Exhibition dates: 17th June – 30th October 2022
Curator: Virginia Chardin
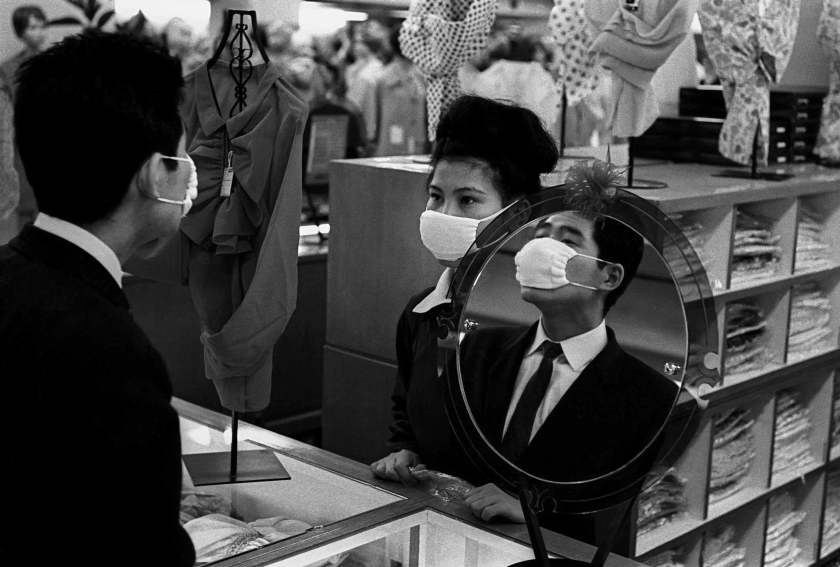
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Muslim wedding, fiancé discovering his fiancée’s face in a mirror, Pakistan
1952
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Another male photographer, this time one who underlines the commonalities between his work as a photo-reporter and his work for fashion. But other than a few transcendent images (the Givenchy Hat duo in particular) I find his work to be very stylised, of the 1950s era, and not particularly memorable.
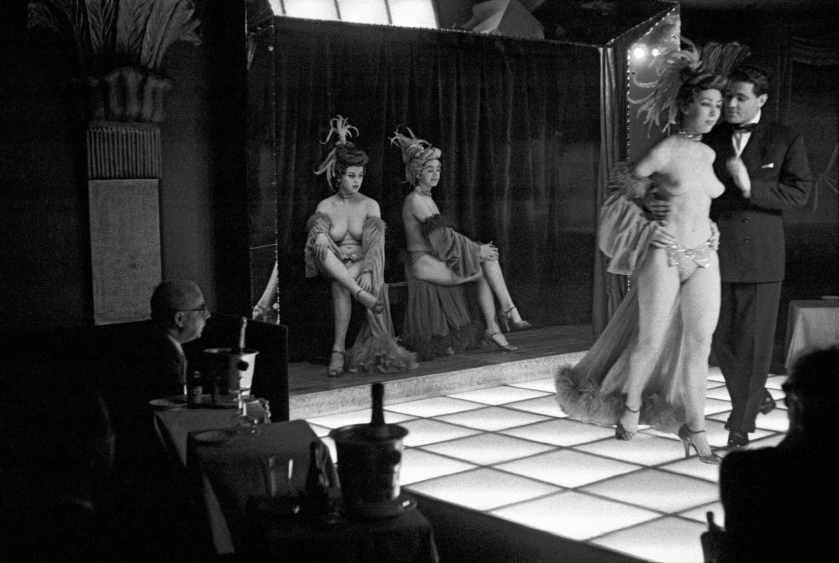
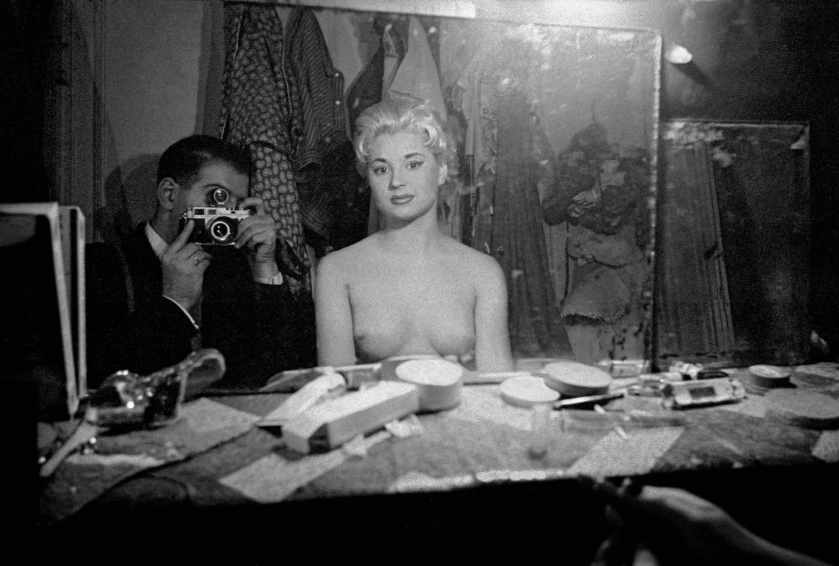
Can you imagine the artist Susan Meiselas in her work Carnival Strippers (1972-1975) taking an image of a naked female and then naming the work for themselves, “self-portrait”, Self-portrait with stripper, The Sphinx, Paris (1956, below) even as the photographer is obscured with the camera machine up to his face recording with the male gaze and the gaze of the camera the body of a anonymous woman? Just a stripper?
I know Meiselas’ work is from a later generation when feminism was rising but the objectification of the female body in Horvat’s work is unsavoury, even as the press release says he ensured the “complicit, amused and moving participation of the young women.” (To be complicit means to be involved with others in an activity that is unlawful or morally wrong)
From the look on the woman’s face, I don’t think so…
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Jeu de Paume for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Thus, putting aside the notions of truth or deception in the representation of women, and in leaning instead on this concept that Griselda Pollock called the woman-as-image, it becomes possible to analyze the mechanisms of fetishism, voyeurism and objectification who form and inform the representation of women.”
Abigail Solomon-Godeau, “Representing Women: The Politics of representation of the self,” in Chair à canons. Photography, discourse, feminism, Paris, Textual, coll. “Photographic writing,” 2016, p. 234.
The Jeu de Paume pays tribute to the photographer Frank Horvat, who died on October 21, 2020 at the age of ninety-two, with an exhibition presented at the Château de Tours from June 17 to October 30, 2022. Accompanied by a monograph, it brings a renewed vision of the fiery activity of the photographer during his first fifteen years of career, from 1950 to 1965, a period during which he affirmed an extraordinary personality as author-reporter and fashion photographer.
Made from the archives kept by the author in his home-studio in Boulogne-Billancourt, the exhibition is based on period documents: vintage, publications, writings, in order to follow and explain the photographer’s approach, in the context of the evolution of the illustrated press at the time. He strives to discern the deep driving forces of the work and to bring out its strength and points of tension. He underlines the commonalities between his work as a photoreporter and his work for fashion. Fascination with beauty, the motif of the viewer-voyeur, attention to physical or amorous disorder, are some of the recurring themes of Frank Horvat, who appears above all as a photographer of the body and the intimate. It also reveals the melancholy facet of an independent and sometimes solitary author, living as an outsider despite his success as a fashion photographer.
The Jeu de Paume pays tribute to the photographer Frank Horvat, who died on October 21, 2020 at the age of ninety-two, with an exhibition presented at the Château de Tours from June 17 to October 30, 2022. Accompanied by a monograph, it brings a renewed vision of the fiery activity of the photographer during his first fifteen years of career, from 1950 to 1965, a period during which he asserted an extraordinary personality as author-reporter and fashion photographer.
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Howrah Bridge, Kolkata, India
1953-1954
vintage contact sheet
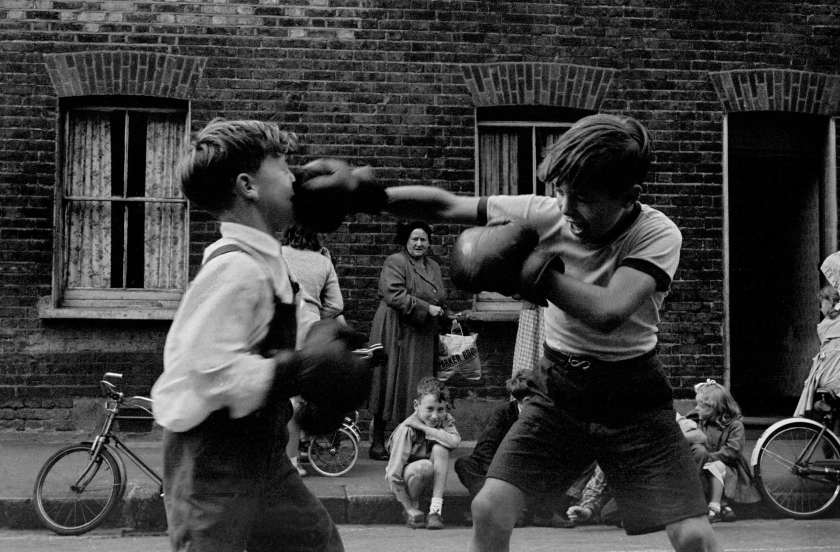
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Boxing fight between children, Cockney Borough of Lambeth, London, England
1955
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Prostitutes in the Bois de Boulogne, Paris
1955
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
1/ The beginnings of a photo-reporter 1928-1954
Francesco Horvat was born on April 28, 1928 in Abbazia, Italy (today Opatija in Croatia). Around 1951, he decided to become photo-reporter, meets Henri Cartier-Bresson, buys a Leica then embarks on a trip to Pakistan and India from 1952 to 1954. His subjects earned him publications in the international press and one of his images is selected for the exhibition “The Family of Man”, presented at Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) in New York in 1955.
2/ London and Realities 1954-1959
In 1954, he moved to London for a few months, where the English inspire him with humorous images, even frankly ironic. Initiating new formal experiences,he crops his images for close-up effects, hardens his prints by accentuating the grain of the image and works his layouts. Settled in Paris at the end of 1955, Francesco, who now signs Frank Horvat, establishes ongoing relationships with the French monthly Réalités, for which he produced a report on pimping, then in 1959 social subjects on the Parisian suburbs, London or the Borinage.
3/ Telephoto Paris 1956
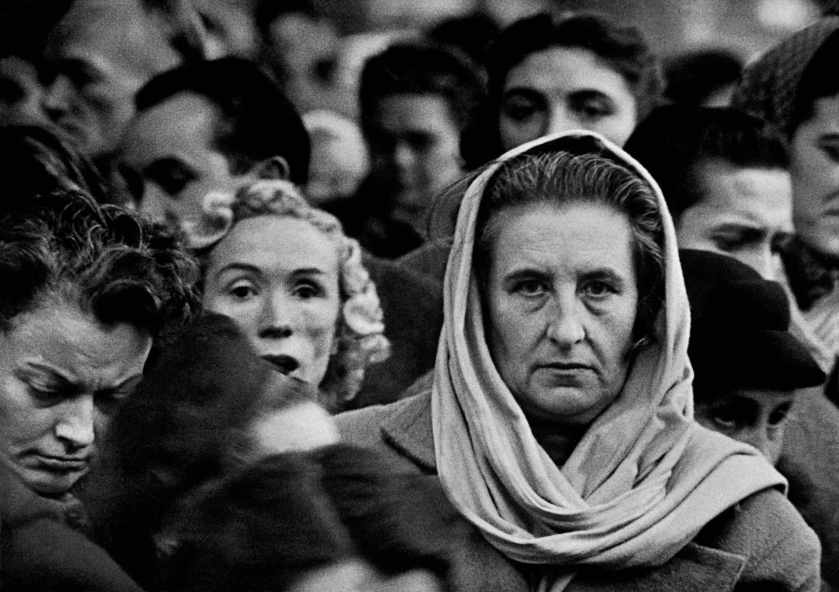
His wanderings in Paris led Frank Horvat to acquire a telephoto lens that he tests on the urban landscape. Intrigued by the effects he obtained from it, he experimented with high views, overlooking monuments and crossroads where crowds and vehicles intermingle. He is interested in graphic games drawn by the signs, the urban furniture, the roofs and the ubiquitous typography of the town. These images earned him significant recognition by international photography journals.
4/ Shows and spectators 1956-1958
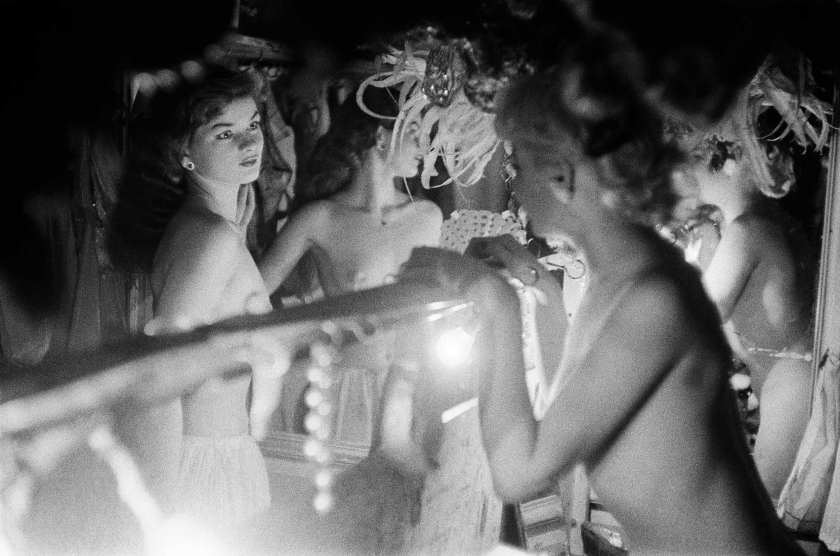
In 1956, the author manages to get behind the scenes the Sphinx striptease cabaret, place Pigalle, and ensures the complicit, amused and moving participation of the young women. This series earned him orders from Jours de France for an “Evenings in Paris” section. The book I like striptease, published in 1962 by Rencontre à Lausanne with an amazing layout by the graphic designer Jacques Plancherel, initiator of the magazine Die Woche, brings together images from these series.
5/ Fashion on the street 1957-1961
In 1957, William Klein introduced Frank Horvat to Jacques Moutin, the artistic director of the magazine Jardin desModes, who offers to transpose the style of his views Parisians in fashion images. Taken with a Leica, without artificial light, the freshness of his images is a sensation, and other magazines appeal to him for his free and natural way to pose his models. He becomes the representative of a “reportage style” in fashion.
6/ Successful fashion photographer and muses 1960-1964
This room brings together some of the iconic images and sophisticated shots made by the photographer for British Vogue and Harper’s Bazaar. Most models represented are exceptional women who have experienced an unusual fate. Maggi Eckardt, Judy Dent, Simone d’Aillencourt, Benedetta Barzini, Deborah Dixon, Carol Lobravico, Vera Valdez, Iris Bianchi or China Machado are the heroines of this room. So many portraits of women only fashion images, these photographs demonstrate a collaborative complicity between the photographer and his models.
7/ A photographer’s world tour 1962-1963
In 1962, the German magazine Revue asked Frank Horvat to produce a report on large non-European cities. Staring games between men and women, fleeting intimacy between watched and watchers, the melancholy and solitude of bodies make this photographic essay one of the most personal of Frank Horvat. The gist of this report having never been published, the vintage prints presented in this room are therefore largely unpublished. Over there following years, Frank Horvat will hardly carry out any more reporting, apart from a few colour subjects for Réalités. This series thus ends his career as a photo-reporter for the press.
