November 2018
Warning: Please be advised that this paper contains images of death and killing. Please do not look if you are upset by such images.
This text was written in 2017 for a special issue of the international magazine Text on the subject ‘Writing Trauma’. While the text was accepted, the peer-reviewers wanted heavy revisions, including reordering the piece and editing out my personal stories. At the time, I was going into hospital for an operation on my hand and such revisions were impossible to undertake.
Now, over a year later, I have reread the text… and I have amended and extended it, but otherwise I am going to leave it as I wrote it in the first place. I like the way I write and I like my personal stories. While it is a long read the writing addresses an important subject with, I hope, some interesting insights along the way.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Word count: 8,137
Download Death and the image (4.3Mb pdf)
Abstract
This text investigates how the act of photography visually writes trauma. Through an analysis of the context of images of death by artists such as Alphonse Bertillon, Robert Capa, Alexander Gardner, and Walker Evans the paper ponders how the camera captures human beings ante-mortem, at the death point, post-mortem and vita ad mortem.
It seeks to understand that line between presence and absence where life was there… and now death is in its place. Death was one step removed, now it is present. How does the act and performance of photography depict the trauma of death, this double death (for the photograph is a memento mori and/or the person in the photograph may already know that they are going to die).
“The text of eternity that the photograph proposes, imparts and imposes a paradoxical state of loss. The secret of telling truth in a photograph is that the more truthful, “the more orgasmic, the more pleasurable, the more suicidal” the pronouncement of the perfect paradox (you are dead but also alive) … then the more we are strangled while uttering it. The language of deferral in the writing of trauma in death and the image becomes the dissolve that seizes the subject in the midst of an eternal bliss. In death and the image we may actually die (be)coming.”
Keywords
Trauma, photography, death, art, memento mori, war, execution, memory, victim, representation, Alphonse Bertillon, Robert Capa, Alexander Gardner, Walker Evans, ante-mortem, point of death, death point, post-mortem, punctum, empathy, vita ad mortem, life after death.
Death and the image
“Photography, because it stops the flow of life, is always flirting with death…”
John Berger1
“On the most fundamental level there are transitions from continuous to discontinuous or from discontinuous to continuous. We are discontinuous beings, individuals who perish in isolation in the midst of an incomprehensible adventure, but we yearn for our lost continuity. We find the state of affairs that binds us to our random and ephemeral individuality hard to bear. Along with our tormenting desire that this evanescent thing should last, there stands our obsession with a primal continuity linking us with everything that is.”
Georges Bataille2
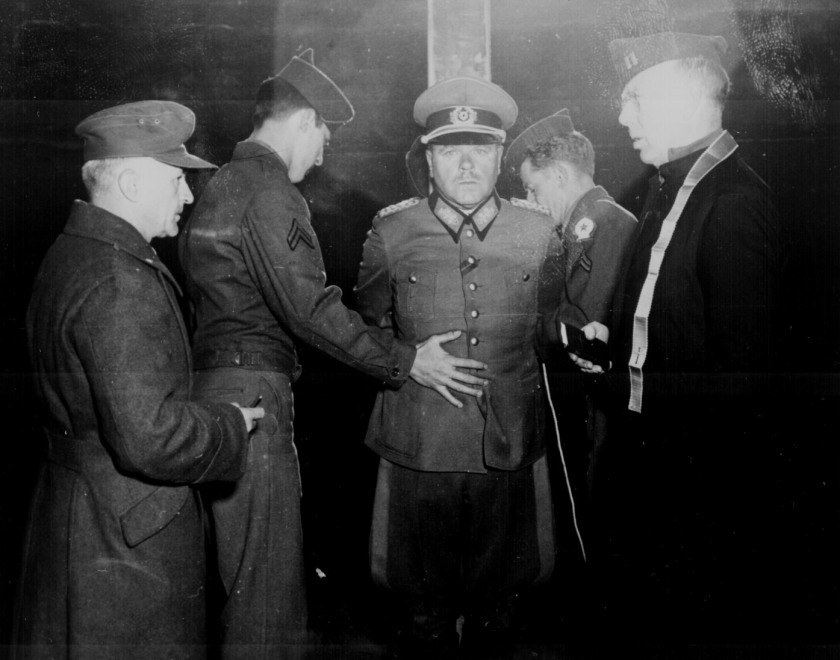
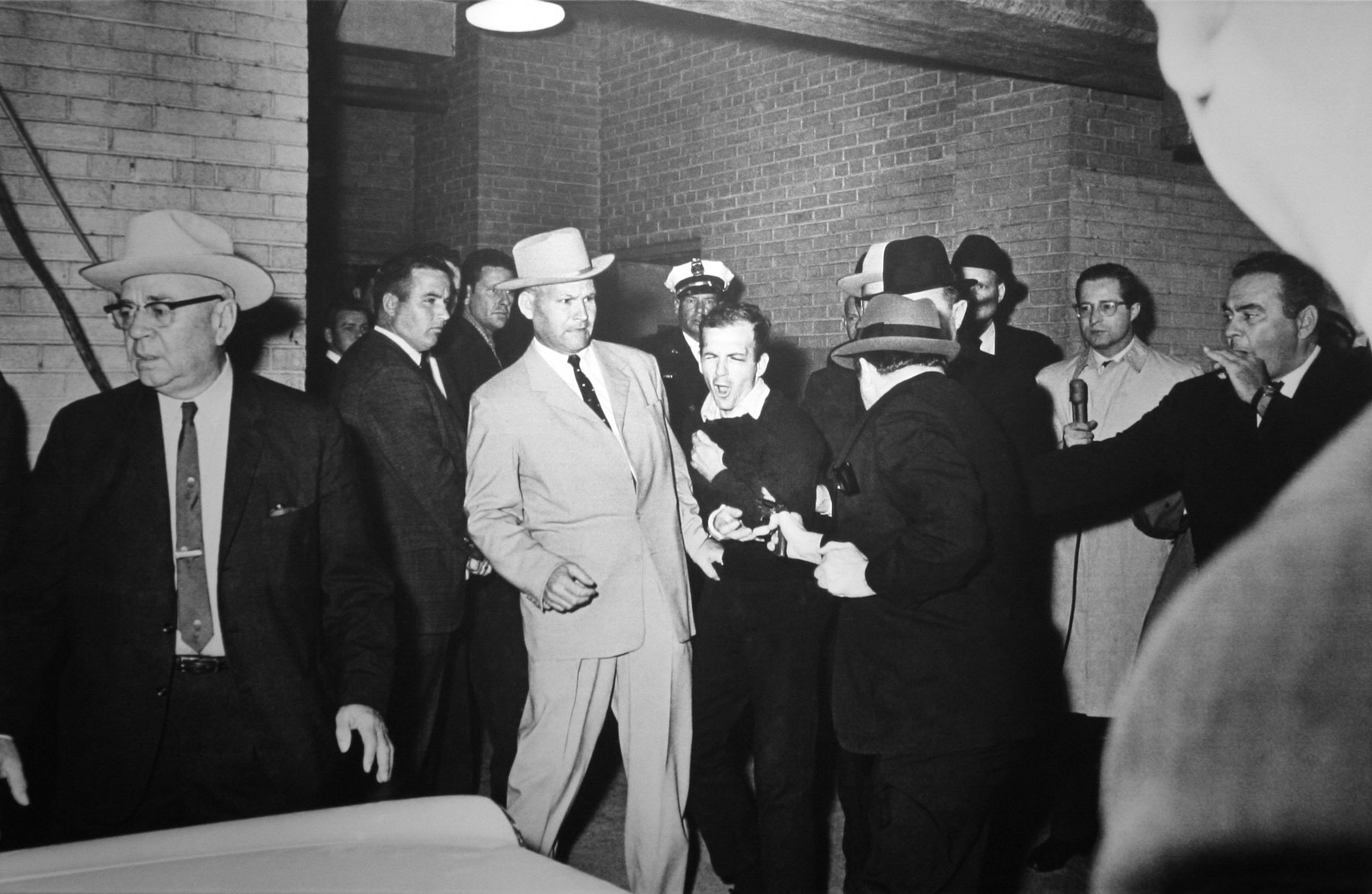
“German General Anton Dostler is tied to a stake before his execution by a firing squad in the Aversa stockade. The General was convicted and sentenced to death by an American military tribunal. Aversa, Italy.” Blomgren, December 1, 1945. 111-SC-225295. National Archives Identifier: 531326
Nazi General Anton Dostler Execution – Italy 1945
The still photograph (above) can be seen being taken by the flash from a still camera that occurs at 1.22 secs in the YouTube film.
* An additional image of Dostler’s execution taken from a different perspective in the Addendum section of this text.
1
One of life’s recurrent themes is mortality. As Bataille notes, we are discontinuous beings: we live, we breathe, and we die. Photography’s recurrent theme is also mortality. In a ghostly evocation, the medium possesses an odour of death that sticks in the throat. So how then does photography visually write the trauma of death – over time, through space, in different contexts, with multiple narratives and different points of view?
As a first point of reference, we need to define trauma. Trauma can be an injury to living tissue; a disordered psychic or behavioural state resulting from severe mental or emotional stress or physical injury; an emotional upset and an agent, force or mechanism that causes all or any of these conditions.3 Atkinson and Richardson note that the work of theorists such as Nicolas Abraham, Maria Torok, Shoshana Felman, Dori Laub, Dominick LaCapra, and Cathy Caruth in broad terms view trauma,
“… as the delayed manifestation of a psychic wound sustained during an experience that has happened too quickly to allow registration and processing of the event at the time of its occurrence. To study trauma in literary or cultural terms, then, is to be concerned with the tension between what is known and what is not known, and with the impact and dynamics of the woundedness and machinations of trauma – not only its purely physical instantiation, but in all its reverberations. This is what brings the study of trauma to the uncertainty of truth, the impossibility of bearing absolute witness to catastrophe, the multiplicity of historical narratives.”4
Constitutive of trauma and its affects is the “piercing of the psychic shield” which protects a fragile subjectivity leaving in its wake shattered individuals, communities and even whole nations.5 Further, Michalinos Zembylas citing Kaplan (2005) notes that “an important distinction that needs to be made here is one’s positioning and context of encountering trauma,”6 between being a primary or secondary witness. Personally, I believe that a testimony (a formal written or spoken statement that something is true) in the first instance… becomes a testament (something that serves as a sign or evidence of a specified fact) in the second.
When looking death in the face, we can state that death is a trauma not only for the physical body and the psyche of the person involved (the direct trauma victim), but also for the witness of the event, be they a primary witness – one who actually witnesses the traumatic event – or a secondary witness, a person “who has no personal connection to the victim but may encounter trauma through other sources such as the media and oral or written accounts of a catastrophe.”7
These secondary encounters can never be the actual experience of trauma but, acting through language (be it oral, written or visual), they may embody sensations that stimulate feelings and thoughts in the secondary observer. A social construction of a testament may produce an empathetic engagement in viewers as “secondary witnesses.”8 Through an understanding of spectatorship, experience, aesthetic effects, narrative strategies and temporal shifts in the polyvocal nature of language we can begin to understand how the affect of secondary traumatisation – on memory, history and the body – can break down the subject-object dichotomy, can break down the realist norms of representation to produce “a mode of cognition involving sensuous, somatic and tactile forms of perception.”9 Here language (the photograph in this case, reinforced by the title of the photograph) stands in for that which is absent, but it is not in opposition to an intensity of feeling. The language of the photograph can intensify the affect of the image, especially if the photograph becomes transcendent, embodied, in the vitality and “aliveness” of the viewer.10
This mimetic experience “promotes a critical and self-reflexive empathy” and knowledge in the secondary witness that LaCapra observes is a “virtual, not vicarious, experience … in which emotional response comes with respect for the other and the realisation that the experience of the other is not one’s own.”11 Essentially, this is a social concept, a social construction of reality, a matrix-like view of the world that draws on relational and contextual dimensions for understanding trauma. This concept requires careful consideration of issues related to history, culture, race, gender, ideology, beliefs, agency and power.
“From a social constructionist and narrative perspective, people reconstruct their selves through the stories they tell about their past and the meaning they ascribe to the present in anticipation of the future. They shape their stories through active and creative interpretation of their lives and are in turn shaped by these stories. However, the self is not only a product of narratives. People are purposeful and moral beings, having the power and agency to change scripts, discourses and ideologies…”12
Here we can ask, what are the machinations of the image in the affective dynamics of photographs of trauma and how are they situated in a certain relation to trauma? What do photographs actually do that give rise to a way of thinking and feeling about trauma?
Although no representation can fully describe the first hand experience of trauma because of the partial nature of language – its gaps, elisions and impossibilities of speech13 – it is because of these very gaps that new spaces of interpretation can open up. Rather than just representing the perceived reality of trauma (this happened, at this time, in this location – an ordering of reality), images have the unique ability to transcend their indexical relationship to the real, pointing and touching (as if with the index finger) to the relationality of trauma as it touches human emotion. With its ability to police and regulate it subject, the implicit violence of photography is a predatory means of taking possession of both its victim (the subject) and its viewer.
Anna Gibbs has stated that we live, “in a more or less continuous state of mediatised emergency and traumatic aftermath, desensitised by the onslaught of images … to the affect we ought to feel.”14 I strongly disagree. I would argue that the traumatic numbing15 and supposed “death of experience”16 allegedly present in the world of image circulation, translation, and accumulation only occurs if the witness lets it be so.
Personally, I believe that something in the image is transferred to the witness pre-cognition – intuitively, imaginatively – which can then be interpreted cognitively and relationally with regard to history and memory, art and culture, politics and experience through an orthogonal movement through time and space. As viewers and interpreters, we are not fixed at a particular point in time and space, nor do we observe from one particular point of view. Our existential engagement provides a space to close the gap between affect and enunciation.
“Facts can vibrate; they can give of colors, sounds, smells, images. To talk of these facts with no recognition of this is to lack any awareness of the act of enunciation, of the gaps between language and experience and the unpredictable ways that sparks can break out of language, leap across the gap and ignite the tinderbox of traumatic memory.”17
2
Surfing Pinterest (a photo sharing website) recently, I absentmindedly clicked on an abstract image of three hanging black shapes from the pantheon of image tiles that presented itself to me. Up popped this horrific image of three Afro-Americans who had been lynched in the Southern United States in the 1920s. I was shocked and dismayed. I had such a strong emotional reaction to the image. But more than that, my feelings and memories of the bigotry that I had faced as a young gay man growing up in the 1970s swelled in my consciousness. This story is a example of how exposure to an image can bring to the surface unresolved aspects of being ‘Other’, of being different, and being persecuted for that difference. I thought about the lives of these people that had led them to that point, their families, their histories and the terror that they must have experienced on that day. You cannot begin to understand that, but you can have empathy and anger against the systems of racism and bigotry that exist in the world.
Then the cognitive part of my brain linked the image to a report I had only just seen a few days before on lynching, which told of the thousands of Afro-Americans who had been killed between 1882 and 1968.18 Mentally, I then linked this to a Facebook posting which put forward the analogy that the current killing of Afro-Americans by police in the United States was akin to a contemporary and publicly endorsed and enforced form of lynching. Finally, in my head I heard Billie Holiday singing that famous song Strange Fruit, “a dark and profound song about the lynching of African Americans in the Southern United States during the Jim Crow Era, “strange fruit,” as they hang from trees, rotting in the sun, blowing in the wind, and becoming food for crows upon being burned.”19 I watched the video of Billie Holiday singing this song on YouTube.20 Every time I think of this image I have these associations of animate thought intrinsic to the original experience,21 where the micro and macro conditions of production work to “embody and register trauma,”22 a communicable language of sensation and affect, time and time again.
Billie Holiday – Strange fruit
These chains of affect, the nexus between affect / feeling / emotion / cognition, are a form of synaesthesia where facts, emotions, feelings, memories, sounds and images vibrate against each other as an active and continuous engagement of the self with the world in which one lives. In a human being who is un/consciously aware, these real and mediated experiences may encourage a sensory intensification that elicits thought and empathic vision in the materiality of embodied experience, something (the punctum?) that takes us out of our selves into a higher register of being.
As part of this system of impressions, of an instantaneous, affective response triggered by an image,23 photographs force us to engage visually and involuntarily. “Impressions that force us to look, encounters which force us to interpret, expressions which force us to think.”24 Encounters which force us to comprehend. The conjunction of affect and critical awareness “constitute the basis of an empathy grounded … on a feeling for another that entails an encounter with something irreducible and different, often inaccessible.”25 This combination of affective and intellectual operations – about forcing oneself to look (and that process of looking/surrendering) but never forgetting your ‘point of view’, your memory, history and identity, is when empathy becomes that process of surrender, “but also the catch that transforms your perception.”26 How is this “catch” enunciated in photographs? I now want to look at a few images that explicate these phenomena.
Ante-mortem: present but absent
3
With the invention of photography in the late 1830s, the photograph as memento mori allows the spectator to observe death not at first hand, but through the representation of the image “taken from life.” Photographs provide a verification of reality through their apparent verisimilitude, while being woven into narratives – oral, textual, intertextual, spatial and temporal – that frame the event in multiple ways.
“Photographs … have come to stand in for reality … despite the fact that it is relatively easy to manipulate their meaning. As a result of their ability to project reality, images, and particularly those that depict death and destruction, are seen as potentially powerful pieces of documentary evidence…”27
Photographs are embedded in “a context of the cultural circumstances at the time, and therefore exist rarely in isolation or without meaning”28 and can be seen as having a denotative level (what they physically represent) and a connotative level (the meanings attached to that representation).29 Photography quickly changed how death was displayed because it introduced a “reality” and immediacy of representation that was democratic, personal and everyday.30
Alexander Gardner (American, 1821-1882)
Lewis Paine
26th April 1865
Albumen silver print from a Collodion glass plate negative
An example of the personal, everyday and documentary nature of photography can be seen in the photograph taken by Alexander Gardner in April 1865. This portrait is of Lewis Thornton Powell (aka Lewis Payne or Paine) who was one of the conspirators in the assassination of Abraham Lincoln which occurred the same month. The photograph has a background of dark metal, and was taken on one of the ironclads U.S.S. Montauk or Saugus, where the conspirators were for a time confined. The reality is Paine was executed in July 1865 just eight short weeks after this photograph was taken, so in effect (and in the affect on us of this knowledge), he is (already) a dead man walking. This is a double death – that death buried in the very act of taking any photograph, La petite mort or “the little death,” an idiom and euphemism for the orgasm of the photographic time freeze; and the fact that we know that he was going to die, those short weeks later.
The photograph forms the central panel of a three-panel Renaissance-like altarpiece, the form in which the three photographs are usually displayed. The left and right hand photographs were taken within minutes of each other, with the camera in the same position, whereas in the centre photograph the camera has been lowered to show more of the body, and the image has been cropped at the top. In the central plate the figure of Paine has been raised up in the frame – almost prematurely brought back to life by his placement. The centre image is the only one where Paine stares directly at the camera. He surveys the viewer with a gaze I find enigmatic.
Alexander Gardner (American, 1821-1882)
Three photographs of Lewis Paine
26th April, 1865
Albumen silver prints from a Collodion glass plate negative
This is a very modern face, a very contemporary face. His hair is similar to Justin Beiber’s. Who brushed his hair across for this picture, and would it normally be this long, or has it just been ignored because of his fate? He still has good muscle tone – has he been exercising in his ironclad cell? And finally, his clothing – are they navy issue, as his top appears to have been given to him, perhaps the coarse, navy blue wool of the Northern states. If we were to place this image within the metaphysical school of photography which peaked with Paul Caponigro and Minor White we could say: Hovering above his head, has his spirit already begun to leave his body?
One reading of his gaze is that he is interested in what the photographer is doing – almost the gaze of an apprentice wanting to apply these skills in the future. Given his fate is he insane because of his interest? Another reading could be that he is looking out to the future in the hope of finding that he will be judged in another way. And another is the immediacy of his gaze – it is a gaze that is happening now!
