September 2018
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Jewel and Harold Walker, 6 and 5 years old, pick 20 to 25 pounds of cotton a day. Father said: “I promised em a little wagon if they’d pick steady, and now they have half a bagful in just a little while.”
Oct. 1916. Comanche County (Geronimo), Oklahoma
Gelatin silver print
Climbing into immortality
In this posting we have a small selection of digitally cleaned images from one of the most influential photographers of the 20th century, Lewis Hine.
Over roughly 30 years Hine, a trained sociologist, used his camera as an educational tool for social reform. He built an incredible body of work focusing mainly on photographs of the poor and underprivileged which captured the lives of immigrants, labourers and child workers in the early 1900’s. After an assignment photographing the building of the Empire State Building in 1930-1931 work dropped off.
“By the late 1930’s he was just about out of work. Roy Stryker, head of the Farm Security Administration, thought he was difficult and past his prime and would not hire him. Assignments were scarce. In Hine’s last couple of years he was so broke that he lost his house, stopped photographing and applied for welfare. He died as destitute as anyone who ever sat for his lens.”1
What a fate for one of the greatest photographers the world have ever known. To add insult to injury, “After his death, the Museum of Modern Art was offered his pictures but did not want them; George Eastman House in Rochester did.”1 More fool MoMa, for in Hine we have the quintessential social documentary modernist photographer, way ahead of his time, taking photographs of child labourers in the first decade of the 20th century. When you think that acknowledged pioneer of modernist photography, Alfred Stieglitz, was still taking Pictorialist photographs such as Excavating, New York (1911), The Ferry Boat (1910) and publishing The Terminal (1892) in Camera Work 36 in 1911… you begin to understand how revolutionary Hine’s stark, perfectly balanced, (sometimes flash) photographs really are, both in terms of their form and their function, that is, the advancement of social change.
In four words we might say: his work is faultless.
Hine’s work emerges out of the American romantic movement with its links to transcendentalism, literary realism and social reform, a movement which included the likes of essayist, lecturer, philosopher, and poet Ralph Waldo Emerson and poet and humanist Walt Whitman. “A core belief of transcendentalism is in the inherent goodness of people and nature, and the belief that society and its institutions have corrupted the purity of the individual, and they have faith that people are at their best when truly “self-reliant” and independent,”2 while “literary realism attempts to represent familiar things as they are. Realist authors chose to depict everyday and banal activities and experiences, instead of using a romanticised or similarly stylised presentation.”3
Hine pictures people and children just as they are, and believes in their innate goodness (as opposed to the hidden power of the body corporate, of industry and the machine). He incorporates both transcendentalism and realism in his works, in an attempt “to represent subject matter truthfully, without artificiality and avoiding artistic conventions…”3 Hine gets down to the subject level of his children. There is no looking down on these people, he gets down to their level, he photographs them as human beings at the level of their incarceration. Whether it be large groups of Breaker Boys or groups of four he photographs at their height, imbuing these portraits with pathos and poignancy. To look into Hine’s photographs is to see into the soul of these human beings, to feel their distress and hurt.
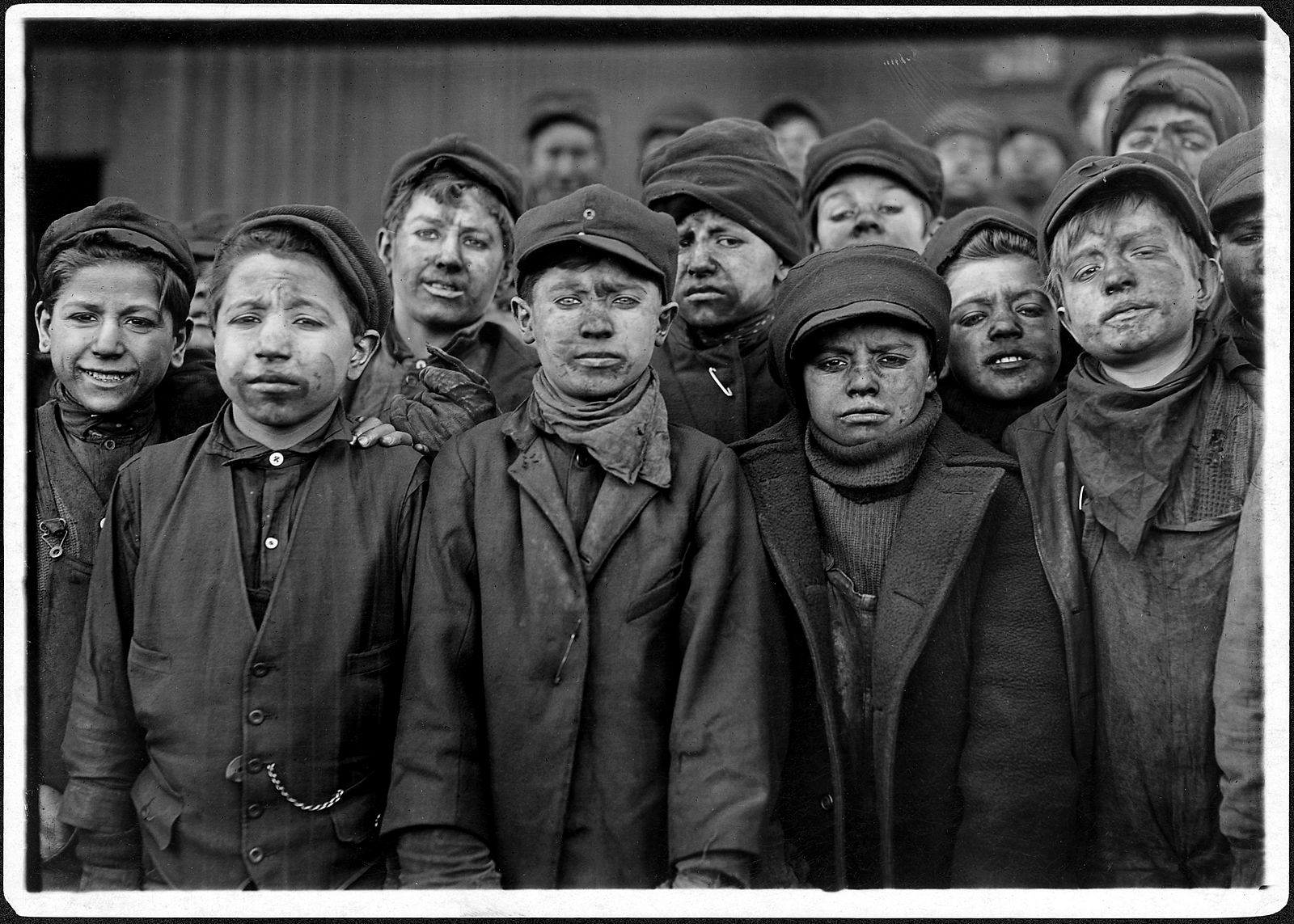
Covered in coal dust the boys rarely smile, and many die in industrial accidents or from Black lung. The image Breaker #9, Hughestown Borough Pa. Coal Co. One of these is James Leonard, another is Stanley Rasmus. Pittston, Pa. (below) subconsciously reminds me of that famous image by Henry Bowers of Scott and his party standing at the South Pole, the party knowing that Roald Amundsen had beaten them to the pole, and that now they had the long, arduous trip back to the Terra Nova pulling heavy sleds. There is a resignation on their faces of their lot, much as Hine’s children stare grimly into the camera knowing that after the photograph has been taken, it will be more of the same. Again and again…
But here in these photographs their spirit is also unbowed. It is almost as though Hine is picturing the relationship between the soul and the surrounding world. They live for eternity in these images which become, as Alexander Nemerov in “Soulmaker: The Times of Lewis Hine” on the Monovisions website (31 May 2016) observes, “A kind of capsule containing the full flow of all we will ever be, and have been. To most, that capsule is almost always invisible, but not to Lewis Hine.” He sees clearly the plight of his people and has left us with photographs which record that plight, photographs which are poignant and profound. They transcend the time in which they were taken and are as relevant today as when they were taken, for we are all still children.
When I think about what photographs represent the first decade of the 20th century, it is Hine’s photographs, amongst others, to which I turn. Personal, objective but sensitive and transcendent, they engage us on an emotional level, human being to human being. These are personal stories – “She had regrets about not getting the education she had desired. She only got as far as the sixth grade. At that point, she started working full time. But she wanted an education, and really valued it, and it was a priority for her that we got a good education – whatever it took to send us to college” – embedded amongst the vast corporations of industry and the might of the machine, the black maw of the industrial revolution. It has taken many years for Hine’s art to ascend to iconic status, a gradual climb into immortality that the destitute condition at the time of his death would have seemingly precluded.
I then think of what photographs represent the first decade of the 21st century and the main event is, of course, the photographs from 9/11. In a century, the personal stories have been subsumed by a universal, industrial ego – the numbers of the dead, the faceless numbers; the velocity of the planes and their thrusting trajectory; the monolithic, corporate, phallic towers with their hidden workers; the war of territory, consumption, oil, power and religion that consumes the world; and the instantaneous “nature” of the transmission of images around the world, where everybody is a photographer, everything is “shot” from as many angles as possible (hoping that one version is the truth? fake news…), where everything is a spectacle to be recorded. There is no slow burn of recognition of the power of individual images, no gradual climb into immortality of the work of artists such as Lewis Hine. You are either dead, or you’re not.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Word count: 1,121
1/ Vicki Goldberg. “The New Season/Photography Critic’s Choice; A Career That Moved From Man to Machine,” on The New York Times website Sept 13, 1998 [Online] Cited 10/09/2018
2/ Anonymous. “Transcendentalism,” on the Wikipedia website [Online] Cited 10/09/2018
3/ Anonymous. “Literary realism,” on the Wikipedia website [Oline] Cited 10/09/2018
Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
I Sit and Look Out
I SIT and look out upon all the sorrows of the world, and upon all oppression and shame;
I hear secret convulsive sobs from young men at anguish with themselves, remorseful after deeds done;
I see in low life the mother misused by her children, dying, neglected, gaunt, desperate;
I see the wife misused by her husband – I see the treacherous seducer of young women;
I mark the ranklings of jealousy and unrequited love attempted to be hid – I see these sights on the earth;
I see the workings of battle, pestilence, tyranny – I see martyrs and prisoners;
I observe a famine at sea – I observe the sailors casting lots who shall be kill’d to preserve the lives of the rest;
I observe the slights and degradations cast by arrogant persons upon laborers, the poor, and upon negroes, and the like;
All these – all the meanness and agony without end I sitting look out upon,
See, hear, and am silent.
Walt Whitman. “I Sit and Look Out,” from Leaves of Grass 1892
“What is so amazing about photographs like this one is the particular poignancy of the moment… Two people are encountering one another in this happenstance way, yet the moment is deeply meaningful in how he manages to imagine a subject’s soul. The moment becomes almost metaphysical. A kind of capsule containing the full flow of all we will ever be, and have been. To most, that capsule is almost always invisible, but not to Lewis Hine.”
Alexander Nemerov quoted in “Soulmaker: The Times of Lewis Hine” on the Monovisions website 31 May 2016 [Online] Cited 21/02/2022
In the 1930s Hine took on small freelance projects but worried his images had fallen out of fashion. His reputation for difficulty, too, scared off potential employers. One former boss praised his talent but noted he was a “true artist type” who “requires some ‘waiting upon’.” Hine applied multiple times for a Farm Security Administration project documenting the impact of the Great Depression, but the head of the project felt he was too uncompromising. When Hine died in 1940, he was destitute and his home was in foreclosure. The photographer who had made a career of capturing the devastation and majesty of American labor couldn’t find work.
Extract from Susie Allen. “Bodies of work: Lewis Hine, EX 1904, captured the changing face of American labor,” in The University of Chicago Magazine – Spring/17 [Online] Cited 21/02/2022
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Noon hour in the Ewen Breaker, Pennsylvania Coal Co., South Pittston, Pennsylvania
January 1911
Gelatin silver print
Library of Congress
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
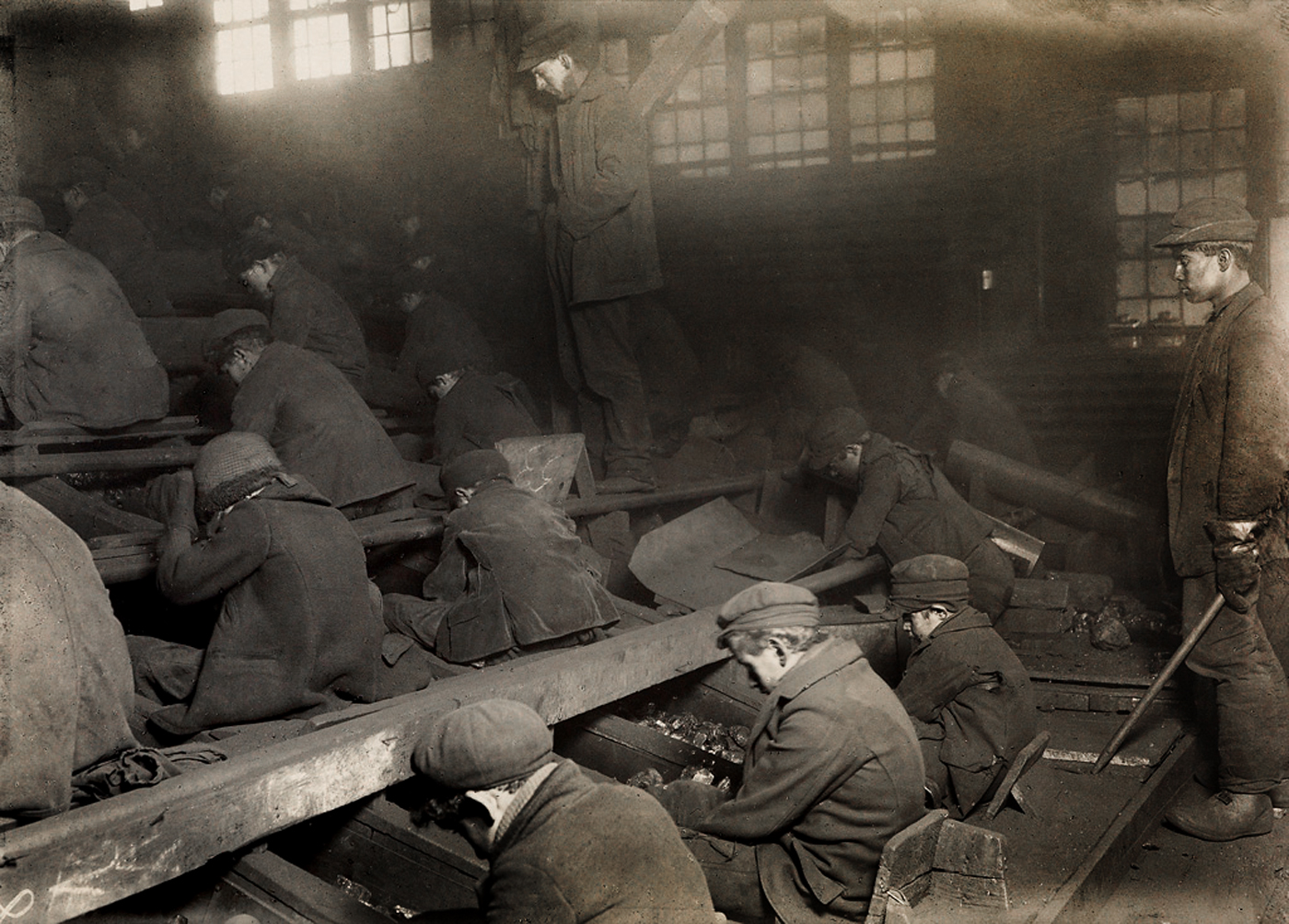
View of the Ewen Breaker of the Pa. Coal Co. The dust was so dense at times as to obscure the view. This dust penetrated the utmost recesses of the boy’s lungs. A kind of slave-driver sometimes stands over the boys, prodding or kicking them into obedience. S. Pittston, Pa.
10 January 1911
Gelatin silver print
U.S. National Archives
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
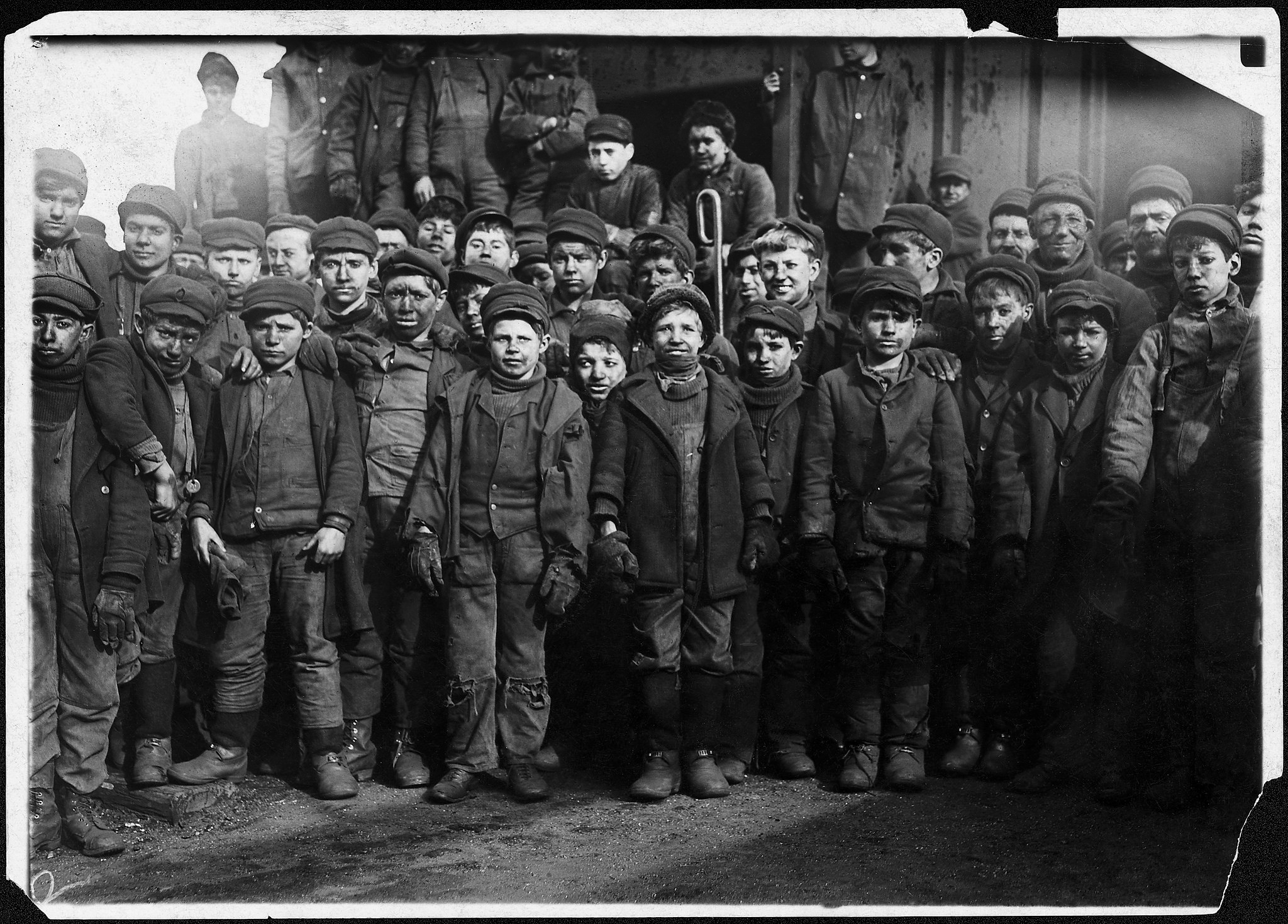
Group of Breaker Boys in #9 Breaker, Hughestown Borough, Pennsylvania Coal Co. Smallest boy is Angelo Ross, Pittston, Pennsylvania
January 1911
Gelatin silver print
Library of Congress
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Breaker boys working in Ewen Breaker. S. Pittston, Pa.
January 1911
Gelatin silver print
U.S. National Archives
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Breaker boys working in Ewen Breaker. S. Pittston, Pa.
January 1911
Gelatin silver print
U.S. National Archives
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Breaker #9, Hughestown Borough Pa. Coal Co. One of these is James Leonard, another is Stanley Rasmus. Pittston, Pa.
16 January 1911
Gelatin silver print
U.S. National Archives
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
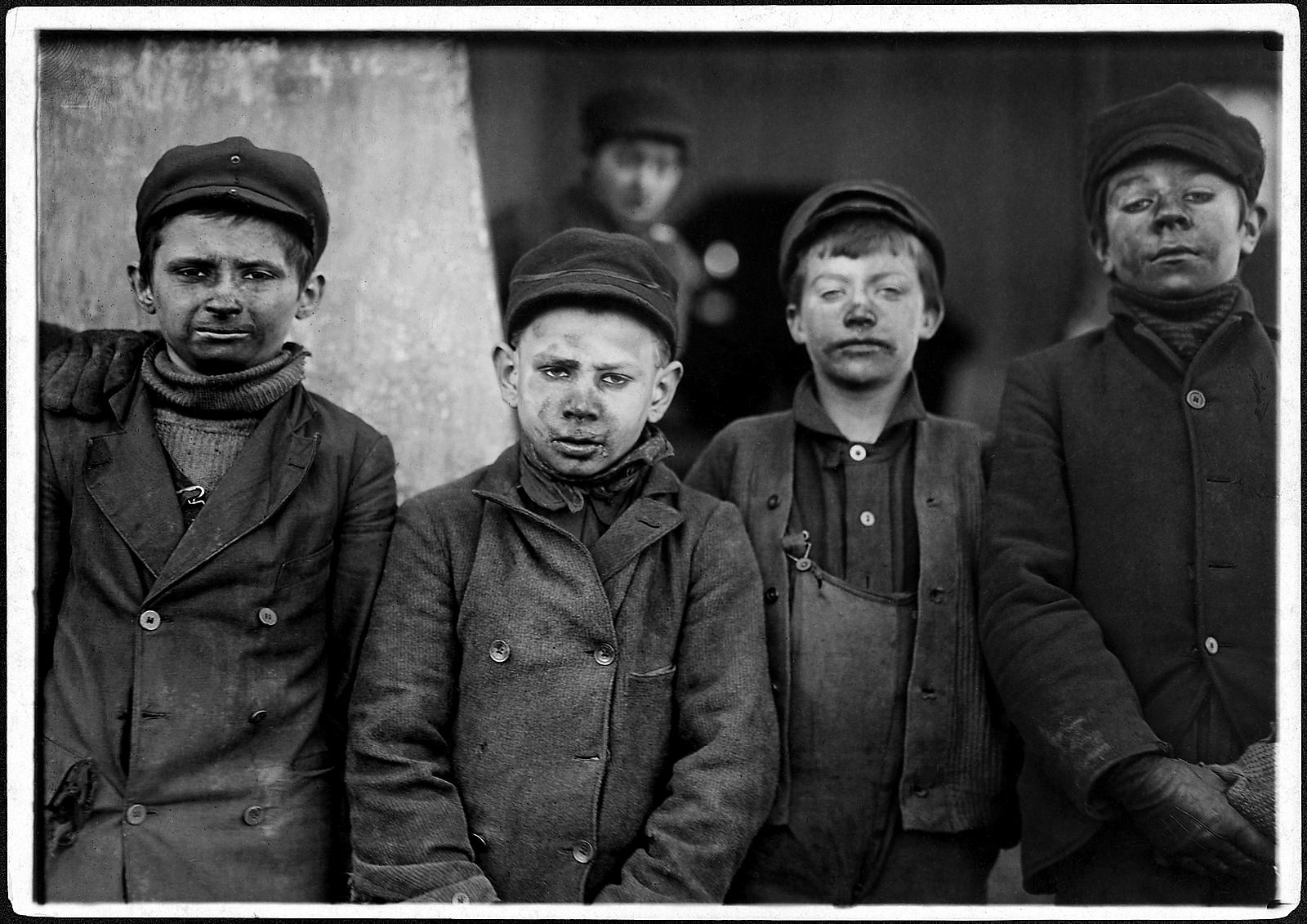
Breaker boys. Smallest is Angelo Ross. Hughestown Borough Coal Co. Pittston, Pa.
16 January 1911
Gelatin silver print
U.S. National Archives
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Group of breaker boys. Smallest is Sam Belloma. Pittston, Pa.
16 January 1911
Gelatin silver print
U.S. National Archives
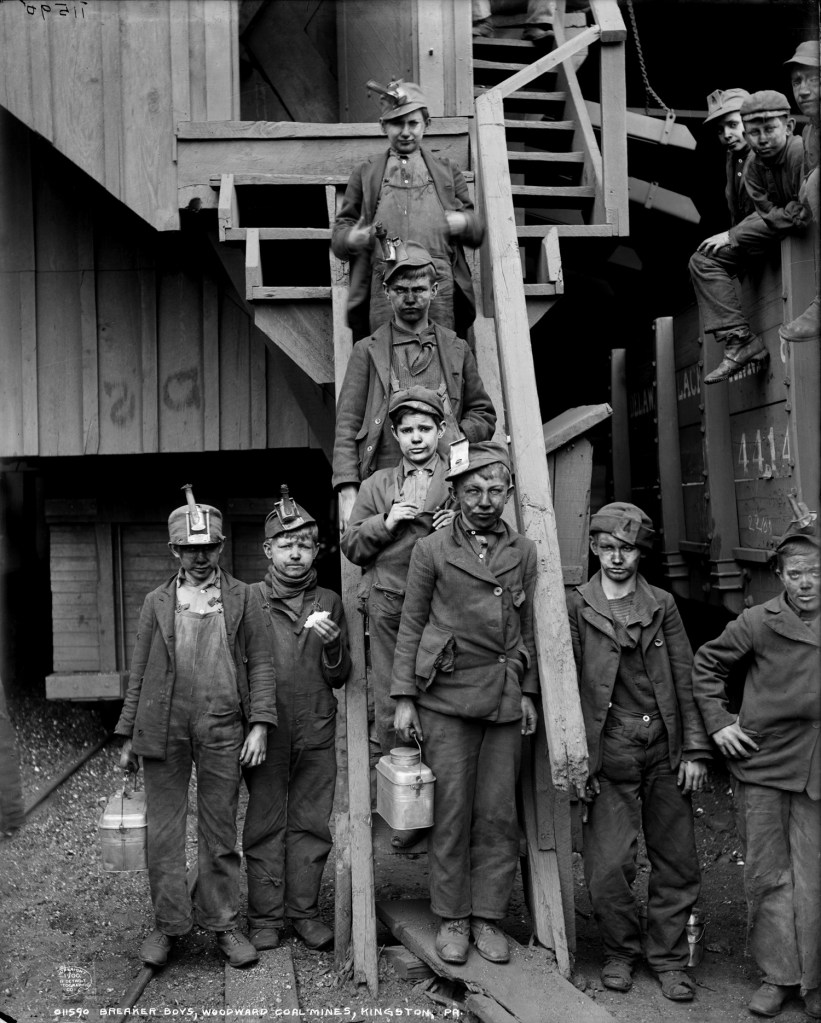

