Exhibition dates: 29th January – 11th May 2014

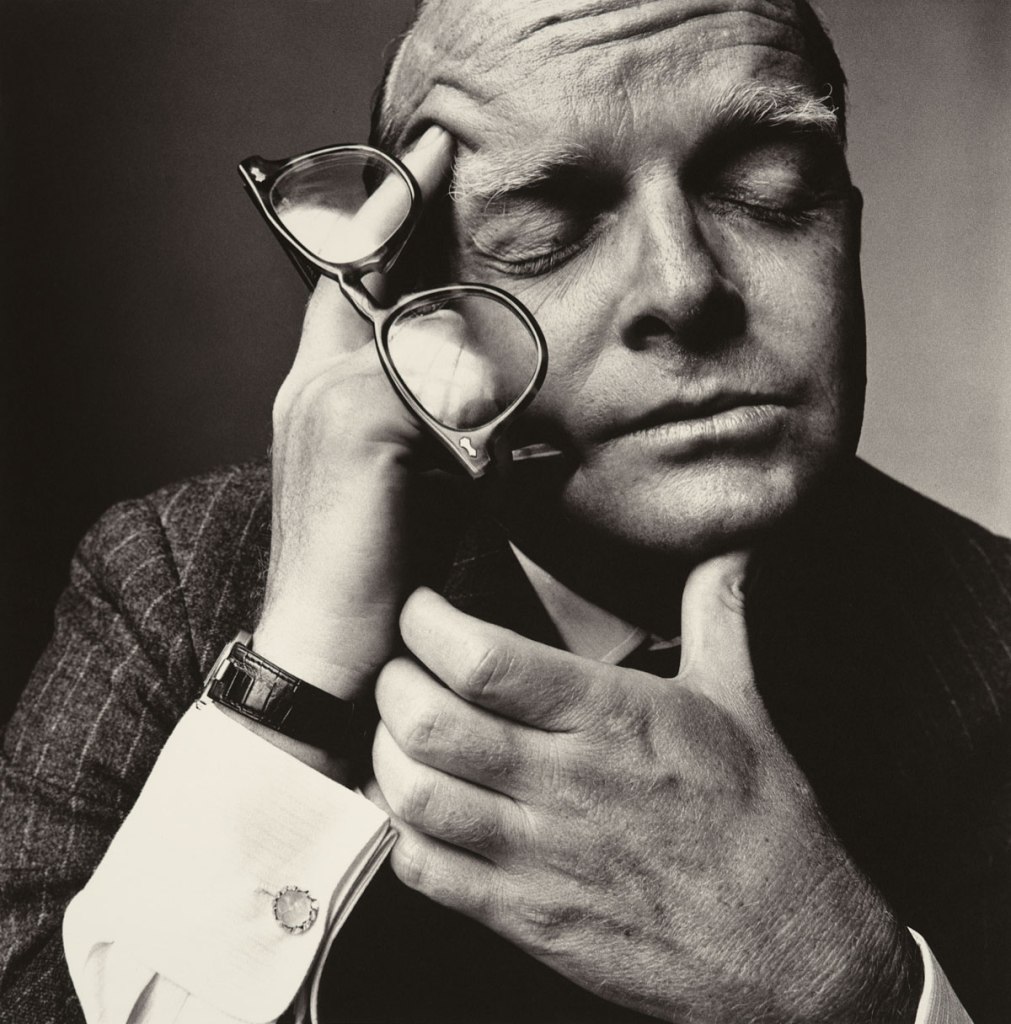
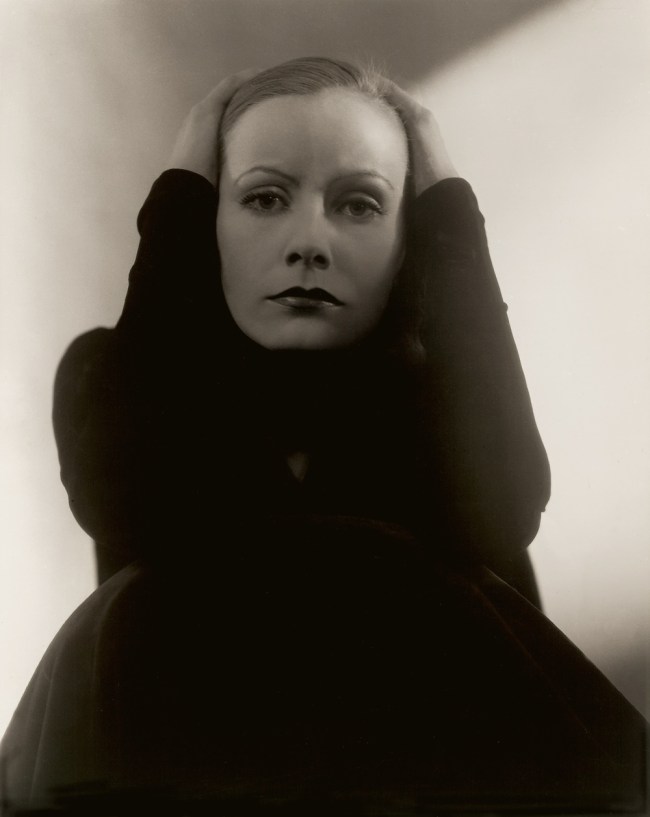
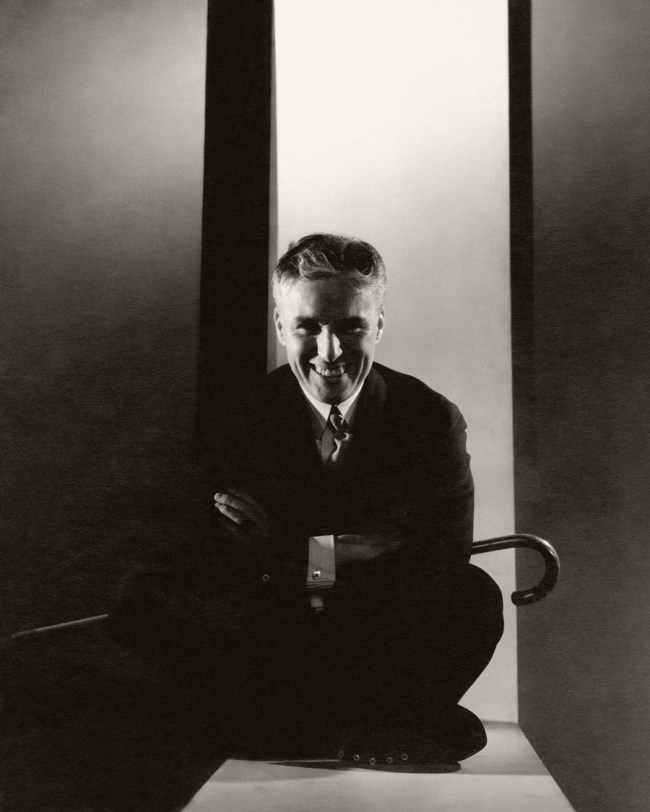
Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
The Versatile Jean Cocteau
1949
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
He “photographed a little bit of everything: animals, Paris, the homeless, underwater, nudes, advertising, fashion and, above all, celebrities portraits, from Ali, Einstein, Churchill, Hepburn, Warhol, Hitchcock and, of course, Marilyn Monroe.”
You could say that he was a versatile photographer, doing everything to pay the bills and anything to make interesting images. He never stopped experimenting with the image, but it is the “straight” portraits that I find are his strongest work. Not the “jump” photos, Monroe, or the surreal experiments with Dalí, much as they delight, but the portraits of Hepburn, Einstein and Churchill for example.
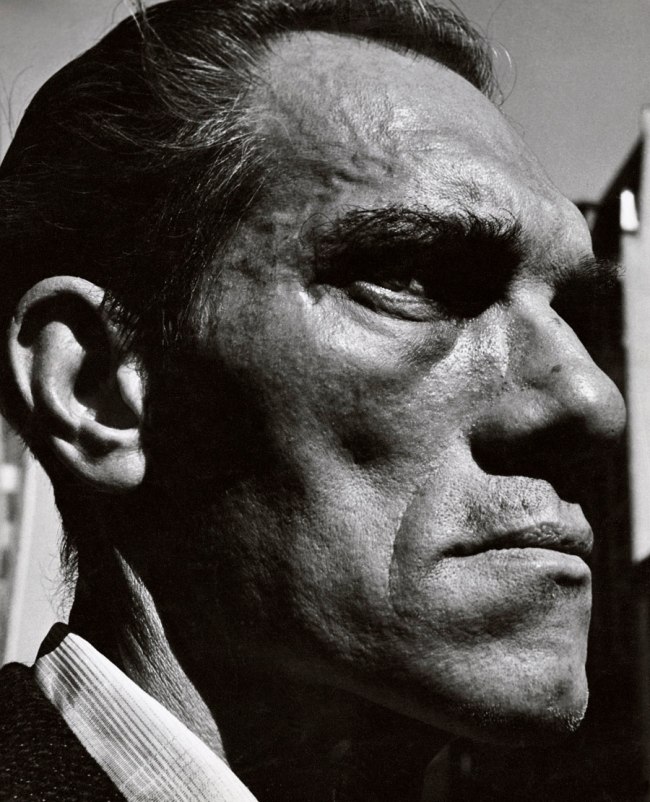
Look at the photograph of Winston Churchill (1951, below). What a way to portray the great man. The bulk of the overcoat, the slope of the shoulders (evincing a certain weariness), the famous Homburg hat pulled down on the head, the leader staring into the tranquil landscape. But what makes the image is the seam down the back of the overcoat which speaks to history itself – the backbone of the country, the never say die spirit, stiff upper lip, the rock of the British empire which Nazism could not defeat – epitomising the British bulldog spirit. Cometh the hour, cometh the man. Solid. Immovable. What a glorious photograph to capture that essence.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Elysée Lausanne for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Shortly before World War I, the greatest sensation in Paris was the Russian Imperial Ballet under Serge Diaghilev. The divine Nijinsky and Pavlova were dancing for him, Stravinsky composed, Picasso, Bakst, and Chagall were painting scenery for him. To work for Diaghilev was the highest accolade for an artist. Jean Cocteau approached Diaghilev and asked: ‘What can I do for you?’ Diaghilev looked at him and answered: ‘Etonne-moi!’ (‘Astonish me!’) These two words can be considered as a motto, as a slogan for the development of the modern art which followed.”
Philippe Halsman
“Photography is a separate form of expression since it falls between two art forms… It’s not only trying to give us a visual impression of reality, like painting and graphic arts, but also to communicate and inform us the way writing does. No writer should be blamed for writing about subjects that exist only in his imagination. And no photographer should be blamed when, instead of capturing reality, he tries to show things that he has only seen in his imagination.”
Philippe Halsman
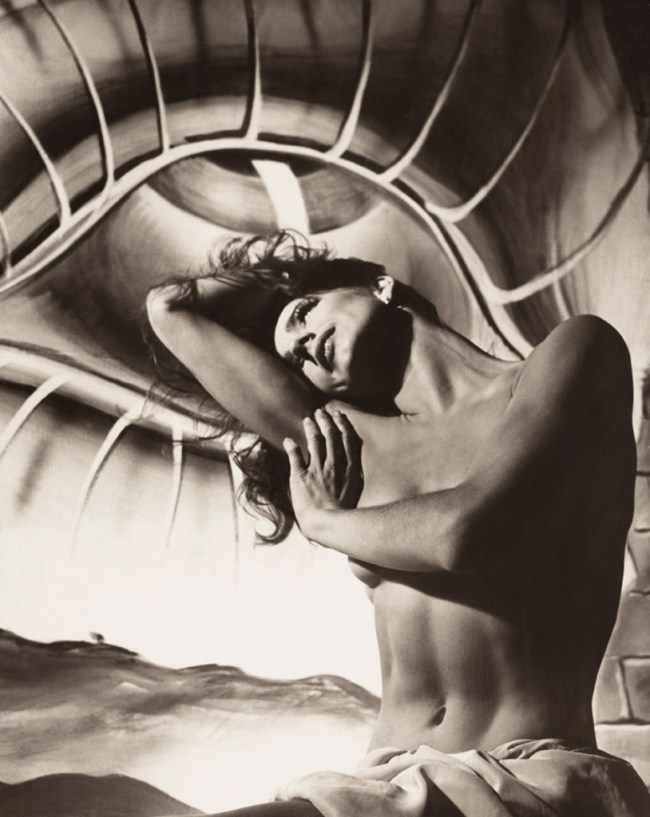

