Exhibition dates: 4th October 2019 – 19th January 2020
Visited October 2019 posted January 2020
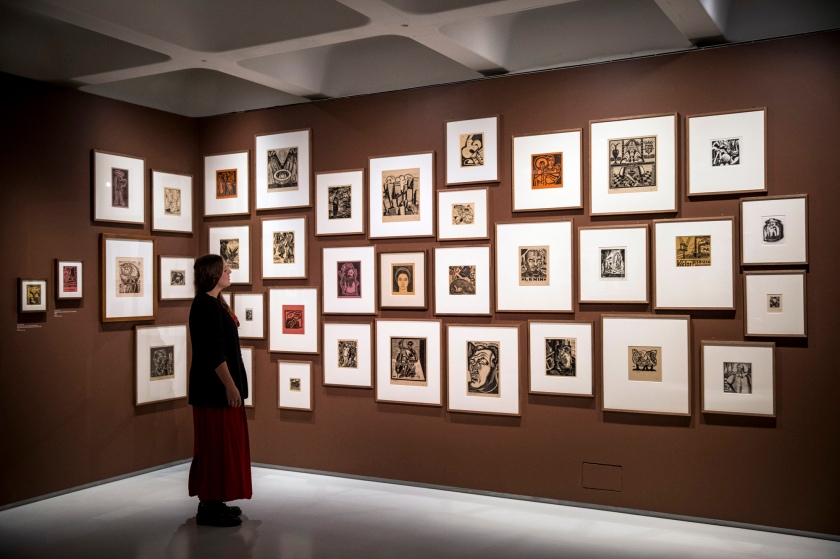
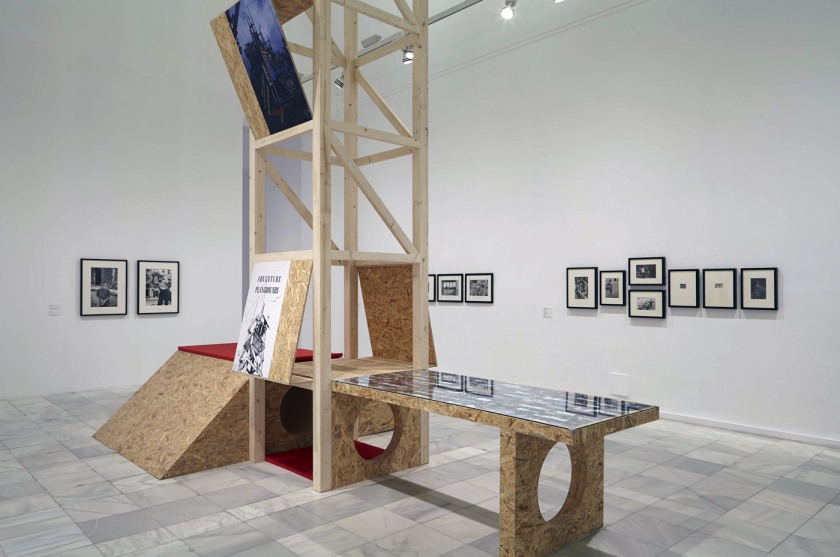
Installation view of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery, London
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
I saw this exhibition in London in October, my last on my European research trip.
Having been a clubber since 1975, I was fascinated to see the history of cabarets and clubs in modern art. I remember going to gay clubs such as Scandals in Soho in the 1970s with their Saturday Night Fever lit up glass dance floor – except this one had a revolving glass turntable at its centre; or Adams under the the Leicester Square Odeon (I think it was the Odeon?) with walls padded and buttoned in red velvet, where they played the latest funk and international disco. Sylvester was the first out and out gay disco star, still beloved, who was taken from us by AIDS. And then there was Heaven, at the time of its opening in December 1979 the biggest gay club in Europe, housed in the arches beneath Charing Cross railway station – the site of many a debauched evening of gay disco, then hi-energy, and sex. We could dance for hours on that huge dance floor, under the lasers and neons, only leaving to get water at the bar, just dancing on pure energy, and then cruise the famous tunnels and bars of the club. Fabulous.
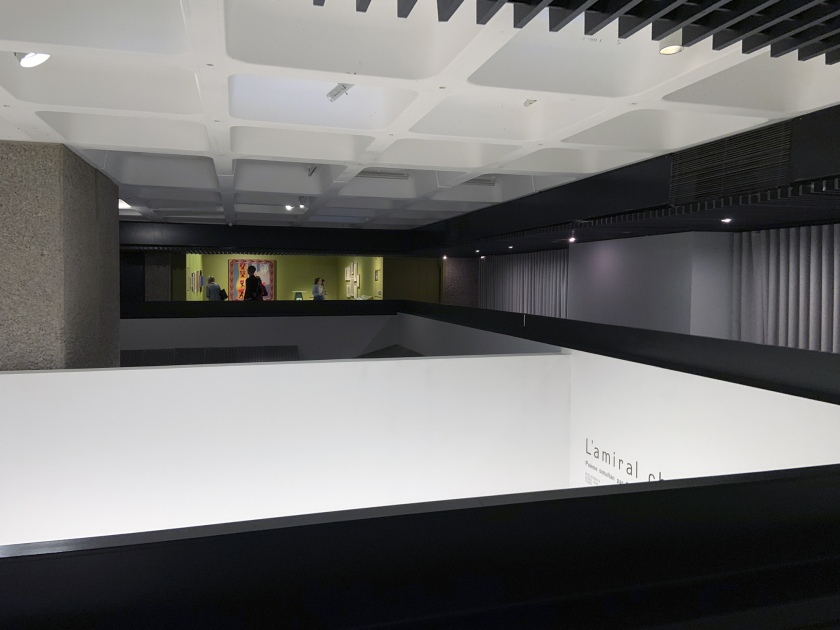
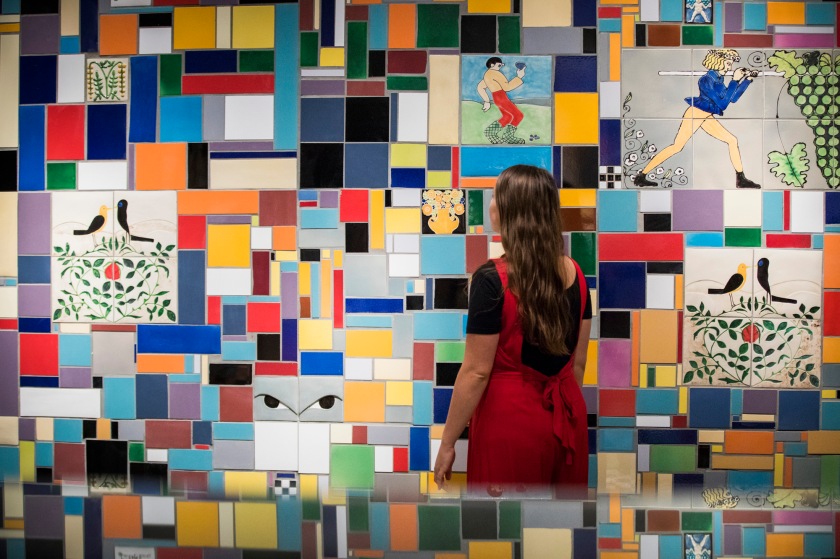
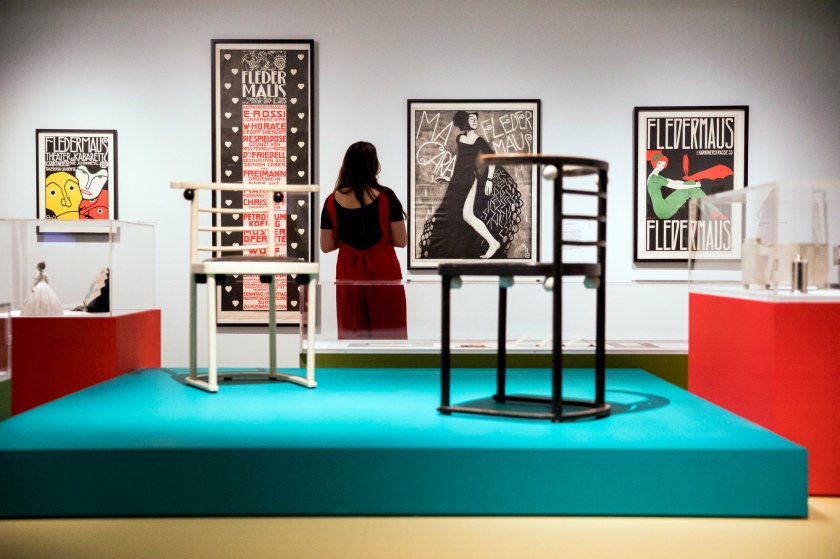
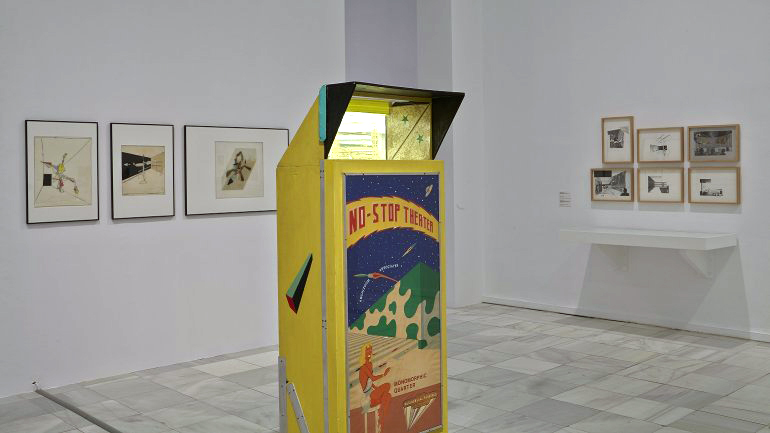
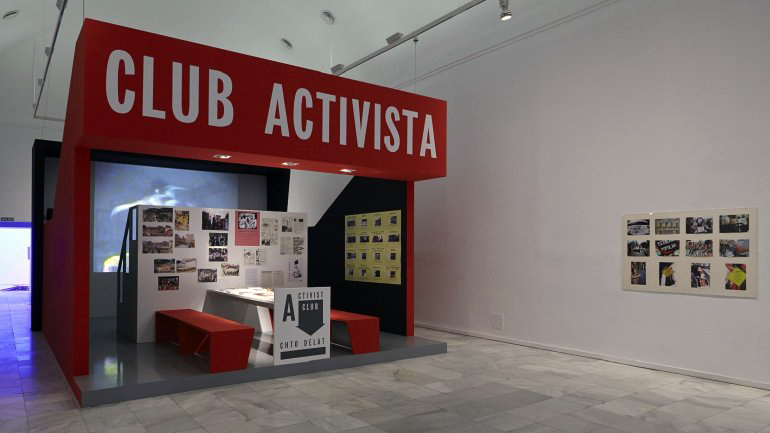
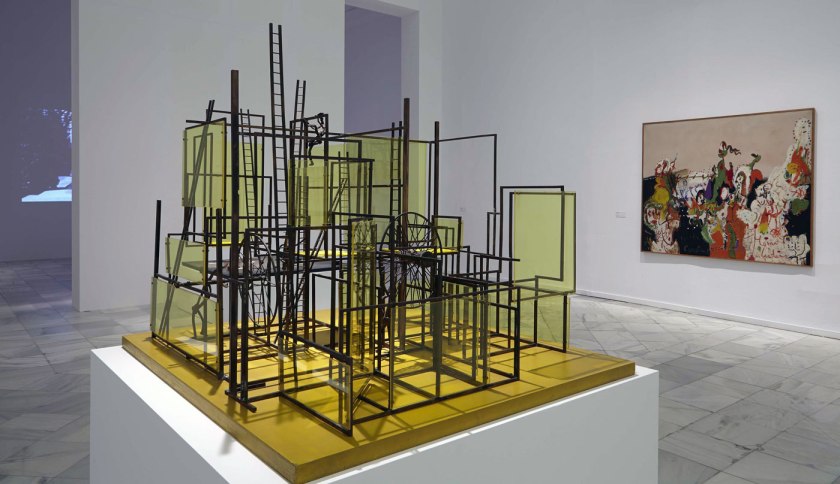
Getting back to the exhibition, Into the Night was a tale of two halves, as can be seen in the installation photographs. The upper level gallery at the Barbican was stirring, intoxicating, mesmerising, especially the sections on Vienna and the Cabaret Fledermaus (see below) and Berlin and the Weimar Nightlife 1920s-1930s, always a favourite avant-garde era of mine (see part 2 of the posting). The lower level featured 3 separate rooms, recreations of the