Exhibition dates: 18th November 2011 – 12th February 2012
Minor White (American, 1908-1976)
Tom Murphy (San Francisco)
1948
from The Temptation of St Anthony is Mirrors 1948
Gelatin silver print
4 5/8 x 3 5/8 in. (11.7 x 9.2cm)
The Minor White Archive, Princeton University Art Museum Bequest of Minor White, MWA 48-136
© Trustees of Princeton University
“The possibility of using our bodies as a possible source of very numerous pleasures is something that is very important. For instance, if you look at the traditional construction of pleasure, you see that bodily pleasure, or pleasures of the flesh, are always drinking, eating and fucking. And that seems to be the limit of the understanding of our bodies, our pleasures ….
It is very interesting to note, for instance, that for centuries people generally, as well as doctors, psychiatrists, and even liberation movements, have always spoken about desire, and never about pleasure. “We have to liberate our desire,” they say. No! We have to create new pleasure. And then maybe desire will follow.” (My bold)
Michel Foucault 1
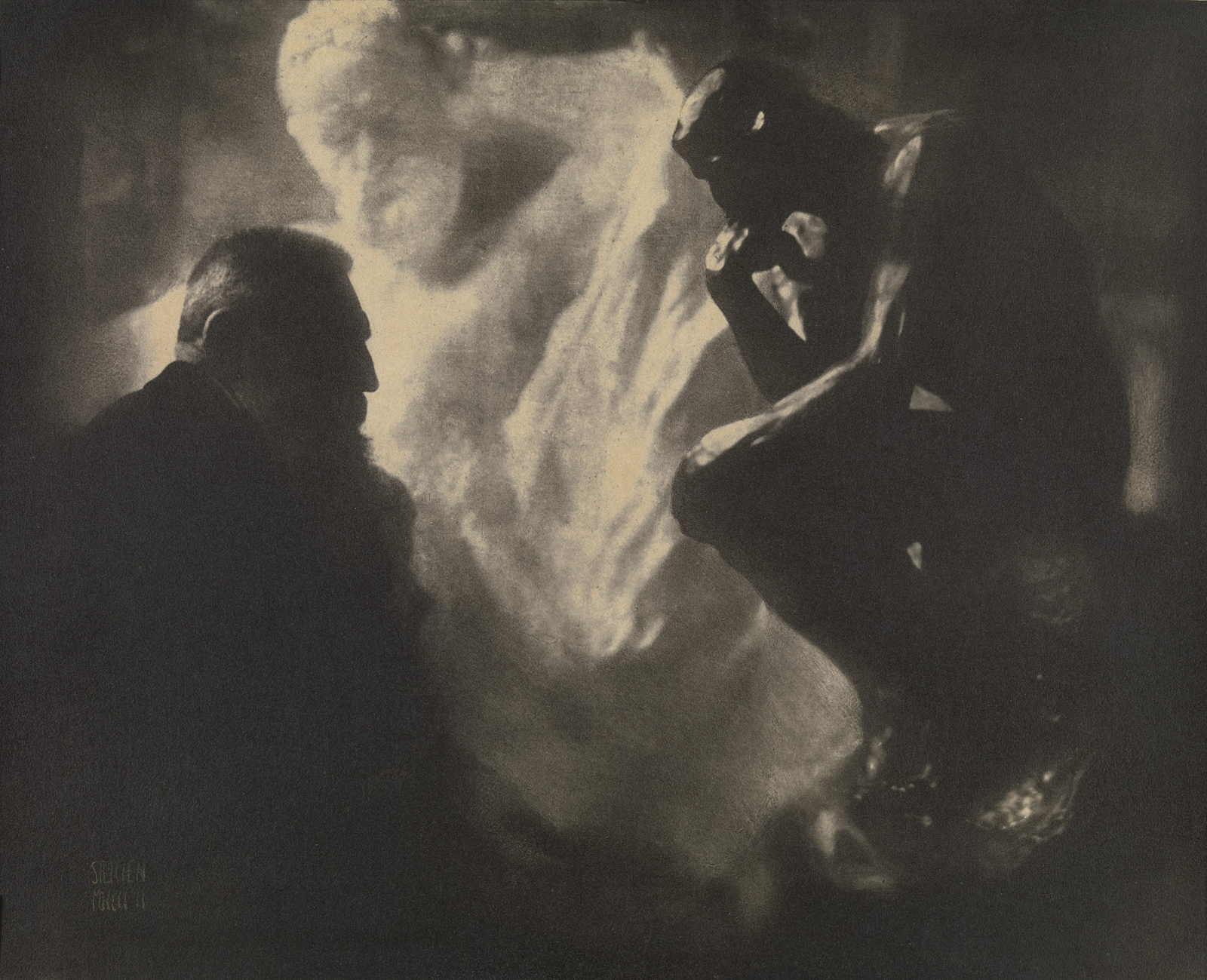
George Platt Lynes, Minor White and The Temptation of Saint Anthony Is Mirrors
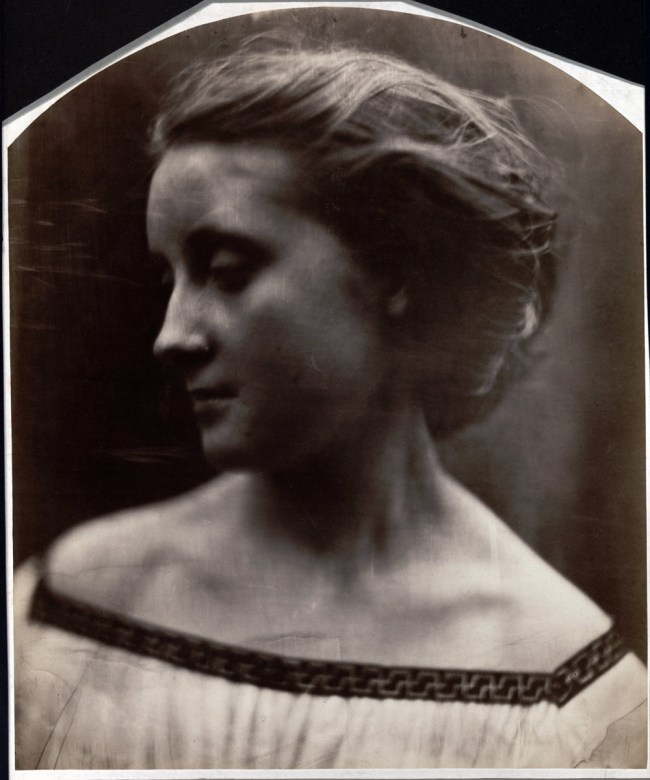