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Breaker boys of the Woodward Coal Mines, Kingston, Pa.
c. 1911
Gelatin silver print
Breaker boy
A breaker boy was a coal-mining worker in the United States and United Kingdom whose job was to separate impurities from coal by hand in a coal breaker. Although breaker boys were primarily children, elderly coal miners who could no longer work in the mines because of age, disease, or accident were also sometimes employed as breaker boys. The use of breaker boys began in the mid-1860s. Although public disapproval of the employment of children as breaker boys existed by the mid-1880s, the practice did not end until the 1920s. …
Use of breaker boys
Until about 1900, nearly all coal breaking facilities in the United States were labour-intensive. The removal of impurities was done by hand, usually by breaker boys between the ages of eight and 12 years old. The use of breaker boys began around 1866. For 10 hours a day, six days a week, breaker boys would sit on wooden seats, perched over the chutes and conveyor belts, picking slate and other impurities out of the coal. Breaker boys working on top of chutes or conveyor belts would stop the coal by pushing their boots into the stream of fuel flowing beneath them, briefly pick out the impurities, and then let the coal pass on to the next breaker boy for further processing. Others would divert coal into a horizontal chute at which they sat, then pick the coal clean before allowing the fuel to flow into “clean” coal bins.
The work performed by breaker boys was hazardous. Breaker boys were forced to work without gloves so that they could better handle the slick coal. The slate, however, was sharp, and breaker boys would often leave work with their fingers cut and bleeding. Breaker boys sometimes also had their fingers amputated by the rapidly moving conveyor belts. Others lost feet, hands, arms, and legs as they moved among the machinery and became caught under conveyor belts or in gears. Many were crushed to death, their bodies retrieved from the gears of the machinery by supervisors only at the end of the working day. Others were caught in the rush of coal, and crushed to death or smothered. Dry coal would kick up so much dust that breaker boys sometimes wore lamps on their heads to see, and asthma and black lung disease were common. Coal was often washed to remove impurities, which created sulfuric acid. The acid burned the hands of the breaker boys.
Public condemnation
Public condemnation of the use of breaker boys was so widespread that in 1885 Pennsylvania enacted a law forbidding the employment of anyone under the age of 12 from working in a coal breaker, but the law was poorly enforced; many employers forged proof-of-age documentation, and many families forged birth certificates or other documents so their children could support the family. Estimates of the number of breaker boys at work in the anthracite coal fields of Pennsylvania vary widely, and official statistics are generally considered by historians to undercount the numbers significantly. One estimate had 20,000 breaker boys working in the state in 1880, 18,000 working in 1900, 13,133 working in 1902, and 24,000 working in 1907. Technological innovations in the 1890s and 1900s (such as mechanical and water separators designed to remove impurities from coal) dramatically lowered the need for breaker boys, but adoption of the new technology was slow.
By the 1910s, the use of breaker boys was dropping because of improvements in technology, stricter child labor laws, and the enactment of compulsory education laws. The practice of employing children in coal breakers largely ended by 1920 because of the efforts of the National Child Labor Committee, sociologist and photographer Lewis Hine, and the National Consumers League, all of whom educated the public about the practice and succeeded in obtaining passage of national child labor laws.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Black lung (Coalworker’s pneumoconiosis)
Coal workers’ pneumoconiosis (CWP), also known as black lung disease or black lung, is caused by long-term exposure to coal dust. It is common in coal miners and others who work with coal. It is similar to both silicosis from inhaling silica dust and to the long-term effects of tobacco smoking. Inhaled coal dust progressively builds up in the lungs and cannot be removed by the body; this leads to inflammation, fibrosis, and in worse cases, necrosis.
Coal workers’ pneumoconiosis, severe state, develops after the initial, milder form of the disease known as anthracosis (anthrac – coal, carbon). This is often asymptomatic and is found to at least some extent in all urban dwellers due to air pollution. Prolonged exposure to large amounts of coal dust can result in more serious forms of the disease, simple coal workers’ pneumoconiosis and complicated coal workers’ pneumoconiosis (or progressive massive fibrosis, or PMF). More commonly, workers exposed to coal dust develop industrial bronchitis, clinically defined as chronic bronchitis (i.e. productive cough for 3 months per year for at least 2 years) associated with workplace dust exposure. The incidence of industrial bronchitis varies with age, job, exposure, and smoking. In nonsmokers (who are less prone to develop bronchitis than smokers), studies of coal miners have shown a 16% to 17% incidence of industrial bronchitis. …
History
Black lung is actually a set of conditions and until the 1950s its dangers were not well understood. The prevailing view was that silicosis was very serious but it was solely caused by silica and not coal dust. The miners’ union, the United Mine Workers of America, realised that rapid mechanisation meant drills that produced much more dust, but under John L. Lewis they decided not to raise the black lung issue because it might impede the mechanisation that was producing higher productivity and higher wages. Union priorities were to maintain the viability of the long-fought-for welfare and retirement fund, which would be sustained by higher outputs of coal. After the death of Lewis, the union dropped its opposition to calling black lung a disease and realised the financial advantages of a fund for its disabled members.
Epidemiology
In 2013 CWP resulted in 25,000 deaths down from 29,000 deaths in 1990. Between 1970-1974, prevalence of CWP among US coal miners who had worked over 25 years was 32%; the same group saw a prevalence of 9% in 2005-2006. In Australia, CWP was considered to be eliminated in the 1970s due to strict hazard control measures. However, there has been a resurgence of CWP in Australia, with the first new cases being detected in May 2015.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Sadie Pfeifer, 48 inches high, has worked half a year. One of the many small children at work in Lancaster Cotton Mills
November 1908. Lancaster, South Carolina
Gelatin silver print
Library of Congress
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
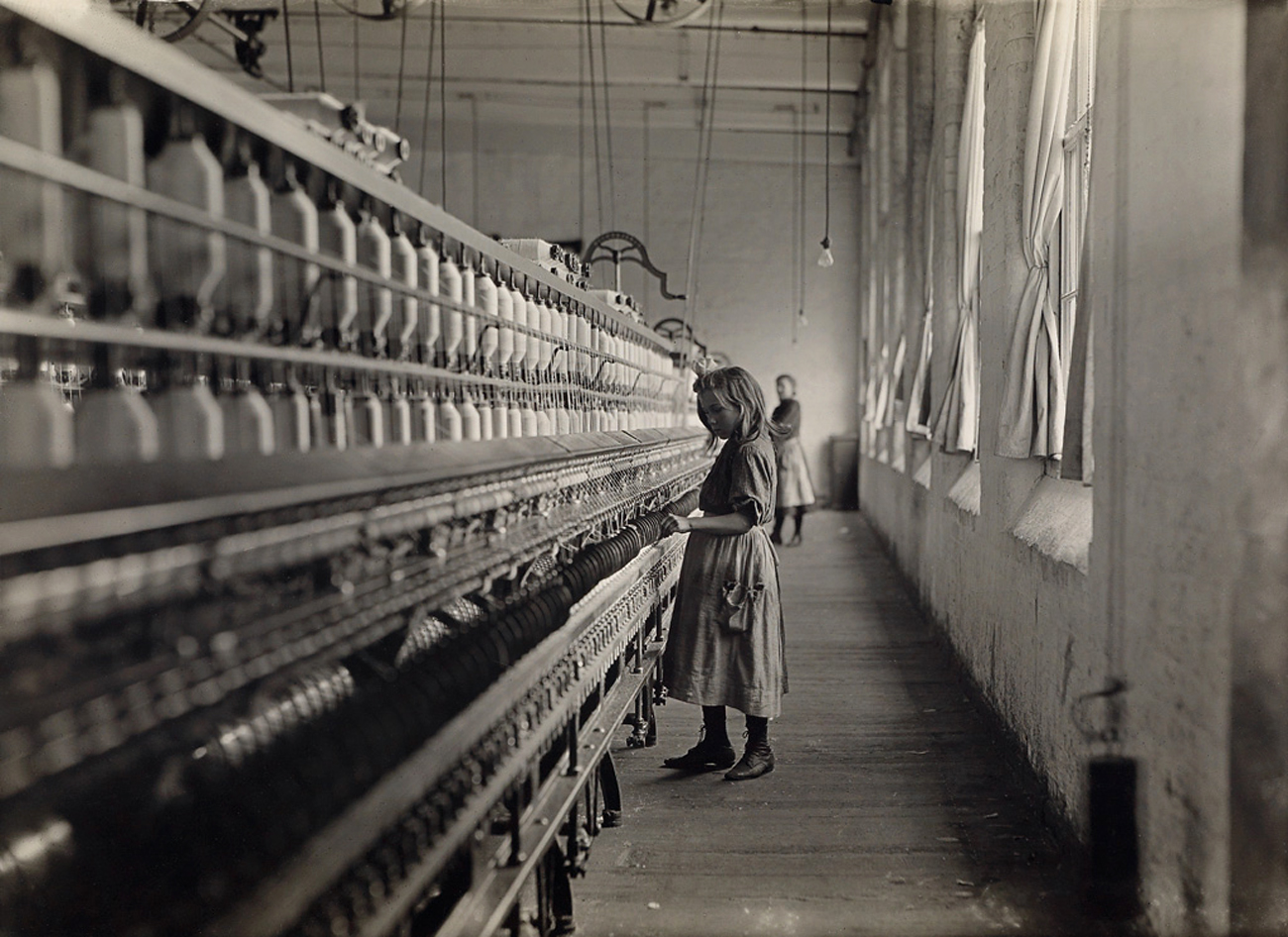
Cora Lee Griffin, spinner in cotton mill, 12 years old, Whitnel, North Carolina
1908
Gelatin silver print
“One of the spinners in Whitnel Cotton Mfg. Co. N.C. She was 51 inches high. Had been in mill 1 year. Some at night. Runs 4 sides, 48 cents a day. When asked how old, she hesitated, then said “I don’t remember.” Then confidentially, “I’m not old enough to work, but I do just the same.” Out of 50 employees, ten children about her size.” ~ Hine’s original caption
“She had regrets about not getting the education she had desired. She only got as far as the sixth grade. At that point, she started working full time. But she wanted an education, and really valued it, and it was a priority for her that we got a good education – whatever it took to send us to college.” ~ Daughter of Cora Lee Griffin
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
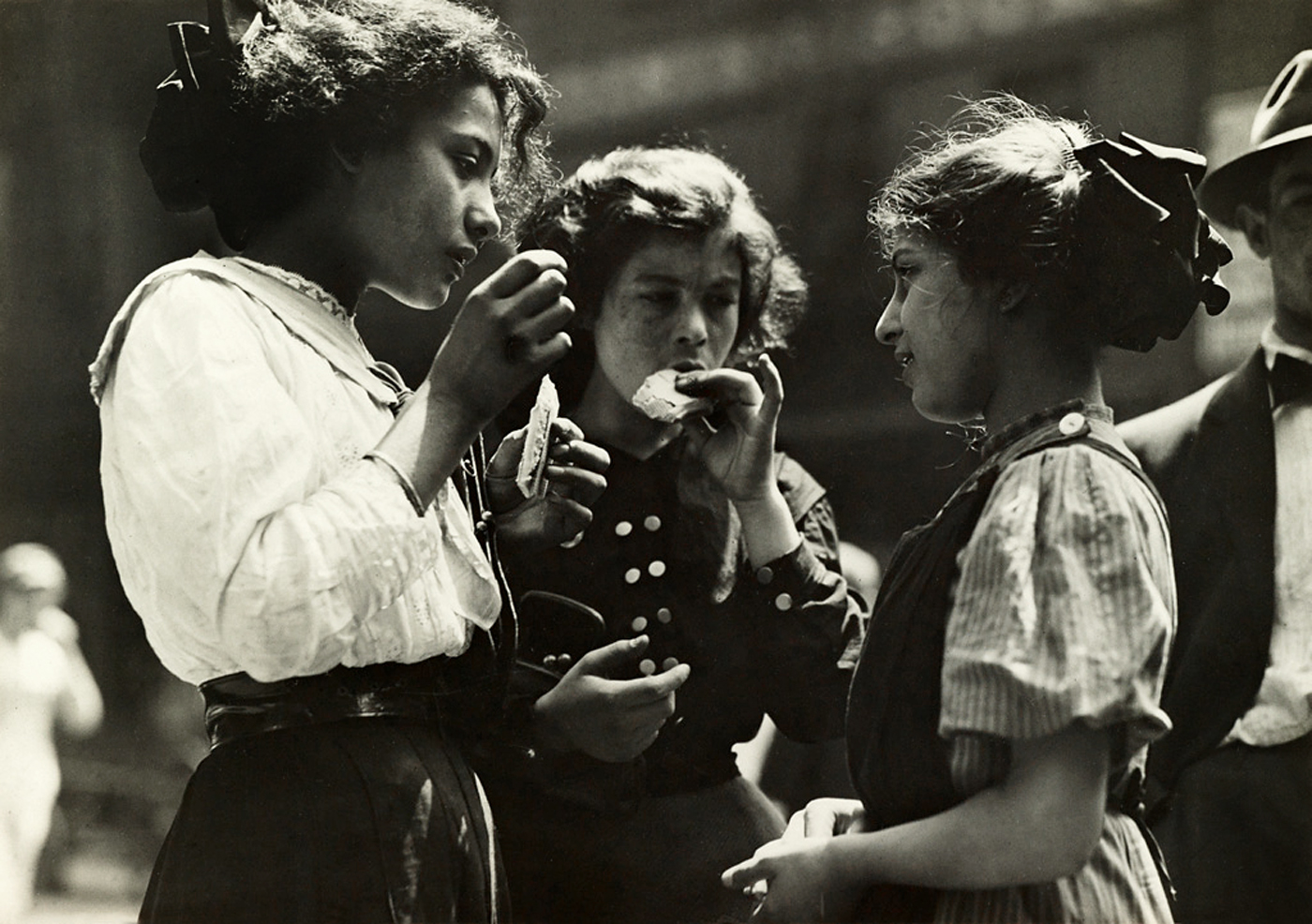
Noon hour in East Side factory district
1912
Gelatin silver print
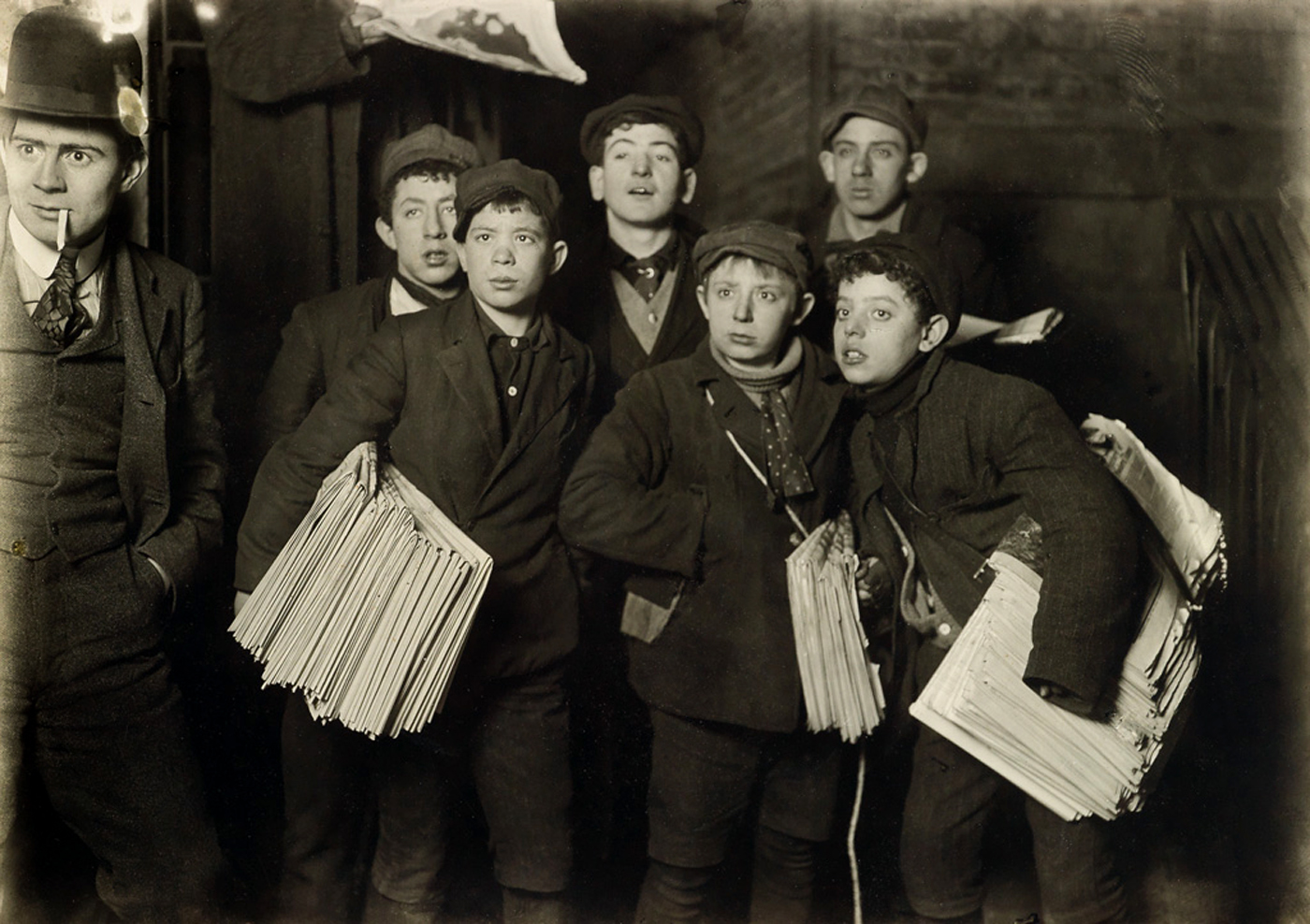
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Newsies, New York
1906
Gelatin silver print
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Nashville
1912
Gelatin silver print
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Tenement family, Chicago
1910
Gelatin silver print
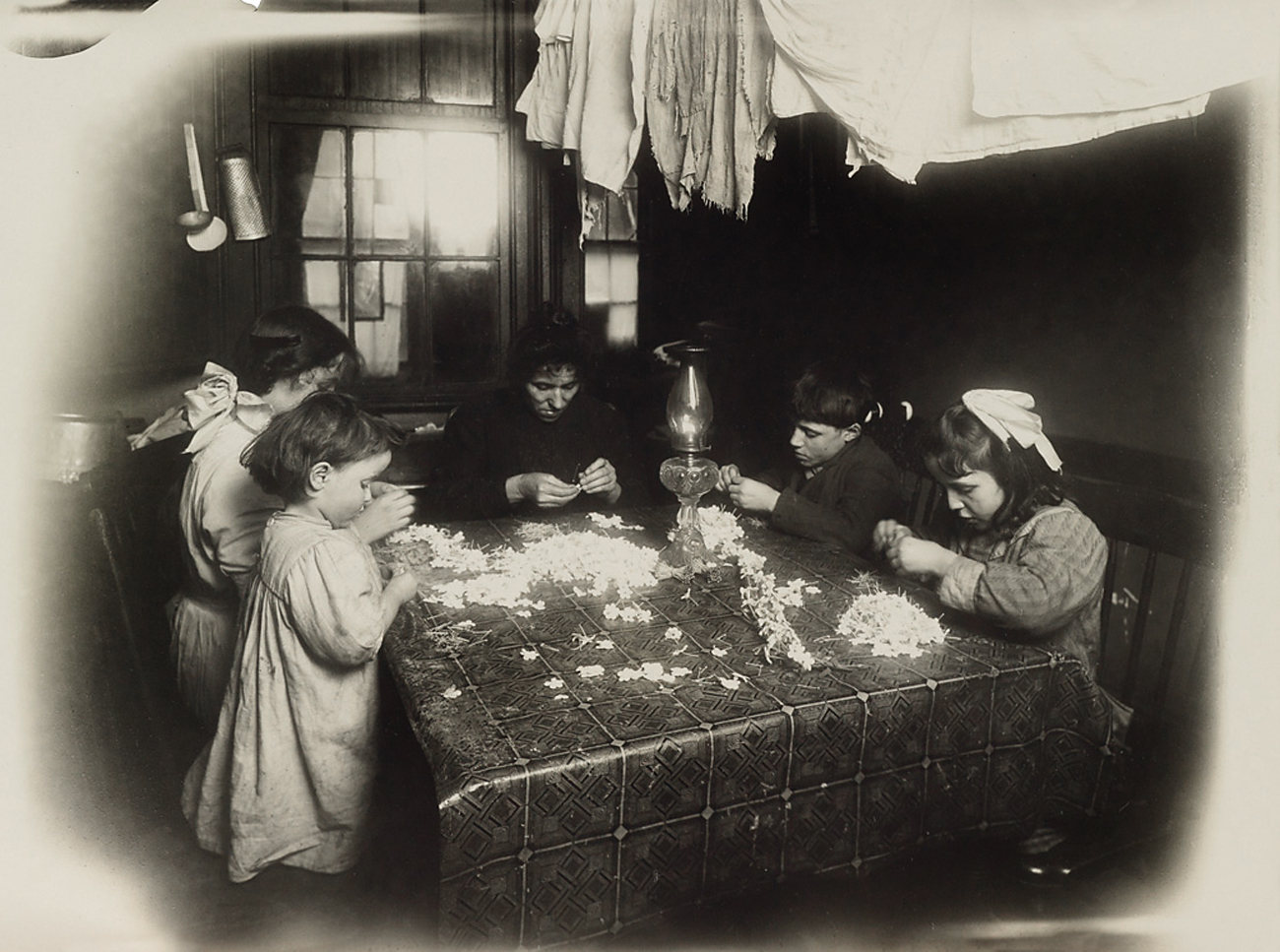
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Artificial flowers, New York City
1912
Gelatin silver print
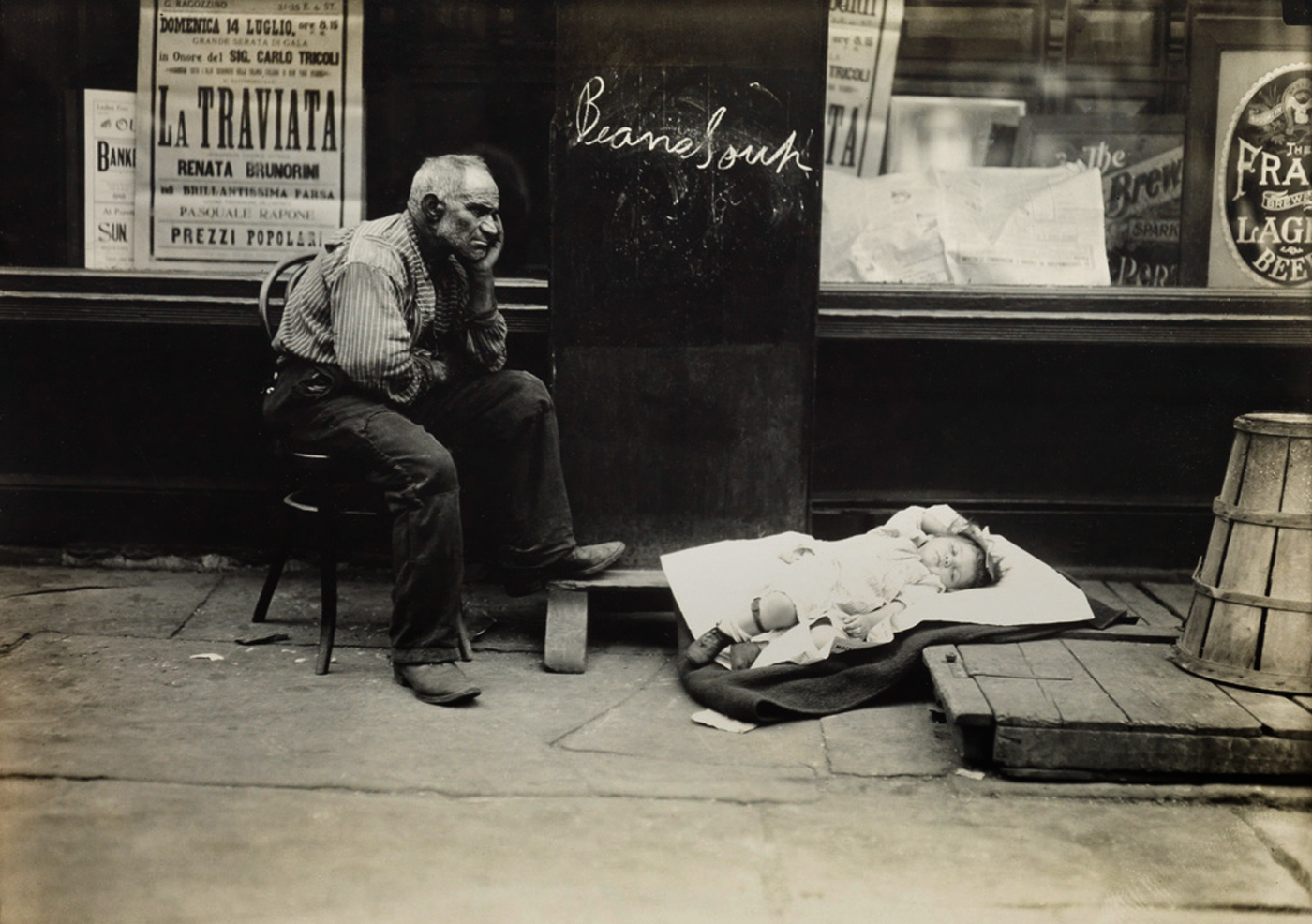
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Hot day on East Side, New York
c. 1908
Gelatin silver print
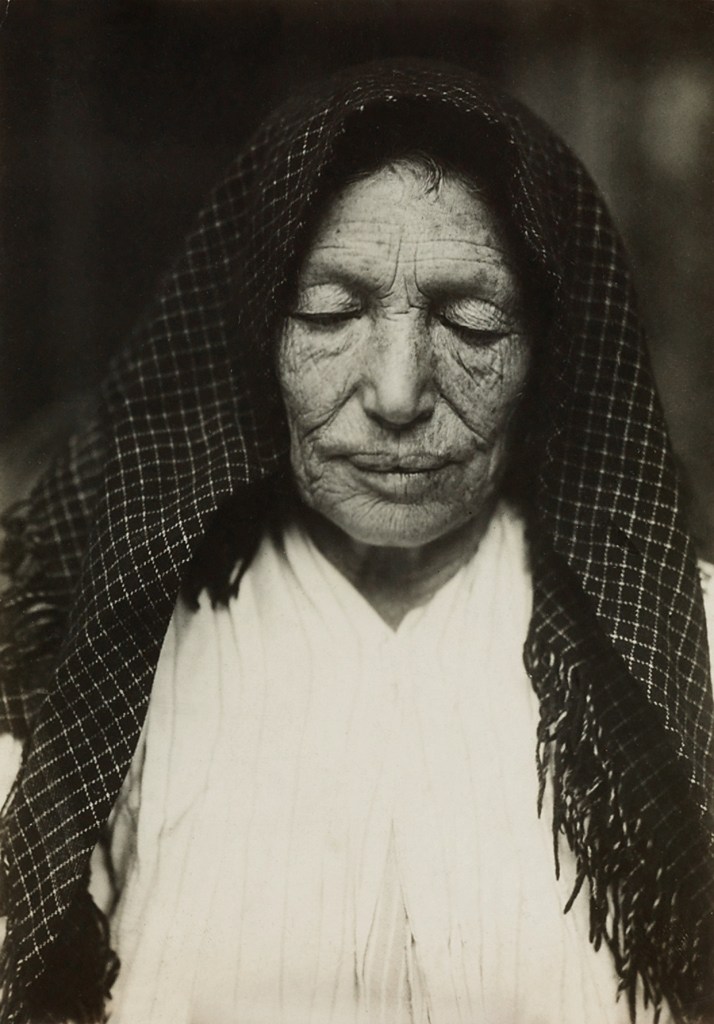

