Exhibition dates: 10th November, 2016 – 7th May, 2017
Curators: Shoair Mavlian with Simon Baker and Newell Harbin, Director of The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
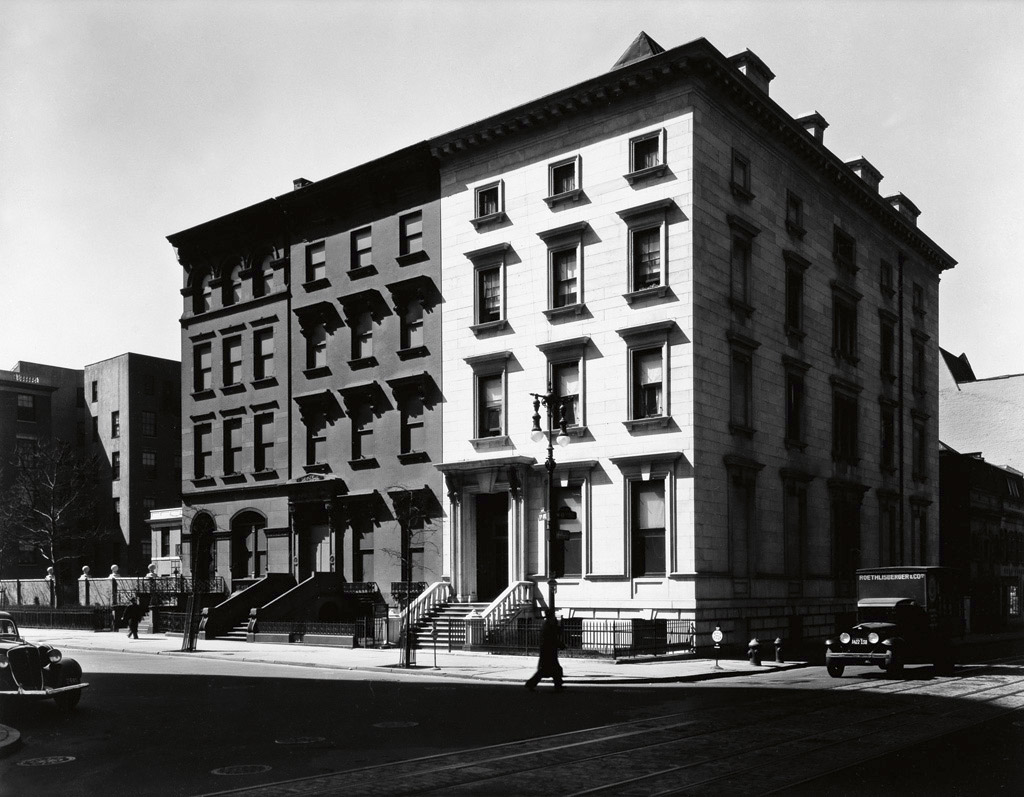
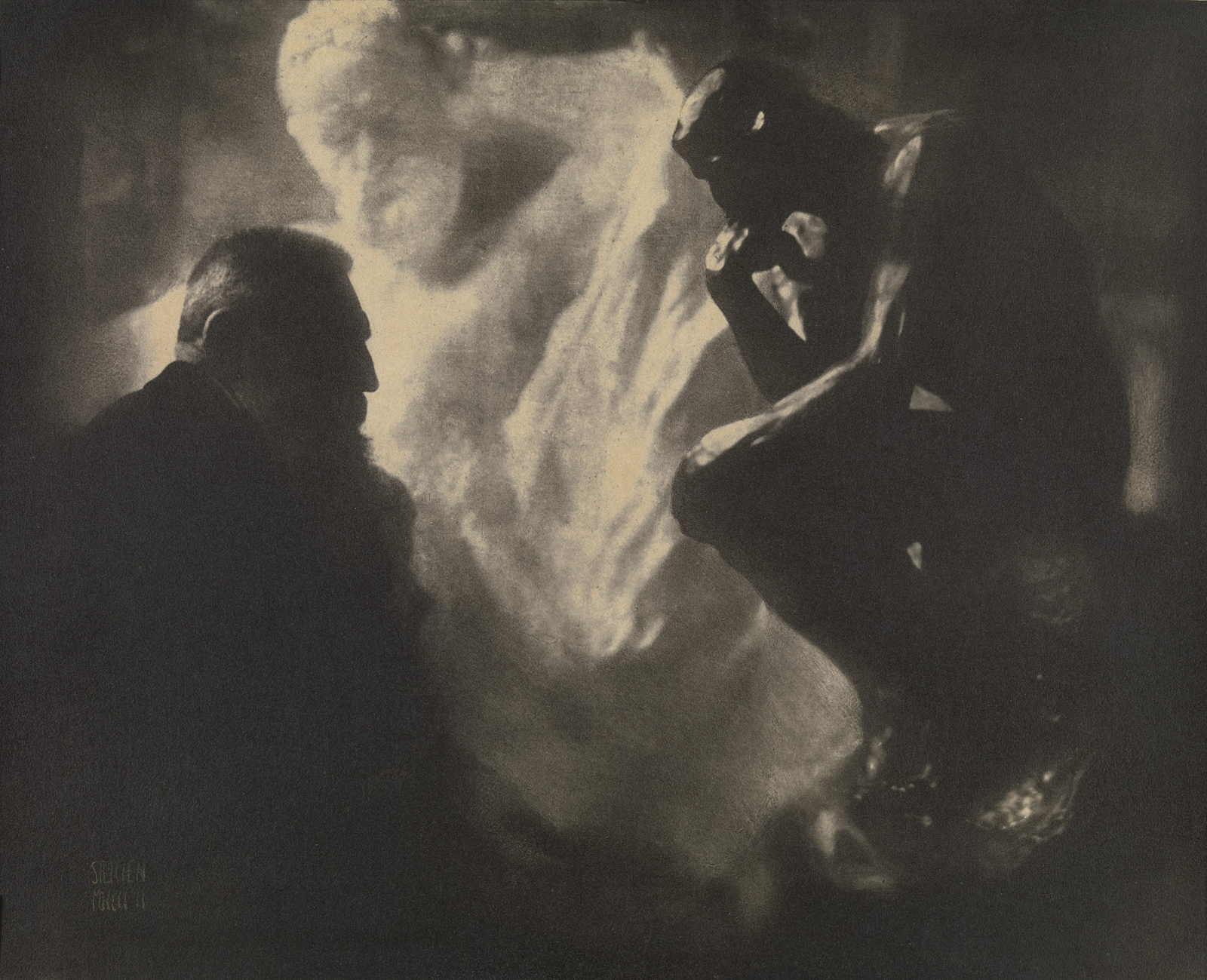
Paul Strand (American, 1890-1976)
Wall Street, New York
1915
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
Many thankx to Tate Modern for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“This is a once-in-a-lifetime chance to see one of the world’s greatest private collections of photography, drawn from the classic modernist period of the 1920s-50s. An incredible group of Man Ray portraits are exhibited together for the first time, having been brought together by Sir Elton John over the past twenty-five years, including portraits of Matisse, Picasso, and Breton. With over 70 artists and nearly 150 rare vintage prints on show from seminal figures including Brassai, Imogen Cunningham, André Kertész, Dorothea Lange, Tina Modotti, and Aleksandr Rodchenko, this is a chance to take a peek inside Elton John’s home and delight in seeing such masterpieces of photography.”
Text from the Tate Modern website
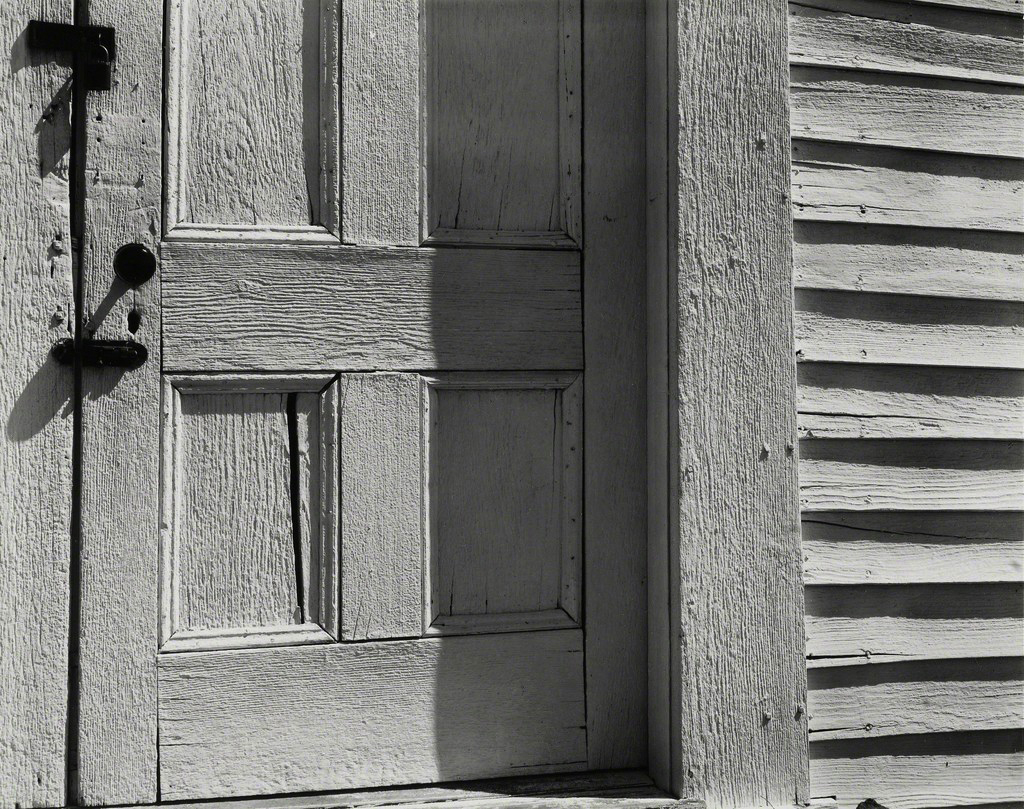
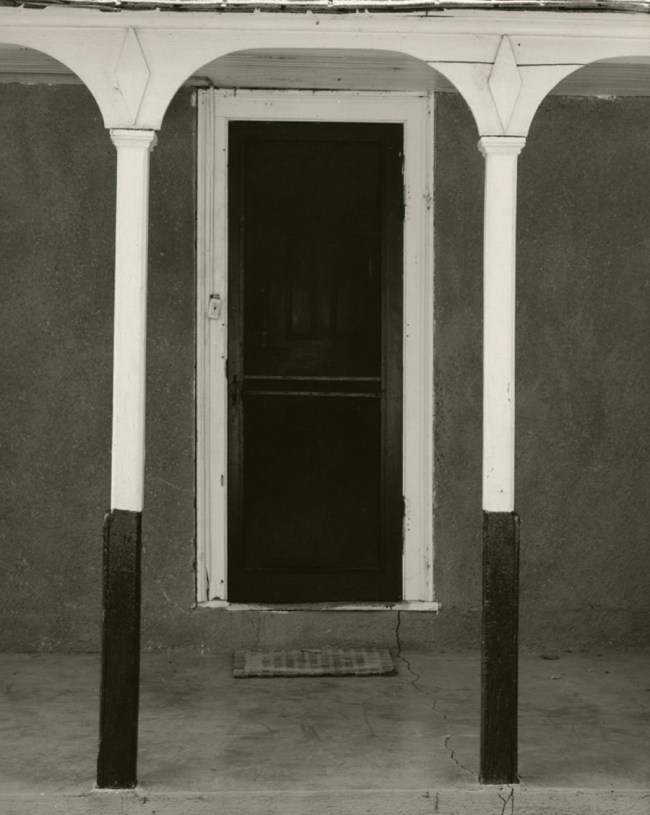
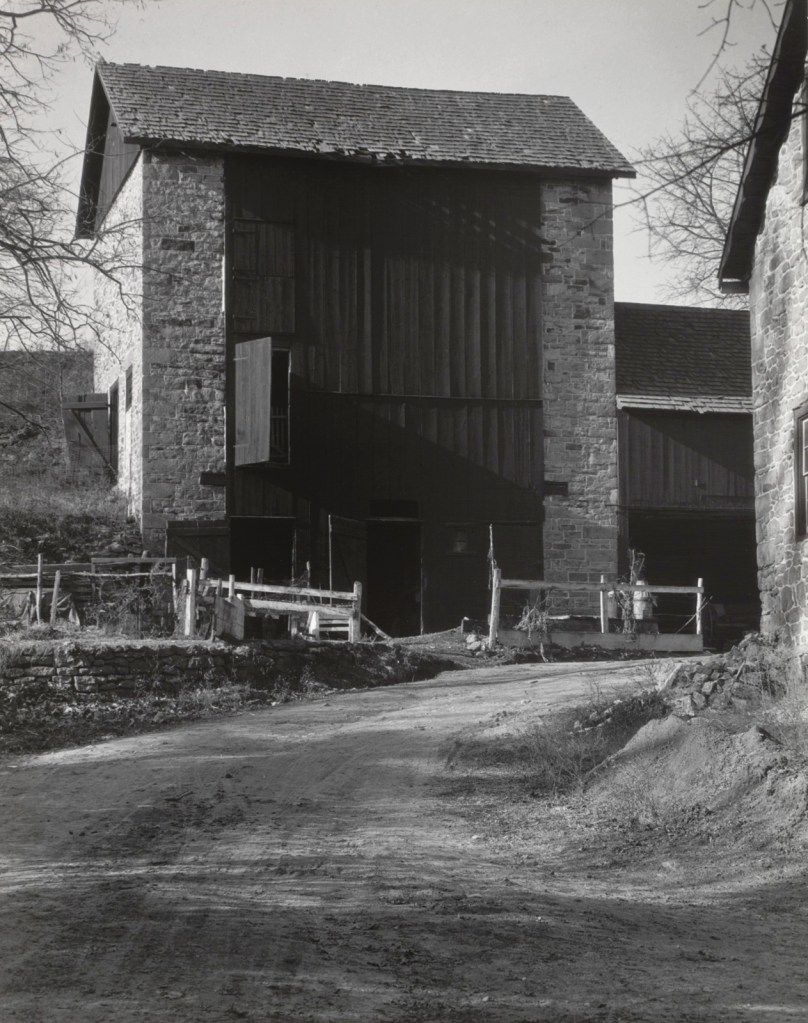
Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
White Door, Hornitos, California
1940
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
Tate Modern presents a major new exhibition, The Radical Eye: Modernist Photography from the Sir Elton John Collection, drawn from one of the world’s greatest private collections of photography. This unrivalled selection of classic modernist images from the 1920s to the 1950s features almost 200 works from more than 60 artists, including seminal figures such as Berenice Abbott, André Kertész, Man Ray, Alexandr Rodchenko and Edward Steichen among many others. The exhibition consists entirely of rare vintage prints, all created by the artists themselves, offering a unique opportunity to see remarkable works up close. The quality and depth of the collection allows the exhibition to tell the story of modernist photography in this way for the first time in the UK. It also marks the beginning of a long term relationship between Tate and The Sir Elton John Collection, as part of which Sir Elton and David Furnish have agreed to give important works to the nation.
The Radical Eye introduces a crucial moment in the history of photography – an exciting rupture often referred to as the ‘coming of age’ of the medium, when artists used photography as a tool through which they could redefine and transform visions of the modern world. Technological advancements gave artists the freedom to experiment and test the limits of the medium and present the world through a new, distinctly modern visual language. This exhibition reveals how the timeless genres of the portrait, nude and still life were reimagined through the camera during this period, also exploring photography’s unique ability to capture street life and architecture from a new perspective.
Featuring portraits of great cultural figures of the 20th century, including Georgia O’Keeffe by Alfred Stieglitz, Edward Weston by Tina Modotti, Jean Cocteau by Berenice Abbott and Igor Stravinsky by Edward Weston, the exhibition gives insight into the relationships and inner circles of the avant-garde. An incredible group of Man Ray portraits are exhibited together for the first time, having been brought together by Sir Elton John over the past twenty-five years, depicting key surrealist figures such as Andre Breton and Max Ernst alongside artists including Henri Matisse, Pablo Picasso and Dora Maar. Ground-breaking experimentation both in the darkroom and on the surface of the print, such as Herbert Bayer’s photomontage and Maurice Tabard’s solarisation, examine how artists pushed the accepted conventions of portraiture.
As life underwent rapid changes in the 20th century, photography offered a new means to communicate and represent the world. Alexandr Rodchenko, László Moholy-Nagy and Margaret Bourke-White employed the ‘worm’s eye’ and ‘bird’s eye’ views to create new perspectives of the modern metropolis – techniques associated with constructivism and the Bauhaus. The move towards abstraction is also explored, from isolated architectural elements to camera-less photography such as Man Ray’s rayographs and Harry Callahan’s light abstractions.
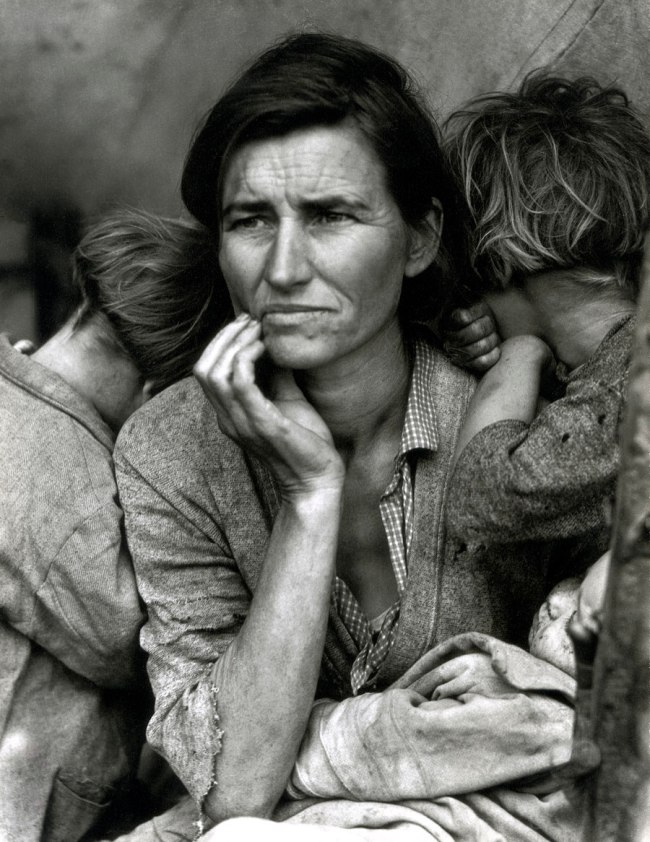
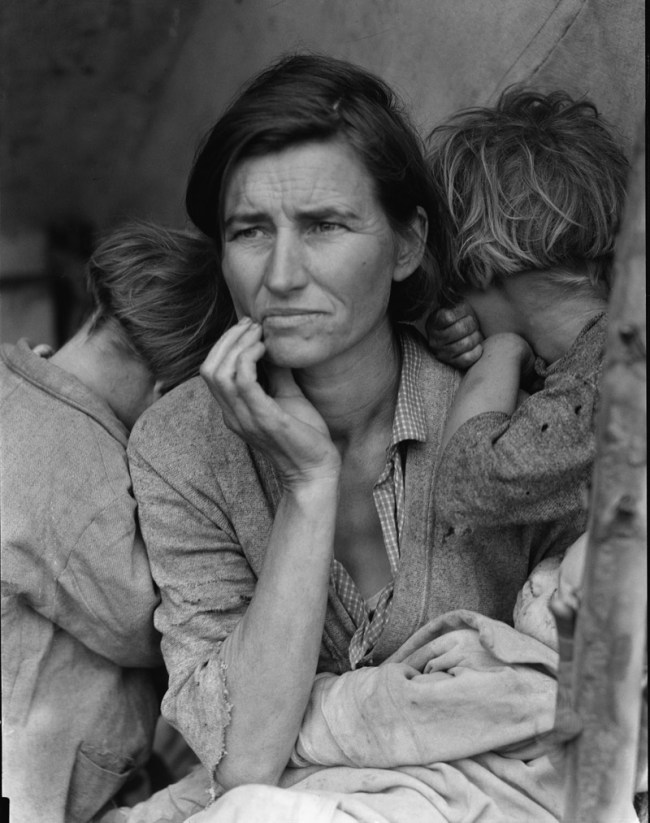
A dedicated section of the exhibition looks at the new approaches that emerged in capturing the human form, highlighted in rare masterpieces such as André Kertész’s Underwater Swimmer, Hungary 1917, while Imogen Cunningham’s Magnolia Blossom, Tower of Jewels 1925 and Tina Modotti’s Bandelier, Corn and Sickle 1927 feature in a large presentation dedicated to the Still Life. The important role of documentary photography as a tool of mass communication is demonstrated in Dorothea Lange’s Migrant Mother 1936 and Walker Evans’ Floyde Burroughs, Hale County, Alabama 1936, from the Farm Security Administration project.
The Radical Eye: Modernist Photography from the Sir Elton John Collection is at Tate Modern from 10 November 2016 until 7 May 2017. It is curated by Shoair Mavlian with Simon Baker and Newell Harbin, Director of The Sir Elton John Photography Collection. The exhibition is accompanied by an exclusive audio tour of the exhibition featuring commentary from Sir Elton John, and a major new catalogue from Tate Publishing including an interview with Sir Elton John by Jane Jackson.
Press release from Tate Modern
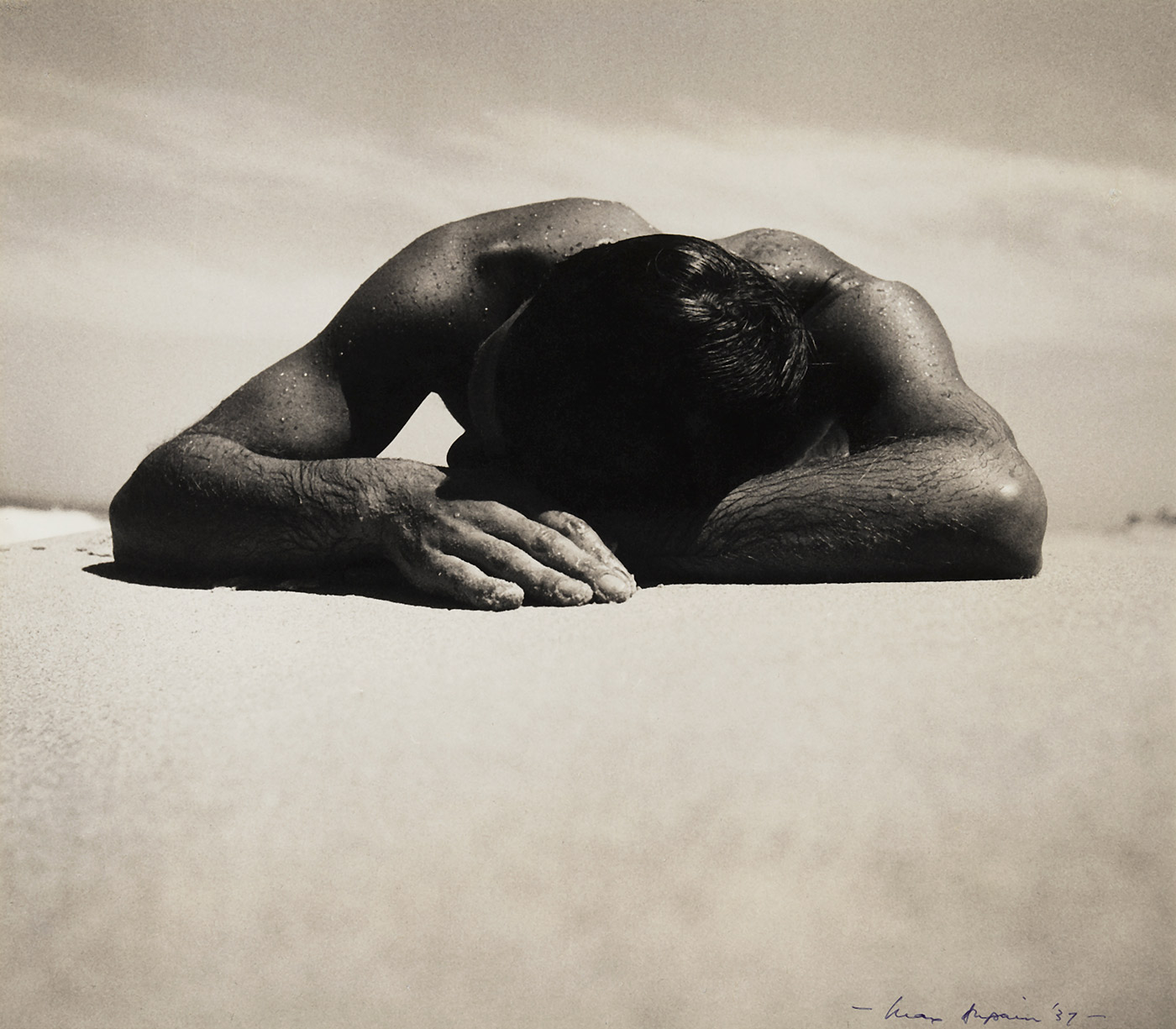
Max Dupain (Australian, 1911-1992)
Sunbaker
1937
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
“We possess an extraordinary instrument for reproduction. But photography is much more than that. Today it is … bringing something entirely new into the world.”
László Moholy-Nagy, 1932
Artists in the modernist period explored what the camera could do that the human eye alone could not, and how this could be harnessed to present a new modern perspective on the world. Artist and theorist László Moholy-Nagy proclaimed that photography could radically change not just what, but how we see. He called this the ‘new vision’. Rather than emulating other art forms, photography began to embrace qualities unique to itself, from its ability to reproduce the world in sharp detail to its capacity to create new realities through the manipulation of light, chemicals and paper.
This re-evaluation of photography coincided with a period of upheaval. War, revolution and economic depression led to mass movements of people and great social change. The idea of the avant-garde took hold and dada and surrealism emerged, challenging both the art and social norms that had come before. At the same time, new art schools such as the Bauhaus in Germany and Vkhutemas in Russia fostered the role of the professional artist and challenged divisions between art and design.
The Radical Eye is arranged thematically and charts a changing emphasis from the subject of an image to the visual qualities of the photograph itself, irrespective of what it represents. The many vintage prints in this exhibition – made soon after the photographs were taken – give a rare insight into the artists’ processes and creative decisions, and foreground the photograph as a physical object. All works are shown in the frames in which they are displayed in the home of Sir Elton John and David Furnish.
Together, the works in this exhibition show how photography pushed the boundaries of the possible, changing the world through the ways in which it was seen and understood. ‘Knowledge of photography is just as important as that of the alphabet. The illiterates of the future will be ignorant of the use of camera and pen alike,’ wrote Moholy-Nagy in 1927, foreseeing the cultural dominance of the photographic image. This extraordinary period still impacts how we, the photo-literate future, read and create images today.
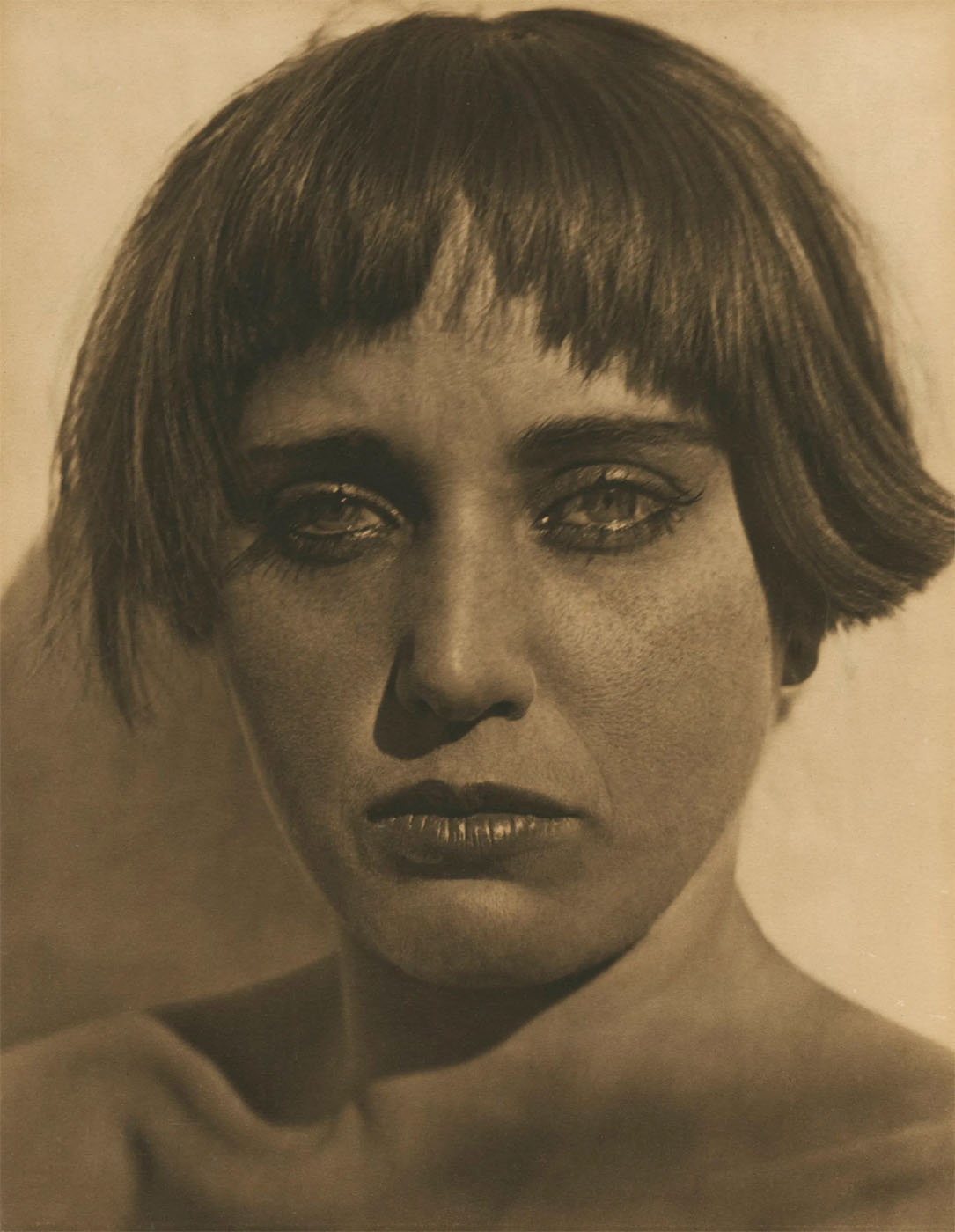
Alfred Stieglitz (American, 1864-1946)
Georgia O’Keeffe
1922
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
“They collect themselves. Carefully, as if tying a cravat, they compose their features. Insolent, serious and conscious of their looks they turn around to face the world.”
From ‘Men before the Mirror’, published alongside portraits by Man Ray, 1934
Portraits
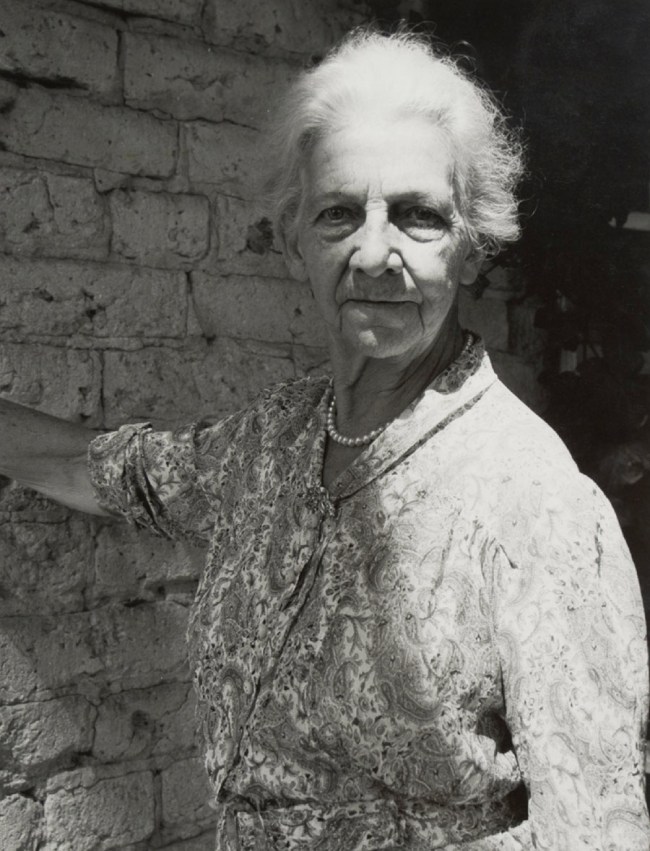
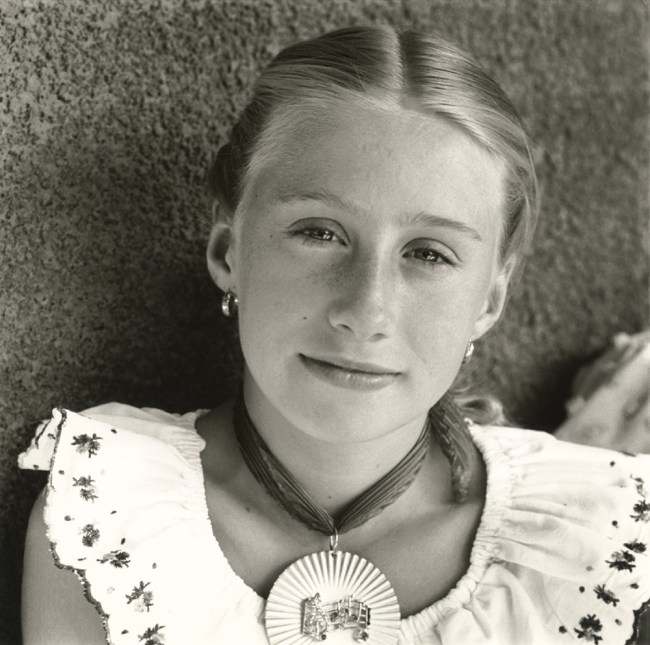
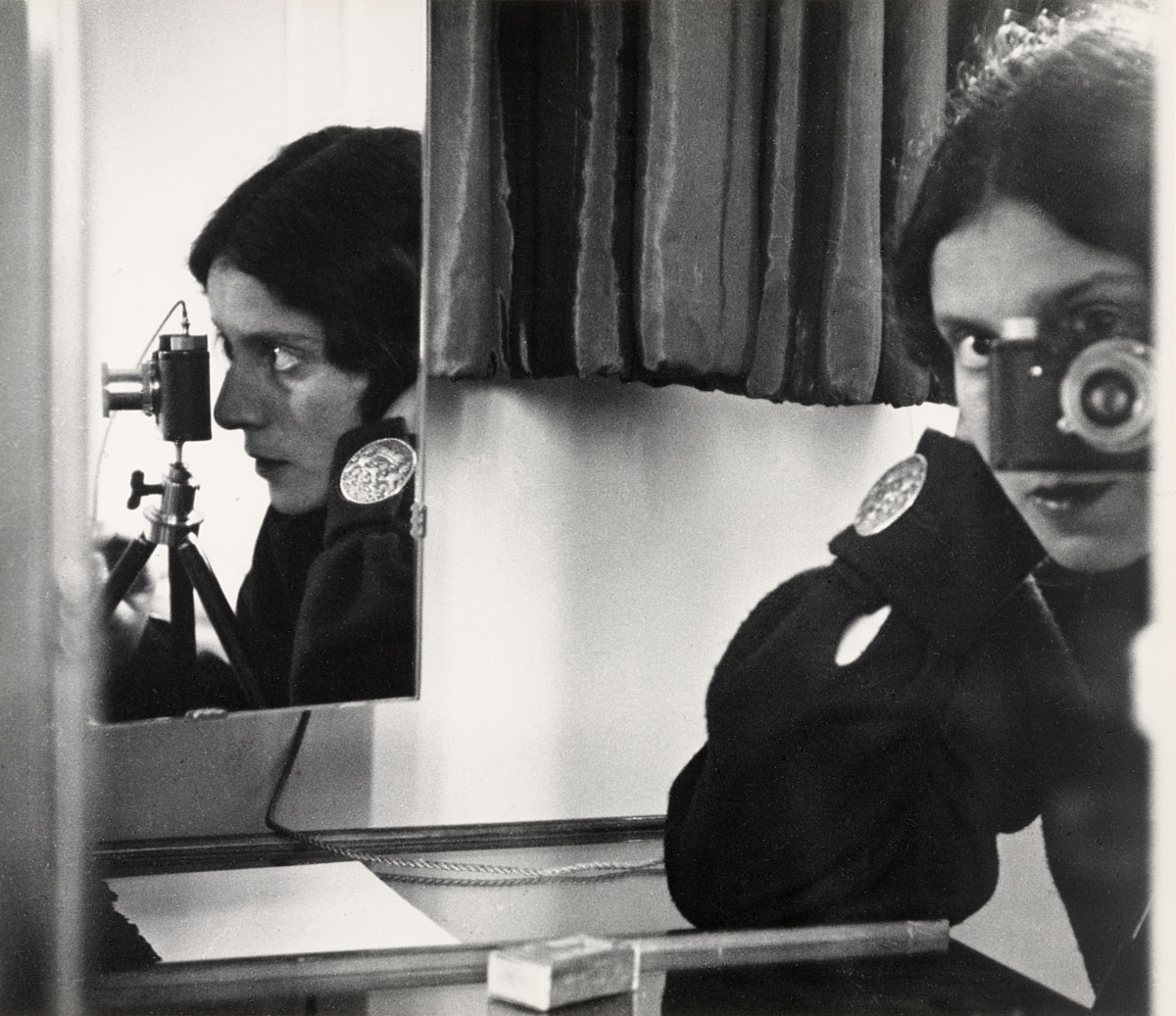
Modernist portraiture harnessed photography’s capacity to render an accurate likeness in clear, sharp focus and detail. But at the same time, artists and sitters pushed the conventions of portraiture with innovations in pose, composition and cropping.
Many of the portraits in this room are of artists, writers and musicians, giving a cross section of key cultural players of the time. Issues of control and collaboration arise particularly when the subject is an artist, raising the question of who is responsible for conveying the sitter’s persona. The modernist period also saw a boom of the illustrated press. Magazines reproduced photographic portraits of well-known figures which were instrumental in shaping their public images.
Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Nusch Éluard
1928
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2016
Nusch Éluard (born Maria Benz; June 21, 1906 – November 28, 1946) was a French performer, model and surrealist artist…
Nusch arrived in France as a stage performer, variously described as a small-time actress, a traveling acrobat, and a “hypnotist’s stooge”. She met Paul Éluard in 1930 working as a model, married him in 1934, produced surrealist photomontage and other work, and is the subject of “Facile,” a collection of Éluard’s poetry published as a photogravure book, illustrated with Man Ray’s nude photographs of her.
She was also the subject of several cubist portraits and sketches by Pablo Picasso in the late 1930s, and is said to have had an affair with him. Nusch worked for the French Resistance during the Nazi occupation of France during World War II. She died in 1946 in Paris, collapsing in the street due to a massive stroke.
Text from the Wikipedia website
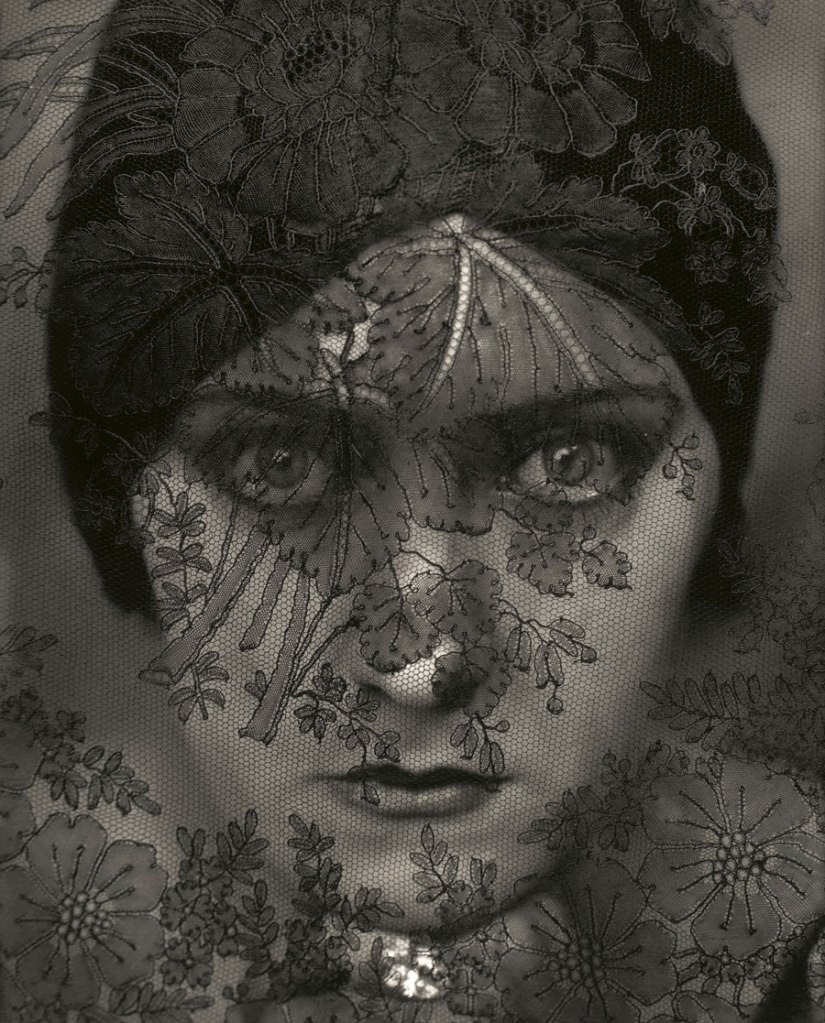

