Exhibition dates: 14th June 2014 – 18th January 2015
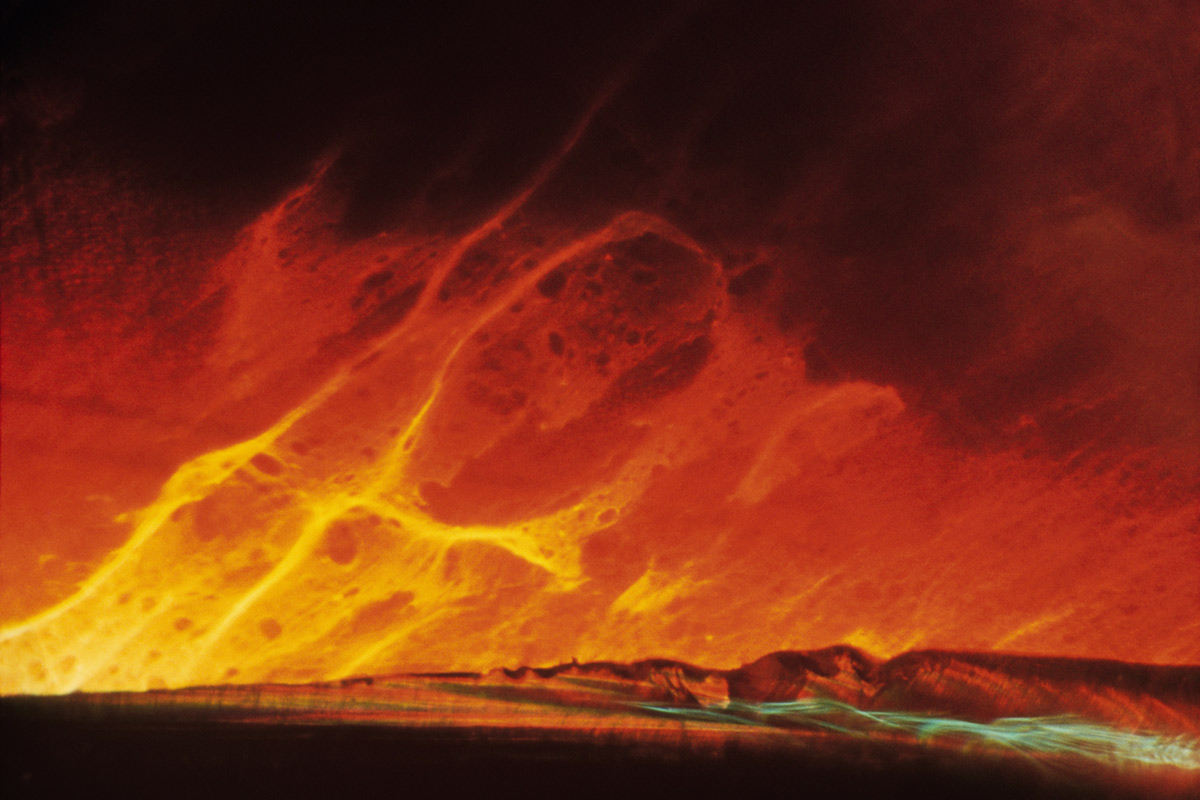
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
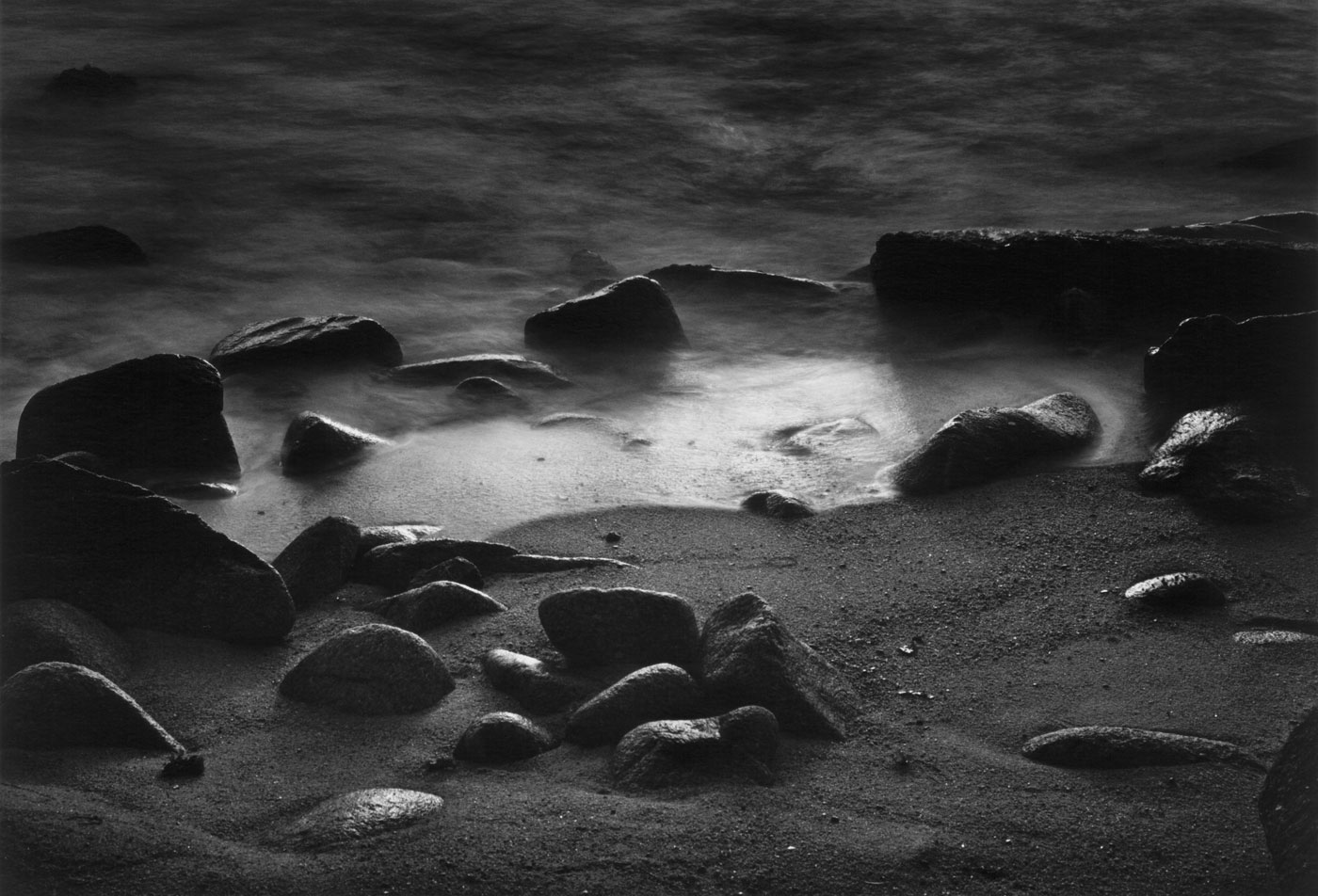
Del Monte Forest
1969
Gelatin silver print
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Being and Becoming in the work of Wynn Bullock
It’s strange how some artists become famous while others wane in relative obscurity. For 50 years after his death, J. S. Bach’s reputation as a composer declined, his work regarded as old-fashioned compared to the new style of the day. Just look at him now.
