Exhibition dates: 31st March – 30th July, 2017
Photographs are in the chronological room order of the exhibition.
Entrance
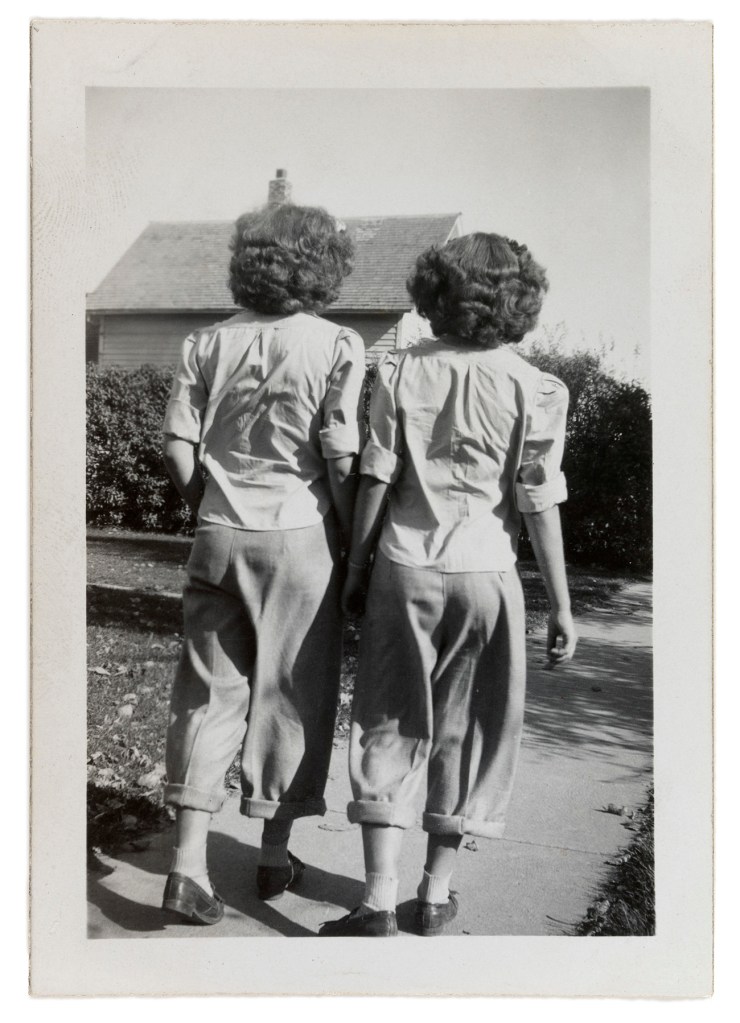

Patrick Pound (New Zealand/Australian, b. 1962)
The entrants (detail)
2016-2017
Site specific installation comprising objects collected by the artist and works from the NGV Collection
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e
E
This polymorphic album of an exhibition by Patrick Pound at NGV Australia, Melbourne is unfortunately stuck with a most ridiculous title.
The great “show and tell” consists of 6 large galleries which are crammed full of thousands of photographs from the artists collection and artefacts from the NGV collection which form a (according to the exhibition blurb) “diagrammatic network of intersections, and in that way shows one of the underlying ideas of the whole exhibition, which is to seek out patterns and similarities and connections across objects and works of art and ideas. In other words, one thing leads to another.”
Not necessarily.
Pound is interested in the writing of Georges Perec (a member of the Oulipo group of writers and mathematicians which formed in France in 1960) and his use of “restrictions in his writing as a way of encouraging new patterns and structures.” Perec wrote a whole novel in 1969, A Void, translated from the original French La Disparition (literally, “The Disappearance”) entirely without using the letter e (except for the author’s name). Oulipo writers sought to produce a document that undermines its own reliability. Through structures – or constraints – on composition, Oulipo writers sought to produce new and interesting works.
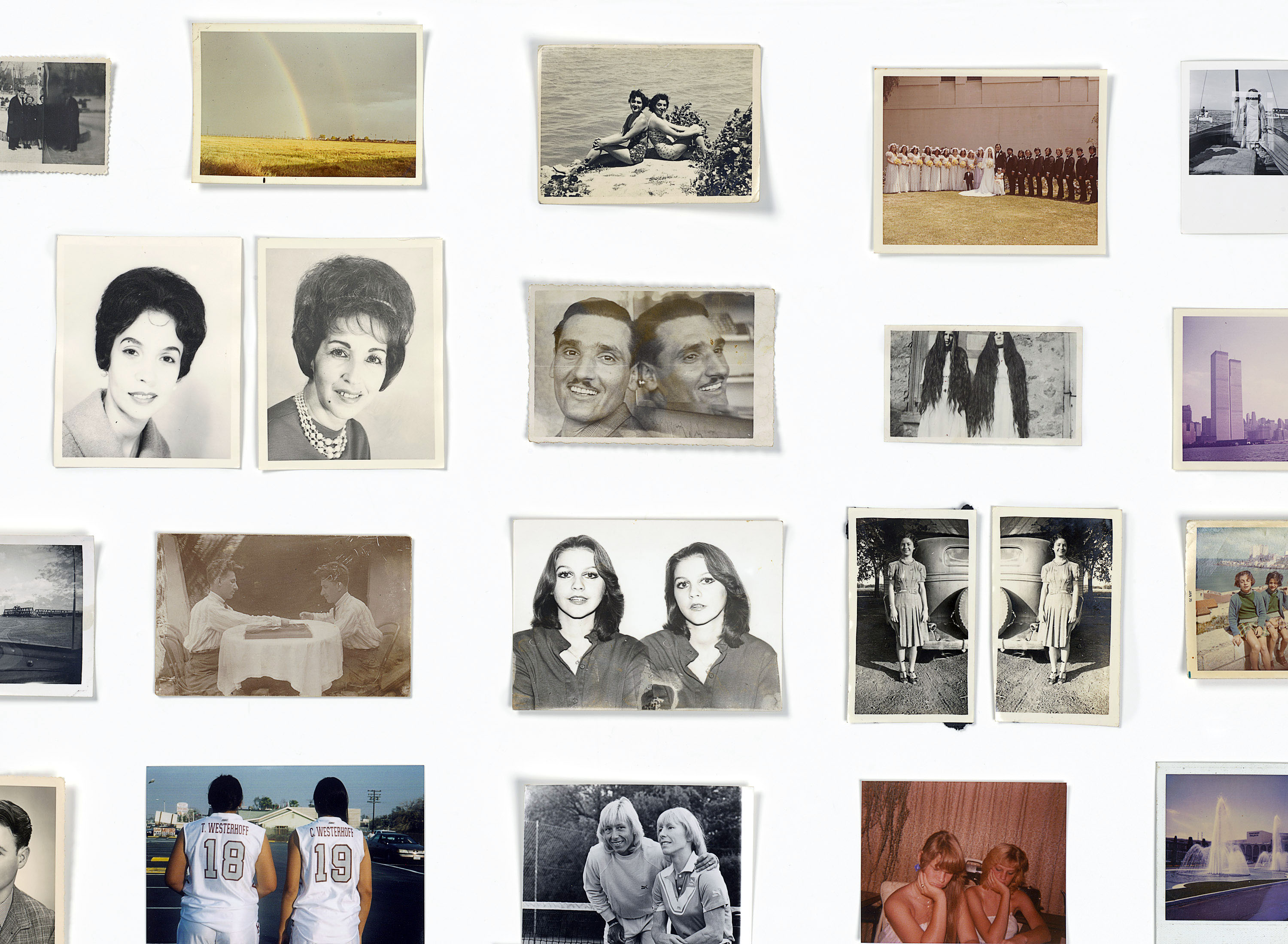
In a similar vein Pound restricts his collections of photographs to restrictive themes, such as people falling, sleepers, holes, readers, the air, lamps, listening to music, hands, shadows, interventions, backs, possibly dead people, holding cameras, self-portraits, doubles, entrants, etc. He seeks to gather his thoughts through these collections, and proposes that collecting found photographs “is like taking cuttings from the world.” A form of collage.
For me the grouping of all these “found” photographs together in display cases is a form of conceptual conceit: the collection of such varied instances of the shadow of the photographer appearing in every image, for example, means very little. Unlike the restrictions that Perec proposes which lead to interesting outcomes, Pound’s restrictions do not enrich the individual photographs by placing them all together, in fact the opposite. The totality is less than the sum of the parts. Reductio ad absurdum.
As individual photographs (as seen below in this posting), the images have presence, they have an aura which emanates from the moment, and context, in which the photograph was taken. Different in each instance. But in this exhibition we are overwhelmed by thousands of images and cannot give them due attention; the photographic “trace” becomes specious. The aura of the singular image is denuded; the aura of the collective does not exist. The collections become the collective photograph (of space) as reassurance: that the interrupting time freeze of individual photographs is not unique and occurs again and again and again. Pound’s collections are a form of photographic cancer… a kind of photographic plate-spinning, where the artist tries to keep all topics rotating in mid-air.
Pound’s existential typologies and classifications are a form of superficial play, using one photo to beget another. The addition of artefacts from the NGV collection only highlights the folly, in which two ceramic parrots paired with a photograph of two parrots is the indulgent nadir. The typologies and collections can, however, be seen as an ironic comment on the nature of our image saturated society, where millions of photographs are uploaded and viewed on the www every day. They can also be seen as a comment on the way people view photography in contemporary culture, where every selfie or picture of what I had for breakfast is posted online for consumption. While I admire Pound’s pugnaciousness and the obsessiveness needed to collect all of these images (being a collector myself) and, further, the tenacity required to catalogue and arrange them all – I really wonder about the clinamen, a term coined by Lucretius to describe the unpredictable swerve of atoms in his version of physics. It was adopted by the Oulipo set as – quoting Paul Klee – ‘the error in the system’. By gathering all of these photographs together in groups, the periphery becomes the centre … AND LOSES ITS UNPREDICTABILITY – the collective photographs loose their punctum, their unpredicatability. The photographs loose their individual transcendence of time. Perec’s missing eeeeeeeeeeeeeee’s at the beginning of this text thus exclude chaos, randomness, the capital E.
Other statements and ideas also grate. “The camera reduces the world to a list of things to photograph. When I click BUY on eBay – for me that’s the equivalent of taking a photograph. The mouse is my camera.” Well, no actually. The camera never reduces the world, it just is, it’s a machine. It is the person who takes the photograph, the human, that reduces the world to what they want to photograph. And when you click BUY on eBay it is not the equivalent of taking a photograph. You have used your money, your capitalism, your CAPITAL, to purchase your DESIRE. You are taking someone else’s vernacular, their moment of deciding what to photograph, to purchase their desire so that you can possess it yourself. You are coveting time and space. “Eventually every photograph is a photograph of a dead person.” Well, no actually, because not every photograph is of a person. “The camera is an idling hearse.” Yes, and so is your body, and the motor car, and walking across the road. The effect of these oblique statements is to further dumb down the public understanding of photography.
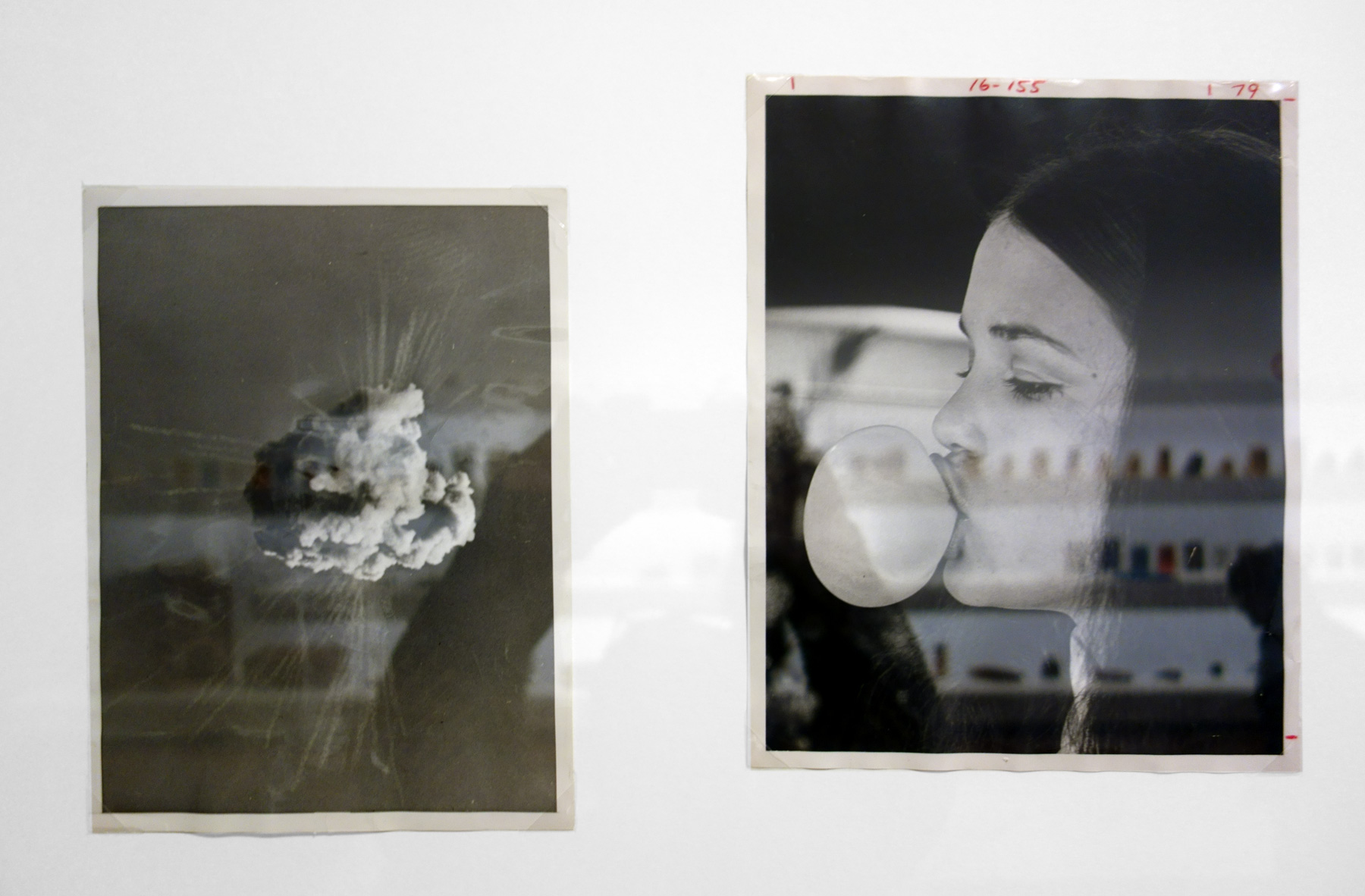
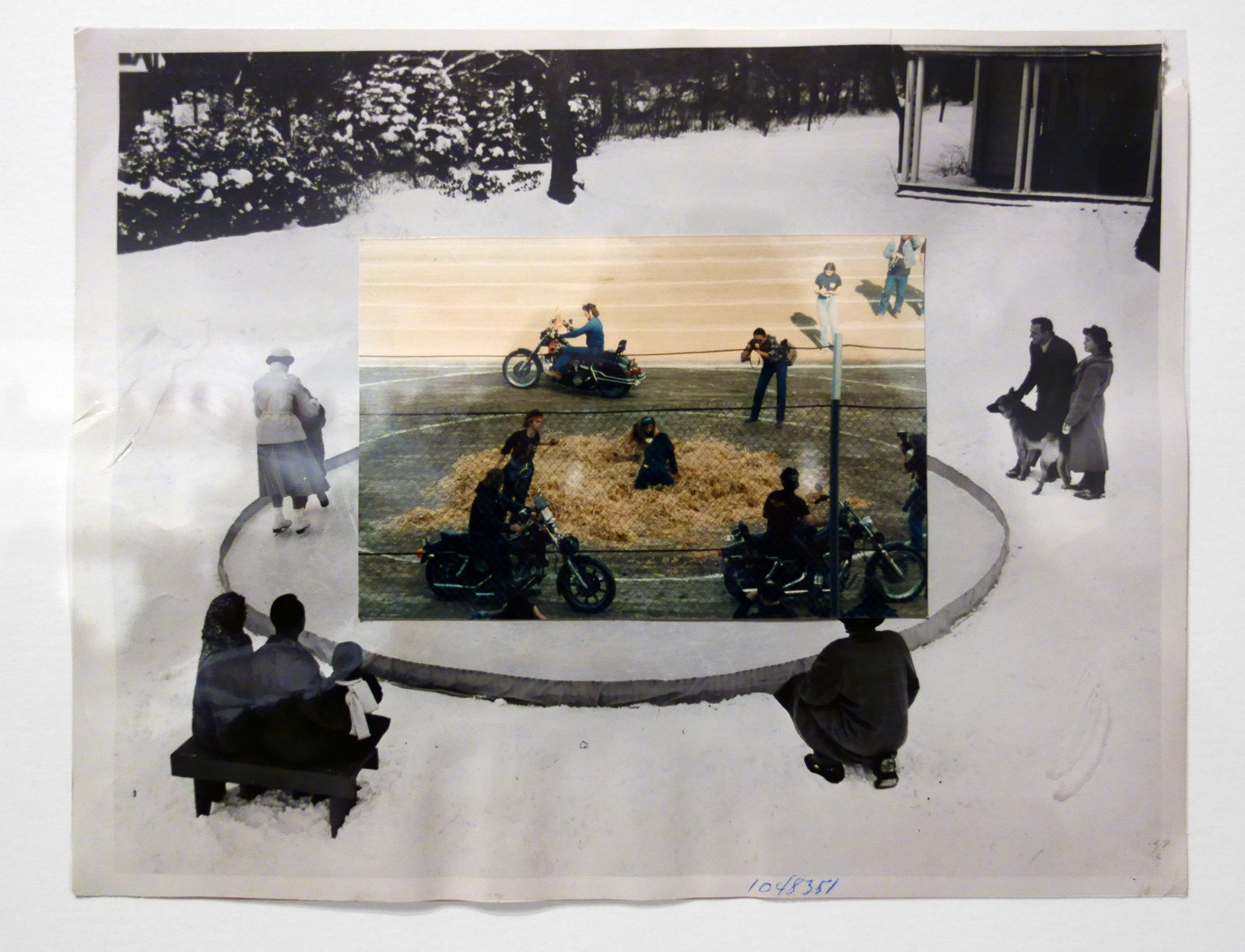
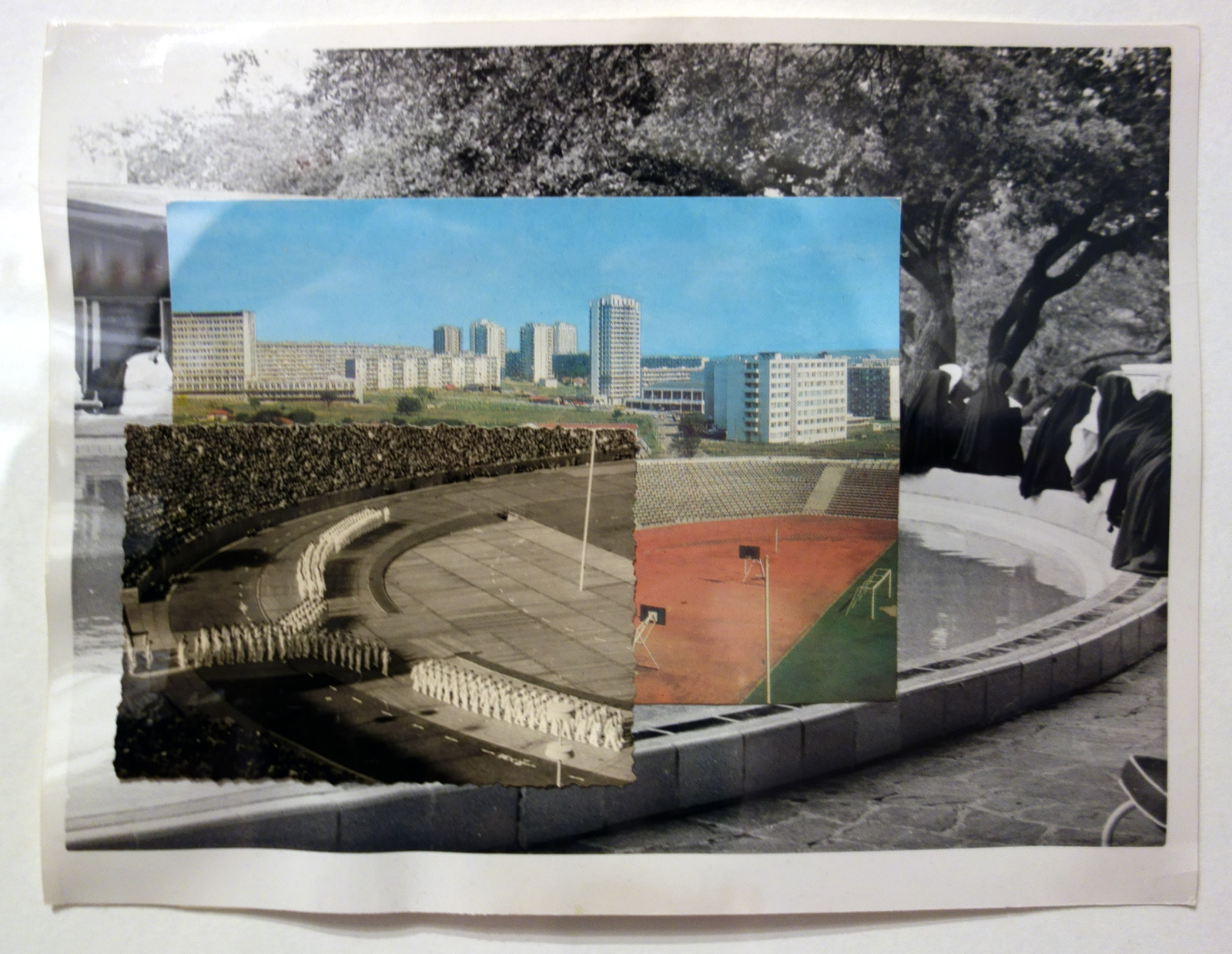
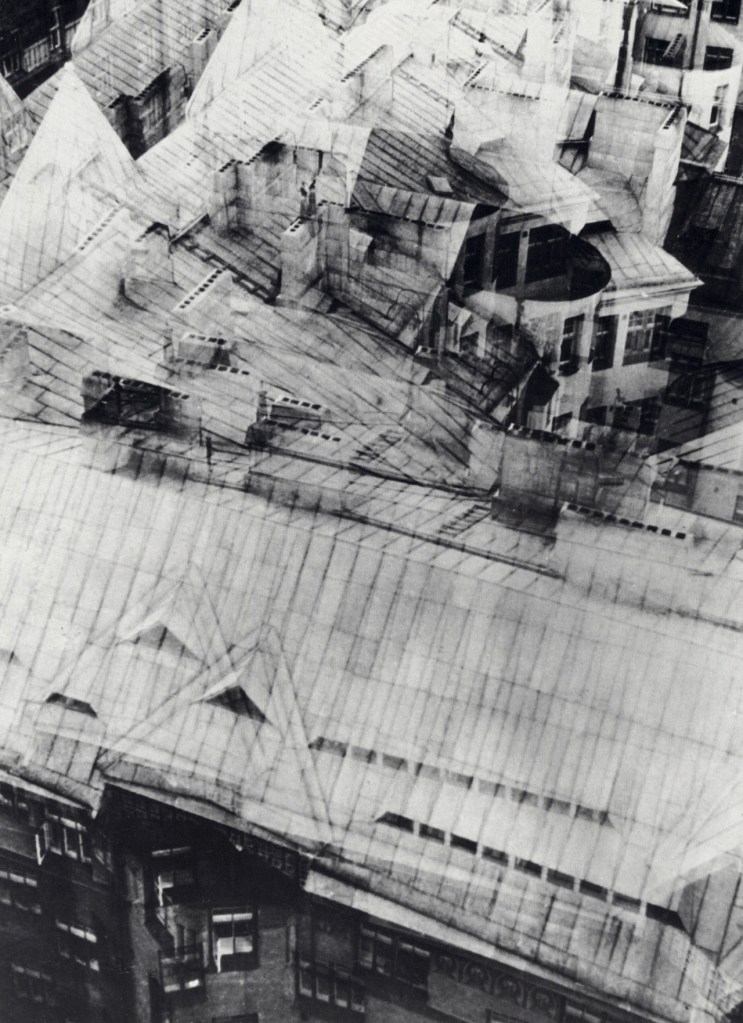
The work in the exhibition starts to come alive in Room 2 The Museum of There / Not there, where all of the things in the room are asked to stand in for an absence, where everything is a remnant or a trace. “Each thing here is a reminder of something else, it can be seen a surrogate or a partial representation.” The dissociative associations challenge the viewer to create their own connections and narratives from the objects placed before them. They mentally challenge the viewer to imagine. This challenge is further heightened in some of the best work in the exhibition, the series Portmanteau – definition: a large travelling bag; a word blending the sounds and combining the meanings of two others: podcast is a portmanteau, a made-up word coined from a combination of the words iPod and broadcast – in which visually disparate images (a cloud, a person blowing gum; a golf ball hovering over the cup, an eclipse) make unusual but sympathetic and intriguing connections across time and space. Photographs such as High wire act (2015) and The Fountainhead (2016, both below) are complex and creative examples of focused image making which reminded me of the Bauhaus collages of Josef Albers where Albers nowhere changes, “the rules of the game more profoundly than in his collages that feature a multitude of photographs. His collage of a bullfight in San Sebastian can be read as a short story or experimental film, where we as viewers recognise that we are being transported to a distant time and place, no less enchanting for its impossibility.” Randomness and synchronicity are back in the game.
Speaking of games, my favourite Pound objects in the exhibition were his Solander box series The game of things (2016, below). Their charm, wittiness, beauty, visual and mental acuity put paid to many other forced associations in the exhibition. He observes that, “Some things have little to do with each other until they come into contact.” But even when they do come into contact, they can still have very little to do with each other. Why The game of things series works so well is that Pound restricts himself (yes that Perec restriction that actually means something) in order / disorder to create something new and interesting, a document that undermines its own reliability (its a game!). The clinamen, the unpredictable swerve which, according to Lucretius occurs “at no fixed place or time” and which provides the “free will which living things throughout the world have” appears. Pound’s free will combines disparate elements in a pared down aesthetic, a playful game, where there is no need for thousands of photographs to focus his ideas.
While Pound’s description of multiplicities, repetitions and differences is engaging in a humorous and ironic way as “lines of escape from the generalities of society,” they create distance from laws and norms even while still re-enacting them. Much more interesting are Pound’s subversions of a singular reality through the overlapping of images – both mental and physical. While existing in a physical space, the “game of things” actually lives in my mind because humanness is the ultimate clinamen.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Word count: 1,372
Many thankx to the National Gallery of Victoria for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image. See Part 1 of the posting.
A page from Georges Perec’s book Species of Spaces (Espèces d’espaces) and Other Pieces 1974
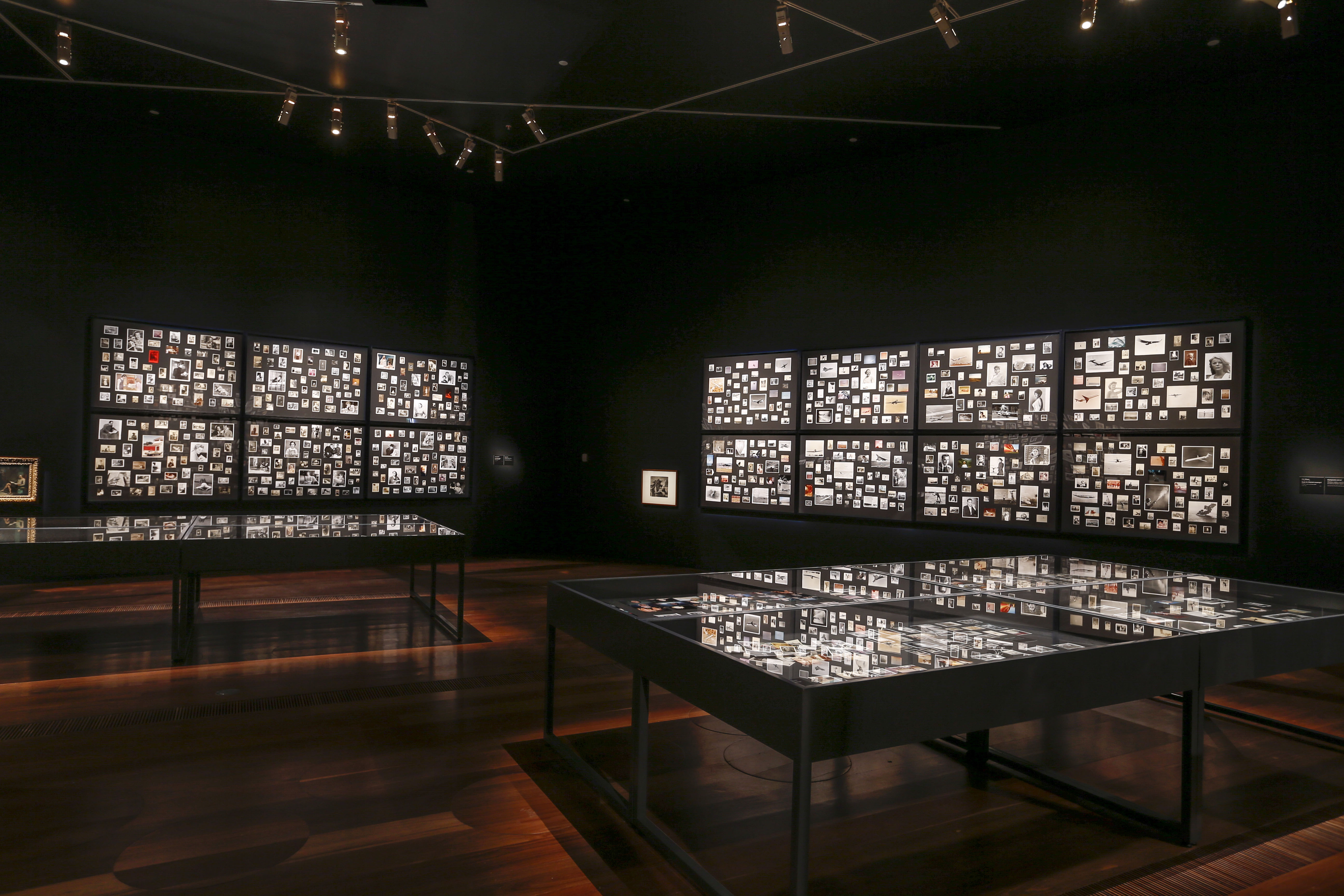
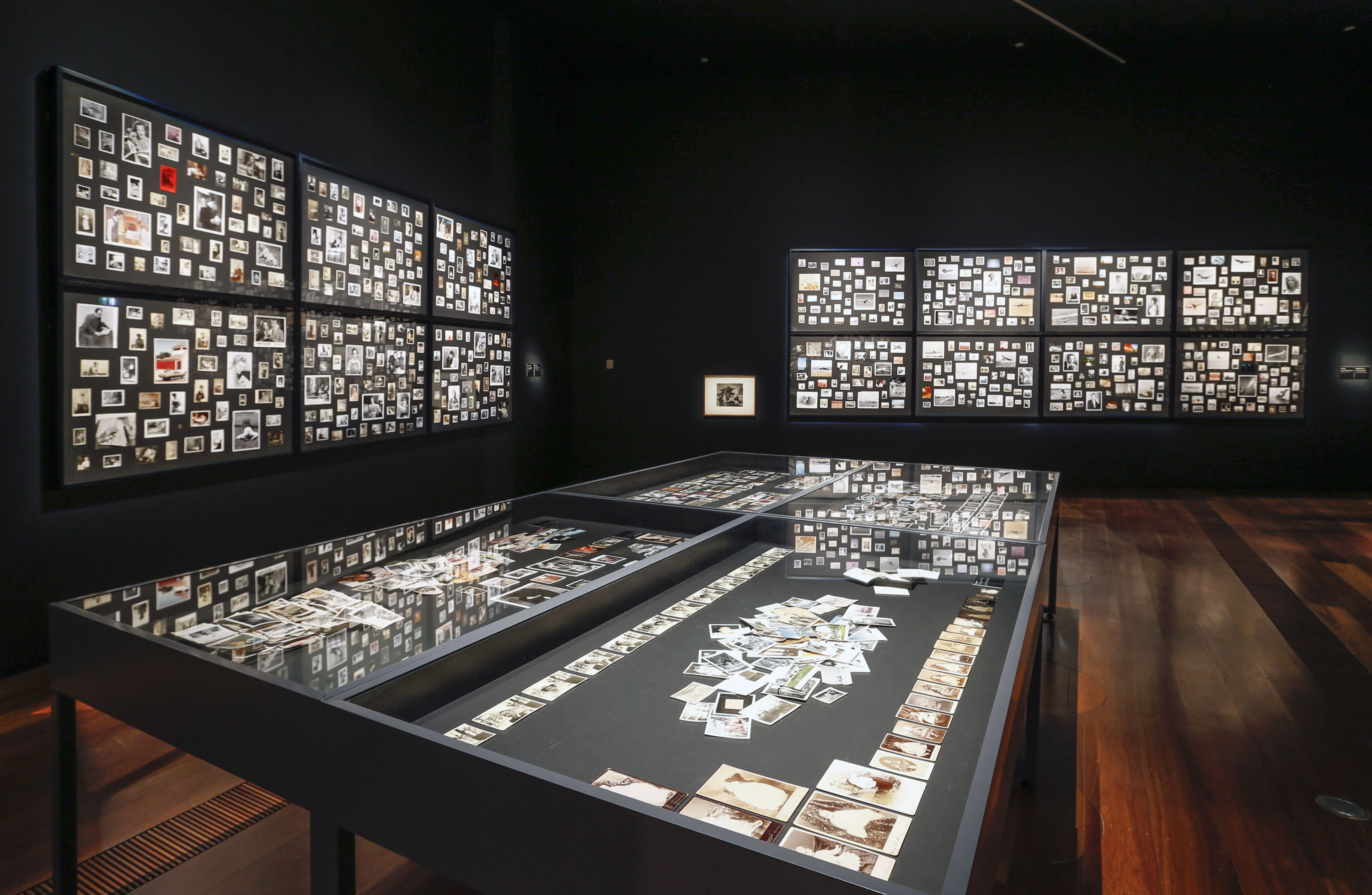
Entrance to the exhibition Patrick Pound: The Great Exhibition with the work The photographer’s shadow (2000-2017) right
Photo: Wayne Taylor
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s work The photographer’s shadow (2000-2017, detail)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s work The photographer’s shadow (2000-2017, detail)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The photographer’s shadow (detail)
2000-2017
Site specific installation comprising photographs collected by the artist
Video: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
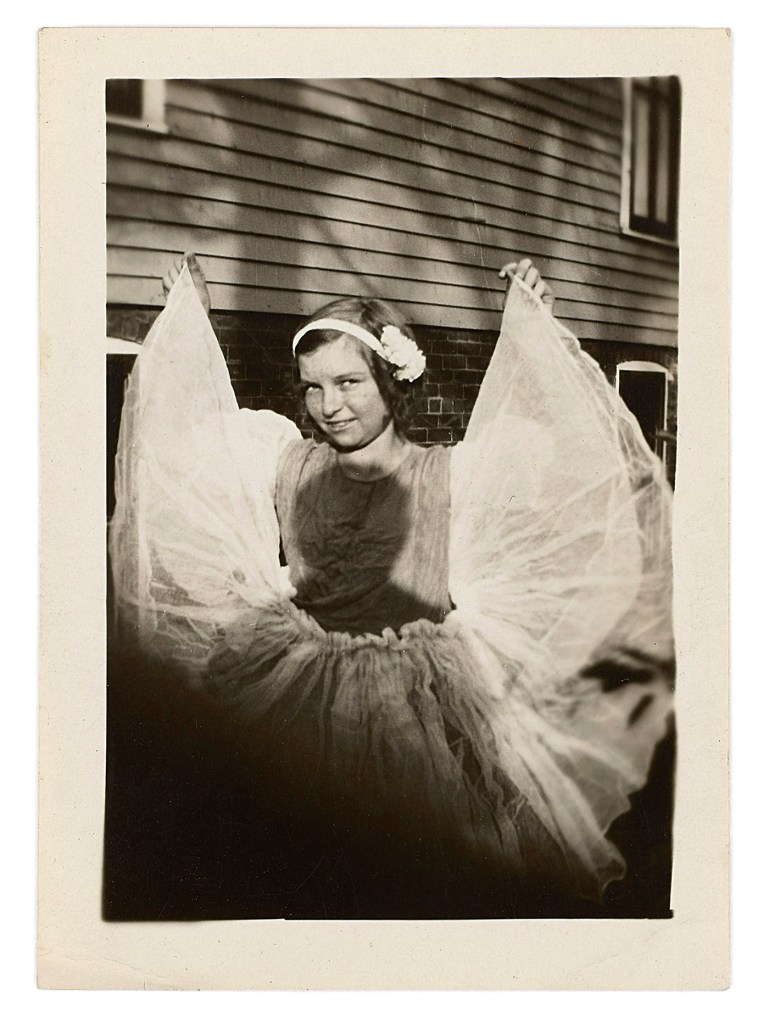

Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The photographer’s shadow (detail)
2000-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
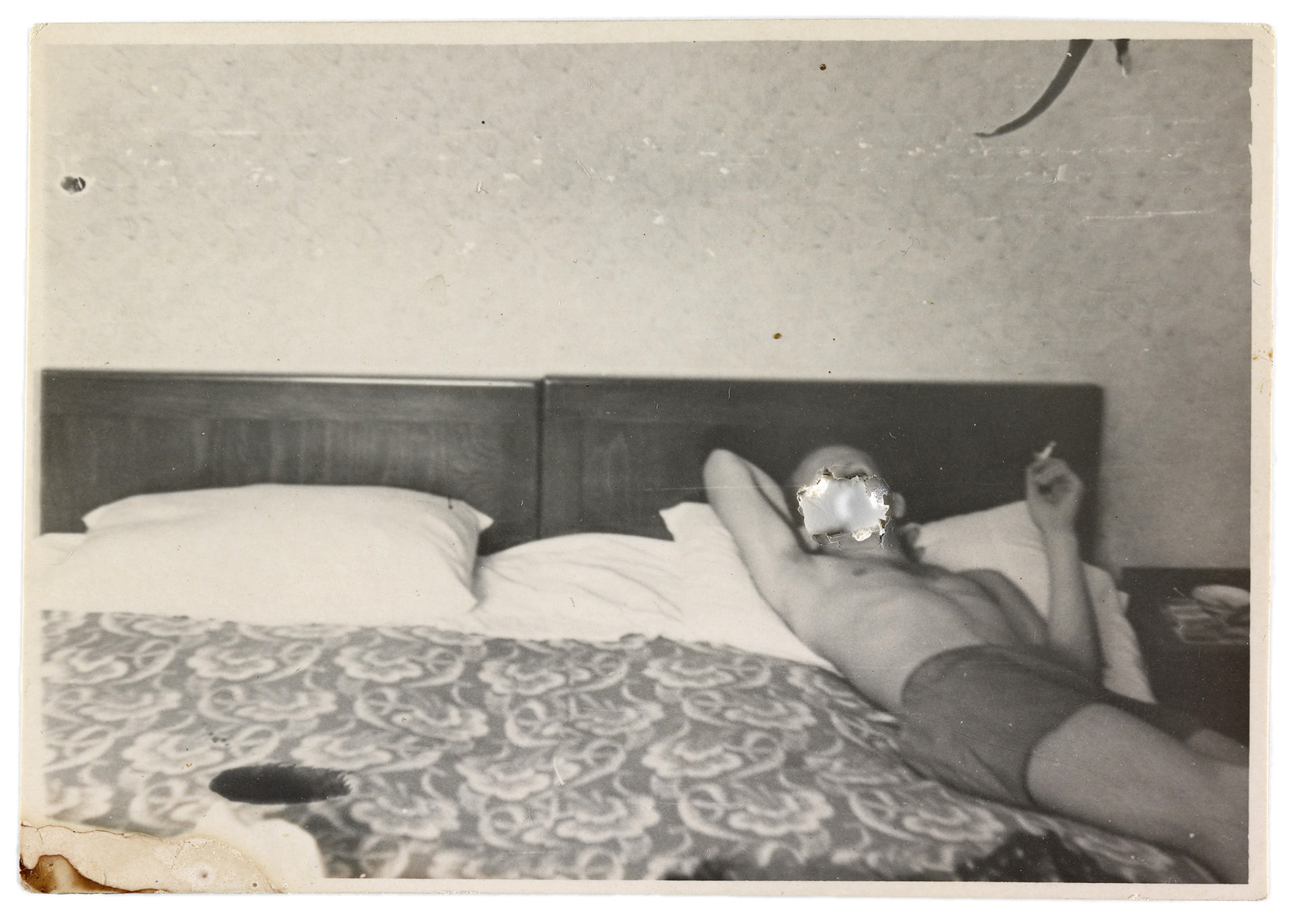
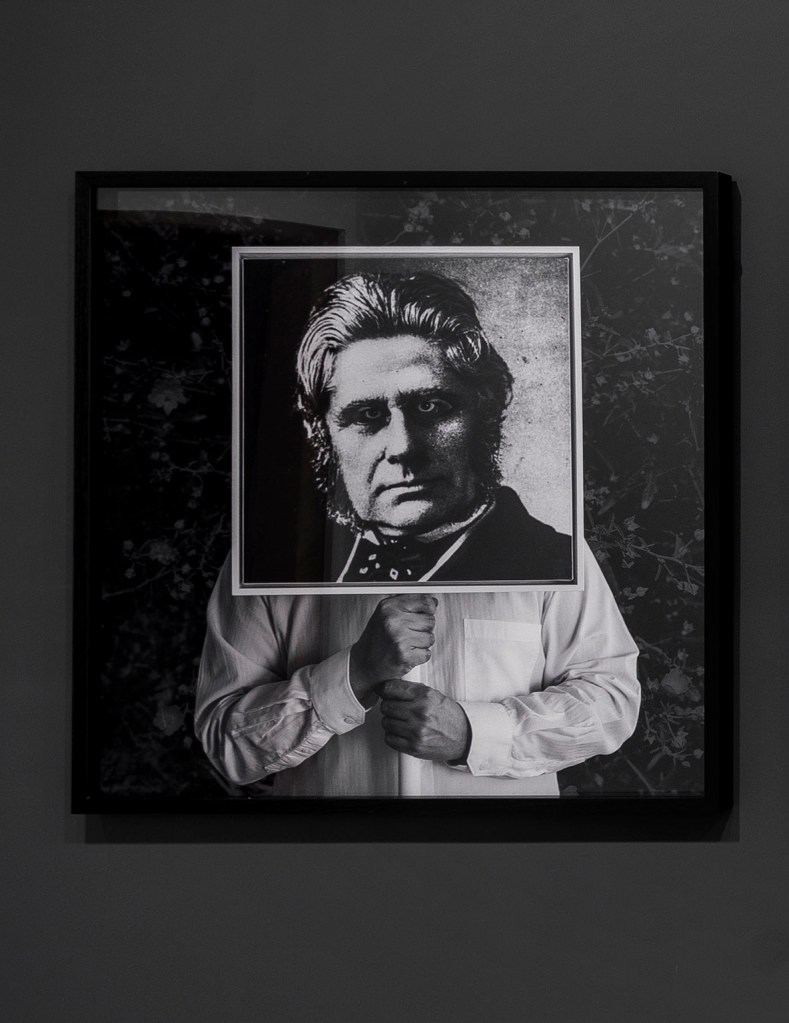
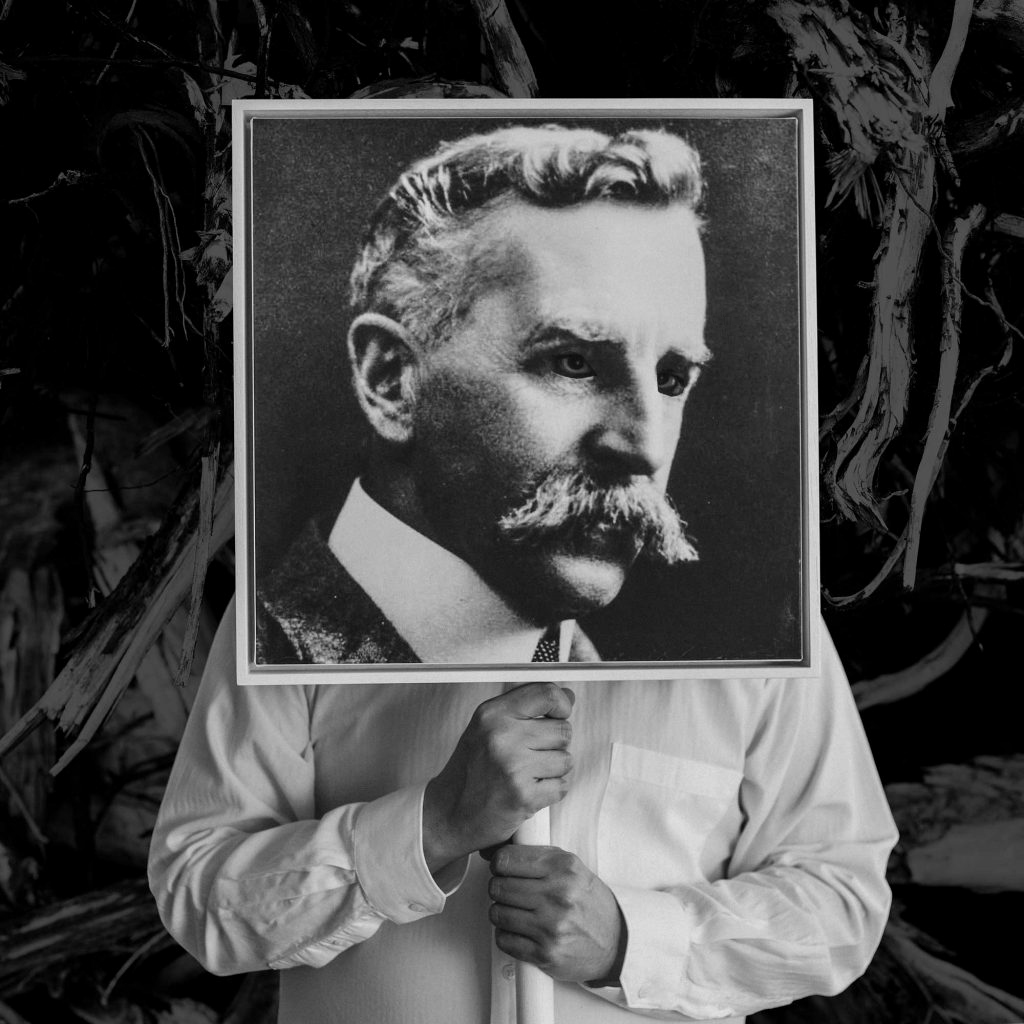
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
People holding cameras (detail)
2007-2017
Site specific installation comprising photographs collected by the artist
Video: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
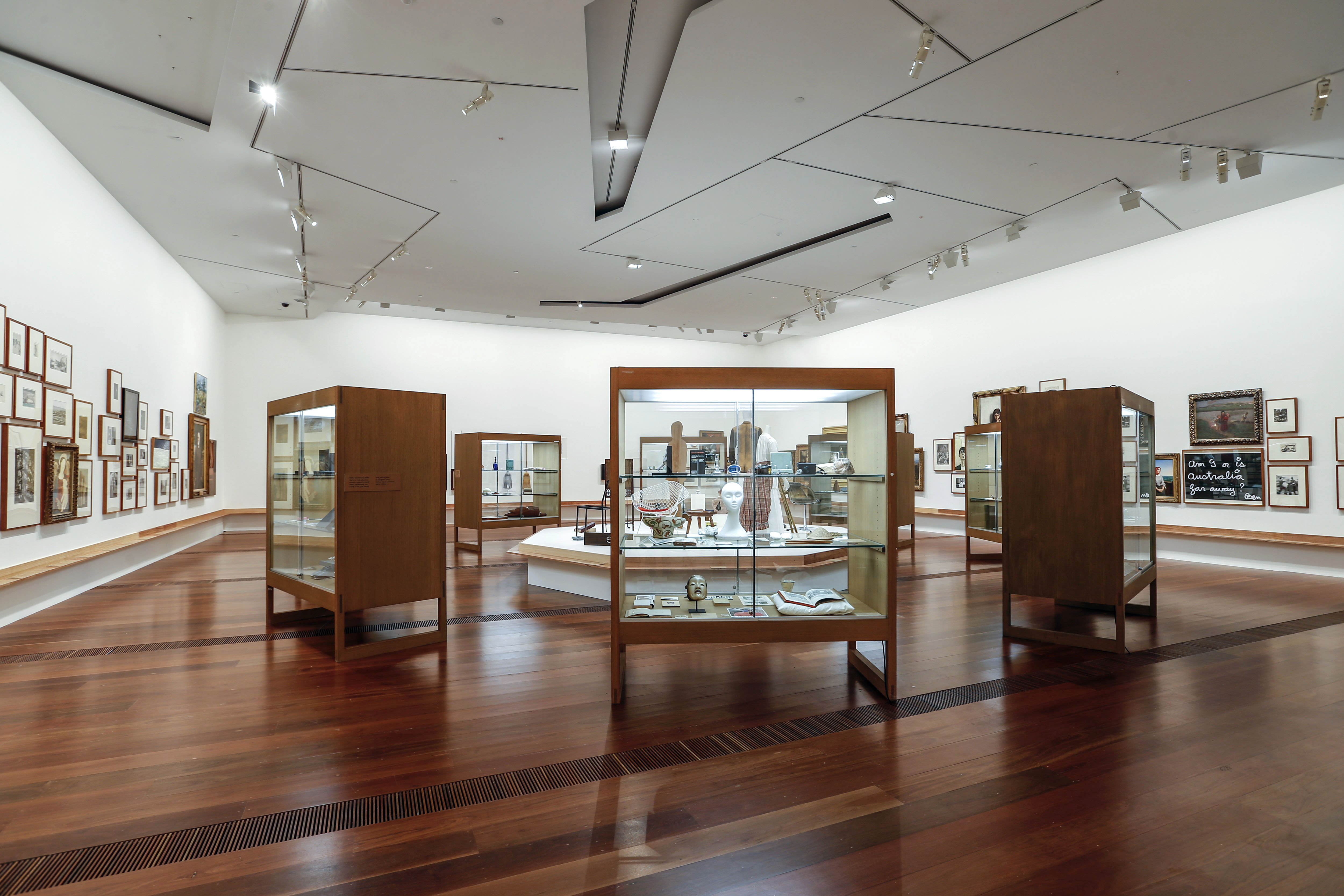
Room 1
Installation views of the exhibition Patrick Pound: The Great Exhibition at NGV Australia, Federation Square. Presented as part of the NGV Festival of Photography.
Photos: Wayne Taylor
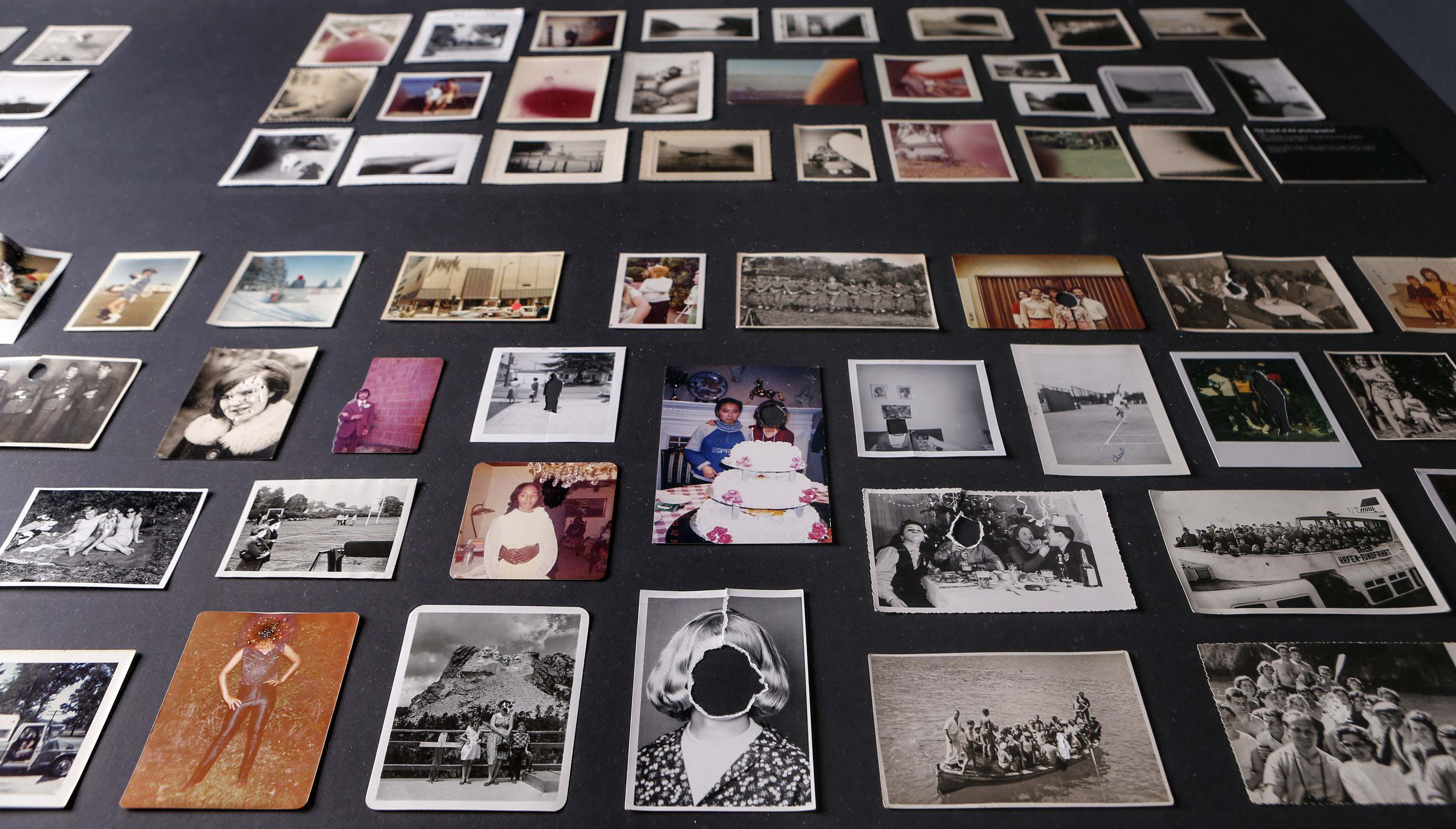
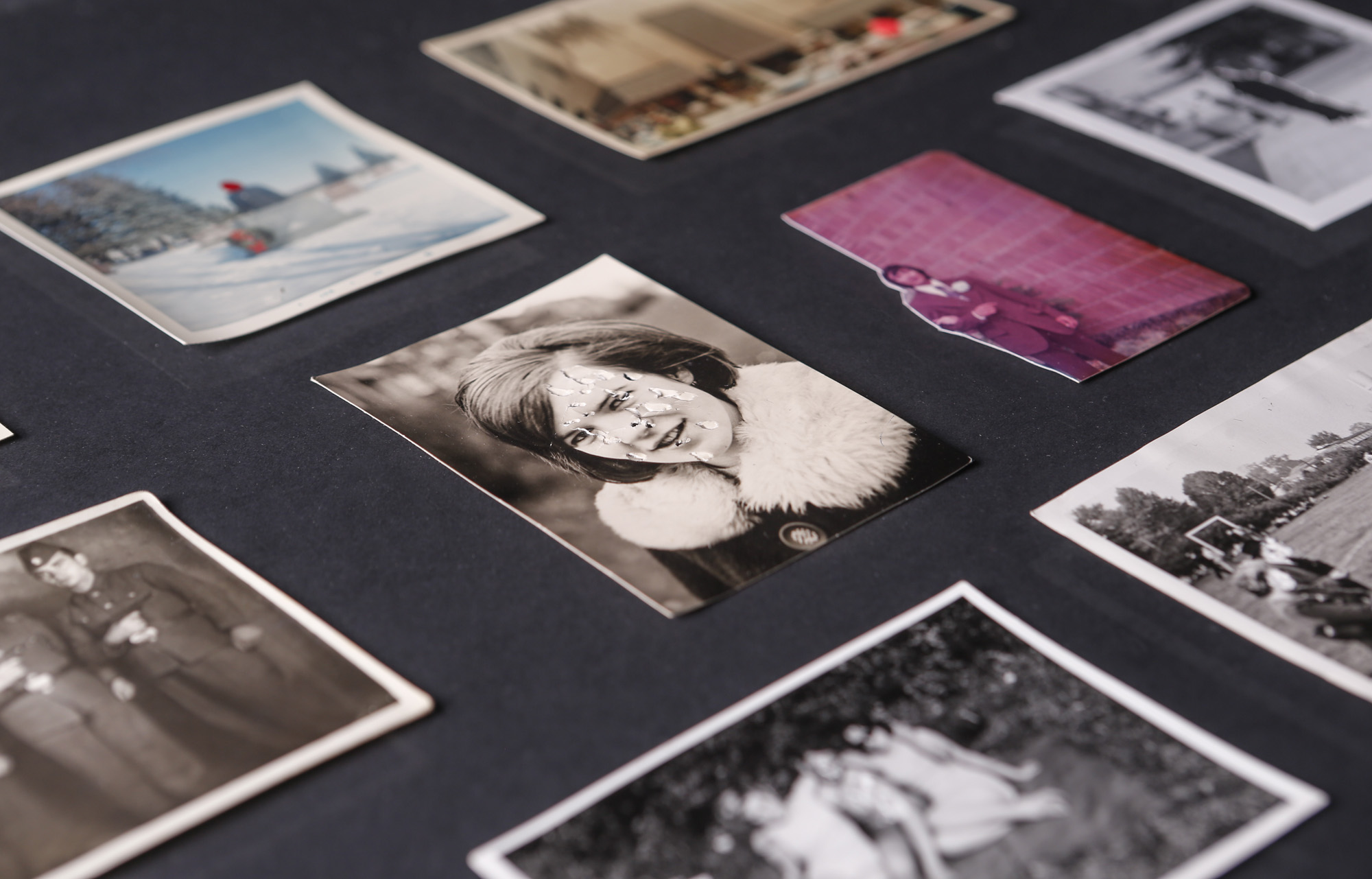
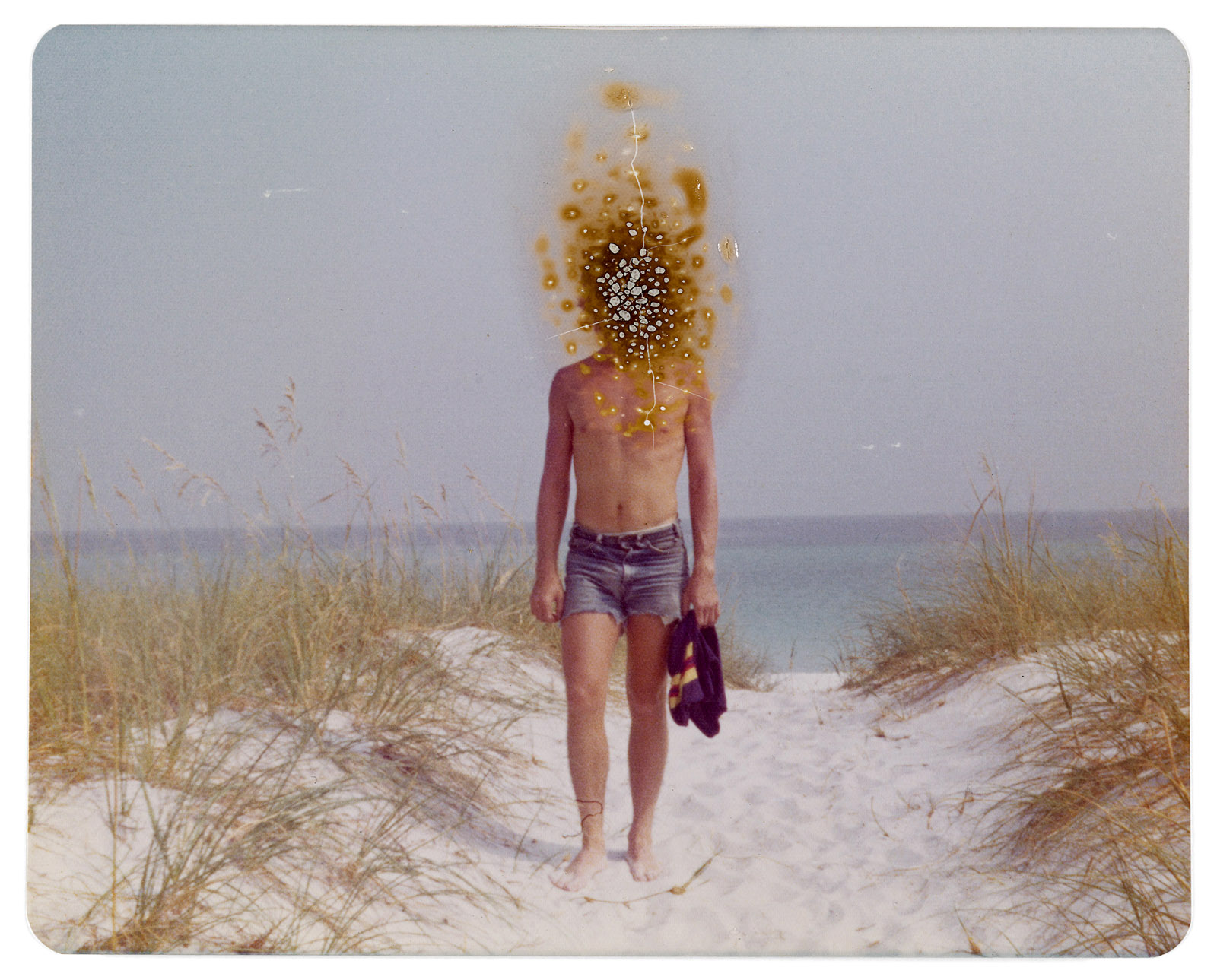
Installation views of Patrick Pound’s work Damaged 2008-2017 (detail)
Photos: Wayne Taylor
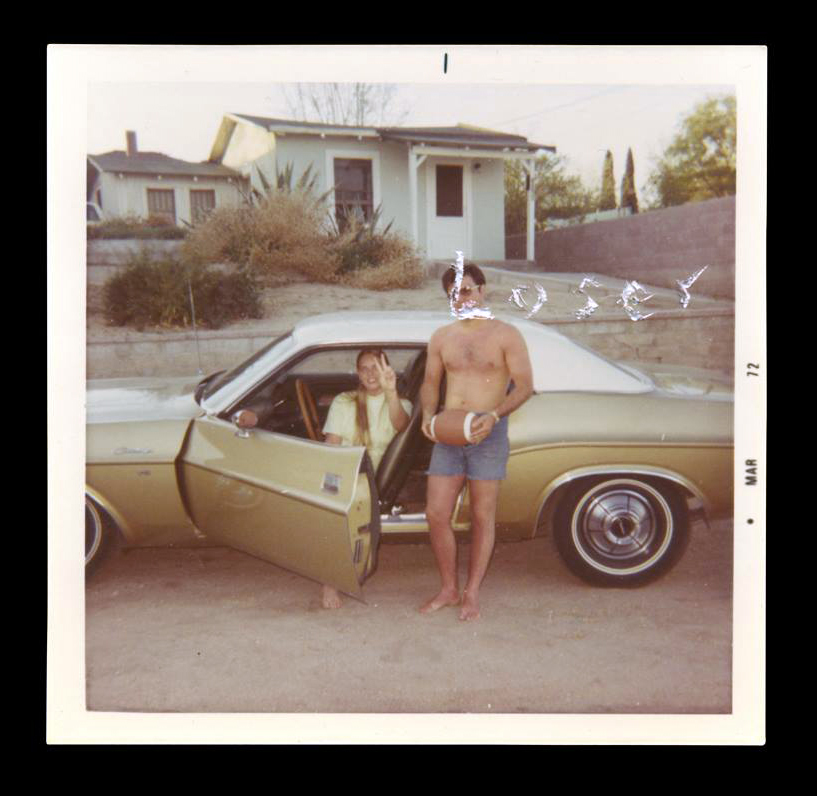


Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Damaged (details)
2008-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s work People holding cameras 2007-2017 (detail)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s work Listen to the music 2016-2017 (detail)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s work Self portraits 2007-2017 (detail)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
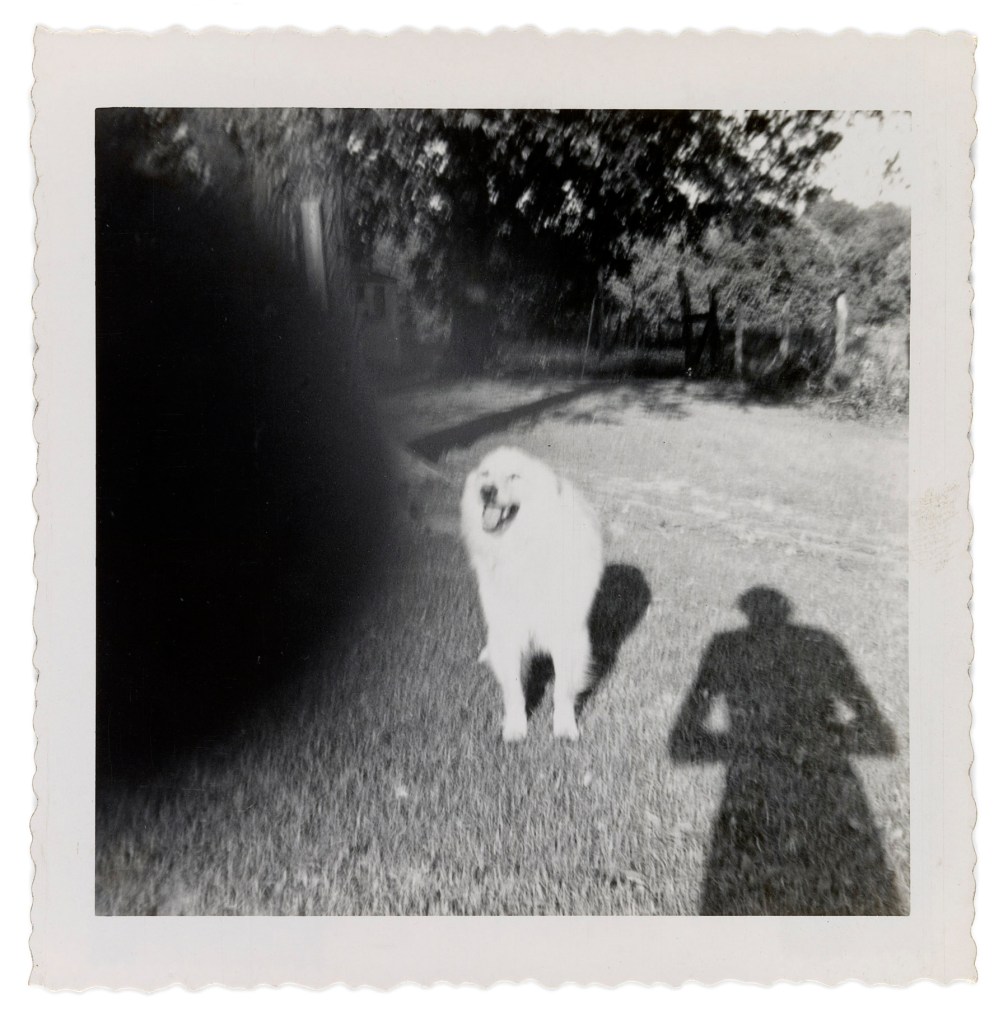
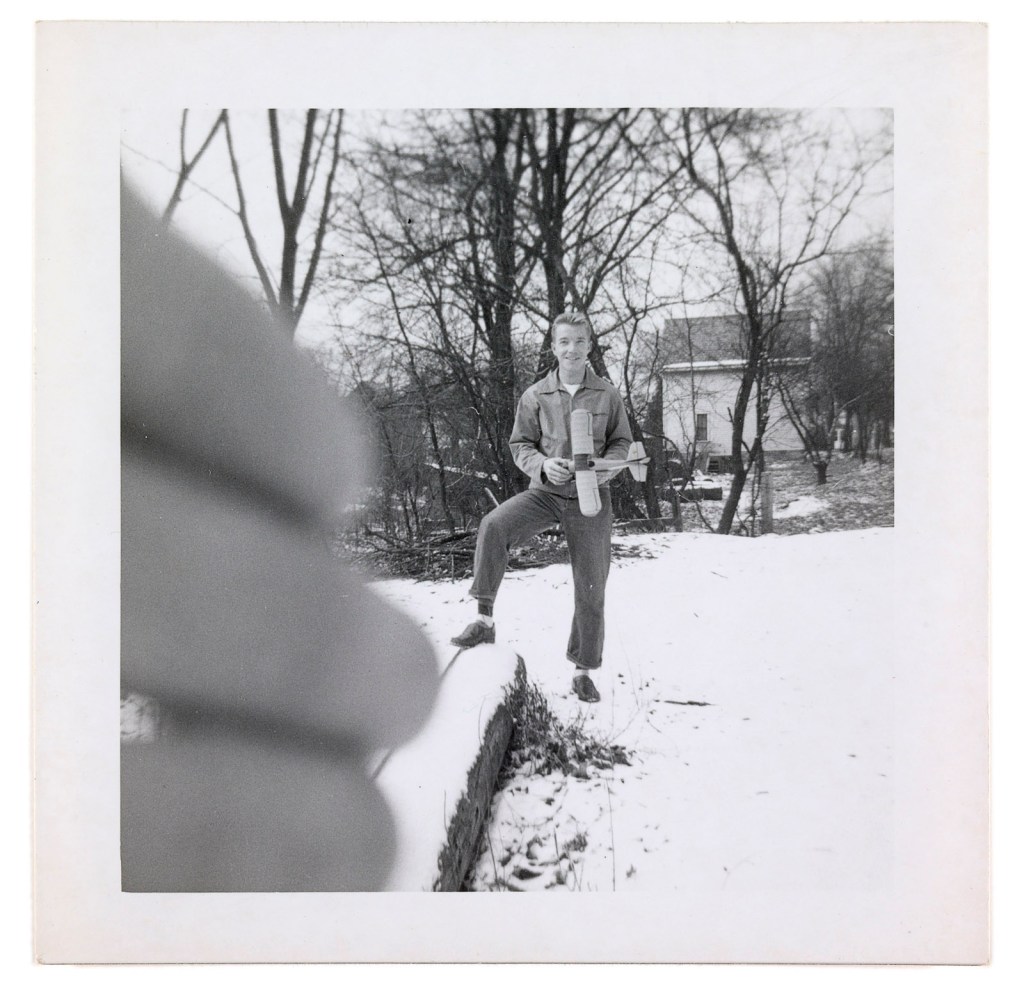


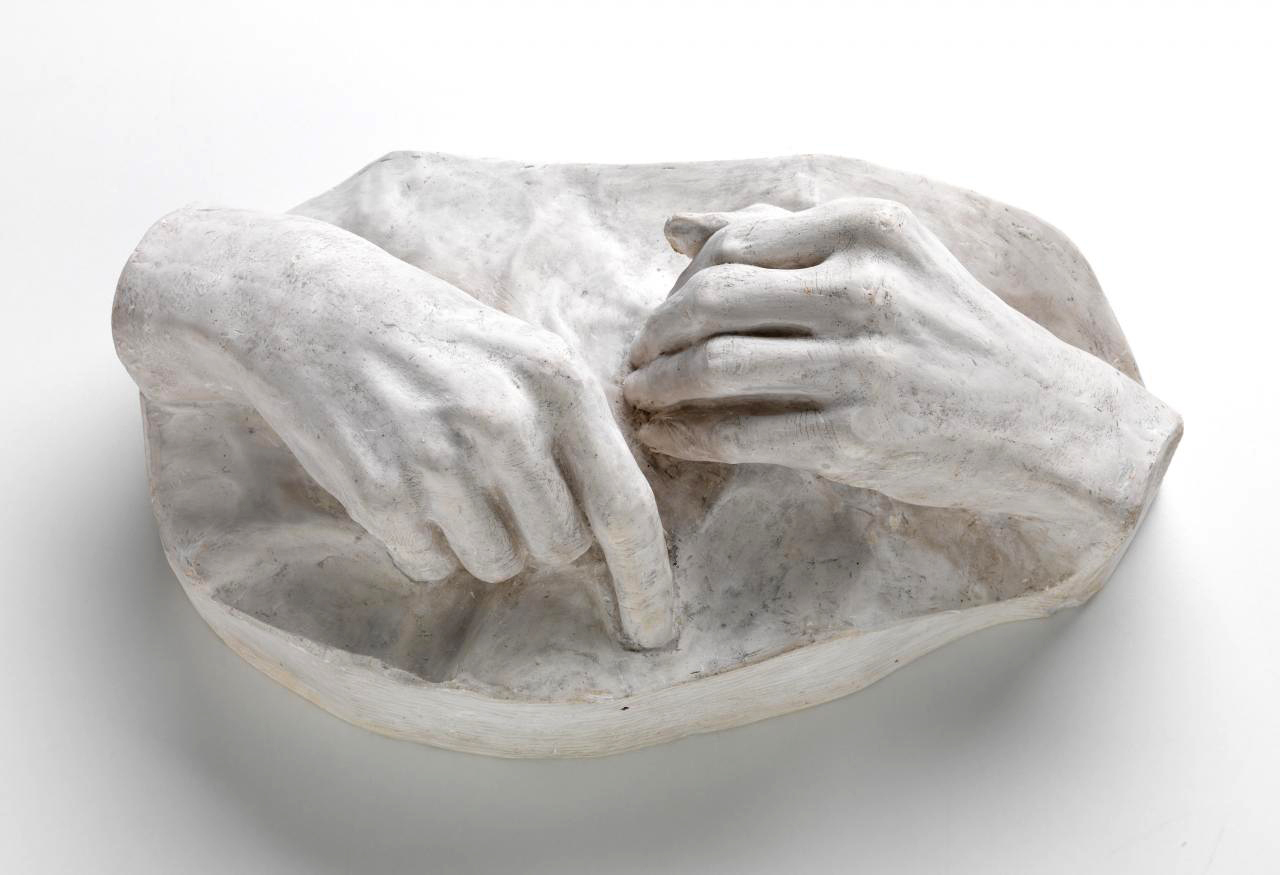
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian 1962- )
The hand of the photographer (details)
2007-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
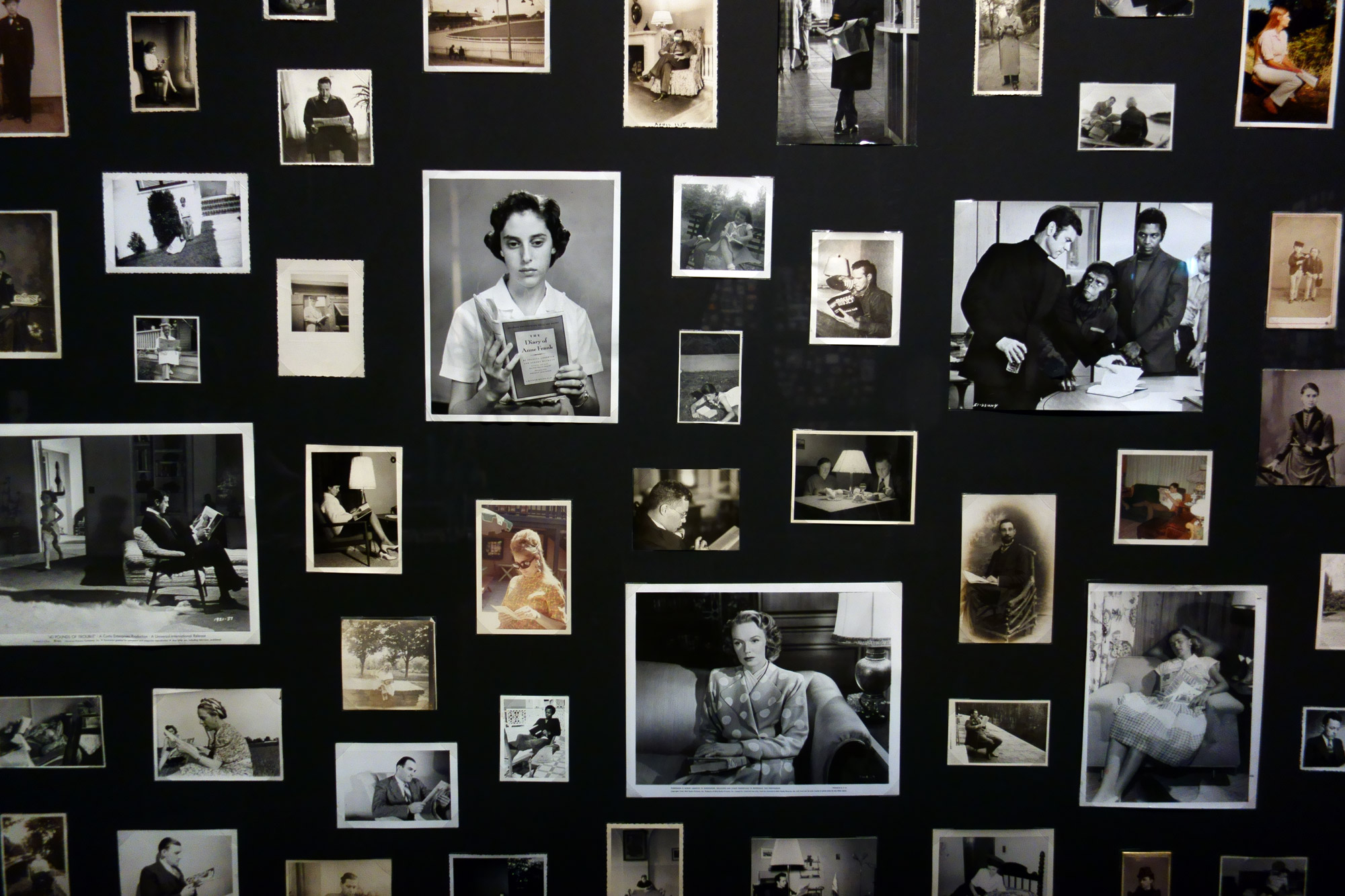

Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian 1962- )
The readers (installation view details)
2016-2017
Site specific installation comprising photographs collected by the artist and works from the NGV Collection
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Photography and air (installation view details)
2016-2017
Site specific installation comprising photographs collected by the artist and works from the NGV Collection
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Room 2
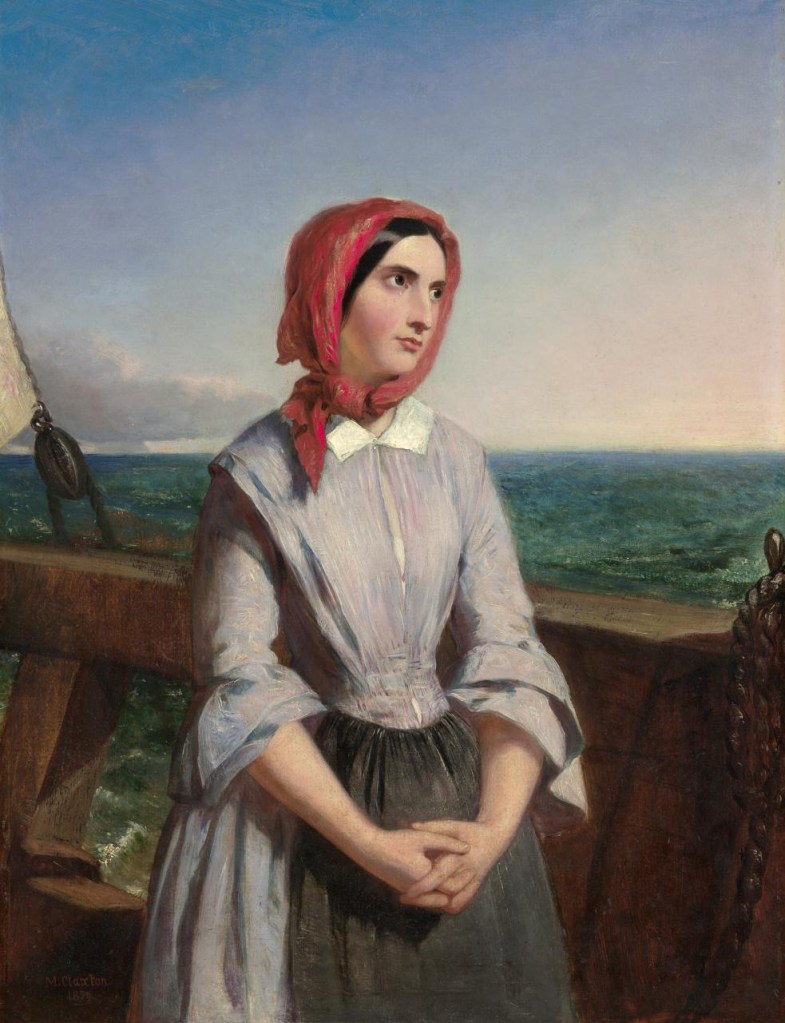
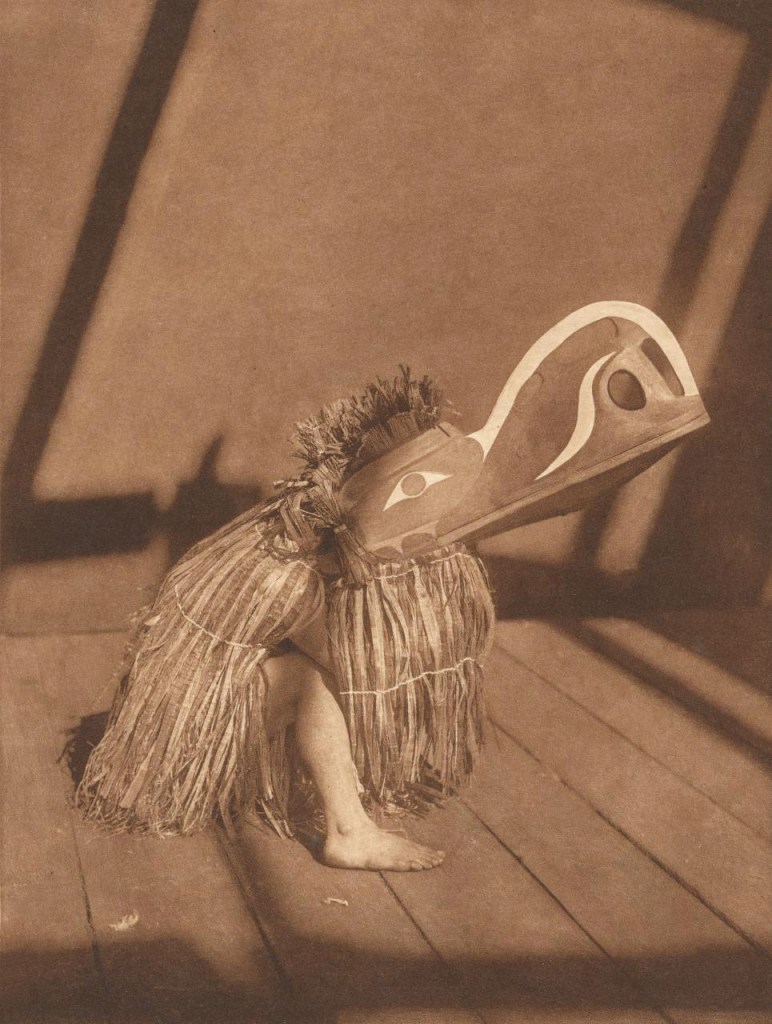
Installation views of The Museum of there / Not there 2016-2017 (detail) with (above) John Brack’s Self-portrait (1955), David Potts Cat show, London (1953), Eugène Atget’s Eclipse (1911, top right), Lee Friedlander’s Mount Rushmore (1969, middle right) and Erich Salomon’s Banquet at the Quai d’Orsay, Paris, August 1931 (bottom right).
Photos: Wayne Taylor
Erich Salomon (German, 1886-1944)
Banquet at the Quai d’Orsay, Paris, August 1931. ‘A le voilà, le roi des indiscrets!’
1931, printed 1970
Gelatin silver photograph, ed. 3/100
Purchased, 1971
Here are some examples of how
The Museum of There / Not there works:
From Rodin’s marble head
without its helmet …
to a sculpture that’s lost its head
yet remains holding onto its hair …
and from a broken comb found in
an Egyptian tomb to a novelty wig …
it is full of missing parts,
surrogates and substitutions,
apparitions and disappearing acts.
Every representation is, after all,
something of a conjurer’s trick.
Patrick Pound
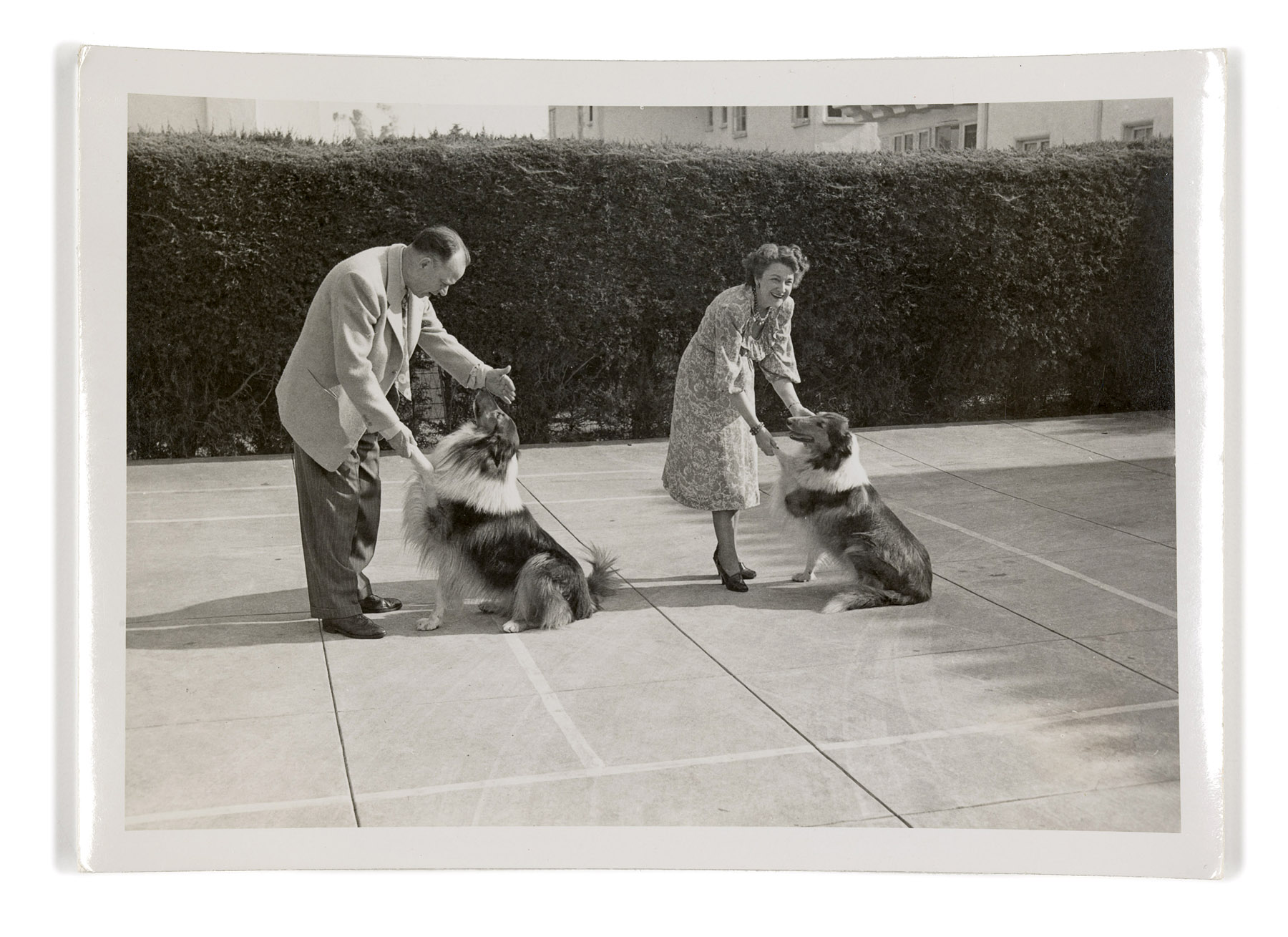
The Museum of There / Not there is a collection of my things, and the NGV’s things. All of the things in this room are asked to stand in for an absence. To make its presence shimmer.
From a ventriloquist’s dummy to a copy of Jean-Paul Sartre’s Being and Nothingness; from a photo of an empty shell to a nineteenth-century bustle; from an American toy border patrol car to a painting of an immigrant – everything in this room is a remnant or a trace. They speak of being there or not being all there.
Each thing here is a reminder of something else, it can be seen a surrogate or a partial representation. There are things that are unfinished or incomplete; there are ghosts and traces; things that are missing parts or that are simply missing. Meanings too might have changed, or become fluid, with the passing of time. In effect, this is a giant collage where things are asked to stand in for other things. They are material realisations of ephemeral and ethereal states.
There is also a soundtrack, featuring music ranging from Tom Petty’s “Refugee” to Aretha Franklin’s “I Wonder (Where You Are Tonight)”.
Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The Museum of There / Not there (installation view details)
2016-2017
Site specific installation comprising objects collected by the artist, a selection of works by the artist, and works from the NGV Collection
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Passageway
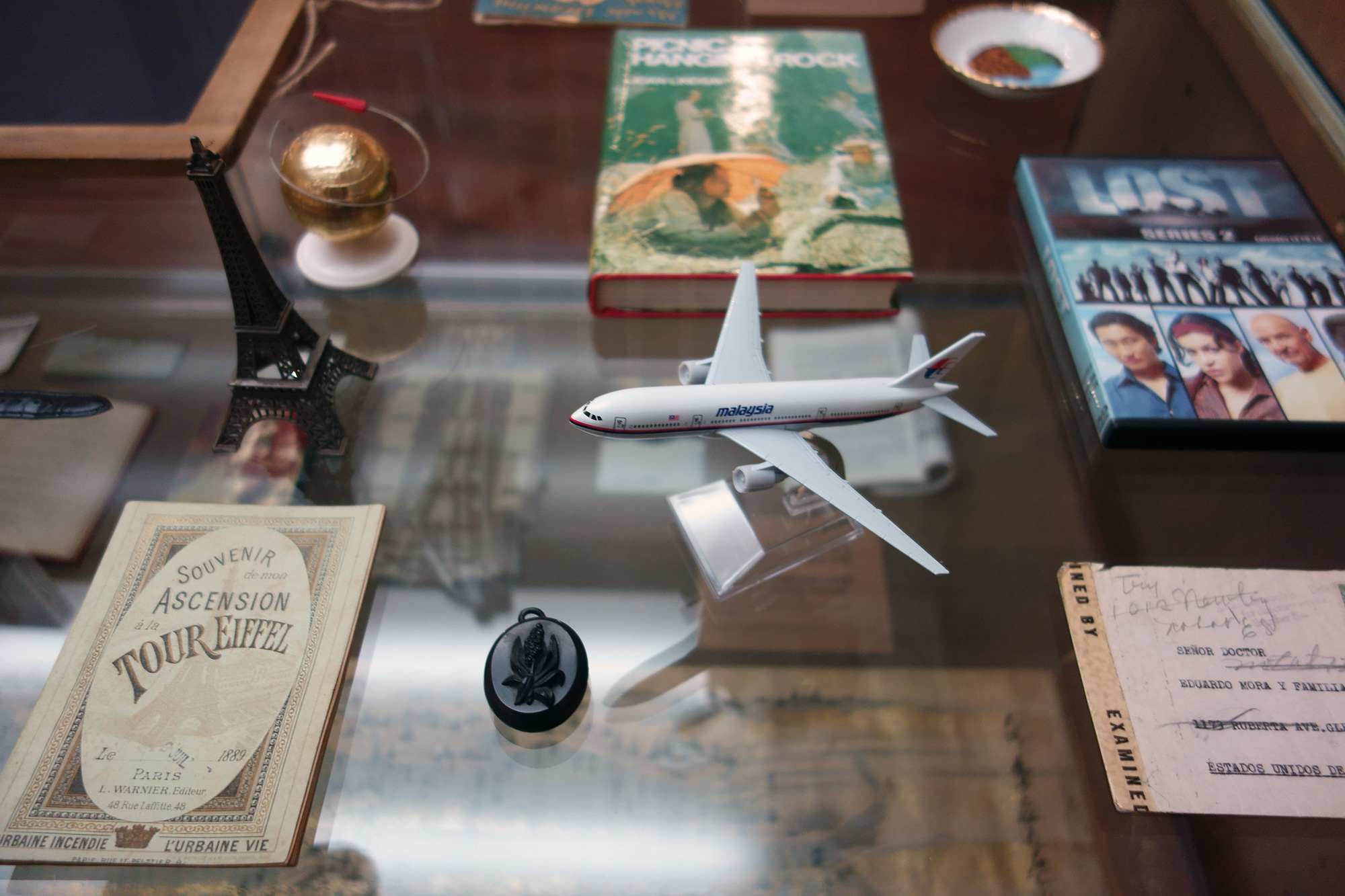
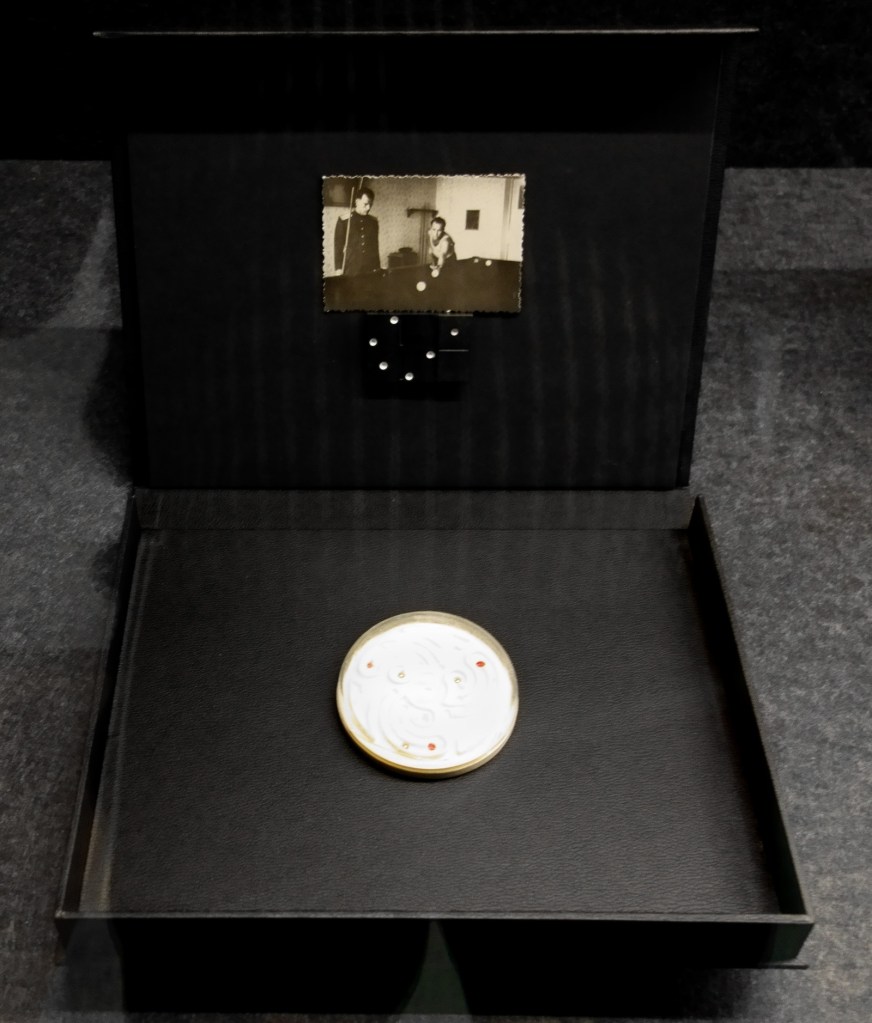
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The game of things (installation view detail)
2016
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
“Photographs and things reflect on each other as if in a game or a puzzle.” ~ Patrick Pound
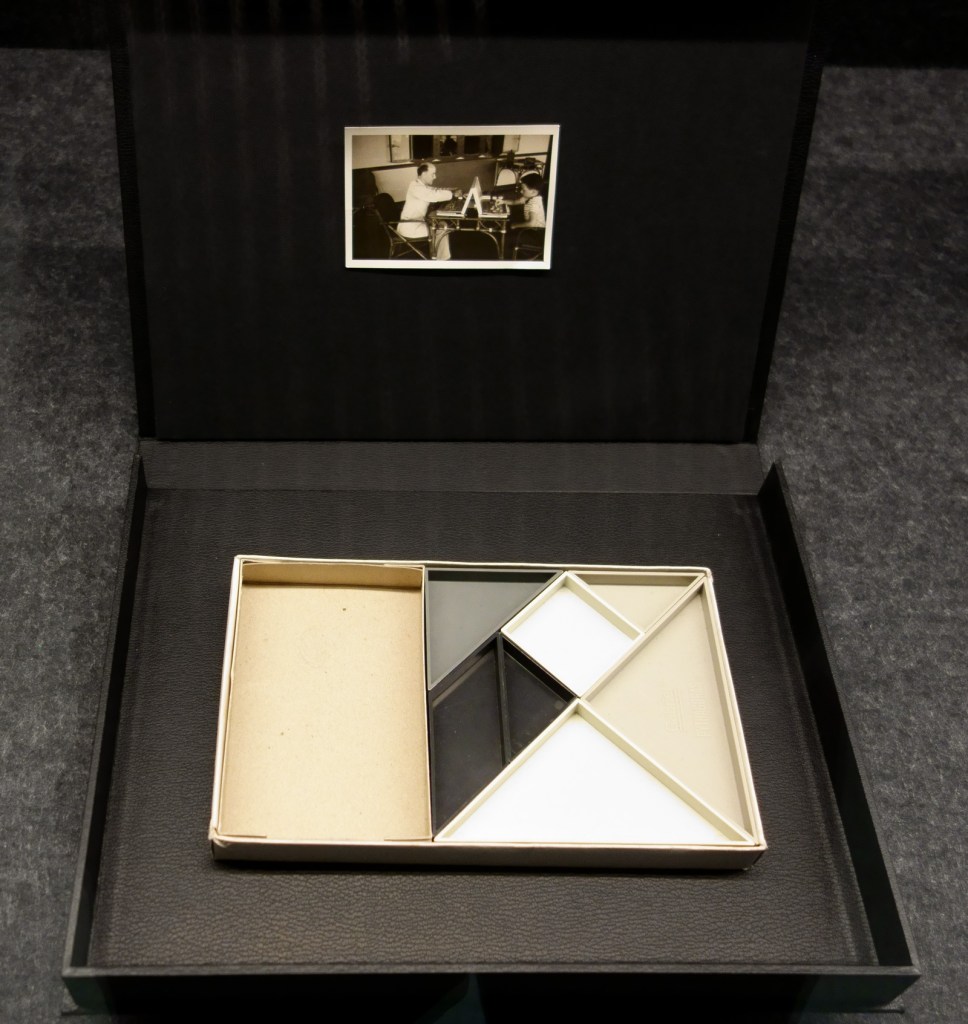
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The game of things (installation view detail)
2016
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
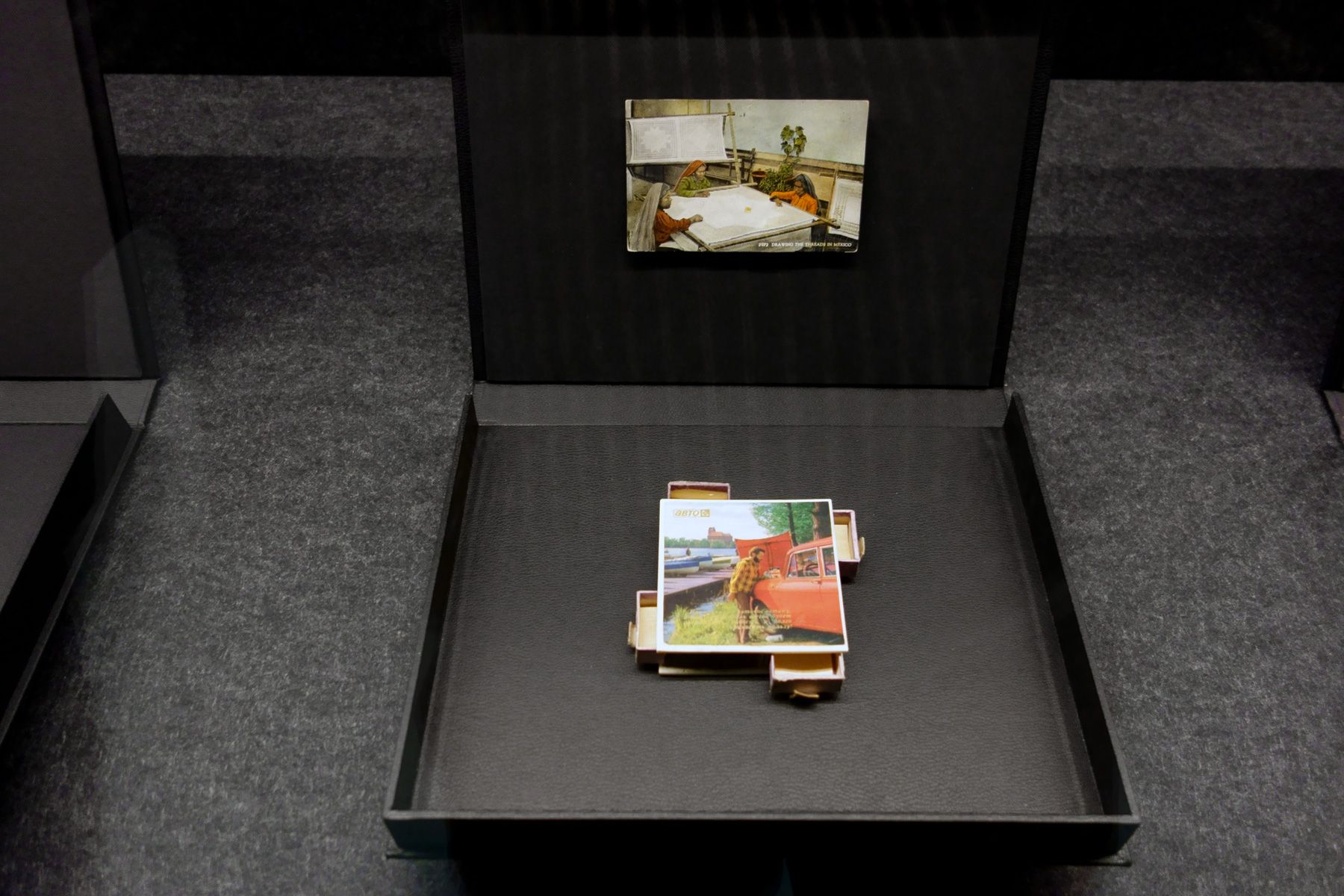
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The game of things (installation view detail)
2016
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
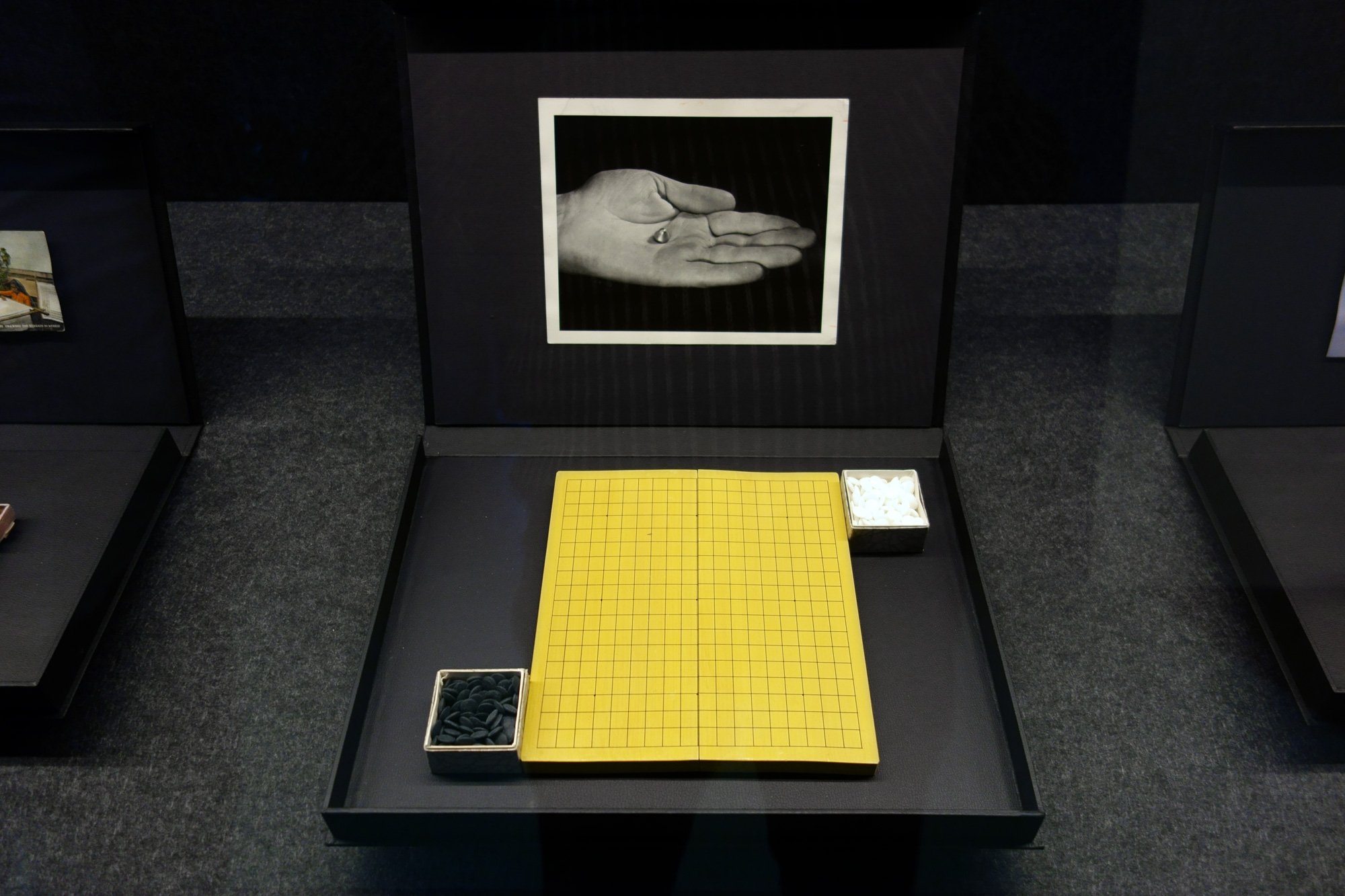
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The game of things (installation view detail)
2016
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The game of things (installation view detail)
2016
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
“To collect is to gather your thoughts through things.”
“When I began collecting photographs I was thinking of the way the camera reduces the world to a list of things to photograph. I thought that to photograph was to collect the world in the form of pictures… As writer Susan Sontag said, photography is not so much a representation of the world but a piece of it. Collecting found photos is like taking cuttings from the world. For me it is a form of collage.”
“I did suggest the call the show ‘Enough Already’ but they went with ‘The Great Exhibition’. Perhaps the best thing about that is that even people who really don’t like it will still have to call it ‘The Great Exhibition’.”
“The camera reduces the world to a list of things to photograph. When I click BUY on eBay – for me that’s the equivalent of taking a photograph. The mouse is my camera.”
“As Honoré de Balzac said, “A hobby, a mania, is pleasure transformed into the shape of an idea!””
“Some things have little to do with each other until they come into contact.”
“To collect is to look for like-minded things. One thing inevitably leads to another. When you pair one thing with another, some things start to make sense – or not. In the end, every collection is, after all, a reflecting pool.”
“Every representation is, after all, something of a conjurer’s trick.”
“Art traditionally becalms her sitters.”
“Photography stops people in their tracks. Eventually every photograph is a photograph of a dead person. The camera is an idling hearse.”
Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound: The Great Exhibition is the first comprehensive exhibition of the New Zealand-born, Melbourne-based artist. An avid collector, Patrick Pound is equally interested in systems and the ordering of objects: an attempt, perhaps, to make things coherent. As Pound says, ‘to collect is to gather your thoughts through things’.
Through complex arrangements and installations of objects drawn from the artist’s expansive archives, Pound’s work playfully and poetically explores the art of collecting, and the ways in which things can hold and project ideas. For this exhibition Pound has created several vast new collections, which he describes as ‘museums of things’. Objects that are seemingly redundant or overlooked are meticulously collected by the artist and put back into ‘use’ in these museums. There are museums of falling, sleepers, and of holes.
The Museum of there / not there houses objects ranging from a souvenir spoon to a mask, a mourning locket to a painted ruin – one thing standing in for another. Within each museum a new logic or narrative is created for the viewer to unravel or identify. In several of Pound’s museums, works from the NGV Collection are grouped into their own categories or sit alongside his ‘things’, with the artist inviting us to rethink these works and consider what it means to collect.
Text from the NGV
Room 3
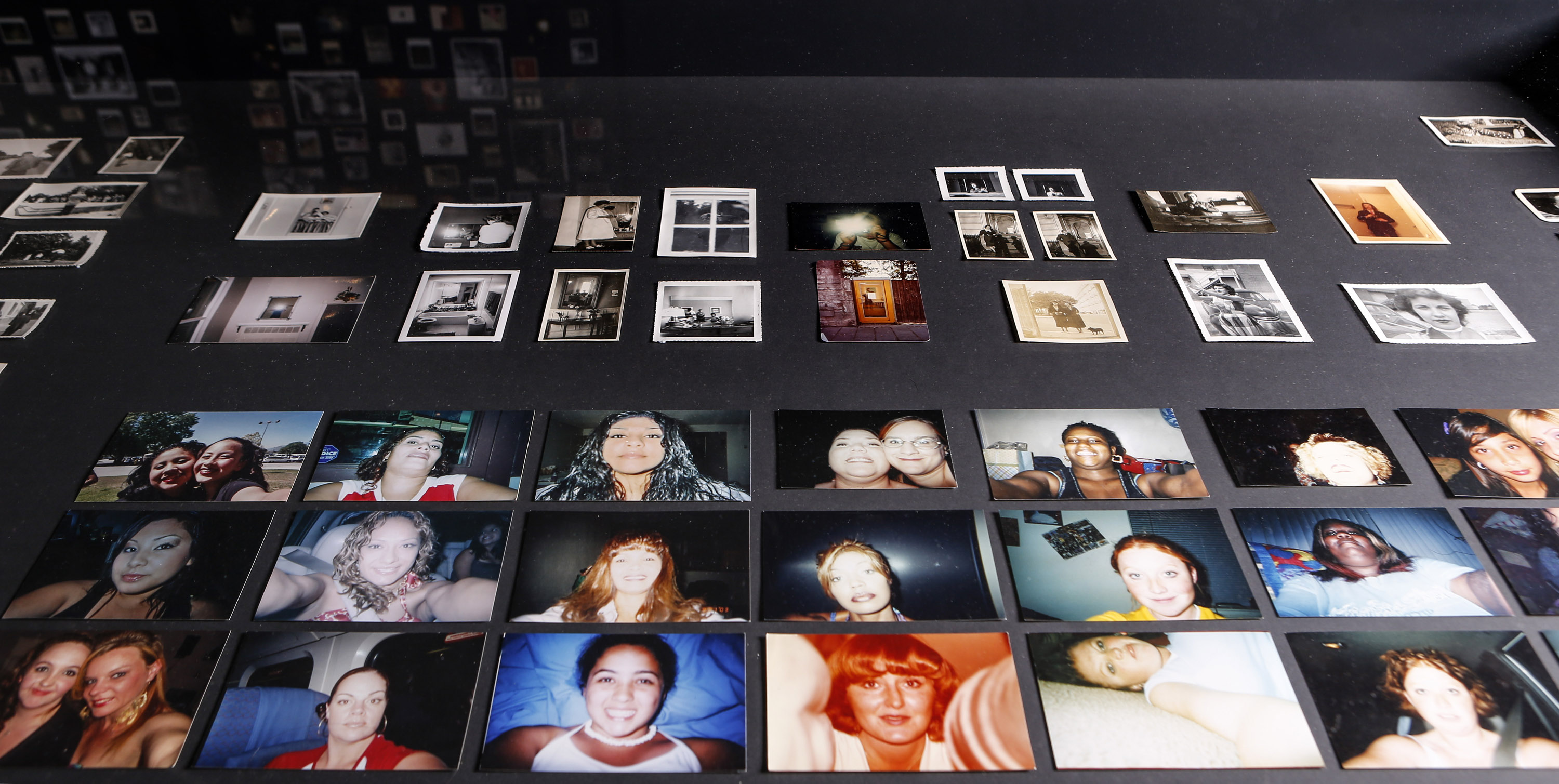
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Pairs (and the double) (detail)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
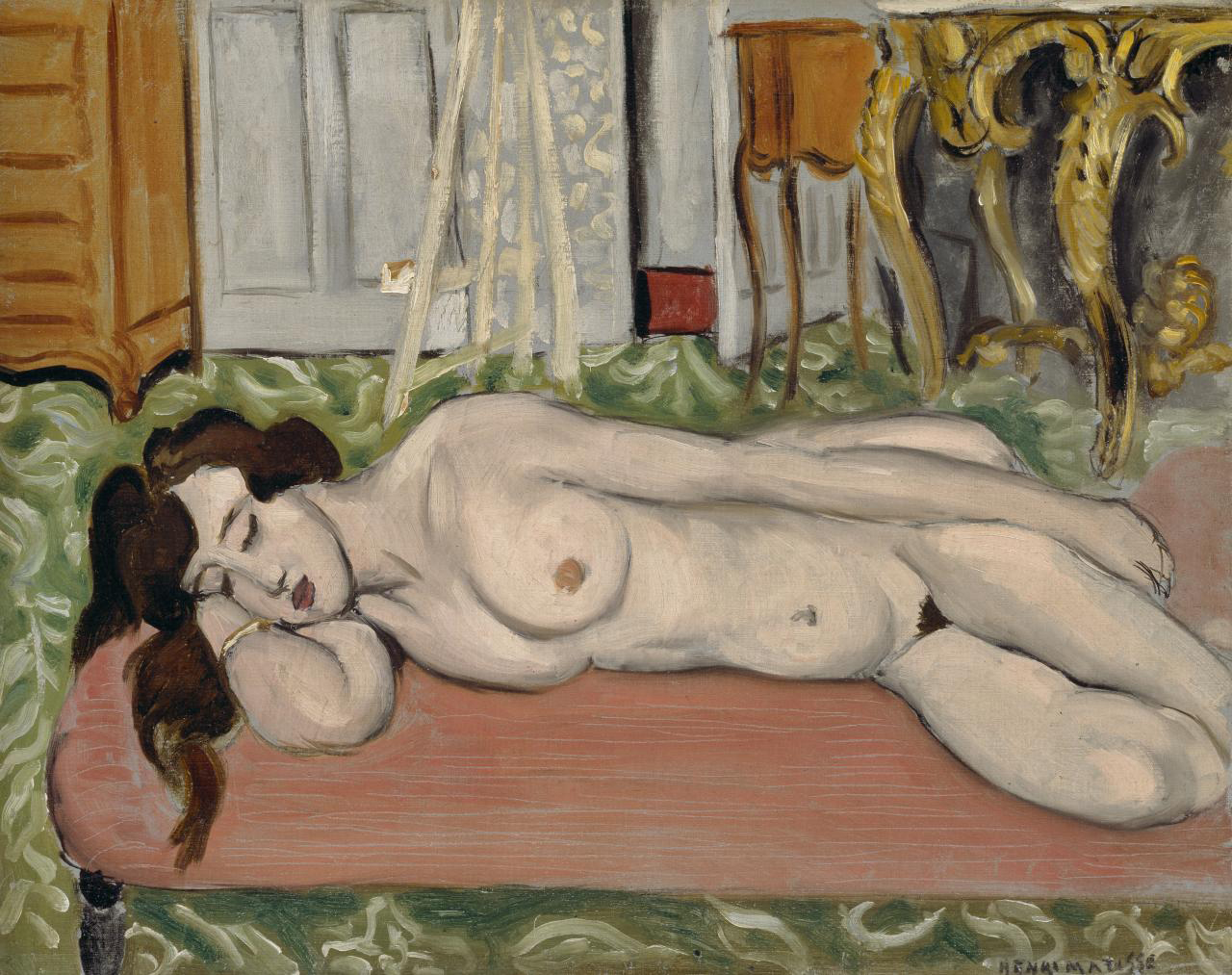
“This room started with my collection of photos of reflections, and of photos of pairs of things; of twins and double exposures. I then began researching the NGV Collection and found an abundance of “pairs and doubles”, assembled within paintings, decorative arts objects, prints and photographs.
To collect is to look for like-minded things. One thing inevitably leads to another. When you pair one thing with another, some things start to make sense – or not. In the end, every collection is, after all, a reflecting pool.”
~ Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Pairs (and the double) (detail)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Pairs (and the double) (detail)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
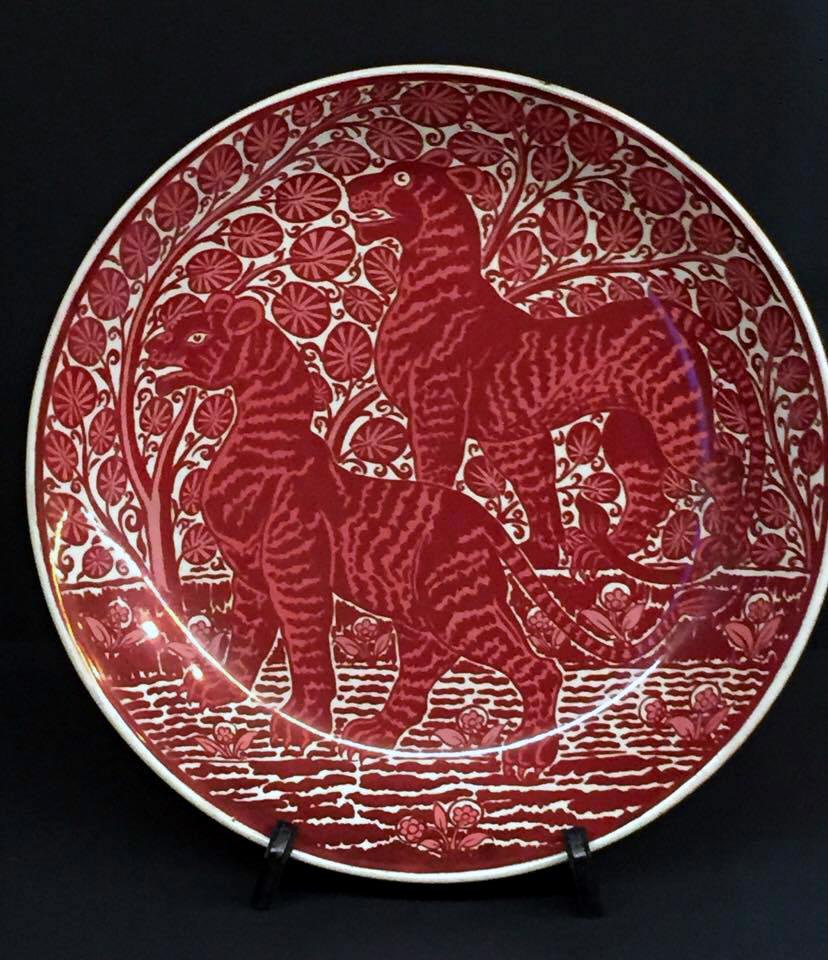
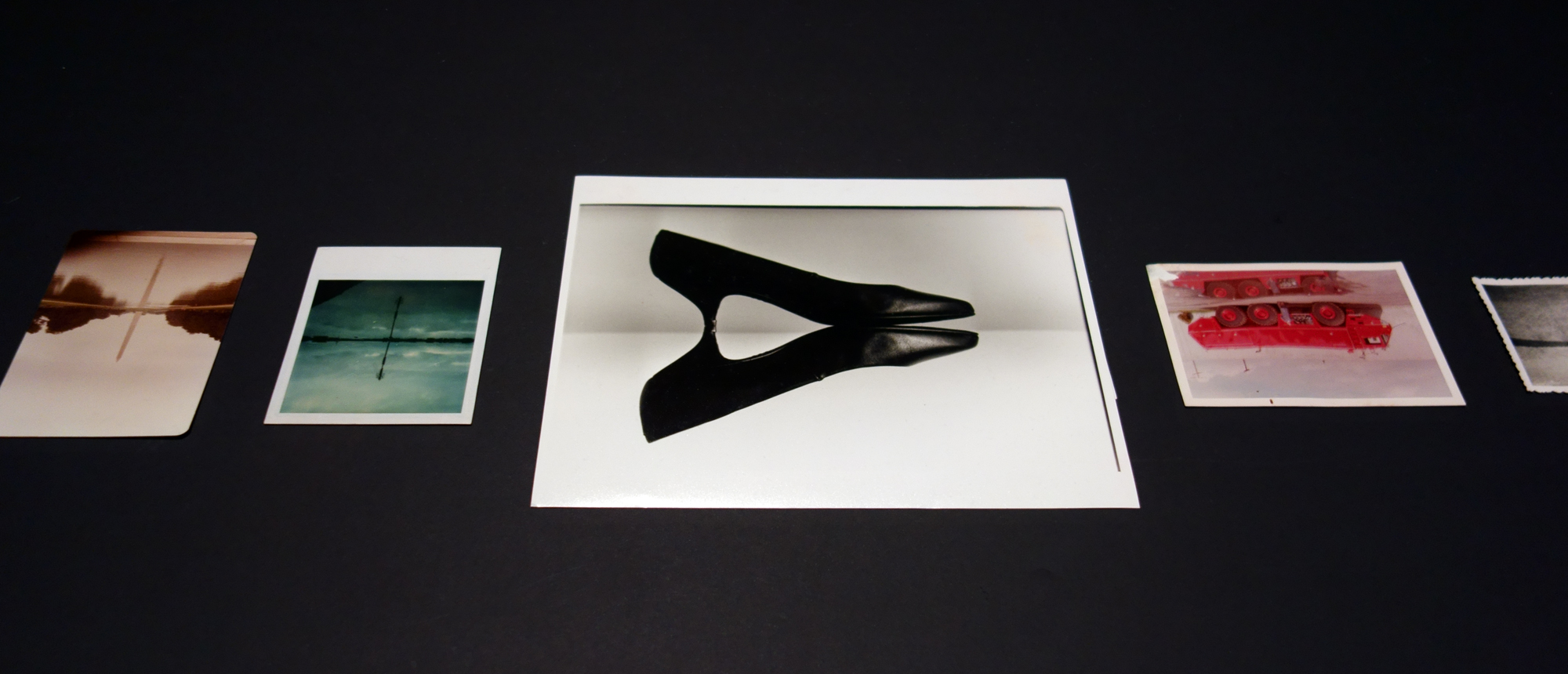

