Exhibition dates: 9th May – 31st August 2014
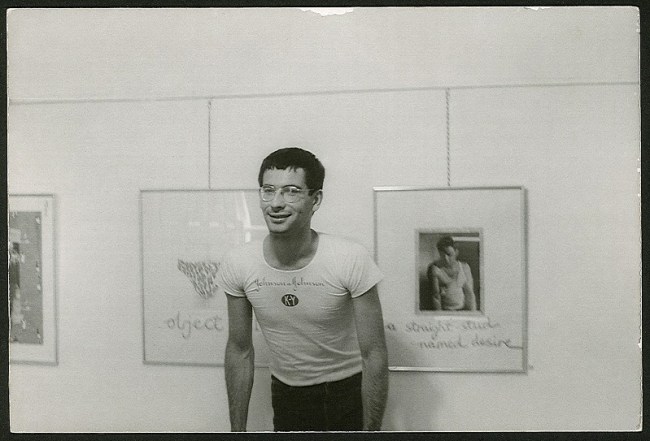

Unidentified photographer
David McDiarmid at his first one-man show ‘Secret Love’, Hogarth Gallery, Sydney, 1976
1976
Silver gelatin photograph
Dennis Altman Collection, Australian Lesbian and Gay Archives (ALGA)
Here’s winking at you, sweetie…
My apologies for the slightly out of focus nature of some of the installation photographs, but I had to take them quickly as I walked through the gallery with co-curator Simon Maidment. If you relied on the nine press images supplied by the NGV (bottom of the posting), you would have no idea of the complexity of this artists work nor would you possess an understanding of the scale, intimacy, brashness, beauty and confrontational visibility of the art. You would also have no idea what a stunning installation the NGV has produced to display the work.
Simply put, this is the best exhibition I have seen in Melbourne this year.
David McDiarmid (1952-1995) – activist (the first gay person ever to be arrested in Australia) and multi-dimensional artist – proves the personal IS political AND influential. His work moves from early personal narratives through decorative to visually commanding and confrontational art. As homosexual identity transits from camp to gay to queer, McDiarmid deconstructs and redefines this identity using context as a FOIL for his art making. As Robert Nelson in his excellent review of the exhibition in The Age newspaper observes, “McDiarmid’s expression of the erotic is an act of protest as well as festivity. When McDiarmid began in full fervour, gay sex was not only reviled but illegal; and as he ended his career, homosexuality seemed to pass from the police to the undertaker. He began his expose of gay eroticism in the spirit of a demonstration and ended it as an act of compassion.”1
Well said. Homosexuality was illegal were McDairmid started making art and was deathly when he himself succumbed to the Grim Reaper. But during the journey that he took the key thing to remember is that McDiarmid never “passed” as something he was not. He was always up front, out there, doing his thing since he was first arrested in 1971. He was always pushing the boundaries, offering a wider perspective on social histories and political contexts. He questioned the marginalisation of minorities (Secret Love, 1976), the boundaries of self and society and examined taboo and transgression in a conservative society. He lived at the cutting edge of culture. Later, he waged a life and death struggle for HIV/AIDS funding, awareness and compassion with a fierce determination combined with sparkling wit, humour and sardonic aphorisms. Sexual politics and safe sex campaigns went hand in hand.
Of course, sexuality and sexual identity were at the core of his creativity. He explored the urban gay male world and the struggle for gay rights, sexual and emotional sensibilities and the cultural politics of HIV/AIDS. Early work was influenced by time spent in New York (where he knew Keith Haring) and San Francisco, where he experienced the development of the clone scene and the music of the clubs. His mode of construction has a lot in common with folk and women’s art (in particular patchwork and quilting) coupled with the use of contemporary materials (such as holographic foil).
McDiarmid’s later work becomes more symbolic and universal but still contains that cutting edge of the personal (DEMENTED QUEEN REMEMBERS HER NAME – forgets to die; POSITIVE QUEEN FEELS NEGATIVE – goes shopping). In the most amazing room of art I have seen this year, McDiarmid uses reflective cut and tiled holographic foils to create moving tribute and biting comment on the HIV/AIDS epidemic. In this darkened room the viewer is surrounded by tiles that “scintillate in spectral transience, changing their colours holographically according to your movement. The image is blunt and horny but also melancholy and scary; and similarly the medium impenetrable, deflecting the gaze and forcing you to change perspective.” (Robert Nelson)
But it’s more than that. You are surrounded by metallic flesh and embedded amongst the iridescence is both love and hate, life and death, winking eyes and holographic rainbow coloured skulls. Body language (1990, below) contains the names of McDairmid’s dead lovers woven into its fabric, a Swastika with the word AIDS for a head and the desire for the anus as a man pulls his arse cheeks apart. But here’s the rub – the tiny, puckered hole contains a holographic image of a winking eye, inviting you in, sharing the death/life joke with you. It’s a classic. In this room it feels as though you are surrounded by the fires of hell as the opalescence of the work changes from footstep to footstep, from positive to negative, from love to hate – and the pure beauty of the work is overwhelming. These are absolutely stunning works of art by any mark of the imagination, up there with the very best art ever made in Australia. His famous Rainbow Aphorisms series 1994 (below) are strong but they are are not a patch on the silver foil works. Less successful are the textile and costume designs, the weakest part of the exhibition.
One question springs to mind. Would his art have been as strong without the impetus of “death art” behind it? What would it have looked like?
I wonder which direction his art would have taken after his initial investigation of gay male identity had he not contracted HIV / AIDS and started making art about the disease. This strong focus gives the work the impetus and grunt it needed to move from the purely decorative and graphic, ney camp in some cases, to work with serious gravitas. In these later works McDiarmid lays it all on the line and just goes for it. I am so glad he did. They are powerful, concise, confrontational, beautiful, shimmering renditions of a soul living life to the full while he still had time.
It’s a pity the NGV has not advertised and promoted this exhibition more extensively. With a stunning catalogue, insightful research, amazing installation and world class art this is one exhibition you shouldn’t miss in Melbourne this winter.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
ART BLART: THE ONLY PLACE TO SEE INSTALLATION PHOTOGRAPHS OF THIS EXHIBITION ON THE WEB.
Many thankx to Simon for allowing me to take the installation photographs during our discussion and to the NGV for allowing me to publish them, along with the nine press images at the bottom of the posting. All installation photographs © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
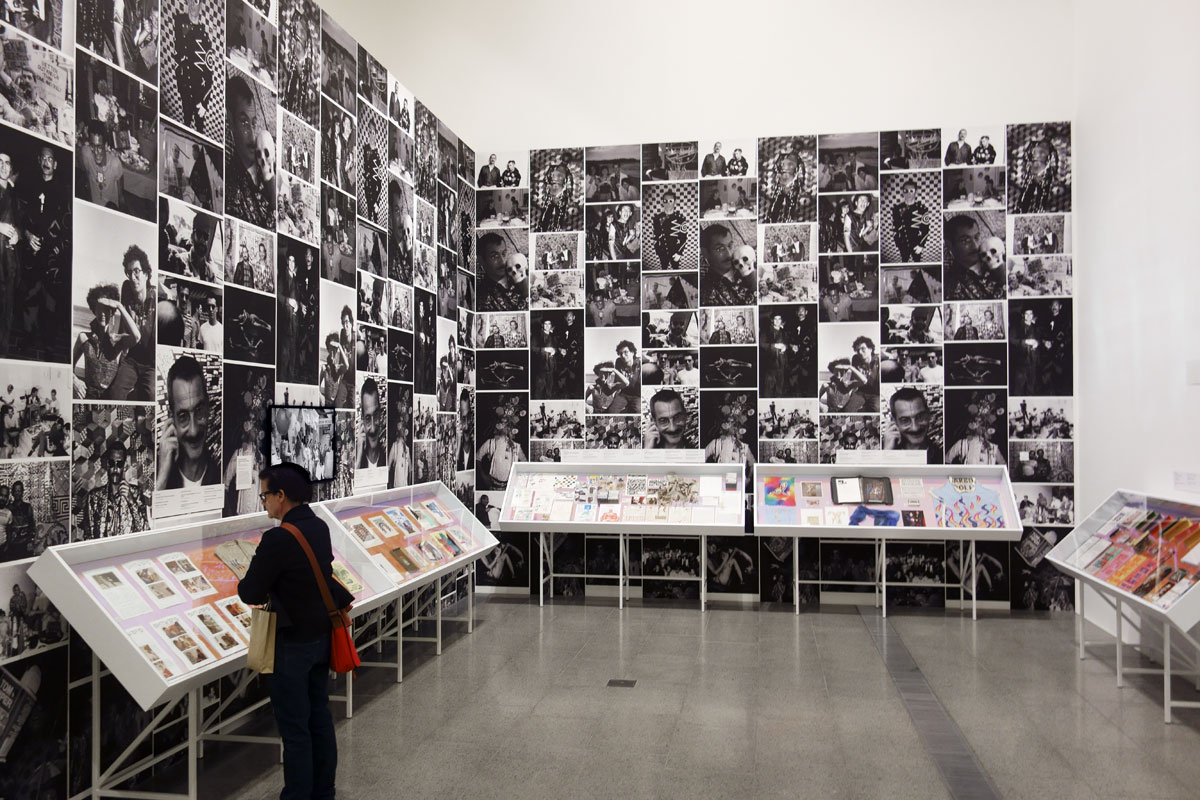
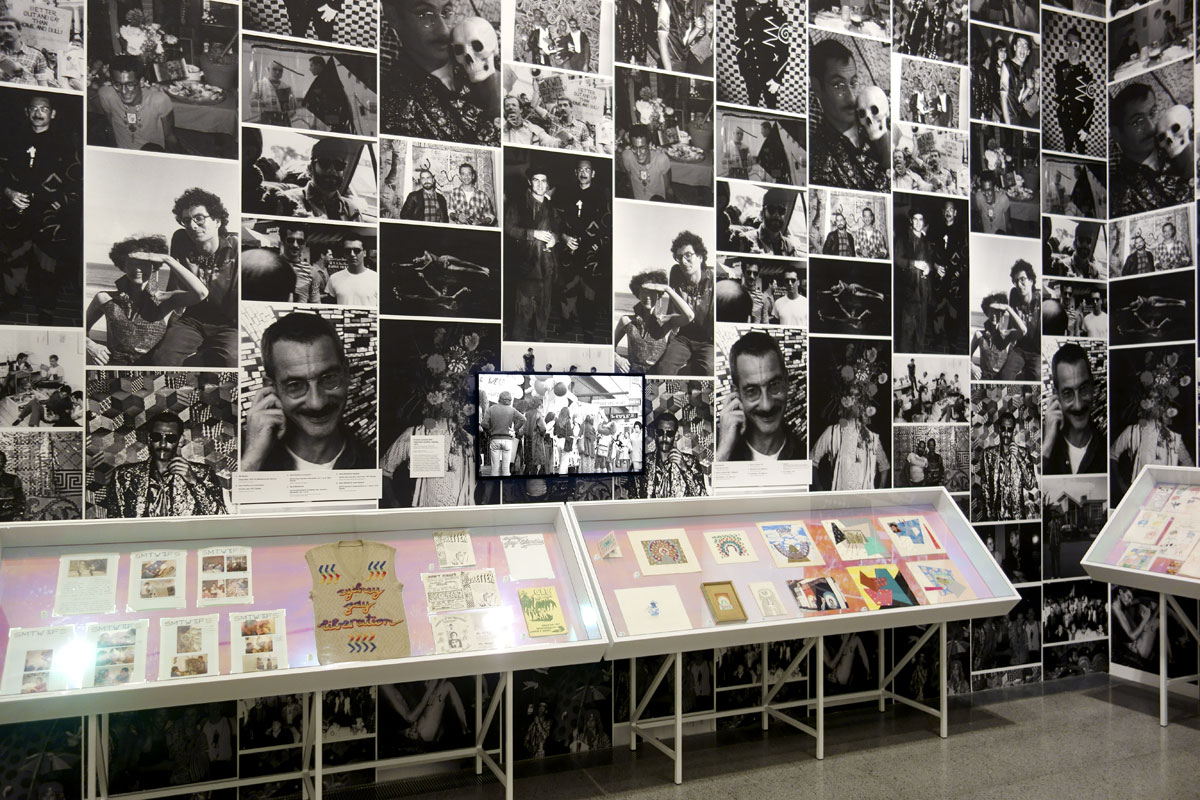


