Exhibition dates: 16th May – 30th October, 2016
Curators: Mia Fineman, Associate Curator; and Beth Saunders, Curatorial Assistant in the Department of Photographs at The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Manuel Alvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1902-2002)
La Buena Fama Durmiendo (The Good Reputation Sleeping)
1939, printed c. 1970s
Gelatin silver print
Mat: 16 × 20 in. (40.6 × 50.8cm)
The Elisha Whittelsey Collection, The Elisha Whittelsey Fund, 1973
The best fun I had with this posting was putting together the first twelve images. They seem to act as ‘strange attractors’, a feeling recognised by the curators of the exhibition if you view the first installation photograph by Anders Jones, below.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to photographer Anders Jones and the Duggal website for allowing me to publish the installation photographs in the posting.
Artists have always turned to dreams as a source of inspiration, a retreat from reason, and a space for exploring imagination and desire. In the history of photography, dreams have been most closely associated with the Surrealists, who pushed the technical limits of the medium to transform the camera’s realist documents into fantastical compositions. Whereas their modernist explorations were often bound to psychoanalytic theories, more recently contemporary photographers have pursued the world of sleep and dreams through increasingly open-ended works that succeed through evocation rather than description.
This exhibition takes a cue from the artists it features by displaying a constellation of photographs that collectively evoke the experience of a waking dream. Here, a night sky composed of pills, a fragmented rainbow, a sleeping fairy-tale princess, and an alien underwater landscape illuminate hidden impulses and longings underlying contemporary life. Drawn entirely from The Met collection, Dream States features approximately 30 photographs and video works primarily from the 1970s to the present.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art
Anselm Kiefer (German born Donaueschingen, b. 1945)
Brünnhilde Sleeps
1980
Acrylic and gouache on photograph
23 x 32 7/8in. (58.4 x 83.5cm)
Denise and Andrew Saul Fund, 1995
© Anselm Kiefer
Near the end of Wagner’s second opera of the Ring Cycle, Die Walküre (The Valkyrie), the Valkyrie Brünnhilde, having attempted to help the sibling lovers Siegmund and Sieglinde against their father’s wishes, is punished for her betrayal. Wotan puts her to sleep and surrounds her with a ring of fire (she will be awakened in turn by her nephew Siegfried, the incestuous son of Siegmund and Sieglinde, in the third opera of the cycle).
Kiefer portrays the dormant Brünnhilde as French actress Catherine Deneuve in François Truffaut’s film Mississippi Mermaid, using a photograph he snapped in a movie house in 1969. In the film, Deneuve plays a deceitful mail-order bride who comes to the island of Réunion to marry a plantation owner, played by Jean-Paul Belmondo. Aside from the parallels of love and betrayal in both the Ring Cycle and Truffaut’s film, Kiefer thought the choice of Deneuve for Brünnhilde both ironic and amusing: she was for him “the contrary of Brünnhilde. Very slim, very French, very cool, very sexy,” hinting that no man would go through fire to obtain Wagner’s corpulent, armoured Valkyrie.
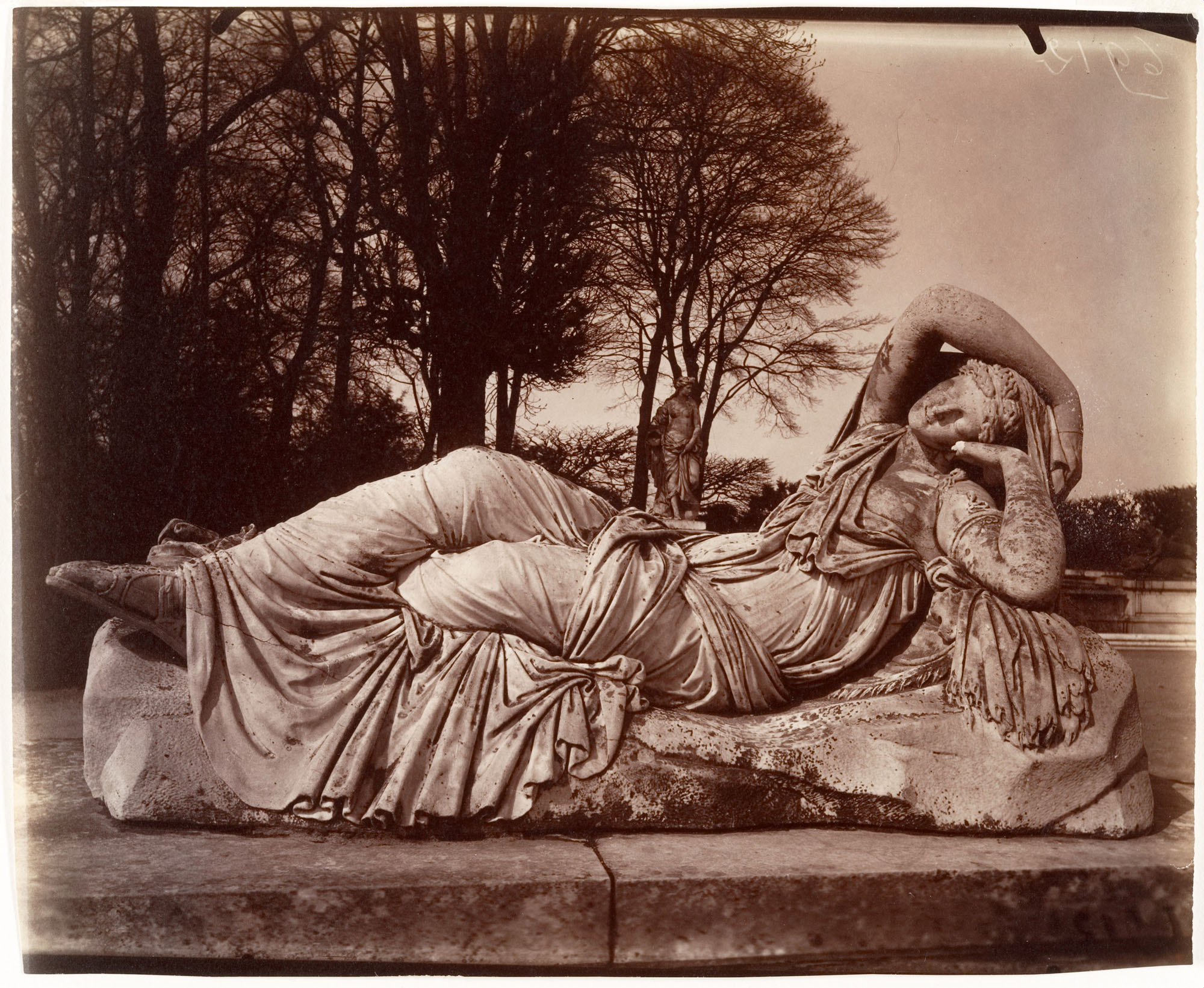
Eugène Atget (French, Libourne 1857-1927 Paris)
Versailles
1924-25
Salted paper print from glass negative
