Exhibition dates: 28th November 2015 – 28th March 2016
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
FORWARD
2008
Mixed media
381 x 604cm
Courtesy of the artists and White Cube
Gentlemen of the gutter
While I admire the mythology of Gilbert and George, that ever so British pair of deviant artists, they have never been among my favourites.
They had a tough road. Imagine meeting in 1967, pre-Stonewall and the beginning of gay liberation, and then moving into the roughest part of London, the East End, to live together and make art, dressed as a pair of besuited businessmen. The prejudice and the abuse would have been intense, but they stuck together, they stuck to their path as artists, and they stuck to each other as human beings. It is fascinating to see the trajectory of their development, to follow the development of the grid, the introduction of one colour and then multiple colours.
I understand what they do, empathise with their endeavour (anti-nationalism, religion, bigotry, racism, homophobia etc etc…) but wonder whether they have not painted themselves and their art into a corner. They are so well known for their long running performance – their vaudeville act reminding me of a contemporary Hieronymus Bosch with text ripped from the headlines / images riffed from hell (portraits of cut up reflections assembled to make surreal creatures with gaping mouths), the gridded works, the colours, the content AS graphic gothic cathedral with stained glass windows – that they seem incapable or willing to push themselves and their art further. To shock us in an altogether different way? Now that would be a greater surprise, than just semen, spit and shit.
What I am saying is that they have got their schtick down pat. They worked hard for their anti-establishment schlock horror. The work has presence and they do know how to reach people with a picture but with each repetition, with each ritual performance the cracks grow ever larger. As John McDonald observes, “They are iconoclastic non-entities making art that attracts and repels.” What actually lies underneath all of this rhetoric. Two caring human beings, two compassionate souls? I think not, therefore I am.**
As can be seen in many of their works, the emperors literally have no clothes…
Dr Marcus Bunyan
** Perhaps it should have been “I care not, therefore I am” … because they don’t really give a dam what people think. This is part of the problem: their rather mean spirited view of the world.
Many thankx to MONA for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition
Gilbert & George In Conversation With Olivier Varenne
“We are unhealthy, middle-aged, dirty-minded, depressed, cynical, empty, tired-brained, seedy, rotten, dreaming, badly-behaved, ill-mannered, arrogant, intellectual, self-pitying, honest, successful, hard-working, thoughtful, artistic, religious, fascistic, blood-thirsty, teasing, destructive, ambitious, colourful, damned, stubborn, perverted and good. We are artists.”
“Art has just become decoration for the very, very rich. We manage to keep our feet on the ground. We have never been part of an elitist art group. Our art is so confrontational that a lot of collectors would never touch it because they don’t want a naked shit picture in their living room… More and more it is difficult to speak as an artist. Nobody hears you because there are too many and there are too many different ways of making art today that there didn’t use to be when we started out in 1969.”
“We never go to the cinema, the theatre, or the ballet or opera. We stopped 40 years ago. We just didn’t want to become contaminated. We know what we’re interested in, we know how we can reach people with a picture. We have a feeling, what we put in that picture that will mean something to somebody.”
Gilbert & George
Two people, but one artist: the legendary Gilbert & George’s first ever exhibition in Australasia, Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition, is now open at the Museum of Old and New Art in Tasmania, Australia, until March 28, 2016.
Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition is a major retrospective, including pictures spanning five decades; dating from 1970 to most recent pictures of 2014. Curated by Gilbert & George with organising curators, Mona’s Co-Directors of Exhibitions and Collections, Olivier Varenne and Nicole Durling, the pictures are installed across the entirety of Mona’s touring galleries, 14 metres underground.
“Our pictures deal with the great universals: death, hope, life, fear, sex, money, race and religion. Seeing is believing. See for yourself: Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition. This is your very first – and last – chance to see one hundred of our pictures, at the wonderful Museum of Old and New Art in Hobart, Tasmania.” ~ Gilbert & George
Since first meeting at St Martin’s school of Art, London, in 1967, Gilbert & George have lived and worked together as one single and fiercely independent artist, dedicated solely to the creation of their art. They have no allegiance to any other trend, school, movement, doctrine, theory or style of art.
Gilbert & George already knew that they were seeking for a form of art that was to them entirely rooted in the real world – in the streets and clamour and traffic and buildings and hearts of strangers: an “Art for All.”
Today, their art continues to be multi-allusive, contemporary and contentious, as their subject is literally at their feet – along countless streets, the thoroughfares of the passage of millions of lives, and dense with the sedimentary tracings of social existence.
