Exhibition dates: 21st September 2012 – 13th January 2013

Unknown artist (American)
Providence Panorama from Grosvenor or Bannigan Building
c. 1900
Six cyanotype prints
RISD Museum: Mary B. Jackson Fund
I hope you enjoy this HUGE posting. There are some rare photographs and little known artists. I have kept the photographs in the sections of the exhibition as explained by the accompanying wall text. Three essays from the catalogue investigating history, landscape and photography can be found as pdfs below, essential reading for anyone interested in the subject (especially the first two essays):
Douglas Nickel. Photography, Perception, and the Landscape 2012 (645kb pdf)
Deborah Bright. Photographing Nature, Seeing Ourselves 2012 (2Mb pdf)
Jan Howard. Landscape as Stage 2012 (775kb pdf)
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design for allowing me to publish the text and most of the photographs in the posting (the others I researched myself). Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“An understanding of landscape theory therefore suggests that not every photograph of land is a landscape, and not every landscape necessarily features the land. The standard definition points to places – places in the world, or places seen in pictures – which take on the quality of a thing. But “landscape” is probably better understood as that set of expectations and beliefs – about both the environment and the conventions of its representation – that we project upon the world. These conventions and expectations are subject to historical change and are culturally specific…”
Douglas Nickel. ‘Photography, Perception, and the Landscape’ 2012 in ‘America in View: Landscape Photography 1865 to Now’ catalogue, p. 26
“Once continental expansion had reached its limits, however, and no existential threats to white settlement remained, American landscape images began to reflect a new criticality – at turns romantic and realistic – that persists to this day. Indeed, for the last century, landscape photography has consistently mirrored Americans’ anxieties about nature, or rather its imminent loss, whether due to industrialisation, pollution, population growth, real estate profiteering, or bioengineering. Alternately portraying nature as a balm for the alienated modern soul or a dystopian fait accompli, modern and postmodern photographic landscapes mark a progressively disquieting understanding of humanity’s relationship to the natural universe.”
Deborah Bright. Photographing Nature, Seeing Ourselves 2012 in America in View: Landscape Photography 1865 to Now catalogue, p. 32
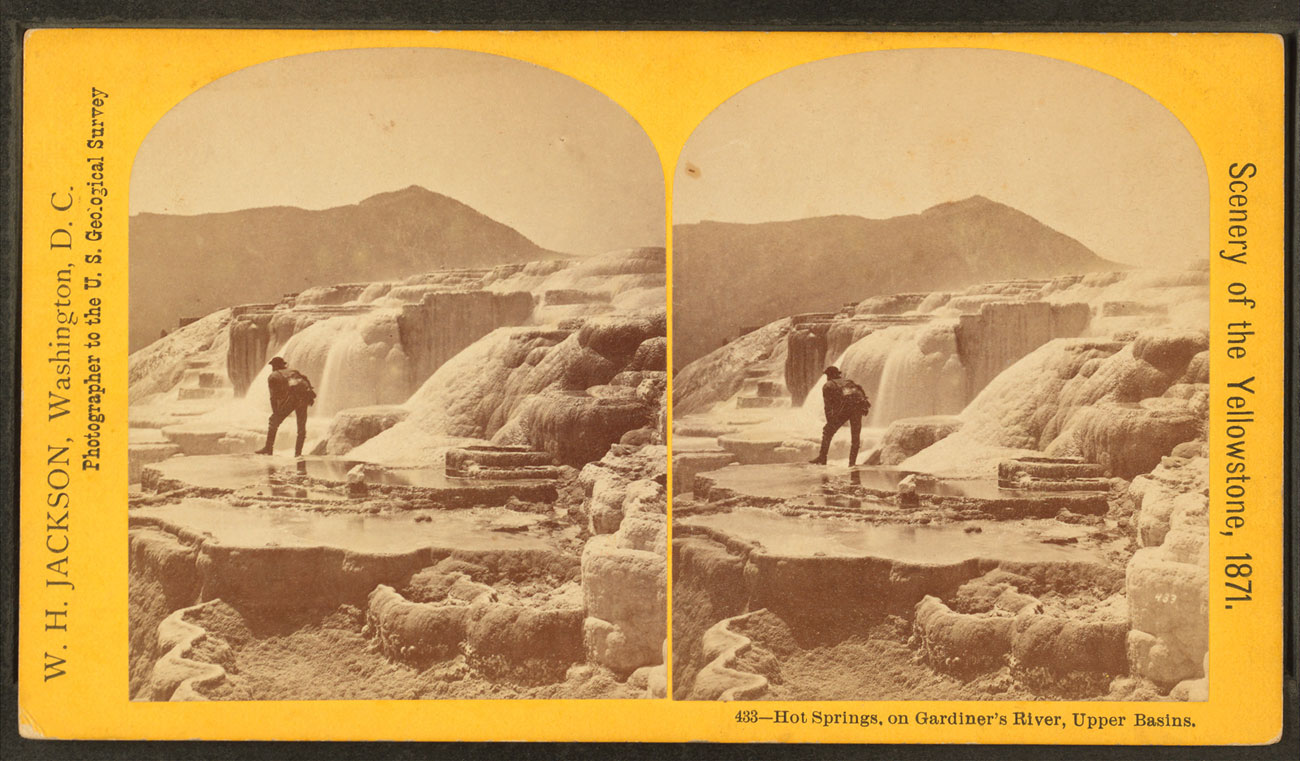

William Henry Jackson (American, 1843-1942)
Gardiners River Hot Springs, Diana’s Baths
1871
From U.S. Geological Survey of the Territories
Albumen print
RISD Museum: Jesse Metcalf Fund
In this photograph William Henry Jackson captures the painter Thomas Moran, who was also part of the 1871 survey team. Shot from slightly below and at a distance, the photograph emphasises the textures of the mineral deposits in the foreground, while Moran’s figure seems dwarfed by the rock formations around him. Jackson often included figures in his photographs to impart a sense of scale. This inclusion of a single figure also heightens the impression that the photograph has captured a moment of discovery, the first contact between intrepid explorers and an uncharted land.

Carleton E. Watkins (American, 1829-1916)
Cape Horn, Columbia River
1867
Helen M. Danforth Acquisition Fund.
Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Cape Horn, Columbia River exemplifies not only the fine detail characteristic of Carleton Watkins’s images, but also his close attention to pictorial structure. Unlike many of the photographers represented in this gallery, Watkins worked independently of industrial concerns or government sponsorship. To make images that would appeal to an audience more familiar with traditional art forms, Watkins borrowed long-established conventions of landscape paintings, in particular carefully modulated lighting effects and harmonious compositions. Like the painters he emulated, Watkins depicts the West as a romantic wilderness and place of spiritual refuge.

William H. Bell (American, 1830-1910)
Perched Rock, Rocker Creek, Arizona
1872
From the album Explorations and Surveys West of the 100th Meridian
Albumen print
Jesse Metcalf Fund. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Surveying the Field
At the end of the American Civil War photographers turned their lenses toward both the wild territories of the West and scenic tourist destinations in the newly established national parks. Although these images are now commonly exhibited in art museums, they were not originally considered art objects, nor were the photographers who made them considered artists. Instead, many of the photographers represented here were hired to document the projects of governmental agencies and the progress of federal survey expeditions to the western territories. Others produced images for the growing tourist market or recorded the construction of tracks through the country’s interior for railroad companies. The majority of these images were published in governmental reports and presentation albums.
The albumen prints produced in America through the 1880s were made from glass-plate negatives created by the laborious process of coating glass plates the size of the prints with a thick photosensitive solution called collodion. These plates had to be prepared on-site, exposed, and developed before the collodion dried, so photographers traveled with portable darkrooms. The prints were made later in a studio by placing paper coated with albumen (solution suspended in egg whites) under a glass-plate negative and exposing the paper to sunlight. By contact printing on this glossy surface, the image was recorded in minute detail.

Timothy O’Sullivan (American born Ireland, 1840-1882)
Water Rhyolites, Near Logan Springs, Nevada
1871
From the album Explorations and Surveys West of the 100th Meridian
Albumen print
RISD Museum: Jesse Metcalf Fund
Timothy O’Sullivan and William H. Bell, official photographers on survey expeditions through Nevada and Arizona from 1871 to 1873, disavowed the traditional conventions of landscape painting in favour of unadorned observation. Spare and anti-picturesque, O’Sullivan’s radical views – depicting the western territories as foreign-looking, even hostile – accorded perfectly with the interests of those invested in seeing these empty territories studied, secured, and settled. One scholar has postulated that O’Sullivan’s photographs were intentionally crafted to look like products of technology – optically precise, printed on glossy albumen papers – a look that stood for industrial progress within a milieu that valued the machine-made over the handmade. In Perched Rock, Rocker Creek, Arizona and Rock Carved by Drifting Sand, Below Fortification Rock, Arizona, the two photographers treat unusual rock formations like specimens, isolating them from the surrounding landscape to be examined and measured.
Luminous Realms
Kodak’s introduction of the handheld camera in 1888 made photography an affordable and popular leisure-time amusement, creating a generation of amateur photographers seemingly overnight. At the same time, photographers with artistic ambitions feared that the mechanical, point-and-shoot approach of the new “button pressers” would jeopardise the medium’s elevation to the status of high art. In response, this group of artists – who called themselves Pictorialists – emphasised the photographer’s expertise and embraced labor-intensive processes to create expressive and impressionistic images. Many favoured platinum prints because of their wide range of tones, soft contrast, and matte surface – qualities of more traditional artistic media such as drawings and etchings. The Pictorialists’ landscape photographs are especially evocative. Rather than capturing a particular place and time, they transformed the landscape into a backdrop for human emotions and actions through visual effects and the inclusion of figures.

Clarence H. White (American, 1871-1925)
Morning
1905
From Camera Work, No. 23, July 1908
Photogravure
RISD Museum: Walter H. Kimball Fund

Laura Gilpin (American, 1891-1979)
Footprints in the Sand
1931
Platinum print
RISD Museum: Museum purchase with funds from the National Endowment for the Arts
Laura Gilpin portrays the Colorado sand dunes in the soft-focus style of the Pictorialists, but the reductive forms of her composition are strikingly modern. The sinuous lines of the wind-sculpted dunes are echoed in the subtle patterning of the figure’s footprints. His presence not only provides a sense of scale, but suggests that the human impact on the landscape can be small, fleeting, and beautiful.
Abstracting Nature
In the 1920s, photographers began to question whether Pictorialism was the style best suited to win acceptance for photography as a fine art. On the east coast, Alfred Stieglitz, who had formerly championed Pictorialism, became its most vocal critic. In northern California, a group of photographers who would come to call themselves Group f/64 developed a new style. Opposing the soft focus, painterly approach, the f/64 photographers embraced a hard-edged, sharp-focus machine aesthetic. Optical reality was transformed into surface pattern, rhythm, tone, and line in prints precisely detailed on glossy, gelatin silver papers. Indeed, f/64 refers to the smallest aperture on their large-format cameras, which resulted in sharp focus from foreground to background.
This period revitalised landscape photography, with many photographers looking to views of nature as a place to escape from the problems of urban life. These photographers captured instants of intensified vision that only the camera offered, creating the photograph mentally before it was realised physically. Whether majestic views of dramatic natural features or abstracted details of quiet settings, these images expressed metaphysical, ethical, or personal reflections on humankind’s relationship to nature.
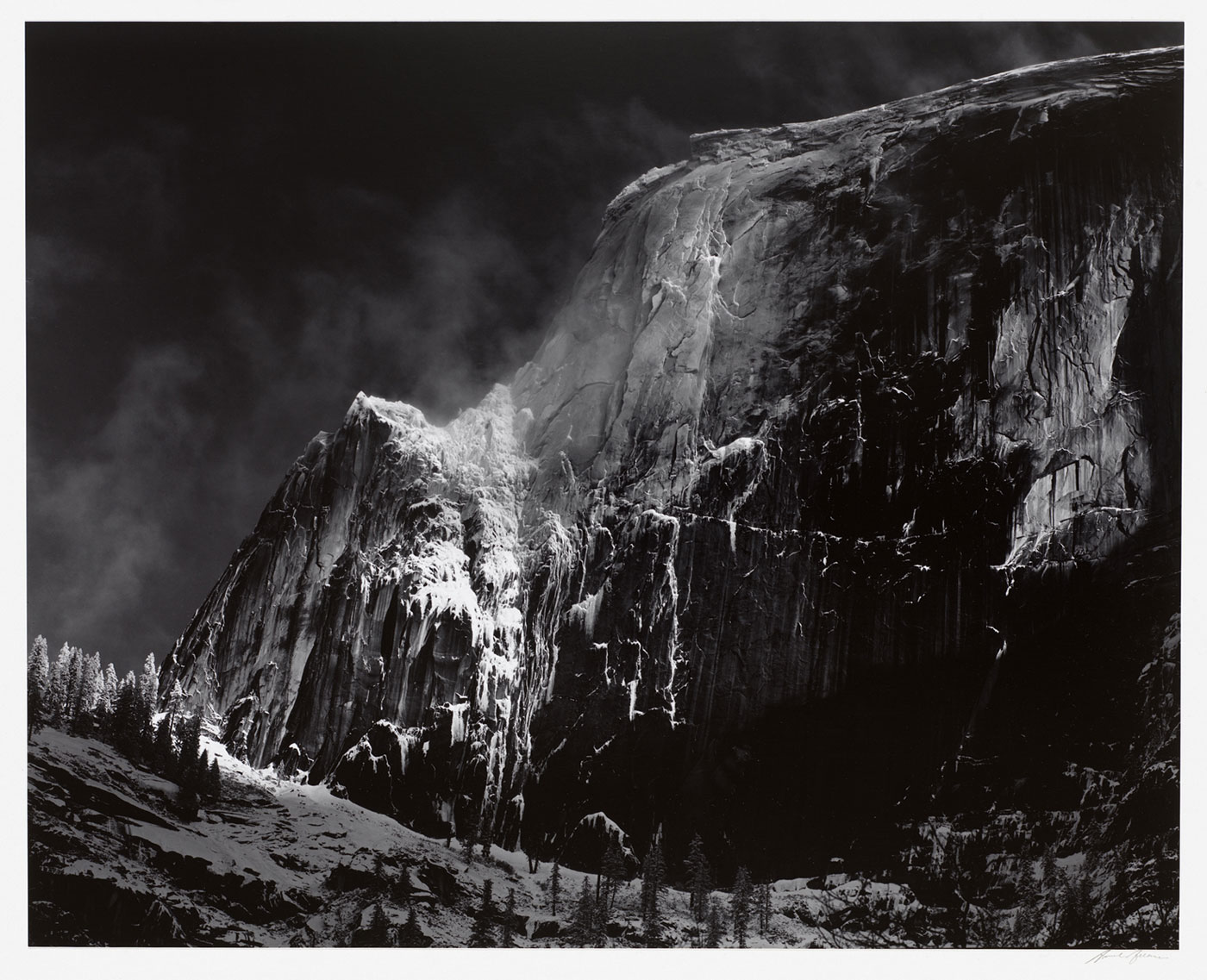

Ansel Adams (American, 1902-1984)
Half Dome, Blowing Snow, Yosemite National Park, California
ca. 1955 (printed 1970s)
Museum purchase with funds from the National Endowment for the Arts
© 2012 The Ansel Adams Publishing Rights Trust. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
This photograph depicts the iconic tourist destination of Yosemite as sublime and untouched. By removing any evidence of human impact, Ansel Adams allows us to escape (at least temporarily) from the intrusions of culture. High contrast adds visual drama to an already majestic view, capturing the textures of the rock wall and the light filtering through the blowing snow. Throughout his life, Adams embraced the notion that nature could provide the harried, urbanised citizen of the modern age with a place of spiritual refuge. A long-time member of the Sierra Club, he was a devoted and vocal advocate for wilderness conservation and his photographs were crucial to the conservation effort.