bar at the Cabaret Fledermaus; the Ciné-Dancing space of L’Aubette; and the shadow theatre of Chat Noir: interesting to see as a walk through but nothing more – then followed by some sparse sections on London’s Cave of the Golden Calf, Harlem’s Jazz Clubs and Cabarets and Tehran’s Rasht 29 (Part 2 of the posting). It felt to me as though the curators ran out of money / time? objects? and curatorial inspiration for the last sections of the exhibition.
Whatever the case, looking at the exhibition as a whole, this was a fascinating insight into cabaret and club art, architecture and design with gems such as Jeanne Mammen’s glorious watercolour paintings on queer female desire and Lohse-Watchler’s dark scenes of Hamburg nightlife. The complex breadth of bohemian and artistic culture covered in the exhibition was truly breathtaking.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Barbican Art Gallery for allowing me to publish the media photographs in the posting. All installation images are iPhone images by Dr Marcus Bunyan. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Catalogue cover for Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery, London
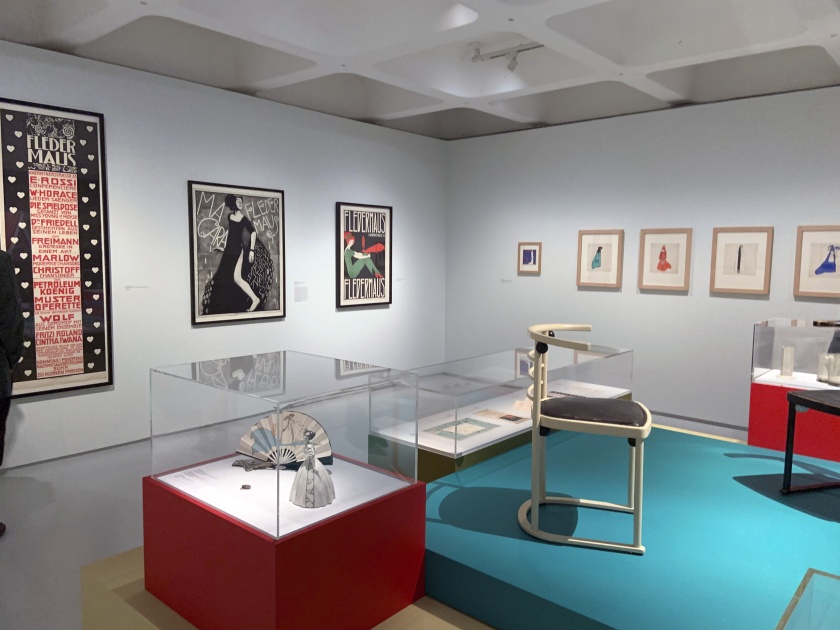
Vienna: Cabaret Fledermaus 1907-1913 wall text
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
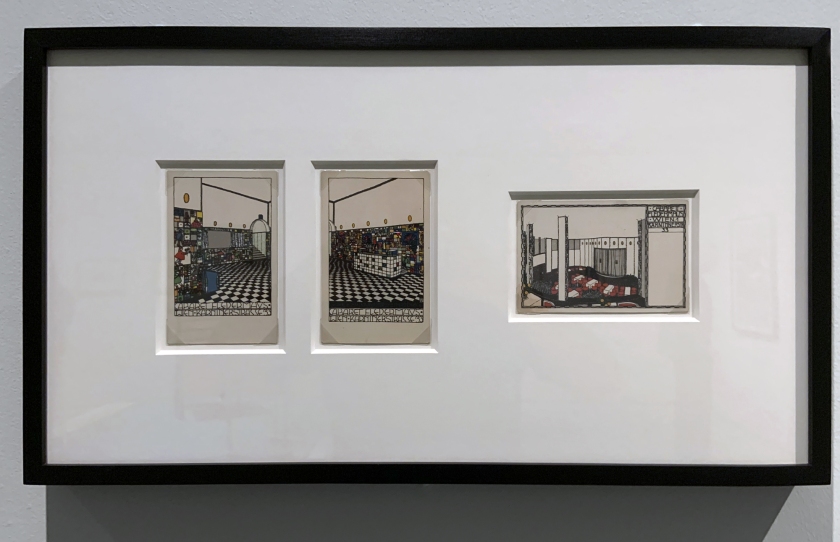
Josef Hoffmann (Austrian, 1870-1956)
Weiner Werkstätte Postkarte (left to right) (installation views)
No. 74 (Interior view of the bar at the Cabaret Fledermaus);
No. 75 (Interior view of the bar at the Cabaret Fledermaus);
No. 67 (Interior view of the auditorium with stage at the Cabaret Fledermaus)
1907
Lithograph postcards
Collection of Leonard A. Lauder
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Wall text about the Weiner Werkstätte postcards
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Josef Hoffmann (Austrian, 1870-1956)
Wiener Werkstätte Postkarte No. 74 (Interior view of the bar at the Cabaret Fledermaus)
1907
Collection of Leonard A. Lauder
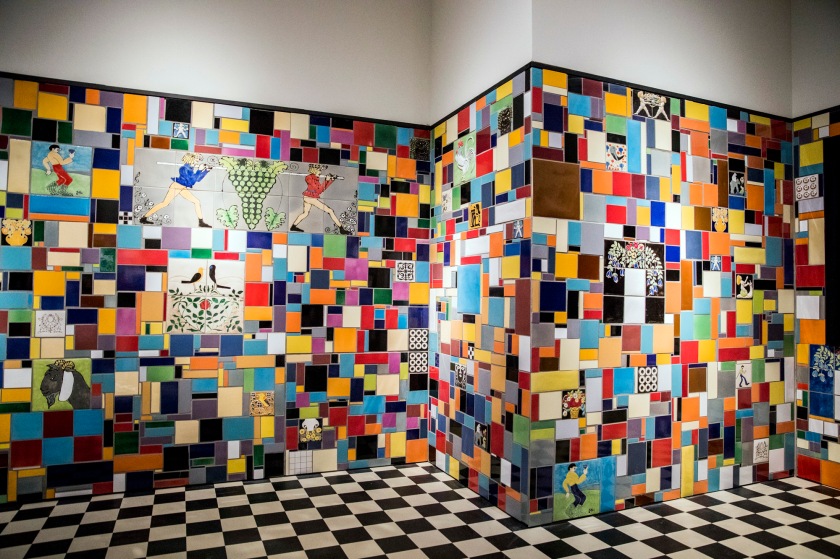
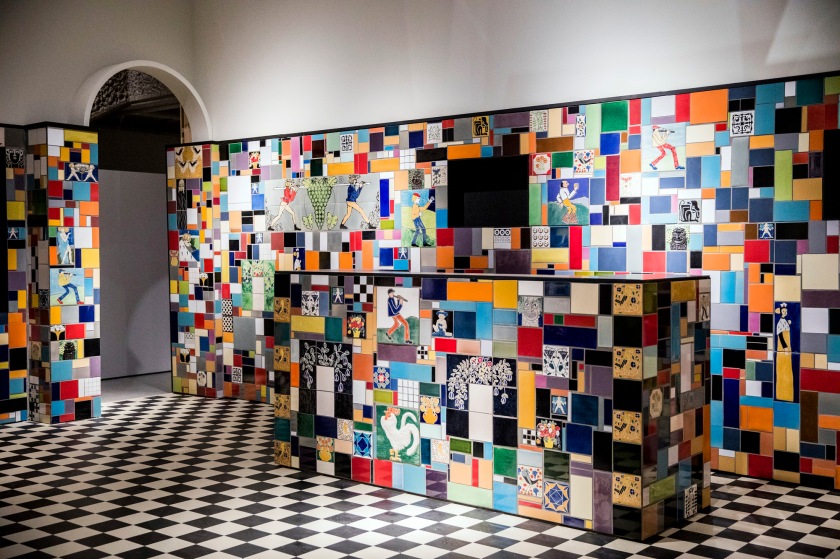
Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art (downstairs gallery, room recreation)
Installation view Barbican Art Gallery 4 October 2019 – 19 January 2020
Recreation of the bar at the Cabaret Fledermaus, originally designed by Josef Hoffmann (1907), 2019
Conceived by the Barbican Art Gallery and Caruso St John, in collaboration with the University of Applied Arts, Vienna
© Tristan Fewings / Getty Images
Downstairs gallery, room recreation
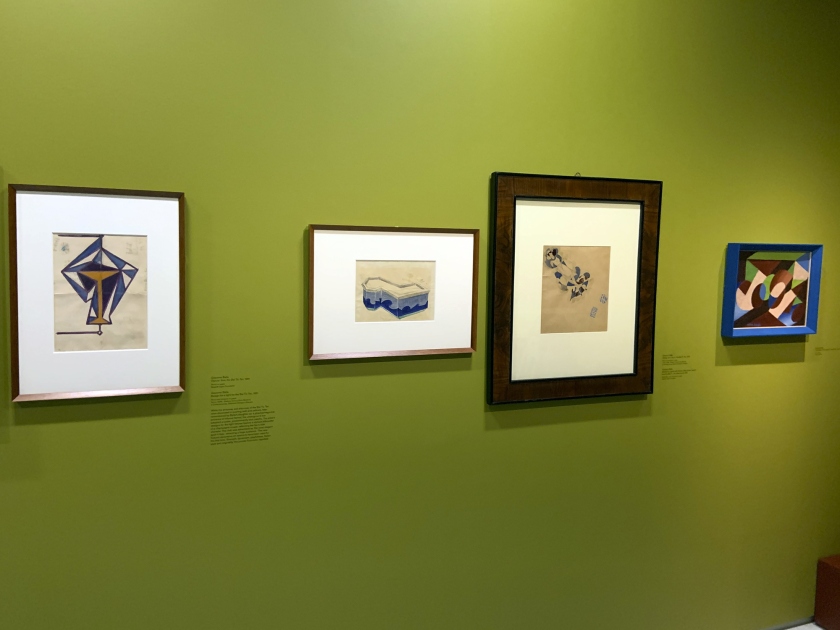
Josef von Divéky (Hungarian, 1887-1951)
Poster design fro the Cabaret Fledermaus (unrealised) (installation views)
1907
Gouache over pencil on paper
University of Applied Arts Vienna, Collection and Archive
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
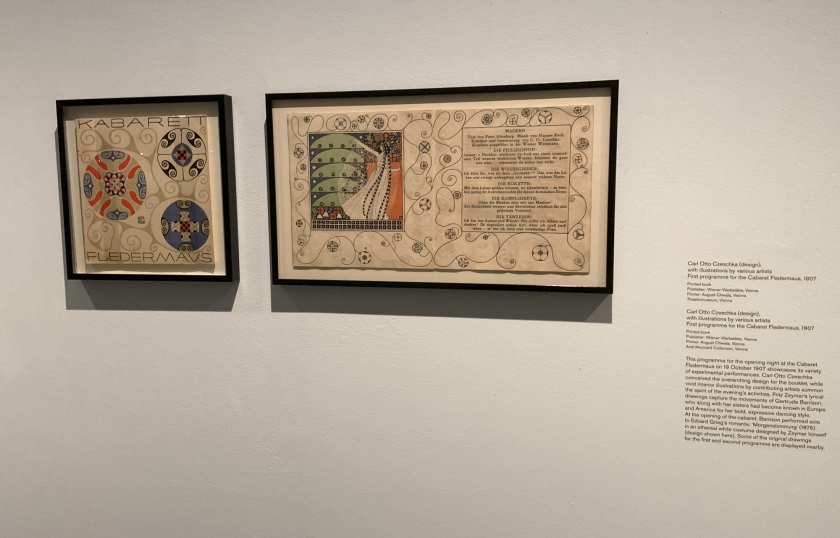
Carl Otto Czeschka (design)(Austrian, 1878-1960)
with illustrations by various artists
First programme for the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation view)
1907
Printed book
Publisher: Wiener Werkstate, Vienna
Printer: August Chwala, Vienna
Theatermuseum, Vienna
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
This programme for the opening night at the Cabaret Fledermaus on 19 October 1907 showcases its variety of experimental performances. Carl Otto Czeschka conceived the overarching design for the booklet, while vivid interior illustrations by contributing artists summon the spirit of the evenings activities.
Carl Otto Czeschka (design)(Austrian, 1878-1960)
with illustrations by various artists
First programme for the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation views)
1907
Printed book
Publisher: Wiener Werkstate, Vienna
Printer: August Chwala, Vienna
Theatermuseum, Vienna
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Fritz Zeymer’s lyrical drawings capture the movements of Gertrude Barrison, who along with her sisters had become known in Europe and America for her bold, expressive dancing style. At the opening of the cabaret, Barrison performed solo to Edvard Greig’s romantic ‘Morgenstimmung’ (1875) in the ethereal white costume design by Zeymer himself (design shown here).