Wynn Bullock, contemporary of Edward Weston, Minor White, Harry Callahan, Aaron Siskind, Imogen Cunningham, Frederick Sommer and Ansel Adams, is not yet as well known as any of them. He should be. As the press release states, “Despite early acclaim, the true breadth and depth of Bullock’s career has remained largely in the shadows.” This first retrospective of his work in 40 years will hopefully start to change that perception. In my estimation he is up there in the pantheon of photographic stars. There are photographers… and there are master photographers. Bullock is one of the latter, in my top ten classical black and white analogue photographers of all time.
Bullock began pursuing “straight” photography after meeting Edward Weston in 1948. Work from the early 1950s has an essential, humanist flavour as can be seen in photographs such as Child in Forest (1951) and Let There Be Light (1951), both images appearing in Edward Steichen’s seminal exhibition The Family of Man at the Museum of Modern Art in 1955, printed at large scale. By the mid-50s Bullock was really hitting his straps and the work starts to become less didactic and more open to multiple interpretations and possibilities.
As Bullock says, the mysteries lie all around us waiting only to be perceived. But it’s more than that… it’s more than “what if”. Bullock claims the existence of these things while at the same time acknowledging that they are not generally accessible within the Western canon. That he expresses their existence is his gift to the world.
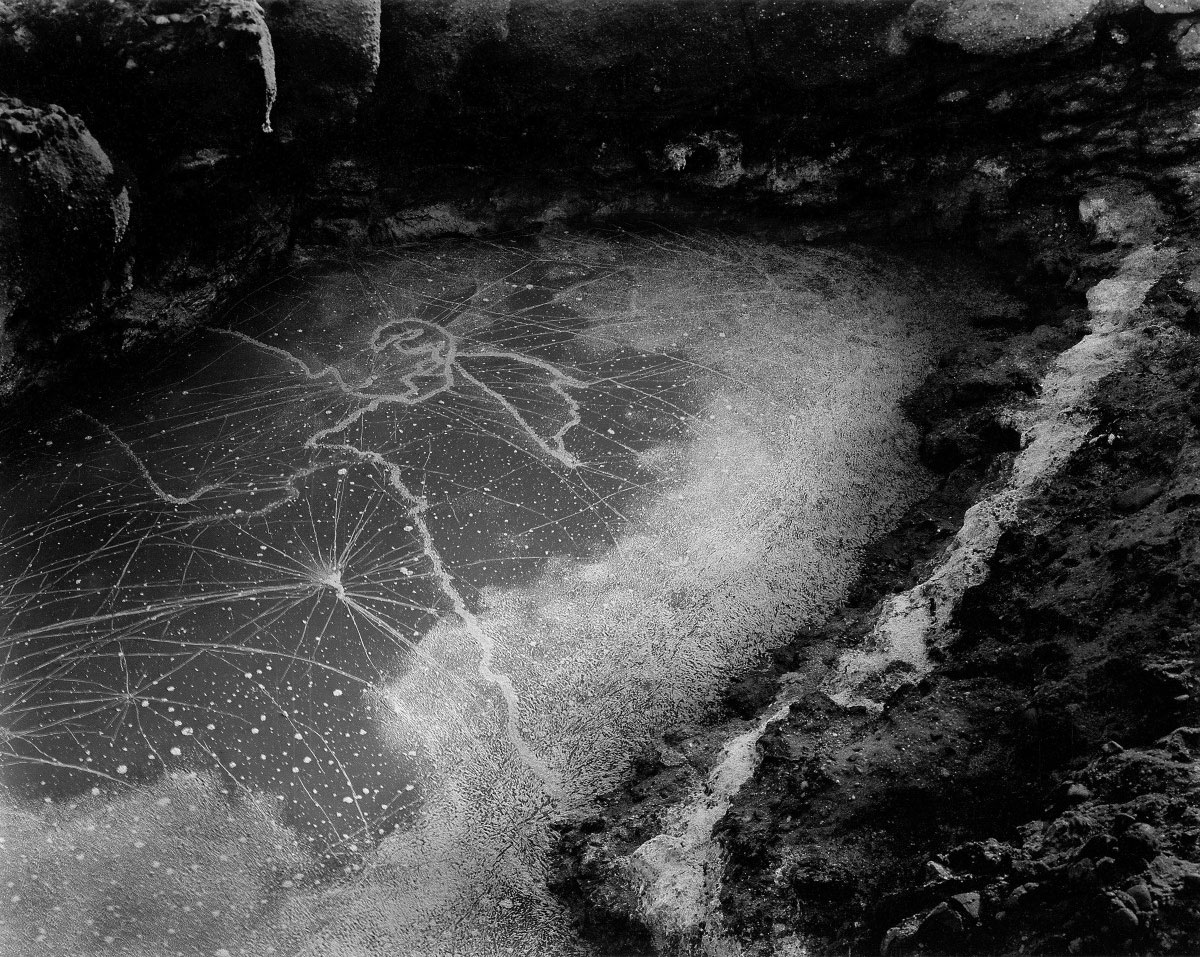
Take, for example, that most complex of images, Point Lobos Tide Pool (1957). Once seen, never forgotten. I remember seeing this image in my first year studying photography at university and it being seared into my brain. How could you get such an image! It encompasses every feeling and emotion about our place in the cosmos that I could ever think of. And then you hear the story (one that I recently confirmed with his daughter Barbara), which I recount here and which appeared in the book Darkroom edited by Eleanor Lewis, published in 1976 by Lustrum Press, and dedicated to Bullock’s memory.
Bullock was only able to make ONE exposure.
“The first photograph I want to discuss is the POINT LOBOS TIDE POOL. This is a contact print from an 8 x 10 negative. The picture was taken at sunset and the light was dim. The sun was striking only the edges of the rocks in the upper-left-hand corner. The tide pool itself was especially dull, and the light was disappearing so fast I had to make a quick exposure. The negative is very soft because in my hurry to capture the picture, I forgot to underexpose the film so that I could expand the contrast by overdeveloping. The tide pool, a critical part of the image, is especially soft.
“For the final print, I used Brovira No. 5 paper, Amidol developer, and developed it for three minutes to keep the dull parts from going flat. As soon as you use high contrast papers, everything gets more critical. A second or two variation in exposure in high contrast areas can mean the difference between seeing what I want to see, and not seeing anything but black or white paper.
“I could think of the negative-making process as one in which I would make a technically perfect negative. But the technically perfect negative doesn’t always give me what I want… By not always reaching for the easily printed negative, I get luminosity I wouldn’t otherwise have.
In the tide pool print, it’s always been a touchy problem to get the brilliance in the pool itself, where the negative is soft. Unless carefully controlled, that part goes muddy. The rest of the photograph is secondary, but requires some burning and dodging to get tonal balance.
“These are problems I’ve been living with. In doing so, I’ve developed printing skills. It’s a way of life with me. In printing, I don’t want to distort the reality of the image, but I don’t want to distort the reality of my feelings for it either. The two go hand in hand. I have no qualms about altering the image by burning and dodging. I’m not a purist in that way. I am a purist in that I don’t want the manipulation to show. As soon as it does, the magic is destroyed.”
As his daughter Barbara notes, “Point Lobos Tide Pool, 1957 is another serendipitous image that took place on the [Point Lobos State] Reserve. The day this photograph was made, Dad was hauling his heavy field camera along the South Shore Trail when he happened upon a tide pool with a galaxy in its midst. He set up his equipment as quickly as he could and made his first exposure. Normally, he liked to bracket his exposures, but before he could make a second one, a gust of wind swept across the pool and the complex pattern of microscopic organisms vanished.
