Exhibition dates: 1st February – 7th May 2023
Curator: Geoffrey Batchen, Professor of the History of Art at the University of Oxford
Artist unknown (England)
Portrait of a man (resembling Jabez Hogg) operating a daguerreotype camera
c. 1845
Oil on canvas
The Bodleian Libraries, University of Oxford
This painting was acquired by the Bodleian Libraries at an auction and is the only known painting of a daguerreotypist at work. The man bears a strong resemblance to the photographer (and later ophthalmic surgeon) Jabez Hogg, who in 1843 published a ‘Manual of Photography’ and worked at the Illustrated London News from 1850 to 1866.
Fickle, fleeting time: illuminating a relationship between adaptability and uncertainty
The new medium – (in art) the substance the artist uses to create a piece of artwork, (in science) the substance that transfers the energy, or light from one substance to another substance or from one place to another, or from one surface to another, (in spirit) a person reputedly able to make contact with the world of spirits – of photography possessed the power to capture a pictorial truth to reality that could liberate, educate and memorialise while at the same time being used by the coercive power of the state, police, scientists and doctors (for example) to classify and control the sick, criminals, deviants, “natives” and “other” subjugated peoples.
In the Age of Machinery this instrument of new power harnessed technology and science to capture light in order to reflect back to man an image of himself as he would like to be seen – freezing a moment in time – as indeed the sitter had to stand still in order for their likeness to be captured in the early photographic processes. This action machine, an all dancing singing mix of paraphernalia, lens, metal, wood, glass and chemical reaction, forced a stillness in the sitter commensurate with the stillness of the resulting portrait image, im/mortal at one and the same time. By then by reflecting on that captured image the viewer could transcend time, bringing past time to present future time.
Imagine having never seen your picture before except in a cut-out silhouette or in a portrait drawing or oil painting. Imagine the shock of seeing your likeness before your eyes as a manifestation of a truth: this is what I look like at this point in time from the camera’s point of view – a manifestation of the energy of a person captured through the suspension of time, through the the spirit of the medium and, perhaps, through the medium of the spirit. That moment when the photograph is taken when you are taken out of yourself into another time and space. And then by looking at that image, coming to the understanding that you were already picturing your own death.
Within this exhibit one could dwell upon the Power of the new medium (to do what? to illuminate – make (something) visible/to help clarify or explain. What something is it helping to explain?) but rather, you might like to consider its adapt/ability to be so many things to so many people, to time travel a singular truth into the many truths to which reality points us. The shadow moves. In a medium where everything is supposedly “fixed” nothing is fixed, for everything is up for negotiation. Despite classification systems used to define categories and stereotypes in a bourgeois capitalist industrial society, this uncertainty of representation would have been incredibly confronting to a Victorian sensibility based on order and control – where everything, and every body (literally), had to be kept in its place.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Bodleian Libraries for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
A New Power: Photography in Britain 1800-1850 is a free exhibition in the Weston Library, running until the 7th May, 2023. This exhibition explores the early history of photography and its impact on British life. It examines the invention of the medium in its earliest incarnation, and how the broad range of uses had an unequivocal impact on British culture. From the invention of celebrity to the very first ‘travel photography’ and how this helped to consolidate colonial sensibilities. By showing how photography intersected with all aspects of a nascent modernity, A New Power reveals photography’s crucial role in making Britain the society it is today.
“The advent of photography was a complex historical event involving social, cultural and technological changes in about equal measure. These changes included significant developments in European society, such as the onset of the Industrial Revolution, but also important advances in scientific thinking and technology, and revolutionary shifts in the experience of time, space and subjectivity. All these elements were necessary to the conception of photography in the early 19th century.” (Exhibition text)
“We are in the infancy of invention with sun pictures, and no man can predict the results which may be obtained from a further advance in the paths of discovery … an instrument of new power [has been] placed at the disposal of Ingenuity and of Art.”
From a leaflet published in 1846
Philippe Jacques de Loutherbourg RA (French, 1740-1812)
Iron Works, Coalbrook Dale
c. 1824
From The romantic and picturesque scenery of England and Wales, London 1805, pl.[7]
Etching, aquatint
“The men, women, children, country and houses are all black … The country continues black, … everywhere, smoking and burning coal heaps, intermingled with wretched huts and carts and little ragged children”
~ The Princess Victoria in a diary entry about a trip to Birmingham, 1832
The advent of photography was a complex historical event involving social, cultural and technological changes in about equal measure. These changes included significant developments in European society, such as the onset of the Industrial Revolution, but also important advances in scientific thinking and technology, and revolutionary shifts in the experience of time, space and subjectivity. All these elements were necessary to the conception of photography in the early 19th century.
“Were we required to characterise this age of ours by any single epithet, we should be tempted to call it … the Mechanical Age. It is the Age of Machinery, in every outward and inward sense of that word”
~ Thomas Carlisle (1829)
J. W. Lowry (British, 1803-1879)
Power loom factory of Thomas Robinson Esqr. Stockport, Cheshire
c. 1849-1850
(after drawing by James Nasmyth)
From Andrew Ure, The Philosophy of Manufactures
Engraving trimmed to platemark
17.5 x 32cm
Science Museum Group Collection
© The Board of Trustees of the Science Museum
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
View of factory interior with five rows of c. 100 power looms using overhead lathe drives, operatives women, visitor and children looking around, spare rollers in corner. [James Nasmyth patents for printing calicoes etc, 1849-1850; Thomas Robinson textile machinery patents, 1844-1849] Factory located in Stockport, Cheshire.
About the exhibition
The announcement of photography’s invention in January 1839, first in Paris and then in London, introduced a ‘new power’ into British life. This new power – derived from photography’s capacity to automatically capture the images created in a camera – was soon being used for every conceivable purpose.
A New Power: Photography in Britain 1800-1850 explores the early history of photography, starting with the invention of the medium and the earliest dissemination of photographic images in Britain and ending with the famous Great Exhibition of 1851. It examines the broad range of uses that photography would quickly come to fill, from documenting the invention of celebrity to the very first ‘travel photography’ and how this helped to shore up colonial sensibilities.
By showing how photography intersected with all aspects of a nascent modernity, A New Power reveals photography’s crucial role in making Britain the society it is today.
Early experiments
In June 1802, Thomas Wedgwood and Humphry Davy co-authored an essay in the Journals of the Royal Institution. It described various experiments the two men had undertaken on making images by exposing to light some pieces of white paper or leather moistened with a solution of silver nitrate. The essay is often considered to be the first to describe specifically photographic experiments. Davy’s colleague Thomas Young made further experiments with silver nitrate in 1804.
“White paper, or white leather, moistened with solution of nitrate of silver, undergoes no change when kept in a dark place; but, on being exposed to the day light, it speedily changes colour, and, after passing through different shades of grey and brown, becomes at length nearly black … Nothing but a method of preventing the unshaded part of the delineation from being coloured by exposure to the day is wanting, to render the process as useful as it is elegant.”
~ Humphry Davy and Thomas Wedgwood (1802)
“I formed an image of the rings, by means of the solar microscope, with the apparatus which I have described in the Journals of the Royal Institution, and I threw this image on paper dipped in a solution of nitrate of silver, placed at the distance of about nine inches from the microscope”
~ Thomas Young (1804)
Scientific entertainments
Scientific experiments were frequently presented as public entertainments in the early 19th century. One satirical cartoon shows an experiment conducted at the Royal Institution in London by Thomas Young. He is seen administering nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, to Sir John Coxe Hippisley, with hilariously unfortunate results. On Young’s left is Humphry Davy, holding a pair of bellows. The audience includes many celebrities of the time. Davy and Young also conducted photographic experiments in this laboratory.
Fleeting time
A number of artists in the early 19th century tried to reconcile ‘fleeting time’ with the stasis of a painted landscape. In 1822, Louis Daguerre and his fellow artist Charles Marie Bouton opened their Diorama building in Paris. In the Diorama, viewers sat on a platform that slowly moved so that different views of the same painted scene, enhanced by special lighting and other effects, could appear to gradually reveal themselves. This apparatus was described by its inventors as ‘imitating aspects of nature as presented to our sight, that is to say, with all the changes brought by time, wind, light, atmosphere’.
“An attempt has been made to arrest the more abrupt and transient appearance of the Chiar’oscuro in Nature … to give ‘to one brief moment caught from fleeting time’ a lasting and sober existence”
~ John Constable (1833)
John Constable (British 1776-1837)
Study of clouds
1822
Oil on paper, laid on canvas [verso inscribed ’31 Sep.r 10-11 o’clock morning looking Eastward a gentle wind to East’]
H 48 x W 59cm
Ashmolean Museum, University of Oxford
Presented by Sir E. Farquhar Buzzard, Bt, 1933
One of a group of cloud studies from 1822 which are so accurate in their record of weather conditions, that Constable’s mistake in dating this example can be silently corrected to 1 October 1822.
Computing and photography
Shortly after his announcement of photography, William Henry Fox Talbot sent Charles Babbage eight examples of his photogenic drawings. Babbage went on to display Talbot’s photographs at his famous London soirées, intellectual gatherings that Talbot and his family occasionally attended in person. The other entertainments included a working model of a portion of Babbage’s first computing machine, the Difference Engine. Visitors therefore encountered photography and computing together, seeing both for the first time at the same time.
“Many thanks for the loan of those beautiful photographs. They were much admired last Saturday Evg … In the meantime, I gave Lady Byron a treat to whom I lent them for a few hours”
~ Charles Babbage, in a letter to William Henry Fox Talbot, 26 February 1844
Women and photography
Women played an often overlooked but important role in the development of British photography. Pioneering scholars like Elizabeth Fulhame and Mary Somerville were among the first to conduct experiments with light-sensitive silver salts and publish their results.
“The possibility of making cloths of gold, silver, and other metals, by chymical processes, occurred to me in the year 1780 ….”
~ Elizabeth Fulhame, from An Essay On Combustion with a View to a New Art of Dying and Painting, wherein the Phlogistic and Antiphlogistic Hypotheses are Proved Erroneous (November 1794)
“In my experiments … I employ the chloride of silver, which Mr Faraday was so kind as to prepare for me, and which, accordingly, was perfectly pure and white. It was liquid and might be uniformly spread over the paper.”
~ Mary Somerville, from ‘Extract of a letter from Mrs Somerville to M. Arago: Chemical Rays of the Solar Spectrum’, The Edinburgh New Philosophical Journal (October 1836 – April 1837)
Beautiful shadows
English scientist William Henry Fox Talbot first conceived of the possibility of a photographic process in 1833 and soon began experimenting with light-sensitive chemistry at his home, Lacock Abbey in Wiltshire. Initially, he only shared the results of his experiments with family members, including his sister-in-law, Laura Mundy. Her reply is the earliest description we have of photographic images.
“Dear Mr Talbot, Thank you very much for sending me such beautiful shadows.”
~ Laura Mundy, in a letter to William Henry Fox Talbot, 13 December 1834
Sir Francis Leggatt Chantrey RA (English, 1781-1841)
Bust of Miss Mundy
1825-1826
Plaster
Ashmolean Museum, University of Oxford
Inventing photography
“The most transitory of things, a shadow, the proverbial emblem of all that is fleeting and momentary, may be fettered by the spells of our natural magic, and may be fixed for ever in the position which it seems only destined for a single instant to occupy.”