I had the great privilege of visiting The Minor White Archive at Princeton University while I was researching for my PhD. While there I studied the work cards and classic prints of the great photographer, paying particular attention to his photography of the male. What was a great surprise and delight to me were the presence of photographs of explicit sexual acts, men photographed with erections – images that have, to my knowledge, never been published. I don’t think that many people would even know that Minor White took such photographs. Although these images would have never been for public consumption it is still very unusual to find a classical photographer with such a public profile taking photographs of erect penises, especially in the 1940s!
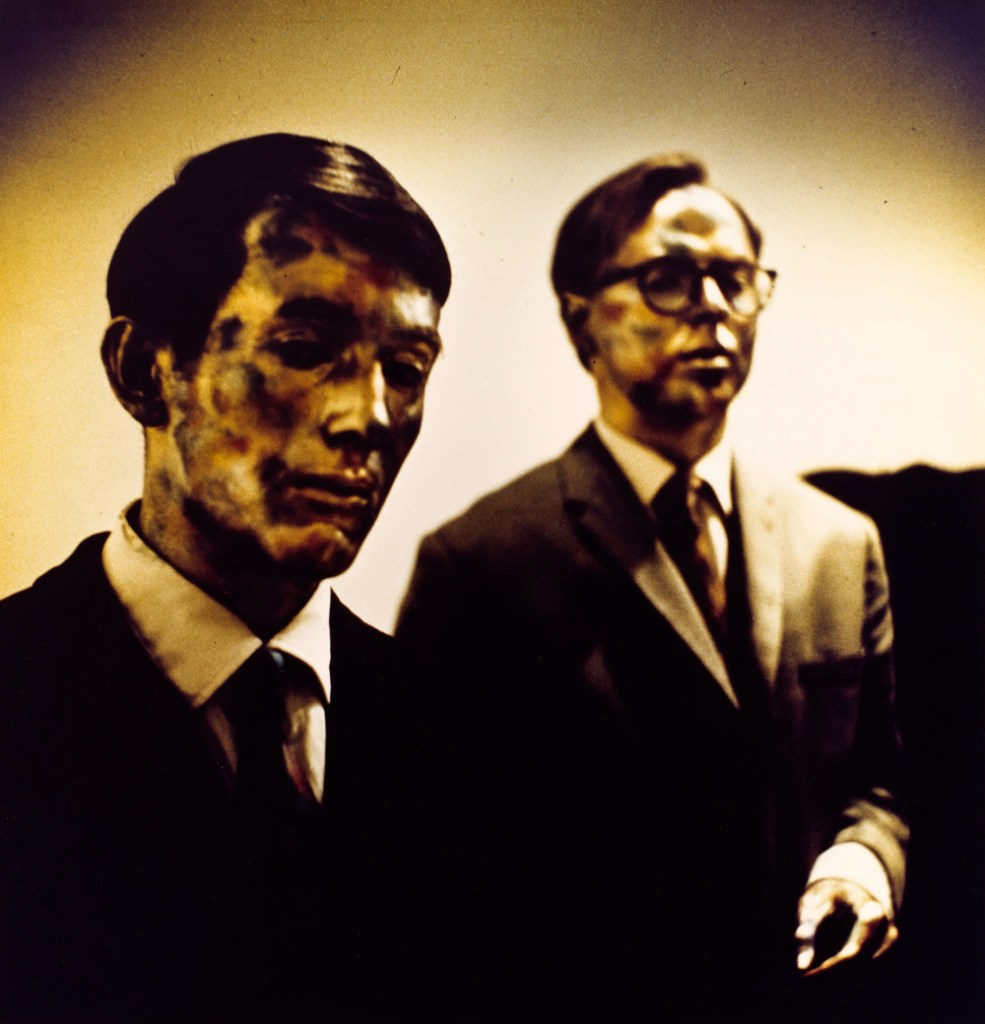
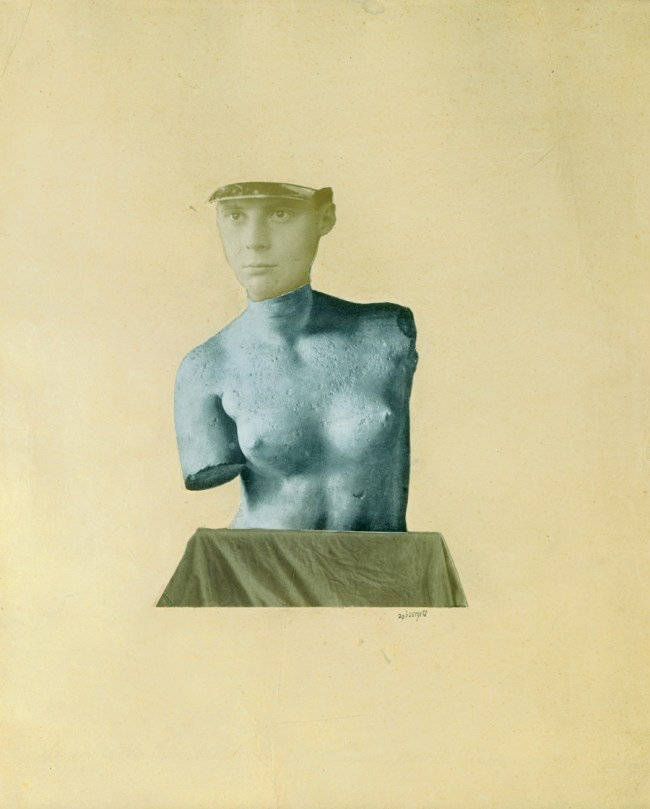
Disturbed by having been in battle in the Second World War and seeing some of his best male friends killed, White’s early photographs of men (in their uniforms) depict the suffering and anguish that the mental and physical stress of war can cause. He was even more upset than most because he was battling his own inner sexual demons at the same time, his shame and disgust at being a homosexual and attracted to men, a difficulty compounded by his religious upbringing. In his photographs White both denied his attraction to men and expressed it. His photographs of the male body are suffused with both sexual mystery and a celebration of his sexuality despite his bouts of guilt. After the war he started to use the normal everyday bodies of his friends to form sequences of photographs, sometimes using the body as a