Text from MONA
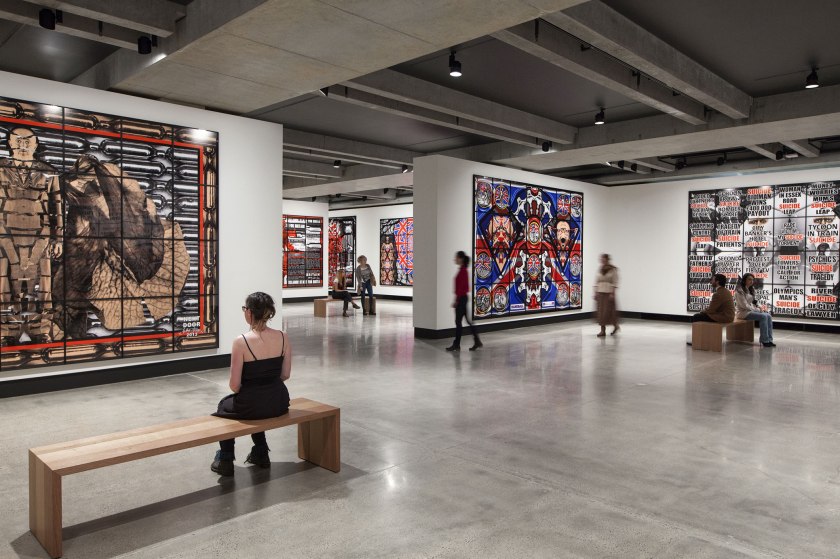
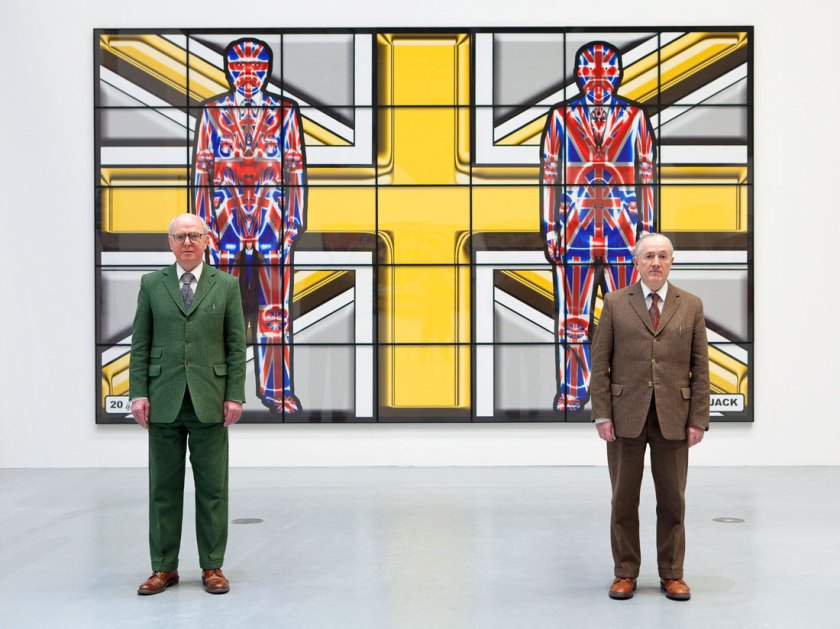
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, BOMBERS (2006), and at right, FORWARD (2008)
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
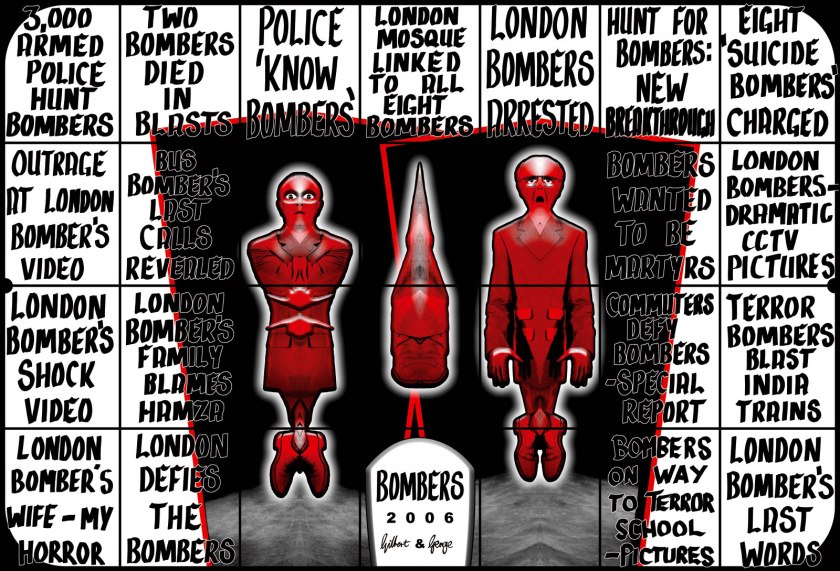
BOMBERS
2006
From Bomb Pictures
Mixed media
336 x 493cm
Courtesy of the artists and White Cube
Gilbert & George created an important group of six pictures for their major retrospective at Tate Modern. The six Bomb Pictures, the only pictures created by the artists in 2006, comprise a 14 metre triptych entitled Bomb and five other pictures: Bombs; Bomber; Bombers; Bombing; and Terror. The artists have described this group of pictures as their most chilling to date. The artists intend the pictures to be seen as modern townscapes reflecting the daily exposure in urban life to terror alerts.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – The Bomb Pictures (2006),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, TOPSY TURVY (1989) from The Cosmological Pictures
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
DEAD HEAD
1989
From The Cosmological Pictures
Picture courtesy of the artists and Mona, Museum of Old and New Art, Tasmania, Australia
With this body of work Gilbert & George stress the power of human thought to remake life and so create the future through a process of communication, discussion and questioning, stimulated by the pictures. The word ‘cosmology’ derives from the Greek words for ‘world’ and ‘discourse’. Since September 1991, The Cosmological Pictures have been touring many European cities. Gilbert and George’s aim – to speak to many people in all of these cities – is at the heart of their cosmology.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – The Cosmological Pictures (1989),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
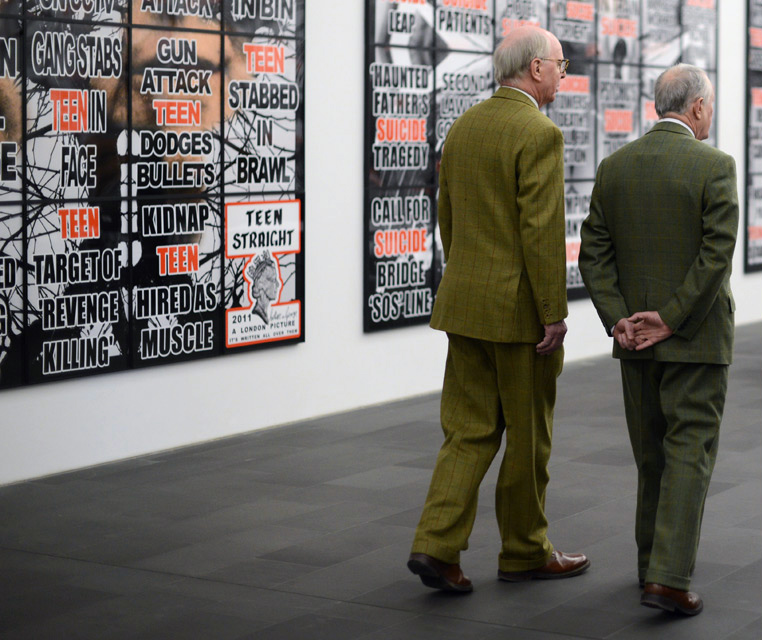
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, NEXT DOOR (2013), in the middle HANDBALL (2008), and at right, SUICIDE STRAIGHT (2011) from The London Pictures
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
KILLERS STRAIGHT
2011
From The London Pictures