Image: 17.5 x 21.9cm (6 7/8 x 8 5/8 in.)
Sheet: 18 × 21.9cm (7 1/16 × 8 5/8 in.)
Mat: 40.6 × 50.8cm (16 × 20 in.)
Gilman Collection, Purchase, Ann Tenenbaum and Thomas H. Lee Gift, 2005
From 1898 until his death in 1927, Atget exhaustively documented the remains of Old Paris: the city’s streets, monuments, interiors, and environs. Among the last entries in this self-directed preservationist effort was a series of images of landscapes and sculpture in the parks of Saint-Cloud and Versailles. Here, the photographer records a statue of a sleeping Ariadne, the mythical Cretan princess abandoned by her lover Theseus on the island of Naxos. Atget’s simultaneously realistic and otherworldly photographs inspired the Surrealist artist Man Ray, who reproduced four of them in a 1926 issue of the journal La Révolution Surréaliste, thus presenting the elder photographer as a modernist forerunner.
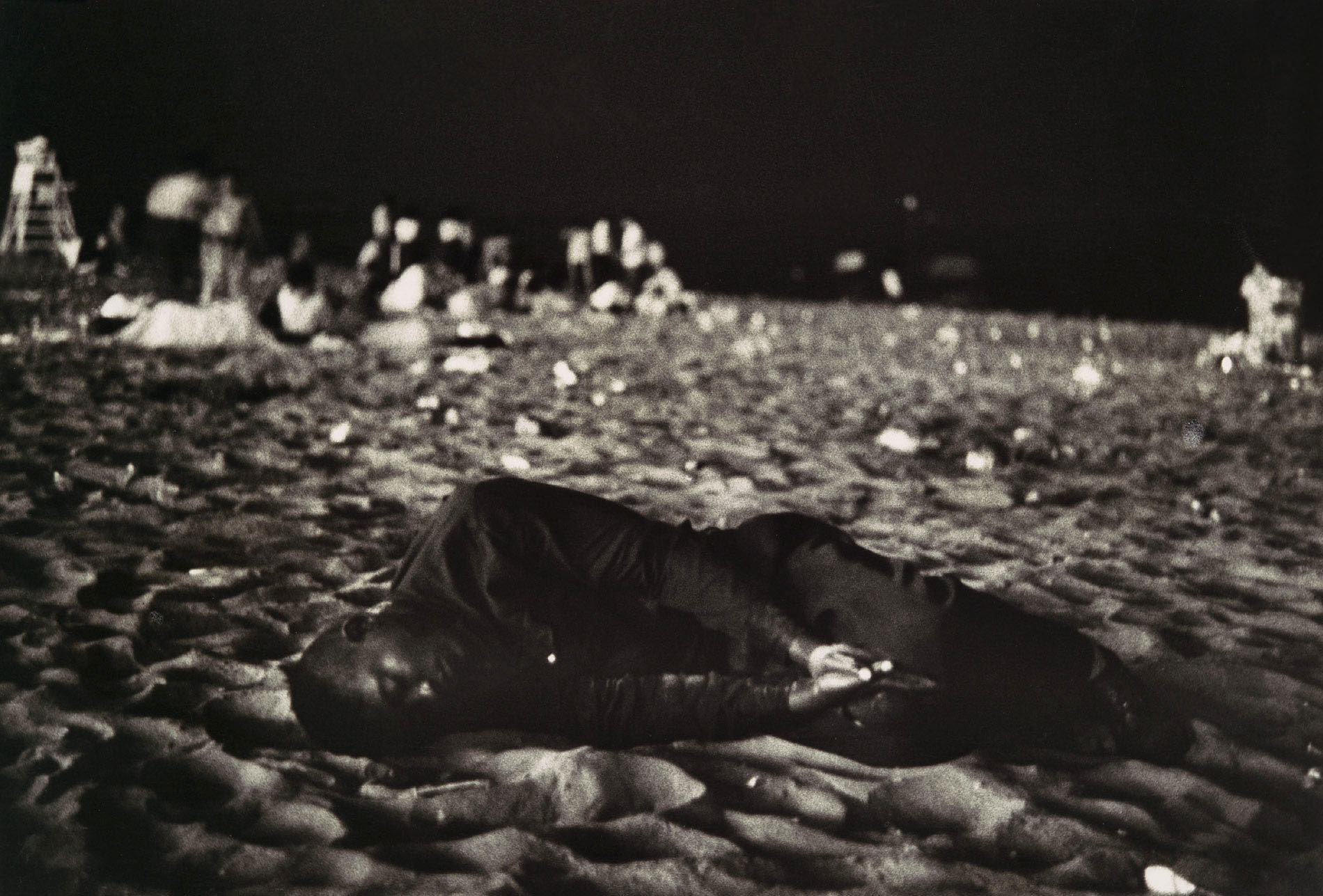
Robert Frank (American, 1924-2019)
Fourth of July, Coney Island
1958
Gelatin silver print
Image: 26 x 35.6 cm (10 1/4 x 14 in.)
Mat: 47 × 57.2cm (18 1/2 × 22 1/2 in.)
Purchase, Alfred Stieglitz Society Gifts, 2002
© 2005 Robert Frank
As he traveled around the country in 1955-1956 making the photographs that would constitute his landmark book, The Americans, Frank’s impression of America changed radically. He found less of the freedom and tolerance imagined by postwar Europeans, and more alienation and racial prejudice simmering beneath the happy surface. His disillusionment is poignantly embodied in this image of a disheveled African-American man disengaged from the crowd and asleep in a foetal position amid the debris of an Independence Day celebration on Coney Island.
This was one of the last still photographs Frank made before he devoted his creative energy to filmmaking in the early 1960s. As such, it may be interpreted as an elegy to still photography; the lone figure functions as a surrogate for Frank himself, as he turned his back on Life – like photojournalism to concentrate on the more personal, dreamlike imagery of his films.
Shannon Bool (Canadian, b. 1972)
Vertigo
2015
Gelatin silver print
Image: 7 13/16 × 11 13/16 in. (19.8 × 30cm)
Gift of Shannon Bool and Daniel Faria Gallery, 2015
© Shannon Bool
This photogram – made without a camera by placing a collage of transparencies on a photosensitive sheet of paper and exposing it to light – is part of a series portraying psychoanalysts and their patients. Here, a patient on a Freudian couch is seen from above; the figure, sheathed in patterns of Maori origin, appears to come apart at the seams under the analyst’s scrutiny.
Nan Goldin (American, born Washington, D.C., 1953)
French Chris on the Convertible, NYC
1979
Silver dye bleach print
Image: 50.8 x 61cm (20 x 24in.)
Mat: 63.5 × 81.3cm (25 × 32 in.)
Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 2001
© Nan Goldin Courtesy Matthew Marks Gallery
Following in the tradition of Robert Frank and Helen Levitt, Goldin is her generation’s greatest practitioner of the “snapshot aesthetic” in photography – the intimate, diaristic mode that yields images that, in the right hands, are both spontaneous and carefully seen, tossed off and irreducibly right. In this early work, the artist has captured her friend as a Chatterton of the Lower East Side, lying across the back of a blue convertible with shirt open, eyes closed, and an empty can of Schaeffer beer by his side instead of arsenic – a contemporary vision of glamorous surrender for our own time.
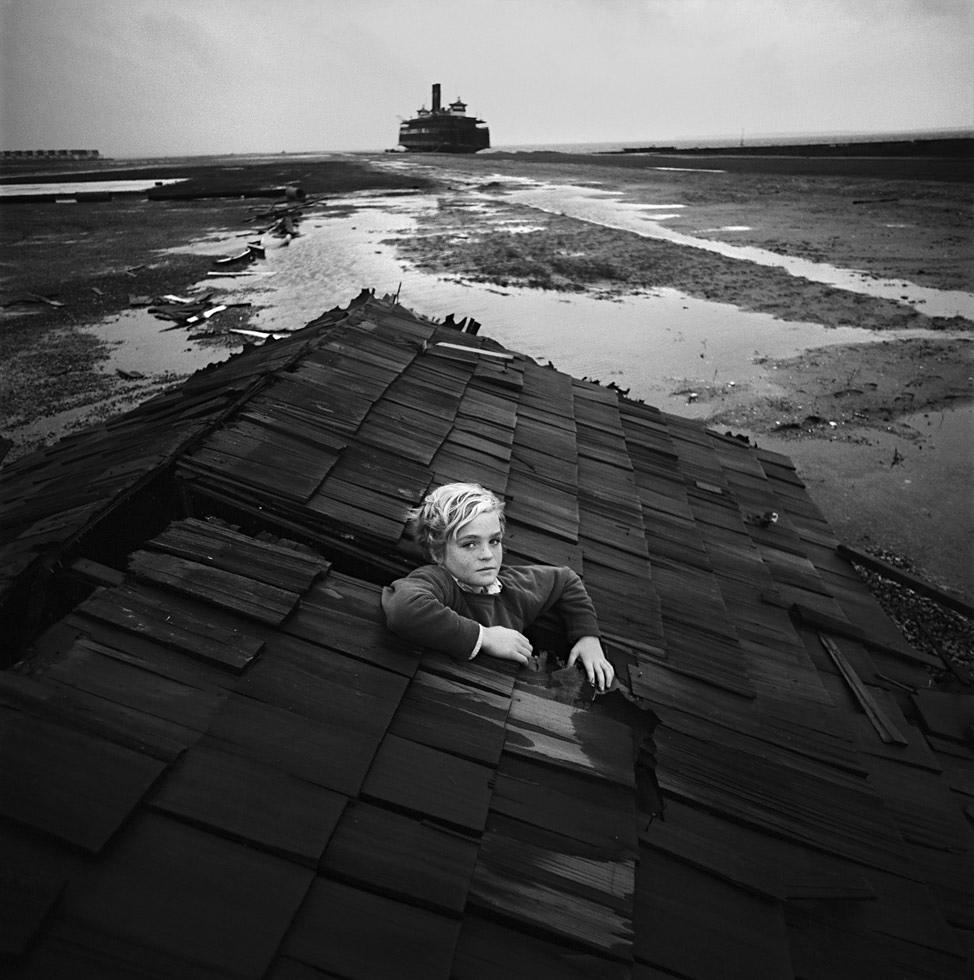