Arthur Rothstein (American, 1915-1985)
Father and Sons Walking in the Face of a Dust Storm, Cimarron County, Oklahoma
1936
Gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Gift of Mr. and Mrs. Gilman Angier
In 1936 Arthur Rothstein traveled to the Oklahoma panhandle, the area of the country most affected by drought, wind, and erosion. In his image (above) he captured one of the few families in the area that had not yet abandoned their farm. His portrayal of the farmer and his sons fighting to make their way home through the elements can be read as a larger statement about the struggle between man and nature. Rothstein’s dark, low contrast print further conveys the oppressive atmosphere of the dust storm.
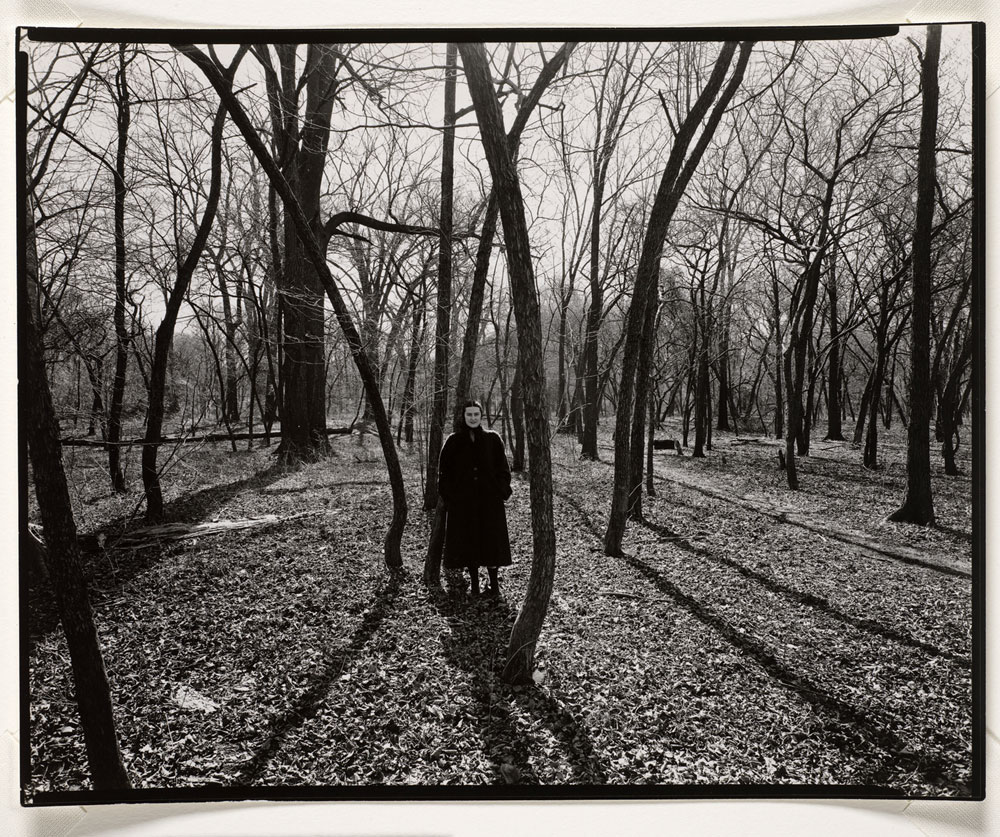

Harry Callahan (American, 1912-1999)
Eleanor, Chicago
c. 1952
Gift from Harry Callahan ca. 1953 Wayne Miller
© The Estate of Harry Callahan, courtesy Pace/MacGill Gallery, New York. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
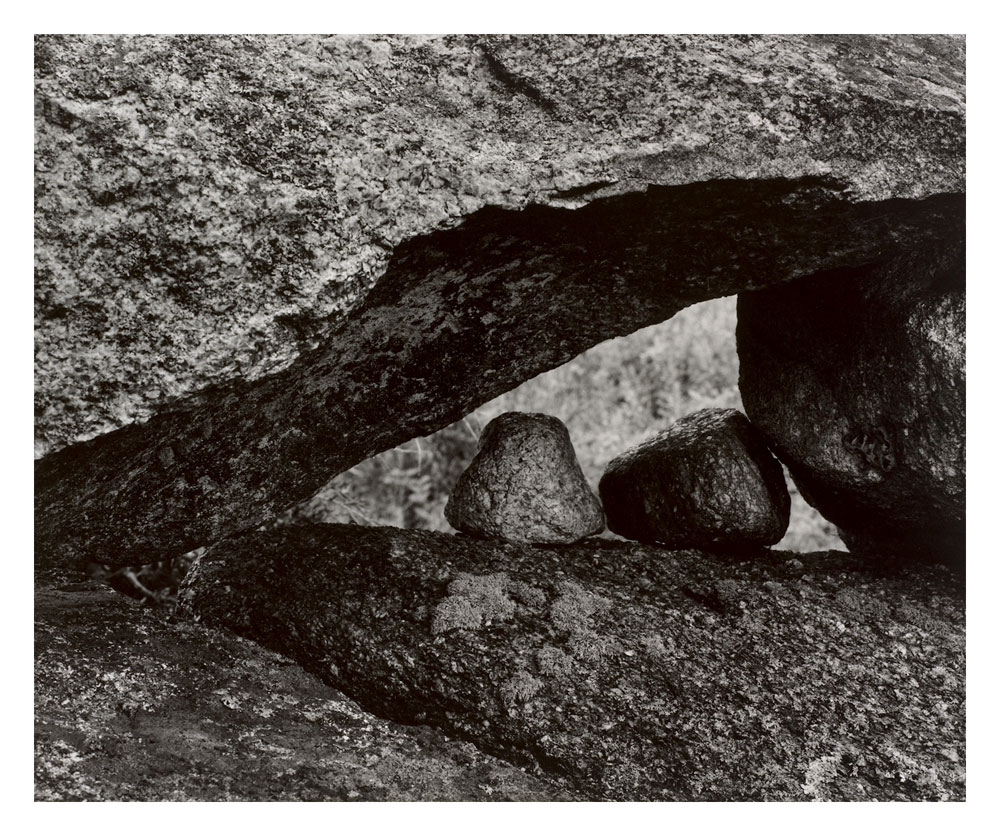

Aaron Siskind (American, 1903-1991)
Martha’s Vineyard, 114B
1954
Gift of Mr. Robert B. Menschel. Courtesy Aaron Siskind Foundation
Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
In Martha’s Vineyard 114B, Aaron Siskind focuses on two small rocks nestled in a stone wall. As Siskind explained, he “began to feel the importance of how these rocks hovered over each other, touched each other, pushed against each other.” He likened this contiguity to family relationships, especially that between mother and child. He believed that the pair of rocks pictured in the photograph would – consciously or not – evoke emotions in the viewer, and that these emotions were both deep-seated and universal. In his depiction of the landscape, he found metaphors for what he called “human drama.”

Frederick Sommer (American, 1905-1999)
Arizona Landscape
1943
Gelatin silver print
Promised gift from the collection of Marc Harrison
Frederick Sommer’s photographs of the Arizona desert, made between about 1939 and 1945, omit the horizon line to create an overall field of pattern where scale and orientation are confounded. The vast space of the desert is pulled to the surface of the image, making the work less a landscape and more an independent construction. Sommer intently considered much of his work before executing it. He might study an area of the desert for days before deciding how to take the picture and then spend weeks in the darkroom perfecting the print.
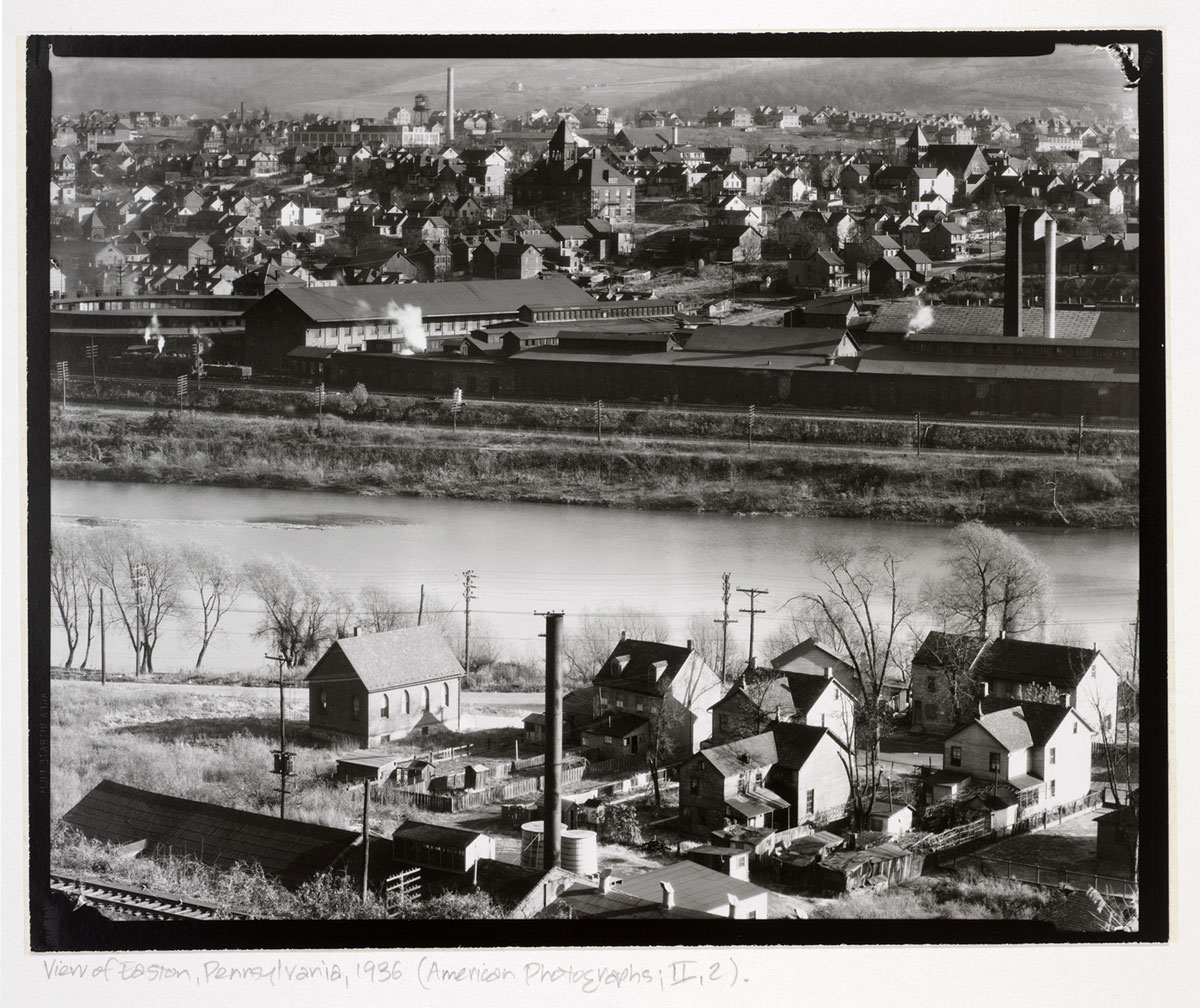

Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975)
View of Easton, Pennsylvania
1936
From the portfolio American Photographs II
Gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Gift of James Dow
By compressing distance and flattening perspective, Walker Evans collapses the two cityscapes of Easton, Pennsylvania, and Phillipsburg, New Jersey, into one plane. Evans’s aesthetically neutral style seems to depict the world without the intervention of the photographer’s point of view. At the same time, he forces the details of every building and smokestack to the surface of the image, making the plight of the cities and their inhabitants – the Depression had crippled the shipping and manufacturing industries that were the lifeblood of both towns – impossible to ignore.

Jack Warren Welpott (American, 1923-2007)
White Sands
1977
Gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Gift of Aaron Siskind

Joe Deal (American, 1947-2010) (RISD Provost 1999-2005, Faculty 2005-2009)
Colton, California
1978
From the portfolio The Fault Zone 1981
Portfolio of 19 gold-toned gelatin silver prints
Museum Purchase: Georgianna Sayles Aldrich Fund and Gift of James D. and Diane D. Burke
© The Estate of Joe Deal, courtesy Robert Mann Gallery. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence

Joe Deal (American, 1947-2010) (RISD Provost 1999-2005, Faculty 2005-2009)
Chatsworth, California
1980
From the portfolio The Fault Zone 1981
Portfolio of 19 gold-toned gelatin silver prints
Museum Purchase: Georgianna Sayles Aldrich Fund and Gift of James D. and Diane D. Burke
© The Estate of Joe Deal, courtesy Robert Mann Gallery. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence

Joe Deal (American, 1947-2010) (RISD Provost 1999–2005, Faculty 2005-2009)
Indio, California
1978
From The Fault Zone 1981
Portfolio of 19 gold-toned gelatin silver prints
RISD Museum: Museum Purchase: Georgianna Sayles Aldrich Fund and Gift of James D. and Diane D. Burke

Joe Deal (American, 1947-2010) (RISD Provost 1999–2005, Faculty 2005-2009)
Santa Barbara, California
1978
From The Fault Zone 1981
Portfolio of 19 gold-toned gelatin silver prints
RISD Museum: Museum Purchase: Georgianna Sayles Aldrich Fund and Gift of James D. and Diane D. Burke
Inspired by conceptual art, Joe Deal generally developed his work in series, choosing a particular location and adhering to a strict visual formula. As in The Fault Zone, his landscapes were typically square in format, viewed from above, lacking a horizon, and empty of people. Edges and divisions in nature and the landscape fascinated him, and the fault lines in California, though invisible on the surface, in many ways define that landscape. Using maps from the Los Angeles County engineering office that indicated where the fault lines were apt to be, Deal looked for sites that would metaphorically suggest volatility. The first image in the series is the only one that was actually taken on the San Andreas Fault; all others symbolically represent the fault lines with torn or disrupted terrain.
Topographic Developments
By the time the landmark exhibition New Topographics: Photographs of a Man-Altered Landscape opened in 1975, the accelerating degradation of the environment had become an inescapable reality. Inverting the Ansel Adams principle of exclusion, the exhibit voiced the belief that the landscape could no longer be portrayed as a refuge from the ills of industrial life: any consideration of the modern environment had to include both wilderness areas and the vacant lot next door.
The New Topographics photographers captured recently constructed tract homes, industrial parks, and highway culture with medium and large format cameras. As aesthetically neutral as real estate snapshots, the photographs showed the facts without offering their opinions about the rapid development they recorded. Seemingly stripped of expressivity, their photographs have the appearance of objective or “topographic” renderings rather than subjective impressions. In emphasising the landscape of the American West and experimenting with anti-Romantic landscape imagery, these photographers looked back to the works of 19th-century survey photographers and to Walker Evans’s documentary style.

Lewis Baltz (American, 1945-2014)
Model Home, Shadow Mountain
1977
From the portfolio Nevada
Gift from the Collection of Joe Deal and Betsy Ruppa
© Lewis Baltz. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
In Nevada, Lewis Baltz alternates unbuilt views with home construction, trailer parks, and roads in a documentation of a rapidly changing landscape in the desert valleys surrounding Reno, an area he once described as “landscape-as-real-estate.” Baltz, like Joe Deal and Harold Jones, whose works are on view in this gallery, developed projects as portfolios, believing that a single photograph cannot capture a complete portrait of a place. In Baltz’s series, a multifaceted, occasionally contradictory image of Nevada emerges through the accumulation of photographs.

Thomas Barrow (American, b. 1938)
f/t/s Cancellations (Brown) – Field Star
1975
Gelatin silver print
Gift from the Collection of Joel Deal and Betsy Ruppa
© Thomas Barrow. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Barrow scratched through his landscape negatives, calling attention to the materiality of the medium itself and the fact that regardless of how much information is given, reality remains an accumulation of belief, knowledge, and one’s own experience.