Carl Otto Czeschka (design)(Austrian, 1878-1960)
with cover design and illustrations by Moriz Jung
Second programme for the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation view)
1907
Printed book
Publisher: Wiener Werkstate, Vienna
Printer: August Chwala, Vienna
Ariel Muzicant Collection, Vienna
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
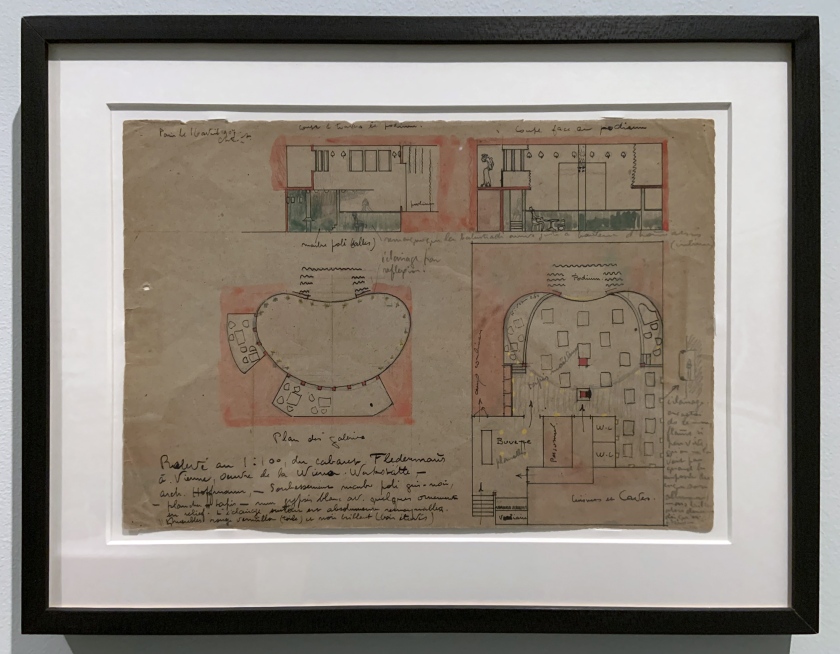
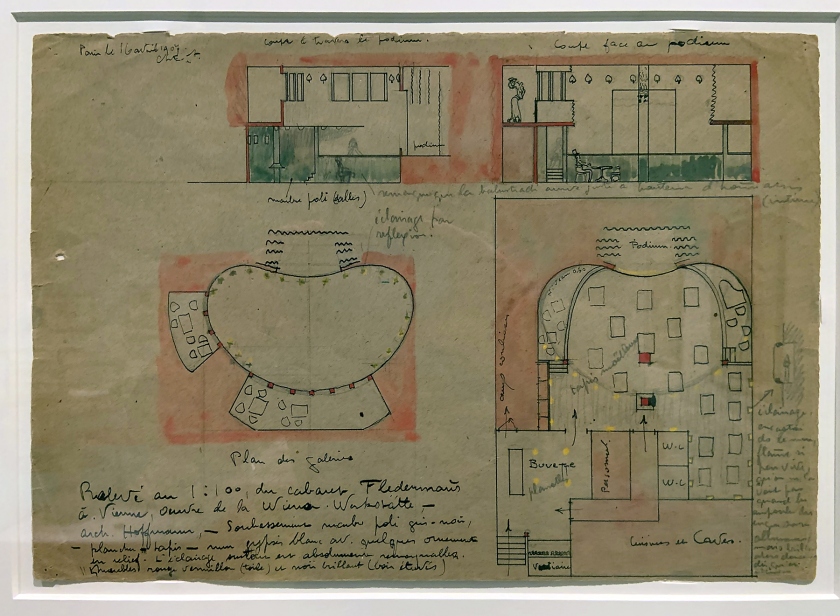
Le Corbusier (Swiss-French, 1887-1965)
Plan at 1:100 for the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation views)
1907
Graphite pencil, ink and wash on paper
Fondation Le Corbusier, Paris
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
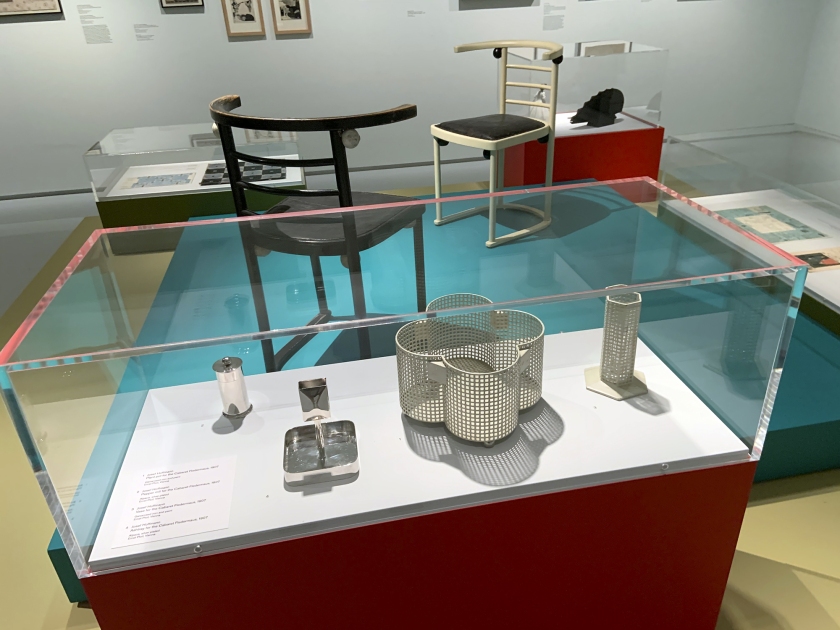
Artefacts in display cabinet include Josef Hoffmann plant pot (1907), pepper mill (1907), vases for the Cabaret Fledermaus (1907) and an ashtray (1907) (installation views)
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Installation views of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art
Installation view Barbican Art Gallery 4 October 2019 – 19 January 2020
© Tristan Fewings / Getty Images
Bertold Löffler (Austrian, 1874-1960)
Poster for the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation view)
1907
Lithograph
The Albertina Museum, Vienna
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Bertold Löffler (Austrian, 1874-1960)
Poster for the Cabaret Fledermaus
1907
The Albertina Museum, Vienna
© The Albertina Museum, Vienna
Bertold Löffler (Austrian, 1874-1960)
Poster for a performance by Miss Macara at the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation view)
1909
Lithograph
The Albertina Museum, Vienna
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Wall text about the poster for a performance by Miss Macara
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Fritz Lang (Austrian-German-American, 1890-1976)
Poster for the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation view)
1911
Lithograph
The Albertina Museum, Vienna
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
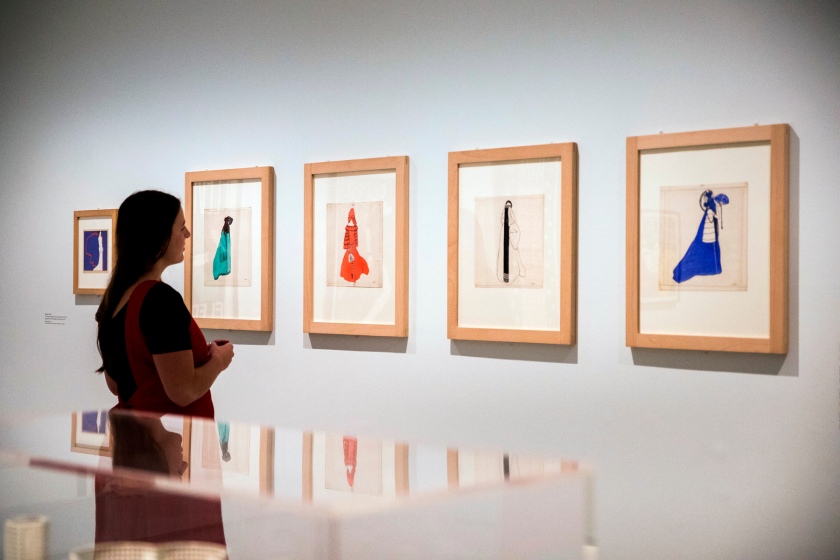
Josef von Divéky (Hungarian, 1887-1951)
Design for ‘Green Domino’, ‘Orange Domino’ and ‘Blue Domino’ for the Cabaret Fledermaus (installation views)
1908
Ink and pencil on paper
MAK – Austrian Museum of Applied Arts, Vienna
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art
Installation view Barbican Art Gallery 4 October 2019 – 19 January 2020
© Tristan Fewings / Getty Images
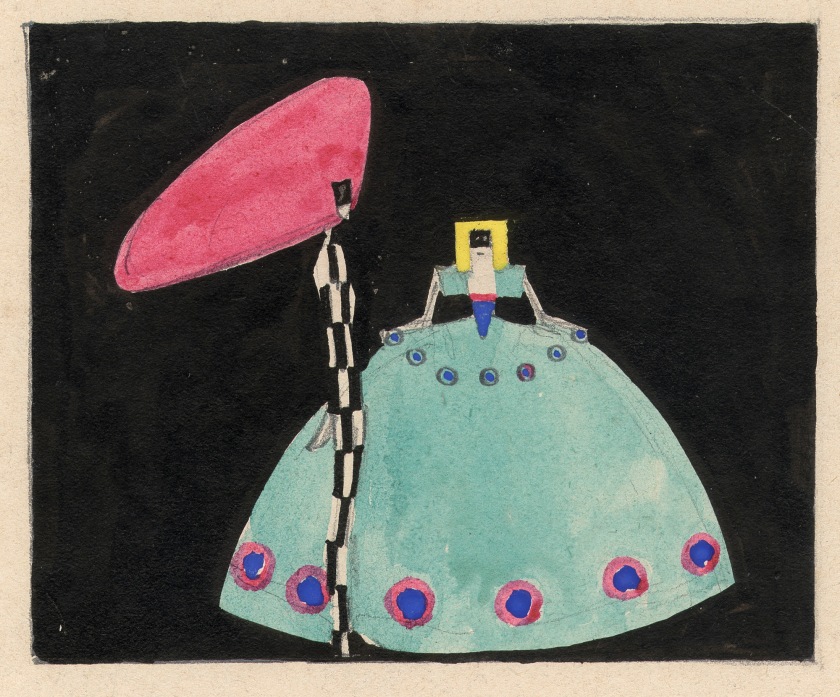
Eduard Josef Wimmer-Wisgrill (Austrian, 1882-1961)
Design for Maskenspiele (Masquerades) (two characters)
1907
MAK – Austrian Museum of Applied Arts, Vienna
© MAK
Opening 4 October 2019, Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art explores the social and artistic role of cabarets, cafés and clubs around the world. Spanning the 1880s to the 1960s, the exhibition presents a dynamic and multi-faceted history of artistic production. The first major show staged on this theme, it features both famed and little-known sites of the avant-garde – these creative spaces were incubators of radical thinking, where artists could exchange provocative ideas and create new forms of artistic expression. Into the Night offers an alternative history of modern art that highlights the spirit of experimentation and collaboration between artists, performers, designers, musicians and writers such as Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Loïe Fuller, Josef Hoffmann, Giacomo Balla, Theo van Doesburg and Sophie Taeuber-Arp, as well as Josephine Baker, Jeanne Mammen, Aaron Douglas, Jacob Lawrence, Ramón Alva de la Canal and Ibrahim El-Salahi.