Arthur Tress (American, b. 1940)
Boy in Flood Dream, Ocean City, New Jersey
1972
Gelatin silver print
Mat: 18 × 18 in. (45.7 × 45.7cm)
Gift of the artist, 1973
In the late 1960s, Tress began audio-recording children recounting their dreams and nightmares. He then collaborated with the young people, who acted out their tales for the camera, and published the resulting surreal images in the 1972 book The Dream Collector. Many of the children shared common nightmare scenarios such as falling, drowning, and being trapped, chased by monsters, or humiliated in the classroom. Here, a young boy clings to the roof of a home that has washed ashore as if after a flood. The desolate landscape evokes the sort of non-place characteristic of dreams and conveys feelings of loneliness and abandonment.
Installation view of the exhibition Dream States: Contemporary Photography and Video at the Metropolitan Museum of Art featuring at lower right, Nan Goldin’s French Chris on the Convertible, NYC (1979)
Photo: Anders Jones
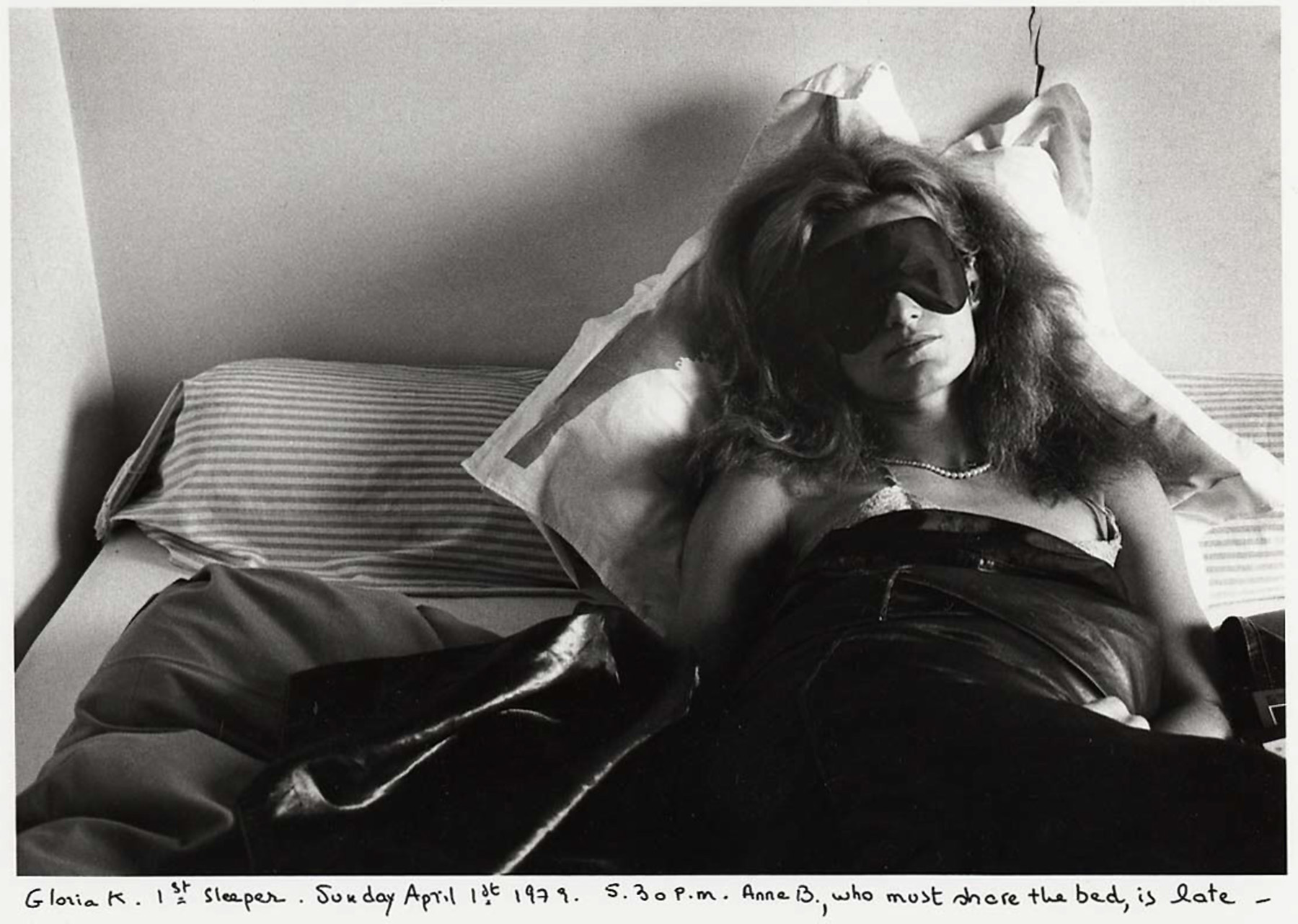
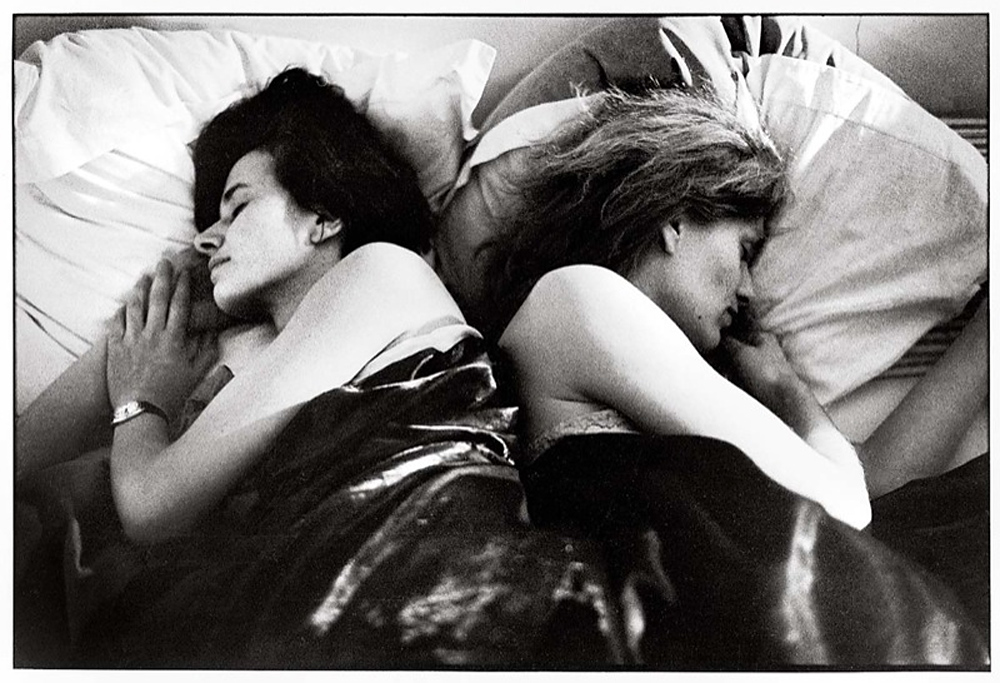
Sophie Calle (French, born Paris, 1953)
Gloria K., first sleeper. Anne B., second sleeper
1979
Gelatin silver prints
Image: 12.6 x 18.4cm (4 15/16 x 7 1/4in.)
Mat: 35.6 × 43.2cm (14 × 17 in.)
Gift of the artist and Olivier Renaud-Clement, in memory of Gilles Dusein, 2000
© Sophie Calle
Sophie Calle (French, born Paris, 1953)
Gloria K., first sleeper. Anne B., second sleeper
1979
Gelatin silver prints
Image: 12.6 x 18.4cm (4 15/16 x 7 1/4in.)
Mat: 35.6 × 43.2cm (14 × 17 in.)
Gift of the artist and Olivier Renaud-Clement, in memory of Gilles Dusein, 2000
© Sophie Calle