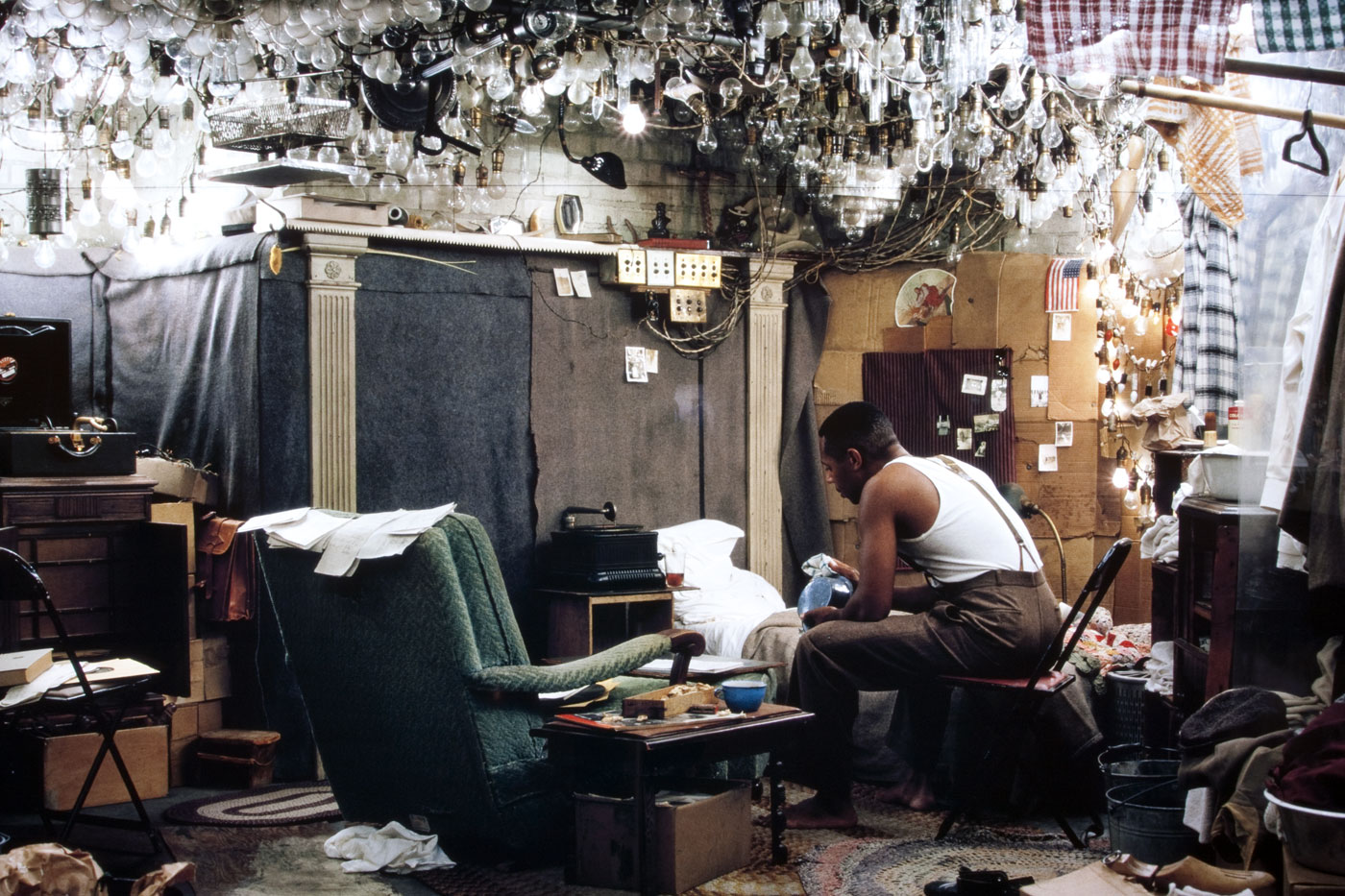
Harold Henry Jones (American, b. 1940)
With Emmet
1978
From the portfolio Tucson
Gelatin silver print
Gift of the artist in honour of Joe Deal
© 1986 Harold Jones. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Harold Jones moved to Tucson sight unseen in 1974. The Tucson Portfolio documents his first years living in, exploring, and adapting to this unfamiliar landscape. In an accompanying text he relates his initial impressions of the Southwest, a landscape he had only seen in Westerns and “in the background of Roadrunner cartoons.” It was, he writes, “white bright and oven hot. Driving through the spiney leafless plants of the desert gave me the impression of being on an ocean floor – except someone had removed the water. A primordial landscape in a sea of light. Shocking and enchanting, at the same time.”
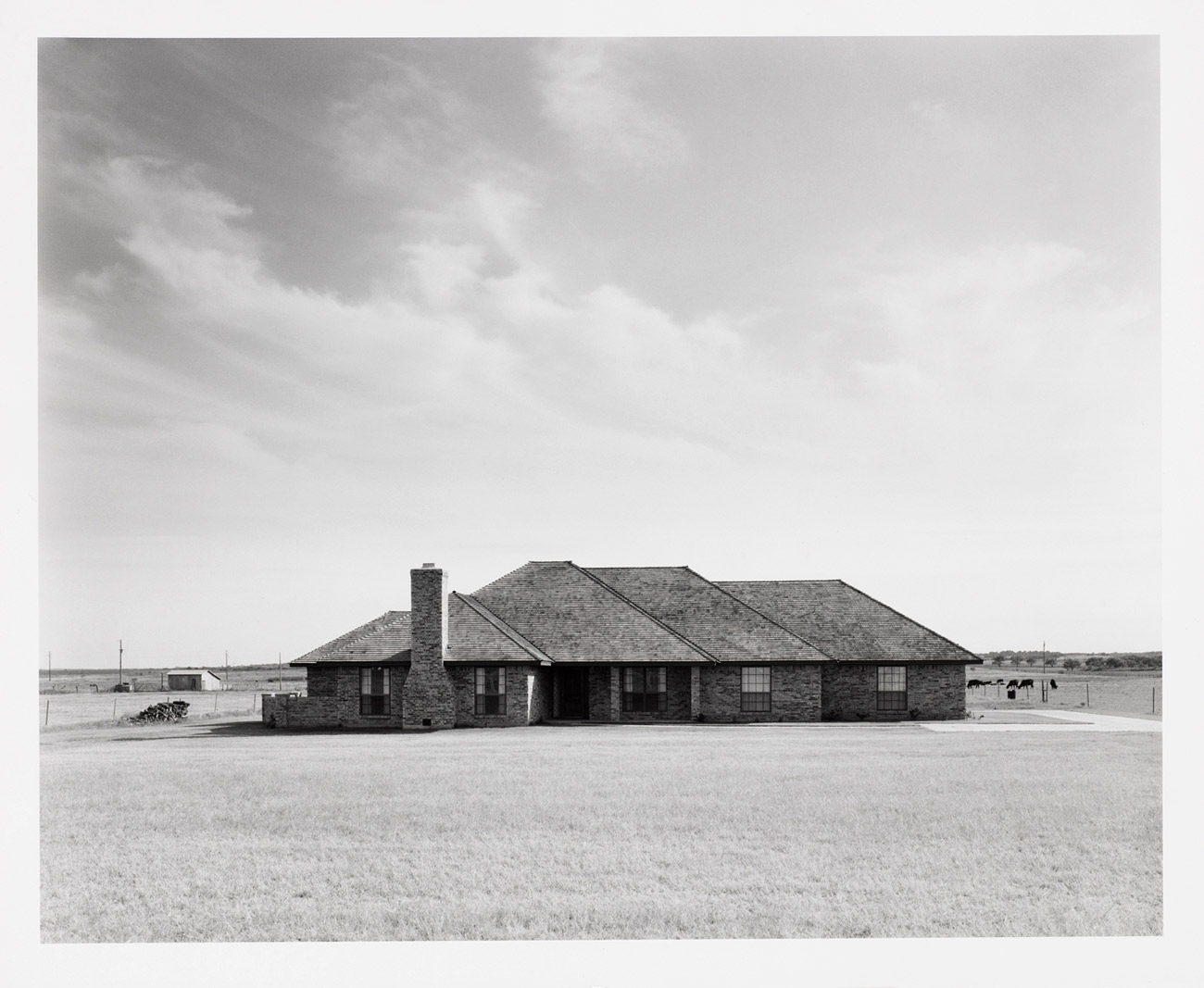

Frank Gohlke (American, b. 1942)
Near Crowley, Texas
1978
Gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Gift from the Collection of Joe Deal and Betsy Ruppa

Lee Friedlander (American, b. 1934)
Atlantic City, New Jersey
1971
Gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Museum purchase with funds from the National Endowment for the Arts

Garry Winogrand (American, 1928-1984)
Utah
1964
From the portfolio Garry Winogrand, 1978
Gelatin silver print
Gelatin silver prints RISD Museum: Gift of Frederick J. Myerson
In the 1960s nature was apt to be viewed from a car window or in a rear-view mirror rather than from a hilltop. The large-format magisterial views of Ansel Adams and Edward Weston were replaced by a 35mm “grab-shot” style that captured the flux and contradictions of modern life with a fresh immediacy. Photographers were among the restless peripatetics crisscrossing the continent on new interstates and side roads, retrieving evidence of the “Americas” they found. The grainy, gritty aesthetic matched the sensations and energy of this environment.
America in View: Landscape Photography 1865 to Now accompanies a major exhibition of that title tracing a history of photographs of the American landscape primarily through the collection of the RISD Museum. The show takes a broad look at the ever-evolving definition of American landscape photography – from seemingly pristine views of nature captured with 19th-century view cameras to images of the decaying contemporary urban streets composed from Google Street View. The RISD Museum’s collection of American landscape photography begins at the end of the Civil War in 1865, when photographers traveled west with government survey teams and railroad companies to record the country’s extraordinary natural features and resources. Ever since, the landscape has remained a compelling subject for photographers who have revealed through their images our nation’s ambition and failings, beauty and degradation, politics and personal stories.
The Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design announces its major fall exhibition, America in View: Landscape Photography 1865 to Now, a broad panorama of our country’s topographies and correlating narratives that reveals a nation’s ambitions and failings, beauty and loss, politics and personal stories through about 150 photographs spanning nearly 150 years. “The landscape has inspired and challenged artists since the earliest days of our nation,” says Museum Director John W. Smith. “The remarkable works in this exhibition not only capture photography’s evolving relationship with the landscape but also trace the larger narrative of America itself.”
From the earliest images in the show, it is clear how purpose guided style. Carlton Watkins’ 1860s painterly and atmospheric views of the sublime landscape portray the wilderness as a place of spiritual renewal and a refuge from urban problems. In contrast, Timothy O’Sullivan, employed for the government’s geological surveys in the 1870s, made purposefully spare and anti-picturesque images that seemingly provide proof of empty territories needing to be studied, secured, and settled.
In her essay for America in View’s accompanying catalogue, photographer Deborah Bright, chair of the Fine Art Department at Pratt Institute, suggests that some of the historical shifts in environmental consciousness seen in the photographs “illuminate how the works also reflect changing conceptions of landscapes as bearers of cultural meaning.” Ansel Adams, whose mid-20th-century views of nature’s majesty and vastness represent many people’s ideals of American landscape photography, omitted human impact on the land. Widely used by the Sierra Club, his stunning images of untouched wilderness encouraged conservation in the face of an increasingly industrial society.
By the 1970s, artists including the late RISD provost and photography professor Joe Deal saw that the environment entailed both wilderness and the vacant lot next door. Their “New Topographics” imagery depicts recently constructed tract homes, industrial parks, and highway culture – inverting Adams’ exclusion. “‘Landscape’ is probably better understood as that set of expectations and beliefs… we project upon the world,” explains Brown University art historian Douglas Nickel, in the catalogue. “Not every photograph of land is a landscape, and not every landscape necessarily features the land.”
The past 20 years reveal a return to romantic views of the landscape, even in its degraded state, often including figures to create narratives. Justine Kurland’s landscape under an overpass shows a stunning place of fantasy and escape. RISD alumnus Justin Kimball explores fantasies of finding wilderness in public parks – where instead we find others seeking the same.
Press release from the RISD website

Barbara Bosworth (American, b. 1953)
Niagara Falls
1986
Gelatin silver print
Private collection

Emmet Gowin (American, b. 1941) (RISD MFA 1967)
Old Hanford City Sites and the Columbia River, Hanford Nuclear Reservation near Richland, Washington
1986
Toned gelatin silver prints
Promised gift of Dr. and Mrs. William G. Tsiaras

Emmet Gowin (American, b. 1941) (RISD MFA 1967)
Alluvial Fan, Natural Drainage near Yuma Proving Ground and the California Arizona Border
1988
Toned gelatin silver prints
Promised gift of Dr. and Mrs. William G. Tsiaras

Emmet Gowin (American, b. 1941) (RISD MFA 1967)
Aeration Pond, Toxic Water Treatment Facility, Pine Bluff, Arkansas
1989
Toned gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Mary B. Jackson Fund
Emmet Gowin’s carefully constructed prints of strip mining sites, nuclear testing fields, large-scale agriculture, and other scars in the natural landscape seductively draw us in to examine what these lushly patterned and toned images represent. Predating Google Earth, these photographs are shot from the air and provide information about the environment that questions our role as stewards of the planet. A master darkroom printer, Gowin makes images come alive through hand-toning. Each print is transformed from grayscale into hues ranging from warm highlights to cool shadows, emphasising the illusion of three-dimensionality.
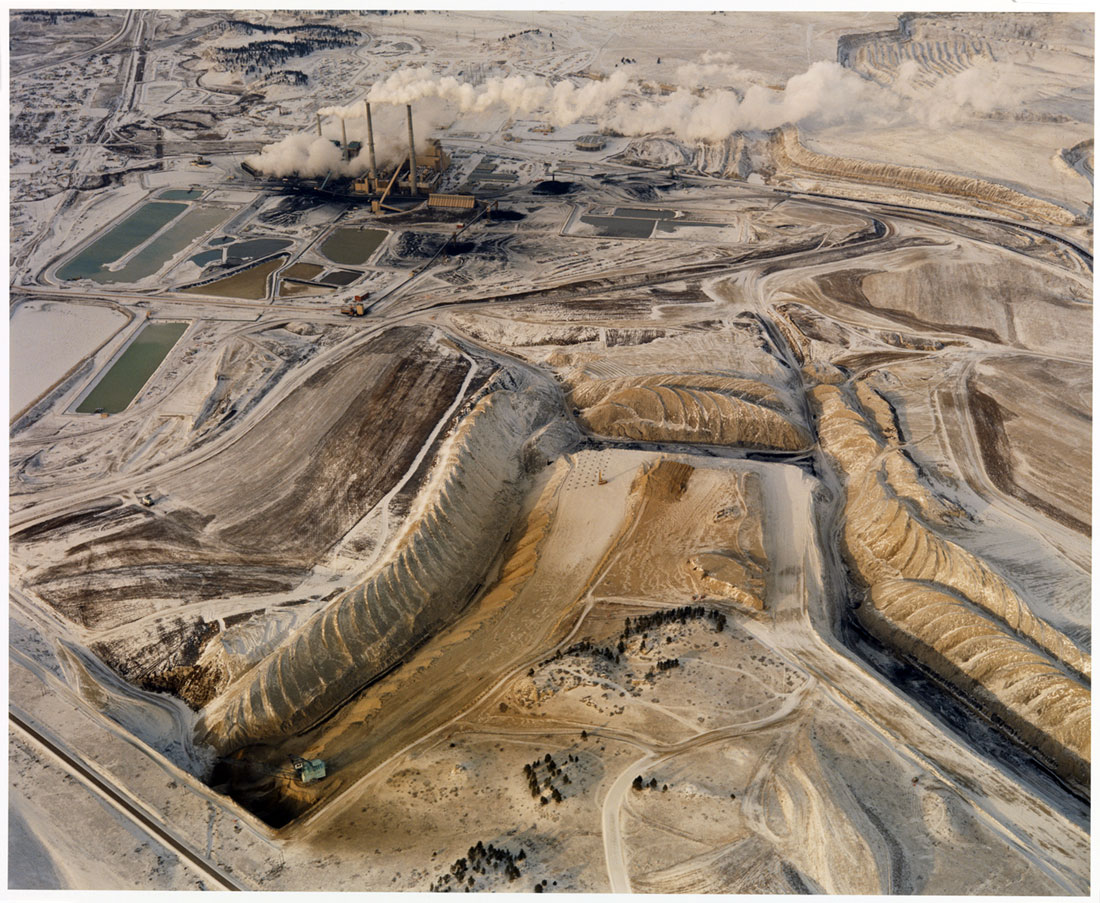

David T. Hanson (American, b. 1948)
Coal Strip Mine, Power Plant and Waste Ponds
1984
Museum Purchase: Gift of the Artist’s Development Fund of the Rhode Island Foundation
© 1984 David T. Hanson, from the book Colstrip, Montana by David T. Hanson (Taverner Press, 2010). Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence

Terry Evans (American, b. 1944)
Terraced Plowing with a Grass Waterway
1991
From the series Inhabited Prairie
Gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Gift of Jan Howard and Dennis Teepe in honour of Joe Deal
Neither the striking abstract design of the terraced field nor the effectiveness of this type of farming are what interests Terry Evans. She is drawn to the specific place and how the marks on the land, as she has said, “contain contradictions and mysteries that raise questions about how we live on the prairie. All of these places are beautiful to me, perhaps because all land, like the human body, is beautiful.”
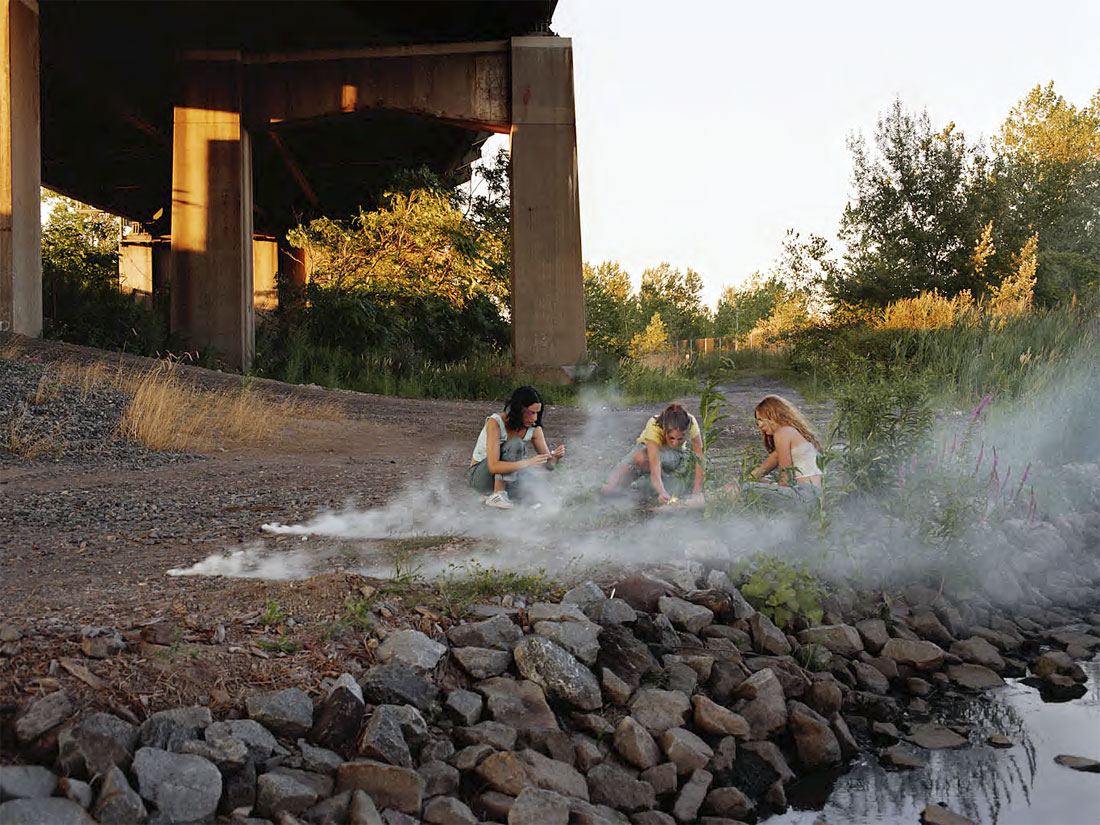

Justine Kurland (American, b. 1969)
Smoke Bombs
2000
From the series Runaway Girls
Colour chromogenic print
RISD Museum: Mary B. Jackson Fund
The neglected space under a New Jersey highway overpass was an ideal spot for three girls to act out Justine Kurland’s fictive story about fugitive teenagers. The figurative grouping recalls pastoral scenes in historical paintings so that the danger of the girls’ pursuit in this dicey no-man’s land is temporarily suspended in the hazy romantic fantasy of escape. The strong light streaming across the scene and the overall beauty of the composition suggests a desire to pursue the sublime even in the most degraded landscapes.

Justin Kimball (American, b. 1961)
Deep Hole, New Hampshire
2002
From the series Where We Find Ourselves
Gift of the artist in honour of Joe Deal
Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Deep Hole, New Hampshire captures light filtering through the trees as a dozen young men and women distribute themselves among rocky outcroppings, poised for adventure in the water below. The composition recalls the quiet drama of Thomas Eakins’s 19th-century painting of nude swimmers. This reference drew Kimball to the picture as it played out in front of him, along with the palpable sense of elation in the youths’ encounter with the landscape, no matter the deteriorating state of the site due to its heavy use. Kimball’s series Where We Find Ourselves explores the fantasy of finding wilderness in state and national parks, where we only find other people looking for it, too.
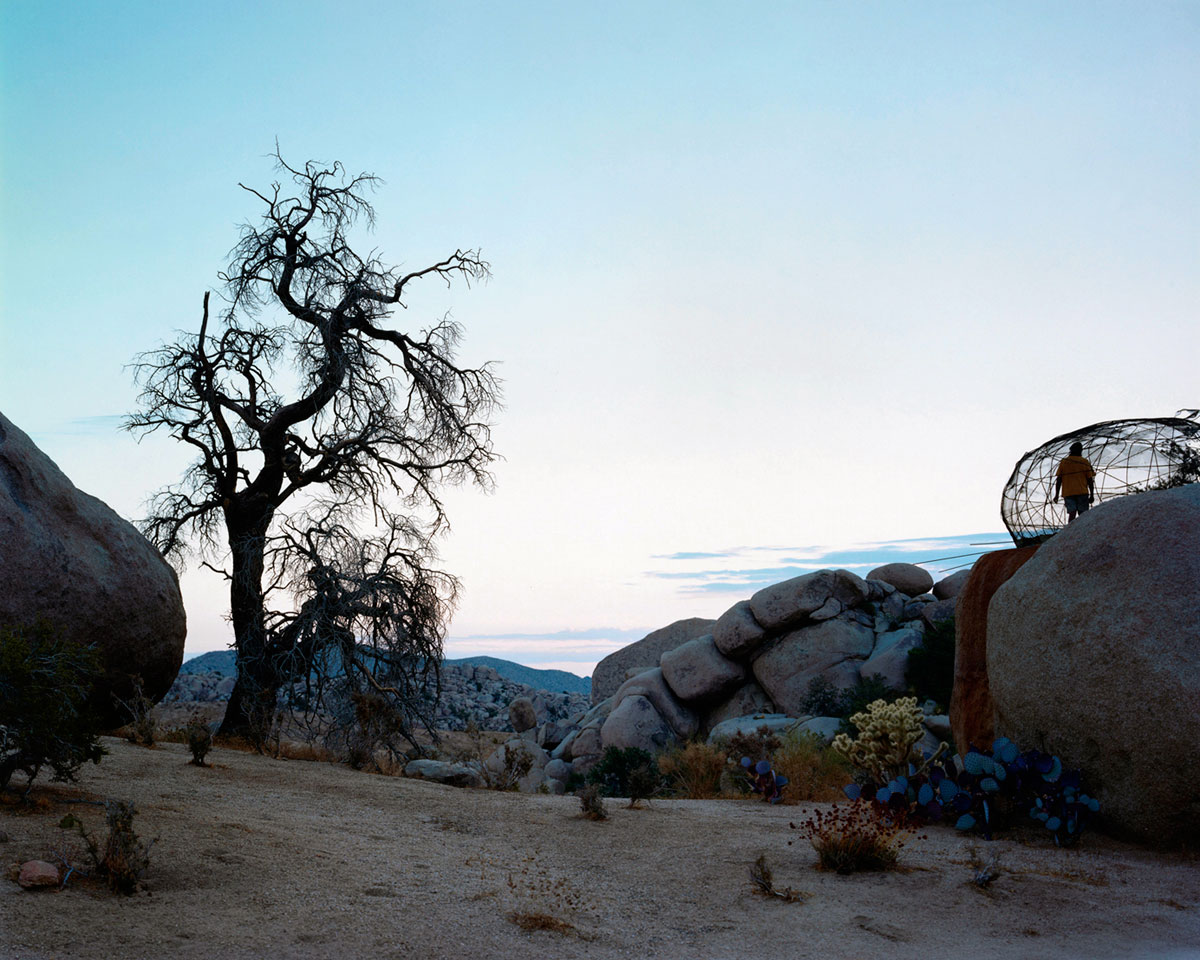

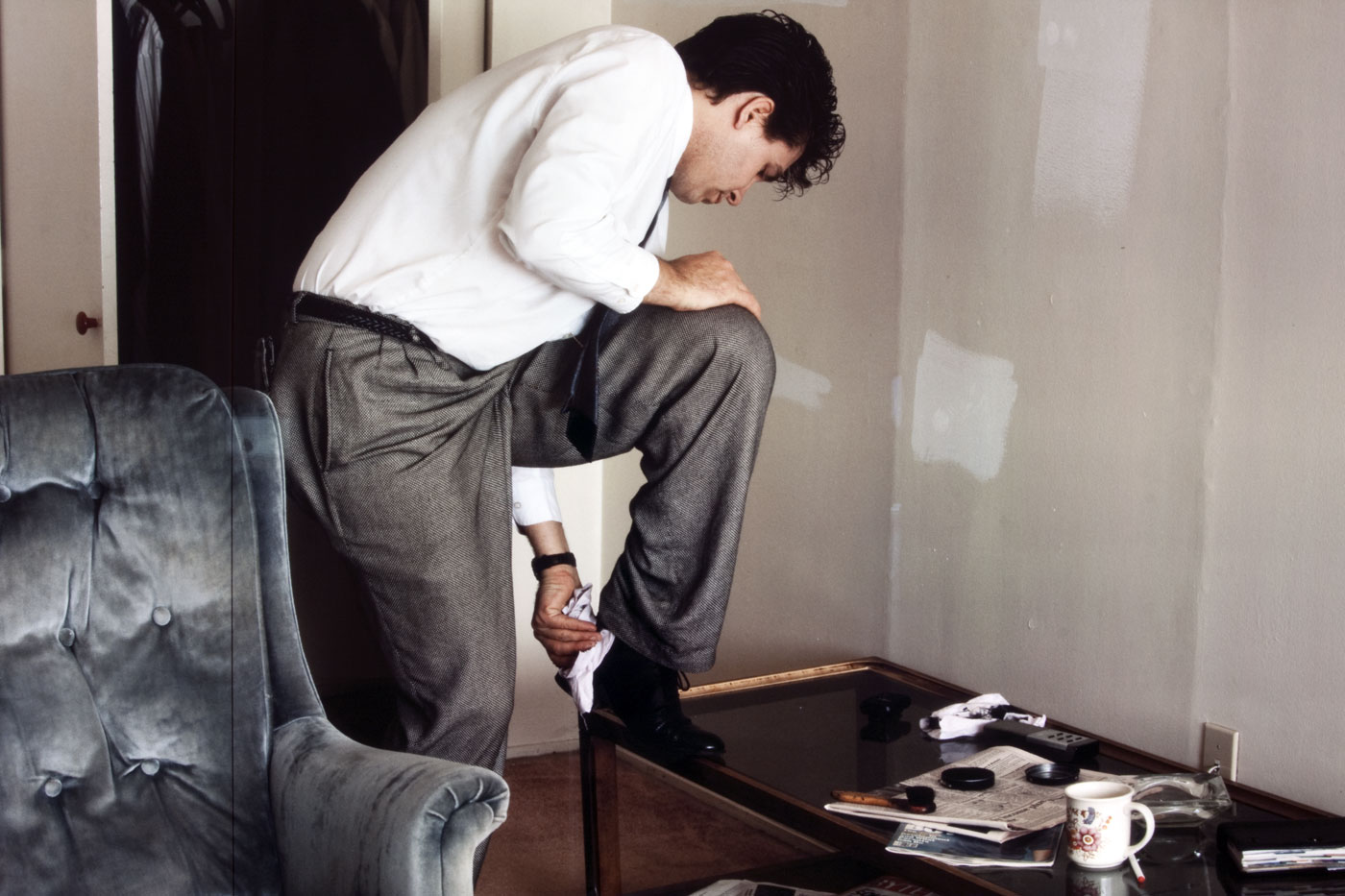
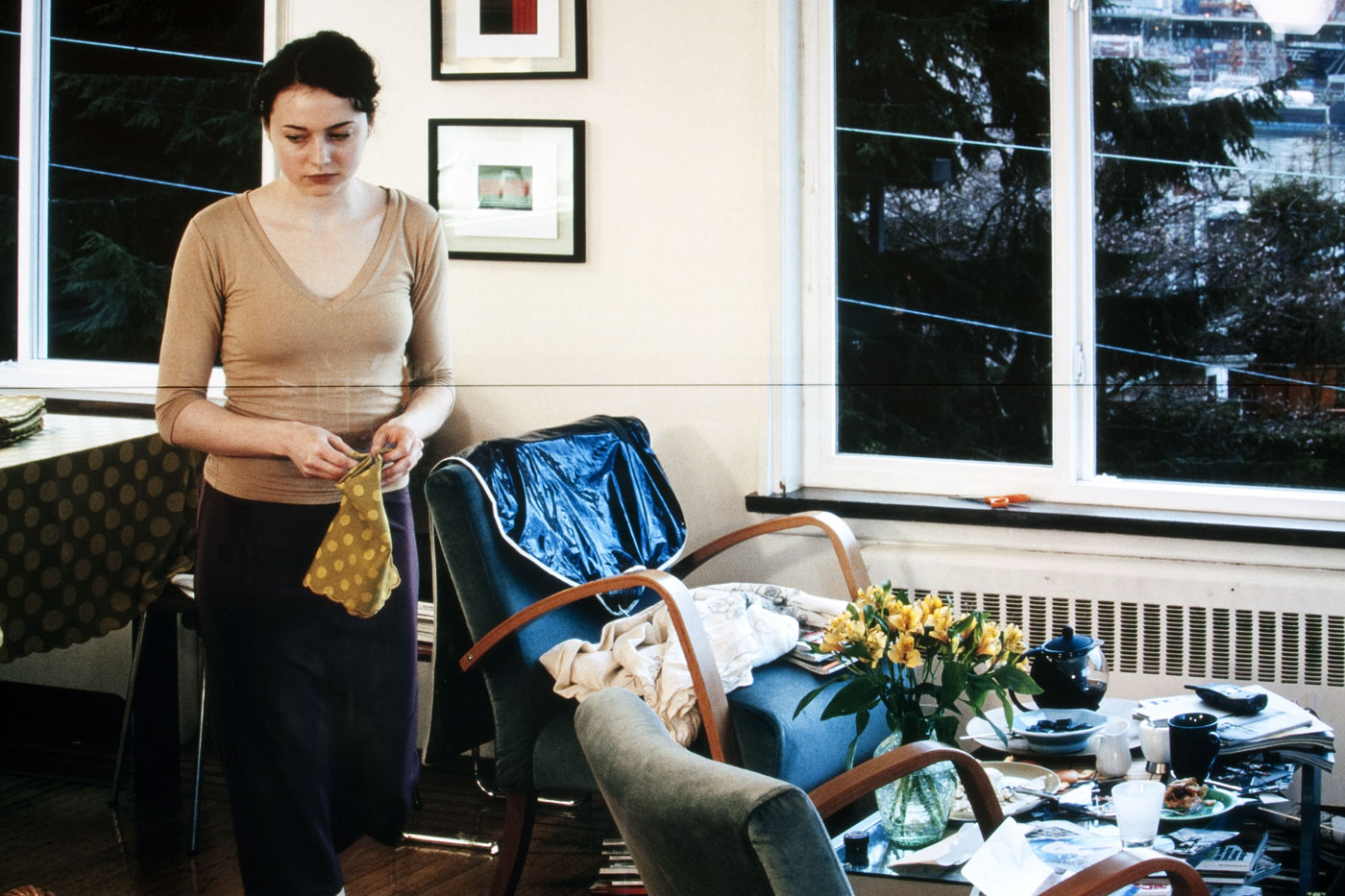
Alec Soth (American, b. 1969)
2008_08zl0031
2008
Mary Ann Lippitt Acquisition Fund
© Alec Soth
Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Where We Find Ourselves
Current representations of the American landscape reveal a continually fraught relationship with the environment. Recent landscape photography reflects its history while constructing new notions of what such an image can be. Some artists continue to see the landscape as a place of refuge or spirituality. Others focus on its more disturbing psychological impact, even haunted with battle scars. Some pick up from the 1970s New Topographics approach with a more pointed investigation of environmentalism, documenting and questioning the impact of industry and development on the natural world. Still others have found that with the introduction of the figure the landscape can act as a stage, albeit one charged with political and social resonance.
Notable shifts have also been driven by new processes and techniques. The photographs of the last several decades are predominantly in colour and are much larger than their precedents. While many artists working today use digital technology, their motive is rarely to alter or fabricate imagery but instead to have easier and better control over how these larger images are presented. Surprisingly, many of today’s photographers are using large format cameras very similar to those of the 19th century to create negatives or digital files capable of being enlarged to the scale of contemporary work.
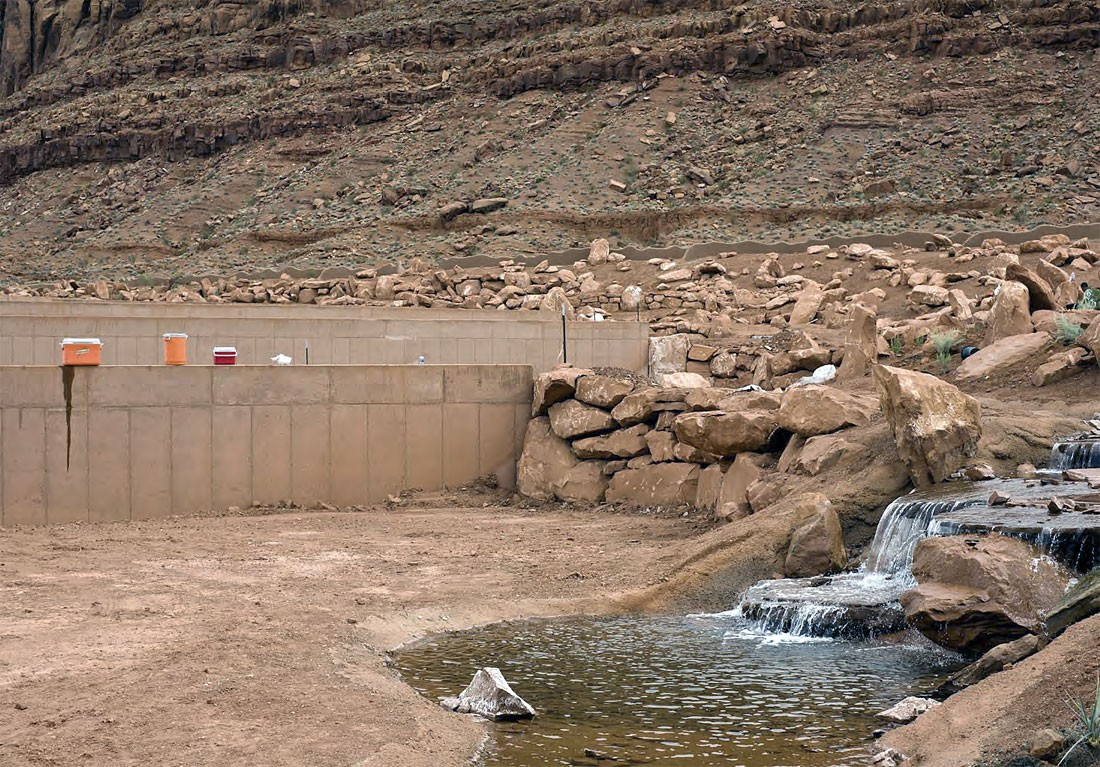