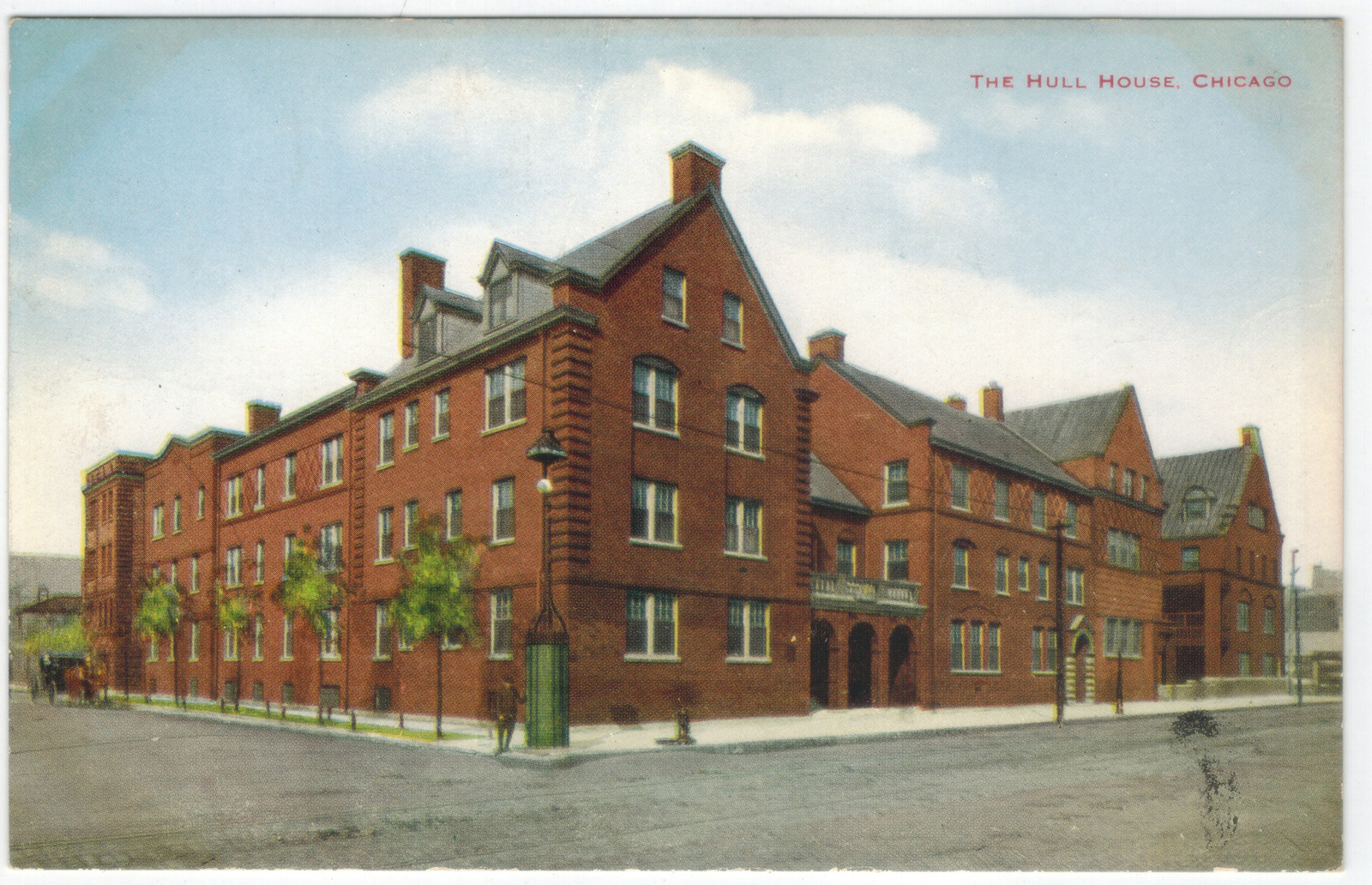
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Hull house beneficiary
1910
Gelatin silver print
Hull House was a settlement house in the United States that was co-founded in 1889 by Jane Addams and Ellen Gates Starr. Located on the Near West Side of Chicago, Illinois, Hull House (named after the original house’s first owner Charles Jerald Hull) opened to recently arrived European immigrants. By 1911, Hull House had grown to 13 buildings. In 1912 the Hull House complex was completed with the addition of a summer camp, the Bowen Country Club. With its innovative social, educational, and artistic programs, Hull House became the standard bearer for the movement that had grown, by 1920, to almost 500 settlement houses nationally…
Most of the Hull House buildings were demolished for the construction of the University of Illinois-Circle Campus in the mid-1960s. The Hull mansion and several subsequent acquisitions were continuously renovated to accommodate the changing demands of the association. The original building and one additional building (which has been moved 200 yards (182.9 m)) survive today.
Text from the Wikipedia website
V.O. Hammon Publishing Co. (publisher)
The Hull House, Chicago
Early 20th century
Postcard
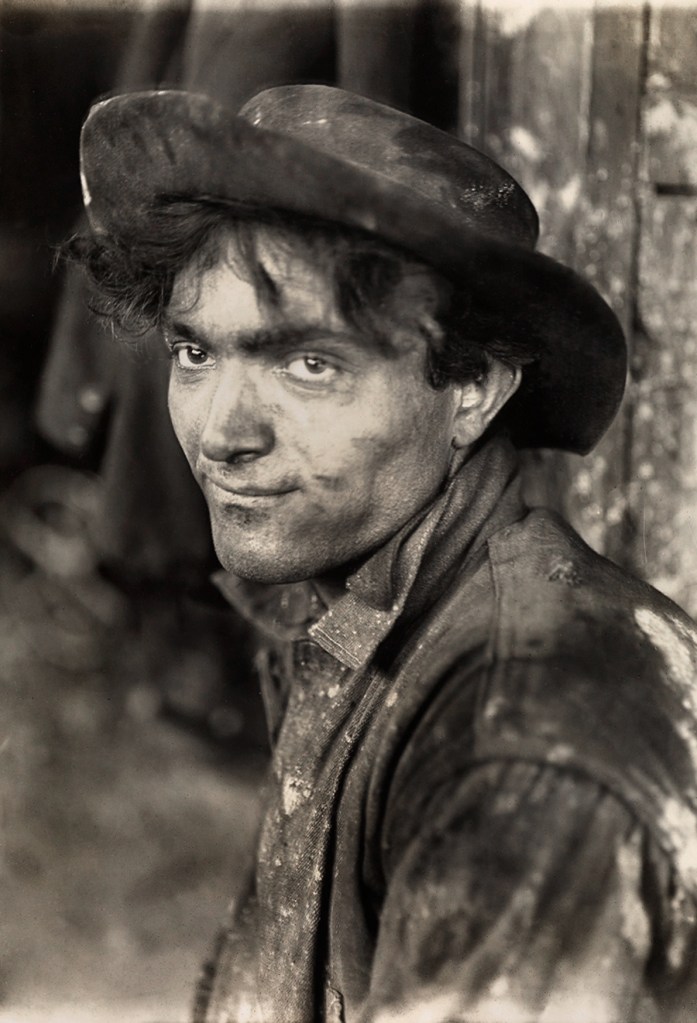