metaphor for the landscape and vice versa. In the above photograph (Tom Murphy, left), based on a religious theme, we see a dismembered hairy body front on, the hands clutching and caressing the body, the lower hand hovering near the exposed genitalia, the upper hand cupping the breast. We see the agony and ecstasy of a homoerotic desire cloaked in a religious theme.
The image comes from the The Temptation of St Anthony is Mirrors (1948), four pages of which can be seen below. While at The Minor White Archive I looked at the only complete, undamaged book in existence. What an experience!
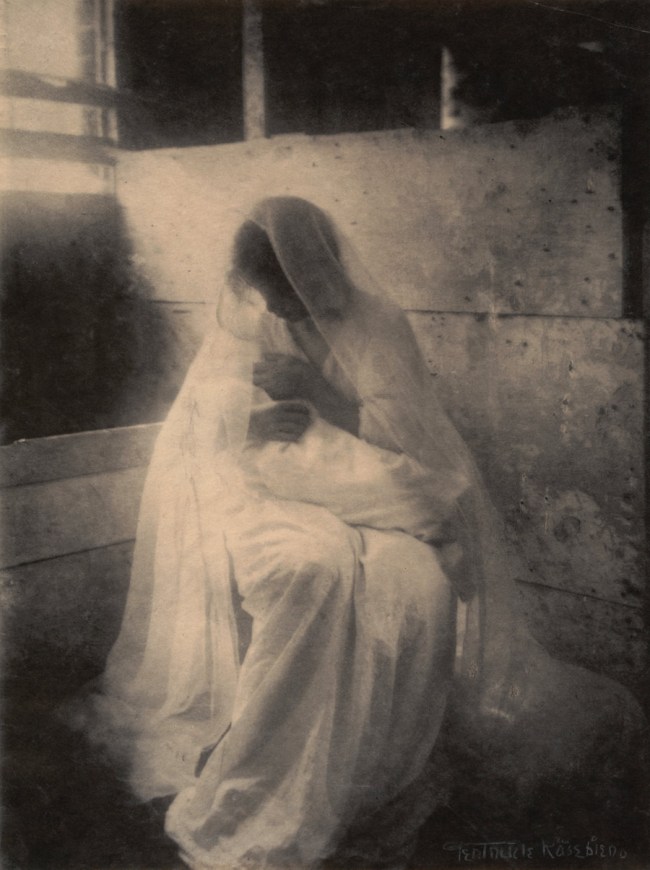
The book has a powerful and intense presence. It was beautifully sequenced as you would expect from Minor White and features photographs of Tom Murphy. There is a series of his hands over the back of a chair in different positions: hanging, curled, splayed, held slightly upwards, and these are paired with photographs of bare feet and turned up jeans, bare feet and rocks, and three other photographs of Tom Murphy. In an excellent paper Cruising and Transcendence in the Photographs of Minor White (Nd. Later published as an online-only feature accompanying Aperture magazine’s Spring 2015 issue, “Queer”), author Kevin Moore observes that the hand-bound volume with images paired on facing pages – “mirrors” to both one another and the artist – is a personal account as well as a meditation on the sins of the flesh.