Edward Steichen (American 1879-1973, emigrated to United States 1881, worked in France 1906-1923)
Actress Gloria Swanson
1924
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
© 1924 Condé Nast Publications
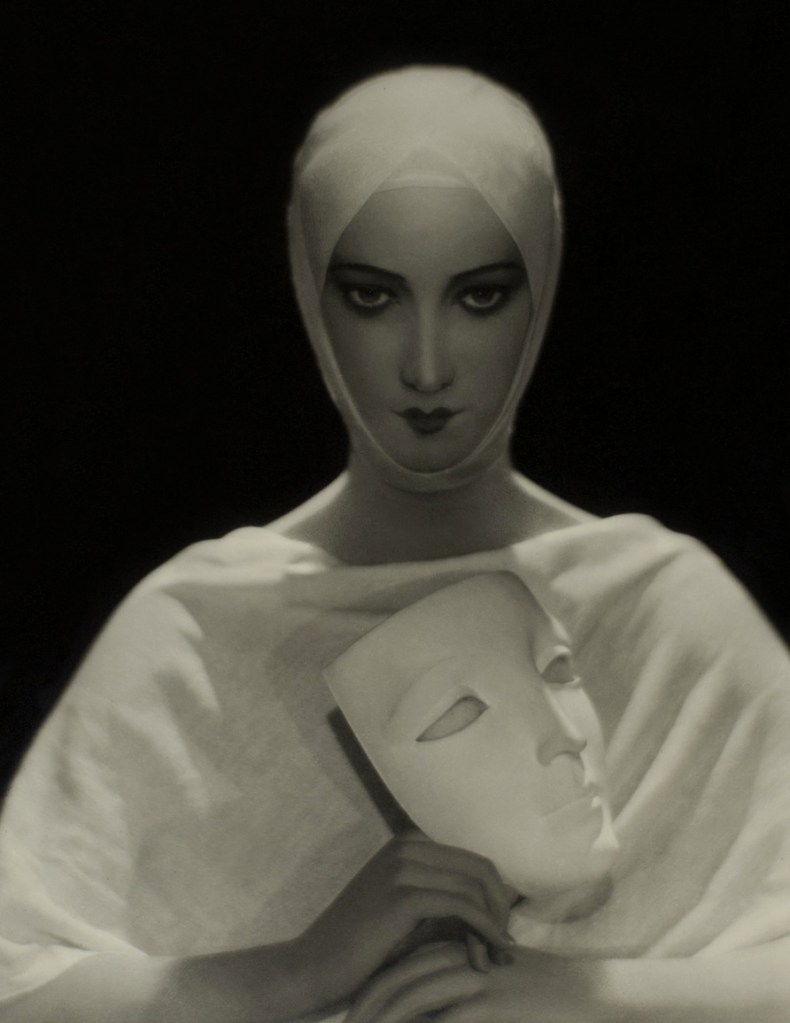