The London Pictures are made up of 292 of the 3,712 newspaper ‘bills’ the pair have doggedly pilfered from outside London newsagents over many years. The pictures present an epic survey of modern urban life in all its volatility, tragedy, absurdity and routine violence. They are Dickensian in scope and ultra-modern in sensibility.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – London Photos (2011),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing in the middle HANDBALL (2008), and at right, SUICIDE STRAIGHT (2011) from The London Pictures
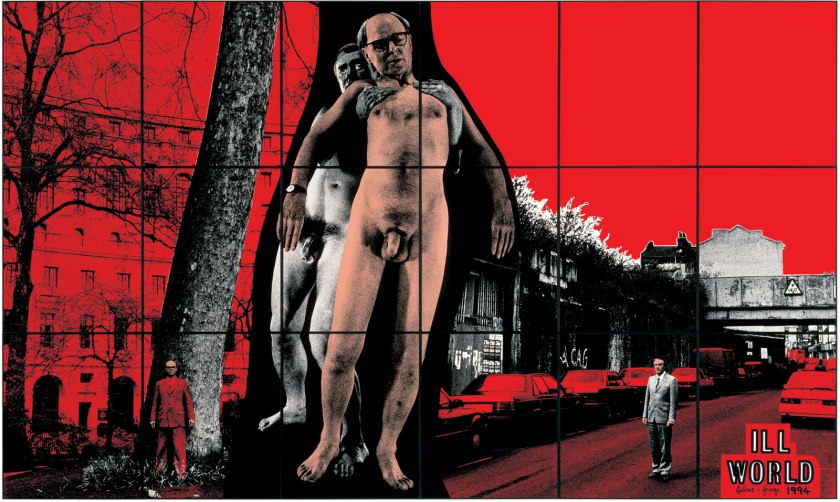
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing from left (large pictures), CITY DROP (1991), FLAT MAN (1991), EIGHT SHITS (1994) and ILL WORLD (1994), both from The Naked Shit Pictures
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
ILL WORLD
1994
Mixed media
253 x 426cm
Courtesy of the artists
The frieze-like composition of The Naked Shit Pictures, with its striking contrasts of scale, was displayed high on the gallery walls. As the title indicates, works in the group depict the artists naked, or semi-dressed, often in conjunction with scaled-up images of faeces. These primary motifs are juxtaposed with urban/parkland scenes, giant anonymous suited bodies and the artists, or set against colour grounds. Marked contrasts in scale are a dominant feature in the series.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – The Naked Shit Pictures (1994),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at middle, IN THEIR ELEMENT (1998) from the series The Rudimentary Pictures (1998) followed by FIVE (1992)
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
IN THEIR ELEMENT
1988
From the series The Rudimentary Pictures
Mixed media
254 x 528 cm
Courtesy of the artists
The Rudimentary Pictures, presents thirty-three new works, in which they explore such themes as alienation, sex, race, and human existence. Many of these striking pictures extend the distinctive range of images they have created exploring city life. In Gum City, City Sweat, Money City, Blood City, Piss City, Sex City and Crying City, backgrounds of London street plans are combined with map-like microscopic details of blood, sweat, tears, urine and semen, together with themselves.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – The Rudimentary Pictures (1998),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at middle, FLYING SHIT WHEEL OF DEATH (1998) and, at right, RAIN WHEEL OF LIFE (1998), both from The Rudimentary Pictures
