Exhibition dates: 21st November, 2015 – 29th May, 2016
Curator: Cynthia Young, curator at Robert Capa archives
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
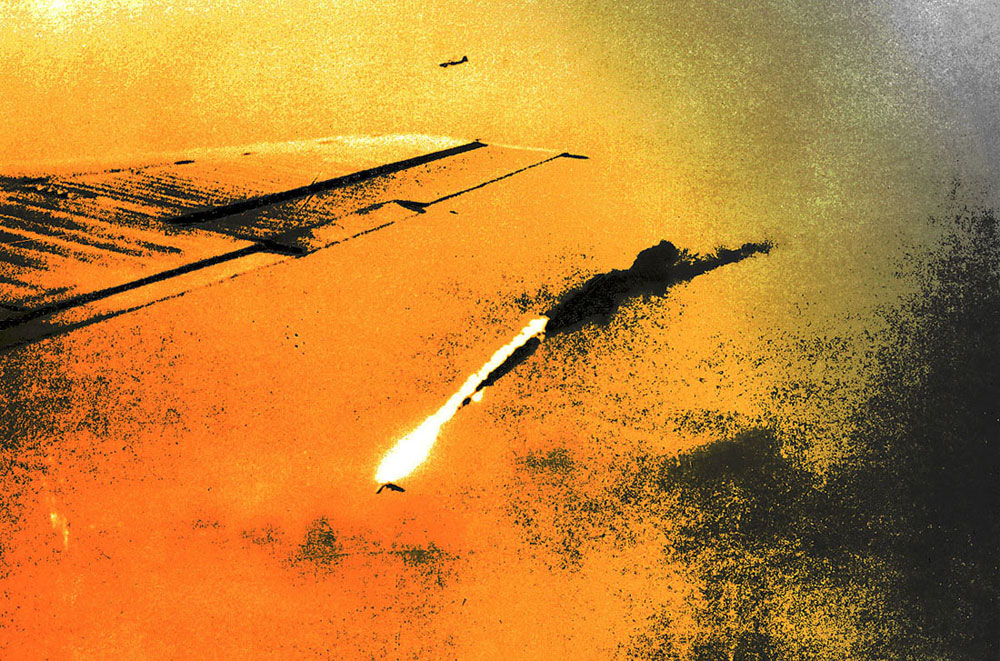
American crewmen stand in front of a B-17 bomber that is being prepared to take off from a Royal Air Force base for a daylight bombing raid over occupied France. This B-17 was one of the first 300 to be brought overseas by the US Army Air Forces
England, 1942
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
To be honest, Robert Capa was not the most natural colour photographer, especially when you compare him to the likes of Paul Outerbridge and Saul Leiter who were working at around the same time. Even the official text from Jeu de Paume that accompanies the exhibition is littered with descriptions like “uninspired”, “the color photographs lack focus”, or worse, “Fleur Cowles at Look and Len Spooner at Illustrated were disappointed with the color images.”
His work in this medium is what I would call “observational” colour photography. The images are best when the subject is intimate, human and ‘on set’, preferably using a limited palette with splashes of subdued colour – such as in the gorgeous Model wearing Dior on the banks of the Seine, Paris, France (1948), the delicate Woman on the beach, Biarritz, France (1951), and the simpatico duo of Humphrey Bogart and Peter Lorre on the set of ‘Beat the Devil’, Ravello, Italy (April 1953) and Truman Capote and Jennifer Jones on the set of ‘Beat the Devil’, Ravello, Italy (April 1953). The photographs of Ava Gardner on set are also cracking images for their vitality and overall balance, as is the almost monochromatic Gen X girl, Colette Laurent, at the Chantilly racetrack, France (1952). Other ensemble tableaux might as well have been shot in black and white, such as Spectators at the Longchamp Racecourse, Paris, France (c. 1952).
Capa too often resorts to one or two strong primary colours for effect, as in Capucine, French model and actress, on a balcony, Rome, Italy (August 1951), Rambaugh Family Circus, Indiana, USA (1949) or American Judith Stanton, Zermatt, Switzerland (1950). In the the former two images the composition doesn’t work with the colour; only in the latter does it become a vigorous and joyous structural element.
Sometimes I think that Capa didn’t exactly know what to do with colour – Woman at an ice bar, Zürs, Austria (1949-1950) and Party, Rome, Italy (August 1951) are not very good at all – but here we must acknowledge an artist experimenting with a relatively new commercial medium, even as he seeks to sell these images to his clients.
Capa in Color is at his best when he employs subtlety, constructing strong human compositions with nuanced placement of shades and hues.
One of the most complex images in the posting is Anna Magnani on the set of Luchino Visconti’s ‘Bellissima’ (Rome, 1951-1952). Just look at this image: your eye plays over the surface, investigating every nook and cranny, every modular plane. The blue of the skirt, the brown of the top, the patterns of the two bikinis and the earthiness of tree and earth. I am reminded of the paintings of Paul Cézanne.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Jeu de Paume for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
The first exhibition dedicated to Capa’s fourteen years of color photographs, Capa in Color has an ambition to evaluate and place these photographs in the timeline of his career and of their period. Capa in Color shows how color photography renewed his vision and how his work gained from a new sensibility after the war, by readapting his compositions in colour, but also to a public attracted to entertainment and to the discovery of new types of images.
Robert Capa et la couleur – Portrait filmé/videoportrait from Jeu de Paume / magazine on Vimeo.
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Regata, Lofoten Island, Hankoe
Norway, 1951
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Recently presented at the International Center of Photography and now available for travel, Capa in Color presents Robert Capa’s colour photographs to the European public for the first time. Although he is recognised almost exclusively as a master of black-and-white photography, Capa began working regularly with colour film in 1941 and used it until his death in 1954. While some of this work was published in the magazines of the day, the majority of these images have never been printed or seen in any form.
Capa in Color includes over 150 contemporary colour prints by Capa, as well as personal papers and tear sheets from the magazines in which the images originally appeared. Organised by Cynthia Young, curator of Capa Collections at ICP, the exhibition presents an unexpected aspect of Capa’s career that has been previously edited out of posthumous books and exhibitions, and show how he embraced colour photography and integrated it into his work as a photojournalist in the 1940s and 1950s.
Robert Capa’s (1913-1954) reputation as one of history’s most notable photojournalists is well established. Born Endre Ernö Friedmann in Budapest and naturalised as a U.S. citizen in 1946, he was deemed “The Greatest War Photographer in the World” by Picture Post in a late 1938 publication of his Spanish Civil War photographs. During World War II, he worked for such magazines as Collier’s and Life, extensively portraying preparation for war as well as its devastating aftermath. His best-known images symbolised for many the brutality and valour of war and changed the public perception of, and set new standards for, war photography.