Adolph de Meyer (European / American, 1868-1946)
For Elizabeth Arden (The Wax Head)
1931
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
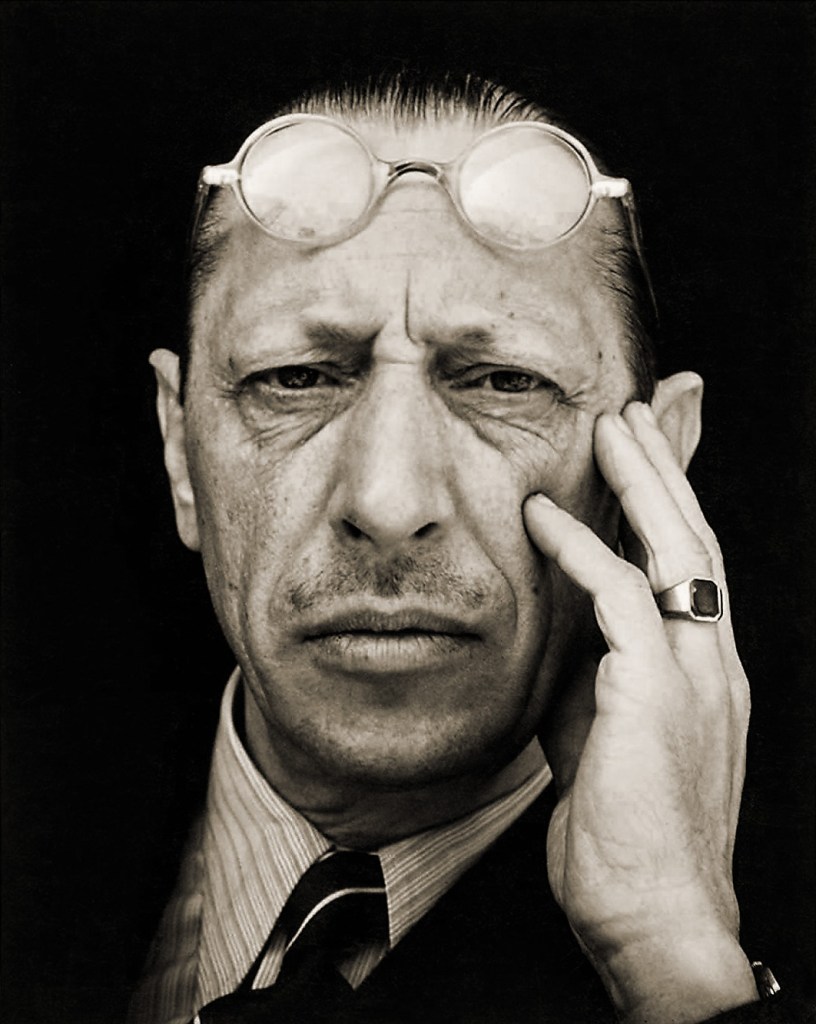

Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
Igor Stravinsky
1935
Silver gelatin print
© 1981 Center for Creative Photography
George Platt Lynes (American, 1907-1955)
A Forgotten Model
c. 1937
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
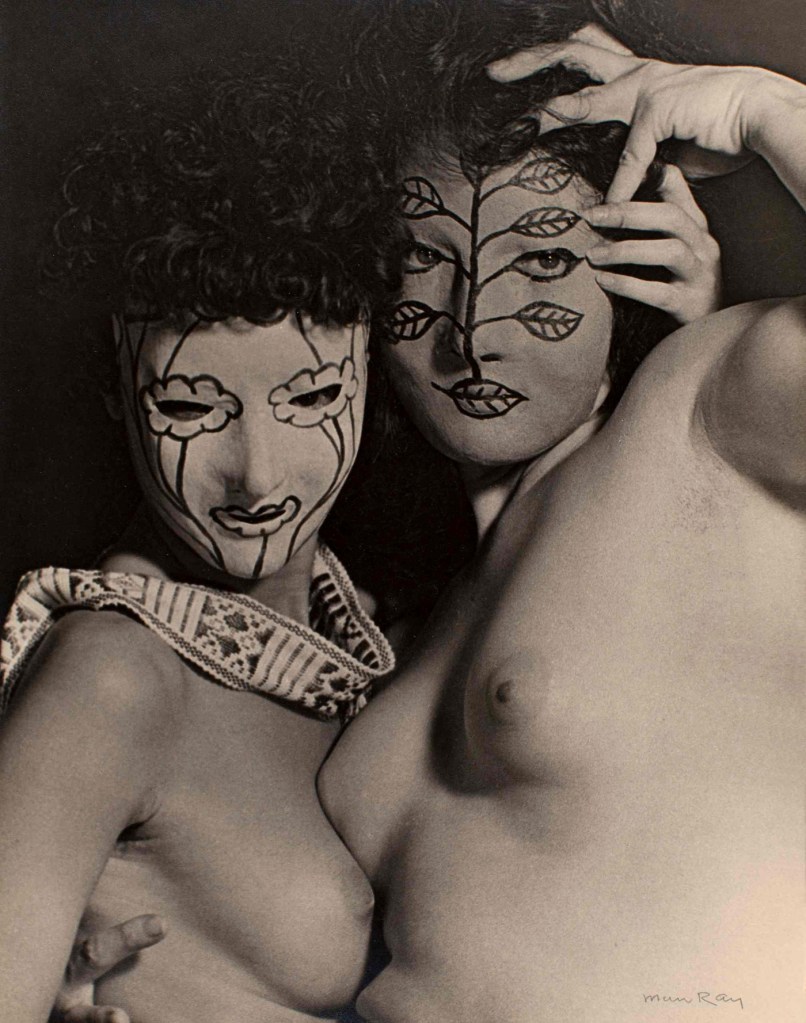