~ William Henry Fox Talbot, writing in January 1839
The invention of the daguerreotype – a photographic process in which an image is recorded on a sheet of silver-plated copper – was announced in Paris on 7 January 1839. Daguerreotypomania ensued. The extraordinary news was reported in British newspapers just a few days later. This prompted English scientist William Henry Fox Talbot to reveal that he, too, had been working on photographic experiments, a paper-based process that he called photogenic drawing. These twin announcements heralded the advent of photography in Britain. Soon, actual examples could be seen in shops or in reproduction.
“M. Daguerre has discovered a method to fix the images which are represented at the back of a camera obscura; so that these images are not the temporary reflection of the object, but their fixed and durable impress.”
~ Hippolyte Gaucheraud, as translated in The Literary Gazette, 12 January 1839
Photogenic drawings
William Henry Fox Talbot published the details of his invention of photogenic drawing in January 1839, so that anyone with the means and some chemical knowledge could use the process. John Herschel soon devised his own light-sensitive formula and made a camera picture, a view of the framework of his father’s forty-foot telescope. He ‘washed out’ the image with hyposulphite of soda, which, unlike Talbot’s use of table salt, entirely prevented further development. In contrast, Talbot’s photogenic drawings remain light sensitive and therefore cannot be displayed in this exhibition.
‘Pictures Formed by the Action of Light’
From The Mechanic and Chemist: a Magazine of the Arts and Sciences (13 April 1839)
Wood engravings after photogenic drawings
Radcliffe Science Library, University of Oxford
“The Mechanic and Chemist was one of the better-established of the pioneering illustrated journals, already entering its fourth year of publication. It was started by George Berger, a publisher and bookseller based in the Strand, who launched a wide range of such publications. Most of these collapsed by the mid-1840s, but were in their heyday in 1839. Wood engravings were the most practical way for these publications to include pictures. Far less expensive and much faster for ‘woodcutters’ or ‘woodpeckers’ to produce than steel or copper engravings, unlike lithographs they were intaglio and could be printed alongside the type in a conventional letterpress. The journal had already published accounts of Daguerre’s and Talbot’s inventions, with a strong bias towards Daguerre, and on 13 April 1839 it attempted to express these inventions in visual form. The photographer here, ‘Q.E.D’, said that the silhouette negative had been “taken with the sun behind, forming a strong contrast of light and shade: the preparation not being sensible enough to show the intermediate shades directly.” Apparently overlooking the fact that Talbot had published the idea of making a print from the negative right from the start, Q.E.D. thought he had invented “a method of transforming such pictures into true representations of nature.””
Larry J Schaaf. “Revelations & Representations,” on the the Talbot Catalogue Raisonné blog 27th May 2016 [Online] Cited 21/02/2023
‘Fac-Simile of a Photogenic Drawing’
From The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction (20 April 1839)
Wood engraving after a photogenic drawing contact photograph by Golding Bird
My personal favourite early woodcut representation of a photogenic drawing is this one, published a week later and coming much closer to mimicking the nature of one of Talbot’s originals. The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction had taken the exceptional step of printing the wood block in a brown ink similar to the tone of photogenic drawings; this would have required a second printing of that sheet in black in for the type and represented a willingness to go to extra expense for the sake of accuracy. (Before colour printing became ubiquitous, I wish that publishers in the 1960s-1980s had recognised the value of this approach more often). The Mirror was one of the older illustrated journals, having started in 1822, and not everyone favoured its antiquarian editor, John Timbs. He explained that “our prefixed engraving is a fac-simile of a photogenic drawing, for which we are indebted to the kindness of Dr. Golding Bird, a distinguished botanist, who has published the following very interesting paper on the application of the photographic art to botanical purposes, in that excellent periodical, the Magazine of Natural History.” Dr. Bird (1814-1854) had been an outstanding chemist ever since a child. By 1836 he held the chair of Natural Philosophy at Guy’s Hospital in London. The next time your physician applies his stethoscope to your chest you will be benefitting from one of Bird’s many inventions. Bird wrote about the effects of light before 1839 and once photography was announced he devoted considerable attention to it in his publications. He at first tried Daguerre’s little-known process on paper, but preferred Talbot’s process, although noting that he wished that Talbot had published even more detailed instructions. Sadly, he died early and none of his own photographs are known to have survived.
Larry J Schaaf. “Revelations & Representations,” on the the Talbot Catalogue Raisonné blog 27th May 2016 [Online] Cited 21/02/2023
‘Fac-Similes of Photogenic Drawings’
From The Magazine of Science (27 April 1839)
Wood engravings after photogenic drawing contact photographs by George William Francis
A very new journal, The Magazine of Science featured the work of a botanist contemporary with Talbot, George William Francis (1800-1865). In 1843 he emigrated to Australia, forming the first Botanic Garden there, in Adelaide. Francis explained that he had photographically sensitised boxwood blocks and made the above photographic impressions directly on them. These were then sent to the wood engraver. The editor felt that the lace was accurately represented but “in the flowers he has failed to express the delicacy and beauty of the drawings.”
Unlike the other journals, The Magazine of Science had delayed publishing about the new invention “because we were desirous in this, as in all things else, to test and, if possible, improve upon the experiments suggested by Mr. Talbot, and since pursued with such ardour by all the philosophers and artists of this country, of France, and of Germany. We now however proceed to give all the information in our power, having tried all the different receipts published.”
Larry J Schaaf. “Revelations & Representations,” on the the Talbot Catalogue Raisonné blog 27th May 2016 [Online] Cited 21/02/2023
Sir John Herschel (British, 1792-1871)
Experimental photogenic drawing of the mounting of Sir William Herschel’s 40-foot telescope in the garden of Herschel’s house at Slough
October 1839
Photogenic drawing
History of Science Museum, University of Oxford
At the time that this was taken, Sir William Herschel’s 40-foot telescope was already a famous astronomical symbol, although it was being demolished – hence the absence of the telescope’s tube. The only camera images Sir John Herschel is know to have taken are of his father’s telescope; they also include the first photograph to be taken on glass (now in the Science Museum, London).
Anonymous. “Photogenic Drawing 5,” on the Museum of the History of Science website Nd [Online] Cited 19/02/2023
Daguerreotypes and their copies
Shortly after the announcement of the invention of the daguerreotype in France, British enthusiasts began to import examples of such photographs. The glass shop owned by Claudet & Houghton also offered their customers a selection of French engravings derived from daguerreotypes. Daguerreotypes were taken in London as public demonstrations for the edification of audiences eager to see the latest advances in science and technology. In September 1840, the English journal Westminster Review published two lithographic images, traced from daguerreotypes that had been made in the Polytechnic Institution in London.
Studio of Noël Marie Paymal Lerebours (France) (French, 1807-1873)
West façade of Notre Dame cathedral, Paris
1839-1840
Daguerreotype
Magdalen College, University of Oxford
Lerebours, an optical instrument maker, quickly embraced photography in his business, and pioneered both the market in architectural and scenic Daguerreotypes, as well as their reproduction as engravings, as witnessed in his serial work Excursions Daguerriennes. The plate size is 8.5 x 6.5 inches, the image is laterally reversed, and there is no gold toning – all characteristics of early Daguerreotypes from the period before portraiture became possible.
Anonymous. “Daguerreotype 1,” on the Museum of the History of Science website Nd [Online] Cited 19/02/2023
Noël Marie Paymal Lerebours (French, 1807-1873)
Plate 6: Egypte: Harem de Méhémet-Ali a Alexandre
c. 1840
From Excursions daguerriennes, vues et monuments les plus remarquables du Globe (Paris: Rittner & Goupil, 1840-1842)
Engraving after daguerreotype
10 13/16 × 15 1/2 × 2 3/16 in. (27.5 × 39.3 × 5.5cm) (Book)
Public domain
This print played an important role in popularising the notion of the artist-daguerreotypist as trustworthy eyewitness. In March 1840, while Goupil-Fesquet and his teacher, Horace Vernet, were on a daguerreotype tour of Egypt and the Levant, a fake story circulated in the Parisian press claiming that Vernet had gained access to Muhammad ‘Ali’s harem. With this print and the accompanying text, Goupil-Fesquet aimed to prove, as “both ocular witness and daguerreotype operator,” that they had seen only the guarded entrance.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Noël Marie Paymal Lerebours (French, 1807-1873)
Plate 4, England, St Pauls and London
c. 1840
From Excursions daguerriennes, vues et monuments les plus remarquables du Globe (Paris: Rittner & Goupil, 1840-1842)
Engraving after daguerreotype
10 13/16 × 15 1/2 × 2 3/16 in. (27.5 × 39.3 × 5.5cm) (Book)
Courtesy of a Private Collection
L.L. Boscawen Ibbetson (English, 1799-1869)
Fossils, engraved on a daguerreotype plate
1840
From The Westminster Review September 1840, p. 460
Ink-on-paper lithograph by A. Friedel
Captain Levett Landon Boscawen Ibbetson (1799 – 8 September 1869) was an English 19th century geologist, inventor, organiser and soldier. He is particularly associated with early developments in photography. He was a member of the London Electrical Society and later a Fellow of the Royal Society (elected 6 June 1850). Capt. Ibbetson developed a method of taking lithographic impressions from daguerreotypes… His illustration of a fossil, “Transverse section of madrepore” in The Westminster Review of September 1840 is credited with being the first example of the use of limelight to shorten exposure times when making daguerreotypes.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Photography and publishing
Paper photographs had one distinct advantage over daguerreotypes: they could be printed in multiple copies and pasted into publications. A number of books and journals containing photographs were produced, seeking to demonstrate the efficacy of the new medium as a means of illustration. These publications met with mixed success, as the unreliable quality of their photographs could not compete with traditional engravings.
Anna Atkins and cyanotype
In a paper delivered to the Royal Society on 13 June 1842, John Herschel proposed a photographic process involving an iron salt that resulted in Prussian-blue images. He decided to call this ‘cyanotype’. Exploiting this invention, the English botanist Anna Atkins issued albums of cyanotype prints of seaweed and algae from 1843, and these are often regarded as the earliest photographic books.
Anna Atkins (British, 1799-1871)
Sargassum bacciferum
1843
From Photographs of British Algae: Cyanotype Impressions (1843-1853)
Cyanotype
25.3 x 20cm (9 15/16 x 7 7/8 in.)
This photograph: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Gilman Collection, Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 2005.
Public domain
The photograph in the exhibition: Oriel College, University of Oxford
The first book to be photographically printed and illustrated, Photographs of British Algae was published in fascicles beginning in 1843 and is a landmark in the history of photography. Using specimens she collected herself or received from other amateur scientists, Atkins made the plates by placing wet algae directly on light-sensitised paper and exposing the paper to sunlight. In the 1840s, the study of algae was just beginning to be systematised in Britain, and Atkins based her nomenclature on William Harvey’s unillustrated Manual of British Algae (1841), labelling each plate in her own hand.
Although artistic expression was not her primary goal, Atkins was sensitive to the visual appeal of these “flowers of the sea” and arranged her specimens on the page in imaginative and elegant compositions. Uniting rational science with art, Photographs of British Algae is an ambitious and effective book composed entirely of cyanotypes, a process invented in 1842 by Sir John Herschel and long used by architects to duplicate their line drawings as blueprints.