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
FLYING SHIT WHEEL OF DEATH (installation view)
1998
from the series The Rudimentary Pictures
Gilbert & George hardcover catalogue
Photo Credit: Mona/Rémi Chauvin
Image Courtesy Mona, Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
RED MORNING DEATH
1977
Mixed media
241 x 201cm
Private collection
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
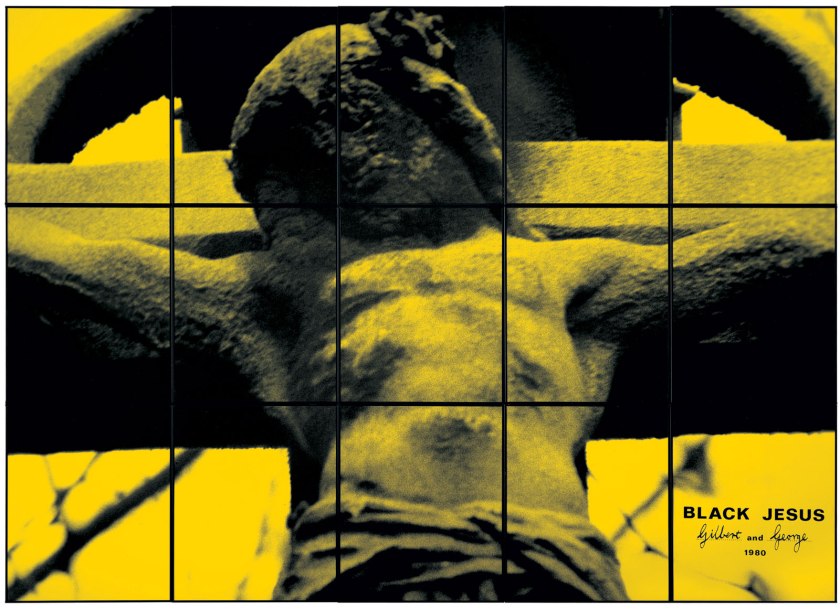
BLACK JESUS
1980
Mixed media
181 x 251cm
Private collection
In the early 1980s, Gilbert & George began to add a range of bright colours to their photographic images. They dramatically expanded their palette although black & white still remained. The series of photo-pieces that emerge during this vibrant period display a heightened reality, moving away from the earlier naturalism. They also began photographing each other as gargoyles, producing large close-ups of their faces, lit from below, grimacing horribly.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – Mixed Media (1980),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
“… In a show as vast as the MONA survey, one sees the shit pictures as only a small chapter in their catalogue of would-be outrages. There are microscopic close-ups of their own sweat, blood, piss and sperm, presented as a form of decorative art. There are galleries of handsome young men, lined up like homoerotic altarpieces. There are works that excoriate religion – all forms of religion – and nationalism.
It would be an understatement to say these works sail close to the edge – they have plunged joyously over the precipice, beyond any conventions of good or bad taste. The “moral dimension” Gilbert & George seek is a systematic attempt to explode everything they see as false morality and hypocrisy. Homophobia is a constant target, as is racism and religious dogmatism. They are not the first to see organised religion as the root of all evil, but few artists or thinkers have been so consistently, so violently anti-religious.
The joke, of course, is that they look and act like conservative businessmen. Even their most confronting works are as bold and colourful as advertising billboards, or perhaps stained glass windows. They are iconoclastic non-entities making art that attracts and repels.