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Telephoto Paris, Strasbourg-Saint-Denis metro station, Paris
1956
Vintage silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Telephoto Paris, traffic in front of Saint-Lazare station, Paris
1956
Vintage silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
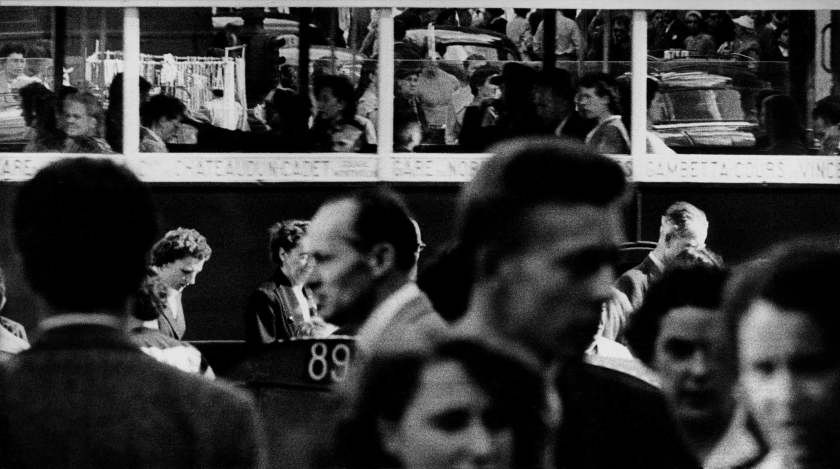
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Telephoto Paris, bus, Paris
1956
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Telephoto Paris, Christmas at Galeries Lafayette
1956
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Telephoto Paris, Christmas at Galeries Lafayette
1956
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
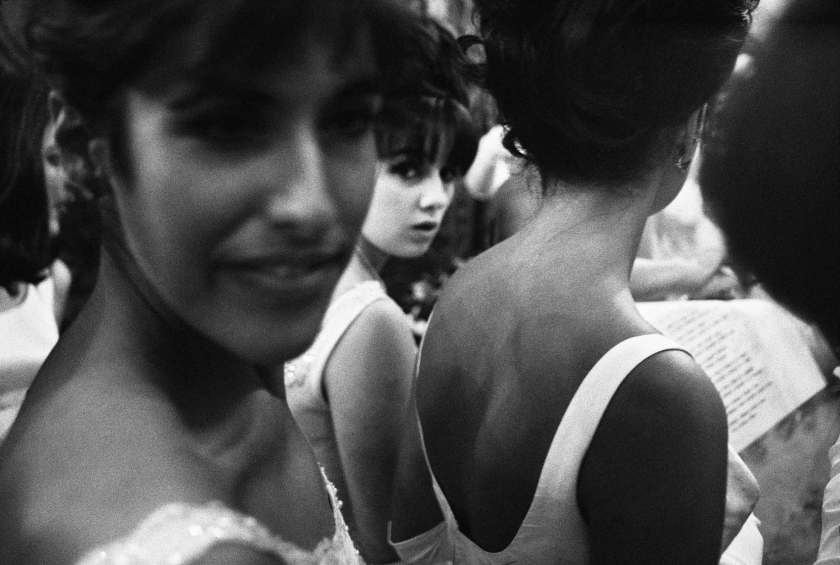
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
The Sphinx, Paris
1956
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Self-portrait with stripper, The Sphinx, Paris
1956
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
The Lido, Paris
1956
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
“If Horvat is a part, along with a few others, of a generation that has indeed renewed photography of fashion by desecrating the mannequin and mixing systematically life to artifice, he no doubt owes it to his training and his work as a photojournalist. This exhibition and this book, with largely unpublished content, focusing for the first time on its first fifteen years as a professional photographer who saw him go from fashionable reportage, precisely intend to reconcile the two sides of his work. On the one hand, his first works for the post-war European and then American press, in the lineage of its elders, Cartier-Bresson at the head, a time of trips that he himself called “the happiest period of his life”; on the other hand, fashion works and the intrusion of colour, which sometimes left him dissatisfied. However, in one case as in the other, the same attention, made of restraint, of empathy and a certain disenchanted sweetness, is brought to the world and, more particularly, to women and relations between the sexes, which are constants in his work – to which we will add, for fashion, a good dose of distance and humour.”
Quentin Bajac, “Foreword,” in Frank Horvat 50-65, Paris, Jeu de Paume / La Martiniere, 2022, p. 3.
The Jeu de Paume and the Château de Tours pay tribute to Frank Horvat who died on October 21, 2020. The exhibition focuses over his first fifteen years of work, during which he affirms an extraordinary personality of author-reporter and of a fashion photographer. Born in Italy in 1928, he started 1951 in Milan a career as a photojournalist which he pursues in Pakistan, India and England in the following years. His first images earned him numerous publications in the international press as well as participation in the famous “The Family of Man” exhibition presented at the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) in New York in 1955.
Settled in Paris in 1955, he was quickly noticed by his telephoto photographs and his subjects on the Paris by night. Managing to capture close-up scenes of a rare intensity, he reveals himself as a photographer of the body and the intimate. This fascination will be found later in his images of fashion for Jardin des Modes, British Vogue or Harper’s Bazaar and in the hallucinatory vibrations of a world tour which he performed in 1962-1963, remained largely unknown. Game of glances, night shows, fragility of masks, complicity with the models, melancholy of the bodies and scintillation love troubles draw an introspective cartography of this photographer moved throughout his life by a inexhaustible quest for new experience.
Produced from the archives left by Horvat in his house-workshop in Boulogne-Billancourt, the exhibition includes over 170 vintage and modern prints. Accompanied publications and original documents, it provides a new light on the work of this major player in French and European photography and present, alongside emblematic images, sets of photographs less known or new. Are thus revealed the wealth and the singularity of a complex and multifaceted work, replaced in the context of the history of photography and the press illustrated post-war.
Exhibition curator: Virginia Chardin
“Photography, for me, was photo-reportage. My photos had to tell stories, like those that the editors of the Berliner Illustrierte, refugees in New York during the war, had taught editors to tell of Life, and that now all the magazines were trying to imitate. With a beginning, a middle, an end and a legend under each photo, so that readers still unaccustomed to this visual language can represent the world, whether magazines are sold and that their collaborators are adequately remunerated.”
Frank Horvat, “Autobiography,” undated manuscript, Boulogne-Billancourt, Studio Frank Horvat archives.
“When I first set foot there, Paris was for me the capital of the world. From fashion of course, but also those of painting, letters, shows and especially – from my perspective – photojournalism, because it was Magnum headquarters. I remember this month of July 1951 as of a triumphal progression: I attended the first Givenchy collection, at Fath’s ball (Dior’s rival), I was received in the editorial offices of Paris-Match and Réalités (which even kept some of my photos), I made the portrait of Maxime de la Falaise, muse of the Parisian intelligentsia, in her boudoir Île Saint-Louis. I told myself that this escalation could only end up at the office on Place Saint-Philippe du Roule, where Cartier-Bresson, every Wednesday at 10 a.m., received young photographers, and where he would certainly have invited me to join his pleiad.
It was a cold shower. “Do you work in 6 × 6? The good God didn’t put your eyes on your stomach! And use flash? This is an arbitrary intervention! And in colour? I would do, if I could have my own palette, but I will never use the Kodak one!” He turned over the pile of my prints, the top of the photos down, so that the expressions of the faces do not distract him from the analysis of the compositions, examined them one after the other, pointed out their faults and concludes: “You have understood nothing. Go to the Louvre and study the compositions of Poussin”.”
Frank Horvat, “Autobiography,” undated manuscript, Boulogne-Billancourt, Studio Frank Horvat archives.
“Following the advice of Henri Cartier-Bresson, Franco Horvat bought a Leica in Munich. He embarked in Trieste on a freighter bound for Karachi in the spring of 1952. This trip to Pakistan, which he will extend to India for two years following, allows him for the first time to give free rein to his imagination by looking for subjects to propose.
Most newspapers and agencies ask photographers to bring them complete reports, that is to say, successions of captioned images telling a story likely to be published on several pages. “The mould of the picture story imposed itself on all those who wanted to work for magazines, they could take advantage of it, a bit like the great filmmakers of Hollywood took advantage of box office constraints, or the Great Century playwrights of the rule of three units”. In Lahore, his intuition or his personal attractions lead him to the “red light district” of Hira Mandi (“market with diamonds”, in Urdu), place of prostitution but also of a annual party where exceptionally unveiled young girls and adorned dance and are exposed to the gaze of men, the latter obtaining at auction the right to converse with the families for a meeting or a marriage – a custom century against which the government is trying to fight. He also photographs opium and hashish smokers, a particular Muslim religious ceremony spectacular, and a wedding during which the fiancé discovers in a mirror the face of his bride. Formally, his images do not deviate from the framework imposed by the codes of the photojournalism of the time, but the choice of subjects reveals a intense fascination for the body and the intimate. The observed woman by men, the viewers themselves captured in their bewilderment, the play of looks between the two are motives that we will find in all of Horvat’s work. […]