Anonymous. “Photographs of British Algae: Cyanotype Impressions,” on the Metropolitan Museum of Art website Nd [Online] Cited 22/02/2023
Success and failure
In 1846, the editor of the journal The Art-Union asked William Henry Fox Talbot to supply approximately 7000 salt prints to accompany a story about the calotype process. These prints were made at the Reading Establishment, a printing business run by Talbot’s former Dutch valet Nicolaas Henneman. Unfortunately for Talbot and Henneman, the Art-Union project proved to be a promotional and financial disaster, with most of the photographs, made in a rush, fading soon after publication.
William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877)
View of one of the towers of Orleans Cathedral
Taken on 21 June 1843
Published in The Art‑Union: Monthly Journal of the Fine Arts and the Arts, Decorative, Ornamental (June 1846)
Salted paper photograph from calotype negatives
16.3 x 20.2cm (6 7/16 x 7 15/16 in.)
This photograph: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Purchase, Barbara Schwartz Gift, in memory of Eugene M. Schwartz, and Rogers Fund, 1996. Public domain
The photograph in the exhibition: Private Collection
In 1840 Talbot devised a negative/positive process that allowed multiple prints of a single image – the procedural basis of nearly all photography since. Talbot’s negatives were made of thin writing paper; the fibrous texture obscured some detail, but it imparted softness and a graded tonality to the resulting print. This photograph, showing the upper levels of one tower of Orléans Cathedral, was made on June 7, 1843, when Talbot was en route to Paris to sell the French rights to his patented process. Because he was unsuccessful in this enterprise, the French did not make paper photographs for another decade.
Anonymous. “Cathedral at Orléans,” on the Metropolitan Museum of Art website Nd [Online] Cited 22/02/2023
Nicolaas Henneman (Netherlands/England, 1813-1898)
The West Façade of Westminster Abbey
Taken before May 1845
Published in The Art-Union: Monthly Journal of the Fine Arts and the Arts, Decorative, Ornamental (June 1846)
Salted paper photograph from calotype negatives
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Jean Horblit, in memory of Harrison D. Horblit, 1994
Talbot’s negative-positive photographic process, first made public in 1839, would change the dissemination of knowledge as had no other invention since movable type. To demonstrate the paper photograph’s potential for widespread distribution – its chief advantage over the contemporaneous French daguerreotype – Talbot produced The Pencil of Nature, the first commercially published book illustrated with photographs. With extraordinary prescience, Talbot’s images and brief texts proposed a wide array of applications for the medium, including portraiture, reproduction of paintings, sculptures, and manuscripts, travel views, visual inventories, scientific records, and essays in art.
Despite the revolutionary nature of Talbot’s undertaking, or perhaps because of it, The Pencil of Nature was not a commercial success. Today fewer than forty substantially complete copies – many quite faded – are extant. The present example, containing all twenty-four plates and still in its rare original fascicle covers, was formerly in the collection of Talbot’s daughter Matilda.
Anonymous. “Westminster Abbey,” on the Metropolitan Museum of Art website Nd [Online] Cited 22/02/2023
Nicolaas Henneman (Netherlands / England, 1813-1898)
Born in the Netherlands village of Heemskerk on December 8, 1813, virtually nothing is known about the life of Nicolaas Henneman, until he was hired as a member of inventor William Henry Fox Talbot’s domestic staff shortly after relocating to England in 1838. He quickly progressed to his master’s valet, and finally his most trusted darkroom assistant. Mr. Henneman was an eager student, and was soon collaborating with Mr. Talbot on a wide range of photographic experiments. He became an expert in the intricate calotype process that required both advanced chemistry knowledge and technical precision, but most of all patience. …
In 1843, Mr. Henneman accompanied his boss to France, where his photographs were subsequently featured in Mr. Talbot’s The Pencil of Nature publication. Buoyed by the critical acceptance, he took the bold move of leaving his employment with Mr. Talbot to open his own full-service calotype business, believed to be the first of its kind. Within the modest grounds of a former schoolyard, Mr. Henneman constructed a glass house to serve as his studio, and he received some modest commissions to illustrate various historical texts, including Mr. Talbot’s Sun Pictures in Scotland and Sir William Stirling’s Annals of the Artists of Spain. In 1848, chemist Thomas Malone became a junior partner, necessitating a name change to Henneman & Malone. With the appointment as “Photographer in Ordinary to Her Majesty,” his conversion to wet-collodion processing, and his successful experiments to reduce exposure times, Mr. Henneman seemed assured of financial prosperity. However, his target market was too small, and his business closed with little notice.
Although Nicolaas Henneman was of the industry’s earliest architects, by the mid-1850s, the London photographic community was becoming exceedingly overcrowded. The soft-spoken Dutchman found himself being pushed out by a younger generation. After Mr. Henneman’s business went bankrupt, his steadfast champion Mr. Talbot quietly paid off his creditors. He moved to Birmingham, where he became an operator for master photographers Napoleon Sarony and Robert White Thrupp, among others. This proved to be both commercially unsuccessful and creatively unsatisfying. Ever the survivor, Mr. Henneman bought and operated a lodging house at 18 Half Moon Street in London during the 1870s. He died on January 18, 1898 at the age of 84, with his photographic contributions virtually forgotten. Fortunately, however, many of Nicolaas Henneman’s photographs have been preserved and can be seen in the collections of Lacock Abbey, Bradford’s National Media Museum, and in Amsterdam’s Rijksmuseum.
Anonymous. “Nicolaas Henneman,” on the Historic Camera website 3rd May 2020 [Online] Cited 22/02/2023
William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877)
Palace of Justice, Rouen
Taken in May 1843
Published in The Art-Union: Monthly Journal of the Fine Arts and the Arts, Decorative, Ornamental (June 1846)
Salted paper photograph from calotype negatives
Talbot may not have intended his brief diversion to Rouen to be as significant as it has become, but during those four days of miserable weather, the creative baton was handed from art to photography – from Turner to Talbot. During a brief “éclairci” from bad weather, Henry took his camera half a mile from the hotel and into another era of history. Le Palais de Justice was one of the secular buildings of medieval Rouen, completed in 1508, occupying three fifths of an acre in a three sided quadrangle. It was described as an elaborately florid style “sumptuous in its decorations both without and within; its triple canopy windows enriched with mullions and tracery.”
Talbot concentrated on the ornate detail of these windows, isolating the intricate elements sculpted by skilled stonemasons over three centuries earlier. Now housing the Rouen criminal courts, Le Palais de Justice represented Henry’s liberation from rain-soaked captivity. The image above stands in magnificent contrast to his study of the lace curtained view from within the Hotel l’Angleterre. This time he was outside looking in.
Rose Teanby. “Talbot’s Rouen, a tale of two cities,” on the the Talbot Catalogue Raisonné blog 9th March 2018 [Online] Cited 21/02/2023
“The most transitory of things, a shadow, the proverbial emblem of all that is fleeting and momentary, may be fettered by the spells of our natural magic, and may be fixed for ever in the position which it seems only destined for a single instant to occupy.”
William Henry Fox Talbot, writing in January 1839
Most extraordinary
A first-hand account of a demonstration of the daguerreotype process was given by two naval architects from India in a book they published in 1841: ‘And we also saw [at the Adelaide gallery in London] the Daguerreotype which is the most extraordinary production of modern times. We know not how better to describe it than to say, that it is embodying a shadow … In a room fitted up as a Theatre, with shutters by which the light can be totally excluded, M. Dele Croix, a French gentleman, explains all the process’.
“The appearance of these drawings is very peculiar. The shadows are a dull grey, varying until they become almost blacky and though the pictures they delineate are accurate in the extreme, they are not pleasing. They appear unnatural and look somewhat like a moonlight scene. The Daguerreotype, with all its necessary apparatus, is manufactured and sold in Paris, for about £20. In Bombay, where the sun is always powerful, pictures of scenery could daily be produced.”
~ Jehangeer Nowrojee and Hirjeebhoy Merwanjee, Journal of residence of two years and a half in Great Britain, London, 1841
Views of London
The earliest photographs of London were taken by visiting Frenchmen. Soon, however, demonstrations of the new process were being offered to audiences at the Polytechnic Institution and Adelaide Gallery in London. In early 1842, Antoine Claudet was commissioned by the newly established Illustrated London News to make a series of daguerreotype views of London. A wood-engraved panorama of the city was then derived from them. This panorama, ‘a picture bigger than anything previously issued’, was promised in the News‘s inaugural issue of 14 May 1842 as a gift to all who subscribed to the journal for six months.
M. de St Croix (French)
Parliament Street from Trafalgar Square
1839
Daguerreotype in wood frame
Victoria & Albert Museum, London
This is the oldest photograph in the Museum’s collection. It is a daguerreotype, a unique image formed on a silvered copper plate. The daguerreotype was the first photographic process, publicised in January 1839. It was named after its inventor, Louis Daguerre. Just a few weeks after the French Government revealed the secrets of daguerreotypy in Paris in August 1839, Monsieur de St Croix organised the first public demonstration of the process in London. This is therefore among the very first photographs taken in London. The scene is reversed – as is characteristic of the process – and the image on the shiny surface is difficult to read. However, once caught at the correct angle, amazing detail emerges. In the foreground there is a statue of Charles I and in the distance the royal Banqueting House. There are also traces of the people who stayed still long enough to register on the exposure, which probably lasted some minutes.
Anonymous. “Parliament Street from Trafalgar Square,” on the V&A website Nd [Online] Cited 22/02/2023
Ebenezer Landells (engraver) et al
‘London in 1842, Taken from the Summit of the Duke of York’s Column (north view)’
From the Illustrated London News (7 January 1843)
Hand-coloured panoramic print, from wood engravings after daguerreotypes by Antoine Claudet taken in 1842
A view of London looking northwards from the summit of the Duke of York’s statue, with Carlton Gardens in the foreground, beyond is Waterloo Place, lower Regent Street and Piccadilly circus.
London labour, London poor
Numerous engraved portraits of members of the working class are featured in Henry Mayhew’s London Labour and the London Poor, first published in 1851. Mayhew’s text provided a richly ethnological and often racialised commentary on London’s street workers, based on interviews and social analysis, given added force by the addition of wood engravings based on daguerreotypes.
Portrait of Henry Mayhew (From a Daguerreotype by BEARD)
“My earnest hope is that the book may serve to give the rich a more intimate knowledge of the sufferings, and the frequent heroism under those sufferings, of the poor.”
The London Coffee-Stall (From a Daguerreotype by BEARD)
“The struggle to get a living is so great, that, what with one and another in the coffee-trade, it’s only those as can get good ‘pitches’ that can get a crust at it.”
The Irish Street-Seller (From a Daguerreotype by BEARD)
From Henry Mayhew’s ‘London labour and the London poor: a cyclopedia of the condition and earnings of those that will work, cannot work, and will not work’, Volume 1 page 97, 1851.
Bodleian Libraries, University of Oxford
“I wish people that thinks we’re idle now were with me for a day. I’d teach them.”
Hindoo Tract-Seller (From a Daguerreotype by BEARD)
“The man whose portrait supplies the daguerreotyped illustration of this number is unable to speak a word of English, and the absence of an interpreter, through some accident, prevented his statement being taken at the time appointed.”
The Blind Boot-Lace Seller (From a Daguerreotype by BEARD)
“I only wish vaccination had been in vogue then as it is now, and I shouldn’t have lost my eyes. God bless the man who brought it up, I say; people doesn’t know what they’ve got to thank him for.”