Focusing on global locations from New York to Tehran, London, Paris, Mexico City, Berlin, Vienna and Ibadan, Into the Night brings together over 350 works rarely seen in the UK, including paintings, drawings, prints, photographs, films and archival material. Liberated from the confines of social and political norms, many of the sites provided immersive, often visceral experiences, manifesting the ideals of the artists and audiences who founded and frequented them. The exhibition features full-scale recreations of specific spaces, such as the multi-coloured ceramic tiled bar of the Cabaret Fledermaus in Vienna (1907), designed by Josef Hoffmann for the Wiener Werkstätte, and the striking abstract composition of the Ciné-Dancing designed by Theo van Doesburg for L’Aubette in Strasbourg (1926-28). The exhibition will feature a soundscape created by hrm199, the studio of acclaimed artist Haroon Mirza, specifically commissioned for the show.
Jane Alison, Head of Visual Arts, Barbican, said: “Into the Night casts a spotlight on some of the most electrifying cabarets and clubs of the modern era. Whether a creative haven, intoxicating stage or liberal hangout, all were magnets for artists, designers and performers to come together, collaborate and express themselves freely. Capturing the essence of these global incubators of experimentation and cross-disciplinarity, immersive 1:1 scale interiors will take the visitor on a captivating journey of discovery.”
Into the Night begins in Paris, on the eve of the 20th century, with two thrilling and iconic locations of the avant-garde. The theatrical shadow plays of the Chat Noir in the 1880s are brought to life through original silhouettes and works that decorated the interior of the cabaret, which acted as a forum for satire and debate for figures such as founder Rodolphe Salis, artist Henri Rivière and composer Erik Satie. The captivating serpentine dances of Loïe Fuller staged at the Folies Bergère in the 1890s were trail-blazing experiments in costume, light and movement. Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec captured her performances in his extraordinary series of delicately hand-coloured lithographs, brought together for the exhibition. Visitors will encounter the immersive “Gesamtkunstwerk” (total work of art) design of the Cabaret Fledermaus (1907) in Vienna by the Wiener Werkstätte, where experimental cabaret productions were staged. The exhibition includes original documentation of Oskar Kokoschka’s exuberant puppet theatre and Gertrude Barrison’s expressionist dance.
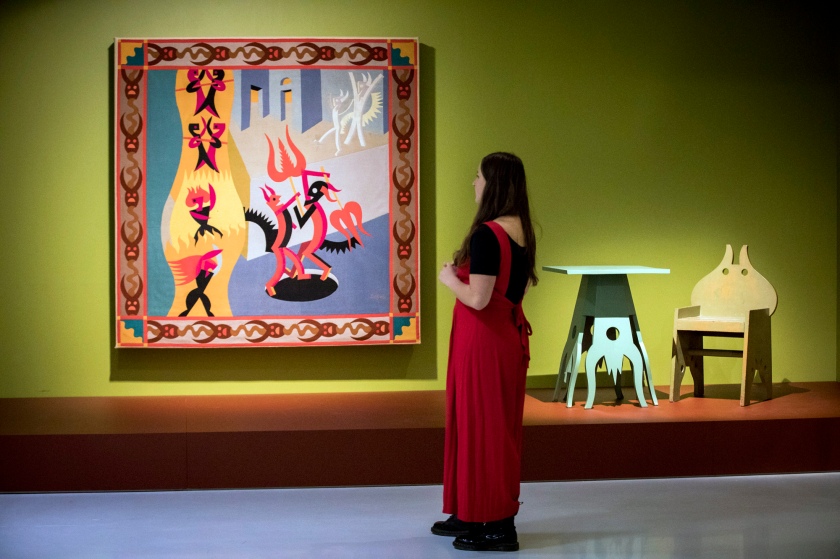
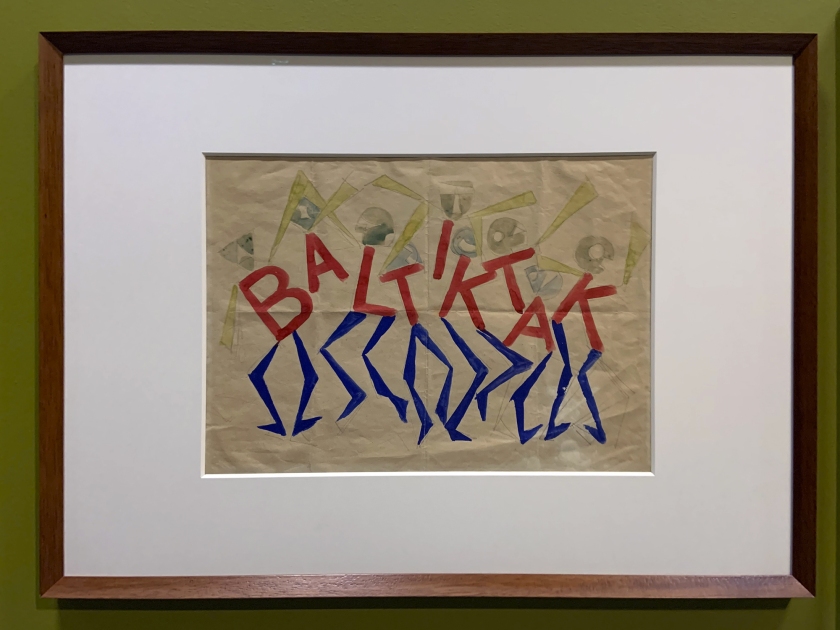
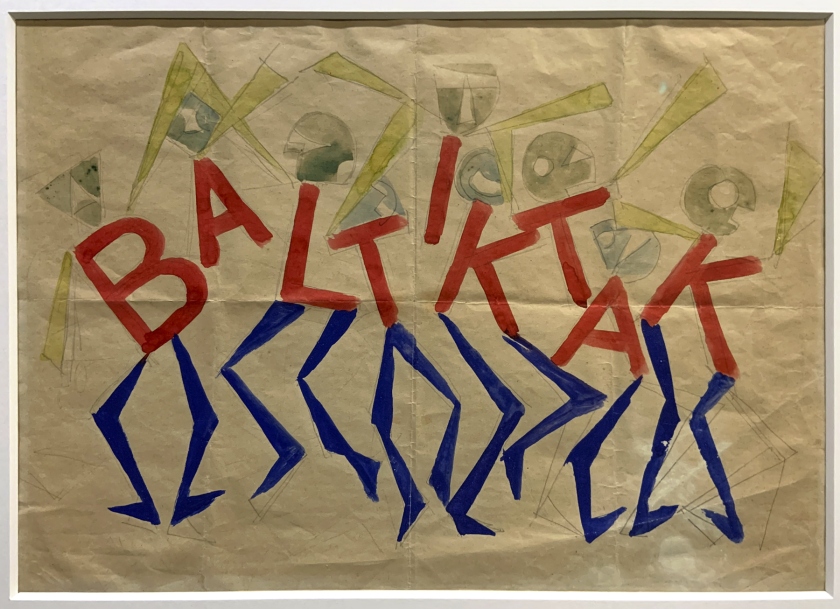
The Cave of the Golden Calf (1912), an underground haunt in Soho epitomising decadence and hedonism, is evoked through designs for the interior by British artists Spencer Gore and Eric Gill, as well as Wyndham Lewis’s highly stylised programmes for the eclectic performance evenings – advertised at the time as encompassing “the picturesque dances of the South, its fervid melodies, Parisian wit, English humour.” In Zurich, the radical atmosphere of the Cabaret Voltaire (1916) is manifested through absurdist sound poetry and fantastical masks that deconstruct body and language, evoking the anarchic performances by Hugo Ball, Emmy Hennings and Marcel Janco. This is the birthplace of Dada, where humour, chaos and ridicule reign. Two significant clubs in Rome provide insights into the electrifying dynamism of Futurism in Italy in the 1920s. Giacomo Balla’s mesmerising Bal Tic Tac (1921) is summoned by colour-saturated designs for the club’s interior, capturing the swirling movement of dancers. Also on show are drawings and furnishings for Fortunato Depero’s spectacular inferno-inspired Cabaret del Diavolo (1922) which occupied three floors representing heaven, purgatory and hell. Depero’s flamboyant tapestry writhes with dancing demons, expressing the club’s motto “Tutti all’inferno!!! (Everyone to hell!!!)”.