David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
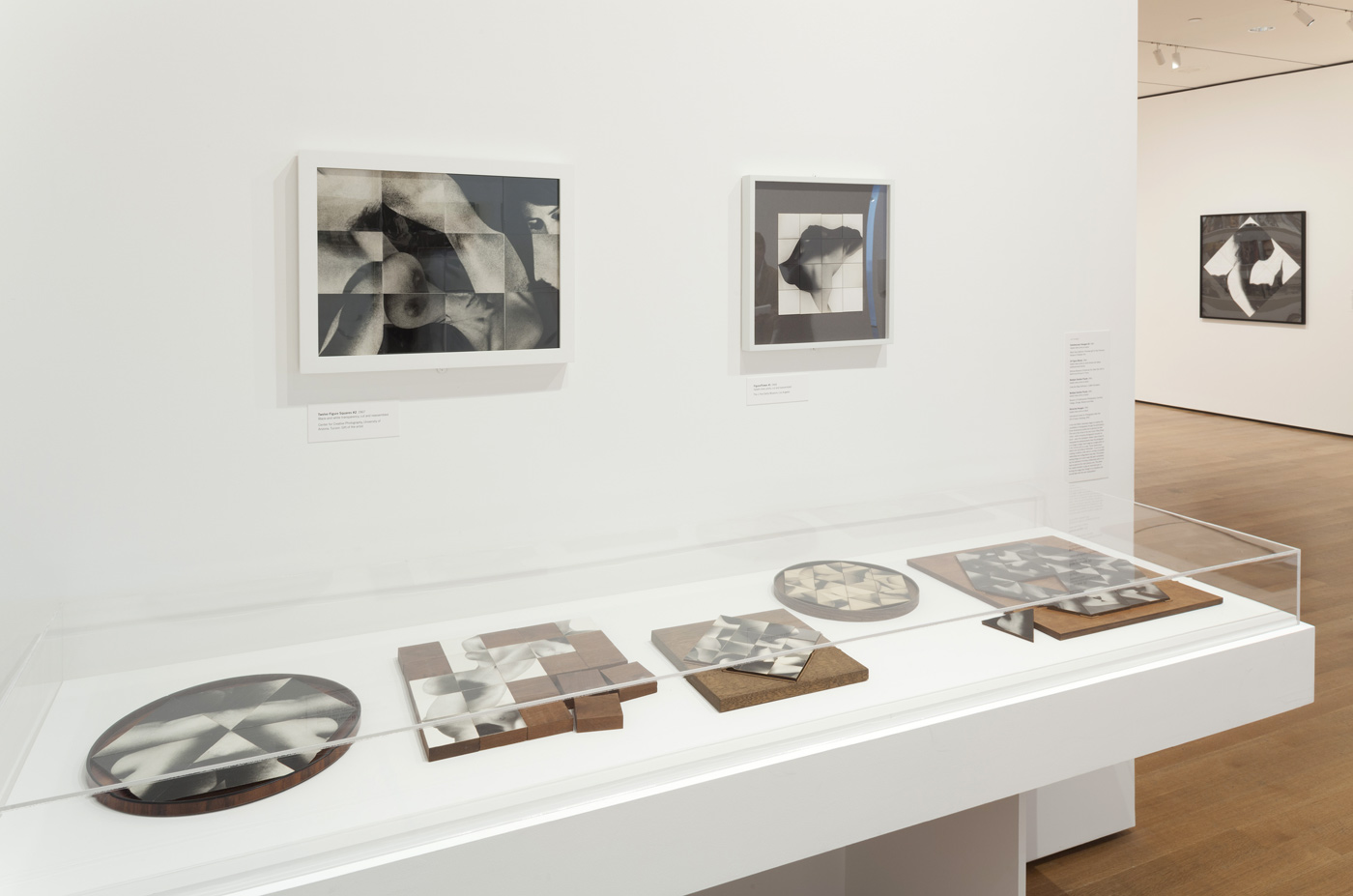
Installation photograph of early works including, in the case, Vest (c. 1972), hand-embroidered by McDiarmid with the words ‘sydney gay liberation’ as a gift for John Lee with photographs of McDiarmid and artist Peter Tully used as a wallpaper on the wall behind at the exhibition David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me at NGV Australia, Melbourne

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
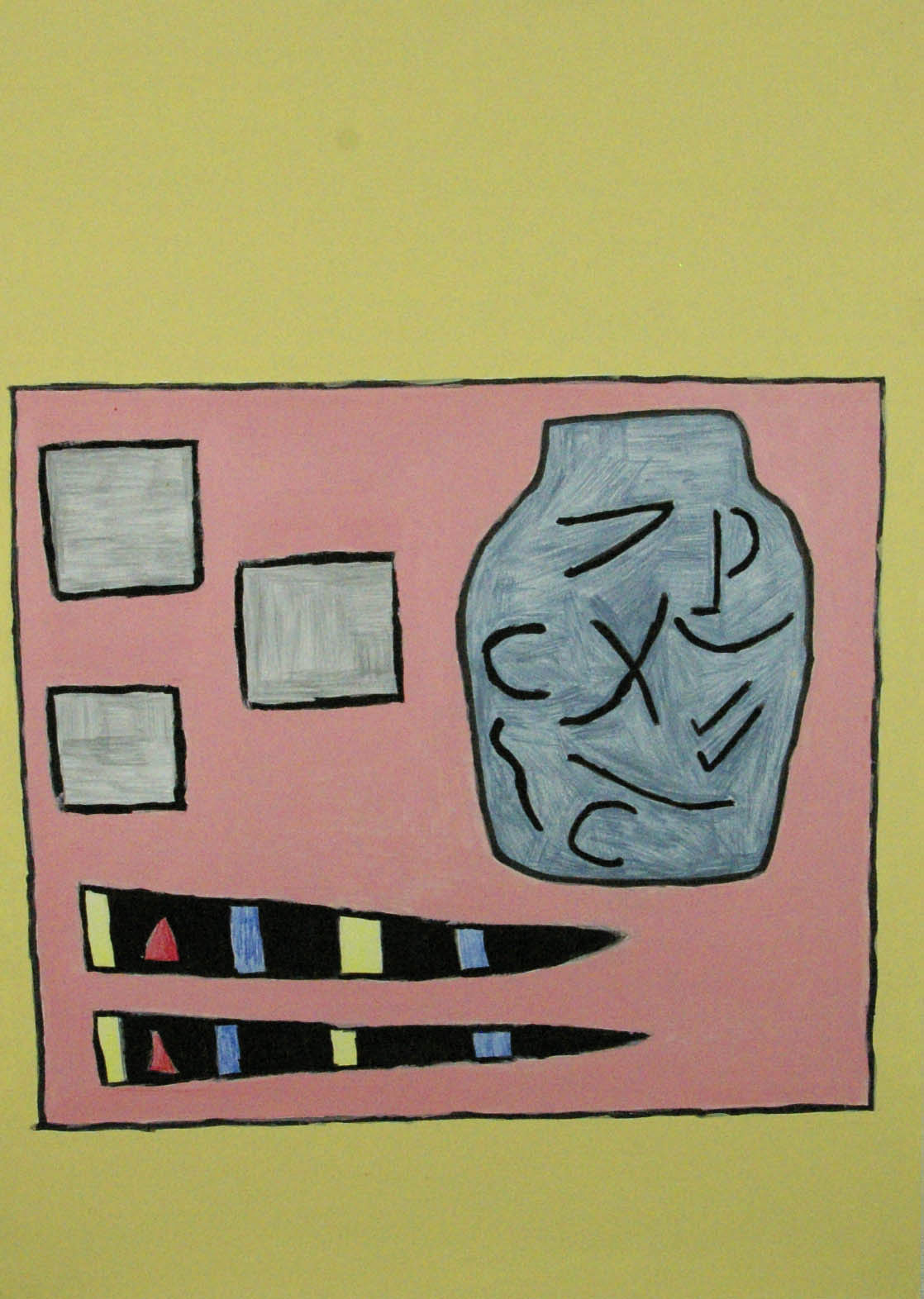
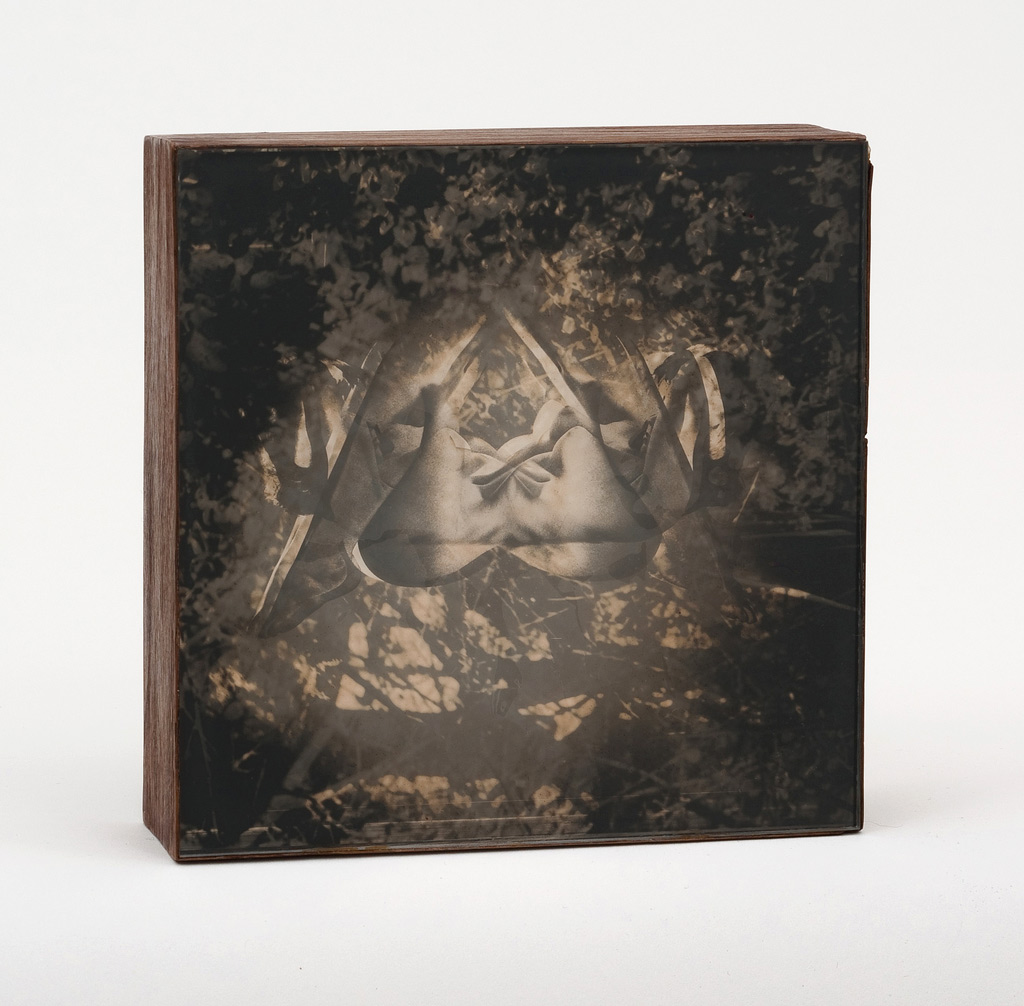
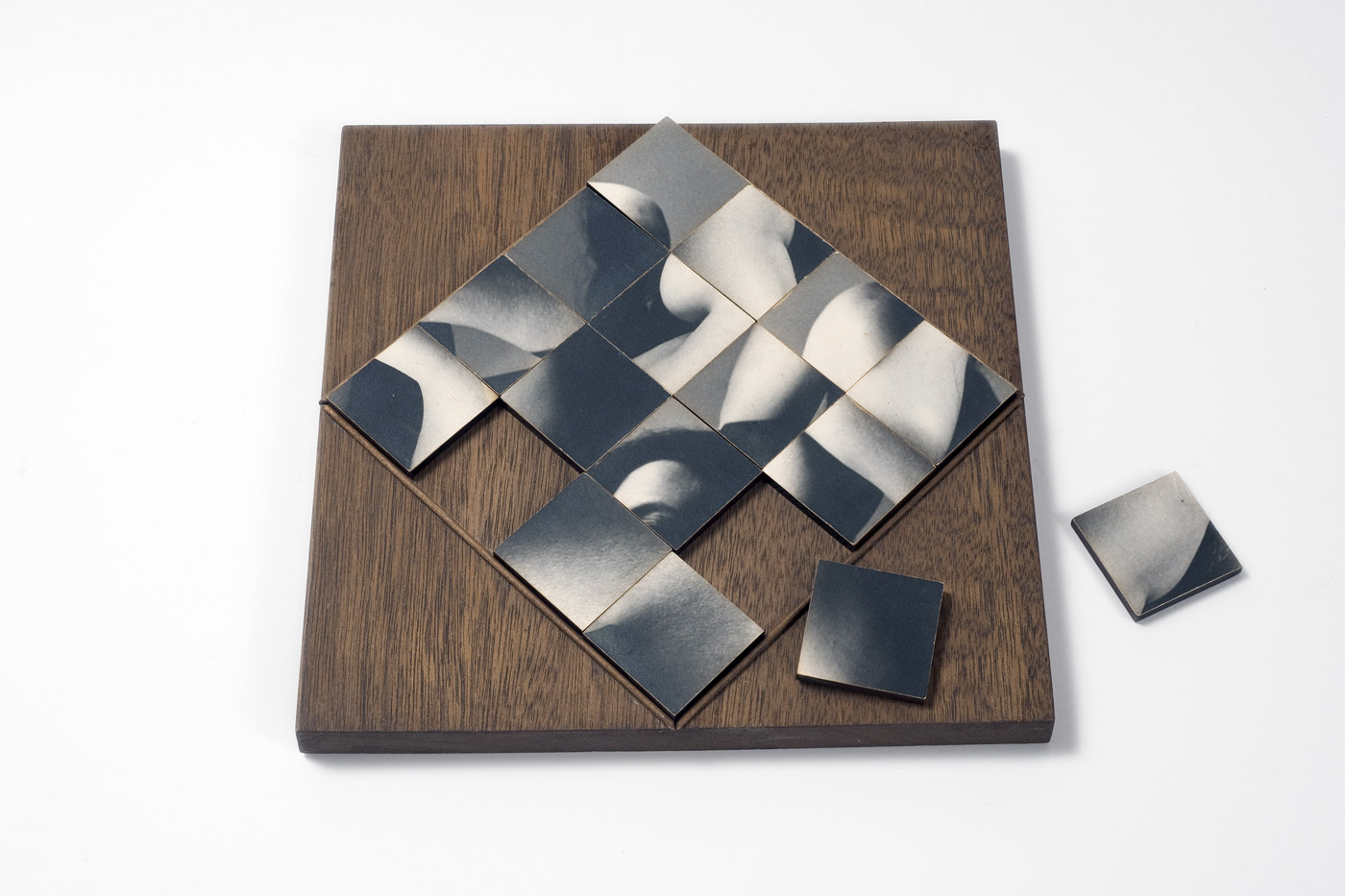
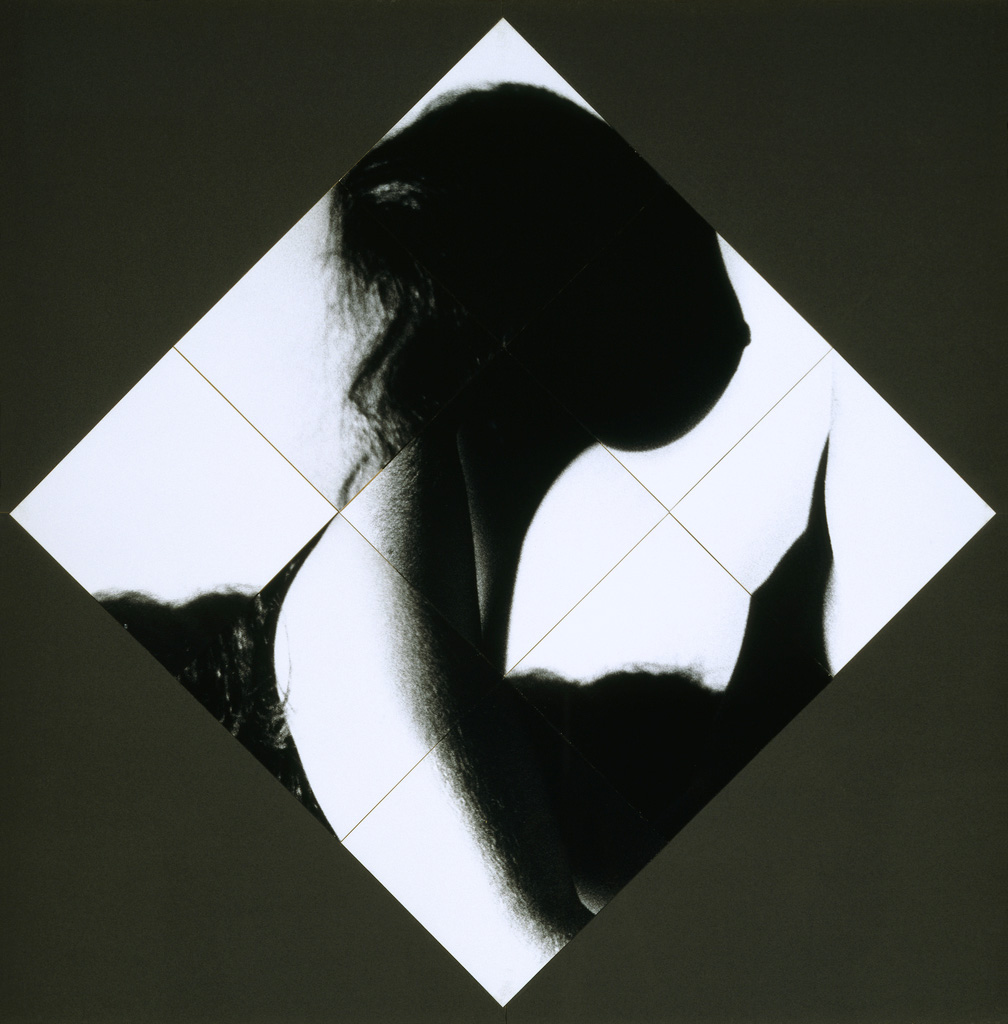
Installation photograph of early works including Secret Love art show, poster (1976, far left), Secret Love (1976, top centre left), Ken’s Karate Klub (1976, centre below left) and Tube of joy (1976, above right) – all from the Secret Love series, 1976 except KKK – at the exhibition David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me at NGV Australia, Melbourne