While obviously indebted to the deadpan photo-text combinations of Conceptualism, Calle’s art is as purely French at its core as the novels of Marguerite Duras and the films of Alain Resnais – an intimate exploration of memory, desire, and obsessive longing. The artist’s primary method involves a perfectly calibrated interplay between narrative and image, both of which steadily approach their object of desire only to find another blind spot-that which can never be captured through language or representation.
This work is the first segment of Calle’s first work, The Sleepers (1979), in which the artist invited twenty-nine friends and acquaintances to sleep in her bed consecutively between April 1 and April 9, during which time she photographed them once an hour and kept notes recording each encounter. All the elements of Calle’s art-from the voyeuristic inversion of the private sphere (rituals of the bedroom) and the public (the book or gallery wall) to the use of serial, repetitive structures-are present here in embryonic form.
Paul Graham (British, b. 1956)
Senami, Christchurch, New Zealand
2011
Chromogenic print
Image: 44 1/4 in. × 59 in. (112.4 × 149.9cm)
Purchase, Vital Projects Fund Inc. Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel and Hideyuki Osawa Gift, 2015
Graham’s series, Does Yellow Run Forever?, juxtaposes three groups of photographs: rainbows arcing over the Irish countryside, the facades of pawn-and-jewellery shops in New York, and tender studies of his partner asleep. The thematic links between the images (the rainbow’s mythical pot of gold, the sparkling objects in the Harlem window display, and a sleeping dreamer) may seem obvious, even pat, but Graham’s photographs transmute those clichés into a constellation of deep feeling. These luminous vignettes evoke a sense of longing and pathos, the quest for something permanent amid the illusory and devalued.
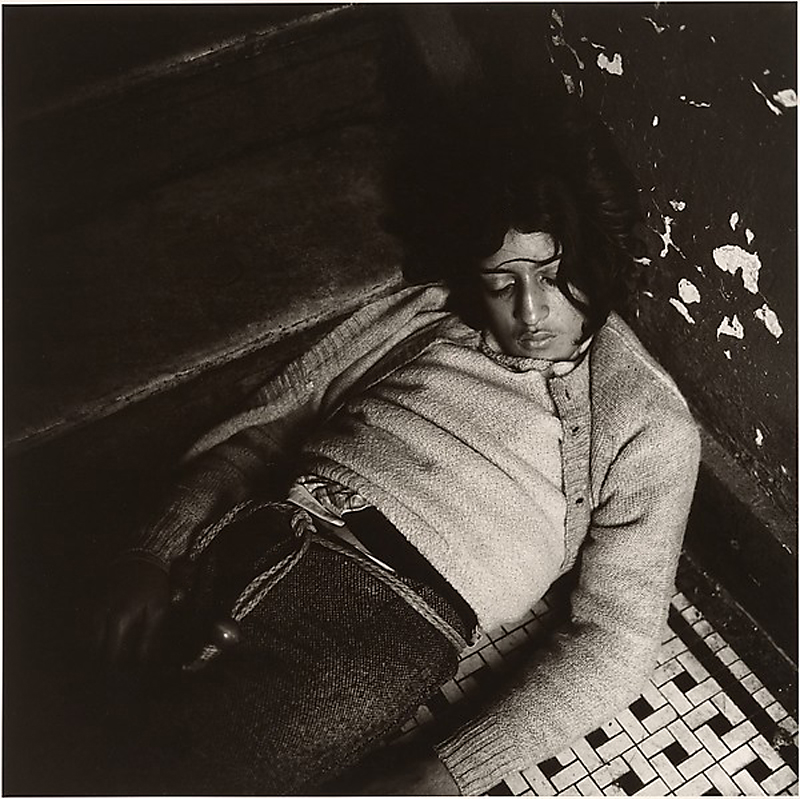