A few years later, a group of artists and writers from the radical movement Estridentismo, including Ramón Alva de la Canal, Manuel Maples Arce and Germán Cueto, began to meet at the Café de Nadie (Nobody’s Café) in Mexico City, responding to volatile Post-Revolutionary change and the urban metropolis. The ¡30-30! group expressed its values by holding a major print exhibition (partially reassembled here) in a travelling circus tent open to all. Meanwhile in Strasbourg, Theo van Doesburg, Hans Arp and Sophie Taeuber-Arp worked together to create the L’Aubette (1926-28), conceived as the ultimate “deconstruction of architecture”, with bold geometric abstraction as its guiding principle. The vast building housed a cinema-ballroom, bar, tearoom, billiards room, restaurant and more, each designed as immersive environments.
After a period of restraint in Germany during the First World War, the 1920s heralded an era of liberation and the relaxation of censorship laws. Numerous clubs and bars in metropolitan cities, such as Berlin, playing host to heady cabaret revues and daring striptease; the notorious synchronised Tiller Girls are captured in Karl Hofer’s iconic portrait. Major works by often overlooked female artists such as Jeanne Mammen and Elfriede Lohse-Wächtler, as well as George Grosz, Otto Dix and Max Beckmann, capture the pulsating energy of these nightclubs and the alternative lifestyles that flourished within them during the 1920s and 1930s. During the same time in New York, the literary and jazz scenes thrived and co-mingled in the predominantly African American neighbourhood of Harlem, where black identity was re-forged and debated. Paintings and prints by Aaron Douglas and Jacob Lawrence convey the vibrant atmosphere and complex racial and sexual politics of the time, while poetry by Langston Hughes and early cinema featuring Duke Ellington shed light on the rich range of creative expression thriving within the city.
Into the Night also celebrates the lesser known but highly influential Mbari Artists and Writers Club, founded in the early 1960s in Nigeria. Focusing on two of the club’s key locations, in Ibadan and Osogbo, the exhibition explores how they were founded as laboratories for postcolonial artistic practices, providing a platform for a dazzling range of activities – including open-air dance and theatre performances, featuring ground breaking Yoruba operas by Duro Ladipo and Fela Kuti’s Afro-jazz; poetry and literature readings; experimental art workshops; and pioneering exhibitions by African and international artists such as Colette Omogbai, Ibrahim El-Salahi and Uche Okeke. Meanwhile in Tehran, Rasht 29 emerged in1966 as a creative space for avant-garde painters, poets, musicians and filmmakers to freely discuss their practice. Spontaneous performances were celebrated and works by artists like Parviz Tanavoli and Faramarz Pilaram hung in the lounge while a soundtrack including Led Zeppelin and the Beatles played constantly.
The exhibition is curated and organised by Barbican Centre, London, in collaboration with the Belvedere, Vienna.
Press release from the Barbican Art Gallery [Online] Cited 28/12/2019
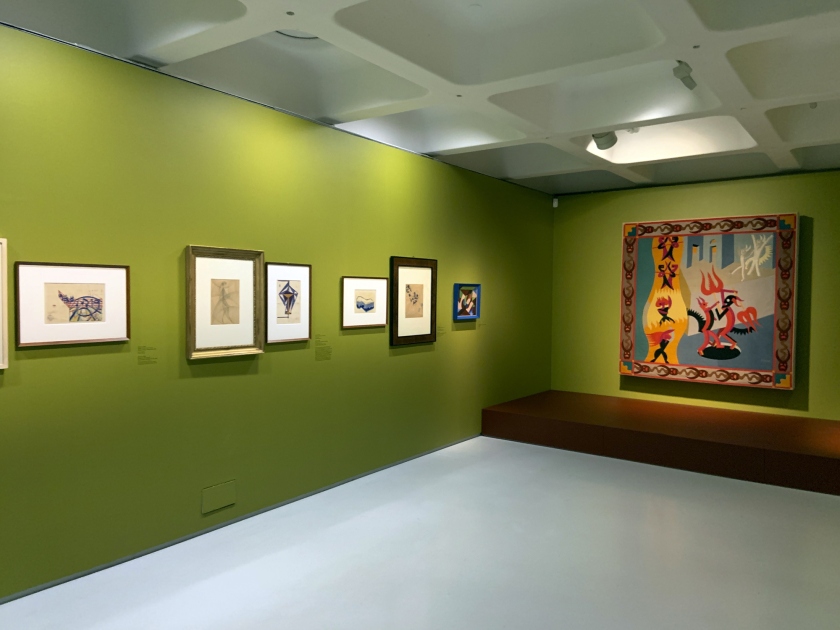
Rome: Cabaret Del Diavolo 1922 wall text
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
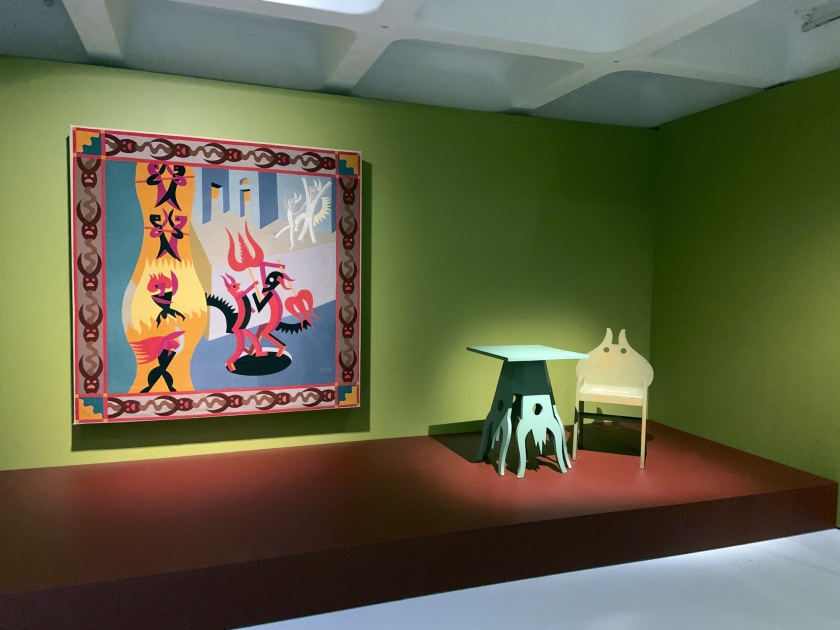
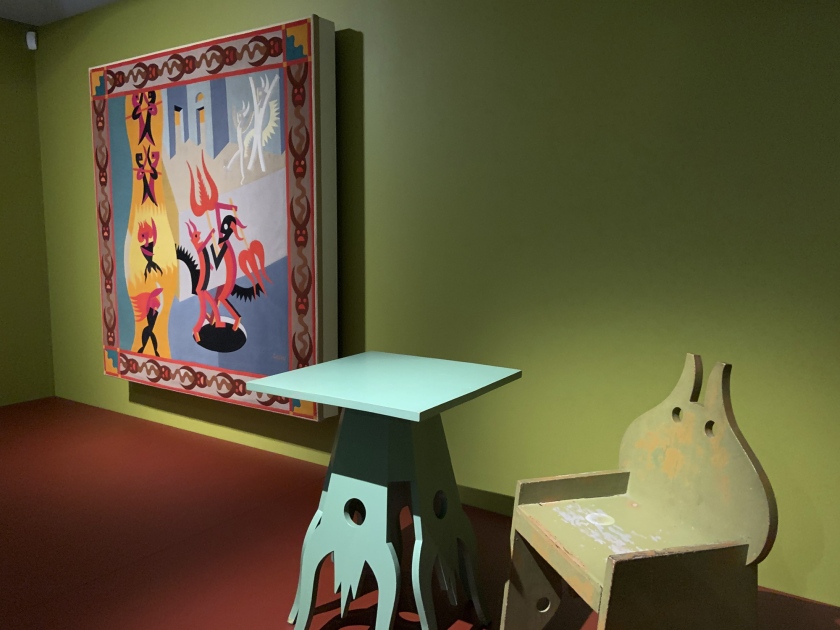
Installation views of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery showing Fortunato Depero’s tapestry Diavoletti neri e bianchi. Danza di diavoli (Black and White Little Devils: Dance of the Devils), 1922
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Fortunato Depero wall text
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art