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Secret Love (installation view)
1976
From the Secret Love series, 1976
Metallic paint, red fibre-tipped pen, coloured pencil, collage of cut photo-offset lithograph and red and black ink on graph paper
78 x 66cm
Collection of Paul Menotti and Bryce Kerr, Sydney

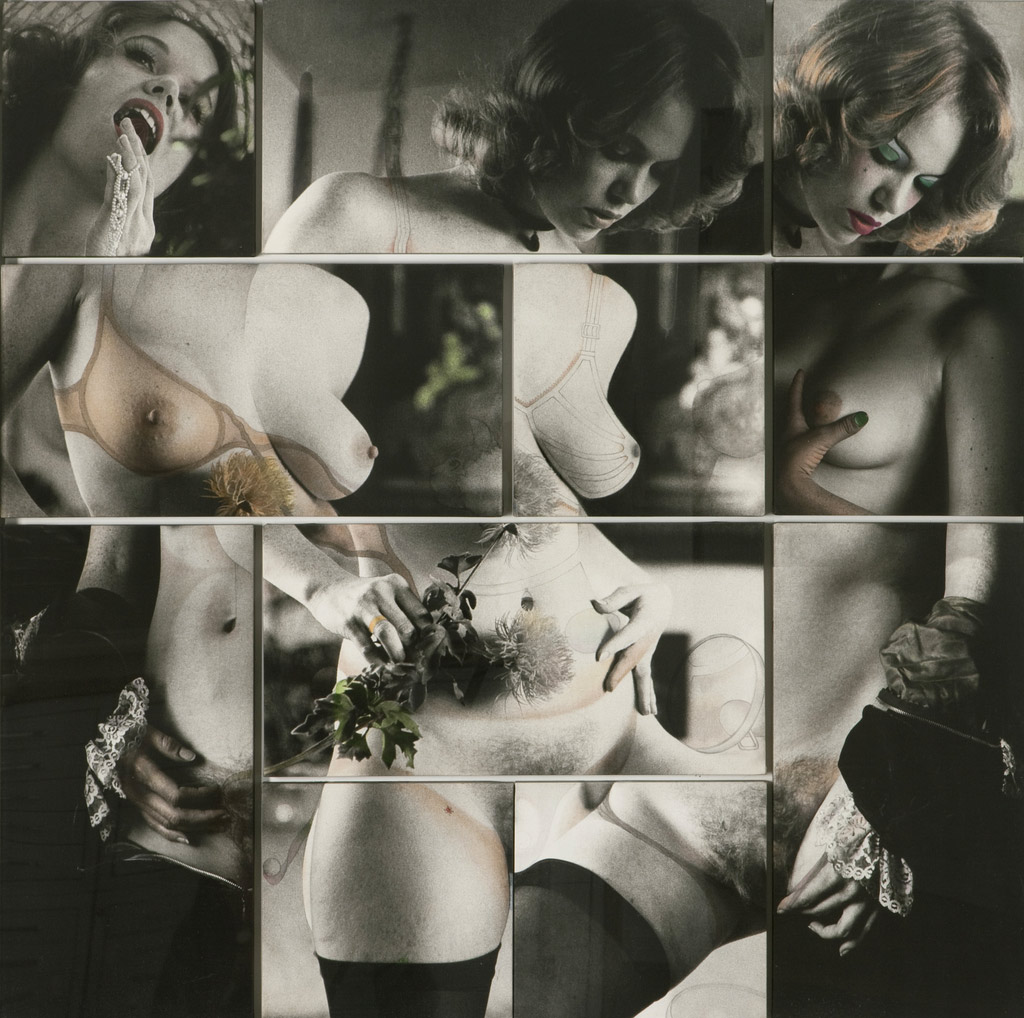
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
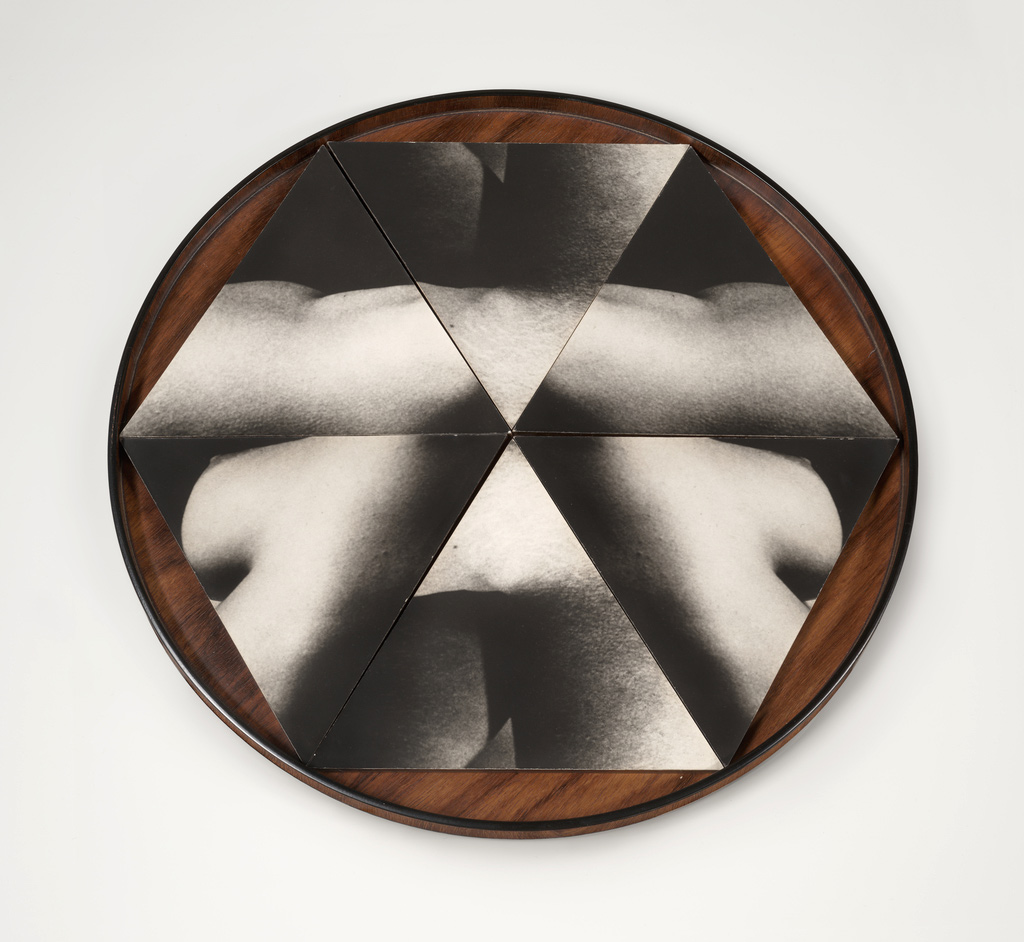
Secret Love (installation view)
1978
Collage of cut colour photo-offset lithographs on plastic, metal and plastic
135 x 142.8cm
Collection of Bernard Fitzgerald, Sydney

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
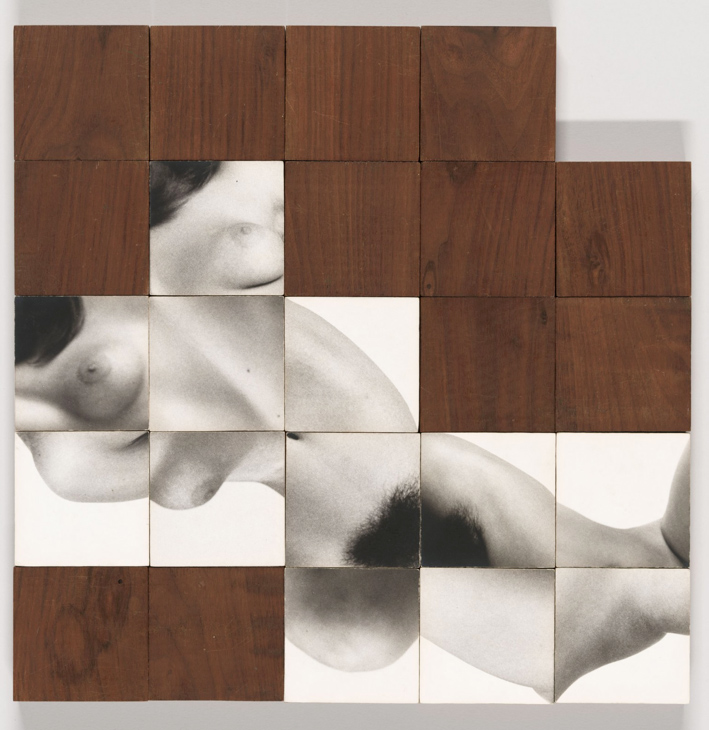
Secret Love (installation view detail)
1978
Collage of cut colour photo-offset lithographs on plastic, metal and plastic
135 x 142.8cm
Collection of Bernard Fitzgerald, Sydney

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Installation view of various artworks from 1978 including Strangers in the night (top second left), Mardi Gras (top fourth left), Juicy fruit (top second right) and Real confessions (bottom second left)
All National Gallery of Victoria