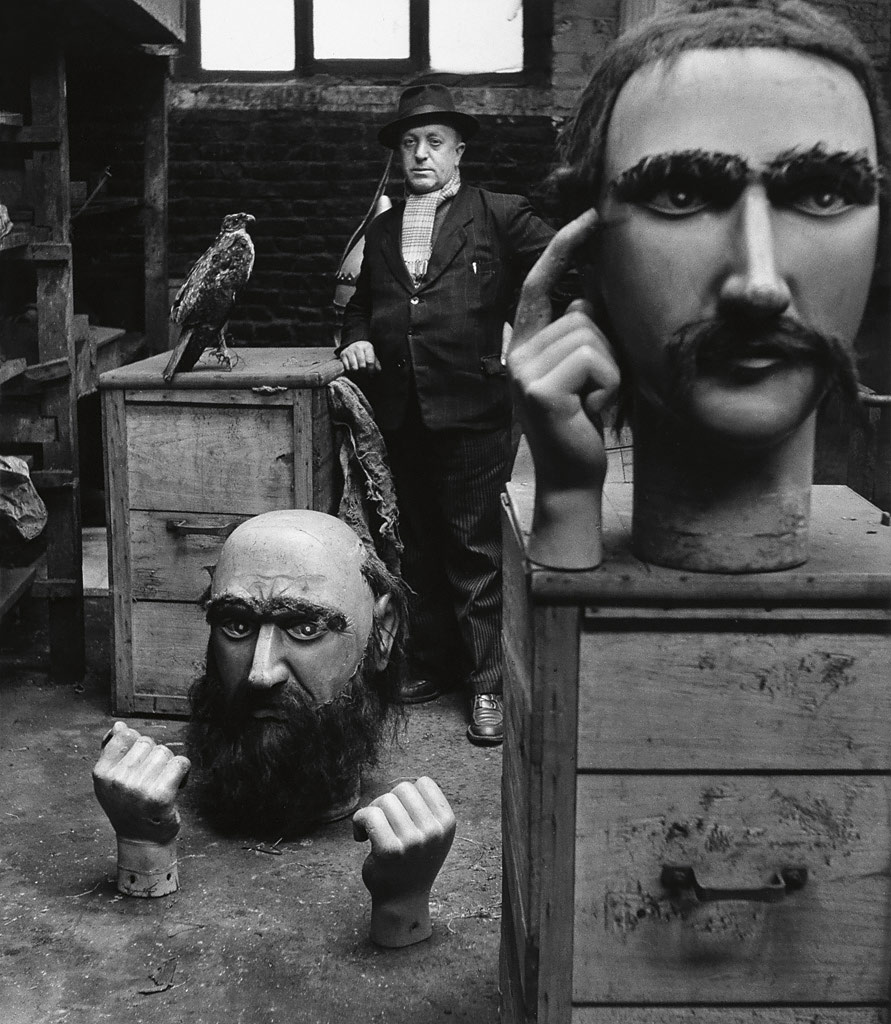
Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Juliet and Margaret Nieman in Papier-Mâché Masks
c. 1945
Gelatin silver print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: © Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2016
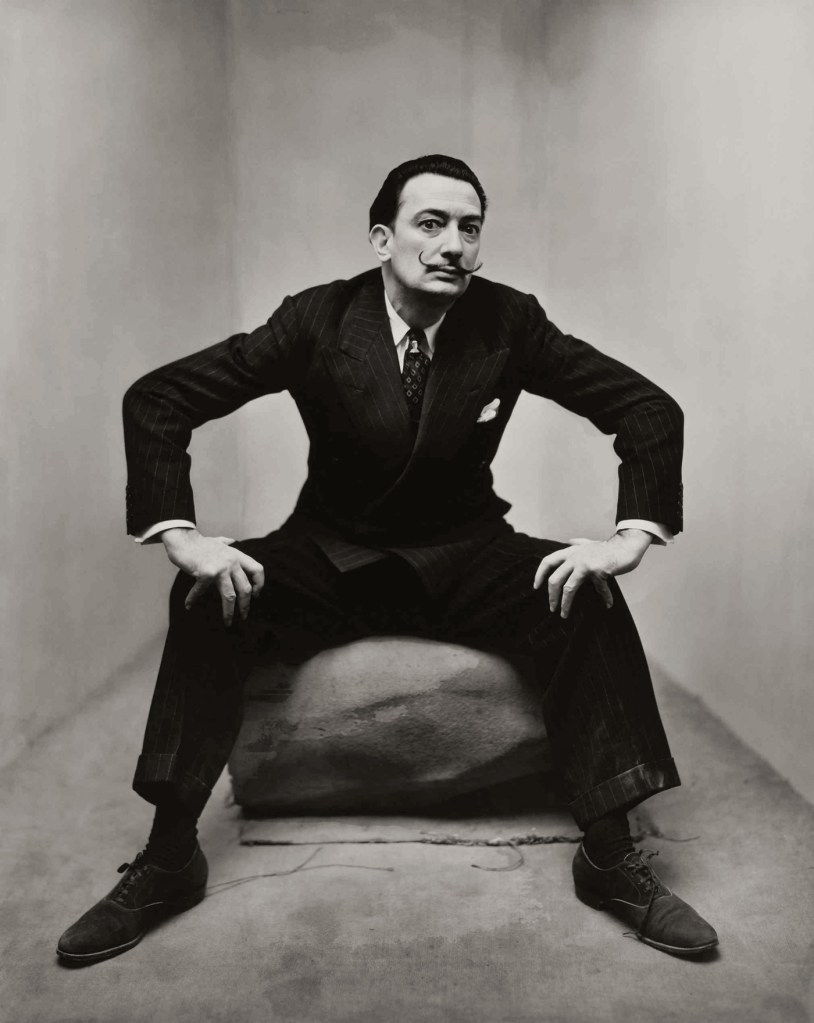

Irving Penn (American, 1917-2009)
Salvador Dali in New York
1947
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: The Irving Penn Foundation
“The enemy of photography is convention, the fixed rules ‘how to do’. The salvation of photography comes from the experiment.”
László Moholy-Nagy, c. 1940
Experiments
This was not a period of discovery but of rediscovery. Artists were rewriting the preceding century’s rules of photographic technique, harnessing ‘mistakes’ such as distortions and double exposures, or physically manipulating the printed image, cutting, marking and recombining photographs. These interventions could occur at any point in the process, from taking the image to the final print.
Used in portraiture, such experiments allowed for more psychologically charged representations. However, the transformative power of a particular technique often becomes much more important than the particular subject of the image. Above all, the rich creative possibilities of the photographic process come to the fore. While artists were seriously investigating the medium, the results are often surprising and playful.
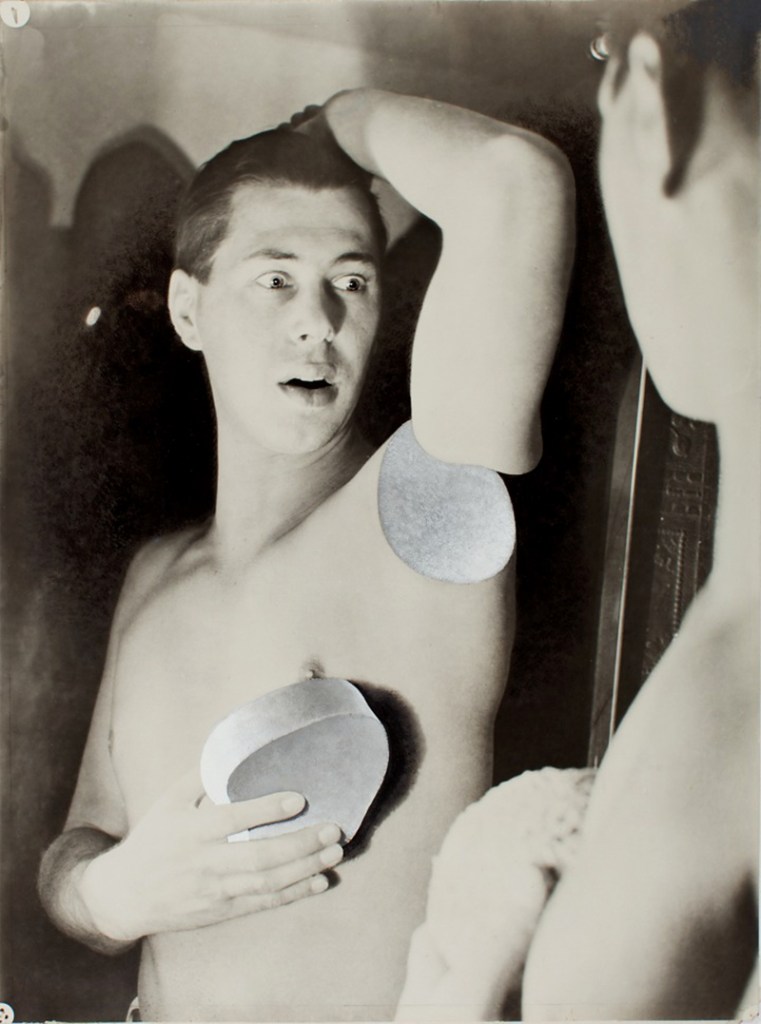

Herbert Bayer (American born Austria, 1900-1985)
Self-Portrait
1932
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
© DACS 2016
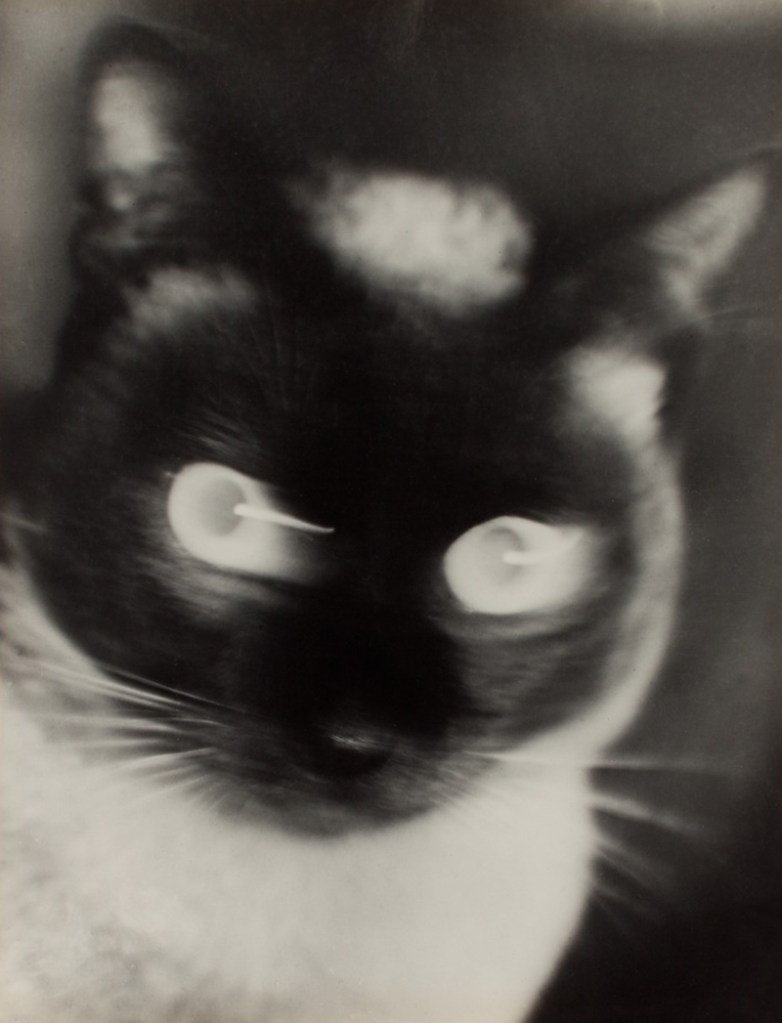

Otto Umbehr (German, 1902-1980)
“Katz” – Cat
1927
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
© Phyllis Umbehr/Galerie Kicken Berlin/DACS 2016
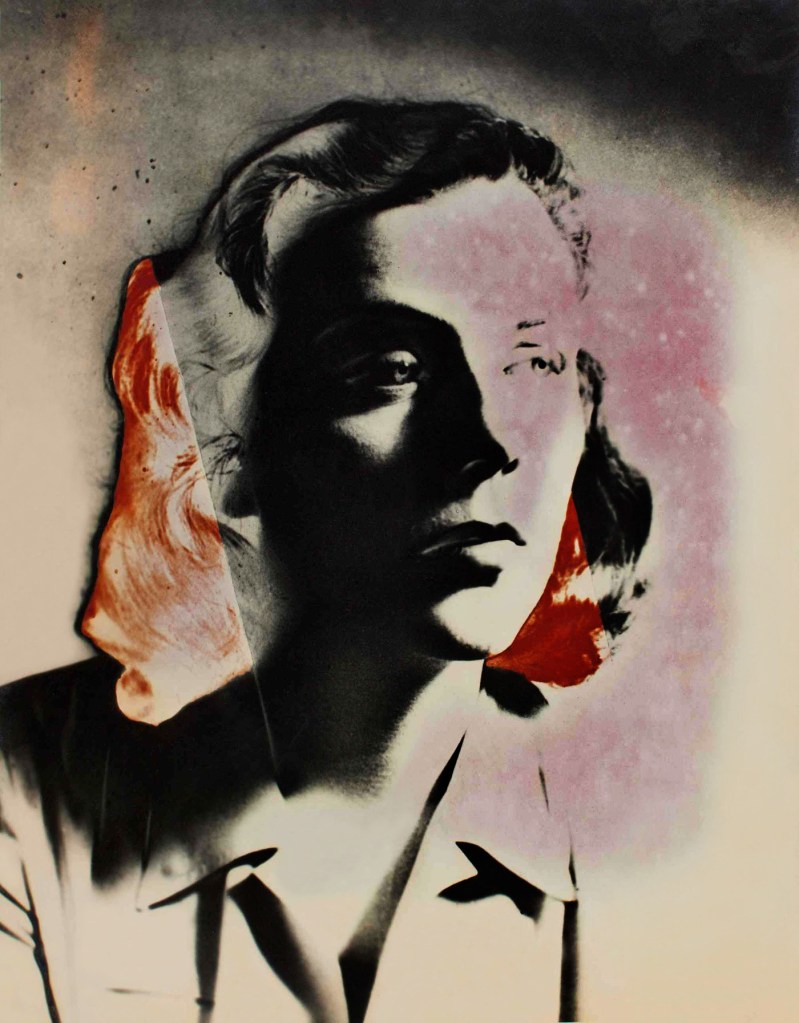