The other thing that I find mysterious is the distance of the photographer from the subject. Was it fear or the presence of the guards that stopped Gardner getting any closer, or are there deck fittings we cannot see that prevented his approach. Imagine being Paine, having a photographer point a damn great view camera at you, documenting your countenance for prosperity. What was going on in Paine’s mind – what is his perspective on this performance by the photographer? And what brought Paine to this place?
Michel Foucault calls the methods and techniques by which human beings constitute themselves, “technologies of the self.” Foucault argued that we as subjects are perpetually engaged in processes whereby we define and produce our own ethical self-understanding. According to Foucault, technologies of the self are the forms of knowledge and strategies that “permit individuals to effect by their own means or with the help of others a certain number of operations on their own bodies and souls, thoughts, conduct, and way of being, so as to transform themselves in order to attain a certain state of immortality.”31 As we look into his eyes he knows that we know he is going to die, has already died but the intensity of that knowledge is brought into present time. In this instant, what Paine emanates is a form of i-mortality.
Roland Barthes in his seminal work Camera Lucida observes in Section 39:
“He is dead and he is going to die… The photograph is handsome, as is the boy: that is the studium. But the punctum is: he is going to die. I read at the same time: this will be and this has been; I observe with horror an anterior future of which death is the stake. By giving me the absolute past of the pose, the photograph tells me death in the future. What pricks me is the discovery of this equivalence.”32
This is Barthes anterior future, a moment where truth is interpreted in the mind of the photographer, not out there but in here (your head and your heart), where past, present and future coalesce into a single point in time: his death and our death connected through his gaze, and the knowledge of our joint discontinuity. In this moment in time, what we are doing is making a list about the human condition when we talk about something that is remarkable. Language can never fully describe the human condition, much as it may try… and this is why this photograph is remarkable, because it is ineffable, unknowable. The photograph inhabits you; it haunts you like few others, because it is a memoriam to a young man and his present death. Here he is present but absent at one and the same time.
As such, this is an image as triple death – the death of the photograph (past time / memento mori / remembrance of death), the death of the person in the photograph and also a third death, the knowledge that Paine is going to die. Death, like life, can be cyclical. This is the catch that transforms your perception, in Barthes terms the punctum of the image, in which the wounding, personally touching detail (past pose, future death) establishes a direct relationship with the object or person within it.
“The punctum (a Latin word derived from the Greek word for trauma [my emphasis]) … inspires an intensely private meaning, one that is suddenly, unexpectedly recognized and consequently remembered (it “shoots out of [the photograph] like an arrow and pierces me”); it ‘escapes’ language (like Lacan’s real); it is not easily communicable through/with language. The punctum is ‘historical’ as an experience of the irrefutable indexicality of the photograph (its contingency upon a referent). The punctum is a detail or “partial object” that attracts and holds the viewer’s (the Spectator’s) gaze; it pricks or wounds the observer.”33
This trauma, prick or wound that lifts the viewer out of themselves, out of their everyday existence, “points to those features of a photograph that seem to produce or convey a meaning without invoking any recognisable symbolic system. This kind of meaning is unique to the response of the individual viewer of the image.”34 This punctum also accounts for the importance of emotion and subjectivity in interacting with photographs; memory of that photograph displaces it from its moment of origin.35 Photography enacts the trauma of death even while being enacted upon.
Now we can read Eduardo Cadava’s comments on Walter Benjamin’s analysis of the photograph:
“As Benjamin suggests … the photograph, like the souvenir, is the corpse of an experience. A photograph therefore speaks as death, as the trace of what passes into history. I, the photograph, the spaced out limit between life and death, I, the photograph, am death. Yet, speaking as death, the photograph can be neither death nor itself. At once dead and alive, it opens the possibility of our being in time.”36
4
Photography then, can be seen as death taken away from itself.
Through the oscillation between studium (historical, social or cultural meanings extracted via semiotic analysis) and punctum (those features of a photograph that seem to produce or convey a meaning without invoking any recognisable symbolic system) the traumatic photograph of death, death’s afterimage, transcends the initial shock inducing signifier leading to a more extended form of engagement that addresses the duration of trauma in memory – through the images elisions, slippages, and conceptual, political and historical complexities. Our negotiation with imaging and imagining, therefore, takes place within ever-expanding contexts of meaning – some relating to the past and some to the present – which impact future interpretations.
I believe that these negotiations are, firstly, linked to what Deleuze calls the encountered sign, a “sign that is felt, rather than recognised, or perceived through cognition.”37 A feeling that is a catalyst for critical enquiry or deep thought. “For Deleuze, affect or emotion is a more effective trigger for profound thought because of the way in which it grasps us, forcing us to engage involuntarily…”38 Secondly, I believe that these negotiations are linked to what Barthes calls the images “third meaning.”
“In Barthes’ view, the image’s third meaning compels viewers after they encounter and deplete both its literal / informational side and its symbolic dimensions. Barthes argued that the third meaning is difficult to locate, because it is not situated structurally or in a certain place of the image. It is similarly difficult to describe, because it involves what he called the image’s obtuseness, its accent or anaphoric side.”39
Again, we have this idea of the catch, accent, or punctum that grasps us and takes us out of ourselves, that modulates the images “voice” (which is how the image takes on an already provided meaning upon its initial appearance), a voice which then also “helps us to understand both the image’s third meaning and the role of contingency in visual memory.”40
Death point
5
“Ah, wretched as I am … to dwell not among the living, not among the dead.”
Sophocles, ‘Antigone’41
Commentators such as Barbie Zelizer observe that images, especially about-to-die images, easily “reduce complex issues and circumstances to memorable but simplistic visual frames.”42 The image,
“… depicts for its onlookers a moment in an event’s unfolding to which they attend while knowing where that unfolding leads. This means that visual work often involves catching the sequencing of events or issues midstream, strategically freezing it at its potentially strongest moment of meaningful representation.”43
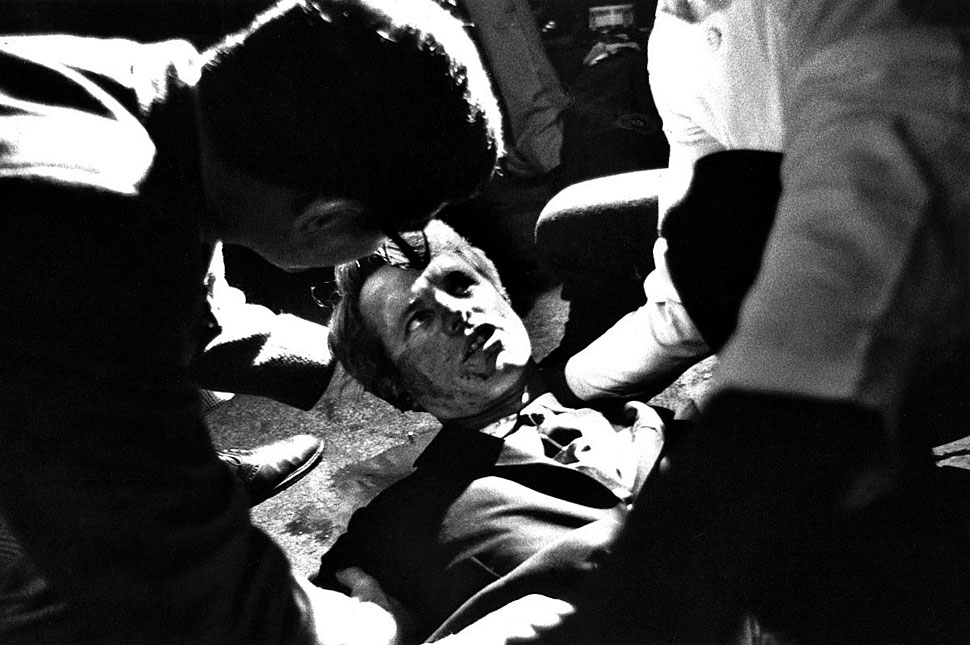
Other writers such as Susan Sontag note that these images have the potential to stir public emotions, simply because they freeze a moment in time and can be looked at again and again… but at the same time the repeated viewing of images of atrocity can have a numbing effect.44 The pain and fear evidenced in the photograph as seen in the victim’s eyes (for example in the photograph of the shooting of Sen. Robert F. Kennedy), expands the literal / informational side and its symbolic dimensions (chivalry, love, devotion, hope – Camelot!) into a Barthes’ third space. While Kennedy is a victim twice over (the victim of the assassin and the camera) in a guttural interpretation of the image he is to remain a victim for eternity in the contingency of the future, as long as we continue to look at this photograph.
For me, this is sad and painful photograph. I remember the day it happened. I was ten years old at the time. It’s one of those events that you will remember for the rest of your life – where you were, who you were with – like the moon landings or 9/11. I was in a car outside a small newsagent when the news came on the radio. Robert F. Kennedy had been shot: first aural, then visual on the black and white TV that night, then textual in the newspapers and then visual again with this photograph, then associative. The pain of the loss of those heady days of hope lessens not.
Boris Yaro (American, 1938-2020)
LOS ANGELES. KENNEDY MOMENTS AFTER SHOOTING. Sen. Robert F. Kennedy Lies Gravely Wounded on the floor at the Ambassador Hotel in Los Angeles shortly after midnight today, moments after he was shot during a celebration of his victory in yesterday’s California primary election
June 5, 1968
Gelatin silver print
17.2 x 21.1cm (6 3/4 x 8 5/16 in.)
Twentieth-Century Photography Fund, 2010
While photographs of the actual moment of death are rare I have been able to find around ten images that capture this vital moment, a freezing of reality at the point of death, the death point: that line between presence and absence where life was there… and now death is in its place. Death was one step removed, now it is present.
However, I would argue that in the contextual language of the photograph, there is no singular death point. I would propose the idea of an extended period of time and space embedded in the spatio-temporal matrix of the image, so that there is no single point, no singular resolution to the traumatic moment of death – either for the person involved, nor the witness or viewer.
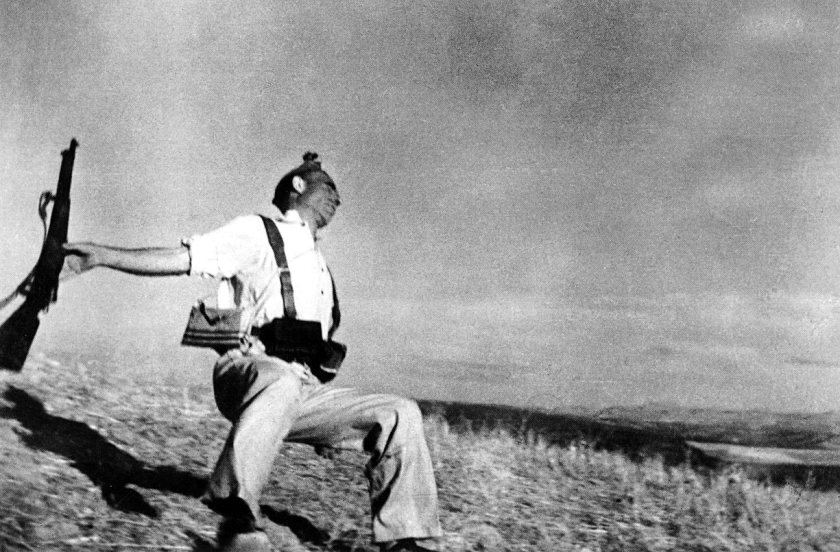
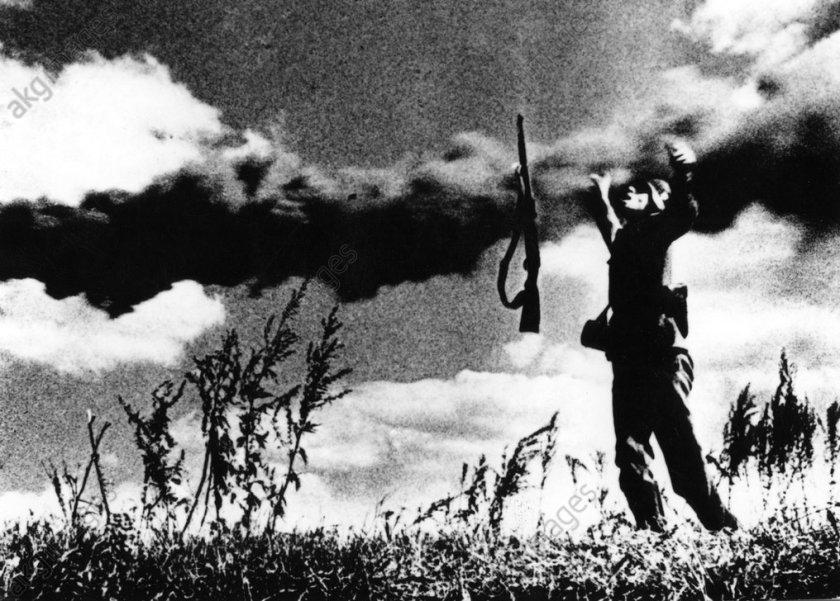
Setting aside the concept that the image could have been staged, in Robert Capa’s famous photograph Loyalist Militiaman at the Moment of Death, Cerro Muriano, September 5, 1936 (below), there is something about this image where space or some basic element is being democratised at the moment of death – or maybe in the choice to struggle with death. In an ontological sense of becoming, perhaps it is this that becomes the pure representation of time. In contrapunto, there is an anonymous image of a German soldier at the point of death on the steppes of Russia that is totally unknown. Why has one become famous and the other not?
Has it to do with the fame of the photographer, the pose of the person, or the agency of photography itself, where one photograph regarding the pain of others is too damning a legacy and of too plain a purpose to bare contemplating, while the other – with its masked face, outflung arm and falling, quasi-religious nature – has become possibly the most famous of war photographs through its proliferation in newspapers and magazines.
Whatever the merits of each image, these death point photographs are noteworthy for what is not said: the violence that is being perpetrated on the victim every time a person looks, and looks again, at the photograph. The writing of trauma by photography never ends, is always and forever infinite.
Robert Capa (American, 1913-1954)
Loyalist Militiaman at the Moment of Death, Cerro Muriano, September 5, 1936
1936
Gelatin silver print
Photograph by Robert Capa © Cornell Capa / Magnum
Anonymous photographer
Falling German Soldier, Eastern Front
c. 1942
akg-images / Interfoto AKG138118
Caption: A German soldier pays the ultimate price of war. German casualties were less than those of the Red Army, but the steady attrition suffered by the Wehrmacht began to undermine its effectiveness.46
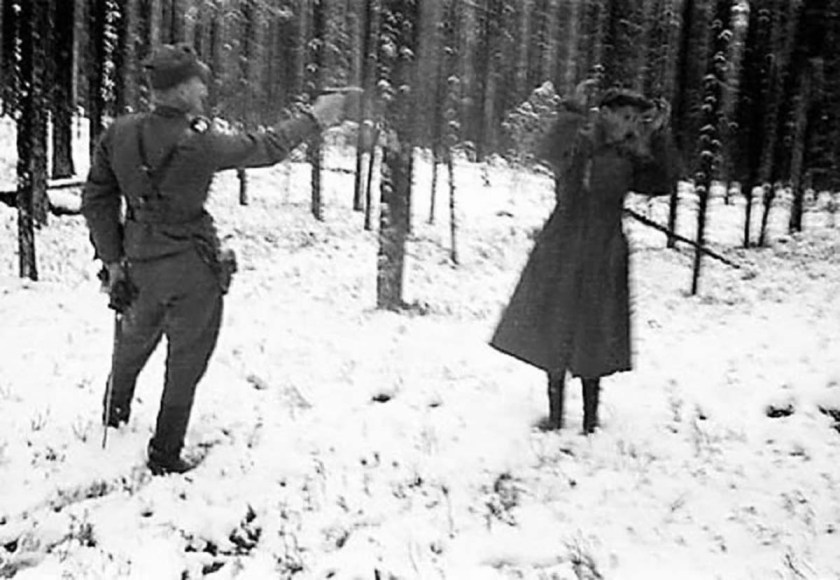
Anonymous photographer
Russian spy laughing through his execution in Finland, 1942
1942
Rare Historical Photos website 2013
Caption: A Soviet spy laughs at his executioner in a picture taken in Rukajärvi, in East Karelia, in November 1942. It has been thought within the Finnish Defence Forces that the decision to withhold pictures of the fate of Russian POWs and spies may also have been prompted by concerns that pro-Soviet elements in Finnish society could have used the images for propaganda purposes. This picture was declassified by the Ministry of Defense of Finland in 2006, with the description: Unknown Soviet intelligence officer before being shot, Finland, 1942.
It’s a pretty amazing picture. To capture the last few moments of life. He knows he will die in a few seconds, in a forest in the snow. And there he will bleed out and be forgotten. His life, his experience, has come to an end. What else could he do but smile? That smile was his final defiance. Death smiles at us all, all a man can do is smile back.47
6
Here we might ask, is it possible, through the use of encountered signs, “voice”, punctum, catch or accent, to extend the unreal time of death?
Personally, I believe it is and I would argue for a sense of a Buddhist “no-time”. A transcendent time embedded into the fabric of the image. In Walker Evans’ terms an “unconscious phenomenon” that culminates in amazing accidents of composition, where things constantly rub up against each other “in the desire to create a type of friction that tests the boundaries of representation.”48 An example of this spatio-temporal dimensionality, third meaning or Thirdspace, can be seen in the interplay between the still image and film footage of the execution of German General Anton Dostler by a firing squad in the Aversa stockade December 1, 1945. By examining the film we see a flash of light at 5.16 secs, which is the still photograph at the top of this text being taken by the flash of a camera. The photographer can then be seen walking off. Later in the film another angle of the execution is shown, again with the flash of the absent camera recorded, starting at 7.10 secs. The displacement of time and space, between one point of view and another, with the absence of the still camera in both instances (in the image and in the film), is uncanny.
The fluidity of Barthes’ third meaning, where the image’s obtuseness compels viewers, has obvious links to Edward Soja’s conceptualisation of “Thirdspace”, which emerged from the spatial trialectics established by Henri Lefebvre in The Production of Space and Michel Foucault’s concept of heterotopia. Soja defines Thirdspace as, “an-Other way of understanding and acting to change the spatiality of human life, a distinct mode of critical spatial awareness that is appropriate to the new scope and significance being brought about in the rebalanced trialectics of spatiality-historicality-sociality.”49 In this amorphous space, “everything comes together… subjectivity and objectivity, the abstract and the concrete, the real and the imagined, the knowable and the unimaginable, the repetitive and the differential, structure and agency, mind and body, consciousness and the unconscious, the disciplined and the transdisciplinary, everyday life and unending history.”50
A further example of the presence of a third meaning in a still photograph can be seen in the image by an unknown photographer Photo taken at the instant bullets from a French firing squad hit a Frenchman who collaborated with the Germans (1944, below). Caught like a rabbit in headlights, the flash illuminates the collaborator kneeling, bound, and masked but it is not quick enough to freeze the explosion of wood, the dynamic breaking of the rope or the slight movement of the hands. The body seems to float on a bed of leaves. The cheap, dirty shoes and striped trousers leading up to the material that covers the victim’s face. Is that his hair, or a hat or another hood over his head? Although we know the what, why, and where of the photograph – an encounter with both its literal/informational side and its symbolic dimensions – the placing of the image, its accent and obtuseness is much more difficult to understand. The photograph and its protagonist seem to exist beyond time and space, the anonymous man surrounded by a death bed of leaves, bursting the bonds that wrapped him and held him tight. Like the mystery of Man Ray’s L’Enigme d’Isidore Ducasse (1920), the photograph has disturbed the trialectics of spatiality-historicality-sociality, destroying the imploring label, “Do not disturb.”
Unknown photographer
Photo taken at the instant bullets from a French firing squad hit a Frenchman who collaborated with the Germans. This execution took place in Rennes, France. 21 November 1944
1944
Silver gelatin photograph
U.S. Army Signal Corps
National Archives Identifier (NAID)
Post-mortem: absent but present
7
Letherolfsvile Oct 29 AD 1859
This is the likeness of Catherine Christ
When I am dead and in my grave
And when my bones are rotten
Remember me
When this you see
Or I shall be forgotten
The grass is green The rose is red
here is my name when I am dead 51
This short poem written on a piece of paper hidden underneath an image in a daguerreotype case implores us to remember the person – a plea to the future to remember them – through a composite narrative of portrait and text. Through the creative addition of text, the language of photographs can be supplemented which adds to the functionality of the photograph as an effective memory object.52 But what if the scene of the text (the photograph) contains an absence, no depiction of the person who has died? What happens to the writing of trauma in images of the dead then?
If we acknowledge that a photograph of a person always prefigures its subjects passing then what we are doing “in reality” is deferring the death of an/other onto the foreseen death of ourselves. In this process, we must remember that every photograph is a construct, a performative act by the photographer. What the photographer chooses to record is an act of will, whether ethical or not. Photographers have the presence of mind to attend to a certain manufacture of history. When viewing this instant narrative the viewer must acknowledge a loss of a sense of time:
“This lost sense could manifest as reliving a traumatic episode as if it is taking place in the present … In the context of trauma… a loss of sense of time deprives one of the ability of remembering and telling one’s narrative in a chronological order.”53
Emmet Gowin (American, b. 1941)
Avebury Stone and Rennie Booher, England and Danville, Virginia
1972
Gelatin silver print
Collection of Emmet and Edith Gowin
© Edith and Emmet Gowin and courtesy of Pace MacGill Gallery, New York