“Temptation (which was never published or exhibited) begins with a sort of prologue, comprising a single full-length nude of Tom Murphy, White’s student and the model most commonly associated with his work. The pose is similar to those found in the beefcake pictures White was producing at this time: Murphy adopts a classical contrapposto stance and is entirely nude, his pale, wiry body positioned against a dark backdrop. A piece of driftwood at the model’s feet proposes a theme of innocence – man in his natural state. The sequence then moves to pairings of images describing man in his civilised state, featuring several loving close-ups of Murphy’s gesturing hands, a shot of his bare feet, and a single shoulder-length portrait, in which he wears a buttoned shirt and looks intently off to the side. Next, there is an interlude suggesting growing dissolution: an image of Murphy’s feet and a petrified stone is paired with a shot of Murphy in full dress slouched on a mass of rocks and staring vacantly off into the distance. The next pairing (images 9 and 10 below) accelerates the descent into temptation. Here, the pose in a second picture of Murphy’s feet suggests agitation, while a three-quarter length portrait of Murphy, crouched in the bushes and looking back over his shoulder, is as emblematic an image of cruising as White ever produced. The photographs that follow descend further into lust and self-recrimination, conveyed through photographs in which Murphy’s naked body alternates between expressions of pain and pleasure. The sequence ends with a series of beatific nudes (images 27 and 28 below), which express redemption through nonsexual treatments of the body and in the body’s juxtaposition with natural forms – a return to nature.
White may have thought at first that the sequence format would help him transcend the limits of personal biography, that he could use the breadth and fluidity of the sequence to emphasize a universal narrative while exercising control over the potentially explosive and revealing content of individual images. This proved to be overly optimistic, at least in his earliest uses of the form. White’s colleagues, for example, immediately understood Temptation for what it really was: an agonized portrayal of White’s love for his male student.”
Moore goes on to conclude that White obsfucated his sexuality, displacing gay ‘cruising’ “by a universalised mystical searching – sexual longing setting in motion a heroic search” using photography as his medium, and that his photographs became a dreamscape, perhaps even a dream(e)scape: “in which meanings are obscured, not clarified; signs are effaced, not illuminated; beauty is closeted, not set out for all to see. White was attracted to the ambiguity of the dream because it offered cover and protection but also freedom to maneuver. The dream supported the irrational, maintained a sense of mystery, and beautified frustration.”
I have to disagree with Kevin Moore. Anyone who has seen The Temptation of Saint Anthony Is Mirrors in the flesh (so to speak) can feel the absolute presence of these images, their reality, the connection between image and viewer. Maybe White was a Romantic but he was realistically romantic; his images are not dreamscapes, they offer multiple readings and contexts, insights into the human condition. Even though there was anguish and guilt present about his sexuality, channelled through his photography, anyone bold enough to take photographs of erections in 1940 has some ticker. It takes a clear eye and a courageous heart to do this, knowing what was at stake in this era of sexual repression. Beauty is not closeted here, unless I am looking at different images from Kevin Moore. In fact the magic of the photography of Minor White is his ability to modulate space, to modulate bodies so that they are beautiful, ambiguous and mystical whatever their context. Not everything in this world has to be in your face. Like a Glen Gould playing the Goldberg Variations revelation of beauty takes time, concentration and meditation.
Also, an overriding feeling when viewing the images was one of loneliness, sadness and anguish, for the bodies seemed to be observed and not partaken of, to be unavailable both physically and in a strange way, photographically. For a photographer who prided himself on revealing the spirit within, through photography, these are paradoxical photographs, visually accessible and mysteriously (un)revealing, photographs of a strange and wonderful ambivalence. Two great words: obsfucation, ambivalence. Clouded with mixed feelings and emotions, not necessarily anything to do with sexuality. Not everything has to be about sexuality. It is the difference between imbibing Freud or Jung – personally I prefer the more holistic, more inclusive, more spiritual Jung.
And so to the image of George Platt Lynes that I have paired with the nude of Tom Murphy (below).
Platt Lynes was another artist who struggled with is sexuality, but seemingly not to such an extent as Minor White did. GPL worked as a fashion photographer and had his own studio in New York where he photographed dancers, artists and celebrities among others. He undertook a series of mythological photographs on classical themes (which are amazing in composition and feature Surrealist motifs). Privately he photographed male nudes but was reluctant to show them in public for fear of the harm that they could do to his reputation and business with the fashion magazines. Generally his earlier male nude photographs concentrate on the idealised youthful body or ephebe.