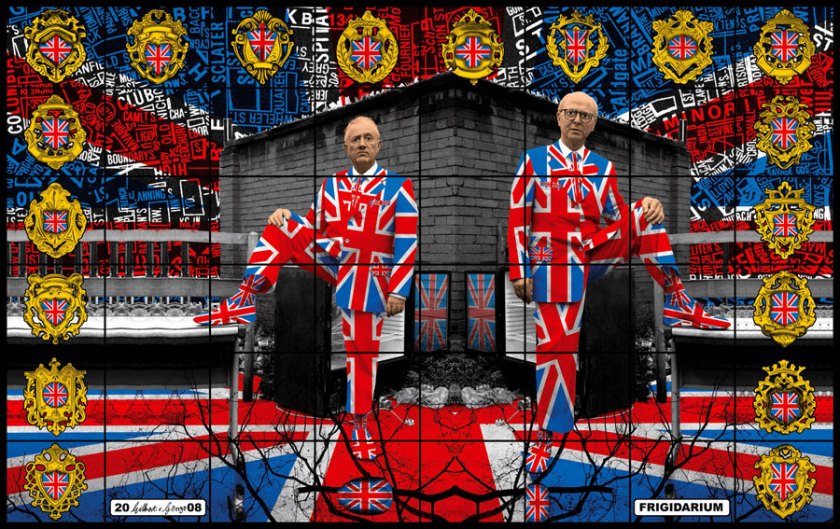
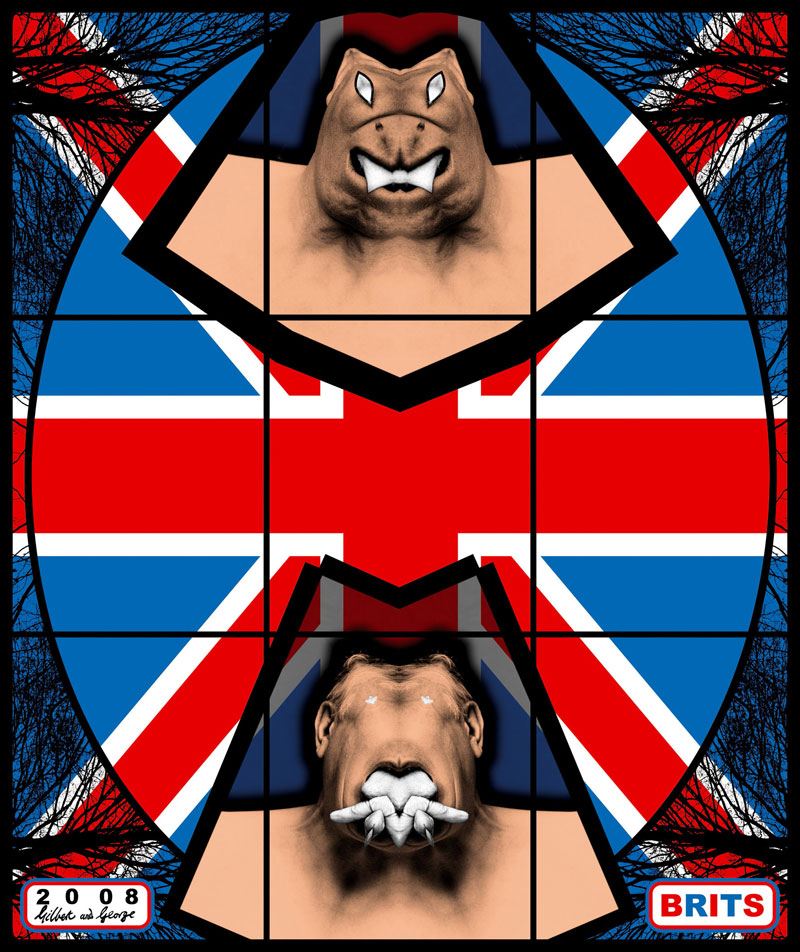
From behind a façade of consummate Englishness they set out to expose the grossness and depravity of the world around them. The Jack Freak Pictures (2008) use images of the Union Jack combined with grotesque morphings of their own figures that make them look like demons or mutants. The London Pictures (2011) use hundreds of daily newspaper banners, purloined from newsagents, to produce a chorus of sordidness and sensationalism.
We see two deadpan comedians enjoying the adolescent humour of exposing themselves to an audience, making wall-sized images of all those things not spoken of in ‘polite’ society. I could almost accept the idea of Gilbert & George as two overgrown children, intent on making mischief, but every so often they hit the mark with surprising force.”
John McDonald. “Gilbert & George,” on the John McDonald website December 4, 2015 [Online] Cited 11/03/2016.