One way that artist’s upset this chronological order is by playing with the fragmentary nature of time, space and memory – of present absence/absent presence. In Emmet Gowin’s accidentally double-exposed negative, Avebury Stone and Rennie Booher, England and Danville, Virginia, 1972 (above), the photograph combines “a funerary image of his wife’s grandmother, Rennie Booher, with the surface of a Neolithic monumental stone he had photographed in England a few days earlier.” Floating through eternity, encased in ancient rock that nourishes her spirit, Gowin’s photograph acts as a kind of testament of absent but present, neither here not there. This loss of sense of space and time can be deeply disturbing (like trauma) as it questions one’s physical presence in the world, but it can also have a transcendental dimension as both time and space are inextricably bound to the very specific conditions of the material world. Photographs like the one of Booher have the potential to draw together what would otherwise seem to be incompatible. To form what Jacob Bronowsi calls a “hidden likeness”, one that transcends time and space, one that is reactivated with every looking.
“The poem or the discovery exists in two moments of vision: the moment of appreciation as much as that of creation; for the appreciator must see the movement, wake to the echo which was started in the creation of the work. In the moment of appreciation we live again the moment when the creator saw and held the hidden likeness. When a simile takes us aback and persuades us together, when we find a juxtaposition in a picture both odd and intriguing, when a theory is at once fresh and convincing, we do not merely nod over someone else’s work. We re-enact the creative act, and we ourselves make the discovery again…”54
An important fact about the nature of trauma is the compulsion of the human psyche to repeat traumatic events over and over again. The reproducibility of photographs and the ability to look at them again and again – their machine-like repeatability, their citationality or iterability to use Derrida’s signature term – feeds into this repetitive “death instinct” (Thanatos). However, Bronowsi’s “hidden likeness” (also the name of one of Emmet Gowin’s exhibitions and a form of punctum) is perhaps a liminal moment, one that may upset the death instinct. These liminal moments may occupy a position at, or on both sides of, a boundary or threshold. By disrupting the threshold – between life and death, between past, present and future time – they are requisite of the ghost (the soul) in the machine (the camera).
As Derrida observes, building on the work of Barthes,
“It belongs to it without belonging to it and is unlocatable in it; it never inscribes itself in the homogenous objectivity of the framed space but instead inhabits, or rather haunts it: “it is the addition [supplement]: it is what I add to the photograph and what is none the less already there.” … Neither life nor death, it is the haunting of the one by the other … Ghosts: the concept of the other in the same, the punctum in the studium, the dead other alive in me.”57
8
In this scenario, perhaps the act of writing trauma through death in the image becomes the true act of learning, and the interpretation of that act becomes an act of creation rather than one of rote memorialisation. These are images that require contemplation, time, analysis, and sensation, where the subject of the photograph is transformed “from somebody merely seen to someone really felt,” which is, as Batchen says, “an emotional exchange transacted in the heart.”58
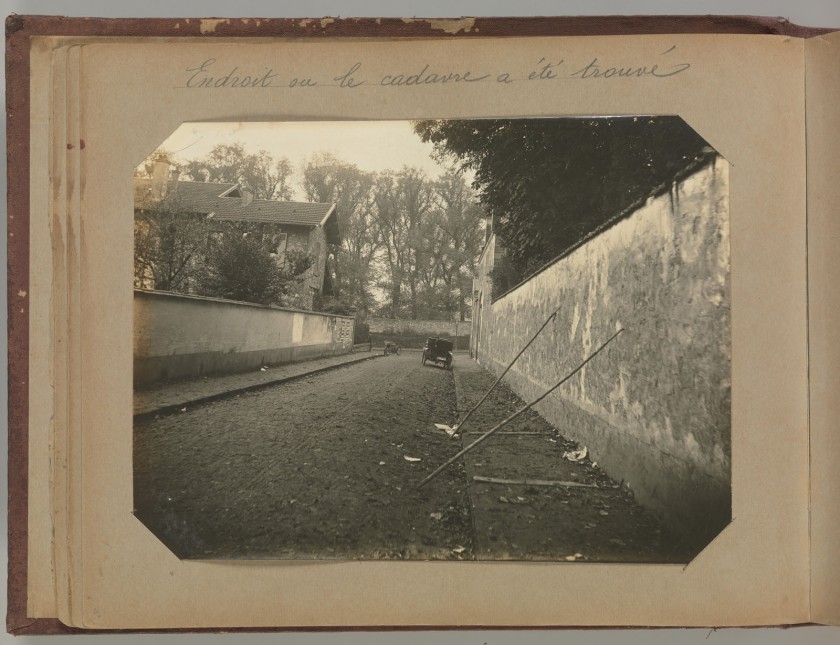
This emotional exchange can take many forms. It can be triggered when the dead body is only metaphorically represented in the image, when the physicality of death has been transmuted. For example, photographs such as Walker Evan’s Child’s grave, Hale County, Alabama (1936, below), or the documentary image Place where the corpse was found (1901-1908, below) by the French photographer Alphonse Bertillon, propose a re-imaging and re-imagining of the life of the person. They do so through an un/ambiguous photographic context, that is, through the marking of place in the photograph. In the latter case, this marking of a life is represented by two pieces of wood lying on the ground and two pieces of wood propped at 45 degrees against the wall. As though this is all that is left of the existence of Mademoiselle Mercier in a street (Rue de l’Yvette) that still exists in Paris to this day. A photograph of pieces of wood and an empty space.
Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975)
Child’s grave, Hale County, Alabama
1936
Silver gelatin print
7 3/8 x 9 7/16″ (18.7 x 23.9cm)
© 2016 Walker Evans Archive, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Attributed to Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914)
Place where the corpse was found
1st November 1902
From Album of Paris Crime Scenes
Gelatin silver print
Overall: 24.3 x 31cm (9 9/16 x 12 3/16 in.)
Page: 23 x 29cm (9 1/16 x 11 7/16 in.)
Gilman Collection, Purchase, The Howard Gilman Foundation Gift, 2001
Other photographs picture the place of death nearly a century later in order to commemorate the traumatic death of “deserters” at the hands of a firing squad during the First World War. These are some of the most traumatic photographs of death I have seen, for they require me to imagine the mise en scène that was enacted at dawn almost 100 years ago, in the very place where these photographs were later “shot” at dawn.
The artist, Chloe Dewe Mathews, realised that “I was placing my tripod around the same spot where the firing squad had stood and looking directly at the place where the victim was placed.” It was, she says, “a solitary and sombre undertaking,” an undertaking (with that name’s etymological link to the word undertaker) which the viewer is invited to partake of, a re-imaging of those traumatic events that requires an active imagining, and thinking, in the neo-spectator. It is this duration of trauma in cultural memory which calls for an active negotiation in ways of seeing, a re-negotiation which can produce an empathic vision that “changes the terms of our engagement” with the image.
Chloe Dewe Mathews (British, b. 1982)
Former Abattoir, Mazingarbe, Nord-Pas-de-Calais
2013
Eleven British soldiers were executed here between 1915-1918
From the series Shot at Dawn
© Chloe Dewe Mathews
Vita ad mortem: life after death
9
“… the life of spirit is not the life that shrinks from death and keeps itself untouched by devastation, but rather the life that endures it and maintains itself in it. It wins its truth only when, in utter dismemberment, it finds itself.”
George Wilhelm Frederich Hegel61
The absence/presence contained within all photographs speaks to the ultimate affect: that of la petite mort – the “little death” – the sensation of orgasm as likened to death, a short period of melancholy or transcendence as a result of the expenditure of the “life force.” While Barthes metaphorically used the concept to describe the feeling one should get when experiencing any great literature, it can also be used when some undesired thing has happened to a person and has affected them so much that “a part of them dies inside.”
A photograph can also contain this melancholy transcendence, a catastrophe that has already occurred.
“Whether or not the subject is already dead, every photograph is this catastrophe… This punctum, more or less blurred beneath the abundance and the disparity of contemporary photographs, is vividly legible in historical photographs: there is always a defeat of Time in them: that is dead and that is going to die… At the limit, there is no need to represent a body [in photographs] in order for me to experience this vertigo of time defeated.”63
Barthes’ concept of an extended punctum may be useful here, when he states, “I now know that there exists another punctum (another ‘stigmatum’) than the ‘detail’. This new punctum, which is no longer of form but of intensity, is Time, the lacerating emphasis of the noeme (‘that-has-been’), its pure representation.”64
Here Barthes is proposing a punctum of intensity; a punctum as lacerating “detail”; and/or “the vertigo of time defeated.” This “temporal hallucination” embedded and embodied in the photograph – the temporality of the “will-have-been”, they are dead (today), they are already dead (yesterday), Barthes’ anterior future – represents a symbolically mediated subject bound up in three extases of time (past, present, and future).65
The subject becomes lost in the language of the photograph, the intersection of Lacan’s the Imaginary (in which the human subject creates fantasy images of both himself and his ideal object of desire), the Symbolic (the social world of linguistic communication and inter-subjective relations), and the Real (defined as what escapes the Symbolic, the Real can be neither spoken nor written, it is impossible, but is ceaselessly writing itself). These concepts serve to situate subjectivity within a system of perception and a dialogue with the external world.
According to Lori Wike, the experience of punctum and the structure of iterability can be aligned to Lacan’s concept of the death drive (or death instinct) present in the Symbolic order, in which the signifier “materializes the agency of death.”66 This may account for the role of the photographic punctum as trauma, in which the punctum opens up “a kind of subtle beyond” where “a blind field is created (is divined)…”67 As Barthes notes, “Photography is a kind of primitive theater, a kind of Tableau Vivant, a figuration of the motionless and made-up face beneath which we see the dead.”68 Further, we can say that, “unlike the symbolic, which is constituted in terms of oppositions such as “presence” and “absence”, there is no absence in the real,” for the real is undifferentiated, “it is without fissure.”
“The symbolic introduces “a cut in the real,” in the process of signification: “it is the world of words that creates the world of things.” Thus the real emerges as that which is outside language: “it is that which resists symbolization absolutely.” The real is impossible because it is impossible to imagine, impossible to integrate into the symbolic order. This character of impossibility and resistance to symbolization lends the real its traumatic quality.”69
The “mark” of photography is eviscerated in the intensity of the real, a traumatic loss of time that confronts us with our own mortality and the knowledge that we will not be remembered. This is where images of death can take us once the initial affective connection is established – to a noumenal space where in the play of representation, the point of origin becomes ungraspable (Lacan’s différance).70
“In French, différance simultaneously contains within its neo-graphism the activities of differing and deferring, a distancing acted out temporally as well as spatially.”71 Where the moment (the time freeze of the shutter) turns in, on and around its own fulcrum, where there is always difference at the point of origin. For all of its instantaneous nature, in photography there is always a perverse moment of displacement and deferral. In its history, “a perverse complicity of continuity and resemblance with its supposed opposite, discontinuity and difference”72 … the latter only existing in a reciprocal relationship to the former.
The circle is closing and we return to where we started.
10
Human beings in their longing for lost continuity are mirrored by their photographs which transition from continuous to discontinuous and back again. While we yearn for our lost continuity, we must acknowledge that death is an unedited event, one that we cannot look back on. There is no following event to blank out that moment… and the dead are always dying. But what images of death in photography do is this: they allow us to approach the noumenal, that state of being of which we can have knowledge of, but can never know. We can approach, touch, feel, analyse, and have empathy for traumatic events in the representation of an unknowable reality. The photograph has the ability to go beyond the symbolic, to approach the impossible, the real.
The photograph may proffer a ‘releasement toward things’,73 a coexistence between a conscious and unconscious way of perceiving which sustains the mystery of the object confusing the distinction between real time and sensual time, between inside and outside, input and output becoming neither here nor there. As Martin Jolly notes, citing John Thompson, “… images of death can be seen a form of “mediated, non-reciprocal intimacy, stretched across time and space” in which we are increasingly unconstrained by our location or our time.”74 Further, John Thompson observes, “While lived experience remains fundamental, it is increasingly supplemented by, and in some respects displaced by, mediated experience, which assumes a greater and greater role in the project of self-formation.”75
In the sense that the photograph becomes la petite mort, the little death, it embodies our desire for the soul to become eternal in the form of this mediated experience… the displacement of the soul via the ghost in the machine, the soul remembered throughout time in the traumatic trace of the photograph. Death in the language of photography is always postponed and deferred: into the physicality of the photograph; into cultural memory; into the gaze (of the photographer, the camera and the viewer); and into the body of the observer. Here, a relationship exists between an impossible reality (an encounter with an “outside” which is unknowable) and a floating referent in an image that is both formative and transformative. And in that relationship, as Donna Haraway observes, “Relationship is multiform, at stake, unfinished, consequential.”76
The text of eternity that the photograph proposes, imparts and imposes a paradoxical state of loss. The secret of telling truth in a photograph is that the more truthful, “the more orgasmic, the more pleasurable, the more suicidal”77 the pronouncement of the perfect paradox78 (you are dead but also alive) … then the more we are strangled while uttering it. The language of deferral in the writing of trauma in death and the image becomes the dissolve that seizes the subject in the midst of an eternal bliss. In death and the image we may actually die (be)coming.
© Dr Marcus Bunyan 2018
Word count: 8,137
Addendum
“Empirically acknowledged as tragic, the photographic print was really just that when, at the turn of the century, it became the instrument of the three great authorities over life and death (the law, the army, medicine). This is when it demonstrated its power to reveal the unfolding of a destiny from the word go. As deus ex machina [god from the machine or, providential intervention], it was to become just as ruthless for the criminal, the soldier or the invalid, the conjunction between the immediate and the fatal only becoming more solid, inevitably, with the progress of representation.”
Virilio, Paul. The Vision Machine (trans. Julie Rose). Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1994, p. 43.
“Written with her trademark flair and force, Sontag’s book [On Photography] inaugurated a wave of criticism, much of it influenced by Foucaultian theory, that underscored the instrumentality and implicit violence of photography, its ability to police and regulate it subjects, especially those lacking social and political power: the poor, presumed “deviants” or “criminals,” and workers. As Sontag herself acknowledged, however, photography is not only a predatory means of taking possession, but also a mode of conferring value; it can potentially be put to counter-hegemonic uses, used to see and frame in ways that affirm and legitimate, rather than strictly contain and control, the presence of culturally disenfranchised persons.”
Entin, Joseph. “Milton Rogovin’s Approach: Photography, Class, and the Aesthetics of Making Space (2008),” on the ASX website July 12, 2010 [Online] Cited 27/10/2018
“The submissions attest to our insatiable hunger for images of suffering. “Sight can be turned off; we have lids on our eyes,” says Sontag5. But sometimes we just can’t resist taking a look. Since its inception photojournalism has traded in images of human suffering. If one of its motivations for representing tragedy has been to change the world then it has been unsuccessful. Instead the profession has turned us into voyeurs, passively consuming these images, sharing in the moment without feeling implicated or responsible for what we are seeing. Roland Barthes summed up the analgesic effect of looking at images of horror when he wrote “someone has shuddered for us; reflected for us, judged for us; the photographer has left us nothing – except a simple right of intellectual acquiescence.”6 Put another way, we look at events in photographs and feel relieved that they’re not happening anywhere near us. …
In the final analysis we were choosing between a French landscape, a dead guerrilla, an HIV positive mother and an American soldier. A strange task. Rather predictably the majority vote went to Tim Hetherington’s soldier. Yet comparing so many diverse images and ultimately declaring one of them a winner feels meaningless. Do we even need to be producing these images any more? Do we need to be looking at them? We have enough of an image archive within our heads to be able to conjure up a representation of any manner of pleasure or horror. Does the photographic image even have a role to play any more? Video footage, downloaded from the internet, conveys the sounds and textures of war like photographs never could. High Definition video cameras create high-resolution images twenty-four photographs a second, eliminating the need to click the shutter. But since we do still demand illustrations to our news then there is a chance to make images that challenge our preconceptions, rather than regurgitate old clichés.”
Adam Broomberg and Oliver Chanarin. “Unconcerned but not indifferent,” on the FOTO8 website 04 Mar 2008 [Online] Cited 20/11/2018
5. Susan Sontag, Regarding The Pain of Others (Penguin, London, 2003) p. 105
6. Roland Barthes, The Eiffel Tower and Other Mythologies (New York, Hill and Wang, 1979) p. 71. quoted in John Taylor, Body Horror: photojournalism, catastrophe and war (Manchester, Manchester University Press, 1988) p. 17
Adrien Constant de Rebecque (Swiss, Lausanne 1806-1876 Lausanne)
(Man in Chainmail Tunic Posing as a Dying Soldier)
c. 1863
Albumen print from collodion glass negative
17.9 x 24.2cm (7 1/16 x 9 1/2 in.)
Gilman Collection, Purchase, The Howard Gilman Foundation Gift, 2012
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
Manuel Álvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1902-2002)
Ouvrier en grève, assassiné (Striking worker, assassinated)
1934
Silver gelatin print
Manuel Alvarez Bravo (Mexican, 1902-2002)
La Buena Fama Durmiendo (The Good Reputation Sleeping)
1939, printed c. 1970s
Silver gelatin print