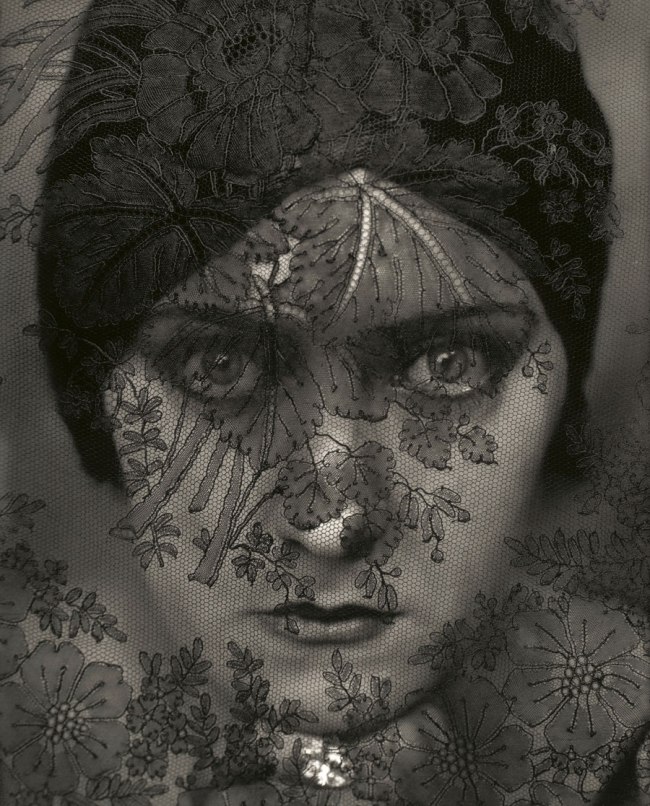
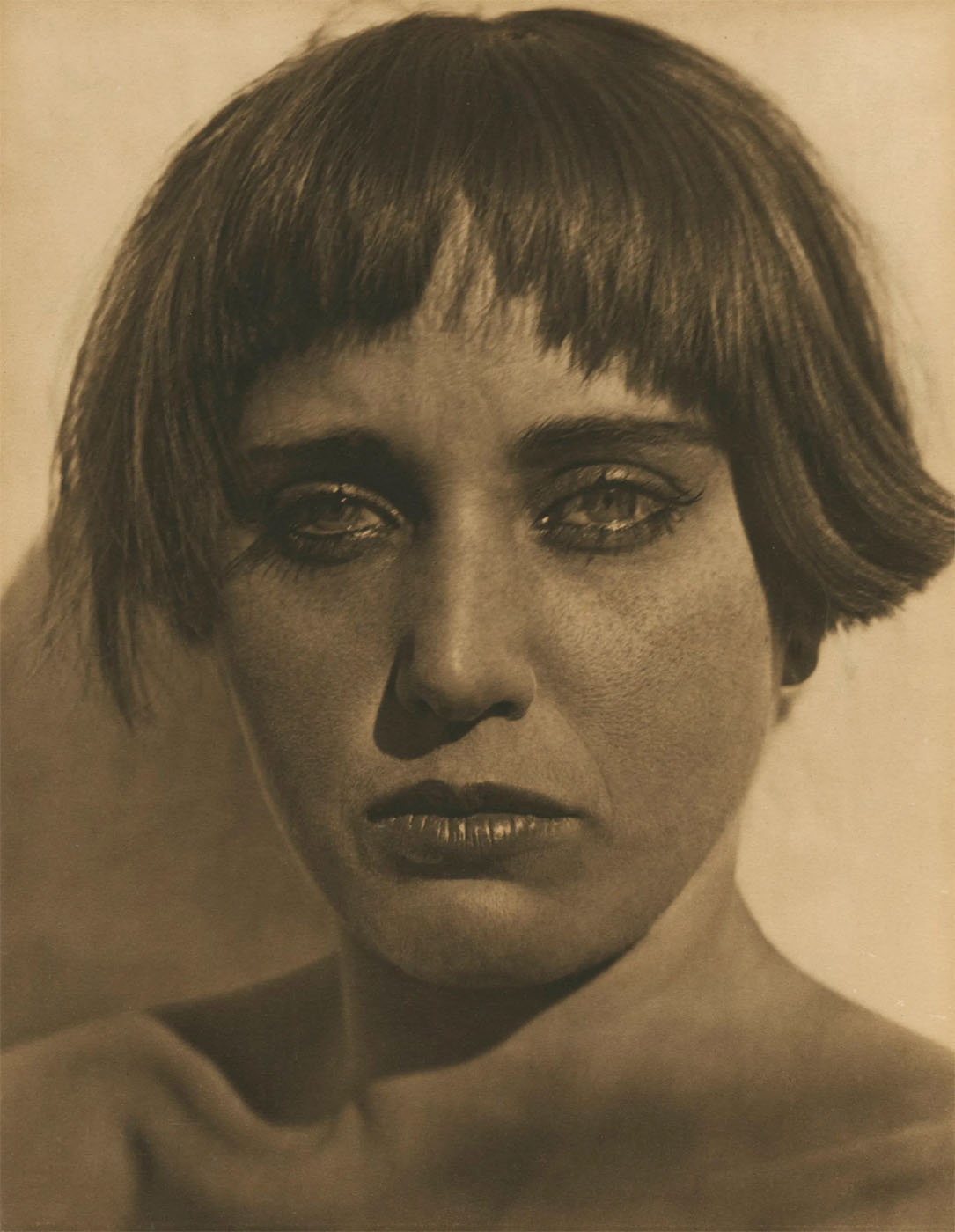
Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
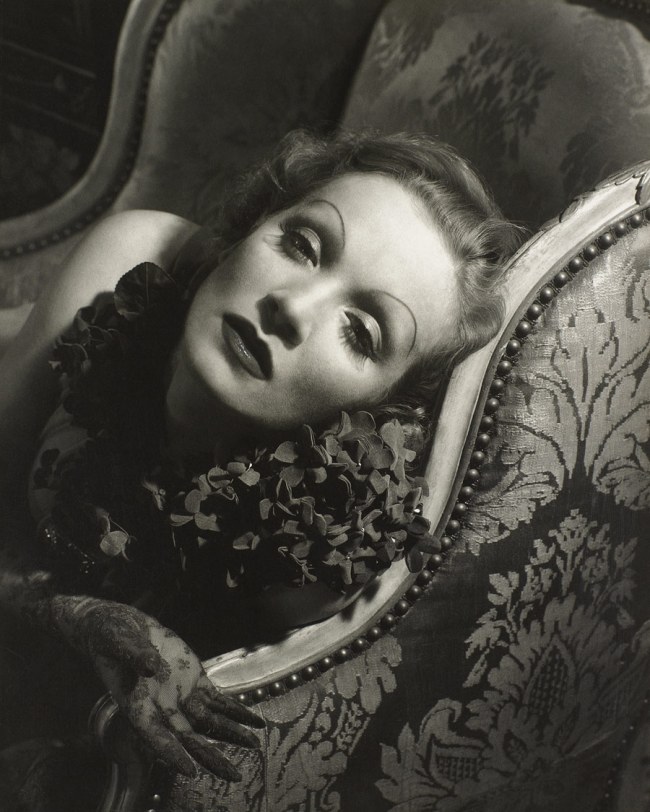
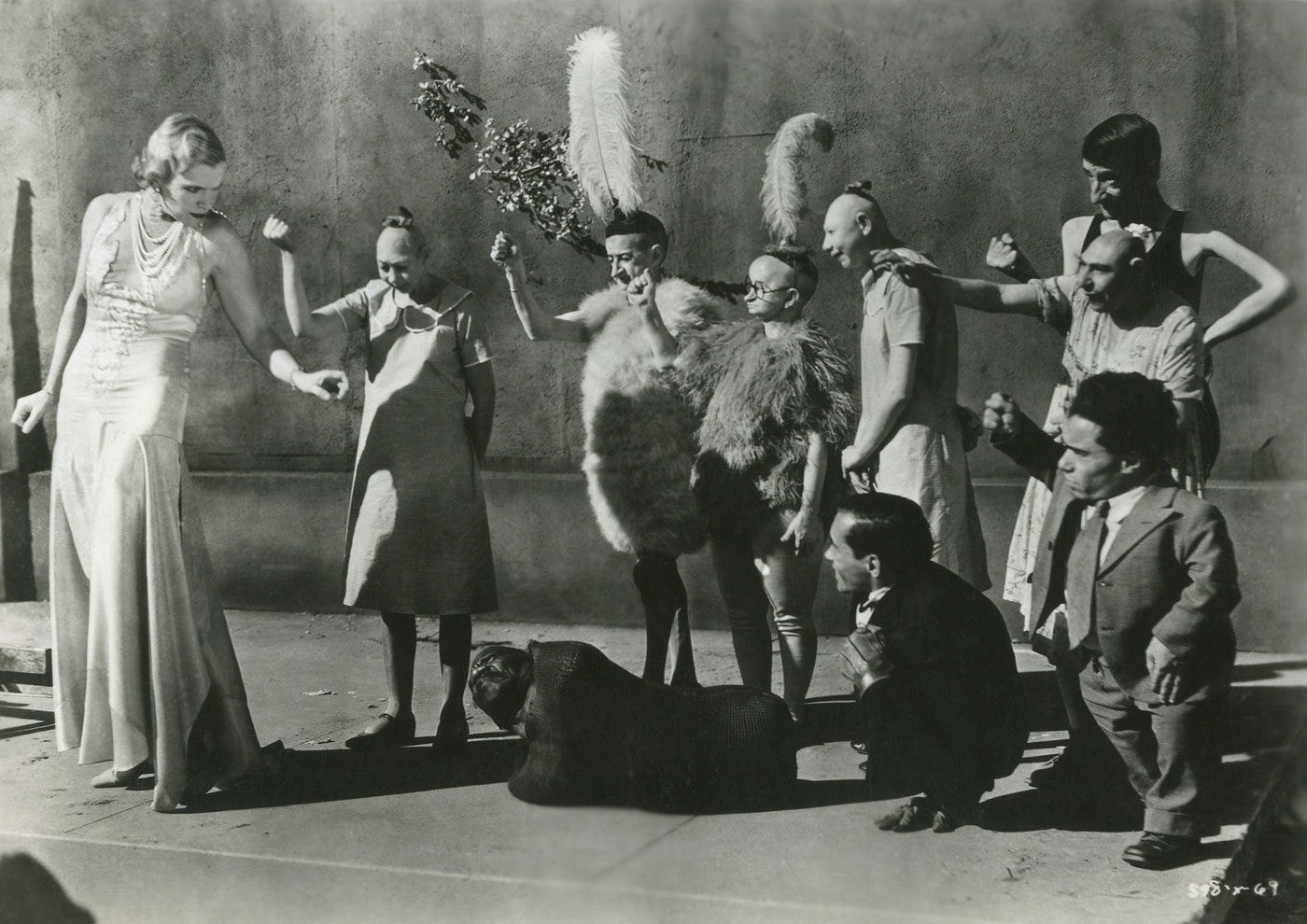
Folle Iseult
1944
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
“In my serious work I am striving for the essence of things and for goals which are possibly unobtainable. On the other hand, everything humorous has great attraction for me, and a childish streak leads me into all kinds of frivolous endeavour.”
Photographer Philippe Halsman had an exemplary career. Over a forty-year period, in Paris during the 1930s and in New York from 1940 on, he developed a broad range of activities (portraits, fashion, reportage, advertisements, personal projects, commissions from individuals and institutions). The Musée de l’Elysée presents the first study dedicated to his entire body of work, with a selection of over 300 pieces.
This project, produced in collaboration with the Philippe Halsman Archive, includes many exclusive unseen elements of the photographer’s work (contact sheets, annotated contact prints, preliminary proofs, original photomontages and mock-ups). The exhibition shows Philippe Halsman’s creative process and reveals a unique approach to photography: a means of expression to explore.
Born in 1906 in Riga, Latvia, Halsman studied engineering in Dresden before moving to Paris, where he opened a photographic studio in 1932. His years in Paris already heralded the approach he was to develop throughout his long career. A studio and reportage photographer, Halsman took inspiration from the contemporary art scene and participated in promoting it. Though he specialised in portraiture, he also branched out into advertising and publishing, which were thriving at the time. In 1940, the German invasion brought Halsman’s prosperous career to a halt, leading him to flee with his family to New York. Though initially unknown, he succeeded in establishing himself on the American market in under a year, and his studio soon became successful. Halsman stood out for his “psychological” approach to portraiture.
He distinguished himself in this area with his vast portrait gallery of celebrities (actors, industrialists, politicians, scientists, writers). Some of these images, such as Audrey Hepburn, Marilyn Monroe, Winston Churchill or Albert Einstein, became icons. He produced the largest number of covers (101) for Life magazine, the first weekly magazine to be illustrated only by photographs.
Halsman’s photography is characterised by a direct approach, masterful technique and a particular attention to detail. His work testifies to his constant research and his interest in all forms of technical and aesthetic experimentation, which he applied to a wide variety of subjects. For Halsman, photography was an excellent way of giving his imagination free reign. He was especially interested in mises en scène – in the form of single images or fictional series. He met Salvador Dalí in 1941 and the artist turned out to be the ideal accomplice. Their fruitful collaboration lasted 37 years. Philippe Halsman also introduced innovations through more personal creations such as the “photo-interview book” or ‘jumpology’.
Press release from the Musée de l’Elysée Lausanne website
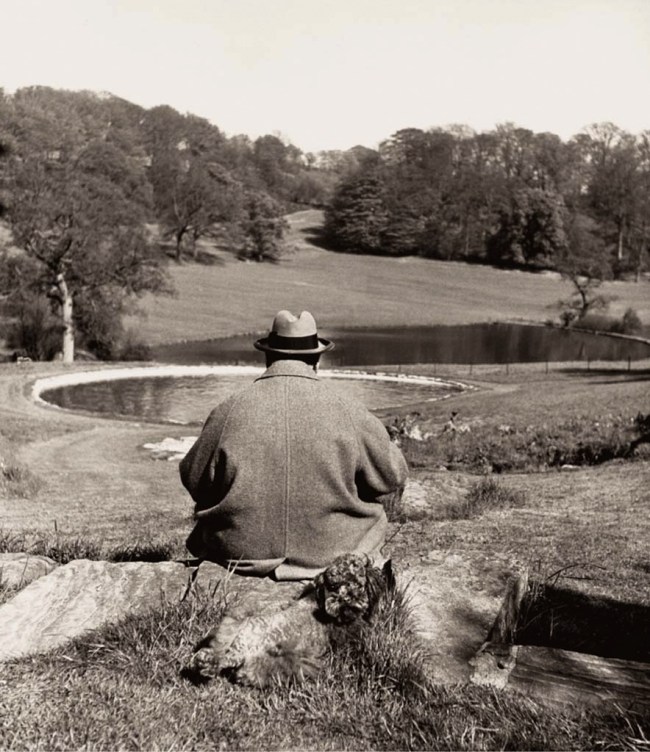