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Italian steel-worker
1909
Gelatin silver print
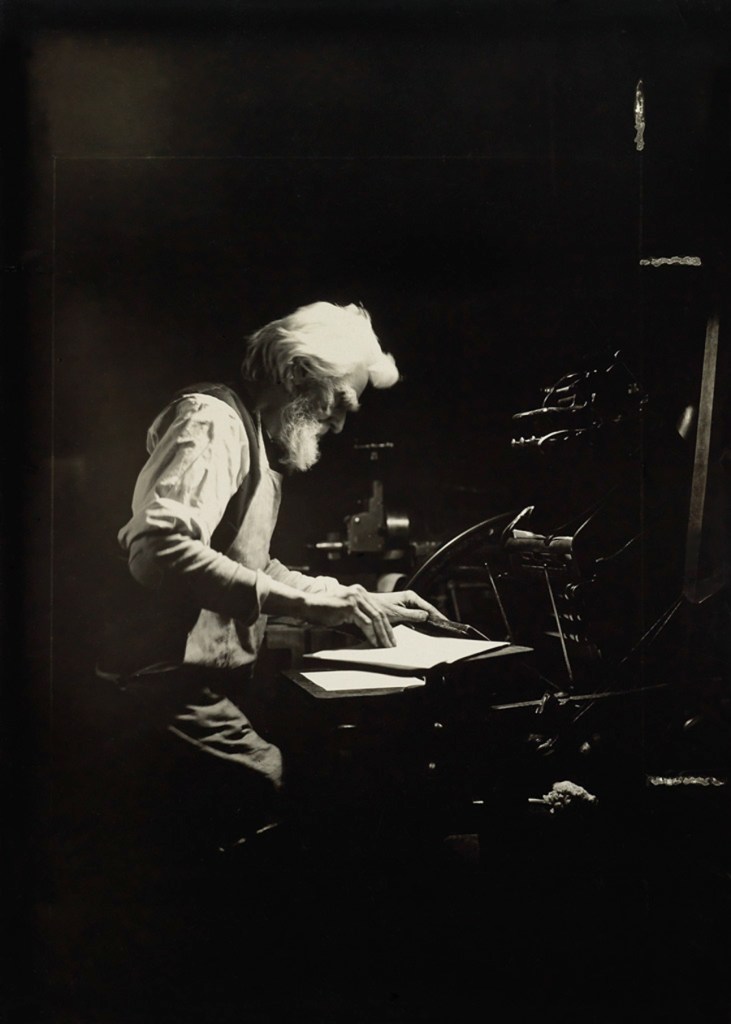

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Printer Ethical Culture School
1905
Gelatin silver print
Ellis Island
Ellis Island, in Upper New York Bay, was the gateway for over 12 million immigrants to the U.S. as the United States’ busiest immigrant inspection station for over 60 years from 1892 until 1954. Ellis Island was opened January 1, 1892. The island was greatly expanded with land reclamation between 1892 and 1934. Before that, the much smaller original island was the site of Fort Gibson and later a naval magazine. The island was made part of the Statue of Liberty National Monument in 1965 and has hosted a museum of immigration since 1990.
Immigrant inspection station
In the 35 years before Ellis Island opened, more than eight million immigrants arriving in New York City had been processed by officials at Castle Garden Immigration Depot in Lower Manhattan, just across the bay. The federal government assumed control of immigration on April 18, 1890, and Congress appropriated $75,000 to construct America’s first federal immigration station on Ellis Island. Artesian wells were dug, and fill material was hauled in from incoming ships’ ballast and from construction of New York City’s subway tunnels, which doubled the size of Ellis Island to over six acres. While the building was under construction, the Barge Office nearby at the Battery was used for immigrant processing…
The present main structure was designed in French Renaissance Revival style and built of red brick with limestone trim. After it opened on December 17, 1900, the facilities proved barely able to handle the flood of immigrants that arrived in the years before World War I. In 1913, writer Louis Adamic came to America from Slovenia, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and described the night he and many other immigrants slept on bunk beds in a huge hall. Lacking a warm blanket, the young man “shivered, sleepless, all night, listening to snores” and dreams “in perhaps a dozen different languages”. The facility was so large that the dining room could seat 1,000 people. It is reported the island’s first immigrant to be processed through was a teenager named Annie Moore from County Cork in Ireland.
After its opening, Ellis Island was again expanded, and additional structures were built. By the time it closed on November 12, 1954, 12 million immigrants had been processed by the U.S. Bureau of Immigration. It is estimated that 10.5 million immigrants departed for points across the United States from the Central Railroad of New Jersey Terminal, just across a narrow strait. Others would have used one of the other terminals along the North River (Hudson River) at that time. At first, the majority of immigrants arriving through the station were Northern and Western Europeans (Germany, France, Switzerland, Belgium, The Netherlands, Great Britain, and the Scandinavian countries). Eventually, these groups of peoples slowed in the rates that they were coming in, and immigrants came in from Southern and Eastern Europe, including Jews. Many reasons these immigrants came to the United States included escaping political and economic oppression, as well as persecution, destitution, and violence. Other groups of peoples being processed through the station were Poles, Hungarians, Czechs, Serbs, Slovaks, Greeks, Syrians, Turks, and Armenians.
Primary inspection
Between 1905 and 1914, an average of one million immigrants per year arrived in the United States. Immigration officials reviewed about 5,000 immigrants per day during peak times at Ellis Island. Two-thirds of those individuals emigrated from eastern, southern and central Europe. The peak year for immigration at Ellis Island was 1907, with 1,004,756 immigrants processed. The all-time daily high occurred on April 17, 1907, when 11,747 immigrants arrived. After the Immigration Act of 1924 was passed, which greatly restricted immigration and allowed processing at overseas embassies, the only immigrants to pass through the station were those who had problems with their immigration paperwork, displaced persons, and war refugees. Today, over 100 million Americans – about one-third to 40% of the population of the United States – can trace their ancestry to immigrants who arrived in America at Ellis Island before dispersing to points all over the country.
Generally, those immigrants who were approved spent from two to five hours at Ellis Island. Arrivals were asked 29 questions including name, occupation, and the amount of money carried. It was important to the American government the new arrivals could support themselves and have money to get started. The average the government wanted the immigrants to have was between 18 and 25 dollars ($600 in 2015 adjusted for inflation). Those with visible health problems or diseases were sent home or held in the island’s hospital facilities for long periods of time. More than 3,000 would-be immigrants died on Ellis Island while being held in the hospital facilities. Some unskilled workers were rejected because they were considered “likely to become a public charge.” About 2% were denied admission to the U.S. and sent back to their countries of origin for reasons such as having a chronic contagious disease, criminal background, or insanity. Ellis Island was sometimes known as “The Island of Tears” or “Heartbreak Island” because of those 2% who were not admitted after the long transatlantic voyage. The Kissing Post is a wooden column outside the Registry Room, where new arrivals were greeted by their relatives and friends, typically with tears, hugs, and kisses.
Text from the Wikipedia website
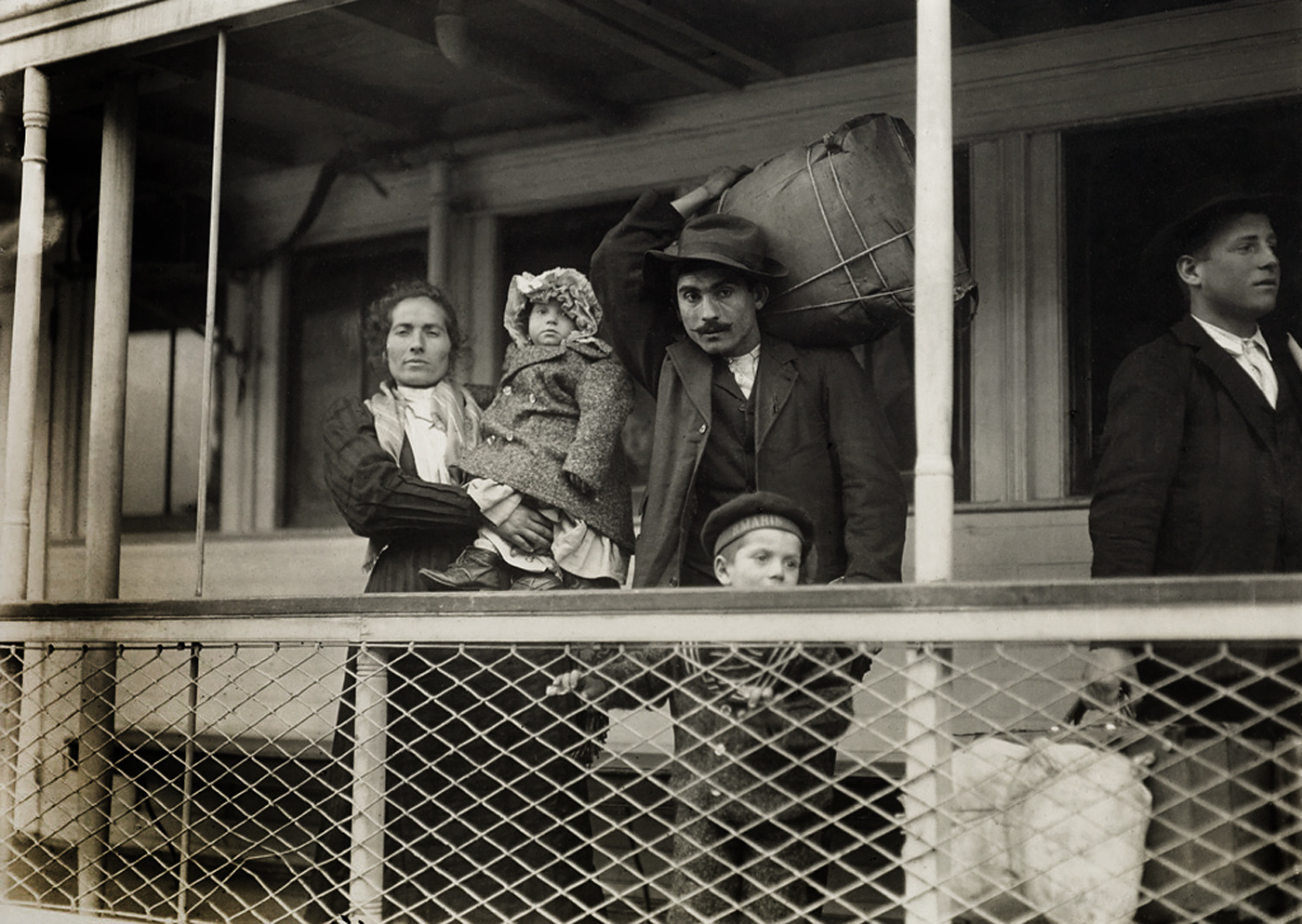
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Italian family on the ferry boat
1905
Gelatin silver print
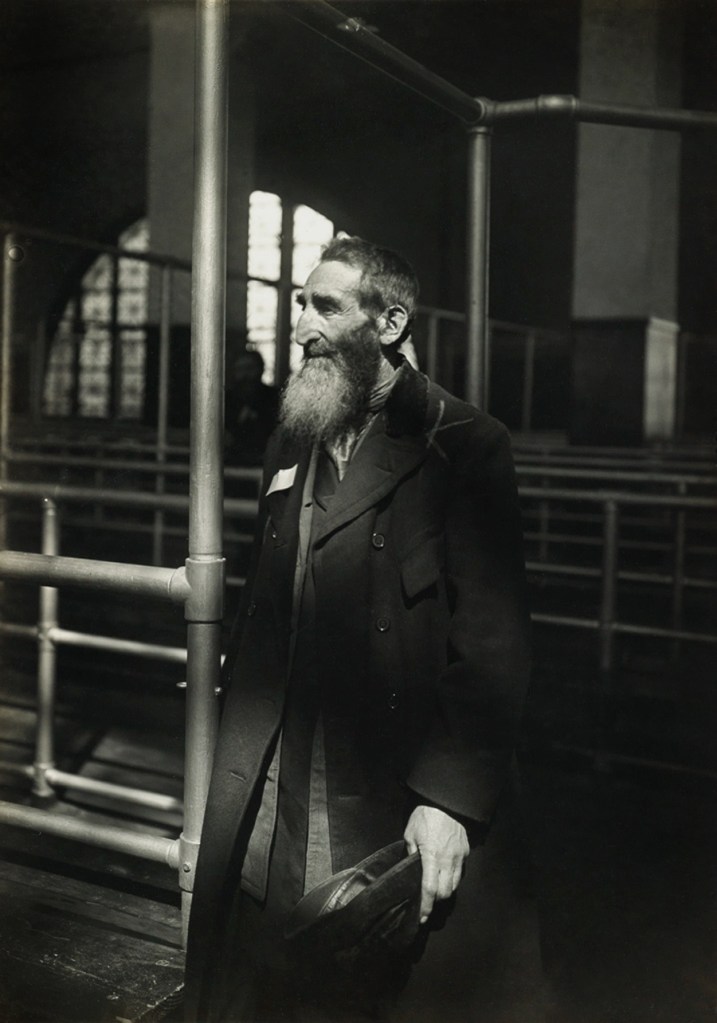

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Patriarch at Ellis Island
1905
Gelatin silver print
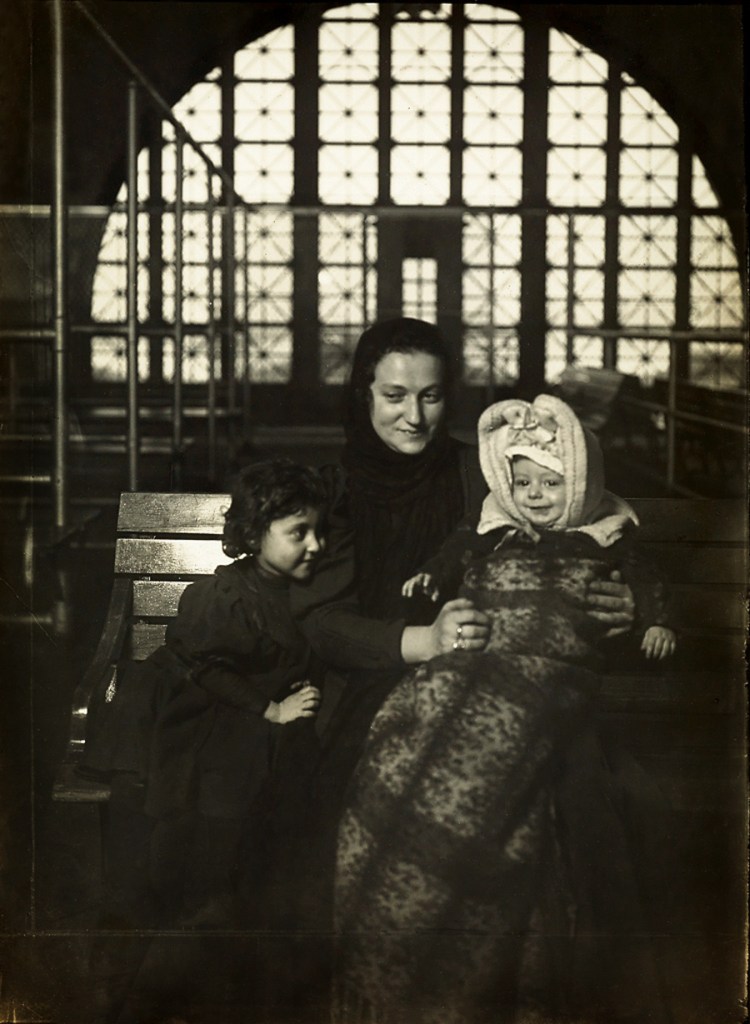