One of my early heroes in photography was Manuel Alvarez Bravo. Many Mexican photographs tell such stories based on the mythology of the country: there are elements of the absurd, surrealism, macabre, revolution, political and socio-economic issues, also of death, violence, beauty, youth, sexuality and religion to name but a few – a search for national identity that is balanced in the photographs of Bravo by a sense of inner peace and redemption. This potent mix of issues and emotions is what makes Mexican photography so powerful and substantive. In the “presence” (or present, the awareness of the here and now) of Mexican photography there is a definite calligraphy of the body in space in most of the work. This handwriting is idiosyncratic and emotive; it draws the viewer into an intimate narrative embrace. Two famous photographs by Bravo illustrate some of these themes (Apollonian / Dionysian; utopian / dystopian). When placed together they seem to have a strange attraction one to the other.
Anne Frank, photograph inscribed with her wish to go to Hollywood, October 10, 1942
Unknown photographer – U.S. Signal Corps Photo
General Anton Dostler
1945
Silver gelatin photograph
From International News Photos
References
Atkinson, Meera and Michael Richardson 2013. ‘Introduction: At the Nexus’, in M Atkinson and M Richardson (eds). Traumatic Affect. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, pp. 1-21
Atkinson, Meera and Michael Richardson (eds) 2013. Traumatic Affect. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing
Barthes, Roland 1981. Camera Lucida – Reflections on Photography. New York: Hill and Wang
Bataille, Georges 1962. Death and Sensuality: A Study of Eroticism and the Taboo. New York: Walker and Company
Batchen, Geoffrey 2004. Forget Me Not: Photography & Remembrance. New York: Princeton Architectural Press
Batchen, Geoffrey 1997. Burning with Desire: The Conception of Photography paperback 1999. Massachusetts: MIT Press
Bennett, Jill 2005. Empathic Vision: Affect, Trauma, and Contemporary Art. Palo Alto: Stanford University Press
Berger, John 1985. The Sense of Sight. New York: Vintage International
Brett, Donna West 2016. ‘Damaged: Ruin and Decay in Walker Evans’ Photographs’ at Walker Evans Symposium. Melbourne: Centre for Contemporary Photography
Bronowski, Jacob 1958. Science and Human Values. New York: Harper and Row
Brown, Andrew (ed. and trans,) 1987. Sophocles: Antigone. Wiltshire: Aris and Phillips Ltd.
Cadava, Eduardo 1992. ‘Words of Light: Theses on the Photography of History’ Diacritics 22 no. 3-4 (Fall-Winter), 84-114
Chaouat, Bruno 2005. ‘Image malgré tout’ (review) in L’Esprit Créateur vol. 45 no. 1, pp. 110-111
Deleuze, Gilles 1964. Proust and Signs. New York: George Braziller, 1972 in English
Edwards, Janis L. 2012. ‘Visual Literacy and Visual Politics: Photojournalism and the 2004 Presidential Debates’ in Communication Quarterly vol. 60 issue 5, pp. 681-197
Foucault, Michel 1988. ‘Technologies of the self’ in L H Martin and H Gutman and P H Hutton (eds). Technologies of the self: A seminar with Michel Foucault. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, pp. 16-49
Gibbs, Anna 2013. ‘Apparently Unrelated: Affective Resonance, Concatenation and Traumatic Circuitry in the Terrain of the Everyday’ in M Atkinson and M Richardson (eds). Traumatic Affect. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, pp. 129-147
Gibbs, Anna 2007. ‘Horrified: Embodied Vision, Media Affect and the Images from Abu Ghraib’ in D Staines (ed). Interrogating the War on Terror. Cambridge: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, pp. 125-142
Hanusch, Folker 2010. Representing death in the news: Journalism, Media and Mortality. London: Palgrave Macmillan
Haraway, Donna and Cary Wolfe 2016. Manifestly Haraway. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press
Hegel, George Wilhelm Frederich 1807. Phenomenology of Spirit Preface (trans. A. V. Miller 1977). Oxford: Oxford University Press
Heidegger, Martin 1966. Discourse on Thinking New York: Harper & Row
Houlihan, Kasia 2004. ‘Annotation on Roland Barthes’ Camera Lucida – Reflections on Photography’ New York: Hill and Wang 1981 in Theories of Media, Winter
Jolly, Martyn 2015. ‘An Australian Spiritualist’s Personal Cartes-de-Visite Album’, in A Maxwell and J Croci (eds). Shifting Focus: Colonial Australian Photography 1850-1920. North Melbourne: Australian Scholarly Publishing, pp. 71-87
Kopelson, Kevin 1990. ‘Wilde, Barthes, and the Orgasmics of Truth’ in GENDERS no. 7 Spring, pp. 22-31
Lacan, Jacques and Jeffrey Mehlman 1972. ‘The Seminar on the ‘Purloined Letter” in Yale French Studies no. 48 French Freud: Structural Studies in Psychoanalysis Yale University Press, pp. 39-72
Martin, Luther H and H Gutman and P H Hutton (eds) 1988. Technologies of the self: A seminar with Michel Foucault. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press
Maxwell, Anne and Josephine Croci (eds) 2015. Shifting Focus: Colonial Australian Photography 1850-1920. North Melbourne: Australian Scholarly Publishing
O’Hagan, Sean 2014. ‘Chloe Dewe Mathews’s Shot at Dawn: a moving photographic memorial’ on The Guardian website Sun 29 Jun 2014
Papastergiadis, Nikos and Mary Zournazi 2002. ‘Faith without certitudes’ in M Zournazi Hope: New Philosophies for Change Annandale. NSW: Pluto Press Australia, pp. 78-97
Randell, Karen and Sean Redmond (eds) 2008. The war body on screen. New York: Continuum
Rastas, David and Maria Schlachter 2016. Art as a Sanctuary for the Mad: Six characteristics of mystical experience and their visual accompaniment in contemporary art
Rogobete, Ileana Carmen 2011. Reconstructing Trauma and Recovery: Life Narratives of Survivors of Political Violence during Apartheid. PhD thesis Cape Town: University of Cape Town
Rutherford, Anne 2013. ‘Film, Trauma and the Enunciative Present’ in M Atkinson and M Richardson (eds) Traumatic Affect. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, pp. 80-103
Sontag, Susan 1977. On Photography New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux
Staines, Deborah (ed) 2007. Interrogating the War on Terror Cambridge: Cambridge Scholars Publishing
Strawberry 2013. ‘Roland Barthes: studium and punctum’ on the Museum of Education website March 12, 2013
Thompson, John 1995. The Media and Modernity: A Social Theory of Media. Cambridge: Polity Press
Virilio, Paul 1994. The Vision Machine (trans. Julie Rose). Bloomington: Indiana University Press
Walsh, Stephen 2000. Stalingrad: The Infernal Cauldron, 1942-43. London: Simon and Schuster
Wike, Lori 2000 ‘Photographs and Signatures: Absence, Presence, and Temporality in Barthes and Derrida’ in InVisible Culture: An Electronic Journal for Visual Studies issue 3, pp. 1-28
Zelizer, Barbie 2002. The Voice of the Visual in Memory. Annenberg School for Communication, University of Pennsylvania
Zembylas, Michalinos 2008. The Politics of Trauma in Education. New York: Palgrave Macmillan
Endnotes
[1] Berger, John 1985. The Sense of Sight. New York: Vintage International, p. 122
[2] Bataille, Georges 1962. Death and Sensuality: A Study of Eroticism and the Taboo. New York: Walker and Company, p. 15
[3] Anonymous 2016 Definition of Trauma by Mirriam-Webster, at http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/trauma (accessed 8 November 2016)
[4] Atkinson, Meera and Michael Richardson 2013. ‘Introduction: At the Nexus’ in M Atkinson and M Richardson (eds). Traumatic Affect. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, p. 5
[5] Rutherford, Anne 2013. ‘Film, Trauma and the Enunciative Present’ in M Atkinson and M Richardson (eds). Traumatic Affect. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, p. 82
[6] Michalinos Zembylas 2008. The Politics of Trauma in Education. New York: Palgrave Macmillan p. 4
[7] Ibid., p. 4
[8] Rutherford Op. cit., p. 87
[9] Rutherford Op. cit., Footnote 49, 93
[10] Rutherford Op. cit., p. 94
[11] Bennett, Jill 2005. Empathic Vision: Affect, Trauma, and Contemporary Art. Palo Alto: Stanford University Press, p. 9
[12] Rogobete, Ileana Carmen 2011. Reconstructing Trauma and Recovery: Life Narratives of Survivors of Political Violence during Apartheid. PhD thesis Cape Town: University of Cape Town, at https://open.uct.ac.za/handle/11427/10884 (accessed 8 November 2016)
[13] Rutherford Op. cit., 85
[14] Gibbs, Anna 2013. ‘Apparently Unrelated: Affective Resonance, Concatenation and Traumatic Circuitry in the Terrain of the Everyday’ in M Atkinson and M Richardson (eds). Traumatic Affect. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 130
[15] “Perhaps rather than numbness, what we actually feel is our own helplessness or impotence, and the shame of helplessness, which robs us of agency. Helplessness is what Tomkins calls an affect complex, and within it distress is the dominant affect, although there may be admixtures in it of fear, anger and shame… Helplessness immobilises, and this is what induces the shame which, as a reduction of interest, makes us lower our gaze and look away.”
Gibbs, Anna 2007. ‘Horrified: Embodied Vision, Media Affect and the Images from Abu Ghraib’ in D Staines (ed). Interrogating the War on Terror. Cambridge: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, pp. 139-140
[16] “To suffer is one thing; another thing is living with the photographed images of suffering, which does not necessarily strengthen conscience and the ability to be compassionate. It can also corrupt them. Once one has seen such images, one has started down the road of seeing more – and more. Images transfix. Images anaesthetize…”
Sontag, Susan 1977. On Photography. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, p. 20
“Are we making too much of images? Are we lured by our own voyeurism and iconophilia, numbed as we are by the democracy of the spectacle? Or, on the contrary, do images open the eyes of our conscience? In other words do images merely entertain and anaesthetize us or do they shame us and awake our conscience?”
Chaouat, Bruno 2005. ‘Image malgré tout’ (review) in L’Esprit Créateur vol. 45 no. 1, at https://muse.jhu.edu/article/265181/pdf (accessed 8 November 2016)
[17] Rutherford Op. cit., 89
[18] Anonymous 2016. ‘Lynching in the United States’, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lynching_in_the_United_States (accessed 11 November 2016)
[19] Anonymous 2016. ‘Strange Fruit: Billie Holiday’, at http://genius.com/Billie-holiday-strange-fruit-lyrics (accessed 11 November 2016)
[20] ‘Billie Holiday – Strange Fruit’, at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dnlTHvJBeP0 (accessed 11 November 2016)
[21] Rutherford Op. cit., Footnote 55, 95
[22] Bennett, Jill 2005. Empathic Vision: Affect, Trauma, and Contemporary Art. Palo Alto: Stanford University Press, p. 4 quoted in Rutherford, p. 95
[23] Ibid., p. 11
[24] Deleuze, Gilles 1964. Proust and Signs. New York: George Braziller (1972 in English) p. 7, in Bennett p. 161
[25] Bennett Op. cit., p. 10
[26] Papastergiadis, Nikos and Mary Zournazi 2002. ‘Faith without certitudes’ in M Zournazi. Hope: New Philosophies for Change pp. 94-95, in Bennett, p. 10
[27] Hanusch, Folker 2010. Representing death in the news: Journalism, Media and Mortality. London: Palgrave Macmillan, p. 55
[28] Ibid., p. 56
[29] Ibid., p. 56
[30] Randell, Karen and Redmond, Sean (eds) 2008. The war body on screen. New York: Continuum, cited in Hanusch, p. 30
[31] Foucault, Michel 1988. ‘Technologies of the self’, in L H Martin and H Gutman and P H Hutton (eds). Technologies of the self: A seminar with Michel Foucault Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, 18
[32] Barthes, Roland 1980 La Chambre Claire (Camera Lucida) (1981 in English) New York: Hill and Wang Section 39, 94
[33] Houlihan, Kasia 2004 ‘Annotation on Roland Barthes’ Camera Lucida – Reflections on Photography’ New York: Hill and Wang 1981 in Theories of Media, Winter at http://csmt.uchicago.edu/annotations/barthescamera.htm (accessed 12 November 2016)
[34] Strawberry 2013. ‘Roland Barthes: studium and punctum’ on the Museum of Education website 12 March, at https://educationmuseum.wordpress.com/2013/03/12/roland-barthes-studium-and-punctum/ (accessed 11 November 2016)
[35] “For memory is always in a state of ruin; to remember something is already to have ruined it, to have displaced it from its moment of origin. Memory is caught in a conundrum – the passing of time that makes memory possible and necessary is also what makes memory fade and die.”
Batchen, Geoffrey 2004. Forget Me Not: Photography & Remembrance. New York: Princeton Architectural Press, p. 78
[36] Cadava, Eduardo 1992. ‘Words of Light: Theses on the Photography of History’ in Diacritics 22 no. 3-4 (Fall-Winter), p. 110 in Batchen, p. 172
[37] Bennett Op. cit., p. 7
[38] Ibid., p. 7
[39] Zelizer, Barbie 2002. The Voice of the Visual in Memory, at http://www.sas.upenn.edu/folklore/center/ConferenceArchive/voiceover/voice_of_the_visual.html (accessed 13 November 2016)
[40] Ibid.,
[41] Brown, Andrew (ed. and trans,) 1987. Sophocles: Antigone, lines 850-52. Wiltshire: Aris and Phillips Ltd., p. 91
[42] Edwards, Janis L 2012. ‘Visual Literacy and Visual Politics: Photojournalism and the 2004 Presidential Debates’ on Taylor Francis Online at http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01463373.2012.725000 (accessed 13 November 2016)
[43] Zelizer Op. cit.,
[44] Sontag Op. cit., 18 cited in F Hanusch 2010 Representing death in the news: Journalism, Media and Mortality London: Palgrave Macmillan, 105
[45] See ‘Robert Capa: The Falling Soldier’, on The Met website, at http://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/283315 (accessed 13 November 2016)
[46] Walsh, Stephen 2000. Stalingrad: The Infernal Cauldron, 1942-43. London: Simon and Schuster, p. 23
[47] Anonymous photographer 2013. ‘Russian spy laughing through his execution in Finland, 1942’, on the Rare Historical Photos website 29 December, at http://rarehistoricalphotos.com/russian-spy-laughing-execution-finland-1942/ (accessed 13 November 2016)
[48] Brett, Donna West 2016. ‘Damaged: Ruin and Decay in Walker Evans’ Photographs’ at Walker Evans Symposium Melbourne: Centre for Contemporary Photography October 7, 5 at https://www.academia.edu/29201498/Damaged_Ruin_and_Decay_in_Walker_Evans_Photographs (accessed 13 November 2016)
[49] Soja, Edward W. 1996. Thirdspace Malden (Mass.): Blackwell, p. 57
[50] Ibid., p. 57
[51] Batchen Op. cit., p. 47
[52] Ibid., p. 48
[53] Rastas, David 2016. Art as a Sanctuary for the Mad: Six characteristics of mystical experience and their visual accompaniment in contemporary art, on the David Rastas website (accessed 19 November 2016. No longer available online)
[54] Bronowski, Jacob 1958. Science and Human Values. New York: Harper and Row, p. 31
[55] Anonymous 2015. ‘Hidden Likeness: Photographer Emmet Gowin at the Morgan’, on The Morgan Library & Museum website May 22 through September 20, 2015 https://www.themorgan.org/exhibitions/emmet-gowin (accessed 08 May 2018)
[56] See Turner, Victor 1966. The Ritual Process: Structure and Antistructure. Chicago: Aldine. For a definition of liminality see Anonymous, ‘Liminality’, on the Wikipedia website https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liminality (accessed 08 May 2018)
[57] Batchen, Geoffrey 1997. Burning with Desire: The Conception of Photography (paperback 1999). Massachusetts: MIT Press, p. 194
[58] Batchen. Forget Me Not, p. 94
[59] O’Hagan, Sean 2014 ‘Chloe Dewe Mathews’s Shot at Dawn: a moving photographic memorial’, on The Guardian website 29 June, at https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2014/jun/29/chloe-dewe-mathews-shot-at-dawn-moving-photographic-memorial-first-world-war (accessed 25 November 2016)
[60] Bennett 2005. Empathic Vision, p. 69
[61] Hegel, George Wilhelm Frederich 1807. Phenomenology of Spirit Preface (trans. A. V. Miller 1977). Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 10
[62] Anonymous 2016. ‘La petite mort’ Wikipedia website at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/La_petite_mort (accessed 25 November 2016)
[63] Barthes, Op. cit., p. 96
[64] Barthes, Op. cit., p. 96
[65] See Wike, Lori 2000. ‘Photographs and Signatures: Absence, Presence, and Temporality in Barthes and Derrida’ in InVisible Culture: An Electronic Journal for Visual Studies issue 3, at http://www.rochester.edu/in_visible_culture/issue3/wike.htm (accessed 25 November 2016)
[66] Lacan, Jacques and Jeffrey Mehlman 1972. ‘The Seminar on the ‘Purloined Letter”, in Yale French Studies, no. 48, p. 53 quoted in Wike, 2000
[67] Barthes. Camera Lucida, pp. 57-58 quoted in Wike, 2000
[68] Barthes. Camera Lucida, pp. 31-32 quoted in Wike, 2000
[69] Anonymous 2016. ‘The Real’, Wikipedia website at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Real (accessed 25 November 2016)
[70] “Derrida sees differences as elemental oppositions working in all languages, systems of distinct signs, and codes, where terms don’t have absolute meanings but instead draw meaning from reciprocal determination with other terms… Différance is the systematic play of differences, of the traces of differences, of the spacing by means of which elements are related to each other… the a of différance also recalls that spacing is temporization, the detour and postponement by means of which intuition, perception, consummation – in a word, the relationship to the present, the reference to a present reality, to a being – are always deferred.”
Anonymous 2016. ‘Différance’ at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Différance (accessed 25 November 2016
[71] Batchen. Burning with Desire p. 179. Information on photography and différance pp. 178-179.
[72] Batchen. Burning with Desire p. 186
[73] “We stand at once within the realm of that which hides itself from us, and hides itself just in approaching us. That which shows itself and at the same time withdraws is the essential trait of what we call the mystery… Releasement towards things and openness to the mystery belong together. They grant us the possibility of dwelling in the world in a totally different way…”
Heidegger, Martin 1966. Discourse on Thinking. New York: Harper & Row, pp. 55-56
[74] Thompson, John 1995. The Media and Modernity: A Social Theory of Media Cambridge: Polity Press, p. 208 quoted in M Jolly 2015. ‘An Australian Spiritualist’s Personal Cartes-de-Visite Album’, in A Maxwell and J Croci (eds). Shifting Focus: Colonial Australian Photography 1850-1920. North Melbourne: Australian Scholarly Publishing, p. 84
[75] Thompson, p. 233 quoted in Jolly, 2015
[76] Haraway, Donna and Cary Wolfe 2016. Manifestly Haraway. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, p. 122, at https://muse.jhu.edu/ (accessed 26 November 2016)
[77] Kopelson, Kevin 1990. ‘Wilde, Barthes, and the Orgasmics of Truth’ in GENDERS no 7 Spring, p. 26
[78] “You are dead but also alive, the dissolution of the distinction between objective and subjective realities, “the image is an interface connecting inner and outer, past and future, affect and cognition.””
Gibbs, Anna 2007. ‘Horrified: Embodied Vision, Media Affect And The Images From Abu Ghraib’, in D Staines (ed). Interrogating the War on Terror. Cambridge: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, p. 130