Bush Couture, Sydney (fashion house) (front)
Linda Jackson (designer)
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987) (painter)
Paua kimono (installation view)
1984
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Interview with co-curator Simon Maidment
MB: First of all Simon, can I ask how long have you been at the National Gallery of Victoria and what brought you to the institution?
SM: I’ve been at the NGV since June 2013 and I joined because of a new vision for the gallery which is making contemporary art a priority, both in collecting practices in the exhibitions that the NGV holds. Recently, there has been a real push for change, precipitated by the appointment of Max Delany who is a friend and colleague I respect a lot and who has been really supportive of my career.
MB: So what was your background in terms of training?
SM: I studied as an artist and immediately before coming to the NGV I was undertaking my PhD at The University of Melbourne’s Victorian College of the Arts Centre for Ideas with Elizabeth Presa as one of my supervisors.
MB: And what new knowledge was your PhD based around?
SM: It investigated curatorial practices that could be thought of as context responsive, looking at artists who seek to enact some sort of social and/or political change.
MB: So this exhibition would be perfect to fit into that…
SM: Yes, indeed… so largely my background has been working with living artists. I have done a few shows in which I have worked with existing bodies of work, but I have done a lot of shows where I have been facilitating artists works. I started as an artist working in media arts – sound, video, projection and digital technologies – and often worked as a studio assistant for more senior artists, people like Sue Ford, Susan Fereday, Ian de Gruchy and my role with them became more and more about facilitation. Then the directorship of Westspace came up and I got that, and my focus turned more from collaboration and working as a studio assistant to facilitation. I became a curator because basically that is what I was doing.
MB: So can you tell me Simon, what was the lead in time for this exhibition? I know it was postponed and delayed at various times, what were the reasons for that?
SM: It was kind of before my time so I am not really sure, but there have been different curators at different times from the NGV involved with the project. So Ted Gott was involved with the exhibition, even before he began work at the NGV. Ted was involved with David’s estate with Sally Gray, my co-curator, right from the start, so he’s been an advisor to Sally right from the start of this long journey. I think the initial discussion about the show was with Ted, and then when Jason Smith was in my position he was involved in this project. When I was talking with Sally the very first discussions about holding the exhibition at the NGV was maybe 15 years ago…
MB: So to finally get it here and up on the walls…
SM: So when I started 11 months ago there was really very little in place. So Max Delany and Sally started a conversation about working towards this show probably about 14 months ago. When Tony Ellwood started he was like, “We’re doing this show.” He’s a big fan of David McDiarmid. He was very familiar with his work so I think that helped speed things along and he really facilitated getting this exhibition done. It was scheduled for 2011.
MB: To get it together from start to finish in 14 months is pretty amazing really…
SM: It was a lot of work but bearing in mind how familiar Sally is with the material we kind of had a real head start.
MB: But then you have to pull it all together from lenders and institutions that hold works and that would have been very intensive. Then to design it all and to make it look like it does. It looks fantastic! Everyone at the opening was just smiling and having a good time, looking at the work, remembering.
SM: I knew the work en masse would blow people away.
MB: Reading the catalogue, you can see that David comes from a period where there was a ground swell of social movements, which was almost like one movement. Everybody went to everyone else’s rallies and they all protested together. David McDiarmid was the very first gay person to get arrested in Australia and at the moment I am digitally restoring the image of him being marched away by two policemen at the ABC protest in Sydney. It is so degraded it will take a long time to restore but it is a really important image. Out of that there comes a real social conscience, fighting for your rights and freedom. So leading on from that, when you think about having this exhibition here now (after Ted Gott’s seminal exhibition Don’t Leave Me This Way: Art in the Age of AIDS at the National Gallery of Australia in 1994), you observe that marginalised voices rarely enter institutional centres of art, rarely enter the mainstream art. It’s usually ARI’s or small public galleries. Not that the artist is gay (because they are just artists) but that the CONTENT addresses gay issues – which is why it’s so fantastic to see this exhibition here at the NGV.
So were there any barriers here to doing David’s show?
SM: No, not really. I think one of the really important things to note is that they show would not have really happened without the large gift from the estate. Becoming the key holder and custodian of David McDiarmid’s work added extra emphasis and responsibility about doing the right thing. At that point the organisation is implicated in that legacy and somehow we have to disseminate the work out into the community.
MB: It is quite a confronting show, how do you think the general public will respond to it?
SM: I have done a couple of tours of people through the exhibition, members and other, and one of the things that has been surprising to me, in a way, which has only become apparent when I have been describing the show in which David makes work in response to particular social and political conditions and contexts… is how different things are. AIDS is now not a terminal illness. To speak to a younger generation than even myself, they have no idea about dying from lack of a viable treatment, of AIDS being a death sentence.
MB: Last night I had a cry for all the people I had loved and lost. But it’s not just the public coming in to see this exhibition, it’s young gay men who don’t ever see anybody ill, don’t understand about the side effects of taking the medication, about what living with HIV is like. They don’t understand the struggle that went on for them to live as they do now. Do you think they will engage with that?
SM: We have structured the show in a way that teases those things out. One of the aspects of McDiarmid as a figure that I find very interesting is that, in 20 short years of practice, he spanned incredible key moments and periods of change in broader society and also within gay society. The legal, medical, institutional change… and really looking at that 20 years is looking at a period of immense social change. The narrative of the exhibition is then to reflect on that broader cultural shift through the biography of one person.
MB: It’s interesting when I looked at the show, when you start making work as an artist it’s always about personal narratives – lovers, friends, places – which then widens out into more universal concerns. You can see in David’s early work him scribbling, writing and really intimately notating his world, investigating his self and his relations to the world around him. And then to take that insight and then to mould it into these reflective images into the Rainbow Aphorisms at the end is an incredible journey. Stephen Alkins was saying to be last night that even the last works were still grounded in this humorous, ironic look at life. He as a really important multimedia artist when you actually study the work.
SM: Just to pick up on one aspect that you are mentioning, and going back into my own background, one of things that Max Delany and I have been talking about that has in some ways illuminated this project is that, in the 1970s and 80s that saying ‘The personal is political’, is very important. David’s work is talking very much about the political as his own biography. Perhaps there is a shift in his later work to a more symbolic realm, and I would argue that nowadays artists working in a political and social context and to affect social change is not so much now as a personal identity – a woman, a black man, a gay man – it’s not necessarily about individual identities anymore, in some ways those battles seem to have been won within Western society. Actually for artists now in this context it’s more about neo-liberalism or capitalism. So it tends to be more on an institutional level and people tackling that in a much more symbolic realm. For instance I am thinking of such people as Jeremy Deller, an English artist who engages with British history and in particular his Battle of Orgreave, a reenactment of the actual Battle of Orgreave which occurred during the UK miners’ strike in 1984.
MB: People like Tom Nicholson in Australia, then, who did the Monument for the flooding of Royal Park (2008-2010), a proposition for the scattering of nardoo sporocarp throughout Royal Park, a vast Park in Melbourne’s inner north which was Burke and Wills departure point, now commemorated by a small cairn.
SM: Exactly. Artists like Tom are working in very propositional ways about memory, social imagination, monuments and memorialisation. All those kind of things are very much within a symbolic realm now. McDiarmid’s work fills the personal and then moves into the symbolic.
MB: But then Stephen Alkins said it was always personal to David, still based in the personal. He was very loyal to his friends, he was a very quiet person, very loving person with great energy. But he didn’t suffer fools gladly, and I think that this comes out of that culture of standing up for yourself and being strong because of the stuff we had to go through to where we are today. Seeing this exhibition actually shows you that difference and what we had to fight for.
SM: There’s a real drive there in that last room. He made so much work, across so much media, at the end of his life – that impending death drive was the source of so much creativity.
MB: McDiarmid was heavily influenced by international artists such as Keith Haring but he never really showed overseas. What do you think about that diaspora, that going overseas and then returning home to then begin exhibiting?
SM: Well the earlier work is, as you say, heavily influenced by the New York scene, the clone scene that was prevalent in the 80s – San Francisco, New York – so he’s definitely channelling those places… Interestingly, unlike many other artists, his art practice is nearly all Australian.
MB: Finally, what do you think is is his legacy in terms of his standing as an artist?
SM: In the last ten years of his life he was heavily involved as a community artist. He was incredibly busy and incredibly involved with things like the organisation of the Sydney Gay Mardi Gras and the design of the posters and floats. He was director of Mardi Gras from 1988-90 and he worked up float designs for various groups. You really get a sense of, as you said, of the solitary work of an artist and a real commitment to that work. In terms of his legacy as an artist, I don’t think that we will know until the exhibition is over. His work, such as the Rainbow Aphorisms, has been distributed widely but not really in an art context, and certainly not in a museum show such as this. People have not had the opportunity to visualise his work as a whole body of work until now.
MB: That brings me to the international context. The Keith Haring Foundation relentlessly promotes his work through books, exhibitions and conferences throughout the world. Do you think that you will start promoting his work overseas to other galleries and getting it into international exhibitions?
SM: I think the book will open a lot of doors. Because his work reproduces so well, because his writing is so interesting there is a broad range of voices for the scholars to investigate. But I think because the work reproduces so beautifully that will be hugely important. One of the aspects that the book will hopefully communicate to a younger audience is that of an infected muscular, sexually active, virile man not an emaciated artist… but to understand that and where that came from, and how radical that was at the time. I think that is one of the legacies that people will take away from David’s work. He is one of the artists that has been really instrumental in redefining that imaginary representation of a dying gay man.
MB: I remember seeing those + and – posters in gay sex venues, and thinking to myself, wow those are so amazing, who did those!
SM: Yes, those posters are about not closing down, about always been open to possibilities.
MB: Thank you so much Simon for taking the time to talk to me, it’s been great.
SM: Always a pleasure.
Dr Marcus Bunyan with Simon Maidment for Art Blart, June 2014
Simon Maidment is Curator of Contemporary Art at the NGV.
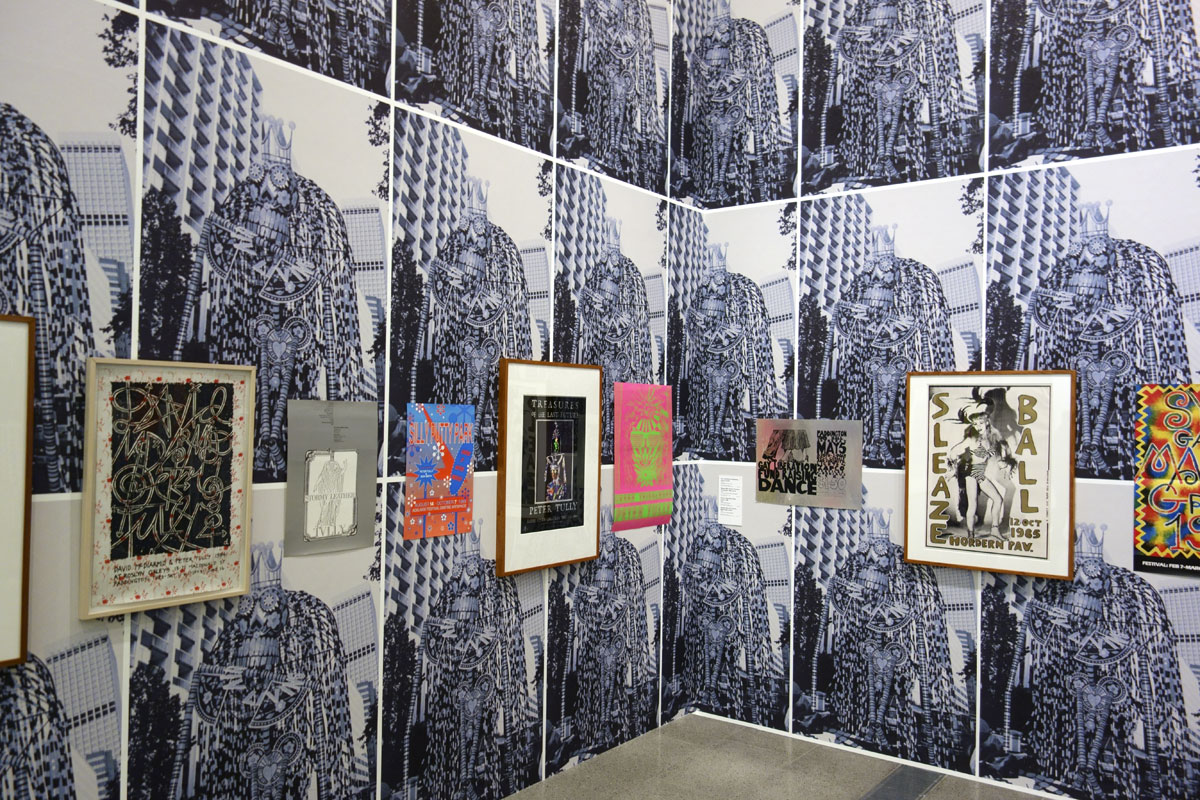


David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
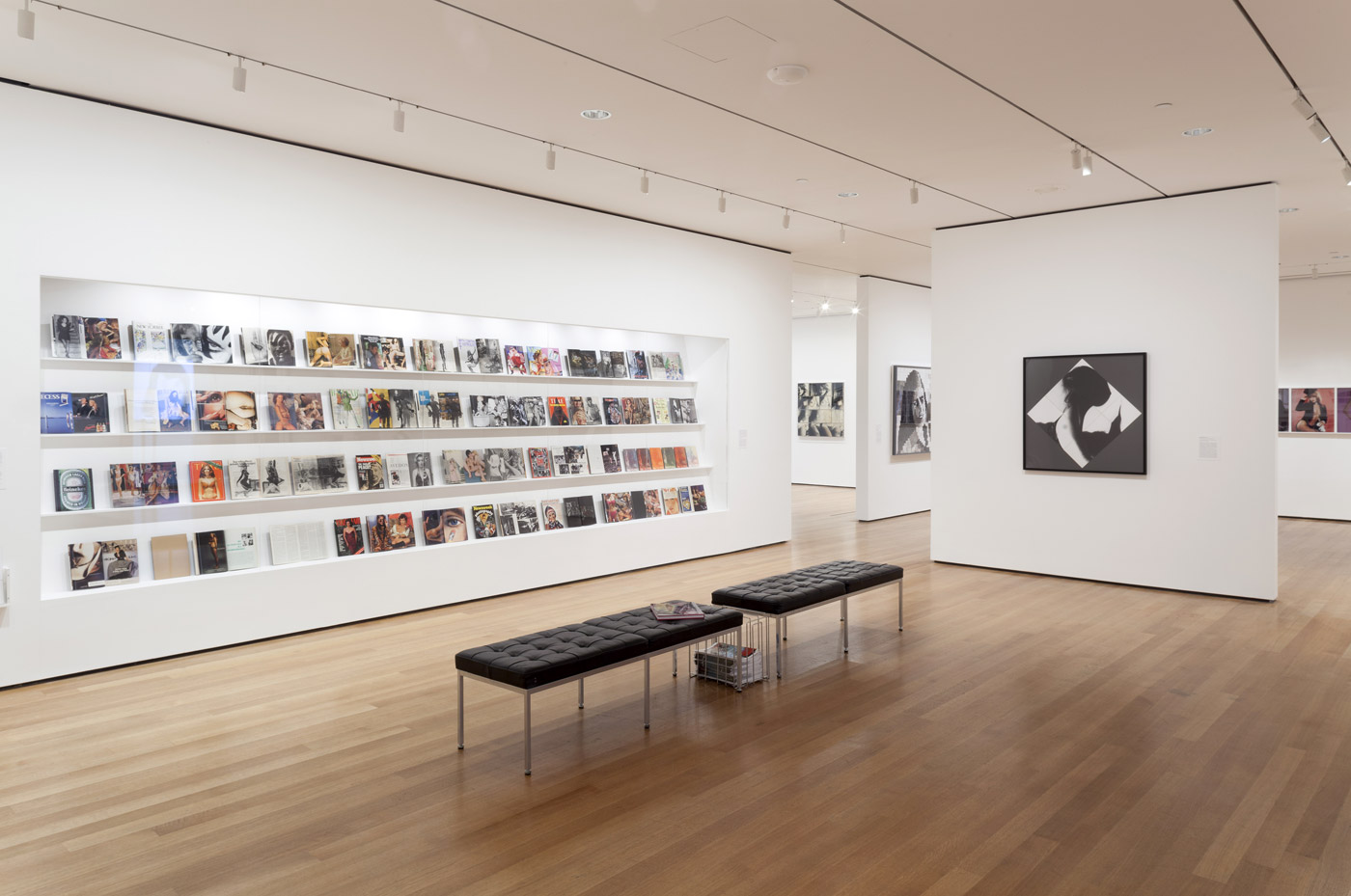
Installation views of various Sydney party posters with a black and white background wallpaper of David and the HIV Living group’s Day of the dead skeleton for the Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras, 1992 (commissioned by the AIDS Council of NSW) at the exhibition David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me at NGV Australia, Melbourne