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Russian family at Ellis Island
1905
Gelatin silver print
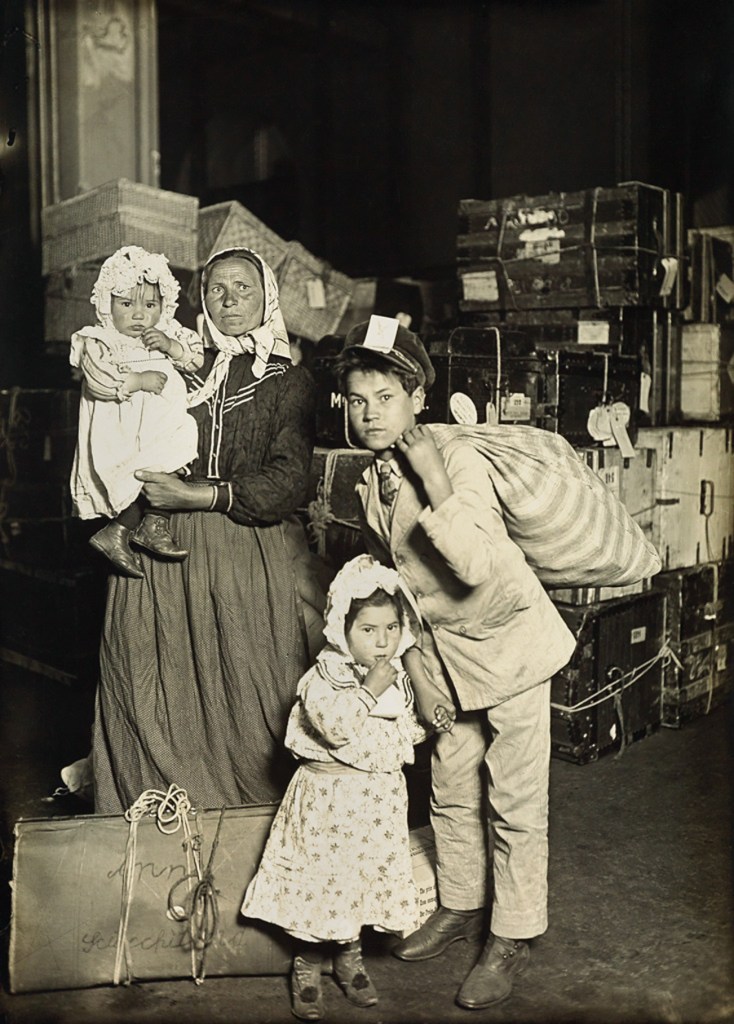

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Italian family in the baggage room
1905
Gelatin silver print
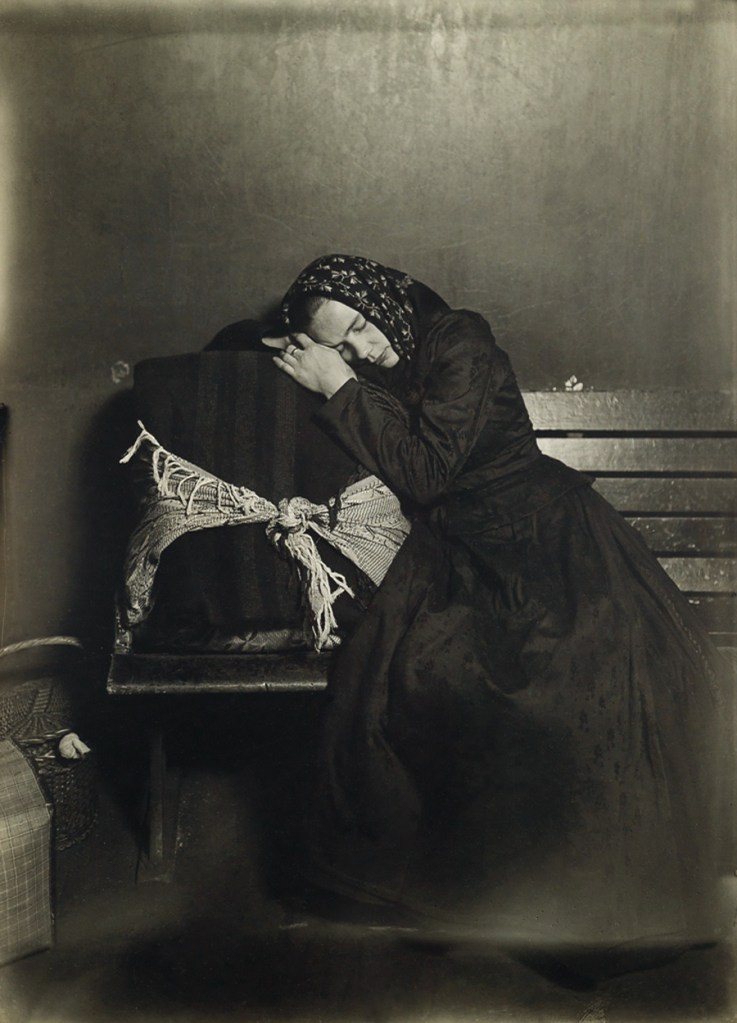

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Slavic immigrant at Ellis Island
1907
Gelatin silver print
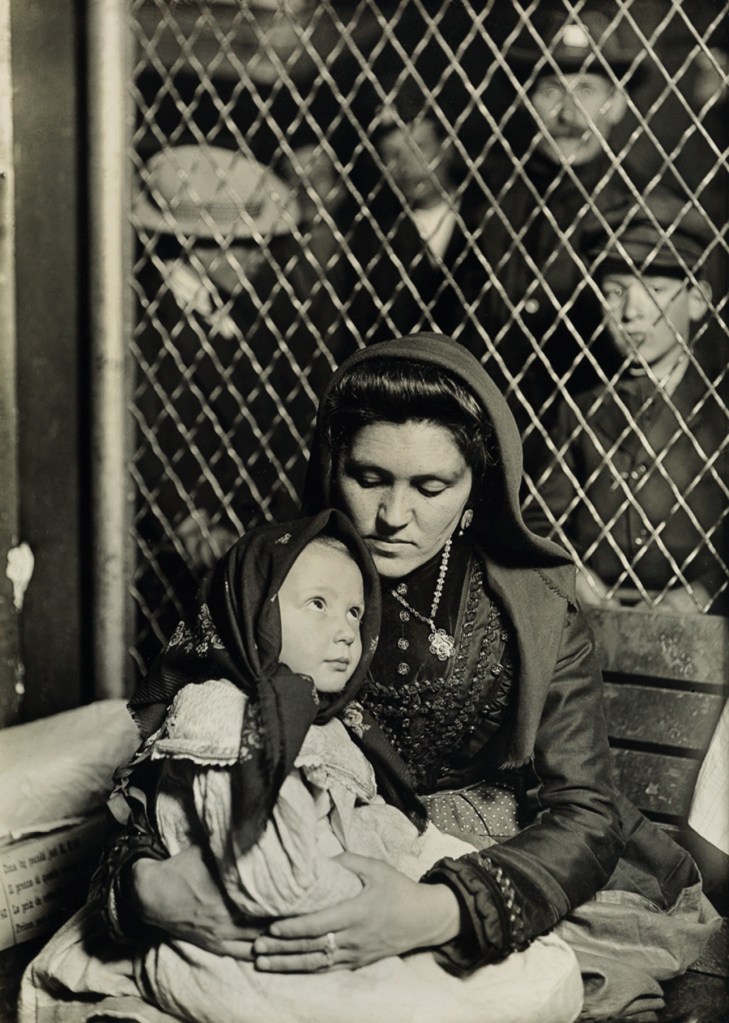

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Mother and child Ellis Island
c. 1907
Gelatin silver print
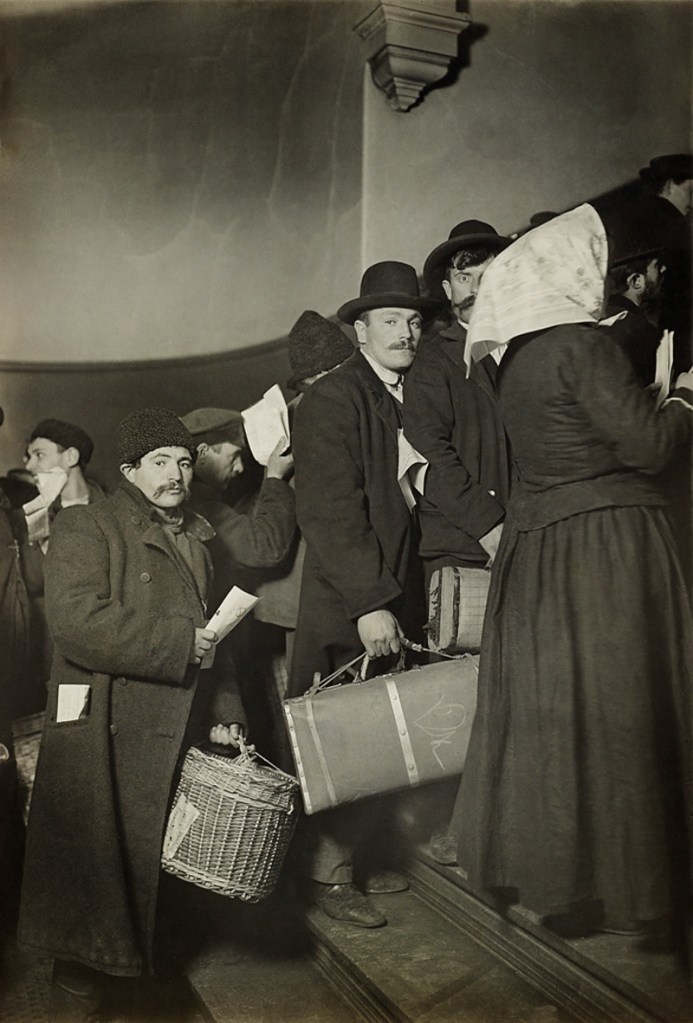

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
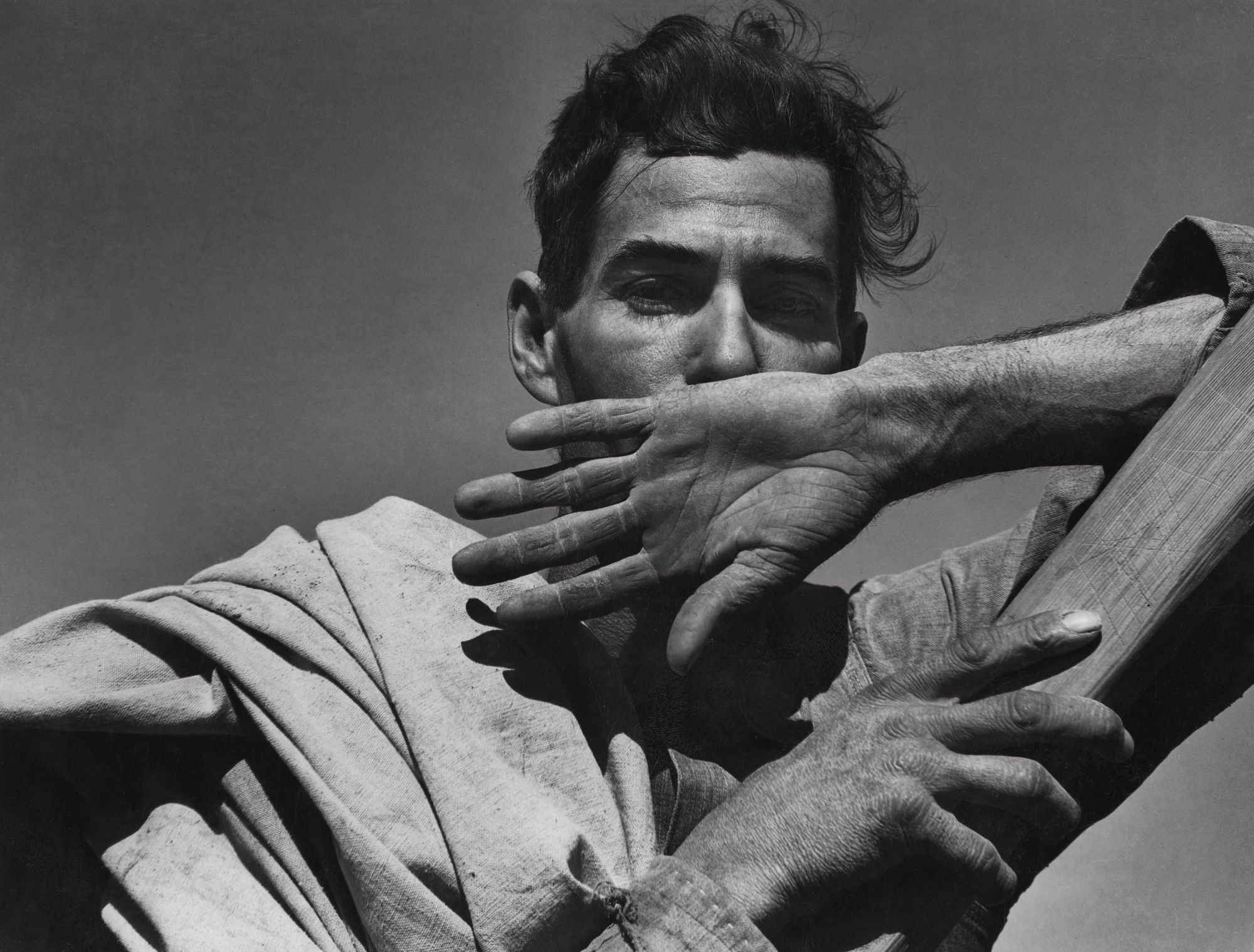
Climbing into America
1908
Gelatin silver print
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Documentary photography
In 1907, Hine became the staff photographer of the Russell Sage Foundation; he photographed life in the steel-making districts and people of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, for the influential sociological study called The Pittsburgh Survey.
In 1908 Hine became the photographer for the National Child Labor Committee (NCLC), leaving his teaching position. Over the next decade, Hine documented child labor, with focus on the use of child labor in the Carolina Piedmont, to aid the NCLC’s lobbying efforts to end the practice. In 1913, he documented child labourers among cotton mill workers with a series of Francis Galton’s composite portraits.
Hine’s work for the NCLC was often dangerous. As a photographer, he was frequently threatened with violence or even death by factory police and foremen. At the time, the immorality of child labor was meant to be hidden from the public. Photography was not only prohibited but also posed a serious threat to the industry. To gain entry to the mills, mines and factories, Hine was forced to assume many guises. At times he was a fire inspector, postcard vendor, bible salesman, or even an industrial photographer making a record of factory machinery.
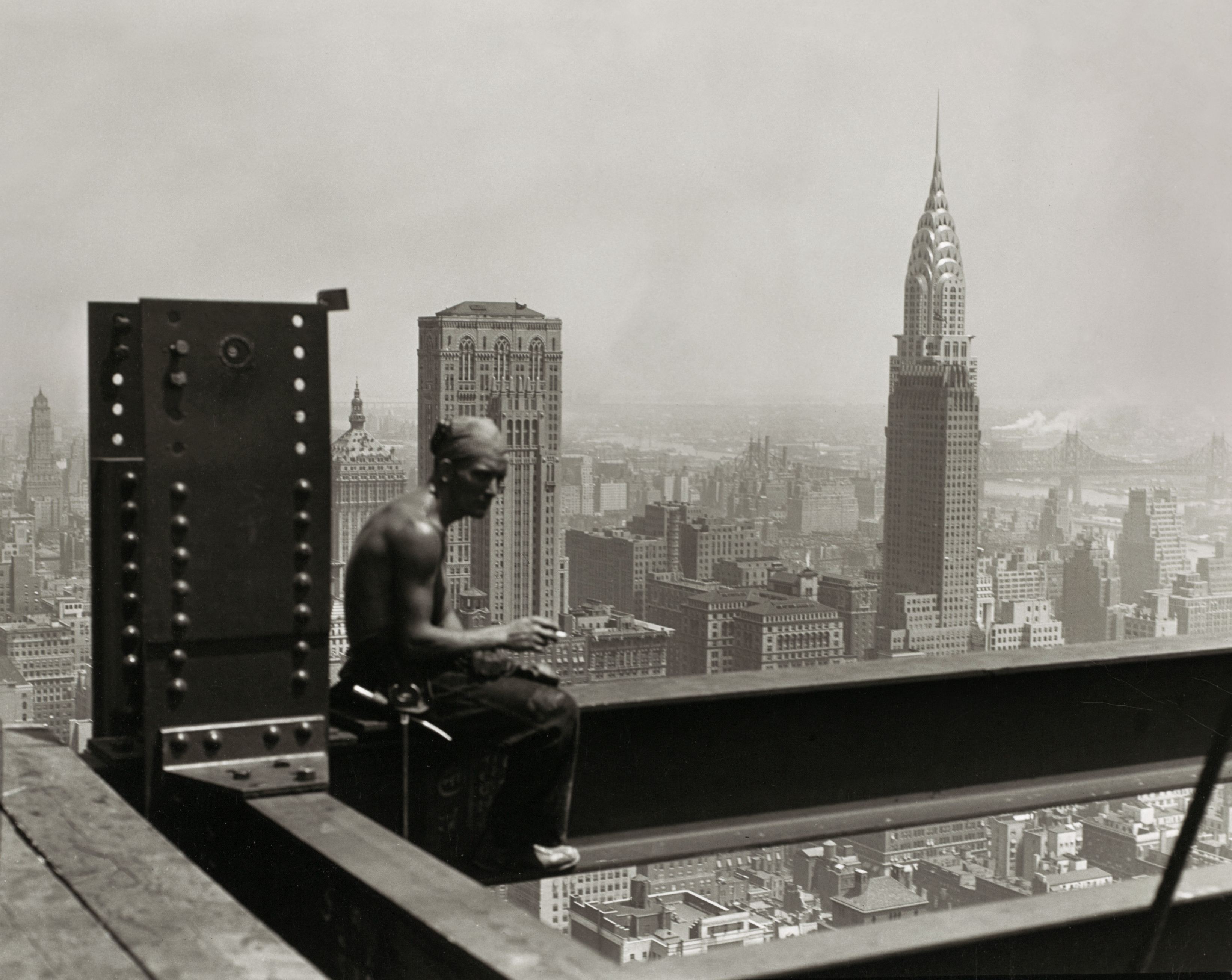
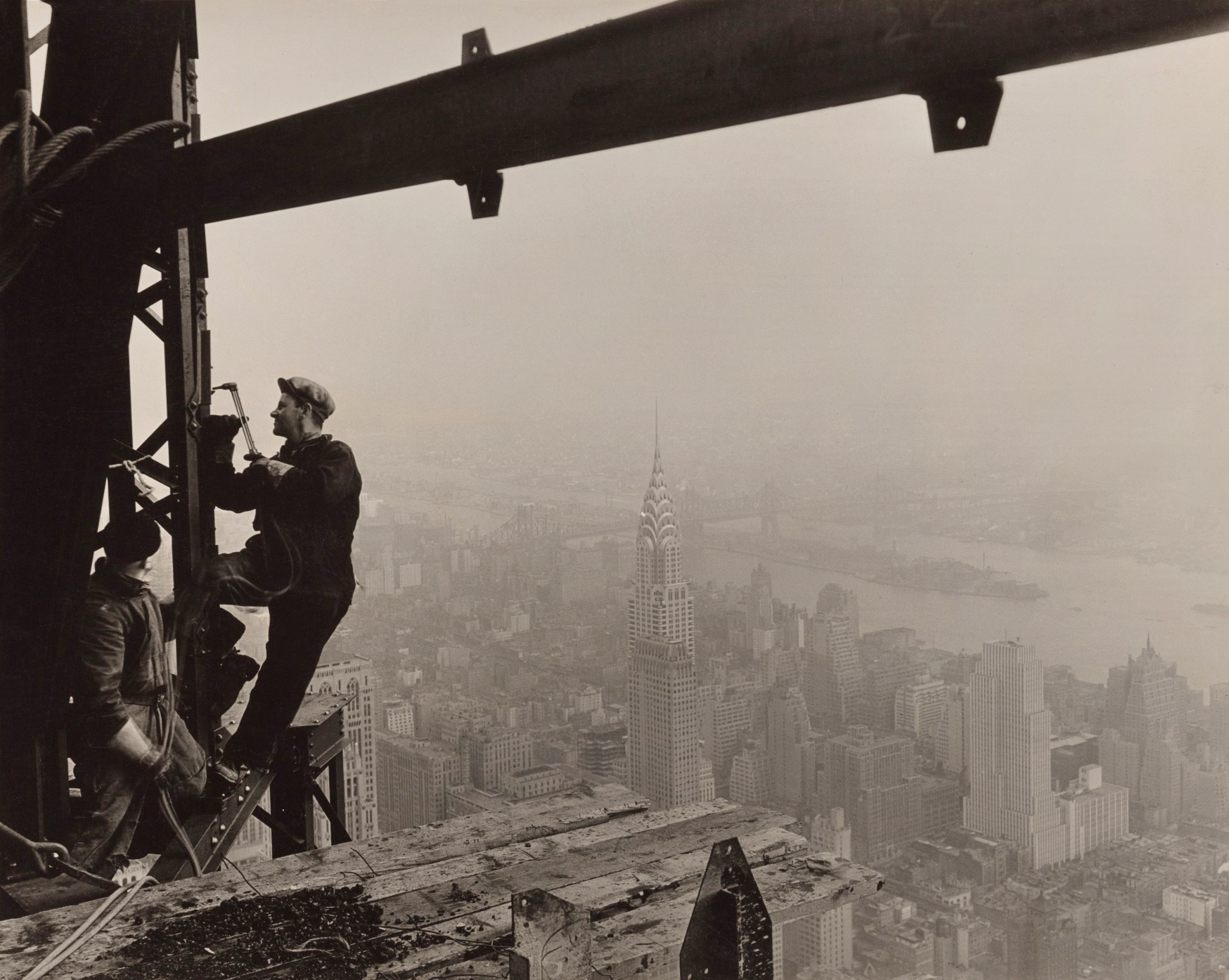
During and after World War I, he photographed American Red Cross relief work in Europe. In the 1920s and early 1930s, Hine made a series of “work portraits,” which emphasised the human contribution to modern industry. In 1930, Hine was commissioned to document the construction of the Empire State Building. He photographed the workers in precarious positions while they secured the steel framework of the structure, taking many of the same risks that the workers endured. In order to obtain the best vantage points, Hine was swung out in a specially-designed basket 1,000 ft above Fifth Avenue.
During the Great Depression Hine again worked for the Red Cross, photographing drought relief in the American South, and for the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), documenting life in the mountains of eastern Tennessee. He also served as chief photographer for the Works Progress Administration’s National Research Project, which studied changes in industry and their effect on employment. Hine was also a faculty member of the Ethical Culture Fieldston School.
Later life
In 1936, Hine was selected as the photographer for the National Research Project of the Works Projects Administration, but his work there was not completed.
The last years of his life were filled with professional struggles by loss of government and corporate patronage. Few people were interested in his work, past or present, and Hine lost his house and applied for welfare. He died on November 3, 1940 at Dobbs Ferry Hospital in Dobbs Ferry, New York, after an operation. He was 66 years old.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Worker on platform
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
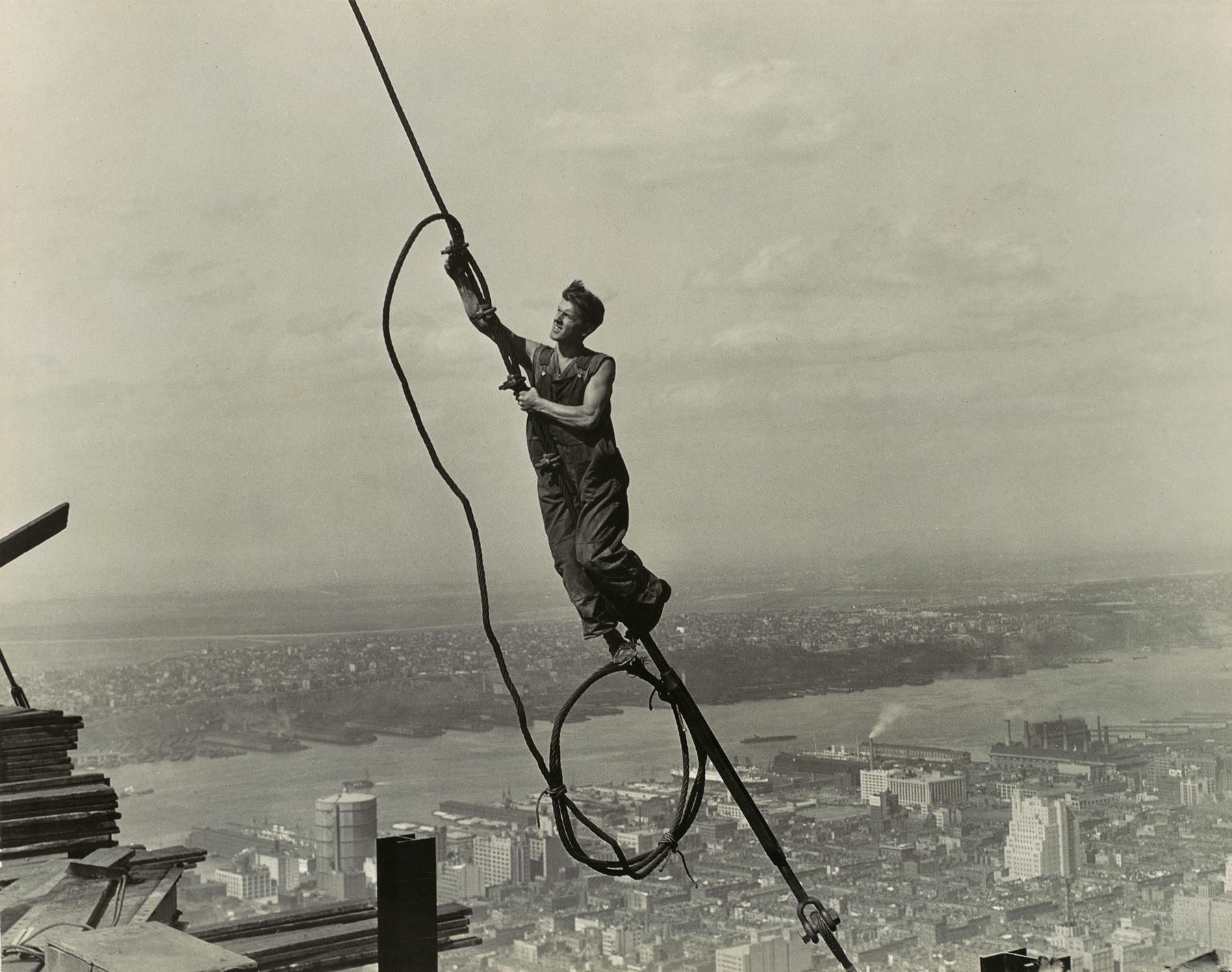
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Icarus, Empire State Building
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
Of the many photographs Hine took of the Empire State Building, this one became the popular favourite. Suspended in graceful sangfroid, the steelworker symbolises daring technical innovation of the sort Daedalus embodied in Greek legend. While Daedulus flew the middle course between sea and sky safely, his son Icarus flew too close to the sun and perished. The optimism of this image suggests that it was not Icarus’s folly but his youth and his ability to fly that prompted Hine’s title.
Text from The Met website
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Empire State Building
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Empire State Building
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Girders and Workers, Empire State Building
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
Same man second left as in the image below.