![Adrien Constant de Rebecque (Swiss, Lausanne 1806-1876 Lausanne) '[Man in Chainmail Tunic Posing as a Dying Soldier]' c. 1863 Adrien Constant de Rebecque (Swiss, Lausanne 1806-1876 Lausanne) '[Man in Chainmail Tunic Posing as a Dying Soldier]' c. 1863](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/09/man-in-chainmail-tunic-posing-as-a-dying-soldier-web.jpg?w=840)





















![Unknown photographer (American) '[Jeff Briggs, Robert Sims, Otis Hall, and Peter Pamphlet; Full-Length Mugshot from the Chicago Police Department]' 1936 Unknown photographer (American) '[Jeff Briggs, Robert Sims, Otis Hall, and Peter Pamphlet; Full-Length Mugshot from the Chicago Police Department]' 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/mug-shot1-web.jpg)
![Unknown photographer (American) '[John Dillinger's Feet, Chicago Morgue]' 1934 Unknown photographer (American) '[John Dillinger's Feet, Chicago Morgue]' 1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/john-dillingers-body-web.jpg)
![Unknown photographer (American) '[Jeff Briggs, Robert Sims, Otis Hall, and Peter Pamphlet; Full-Length Mugshot from the Chicago Police Department]' 1936 Unknown photographer (American) '[Jeff Briggs, Robert Sims, Otis Hall, and Peter Pamphlet; Full-Length Mugshot from the Chicago Police Department]' 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/mug-shot2-web.jpg)
![Walker Evans (American, St. Louis, Missouri 1903–1975 New Haven, Connecticut) '[Subway Passengers, New York City]' 1938 Walker Evans (American, St. Louis, Missouri 1903–1975 New Haven, Connecticut) '[Subway Passengers, New York City]' 1938](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/walker-evans-subway-passengers-new-york-city-web.jpg)