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Sleaze Ball, Horden Pavilion, 12 October 1985 (installation view)
1985
Screenprint printed in black and gold ink
91.2 x 65cm (sheet)
National Gallery of Australia, Canberra
Gift of the artist, 1991
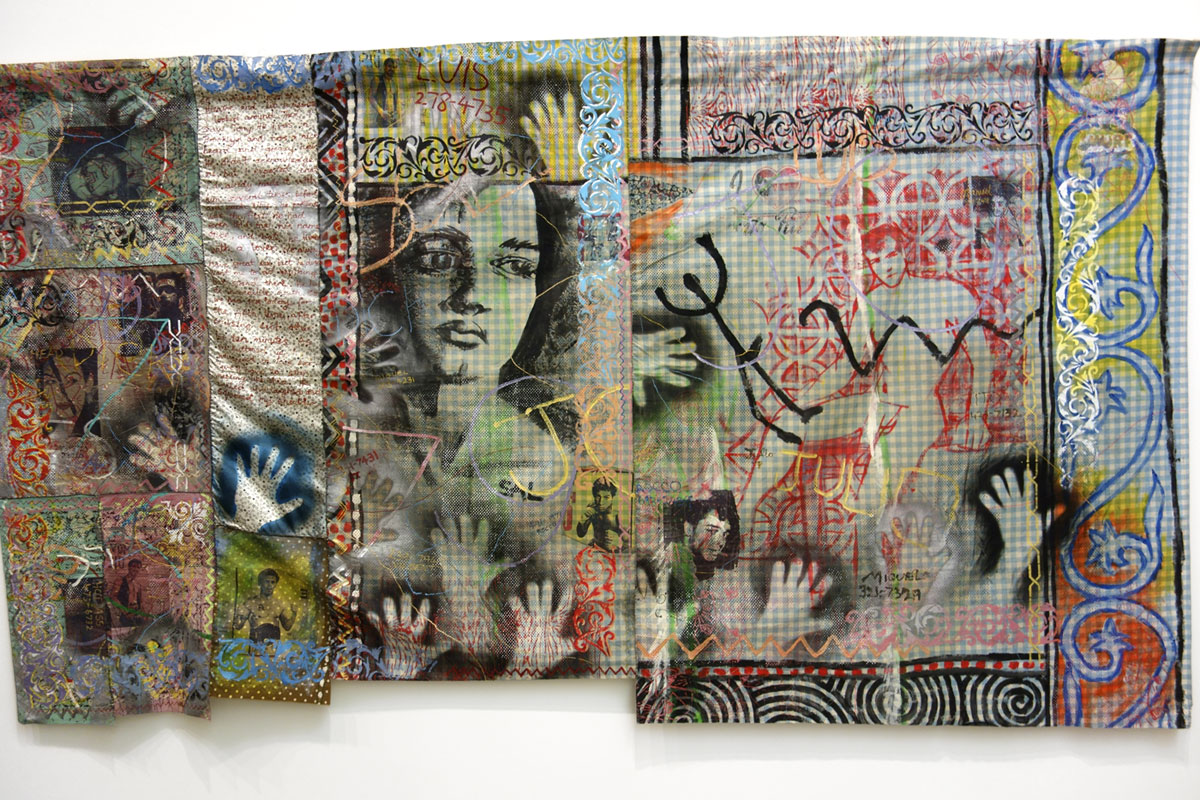

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
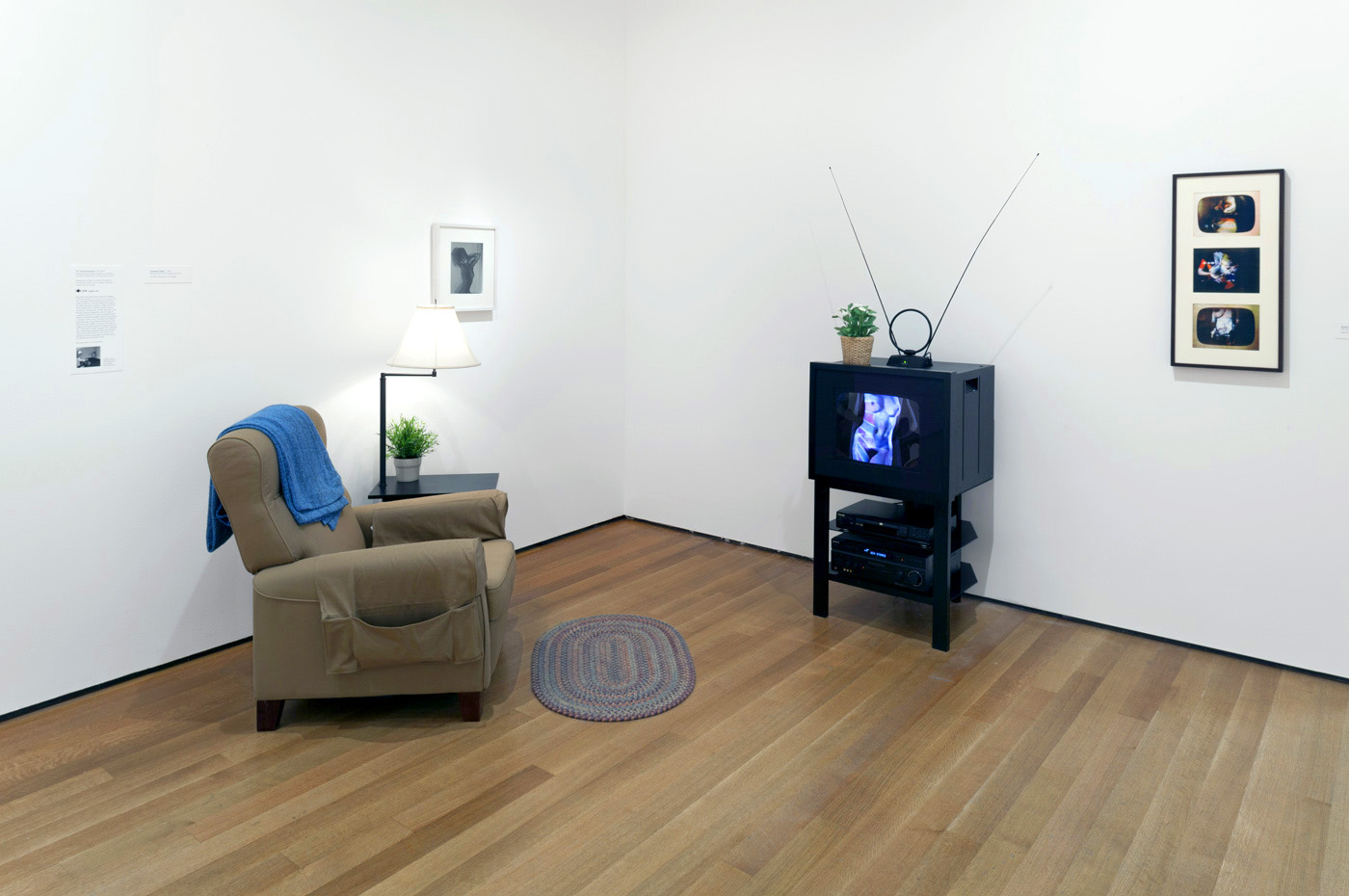
So I walked into the theatre (installation view)
1984-1985
Synthetic polymer paint, iron-on transfer, and cotton thread on cotton
Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne
Gift of the Estate of David McDiarmid, 1998
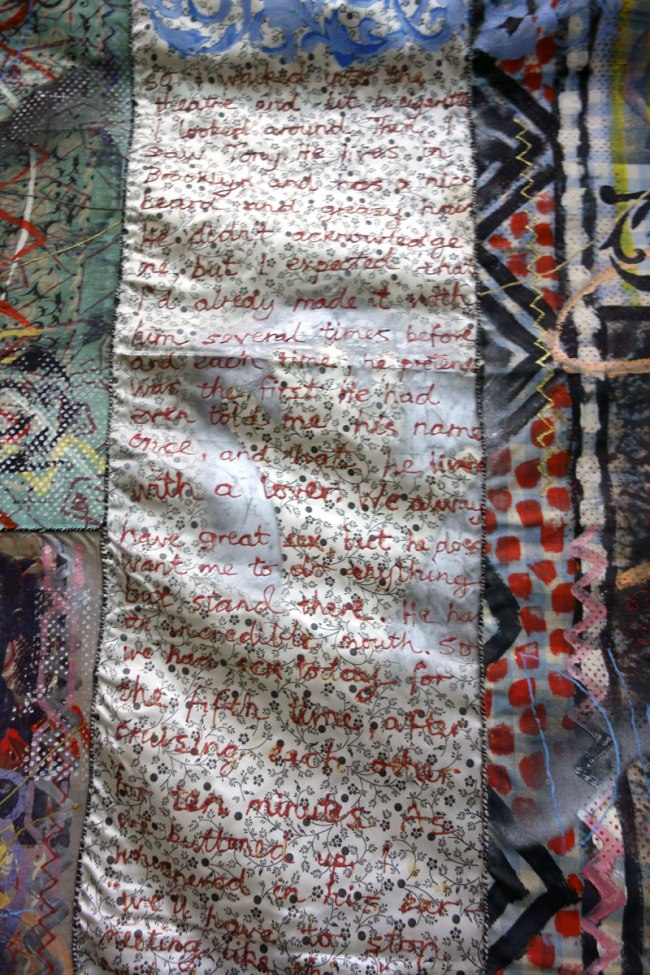

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
So I walked into the theatre (installation view detail)
1984-1985
Synthetic polymer paint, iron-on transfer, and cotton thread on cotton
Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne
Gift of the Estate of David McDiarmid, 1998
So I walked into the
theatre and lit a cigarette
I looked around. Then I
saw Tony. He lives in
Brooklyn and has a nice
beard and greasy hair.
He didn’t acknowledge
me, but I expected that.
I’d already made it with
him several times before
and each time, he pretended
was the first. He had
even told me his name
once, and that he lived
with a lover. We always
have great sex, but he doesn’t
want me to do anything
but stand there. He has
an incredible mouth…

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Disco kwilt (installation view)
c. 1980
Artbank collection

