was unheard of to dress in a “gay” manner or to act in any way which might lead others to suspect that you were a homosexual. Now, almost overnight, we have “gay” bars “gay” dance clubs, “gay” books, even business firms openly soliciting the business of homosexuals.
While this is good in the sense that it gives the homosexual a right to live like the rest of humanity, it has led to problems which were heard of in the past. Perhaps a slave needs his chains let loose slowly if he worn them for many years. Perhaps the “gay” world was not ready for this freedom or maybe it came to quickly. However, the homosexual now finds himself in a position where his “public image” is not that it should be. The blame for this lies mainly with those who flaunt their homosexuality in the faces of the general public.
A homosexual, as defined by most medical authorities, is one who seeks love and sexual satisfaction from his or her own sex. The majority of today’s homosexuals (or so it seems to the general public) could best be described as persons who look for as much sexual satisfaction from as many of their own sex as they can, without giving their love to any of them. This has come about because of the so-called “emancipation” mentioned previously. A homosexual can gratify his passions so easily now that the finer things in life seem to be cast aside …
Inside the “gay” bars, the tourist or outsider can walk in, and with no effort, behold the spectacle of people openly trying to make a one-night stand with each other. Outside the bar, the same tourist or outsider can hear those who failed in their mission inside the bar bargaining with someone on the street for the use of his body for the night … This is the image today’s homosexual is giving to the general public …
Why not get back to caring for one another? Hurt each other if you have to – you can start over again and learn from your mistake. Stop chalking up your conquests as if sex were a commodity.
Why not see how long you can stay with one person? Put love back into homosexual life.
Stop poking fun at the person who seeks love and friendship instead of one-night stands.
Let the love that is locked away and going to waste inside yourself be let loose and given to someone who will return it with interest. Don’t be afraid of your emotions. Get back to making the “gay” life what it should be – two people living together who need love of their own kind.”
Lady Beesborough. “The Public is Watching,” in The Greyhuff Review. 1st Edition. Minneapolis, Minn: Directory Services Inc., 1965, pp. 24-25. Sourced at The Kinsey Institute, University of Indiana, USA.
Even at this date (1965, which is pre-Stonewall), some people obviously saw gay male sex (and inherently the gay male body) as being a promiscuous commodity, which is quite amazing because nothing much has changed today. It is still a sellers market and gay men still go for it! The advice not to be afraid of your emotions is a good one – but that will naturally open gay men up to experiences, including many sexual interactions and not just love! As I comment elsewhere in the Re-Pressentation chapter, gay men are paradoxically both seeking sexual release and intimate connection whilst at the same time being afraid of that connection and revealing themselves to others.
4/ Swift, Michael. “Darkside,” in Blue Magazine. Sydney: Studio Magazines, April 1997, p. 106.
5/ Parry, Tracey. “Access All Areas,” in Blue Magazine. Sydney: Studio Magazines, February 1999, p. 66.
6/ Massengill, Reed. “Sand Man,” in Blue Magazine. Sydney: Studio Magazines, February 1999, p. 90.
7/ “Lifestyle refers to a relatively integrated set of practices chosen by an individual in order to give material form to a particular narrative of self-identity. The more tradition loses its ability to provide people with a secure and stable sense of self, the more individuals have to negotiate lifestyle choices, and attach importance to these choices.”
Schilling, Chris. The Body and Social Theory. London: Sage Publications, 1993, pp. 181-183. See also Giddens, A. Modernity and Self-Identity. Cambridge: Polity Press, 1991, p. 2, 5, pp. 80-81.
8/ Schilling, Chris. The Body and Social Theory. London: Sage Publications, 1993, p. 143. See also Featherstone, Mike. “Perspectives on Consumer Culture,” in Sociology 24(1). 1990, pp. 5-22.
9/ Below are four quotations about the definition and effects of narcissism.
“Notwithstanding his occasional illusions of omnipotence, the narcissist depends on others to validate his self-esteem. He cannot live without an admiring audience. His apparent freedom from family ties and institutional constraints [especially gay men] does not free him to stand alone or to glory in his individuality. On the contrary, it contributes to his insecurity, which he can overcome only by seeing his “grandiose self” reflected in the attentions of others, or by attaching himself to those who radiate celebrity, power and charisma. For the narcissist the world is a mirror…” (My italics)
Lasch, Christopher. The Culture of Narcissism. New York: W.W. Norton and Company, 1978, p. 10.
“Central to the narcissistic personality is an orientation to the body as youthful, enduring and constitutive of the self. The narcissistic body is open to new experiences, but only as long as they can be easily appropriated and consumed to reinforce its own sense of self as sacred and immortal.” (My italics)
Schilling, Chris. The Body and Social Theory. London: Sage Publications, 1993, p. 194.
“Narcissism presumes a constant search for self-identity, but this is a search that remains frustrated, because the restless pursuit of ‘who I am’ is an expression of narcissistic absorption rather than a realisable quest … Narcissism treats the body as an object of sensual gratification, rather than relating sensuality to communication with others.”
Giddens, Anthony. Modernity and Self-Identity: Self and Society in the Late Modern Age. California: Stanford University Press, 1991, p. 170.