Initially, Réalités commissioned a subject from him which going to fascinate him, on pimping in Paris. Remote or hidden behind the wheel of his car, he explores by night or day the streets and cafés of Pigalle, rue Saint-Denis, as well as the alleys of the Bois de Boulogne, in a sort of long tracking shot which is reminiscent of the world of cinema or the novel policeman. The magazine announces on the cover: “A document exceptional. Réalités denounces one of the biggest scandals in our time”. Frank Horvat’s archives keep period prints that he had made by Georges Fèvre, one of of the main printers of the Pictorial Service laboratory (Picto) created by Pierre Gassmann. The latter then has the exclusive Magnum prints and gathers around him many French and international authors. This report, which Anne by Mondenard and Michel Guerrin, authors of a book on this magazine, consider it “one of the most strong of Realities” testifying to the “tragic realism of Horvat”, is amazing. The theme of voyeurism captivates the photographer whom he follows for several weeks the thread of Paris by night: the Folies-Bergère, a premiere of the Lido to which assist Charlie Chaplin, Brigitte Bardot and Jean Cocteau, fairground booths for light shows, several boxes of striptease. In a masterful series on the Sphinx at Pigalle, the photographer manages to ensure, behind the scenes, the participation accomplice and moving strippers while leaving to their pathetic loneliness the spectators-voyeurs.”
Virginie Chardin, “Frank Horvat, the inner journey,” in Frank Horvat 50-65, Paris, Jeu de Paume / La Martinière, 2022, p. 13 and 17.
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Tan Arnold at The Smoking Dog, Paris, for Jardin des Modes
1957
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancour
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Fashion at Les Invalides, Paris, pour Jardin des Modes
1958
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
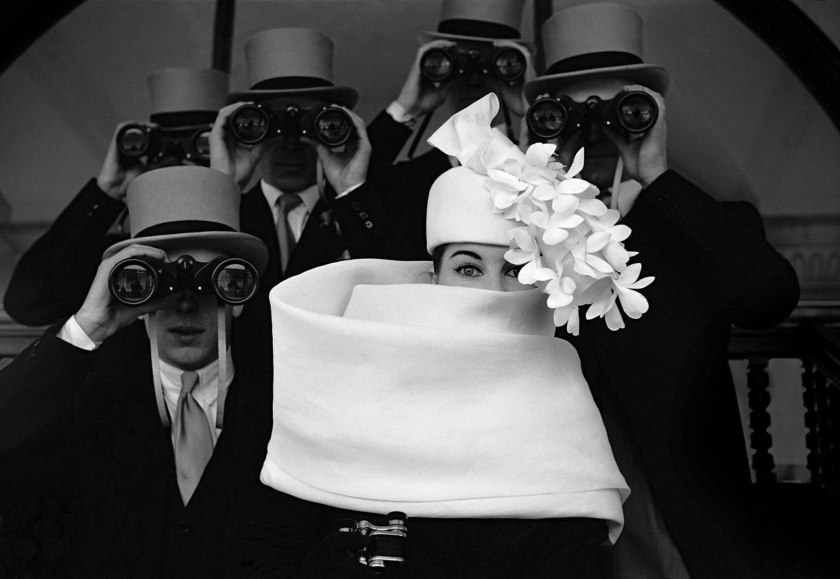
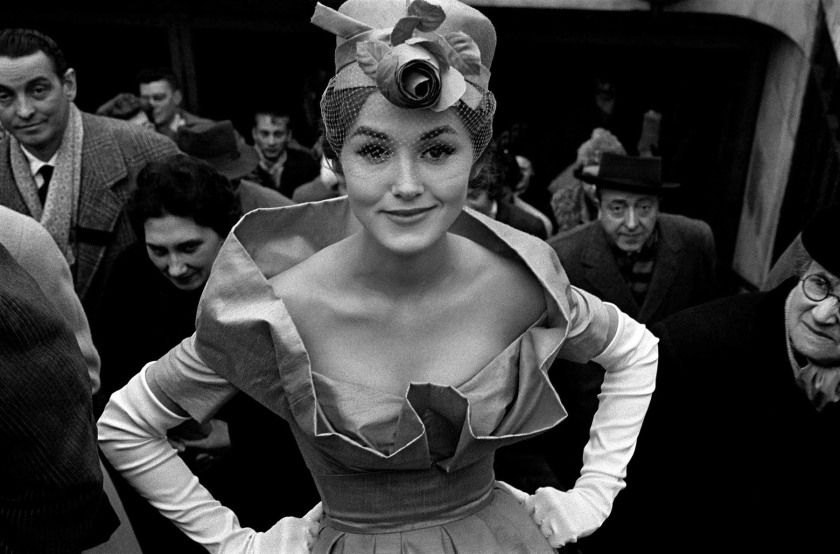
Givenchy Hat, Paris, for Jardin des Modes
1958
Modern inkjet print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Givenchy Hat For Jardin des Modes
1958
Modern inkjet print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
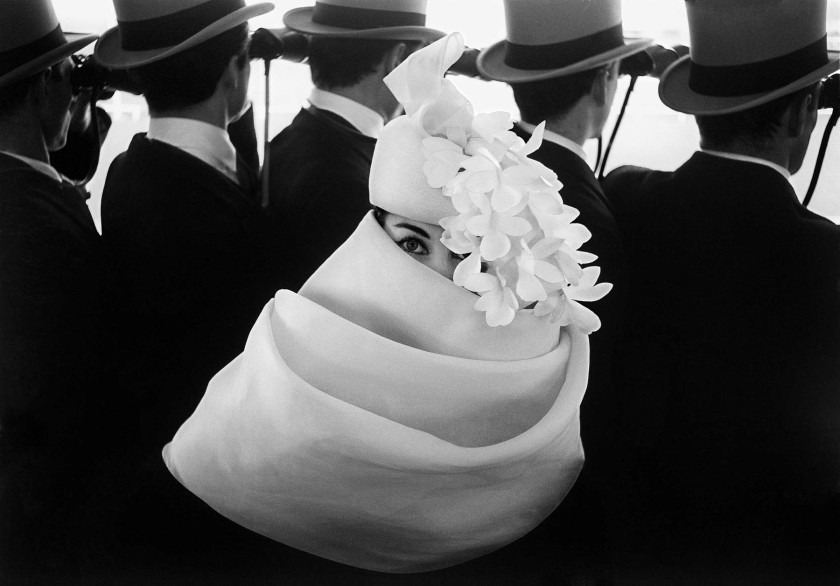
Mode à Longchamp, Givenchy hat, Paris For Jardin des Modes
1958
Vintage silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Monique Dutto at the Metro exit, Paris, for Jours de France
1959
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Commuter train hall, Saint-Lazare station, for Réalités, Femina-Illustration
1959
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
City, London, England, for Realities
1959
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
“As far as I am concerned, I had not yet realized that I lived “in the century of the body” – as it was to be called, forty years later, an exhibition of photographs, where one of the present images was going to be in the right place – and I had no intention of investigating this theme. But I had just moved to Paris, the orders were not legion and it was difficult for me to refuse that of a “men’s magazine” of New York, which offered two hundred dollars for a report on “Parisian life”.
On the sidewalks of Pigalle, the braided doormen addressed me expressions of welcome, quickly transformed into pouts disdainful as soon as I expressed the wish to photograph behind the scenes. At two o’clock in the morning, having wiped the refusals of all the establishments of the square and the alleys neighbours, I decided to go to great lengths. I slipped a five thousand franc note – of the time – in the hand of the doorman of the Sphynx, although the neon lights of this place were a slightly bald and the man’s uniform not brand new. That has been perhaps these imperfections that decided him to pocket the money and to let me enter, without further ceremony, into the sanctuary for strippers.
These young ladies gave me a rather warm welcome, perhaps because that the audience that night was so gloomy that the mere fact that a paparazzo takes care of them gave them a little feeling important. For my part, I machine-gunned hastily, as sensing that my luck would not last. Effectively, at after four or five spools, one of them said to me: “What are you paying for?” The demand was not unjustified, but I I couldn’t satisfy her. I turned a deaf ear and, without waiting for the others to join in, beat a retreat. The next day, while going through the contacts, I realized that “I had a story” […].”
Frank Horvat, Strip-tease, Paris, Galerie Nina Verny, 2001, n. p.
“[…] for now, his work is leading him to acquire a telephoto lens, which he tests on the urban landscape. Intrigued by the effects he obtains from it, he then abandons the motif of cabarets and of the night to experience many views taken in height, on foot, and overlooking monuments and crossroads where crowds and vehicles intermingle. He is interested in games graphics drawn by the signs, the signage, the street furniture, rooftops and the ubiquitous typography in the city. Positioning himself in the middle of the crowd, he captures close-ups of faces or bends down to child’s height. The objectives of long focal length put on the market are then the subject of a real infatuation. Frank Horvat shows a selection of his images to Romeo Martinez, the editor-in-chief of Camera magazine who, enthusiastic, decides to devote an important article to them and to exhibit them at the first Biennale of photography in Venice. This recognition will be crucial for the rest of his career, although the technique and use the telephoto lens only interested him for a short time. It earned him interviews and portfolios in magazines international photography exhibitions and to be exhibited alongside authors like Peter Keetman or William Klein. The same moment, as the exhibition “The Family of Man” arrives at Paris and that Frank Horvat surveys the city with his telephoto lens, published by Editions du Seuil, the book on New York by William Klein, who won the Nadar Prize the following year. It’s a real stylistic revolution in the world of photography, which coincides with the end of the golden age of humanist photography and the decline of photojournalism, and which marks the beginning of a new era of the press, in close correlation with the explosion of the society of consumption.”
Virginie Chardin, “Frank Horvat, the inner journey,” in Frank Horvat 50-65, Paris, Jeu de Paume / La Martinière, 2022, p. 18-21.
“Models who take stereotypical expressions bore me. I forced them to become what I call naively “real women”. It was a war against a lot of people; I went against the preconceived image of editors, models, makeup artists and hairstylists… and even against the necessity of having to represent a illusion. Certainly, I understand the desire for idealization that exists in fashion photography. But I wanted to realize my ideal and not that of an era. I wish that the models do not look like models. I had at first introduces passers-by, dogs, characters into the street. And then I tried to find the same truth in the studio, using white backgrounds. Sometimes I was wrong. This form of democratization of fashion has been favored by political actions. But I arrived at the right time.”
Frank Horvat, “Photographing the relationship”, interview by Muriel Berthou Crestey, October 19, 2013 (online: https://regard.hypotheses.org/1232)
“The greatest models of Horvat possess a beauty nonconformist, and their personality shines through the pages magazines. However, the woman in his photograph most famous remains an enigma. She stares at the lens, one eye visible under one flawless brow bone, the other obscured by the cascade of white silk flowers from her Givenchy hat. Unusually, it is not she who concentrates the attention of the other protagonists: around her, the men in top hats point their binoculars in the distance, to a horse race.”
Susanna Brown, “A beautiful chimera: Frank Horvat and fashion,” in Frank Horvat 50-65, Paris, Jeu de Paume / La Martinière, 2022, p. 38.
