Exhibition dates: 25th February – 3rd June 2012
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait
1929
Gelatin silver print
24 x 19cm
Musée des Beaux-Arts de Nantes
© RMN/Gérard Blot
“In many ways, Cahun’s life was marked by a sense of role reversal, and her public identity became a commentary upon not only her own, but the public’s notions of sexuality, gender, beauty, and logic. Her adoption of a sexually ambiguous name, and her androgynous self-portraits display a revolutionary way of thinking and creating, experimenting with her audience’s understanding of photography as a documentation of reality. Her poetry challenged gender roles and attacked the increasingly modern world’s social and economic boundaries. Also Cahun’s participation in the Parisian Surrealist movement diversified the group’s artwork and ushered in new representations. Where most Surrealist artists were men, and their primary images were of women as isolated symbols of eroticism, Cahun epitomised the chameleonic and multiple possibilities of the female identity. Her photographs, writings, and general life as an artistic and political revolutionary continue to influence countless artists, namely Cindy Sherman, Nan Goldin and Del LaGrace Volcano.”
Text from the Wikipedia website
Cahun was a resistance fighter during the Second World War, was arrested, sentenced to death and survived. She lived with her longtime female partner and collaborator on Jersey from 1937 until 1954, the year of her death. Entre Nous means “Between Us,” such an appropriate title for their collaboration, love and partnership. What a talent, what a woman and gay to boot!
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Art Institute of Chicago for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait
1929
Gelatin silver print
11.5 x 8.5cm
Jersey Heritage Collection
© Jersey Heritage
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait
1928
Gelatin silver print
13.9 x 9cm
Jersey Heritage Collection
© Jersey Heritage
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait
1927
Gelatin silver print
10.4 x 7.6cm
Soizic Audouard Collection
Claude Cahun (1894-1954) has something approaching cult status in today’s art world. However, her work was almost unknown until the early 1980s, when it was championed by the research of François Leperlier, after which exhibitions at the Musée des Beaux-Arts in Nantes (1994) and the Musée d’Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris (1995) brought it to public attention. Her life and work (both literary and artistic) bespeak an extraordinary libertarian personality who defied sexual, social and ethical conventions in what was an age of avant-garde and moral upheaval. Among her many photographs, it is undoubtedly her self-portraits that have aroused the greatest interest in recent years. Throughout her life, Cahun used her own image to dismantle the clichés surrounding ideas of identity. She reinvented herself through photography, posing for the lens with a keen sense of performance and role-play, dressed as a woman or a man, as a maverick hero, with her hair long or very short, or even with a shaved head. This approach was extended in innovative ways in her photographs of objects and use of photomontages, which asserted the primacy of the imagination and of metamorphosis.
By exploring the many different analyses made of Cahun’s work since the 1990s, and ranging across its different themes: from the subversive self-portraits that question identity, to her surrealist compositions, erotic metaphors and political forays, this exhibition confirms the modernity of a figure who, as a pioneer of self-representation and the poetry of objects, has been an important influence for many contemporary artists.
Metamorphoses of identity and the subversion of gender (I)
This set of photographs, going from 1913 to the end of the 1920s, includes some of Cahun’s major works, in which she staged her own persona, emphasising disguise and masks, and working through variations on gender: feminine, masculine, androgyne, undifferentiated. Sexual ambiguity is consciously cultivated and calls into question established norms and conventions. In 1928, she even represented herself with her head shaved, wearing a singlet, in profile, or with her hands against her face, or wearing a loose man’s jacket. Some of the mise-en-scènes from this period seem to anticipate contemporary performance.
Poetics of the object
The “assemblages of objects,” which make their appearance in around 1925, inventively explore what at the time was still a rather new form. This work came to wider attention in the Surrealist exhibition at the Charles Ratton gallery, in May 1936, and then with the commissioning of 22 photographic plates to illustrate a book of poems by Lise Deharme, Le Coeur de Pic (1937), prefaced by Paul Eluard. These photographs capture ephemeral set-ups, often in a natural setting (garden, beach). Each “sketch” is a composition of heterogeneous elements, both found and made, such as knickknacks in spun glass, sewing items, twigs, bones, insects, feathers, gloves, pieces of fabric, shoes, tools, etc. This “theatre of objects” has both a visual and symbolic significance, which Cahun explained in her text Prenez garde aux objets domestiques (1936).