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, MONEY (2011) from The London Pictures and, at right, Raack (2005) from Ginkgo Pictures
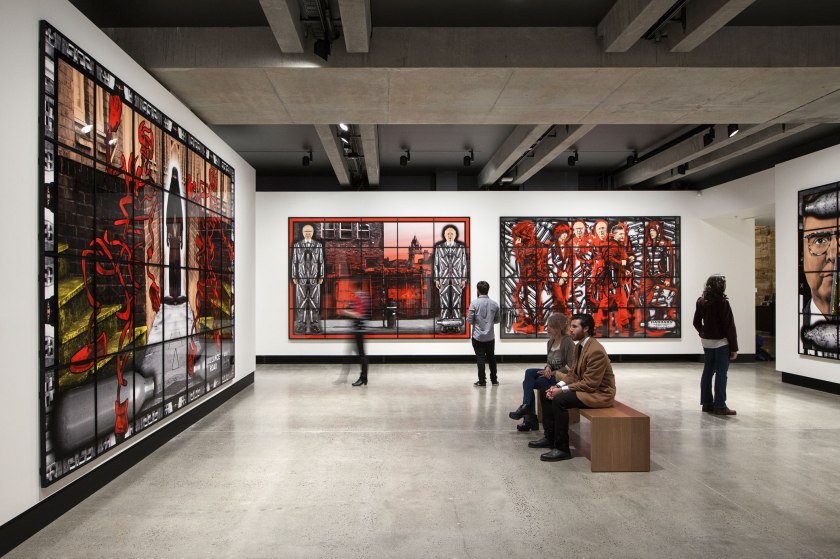
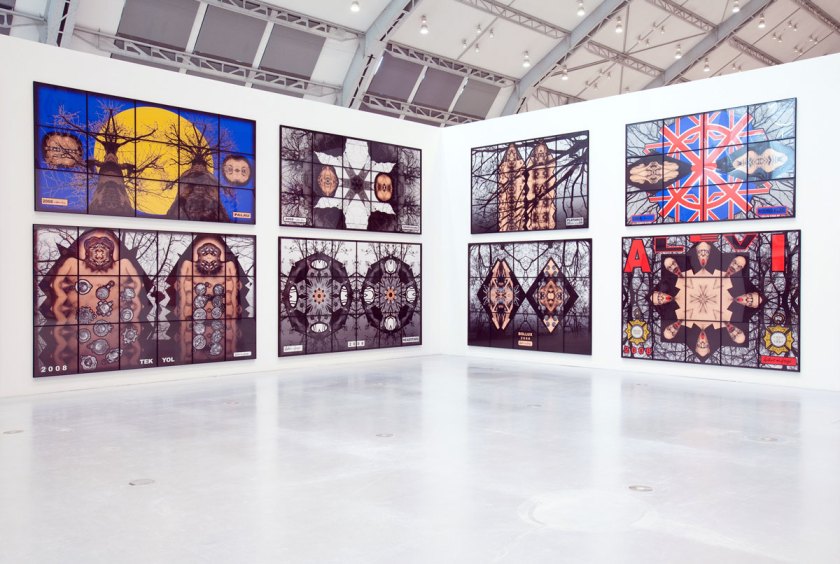
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, VALLANCE ROAD (2013); at centre left RIDLEY ROAD (2013) and at centre right HABDABS (2013) all from the series Scapegoating Pictures
There are 292 pieces in this series featuring whippets and hippy crack (laughing gas). The SCAPEGOATING PICTURES unflinchingly describe the volatile, tense, accelerated and mysterious reality of our increasingly technological, multi-faith and multi-cultural world. It is a world in which paranoia, fundamentalism, surveillance, religion, accusation and victimhood become moral shades of the city’s temper.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – Scapegoating Pictures for London (2013),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
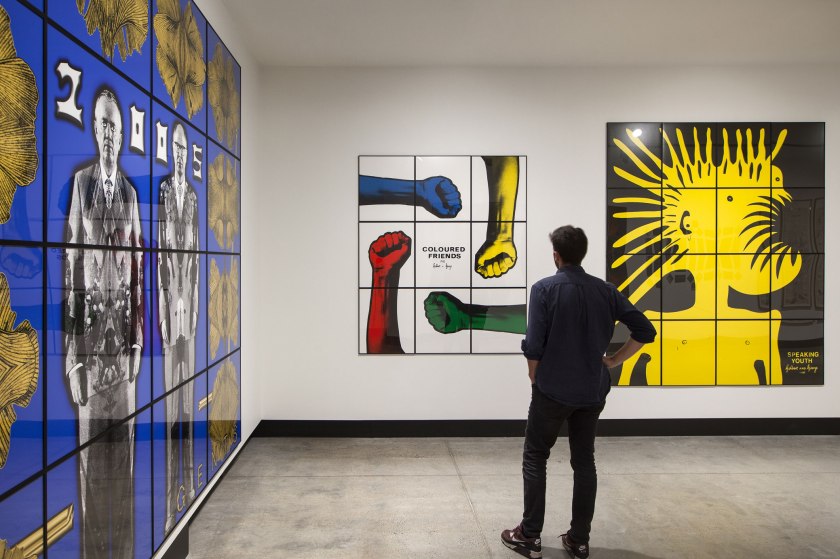
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, Citied Gents (2005) from Ginkgo Pictures; at left rear, COLOURED FRIENDS (1982); and at right rear SPEAKING YOUTH (1981)
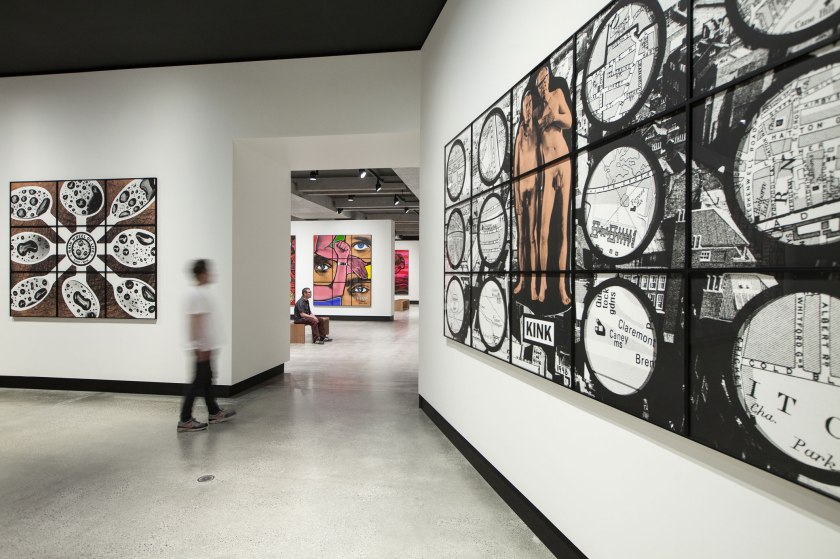
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, RAIN WHEEL OF LIFE (1998), and at right KINK (1998), both from The Rudimentary Pictures
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, TONGUES (1992) followed by IN THEIR ELEMENT (1998) from the series The Rudimentary Pictures followed by FIVE (1992); to the right TOFF’S OUT! (2014) followed by THEY SHOT THEM! (2014), both from the series Utopian Pictures
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
THEY SHOT THEM!
2014
Mixed media
254 x 453 cm
Courtesy of ARNDT and Gilbert & George