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Simone d’Aillencourt with designer Hardy Friends drinking tea, British high fashion, London, England, for British Vogue
1961
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Deborah Dixon and Federico Fellini, Italian haute couture, for Harper’s Bazaar, Rome, Italy
1962
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Iris Bianchi and Agnès Varda, Paris, French haute couture, for Harper’s Bazaar
1962
Modern inkjet print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Deborah Dixon on the steps of Piazza di Spagna, Italian haute couture, Rome, Italy, for Harper’s Bazaar
1962
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Deborah Dixon eating spaghetti with writer Antero Piletti, Italian haute couture, Rome, Italy, for Harper’s Bazaar
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Carol Lobravico au café de Flore, haute couture française, Paris, pour Harper’s Bazaar
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Carol Lobravico et Iris Bianchi au café de Flore, haute couture française, Paris, for Harper’s Bazaar
1962
Gelatin silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
“This photo [“Hat Givenchy, Paris, for Jardin des Modes,” 1958] would become my [most] iconic image, that is to say the one most often associated with my name. Maybe that’s why she’s not among the ones I prefer, to the point that I’m almost annoyed when it’s designate as my masterpiece. Another reason for my reluctance is that it was not really my idea, but the one of the artistic director, who even made, before the session, a sketch, which I was supposed to get as close as I could. I have never liked being directed, to the point that the concept of an “artistic direction” seems to me a contradiction in the terms: can we direct art? On the other hand, I have to admit that Jacques Moutin did not lack good ideas, and that this one was excellent. I owe him a big part of the success of this image and the benefits it has earned me.”
Frank Horvat, A look at the 60s, Paris, Loft Publications, Cyel editions, 2012, ill. 37.
“Thus, putting aside the notions of truth or deception in the representation of women, and in leaning instead on this concept that Griselda Pollock called the woman-as-image, it becomes possible to analyze the mechanisms of fetishism, voyeurism and objectification who form and inform the representation of women.”
Abigail Solomon-Godeau, “Representing Women: The Politics of representation of the self,” in Chair à canons. Photography, discourse, feminism, Paris, Textual, coll. “Photographic writing,” 2016, p. 234.
“Life had finally arrived on newsstands, imitated in everything the “free world” by magazines of the same format, such as Match in Paris, Stern in Hamburg and Epoca in Milan. We admired the Magnum photographers – Cartier-Bresson, Capa, Seymour and Bischof – both artists and adventurers. Far from a stopgap measure, photojournalism appeared to me as a way to reach my ideal from a creative activity to my desire to travel the world.”
Frank Horvat, “Pre-history,” in Frank Horvat. Please don’t smile, Berlin, Hatje Cantz Verlag, 2015, p. 232.
“If I had to sum up the photogenicity of Paris in a few words, I would would say that it comes from its facets. We can realize that on any street corner, looking in any direction through a viewfinder: details accumulate in the frame and repeat themselves as in a game of mirrors, disparate but always granted between them […]. The effect can be enhanced by a focal length of telephoto lens, which crushes perspectives and tightens distances.”
Frank Horvat, “Cities and Languages,” in Frank Horvat, Paris-Londres, London-Paris, 1952-1962, Paris, Paris Museums, Carnavalet Museum, 1996, p. 6-7.
“The spectator is a recurring presence in the work of Frank Horvat, and we could interpret this male figure anonymous as a representation of the photographer himself. In his exploration of the dichotomy between manifest gaze and hidden gaze, he often uses reflective surfaces, exploiting the properties of the mirror which induce a disturbance of three-dimensional space and a fragmentation of the picture plane.”
Susanna Brown, “A beautiful chimera: Frank Horvat and fashion,” in Frank Horvat 50-65, Paris, Jeu de Paume / La Martiniere, p. 33.
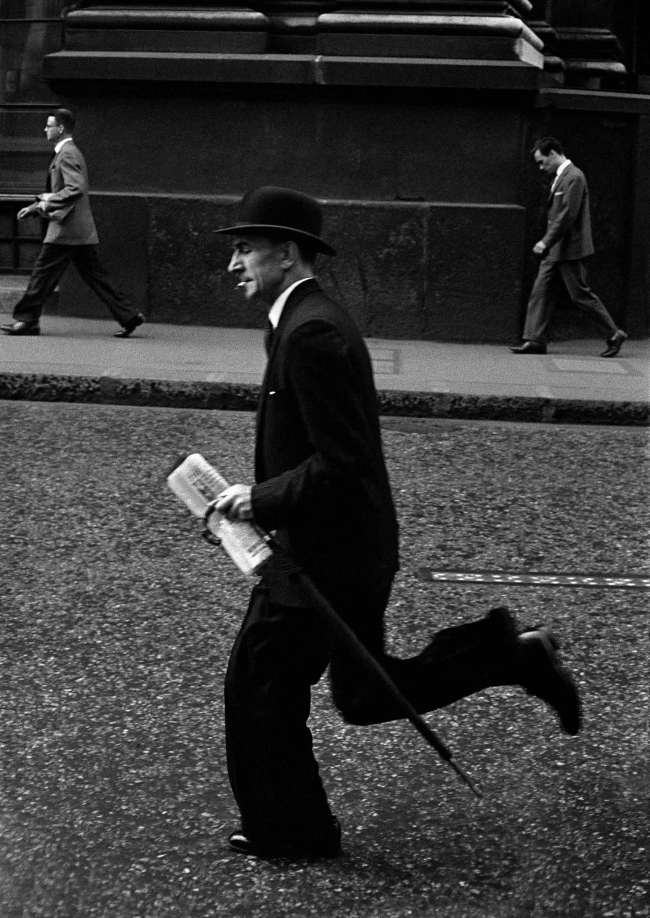
“For the “continental” that I was, England in the 1950s was as exotic as India – my teenage dreams in less. Immigration and globalization not yet on the agenda, the male population was divided into two classes: those who wore a cap and who in the métro – the tube – read the Daily Mirror, and those who wore the bowler hat and read the Times (whose titles were inside, the first page being reserved for small advertisement). The social class of women was recognized less easily: most looked like faded flowers, wore little hats and knitted. The light of a sky of lead suited me almost better than that of the sheer sun, but I know my London pictures stayed closer caricature than miracle: I had neither the knowledge nor the imagination to superimpose on this universe another grid than that of an ironic look.
In Paris, where I transferred myself the following year, it was all contrary: the references jostled, to the point of seeming sometimes too easy. Montmartre stairs, children brandishing chopsticks, the street lamps in the fog and the fairgrounds inevitably reminded me of the movies of the 1930s, but also the so-called humanist photographers who were inspired by it and of which I did not share some tenderness. Other associations of ideas, however, were irresistible. The gaze of a passer-by as in The Flowers of Evil: “O you whom I had loved, oh you who knew it”. The ghosts of demolished houses, like in Malta Laurids Brigge: “…it wasn’t, so to speak, the first wall of the remaining houses, but the last wall of the old. We saw the inside. We could see on the different floors the walls where hangings had remained pasted, here and there the beginning of a floor or a ceiling…” And of course the Mirabeau d’Apollinaire bridge, the grand boulevards of novels by Balzac, the Quai des Orfèvres by Edgar Poe, coffee Flore de Sartre… To literary memories were added the seductions of shop windows, restaurant menus, posters theater, and of course and above all women, interviews and unapproachable behind car windows or disturbing by their availability on the sidewalks of rue Saint-Denis.
For me, these were not so much reporting themes, as I had found in India and England, only entries in the diary of my wonders, my desires, of my fears and my mistakes. As were, on other registers, the subjects of the images on the run from Cartier-Bresson and Boubat, for whom photojournalism was, in the end, only a pretext for their own quests – or simply a livelihood.”
Frank Horvat, “Autobiography,” undated manuscript, Boulogne-Billancourt, archives from Studio Frank Horvat.
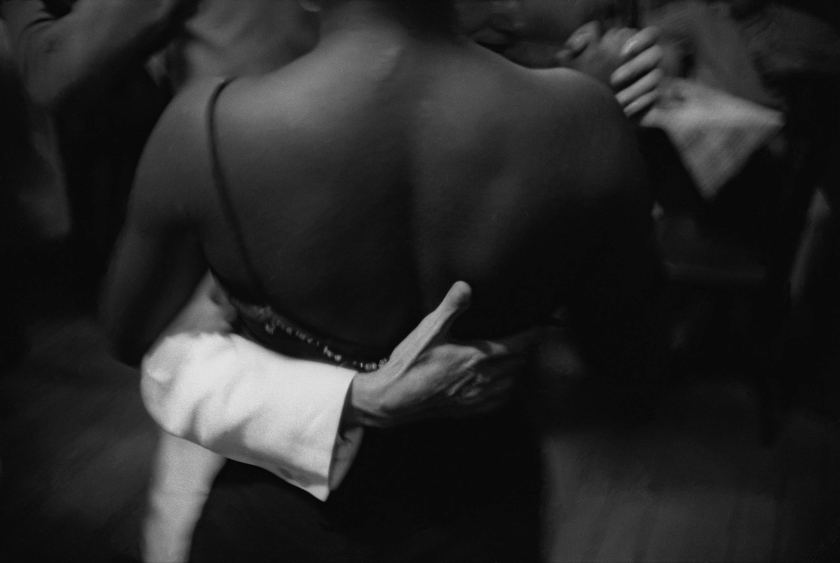
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
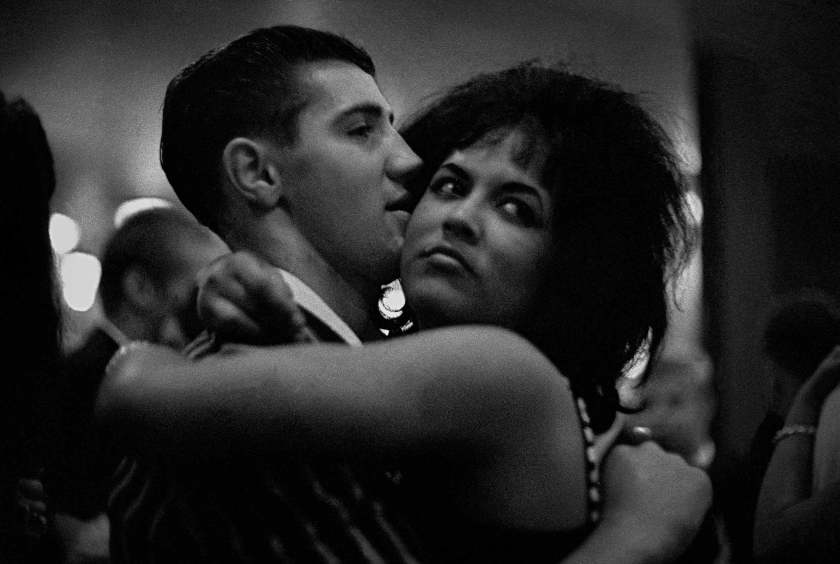
Christmas night, couple dancing in sailor bar, Calcutta, India
1962
Vintage silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Department store, Tokyo, Japan
1963
Vintage silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Couple dancing in a gafeira (popular ball), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
1963
Modern silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
15th anniversary celebration, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
1963
Silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Entrance to Luna Park, Sydney, Australia
1963
Vintage silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
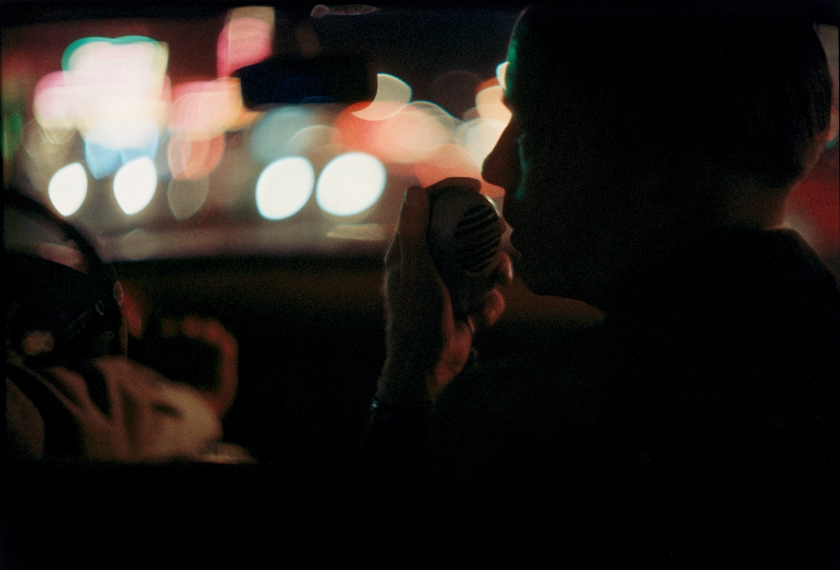
Frank Horvat (Italian, 1928-2020)
Lovers, Sydney, Australia
1963
Vintage silver print
© Studio Frank Horvat, Boulogne-Billancourt
Frank Horvat Photography, 1955
Frank Horvat Jardin des Modes, France, 1958
Jeu de Paume at the Château de Tours
25 avenue André Malraux, 37000 Tours
Phone: 02 47 70 88 46
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Sunday 2pm – 6pm
Closed on Monday
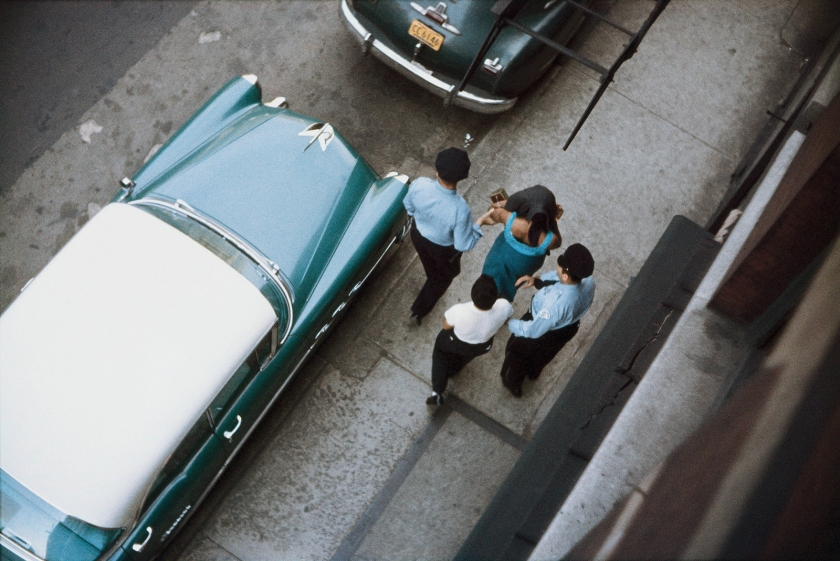
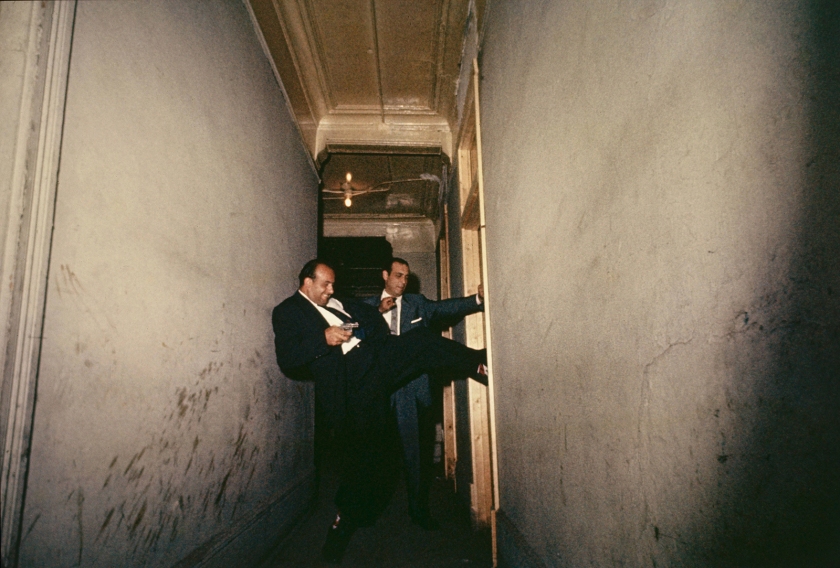
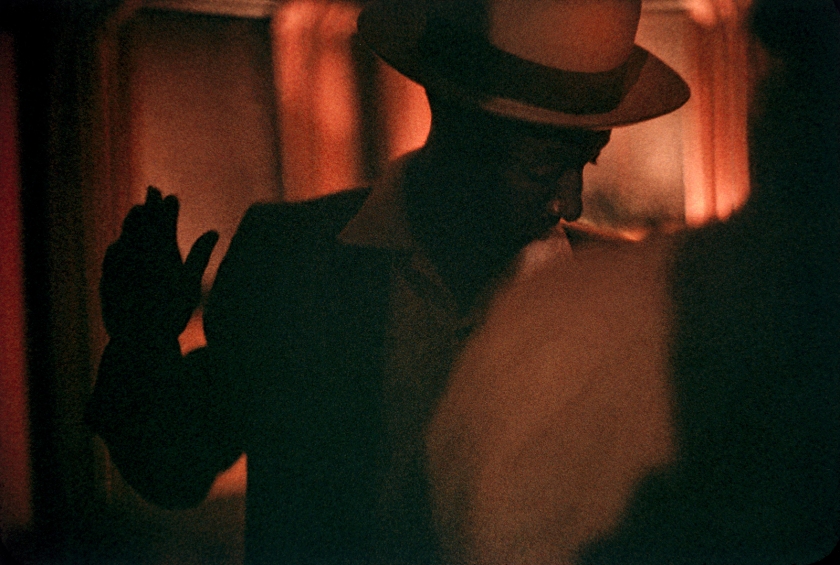
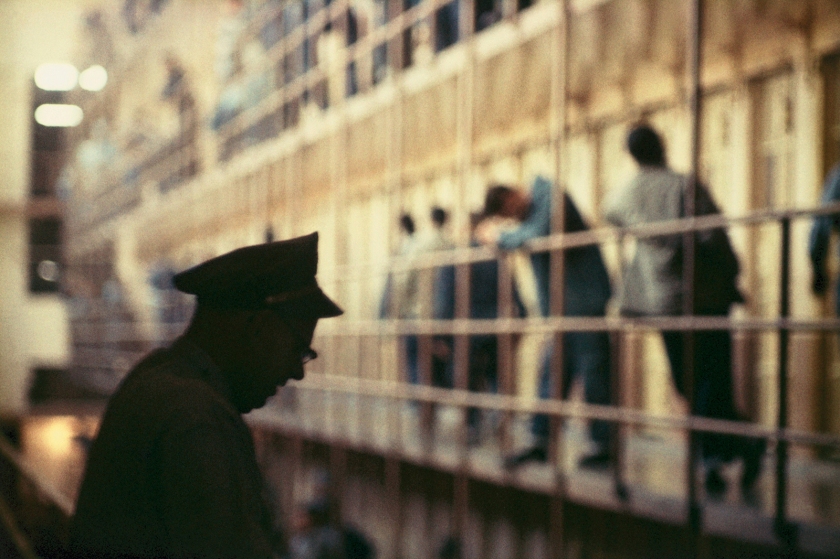