Installation view Barbican Art Gallery 4 October 2019 – 19 January 2020 showing at left Fortunato Depero’s tapestry Diavoletti neri e bianchi. Danza di diavoli (Black and White Little Devils: Dance of the Devils), 1922
© Tristan Fewings / Getty Images
Fortunato Depero (Italian, 1892-1960)
Diavoletti neri e bianchi. Danza di diavoli (Black and White Little Devils: Dance of the Devils)
1922
Mart, Museo di arte moderna e contemporanea di Trento e Rovereto / Fondo Depero
© DACS 2019. Archivo Depero, Rovereto. Courtesy Mart – Archivio Fotografico e Mediateca
Rome: Bal Tic Tac 1921 wall text
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Giacomo Balla (Italian, 1871-1958)
Design for the sign and flashing light for the facade of the Bal Tic Tac (installation views)
1921
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Giacomo Balla wall text
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Giacomo Balla (Italian, 1871-1958)
Design for the sign and flashing light for the facade of the Bal Tic Tac
1921
© DACS, 2019. Reproduced by permission of the Fondazione Torino Musei
Photo: Studio Fotografico Gonella 2014
Installation views of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Giacomo Balla (Italian, 1871-1958)
Dancer from the Bal Tic Tac (installation views)
1921
Pencil on paper
Biagiotti Cigna Foundation
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Giacomo Balla (Italian, 1871-1958)
Design for a light for the Bal Tic Tac (installation view)
1921
Pencil and tempera on paper
Torino, GAM – Galleria Civica d’Arte moderna e Contemporanea, Gabinetto Disegni e Stampe
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Giacomo Balla wall text
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Installation views of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
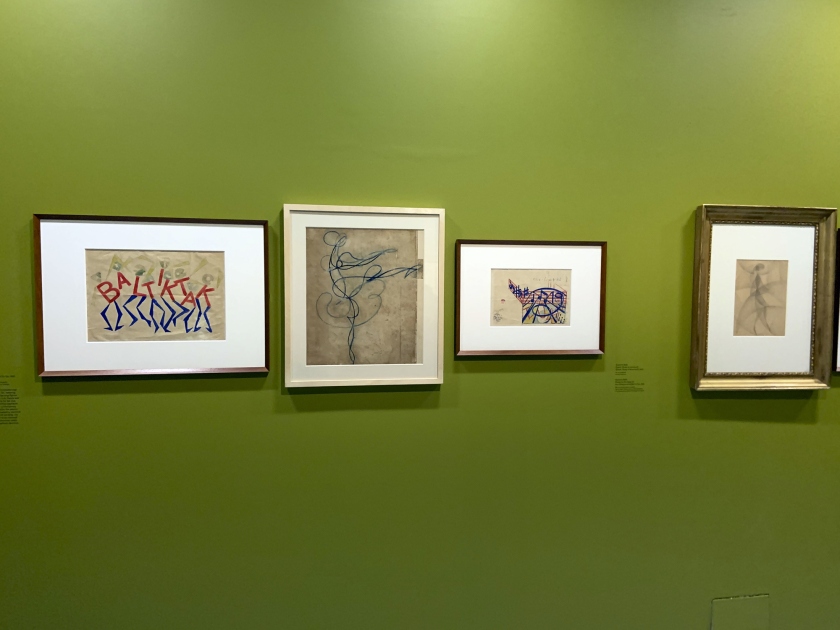
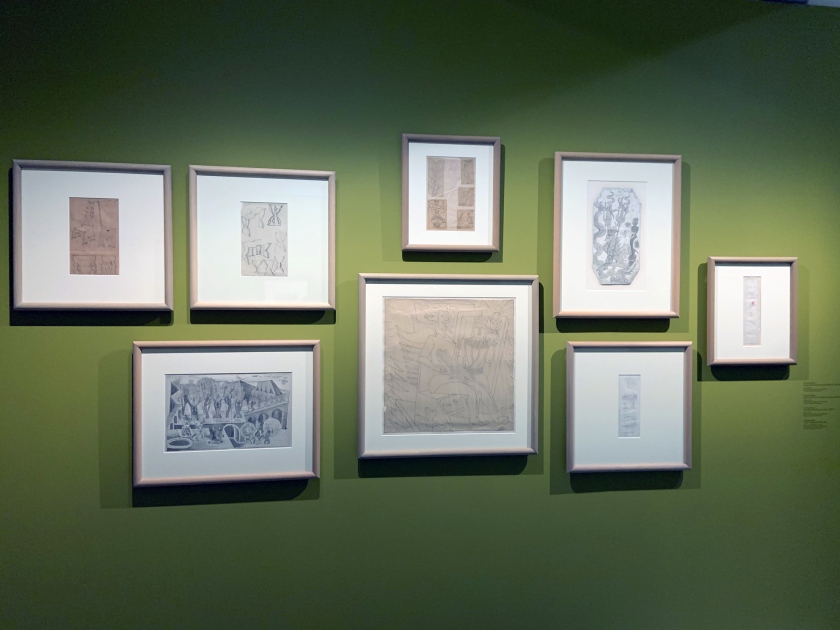
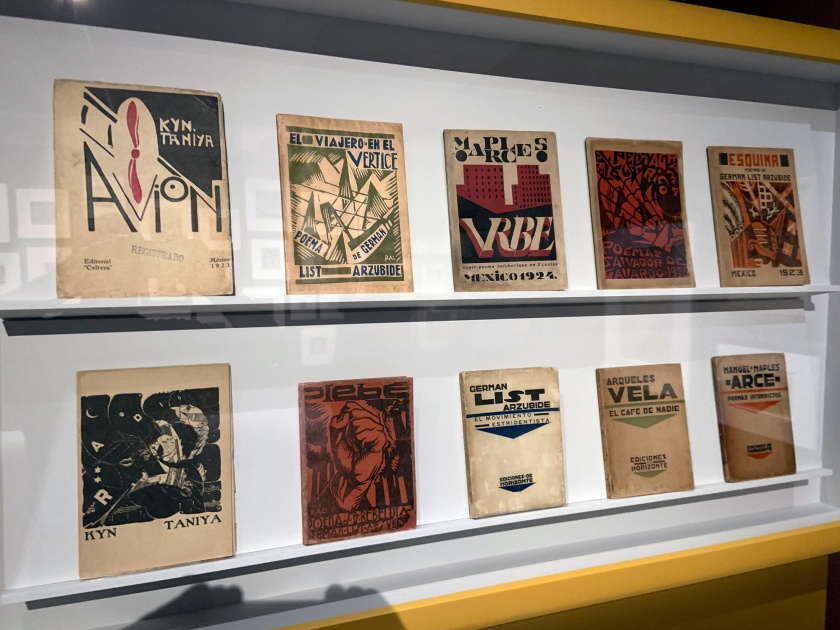
Mexico City: Cafe De Nadie & Carpa Amaro 1920s wall text
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Installation views of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery showing a group of Mexican woodcuts 1922-1928
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Justino Fernandez (Mexican, 1904-1972)
El corrido (The Corrido) (installation views)
1928
Woodcut
Fondo Diaz de León
Colección Andres Blastien, Mexico
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Justino Fernandez (Mexican, 1904-1972)
La hora del mando (Market Time) (installation views)
1928
Woodcut
Fondo Diaz de León
Colección Andres Blastien, Mexico
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Fernando Leal (Mexican, 1896-1964)
Danzantes (Dancers) (installation view)
1922
Woodcut
Fondo Diaz de León
Colección Andres Blastien, Mexico
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Francisco Diaz de León (Mexican, 1897-1975)
Retablo (Altarpiece)
1928
Woodcut
Fondo Diaz de León
Colección Andres Blastien, Mexico
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Isabella Villaseñor (Mexican, 1909-1953)
Autorretrato (Self-portrait) (installation view)
1928
Woodcut
Colecciones Carlos Monsivais
Museo del Estanquillo
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Fernando Leal (Mexican, 1896-1964)
Dance of the Crescent Moon (installation view)
1922
Woodcut
Museo Nacional de Arte, INBA
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gabriel Fernández Ledesma (Mexican, 1900-1983)
Cabeza de Lenin (Head of Lenin) (installation view)
1927
Woodcut
Fondo Diaz de León
Colección Andres Blastien, Mexico
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gabriel Fernández Ledesma (Mexican, 1900-1983)
Tlacuache (Opposum) (installation view)
c. 1920s
Woodcut
Fondo Diaz de León
Colección Andres Blastien, Mexico
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Gabriel Fernández Ledesma (Mexican, 1900-1983)
Patos Chinos (Chinese Ducks) (installation view)