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Winston Churchill
1951
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
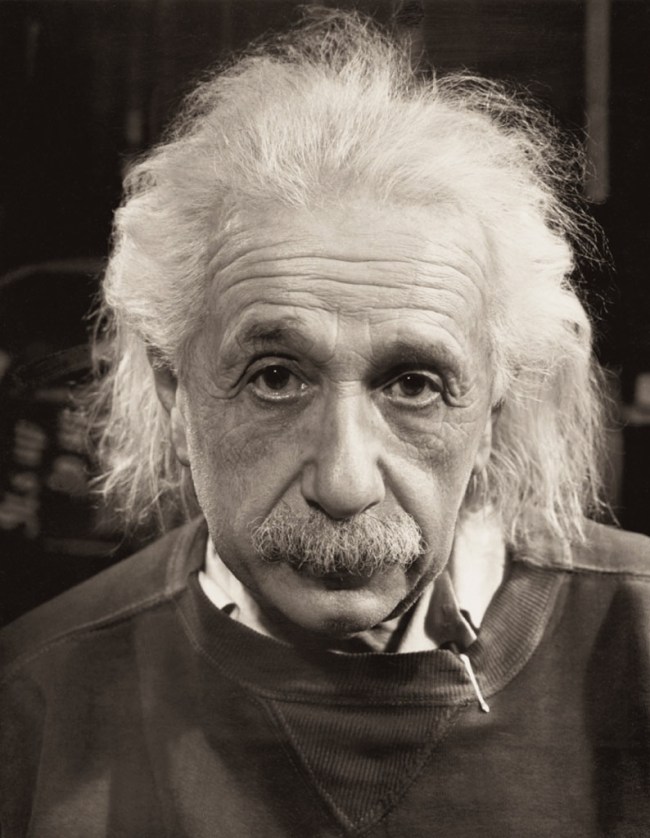