Metamorphoses of identity and the subversion of gender (continued)
The 1930s saw Cahun continuing to explore images of the self. However, questions of sexual difference and its social and cultural construction were now less to the fore as she went deeper into the potential of situations and disguises and experimented with duplication in a way that extended the work of the photomontages from the late 1920s.
Metaphors of desire
Eschewing the direct and sometimes reifying display of the female body found in many paintings and photographs, Cahun opted for a more subtle kind of “veiled eroticism” using distance and irony. Here we find some very evocative examples of her calculating games with desire. Whether through the contained display of the body, allegory (the bacchante or faun, surrounded by sensuous vegetation), or anthropomorphic objects (the hermaphroditic “père”), she aimed to capture the essence of desire, to bring out its essential grounding in fantasy.
The two of us. Claude Cahun and Suzanne Malherbe (Marcel Moore)
The photograph Entre nous (1926) clearly establishes the spirit of this section, which evokes various aspects of Claude Cahun’s intimate relationship and artistic collaboration with her partner, Suzanne Malherbe. In fact, a number of the photographs here were taken by Suzanne following Claude’s suggestions. A double portrait from 1921 shows a surprising parallel which could be read as a metaphor of their relationship, a deep closeness and understanding between two strong personalities. The linchpin of this section is constituted by the four photomontages used to illustrate Aveux non avenus (1930), Cahun’s most significant literary work, gathering together all the artist’s main themes and obsessive metaphors. The plates were executed by Moore in collaboration with Claude Cahun.
Elective encounters
This series of portraits, which reflect the importance of friendship in the development of Cahun’s work, gives an idea of the figures who were important to her and influenced her, or to whom she felt close, among them Henri Michaux, Robert Desnos, André Breton, Jacqueline Lamba and Suzanne Malherbe. There are also two photographs from performances at Pierre Albert-Birot’s theatre Le Plateau (1929). They attest Cahun’s keen interest in theatre and acting.
Poetry and politics
In the 1930s Cahun’s positions grew increasingly radical in response to the rise of totalitarianism. She joined the Surrealists and associated with a number of groups on the left and far left. This radicalisation is reflected in her aesthetic. In line with the ideas put forward in her pamphlet Les Paris sont ouverts (1934), she exploited the subversive qualities of “indirect action” in the sphere of symbolic expression, making a number of objects in which poetry and politics are intimately intertwined. This process culminated when she used these pieces for two big series of photographs dominated by a mood of irony, revolt and provocation: “La Poupée” (The Doll), a figure fashioned out of newspaper, and “Le Théâtre” (The Theatre), a wooden mannequin surrounded by various elements and placed under a glass dome.
Beyond the visible. The last self-portraits
Close study of Cahun’s photographs reveals the presence of allusions to non-visible phenomena, pointing the way to other realities – and perhaps, too, beyond death. Her attraction to symbolism, her interest in Eastern doctrines and her closeness to Surrealism only confirmed the primacy of fantasy and metamorphosis evidenced in the intellectual and aesthetic approaches she took throughout her life. The series Le Chemin des chats (The Way of Cats, around 1949 and 1953), suggests a mediation on and questioning of reality and appearance. Cahun was a true cat lover: for her, this animal was the great intercessor, the medium of an intuitive contact between the visible and the invisible, leading to sensorial worlds that are both unfamiliar and yet very near.