Josef Breitenbach (German, 1896-1984)
Patricia, New York
c. 1942
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: Josef and Yaye Breitenbach Charitable Foundation, Courtesy Gitterman Gallery
“The camera should be used for a recording of life, for rendering the very substance and quintessence of the thing itself, whether it be polished steel or palpitating flesh.”
Edward Weston, 1924
Bodies
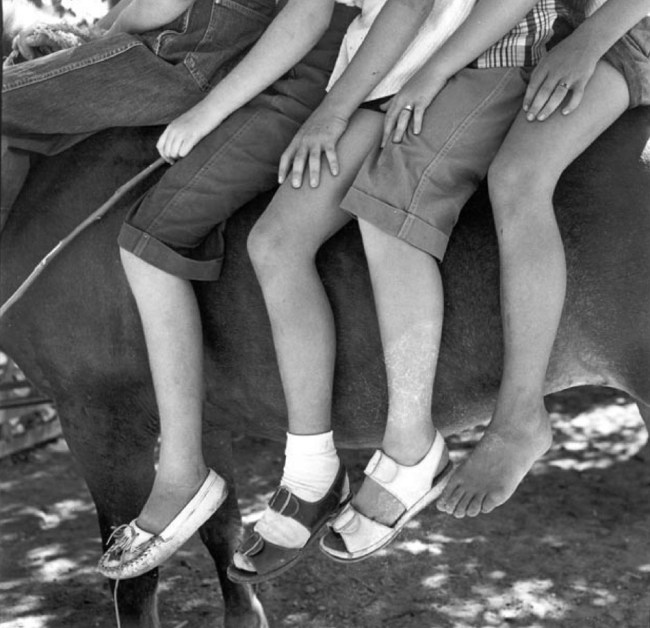
Experimental approaches to shooting, cropping and framing could transform the human body into something unfamiliar. Photographers started to focus on individual parts of the body, their unconventional crops drawing attention to shape and form, accentuating curves and angles. Fragmented limbs and flesh were depersonalised and could be treated like a landscape or still life, dissolving distinctions between different genres. Thanks to faster shutter speeds and new celluloid roll film, photographers could also freeze the body in motion outside of the studio for the first time, capturing dancers and swimmers with a clarity impossible for the naked eye.
André Kertész (Hungarian, 1894-1985)
Underwater Swimmer, Esztergom, Hungary, 30 June 1917
1917
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
© Estate of André Kertész/Higher Pictures
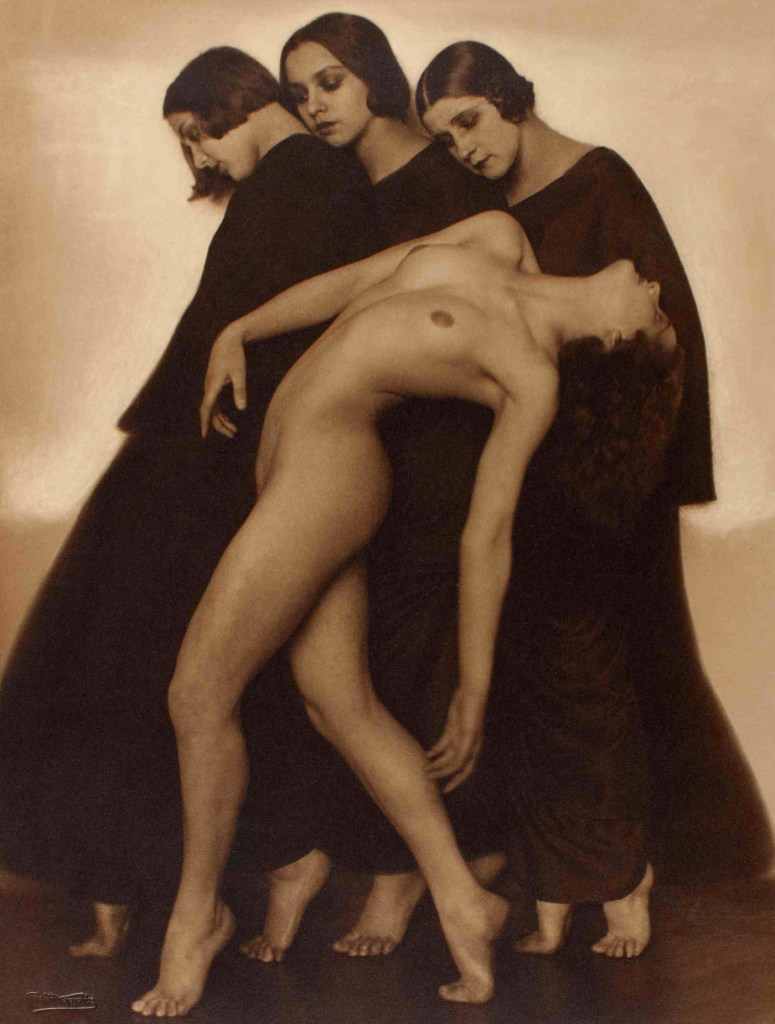

Rudolph Koppitz (Austrian, 1884-1936)
Movement Study
1925
Gelatin silver print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: ADAGP, Paris and DACS London 2016
Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Noire et Blanche
1926
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2016
Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Glass Tears (Les Larmes)
1932
Gelatin silver print on paper
229 x 298 mm
Collection Elton John
© Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2016
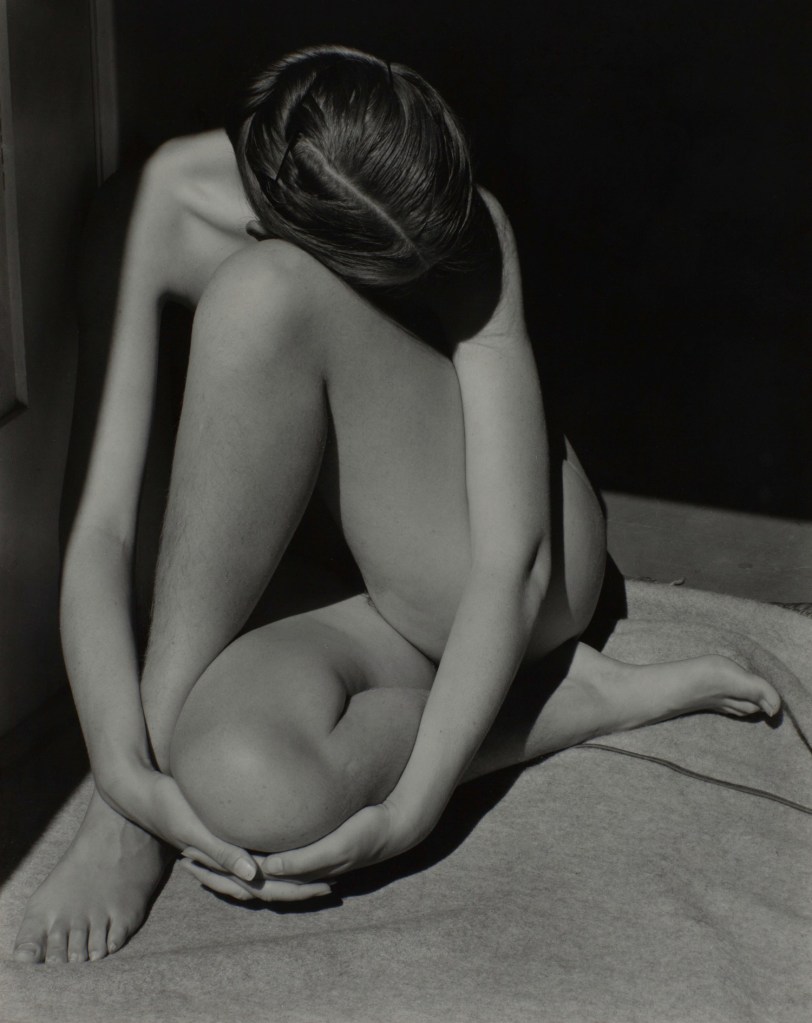

Edward Weston (American, 1886-1958)
Nude
1936
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: 1981 Center for Creative Photography, Arizona Board of Regents
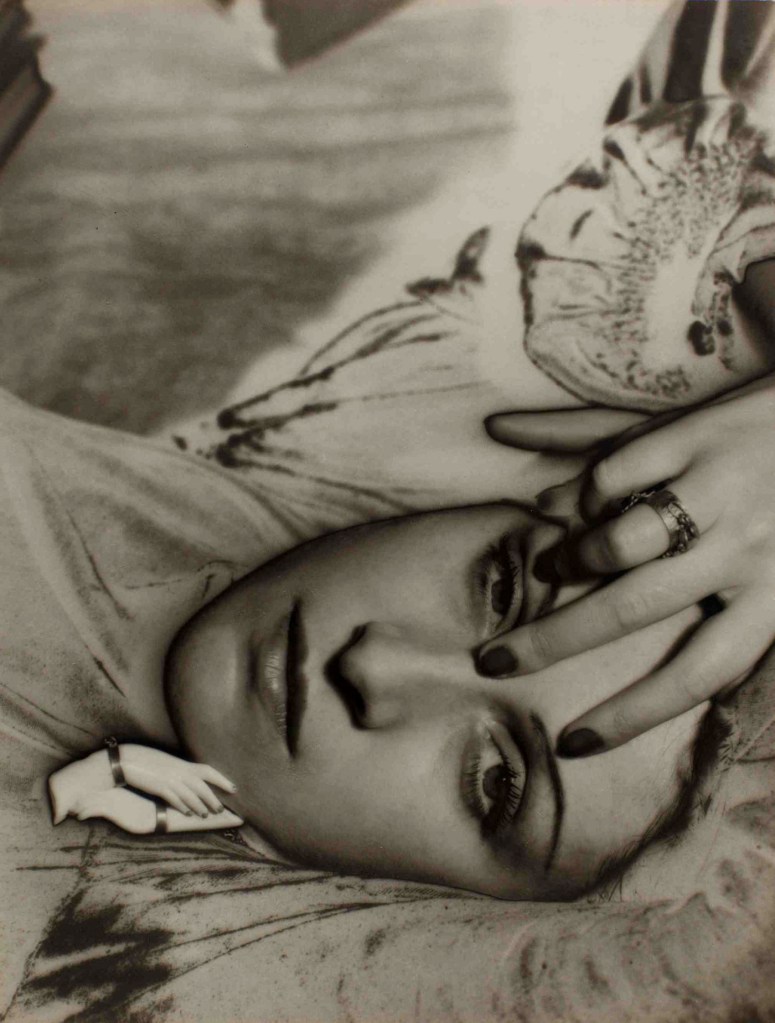

Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Dora Maar
1936
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2016
Nino Migliori (Italian, b. 1926)
Il Tuffatore (The Diver)
1951
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
“The documentary photographer is trying to speak to you in terms of everyone’s experience.”
Dorothea Lange, 1934
Documents
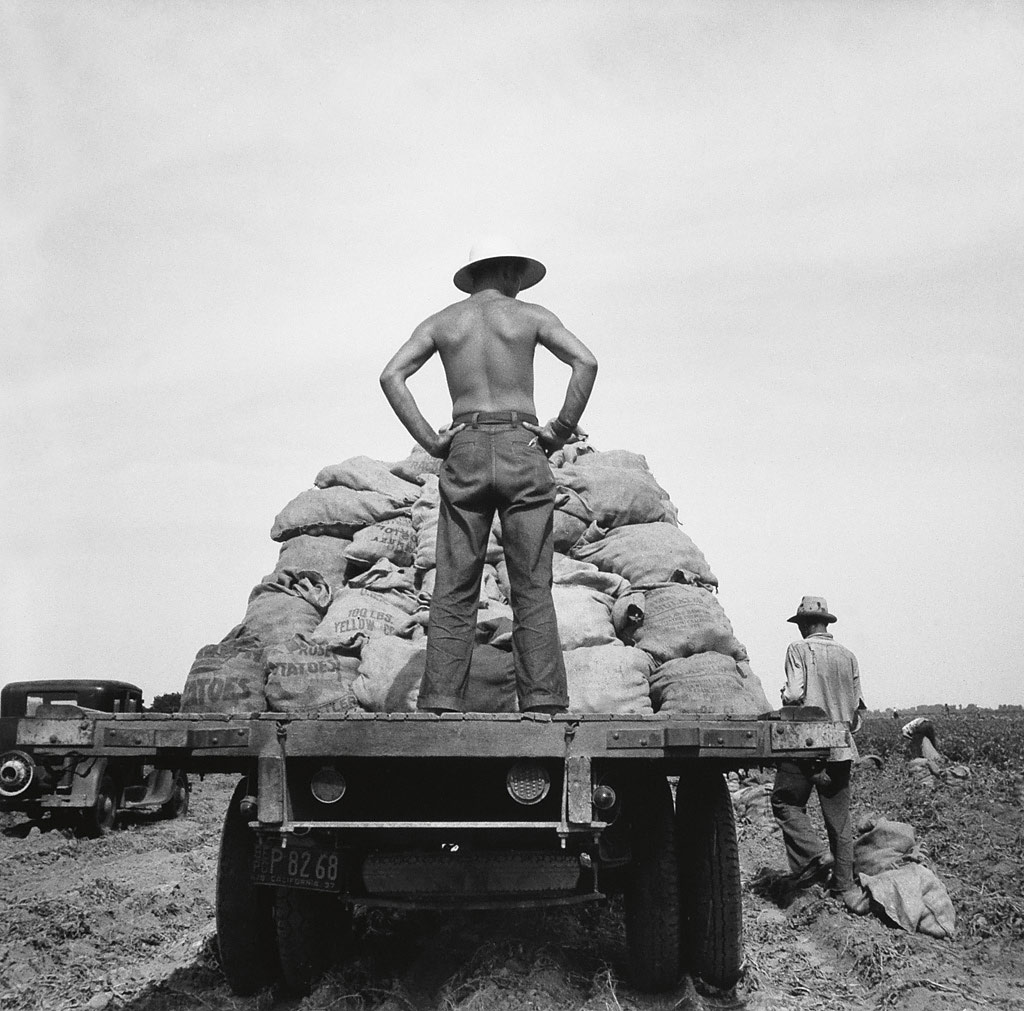
During the 1930s, photographers refined the formula for what we now know as social documentary. To compel the public to look at less palatable aspects of contemporary society they married creative manipulation with an appeal to viewers’ trust in the photograph as an objective visual record. This combination proved itself uniquely capable of eliciting empathy but is fraught with artistic and ethical complexity. These works highlight the vexed position of documentary photographs: historical evidence, instruments of propaganda and, latterly, works of art.
The development of new technology – particularly the portable camera and roll film – allowed photographers to capture spontaneous moments unfolding in the everyday world. Taking viewers into neighbourhoods where they might never set foot, street photography and documentary opened up new perspectives socially as much as visually.
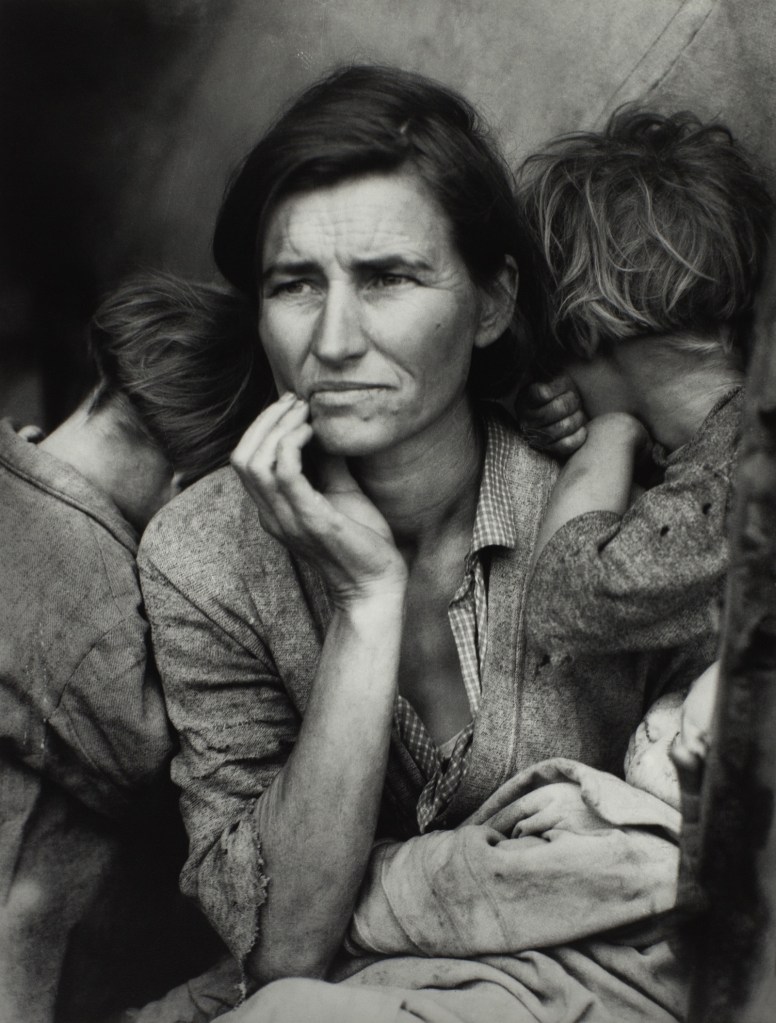