All from
Henry Mayhew (English, 1812-1887)
London labour and the London poor; a cyclopedia of the condition and earnings of those that will work, those that cannot work, and those that will not work: The London street-folk; comprising, street sellers. Street buyers. Street finders. Street performers. Street artizans. Street labourers. With numerous illustrations from photographs
London, 1851
‘London Labour and the London Poor’ is an oral account of London’s working classes in the mid-19th century. Taking the form of verbatim interviews that carefully preserve the grammar and pronunciation of every interviewee, the completed four-volume work amounts to some two million words: an exhaustive anecdotal report on almost every aspect of working life in London.
Henry Mayhew (25 November 1812 – 25 July 1887) was an English journalist, playwright, and advocate of reform. He was one of the co-founders of the satirical magazine Punch in 1841, and was the magazine’s joint editor, with Mark Lemon, in its early days. He is also known for his work as a social researcher, publishing an extensive series of newspaper articles in the Morning Chronicle that was later compiled into the book series London Labour and the London Poor (1851), a groundbreaking and influential survey of the city’s poor.
Henry Mayhew (English, 1812-1887)
London labour and the London poor; a cyclopedia of the condition and earnings of those that will work, those that cannot work, and those that will not work: The London street-folk; comprising, street sellers. Street buyers. Street finders. Street performers. Street artizans. Street labourers. With numerous illustrations from photographs
London, 1851
Priests and politicians
All sorts of celebrities were celebrated in engravings based on daguerreotypes, from priests to politicians. One example is Lájos Kossuth, former regent-president of the Kingdom of Hungary, who arrived as an exile at the port of Southampton on 23 October 1851. Over the next three weeks he toured Britain, giving lectures in support of the struggle to free Hungary from the Hapsburg Empire. During this period, he and his family visited Antoine Claudet’s studio in London to have a number of daguerreotype portraits made. Versions of these images were subsequently distributed around the world in the form of lithographs or engravings.
Alonzo Chappel (American, 1828-1887)(engraver)
Thomas Chalmers: Likeness from a daguerreotype by Claudets [sic]
1873
Steel engraving of a Scottish clergyman after a daguerreotype by Antoine Claudet studio in c. 1847
Public domain
Alonzo Chappel (March 1, 1828 – December 4, 1887) was an American-Spanish painter, best known for paintings depicting personalities and events from the American Revolution and early 19th-century American history.
Thomas Chalmers FRSE (17 March 1780 – 31 May 1847), was a Scottish minister, professor of theology, political economist, and a leader of both the Church of Scotland and of the Free Church of Scotland. He has been called “Scotland’s greatest nineteenth-century churchman.”
Notable commissions
A particularly notable commission for the Beard studio involved making daguerreotype portraits in May 1845 on the deck of the H.M.S. Erebus. The subjects were fourteen of the officers about to set out under the command of Sir John Franklin in search of the Northwest Passage above Canada. These pictures became particularly famous when the entire expedition disappeared, never to be heard from again. After a public campaign by Lady Franklin in the illustrated press, many other ships were sent over during the ensuing years to try and find the expedition.
Installation view of Studio of Richard Beard daguerreotypes of Sir John Franklin (May 1845, below) and Lieutenant Graham Gore, Commander (May 1845, below)
Studio of Richard Beard (English, 1801-1885)
Sir John Franklin
May 1845
Daguerreotype in leather case
The Scott Polar Institute, University of Cambridge
Public domain
Sir John Franklin, 16 May 1845, suffering from influenza before leaving for the Arctic. He is wearing the 1843-1846 pattern Royal Navy undress tailcoat with cocked hat.
Lady Franklin commissioned daguerreotype photographs of the twelve senior officers of HMS Erebus and Captain Crozier of HMS Terror. They were taken on board the Erebus at the dockside in Greenhithe on 16 May 1845, just before the ships sailed. Franklin was fascinated by this new technology and included photographic apparatus as part of the expedition’s equipment.
Sir John Franklin KCH FRS FLS FRGS (16 April 1786 – 11 June 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. After serving in wars against Napoleonic France and the United States, he led two expeditions into the Canadian Arctic and through the islands of the Arctic Archipelago, in 1819 and 1825, and served as Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen’s Land from 1839 to 1843. During his third and final expedition, an attempt to traverse the Northwest Passage in 1845, Franklin’s ships became icebound off King William Island in what is now Nunavut, where he died in June 1847. The icebound ships were abandoned ten months later and the entire crew died, from causes such as starvation, hypothermia, and scurvy.
Richard Beard (22 December 1801 – 7 June 1885) was an English entrepreneur and photographer who vigorously protected his photographic business by litigation over his photographic patents and helped to establish professional photography in the UK.
Studio of Richard Beard (English, 1801-1885)
Lieutenant Graham Gore, Commander
May 1845
Daguerreotype in leather case
The Scott Polar Institute, University of Cambridge
Public domain
Studio of Richard Beard Jr. (London)
Tyrolese Singers
1851-1852
Hand-coloured enamelled daguerreotype
14.1 x 10.3cm
Royal Collection Trust
Acquired by Queen Victoria and Prince Albert in 1852
© His Majesty King Charles III 2022
This daguerreotype, produced and enamelled by the studio of Richard Beard, was purchased by Queen Victoria in 18522, the same year in which her mother, the Duchess of Kent, arranged for the Tyrolese minstrels to surprise the Queen with a serenade at breakfast for her birthday at Osborne. About the event, the Duchess wrote: “Victoria appeared very much pleased with the surprise.”
Hand-coloured enamelled daguerreotype of a group of Tyrolese singers called Klier, Rainer, Margreiter, Rahm and Holaus. Rahm is seated facing partly left playing a dulcimer and Rainer holds a guitar. All are wearing traditional Tyrolese costume, coloured with both dark and pastel tones. The daguerreotype is mounted in a large dark blue leather case with a red velvet interior. Queen Victoria had first seen this troupe of Tyrolese singers at Kensington Palace in 1833. Her mother, the Duchess of Kent, later arranged for the singers to perform at Osborne on her birthday in 1852. The Duchess recorded in her diary that ‘dearest Victoria appeared very much pleased with the surprise’. Later the same year Queen Victoria acquired this daguerreotype. Beard had shown examples of his enamelled daguerreotypes at the Great Exhibition in 1851. The process involved varnishing the daguerreotype and then heating and adding another coat of varnish after the colour pigments had been added.
Text from the Royal Collection Trust website
Tyrolese minstrels
This daguerreotype shows Tyrolese minstrels in carefully tinted folkloric costumes and holding musical instruments. A variant view was the basis of a wood engraving published in the Illustrated London News in 1851 (below). For Queen Victoria’s birthday at Osborne in 1852, her mother, the Duchess of Kent, arranged for the singers to serenade her at breakfast. ‘Victoria appeared very much pleased with the surprise’, the Duchess wrote. This daguerreotype, enamelled according to Beard’s patented formula, was purchased by the Queen in the same year.
Smyth (engraver)
‘The Tyrolese Minstrels – from a photograph taken by Beard, by desire of H.R.H. The Duchess of Kent’
From the Illustrated London News (6 December 1851)
Wood engraving after a daguerreotype by Richard Beard Jr.
Private Collection
Fascinating people
The popular press, and especially the Illustrated London News, soon included wood engraved copies of photographic portraits of celebrities and indigenous people from the colonies of the British Empire. Equally exotic to middle-class viewers, however, were photographic illustrations of members of the British working class. In every case, the daguerreotype was destroyed during the tracing process that led to its wood-engraved copy, leaving these reproductions behind as a kind of shadow history of the medium. In this form, photographic images circulated all around the globe.
Photographer unknown (English)
Seated man holding a copy of the Illustrated London News
c. 1850
Hand-painted daguerreotype in leather case
Private Collection
Engraver unknown (England)
‘The Walpole Islanders at the Panopticon. – From a photograph by Claudet’
1856
From the Illustrated London News (12 July 1856), page 41
Courtesy of a Private Collection
Modern art and swansdown
These ‘lords and ladies’ dressed in historical costumes for a ball appeared as wood engravings after daguerreotypes taken by Richard Beard Jr. in the Illustrated London News in July 1848. A review in the Nottingham Mercury on 6 October 1848 commended the photographer for the quality of his work, calling it ‘modern art combined with science’.
“Swansdown on black is produced in the most exquisite style, and the finest white lace brought out in bold relief on a dress of white satin.”
~ Nottingham Mercury (6 October 1848)
Smyth (engraver)
‘The Spitalfields Ball. Costume Portraits, from daguerreotypes, by Beard’
From the Illustrated London News (15 July 1848, p. 24)
Wood engravings after daguerreotypes by Richard Beard Jr.
Bodleian Libraries, University of Oxford
Extraordinary Australians
The English-born photographer Douglas T. Kilburn (brother of Edward Kilburn) arrived in Melbourne, Australia, in 1847. Kilburn made a series of daguerreotypes of local indigenous people in about October of that same year. These daguerreotype images were then reproduced around the world in various media. They found their widest audience when a number of them were reproduced as wood engravings in an 1850 issue of the Illustrated London News, along with an accompanying text that expressed the usual racial prejudices of the time.
Unknown engravers (England)
‘Australia Felix’
From the Illustrated London News (26 January 1850, p. 53)
Wood engravings after daguerreotypes by Douglas Kilburn, Melbourne
Private Collection
Daguerrotype studios
The first commercial photography studio in England was opened by Richard Beard in the Royal Polytechnic Institution in London in March 1841. It made small daguerreotype portraits using an American invention, a camera that employed a concave mirror rather than a lens to focus the light. Soon, superior, lens-enhanced cameras and more light-sensitive plates allowed for larger and more lively portraits to be made by an ever-increasing number of professional studios.
One of the earliest clients of the Richard Beard studio in London was the 73-year-old Anglo-Irish writer Maria Edgeworth. She had several portraits taken, at a guinea each, during mid-morning on 25 May 1841. About five years later, she returned to the same studio and had a second portrait made.
Her letter to her half-sister Fanny Wilson describes her first portrait session.
“I fear you will not like any of my daguerreotype faces – I am sure I do not – the truer, the worse”
~ Maria Edgeworth, in a letter to Fanny Wilson, 28 May 1841
‘Lestock came with me to breakfast here at 8 o’clock and then he took Honora and Captain Beaufort and me to the Polytechnic and we all had our likenesses taken and I will tell you no more lest I should some way or other cause you disappointment. For my own part my object is secure for I have done my dear what you wished. It is a wonderful mysterious operation. You are taken from one room into another up stairs and down and you see various people whispering and hear them in neighbouring passages and rooms unseen and the whole apparatus and stool on high platform under a glass dome casting a snap-dragon blue light making all look like spectres and the men in black gliding about like &c. I have not time to tell you more of that’.