As Lynes became more despondent with his career as a fashion photographer his private photographs of male nudes tended to take on a darker and sharper edge. After a period of residence in Hollywood he returned to New York nearly penniless. His style of photographing the male nude underwent a revision. While the photographs of his European colleagues still relied on the sun drenched bodies of young adolescent males evoking memories of classical beauty and the mythology of Ancient Greece the later nudes of Platt Lynes feature a mixture of youthful ephebes and heavier set bodies which appear to be more sexually knowing. The compositional style of dramatically lit photographs of muscular torsos of older men shot in close up (see photograph below for example) were possibly influenced by a number of things – his time in Hollywood with its images of handsome, swash-buckling movie stars with broad chests and magnificent physiques; the images of bodybuilders by physique photographers that George Platt Lynes visited; the fact that his lover George Tichenor had been killed during WWII; and the knowledge that he was penniless and had cancer. There is, I believe, a certain sadness but much inner strength in his later photographs of the male nude that harnesses the inherent sexual power embedded within their subject matter.
When undertaking research into GPL’s photographs at The Kinsey Institute as part of my PhD I noted that most of the photographs had annotations in code on the back of them giving details of age, sexual proclivities of models and what they are prepared to do and where they were found. This information gives a vital social context to GPL’s nude photographs of men and positions them within the moral and ethical framework of the era in which they were made. The strong image (below) is always quoted as an example of GPL’s more direct way of photographing the male nude in the last years of his life. The male is solid, imposing, lit from above, heavy set, powerful, massive. The eyes are almost totally in shadow. Later photos have more chiaroscuro than earlier work, more use of contrasting light (especially down lit or uplit figures) but are they more direct? Yes. The men look straight into camera.
This monumentality of body and form was matched by a new openness in the representation of sexuality. There are intimate photographs of men in what seem to be post-coital revere, in unmade beds, genitalia showing or face down showing their butts off. Some of the faces in these later photographs remain hidden, as though disclosure of identity would be detrimental for fear of persecution. The photograph above is very ‘in your face’ for the conservative time from which it emerges, remembering it was the era of witch hunts against communists and subversives (including homosexuals). Conversely, this photograph is quite restrained compared to the most striking series of GPL’s photographs that I saw at The Kinsey Institute which involves an exploration the male anal area (a photograph from the 1951 series can be found in the book titled George Platt Lynes: Photographs from The Kinsey Institute). This explicit series features other photographs of the same model – in particular one that depicts the male with his buttocks in the air pulling his arse cheeks apart. After Lynes found out he had cancer he started to send his photographs to the German homoerotic magazine Der Kries under the pseudonym Roberto Rolf, and in the last years of his life he experimented with paper negatives, which made his images of the male body even more grainy and mysterious.
I believe that Lynes understood, intimately, the different physical body types that gay men find desirable and used them in his photographs. He visited Lon of New York (a photographer of beefcake men) in his studio and purchased photographs of bodybuilders for himself, as did the German photographer George Hoyningen-Huene. It is likely that these images of bodybuilders did influence his later compositional style of images of men; it is also possible that he detected the emergence of this iconic male body type as a potent sexual symbol, one that that was becoming more visible and sexually available to gay men.
The differences between the White and GPL nudes is instructive. White: introspective, haunted, religious with an unrequited sense of longing – hands clutching self, inward pointing; GPL: more closely cropped, more open, one hand firmly grasping but the other hand open, receptive, presented to the viewer above the available phallic organ. It reminds me for some unknown reason, some quirk of my brain association, of the shell of Botticelli’s Birth of Venus (1486) inverted. There is difference between the two artists – one struggling with his sexuality, being realistically romantic, the other physically doing something about it – posting his photographs to one of the first gay magazines in the world. But both were taking photographs of intimate sexual acts that could never have been published in their lifetimes – that are still are hidden from view today. When, oh when, will someone have the courage to publish this work?
Dr Marcus Bunyan
My notes on Minor White’s photographs and notes on George Platt Lynes photographs from my Phd thesis Pressing the Flesh: Sex, Body Image and the Gay Male (2001) can be found below.
Many thankx to the Brooklyn Museum for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
1/ Gallagher, Bob and Wilson, Alexander. “Sex and the Politics of Identity: An Interview with Michel Foucault,” in Thompson, Mark. Gay Spirit: Myth and Meaning. New York: St. Martin’s Press, 1987, p.31.