“According to what I said about the nature of love, the main condition for the achievement of love is the overcoming of one’s narcissism. The narcissistic orientation is one which one experiences as real only that which exists within oneself, while the phenomena in the outside world have no reality in themselves, but are experienced only from the viewpoint of their being useful or dangerous to one. The opposite pole to narcissism is objectivity; it is the faculty to see people and things as they are, objectively, and to be able to separate this objective picture from a picture which is formed by one’s desires and fears.”
Fromm, Erich. The Art of Loving. London: Allen and Unwin, 1957, p. 118.
10/ Giddens, Anthony. Modernity and Self-Identity: Self and Society in the Late Modern Age. California: Stanford University Press, 1991, p. 172.
11/ Burns, Tom. Erving Goffman. London: Routledge, 1992, p. 38, quoted in Schilling, Chris. The Body and Social Theory. London: Sage Publications, 1993, p. 85.
12/ “The penis can never live up to the mystique implied by the phallus. Hence the excessive, even hysterical quality of so much male imagery. The clenched fists, the bulging muscles, the hardened jaws, the proliferation of phallic symbols – they are all straining after what can hardly ever be achieved, the embodiment of the phallic physique.” (My italics)
Dyer, R. Only Entertainment. London: Routledge, 1992, p. 116, quoted in Stratton, Jon. The Desirable Body. Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1996, p. 195.
13/ Interview with Jim Sotiropolous, Melbourne. 23/09/1997. Co-ordinator of 3 different programmes at The Victorian AIDS Council / Gay Mens Health Centre, Melbourne, Victoria.
14/ For a discussion of these issues please see Mishkind, Marc, Rodin, Linda, Silberstein, Lisa and Striegel-Moore, Ruth. “The Embodiment of Masculinity: Cultural, Psychological and Behavioural Dimensions,” in Kimmel, M. (ed.,). Changing Men: New Directions in Research on Men and Masculinity. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications, 1987, pp. 37-47. An extract from this paper can be found in Appendix A of the Bench Press chapter.
15/ Lakoff, Robin and Scherr, Raquel. Face Value: The Politics of Beauty. Boston: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1984, pp. 292-293.
16/ Jordaan, Peter. “The Naked VCR,” in Outrage Magazine No. 131. Melbourne: Bluestone Media, 1994, p. 45.
17/ “Some people are so horny and desperate to have a connection that they will do anything to have sex, especially with someone who they find attractive. Sometimes sexually they even step over the line of physical attraction … and this can indicate compulsive sexual behaviour. I’M SO HORNY I JUST HAVE TO HAVE SEX!”
Interview with Greg Adkins. Melbourne. 02/10/1997. Outreach Beats Education Officer at The Victorian AIDS Council / Gay Mens Health Centre, Melbourne, Victoria.
18/ “We find it more important to preserve and foster the myth of sexuality as mechanical process than we do to develop any kind of detailed or sensitive phenomenology of sexual experience (ie., establishing how in fact people experience their sexual needs and feelings). I suspect that a vast proportion of people live in secret unhappiness about their sexuality because they are unable to meet what are in truth entirely mythical ‘norms’ of ‘performance’.”
Smail, David. Illusion and Reality: The Meaning of Anxiety. London: J.M. Dent & Sons, 1984, p. 113.
19/ Signorile, Michelangelo. Life Outside: The Signorile Report on Gay Men: Sex, Drugs, Muscles, and the Passages of Life. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 1997, p. 68.
20/ “Big Ears has heard of at least two cases of ‘roid rage in Sydney this week as the countdown to Mardi Gras and bodily perfection reaches its climax. One Big Ears associate minding his own business in a well known Oxford St. venue this week was set upon by an incredible hulk wielding a broken bottle after he tried to help up the hulk’s substance affected, brick shit-house of a friend who had toppled over and landed on top of him, all but crushing him to death. Meanwhile, in an inner Sydney gym, another Big Ears associate witnessed a similar savage and unprovoked attack this week. Enraged that someone was using a machine he wanted to use, brick shit-house #3 dragged off the poor girl in question, threw her against the wall and all but choked her until gym staff managed to pull him off. Hello? Mardi Gras is supposed to be a party not a battle to the death. Gone, it seems, are the days when all you needed to get yourself through an all night party were a jazzy pair of shorts and a bubbly personality…”
Big Ears. Melbourne Star Observer. Melbourne: Bluestone Media, 26th February, 1999, p. 15.
21/ Rod Pounder. “Video Review: One Hot Summer,” in Brother Sister Magazine. Melbourne, 9th May, 1997, p. 29.
22/ Jordaan, Peter. “The Naked VCR,” in Outrage Magazine No. 131. Melbourne: Bluestone Media, 1994, p. 50.
23/ Ward, Stan. “‘Sauna Paradiso’ review,” in Douglas, Jerry (ed.,). Manshots: The Firsthand Video Guide Vol. 7 No. 2. Teaneck, N.J.: FirstHand Ltd., December 1994, p. 46.


































































































![Installation view of the exhibition 'Documentary Genealogies: Photography 1848-1917' at the Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid showing at left rear, pages from Carl Dammann's '[Races of Mankind]: Ethnological Photographic Gallery of the Various Races of Men' 1876 Installation view of the exhibition 'Documentary Genealogies: Photography 1848-1917' at the Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid showing at left rear, pages from Carl Dammann's '[Races of Mankind]: Ethnological Photographic Gallery of the Various Races of Men' 1876](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/documentary-genealogies-installation-d.jpg)
































































































![Chris Killip (British, 1946-2020) 'Untitled? [Shipbuilding on Tyneside]' 1975-1977 Chris Killip (British, 1946-2020) 'Untitled? [Shipbuilding on Tyneside]' 1975-1977](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/killip-shipbuilding-on-tyneside.jpg?w=910)











































































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.