Maria Edgeworth, Letter to Fanny Wilson, 25 May 1841
MS. Eng. Lett. c. 710, fol. 1r
Studio of Richard Beard (English, 1801-1885) (Royal Polytechnic Institution, London)
Portrait of Maria Edgeworth
May 1841
Daguerreotype in vertical leather case
Studio of Richard Beard (English, 1801-1885) (Royal Polytechnic Institution, London)
Portrait of an older man
c. 1841
Courtesy of a Private Collection
Forty a day
Using a number of different operators, the studio owned by Richard Beard claimed to make about 40 daguerreotype portraits per day. Soon he ran three such studios in London and had licensed a dozen more elsewhere in England. As the English patent holder for the daguerreotype process, Beard insisted that each of these daguerreotypes be stamped with the words ‘Beard Patentee’, wherever they were made. Having established photography as a franchise system, he became, in effect, the Colonel Sanders of early English photography.
Laman Blanchard ed.
‘Photographic Phenomena’
George Cruikshank’s Omnibus (London Tilt and Borgue, 1842)
London, 1842
Wood engraving by George Cruikshank of the Beard Studio and a poem by S.L. Blanchard
Courtesy of a Private Collection
Fierce enemy
Disputing who had exclusive rights to the commercial use of the daguerreotype process, Richard Beard and Antoine Claudet took several legal actions against each other. In a letter to William Henry Fox Talbot dated 18 January 1843, Claudet refers to Beard as his ‘competitor and fierce enemy’. Having overturned an injunction prohibiting his use of the process, Claudet quickly became Beard’s greatest rival. Soon, however, other competitors also opened studios in London, with those run by Edward Kilburn and John Mayall among the most significant.
Studio of Antoine Claudet (French, 1797-1867) (Adelaide Gallery, London)
Portrait of Michael Faraday
c. 1848
Daguerreotype and leather case
History of Science Museum, University of Oxford
Claudet invented one of the improvements that made the Daguerreotype fast enough to take portraits; Faraday’s association with photography began in January 1839 when he announced Talbot’s discovery at the Royal Institution in London.
Michael Faraday FRS (22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English natural philosopher who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis.
Antoine François Jean Claudet (French, 1797-1867)
Antoine François Jean Claudet (August 18, 1797 – December 27, 1867) was a French photographer and artist active in London who produced daguerreotypes. …
Early in his career Claudet headed a glass factory at Choisy-le-Roi, Paris, together with Georges Bontemps, and moved to England to promote the factory with a shop in High Holborn, London. Having acquired a share in L. J. M. Daguerre’s invention, he became one of England’s first commercial photographers using the daguerreotype process for portraiture, improving the sensitising process by using chlorine (instead of bromine) in addition to iodine, thus gaining greater rapidity of action.
He invented the red darkroom safelight, and it was he who suggested the idea of using a series of photographs to create the illusion of movement. The idea of using painted backdrops has also been attributed to him.
From 1841 to 1851 he operated a studio on the roof of the Adelaide Gallery (now the Nuffield Centre), behind St. Martin’s in the Fields church, London, where in 1843 he took one of only two surviving photographs of Ada Lovelace. He opened additional studios at the Colosseum, Regent’s Park (1847-1851) and in 1851 he moved his entire business to 107 Regent Street, where he established what he called a “Temple to Photography.”
It has been estimated that he made 1,800 pictures every year with subjects including Michael Faraday and Charles Babbage. His daguerreotype of Hemi Pomara, in the National Library of Australia, is the oldest known photograph of any Māori person.
In 1848 he produced the photographometer, an instrument designed to measure the intensity of photogenic rays; and in 1849 he brought out the focimeter, for securing a perfect focus in photographic portraiture.
He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 1853, and in 1858 he produced the stereomonoscope, in reply to a challenge from Sir David Brewster.
Claudet received many honours, among which was the appointment, in 1853, as “Photographer-in-ordinary” to Queen Victoria, and the award, ten years later, of an honor from Napoleon III of France.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Antoine Claudet (French, 1797-1867) (18 King William St Strand)
Portrait of seated man and woman
c. 1850
Half-plate daguerreotype with applied colour in stamped leather case
Courtesy of a Private Collection
Claudet learned photography from Louis Daguerre in the late 1830s, and established his first daguerreotype studio in London in 1841 behind St Martin-in-the-Fields church, receiving honours from both Queen Victoria and Napoleon III for his skills as a photographer. However, he is best known for his experiments with photographic instruments and his chemical experiments, which succeeded in speeding up the photographic process.
Unfortunately horrid
François Arago, in a report to the Chamber of Deputies in Paris on 3 July 1839, warned that touching the surface of a daguerreotype was like ‘brushing the wings of a butterfly’. This fragility is demonstrated in an 1852 group portrait of Queen Victoria and her family. Apparently, Victoria had been captured with her eyes closed. So, she scratched out her face on the plate in a blizzard of annoyance, leaving herself decapitated but the children unblemished. Despite this experience, Victoria and Albert were enthusiastic patrons of photography.
William Edward Kilburn Studio (English, 1818-1881)
Queen Victoria et al
17 January 1852
Scratched daguerreotype
Royal Collection Trust
© His Majesty King Charles III 2022
This group portrait of Queen Victoria with her five eldest children was taken in January 1852 by William Edward Kilburn, who, as one of the leading photographers in London, was commissioned to photograph the Royal family on a number of occasions. The Queen was portrayed with her eyes closed, which is why she wiped out her face on the plate, but spared the images of the children.
“Went back to the Gardens, where a Daguerreotype by Mr. Kilburn was taken of me & 5 of the children. The day was splendid for it. Mine was unfortunately horrid, but the children’s were pretty.”
~ Queen Victoria, from a diary entry, 1852
William Edward Kilburn Studio (English, 1818-1881)
Prince Albert (1819-1861)
1848
Hand-coloured daguerreotype
6.3 x 8.7cm
Royal Collection Trust RCIN 2932486
© His Majesty King Charles III 2022
Hand-coloured daguerreotype of Prince Albert, seated and facing partly right. His left arm rests on the arm of the chair and his right rests on his lap. He is wearing a beige jacket and a dark brown waistcoat. The background is painted blue with white clouds and the daguerreotype is mounted under glass. On the reverse there is a label reading ‘The Prince from Life 1848’, handwritten by Queen Victoria. Prince Albert was an early enthusiast of photography and closely followed the development of the medium. In February 1847 Kilburn showed examples of his coloured daguerreotypes, made by adding fine coloured powders to the photographic plate, to the Society of Arts. In 1848 Prince Albert commissioned a portrait using the new technique. This is one of two surviving hand-coloured daguerreotypes produced from the sitting. Commissioned by Prince Albert in 1848
Anonymous. “Prince Albert (1819-1861),” on the Royal Collection Trust website Nd [Online] Cited 23/02/2023
Applied colour
By the mid-1840s, it was common for middle-class British citizens to have a daguerreotype portrait made. Often, these were enhanced with applied colour, giving a touch of life to an otherwise monochrome medium.
Studio of Richard Beard (English, 1801-1885)
Portrait bust of a man
c. 1845
Hand-painted daguerreotype in vertical leather case
Courtesy of a Private Collection
Richard Beard was a businessman who purchased a licence to use the daguerreotype process in 1841 and opened the world’s first photographic studio. It was set up in a glasshouse on the roof of London’s Royal Polytechnic Institution to provide all-round lighting necessary to the daguerreotype process. There were huge profits from his studios in London and Liverpool and from the sale of licences to take daguerreotypes, but Beard was ruined by his many legal actions against rivals, and went bankrupt in 1850.
Itinerant and transnational
The career of James William Newland exemplifies the itinerant, transnational character of many early photographers. Born in Suffolk in about 1810, Newland opened his first daguerreotype studio in 1845 in New Orleans in the USA. He subsequently travelled throughout Central and South America and then across the Pacific to Sydney, Australia. In 1848, he established a studio there and exhibited 200 daguerreotypes he had taken during his journey. After Australia, he headed back to England for a brief visit, before moving to India to set up a studio in Calcutta. It was there that he died, killed during the Indian Uprising of 1857.
J.W. Newland (English, c. 1810-1857)
Portrait of a standing man, Calcutta
c. 1855
Quarter-plate daguerreotype in leather case with red velvet pad
Courtesy of a Private Collection
Photo journalism
This daguerreotype records the immense crowds at one of the Chartist rallies held in South London in 1848. Calling for political reform, the Chartist movement was seen by many as a terrifying threat to the established order. Fears were so great, the Duke of Wellington stationed troops across London and the royal family was moved to Osborne House on the Isle of Wight. In the event, the rally passed peacefully, and Prince Albert himself purchased this record of it.
Studio of William Edward Kilburn (English, 1818-1881) (234 Regent St, London)
The Chartist Meeting on Kennington Common, 10 April 1848
10 April 1848
Daguerreotype Royal Collection, London
Daguerreotype of a large crowd of supporters of the Chartist movement gathered together on Kennington Common. At the centre of the crowd there is a platform for the speakers, and a number of people hold banners and flags. Behind the crowd there is a tall factory chimney and a large house to the right. In the foreground a man stands facing the crowds in a horse-drawn cart. The daguerreotype is mounted under glass.
This daguerreotype records the immense crowds at one of the Chartist rallies held in South London in 1848. Calling for political reform, and spurred on by the recent February Revolution in France, the Chartist movement was seen by many as a terrifying threat to the established order. Fears were so great that on the eve of the meeting, the Duke of Wellington stationed troops across London and the royal family were moved to Osborne House on the Isle of Wight. In the event the rally passed peacefully. Prince Albert later spoke about his concern for the working classes at a meeting of the Society for the Improvement of the Condition of the Labouring Classes, 18 May 1848. This is one of a pair of daguerreotypes of the event acquired by Prince Albert.
One of a pair of daguerreotypes of the Chartist Meeting on Kennington Common purchased by Prince Albert in 1848
Anonymous. “The Chartist Meeting on Kennington Common, 10 April 1848,” on the Royal Collection Trust website Nd [Online] Cited 23/02/2023
Ruskin and photography
Although his opinion of photography evolved over the years, John Ruskin was initially enthusiastic about the daguerreotype, importing early examples from France and learning the process himself in order to make photographic sketches of architecture and landscape.
“Daguerreotypes taken by this vivid sunlight are glorious things. It is very nearly the same thing as carrying off the palace itself: every chip of stone and stain is there, and of course there is no mistake about proportions… It is a noble invention.”
~ John Ruskin, in a letter to his father from Venice, 7 October 1845
John Ruskin (English, 1819-1900) and John Hobbs (?)
View of the façade of a building in Venice
c. 1850
Daguerreotype
History of Science Museum, University of Oxford
Minn Collection
Bequeathed by Henry Minn in 1961
John Ruskin (8 February 1819 – 20 January 1900) was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and political economy.
Ruskin’s writing styles and literary forms were equally varied. He wrote essays and treatises, poetry and lectures, travel guides and manuals, letters and even a fairy tale. He also made detailed sketches and paintings of rocks, plants, birds, landscapes, architectural structures and ornamentation. The elaborate style that characterised his earliest writing on art gave way in time to plainer language designed to communicate his ideas more effectively. In all of his writing, he emphasised the connections between nature, art and society.
Ruskin was hugely influential in the latter half of the 19th century and up to the First World War. After a period of relative decline, his reputation has steadily improved since the 1960s with the publication of numerous academic studies of his work. Today, his ideas and concerns are widely recognised as having anticipated interest in environmentalism, sustainability and craft.