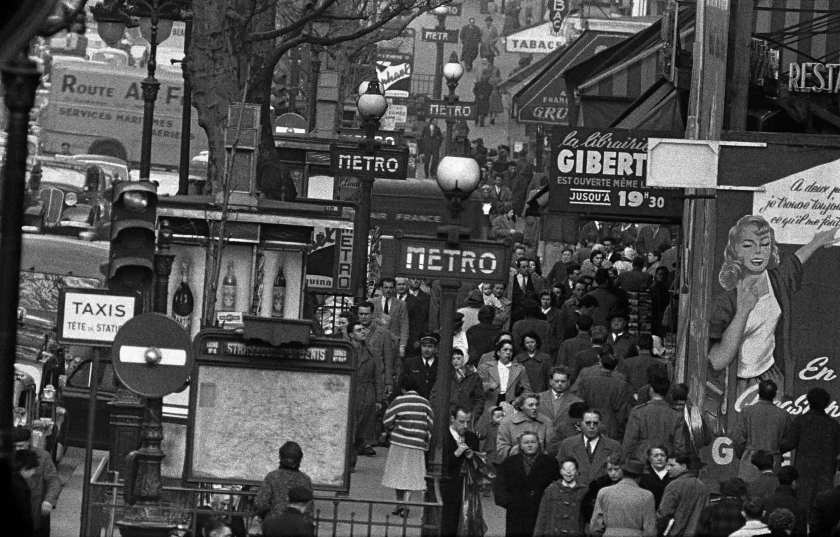
































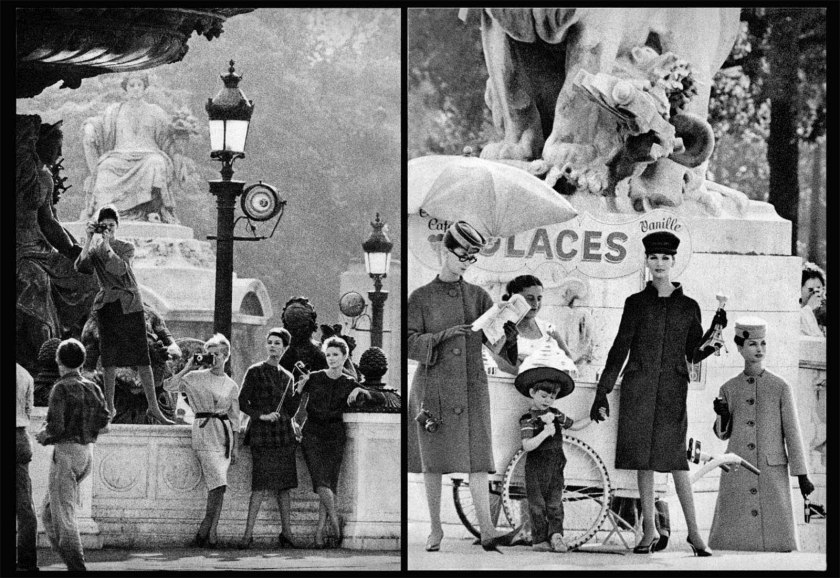




































![Roman Vishniac (1897-1990) '[David Eckstein, seven years old, and classmates in cheder (Jewish elementary school), Brod]' c. 1938 Roman Vishniac (1897-1990) '[David Eckstein, seven years old, and classmates in cheder (Jewish elementary school), Brod]' c. 1938](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/08/icp_vishniac_pressimage_8-web.jpg?w=650&h=794)
![Roman Vishniac (1897-1990) '[Grandmother and grandchildren in basement dwelling, Krochmaina Street, Warsaw]' c. 1935-1938 Roman Vishniac (1897-1990) '[Grandmother and grandchildren in basement dwelling, Krochmaina Street, Warsaw]' c. 1935-1938](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2019/02/vishniac-grandmother-and-grandchildren-web.jpg?w=650&h=698)
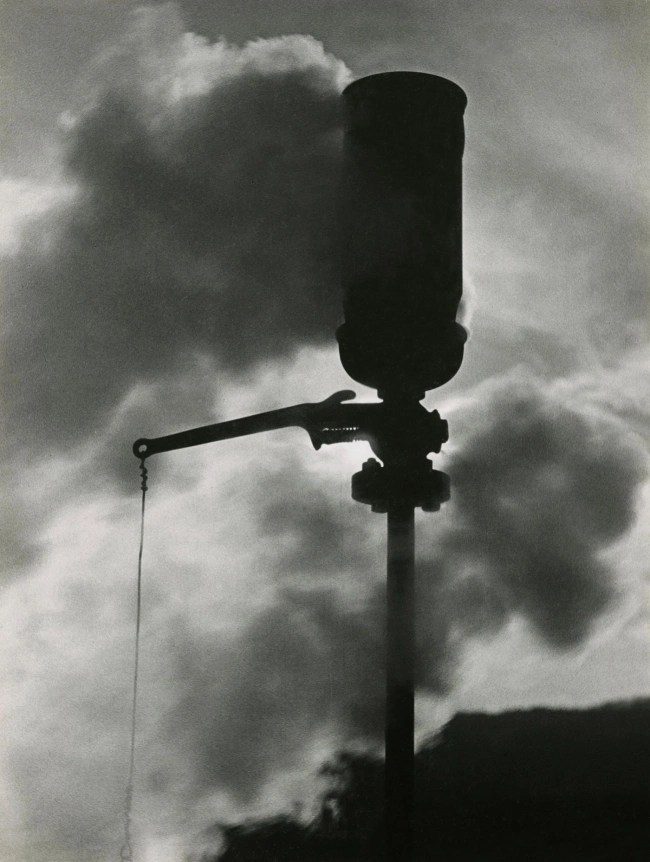


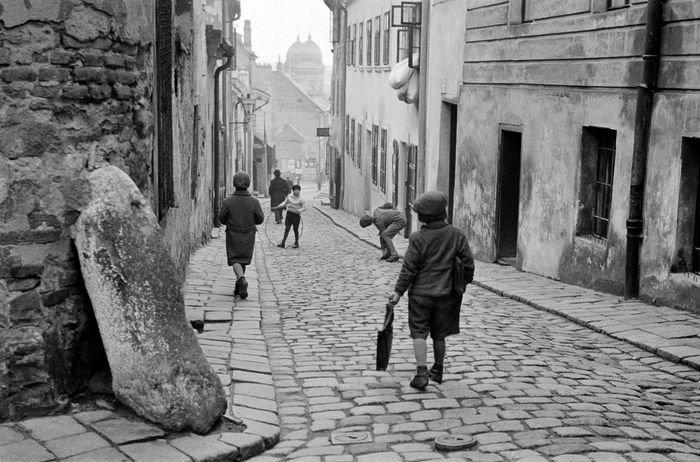










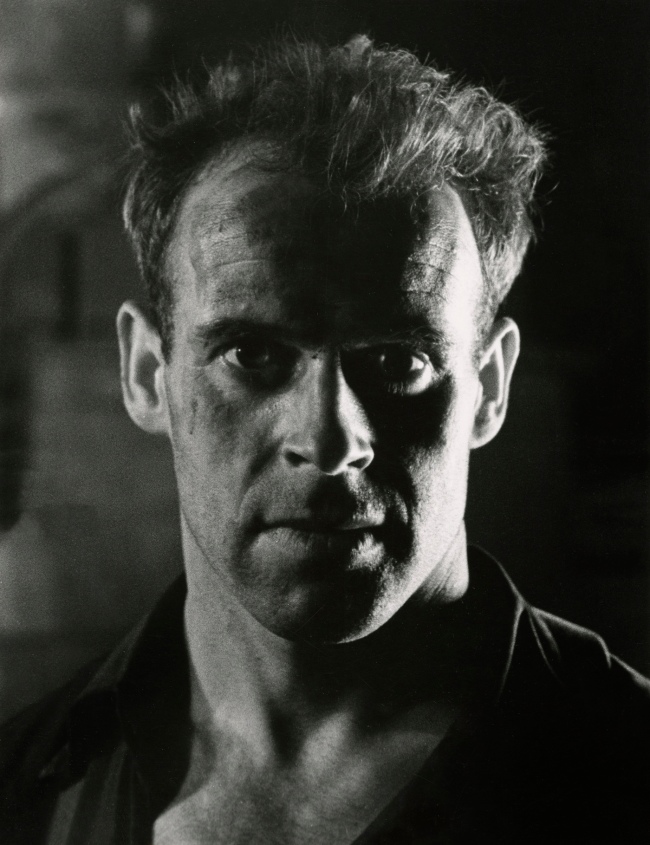
![Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Autoritratto, Zurigo [Self-portrait, Zurich]' 1927 Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Autoritratto, Zurigo [Self-portrait, Zurich]' 1927](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/jakob-tuggener-autoritratto-zurigo-1927-web.jpg?w=650&h=807)
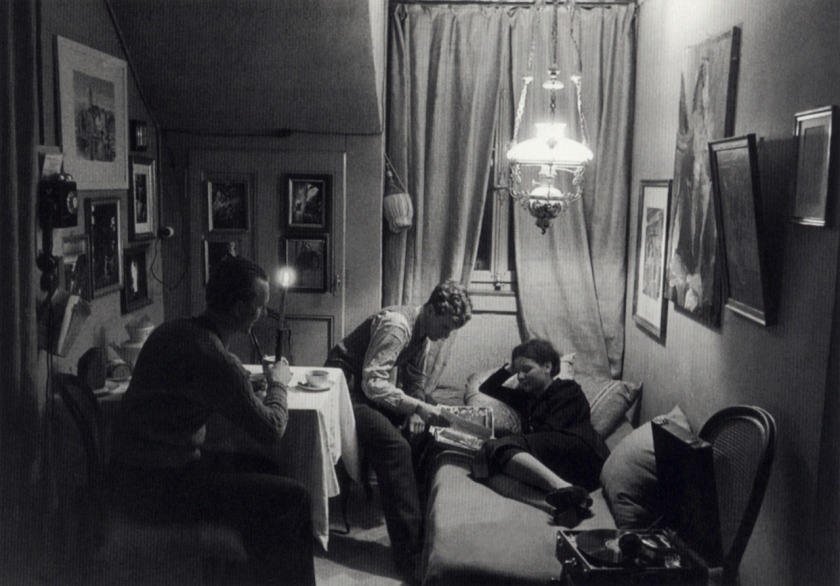
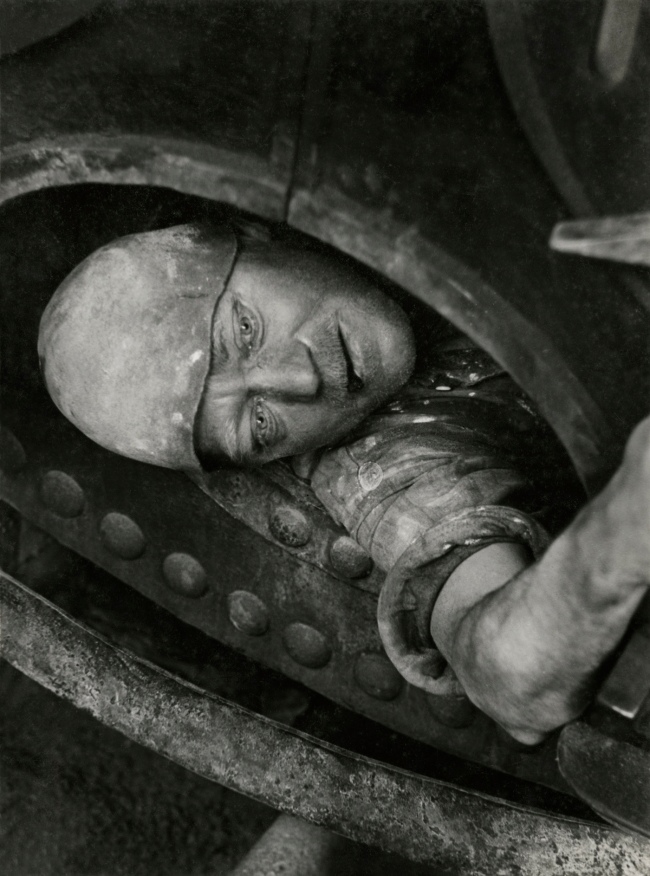
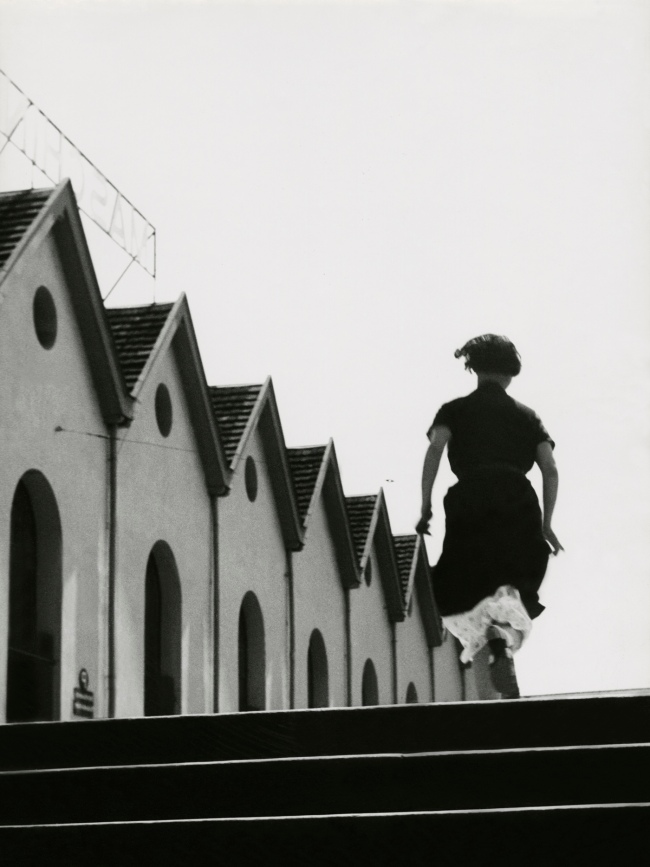
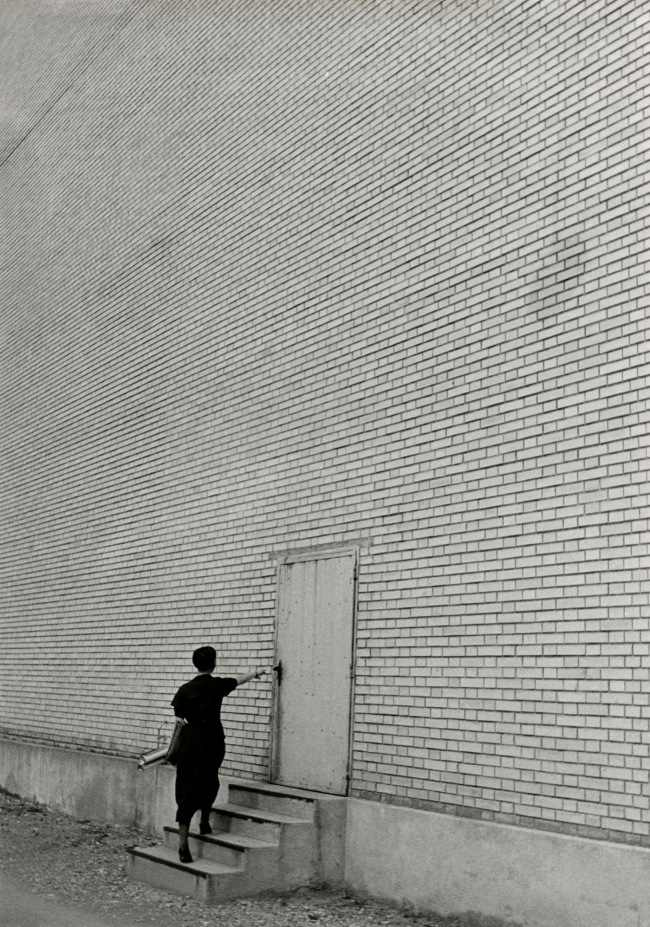






![Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Nell'ufficio della fonderia, fabbrica di costruzioni meccaniche Oerlikon' [In the foundry office, Oerlikon mechanical engineering factory] 1937 Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Nell'ufficio della fonderia, fabbrica di costruzioni meccaniche Oerlikon' [In the foundry office, Oerlikon mechanical engineering factory] 1937](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/jakob-tuggener-nellufficio-della-fonderia-web.jpg?w=650&h=869)
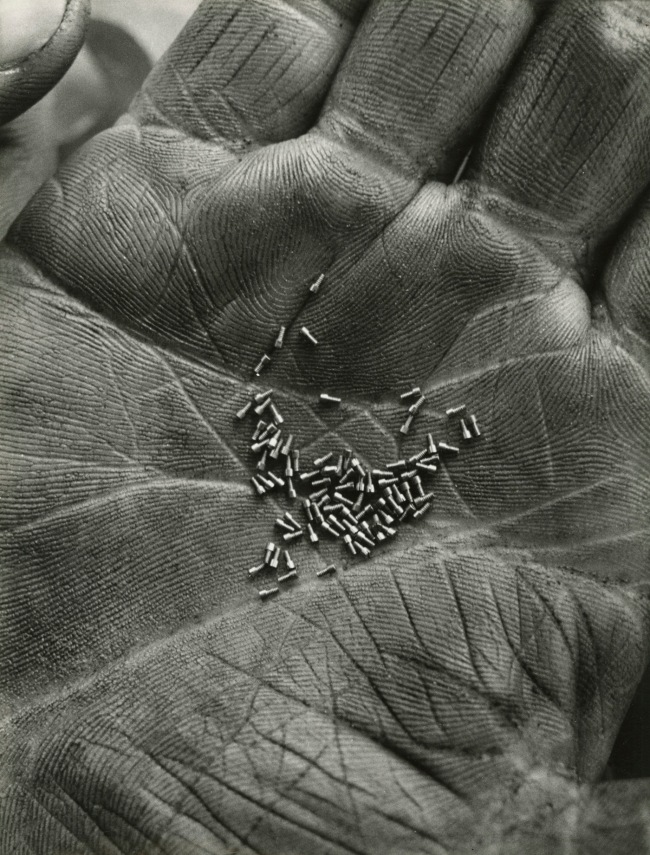

![Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Navy Cut, Ateliers de construction mécanique Oerlikon (MFO)' [Navy Cut, Machine Shops Oerlikon (MFO)] 1940 Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Navy Cut, Ateliers de construction mécanique Oerlikon (MFO)' [Navy Cut, Machine Shops Oerlikon (MFO)] 1940](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/tuggener-navy-cut-web.jpg?w=650&h=872)
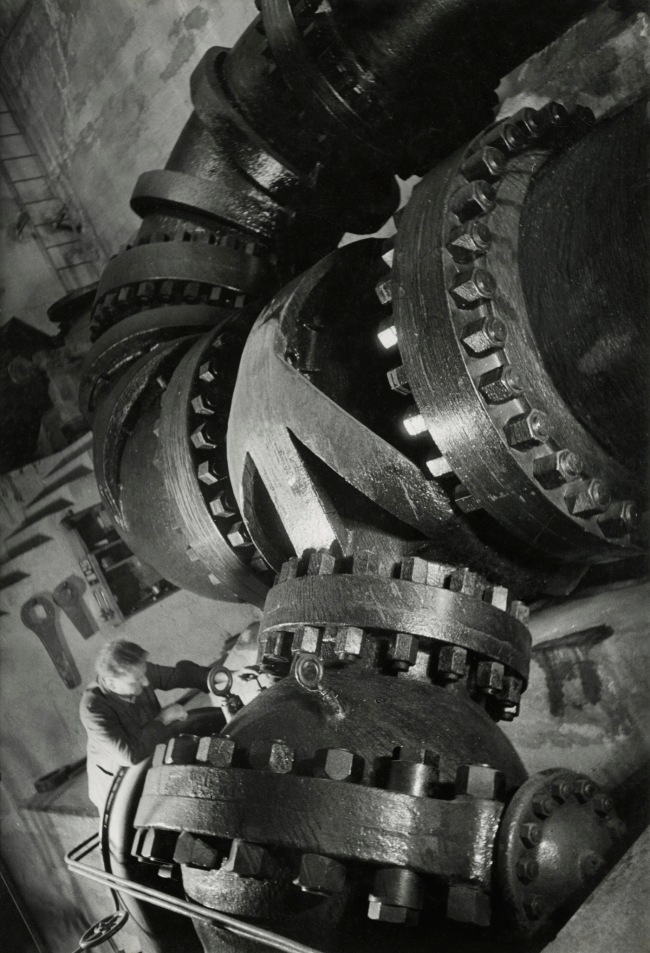
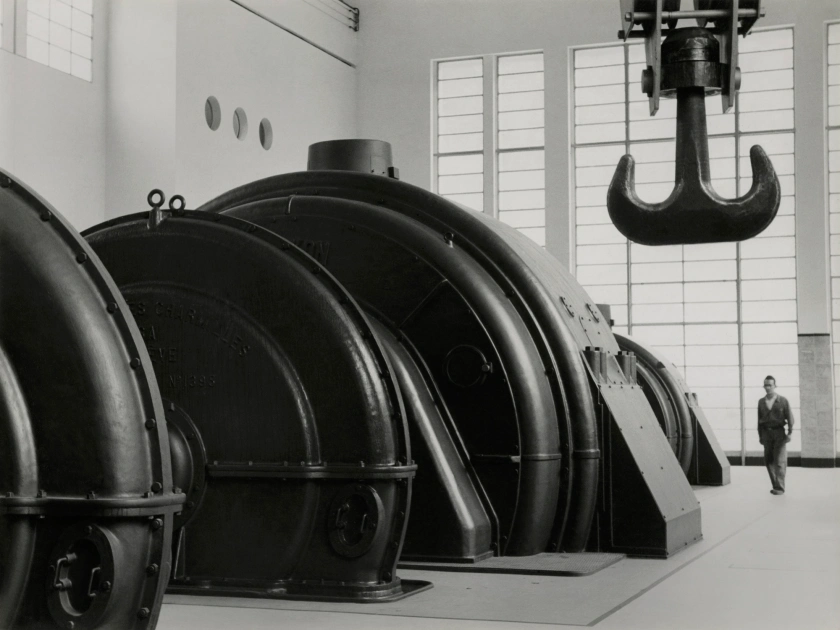


![Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Laboratorio di ricerca, fabbrica di costruzioni meccaniche Oerlikon' [Research laboratory, Oerlikon mechanical engineering factory] 1941 Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Laboratorio di ricerca, fabbrica di costruzioni meccaniche Oerlikon' [Research laboratory, Oerlikon mechanical engineering factory] 1941](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/jakob-tuggener-laboratorio-di-ricerca-web.jpg?w=650&h=939)
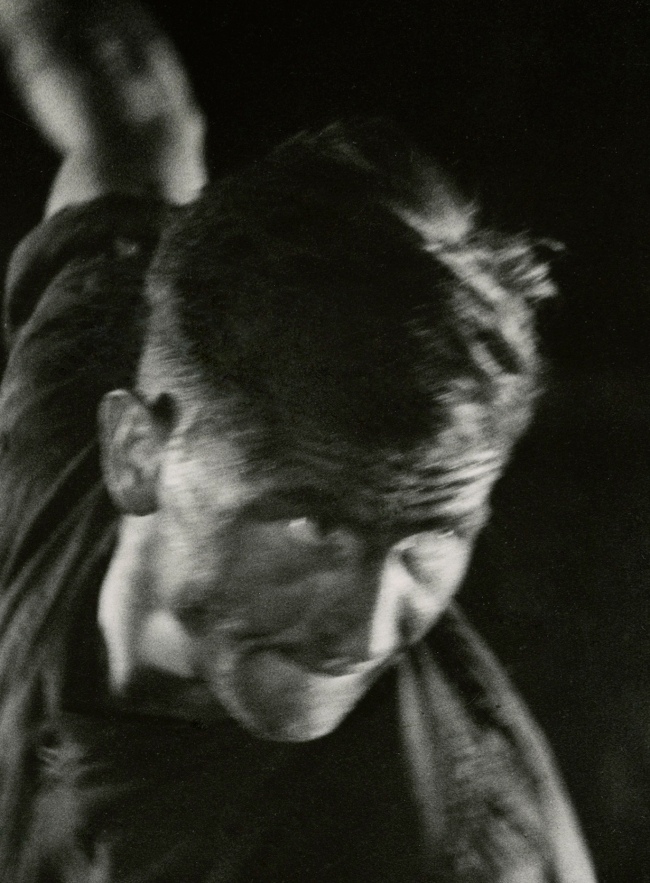
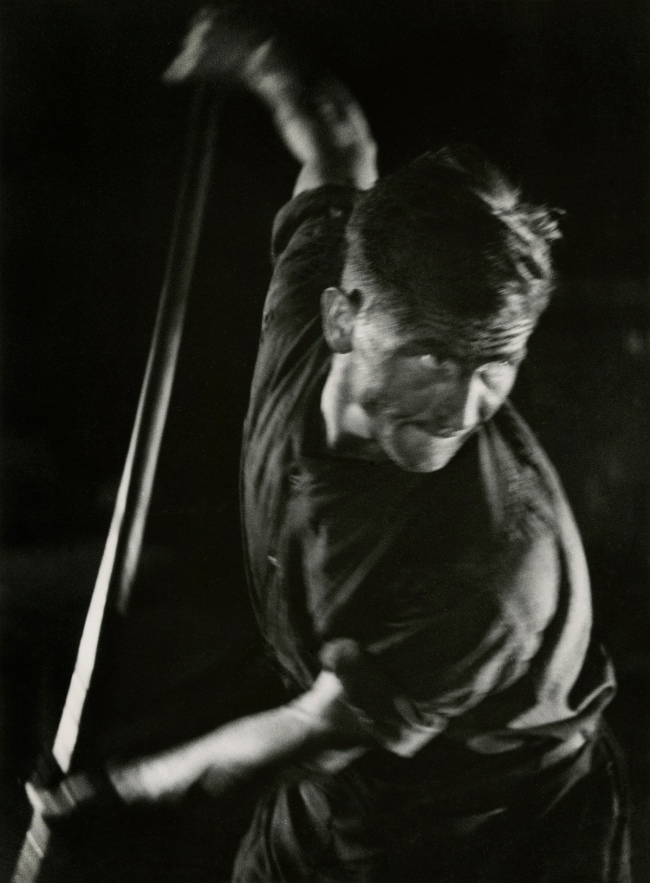
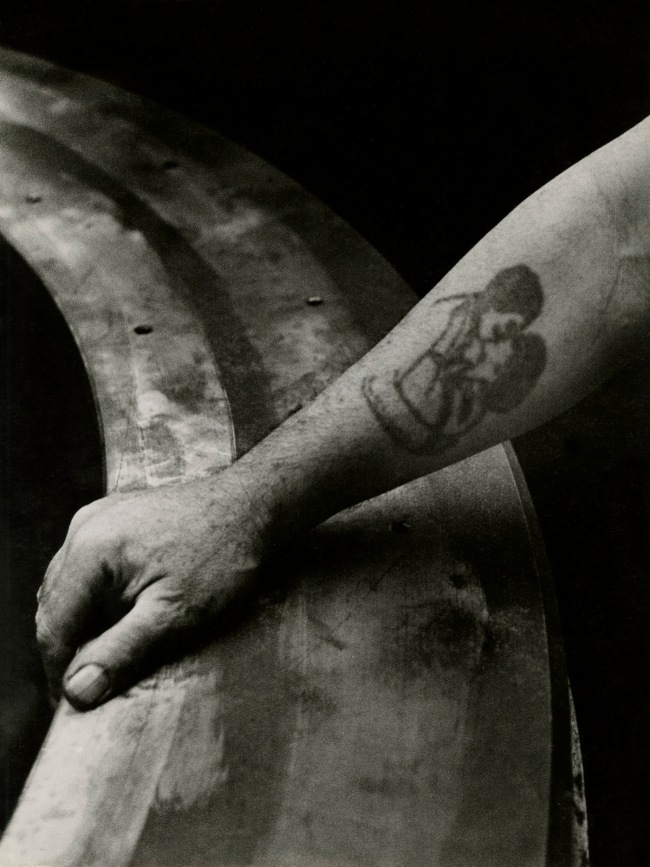
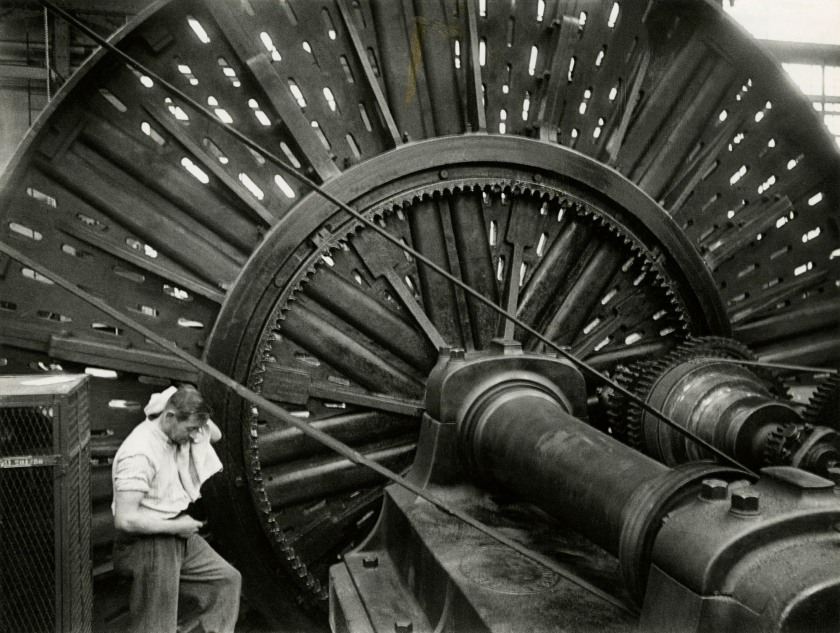
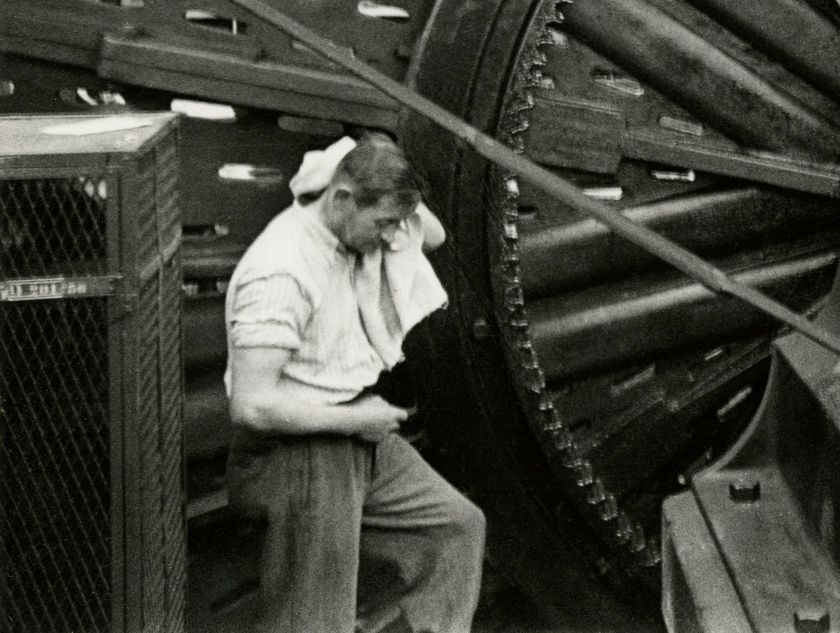




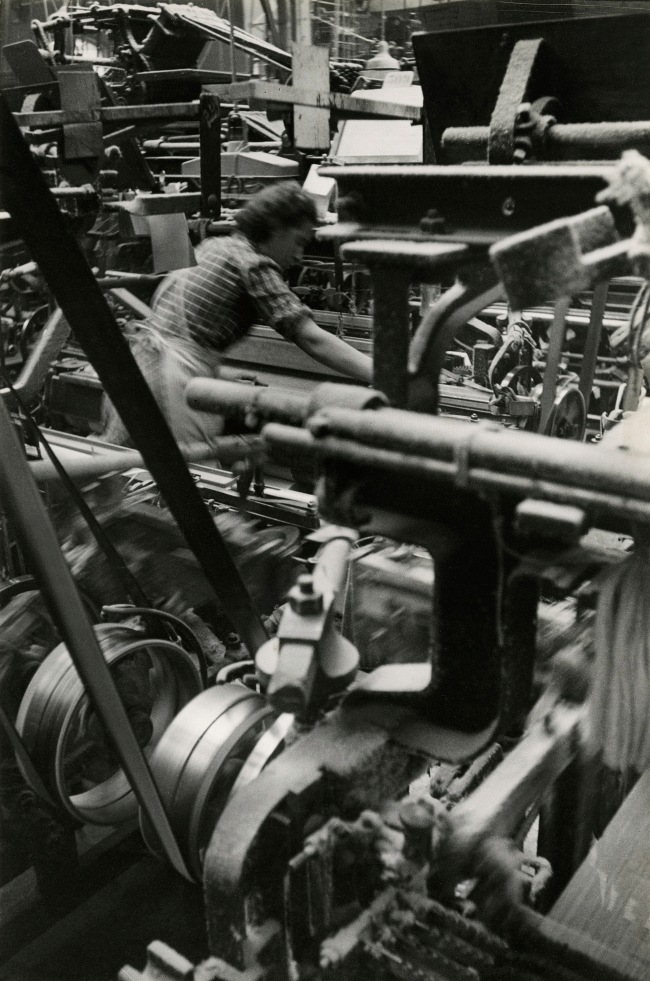



![Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Forgeron dans une fabrique de wagons de Schlieren' [Blacksmith in a Schlieren wagon factory] 1949 Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Forgeron dans une fabrique de wagons de Schlieren' [Blacksmith in a Schlieren wagon factory] 1949](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/tuggener-forgeron-dans-une-fabrique-de-wagons-web.jpg?w=650&h=898)
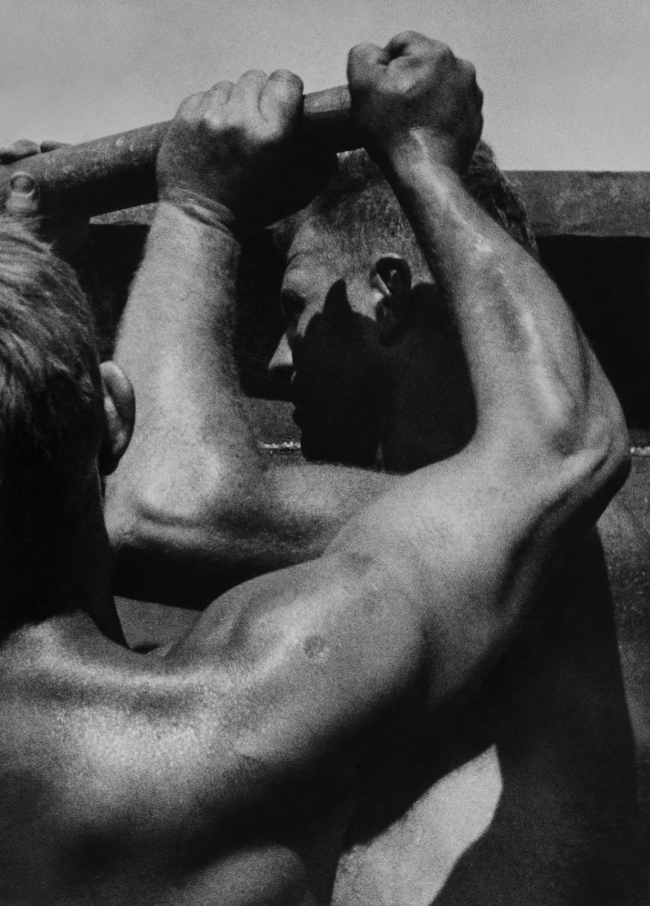
