Steven B. Smith (American, b. 1963) (RISD Faculty 1996-present)
Coolers, Ivins, Utah
2007
From the series Irrational Exuberance
Colour inkjet print
RISD Museum: Gift of Heather Smith in honour of Joe Deal
Steven Smith’s subject matter follows in the tradition of the 1970s New Topographic artists. What differentiates Smith’s view of a recently suburbanised desert from his predecessors is the humour with which he captures the extravagant building in this arid place. In this image, from the aptly titled series Irrational Exuberance, fluorescent-coloured coolers, like the red rocks, become part of the landscape, even creating their own waterfall.
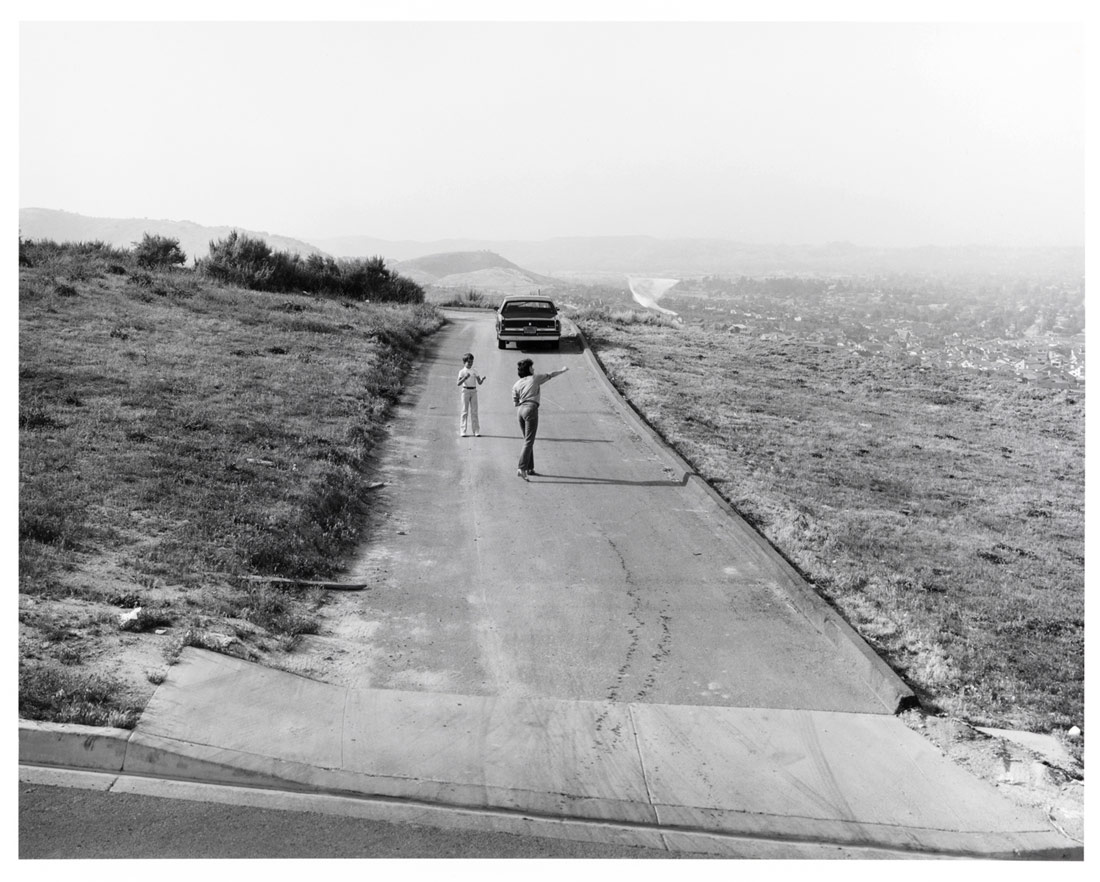

Joe Deal (American, 1947-2010) (RISD Provost 1999-2005, Faculty 2005-2009)
Kite, Chino Hills, California
1984
From the portfolio Subdividing the Inland Basin
Gift of the artist
© The Estate of Joe Deal, courtesy Robert Mann Gallery. Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Joe Deal often found his picture at the border between the built and unbuilt landscape. The driveway makes for a convenient spot to fly a kite, surrounded as it is here with a bit of open space remaining in a new development. In the distance to the right the residential growth that will soon cover this piece of land is visible through the atmospheric smog. In the distance to the left are still untouched hills. The inclusion of people – evidence of a rapidly exploding community near the intersection of the Pomona and Orange freeways – marks a shift in Deal’s photography to embracing the landscape as a site for narrative.
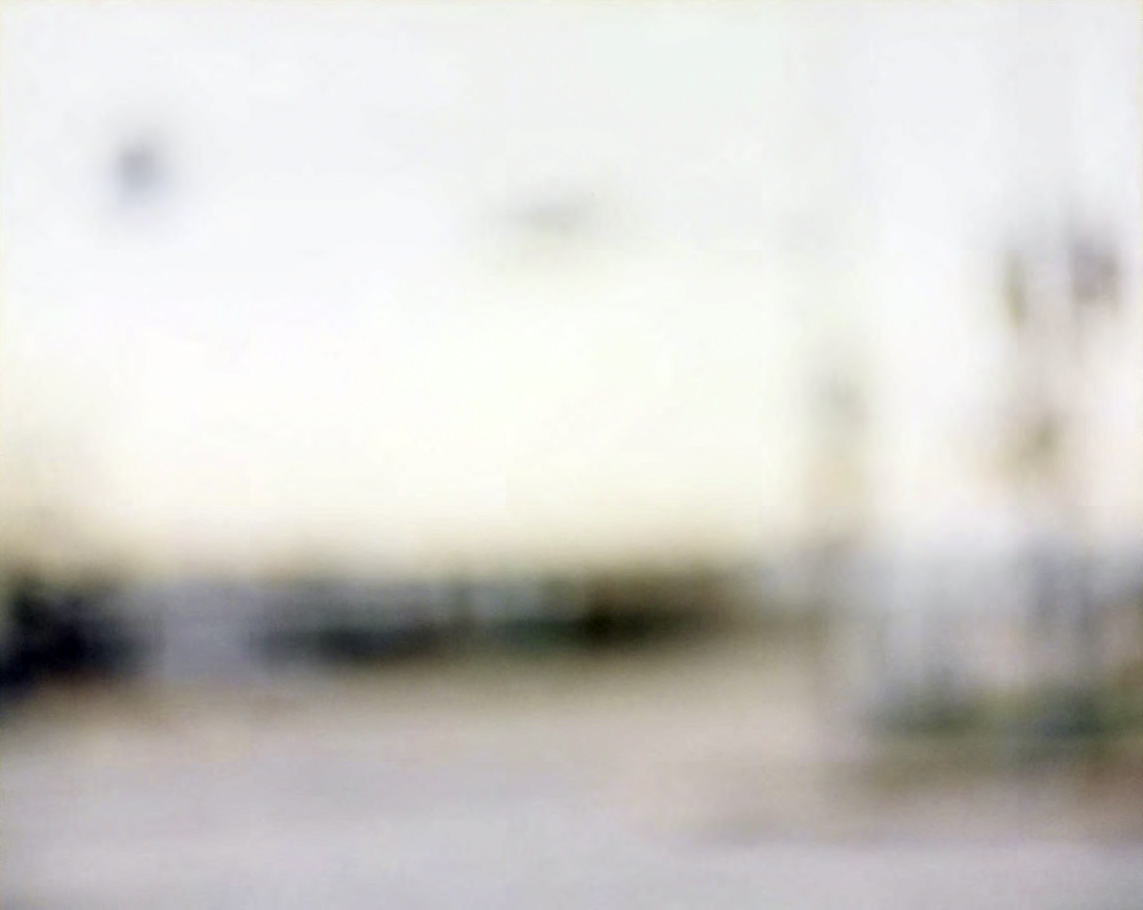

Uta Barth (German, b. 1958)
Field #14
1996
Colour chromogenic print
RISD Museum: Gift of the Buddy Taub Foundation, Jill and Dennis Roach, Directors
Uta Barth radically softens the camera’s focus to remove all signs of historical specificity and to saturate a flat industrial-looking non-place with a dream-like atmosphere. As such she creates a generic landscape as viewed through a heavily fogged window, with an uncanny sense that is deeply familiar.

Henry Wessel (American, b. 1942)
Night Walk, Los Angeles, No. 28
1995
From the series Night Walk: LA
Gelatin silver print
RISD Museum: Gift of Mark Pollack
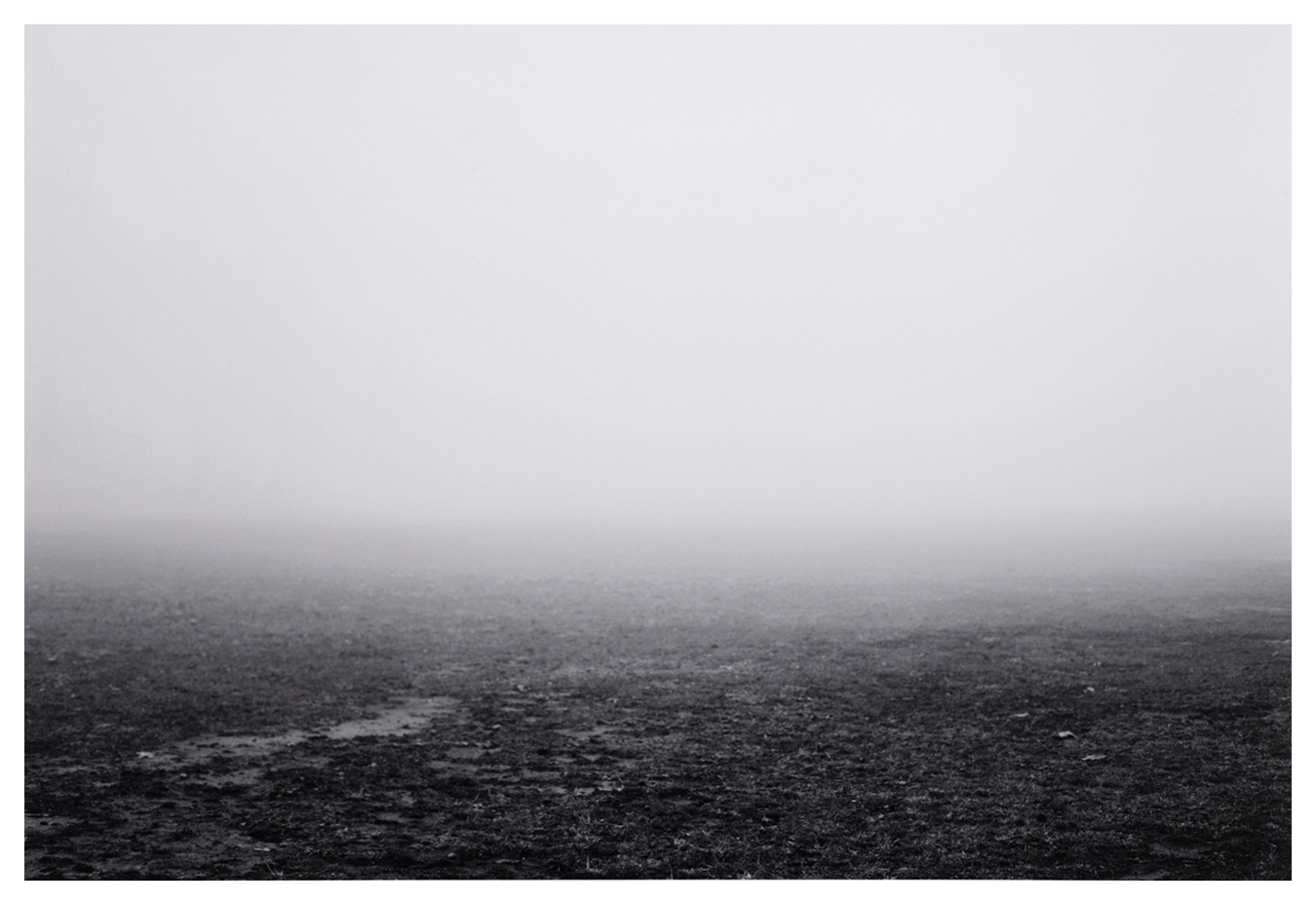

Millee Tibbs (American, b. 1976) (RISD MFA 2007)
Self-Portrait in the Fog
2009
From the portfolio Self Portraits
Colour inkjet print
RISD Museum: Gift of the artist in honour of Joe Deal