Ruskin first came to widespread attention with the first volume of Modern Painters (1843), an extended essay in defence of the work of J. M. W. Turner in which he argued that the principal role of the artist is “truth to nature”. From the 1850s, he championed the Pre-Raphaelites, who were influenced by his ideas. His work increasingly focused on social and political issues. Unto This Last (1860, 1862) marked the shift in emphasis. In 1869, Ruskin became the first Slade Professor of Fine Art at the University of Oxford, where he established the Ruskin School of Drawing. In 1871, he began his monthly “letters to the workmen and labourers of Great Britain”, published under the title Fors Clavigera (1871-1884). In the course of this complex and deeply personal work, he developed the principles underlying his ideal society. As a result, he founded the Guild of St George, an organisation that endures today.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Stereoscopic still life
This stereo-daguerreotype includes a selection of the instruments found in the studio of London photographer Antoine Claudet in 1853. They include a focimeter (a device of his own devising that aided focus), a distillation device hanging on the back wall, a telescope on a stand, an upside-down globe, an array of chemical jars and glass vessels, a centrifugal force speed controller, a photographometer (an early kind of light metre), three different kinds of stereoscope, the Post Office London Directory of 1852, a magnifying glass, a slide rule, a glass prism, a French treatise on photography, two of his dynactinometers (another device of his own invention), a mortar and pestle, and an apothecary’s scales.
Photographs of paintings
Daguerreotypes were used to make records of paintings and prints. Sometime in the 1850s, the studio of London-based photographer Edward Kilburn was commissioned to make a daguerreotype of a painting then thought to be by Raphael. The client was the British art dealer Morris Moore. Moore engaged in a decades-long struggle to have this painting, now titled Apollo and Marsyas and attributed to Perugino, accepted as an early work by Raphael. This daguerreotype no doubt played a part in that campaign. Moore displayed it, for example, in Berlin in 1856.
Keepsake and memory
Ada Lovelace, the English mathematician and computing pioneer, had a number of daguerreotype portraits made of herself. The last of these, taken by an unknown photographer, is of a small painted portrait of Lovelace. Frail and thin and suffering from cancer, she is shown sitting at her piano. Shortly before she died, Lovelace wrote a note in which she leaves ‘a daguerreotype from Philips’s picture of me’ to her mother’s friend, a Mary Millicent Montgomery.
Photographer unknown (English)
Copy of an 1852 painting of Ada Lovelace by Henry Wyndam Phillips
13 August 1852
Daguerreotype
Private Collection
Reproduction courtesy of Geoffrey Bond
Public domain
Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (née Byron; 10 December 1815 – 27 November 1852) was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage’s proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognise that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
Text from the Wikipedia website
2th Sept 1852
I leave to my Mother’s oldest
Friend, Mary Millicent Mont=
=gomery, three articles, viz:
1. A Red Cornelian Brooch which
I have much used I have much used, & to which
I desire my Hair to be added;
2. A Daguerreotype from Philip’s
Picture of me;
3. 4 Books printed out by me.
I request this Paper also to be
given to Mary Millicent Mont=
=gomery; & I wish her to
understand that I leave her …
As well as being customers of the new photographers, Ada Lovelace and her circle were intrigued by the science of photography and the contribution photographic processes might make to science. Apart from her famous paper on Babbage’s Analytical Engine, her only other known publication is in the form of long footnotes to an article by her husband, William Earl of Lovelace, in the Royal Agricultural Society journal. The article, which he describes as being written for the ‘leather-gaiter-and-top-boot-mind’, reviews a paper by the French economist Gasparin, about possible laws linking climate and the yield of crops, referring to a wide variety of observations of weather and plants collected by both professionals and amateurs. Ada Lovelace observes that photographic devices, such as the actinograph designed by her friend John Herschel, allow the construction of ‘meteorological instruments of the utmost delicacy’, and criticises Gasparin ‘who seems to write unaware of the means which photography has offered’.
In similar vein, she reflected on the potential of photography in providing objective evidence of psychic phenomena. In an unpublished article she writes, ‘If amateurs, of either sex, would amuse their idle hours with experimenting on this subject, & would keep an accurate journal of their daily observations, we should in a few years have a mass of registered facts to compare with the observation of the Scientific’, concluding that ‘we believe that it is as yet quite unsuspected how important a part photography is to play in the advancement of human knowledge’.
A third poignant daguerreotype, by an unknown photographer, is a photograph of a small portrait of Ada Lovelace, frail and thin, painted by Henry Wyndham Phillips in the last months of her life, when she was in great pain from uterine cancer. Her husband recorded progress on the portrait in his diary – on 2 August ‘she managed to remain long enough when he came for him to make some progress’, on 3 August that he was ‘getting on with the portrait’, and on 13 August that though ‘the suffering was so great that she could scarce avoid crying out’, yet ‘she sat at the piano some little time so that the artist could portray her hands’. The Bodleian archives contain a note written in her last days, in which she leaves ‘a daguerreotype from Philips’s portrait of me’ to her mother’s friend, Miss Montgomery.
Professor Ursula Martin CBE, University of Oxford. “Only known photographs of Ada Lovelace in Bodleian Display,” on the Bodleian blogs Ada Lovelace website 14 October 2015 [Onlinr] Cited 23/02/2023
George Hollis (British, 1793-1842) (engraver)
Mr Couldock as Richard III
1851
From Tallis’s Drawing Room Table Book of Theatrical Portraits, Memoirs and Anecdotes
Hand-coloured steel engraving after daguerreotype by William Paine of Islington
This engraving: The British Museum CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
The engraving in the exhibition: Private collection
Celebrity actors
Tallis’s Drawing Room Table Book of Theatrical Portraits, Memoirs and Anecdotes offered a series of engraved copies of daguerreotype portraits of celebrated Shakespearean actors. Sometimes these actors are shown as if in a portrait studio, but more often they are posing in costume (and even in blackface), as if in the midst of a performance. The series is a reminder of the popularity of the theatre and actors in the mid-19th century (even Queen Victoria bought a copy of this publication), but also of the casual racism that was part of everyday British life.
Engraver unknown (British)
Mr Charles Kean as Hamlet
1851
From Tallis’s Drawing Room Table Book of Theatrical Portraits, Memoirs and Anecdotes
Steel engraving after daguerreotype by William Paine of Islington
This engraving: The British Museum CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
The engraving in the exhibition: Private collection
‘Mr Ira Aldridge as Aaron in Titus Andronicus’
From Tallis’s Drawing Room Table Book of Theatrical Portraits, Memoirs and Anecdotes
c. 1851
Steel engraving after daguerreotype by William Paine of Islington
Bodleian Libraries, University of Oxford
Ira Aldridge
Born in New York, Ira Aldridge (1807-1867) was an African-American actor, playwright, and theatre manager. From 1824, the year he emigrated to the UK, Aldridge made his career largely on the London stage and in Europe. He became well known as a performer in plays by Shakespeare, including roles usually played by white actors, such as Richard III, King Lear and Macbeth. Aldridge’s career took off at the height of the movement to abolish slavery throughout the British Empire. He chose to play a number of anti-slavery roles and often addressed his audiences on closing night, speaking passionately about the injustice of slavery.
The Great Exhibition
Six million people – equivalent to a third of the entire population of Britain at the time – visited the Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, an international showcase for goods, raw materials and industrial products and machinery. It took place in Hyde Park, London, from 1 May to 15 October in 1851. Photographs were among the thousands of exhibits, but the Great Exhibition was itself much photographed, as evidenced in the many photographic images reproduced in the illustrated press.
“Today is sunshine and mild weather. I peeped in thro’ a window at the East End of the Crystal palace, and found myself in the territories of the United States, who ought rather to have been located in the Far West of the building. The perspective looked beautiful.”
~ William Henry Fox Talbot, in a letter to his wife Constance, 30 April 1851
Engravers unknown (English)
The Great Exhibition: The east nave, viewed from the south-western gallery
1851
From Illustrated London News, 6 September 1851, p. 296
Stipple and line engraving from daguerreotype by William Edward Kilburn
210 x 270 mm
Courtesy of a Private Collection
Held at Crystal Palace in London in 1851, the Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations was one of the most influential cultural events of the 19th century and the Illustrated London New did not fail to record its scale and significance using an equally influential invention that would shape the current century and those to come.
Sir Joseph Paxton (1801-1865) began his career as a gardener’s boy, eventually becoming head gardener for the Duke of Devonshire. He remodelled the Duke’s gardens at Chatsworth and Chiswick, designing large glass and iron conservatories for them. These later became the model for his design of the Great Exhibition building, now known as the Crystal Palace, for which he received his knighthood. After this success, Paxton continued to work on landscape gardening and public parks as well as designing various country houses. Published by Peter Jackson, London.
Sir Joseph Paxton (English, 1801-1865)
Sir Joseph Paxton, (born Aug. 3, 1801, near Woburn, Bedfordshire, Eng. – died June 8, 1865, Sydenham, near London), English landscape gardener and designer of hothouses, who was the architect of the Crystal Palace for the Great Exhibition of 1851 in London.
He was originally a gardener employed by the duke of Devonshire, whose friend, factotum, and adviser he became. From 1826 he was superintendent of the gardens at Chatsworth, the duke’s Derbyshire estate; he built in iron and glass the famous conservatory there (1840) and the lily house for the duke’s rare Victoria regia (1850). Also in 1850, after a cumbersome design had been officially accepted by the Great Exhibition’s organisers, Paxton’s inspired plan for a building of prefabricated elements of sheet glass and iron was substituted. His design, based on his earlier glass structures, covered four times the area of St. Peter’s, Rome, and the grandeur of its conception was a challenge to mid-19th-century technology. Although it was built within six months and he was knighted for his efforts (1851), it was not until later that the structure was seen as a revolution in style. In 1852-1854 its components were moved to Sydenham Hill in Upper Norwood, where they remained (reerected in a different form from the original) until destroyed by fire in 1936.
Paxton was a member of Parliament for Coventry from 1854 until his death. During the period of his glass structures, he also designed many houses in eclectic styles and laid out a number of public parks.
Kathleen Kuiper. “Sir Joseph Paxton,” on the Britannica website Nd [Online] Cited 23/02/2023
Joseph John Jenkins (English, 1811-1885) (engraver)
Joseph Paxton, designer of the Crystal Palace
c. 1851
Stipple and line engraving from daguerreotype by William Edward Kilburn
This engraving: from the Britannica website
The engraving in the exhibition: Private collection
Joseph John Jenkins (1811 – 9 March 1885) was a British engraver and watercolour painter. He is best known for his portraits and landscapes paintings.
Jenkins engraved many portraits, and among other works, Susanna and the Elders, after Francesco Mola, and The Greenwich Pensioner and The Chelsea Pensioner, after Michael William Sharp. He engraved plates and drew illustrations for the annuals, such as The Keepsake and Heath’s Book of Beauty, Plates from his drawings are in Charles Heath’s Illustrations to Byron and similar works.
Grand Panorama
The Illustrated London News issued a commemorative Grand Panorama of the Great Exhibition of All Nations 1851 in its December issue. Comprising fold-out pages, each sheet was based on daguerreotypes of the interior of the Exhibition taken by an operator from the Beard studio. The panorama showed frontal views of each side of the interior of the Crystal Palace, with distinct sections suitably captioned and clusters of figures added to give interest to an otherwise drab set of facades.