Dorothea Lange (American, 1895-1965)
Migrant Mother
1936
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
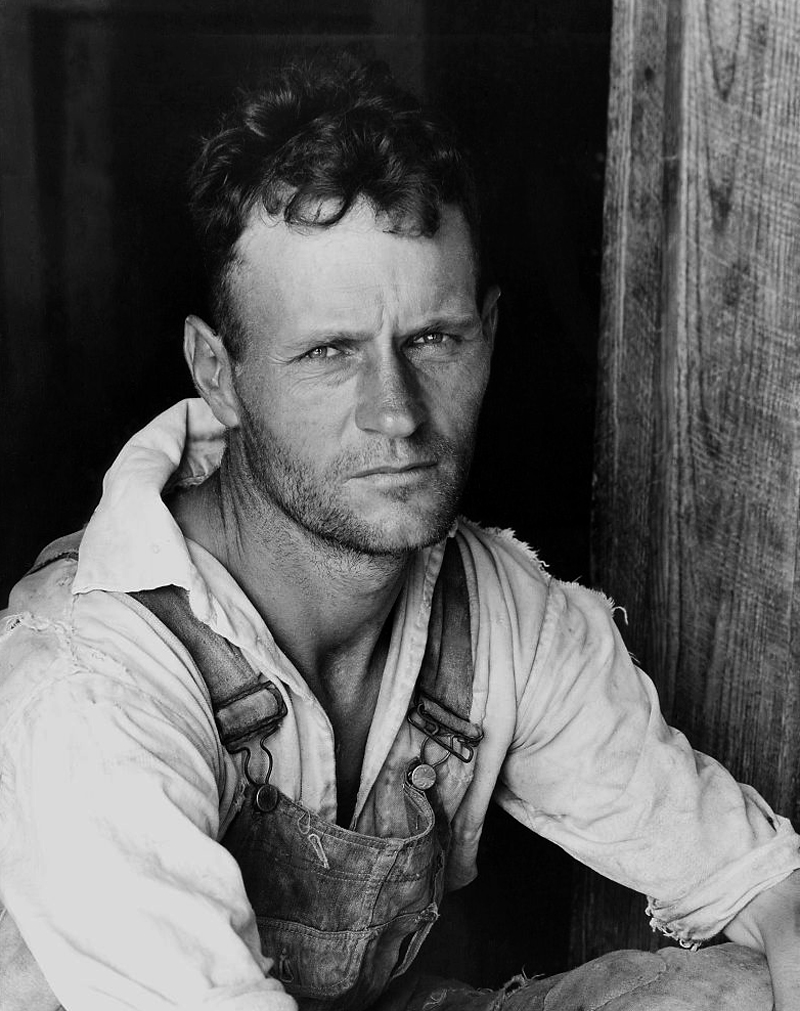

Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975)
Floyde Burroughs, a cotton sharecropper, Hale County, Alabama
1936
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
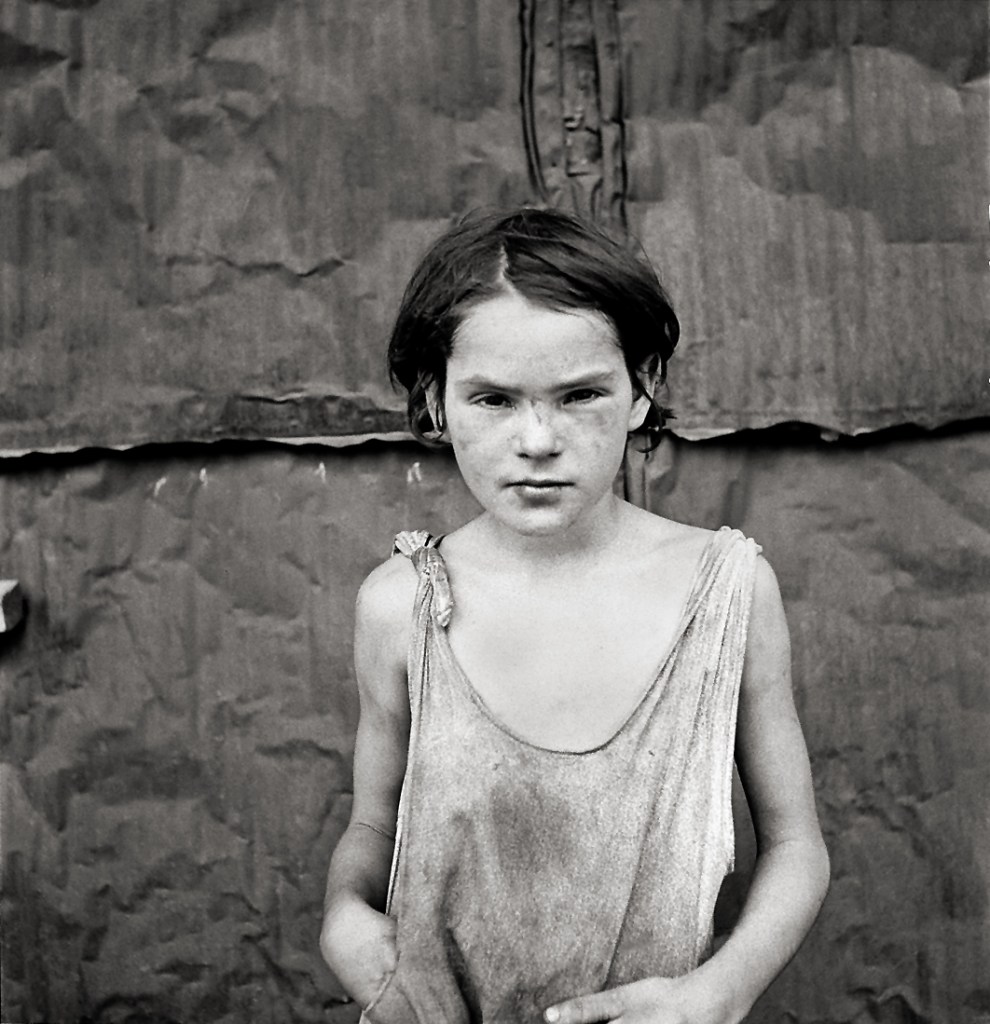

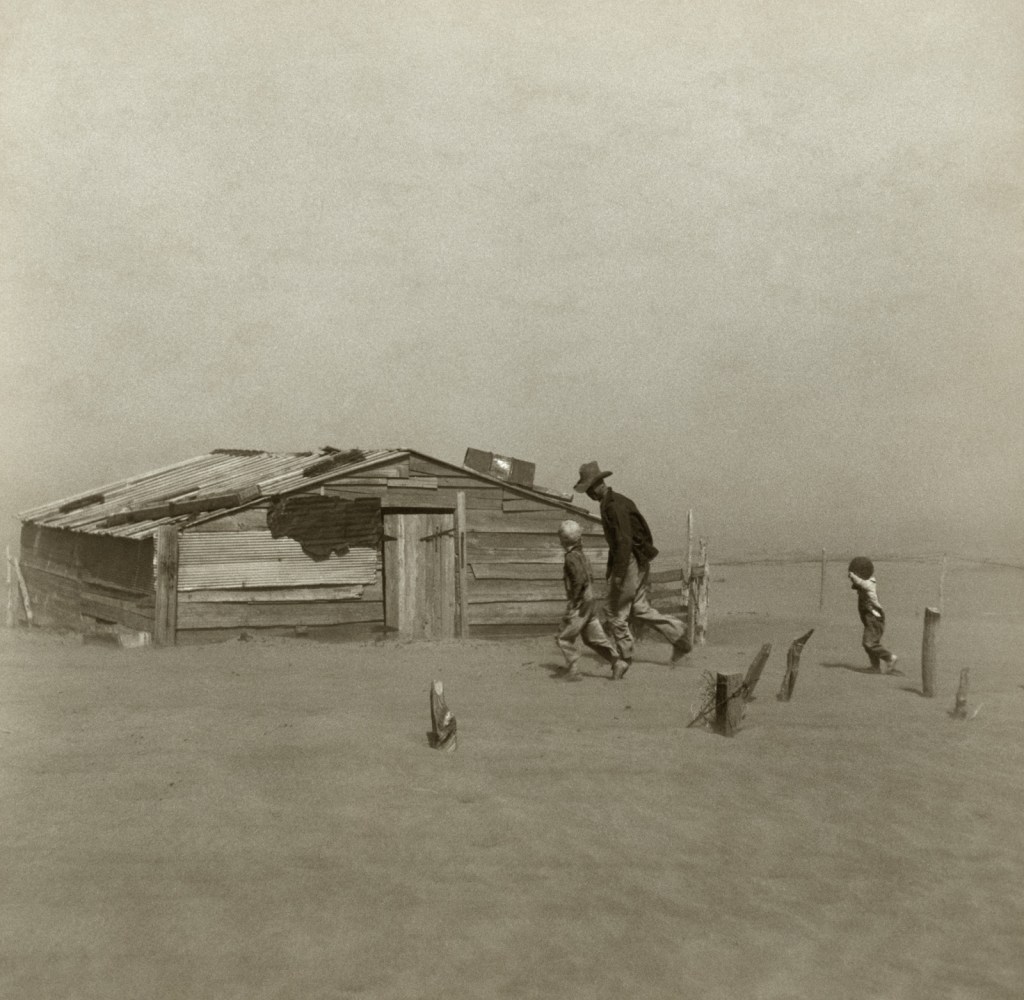
Dorothea Lange (American, 1895-1965)
A young girl living in a shack town near Oklahoma City, Oklahoma
1936
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
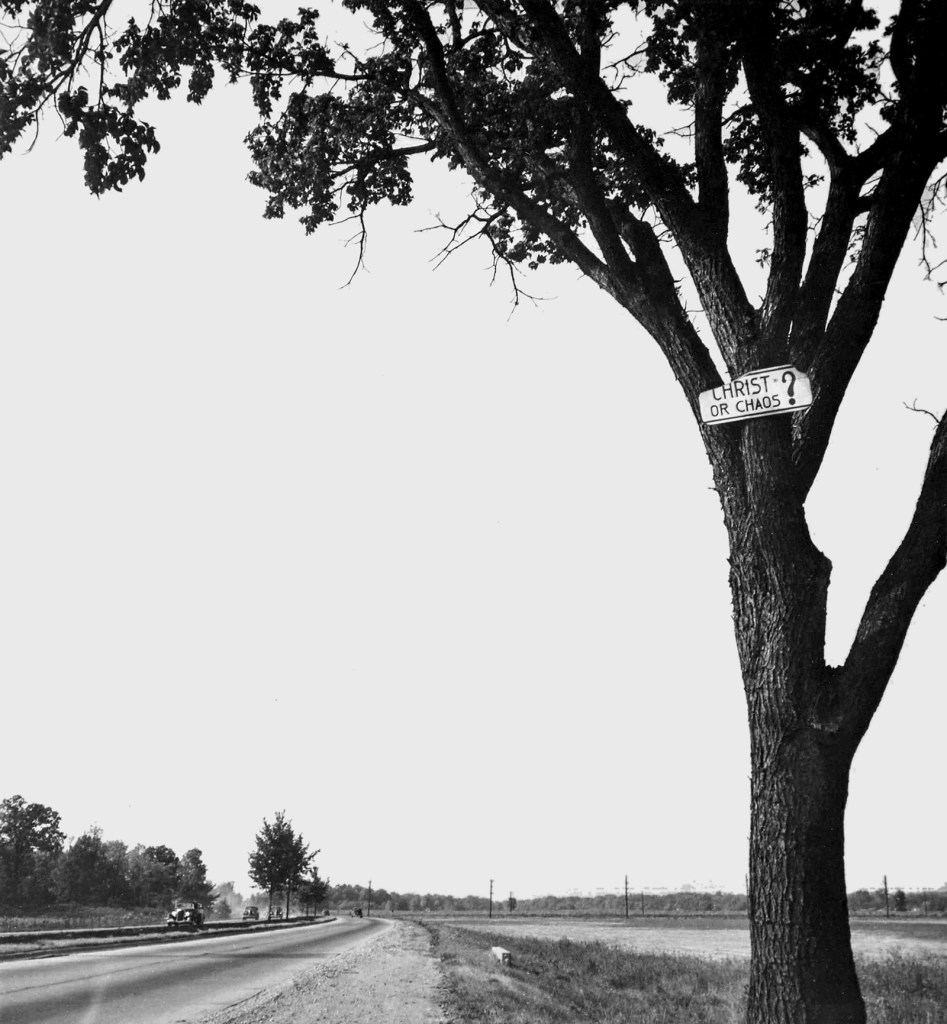

Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975)
Christ or Chaos?
1946
Gelatin silver print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: Walker Evans Archives, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
“Contradictions of perspective. Contrasts of light. Contrasts of form. Points of view impossible to achieve in drawing and painting.”
Aleksandr Rodchenko, 1920s
Objects, Perspectives, Abstractions
The subjects and approaches of modernist photography vary widely, but are united by a fascination with the medium itself. Every image asks what photography is capable of and how it can be pushed further. This final room brings together three interlinked approaches. It shows the still life genre reimagined by photographers who used the technical capabilities of the camera to reveal the beauty of everyday things. Objects captured at unconventional angles or extreme close-up become strange, even unrecognisable.
A similar effect of defamiliarisation was accomplished by taking photographs from radically new perspectives, positioning a camera at the point of view of the ‘worm’s eye’ or ‘bird’s eye’. This created extreme foreshortening that transformed photographs from descriptive images of things into energetic compositions hovering between abstraction and representation.
Abstraction pushes against photography’s innate ability to record objectively. Radical techniques such as cameraless image-making simplified the medium to the point of capturing the play of light on photosensitive paper. By stripping it back to its most basic components, artists celebrated photography, not as a tool for reproduction, but as a creative medium capable of producing new imagery.
Alexander Rodchenko (Russian, 1891-1956)
Shukov Tower
1920
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
© A. Rodchenko & V. Stepanova Archive, DACS, RAO 2016
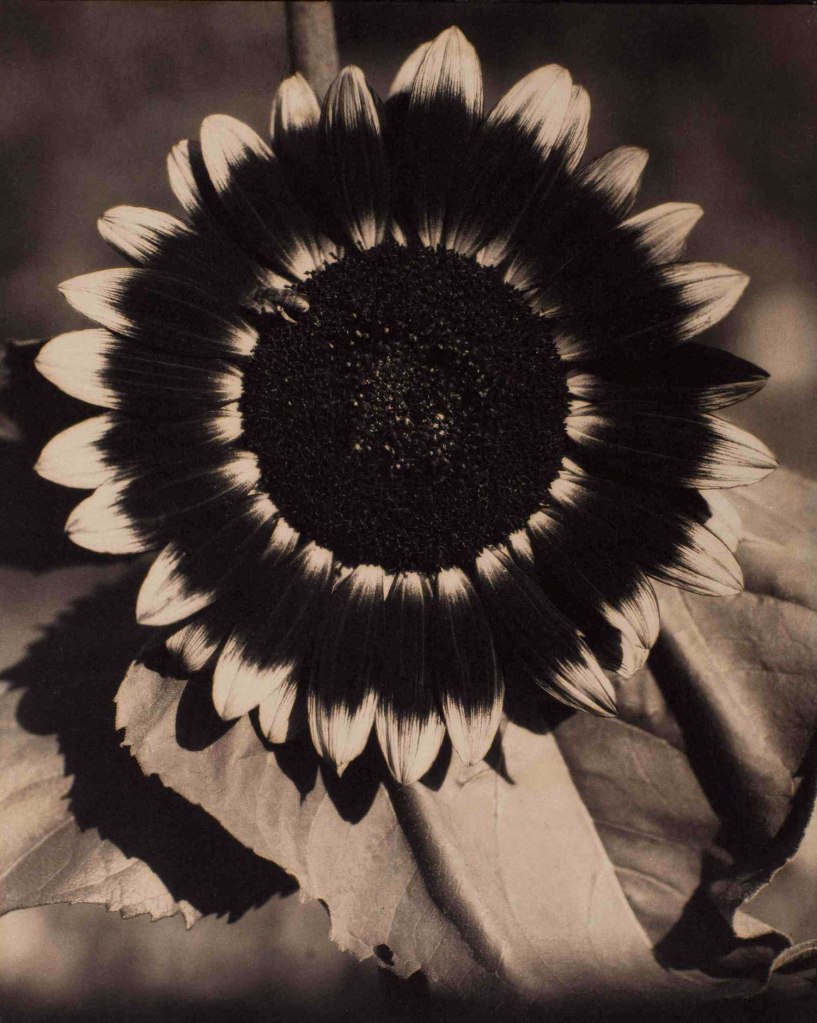

Edward Steichen (American, 1879-1973)
A Bee on a Sunflower
c. 1920
Gelatin silver print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection

Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
“Rayograph”
1923
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
Photograph: Man Ray Trust/ADAGP, Paris and DACS, London 2016
André Kertész (Hungarian, 1894-1985)
Mondrian’s Glasses and Pipe
1926
Gelatin silver print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
© Estate of André Kertész/Higher Pictures
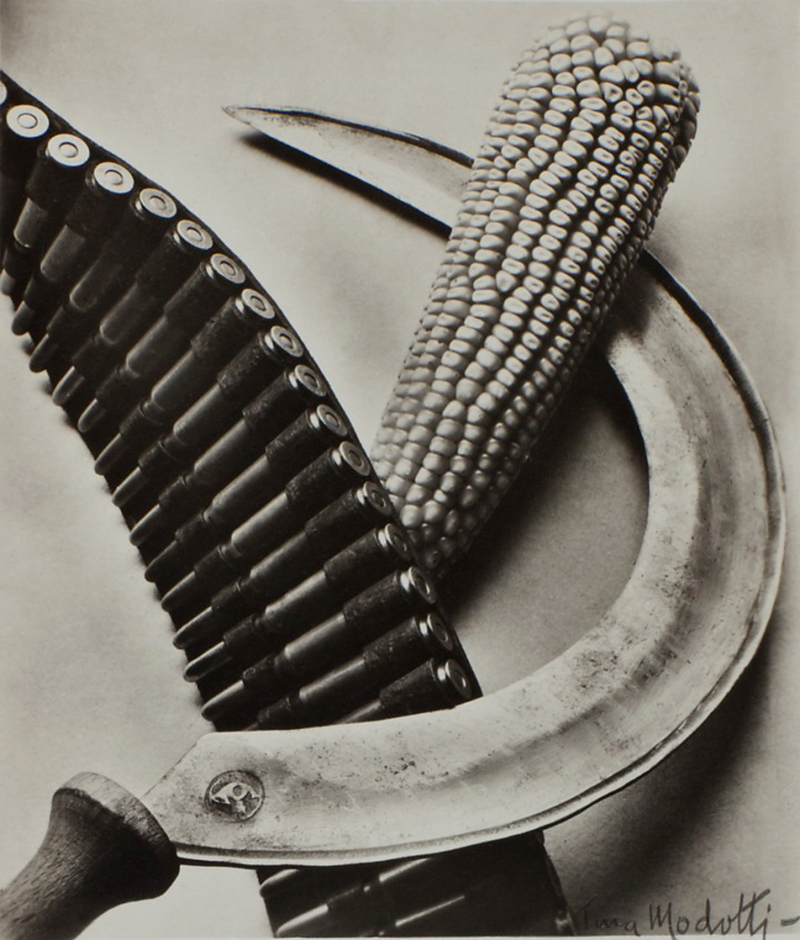

Tina Modotti (Italian American, 1896-1942)
Bandelier, Corn and Sickle
1927
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
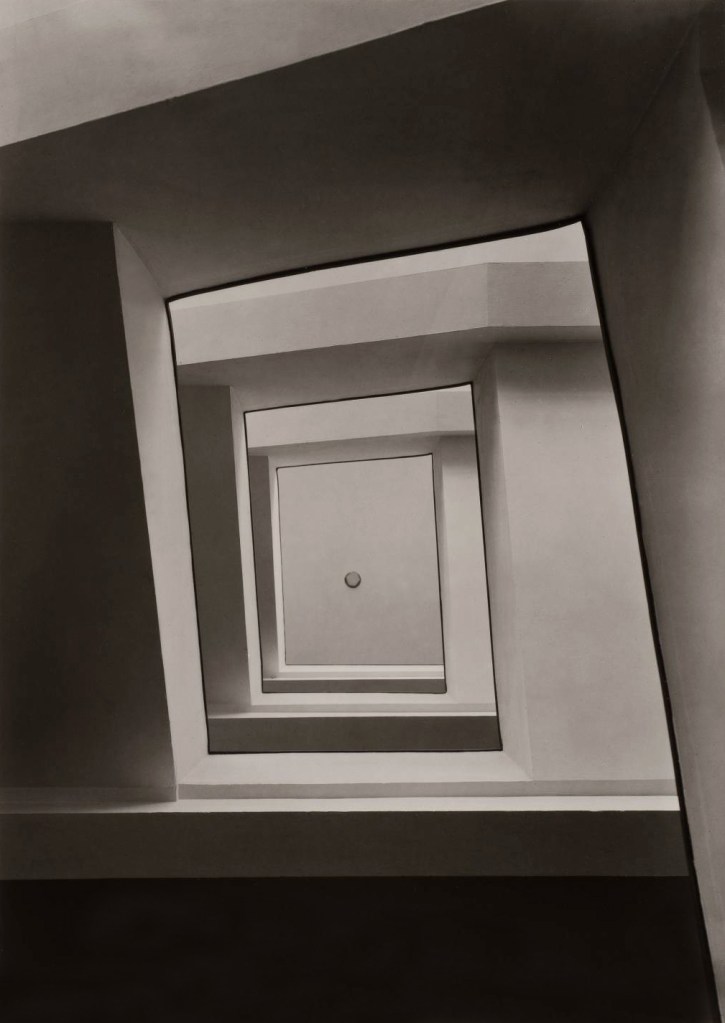

Werner Mantz (German, 1901-1983)
Staircase Ursuliner Lyzeum Cologne 1928
1928
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
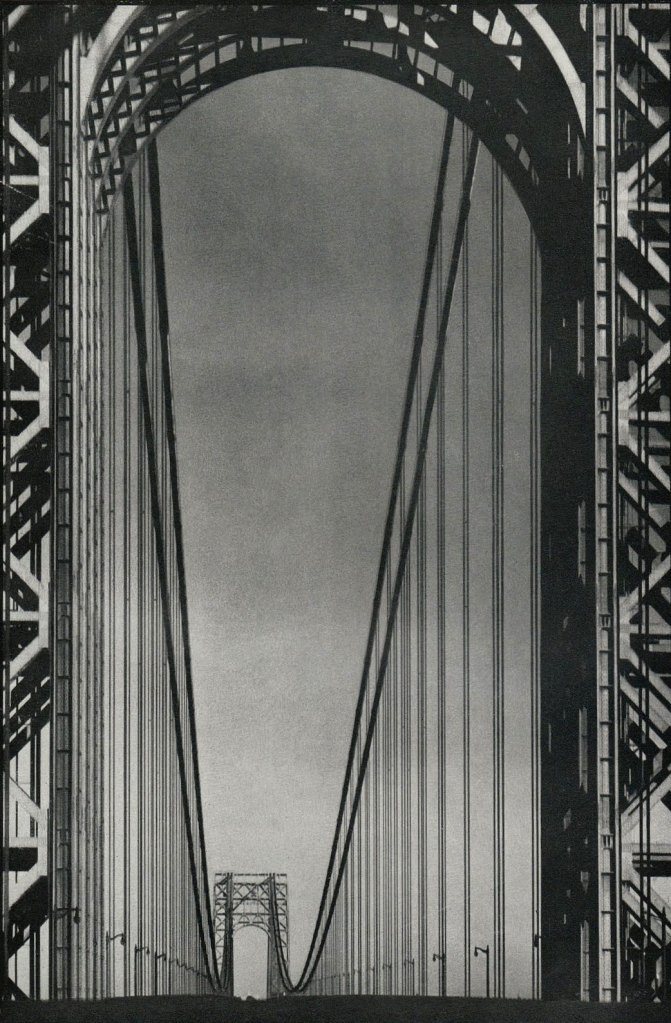

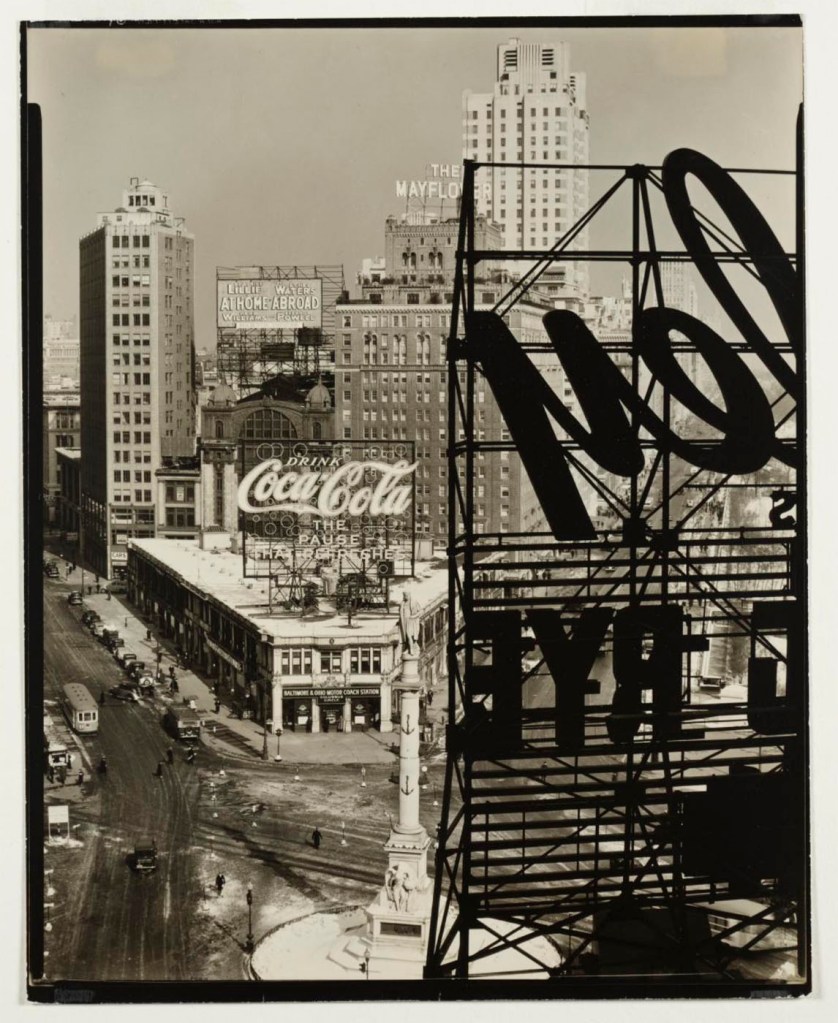
Margaret Bourke-White (American, 1904-1971)
George Washington Bridge
1933
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photography Collection
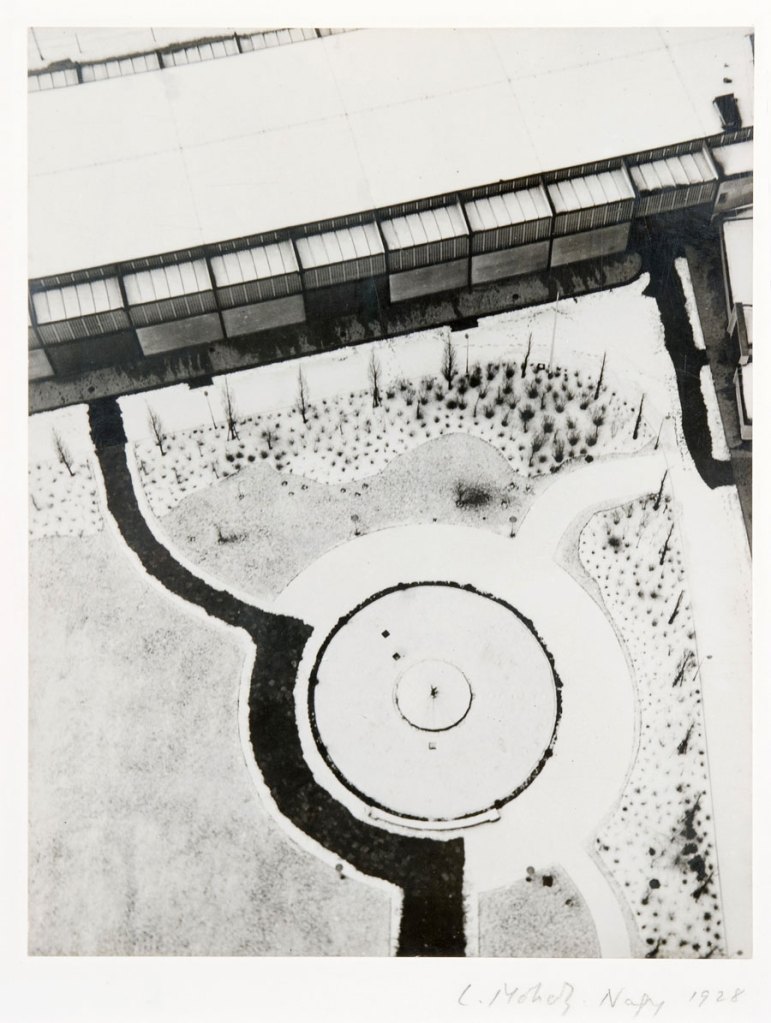

László Moholy-Nagy (Hungarian, 1895-1946)
View from the Berlin tower
1928
Silver gelatin print
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
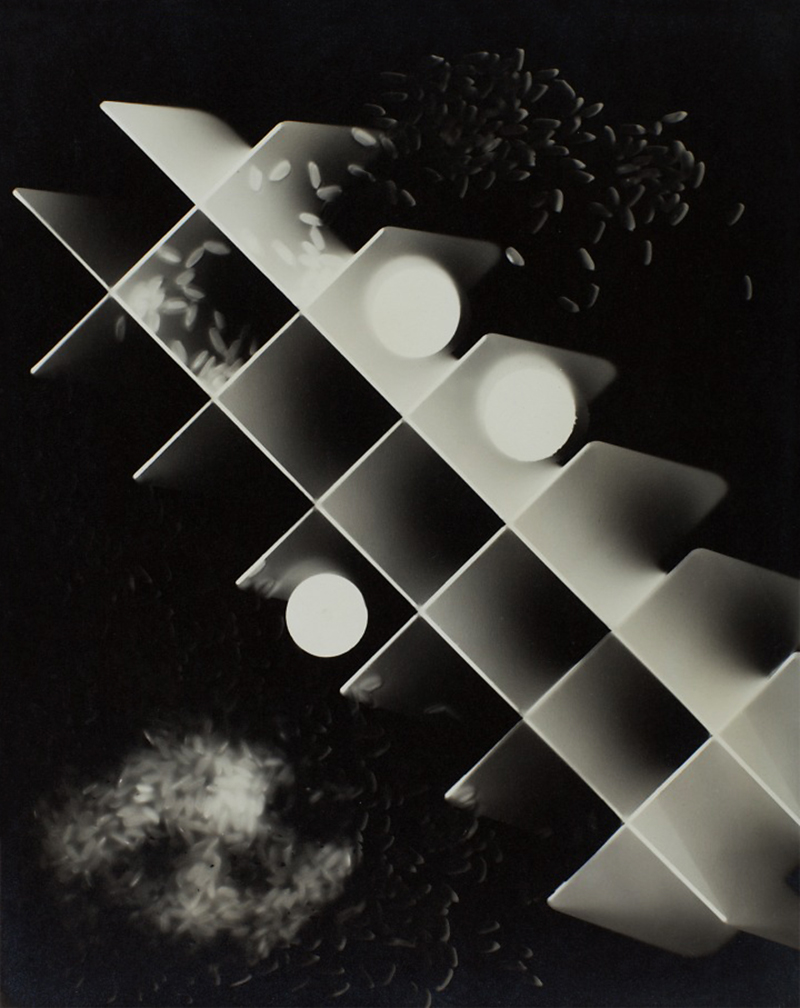

Margaret de Patta (American, 1903-1964)
Ice Cube Tray with Marbles and Rice
1939
The Sir Elton John Photographic Collection
© Estate of Margaret de Patta
Tate Modern
Bankside
London SE1 9TG
United Kingdom
Opening hours:
Sunday – Thursday 10.00 – 18.00
Friday – Saturday 10.00 – 22.00




