July 27, 1938, while in China for eight months covering the Sino-Japanese war, Robert Capa wrote to a friend at his New York agency, “… send 12 rolls of Kodachrome with all instructions; … Send it “Via Clipper” because I have an idea for Life“. Although no colour film from China survives except for four prints published in the October 17, 1938, issue of Life, Capa was clearly interested in working with colour photography even before it was widely used by many other photojournalists.
In 1941, he photographed Ernest Hemingway at his home in Sun Valley, Idaho, in colour, and used colour for a story about crossing the Atlantic on a freighter with an Allied convoy, published in the Saturday Evening Post. While Capa is best known for the black-and-white images of D-Day, he also used colour film sporadically during World War II, most notably to photograph American troops and the French Camel Corps in Tunisia in 1943.
Capa’s use of colour film exploded in his postwar stories for magazines such as Holiday (USA ), Ladies’ Home Journal (USA ), Illustrated (UK), and Epoca (Italy). These photographs, which until now have been seen only in magazine spreads, brought the lives of ordinary and exotic people from around the world to American and European readers alike, and were markedly different from the war reportage that had dominated Capa’s early career. Capa’s technical ability coupled with his engagement with human emotion in his prewar black-and-white stories enabled him to move back and forth between black and white and colour film and integrate colour to complement the subjects he photographed. These early stories include photographs of Moscow’s Red Square from a 1947 trip to the USS R with writer John Steinbeck and refugees and the lives of new settlers in Israel in 1949-50. For the Generation X project, Capa traveled to Oslo and northern Norway, Essen, and Paris to capture the lives and dreams of youth born before the war.
Capa’s photographs also provided readers a glimpse into more glamorous lifestyles that depended on the allure and seduction of colour photography. In 1950, he covered fashionable ski resorts in the Swiss, Austrian, and French Alps, and the stylish French resorts of Biarritz and Deauville for the burgeoning travel market capitalised on by Holiday magazine. He even tried fashion photography by the banks of the Seine and on the Place Vendôme. Capa also photographed actors and directors on European film sets, including Ingrid Bergman in Roberto Rossellini’s Viaggio in Italia, Orson Welles in Black Rose, and John Huston’s Moulin Rouge. Additional portraiture in this period included striking images of Picasso, on the beach near Vallauris, France with his young son Claude.
Capa carried at least two cameras for all of his postwar stories: one with black-and-white film and one with colour, using a combination of 35mm and 4 x 5 Kodachrome and medium-format Ektachrome film, emphasising the importance of this new medium in his development as a photographer. He continued to work with colour until the end of his life, including in Indochina, where he was killed in May 1954. His colour photographs of Indochina presage the colour images that dominated the coverage from Vietnam in the 1960s.
Capa in Color is the first museum exhibition to explore Capa’s fourteen-year engagement with colour photography and to assess this work in relation to his career and period in which he worked. His talent with black-and-white composition was prodigious, and using colour film halfway through his career required a new discipline. Capa in Color explores how he started to see anew with colour film and how his work adapted to a new postwar sensibility. The new medium required him to readjust to colour compositions, but also to a postwar audience, interested in being entertained and transported to new places.
Press release from Jeu de Paume
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
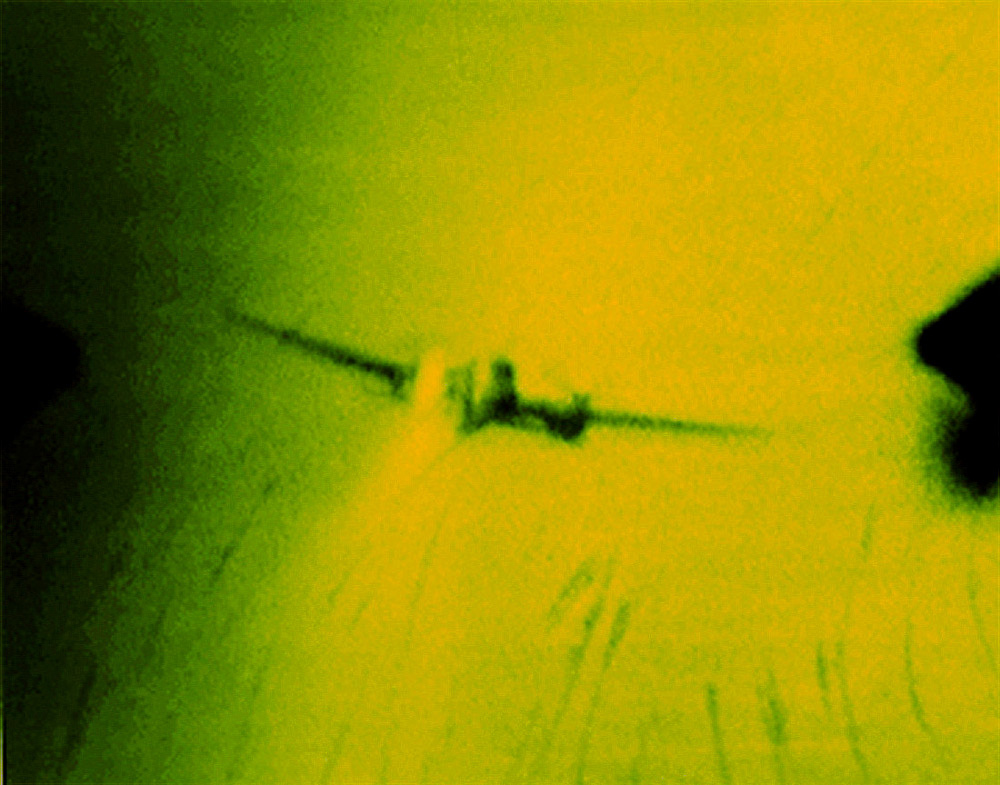
A crewman signals another ship of an Allied convoy across the Atlantic from the US to England
1942
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
It is surprising, even shocking to some, that famous photojournalist Robert Capa (born Budapest 1913, died Indochina 1954) photographed in colour, and not just occasionally, but regularly after 1941. His coloured work is essentially unknown. Capa is considered a master of black-and-white war photography, a man who documented some of the most important political events of Western Europe in the mid-twentieth century. His photographs of 1930s Paris, the Spanish Civil War, World War II, postwar Europe, and his last images in Indochina are known to us in black-and-white. None of the posthumous retrospective projects of his work have included colour, with a few rare exceptions..
Capa first experimented with colour in 1938, two years after Kodak developed Kodachrome, the first colour roll film. While in China covering the Sino-Japanese War, he wrote to a friend at his New York agency, Pix, “Please immediately send 12 rolls of Kodachrome with all instructions; whether special filters are needed, etc. – in short, all I should know. Send it ‘Via Clipper’, because I have an idea for Life“. Only four colour images from China were published, but Capa’s enthusiasm for colour was born. He photographed with colour film again in 1941 and for the next two years he fought hard to persuade editors to buy his colour images in addition to the black-and-white. After the war, the magazines were eager to include colour and his colour assignments increased. For the rest of his life, he almost always carried at least two cameras: one for black-and-white and one for colour film.