Commodities and things
The taking of photographs inside the building was restricted to between 6 and 9 am, before it opened to the public, or on Sundays, when it was otherwise closed. Often, the resulting views are undemonstrative and frontal, even if they are also sometimes animated by the engraver through the addition of figures peering at the exhibits. These scenes confirm the fetishisation of the commodity that was the Great Exhibition’s singular attraction, turning that spectacle into a picture to be gazed at in its turn.
John Tallis (English, 1817-1876) and Jacob George Strutt (British, 1790-1864)
Tallis’s history and description of the Crystal Palace, and the exhibition of the world’s industry in 1851 (p. 13)
1852
Steel engravings, from original drawings and daguerreotypes by Beard and Mayall studios
The Swedish Nightingale
Prizes were awarded to photographers whose displays at the Great Exhibition were considered to be particularly notable. One of those prizes was awarded to Edward Kilburn. The jury was particularly impressed by a full-length daguerreotype portrait made by Kilburn in 1848 of Swedish opera singer Jenny Lind, known as the Swedish Nightingale. Lind is posed so that her image is reflected in a large mirror; ‘that the reflection in the glass is equally perfect with the original is the point worthy of remark and commendation’.
“… a masterpiece of this art, not excelled, if equalled, by any other specimen exhibited throughout the entire building.”
~ Illustrated London News (1851)
Studio of William Edward Kilburn (English, 1818-1881) (234 Regent St, London)
Portrait of Jenny Lind standing at a piano
1848
Daguerreotype
11.5 x 9.1cm
© Royal Collection, London
Daguerreotype of a full length portrait of Jenny Lind standing beside a piano, facing away from the camera, with her head and upper body turned left towards the camera. Her right hand rests on the top of the piano and her left hand is touching the keys. She is wearing a long dress and a dark colour lace shawl. The mirror on the wall to the right reflects her back and there is an ornate side table beneath it. The daguerreotype is mounted under glass.
Queen Victoria attended the first London performance given by the Swedish soprano Jenny Lind on the 4th of May 1847. She described the occasion in her journal: ‘The great event of the evening however was Jenny Lind’s appearance & her complete triumph. She has the most exquisite, powerful, & really quite peculiar voice’. She later sang among the choristers at the wedding of the Prince of Wales in St George’s Chapel in 1863.
William Kilburn exhibited several daguerreotypes at the 1851 Great Exhibition, with this image being particularly well received. The exhibition jury commented: ‘For novelty of design we may mention a small picture of the interior of a room, including a whole-length portrait of Jenny Lind: beside, and near her, is a large mirror, in which the figure is reflected. That the reflection in the glass is equally perfect with the original is the point worthy of remark and commendation’.
The daguerreotype was also reproduced with significant cropping in carte-de-visite format, such as in the example today kept at the Victoria & Albert Museum, London (Museum Number S.138:66-2007). Acquired by Queen Victoria and Prince Albert in 1849.
Anonymous. “Jenny Lind (1820-1887),” on the Royal Collection Trust website Nd [Online] Cited 23/02/2023
Really marvellous
Stuffed frogs being shaved and promenading under an umbrella were among the most remarkable of the exhibits daguerreotyped by the Claudet studio at the Great Exhibition. The animals were prepared for anthropomorphic display by Hermann Ploucquert, a taxidermist at the Royal Museum in Stuttgart. The stall at which these creations were exhibited was apparently perpetually surrounded by a crowd. Queen Victoria herself described them in her diaries as ‘really marvellous’. Claudet’s images were issued as a book of coloured wood engravings titled The Comical Creatures from Wurtemberg.
News from home
The dissemination of engravings after daguerreotypes in the Illustrated London News meant that photographic images became itinerant entities. Distributed all over the world, the same image was capable of being experienced, simultaneously, in – say – Sydney, Hong Kong, Calcutta, New York, and London. By 1851, when Harden Melville completed the painting that this coloured engraving commemorates – titled Australia: News from Home – even settlers in outback Australia were able to get copies. One of them is looking at an issue of the Illustrated London News that celebrates the opening of the Great Exhibition in London.
Official reports
Not one of the many photographs exhibited in the Great Exhibition was by William Henry Fox Talbot, England’s claimant to the medium’s invention. Nevertheless, Talbot’s calotype process was chosen to illustrate the official reports on the event, even if the majority of these illustrations was shot and printed by French photographers rather than English ones. The other claimant to photography’s invention, the Frenchman Louis Daguerre, lived long enough to read about London’s Great Exhibition but died two months after it opened. Fittingly, his obituary in the Illustrated London News was accompanied by a wood-engraved portrait based on a daguerreotype.
The Duke of Wellington
The Ryall engraving faithfully imitates the composition and details of the daguerreotype made by the Claudet studio, but reverses the orientation of the Duke’s body. A story in the Illustrated London News, published on 13 November 1852, tells us that the Duke himself was not particularly impressed by the print. Apparently, ‘he looked at it for a moment, shook his head, and, with a half smile and half frown of recognition, muttered “Very old! Hum!” and turned away in thought’. This engraving was in turn copied by others, reappearing in a variety of media over the next few decades, and especially in 1852, the year of Wellington’s death.
Edward J. Pickering, for studio of Antoine Claudet (London)
Portrait of the Duke of Wellington
1 May 1844
Daguerreotype
This image: Getty
Public domain
Image in the exhibition: Wellington Collection, Stratfield Saye House
John Sartain (English, 1808-1897)
The Duke of Wellington
1852
Mezzotint, etching and aquatint engraving (‘engraved by J. Sartain after Claudet’s portrait’)
7 x 4 15/16 in. (17.78 x 12.54cm)
This engraving: Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts
Bequest of Dr. Paul J. Sartain
Public domain
The engraving in the exhibition: Private collection
Salt prints
In September 1840, William Henry Fox Talbot discovered how to greatly increase his photographic paper’s sensitivity to light. This new process produced a latent image which remained invisible to the eye until it was developed for a second time. The result was a sharp negative from which numerous positive salt prints could be made. Resisting his mother’s entreaty to call this process ‘Talbotype’, after himself, he gave it the more modest name of ‘calotype’ (‘beautiful picture’). Other photographers soon took up this new process, including Welshman Calvert Richard Jones and the Scottish duo of David Hill and Robert Adamson.
“A better picture can now be obtained in a minute than by the former process in an hour.”
~ William Henry Fox Talbot, in a letter to the Literary Gazette, 13 February 1841
William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877)
Lace
Early 1840s
Salt print from a calotype negative
22.7 x 18.7cm
Rev. Calvert Richard Jones (Welsh, 1804-1877)
Colosseum, Rome, 2nd view
1846
Salt print (printed by Nicolaas Henneman) from a calotype negative
This image: Metropolitan Museum of Art
Public domain
Image in the exhibition: MS. WHF Talbot photogr. 6
The Reverend Calvert Richard Jones was the son of a landowner from Wales. He became a marine painter, draftsman, and daguerreotypist before turning to the calotype, the negative/positive paper process invented by William Henry Fox Talbot, with whom Jones occasionally photographed. During travels to Italy in 1841, Jones stopped in France, where he met and photographed with Hippolyte Bayard, the French inventor of direct positive prints on paper. Through Jones, Bayard and Talbot were introduced to each other and their respective pioneering processes.
Jones was enthusiastic about the creative possibilities of photography. He used the photographic panorama, a device that provided the viewer with a wide-angle view of a given scene. His body of work includes marine landscapes and genre portraits of local men and women at work and leisure, as well as travel landscapes of Italy and France. After 1856 Jones apparently gave up photography, although he continued to paint.
Text from the J. Paul Getty Museum website
William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877)
Loch Katrine
1844
Salt print (printed by Nicolaas Henneman) from a calotype negative
David Octavius Hill and Robert Adamson (Scottish, 1802-1870 and Scottish, 1821-1848)
Portrait of James Inglis
2 October 1844
Salt print from a calotype negative
History of Science Museum, University of Oxford
Presented by Sir John R. Findlay in 1929
Calotype (salted paper print from a calotype negative) of James Inglis, a doctor from Halifax, seated nearly three-quarter length, head very nearly in profile looking left, a leather glove on his left hand; photographed at the British Association for the Advancement of Science meeting at York in 1844. Mostly greenish sepia, pale at edges, retaining the original brown only at centre; discolouration mark from juxtaposed paper on back. For fuller descriptive and historical commentary see narratives.
David Octavius Hill (1802-1870) and Robert Adamson (1821-1848)
Brewster, sensing that Hill’s intention to sketch each of the several hundred ministers before they returned to the far corners of Scotland would be close to impossible, suggested that the painter use the services of the newly established Adamson to make photographic sketches instead. “I got hold of the artist,” Brewster wrote to Talbot in early June, “showed him the Calotype, & the eminent advantage he might derive from it in getting likenesses of all the principal characters before they were dispersed to their respective homes. He was at first incredulous, but went to Mr. Adamson, and arranged with him preliminaries for getting all the necessary portraits.” Within weeks Hill was completely won over, and the two were working seamlessly in partnership. As artistic director, Hill composed each picture, placing his sitters as they might appear in the finished painting.
Adamson operated the camera and carried out the chemical manipulations. Hill and Adamson were a perfect team. Hill, twenty years older than Adamson, was trained as a painter and had important connections in artistic and social circles in Edinburgh; he easily attracted a distinguished clientele to the team’s portrait studio at Adamson’s home, Rock House. Most of all, he possessed a geniality, a “suavity of manner and absence of all affectation,” that immediately set people at ease and permitted him to pose his sitters without losing their natural sense of posture and expression. Adamson was young but had learned his lessons well. He was a consummate technician, excelling in – and even improving upon – the various optical and chemical procedures developed by Talbot. Both men had a profound understanding of the way the world would translate into monochrome pictures.
If in May Hill had been incredulous, by June he was convinced; by July he was proud to exhibit the first photographs as “preliminary studies and sketches” for his picture, and by the end of the year he and his partner had photographed nearly all the figures who would have a place in his grand painting. Their hundreds of preparatory “sketches” ranged from single portraits to groups of as many as twenty-five ministers posed as Hill envisioned them in his ambitious composition. Some portraits, such as that of Thomas Chalmers, first moderator of the Free Church, were used as direct models for the finished work. However, at each sitting, Hill and Adamson made numerous photographs in various poses, and many photographs of the ministers have no direct correspondence with the painting. Still other portraits, of people who were not present for the signing of the Deed of Demission – but whom Hill apparently thought should have been – were used as models for the painting.
“The pictures produced are as Rembrandt’s but improved,” wrote the watercolorist John Harden on first seeing Hill and Adamson’s calotypes in November 1843, “so like his style & the oldest & finest masters that doubtless a great progress in Portrait painting & effect must be the consequence.” In actuality, though, it was so easy to make the portrait “sketches” by means of photography that Hill’s painting was ultimately overburdened by a surfeit of recognizable faces: 450 names appear on his key to the painting. The final composition – not completed for two decades and as dull a work as one can imagine – lacks not only the fiery dynamism of Hill’s first sketches of the event but also the immediacy and graphic power of the photographs that were meant to serve it.
By August 1844, Hill and Adamson clearly understood the value of their calotypes as works of art in their own right and decided to expand their collaboration far beyond the original mission, announcing a forthcoming series of volumes illustrated with photographs of subjects other than the ministers of the Free Church: The Fishermen and Women of the Firth of Forth; Highland Character and Costume; Architectural Structures of Edinburgh; Architectural Structures of Glasgow, &c.; Old Castles, Abbeys, &c. in Scotland; and Portraits of Distinguished Scotchmen. Although these titles were never issued as published volumes, photographs intended for each survive, and those made in the small fishing town of Newhaven are a particularly noteworthy group.