Peter Hujar (American, Trenton, New Jersey 1934-1987 New York)
Girl in My Hallway
1976
Gelatin silver print
Image: 37 x 37.1cm (14 9/16 x 14 5/8 in.)
Mat: 63.5 × 63.5cm (25 × 25 in.)
Purchase, Alfred Stieglitz Society Gifts, 2006
© The Peter Hujar Archive, L.L.C.

Brassaï (French born Romania, Brașov 1899-1984 Côte d’Azur)
A Vagrant Sleeping in Marseille
1935, printed 1940s
Gelatin silver print
Image: 17.2 x 23.3cm (6 3/4 x 9 3/16in.)
Mat: 43.2 × 35.6cm (17 × 14 in.)
Gift of the artist, 1980
Copyright © Gilberte Brassaï
The inevitable suggestion that the homeless, hungry man sprawled on the sidewalk might be dreaming of a finely dressed and improbably large salad links Brassaï’s photograph to the work of the Surrealists. Although he frequently depicted thugs, vagrants, and prostitutes, he did so without judgment or political motive; his were pictures meant to delight or perplex the eye and mind-not to prompt a social crusade.
Installation view of the exhibition Dream States: Contemporary Photography and Video at the Metropolitan Museum of Art showing at left, Paul Graham’s Gold Town Jewellery, East Harlem, New York (2012); and at right, Paul Graham’s Senami, Christchurch, New Zealand (2011), both from the series Does Yellow Run Forever?
Photo: Anders Jones
The psychological fluidity of the medium has been noted before by the Met. In 1993, to celebrate its purchase of the Gilman Collection, the curator Maria Morris Hambourg chose to call her exhibition The Waking Dream. The title came from Keats’s “Ode to a Nightingale” and suggested, in Hambourg’s words, “the haunting power of photographs to commingle past and present, to suspend the world and the artist’s experience of it in unique distillations.”
Conceptual latitude can benefit curators, giving them plenty of room to manoeuvre in making their selections, or it can be a detriment if a loose framework has so many sides that it won’t support an argument.
Dream States suffers from the latter, even though the leeway of the title allows splendid pictures in disparate styles to be displayed together. Organised by associate curator Mia Fineman and assistant curator Beth Saunders around a theme that isn’t notably pertinent or provocative, the show has no discernible reason for being. It isn’t stocked with recent purchases – fewer than ten of the works entered the collection in this decade – and it isn’t tightly edited. To quality for inclusion here a photograph need only depict someone lying down or with eyes closed. A “dream state” seems to be loosely defined. It can be as a starry or cloudless sky; a tree-less landscape; inverted or abstract imagery; or something blurry.
Richard B. Woodward. “Dream States: Contemporary Photography and Video @Met,” on the Collector Daily website July 11, 2016 [Online] Cited 06/10/2016
Jack Goldstein (American born Canada, 1945-2003)
The Pull
1976
Chromogenic prints
Frame: 76.2 x 101.6cm (30 x 40 in.) each
Purchase, The Buddy Taub Foundation Gift and Vital Projects Fund Inc. Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 2009
© The Estate of Jack Goldstein
Born in the postwar baby boom, Goldstein grew up surrounded by the products of the rapidly expanding media culture-movies, television, newspapers, magazines, and advertisements of all kinds. Young artists such as Goldstein went on to be educated in the rigorous and reductive principles of Minimal and Conceptual art during the 1970s but knew from personal experience that images shape our sense of the world and who we are, rather than vice versa; they made their art reflect that secondhand relationship to reality.
In this early work, Goldstein has lifted, or “appropriated,” images of a deep sea diver, a falling figure, and a spaceman from unknown printed sources – isolating them from their original contexts and setting them at a very small scale against monochromatic backgrounds (green for sea, blue for sky, and white for space), as if the viewer were seeing them from a great distance. Because the viewer is unlikely to have seen such figures firsthand, that distance is not merely spatial but also epistemological in nature-the images trigger memories based not on original encounters but on reproductions of experience. The Pull – Goldstein’s only photographic work in a career that spanned painting, performance, film, and sound recordings – was included in “Pictures,” a seminal 1977 exhibition at Artist’s Space in New York, which also introduced the public to other young artists making use of appropriation, such as Sherrie Levine, Robert Longo, and Troy Brauntuch.
Sarah Anne Johnson (Canadian, b. 1976)
Glitter Bomb
2012
Chromogenic print with glitter and acrylic paint
Sheet: 29 7/8 in. × 53 in. (75.9 × 134.6cm)
Purchase, Funds from Various Donors in memory of Randie Malinsky, 2016
© Sarah Anne Johnson
Johnson works primarily with photography but also employs a variety of other media – sculpted figurines, dioramas, paint, ink, and bursts of glitter – to amplify the emotional power of her images. Glitter Bomb belongs to a series exploring the bacchanalian culture of summer music festivals. At once ominous and ecstatic, the image evokes the blissed-out mind-set of young revellers taking part in a modern-day rite of passage.
Oliver Wasow (American, b. 1960)
Float
1984-2008, printed 2009
Inkjet prints
Frame: 17.3 x 22.3cm (6 13/16 x 8 3/4 in.)
Overall: 116.8 x 152.4cm (46 x 60 in.)
Purchase, Vital Projects Fund Inc. Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 2010
© Oliver Wasow
Wasow has a long-standing fascination with science fiction, apocalyptic fantasies, and documentation of unidentified flying objects. In his many pictures of mysterious floating disks and orbs, the artist courts doubt by running found images through a battery of processes, including drawing, photocopying, and superimposition, to create distortions. The resulting photographs play with the human propensity to invest form with meaning, offering just enough detail to spur the imagination.
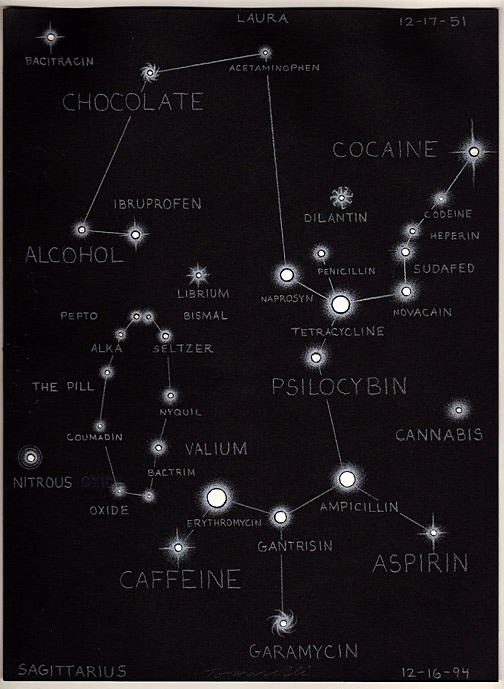
Fred Tomaselli (American born Santa Monica, California, 1956)
Portrait of Laura
2015
Gelatin silver print with graphite
Image: 16 in. × 19 15/16 in. (40.6 × 50.6cm)
Mat: 24 3/4 × 25 3/4 in. (62.9 × 65.4cm)
Purchase, Vital Projects Fund Inc. Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 2016
© Fred Tomaselli
This “portrait” of the artist’s wife, Laura, belongs to an ongoing series he calls “chemical celestial portraits of inner and outer space.” Tomaselli creates likenesses based on each sitter’s astrological sign and the star map for his or her date of birth. Placing sugar and pills on photographic paper and exposing it to light, he produces a photogram of the corresponding constellation and names the stars after the various drugs the subject remembers consuming, from cold medicine to cocaine. The result is an unconventional map of identity that cleverly weds the mystical and the pharmacological.
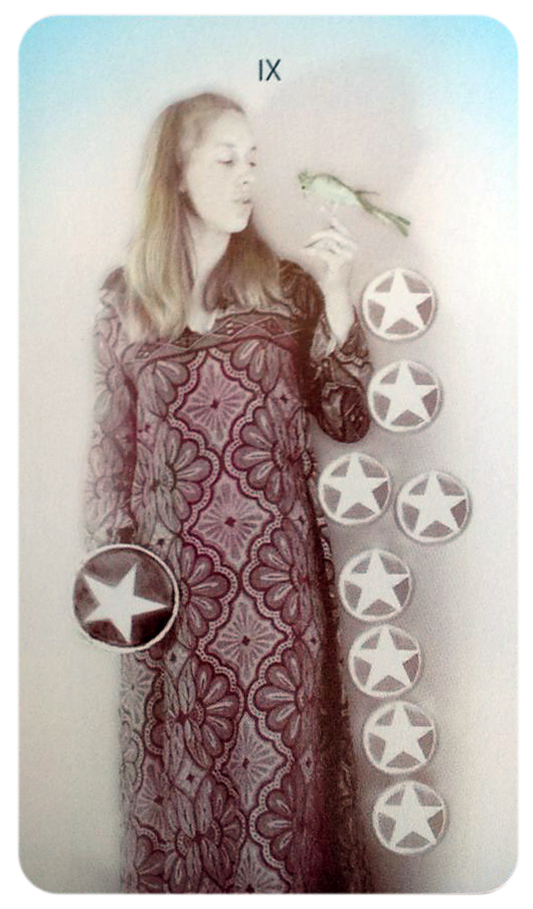