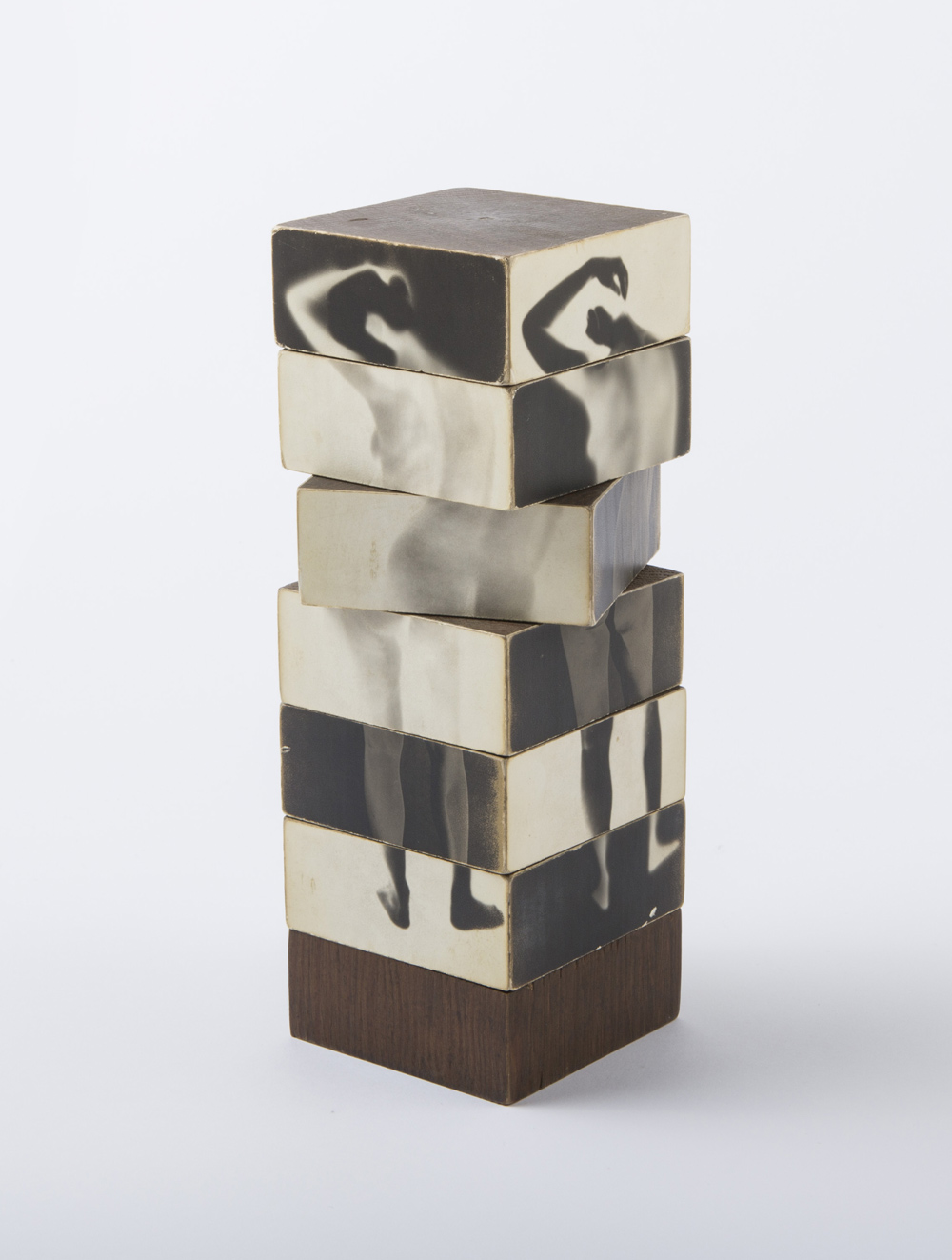
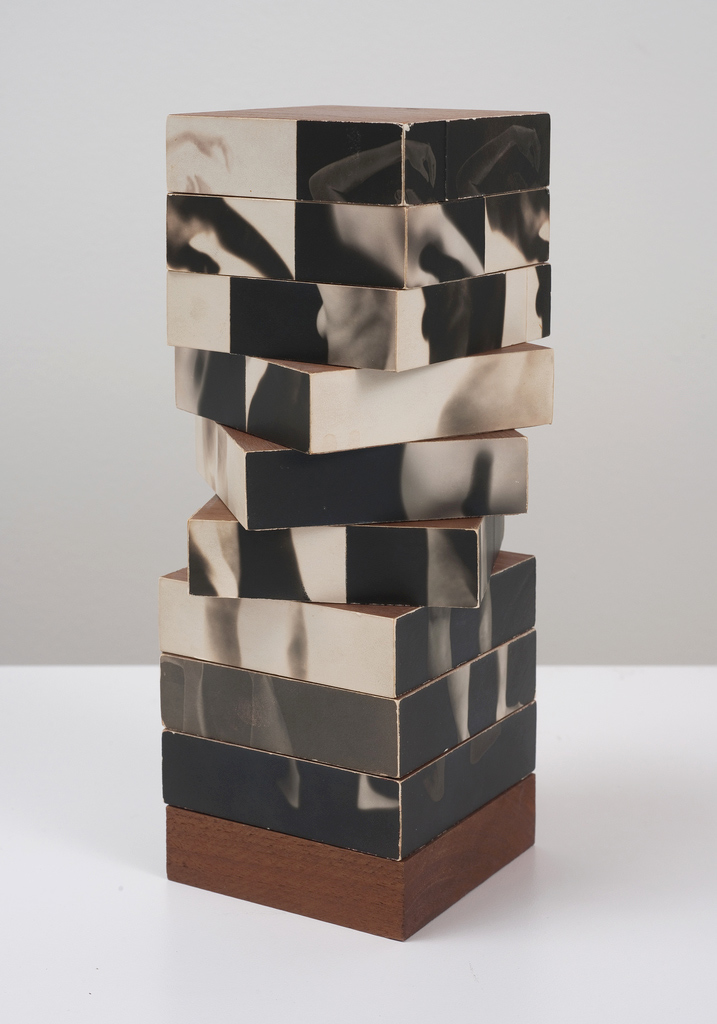
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
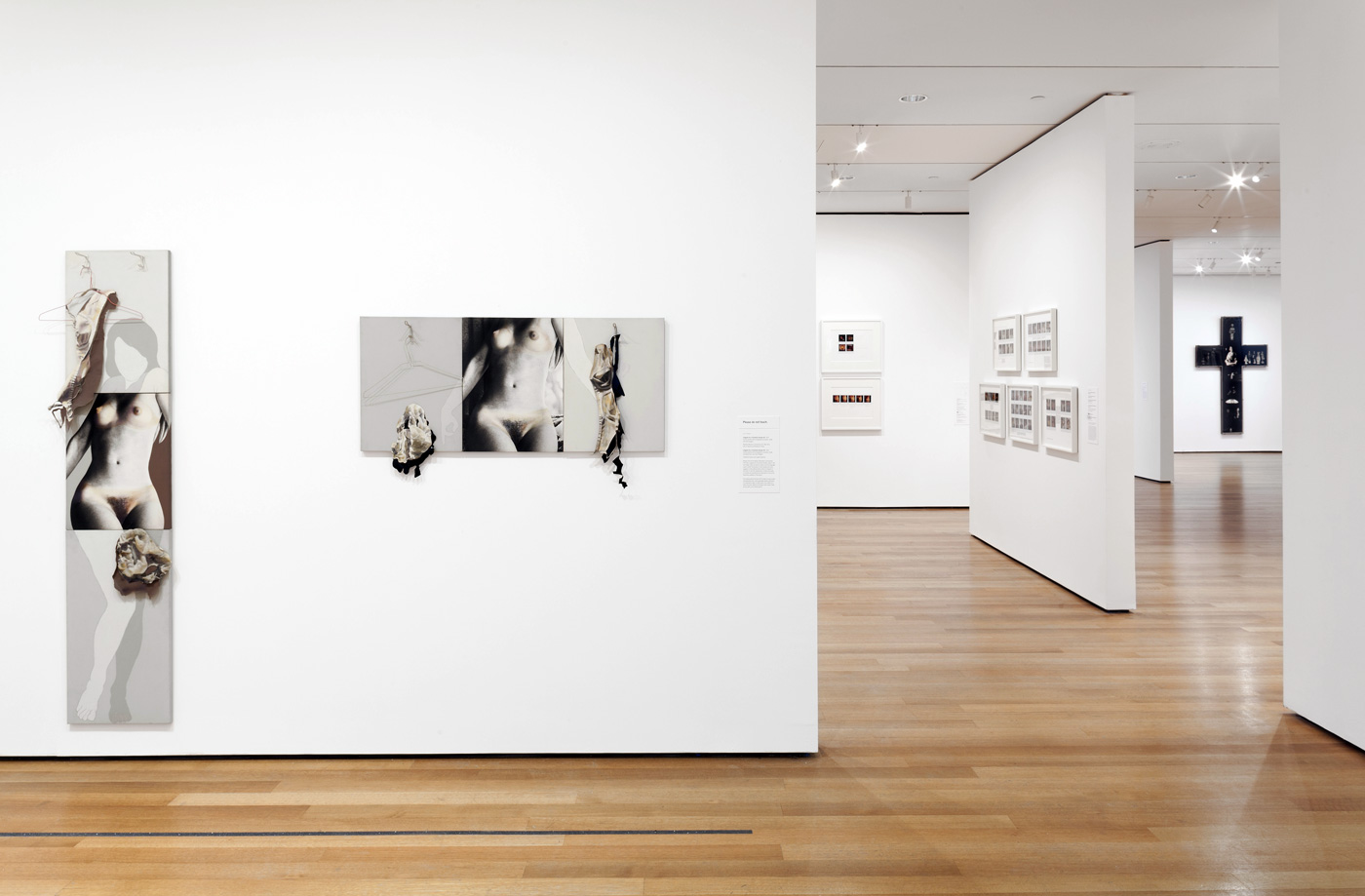
Installation view of works from the series Kiss of Light, 1990-92 including at left Mighty real 1991 with Kiss of Light 1990 right at the exhibition David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me at NGV Australia, Melbourne
Collage of cut self-adhesive holographic film on enamel paint on plywood

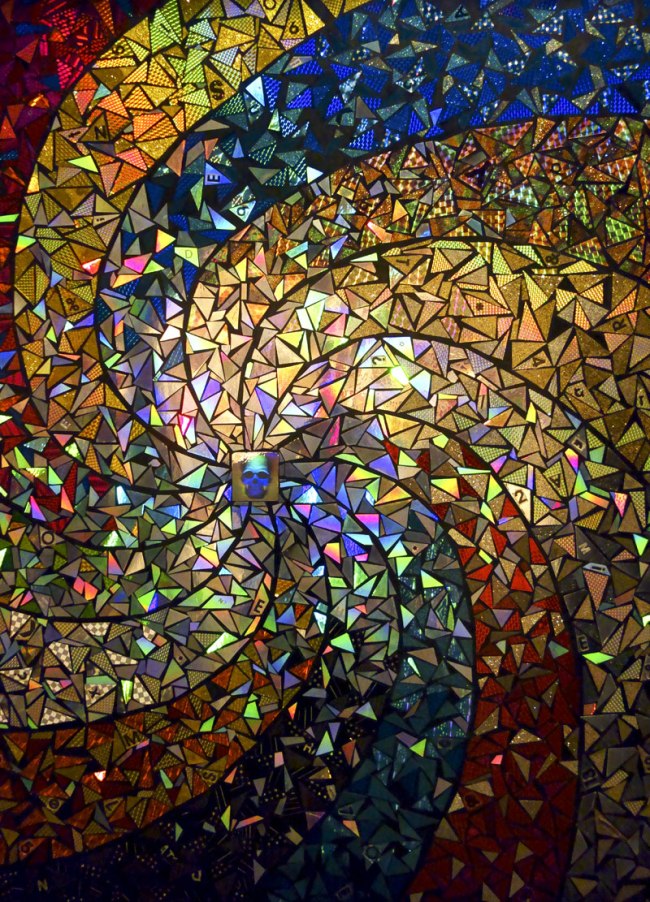
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Mighty real (installation view detail)
1991
From the Kiss of light series 1990-1992
Collage of cut self-adhesive holographic film on enamel paint on plywood
144.5 x 123.6cm
Collection of Bernard Fitzgerald, Sydney

Detail of one of David McDiarmid’s holographic film art works showing the winking eyes
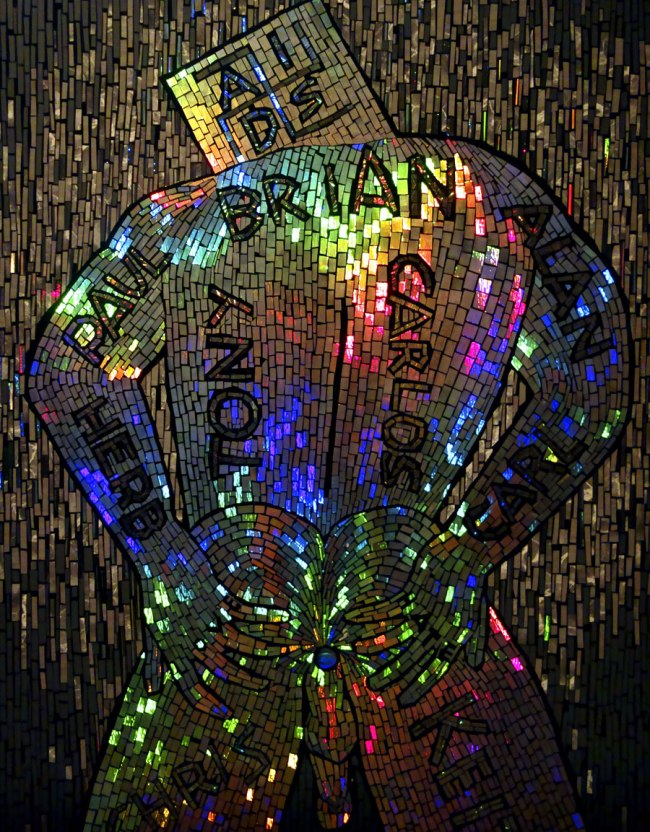

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Body language (installation view)
1990
From the Kiss of light series 1990-1992
Collage of cut self-adhesive holographic film on enamel paint on plywood
152.4 x 121.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
There is a holographic winking eye in the arsehole of this work

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Thinking of you (installation view detail)
1990
Collage of cut self-adhesive holographic film on enamel paint on plywood
140 x 120cm
Collection of Steven Alkins, Mullumbimby, New South Wales

Installation photograph of the last room showing, at left on the wall, work from the Rainbow Aphorisms series 1994 with in front Totem works 1992-1995 at the exhibition David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me at NGV Australia, Melbourne