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Albert Einstein
1947
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
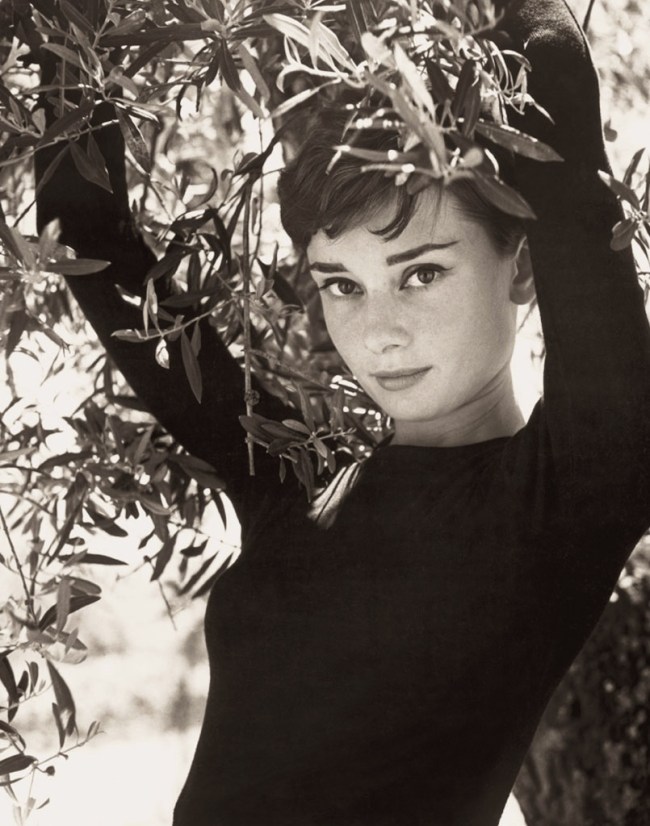

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Audrey Hepburn
1955
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
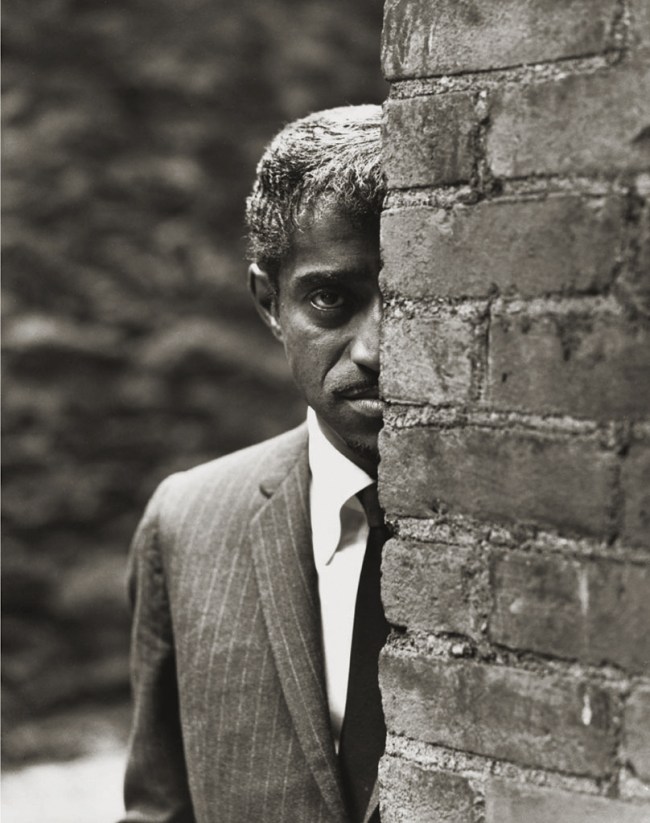

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Sammy Davis Jr
1965
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
Presentation of the exhibition
In 1921, Philippe Halsman found his father’s old camera, and spoke of a “miracle” when he developed his first glass plates in the family’s bathroom sink. He was 15 years old, and this was the first encounter with photography of someone who was to become one of the leading photographers of the 20th century. This exhibition, produced by the Musée de l’Elysée in collaboration with the Philippe Halsman Archive, showcases the American photographer’s entire career for the first time, from his beginnings in Paris in the 1930s to the tremendous success of his New York studio between 1940 and 1970.
Halsman was able to go to Paris thanks to the support of French minister Paul Painlevé – whose son Jean, a scientific filmmaker, gave him one of the best cameras of the time upon his arrival. He remained in Paris for ten years, until 1940. Over that period, he collaborated with the magazines Vogue, Vu and Voilà and created portraits of numerous celebrities like Marc Chagall, Le Corbusier and André Malraux. He exhibited his work several times at the avant-garde Pléiade gallery, alongside photographers like Laure Albin Guillot, whose work was exhibited at Musée de l’Elysée in 2013.
Fleeing Nazism, he left Paris in 1940 and moved to New York. There, he worked for many American magazines including Life, which brought him into contact with the century’s top celebrities – Marilyn Monroe, Rita Hayworth, Duke Ellington, the Duke and Duchess of Windsor, Richard Nixon, Albert Einstein to name only a few. Halsman shot 101 covers for Life magazine. Far from restricting himself to photographing celebrities, throughout his whole life Halsman never stopped experimenting and pushing the limits of his medium. He collaborated with Salvador Dalí for over thirty years and invented ‘jumpology’, which consisted in photographing personalities in the middle of jumping, offering a more natural, spontaneous portrait of his subjects.
The exhibition Philippe Halsman, Astonish me! is divided into four sections illustrating memorable periods, collaborations and themes in the photographer’s work and life.
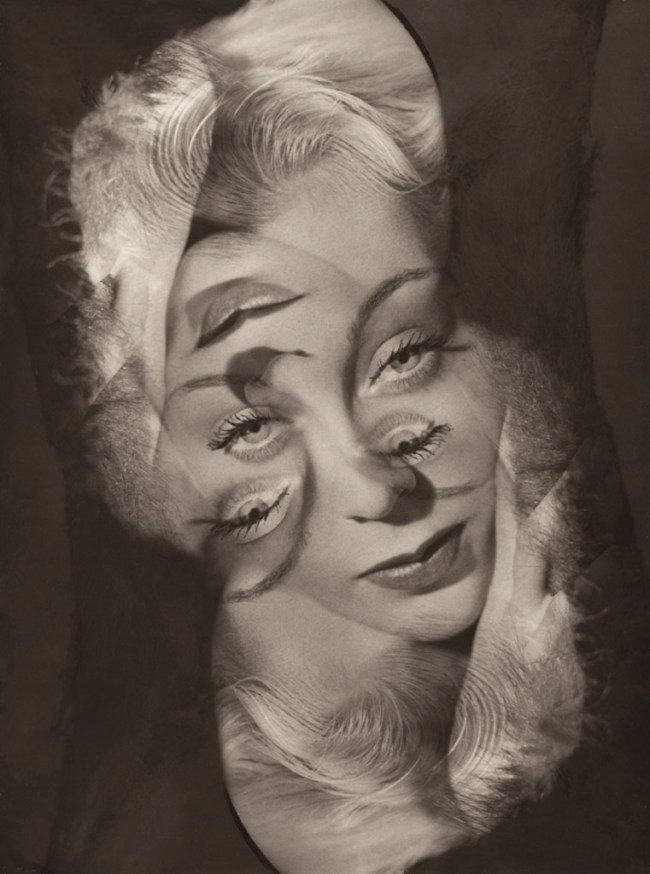