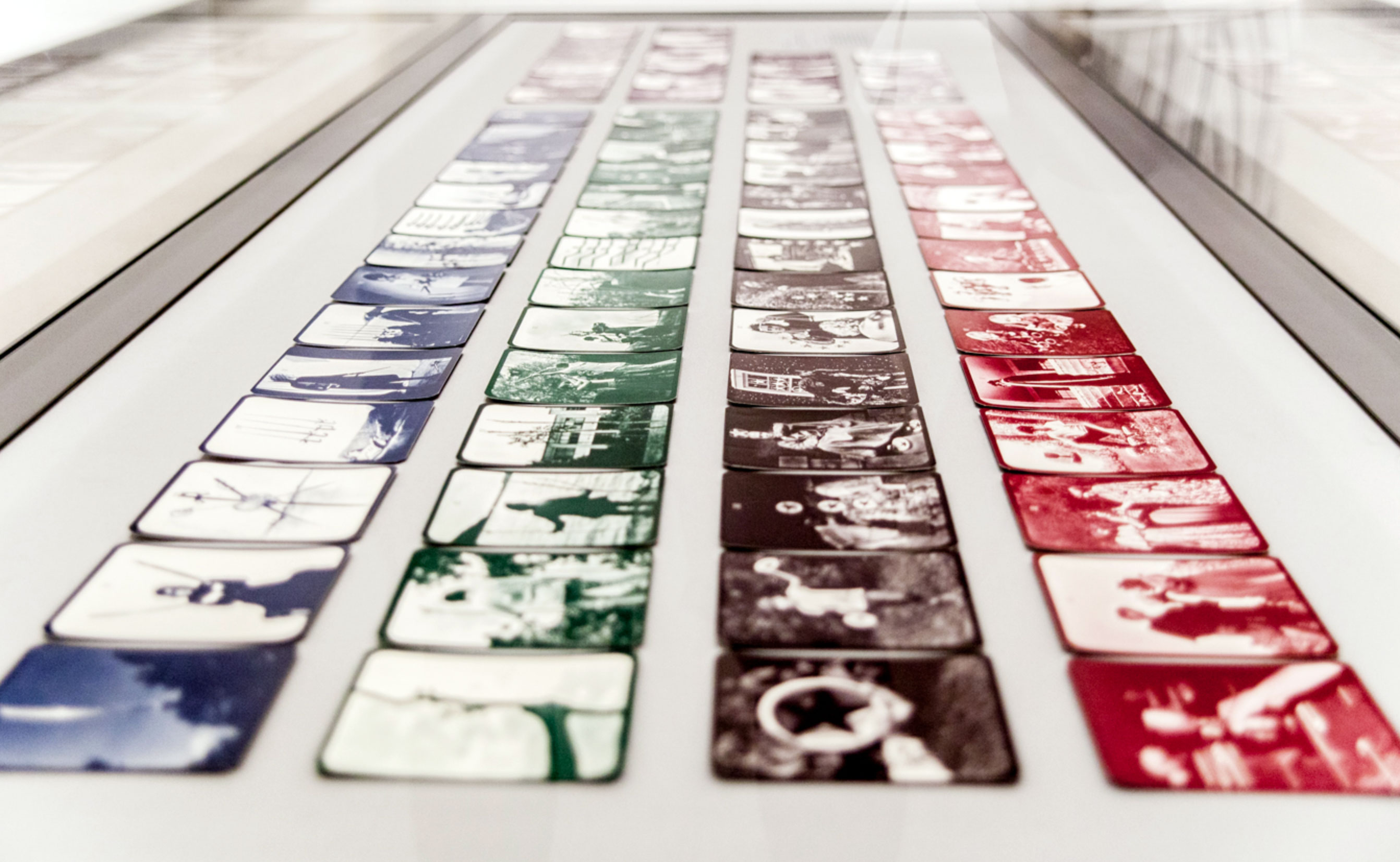
Bea Nettles (American, born Gainesville, Florida, 1946)
Mountain Dream Tarot: A Deck of 78 Photographic Cards
1975
Photographically illustrated tarot cards
Purchase, Dorothy Levitt Beskind Gift, 1977
The idea to create a set of photographic tarot cards came to Nettles in a dream during the summer of 1970, while she was on an artist’s residency in the mountains of North Carolina. She subsequently reinterpreted the ancient symbolism of the traditional tarot deck, enlisting friends and family members as models for photographs that she augmented with hand-painted additions. In 2007 the image Nettles created for the Three of Swords card was used as the disc graphic for Bruce Springsteen’s album Magic.
Installation view of the exhibition Dream States: Contemporary Photography and Video at the Metropolitan Museum of Art showing Bea Nettles’ Mountain Dream Tarot: A Deck of 78 Photographic Cards (1975)
Photo: Anders Jones
Artists often turn to dreams as a source of inspiration, a retreat from reason, and a space for exploring imagination and desire. In the history of photography, dream imagery has been most closely associated with the Surrealists, who used experimental techniques to bridge the gap between the camera’s objectivity and the internal gaze of the mind’s eye. While those modernist explorations were often bound to psychoanalytic theories, other photographers have pursued the world of sleep and dreams through deliberately open-ended works that succeed through evocation rather than description. The exhibition Dream States: Contemporary Photographs and Video presents 30 photographs and one video drawn from The Met collection, all loosely tied to the subjective yet universal experience of dreaming. The exhibition is on view at the Museum from May 16 through October 30, 2016.
Many of the works take the surrender of sleep as their subject matter. In photographs by Robert Frank, Danny Lyon, and Nan Goldin, recumbent figures appear vulnerable to the wandering gaze of onlookers, yet their inner worlds remain out of reach. Images of bodies floating and falling conjure the tumultuous world of dreams, and landscapes are made strange through the camera’s selective vision. Highlights include photographs by Paul Graham from his recent series Does Yellow Run Forever (2014); images from Sophie Calle’s earliest body of work, The Sleepers (1979), in which she invited friends and acquaintances to sleep in her own bed while she watched; and Anselm Kiefer’s Brünnhilde Sleeps (1980), a hand-painted photograph featuring French actress Catherine Deneuve recast as a Wagnerian Valkyrie. Also featured are recently acquired works by Shannon Bool, Sarah Anne Johnson, Jim Shaw, and Fred Tomaselli.
Dream States: Contemporary Photographs and Video is organised by Mia Fineman, Associate Curator; and Beth Saunders, Curatorial Assistant in the Department of Photographs at The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art
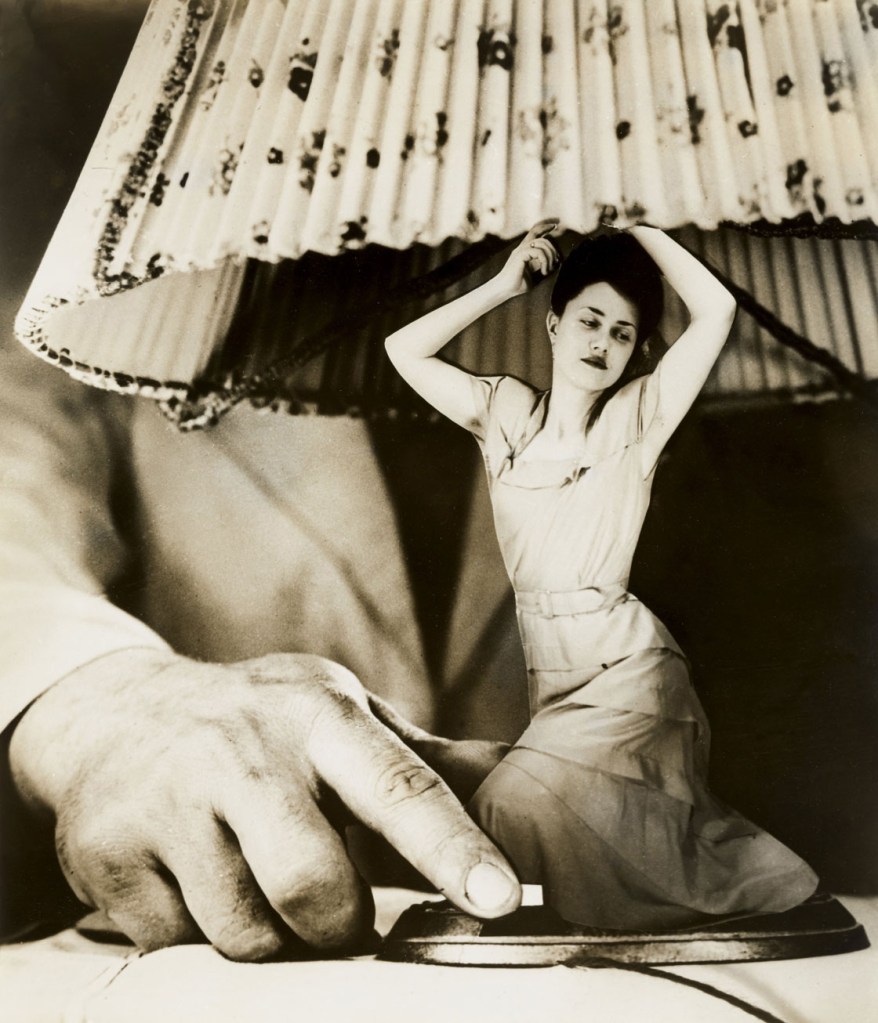