Fortunately, one exposure was good enough. Whenever he told the story, Dad would laugh and say, “I was just damn lucky that day!” What he often left unexpressed was the lasting impression of the experience that exemplified for him the continual being-and-becoming nature of the universe as well as the kinship of its microcosmic and macrocosmic dimensions. The image remained a personal favourite for the rest of his life.” (Barbara Bullock-Wilson. “Point Lobos Tide Pool, 1957” Commentary © 2013/2015 Barbara Bullock-Wilson. All rights reserved.)
It is as if the universe stood still for the length of time that it took Bullock to expose his plate, as though the universe was giving him permission for his previsualisation … … … before it moved on, in a gust of wind. But that is not the end of it, no! Because of the thin negative Bullock had to print on grade 5 paper, the most contrasty paper that you can get. And because the area of the tide pool was especially thin, the exposure time is absolutely critical for this print, to get the luminosity in the pool that the artist required. In the whole scheme of things there is a tiny window of opportunity with the exposure of this negative to get a glorious print. This is far from a straight print, and what makes the story even more remarkable is that Bullock had to delve into his scientific knowledge, had to experiment with his feelings (his exposure time), with the magic of the analogue print, to make this apparition appear!
The whole story is quite thrilling really. As my mentor observes, “Point Lobos is several km of coast if you measured into every bay – but there aren’t that many spots where you can photograph the actual tide zone – probably 7 or 8 inlets – some smaller than a basketball court. The spot that Minor White talks about as Weston cove is about basketball court size from memory. You can walk around above it a few metres in the air and see it all. Only someone with a specific aim would scramble down to be amongst what could already be clearly seen. There are just as many spots where you can’t get down like Weston’s sparkle on the sea shot. Weston cove feels amazing; full of ghosts. Bullock would have been very familiar with what would be likely to come around again and what would not.”
Close your eyes and just imagine dragging an 8 x 10 camera down there and finding that image.
Readers, you know that I am a passionate person, that I am passionate about photography. As I relatively young man what these great artists seemed to me to be doing were noble artistic things; I still feel that. You cannot talk about photography like other mediums that define themselves – not in a modernist sense of materials – Rothko can only be talked about by referring to Rothko, Beethoven, Mozart, etc… Much as Bullock says that light “permits the same freedom of expression as paint for the painter, words for the writer, numbers for the mathematician, or sound for the composer,” photography is of a different order. You are comparing a system of making using the hand with a system using a photo-mechanical eye. Making great images is of necessity much more difficult within this process (as can be see in the millions of meaningless images that flood the world today).
I believe that inherent to any photograph is the ability to transcend the medium – whether that is in vernacular photography (by chance) or through astute observation and meditation (MW and WB). Whether the person then recognises these images as such is another matter, but it only happens on limited occasions. But when you get something, the magic just works. In his Point Lobos Tide Pool (1957), Navigation without Numbers (1957), Under Monterey Wharf (1969) and Erosion (1959), Bullock is like a mystical time traveller – of both the body and the landscape. You only have to look at the timbre of the prints and the layering of tones. These images can’t be judged on any terms other than the terms the image itself lays down. They are beyond serious: and it shows how difficult photography really is – and how rare the good photograph is – that most photographers don’t really have a count that gets into double figures for a decade’s work. It doesn’t add up to much of a crop for a lifetimes work but does Bullock care… hell no!
As he says, “You really have to give of yourself to make good pictures… The fact that good pictures are rare, however, has never slowed me down. Just going out and looking at things and using a camera is therapeutic. I deeply love the whole process.”
A deep love of the whole process, a deep love of being and becoming.
The ability of the photographer is that they can massage the medium – through imagination, surrealism, reality, space / time etc… that ENACTS a difference that painters, musicians can only dream of – through a manipulation of reality, through a form of hyper-reality. In Bullock’s case it is the recognition of the mysteries that lie all around us in which the images take on a symbiotic relationship with an observation of the human mind THROUGH photography.
Openly talking in a clear language from a lifetime of meditation.
A clear language where words don’t quite equal the meanings normally attached to them.
From another dimension.
“In streams of light I clearly saw
The dust you seldom see,
Out of which the Nameless makes
A Name for one like me.
I’ll try to say a little more:
Love went on and on
Until it reached an open door –
Then Love Itself
Love Itself was gone.
All busy in the sunlight
The flecks did float and dance,
And I was tumbled up with them
In formless circumstance.
I’ll try to say a little more:
Love went on and on
Until it reached an open door –
Then Love Itself
Love Itself was gone.”
(from “Love Itself” lyrics by Leonard Cohen)
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the High Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs and text in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Mysteries lie all around us, even in the most familiar of things, waiting only to be perceived.”
“Light to me is perhaps the most profound truth in the universe… [It] permits the same freedom of expression as paint for the painter, words for the writer, numbers for the mathematician, or sound for the composer.”
“You really have to give of yourself to make good pictures. Well, that giving takes a lot out of you, and you simply can’t operate at that intense level all the time. Neither can you predetermine what happens outside you.The fact that good pictures are rare, however, has never slowed me down. Just going out and looking at things and using a camera is therapeutic. I deeply love the whole process.”
Wynn Bullock
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Point Lobos Tide Pool
1957
Gelatin silver print
7 9/16 x 9 1/2 in.
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Point Lobos Tide Pool appears simultaneously to resemble both a galaxy and a bacterial growth across a petri dish, when in fact it is neither so large nor so small a subject, but rather a pool arrayed with microorganisms along the Carmel coast, transformed into a picture of astounding beauty.