Robert Frank (Swiss, 1924-2019)
U.S. 285, New Mexico
1955
Silver gelatin photograph
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
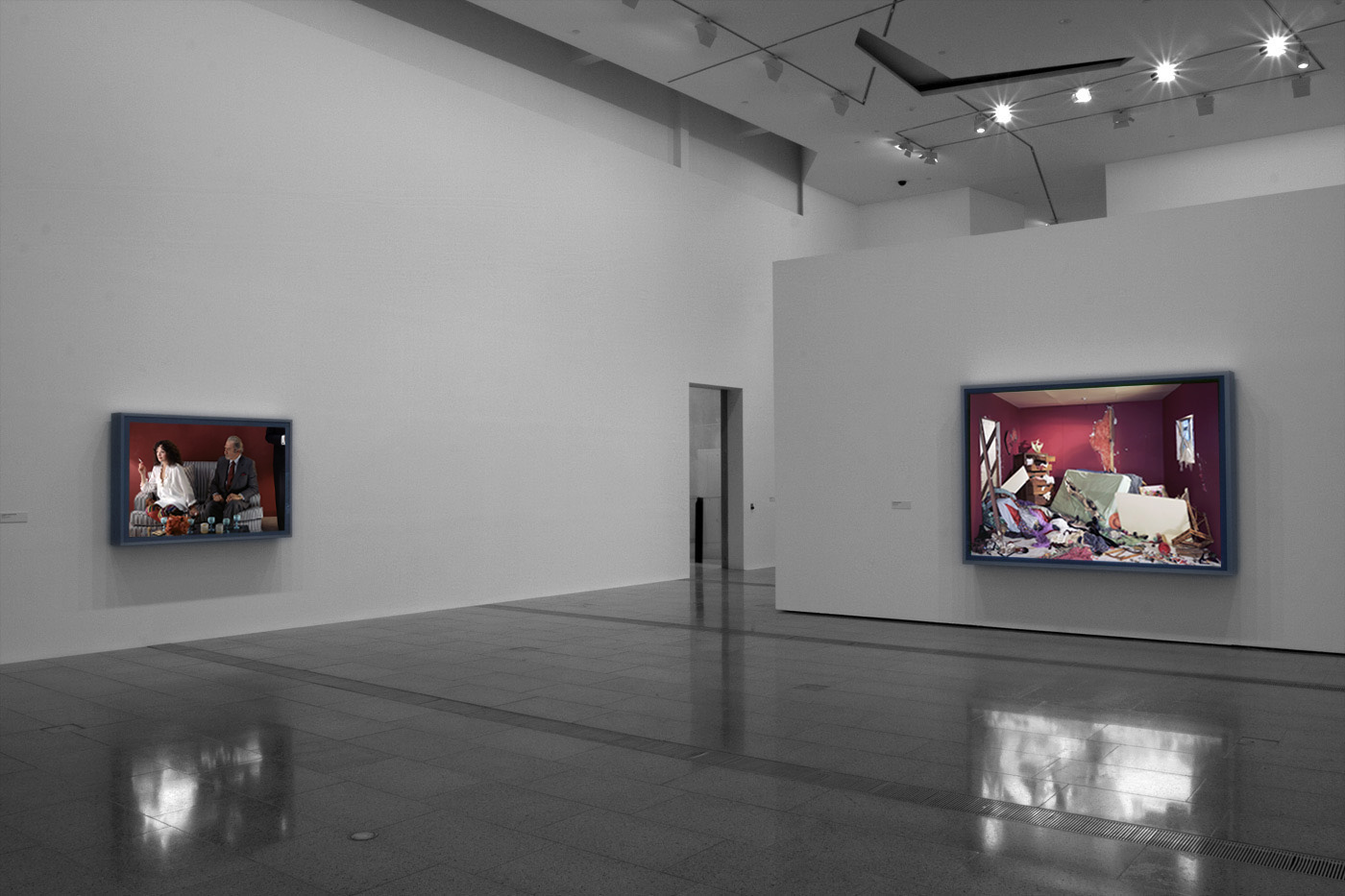
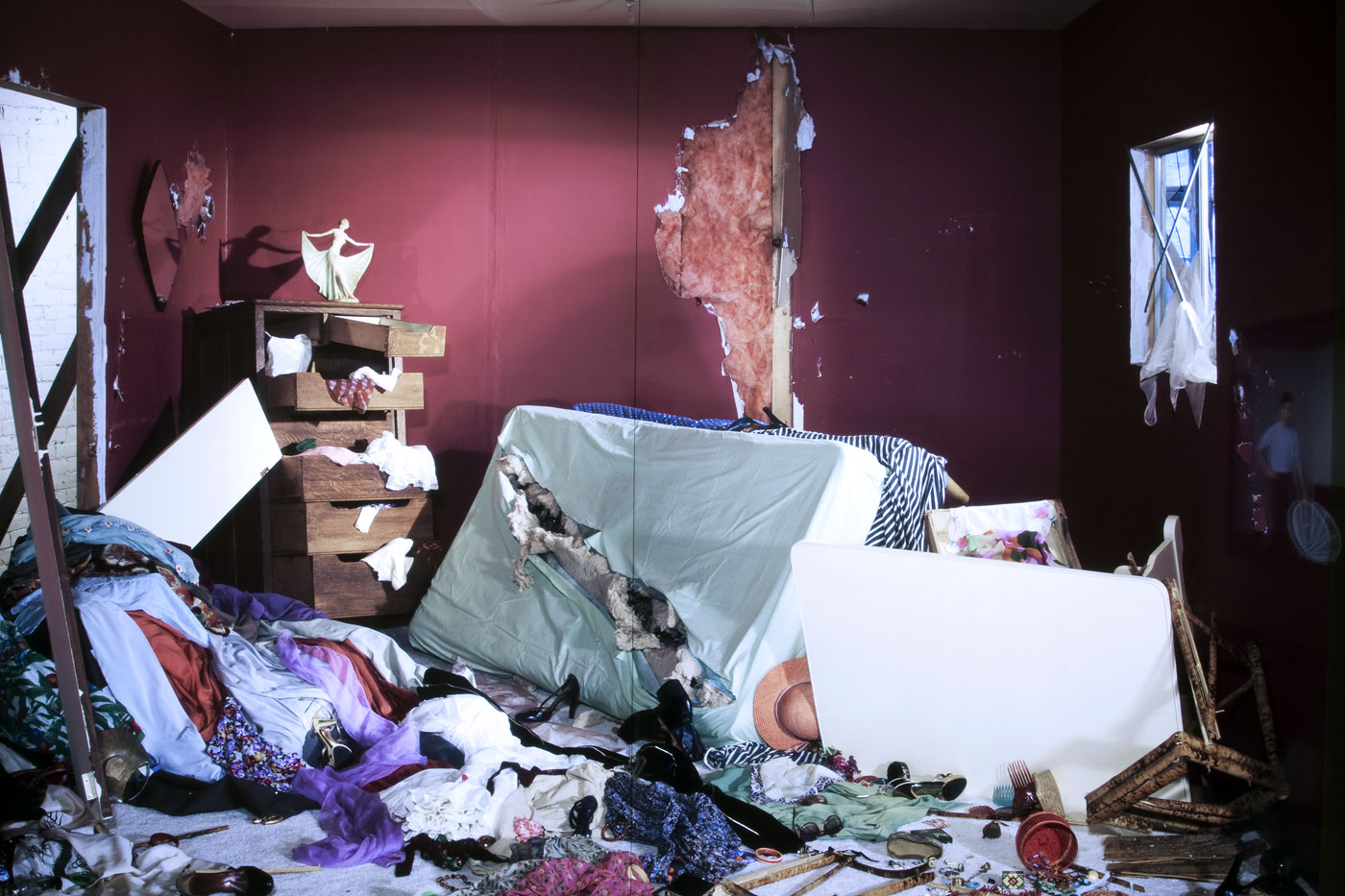
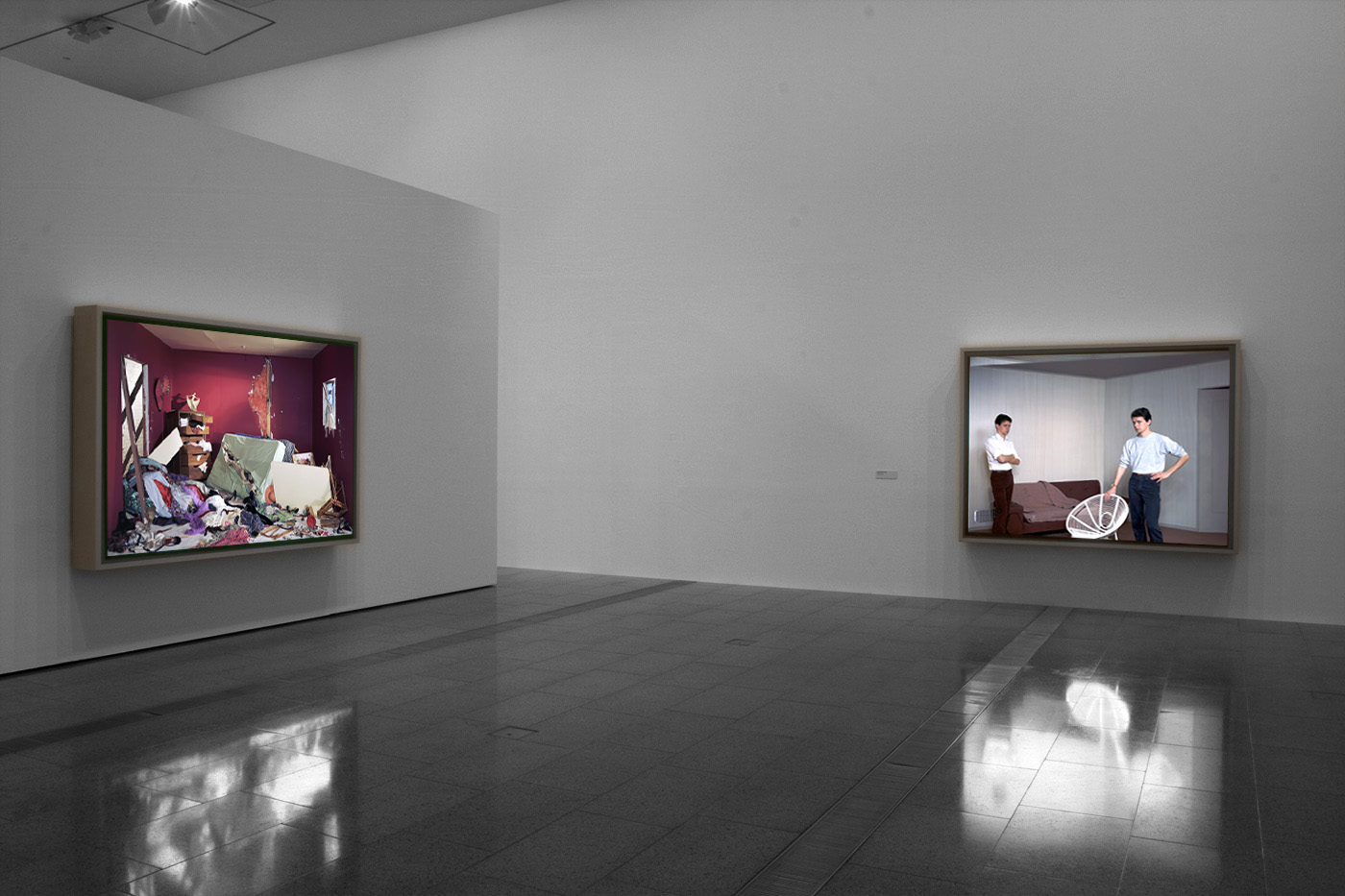
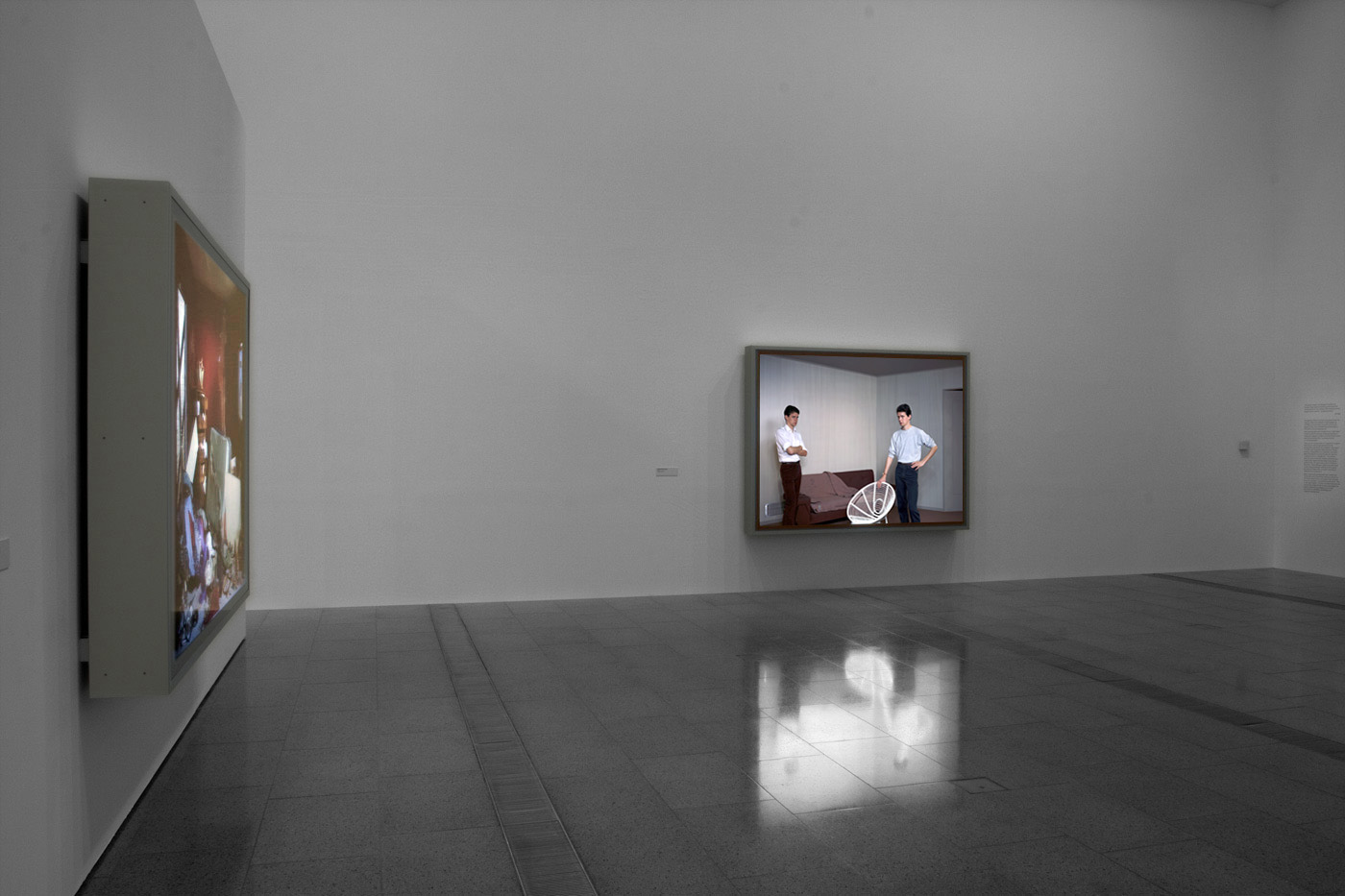
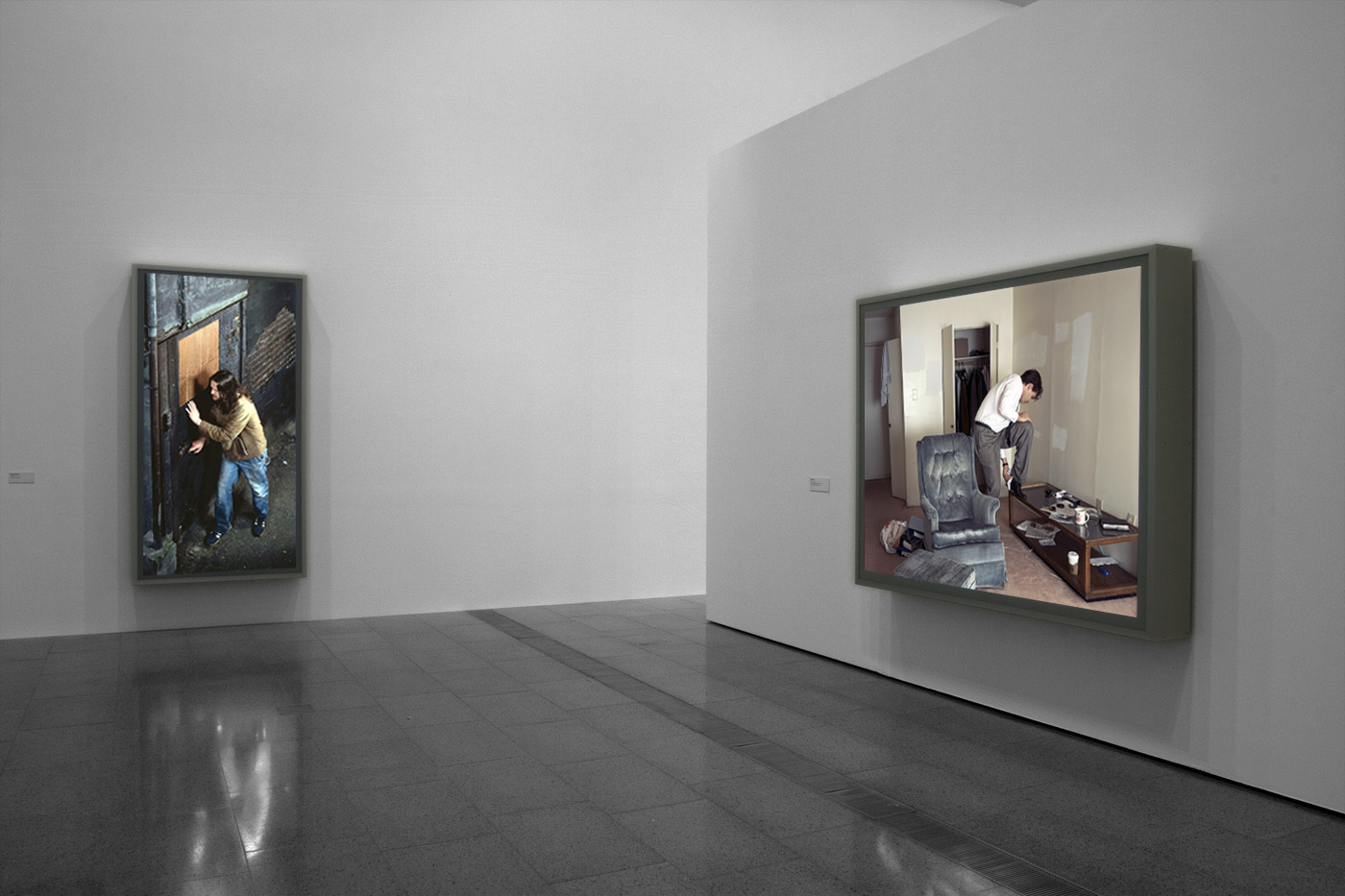
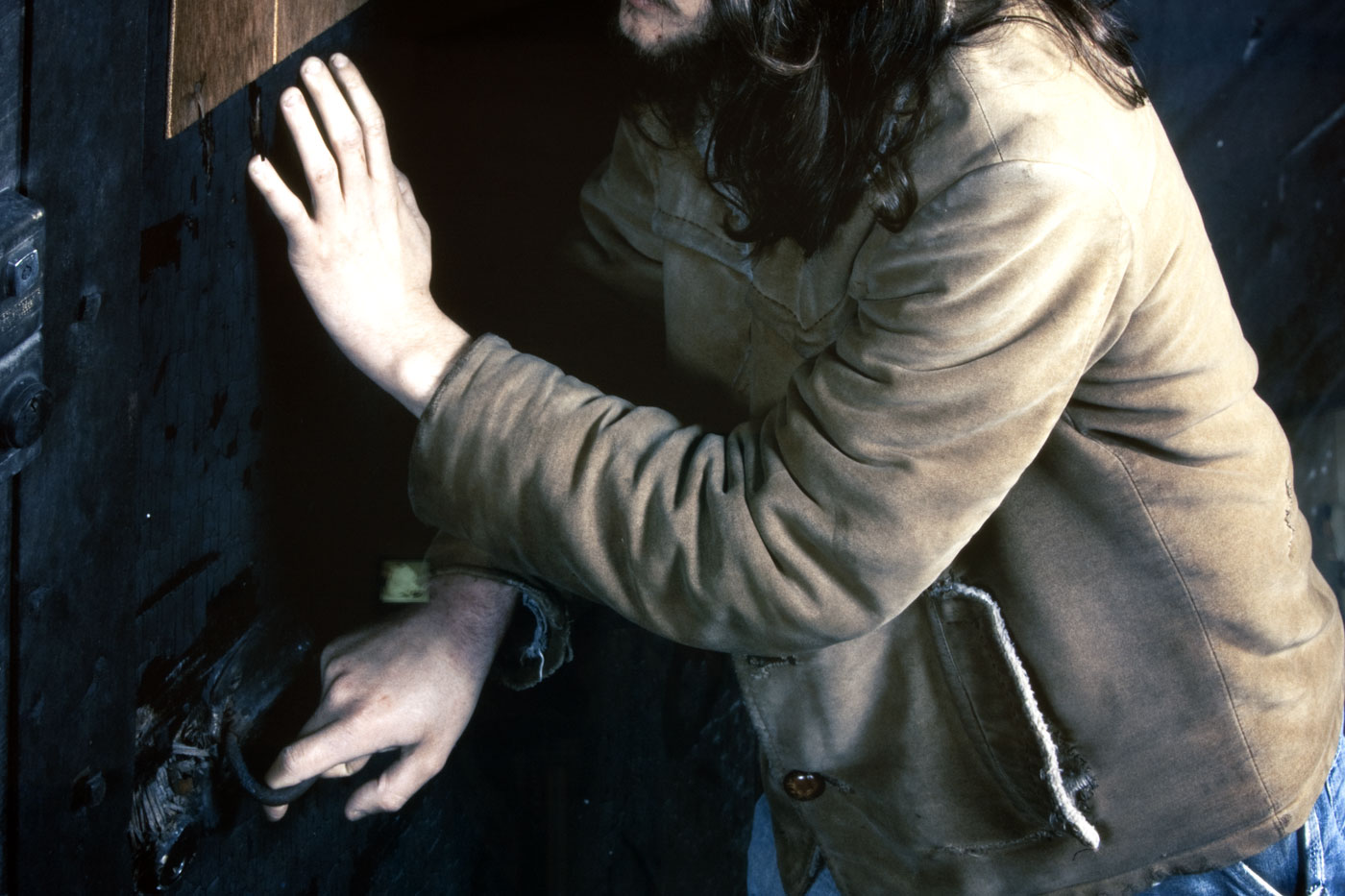
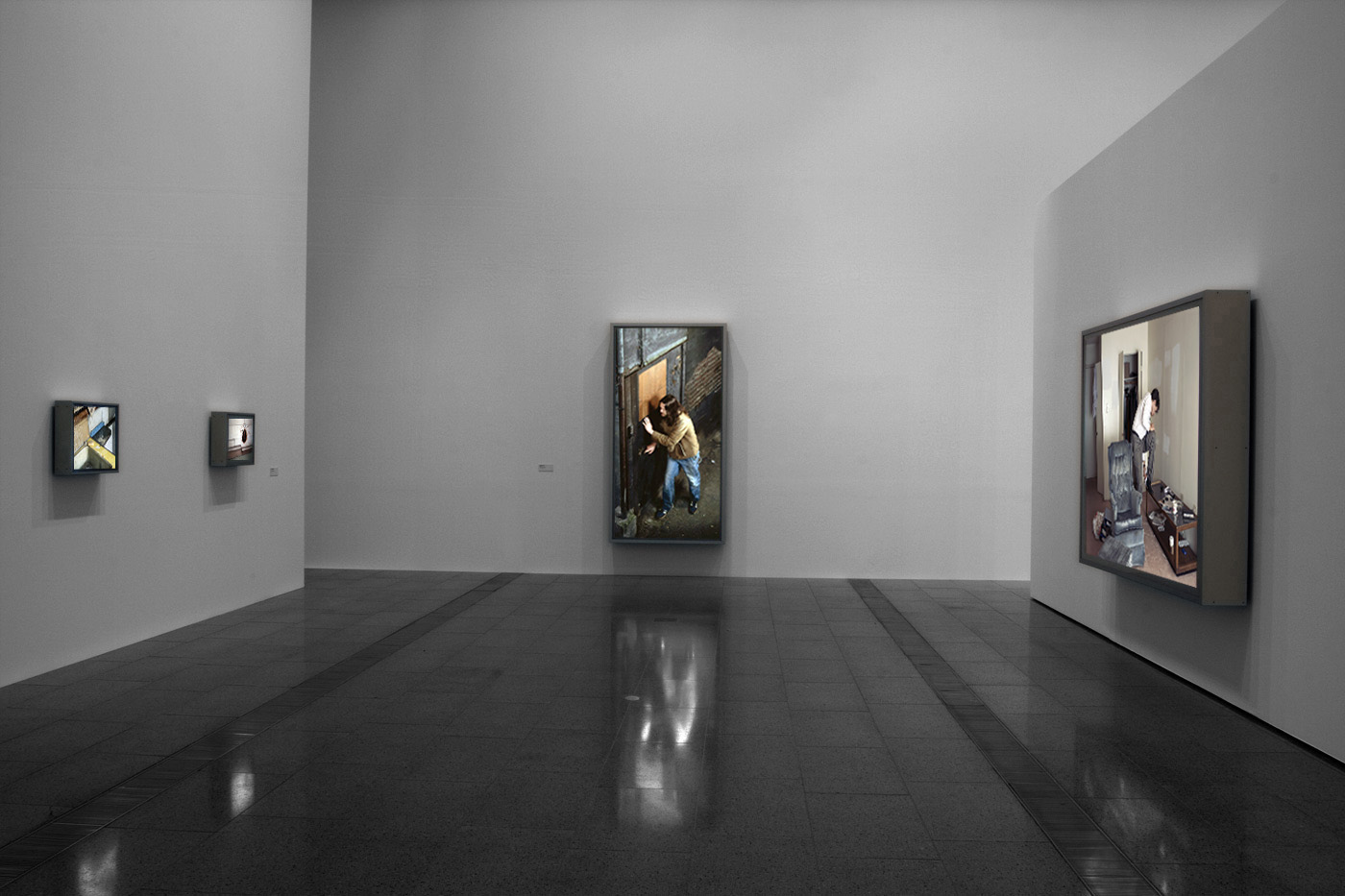
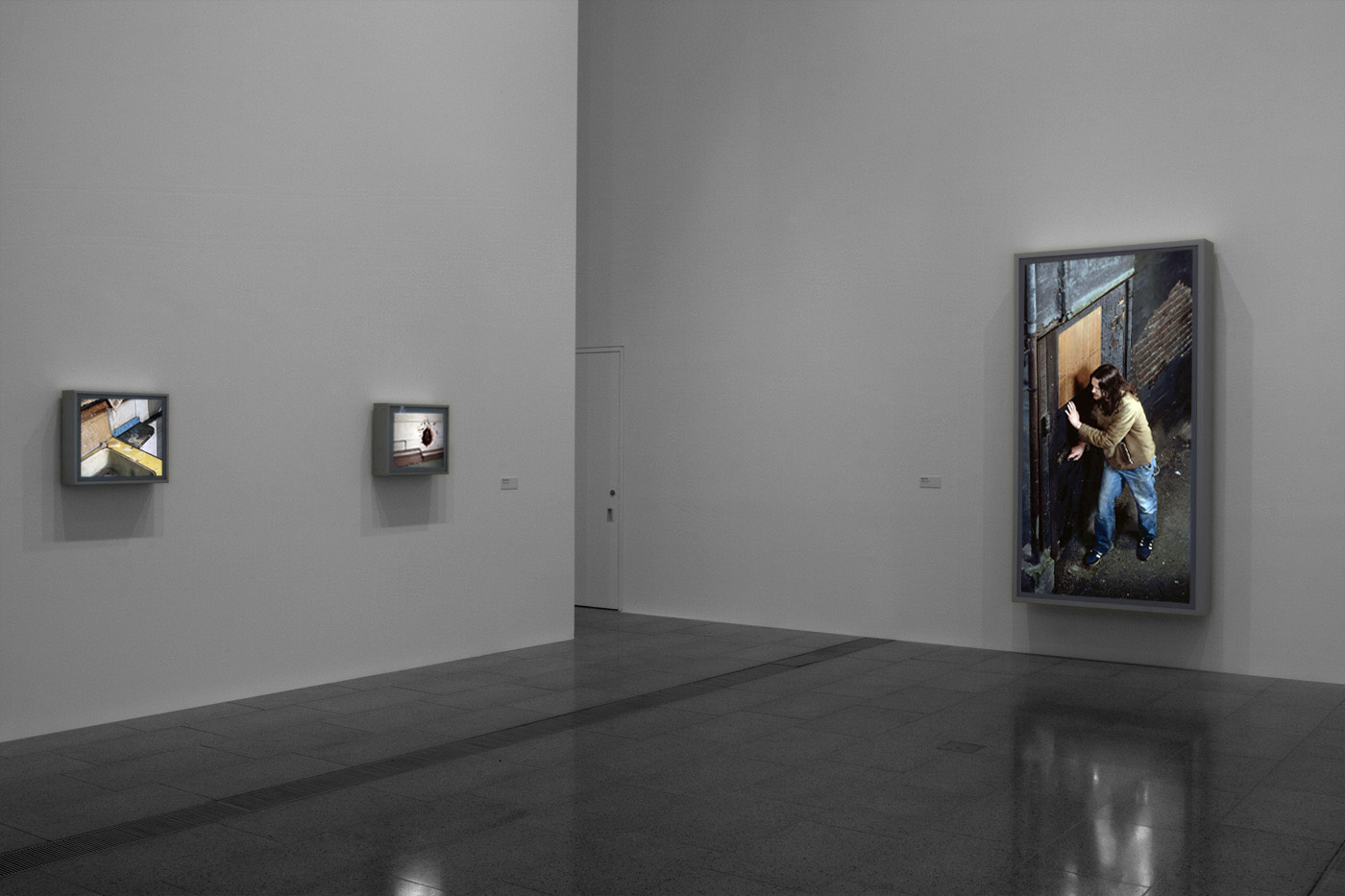
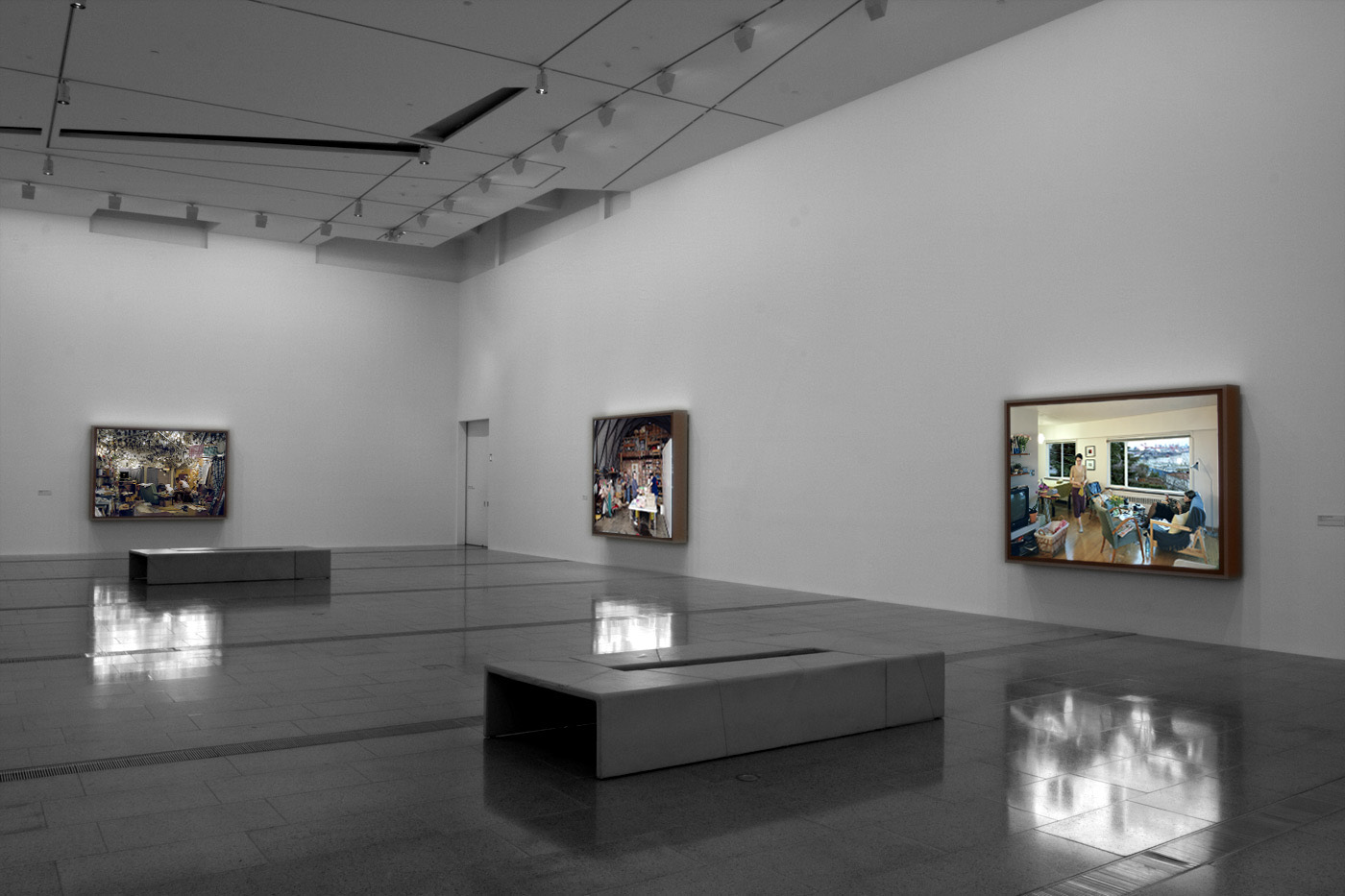
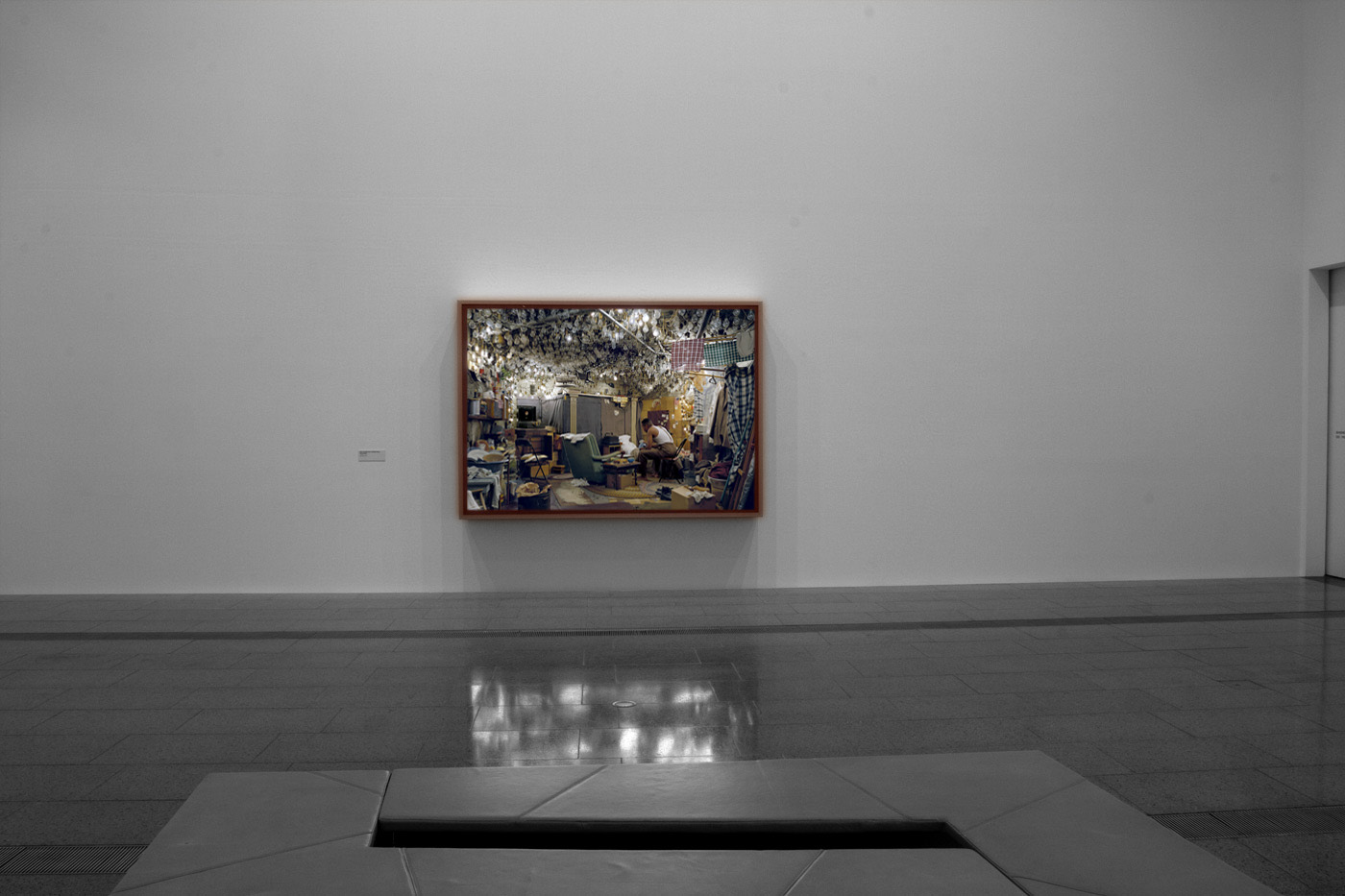
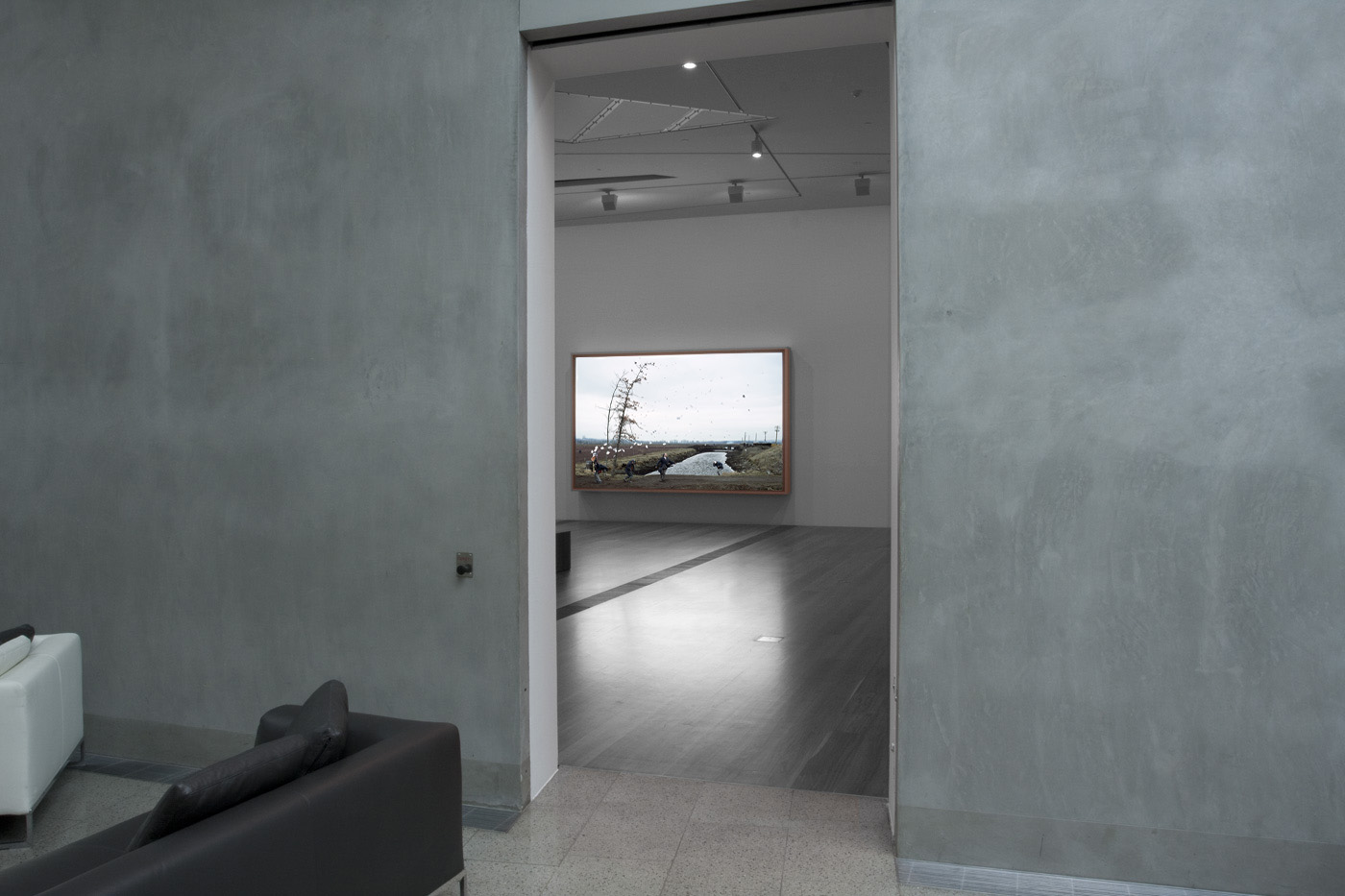