Grete Stern (Argentinian born Germany, 1904-1999)
Sueño No. 1: “Articulos eléctricos para el hogar” (Dream No. 1: “Electrical Household items”)
c. 1950
Gelatin silver print
Image: 26.6 x 22.9cm (10 1/2 x 9 in.)
Frame: 63.5 x 76.2cm (25 x 30 in.)
Twentieth-Century Photography Fund, 2012
In 1948 the Argentine women’s magazine Idilio introduced a weekly column called “Psychoanalysis Will Help You,” which invited readers to submit their dreams for analysis. Each week, one dream was illustrated with a photomontage by Stern, a Bauhaus-trained photographer and graphic designer who fled Berlin for Buenos Aires when the Nazis came to power. Over three years, Stern created 140 photomontages for the magazine, translating the unconscious fears and desires of its predominantly female readership into clever, compelling images. Here, a masculine hand swoops in to “turn on” a lamp whose base is a tiny, elegantly dressed woman. Rarely has female objectification been so erotically and electrically charged.

Adam Fuss (British, b. 1961)
From the series “My Ghost”
1999
Gelatin silver print
184.9 x 123.3cm (72 13/16 x 48 9/16 in.)
Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 2000
© Adam Fuss
With his large-scale photograms, Fuss has breathed new life into the cameraless technique that became the hallmark of modernist photographers such as Man Ray and László Moholy-Nagy in the 1920s. He created this image by blowing thick clouds of smoke over a sheet of photographic paper and exposing it to a quick flash of light. Evoking the wizardry of a medieval alchemist, Fuss fixes a permanent image of evanescence.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
1000 Fifth Avenue at 82nd Street
New York, New York 10028-0198
Phone: 212-535-7710
Opening hours:
Sunday – Tuesday and Thursday: 10am – 5pm
Friday and Saturday: 10am – 9pm
Closed Wednesday









































![Franck-François-Genès Chauvassaignes (French, 1831 - after 1900) 'Untitled [Female Nude in Studio]' 1856-1859 Franck-François-Genès Chauvassaignes (French, 1831 - after 1900) 'Untitled [Female Nude in Studio]' 1856-1859](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/chauvassaignes_seated-nude-web.jpg?w=650)
![Félix-Jacques-Antoine Moulin (French, 1800 - after 1875) 'Untitled [Two Standing Female Nudes]' c. 1850 Félix-Jacques-Antoine Moulin (French, 1800 - after 1875) 'Untitled [Two Standing Female Nudes]' c. 1850](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/moulin_two-nudes-standing-web.jpg?w=650)
![Unknown photographer (French) '[Seated Female Nude]' c. 1850 Unknown photographer (French) '[Seated Female Nude]' c. 1850](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/seated-female-nude.jpg)
![Julien Vallou de Villeneuve (French, 1795-1866) '[Standing Female Nude]' c. 1853 Julien Vallou de Villeneuve (French, 1795-1866) '[Standing Female Nude]' c. 1853](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/julien-vallou-de-villeneuve-standing-female-nude.jpg)
![Eugène Durieu (French, 1800-1874) 'Untitled [Seated Female Nude]' 1853-1854 Eugène Durieu (French, 1800-1874) 'Untitled [Seated Female Nude]' 1853-1854](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/durieu_nude_ph8976-web.jpg?w=650)
![Charles Alphonse Marlé (French, 1821 - after 1867) 'Untitled [Standing Male Nude]' c. 1855 Charles Alphonse Marlé (French, 1821 - after 1867) 'Untitled [Standing Male Nude]' c. 1855](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/marle_standing-male-nude-web.jpg?w=650)
![Nadar (French, Paris 1820 - 1910 Paris) '[Standing Female Nude]' 1860-1861 Nadar (French, Paris 1820 - 1910 Paris) '[Standing Female Nude]' 1860-1861](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/nadar-standing-female-nude.jpg)
![Unknown photographer (French) '[Nude with Mirror]' c. 1850 Unknown photographer (French) '[Nude with Mirror]' c. 1850](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/nude-with-mirror.jpg)
![Julien Vallou de Villeneuve (French, 1795-1866) '[Reclining Female Nude]' c. 1853 Julien Vallou de Villeneuve (French, 1795-1866) '[Reclining Female Nude]' c. 1853](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/julien-vallou-de-villeneuve-reclining-female-nude.jpg)