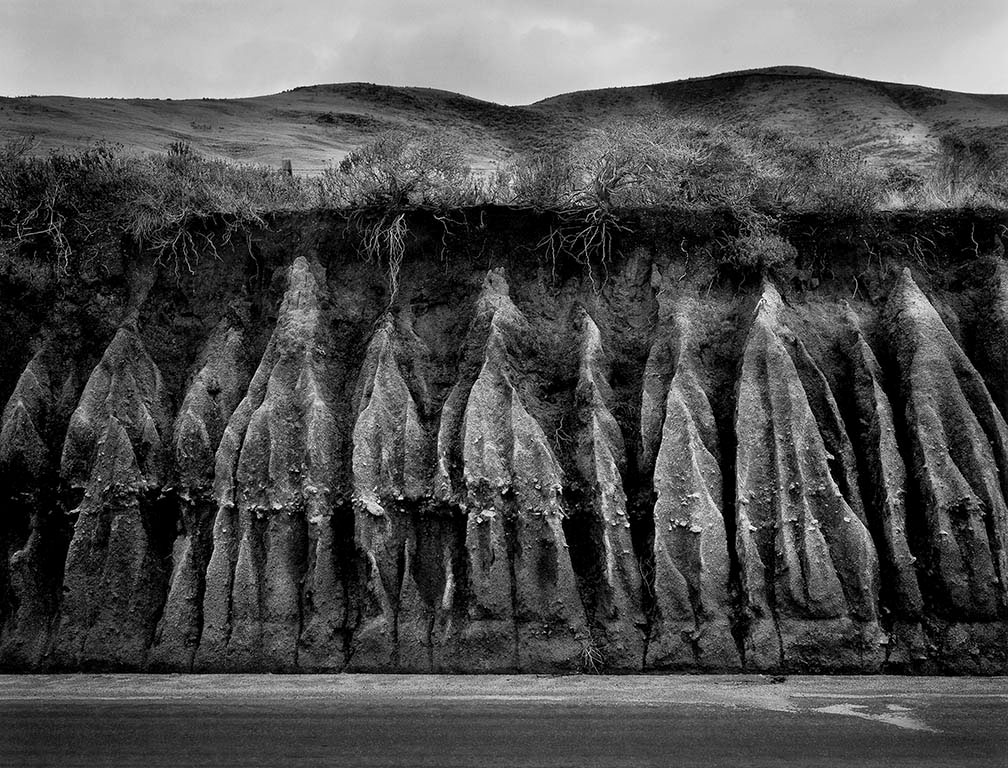
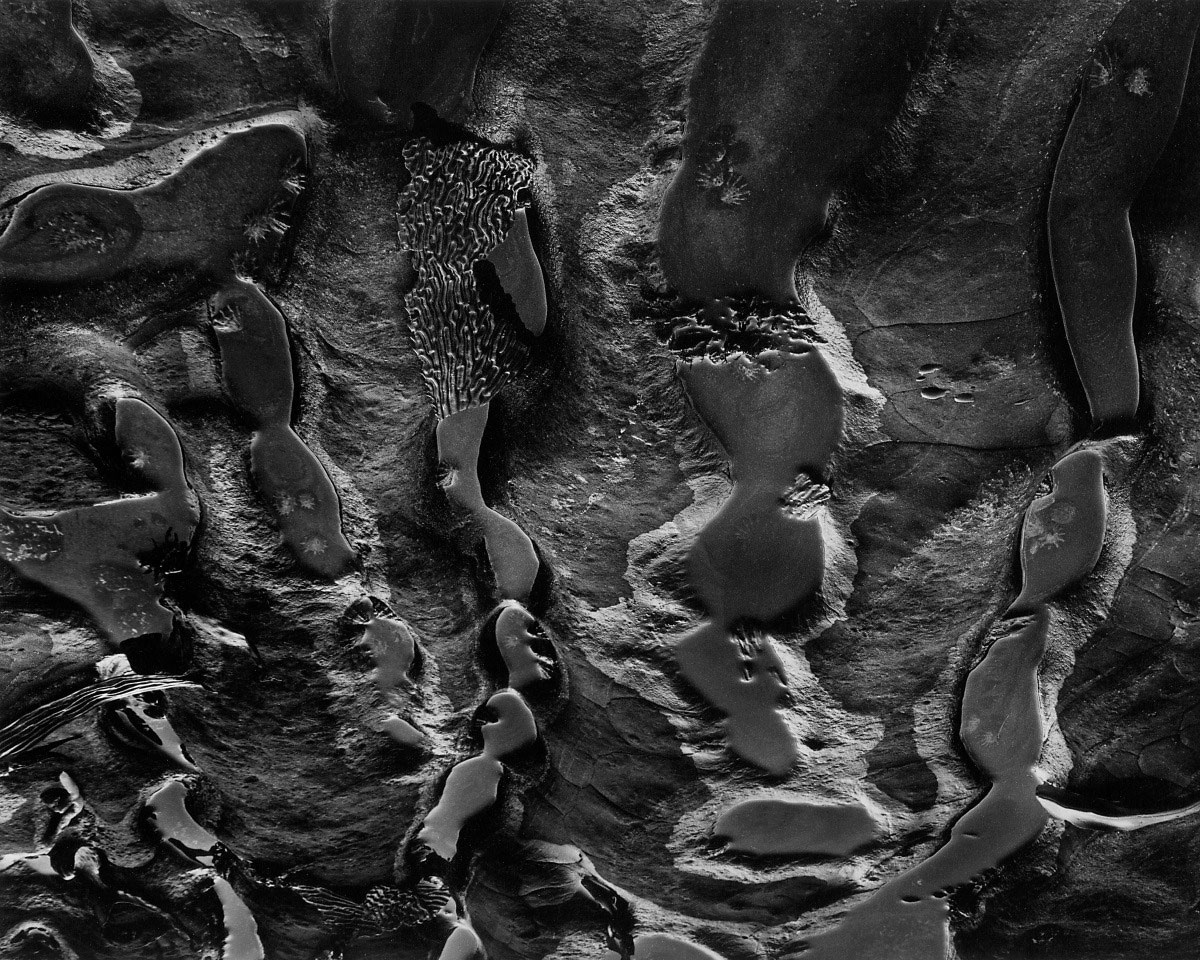
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Erosion
1959
Gelatin silver print
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Bullock found this scene along a California roadway and was drawn to the insight it provides into what goes on in spaces that normally lie beyond our perception. The eroded embankment reveals the slow evolution of the world across centuries, with organic and inorganic elements coexisting together at different stages of growth and decay. Stripped of its skin and flayed by the corrosive power of water, the hill in Bullock’s picture reveals a powerfully foreign world as real and as beautiful as anything on the surface of the earth. Bullock’s efforts were decidedly pointed toward making the ordinary profound and in revealing a complexity beyond the surface of things.
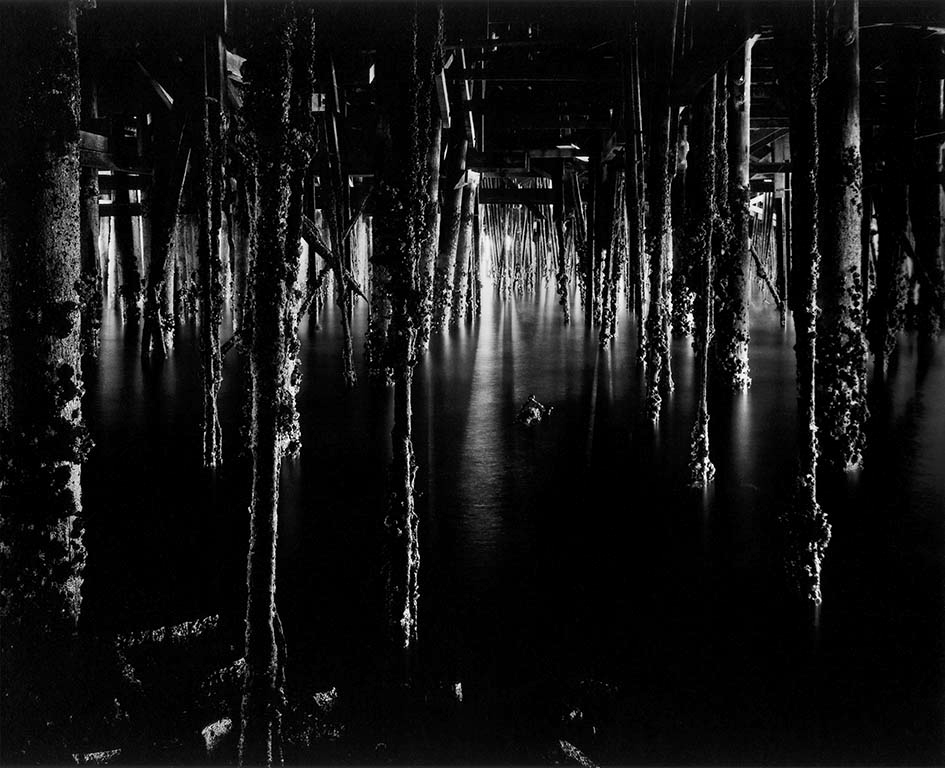
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Under Monterey Wharf
1969
Gelatin silver print
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Navigation without Numbers
1957
Gelatin silver print
6 13/16 x 8 15/16 in.