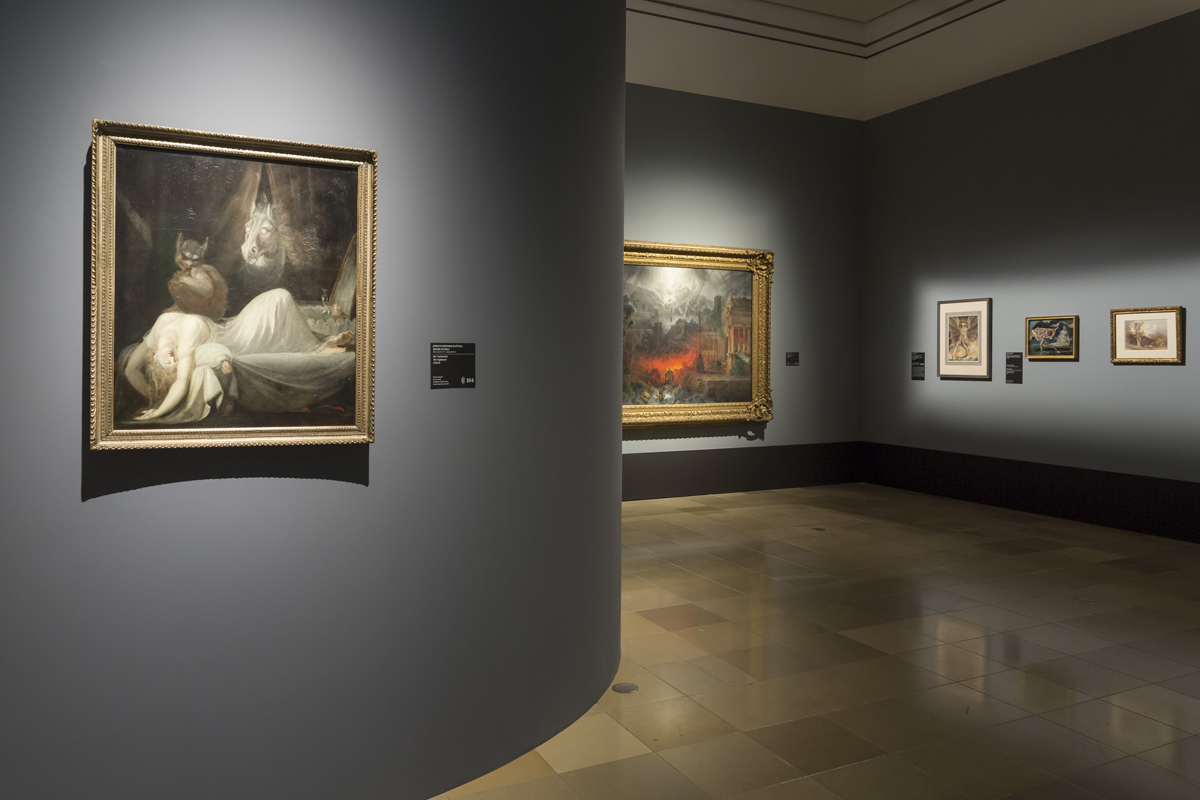
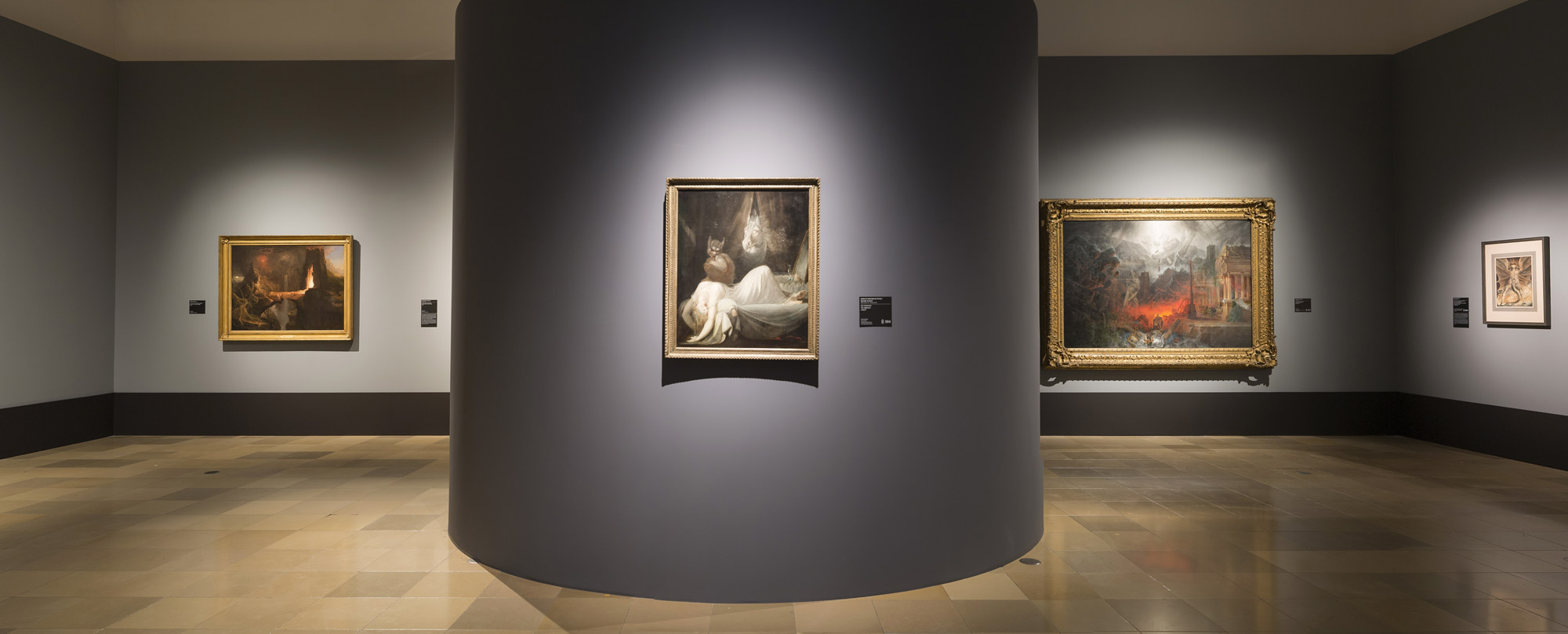
Installation views of America in View: Landscape Photography 1865 to Now at the Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design, Providence
Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design (RISD)
224 Benefit Street, Providence, RI 02903
Phone: 401 454-6500
Opening hours:
Tuesdays Wednesdays, Saturdays, Sundays 10am – 5pm
Thursdays – Fridays 12 – 7pm
Closed Mondays
Museum of Art Rhode Island School of Design (RISD) website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top













































![Fritz Winter (German, 1905-1976) 'Stufungen [Gradations]' 1934 Fritz Winter (German, 1905-1976) 'Stufungen [Gradations]' 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/fritz-winter-stufungen-1934-web.jpg?w=650&h=921)

![Fritz Winter (German, 1905-1976) 'Weiß in Schwarz [White in Black]' 1934 Fritz Winter (German, 1905-1976) 'Weiß in Schwarz [White in Black]' 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/fritz-winter-weic39f-in-schwarz-1934-web.jpg?w=650&h=880)



































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.