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
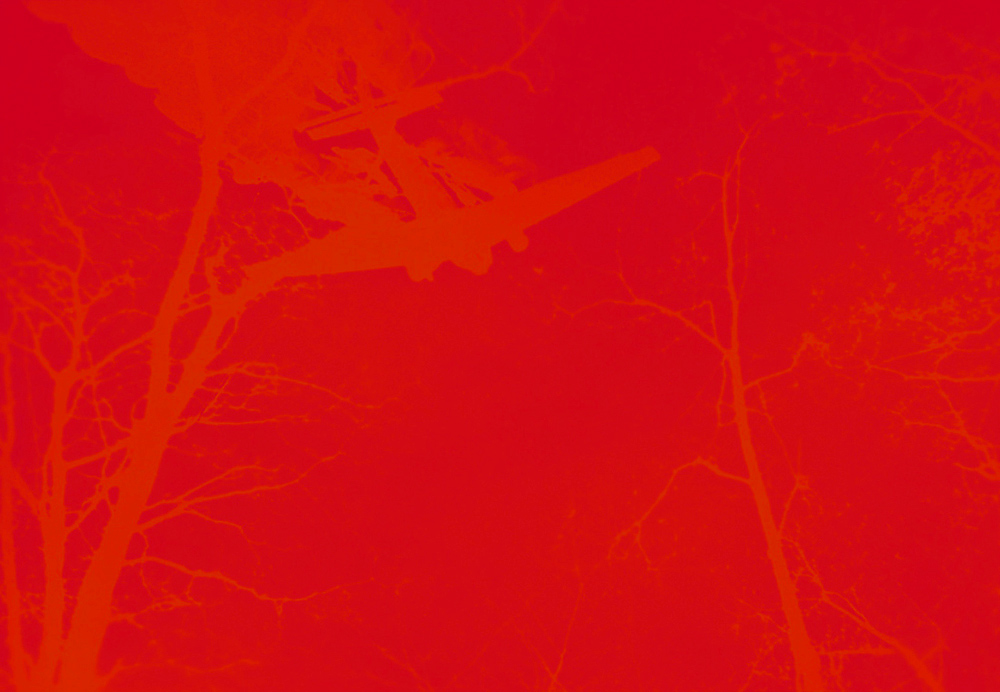
American Captain Jay F. Shelley stands in front of “The Goon,” a B-17 bomber, before a raid over Italy, Tunisia, 1943
1943
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Jay F. Shelley, Sr., 88, of Yuma,formerly of Scottsdale, Arizona, entered Eternity on June 6, 2004. Jay was born May 16, 1916, in Long Beach, California. He was a decorated B-17 Bomber Pilot during WWII and flew 54 combat missions. He received a degree in business administration with a major in accounting from University of Montana. Jay worked as an accountant until 1979 when he retired with his wife to Scottsdale, Arizona. Capt. Jay F Shelley was assigned to the 301st BG 32nd Squadron.
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Damaged plane hosed down with chemicals after landing on belly following a raid over Occupied France, England, July 1941
1941
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
The plane is a Bristol Blenheim.
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
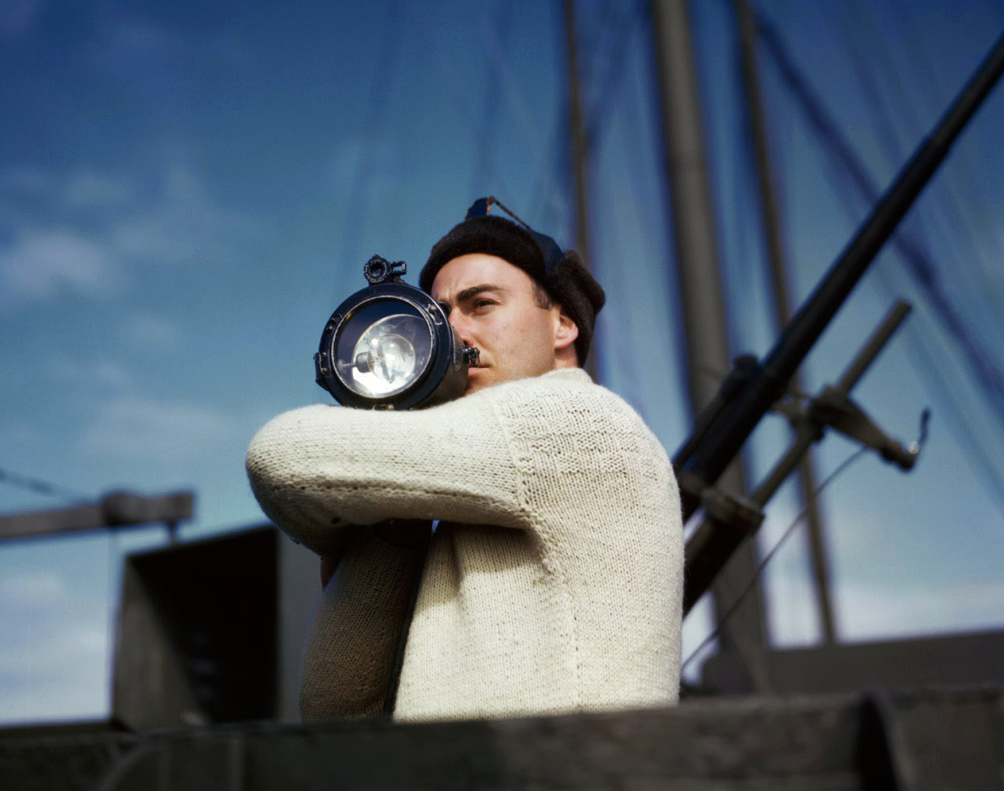
An American B-17 gunner awaits take off from a Royal Air Force base for a daylight bombing raid over occupied France
England, 1942
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
World War II
In 1941, Capa produced his first colour film story for the Saturday Evening Post, about crossing the Atlantic from New York on a convoy. Once in England, he was also able to sell these images to the English magazine Illustrated, because the two magazines did not have the same readerships.
He made the crossing again the next year, carrying a larger format camera that made bigger, more spectacular portraits of the ship’s crew. The turnaround time for Kodachrome film was several weeks. As Kodak maintained secrecy surrounding the formula, the undeveloped film had to go to a special Kodak processing plant and then returned to the photographer. It was not ideal for timely news. The magazines published few of Capa’s colour images from the UK, but he persisted in using it. In 1943, he entered the battlefields of World War II in North Africa, first traveling on a troop ship from England to Casablanca. His last colour images from the war were taken on a boat from Tunisia to Sicily in July 1943, where he debarked and moved up to Naples with America soldiers over the following months. It appears that for the rest of the war he did not use colour film, apparently discouraged by a combination of the slow shutter speed of the film, long processing times, and the uneven commitment to his colour images by the magazines.