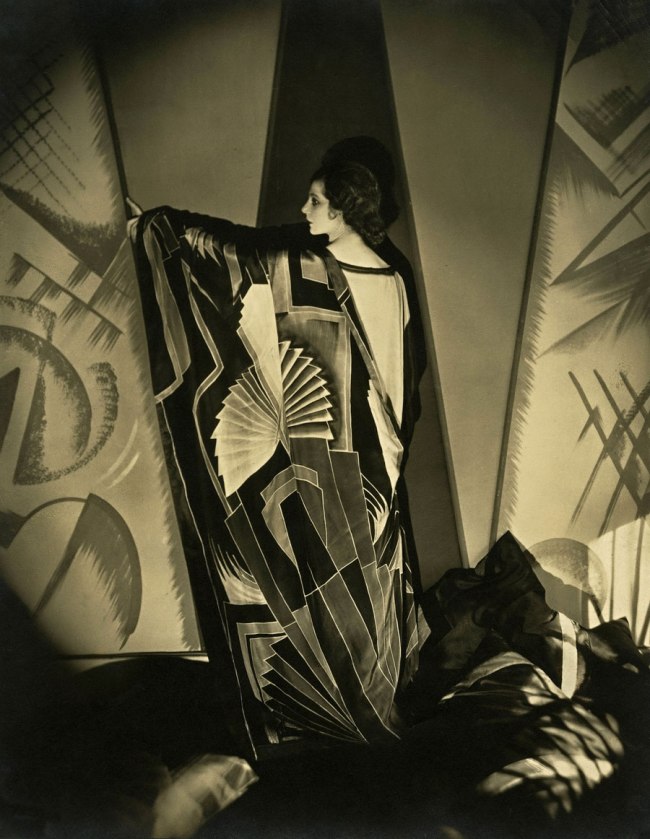
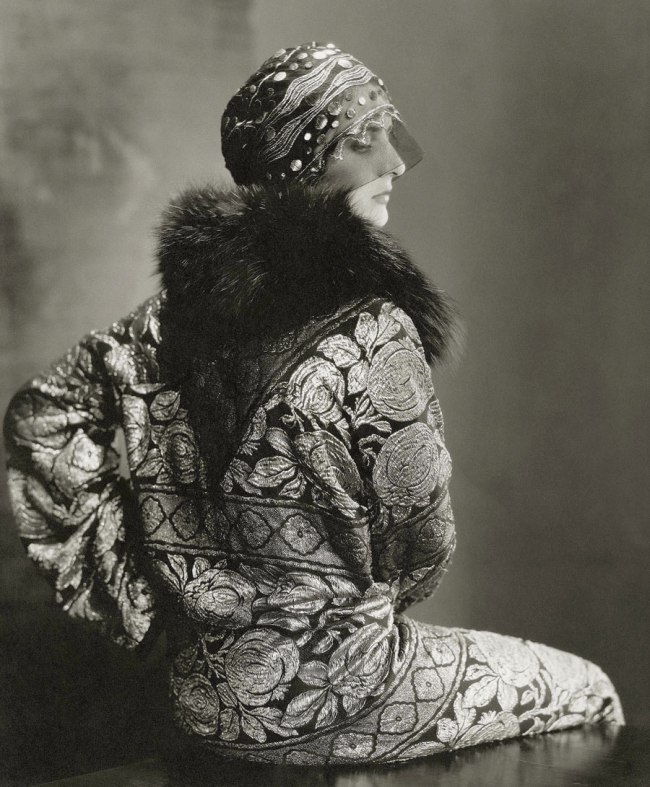
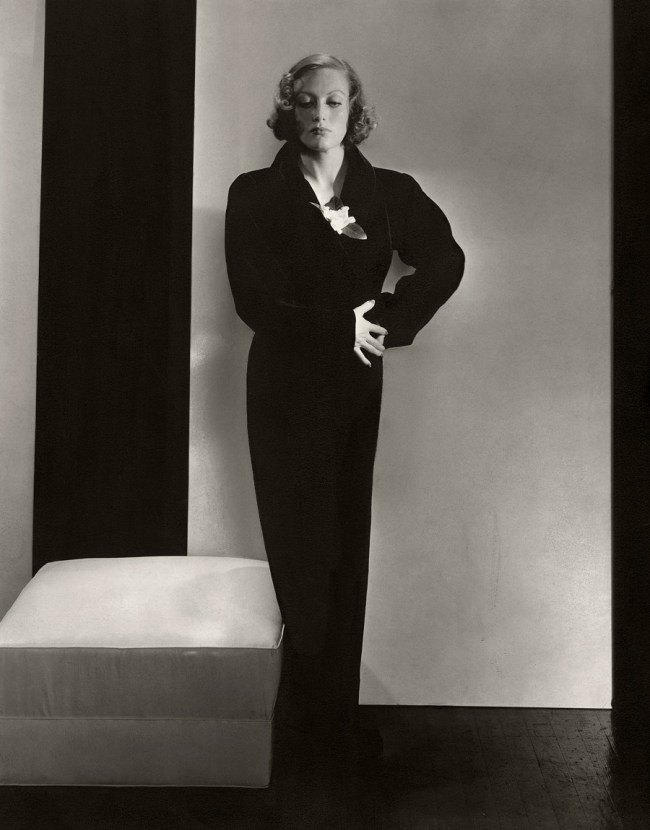
Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Expérimentation pour un portrait de femme (Experimentation for a portrait of a woman)
1931-1940
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos

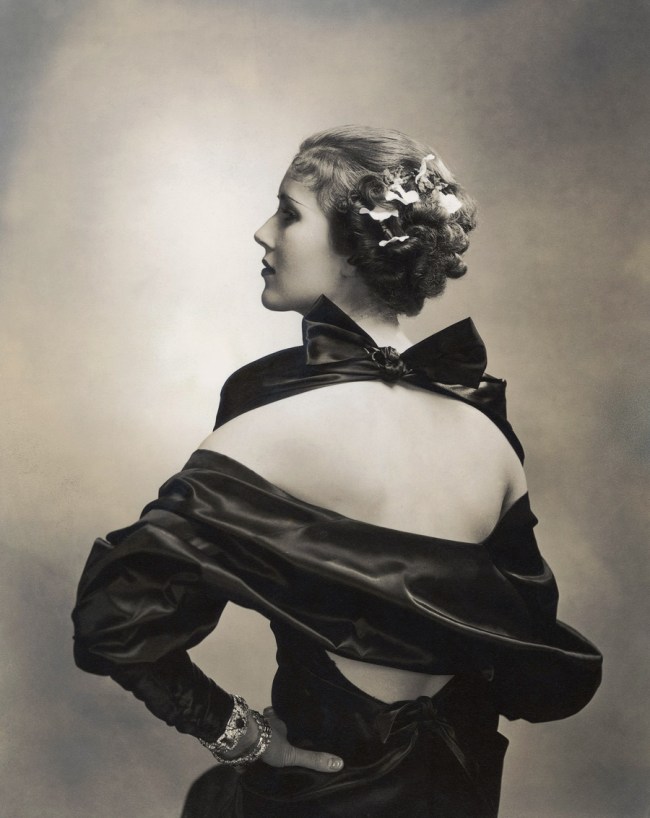
Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Affiche exposition Pleiade (Poster for exhibition at La Pléiade gallery)
1936
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
“When I arrived in America in 1940 I had to adapt to the American style, that is to say, produce photographs that were technically perfect, clear, precise and properly modelled by the light without being distorted. Once, to accentuate the coldness of a rainy landscape I added a blue gelatin to my transparent film. Wilson Hicks took this gelatin off saying: ‘You’re cheating, Philippe’. Any hint of artifice was considered dishonest.”
Philippe Halsman
Paris in the 1930s
Philippe Halsman was born in Riga, Latvia in 1906. When he was 22, his father died in a hiking accident in Austrian Tyrol, and Philippe Halsman was wrongly convicted of his murder in a highly anti-Semitic climate. He was freed thanks to his sister’s support; she organised the support of prominent European intellectuals, who endorsed his innocence.
He went to Paris, where he began his career as a photographer, quickly distinguishing himself through his portrait technique. He explored various genres, such as views of Paris, nudes and fashion. His work was exhibited three times at the La Pléiade gallery, a famous avant-garde gallery where artists like Man Ray, André Kertész and Brassaï presented their works.
Focus on La Pléiade gallery
Founded by publisher Jacques Schiffrin in the spring of 1931 and located in the heart of the Latin Quarter, this art gallery was one of the first to present photographic exhibitions, and it started specialising in this field in April 1933 under directorship of Rose Sévèk. Dedicated to contemporary photography, the program incorporated its new practices and applications. It was one of the places where New Photography was promoted in the form of solo, group or thematic exhibitions.
It was probably through his friend Jean Painlevé that Halsman entered in contact with La Pléiade gallery. He was given a first solo exhibition, Portraits and Nudes, which ran from March 28 to April 30, 1936. The following year, his name became associated with the New Vision movement in the context of two group exhibitions: Portraits of Writers (April 17 to May 14, 1937) which included Emmanuel Sougez, Rogi André, Roger Parry and others; La Parisienne de 1900… à 1937 (June 4-30, 1937), which included photographs by Florence Henri and Maurice Tabard. It was one of the last exhibitions at the gallery, which was sold a few months later in October, to Paul Magné.
Having initially been unable to flee wartime Paris, Halsman finally received an emergency visa in 1940 thanks to a letter from Albert Einstein to Eleanor Roosevelt, making it possible for him to join his family, who had left six months earlier.
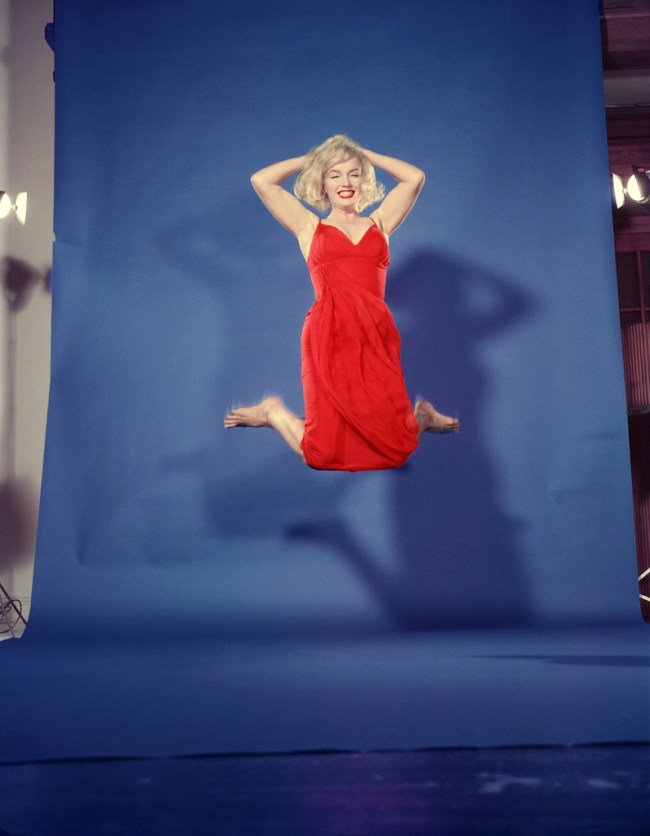