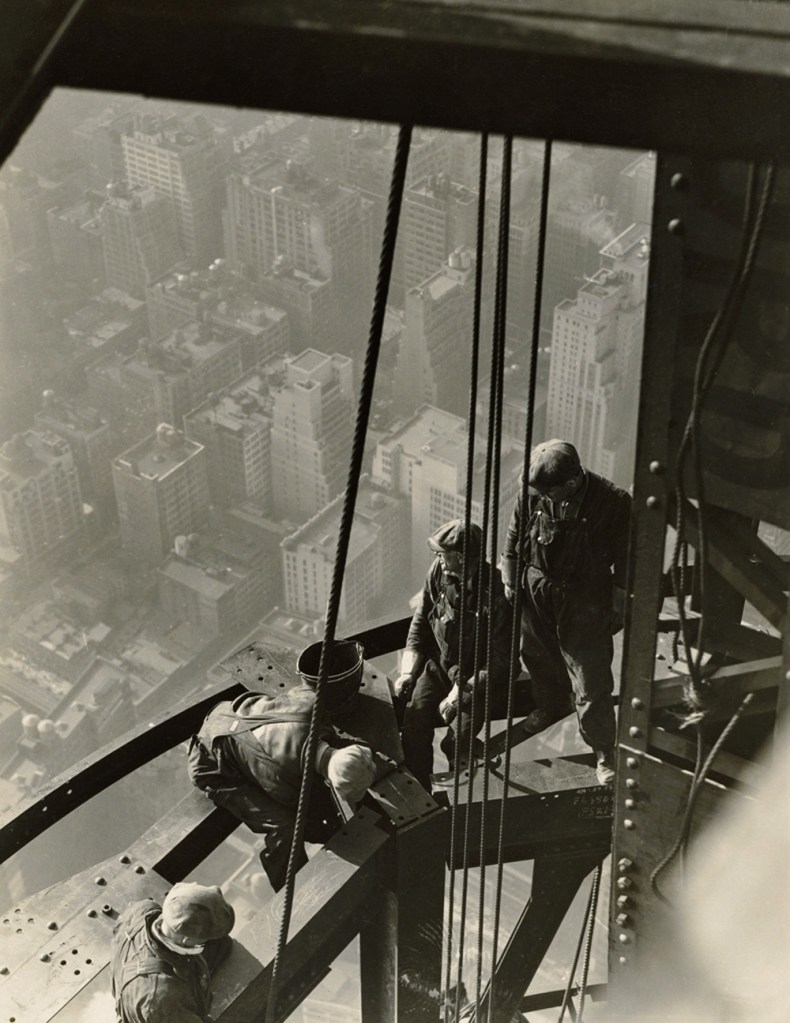
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Laborer on connector
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Workers on girder
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
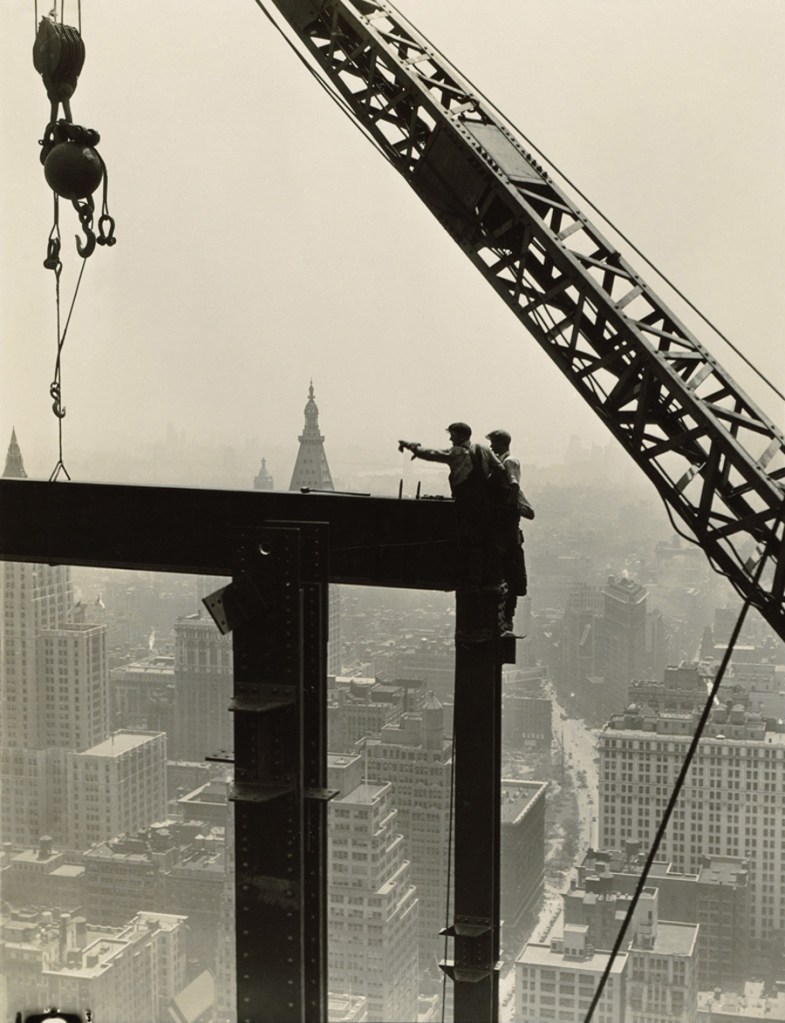

Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Derrick and workers on girder
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
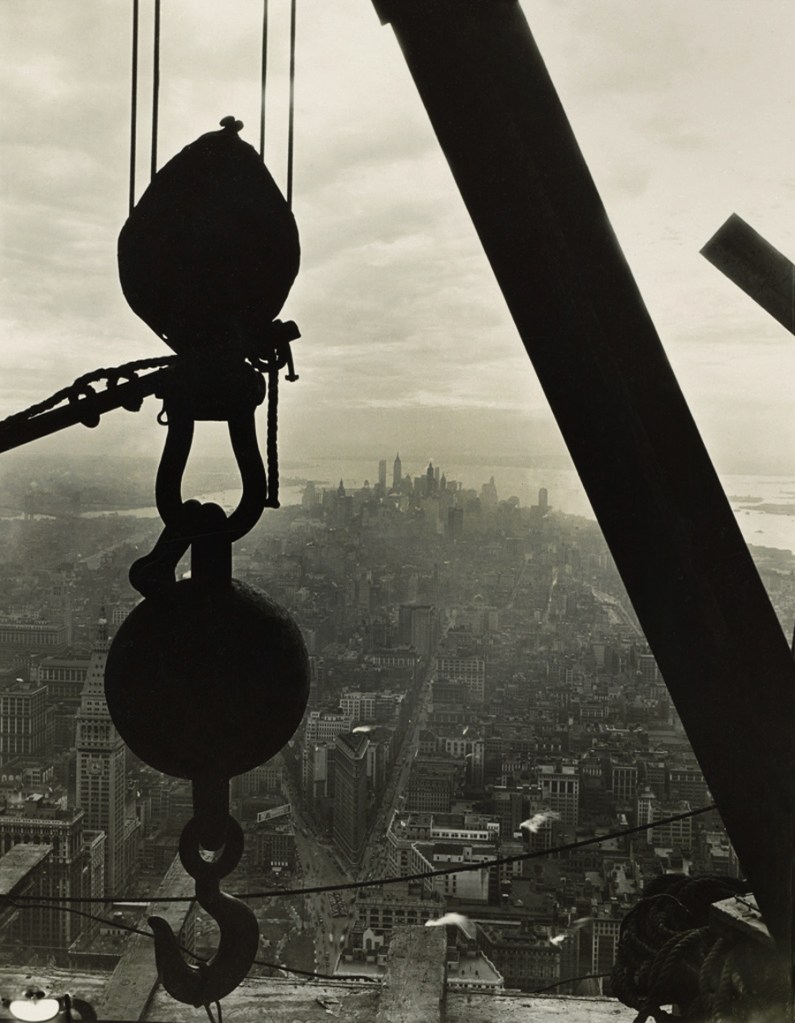