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Rambaugh Family Circus, Indiana, USA
1949
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
USA
Soon after his return from England, in the fall of 1941, Capa traveled to Sun Valley, Idaho, to do a story for life on his friends, the writers Ernest Hemingway and Martha Gellhorn, whom he had met during the Spanish Civil War. After World War II, Capa sought out new relationships with magazines and holiday became one of his most important supporters.
A glamorous travel magazine that featured New Yorker – caliber writers, Holiday was launched in 1946 by the Philadelphia-based Curtis Publishing Company, which also carried The Saturday Evening Post and Ladies’ Home Journal. Born in full colour, it was a peacetime publication catering to an ideal of American postwar prosperity. Holiday covered American cities, but immediately assigned stories on stylish international hot spots, places readers could dream of visiting with the advent in 1947 of nonstop transatlantic flights. In 1950, Holiday sent Capa to Indianapolis, and while his pictures of a nuclear family of five exploring the city are uninspired, he also photographed a family-run traveling circus. Despite Capa’s lukewarm attitude toward American culture, the colour images present a strong vision of American small-town life.

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Young visitors waiting to see Lenin’s Tomb at Red Square
Moscow, 1947
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
USSR
The year 1947 was a turning point in Capa’s life. He founded Magnum, the photographers cooperative agency he had dreamed of since 1938. The same year, he traveled to the Soviet Union, a trip that he had wanted to make in 1937 and then in 1941, both times unable to obtain a visa or magazine support for the trip.
He teamed up with writer John Steinbeck to report on the lives and opinions of ordinary Russians in opposition to Cold War rhetoric. Their adventures were published in the book A Russian Journal the following year and syndicated in newspapers and international picture magazines. Although the colour images were well represented in the magazines and on the cover of Illustrated for a special issue, Capa did not shoot much colour film in the Soviet Union, and no colour was included in A Russian Journal, except for the cover. Either he deemed only a few places worthy of the new medium format Ektachrome colour film that did not require special processing – chiefly Moscow and collective farms in the Ukraine and Georgia – or he had only a limited amount of film and used it sparingly. The images of Red Square take full advantage of colour film.
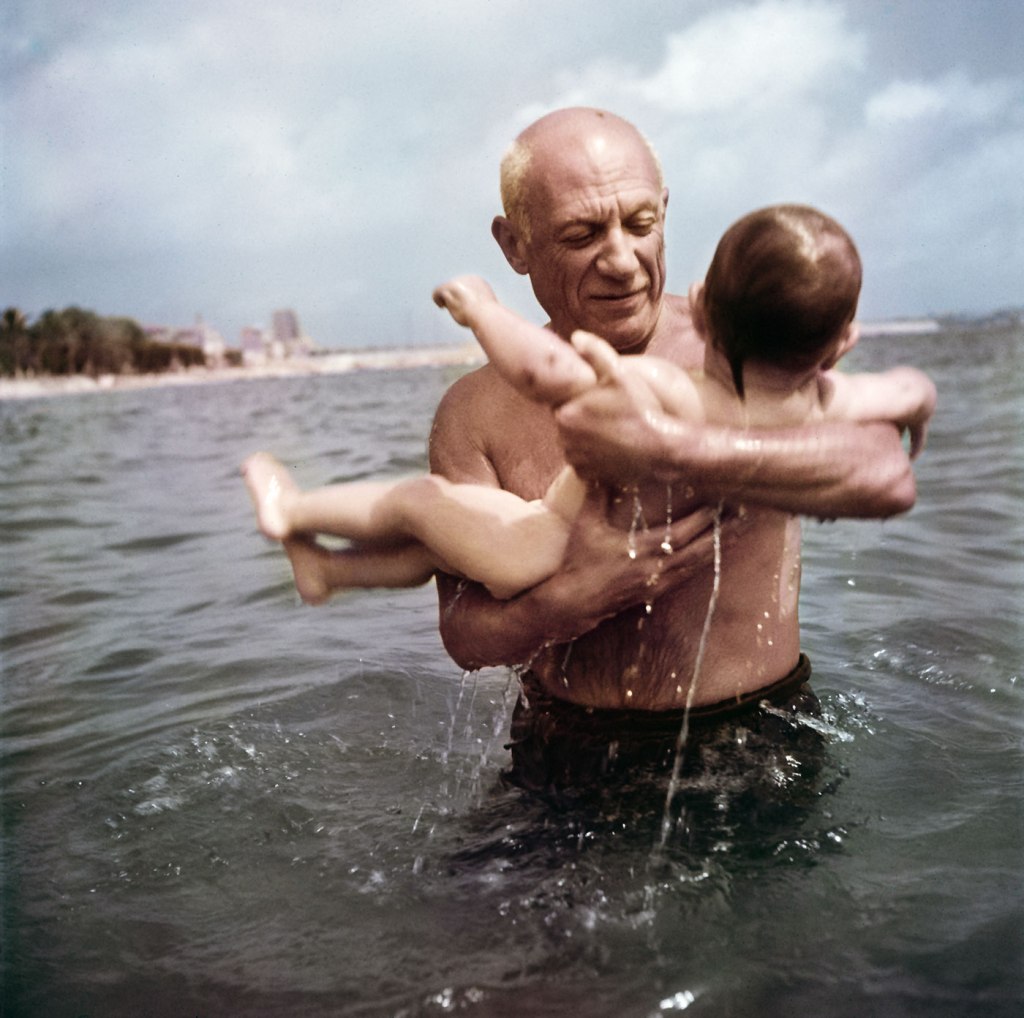
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Pablo Picasso playing in the water with his son Claude, near Vallauris, France
1948
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Picasso
Some of Capa’s colour works were considerably less successful than his black-and-white photographs. This was the case with his 1948 feature on Picasso, originally sold to look as a story about the artist’s pottery, but as Capa failed to take pictures of the pottery, it became a story about Picasso and his family.
He instructed his Magnum colleague Maria Eisner: “Look gave me a definite assignment but no price so you have to insist on $200 pro black and white and $300 pro coloured page, and $250 for expenses. If they are not willing to pay a reasonable sum, you can withdraw, but Madame Fleurs Cowles was so positive on this matter and the pictures are so exclusive that I could be very surprise[d] if this doesn’t work”. Both Fleur Cowles at Look and Len Spooner at Illustrated were disappointed with the colour images, although delighted with the story, which included Capa’s now famous picture of Picasso holding a sun umbrella over his ravishing young artist girlfriend, Françoise Gilot, parading on the beach.
Hungary
In 1948, Holiday sent Capa to his native Budapest and commissioned him to write the accompanying article. Capa had been widely praised for the hilarious and self-deprecating 1947 book about his wartime exploits, slightly out of focus, so the editors were hardly taking risk by asking him to write a long article.
Holiday used four colour images in the November 1949 issue. Unlike the glamorous destinations the magazine usually covered or that Capa would later cover for them, the images and accompanying article, one of the strongest texts he wrote about a place, functioned more as a letter from Budapest. He observes with fascination and humour the clashing end of one empire with the start of another, bittersweet against the reality of what his childhood city had become. While he seemed to have had more colour film on this assignment than in Russia, it was expensive to buy and process, so he still conserved, and there are many more black-and-white negatives of similar scenes than in colour.
Morocco
Capa’s 1949 trip to Morocco was one of the few postwar stories he made concerning a political subject, but it was a complicated sell and failed as an international news story.
The assignment was muddled from the start, as it combined Moroccan politics, lead mines, and the filming of The Black Rose with Orson Welles. Paris Match first published some of the pictures in a piece about the annual tour of the country by the Moroccan leader Sultan Sidi Mohammed. Illustrated published a story with only black-and-white images about the strange effects of the Marshall Plan, in which as a French colony Morocco received American aid through France, although the French General was not recognised as the leader in charge by the U.S. State Department. Some of the best images are portraits of the Moroccan people.