Juan Vicente Aliaga and François Leperlier, curators of the exhibition
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait
1939
Gelatin silver print
10 x 8cm
Jersey Heritage Collection
© Jersey Heritage
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Autoportrait
1926
Gelatin silver print
11.1 x 8.6cm
IVAM, Institut Valencià d’Art Modern, Generalitat
Born Lucy Schwob to a family of French intellectuals and writers, Claude Cahun (who adopted the pseudonym at age 22) is best known for the staged self-portraiture, photomontages, and prose texts she made principally between 1920 and 1940. Rediscovered in the late 1980s, her work has not only expanded our understanding of the Surrealist era but also serves as an important touchstone to later feminist explorations of gender and identity politics. In her self-portraits, which she began creating around 1913, Cahun dismantled and questioned preexisting notions of self and sexuality. Posing in costumes and elaborate make-up, Cahun appears masked as various personae: man or woman, hero or doll, both powerful and vulnerable. Almost a century after their making, these innovative photographs and assemblages remain remarkably relevant in their treatment of gender, performance, and identity.
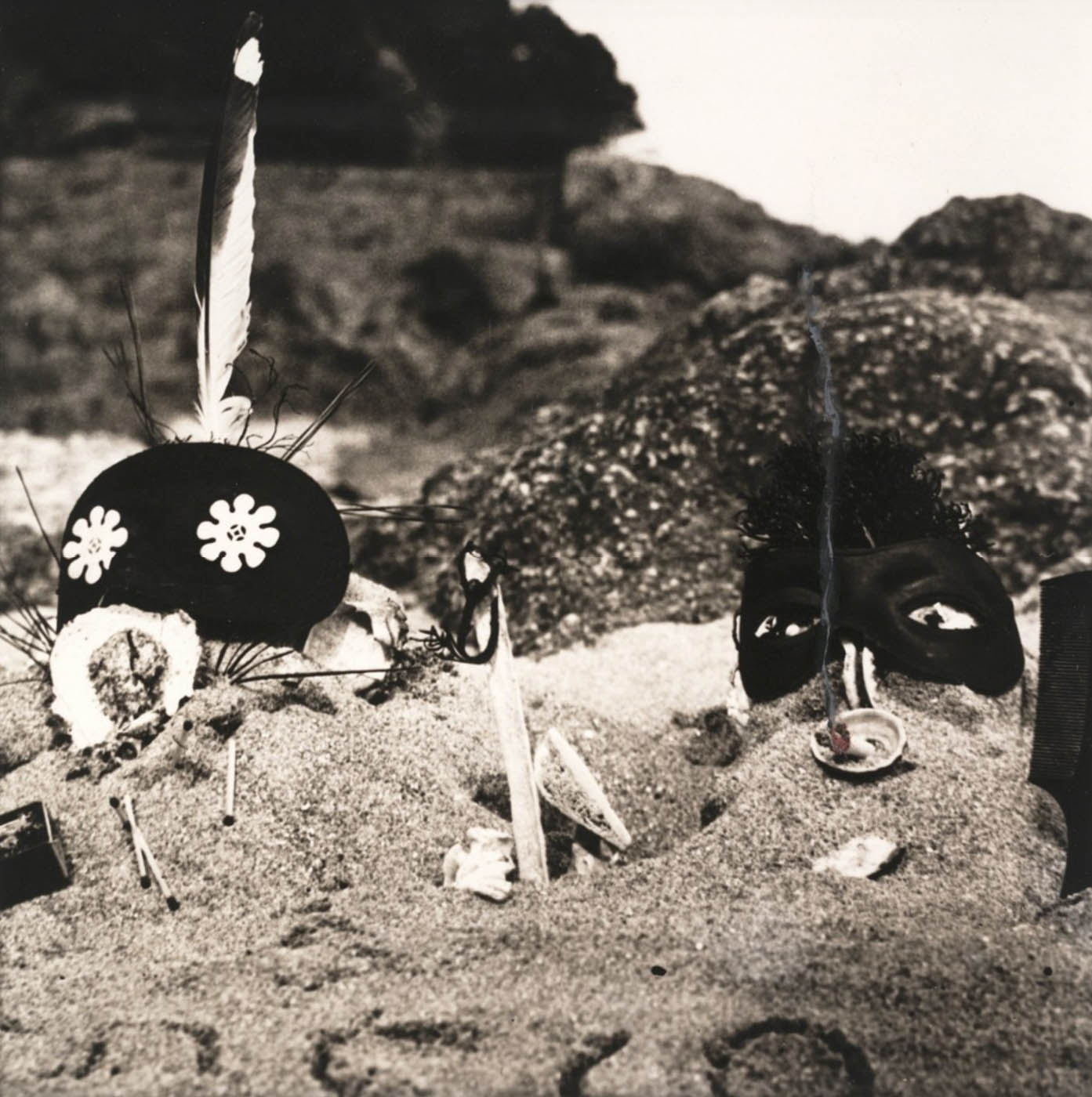
From her university years until her death, Cahun was accompanied by her partner and artistic collaborator, Suzanne Malherbe, a childhood friend and stepsister. They surrounded themselves with members of the Surrealist movement and created work that embraced leftist politics. Cahun, with assistance from Malherbe (under the pseudonym Marcel Moore), produced photographs, assemblages, and publications from the 1920s on. The photograph Entre Nous (Between Us), featuring a pair of masks embedded in sand, gives the title to this show and is emblematic of their multifaceted relationship.