Research notes on photographs from the Minor White Archive, Princeton University, New Jersey 06/08/1999
Download the Minor White research notes (85kb pdf)
Research at The Kinsey Institute , Bloomington, Indiana 16/08/1999 – 19/08/1999. George Platt Lynes photographs from the Collection at The Kinsey Institute
Download the George Platt Lynes research notes (55kb pdf)
(top)
Minor White (American, 1908-1976)
Images 9 and 10 in the bound sequence The Temptation of Saint Anthony Is Mirrors
1948
9.3 x 11.8cm; 11.2 x 9.1cm
(bottom)
Minor White (American, 1908-1976)
Images 27 and 28 in the bound sequence The Temptation of Saint Anthony Is Mirrors
1948. 5.3 x 11.6cm; 10.6 x 8.9cm
 |
 |
(left)
Minor White (American, 1908-1976)
Tom Murphy (San Francisco)
1948
from The Temptation of St Anthony is Mirrors 1948
Gelatin silver print
4 5/8 x 3 5/8 in. (11.7 x 9.2 cm)
(right)
George Platt Lynes (American, 1907-1955)
Untitled
Nd
Gelatin silver print
George Platt Lynes (American, 1907-1955)
Untitled (Frontal Male Nude)
Nd (early 1950s)
Gelatin silver print
Thomas Eakins (American, 1844-1916)
Walt Whitman (American, 1818-1892)
1891
10.3 x 12.2cm
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institute
Charles Demuth (American, 1883-1935)
Dancing Sailors
1917
Watercolour and pencil on paper
20.3 x 25.4cm
Cleveland Museum of Art, Ohio; Mr and Mrs William H Marlatt Fund
George Wesley Bellows (American, 1882-1925)
Riverfront No.1
1915
Oil on canvas
115.3 x 160.3cm
Columbus Museum of Art, Ohio: Howald Fund Purchase
Marsden Hartley (American, 1877-1943)
Eight Bells Folly: Memorial to Hart Crane
1933
Oil on canvas
Gift of Ione and Hudson D. Walker
Frederick R. Weisman Art Museum, University of Minnesota
Harold Hart Crane (July 21, 1899 – April 27, 1932) was an American poet. Finding both inspiration and provocation in the poetry of T. S. Eliot, Crane wrote modernist poetry that is difficult, highly stylised, and very ambitious in its scope. In his most ambitious work, The Bridge, Crane sought to write an epic poem in the vein of The Waste Land that expressed something more sincere and optimistic than the ironic despair that Crane found in Eliot’s poetry. In the years following his suicide at the age of 32, Crane has come to be seen as one of the most influential poets of his generation…
Crane visited Mexico in 1931-32 on a Guggenheim Fellowship and his drinking continued as he suffered from bouts of alternating depression and elation … While on board the steamship SS Orizaba enroute to New York, he was beaten after making sexual advances to a male crew member, seeming to confirm his own idea that one could not be happy as a homosexual. Just before noon on April 27, 1932, Hart Crane jumped overboard into the Gulf of Mexico. Although he had been drinking heavily and left no suicide note, witnesses believed his intentions to be suicidal, as several reported that he exclaimed “Goodbye, everybody!” before throwing himself overboard. (The legend among poets is: He walked to the fantail, took off his coat quietly, and jumped.) His body was never recovered.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Peter Hujar (American, 1937-1987)
Susan Sontag (American, 1933-2004)
1975
Gelatin silver print
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institute
© Estate of Peter Hujar
Keith Haring (American, 1958-1990)
Unfinished Painting
1989
Acrylic on canvas
100 x 100cm
Courtesy of Katia Perlstein, Brussels, Belgium
© Keith Haring Foundation
David Wojnarowicz (American, 1954-1992)
A Fire In My Belly (Film In Progress) (film still)
1986-1987
Super 8mm film
black and white & color (transferred to video)
Courtesy of The Estate of David Wojnarowicz and P.P.O.W Gallery, New York and The Fales Library and Special Collection
One day before World AIDS Day, the renown painter, photographer, writer, filmmaker, performance artist and activist David Wojnarowicz, who died in 1992 at the age of 37 from AIDS-related complications, has had one of his most important works, A Fire In My Belly, pulled from The Smithsonian Institution’s National Portrait Gallery’s HIDE / SEEK exhibit because of pressure from conservative politicians and the Catholic League.”
HIDE/SEEK: Difference and Desire in American Portraiture, the first major museum exhibition to explore how gender and sexual identity have shaped the creation of American portraiture, organised by and presented at the National Portrait Gallery last fall, will be on view at the Brooklyn Museum from November 18, 2011, through February 12, 2012. With the cooperation of the National Portrait Gallery, the Brooklyn Museum has reconstituted the exhibition in concert with the Tacoma Art Museum, where it will be on view from March 17 through June 10, 2012.
HIDE/SEEK includes approximately a hundred works in a wide range of media created over the course of one hundred years that reflect a variety of sexual identities and the stories of several generations. Highlighting the influence of gay and lesbian artists, many of whom developed new visual strategies to code and disguise their subjects’ sexual identities as well as their own, HIDE/ SEEK considers such themes as the role of sexual difference in depicting modern Americans, how artists have explored the definition of sexuality and gender, how major themes in modern art – especially abstraction – have been influenced by marginalisation, and how art has reflected society’s changing attitudes.
Announcing the Brooklyn presentation, Museum Director Arnold L. Lehman states, “From the moment I first learned about this extraordinary exhibition in its planning stages, presenting it in Brooklyn has been a priority. It is an important chronicle of a neglected dimension of American art and a brilliant complement and counterpoint to ‘Youth and Beauty: Art of the American Twenties’, a touring exhibition organised by the Brooklyn Museum, also on view this fall.”