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Construction of the new settlements for workers, Neguev Desert, outside Be’er Sheva, Israel
1949-1950
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Former shop near Jaffa gate, Jerusalem, Israel
1949
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Israel
Capa’s big geopolitical assignment of the late 1940s took him to Israel. He first traveled there in 1948 to cover the Arab-Israeli war, then returned in 1949, for Holiday and Illustrated, with writer Irwin Shaw.
He came back in 1950 to continue photographing the new nation in transition, focusing on the influx of refugees arriving from Europe and neighbouring Arab countries, the ongoing repair of the physical destruction, portraits of immigrants, agricultural work, kibbutzim, and various Jewish festivities. While there is only one colour image from the 1948 trip, of the Altalena ship burning in the water off the beach in Tel Aviv – a result of the conflict between extreme right-wing Irgunists and the Israeli government – by the time Capa arrived in 1949, he seemed to have all the colour film he needed. His Israel stories were picked up by all the major international picture news magazines, spurred by the 1950 publication Report on Israel, with text by Shaw and photos by Capa.
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Jetty, Socoa, near Saint-Jean-de-Luz, France
August 1951
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
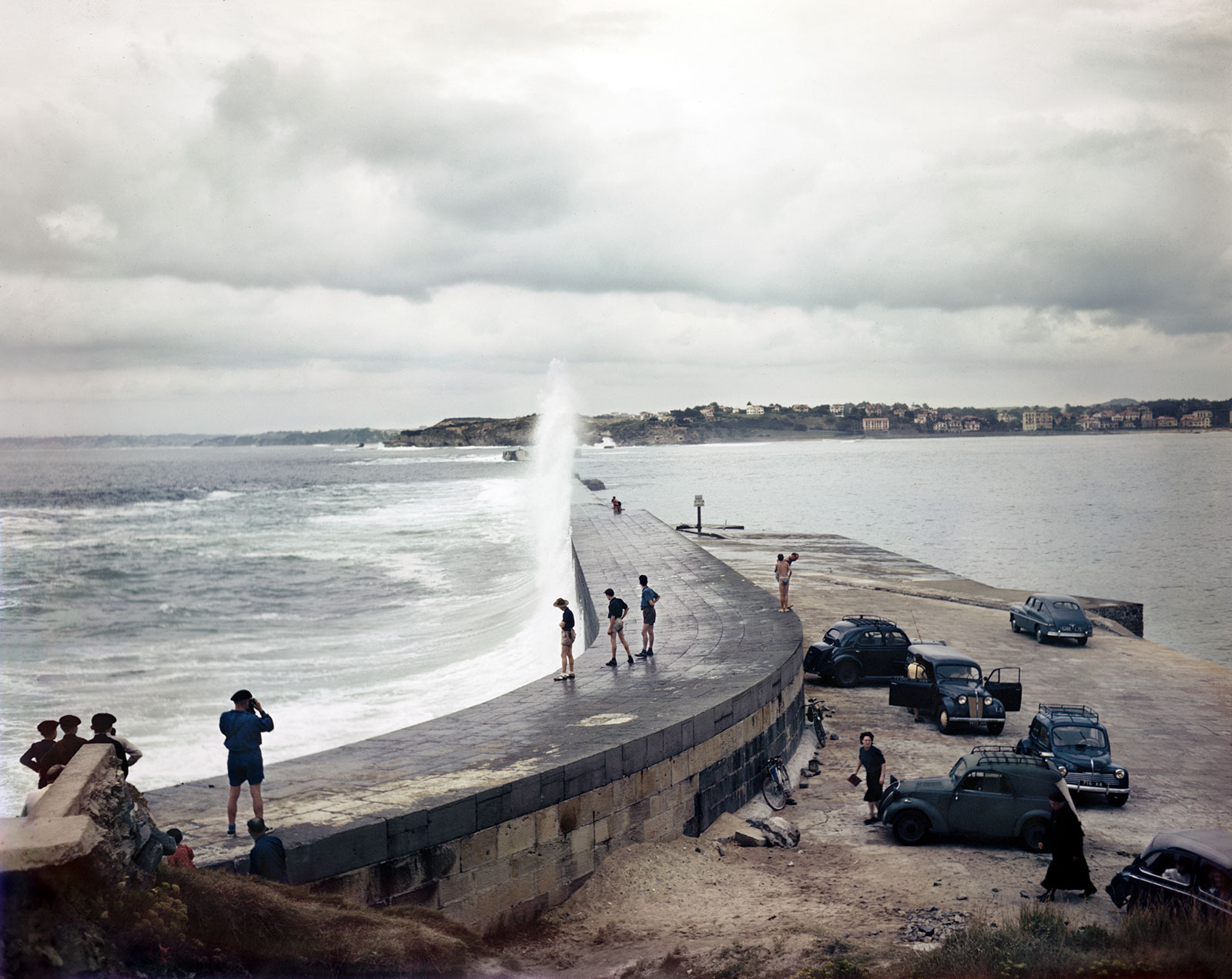
Woman on the beach, Biarritz, France
August 1951
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Deauville and Biarritz
Following the success of his skiing story, Capa proposed a piece on French seaside resorts. In the summer of 1950, he traveled to Deauville in Normandy, with its racetrack and casino, photographing only in black-and-white (all that appeared in Illustrated).
He knew he could do more with the story and pitched it to Holiday as a double feature with Biarritz, in Basque Country. A year later, he returned to Deauville with colour film to photograph the scene, capturing the mix of social classes at the horse races. He then traveled to Biarritz, covering the beach, nightlife, and traditional folklore. For this story, the black-and-white and colour images complement each other – the colour adding details to the black-and-white, which set the stage. The layout, not published until September 1953, balances the colour and black-and-white with Capa’s humorous, self-deprecating text about his time in each resort.
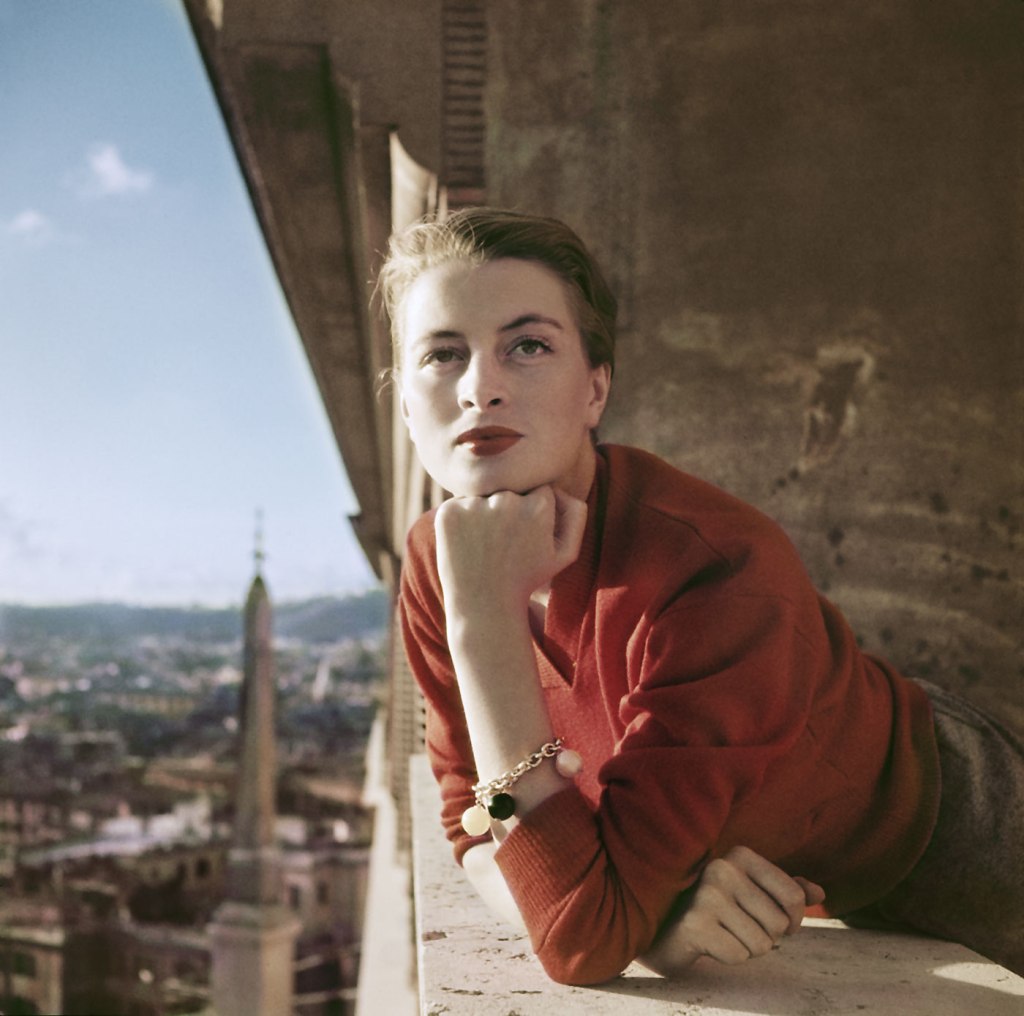