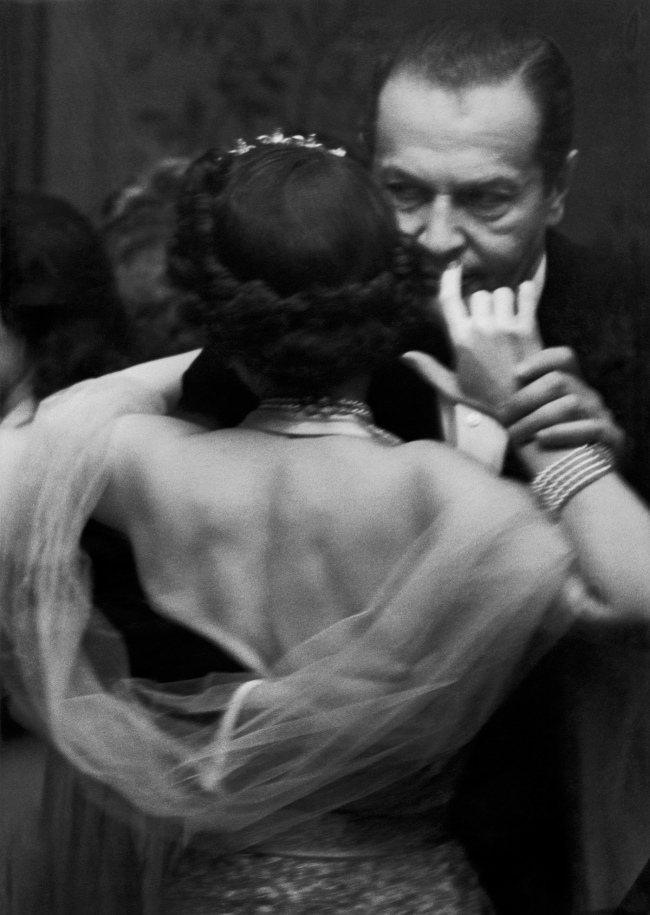
![Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Ballo ungherese, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurigo, 1935' [Hungarian dance, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurich, 1935] 1935 Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Ballo ungherese, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurigo, 1935' [Hungarian dance, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurich, 1935] 1935](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/tuggener-ballo-ungherese-web.jpg?w=650&h=879)
![Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Ballo ungherese, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurigo, 1935' [Hungarian dance, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurich, 1935] 1935 Jakob Tuggener (Swiss, 1904-1988) 'Ballo ungherese, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurigo, 1935' [Hungarian dance, Grand Hotel Dolder, Zurich, 1935] 1935](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/jakob-tuggener-ballo-ungherese-web.jpg?w=650&h=953)
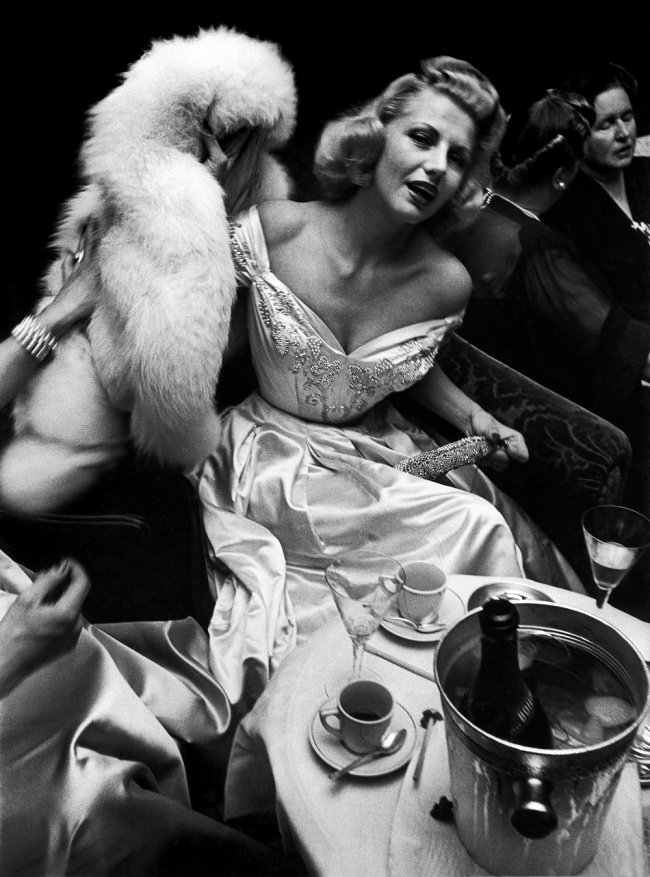
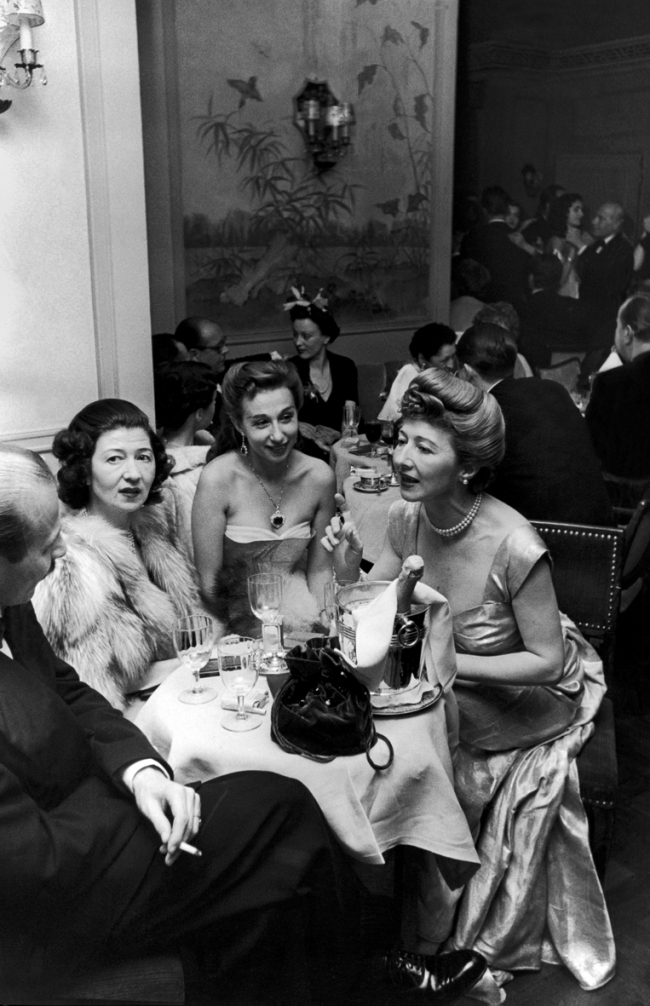
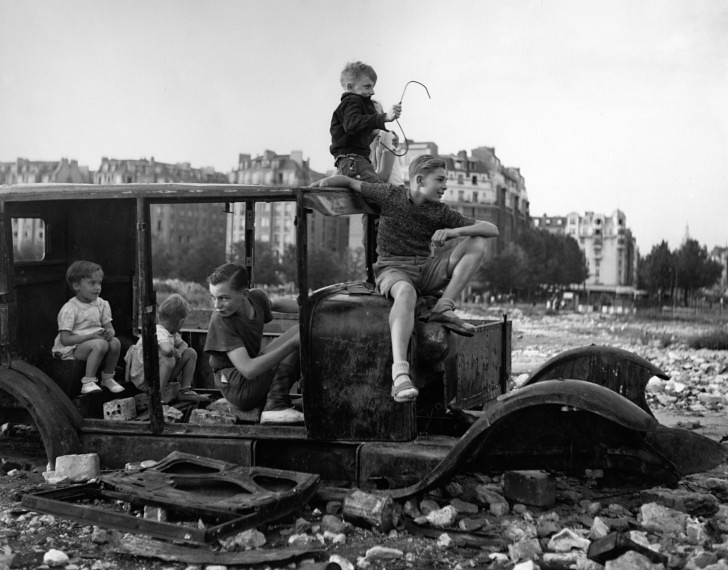
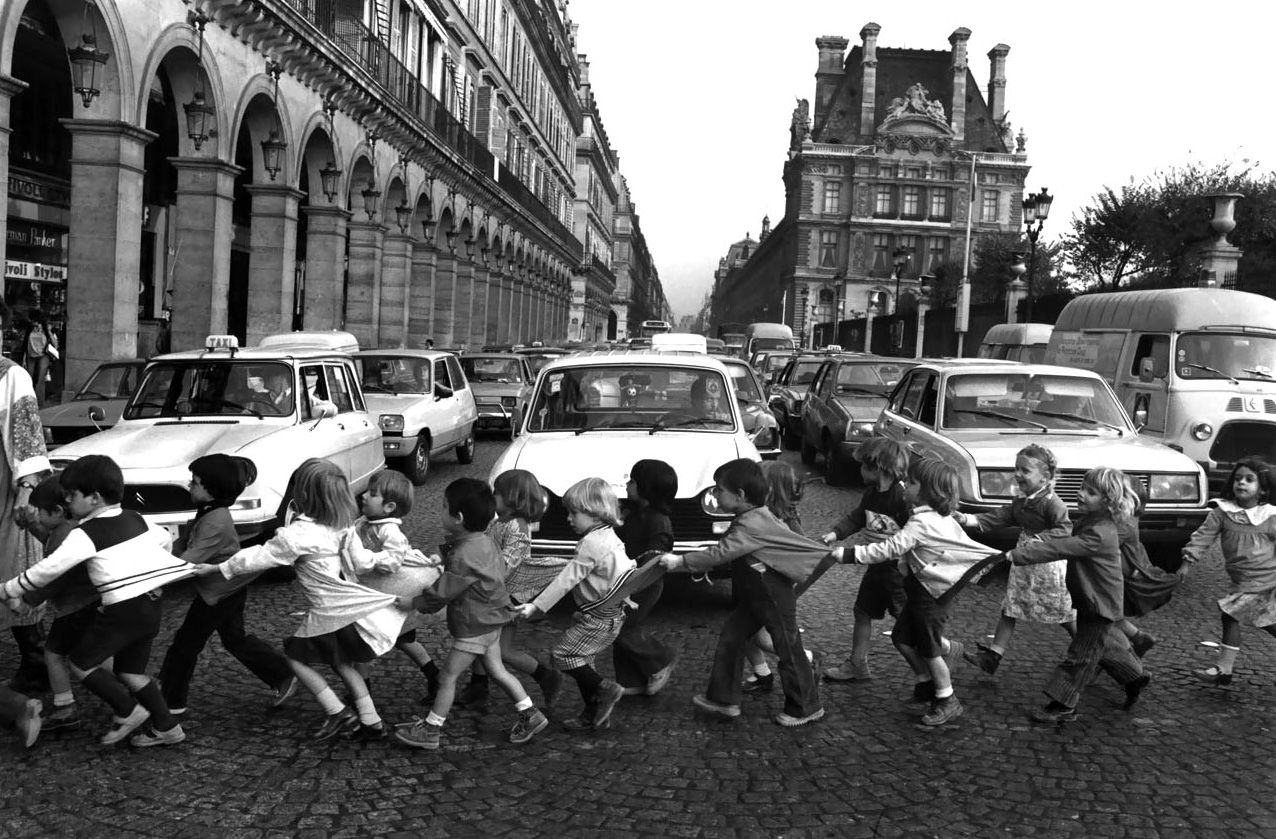
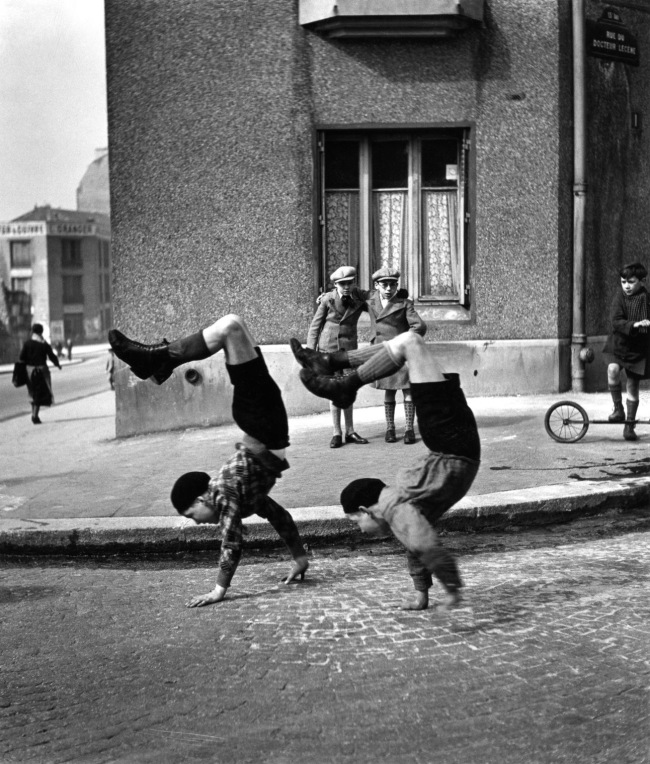
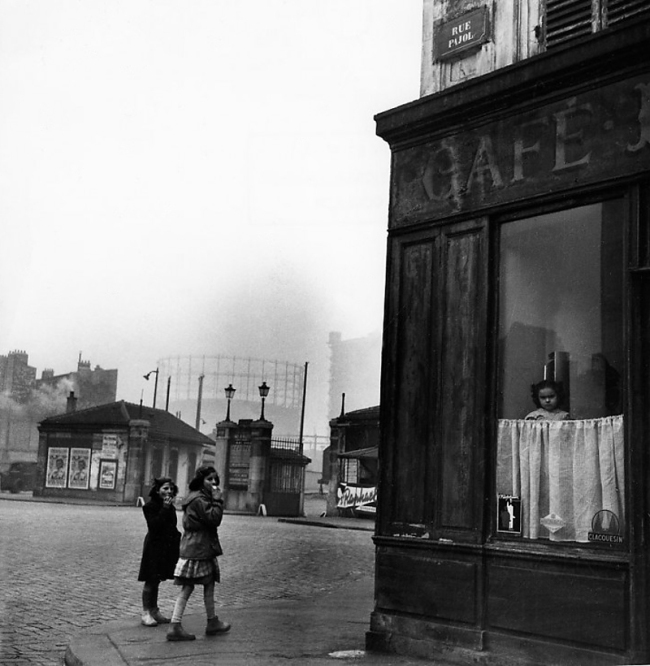
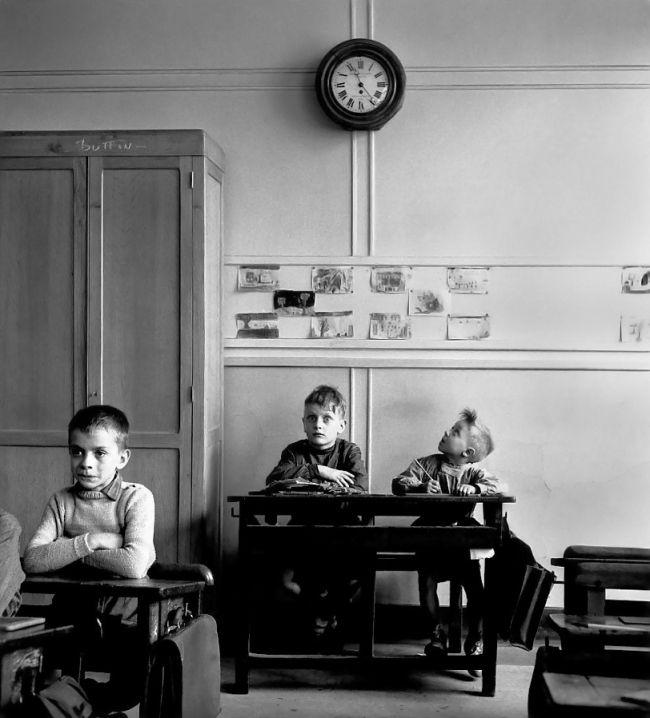






























































![Sabine Weiss (Swiss-French, 1924-2021) 'Enfants jouant, rue Edmond-Flamand' [Children playing, rue Edmond-Flamand] Paris, 1952 Sabine Weiss (Swiss-French, 1924-2021) 'Enfants jouant, rue Edmond-Flamand' [Children playing, rue Edmond-Flamand] Paris, 1952](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/10/weiss-children-playing-web.jpg?w=650&h=834)




![Sabine Weiss (Swiss-French, 1924-2021) 'Anna Karina pour la marque Korrigan' [Anna Karina for the brand Korrigan] 1958 Sabine Weiss (Swiss-French, 1924-2021) 'Anna Karina pour la marque Korrigan' [Anna Karina for the brand Korrigan] 1958](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/10/weiss-karina-web.jpg?w=650&h=820)



![George Baron Goodman, d. 1851. [Dr William Bland, ca. 1845 - portrait] c. 1845](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/07/goodman-dr-george-bland-1845-web.jpg?w=840)























































You must be logged in to post a comment.