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
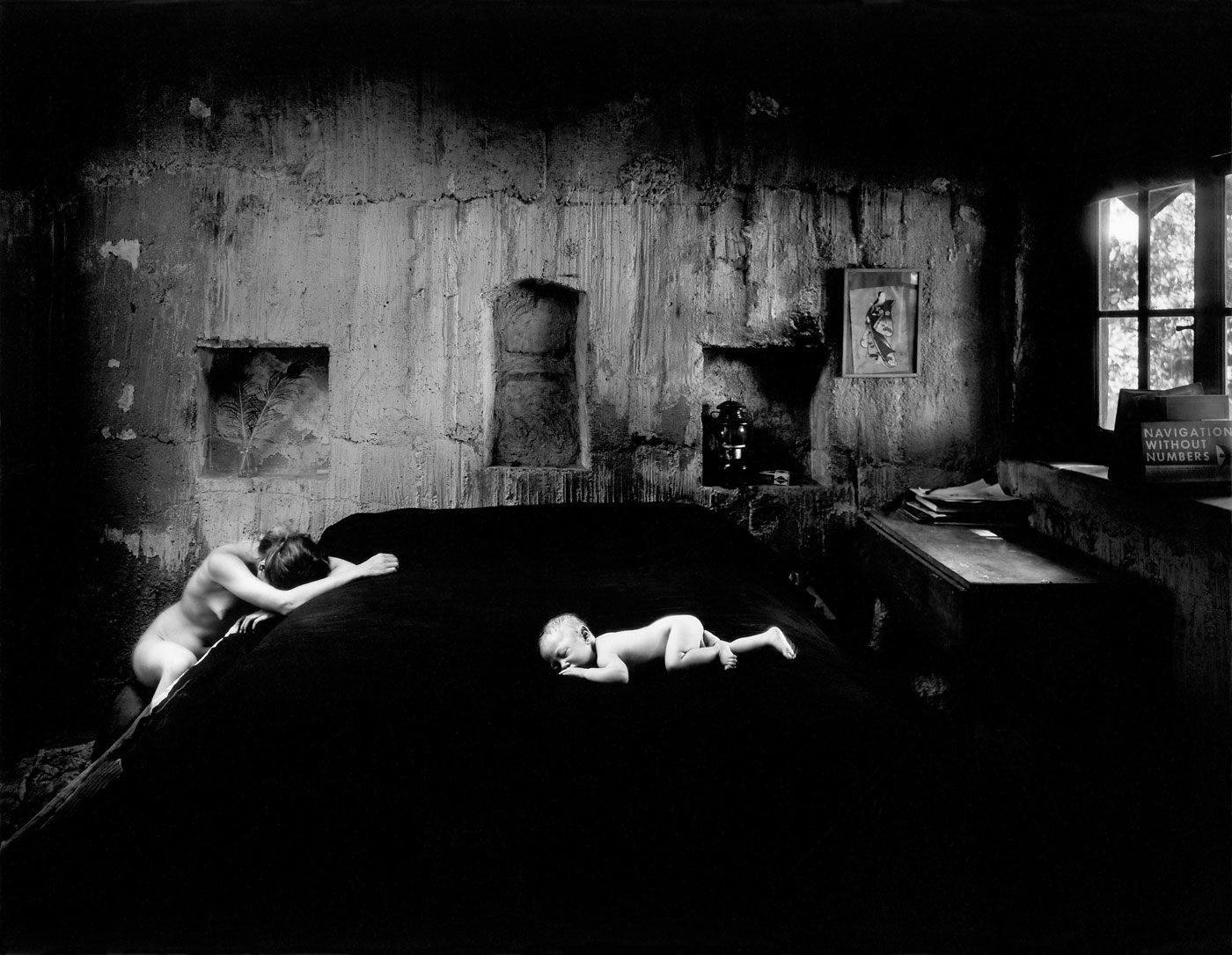
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Nude by Sandy’s Window
1956
Gelatin silver print
Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
In this picture, a brightly lit window occupies the bulk of Bullock’s composition, hovering over a woman who appears to be asleep; light shines in through the glass with a blinding intensity that obscures a clear view of the exterior while alluding to the existence of a world of indefinite proportions beyond.
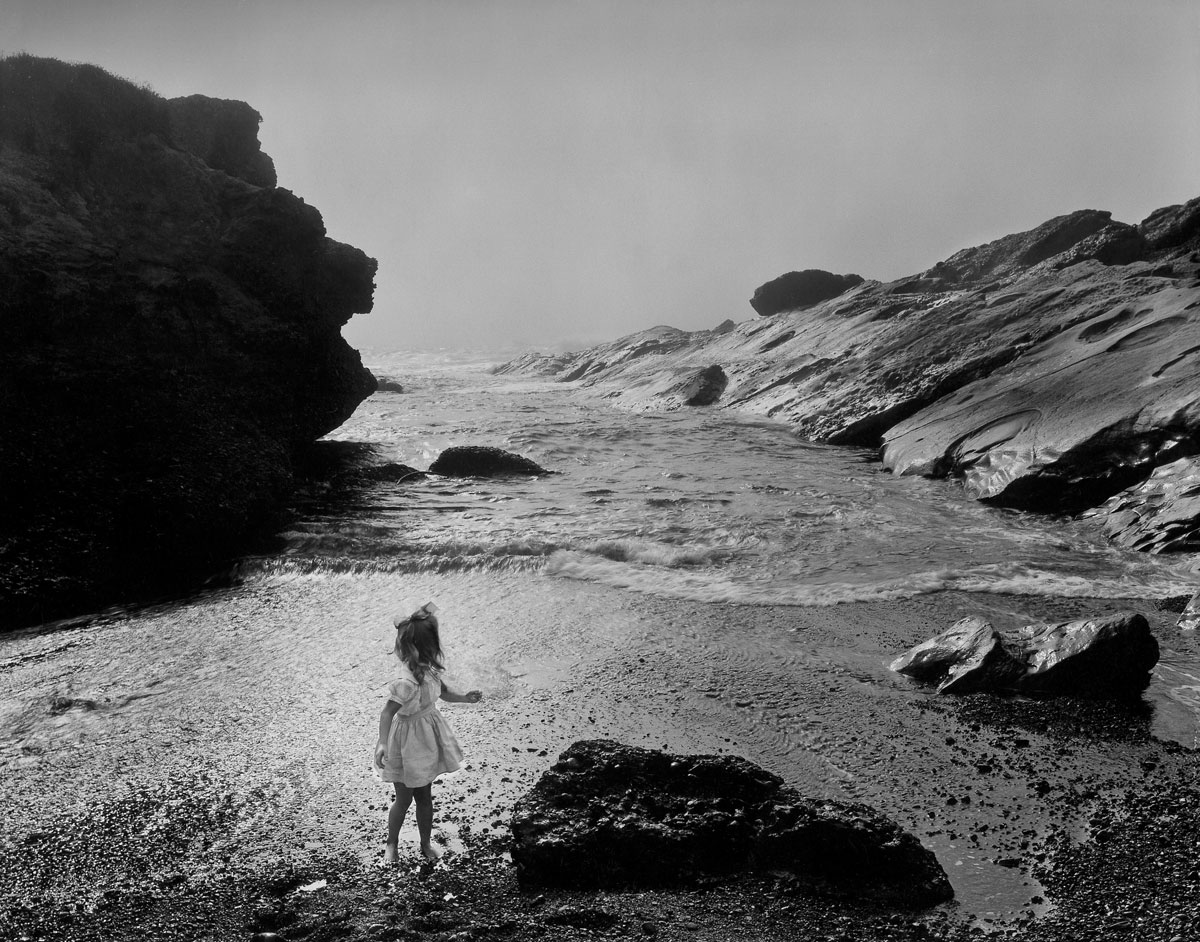
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Lynne, Point Lobos
1956
Gelatin silver print
7 1/2 x 9 7/16 in.