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Capucine, French model and actress, on a balcony, Rome, Italy
August 1951
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Capucine (French, 1928-1990)
Capucine (6 January 1928 – 17 March 1990) was a French fashion model and actress known for her comedic roles in The Pink Panther (1963) and What’s New Pussycat? (1965). She appeared in 36 films and 17 television productions between 1948 and 1990. At age 17, while riding in a carriage in Paris, she was noticed by a commercial photographer. She became a fashion model, working for fashion houses Givenchy and Christian Dior. She adopted the name, “Capucine” (French for nasturtium). She met Audrey Hepburn while modelling for Givenchy in Paris. The two would remain close friends for the rest of Capucine’s life.
In 1957, film producer Charles K. Feldman spotted Capucine while she was modelling in New York City. Feldman brought her to Hollywood to learn English and study acting under Gregory Ratoff. She was signed to a contract with Columbia Pictures in 1958 and landed her first English-speaking role in the film Song Without End (1960) for which she was nominated for a Golden Globe Award. Over the next few years, Capucine made six more major motion pictures. They included North to Alaska (1960), a comedy, as a prostitute who becomes the love interest of John Wayne, and Walk on the Wild Side (1962), in which she portrayed a redeemed hooker, before moving to Switzerland in 1962.
Much of 1963’s hit film The Pink Panther was shot in Europe. A crime comedy that led to a number of sequels, the film starred David Niven and Peter Sellers along with Capucine. The risqué comedy What’s New Pussycat? (1965), which co-starred Sellers and Peter O’Toole, was filmed entirely in France. She continued making films in Europe until her death.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Party, Rome, Italy
August 1951
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Rome
In his article on Norway for Holiday, Capa wrote: “I have revisited Budapest because i happen to have been born there, and because the place offered only a short season for revisiting. I even got to Moscow, which usually offers no revisiting at all. I kept on revisiting Paris because I used to live there before the war; London, because I lived there during the war; and Rome, because I was sorry that I had never lived there at all.”
Capa traveled to Rome for Holiday in 1951 and his pictures were published in April 1952, with a text authored by Alan Moorehead. A writer for The New Yorker at the time of the Rome assignment, Moorehead had been a correspondent for the Daily Express of London during World War II, and he and Capa had been together in North Africa, Sicily, and Normandy. Capa’s accompanying colour photographs pursued a glamorous city filled with beautiful people engaged in endless partying, reflecting a Rome removed from postwar destruction and entering the period of La Dolce Vita.

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
American Judith Stanton, Zermatt, Switzerland
1950
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Woman at an ice bar, Zürs, Austria
1949-1950
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Skiing
Skiing was one of Capa’s favourite pastimes and he vacationed annually in Klosters, Switzerland, to relax and recuperate. In 1948, he and a Magnum colleague were trying to drum up a story on Megève, France, a popular ski resort for Parisians, on its “dual personality … simple peasant life and gay, café society set.”
Capa photographed in Zürs, Austria, in early 1949, for a Life story, although the magazine ultimately killed it. Holiday pulled in after Life dropped out and, in late 1949, signed on to a feature about the great skiing resorts of Austria, Switzerland, and France, which would become one of Capa’s most joyous and successful colour stories. In fact, it was arguably better in colour, which provided the additional elements of glitter and humour that black-and-white often missed. For two months, he traveled from the Austrian resorts of Kitzbühel, St. Anton, Zürs, and Lech, to the Swiss towns of Davos, Klosters, and Zermatt, then over the French border to Val d’Isère. In each place, he found a glamorous circle to depict: director Billy Wilder and writer Peter Viertel from Hollywood, young international ski champions, and current and ex-European royalty, including the Queen and Prince of Holland. Everyone was healthy and the mood festive. Capa found a relaxed, casual confidence in his subjects.
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Spectators at the Longchamp Racecourse, Paris, France
c. 1952
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
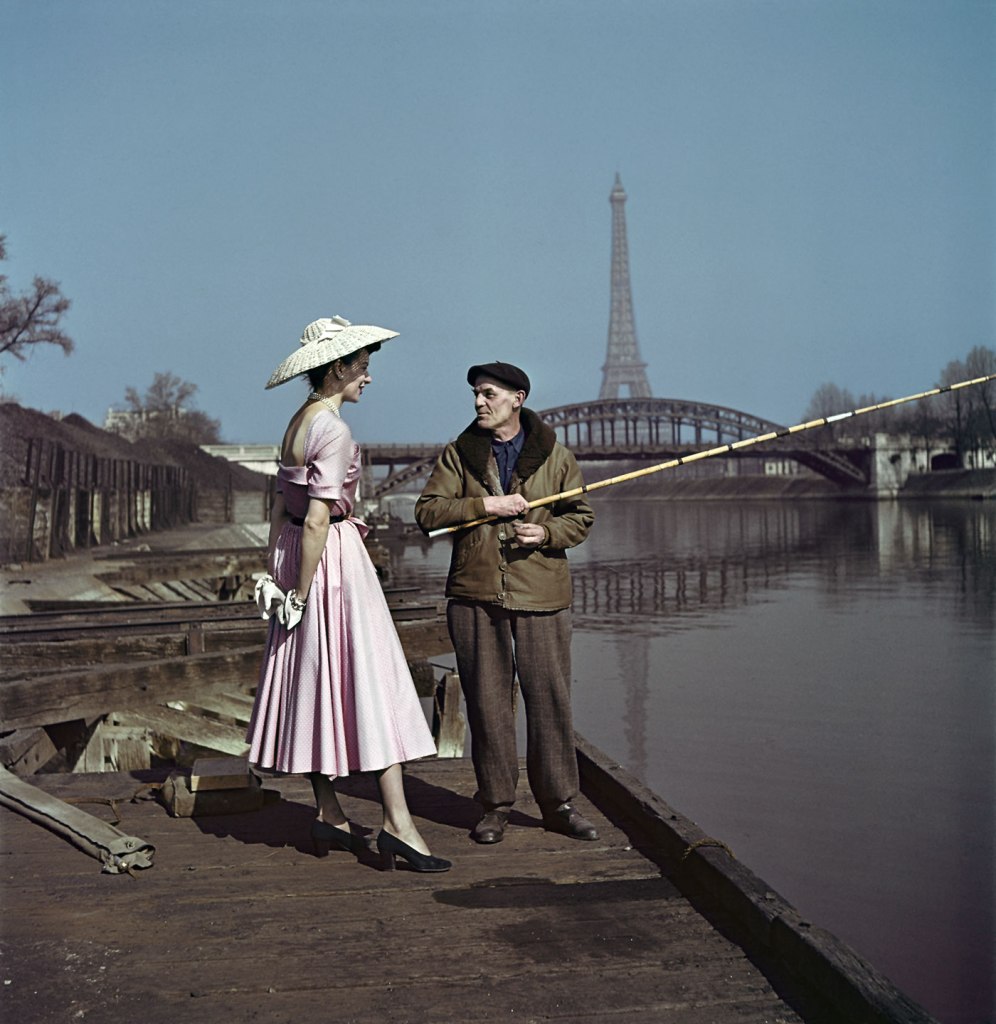