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Marilyn Monroe jump
1959
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
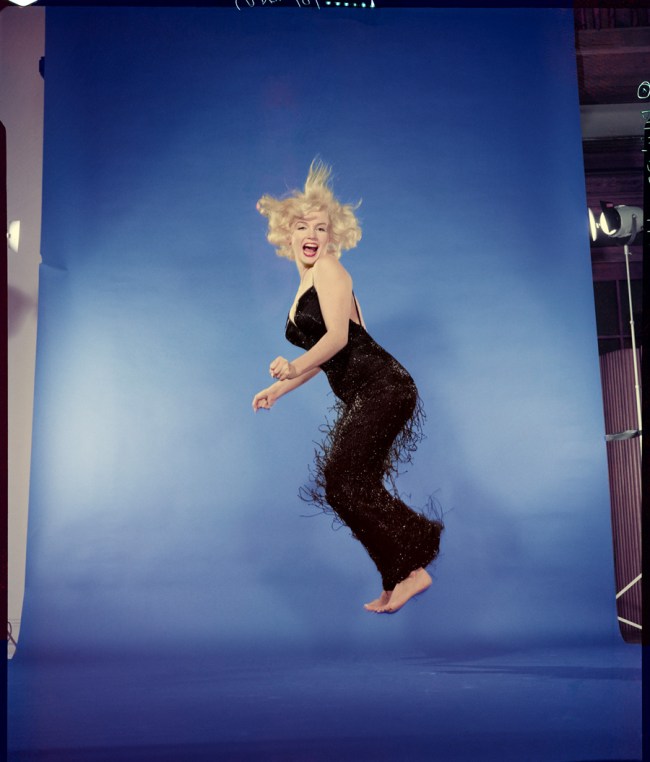

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Marilyn Monroe jump
1959
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
“Of the group of starlets only Marilyn emerged. Still photographers discovered her natural talent for flirting with the camera lens, and her blond looks of instant availability made her America’s most popular pin-up girl. Marilyn felt that the lens was not just a glass eye, but the symbol of the eyes of millions of men. She knew how to woo this lens better than any actress I ever photographed.”
Philippe Halsman
Portraits
Champion of the direct approach, Philippe Halsman also experimented with a wide range of techniques in order to capture the essence of his subjects and express their individuality. Many portraits became iconic images such as his 101 Life magazine covers.
Focus on Marilyn Monroe
Philippe Halsman photographed Marilyn Monroe on several occasions between 1949 and 1959. This important corpus traces the actress’s career and reveals the photographer’s varied approach during this period. In the autumn of 1949, Halsman was sent to Hollywood by Life magazine to do a report on eight young models embarking on acting careers. Halsman photographed them in four scenes he imposed (the approach of a monster, embracing a lover, reacting to a funny story and drinking a favourite drink). He quickly noticed the talents of the young Marilyn Monroe.
This opinion was confirmed three years later when Life commissioned him to do a feature on the actress entitled “The Talk of Hollywood”. These shots, some in colour and some in black and white, illustrated the actresses’s everyday life and talents. She acted out a series of scenes, humorously presenting the different stages of the strategy she used when being interviewed for roles. Most importantly, Halsman created several emblematic images of the actress and helped promote her by giving her a chance to have her first Life magazine cover.
In 1954, Halsman welcomed Marilyn Monroe to his New York studio. Halsman’s photographs reflect the ‘sex symbol’ image she cultivated. However, he managed to shoot a more natural portrait of the actress by asking her to jump in the air. There was only a few images of this type because when Halsman explained his ‘jumpology’ concept, Marilyn Monroe, frightened by the idea of revealing her personality, refused to repeat the experiment.
It took five years before she agreed to go along with ‘jumpology’. Marilyn Monroe had become a star by the time Life magazine offered to feature her on its cover in 1959 to illustrate a major article on Philippe Halsman’s ‘jumpology’. She treated it as a request for a performance. Over the course of three hours, the actress jumped over 200 times in front of Halsman’s lens, in order to achieve the “perfect jump”.
Several times Halsman suggested to Marilyn Monroe that they continue this collaboration, but without success. The actress was then at a turning point in her life that was foreshadowing her decline. However, Halsman continued his photographic work on the actress by creating new images, or more precisely variations of portraits he had previously shot. These compositions – montages of prints cut out and rephotographed together expressing the idea of movement, or reworked images transposed in negative format are characteristic of Halsman’s approach in the 1960s. Ten years later, he created a portrait of Marilyn Monroe as Chairman Mao, as requested by Salvador Dalí during his guest editorship of the French edition of Vogue magazine (December 1971 – January 1972).

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Alfred Hitchcock for the promotion of the film ‘The Birds’
1962
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos

Cover of Life magazine with a portrait of Marilyn Monroe jumping by Philippe Halsman, November 9, 1959
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
Mises en scène
Halsman was often commissioned to photograph the contemporary art scene for magazines including dance, cinema and theatre. Collaborations with artists were important in Halsman’s career and inspired performances resulting in picture stories or striking individual images.
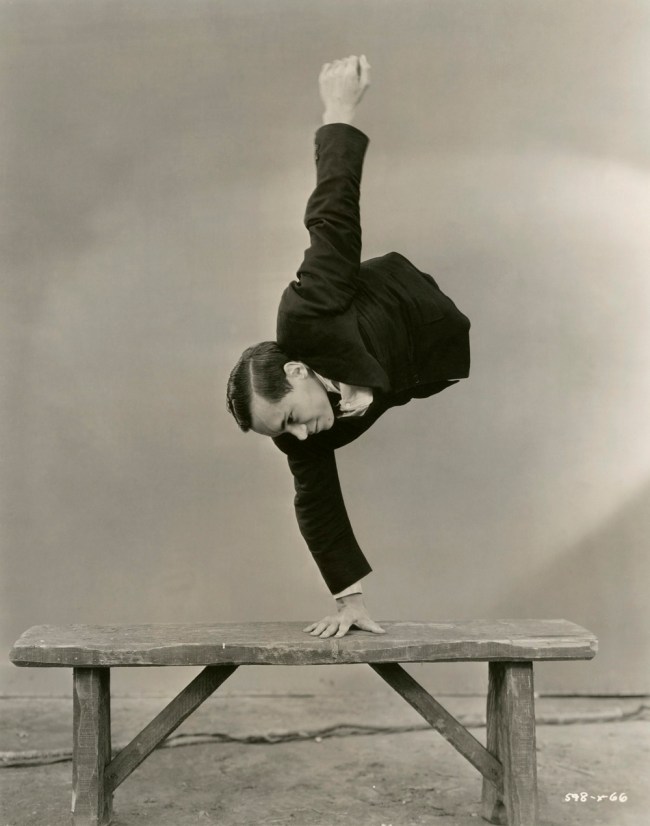
Focus on ‘Jumpology’
In 1950, Halsman invented ‘jumpology’, a new way of creating spontaneous, authentic portraits: “When you ask a person to jump, his attention is mostly directed toward the act of jumping and the mask falls so that the real person appears”. Over a period of ten years, Halsman created an extraordinary gallery of portraits of American society.
Containing over 170 portraits, Philippe Halsman’s Jump Book illustrated a new “psychological portrait” approach developed by Philippe Halsman in the 1950s. His method was systematic. During commissioned work, at the end of shooting sessions Halsman would ask his subjects if they would agree to take part in his personal project, and then the jumps were done on the spot. In this way he managed to photograph hundreds of jumps. Producing these shots was in fact simple: his equipment was limited to a Rolleiflex camera and an electronic flash, and as he pointed out, the only constraint was the height of the ceiling.
Although these portraits are characterised by their lightheartedness, Halsman viewed ‘jumpology’ as a new scientific tool for psychology. While the subject was concentrating on his jump, “the mask” fell, and it was this moment that the photographer needed to capture. Over the time that he was conducting this experiment, Halsman noticed the great diversity of the various participants’ postures, and discerned in these gestures – leg positions, arm positions, facial expressions and other details revealing signs of their character, expressed unwillingly.
The arrangement of the portraits in Philippe Halsman’s Jump Book illustrated these views. Halsman made a distinction in the form of two corpuses. First he presented influential personalities from different fields (political, industrial, scientific, theological, literary, etc…) resulting in a gallery of unexpected portraits that contrasted with their official image. For this project, Halsman also enjoyed the collaboration of actors, singers, dancers, etc… Conscious of the special character of their performances, Halsman assembled their images in a second part, categorised by discipline. This organisation was punctuated by various themes like American flamboyance, British reserve, and the eloquence of actresses’ legwork. The layout played with different photograph formats and assemblages.
Although it only presented well-known personalities, the publication nevertheless encouraged the democratisation of this practice: it ended with a photograph of Philippe Halsman jumping on a beach, with a caption asking: “How do you jump?”
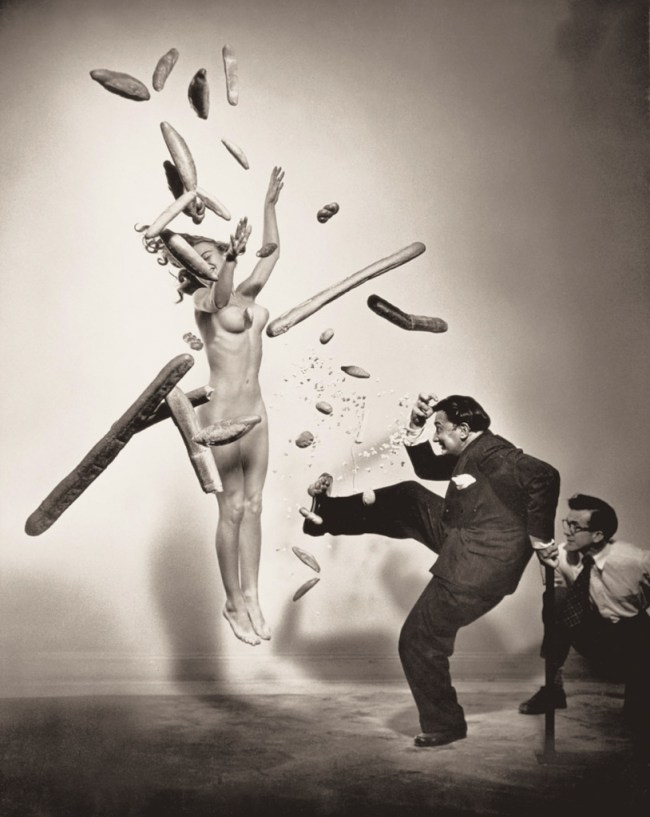
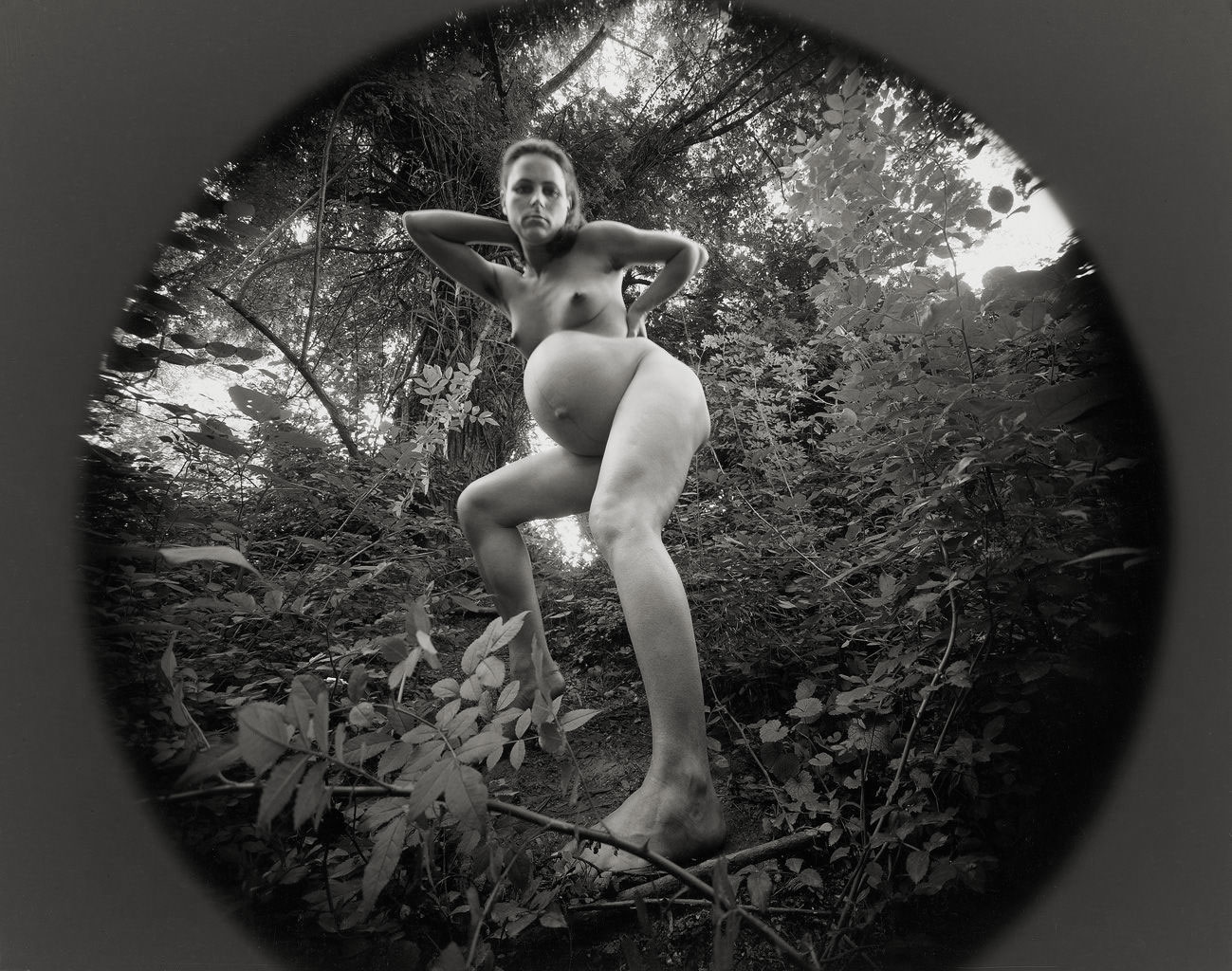
Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Nu au pop-corn (Popcorn nude)
1949
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
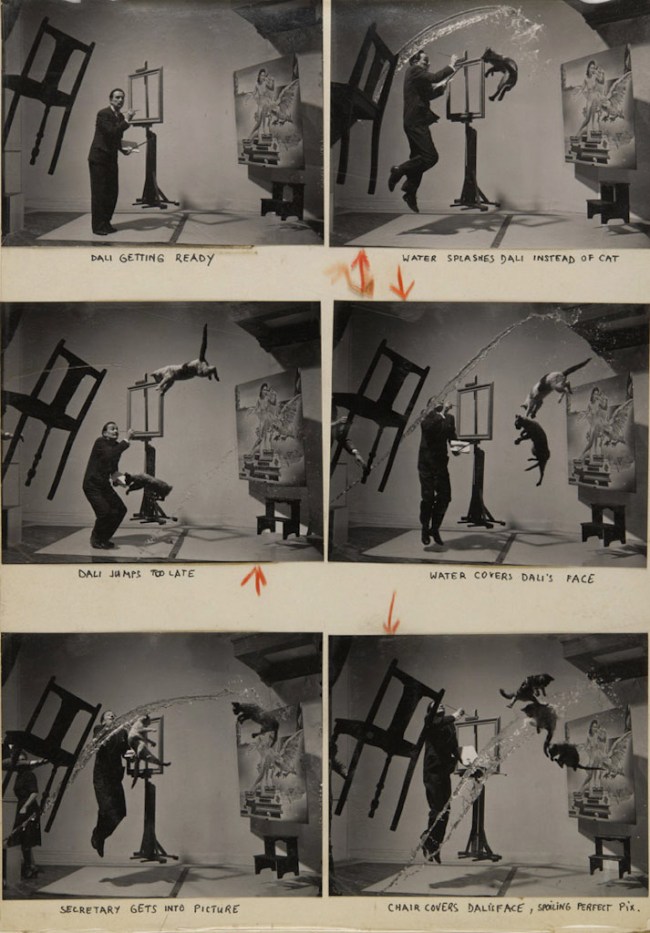

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Dalí Atomicus
1948
Contact sheet
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
Exclusive rights for images of Salvador Dalí: Fundació Gala-Salvador Dalí, Figueres, 2014
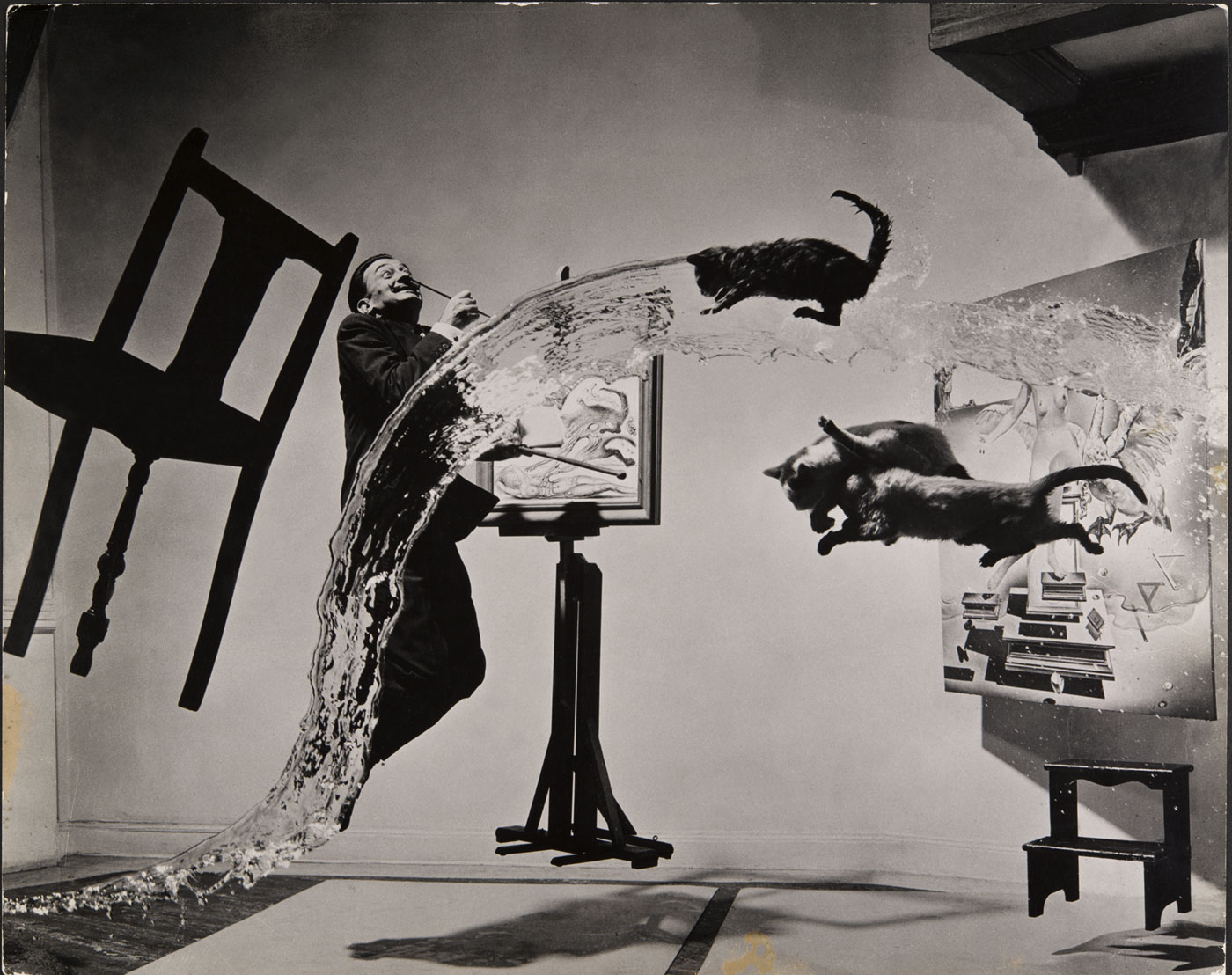