The 26 UTOPIAN PICTURES convey, like an energy storm, the frenetic forces of an endlessly embattled state: between the voices of authority and civic order. These pictures depict a modern world in which authority and the resentment of authority, rules and rebellion, advertising and public information, dogma and warning, boasts and threats co-exist in seemingly endless proclamations.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – Utopian Pictures (2014),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing from left to right, SHIT ON SPIT (1997) from The New Testamental Pictures, BLOOD ROADS (1998), BLOOD CITY (1998) and PISS GARDEN (1998) from The Rudimentary Pictures
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
BLOOD CITY
1988
Mixed media
151 x 127 cm
Courtesy of the artists
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, KINK (1998), and at rear, COLD STREET (1991)
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing from left to right, BLOODY LIFE No. 4 (1975), AKIMBO (2005) from Sonofagod Pictures, SHITTY WORLD (1994), DEAD HEAD (1989), and CHRISTS (1992) from The China Pictures
In the BLOODY LIFE pictures, from 1975, Gilbert & George strike poses with clenched fists and legs kicking. Even the introspective image of the artists in BLOODY LIFE NO.3 is embedded within a frame of alcohol and the boxing ring. The brutality of these pictures reflects their experience at the time. ‘We went through this big destructive period of the drunken scenery, exploring ourselves, exploring our dark side, going out, getting drunk, all those destructive elements’.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – Bloody Life (1975),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
The SONOFAGOD PICTURES consist of 20 paintings that possess a darkly graven strangeness, at once archaic and ultra-modern, in which their temper no less than their signage appears deeply contemporary, ritualistic and disturbed and have all of the dramatic visual impact which one might expect to find in neo-Gothic medievalism.
Christs shows a local youth imagining a butterfly Christ with Gilbert and George wings.