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Model wearing Dior on the banks of the Seine, Paris, France
1948
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Paris
Paris was Capa’s de facto home from 1933 to 1939 and then as his postwar base, usually in a back room of the elegant Hotel Lancaster off the Champs-Élysées, where he was friend with the owner.
Holiday‘s editor Ted Patrick commissioned Capa to provide photographs for a special issue on Paris in 1952, and Capa brought in other Magnum colleagues – Henri Cartier-Bresson, Chim, and the young Dennis Stock. The magazine included texts by Irwin Shaw, Paul Bowles, Ludwig Bemelmans, Art Buchwald, and Colette, among others, and is a romantic paean to the city, almost a stage set for romance, gastronomy, and history. Some of Capa’s best images from this story are the quirkiest ones and play with the contrasts that he seemed to revel in, between the young and old, human and animal, high-life and low-life, particularly at the horse races, about which he noted: “The sport of kings is also the sport of concierges”. For his photographs of plein air painters, Capa wrote: “Place du Tertre is a painter’s paradise. A few stops from Sacré Coeur we find an old gentleman in beard and beret looking like an American movie producer’s idea of the kind of French painter found in Montmartre”.
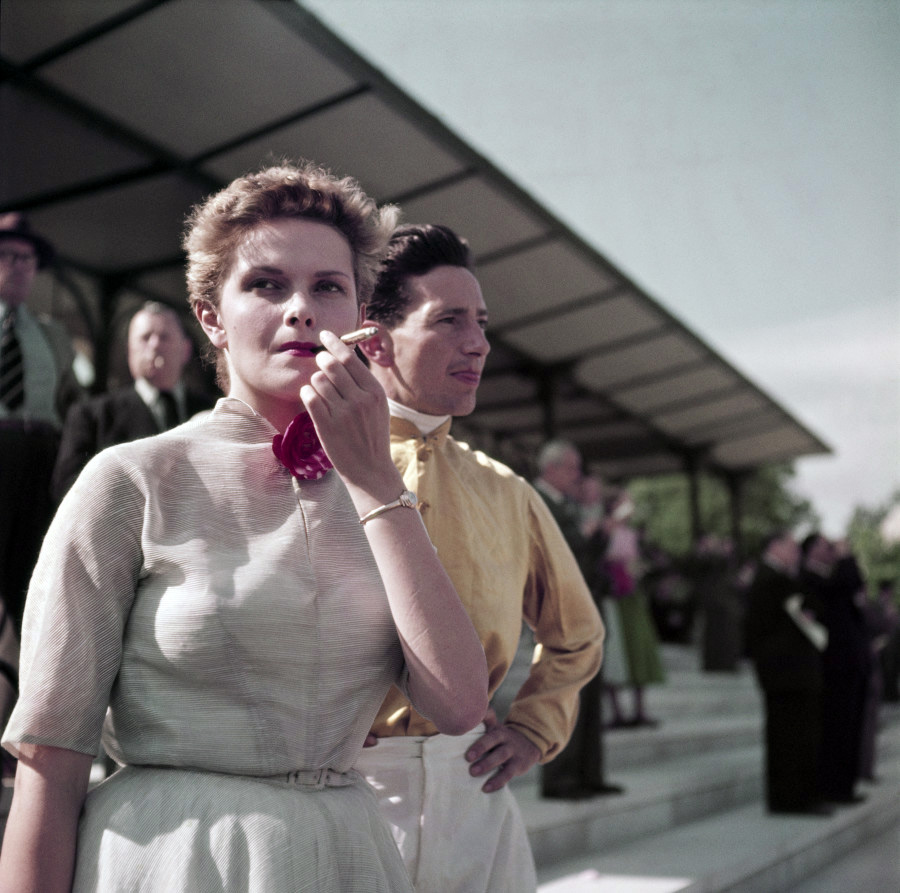

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Gen X girl, Colette Laurent, at the Chantilly racetrack, France
1952
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Generation X
Capa developed Generation X, also known as Gen X, for Magnum on the mark of the half century in late 1949. McCall’s was originally behind the project, but had pulled out by 1951, when Capa insisted on injecting more political content.
Holiday filled the void and supported the project all the way to a three-part series published in early 1953. Capa observed, “it was one of those projects, of which many are born in the minds of people who have big ideas and little money. The funny thing about this project is that it was accomplished.” He assigned the photographers, including Chim, Cartier-Bresson, and Eve Arnold, to each create a portrait of a boy and/or girl in countries where they were already working or had worked. Each subject answered a detailed questionnaire about his or her life, family, personal beliefs, and goals. The project eventually included twenty-four individuals in fourteen countries on five continents. Capa photographed all his subjects – a French girl, a German boy, and Norwegian boy and girl – in colour and black-and-white, but only the Norwegian photos were published in colour. Capa’s biographer Richard Whelan suggested that Capa’s depiction of the French girl, Colette Laurent, was an oblique portrait of himself at the time: “Her life is superficial, artificial on the surface and holds none of the good things except the material ones.”

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Ava Gardner on the set of ‘The Barefoot Contessa’, Tivoli, Italy
1954
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Ava Gardner on the set of ‘The Barefoot Contessa’, Tivoli, Italy
1954
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Humphrey Bogart and Peter Lorre on the set of ‘Beat the Devil’, Ravello, Italy
April 1953
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
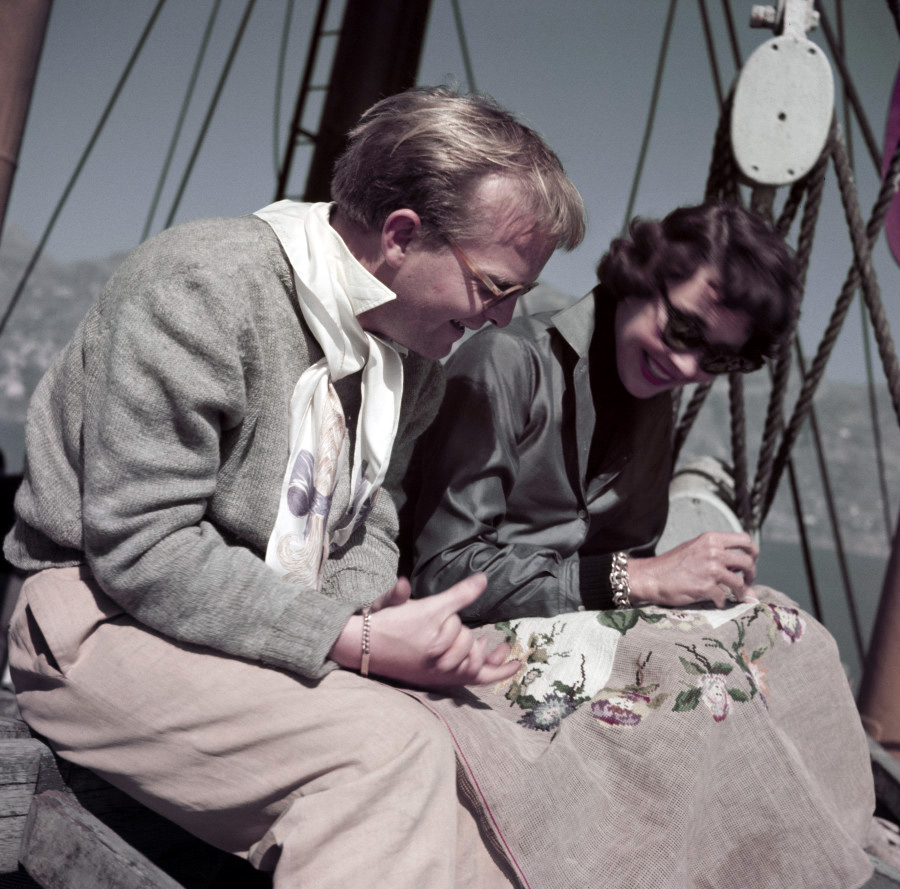