![Unknown photographer (French) '[Standing Female Nude]' c. 1856 Unknown photographer (French) '[Standing Female Nude]' c. 1856](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/standing-female-nude.jpg)
![Unknown photographer (French) '[Standing Male Nude]' c. 1856 Unknown photographer (French) '[Standing Male Nude]' c. 1856](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/standing-male-nude.jpg)

![Unknown photographer (French) '[Female Nude with Mask]' c. 1870 Unknown photographer (French) '[Female Nude with Mask]' c. 1870](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/female-nude-with-mask.jpg)





![Albert Londe (French, 1858-1917) Paul Marie Louis Pierre Richer (French, 1849-1933) '[Male Musculature Study]' c. 1890 Albert Londe (French, 1858-1917) Paul Marie Louis Pierre Richer (French, 1849-1933) '[Male Musculature Study]' c. 1890](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/male-study.jpg)
![Guglielmo Plüshow (Italian born Germany, 1852–1930) '[Young Male Nude Seated on Leopard Skin]' 1890s-1900s Guglielmo Plüshow (Italian born Germany, 1852–1930) '[Young Male Nude Seated on Leopard Skin]' 1890s-1900s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/plushow-young-male-nude-seated-on-leopard-skin.jpg)


![Lady Ottoline Violet Anne Cavendish-Bentinck Morrell (British, 1873-1938) '[Cavorting by the Pool at Garsington]' c. 1916 Lady Ottoline Violet Anne Cavendish-Bentinck Morrell (British, 1873-1938) '[Cavorting by the Pool at Garsington]' c. 1916](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/cavendish-bentinck-morrell-cavorting-by-the-pool-at-garsington.jpg)
![Lady Ottoline Violet Anne Cavendish-Bentinck Morrell (British, 1873-1938) '[Cavorting by the Pool at Garsington]' c. 1916 Lady Ottoline Violet Anne Cavendish-Bentinck Morrell (British, 1873-1938) '[Cavorting by the Pool at Garsington]' c. 1916](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/cavendish-bentinck-morrell-cavorting-by-the-pool-at-garsington-a.jpg)
![Edward Weston (American, Highland Park, Illinois 1886 - 1958 Carmel, California) '[Nude]' 1925 Edward Weston (American, Highland Park, Illinois 1886 - 1958 Carmel, California) '[Nude]' 1925](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/weston-nude.jpg)
![George Platt Lynes (American, East Orange, New Jersey 1907–1955 New York) '[Male Nude]' 1930s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/lynes-male-nude-1.jpg)













![Mark Morrisroe (American, 1959-1989) 'Untitled [Two Men in Silhouette]' c. 1987 Mark Morrisroe (American, 1959-1989) 'Untitled [Two Men in Silhouette]' c. 1987](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/16_morrisroe_untitled-web.jpg?w=650)




































![Adolph de Meyer (American born France, 1868-1949) '[Dance Study]' c. 1912 Adolph de Meyer (American born France, 1868-1949) '[Dance Study]' c. 1912](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/adolf-de-meyer-dance-study-web.jpg)












![Morton Schamberg (American, 1881–1918) '[View of Rooftops]' 1917 Morton Schamberg (American, 1881–1918) '[View of Rooftops]' 1917](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/schamberg-view-of-rooftops.jpg?w=815)







![Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Head of Man with Hat and Cigar]' c. 1960 from the exhibition 'Hipsters, Hustlers, and Handball Players: Leon Levinstein's New York Photographs, 1950-1980' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, June - October, 2010 Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Head of Man with Hat and Cigar]' c. 1960 from the exhibition 'Hipsters, Hustlers, and Handball Players: Leon Levinstein's New York Photographs, 1950-1980' at The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, June - October, 2010](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/leon-levinstein-head-of-man-with-hat-and-cigar.jpg)
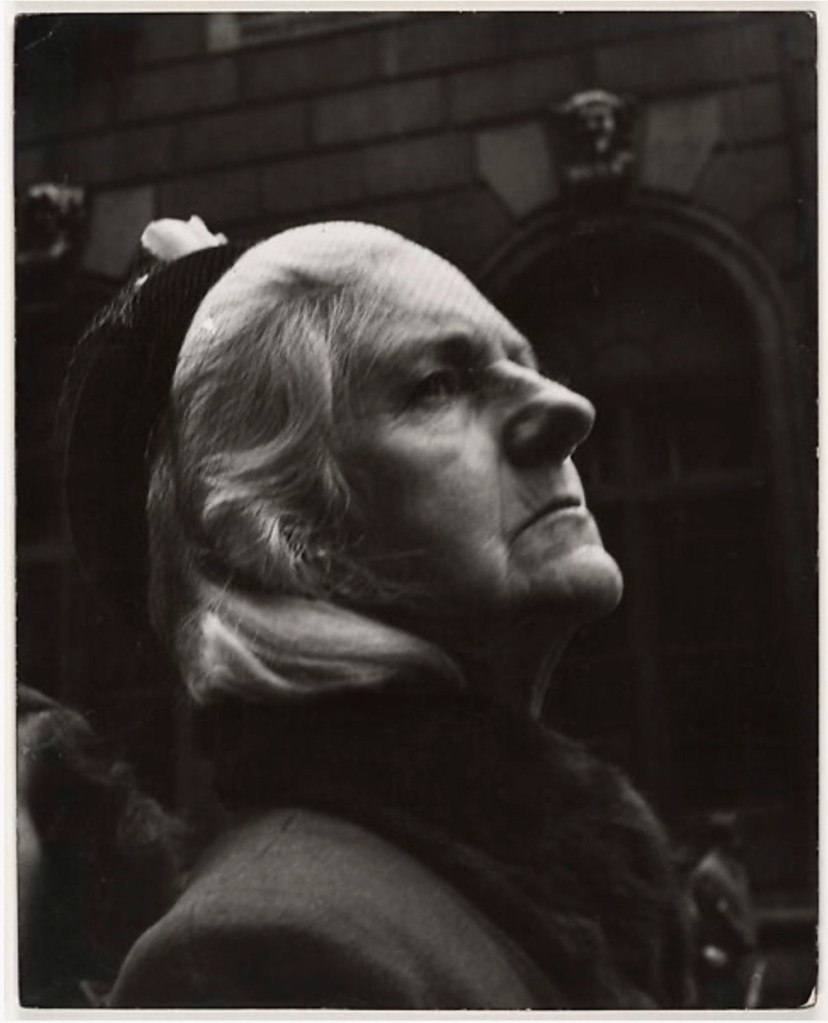








![Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Beach Scene: Woman Wearing Paper Bag Hat, Coney Island, New York]' 1950s Leon Levinstein (American, 1910-1988) 'Untitled [Beach Scene: Woman Wearing Paper Bag Hat, Coney Island, New York]' 1950s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/leon-levinstein-beach-scene.jpg?w=809)



























You must be logged in to post a comment.