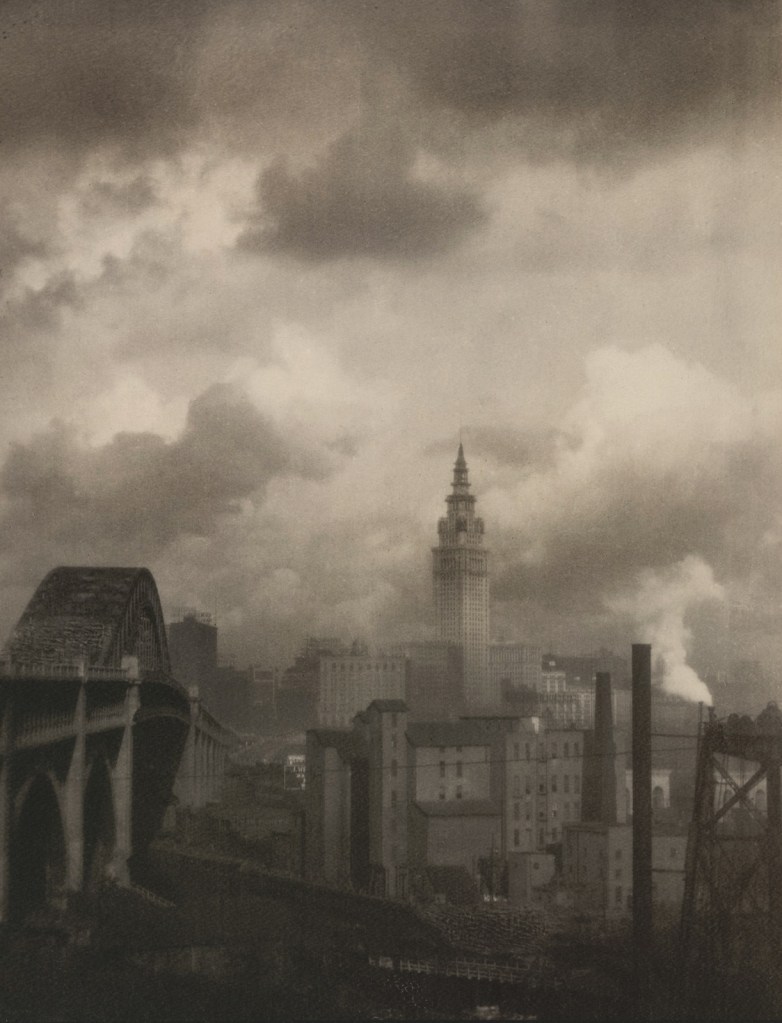
![Margaret Bourke-White (American, 1904-1971) 'Terminal Tower [Cleveland]' c. 1928 Margaret Bourke-White (American, 1904-1971) 'Terminal Tower [Cleveland]' c. 1928](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/margaret-bourke-white-terminal-tower-cleveland-web.jpg?w=719)
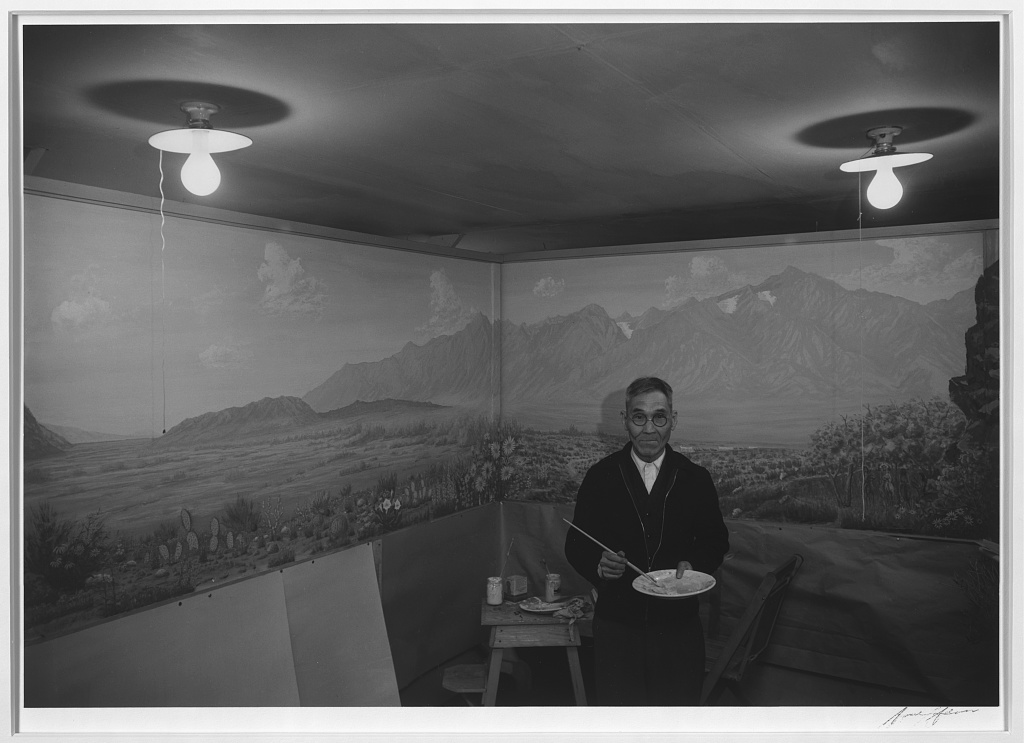




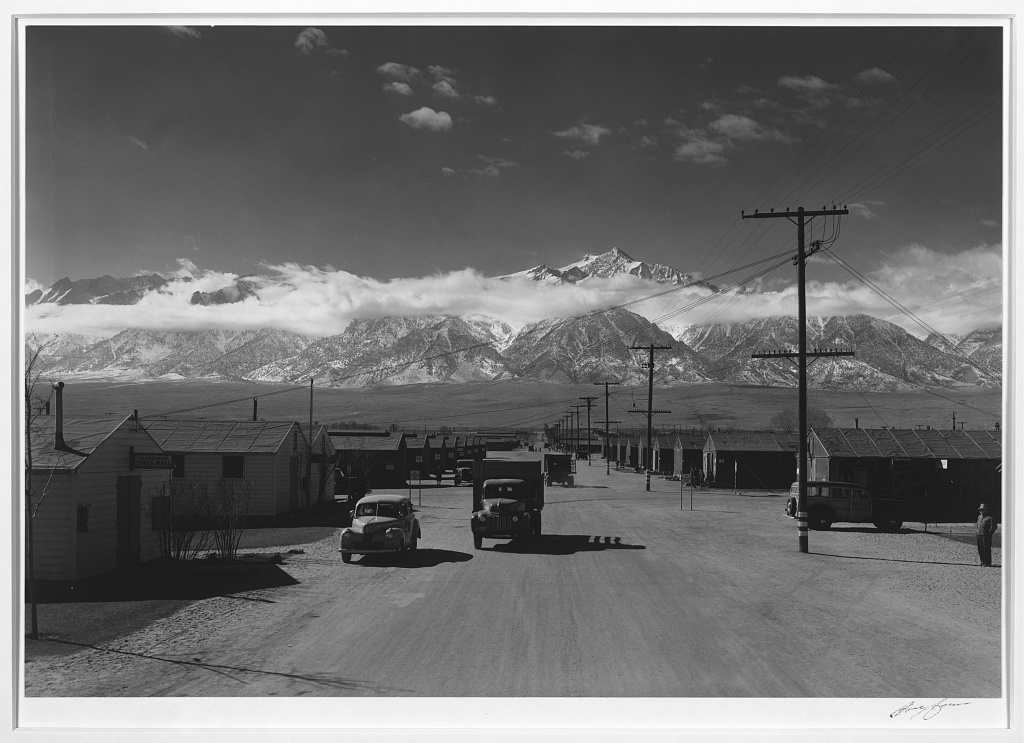
![Ansel Adams (American, 1902-1984) 'Frank Hirosama [i.e., Hirosawa] in laboratory, Manzanar Relocation Center' 1943 Ansel Adams (American, 1902-1984) 'Frank Hirosama [i.e., Hirosawa] in laboratory, Manzanar Relocation Center' 1943](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/frank-hirosama-i-e-hirosawa-in-laboratory-1943.jpg)















































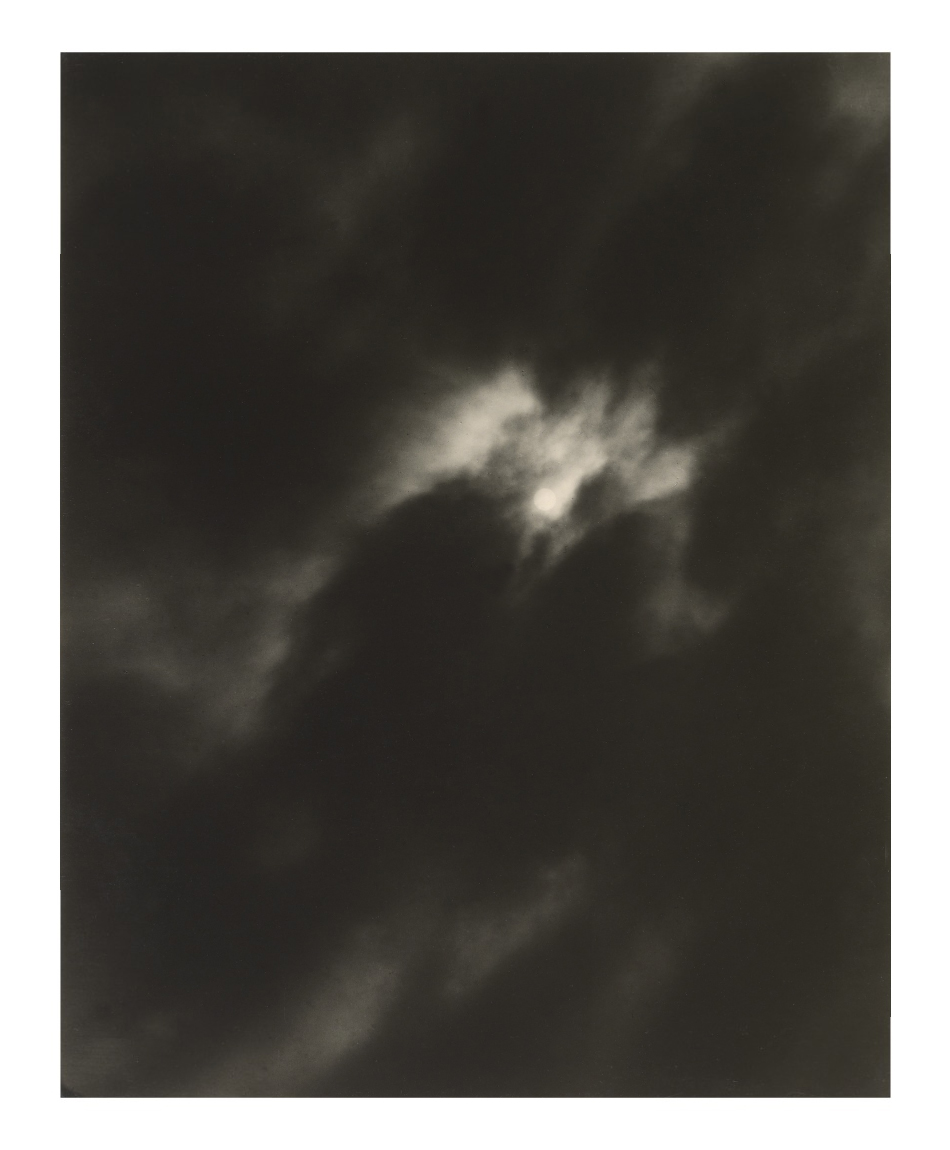
![Carleton Watkins (American, 1829-1916) '[Solar Eclipse]' January 1, 1889 Carleton Watkins (American, 1829-1916) '[Solar Eclipse]' January 1, 1889](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/carleton-watkins-solar-eclipse.jpg)

















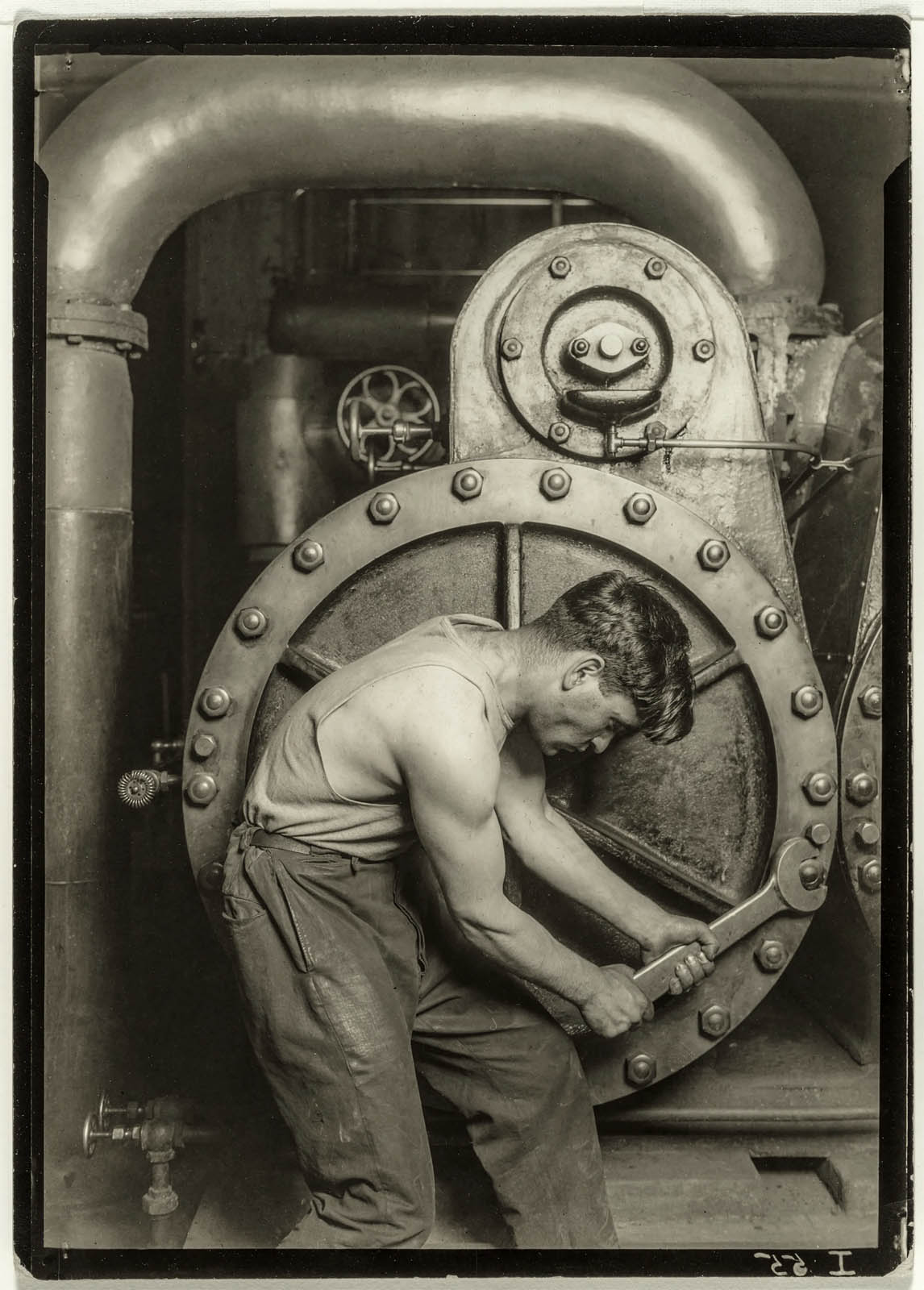
![Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Powerhouse mechanic]' 1920 catalogue size Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Powerhouse mechanic]' 1920 catalogue size](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/hine_powerhousemechanic-actual.jpg)
![Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Powerhouse mechanic]' 1920 catalogue size Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Powerhouse mechanic]' 1920 catalogue size](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/hine_powerhousemechanic-print2.jpg)







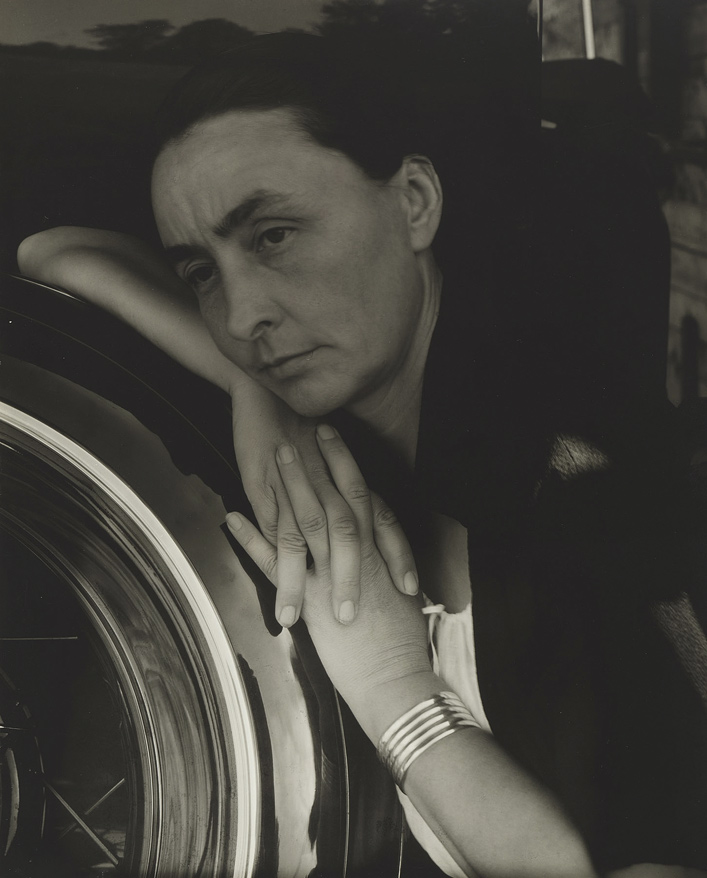
![Alfred Steiglitz (American, 1864-1946) '[Georgia O'Keefe hand on back tire of Ford V8]' 1933 Alfred Steiglitz (American, 1864-1946) '[Georgia O'Keefe hand on back tire of Ford V8]' 1933](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/stieglitz_alfred_portraitgeorgiaokeefe-web3.jpg?w=650)





![W. Eugene Smith (American, 1918-1978) '[Frontline Soldier with Canteen at Saipan]' June 1944 W. Eugene Smith (American, 1918-1978) '[Frontline Soldier with Canteen at Saipan]' June 1944](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/w.-eugene-smith-soldier.jpg)












































You must be logged in to post a comment.