In addition to its commentary on a marginalised cultural history, HIDE/ SEEK offers an unprecedented survey of more than a century of American art. Beginning with late nineteenth-century portraits by Thomas Eakins and John Singer Sargent, it includes works from the first half of the 1900s by such masters as Romaine Brooks, George Bellows, Marsden Hartley, and Georgia O’Keeffe; the exhibition continues through the postwar period with works by Jasper Johns, Robert Rauschenberg, Agnes Martin, and Andy Warhol, and concludes with major works by late twentieth-century artists such as Keith Haring, Glenn Ligon, Nan Goldin, Felix Gonzalez-Torres, and Catherine Opie.
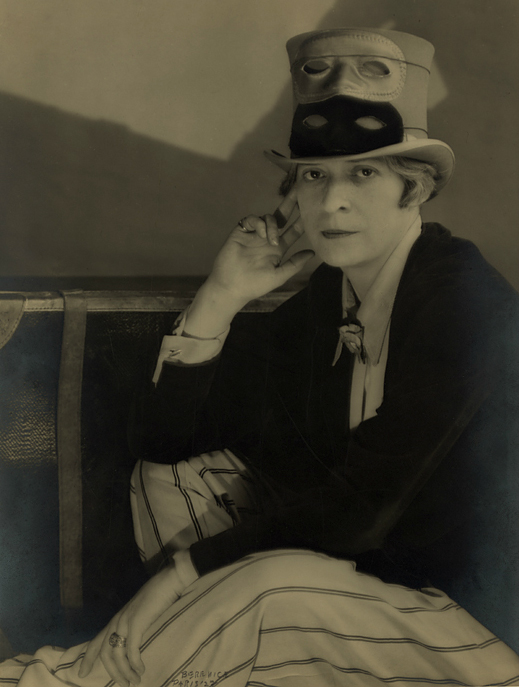
The Brooklyn presentation will feature nearly all of the works included in the National Portrait Gallery exhibition. Among them are rarely seen paintings by Charles Demuth, whose better-known industrialised landscapes are on view in the Brooklyn Museum exhibition Youth and Beauty; a poignant portrait of New Yorker writer Janet Flanner wearing two masks, taken by photographer Bernice Abbott; Andrew Wyeth’s painting of a young neighbour standing nude in a wheat field, much like Botticelli’s Venus emerging from her shell; Robert Mapplethorpe’s photograph riffing on the classic family portrait, in which a leather-clad Brian Ridley is seated on a wingback chair shackled to his whip-wielding partner, Lyle Heeter; and Cass Bird’s photographic portrait of a friend staring out from under a cap emblazoned with the words “I look Just Like My Daddy.” The exhibition will also include David Wojnarowicz’s A Fire in My Belly, an unfinished film the artist created between 1986 and 1987.
Press release from the Brooklyn Museum website
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Janet Flanner (American, 1892-1978)
1927
Photographic print
23 x 17.3cm
Prints and Photographs Division, Library of Congress, Washington, D.C
C Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd., Inc.
Thomas Eakins (American, 1844-1916)
Salutat
1898
Oil on canvas
127.0 x 101.6cm
Addison Gallery of American Art, Phillips Academy, Andover, Massachusetts
Gift of anonymous donor
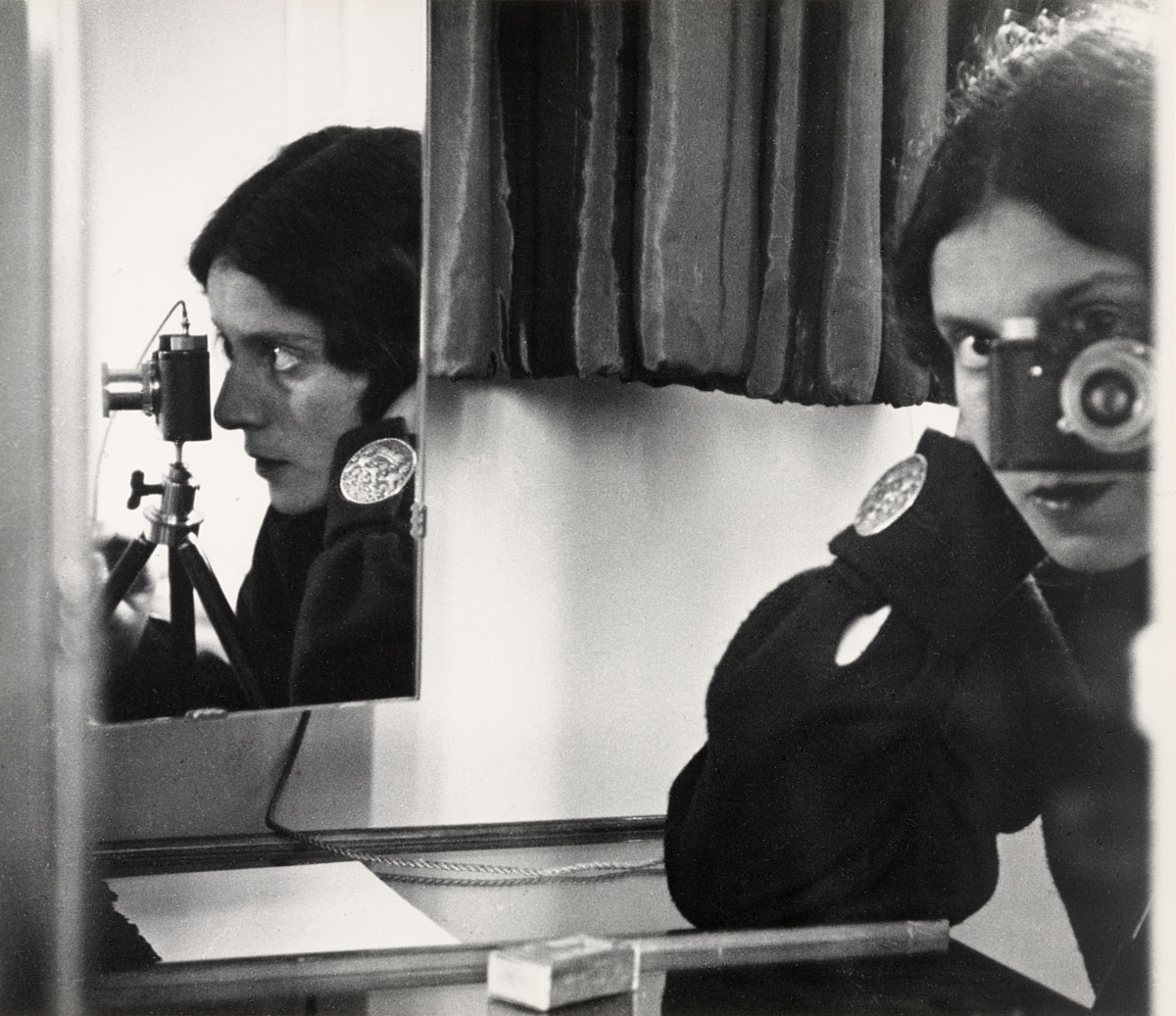
Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975)
Lincoln Kirstein (American, 1907-1996)
1930
Gelatin silver print
16.1cm x 11.4cm
The Metropolitan Msuem of Art, Ford Motor Company Collection