![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-a-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-a-detail.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-b-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-b-detail.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-c-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-c-detail.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-d-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-d-detail.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-h-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-h-detail.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-e-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-e-detail.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-f-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-f-detail.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-g-web.jpg)
![Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail) Alphonse Bertillon (French, 1853-1914) '[Album of Paris Crime Scenes]' 1901-1908 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/bertillon-g-detail.jpg)



























![Unknown photographer (American) '[Broadside for the Capture of John Wilkes Booth, John Surratt, and David Herold]' 1865 Unknown photographer (American) '[Broadside for the Capture of John Wilkes Booth, John Surratt, and David Herold]' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp274835-murder-web.jpg?w=650&h=1223)
![Alexander Gardner (American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821 - 1882 Washington, D.C.) 'Lewis Powell [alias Lewis Payne]' April 27, 186 Alexander Gardner (American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821 - 1882 Washington, D.C.) 'Lewis Powell [alias Lewis Payne]' April 27, 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/07/lewis-powell-web.jpg?w=650&h=821)


![Unknown photographer (American). '[Five Members of the Wild Bunch]' c. 1892 Unknown photographer (American). '[Five Members of the Wild Bunch]' c. 1892](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/07/the-wild-bunch-web.jpg?w=650&h=894)
![Tom Howard (American, 1894-1961) '[Electrocution of Ruth Snyder, Sing Sing Prison, Ossining, New York]' 1928 Tom Howard (American, 1894-1961) '[Electrocution of Ruth Snyder, Sing Sing Prison, Ossining, New York]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/07/electrocution-of-ruth-snyder-web.jpg?w=650&h=810)