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
“The most beautiful thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the source of all true art and science.
He to whom this emotion is a stranger, who can no longer pause to wonder and stand rapt in awe, is as good as dead: his eyes are closed.”
Albert Einstein, quoted by Wynn Bullock
In June 2014, the High Museum of Art will become the first major museum in nearly 40 years to mount a retrospective of work by Wynn Bullock (1902-1975) with the exhibition Wynn Bullock: Revelations, organised by the High in collaboration with the Center for Creative Photography.
One of the most significant photographers of the mid-20th century, Bullock worked in the American modernist tradition alongside Edward Weston, Harry Callahan and Ansel Adams. More than 100 black-and-white and colour works by Bullock will come together for the exhibition, which will coincide with a major gift to the High from the Bullock Estate of a large collection of vintage photographs, making the Museum one of the most significant repositories of Bullock’s work in the U.S.
The High is home to the most robust photography program in the American Southeast with particularly distinct holdings in the classic modernist tradition. Wynn Bullock: Revelations offers an unprecedentedly holistic look at Bullock’s innovative career, beginning with his early light abstractions and moving through his landscapes, figure studies, colour work, negative images and late abstractions. The exhibition will be on view June 14, 2014 through Jan. 18, 2015.
A close friend of influential West Coast artists Ansel Adams and Edward Weston, and a contemporary of Minor White, Harry Callahan, Aaron Siskind, Imogen Cunningham and Frederick Sommer, Bullock created a body of work marked by a distinct interest in experimentation, abstraction and philosophical exploration. His images Let There Be Light and Child in Forest (both of which will be included in the High’s exhibition) became icons in the history of photography following their prominent inclusion in Edward Steichen’s landmark 1955 exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art, The Family of Man.
Bullock’s photography received early recognition in 1941, when the Los Angeles County Museum of Art staged his first solo exhibition. His mature work appeared in one-man shows at the Bibliotèque Nationale, Paris; the Royal Photographic Society, London; the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York; and the Art Institute of Chicago; among other prestigious venues. His archive was a foundational collection for the Center for Creative Photography in Tucson, Ariz., which is recognised as one of the most important photographic resources in the world.
Despite early acclaim, the true breadth and depth of Bullock’s career has remained largely in the shadows. Wynn Bullock: Revelations offers the most comprehensive assessment of the photographer’s extraordinary career in nearly 40 years. This retrospective traces Bullock’s evolution from his early experimental work of the 1940s, through the mysterious black-and-white imagery of the 1950s and colour light abstractions of the 1960s, to his late metaphysical photographs of the 1970s.
“Bullock’s arresting work was integral to codifying what we now think of as quintessential mid-century style, which in turn paved the way for every stage of photography that has followed,” said Brett Abbott, curator of photography and head of collections at the High. “Presenting this exhibition and acquiring this generous body of work from Bullock’s estate will allow us to play a role in bringing him back into the popular consciousness. Our photography department has expanded greatly over the last few years, in terms of the work we own and the exhibitions we mount, giving us the ability to position this pivotal body of work as part of the nearly two-century-long story of the development of photography.”
Wynn Bullock: Revelations will be accompanied by a fully illustrated catalogue to be produced by the High in collaboration with the University of Texas Press. The book presents 110 images, including some from the Bullock Estate that have never been published before. An essay by Abbott explores the nuances of Bullock’s approach to photography and its fascinating relationship to the history of science and philosophy. The volume also includes an illustrated chronology, bibliography, selected collections, exhibitions history, plate list and notes.
About Wynn Bullock
Wynn Bullock was born on April 18, 1902, in Chicago, Ill. After graduating from high school, Bullock worked as a professional singer in New York City and across Europe. In 1938 he moved to Los Angeles to pursue a law degree but soon dropped out of school to become a photography student at Art Center School, where he became deeply involved in exploring alternative processes such as solarisation and bas relief and began building a career in commercial photography. Bullock went on to serve in the military and then to build a successful private photography business, where he developed a way to control the line effect of solarisation, a discovery for which he was awarded patents. Bullock began pursuing “straight” photography after meeting Edward Weston in 1948. Throughout the 1950s he explored the natural world from his own unique perspective in photography and came into the public spotlight through exhibitions at the Museum of Modern Art in New York City and the Corcoran Gallery in Washington, D.C. In the 1960s he created an innovative body of abstract colour images. He later returned to experimental black and white, on which he continued to focus until his death in 1975. Bullock’s work is part of the collections of more than 90 major institutions throughout the world.
Press release from the High Museum of Art website
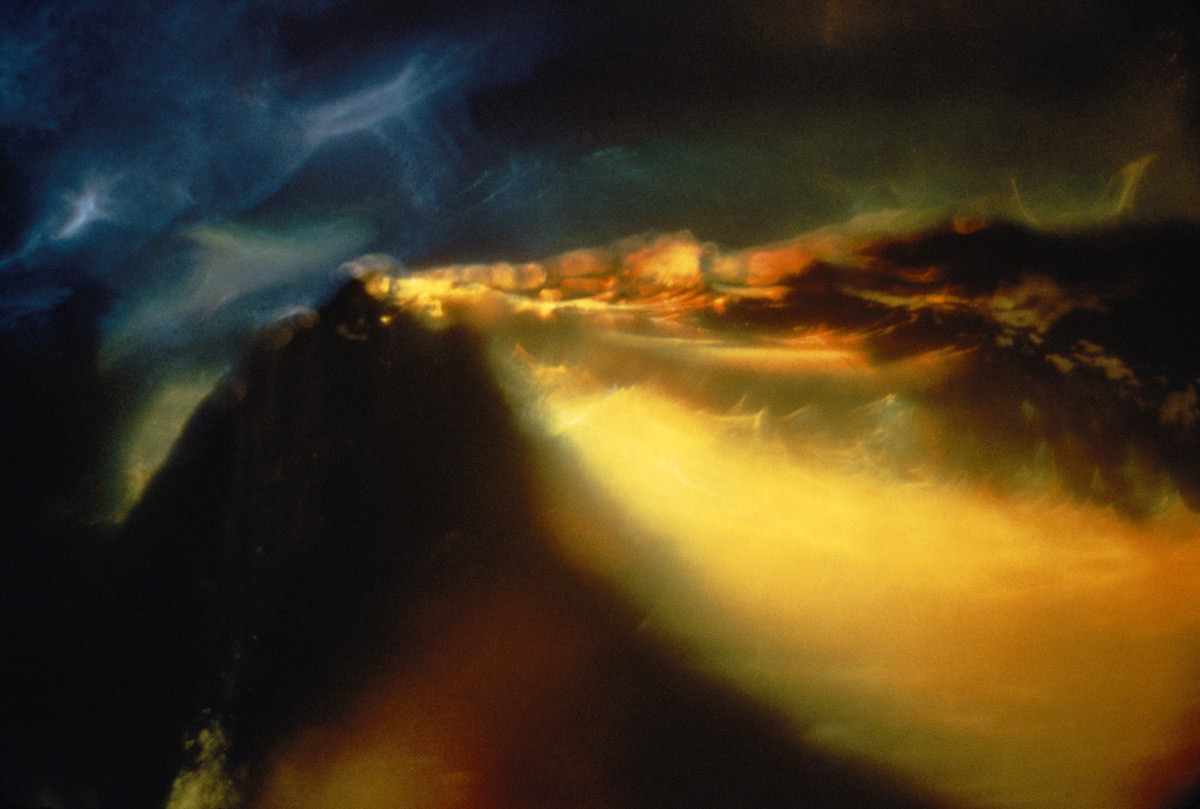
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Color Light Abstraction 1076
1963
Inkjet print
14 x 21 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Color Light Abstraction 1075
1963
Inkjet print
14 x 21 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock: Revelations installation at the High Museum of Art, Atlanta
Entrance mural with glimpses of Galleries 1 and 3 (top), Galleries 1, 2 and 3 (bottom)
“Love Itself”
The light came through the window,
Straight from the sun above,
And so inside my little room
There plunged the rays of Love.