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Standard bold condensed (installation view)
1994
Screenprint on mylar on colour laser print
255.7 x 242.3cm (overall)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift of the Estate of David McDiarmid, 1998
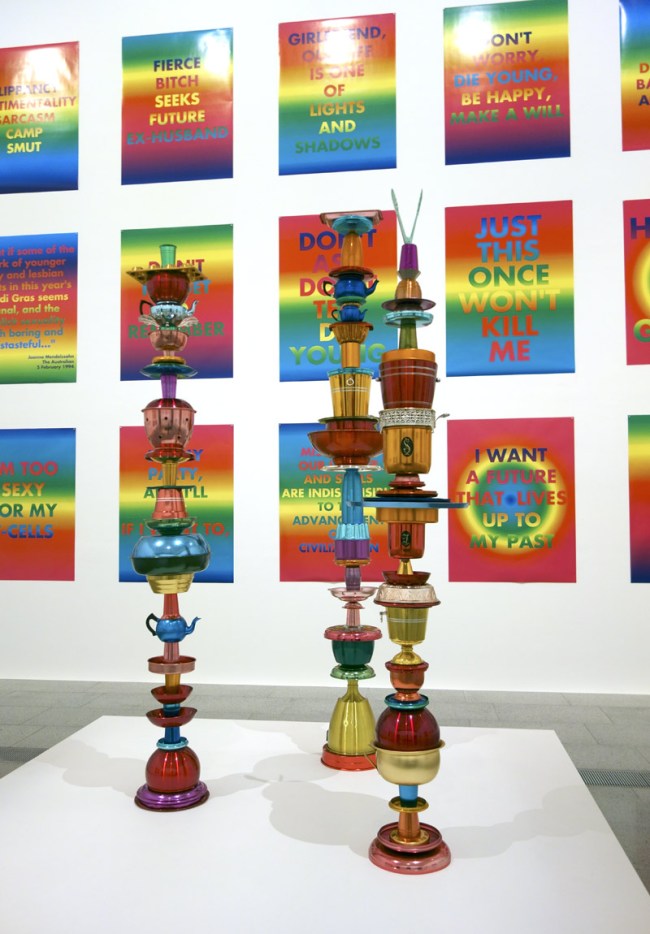


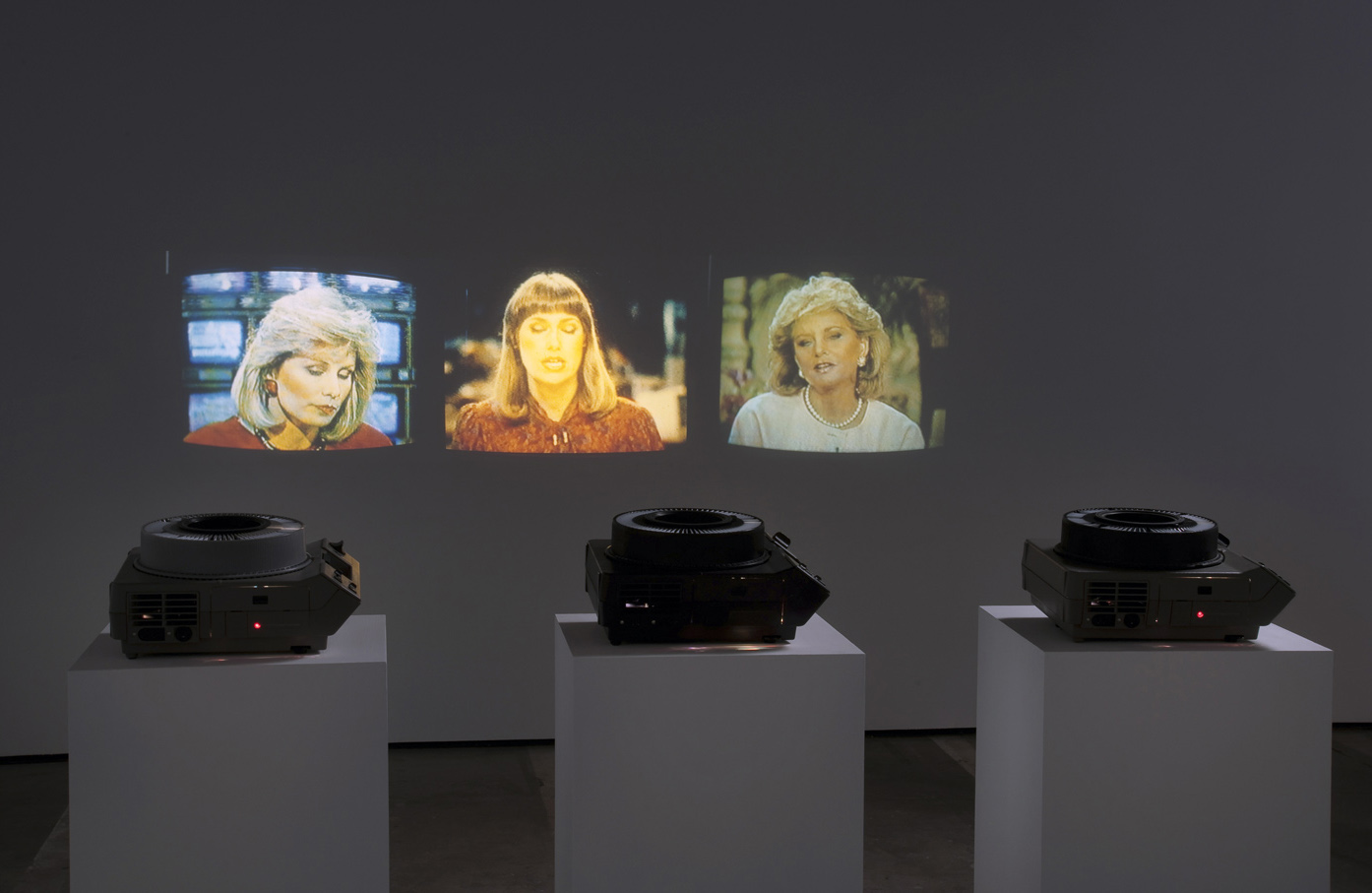
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Works from the Rainbow Aphorisms series (installation views)
1994, printed 2014
Computer generated colour inkjet prints
149.1 x 110cm (image and sheet each)
Collection of the McDiarmid Estate, Sydney
Peter Tully (Australian, 1947-1992)
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Lived in United States 1979-1987
Ron Smith (Australian, b. 1950s)
Totem works
1992-1995
Anodised aluminium, found objects (installation)
Dimensions variable
Collection of Ron Smith, Woonona, New South Wales
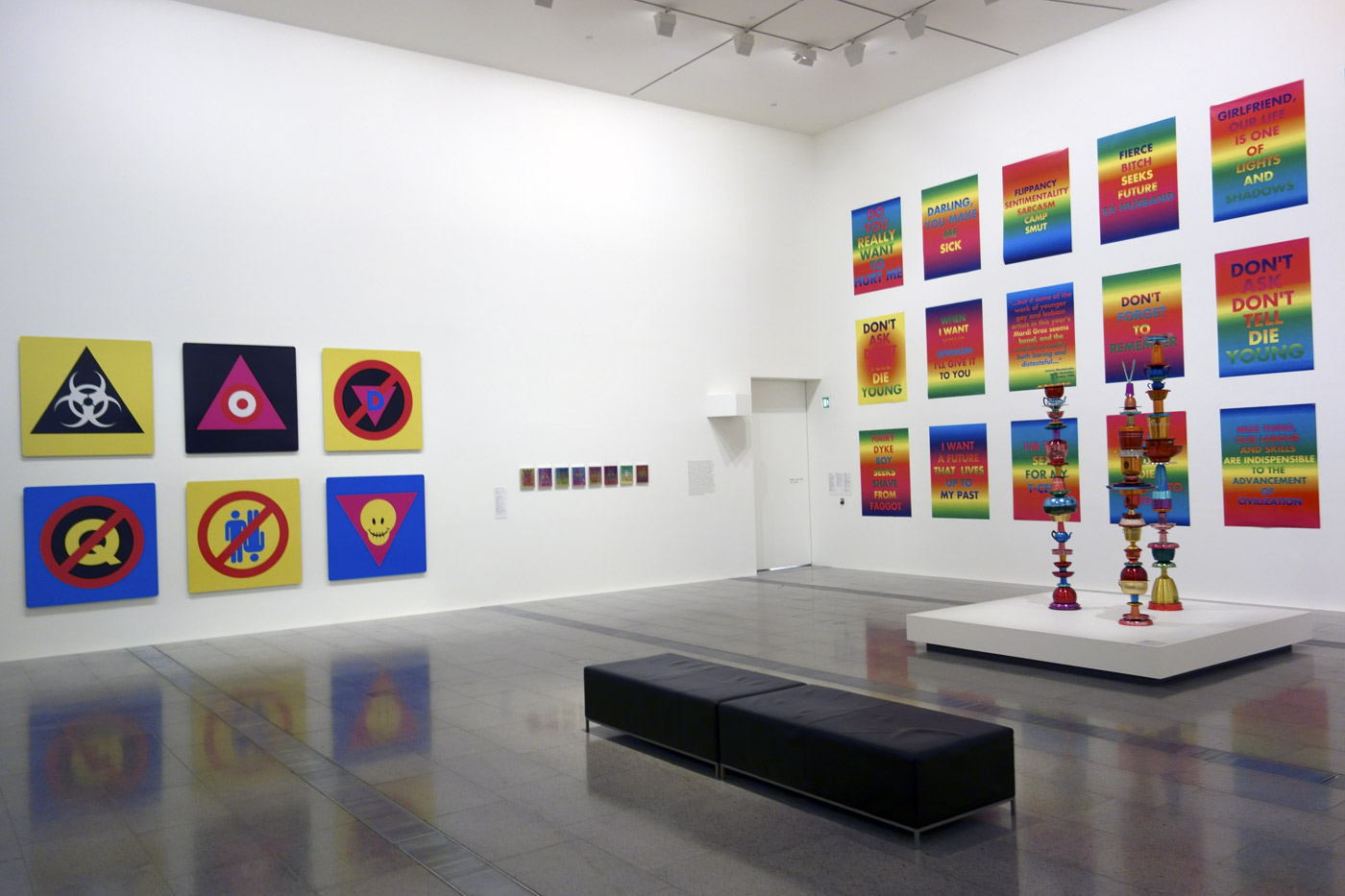

Installation photograph of the last room showing, at right on the wall, work from the Rainbow Aphorisms series 1994 with in front Totem works 1992-95, then at left on the wall Pictograms 1995 at the exhibition David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me at NGV Australia, Melbourne

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Pictograms
1995
Vinyl and reflective plastic on aluminium
“I never saw art as being a safe thing. I know that exists but that’s not something that involves me.”
David McDiarmid, 1993
The vibrant, provocative and pioneering work of leading Australian artist, designer and gay activist David McDiarmid will be presented in a retrospective exhibition at the National Gallery of Victoria. Defying classification, McDiarmid’s work encompasses the complex and interconnected histories of art, craft, fashion, music, sex, gay liberation and identity politics.
David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Mewill bring together more than 200 works, including the artist’s early gay liberation work; New York graffiti and disco quilts; fashion collaborations with Linda Jackson; his pioneering Rainbow aphorisms andGothic aphorisms digital work; material he produced as Sydney Mardi Gras Artistic Director; posters created for the AIDS Council of NSW; and, his significant and highly influential international campaigns developed in the context of AIDS, sexual politics and safe sex in the 1990s.
Tony Ellwood, Director, NGV, said, “The NGV is pleased to be staging this retrospective of an artist whose work had enormous impact on both the gay liberation movement and the international dialogue around AIDS, and whose clear messages of liberation, equality and emancipation continue to resonate today. David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me explores the social history, as well as political and art historical context, that informed McDiarmid’s work, which inspires through its courage, poetry, exuberance and cultural impact.”
Defying classification, the work of David McDiarmid encompasses the complex and interconnected histories of art, craft, fashion, music, sex, gay liberation and identity politics; happily residing in the spaces between high and low art, popular culture and community engagement. At once kaleidoscopic, celebratory and darkly humorous in tone, the artist’s idiosyncratic, highly personal and at times, confessional work highlights the redefinition and deconstruction of identities – “from camp to gay to queer” – drawing on the experiences of a life intensely lived in Melbourne, Sydney and New York. Charting the shifts in politics and individual and community expression that unfold across the decades of the 1970s, 80s and 90s, this exhibition also reveals McDiarmid’s artistic and grassroots political response to the impact of HIV/AIDS during the 1980s and beyond, for which he is best known internationally.
Recognising the cultural climate in which the artist worked, including the burgeoning of the gay rights movement, and a decade later, the advent of the AIDS crisis, the playful and provocative nature of McDiarmid’s work was critically related to changes that were occurring throughout this time to sexual identity and politics in Australia.
Dr Sally Gray, Guest Curator, said, “McDiarmid’s work speaks so eloquently of its time yet its importance and relevance endures today. David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me is the first exhibition in which the full scope of McDiarmid’s creative oeuvre is on display and is the culmination of painstaking research, with the support of many of his collaborators, friends and fans.”
David McDiarmid: When This You See Remember Me will coincide with the 20th International AIDS Conference in Melbourne in July 2014.
This exhibition includes coarse language and sexual content. Press release from the NGV website
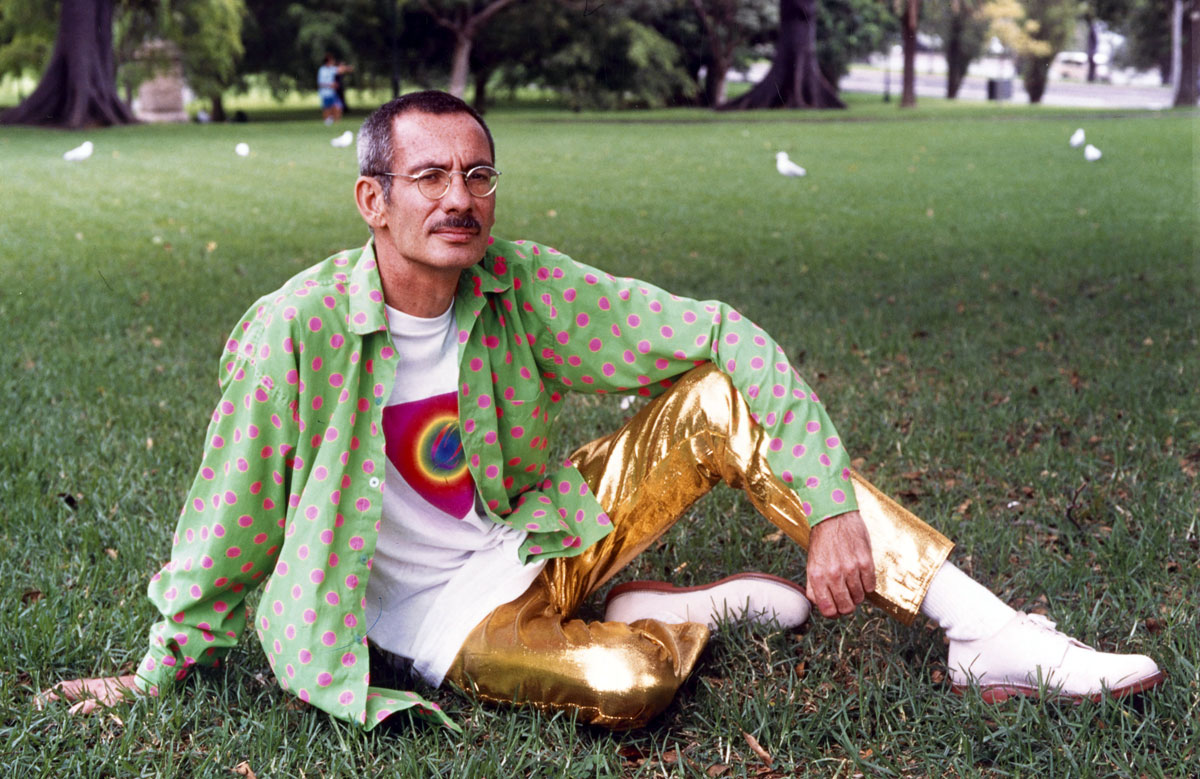