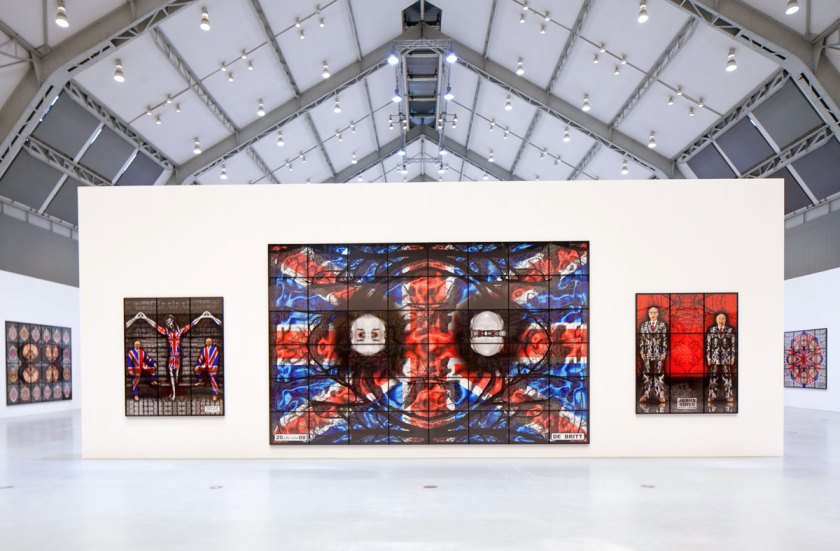
Installation view of the exhibition Gilbert & George: The Art Exhibition at the Museum of Old and New Art, Hobart showing at left, FORWARD (2008) and in the middle right, SCAPEGOATING (2013)
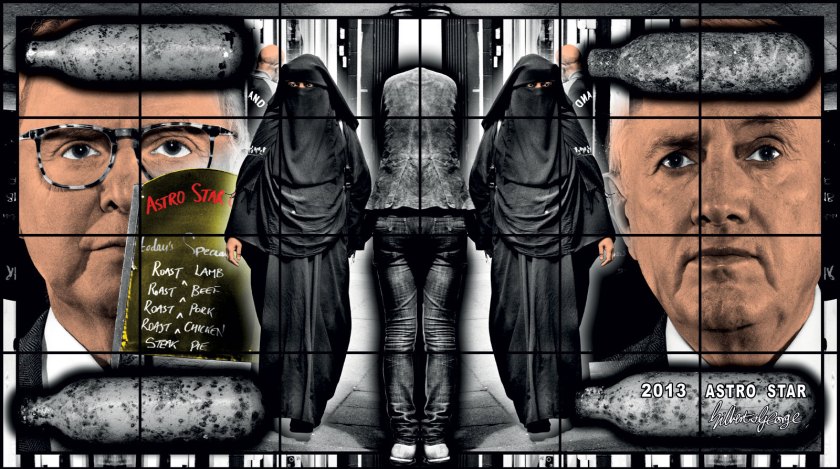
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
ASTRO STAR
2013
From Scapegoating Pictures
Picture courtesy of the artists and Mona, Museum of Old and New Art, Tasmania, Australia
There are 292 pieces in this series featuring whippets and hippy crack (laughing gas). The SCAPEGOATING PICTURES unflinchingly describe the volatile, tense, accelerated and mysterious reality of our increasingly technological, multi-faith and multi-cultural world. It is a world in which paranoia, fundamentalism, surveillance, religion, accusation and victimhood become moral shades of the city’s temper.
Barry Grayshon. “Gilbert and George – Scapegoating Pictures for London (2013),” on the Pinterest website [Online] Cited 16/03/2016
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
FIGHT BACK
2014
From the series Utopian Pictures
Mixed media
254 x 377cm
Courtesy of ARNDT and Gilbert & George
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
ONE WORLD
1988
Mixed media
226 x 254cm
Courtesy of the artists
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
ALL MY LIFE I GIVE YOU NOTHING AND STILL YOU ASK FOR MORE (Gilbert)
1970
Mixed media
Each 193 x 75cm
Private collection
Gilbert & George (Gilbert Prousch, British born Italy, 1943; George Passmore, British, b. 1942)
ALL MY LIFE I GIVE YOU NOTHING AND STILL YOU ASK FOR MORE (George)
1970
Mixed media
Each 193 x 75cm
Private collection
Museum of Old and New Art
655 Main Road Berriedale
Hobart Tasmania 7011, Australia
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 6pm























































![Egon Schiele (Austrian, 1890-1918) '“Prediger” (Selbstakt mit blaugrünem Hemd) ["Preacher" (Nude with teal shirt)]' 1913 Egon Schiele (Austrian, 1890-1918) '“Prediger” (Selbstakt mit blaugrünem Hemd) ["Preacher" (Nude with teal shirt)]' 1913](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/egon_schiele_prediger_selbstakt_mit_blaugruenem_hemd_1913-web.jpg?w=650&h=982)




![Pierre & Gilles (Pierre Commoy and Gilles Blanchard) 'Vive la France [Long live France]' 2006 Pierre & Gilles (Pierre Commoy and Gilles Blanchard) 'Vive la France [Long live France]' 2006](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/pierre_gilles_vive_la_france-2006-web.jpg?w=650&h=769)


























































You must be logged in to post a comment.