1928
Woodcut
Fondo Diaz de León
Colección Andres Blastien, Mexico
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art
Installation view Barbican Art Gallery 4 October 2019 – 19 January 2020 showing a group of Mexican woodcuts 1922-1928
© Tristan Fewings / Getty Images
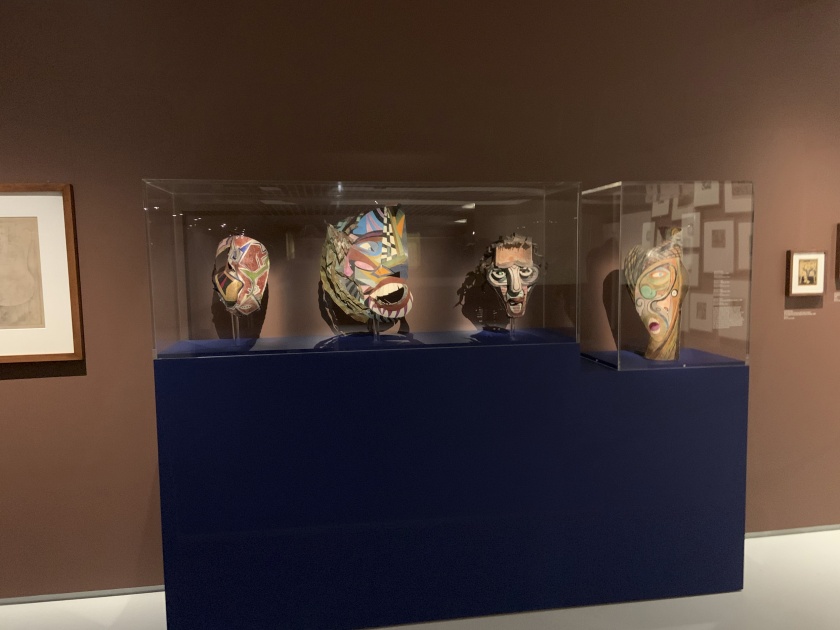
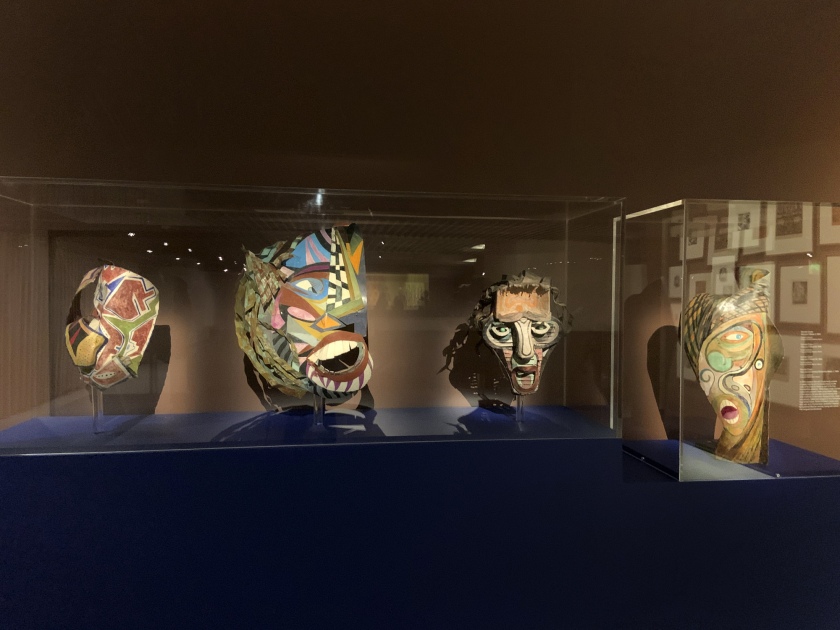
Installation view of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery showing Germán Cueto’s Máscara estridentista (Stridentist Masks), c. 1924
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Germán Cueto (Mexican, 1893-1975)
Máscara estridentista (Stridentist Mask)
c. 1924
Colección Ysabel Galán, México
Photo: Cortesia del Museo Frederico Silva Escultura Contemporeana, San Luis Potosi, Mexico
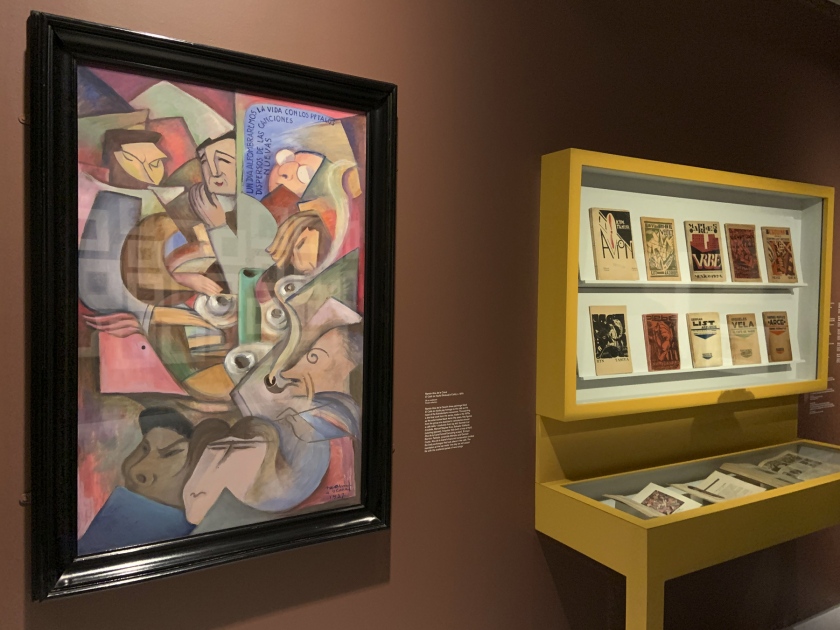
Installation views of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery showing Ramón Alva de la Canal’s painting El Café de Nadie (Nobody’s Café), c. 1970
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art
Installation view Barbican Art Gallery 4 October 2019 – 19 January 2020 showing Ramón Alva de la Canal’s painting El Café de Nadie (Nobody’s Café), c. 1970
© Tristan Fewings / Getty Images
Ramón Alva de la Canal (Mexican, 1892-1985)
El Café de Nadie (Nobody’s Café)
c. 1970
© DACS, 2019
Courtesy Private Collection
Installation views of the exhibition Into the Night: Cabarets and Clubs in Modern Art at the Barbican Art Gallery showing Mexican printed books 1923-1927
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Ramón Alva de la Canal (Mexican, 1892-1985)
El movimiento estridentista (The Stridentist Movement) (installation views)
1926
Woodcut
Francisco Reyes Palma Collection
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Ramón Alva de la Canal (Mexican, 1892-1985)
Manuel Maples Arce en el Café de Nadie (Manuel Maples Arce in the Café de Nadie) (installation view)
c. 1924
Woodcut
Museo Nacional de Arte, Mexico City
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Barbican Art Gallery
Silk Street, London
EC2Y 8DS
Opening hours:
Sat – Wed 10am – 6pm
Thu – Fri 10am – 8pm












































































































![Irving Penn (American, Plainfield, New Jersey 1917-2009 New York) 'Ballet Society, New York [Tanaquil Le Clercq with Corrado Cagli, Vittorio Rieti, and George Balanchine]' March 5, 1948, printed November 1976 Irving Penn (American, Plainfield, New Jersey 1917-2009 New York) 'Ballet Society, New York [Tanaquil Le Clercq with Corrado Cagli, Vittorio Rieti, and George Balanchine]' March 5, 1948, printed November 1976](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/penn-ballet-society-web.jpg?w=650&h=815)







































![Max Dupain (Australian, 1911-1992) 'Untitled rayograph [with water]' 1936 Max Dupain (Australian, 1911-1992) 'Untitled rayograph [with water]' 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/dupain-rayograph-water.jpg?w=650&h=830)

































![Agustí Centelles. 'Barcelona, España. Guardería infantil en Vía Layetana' [Babysitting in Layetana Road] 1936-39](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/agusti_centelles-guarderia_infantil-web.jpg?w=840)
![Fernand Léger. 'Les Loisirs - Hommage à Louis David' [Leisure - Homage to Louis David] 1948-1949](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/leger-les_loisirs-web.jpg?w=840)
![Louis Sciarli. 'Le Corbusier. Marseille: Unité d'habitation, École Maternelle' [Le Corbusier. Marseille: housing unit, Kindergarten] 1945/2014](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/sciarli-le_corbusier_marseille-web.jpg?w=840)





















































You must be logged in to post a comment.