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Dalí Atomicus
1948
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
Exclusive rights for images of Salvador Dalí: Fundació Gala-Salvador Dalí, Figueres, 2014
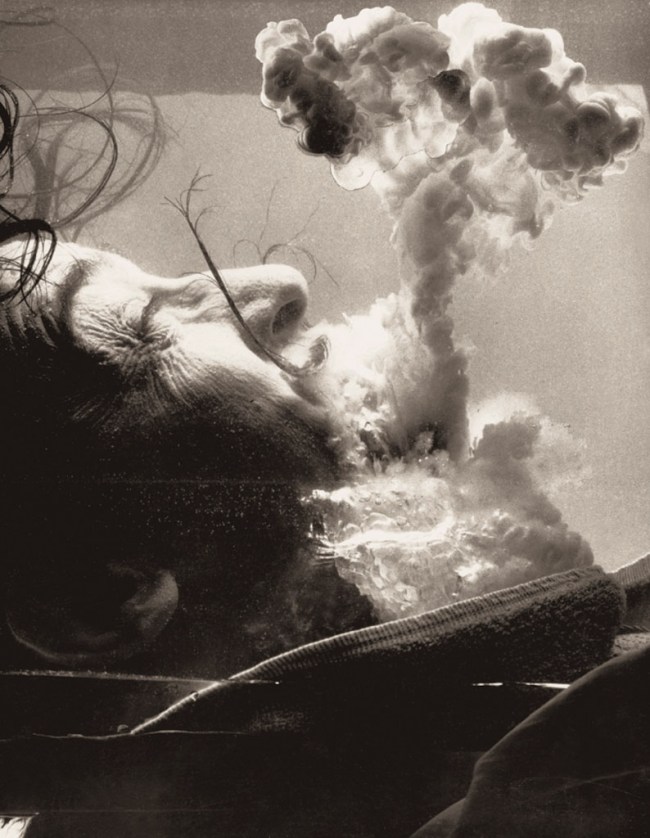

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Épreuve préparatoire pour “Certainement. Je m’adonne personnellement à des explosions atomiques,” Dalí’s Mustache
(Test event for “Certainly. I personally engaged in atomic explosions,” Dalí’s Mustache)
1953-1954
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Portrait de Salvador Dalí avec casque de footballeur américain (Portrait of Salvador Dalí with American football helmet)
1964
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Dalí Cyclops
1949
Musée de l’Elysée
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
“In the thirty years of our friendship I have made countless photographs showing the surrealist painter in the most incredible situations. Whenever I needed a striking or famous protagonist for one of my wild ideas, Dalí would graciously oblige. Whenever Dalí thought of a photograph so strange that it seemed impossible to produce, I tried to find a solution. ‘Can you make me look like Mona Lisa?… Can you make a man one half of whom would look like Dalí and the other half like Picasso?’ I could and I did.”
Philippe Halsman
Halsman/Dalí
One of Halsman’s favourite subjects was Salvador Dalí with whom he shared a unique collaboration that spanned 37 years. Their 47 sittings, combining Dalí’s talent for performance and Halsman’s technical skill and inventiveness, resulting in an impressive repertoire of “photographic ideas”.
Focus on Dalí’s Mustache
As Halsman explains, Dalí’s Mustache is the fruit of this marriage of the minds. They conceived this book entirely dedicated to Dalí’s moustache, and created over thirty portraits of the painter absurdly answering Halsman’s questions. In 1953 Halsman realised that Salvador Dalí’s expanding moustache gave him the “chance to fulfil one his most ambitious dreams yet and create an extraordinarily eccentric work”. Dalí was enormously fond of his own person and of his mustache in particular, which he saw as a symbol of the power of his imagination, and was immediately thrilled at the idea. To create a “picture book” containing an interview with Salvador Dalí, Halsman reused an editorial concept he had introduced five years earlier with French actor Fernandel: a question asked of the artist was printed on one page, and the answer appeared on the following page in the form of a captioned photograph.
For this project, it was no longer just a matter of photographic expression, but of genuine mise en scène, combining Dalí’s theatrical character with Halsman’s impressive inventiveness and technical skill. Halsman presented the book as a genuine collaboration between two artists, representing their mutual understanding.
Halsman photographed Dalí with his 4×5 camera and his electronic flash through many sessions over a period of two years. Most of the plates in the book are portraits of the artist posing in a variety of positions, playing with his moustache in various ways, accentuated by light and framing effects. Dalí was ready to go along with any whim to create the scenes: he styles his precious moustache with the help of Hungarian wax, and agrees to take part in incongruous mises en scène, pressing his head behind a round of cheese to put the ends of his moustache through its holes, or plunging his head into a water-filled aquarium, his mouth full of milk.
As for Halsman, he put a lot of his effort into the post-production work in order to give concrete expression to their ideas. It sometimes took a laborious process to achieve images like the Mona Lisa portrait, inner conflicts, surrealism or the essence of Dalí, which not only required work on the print or negative (cutting, enlargement, deformation, double exposure) but also a montage and a new shot to create a negative of the final image. For the portrait of the artist in the form of a “soft watch”, Halsman worked around one hundred hours. He photographed Dali close up, then tacked a wet print of the image onto the edge of a table and re-photographed it at an angle that matched the angle of the original painting. He then cut it out, made a collage, and re-photographed it again – creating an image of Dali’s melted face. For the photographer, it was a genuine technical challenge, which he seized with patience and success.
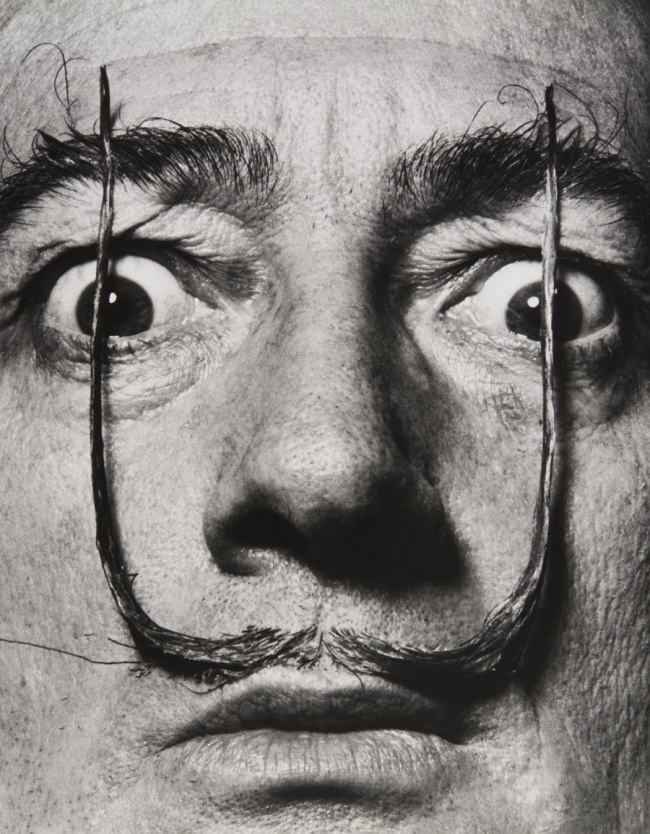

Philippe Halsman (American, 1906-1979)
Like Two Erect Sentries, My Mustache Defends the Entrance to My Real Self, Dalí’s Mustache
1954
Philippe Halsman Archive
© 2013 Philippe Halsman Archive / Magnum Photos
Exclusive rights for images of Salvador Dalí: Fundació Gala-Salvador Dalí, Figueres, 2014
The Musée de l’Elysée
18, avenue de l’Elysée
CH - 1014 Lausanne
Phone: + 41 21 316 99 11
Opening hours:
Wednesday – Monday 10am – 6pm
Closed Tuesday
The Musée de l’Elysée website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top
0.000000
0.000000




































































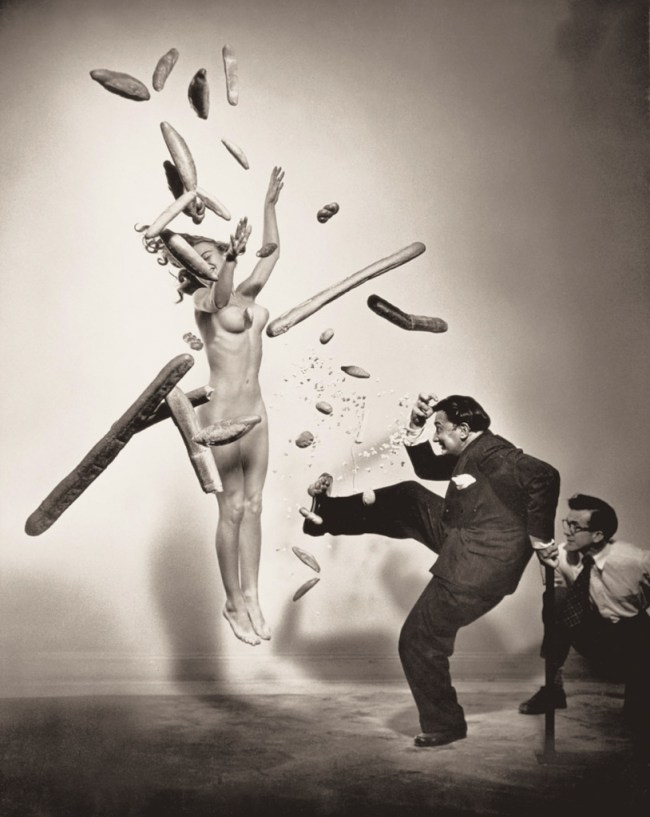























































































You must be logged in to post a comment.