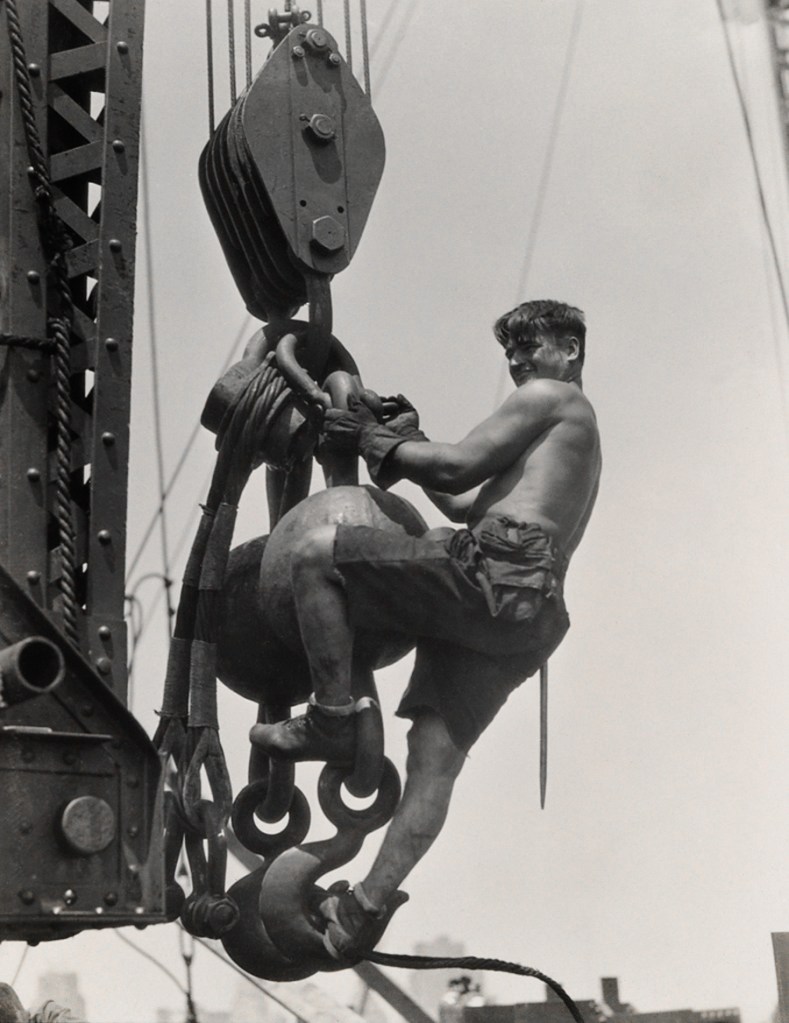
Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940)
Silhouetted crane hook
1930-1931
Gelatin silver print
Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and completed in 1931, the building has a roof height of 1,250 feet (380 m) and stands a total of 1,454 feet (443.2 m) tall, including its antenna. Its name is derived from “Empire State”, the nickname of New York. As of 2017 the building is the 5th-tallest completed skyscraper in the United States and the 28th-tallest in the world. It is also the 6th-tallest freestanding structure in the Americas.
The site of the Empire State Building, located on the west side of Fifth Avenue between West 33rd and 34th Streets, was originally part of an early 18th century farm. In the late 1820s, it came into the possession of the prominent Astor family, with John Jacob Astor’s descendants building the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel on the site in the 1890s. By the 1920s, the family had sold the outdated hotel and the site indirectly ended up under the ownership of Empire State Inc., a business venture that included businessman John J. Raskob and former New York governor Al Smith. The original design of the Empire State Building was for a 50-story office building. However, after fifteen revisions, the final design was for a 86-story 1,250-foot building, with an airship mast on top. This ensured it would be the world’s tallest building, beating the Chrysler Building and 40 Wall Street, two other Manhattan skyscrapers under construction at the time that were also vying for that distinction. …
The project involved more than 3,500 workers at its peak, including 3,439 on a single day, August 14, 1930. Many of the workers were Irish and Italian immigrants, with a sizeable minority of Mohawk ironworkers from the Kahnawake reserve near Montreal. According to official accounts, five workers died during the construction, although the New York Daily News gave reports of 14 deaths and a headline in the socialist magazine The New Masses spread unfounded rumours of up to 42 deaths. The Empire State Building cost $40,948,900 to build, including demolition of the Waldorf-Astoria (equivalent to $533,628,800 in 2016). This was lower than the $60 million budgeted for construction.
Lewis Hine captured many photographs of the construction, documenting not only the work itself but also providing insight into the daily life of workers in that era. Hine’s images were used extensively by the media to publish daily press releases. According to the writer Jim Rasenberger, Hine “climbed out onto the steel with the ironworkers and dangled from a derrick cable hundreds of feet above the city to capture, as no one ever had before (or has since), the dizzy work of building skyscrapers”. In Rasenberger’s words, Hine turned what might have been an assignment of “corporate flak” into “exhilarating art”. These images were later organised into their own collection. Onlookers were enraptured by the sheer height at which the steelworkers operated. New York magazine wrote of the steelworkers: “Like little spiders they toiled, spinning a fabric of steel against the sky”.
Text from the Wikipedia website
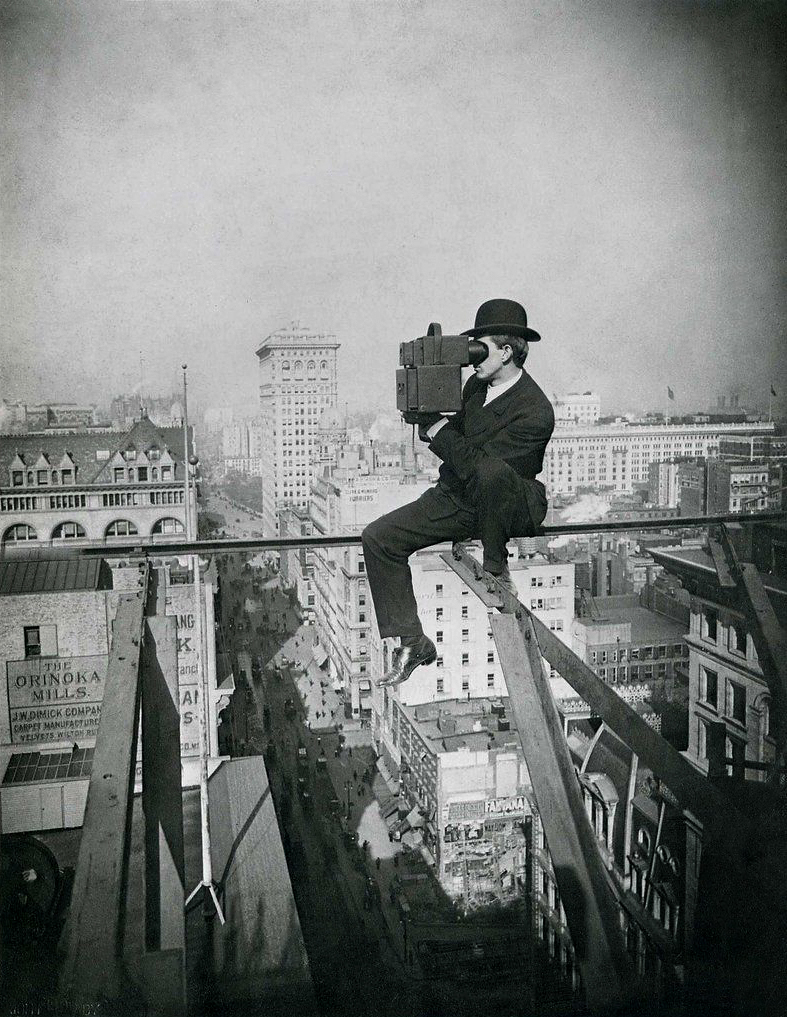

Anonymous photographer
Untitled (Lewis Hine with camera)
c. 1900-1910s
Gelatin silver print


























![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web2.jpg)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web9.jpg)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 compilation of three Weegee crime scene photographs Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 compilation of three Weegee crime scene photographs](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web1-and-6b.jpg)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web6.jpg?w=791)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web1.jpg?w=769)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web3.jpg?w=760)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 compilation of two Weegee crime scene photographs Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 compilation of two Weegee crime scene photographs](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web4-and-5.jpg)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web4.jpg?w=705)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web5.jpg?w=791)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web7.jpg)
![Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930 Weegee (Arthur Fellig) (American, 1899-1968) 'Untitled [Crime scene]' c. 1930](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/weegee-a-group-of-9-crime-scene-photographs-c-1930-web8.jpg?w=648)









































































































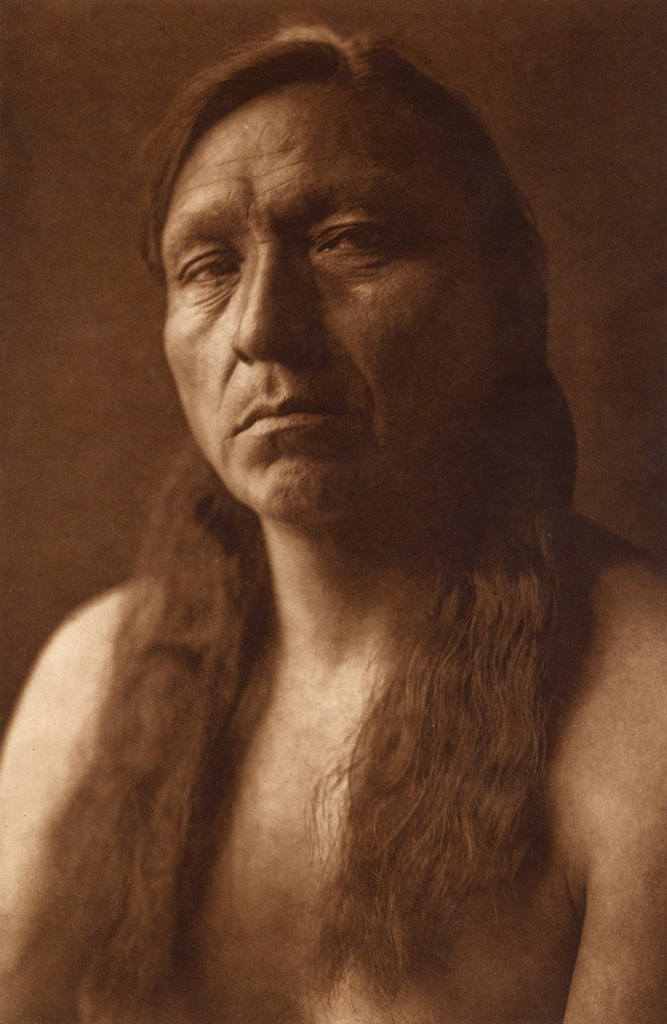
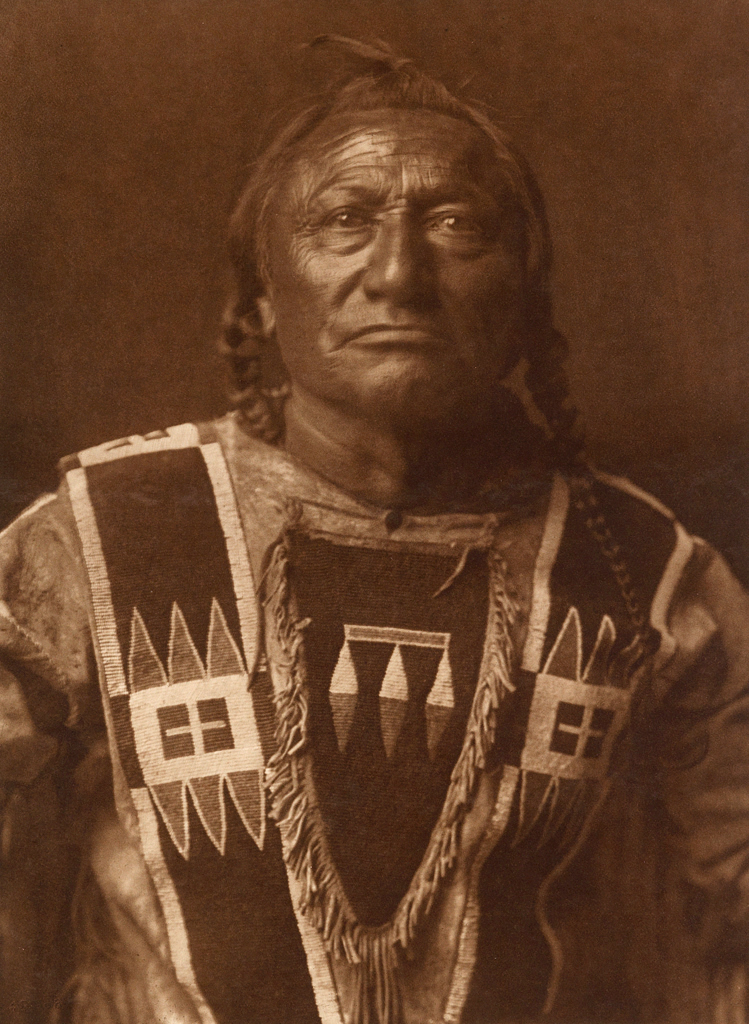
![Edward S. Curtis (American, 1868-1952) '[Bear's Belly, Arikara Indian half-length portrait, facing front, wearing bearskin]' c. 1908 from 'Edward S. Curtis (1868-1952) – The North American Indian' List of Large Plates Supplementing Volume V Edward S. Curtis (American, 1868-1952) '[Bear's Belly, Arikara Indian half-length portrait, facing front, wearing bearskin]' c. 1908 from 'Edward S. Curtis (1868-1952) – The North American Indian' List of Large Plates Supplementing Volume V](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/edward-s-curtis-1868-1952-the-north-american-indian-portfolio-v-1907-photogravure-on-vellum1-web.jpg?w=770)
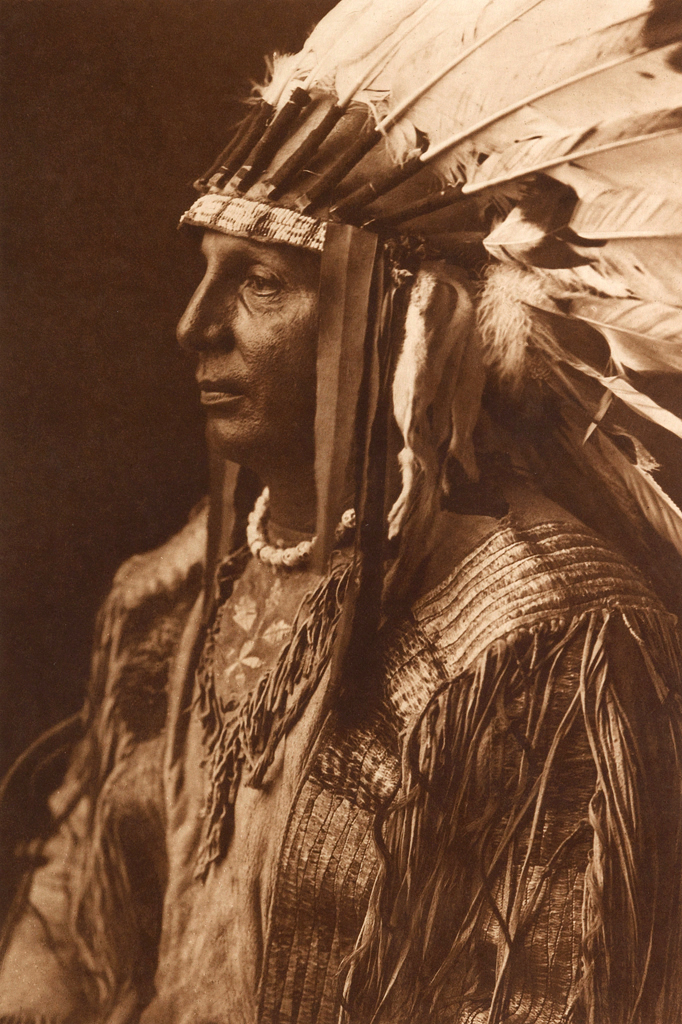
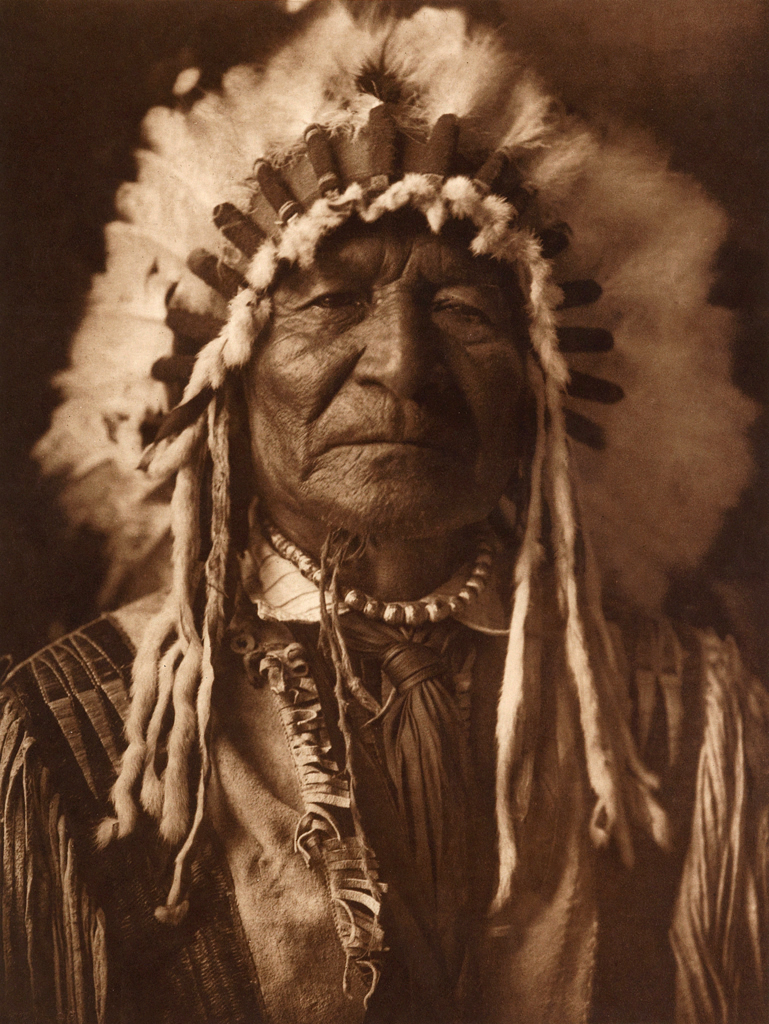
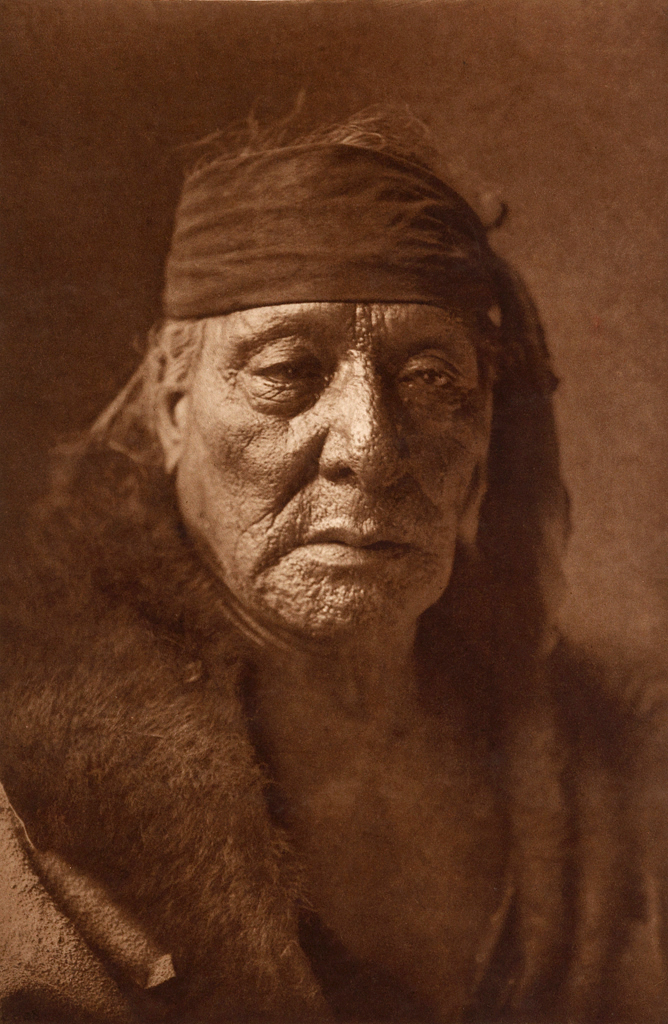