![Unknown photographer (American) '[Automobile Murder Scene]' c. 1935 Unknown photographer (American) '[Automobile Murder Scene]' c. 1935](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/07/automobile-murder-scene-circa-1935-web.jpg?w=650&h=815)


![Weegee (American, born Ukraine (Austria), Złoczów (Zolochiv) 1899 - 1968 New York) '[Outline of a Murder Victim]' 1942 Weegee (American, born Ukraine (Austria), Złoczów (Zolochiv) 1899 - 1968 New York) '[Outline of a Murder Victim]' 1942](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/weegee-outline-web.jpg)







![United Press International (American) '[Bank Robber Aiming at Security Camera, Cleveland, Ohio]' March 8, 1975 United Press International (American) '[Bank Robber Aiming at Security Camera, Cleveland, Ohio]' March 8, 1975](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2016/07/cleveland-1975-web1.jpg?w=650&h=893)
![Mathew B. Brady. 'Untitled [Spectators massing for the Grand Review of the Armies, 23-24 May 1865, at the side of the crepe-draped U.S. Capitol, flag at half mast following the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln]' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/matthew-brady-captured-spectators-massing-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-b.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-b-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-b-detail.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-c-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-c-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-c-detail.jpg?w=840)















![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-d-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-d-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-d-detail.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-e-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-e-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-f-detail.jpg?w=650&h=464)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-f-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-f-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-g-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-g-whole.jpg?w=840)


![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-h-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-h-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-i-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-i-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-i-detail.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-j-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-j-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-k-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-k-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-k-detail.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-l-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-l-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-web.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-whole.jpg?w=840)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-detail.jpg?w=840)
![Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/reviewing-stand-web.jpg?w=650&h=644)
![Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 (detail) Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/reviewing-stand-detail.jpg?w=650&h=644)
![Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2015/07/brady-reviewing-stand.jpg?w=840)
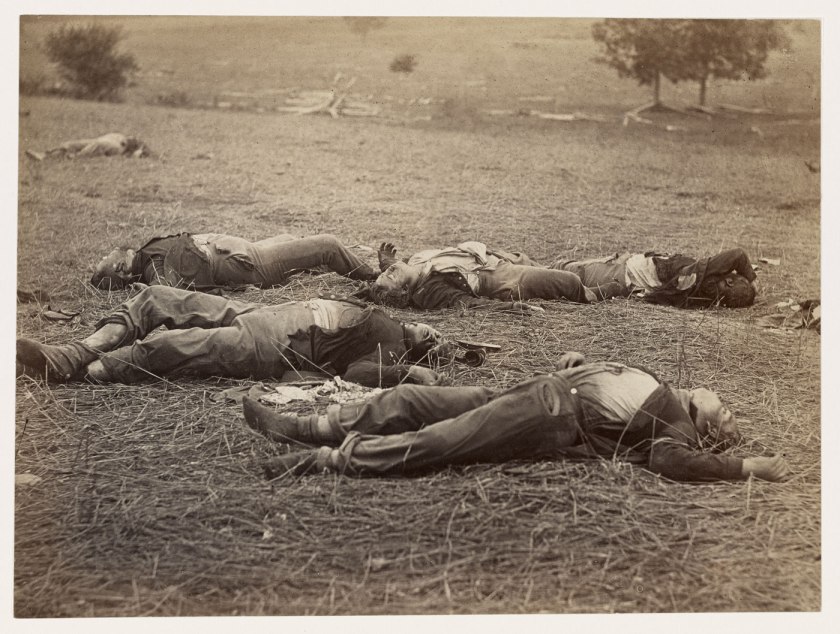
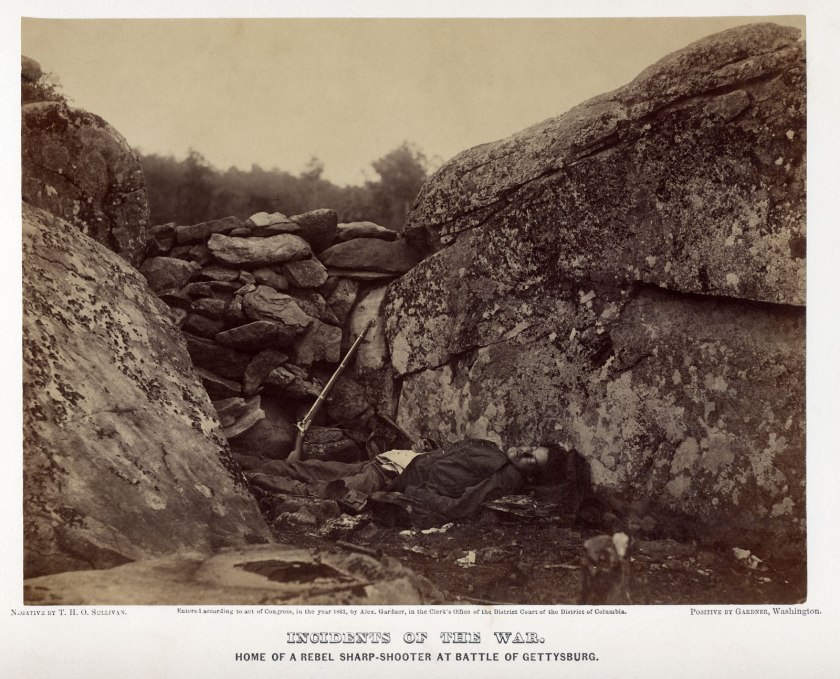
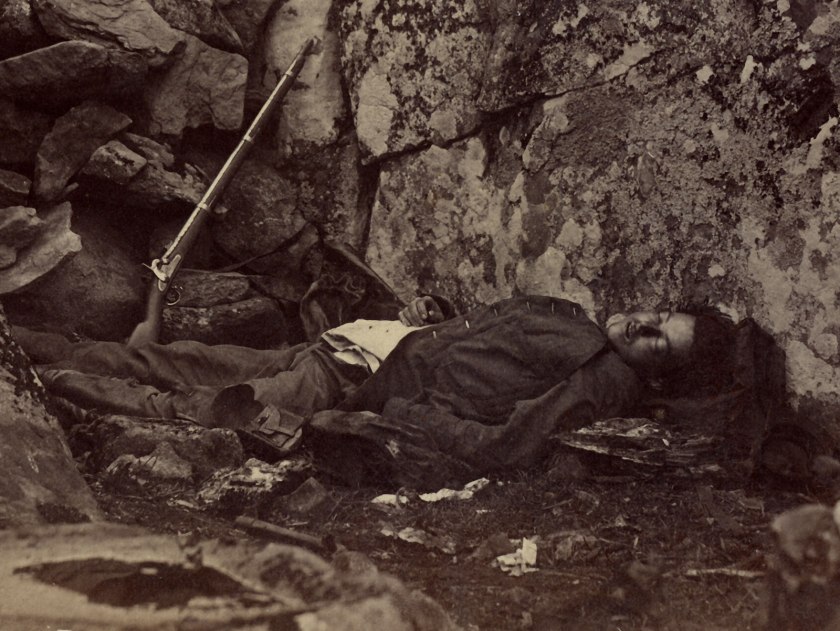
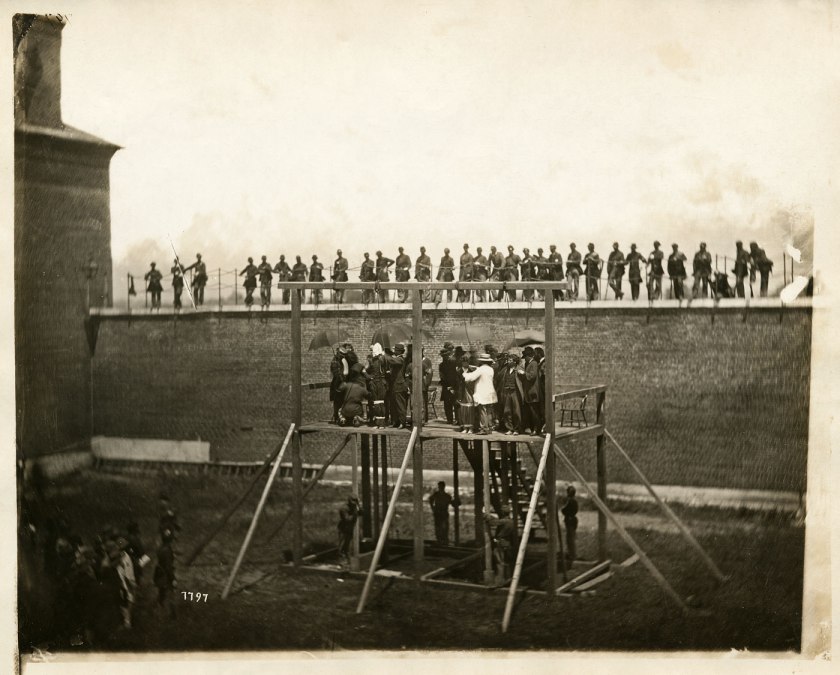











































































![Unknown '[The Pattillo Brothers (Benjamin, George, James, and John), Company K, "Henry Volunteers," Twenty-second Regiment, Georgia Volunteer Infantry]' 1861-63](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/patillo-brothers-close-up-web.jpg?w=840&h=719)
![Unknown '[The Pattillo Brothers (Benjamin, George, James, and John), Company K, "Henry Volunteers," Twenty-second Regiment, Georgia Volunteer Infantry]' (detail) 1861-63](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/patillo-brothers-close-up-detail.jpg?w=840&h=640)





![Maker: Unknown '[Civil War Portrait Lockets]' 1860s Maker: Unknown '[Civil War Portrait Lockets]' 1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp273827-lockets-web.jpg?w=840&h=573)
![Maker: Unknown '[Civil War Portrait Lockets]' (detail) 1860s Maker: Unknown '[Civil War Portrait Lockets]' (detail) 1860s](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp273827-lockets-detail.jpg?w=840&h=900)
![Alexander Gardner (American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821-1882 Washington, D.C.;) '[President Abraham Lincoln, Major General John A. McClernand (right), and E. J. Allen (Allan Pinkerton, left), Chief of the Secret Service of the United States, at Secret Service Department, Headquarters Army of the Potomac, near Antietam, Maryland]' October 4, 1862 Alexander Gardner (American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821-1882 Washington, D.C.;) '[President Abraham Lincoln, Major General John A. McClernand (right), and E. J. Allen (Allan Pinkerton, left), Chief of the Secret Service of the United States, at Secret Service Department, Headquarters Army of the Potomac, near Antietam, Maryland]' October 4, 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp248329-abraham-lincoln-web.jpg?w=826&h=1024)
![Alexander Gardner (American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821-1882 Washington, D.C.;) '[President Abraham Lincoln, Major General John A. McClernand (right), and E. J. Allen (Allan Pinkerton, left), Chief of the Secret Service of the United States, at Secret Service Department, Headquarters Army of the Potomac, near Antietam, Maryland]' (detail) October 4, 1862 Alexander Gardner (American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821-1882 Washington, D.C.;) '[President Abraham Lincoln, Major General John A. McClernand (right), and E. J. Allen (Allan Pinkerton, left), Chief of the Secret Service of the United States, at Secret Service Department, Headquarters Army of the Potomac, near Antietam, Maryland]' (detail) October 4, 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp248329-abraham-lincoln-detail.jpg?w=840&h=611)
![Maker: Unknown, American; Photography Studio: After, Brady & Co., American, active 1840s–1880s '[Mourning Corsage with Portrait of Abraham Lincoln]' (detail) Photograph, corsage April 1865 Maker: Unknown, American; Photography Studio: After, Brady & Co., American, active 1840s–1880s '[Mourning Corsage with Portrait of Abraham Lincoln]' (detail) Photograph, corsage April 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/lincoln-mourning.jpg?w=768&h=1024)
![Maker: Unknown, American; Photography Studio: After, Brady & Co., American, active 1840s–1880s '[Mourning Corsage with Portrait of Abraham Lincoln]' (detail) Photograph, corsage April 1865 Maker: Unknown, American; Photography Studio: After, Brady & Co., American, active 1840s–1880s '[Mourning Corsage with Portrait of Abraham Lincoln]' (detail) Photograph, corsage April 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp265063-lincoln-memorial-button-web.jpg?w=768&h=1024)

![Maker: Unknown '[Game Board with Portraits of President Abraham Lincoln and Union Generals]' 1862 Maker: Unknown '[Game Board with Portraits of President Abraham Lincoln and Union Generals]' 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp269309-chess-board-web.jpg?w=840&h=827)
![Maker: Unknown '[Game Board with Portraits of President Abraham Lincoln and Union Generals]' (detail) 1862 Maker: Unknown '[Game Board with Portraits of President Abraham Lincoln and Union Generals]' (detail) 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp269309-chess-board-detail.jpg?w=840&h=503)
![Unknown photographer (American) '[Confederate Sergeant in Slouch Hat]' 1861-1862 Unknown photographer (American) '[Confederate Sergeant in Slouch Hat]' 1861-1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/confederate-with-clown-like-chevrons-closeup-web.jpg?w=840&h=890)