The first retrospective exhibition in the United States of Cahun’s work, Entre Nous: The Art of Claude Cahun brings together over 80 photographs and published material by Cahun and Moore, including several photomontages from their 1930 collaborative publication Aveux non avenus (Disavowals), and the only surviving object by Cahun, which is in the Art Institute’s permanent collection.
Organiser: This exhibition was organised by the Jeu de Paume, Paris, and coproduced with La Virreina Centre de la Imatge, Barcelona.
Press release from the Art Institute of Chicago website
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Combat de pierres
1931
Gelatin silver print
21 x 15.5cm
Private collection
© Béatrice Hatala
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Le Père
1932
Gelatin silver print
23.6 x 17.7cm
LAC
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954) Marcel Moore (French, 1892-1972)
Entre nous (Between Us)
1926
Gelatin silver print
4 11/16 × 4 5/8 in (11.9 × 11.7cm)
While the motivation for these remarkable self-portraits seems rooted in a commitment to leftist politics and subversion of gender norms, I also feel a great sense of intimate domesticity beneath the surface. Cahun and Moore first met in 1909 when they were both teenagers. Eight years later, Cahun’s father married Moore’s mother, which must have given the couple a convenient excuse for their close relationship at a time when such lifestyle choices were less than accepted.
Our curators have surmised that Cahun’s camera did not have a timer on it, so many if not all of these self-portraits must have been created with Moore’s assistance. When the two moved to the Isle of Jersey in the 1930s to escape the political climate developing in France, they began to live in almost total seclusion. Though often taken outside around the grounds of their estate, the photographs from this period seem to the most private and familiar. Beyond the thoughtful self-presentation and artistic experimentation, there is a palpable sense of play, of close friends having fun.
An interesting aside: In July of 1940, the Nazis invaded Jersey where Cahun and Moore were still living. For the next four years, they engaged in active resistance against the Germans, producing and distributing counterpropaganda leaflets to Nazi soldiers on the island. Continuing the kind of dress-up they’d played together for years, the two would dress in disguises to infiltrate German outposts where they would disseminate anti-Nazi leaflets signed as “der Soldat ohne Namen” (the solider with no name). They were eventually arrested in 1944 and sentenced to death. Fortunately, the island was liberated before the executions could be carried out.
Extract from Robby Sexton, “Between You and Me,” on the Art Institute of Chicago website March 15, 2012 [Online] Cited 08/10/2024
Claude Cahun (French, 1894-1954)
Aveux non avenus, planche III
1929-1930
Gelatin silver print photomontage
15 x 10cm
Private collection
The Art Institute of Chicago
111 South Michigan Avenue
Chicago, Illinois 60603-6404
Phone: (312) 443-3600
Opening hours:
Thursday – Monday 11am – 5pm
Closed Tuesdays and Wednesdays

















































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.