In streams of light I clearly saw
The dust you seldom see,
Out of which the Nameless makes
A Name for one like me.
I’ll try to say a little more:
Love went on and on
Until it reached an open door –
Then Love Itself
Love Itself was gone.
All busy in the sunlight
The flecks did float and dance,
And I was tumbled up with them
In formless circumstance.
I’ll try to say a little more:
Love went on and on
Until it reached an open door –
Then Love Itself
Love Itself was gone.
Then I came back from where I’d been.
My room, it looked the same –
But there was nothing left between
The Nameless and the Name.
All busy in the sunlight
The flecks did float and dance,
And I was tumbled up with them
In formless circumstance.
I’ll try to say a little more:
Love went on and on
Until it reached an open door –
Then Love itself,
Love Itself was gone.
Love Itself was gone.
Lyrics by Leonard Cohen
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Child in Forest
1951
Gelatin silver print
7 7/16 x 9 3/8 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, purchase
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Stark Tree
1956
Gelatin silver print
7 5/8 x 9 1/16 in.
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Let There Be Light
1954
Gelatin silver print
7 3/8 x 9 7/16 in.
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Old Typewriter
1951
Gelatin silver print
7 1/16 × 9 7/16 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, Gift of Lucinda W. Bunnen for the Bunnen Collection
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
The Shore
1966
Gelatin silver print
9 1/4 x 13 5/8 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
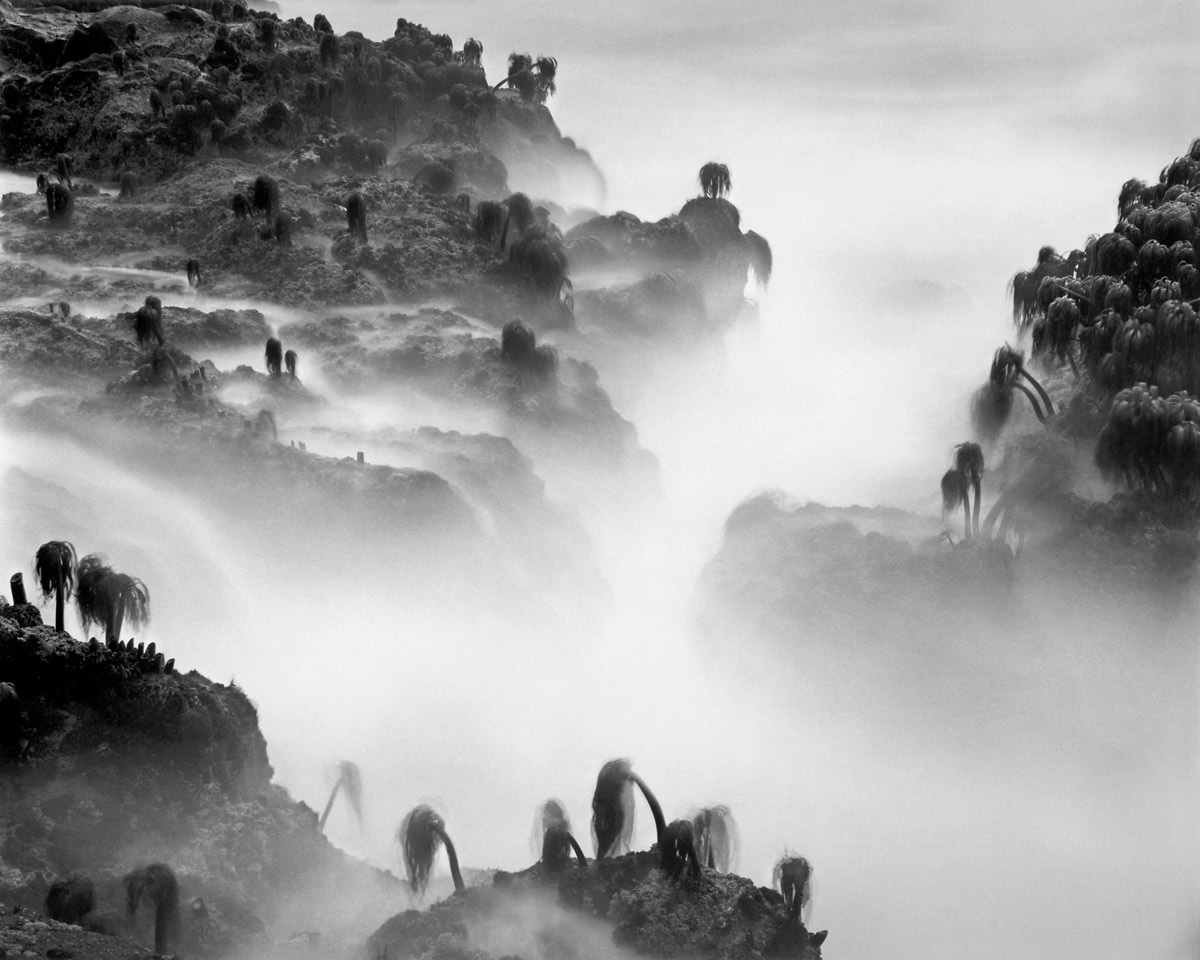
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Sea Palms
1968
Gelatin silver print
7 1/2 x 9 1/4 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
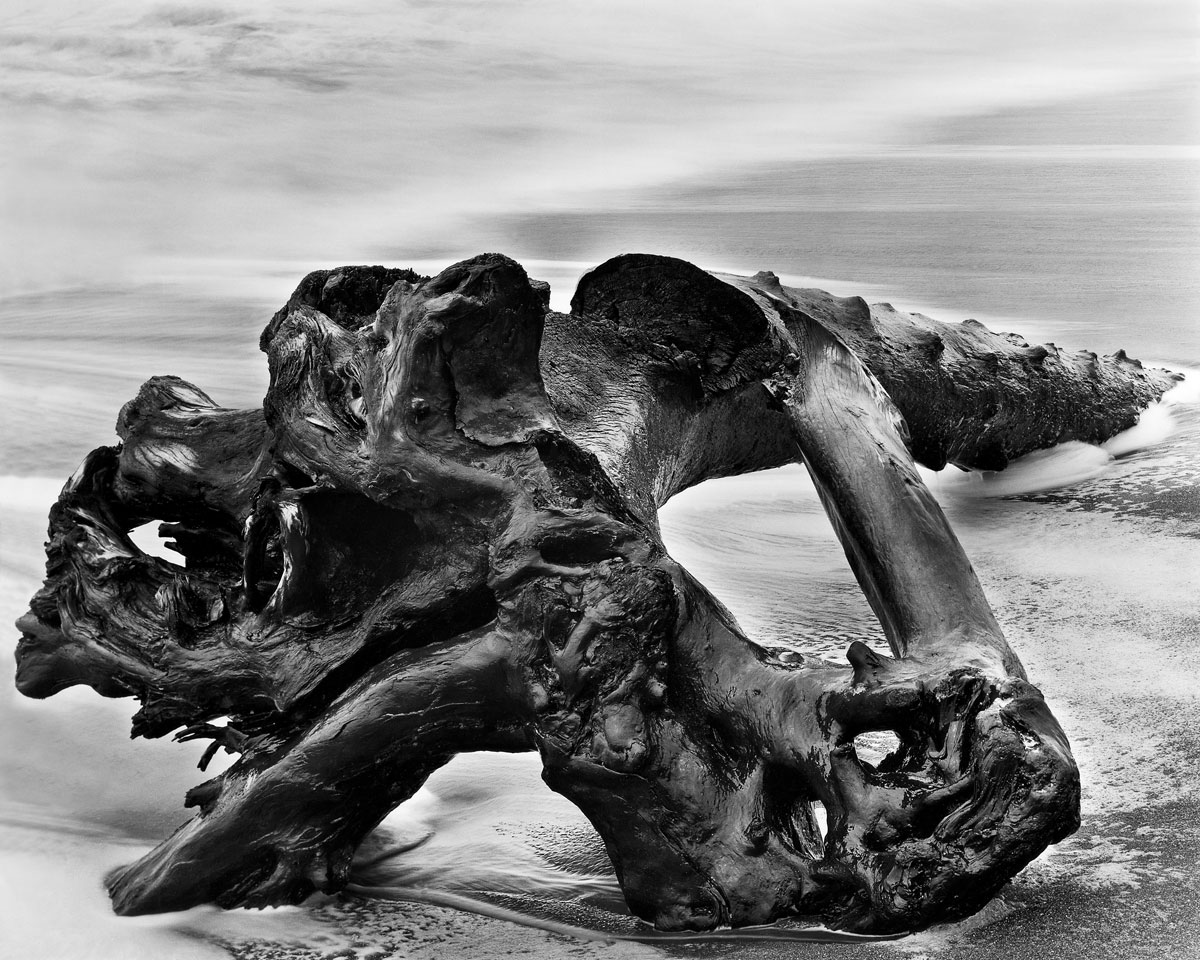
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Driftwood
1951
Gelatin silver print
7 1/2 x 9 1/2 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Point Lobos Tide Pools
1972
Gelatin silver print
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Early Solarization
1940
Gelatin silver print
6 1/4 x 8 in.
Collection of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Edna
1956
Gelatin silver print
7 1/2 x 7 1/2 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Portrait of Edna, Cannery Row