![Unknown photographer (American) '[James A. Holeman, Company A, "Roxboro Grays," Twenty-fourth North Carolina Infantry Regiment, Army of Northern Virginia]' 1861-1862 Unknown photographer (American) '[James A. Holeman, Company A, "Roxboro Grays," Twenty-fourth North Carolina Infantry Regiment, Army of Northern Virginia]' 1861-1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/james-holeman-closeup-web.jpg?w=840&h=975)

![Maker: Unknown (American; Alexander Gardner, American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821–1882 Washington, D.C.; Photography Studio: Silsbee, Case & Company, American, active Boston) '[Broadside for the Capture of John Wilkes Booth, John Surratt, and David Herold]' April 20, 1865 Maker: Unknown (American; Alexander Gardner, American, Glasgow, Scotland 1821–1882 Washington, D.C.; Photography Studio: Silsbee, Case & Company, American, active Boston) '[Broadside for the Capture of John Wilkes Booth, John Surratt, and David Herold]' April 20, 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/dp274835-murder-web.jpg?w=544&h=1024)











![Unknown, American. '[Broadside for the Capture of John Wilkes Booth, John Surratt, and David Herold]' April 20, 1865 Unknown, American. '[Broadside for the Capture of John Wilkes Booth, John Surratt, and David Herold]' April 20, 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/08/broadside-for-the-capture-of-john-wilkes-booth-web.jpg?w=534&h=1016)
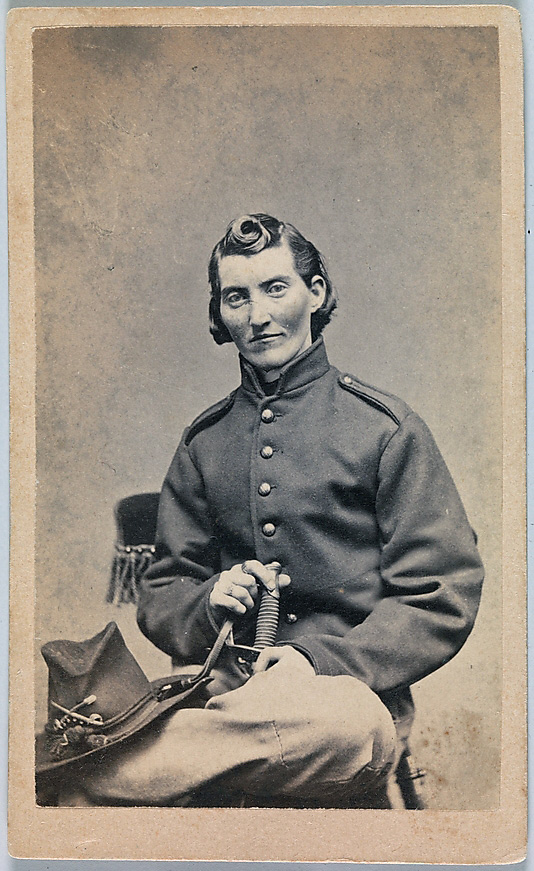












![Unknown. '[Private James House with Fighting Knife, Sixteenth Georgia Cavalry Battalion, Army of Tennessee]' 1861-62? Unknown. '[Private James House with Fighting Knife, Sixteenth Georgia Cavalry Battalion, Army of Tennessee]' 1861-62?](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/08/39-james-house-web.jpg?w=840&h=975)
![Unknown. '[Private James House with Fighting Knife, Sixteenth Georgia Cavalry Battalion, Army of Tennessee]' 1861-62? (detail) Unknown. '[Private James House with Fighting Knife, Sixteenth Georgia Cavalry Battalion, Army of Tennessee]' 1861-62? (detail)](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/08/39-james-house-detail.jpg?w=840&h=974)

![Unknown. '[Private Thomas Gaston Wood, Drummer, Company H, "Walton Infantry," Eleventh Regiment Georgia Volunteer Infantry]' 1861 Unknown. '[Private Thomas Gaston Wood, Drummer, Company H, "Walton Infantry," Eleventh Regiment Georgia Volunteer Infantry]' 1861](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/08/private-thomas-gaston-wood-web.jpg?w=840&h=921)




![Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Dead Confederate sharpshooter in "The devil's den."]' July 1863 Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Dead Confederate sharpshooter in "The devil's den."]' July 1863](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/gardner-sharpshooter-web.jpg?w=840&h=678)
![Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Antietam, Md. President Lincoln with Gen. George B. McClellan and group of officers]' 3rd October 1862 Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Antietam, Md. President Lincoln with Gen. George B. McClellan and group of officers]' 3rd October 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/abraham-lincoln-and-generals-web.jpg?w=840&h=673)
![Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Antietam, Md. President Lincoln with Gen. George B. McClellan and group of officers]' (detail) 3rd October 1862 Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Antietam, Md. President Lincoln with Gen. George B. McClellan and group of officers]' (detail) 3rd October 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/abraham-lincoln-and-generals-detail.jpg?w=840&h=972)

![Timothy H. O'Sullivan (1840-1882). '[Fort Pulaski, Ga. The "Beauregard" gun]' April 1862 Timothy H. O'Sullivan (1840-1882). '[Fort Pulaski, Ga. The "Beauregard" gun]' April 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/big-gun-web.jpg?w=840&h=870)
![Alexander Gardner (1821-1882). '[Richmond, Va. Grave of Gen. J. E. B. Stuart in Hollywood Cemetery, with temporary marker]' Richmond, April-June 1865 Alexander Gardner (1821-1882). '[Richmond, Va. Grave of Gen. J. E. B. Stuart in Hollywood Cemetery, with temporary marker]' Richmond, April-June 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/general-stuart-web.jpg?w=840&h=822)
![James F. Gibson. '[James River, Va. Deck and turret of U.S.S. Monitor seen from the bow (ie. stern)]' 9th July, 1862 James F. Gibson. '[James River, Va. Deck and turret of U.S.S. Monitor seen from the bow (ie. stern)]' 9th July, 1862](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/james-river-va-deck-and-turret-of-uss-monitor-seen-from-the-bow-web.jpg?w=840&h=838)

![Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Washington Navy Yard, D.C. Lewis Payne, the conspirator who attacked Secretary Seward, standing in overcoat and hat]' April 1865 Alexander Gardner (1821-1882) '[Washington Navy Yard, D.C. Lewis Payne, the conspirator who attacked Secretary Seward, standing in overcoat and hat]' April 1865](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/payne-a-web1.jpg?w=834&h=1024)
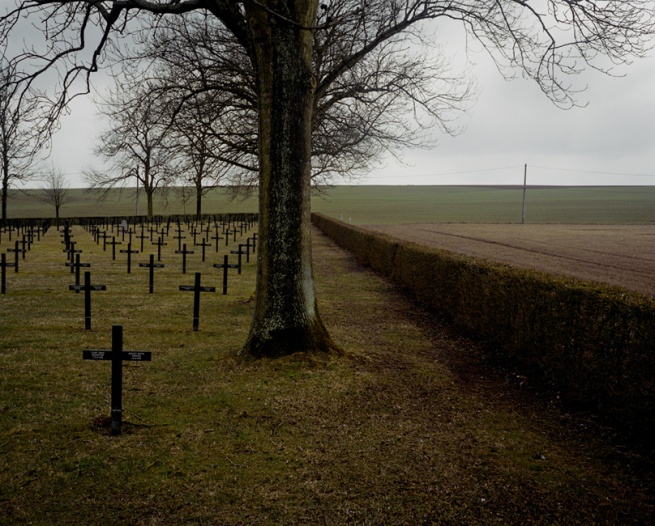
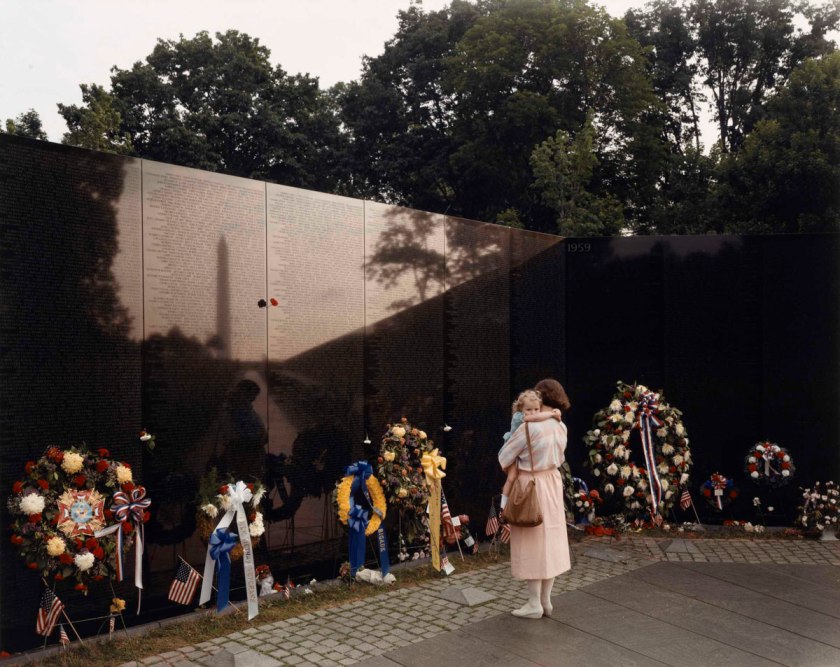
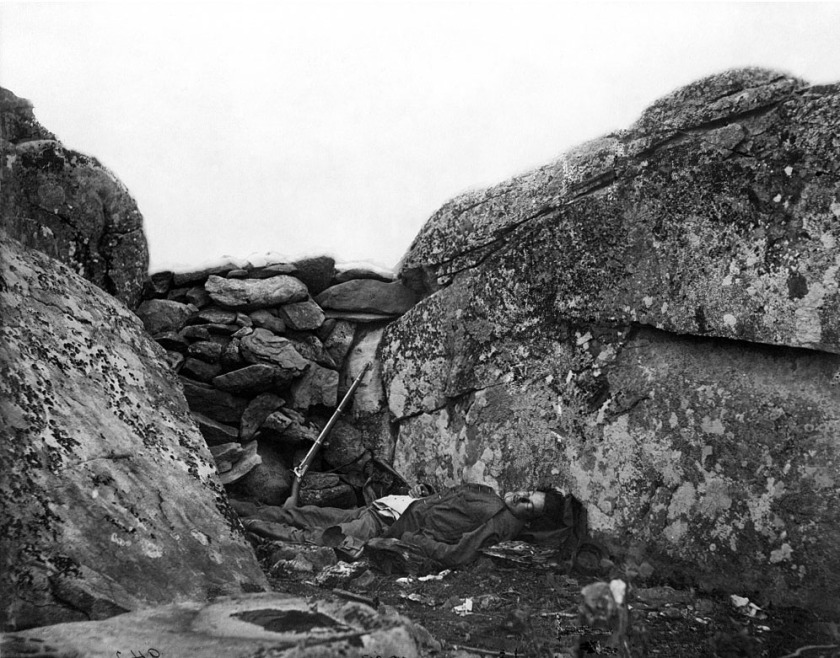





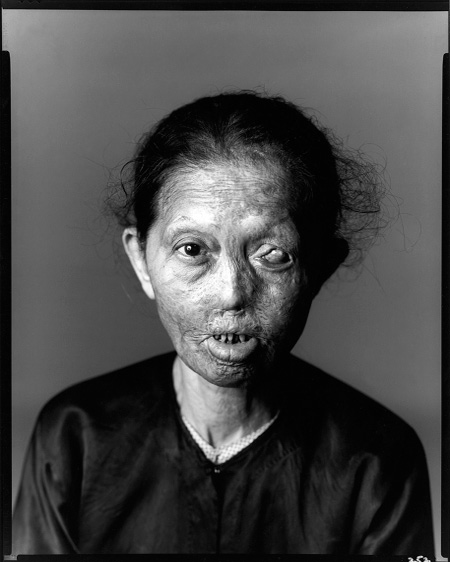

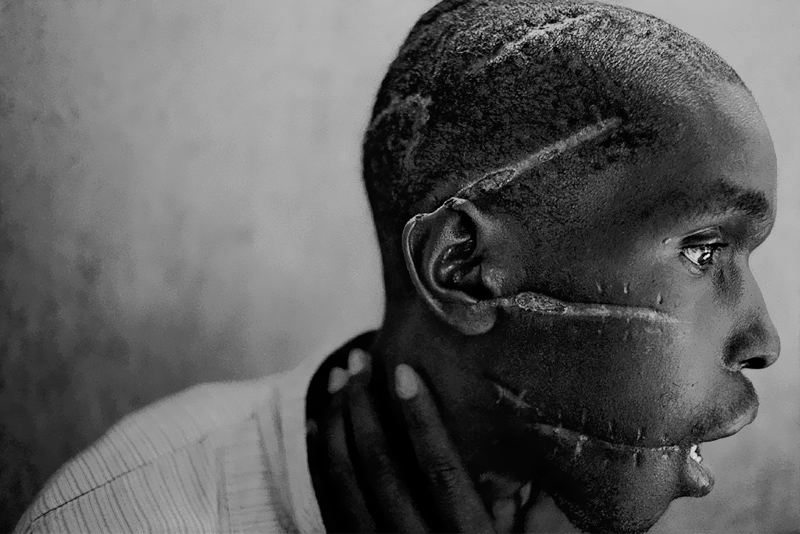







You must be logged in to post a comment.