© Walker Evans Archive, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Lincoln Edward Kirstein (May 4, 1907 – January 5, 1996) was an American writer, impresario, art connoisseur, philanthropist, and cultural figure in New York City, noted especially as co-founder of the New York City Ballet. He developed and sustained the company with his organising ability and fundraising for more than four decades, serving as the company’s general director from 1946 to 1989. According to the New York Times, he was “an expert in many fields,” organising art exhibits and lecture tours in the same years.
Marsden Hartley (American, 1877-1943)
Painting No. 47, Berlin
1915
Oil on canvas
39 7/16 x 32 in (100.1 x 81.3cm)
Hirshhorn Museum and Sculpture Garden, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
Gift of Joseph H. Hirshhorn, 1972
George Platt Lynes (American, 1907-1955)
Marsden Hartley
1942
Gelatin silver print
23.5 x 19.1cm
Bates College Museum of Art, Lewiston, ME, Marsden Hartley Memorial Collection
© Estate of George Platt Lynes
Beauford Delaney (American, 1901-1979)
James Baldwin
1963
Pastel on paper
64.8 x 49.8cm
National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Cass Bird (American, b. 1974)
I Look Just Like My Daddy
2003
C-type print
72.6 x 101.6cm
Collection of the artist, New York
© Cass Bird
Brooklyn Museum
200 Eastern Parkway
Brooklyn, NY 11238-6052
Phone: (718) 638-5000
Opening hours:
Wednesday – Sunday 11am – 6pm
Monday and Tuesday closed




















![Carleton Watkins (American, 1829-1916) '[Solar Eclipse]' January 1, 1889 Carleton Watkins (American, 1829-1916) '[Solar Eclipse]' January 1, 1889](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/carleton-watkins-solar-eclipse.jpg)
















































![Margaret Bourke-White (American, 1906-1971) '[Iron Mountain, Tennessee]' 1937 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas Margaret Bourke-White (American, 1906-1971) '[Iron Mountain, Tennessee]' 1937 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/12/margaret-bourke-white-iron-mountain-tennessee-1937.jpg)





![Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975) '[Lunchroom Window, New York City]' 1929 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975) '[Lunchroom Window, New York City]' 1929 from the exhibition 'American Modern: Abbott, Evans, Bourke-White' at the Amon Carter Museum of American Art, Fort Worth, Texas](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/12/walker-evans-lunchroom-window-new-york-city-1929.jpg)









































































You must be logged in to post a comment.