![Edward S. Curtis (American, 1868-1952) '[Arikara medicine ceremony - the Bears]' c. 1908 Edward S. Curtis (American, 1868-1952) '[Arikara medicine ceremony - the Bears]' c. 1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/edward-s-curtis-1868-1952-the-north-american-indian-portfolio-v-1907-photogravure-on-vellum6-web.jpg)
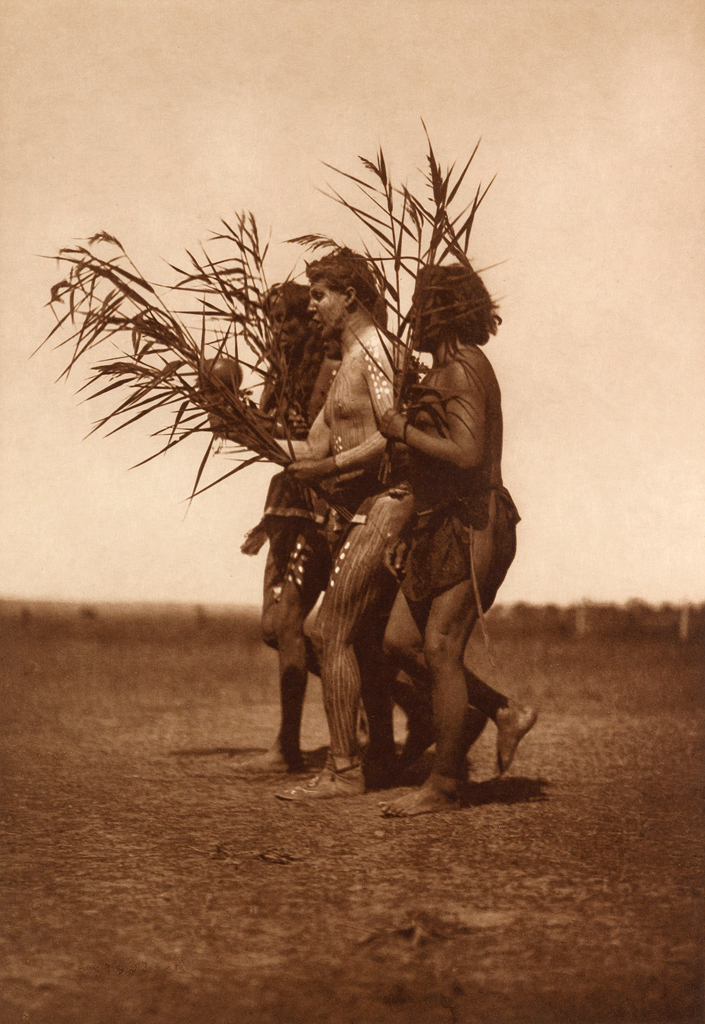
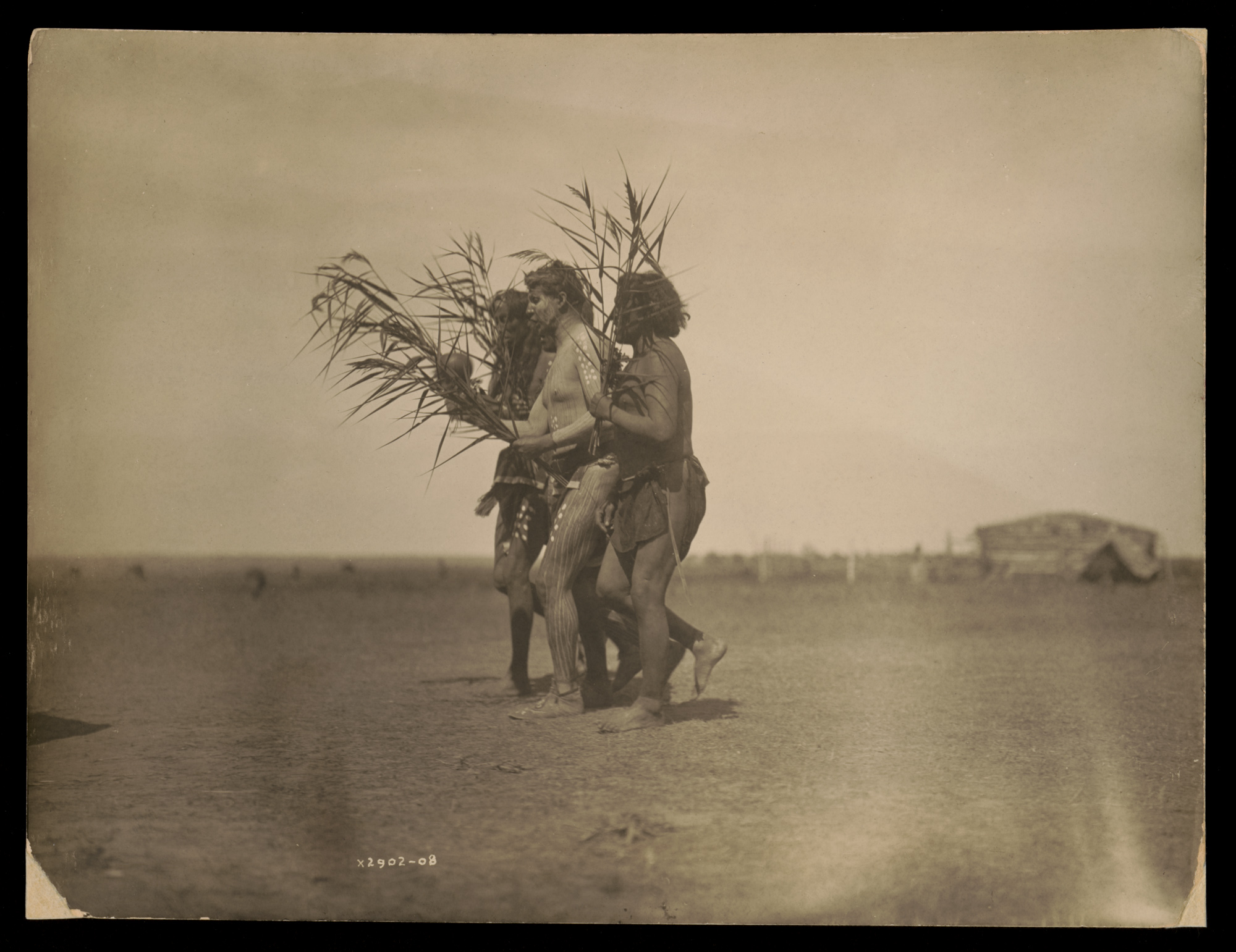
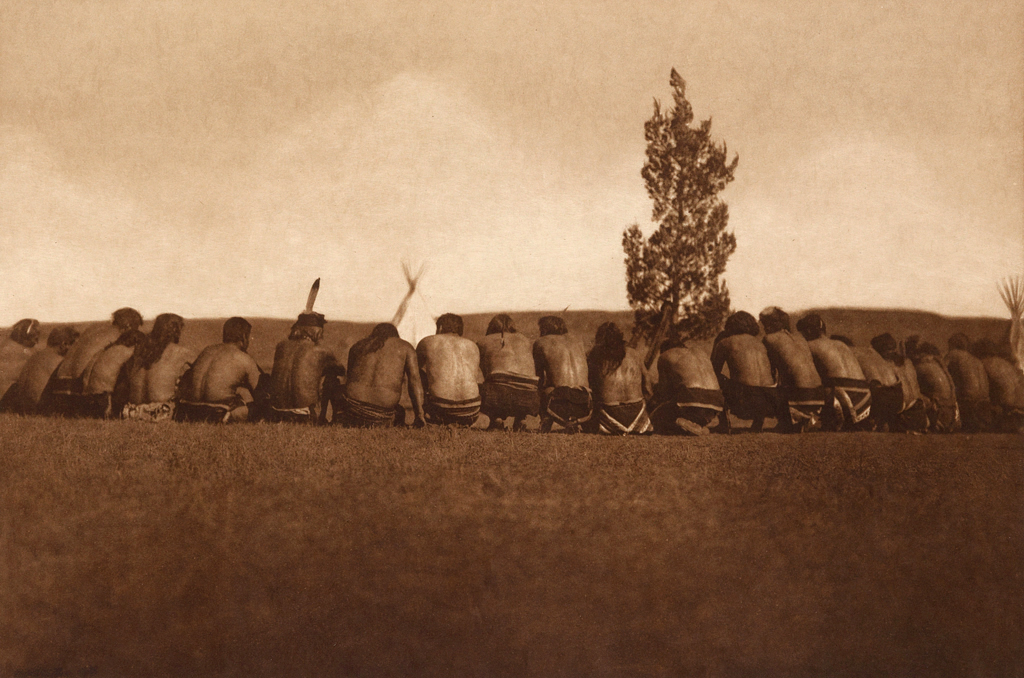
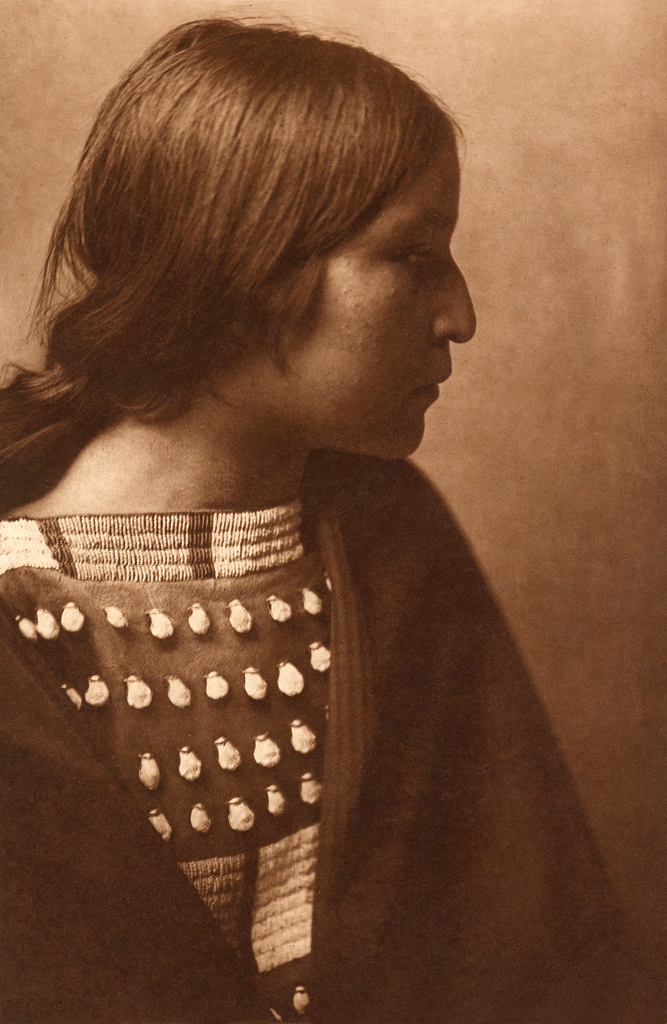
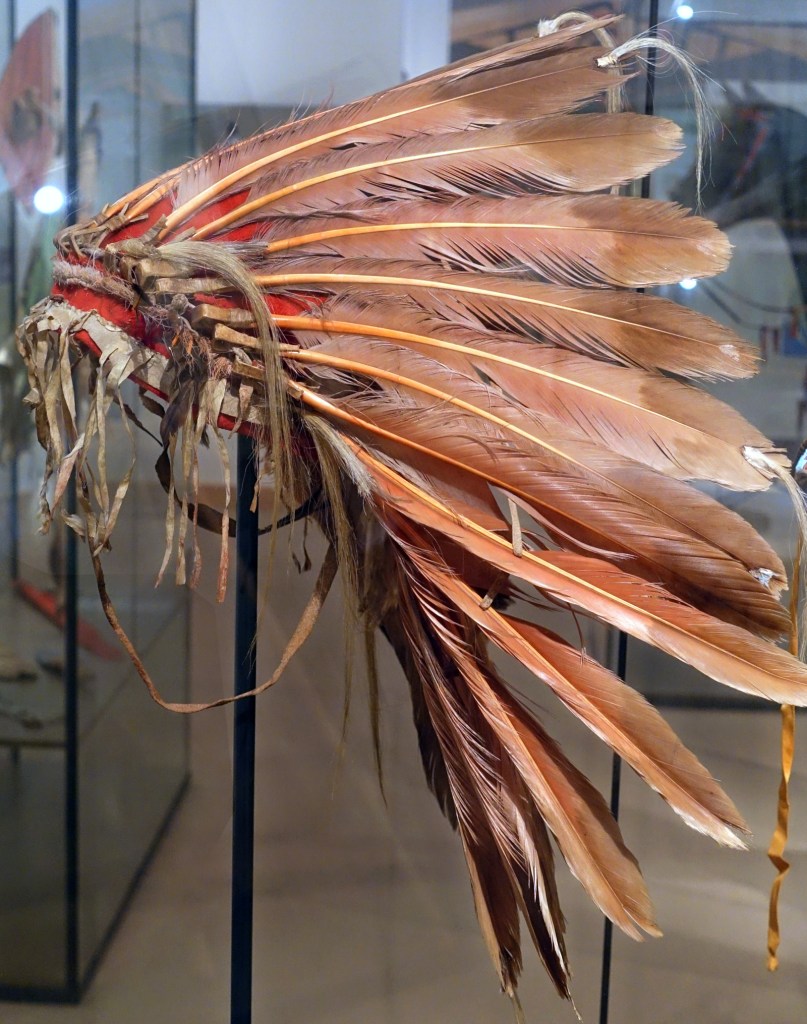
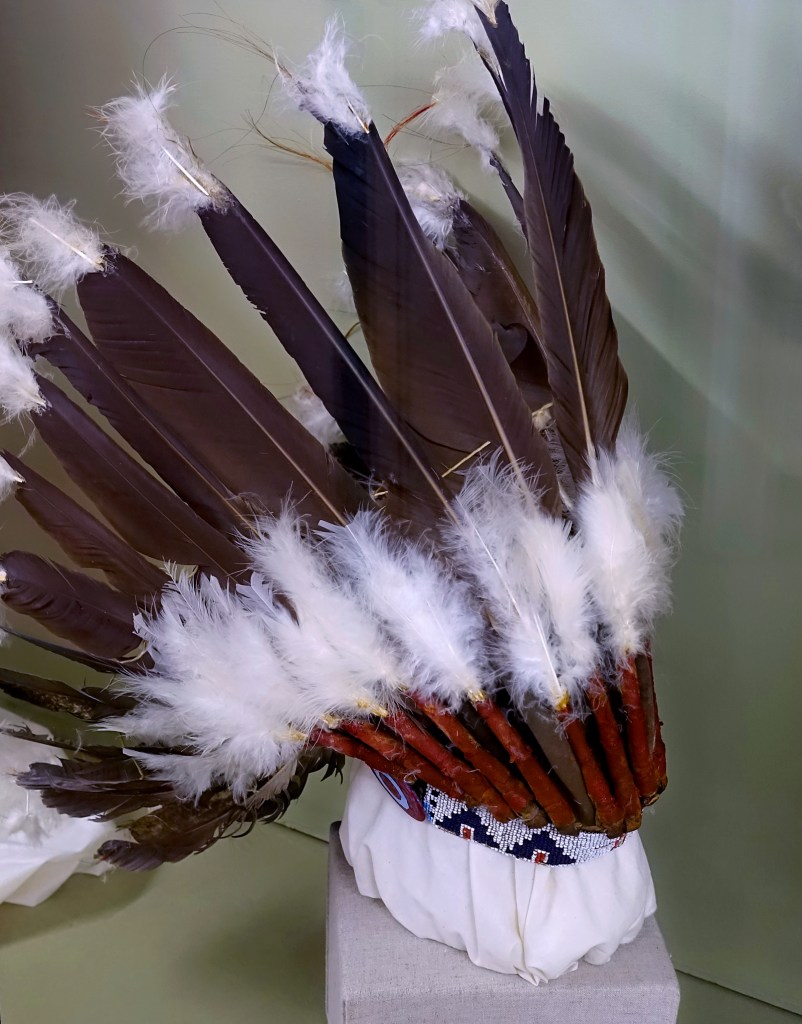
















![Edward S. Curtis (American, 1868-1952) '[Atsina Indian, Red Whip, half-length portrait, seated, facing front, wearing feather, beaded buckskin shirt, holding pipe in left hand]' c. 1908 Edward S. Curtis (American, 1868-1952) '[Atsina Indian, Red Whip, half-length portrait, seated, facing front, wearing feather, beaded buckskin shirt, holding pipe in left hand]' c. 1908](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/edward-s-curtis-1868-1952-the-north-american-indian-portfolio-v-1907-photogravure-on-vellum19-web.jpg?w=671)
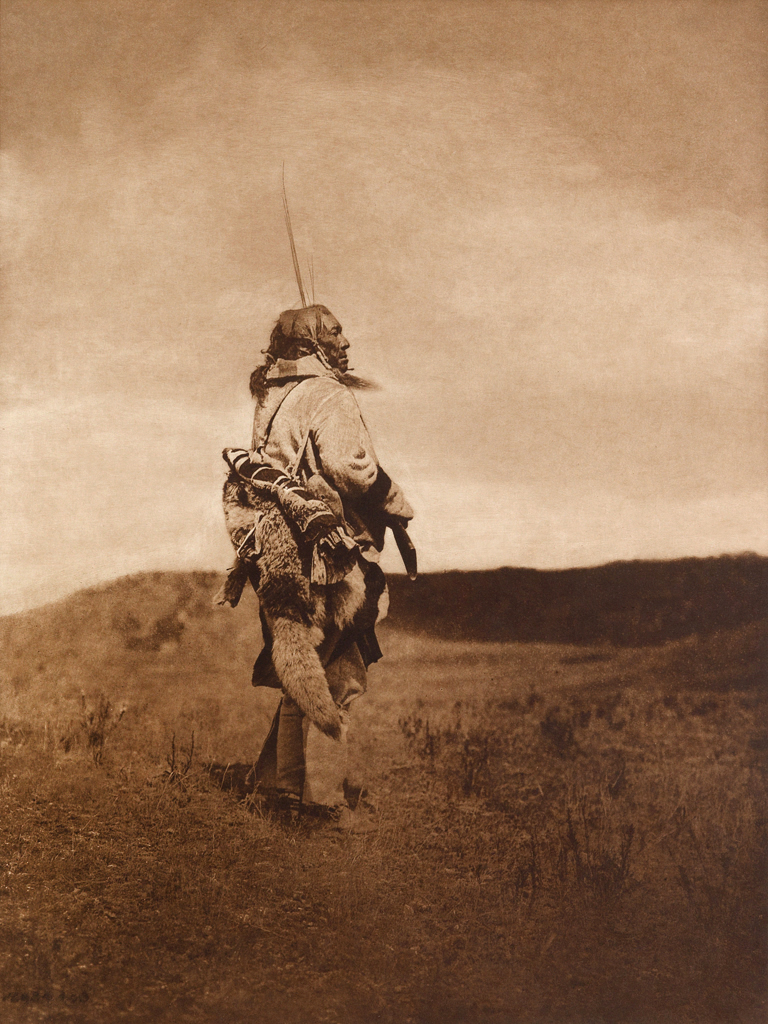
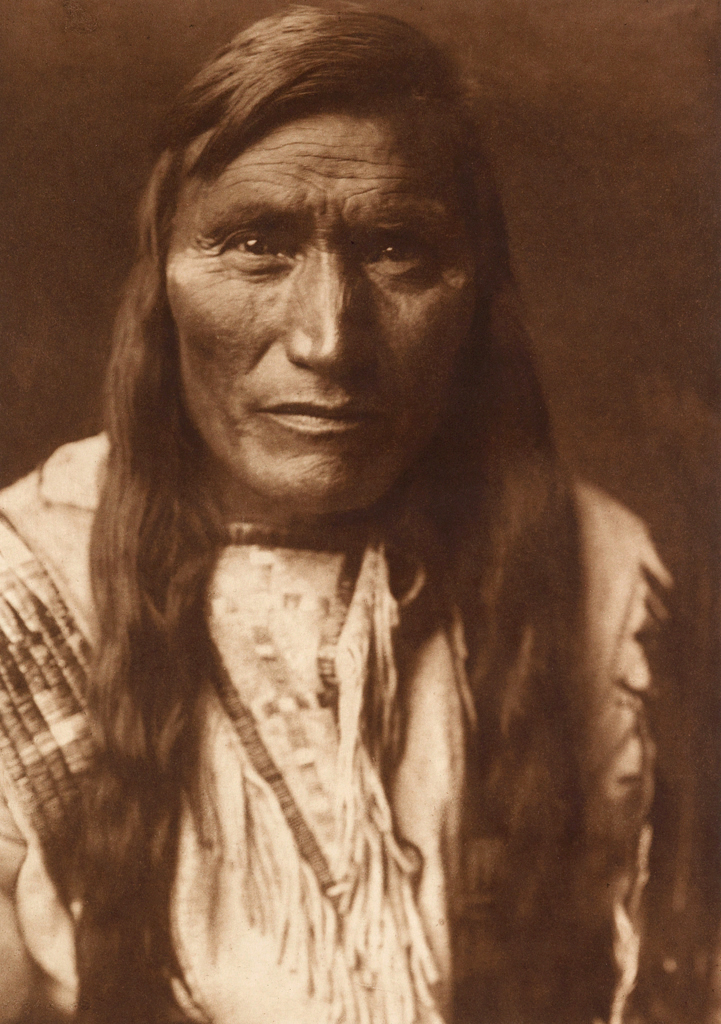

































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.