William De Morgan & Co., London (manufacturer, England 1872-1911)
William De Morgan (designer, England 1839-1917)
Startled tigers, dish
c. 1880
Earthenware
Felton Bequest, 1980
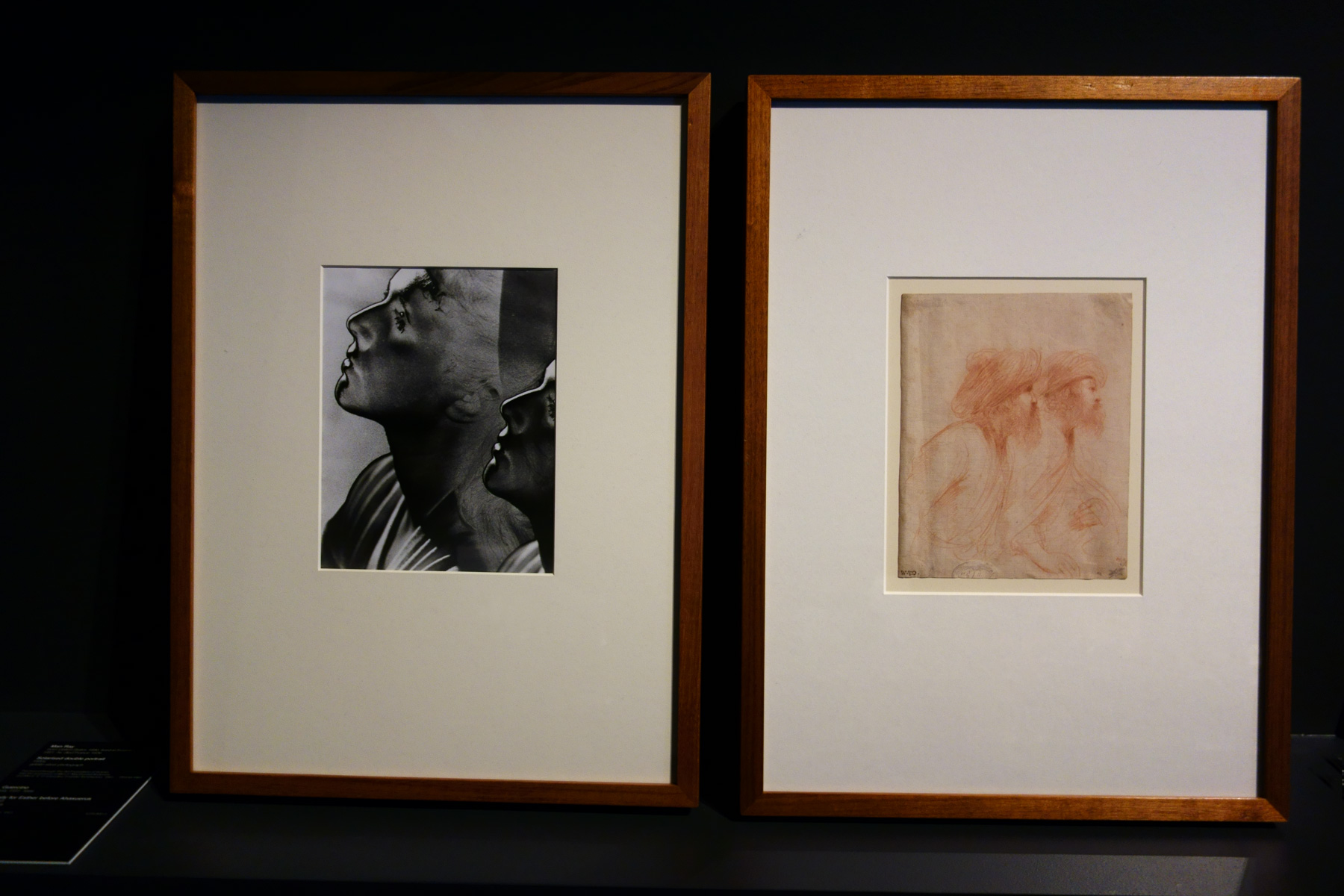

Man Ray (born United States 1890, lived in France 1921-1939, 1951-1976, died France 1976)
Solarised double portrait
1930s
Gelatin silver photograph
Purchased through The Art Foundation of Victoria with the assistance of Miss F. MacDonald Anderson and Mrs E. E. O. Lumsden, Founder Benefactors, 1983
Guercino (Italian, 1591-1666)
Study for Esther before Ahasuerus
c. 1639
Red chalk
Felton Bequest, 1923
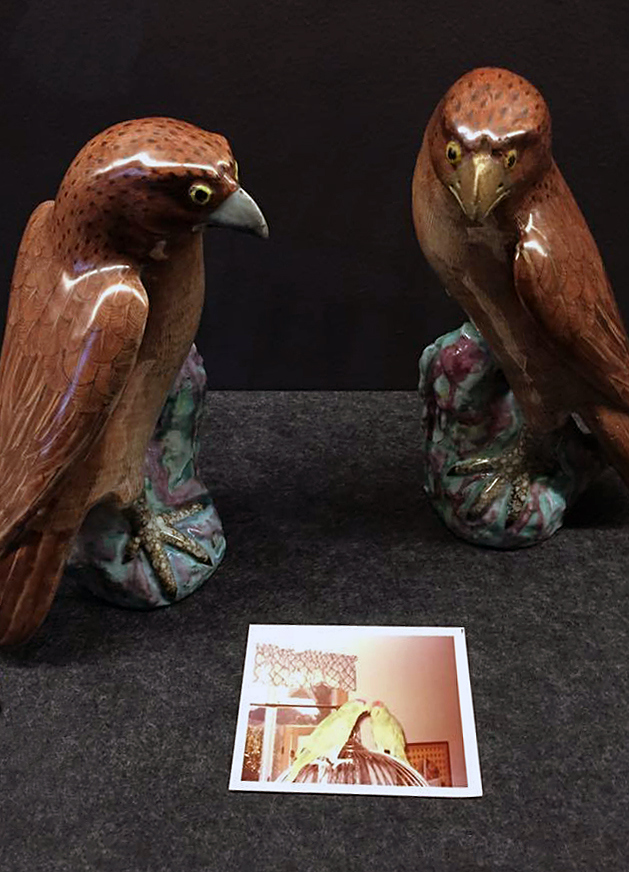

Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Pairs (and the double) (installation view details)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
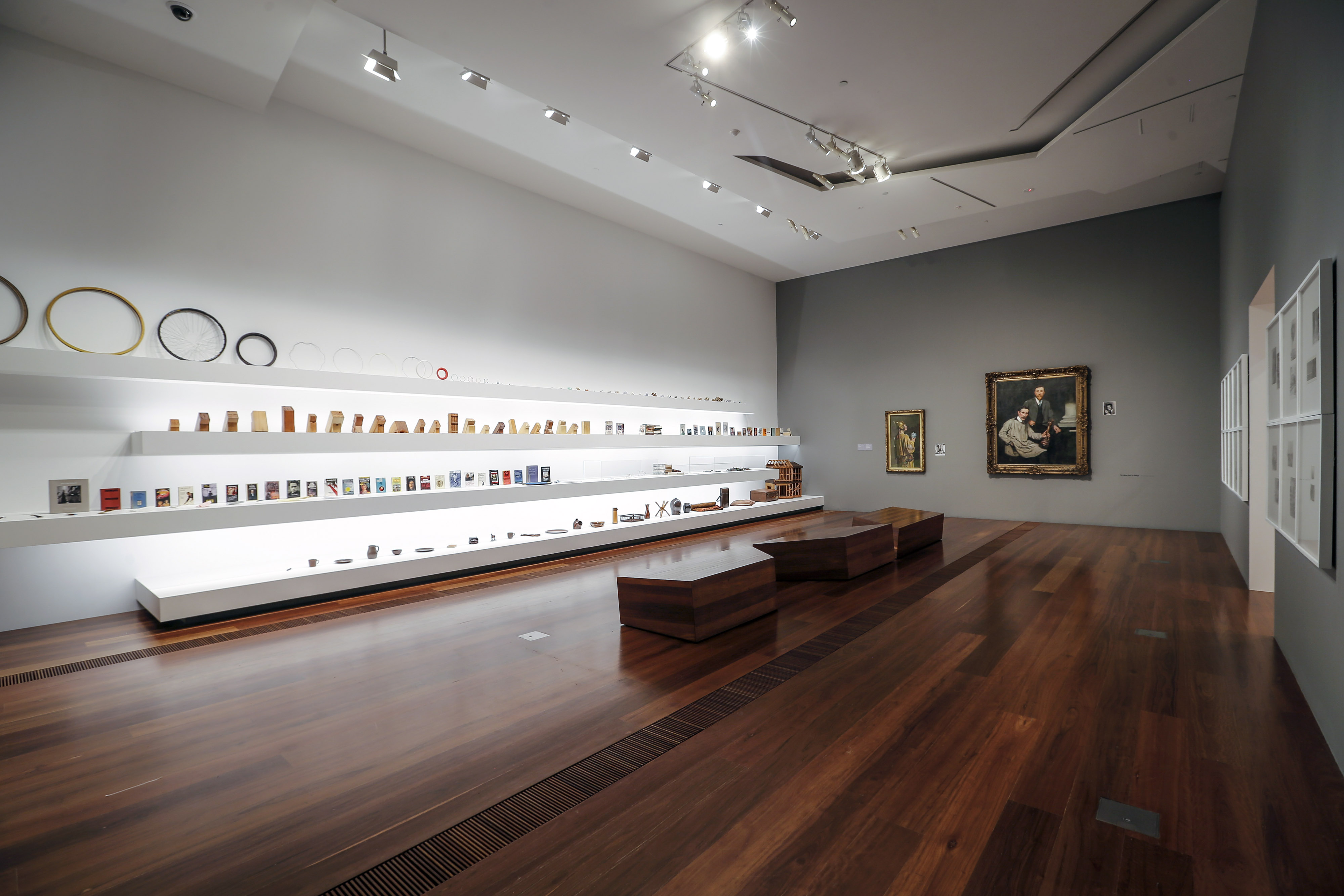
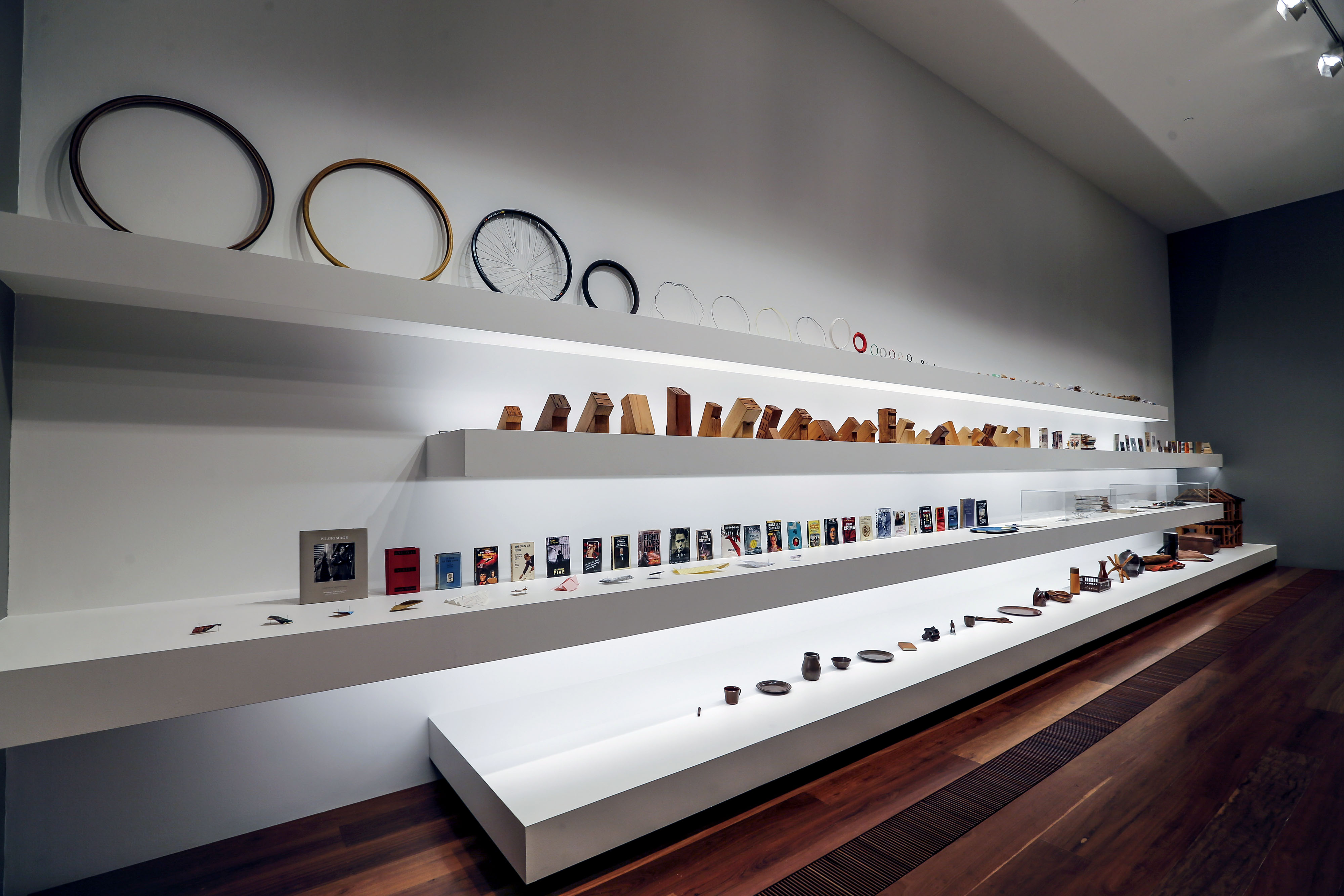
Room 4
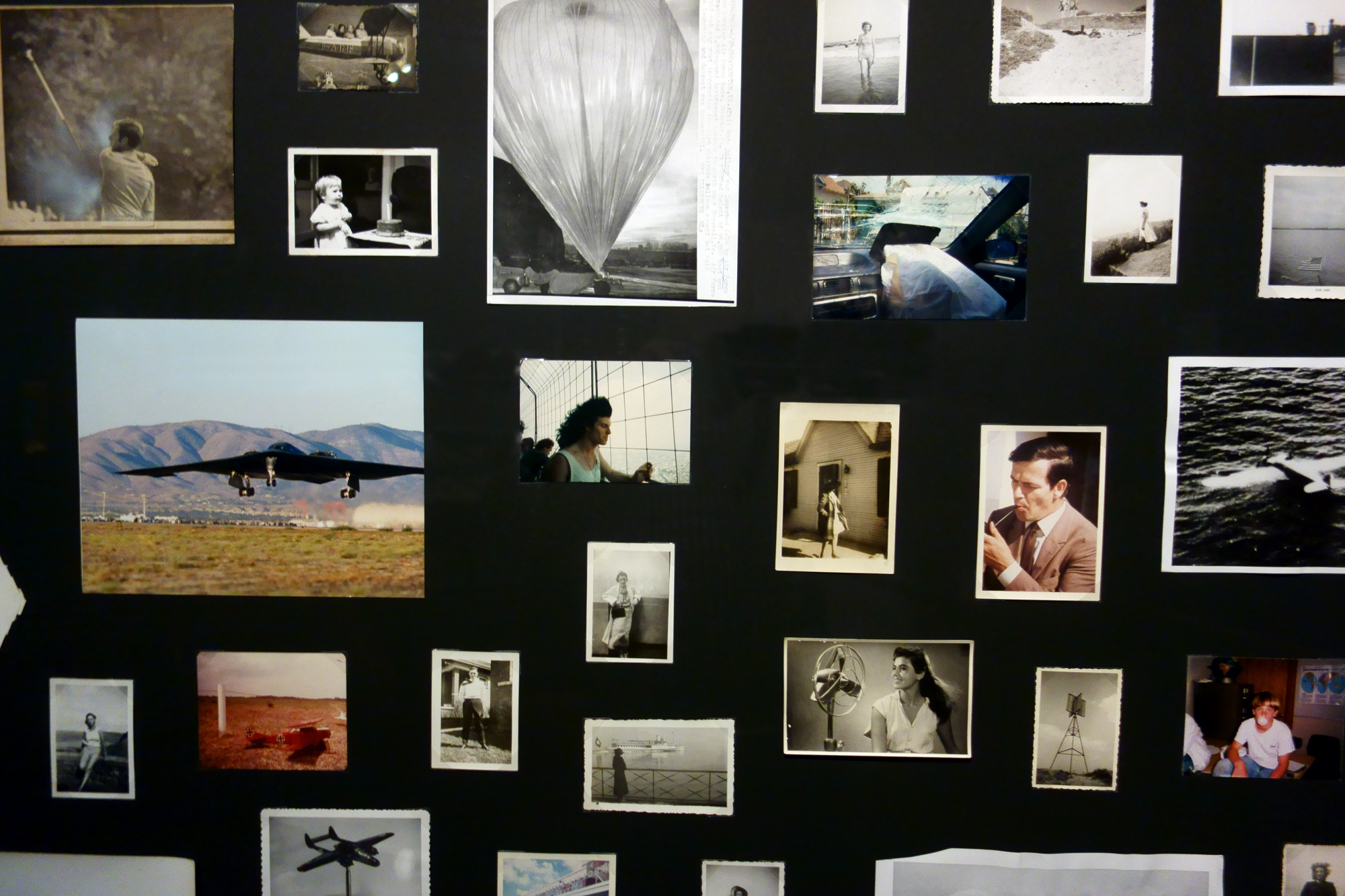
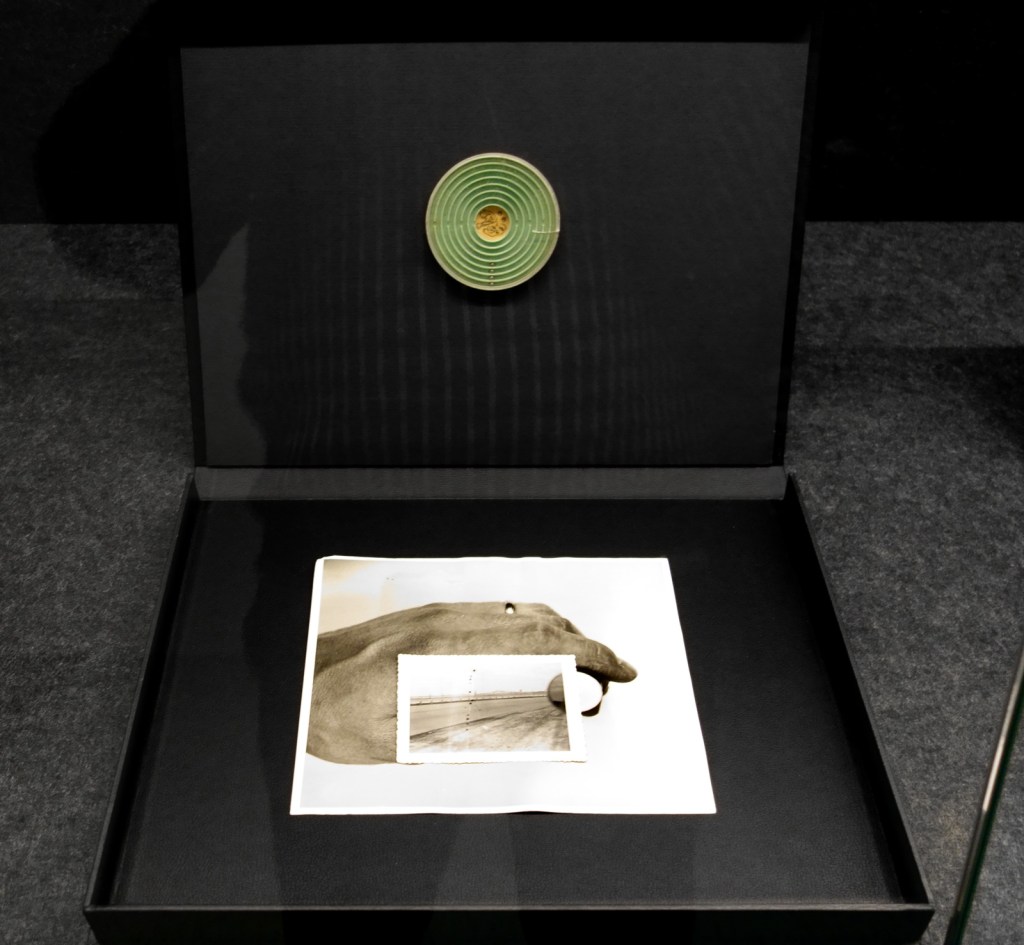
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The collection of shelves (installation view)
1999-2017
Circles 1999-2015
28 (screwed) 2004
Knife blocks 1999-2017
Things Change 2015
The Collector 2000-2017
Some French things 2014
Museum darts 1989-2017
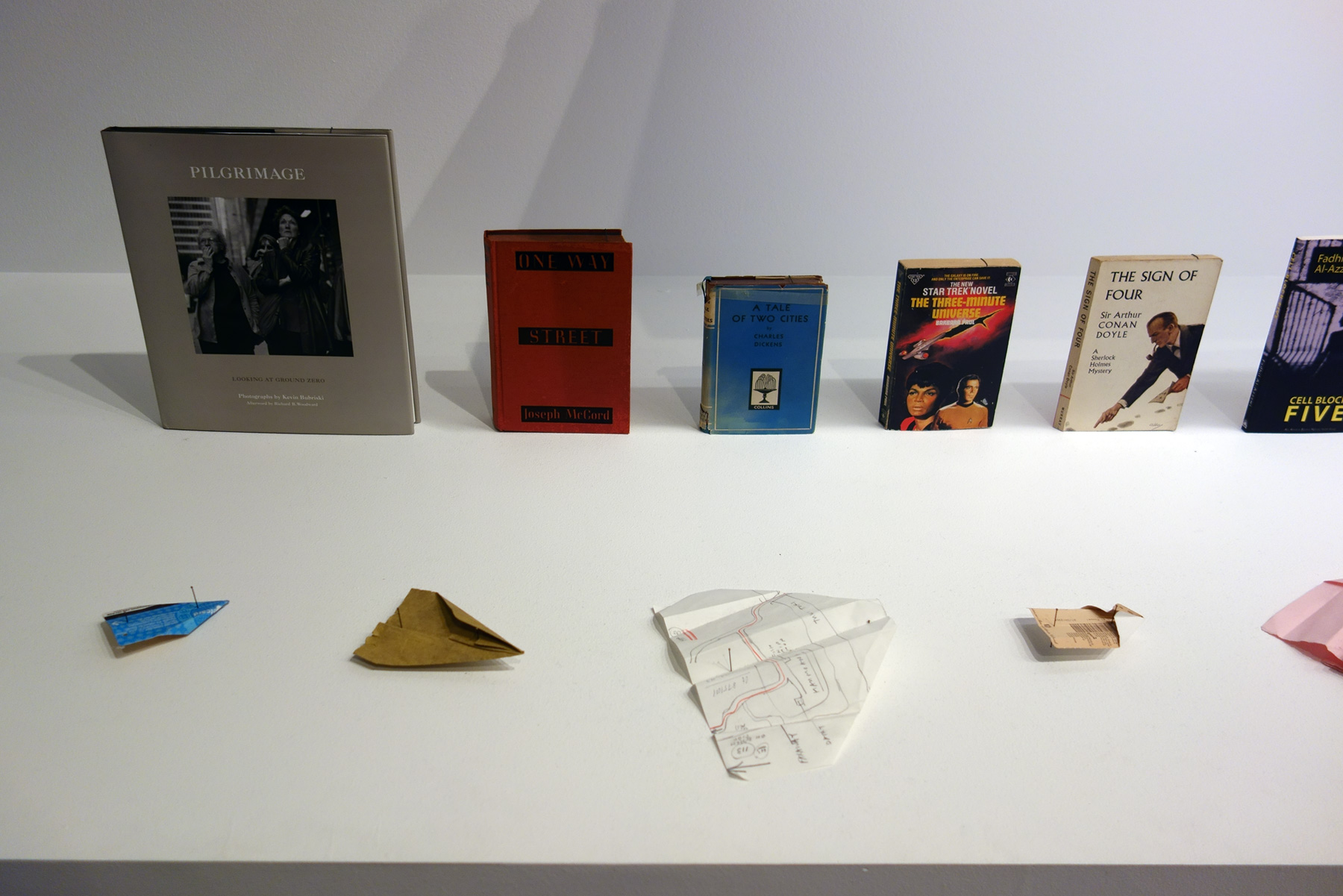
Twenty six and one books 2010
Tangled 2012-2015
Blade magazine 2014
Criminal records 2012
Index cards 2012
Lost birds 1999-2014
Index photos 2013
The names 2007
Small arms 2000-2017
Soldiers 2009
Lockets 1989-2016
26 brown things 2002
Site specific installation comprising objects collected by the artist
Photos: Wayne Taylor
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s work Twenty six and one books 2010 (detail)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Twenty six and one books (installation view detail)
2010
Museum darts (detail)
1989-2017
From the work Twenty six and one books 2010
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
These shelves house a range of collections which Pound has been gathering over many years: they demonstrate how collections of things gradually evolved into works of art. These collections tend to be smaller than others seen throughout this exhibition, and each one operates according to a very specific constraint. Their organisational technique derives from Pound’s interest in the Oulipo group of writers and mathematicians which formed in France in 1960 and, specifically, in the writing of key member Georges Perec. Pound is fascinated by Perec’s use of restrictions in his writing as a way of encouraging new patterns and structures, and has translated some of those ideas into the formation of these collections.
In Pound’s work Twenty six and one books, 2010, each book has a number in the title, starting with Ground Zero, all the way through to Maxim Gorky’s story collection Twenty-Six and One. The entire 26 brown things, 2002, collection was found and purchased by the artist in one shop, on the same day, with everything being – you guessed it – brown.
Like some vast novel cycle, collections reflect the world. The use of such constraints when organising the collections allows for surprising and poetic responses. If we look closely enough, things are found to reflect, to hold and to project ideas.

Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Tangled (installation view details)
2012-2015
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
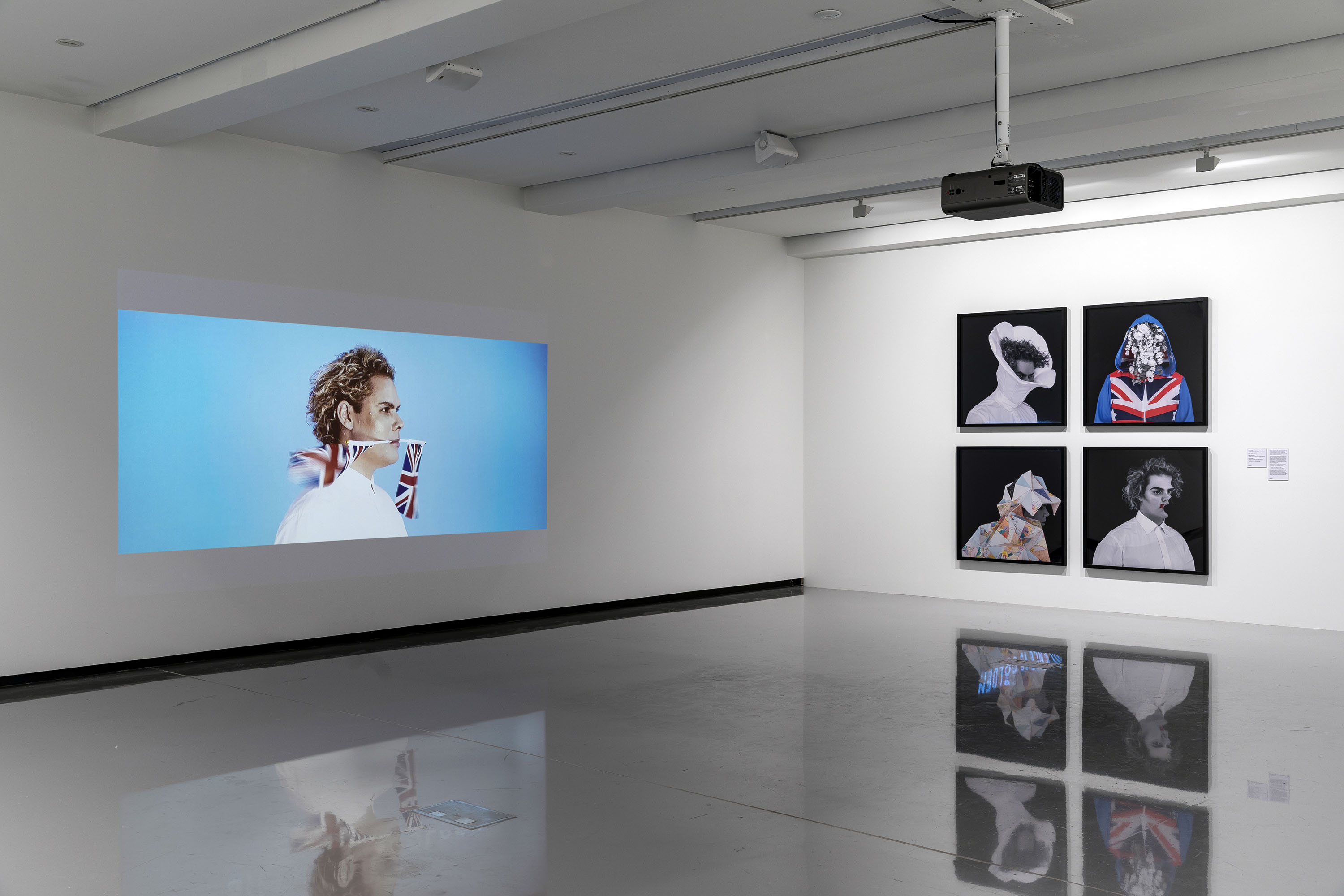
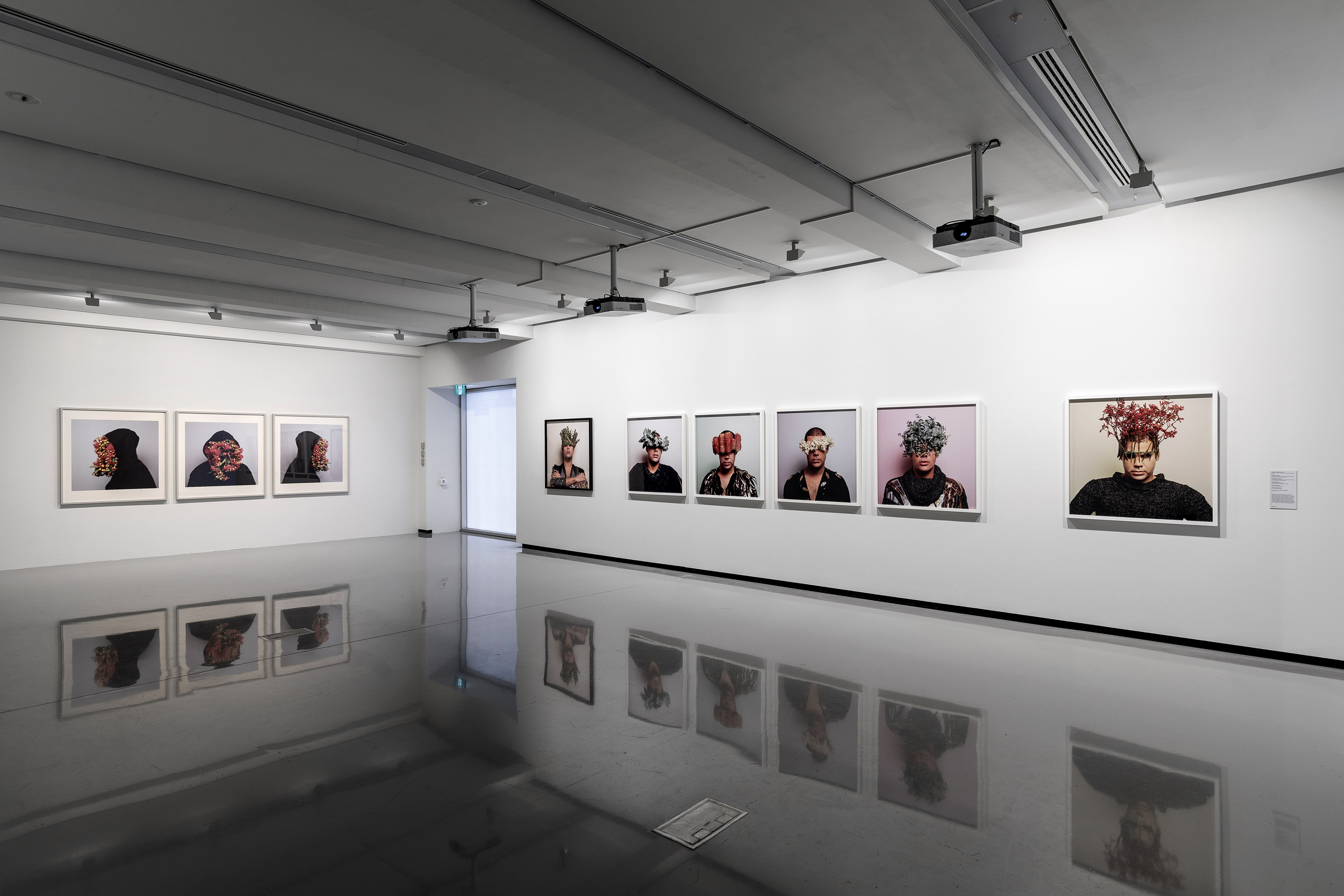
Installation view of the exhibition Patrick Pound: The Great Exhibition at NGV Australia with the work Portmanteau (2015-2017) at middle centre. Presented as part of the NGV Festival of Photography.
Photo: Wayne Taylor
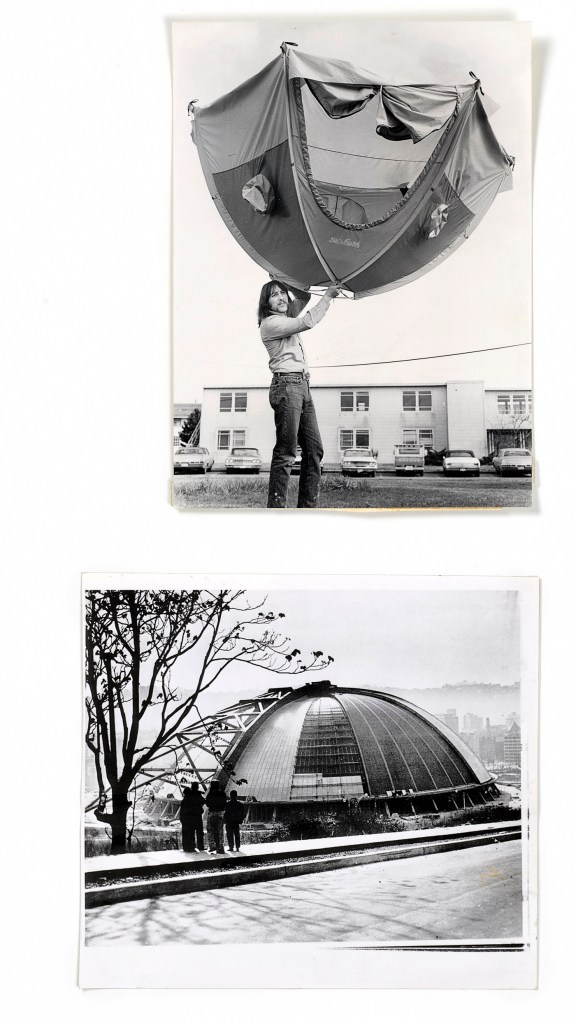

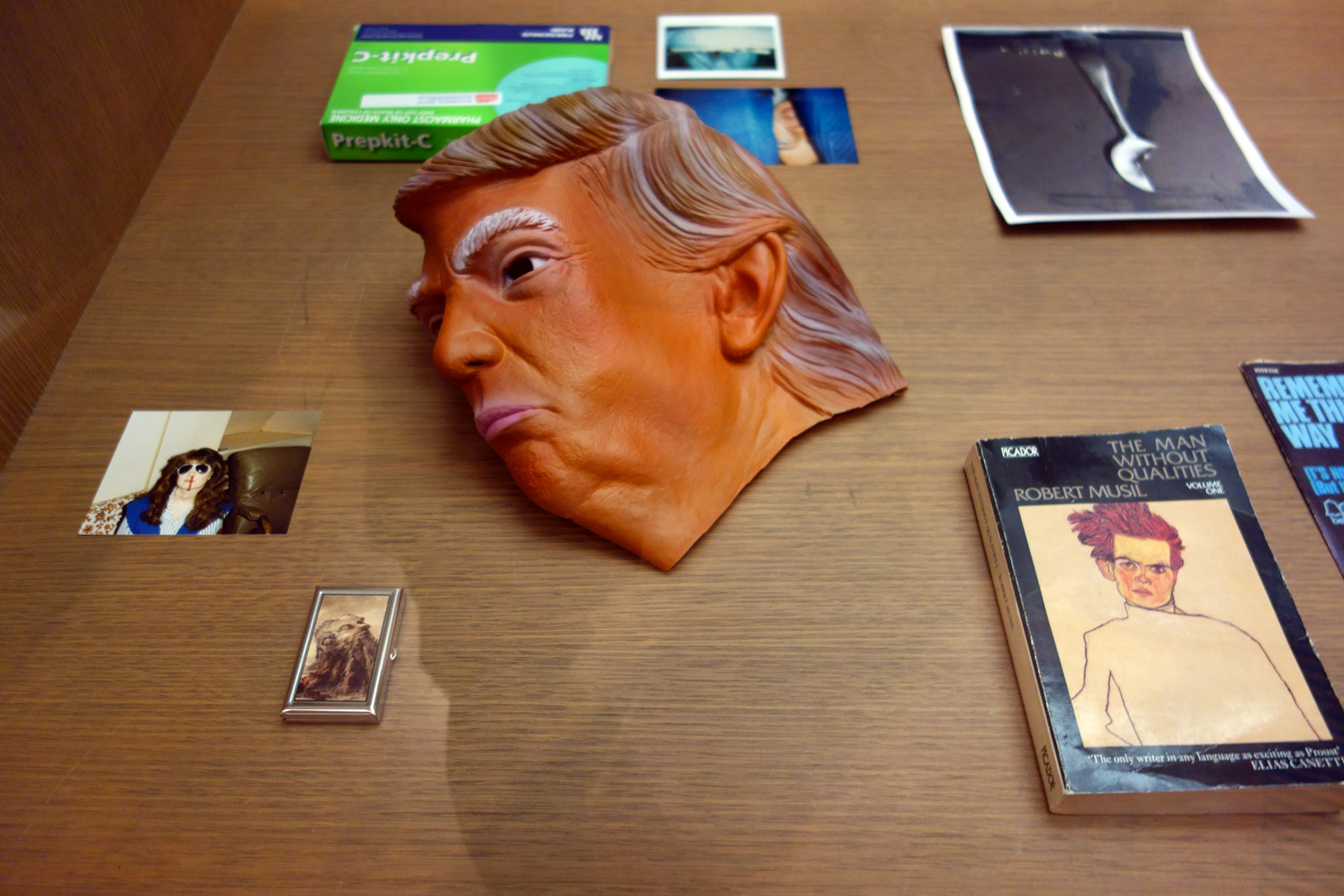
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Portmanteau (detail)
2015-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Portmanteau (installation view detail)
2015-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
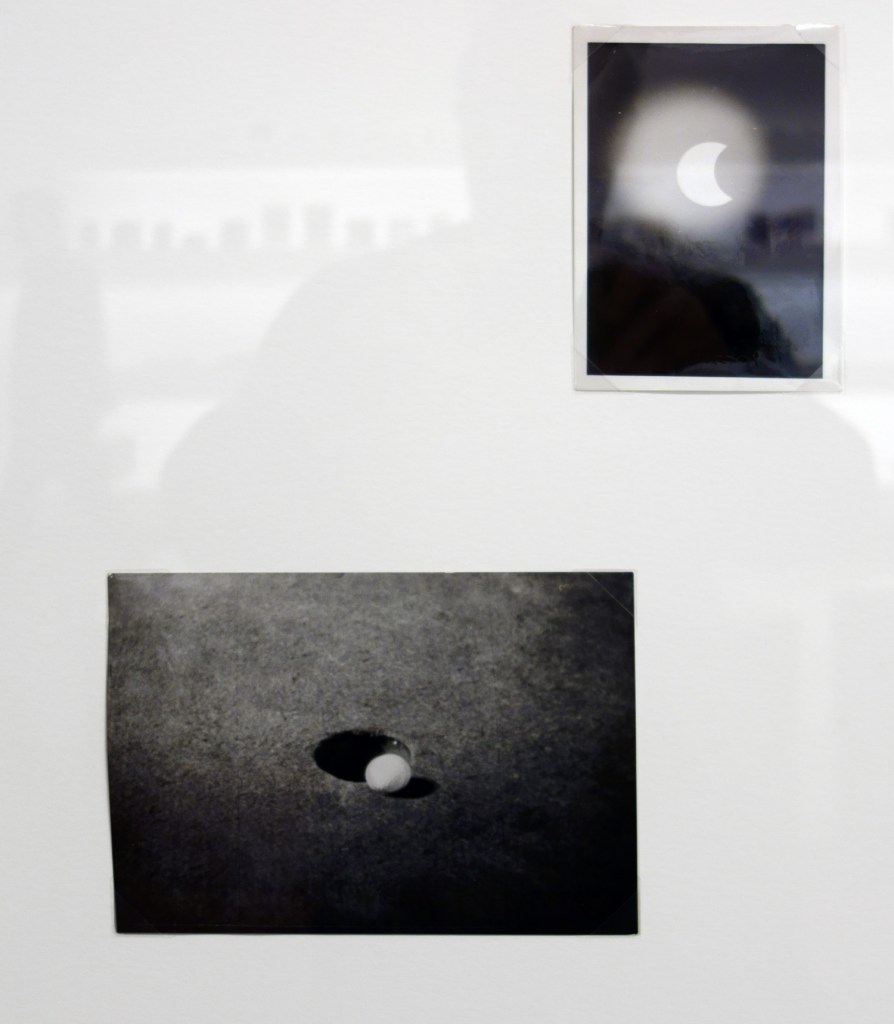

Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Portmanteau (installation view detail)
2015-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
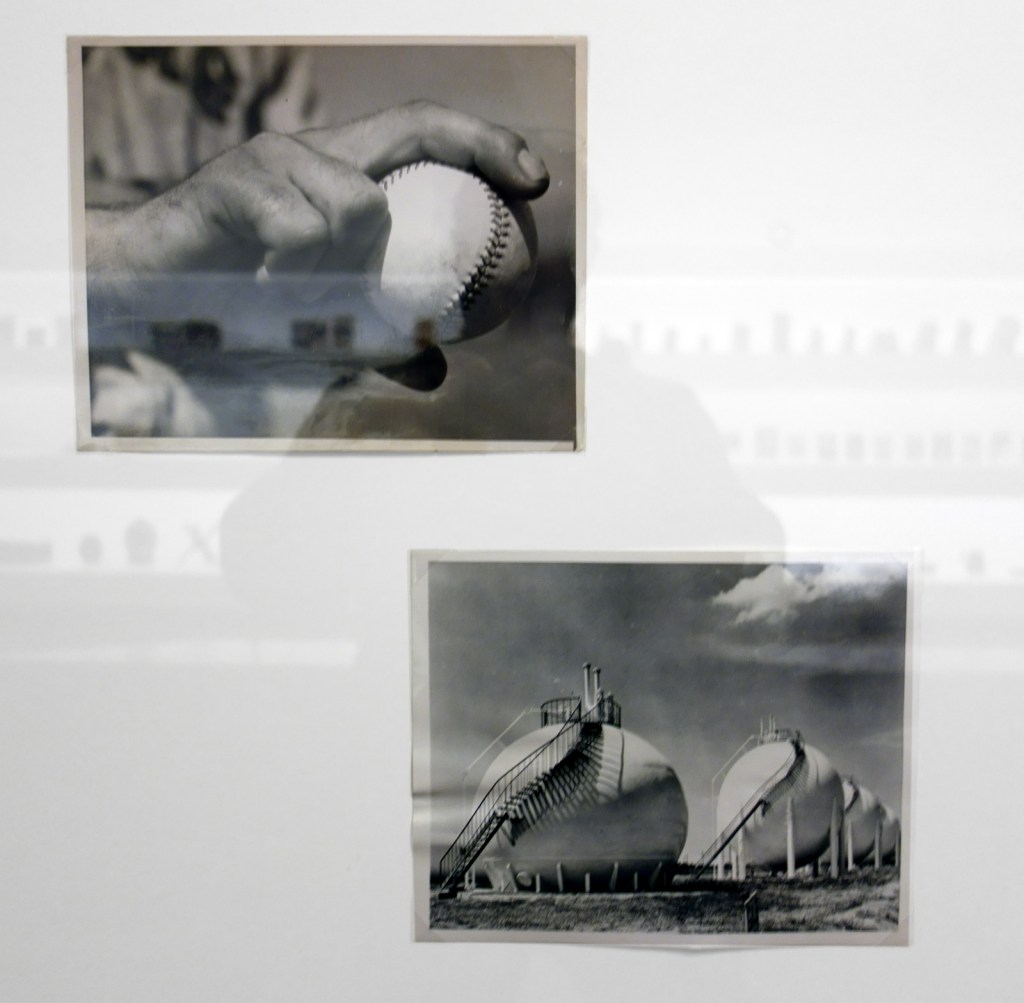

Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Portmanteau (installation view detail)
2015-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
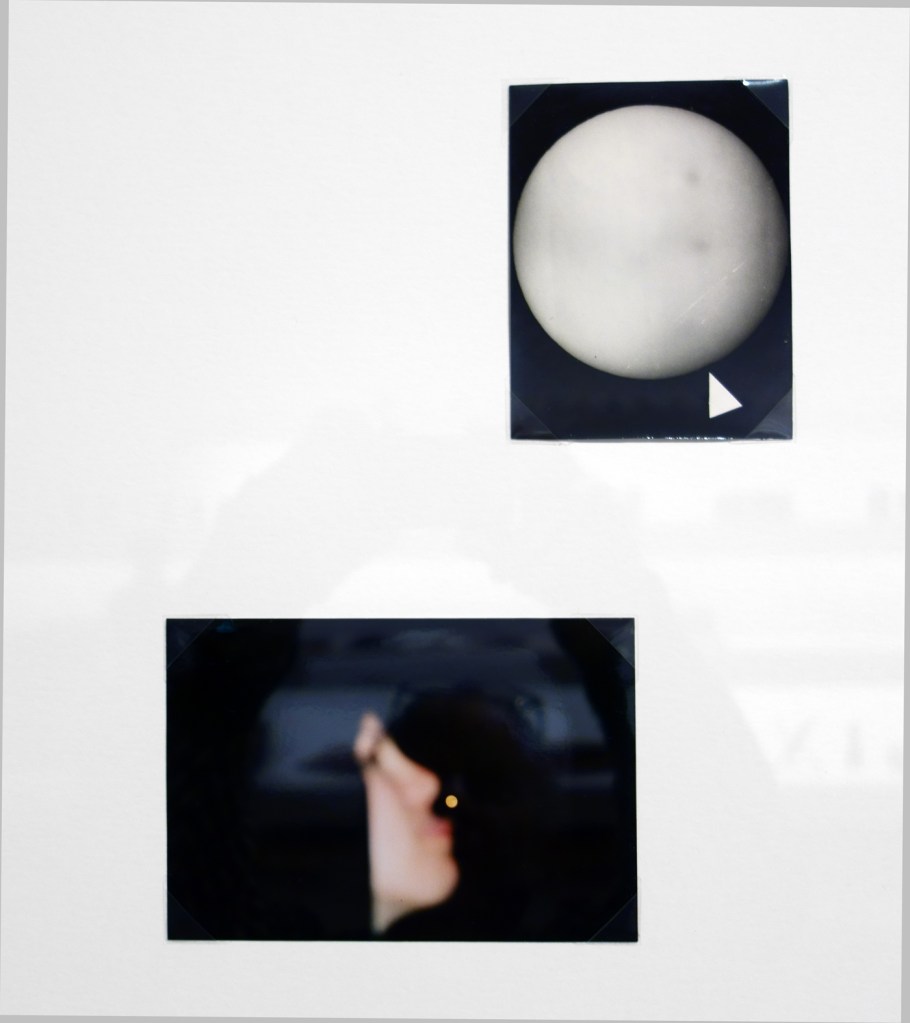
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Portmanteau (installation view detail)
2015-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Portmanteau (installation view detail)
2015-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
High wire act (installation view)
2015
Collage of photographs
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The Fountainhead (installation view)
2016
Collage of photographs
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Photographs, objects and curios sourced from the internet and op shops will be organised alongside artworks from the NGV Collection in a wondrous series of encyclopaedic displays for Patrick Pound’s major exhibition Patrick Pound: The Great Exhibition.
An avid collector, the New Zealand-born, Melbourne-based artist is fascinated by the categorisation and ordering of objects. Irreverently titled The Great Exhibition, with a knowing nod to the epic ambitions of the famous London exposition of 1851, in his largest ever presentation Pound will showcase more than 50 collections, which he describes as ‘museums of things’, featuring hundreds of items from the artist’s expansive archives.
Pound has also extensively researched the scope of the NGV Collection, identifying more than 300 works from across all of the NGV collecting departments to incorporate into his ‘museums of things’. The connections that Pound draws between objects will allow audiences to see the NGV’s diverse holdings in surprising new contexts.
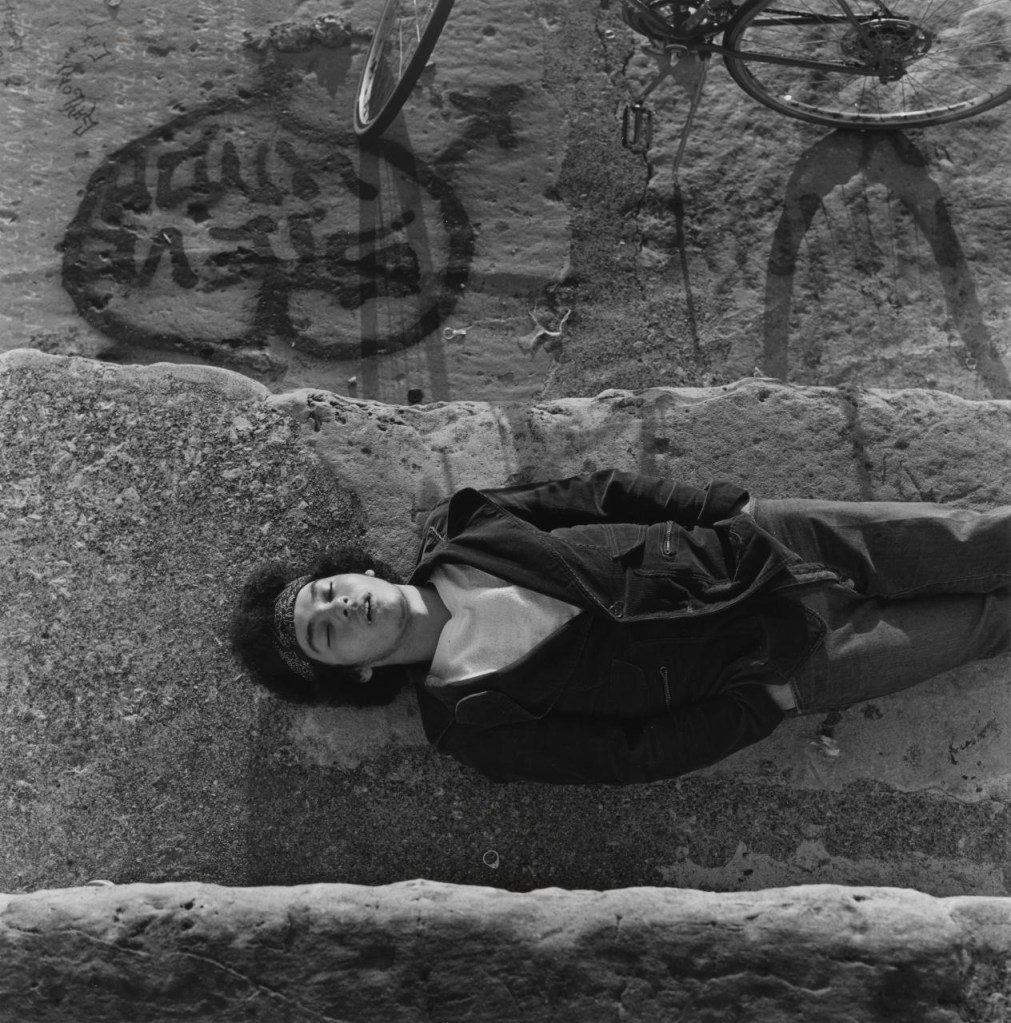
Among the ‘museums’, viewers will encounter vast displays of found photographs which, at closer glance, reveal their common thread, such as The hand of the photographer, a display in which the eclipsing thumb of the photographer is ever-present, and Damaged, a huge display of photographs which have been defaced by their original owners; faces marred by cigarette burns, marker or ripped out of the photo entirely.
Other ‘museums’ incorporate seemingly disparate items, like The Museum of there / Not there, which explores the idea of absence and presence, illustrated by a curated selection of objects such as an obsolete Australian $2 banknote and a mourning locket alongside a milk jug produced to commemorate the forthcoming coronation of King Edward VIII, who abdicated before he was crowned.
Tony Ellwood, Director, NGV, commented, “Through complex arrangements of items drawn from the artist’s archives alongside works from the NGV Collection, Pound’s installations playfully explore the art of collecting, and the ways in which things can hold and project ideas. Within each museum a new logic or exciting narrative is created for the viewer to unravel or identify.”
Pound last exhibited at the NGV in the 2013 exhibition Melbourne Now with his popular “Gallery of Air”, a wunderkammer of diverse artworks and objects that held the idea of air, drawn from the NGV Collection and the artist’s archives.
Press release from the NGV
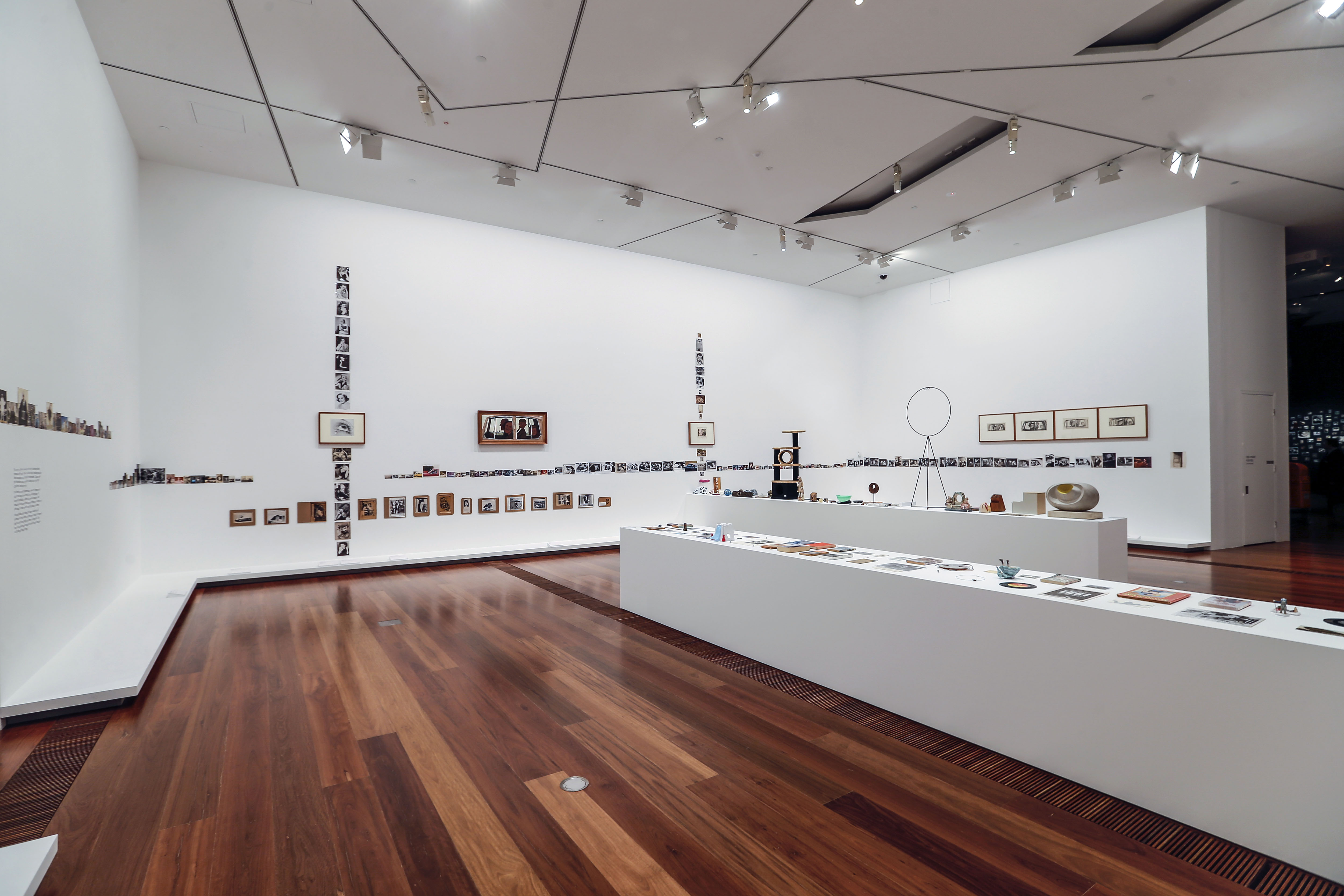
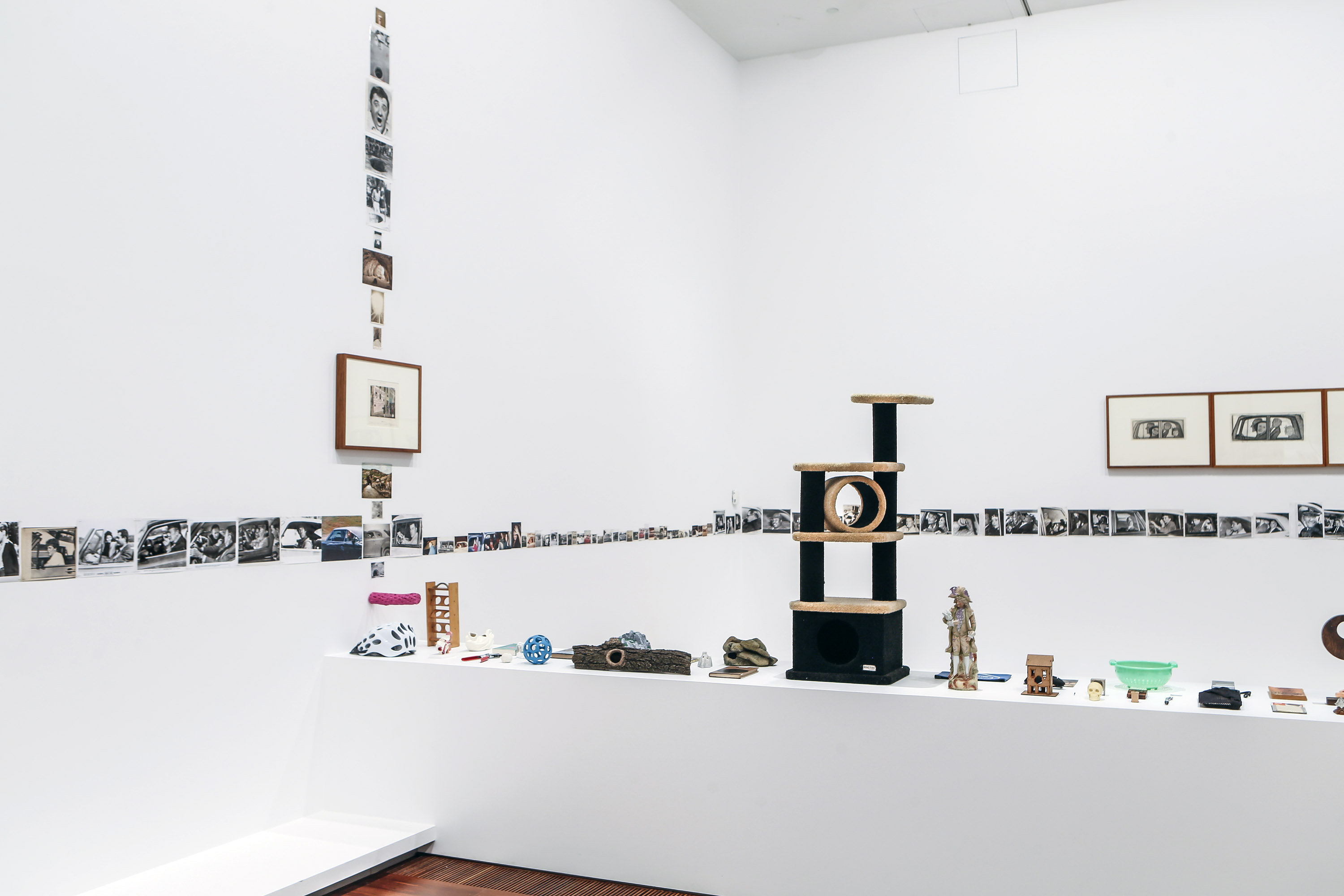
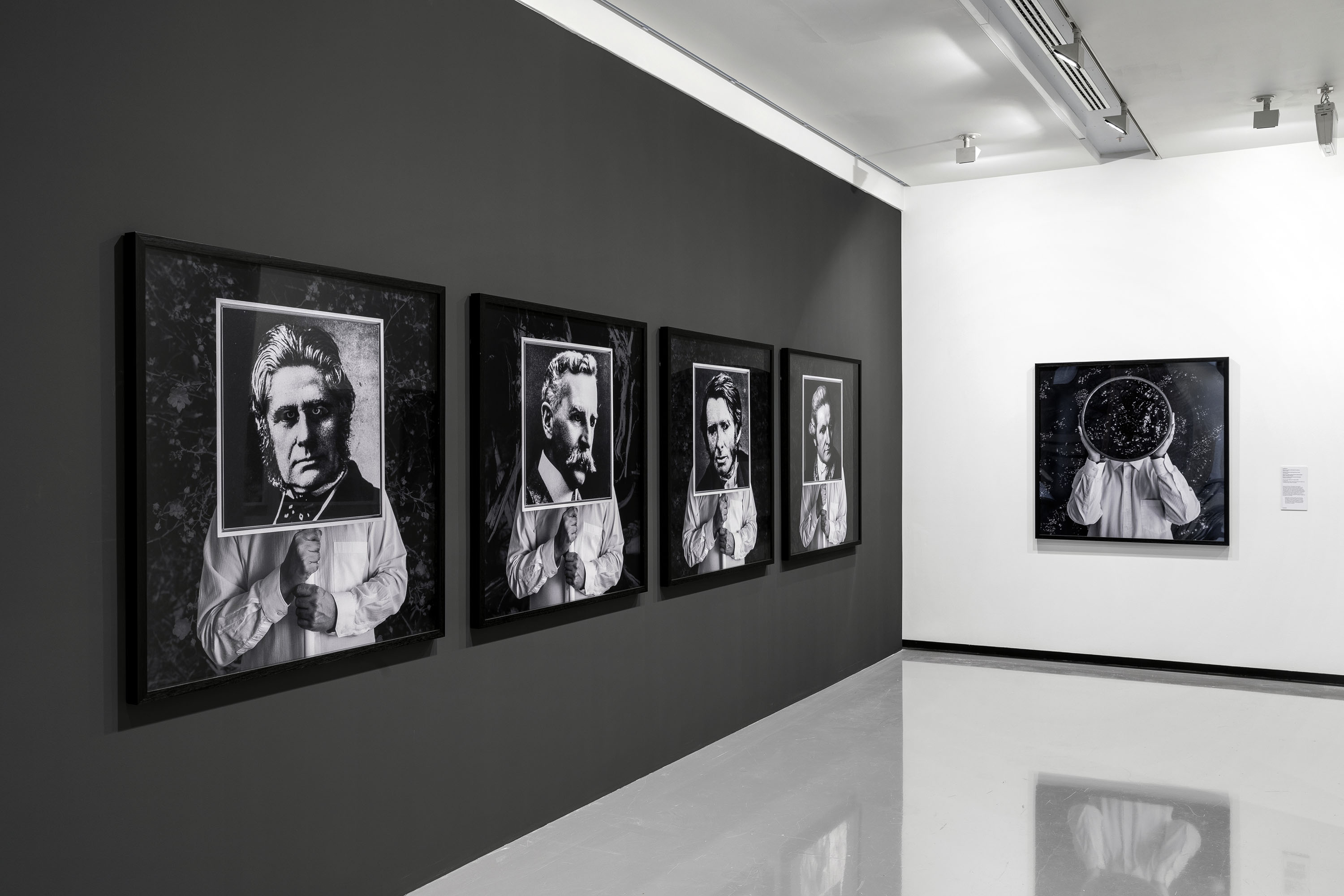
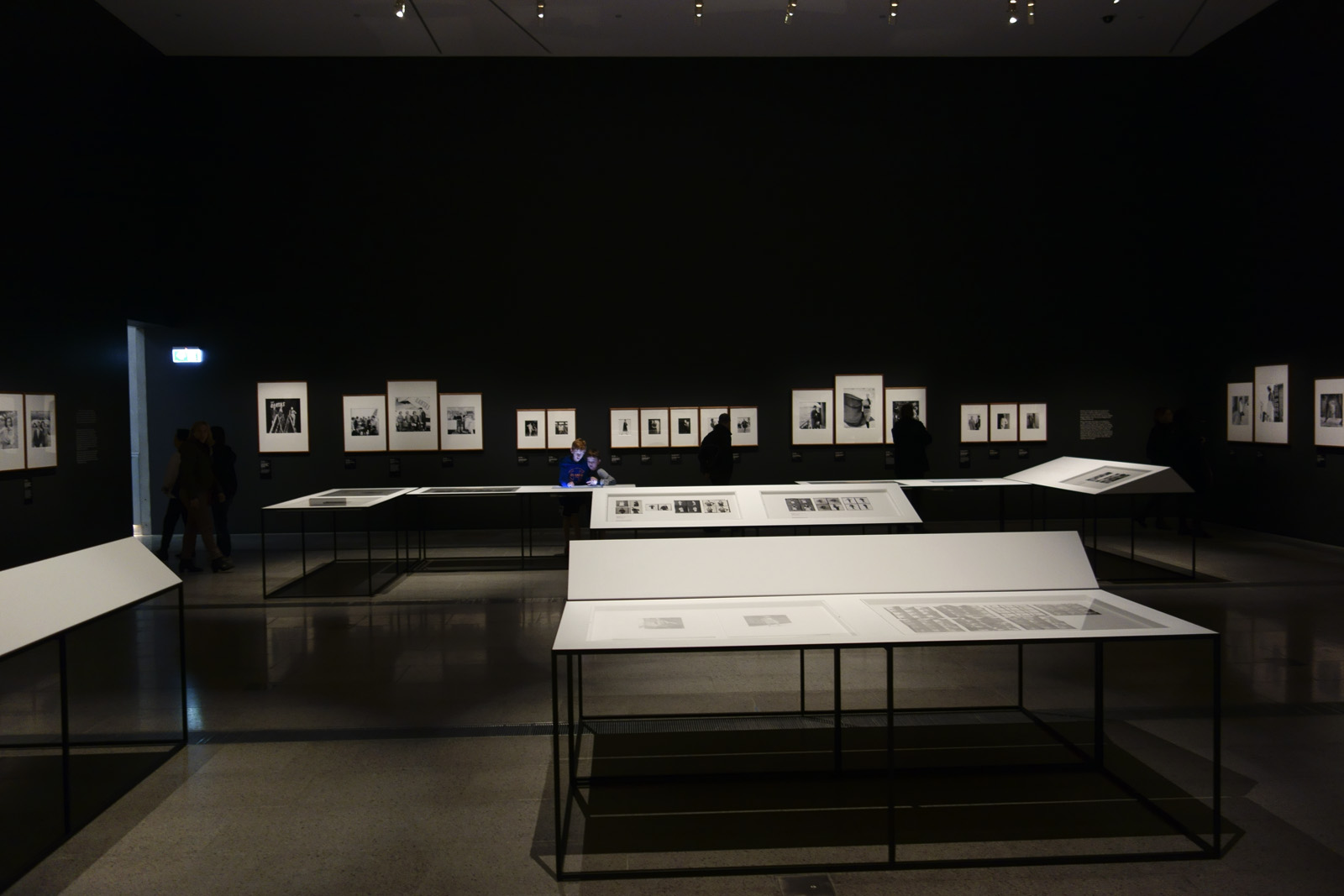
Room 5
Installation views of the exhibition Patrick Pound: The Great Exhibition at NGV Australia, Federation Square. Presented as part of the NGV Festival of Photography.
Photos: Wayne Taylor
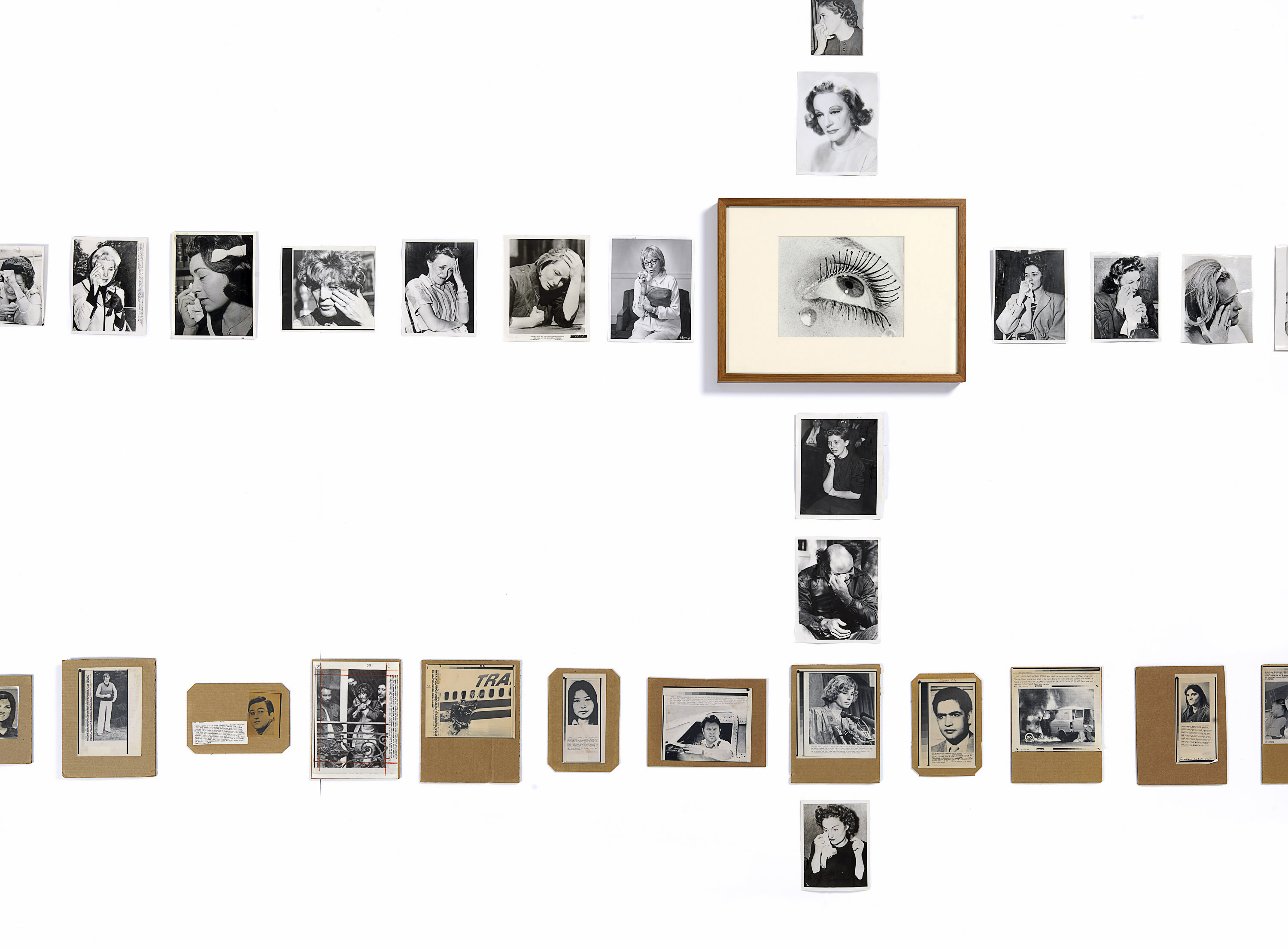
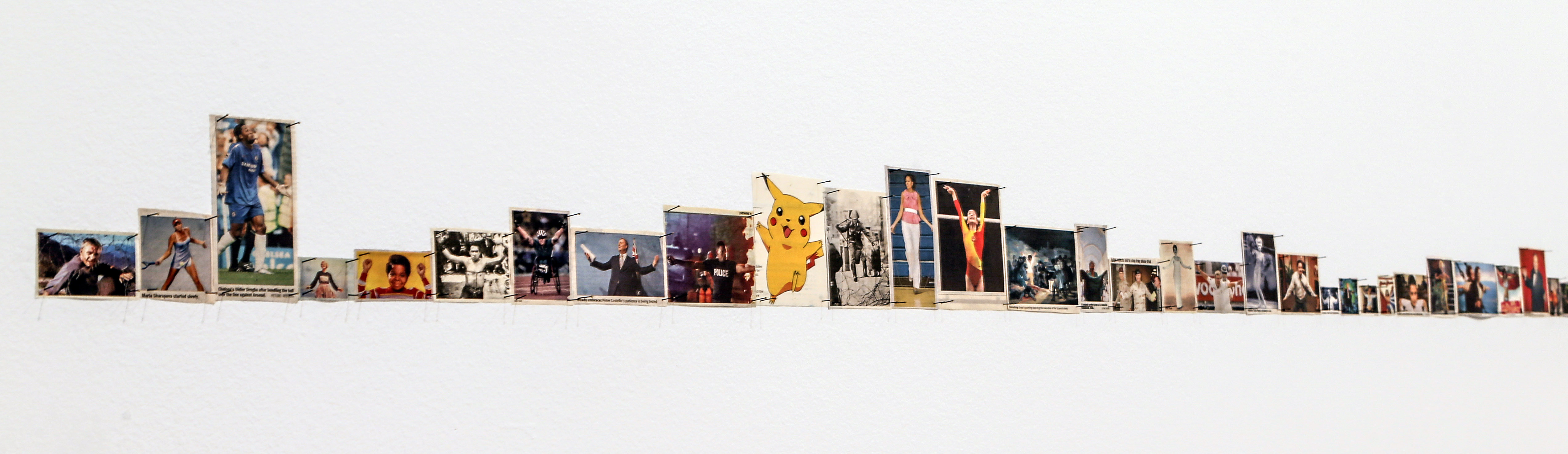
This room contains several of Pound’s collections which intersect with each other in various ways, revealing what the artist describes as a ‘matrix of connections’. Occasionally the collections also connect to works of art in the NGV Collection, and vice versa. The room is a vast diagrammatic network of intersections, and in that way shows one of the underlying ideas of the whole exhibition, which is to seek out patterns and similarities and connections across objects and works of art and ideas. In other words, one thing leads to another.
This installation also reflects the way in which Pound searches on the internet, and the ways in which the internet leads us from one thing to another via algorithms. The room is a visual representation of what Pound describes as ‘thinking through things’.
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
In tears (installation view)
2016-2017
Site specific installation comprising photographs collected by the artist
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Man Ray (born United States 1890, lived in France 1921-1939, 1951-1976, died France 1976)
Eye and tears
1930s, printed 1972
Gelatin silver photograph
Purchased, 1973
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian 1962- )
With arms outstretched (installation view detail)
2016-2017
Site specific installation comprising photographs collected by the artist
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
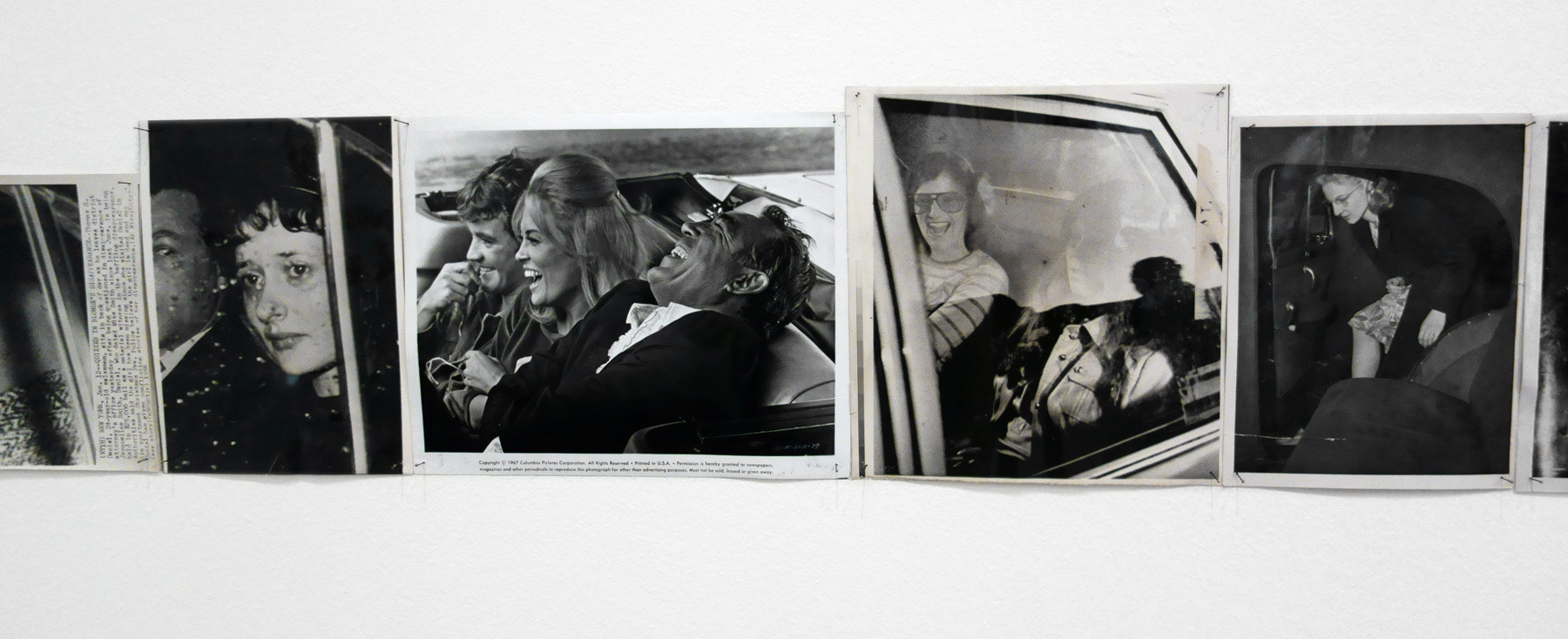
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Drive by (en passant) (detail)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Drive by (en passant) (installation view detail)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
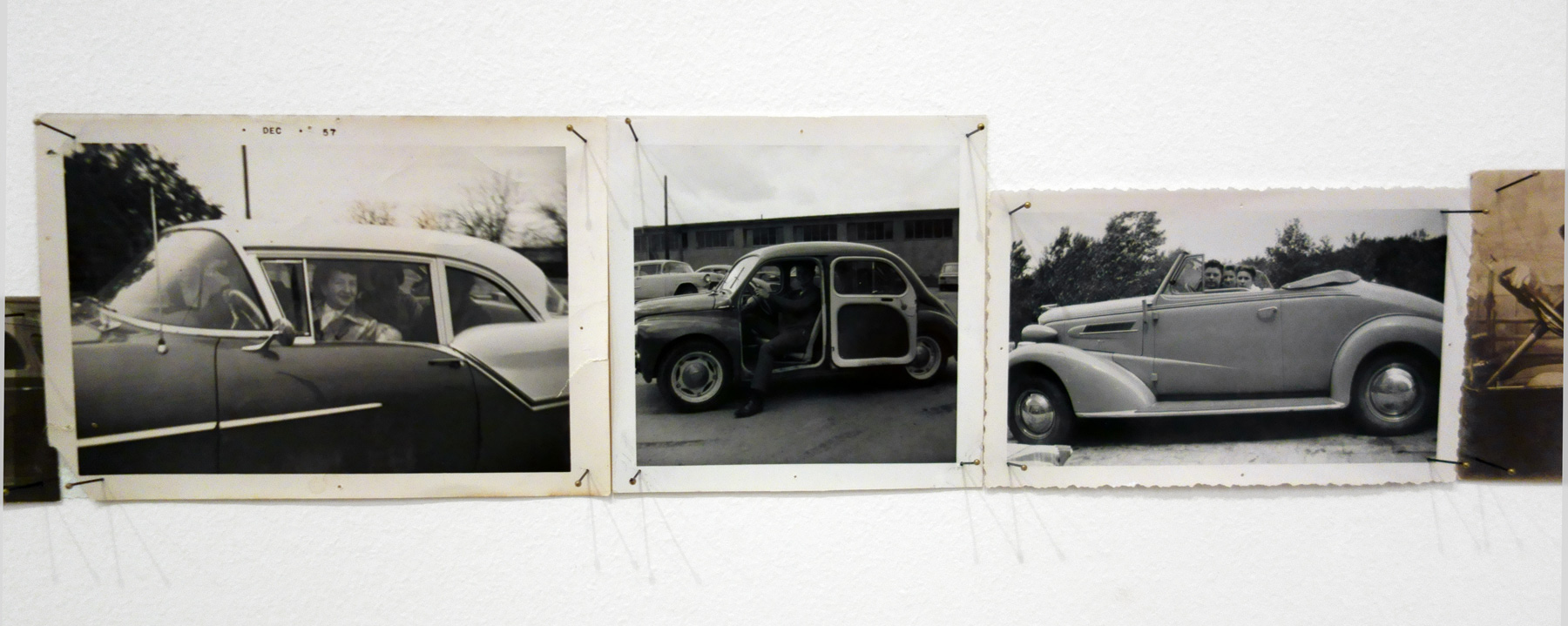
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Drive by (en passant) (installation view detail)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
Drive by (en passant) (installation view detail)
2016-2017
Collection of the artist
Courtesy of Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
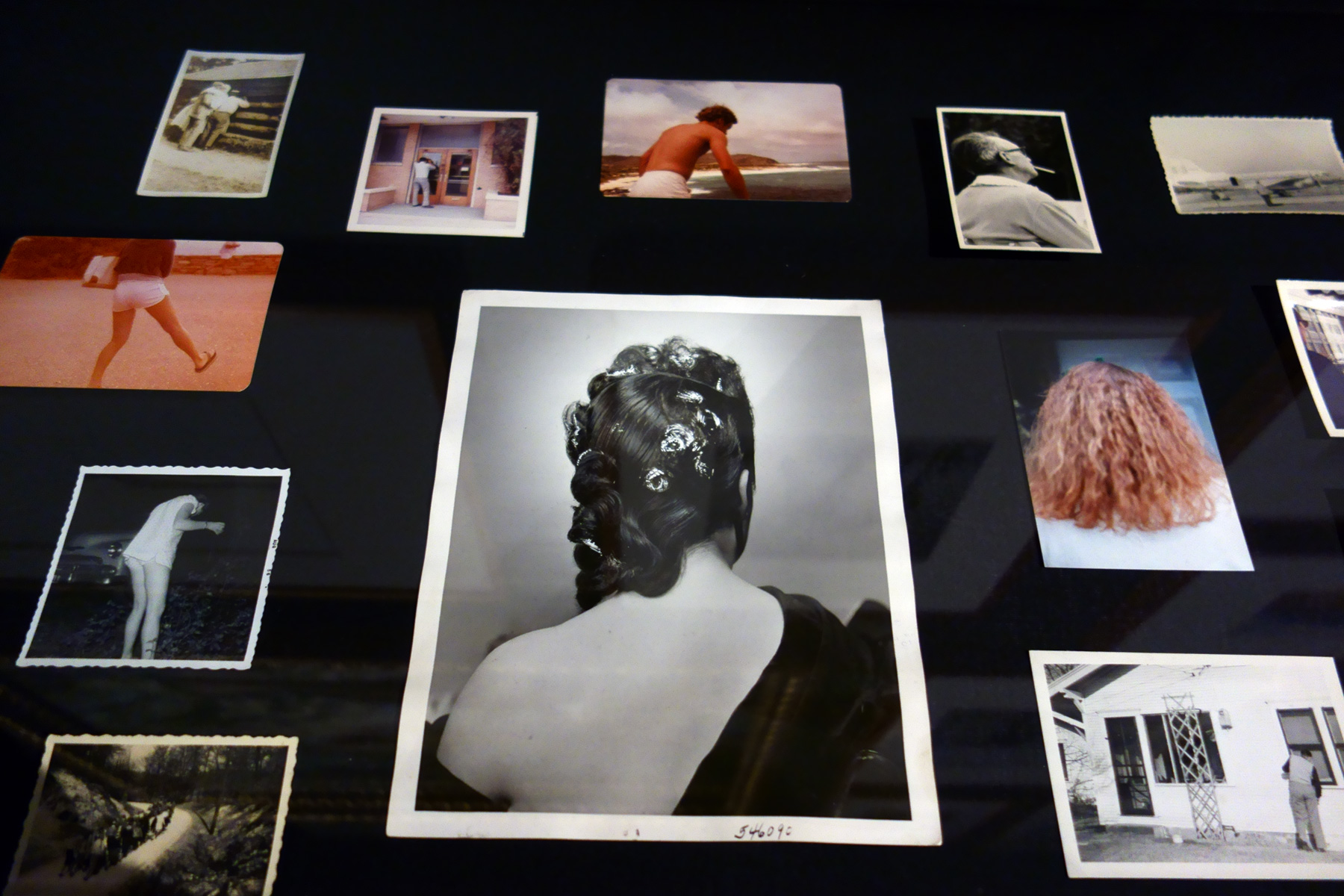
The photographs collected by Patrick Pound include masses of family and vernacular snapshots, as well as newspaper archives and movie stills, which he describes as being ‘unhinged’ from their original sources. Pound does not create photographs in the traditional sense; rather, he spends hours searching for, sorting and buying prints on the internet. He describes this process as a form of ‘retaking’ the photograph.
The images are then organised according to an idea or theme or pattern, such as: ‘readers’, ‘the air’, ‘lamps’ or ‘listening to music’. Pound says he likes the idea of photographing something you cannot otherwise see. Unexpected connections, repetitions and coincidences emerge when the images are placed together in this way. Looking through these images reminds the viewer of the dramatic changes that have occurred in photography – not only in terms of the evolving technology of cameras and prints, but also in terms of what people photograph, why, and how these photographs are shared.
“When I began collecting photographs I was thinking of the way the camera reduces the world to a list of things to photograph. I thought that to photograph was to collect the world in the form of pictures. I love the way photography is so directly connected with the world. It has a remarkable familiarity. We all think we can understand it immediately. As writer Susan Sontag said, photography is not so much a representation of the world but a piece of it. Collecting found photos is like taking cuttings from the world. For me it is a form of collage.
Typically, the analogue photograph stopped life in its tracks. It couldn’t stop time, of course, but it could hold it up to a mirror. The vernacular snap reminds us that the camera is both a portal and a mirror. Photographers used to put photographs in albums and in boxes to be viewed and reviewed at will. Photographs were never made to be scanned and redistributed on eBay. Whether they are analogue or digital, printed photographs have an afterlife that no one saw coming. Photography used to be the medium of record. Now it is equally the medium of transmission.”
Wall text from the exhibition
Room 6
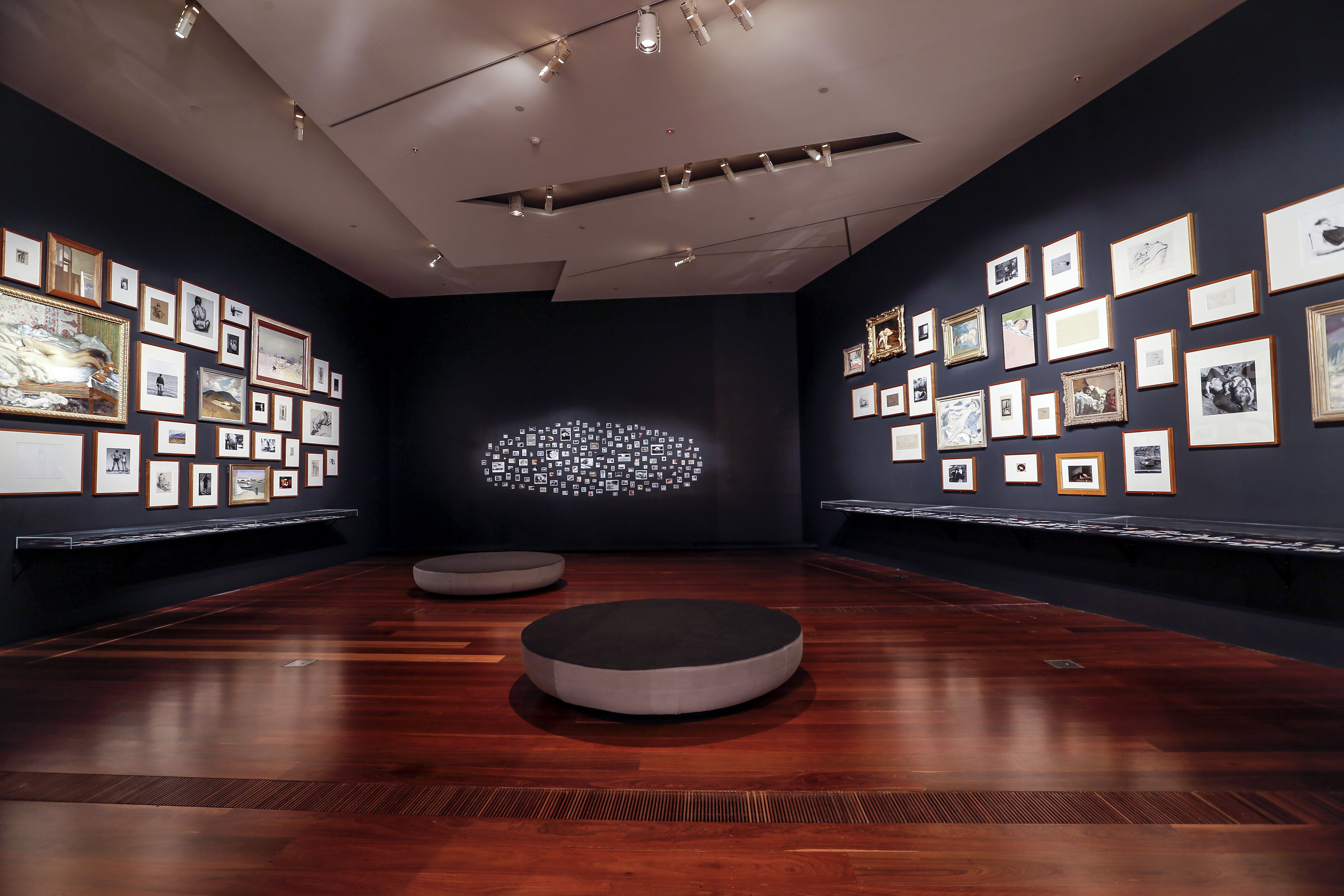
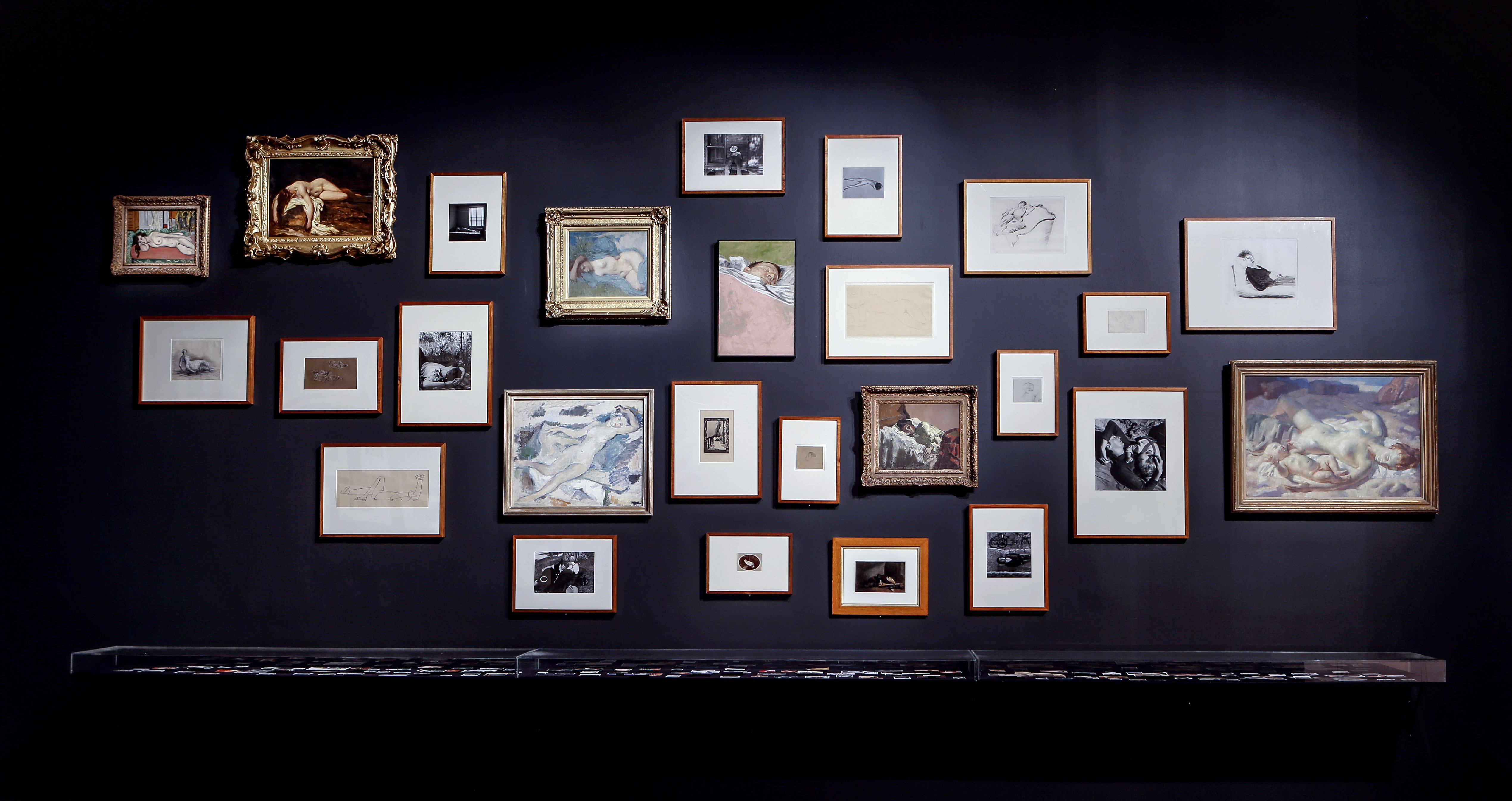
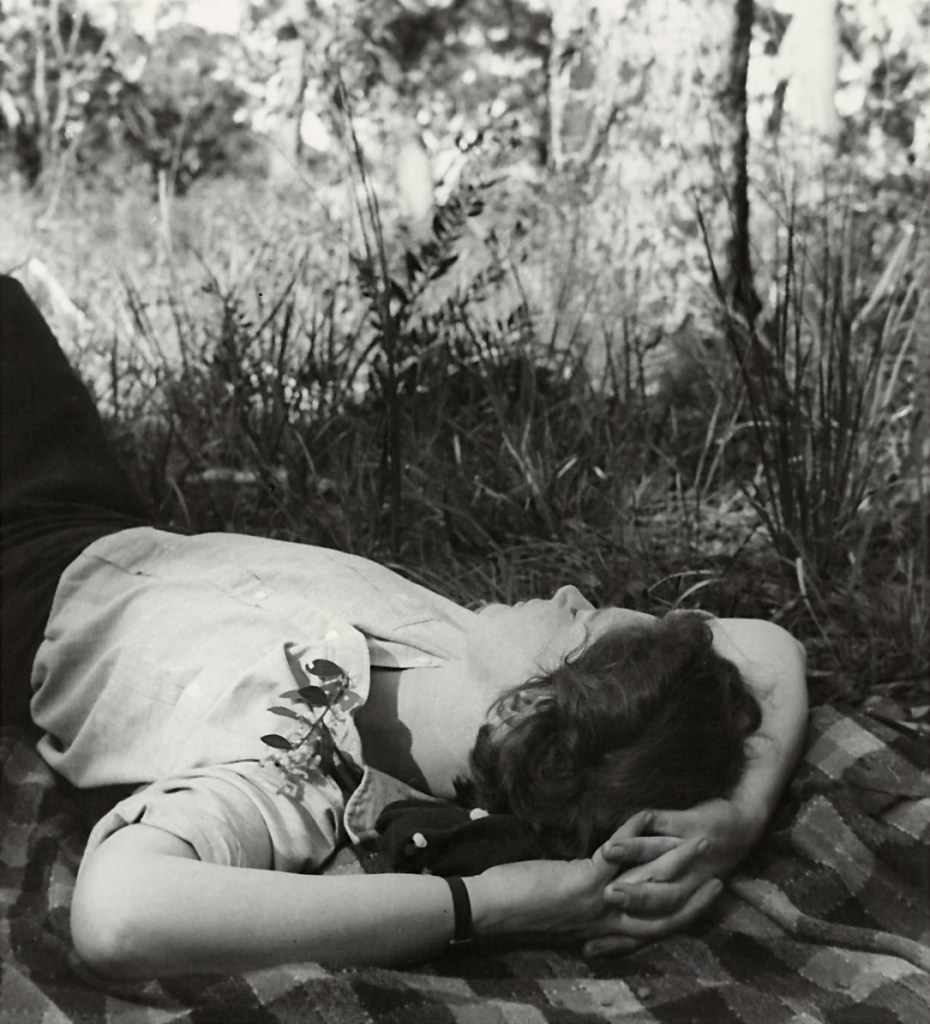
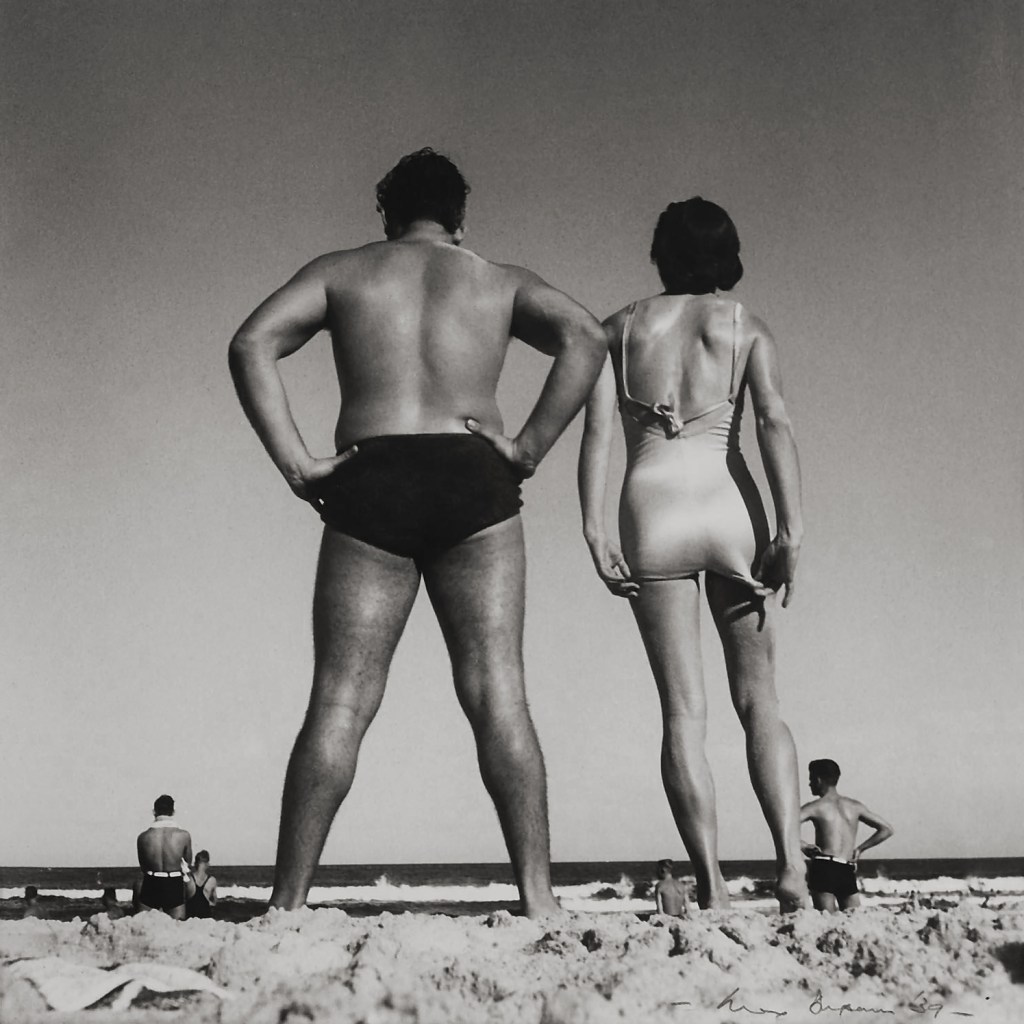
Installation view of the exhibition Patrick Pound: The Great Exhibition at NGV Australia with at left, People from behind 2016-2017; at centre, People who look dead but (probably) aren’t 2011-2014; and at right, The sleepers 2007-2017. Presented as part of the NGV Festival of Photography.
Photo: Wayne Taylor
The exhibition ends as it began, with figures whose backs are turned to us. Alongside are images of people who are asleep for the moment, and some forever; this gallery houses images of people who are all somehow removed from us. They are absorbed in their actions; they are unconscious, or not conscious, of us as they look away. There is a peculiar aspect of voyeurism that is afforded by the camera; the people in these photographs cannot see us looking at them. The camera also has a long association with the idea of stopping time – of freezing, or embalming, fleeting moments.
As Pound says, “Photography stops people in their tracks. Eventually every photograph is a photograph of a dead person. The camera is an idling hearse.”
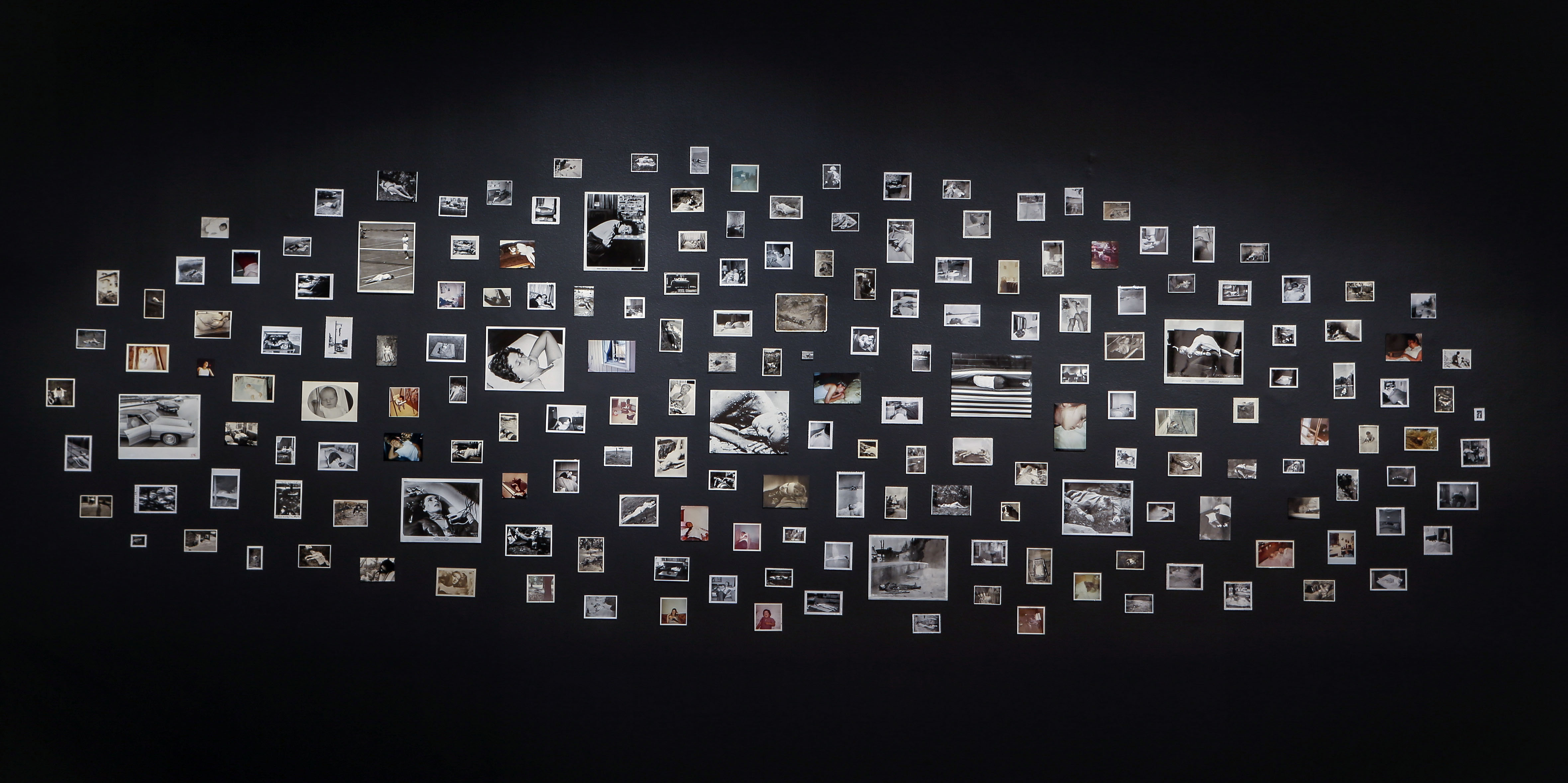
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
People who look dead but (probably) aren’t
2011-2014
Gelatin silver photographs and type C photographs
Yvonne Pettengell Bequest, 2014
© Patrick Pound
Photo: Wayne Taylor
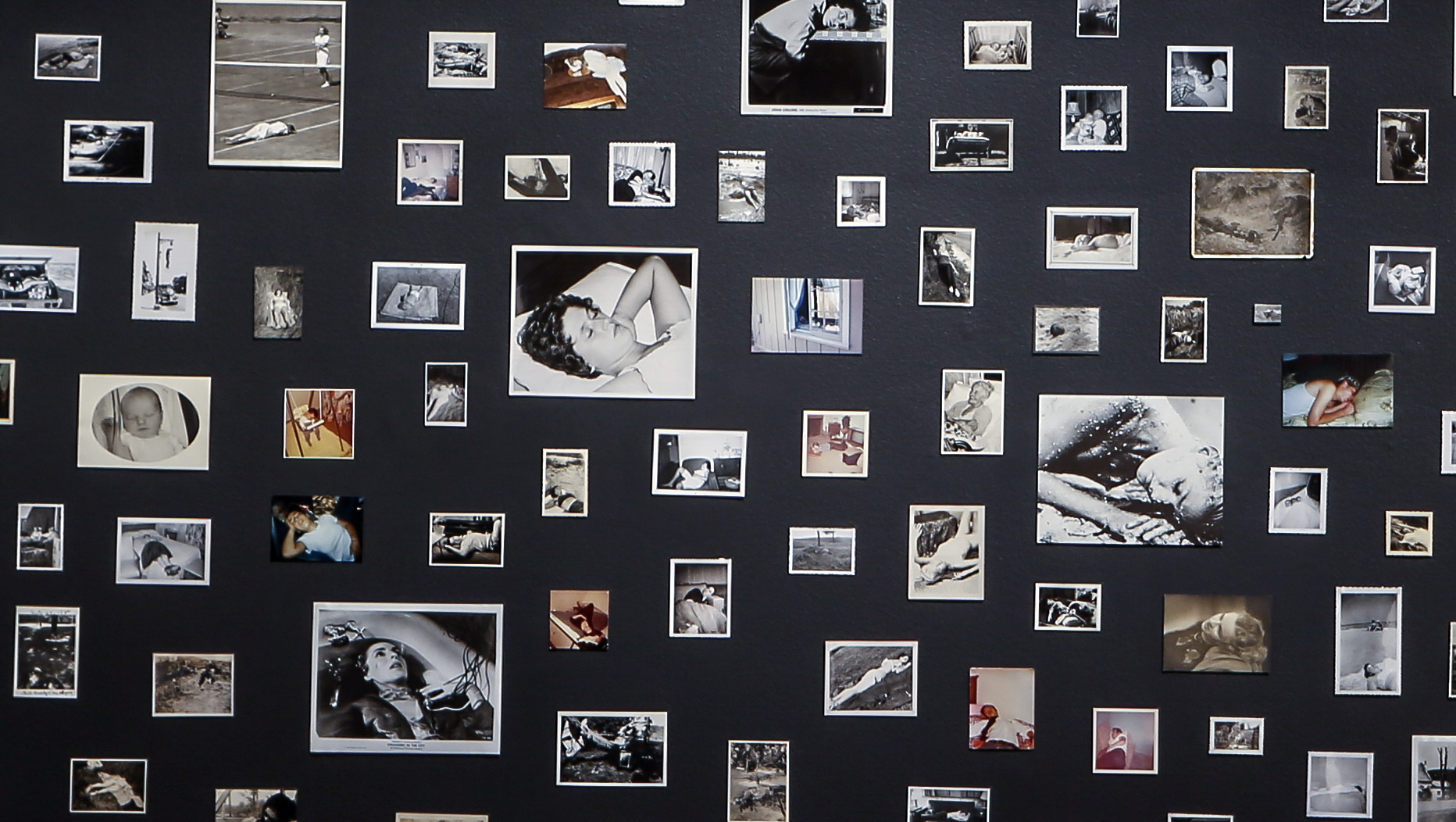
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s People who look dead but (probably) aren’t 2011-2014 (installation view detail)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
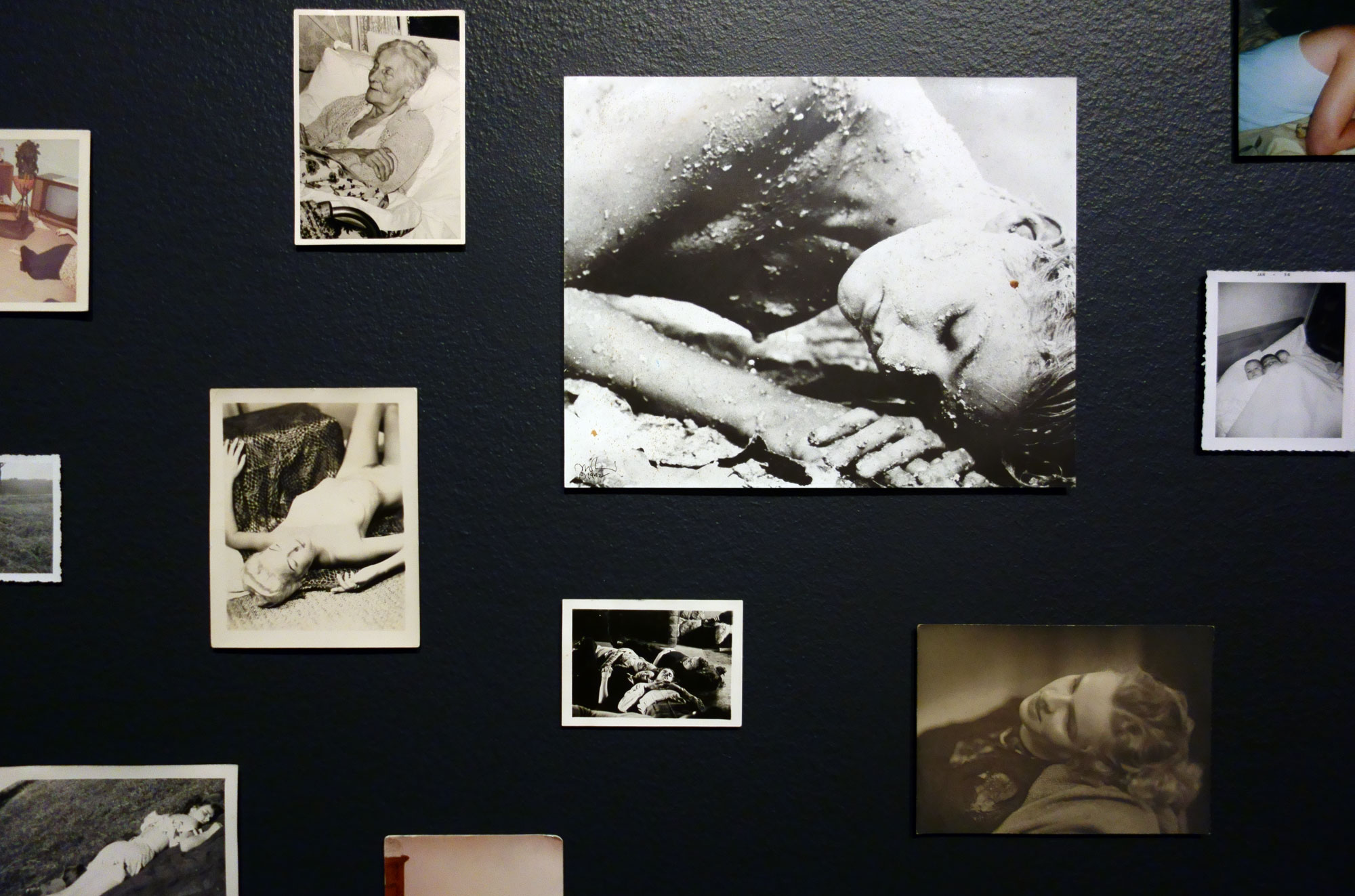
People who look dead but (probably) aren’t (installation view detail)
2011-2014
Gelatin silver photographs and type C photographs
Yvonne Pettengell Bequest, 2014
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s The sleepers 2007-2017 (installation view)
Photo: Wayne Taylor

Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
The sleepers (installation view detail)
2007-2017
Site specific installation comprising photographs collected by the artist
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photo: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
Installation view of Patrick Pound’s People from behind 2016-2017 (installation view)
Photo: Wayne Taylor
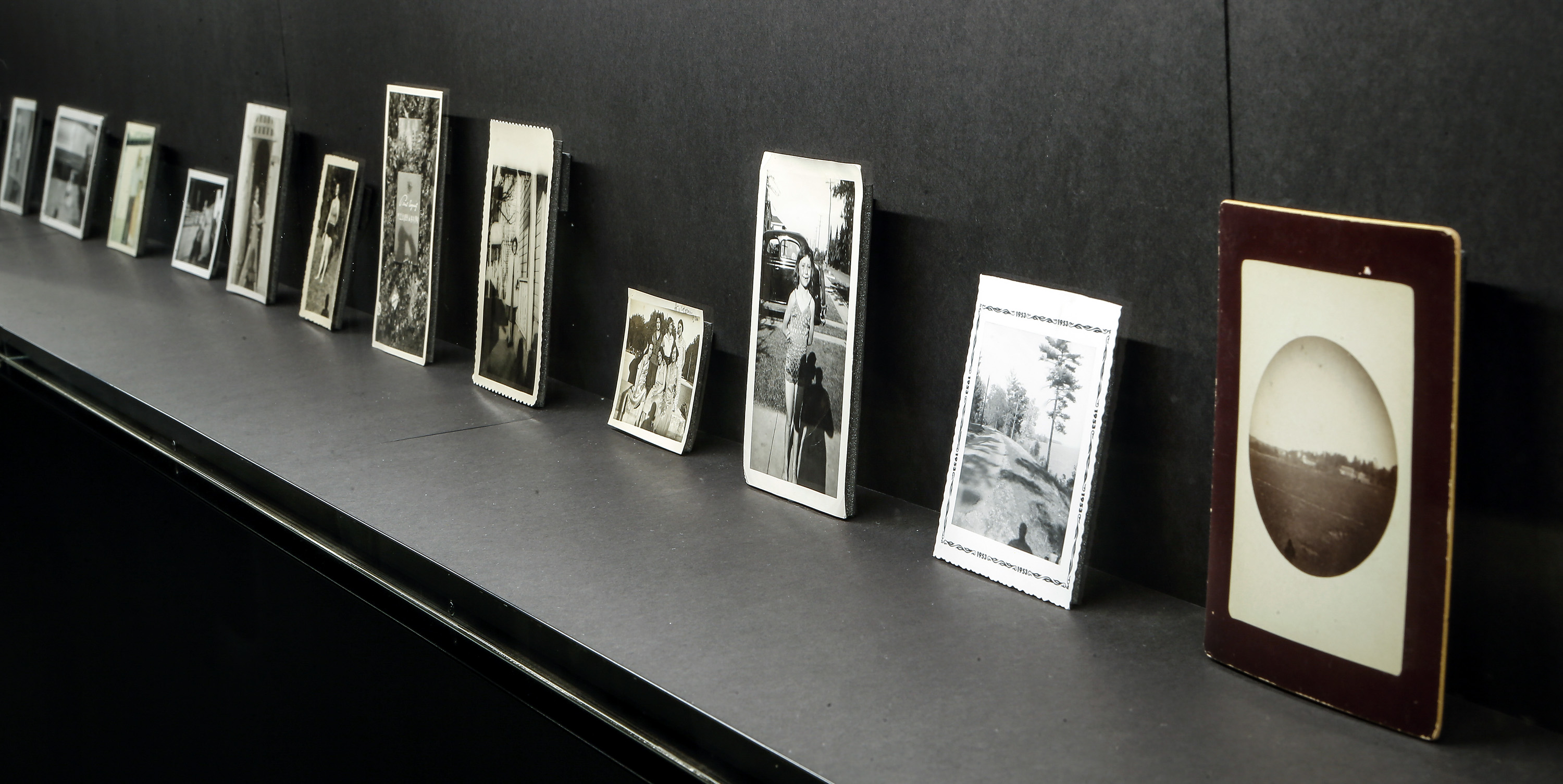
Patrick Pound (New Zealander/Australian, b. 1962)
People from behind (installation view details)
2016-2017
Site specific installation comprising works from the NGV Collection
Courtesy of the artist, Station, Melbourne, Stills Gallery, Sydney, Hamish McKay Gallery, Wellington and Melanie Roger Gallery, Auckland
© Patrick Pound
Photos: © Dr Marcus Bunyan, National Gallery of Victoria and Patrick Pound
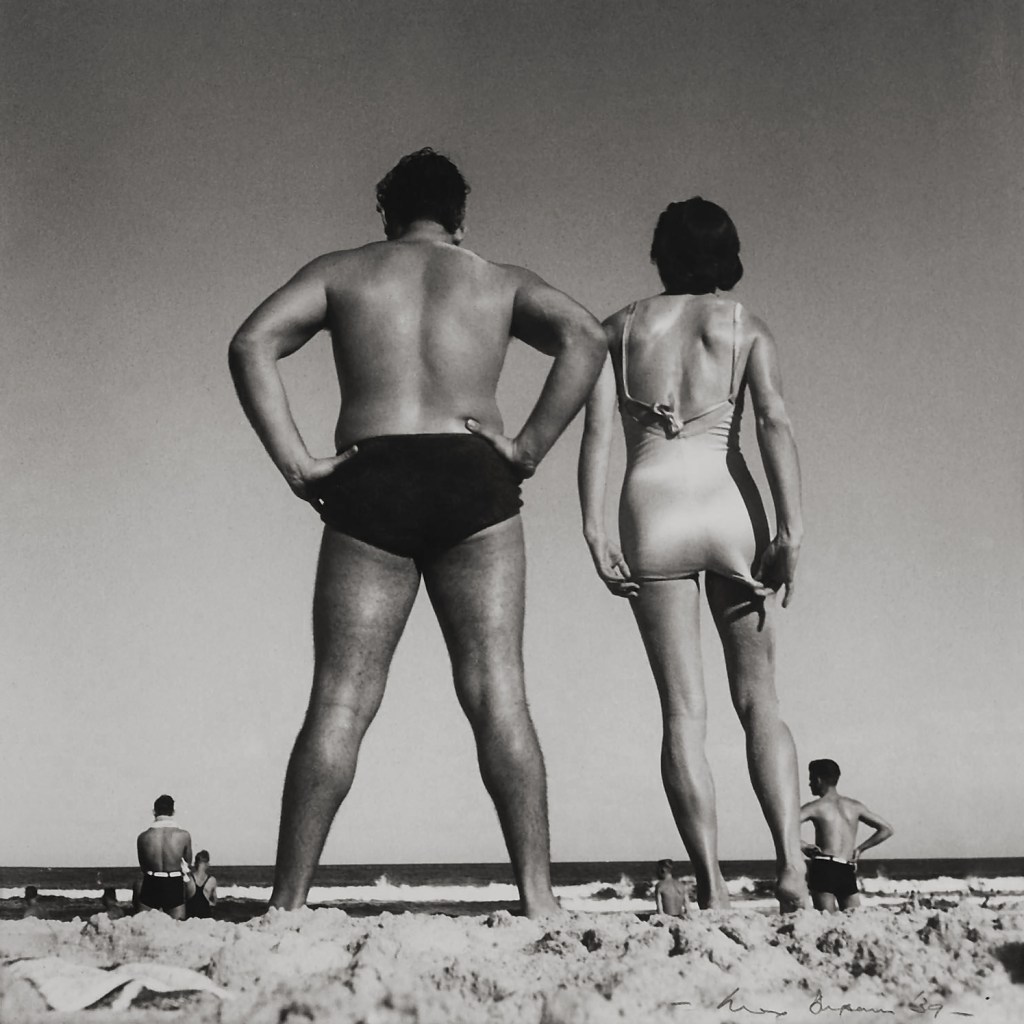

Max Dupain (Australian, 1911-1992)
Bondi
1939, printed c. 1975
Gelatin silver photograph
Purchased with the assistance of the Visual Arts Board, 1976
The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia
Federation Square
Corner of Russell and
Flinders Streets, Melbourne
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm








































































































































































































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.