1955
Gelatin silver print
9 1/2 x 7 1/2 in.
Collection of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Barbara through Window
1956
Gelatin silver print
9 1/2 x 7 1/2 in.
Collection Center for Creative Photography
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Nude Torso in Forest
1958
Gelatin silver print
9 1/2 x 6 1/4 in.
Collection of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Child on Forest Road
1958
Gelatin silver print
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Fallen Tree Trunk
1972
Gelatin silver print
8 5/8 x 7 1/2 in.
High Museum of Art, Atlanta, promised gift of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
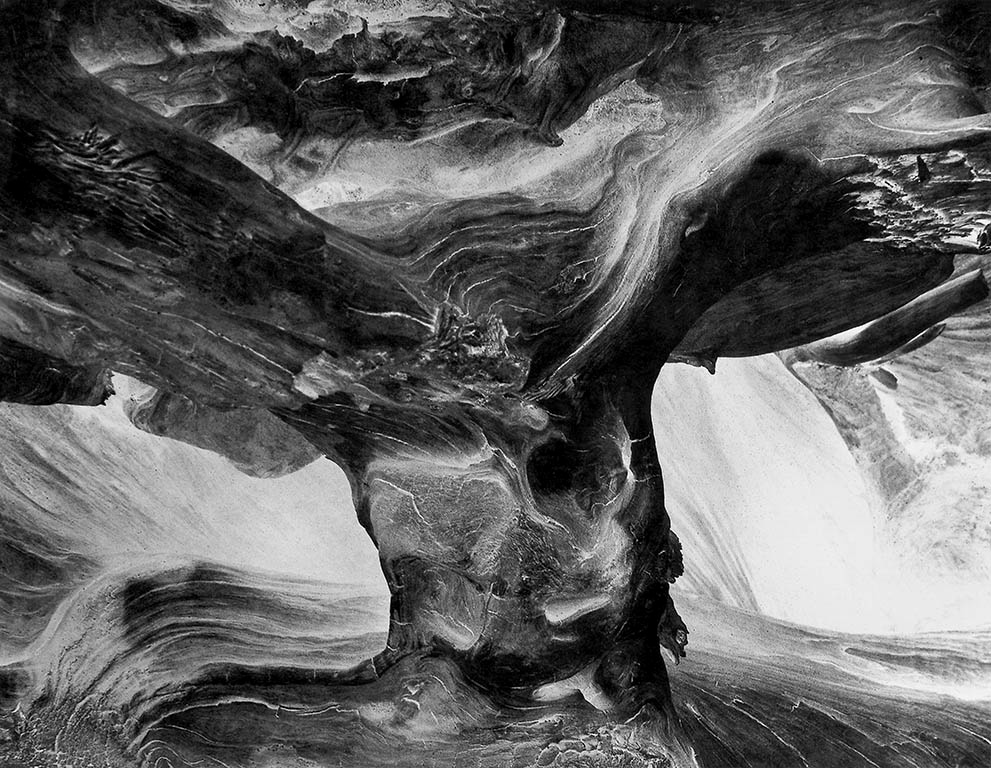
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Tree Trunk
1971
Gelatin silver print
Promised Gift of Lynne Harrington-Bullock
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
To create this image, Bullock reversed the positive and negative values of his rendering of a tree trunk, and then turned the composition upside down. In so doing, he disrupts a habitual reading of the natural world, creates an experience of disorientation, and allows the forms pictured to engage the eye in freshly invigorating ways.
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Photogram
1970
Gelatin silver print
9 1/8 x 7 3/8 in.
Collection of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
Wynn Bullock (American, 1902-1975)
Rock
1973
Gelatin silver print
8 5/8 x 6 3/4 in.
Collection of Barbara and Gene Bullock-Wilson
© Bullock Family Photography LLC. All rights reserved
High Museum of Art
1280 Peachtree Street,
N.E. Atlanta, GA 30309
Opening hours:
Monday Closed
Tuesday – Saturday 10am – 5pm
Sunday 12 noon to 5pm
Wynn Bullock Photography website
Wynn Bullock Photography web page dedicated to the exhibition










































































![Claude Dityvon (French, 1937-2008) '"L'homme à la chaise", Bd St. Michel, 21 May 1968' 1968 [The main the chair] Claude Dityvon (French, 1937-2008) '"L'homme à la chaise", Bd St. Michel, 21 May 1968' 1968 [The main the chair]](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/1968_dityvon__68_bd_st_michel-_21mai08_web.jpg)































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.