William Yang (Australian, b. 1943)
Artist David McDiarmid photographed at the Art Gallery of New South Wales adjacent to his giant Q artwork on the gallery’s facade for Perspecta May, 1995
1995
© Reproduced with permission of William Yang

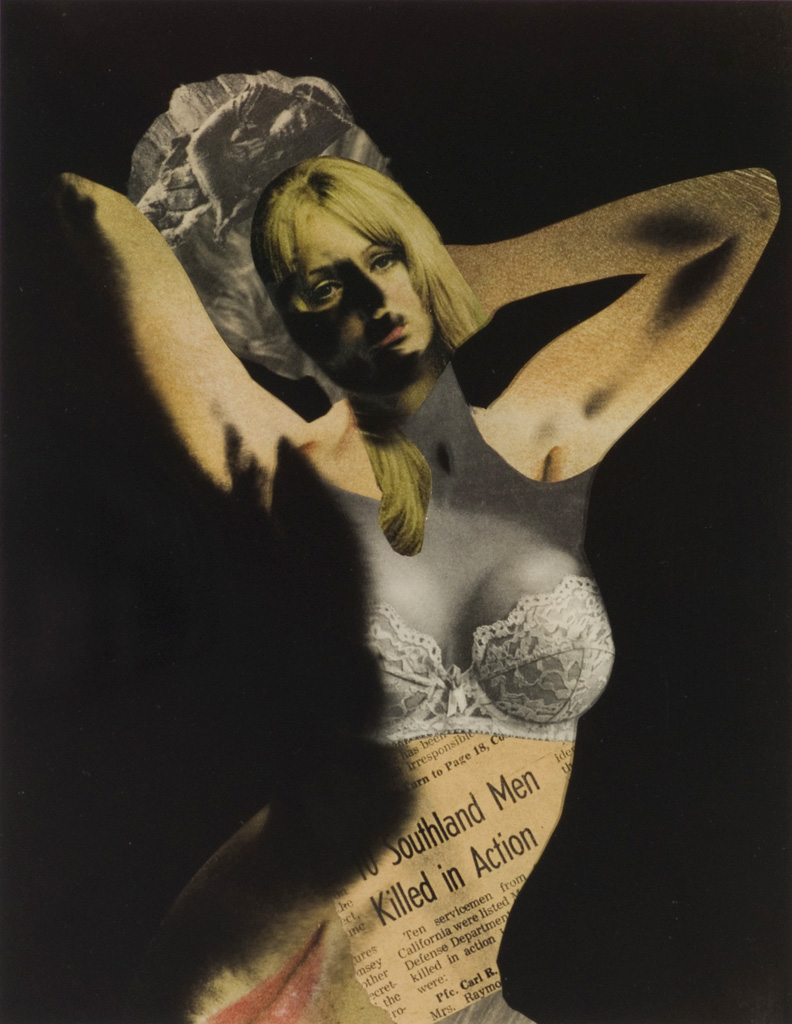
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Judy
1976
From the Secret love series 1976
Metallic paint, red fibre-tipped pen, cut photo-offset lithograph and red and black ink on graph paper
78.0 x 66.0cm
Collection of Paul Menotti and Bryce Kerr, Sydney
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Strangers in the night (installation view)
1978
Collage of cut coloured paper and photocopy on mulberry paper
62.6 x 50.7cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Proposed acquisition
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Hand and heart
1984
Synthetic polymer paint on cotton
250.0 x 230.0cm
Powerhouse Museum, Sydney
Gift of the Estate of the late David McDiarmid, 1998
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras, poster
1989-1990
Colour photo-offset lithograph
69 x 49cm
Powerhouse Museum, Sydney
Gift of Sydney Gay & Lesbian Mardi Gras Limited, 1995
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Untitled
1990-1995
Self-adhesive holographic film and self-adhesive colour plastic on plastic
122.7 x 122.7cm
Collection of Bernard Fitzgerald, Sydney
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate
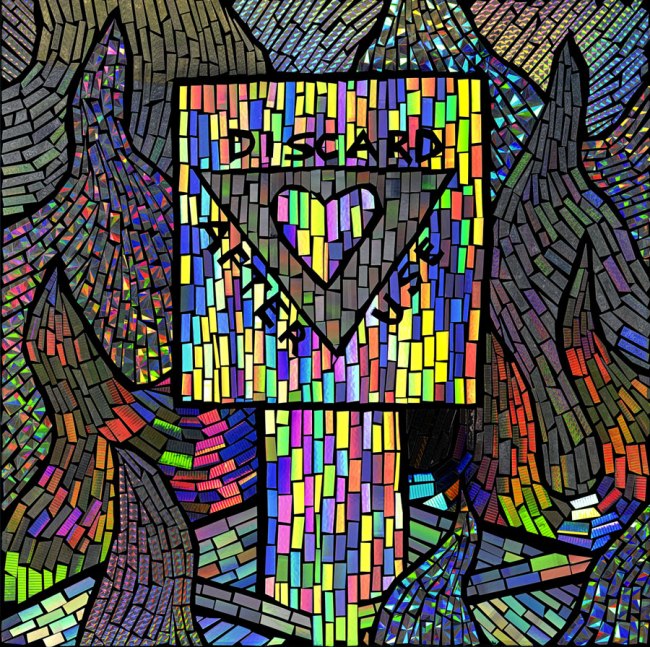

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Discard after use
1990
From the Kiss of light series 1990-1992
Collage of self-adhesive holographic film on enamel paint on plywood
61.2 x 61.2cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Gift from the Estate of David McDiarmid, 1998
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate

David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
I want a future that lives up to my past
From the Rainbow aphorisms series 1994, printed 2014
Computer generated colour inkjet prints
149.1 x 110.0cm
Collection of the McDiarmid Estate, Sydney
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate

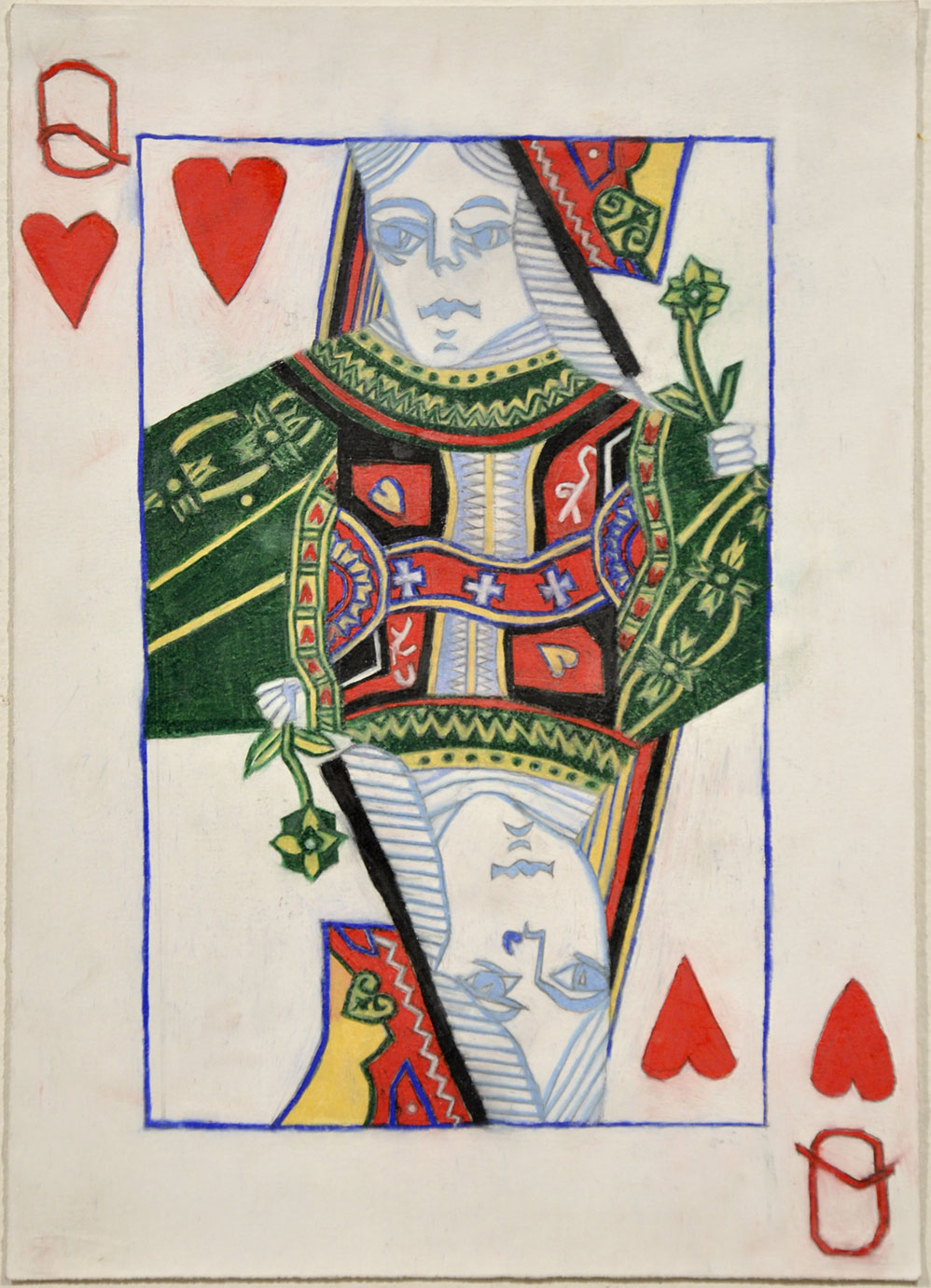
David McDiarmid (Australian 1952-1995, worked in United States 1979-1987)
Q
From the Rainbow aphorisms series 1994, printed 2014
Computer generated colour inkjet prints
149.1 x 110.0cm
Collection of the McDiarmid Estate, Sydney
© Reproduced with the permission of the David McDiarmid estate
The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia
Federation Square
Corner of Russell and
Flinders Streets, Melbourne
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm
National Gallery of Victoria website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top

































![Agustí Centelles (Catalan, 1909-1985) 'Barcelona, España. Guardería infantil en Vía Layetana' [Babysitting in Layetana Road] 1936-1939 Agustí Centelles (Catalan, 1909-1985) 'Barcelona, España. Guardería infantil en Vía Layetana' [Babysitting in Layetana Road] 1936-1939](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/agusti_centelles-guarderia_infantil-web.jpg)
![Fernand Léger (French, 1881-1951) 'Les Loisirs - Hommage à Louis David' [Leisure - Homage to Louis David] 1948-1949 Fernand Léger (French, 1881-1951) 'Les Loisirs - Hommage à Louis David' [Leisure - Homage to Louis David] 1948-1949](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/leger-les_loisirs-web.jpg)
![Louis Sciarli (French, b. 1925) 'Le Corbusier. Marseille: Unité d'habitation, École Maternelle' [Le Corbusier. Marseille: housing unit, Kindergarten] 1945/2014 Louis Sciarli (French, b. 1925) 'Le Corbusier. Marseille: Unité d'habitation, École Maternelle' [Le Corbusier. Marseille: housing unit, Kindergarten] 1945/2014](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/sciarli-le_corbusier_marseille-web.jpg)




































































![Giacomo Balla (Italian, 1871-1958) 'The Hand of the Violinist (The Rhythms of the Bow)' (La mano del violinista [I ritmi dell’archetto]) 1912 Giacomo Balla (Italian, 1871-1958) 'The Hand of the Violinist (The Rhythms of the Bow)' (La mano del violinista [I ritmi dell’archetto]) 1912](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/01_balla_handoftheviolinist-web.jpg)



























































![Neo Rauch (German, b. 1960) 'Goldgrube' [Goldmine] 2007 Neo Rauch (German, b. 1960) 'Goldgrube' [Goldmine] 2007](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/22_neo_rauch_goldgrube-web.jpg)

![Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (Dutch, 1606-1669) 'Sogenannter Faust' [Allegedly Faust] c. 1651‑1653 Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (Dutch, 1606-1669) 'Sogenannter Faust' [Allegedly Faust] c. 1651‑1653](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/12_rembrandt_sogenannter_faust-web.jpg)




![Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962) 'Relief éponge bleu (RE 18)' (blue sponge relief [re 18]) 1960 Yves Klein (French, 1928-1962) 'Relief éponge bleu (RE 18)' (blue sponge relief [re 18]) 1960](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/16_klein_schwammrelief-web.jpg?w=650)











You must be logged in to post a comment.