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Truman Capote and Jennifer Jones on the set of ‘Beat the Devil’, Ravello, Italy
April 1953
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Jeffrey Hunter on the set of ‘Single-Handed (Sailor of the King)’
Malta, 1952
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
John Huston at the café Les Deux Magots during the filming of ‘Moulin Rouge’
Paris, 1952
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Anna Magnani on the set of Luchino Visconti’s ‘Bellissima’
Rome, 1951-1952
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Ingrid Bergman and George Sanders on the set of ‘Viaggio in Italia’
Naples, April 1953
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
On the set
Capa was friends with a number of movie stars and directors and incorporated them into his professional work. He met John Huston in Naples in 1944, while Huston was making films for the Army Signal Corps, and Ingrid Bergman in 1945 when she was filming in Paris, before beginning a one-year love affair.
As part of his 1948 trip to Morocco, he included a story on The Black Rose and its star Orson Welles. He photographed the set of Huston’s Beat the Devil, written by Truman Capote and filmed in the hillside town of Ravello, Italy. The cast visited the set of Viaggio in Italia in nearby Almalfi with Bergman, Roberto Rossellini, and George Sanders and Capa also dipped down to Paestum with his friend Martha Gellhorn, casting her as a caryatid in the ancient ruins. Capa covered another Huston film, Moulin Rouge, about the life of painter Toulouse Lautrec, shot in Paris and at Shepparton Studios near London. Capa’s colour portraits of the actors eschew traditional head shots and capture the varied pace and playful moments on the set.

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Spectators along the procession route in Piccadilly Circus before the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II, London, England
February 6, 1953
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
London and Japan
In 1953, Capa traveled to London to cover the coronation of the young Elizabeth II with friends Humphrey Bogart and John Huston. His colour images of crowds waiting for the parade of guests before the coronation, for which he used 35mm Kodachrome, suggest a new interest in colour for colour’s sake.
In 1954, he received an invitation from Mainichi Press to travel to Japan for six weeks with Japanese cameras and an unrestricted amount of film to shoot what he liked in return for images they could publish. The trip was an easy one, but the colour photographs lack focus. He wandered around markets, documented foreign signs, watched people visiting temples and shrines, and photographed Children’s Day in Osaka, but they are little better than tourist snaps. Only a few images of a May Day workers’ celebration in Tokyo, in bright colours, show some engagement, reminiscent of his 1930s images of workers in France and Spain.
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
On the road from Namdinh to Thaibinh, Indochina (Vietnam)
May 1954
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
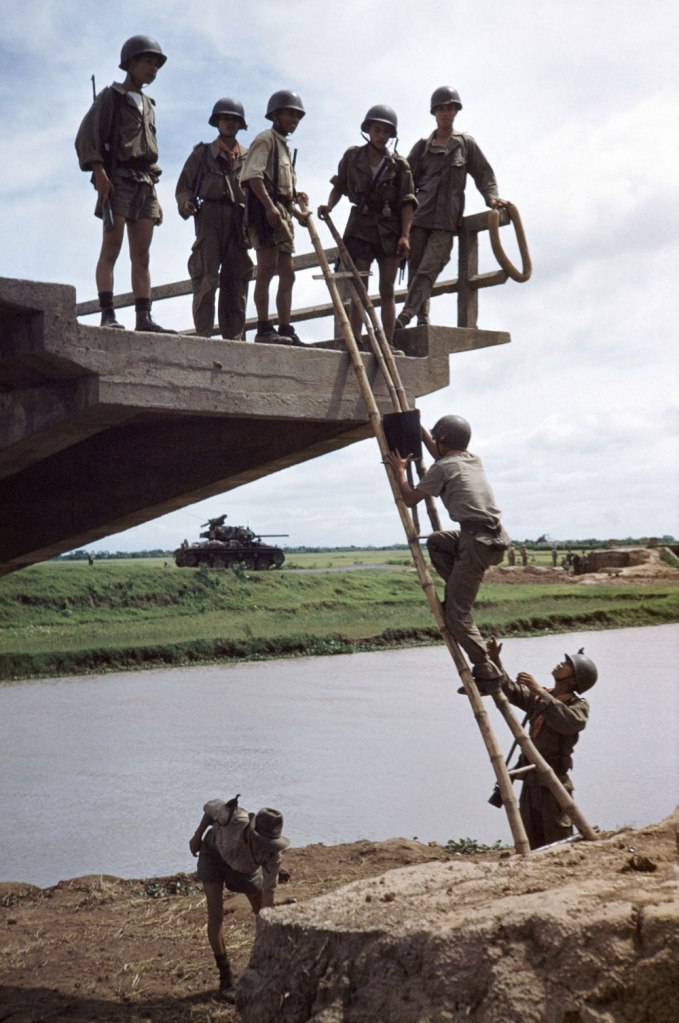

Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
West of Namdinh, Indochina (Vietnam)
May 1954
International Center of Photography, New York
© Robert Capa/International Center of Photography/Magnum Photos
Indochina
In 1953, Capa expressed his readiness “to get back to real work, and soon. What and where I do not know, but the Deauville and Biarritz and motley movie period is over.”
In the same letter, he writes of his desire to go to “Indochina, or any other proposition which would get me back to reporting on my own type of territory”. While in Japan the next year, Capa received a cable from Life asking him to cover for their photographer in Indochina. The assignment was only for a few weeks and would bring in some needed money. He reached Hanoi on May 9 and on May 25, with Time reporter John Mecklin and Scripps-Howard correspondent John Lucas, left Mandihn with two cameras, a Contax with black-and-white film, and a Nikon with colour film. Their convoy traveled along a dirt road lined by rice paddies. Moving toward Thaibinh, Capa left the convoy and walked on by himself. He photographed the soldiers advancing through the fields, and as he climbed the dike along the road, he stepped on a land mine and was killed. While the colour images are some of the strongest war pictures he made, none were used in the press at the time, probably in part because of the extra time required to process the colour film.
Jeu de Paume – Château de Tours
25 avenue André Malraux
37000 Tours
Opening hours:
Tuesday to Sunday: 2pm – 6pm
Closed Mondays


















![Dallaporte (Portugal) 'Batalha – Mosteiro, Fachada das Capelas Imperfeitas [Monastery of Batalha, façade of the Imperfect Chapels]' Nd Dallaporte (Portugal) 'Batalha – Mosteiro, Fachada das Capelas Imperfeitas [Monastery of Batalha, façade of the Imperfect Chapels]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/batalha-web.jpg)





![Luigi Grassi, Milano (Italian) 'Milano, Facciata della Cattedrale [Facade of Milan Cathedral]' Nd Luigi Grassi, Milano (Italian) 'Milano, Facciata della Cattedrale [Facade of Milan Cathedral]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/milan-catherdral-web.jpg?w=670)







![Nels (Belgium, 1898 - ) 'S. A. des Grottes de Han-sur-Lesse et de Rochefort - Le Trophée [Caves of Han-sur-Lesse and Rochefort - The Trophy]' Nd Nels (Belgium, 1898 - ) 'S. A. des Grottes de Han-sur-Lesse et de Rochefort - Le Trophée [Caves of Han-sur-Lesse and Rochefort - The Trophy]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/grottes-de-han-web.jpg?w=676)


































































































































![Ana Mendieta (Cuban-American, 1948-1985) 'Itiba Cahubaba (Esculturas Rupestres)' [Old Mother Blood (Rupestrian Sculptures)] 1982 Ana Mendieta (Cuban-American, 1948-1985) 'Itiba Cahubaba (Esculturas Rupestres)' [Old Mother Blood (Rupestrian Sculptures)] 1982](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/ana-mendieta_itiba-cuhababa-web.jpg)









































You must be logged in to post a comment.