Malcolm Daniel. “David Octavius Hill (1802-1870) and Robert Adamson (1821-1848),” on the Metropolitan Museum of Art website October 2004 [Online] Cited 23/02/2023
William Henry Fox Talbot (English, 1800-1877)
An Ancient Door in Magdalen College, Oxford
April 1843
Salted paper print from paper negative
Dimensions overall: 18.8 x 22.7cm (7 3/8 x 8 15/16 in.)
This image: National Gallery of Art, Robert B. Menschel Fund
CC0 1.0 Universal
Image in the exhibition: MS. WHF Talbot photogr. 4, item 3
A New Power: Photography in Britain 1800-1850 is made possible through the generosity of donors and lenders. In particular the Bodleian Libraries would like to thank: Professor Raymond Dwek CBE FRS and Mrs Sandra Dwek Sir Brian and Lady Pomeroy Ian and Caroline Laing
Lenders
His Majesty King Charles III
Blackie House Library and Museum, Edinburgh
The Trustees of the British Museum
English Heritage Trust
Polar Museum, Scott Polar Research Institute, University of Cambridge
Victoria and Albert Museum
The Wellington Collection, Stratfield Saye House
Ashmolean Museum, University of Oxford
History of Science Museum, University of Oxford
Oxford University Museum of Natural History
The President and Fellows of Magdalen College
The Provost and Fellows of Oriel College
The Principal and Fellows of Somerville College
Geoffrey Batchen
G C Bond
K & J Jacobson
Gregory Page-Turner
William Zachs
We would like to thank HM Government for providing Government Indemnity for the loans and the Department for Culture, Media and Sport and Arts Council England for arranging the indemnity. We are also grateful to those whose skill and labour have made this exhibition possible.
A New Power: Photography in Britain 1800-1850 exhibition poster
Weston Library
Broad Street, OX1
Opening hours:
Monday – Saturday: 10am – 5pm
Sunday: 11am – 4pm
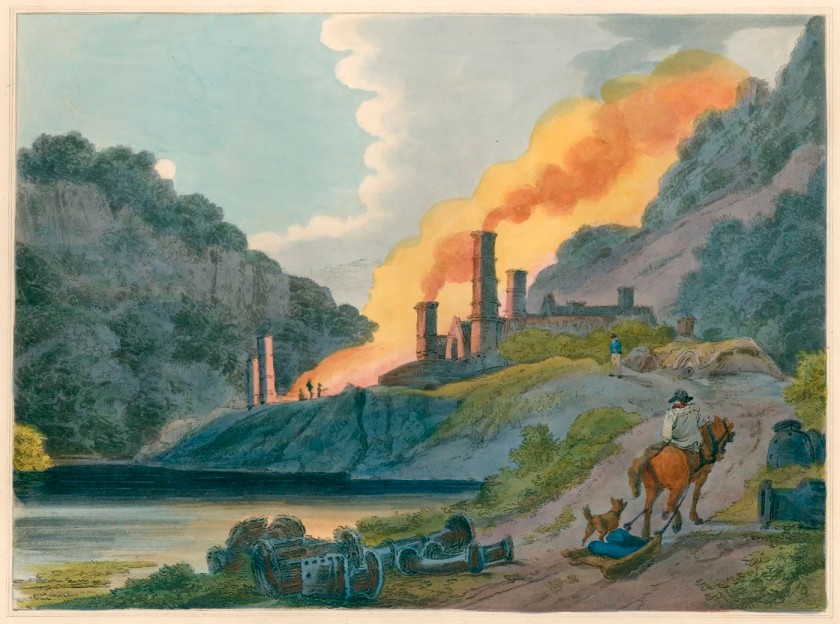
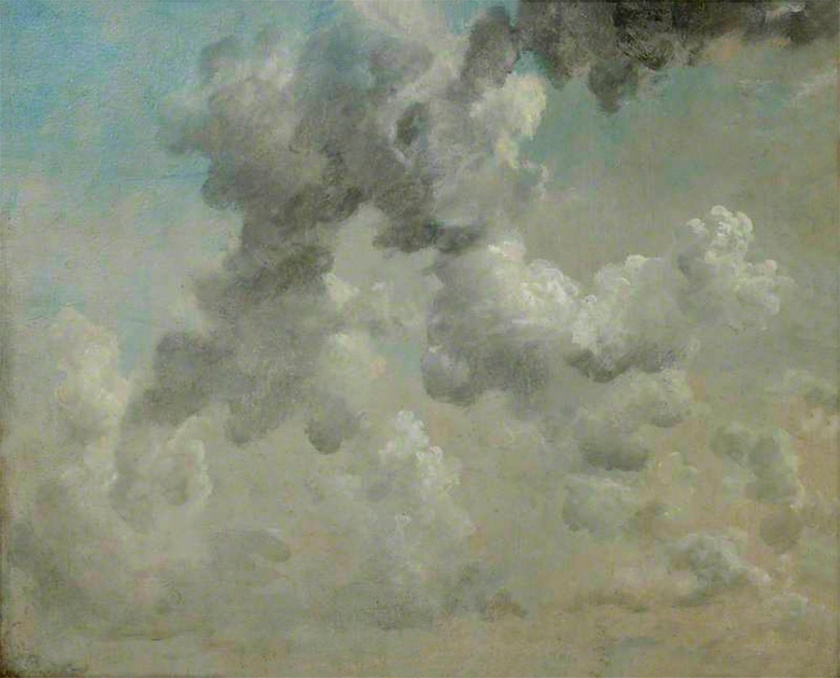
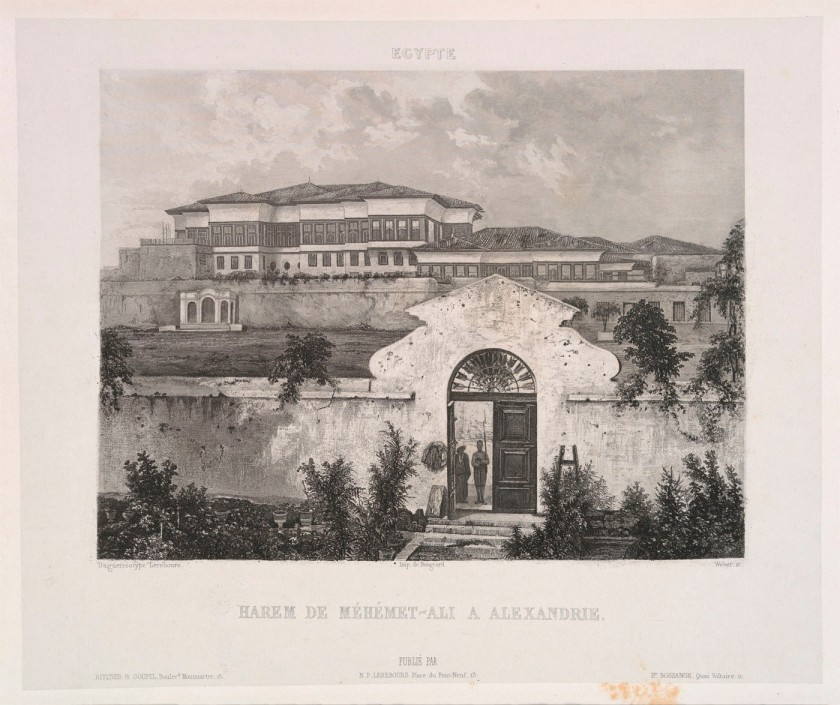
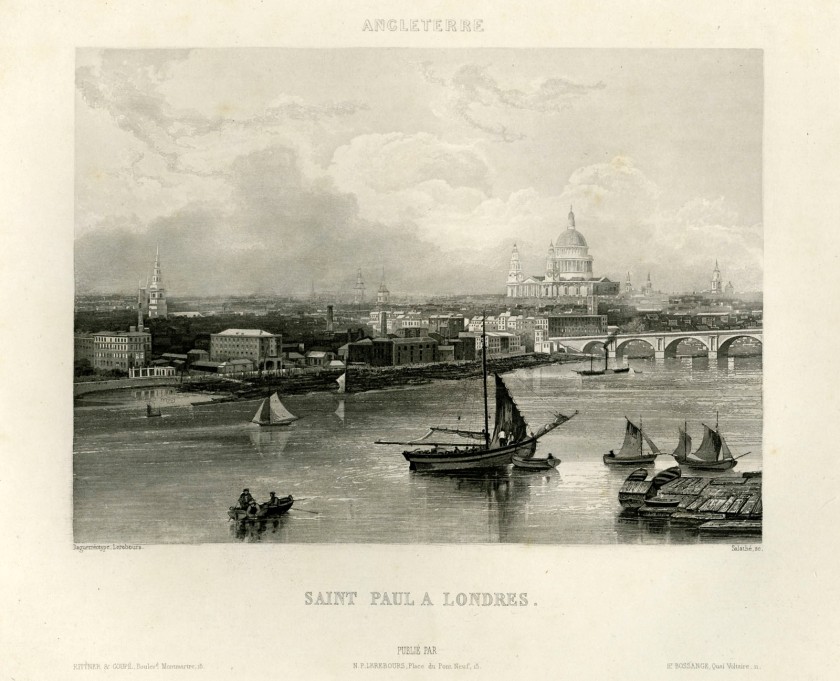
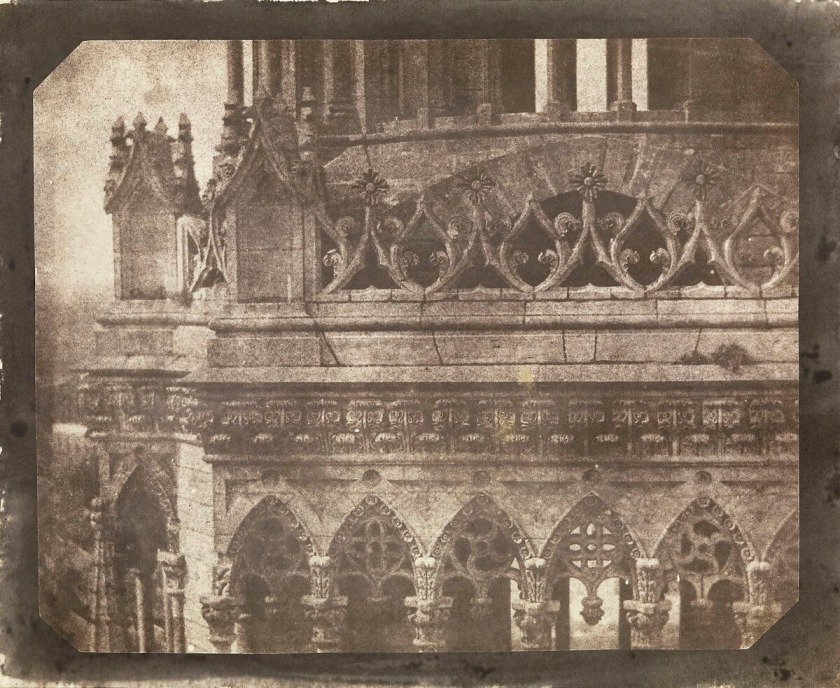
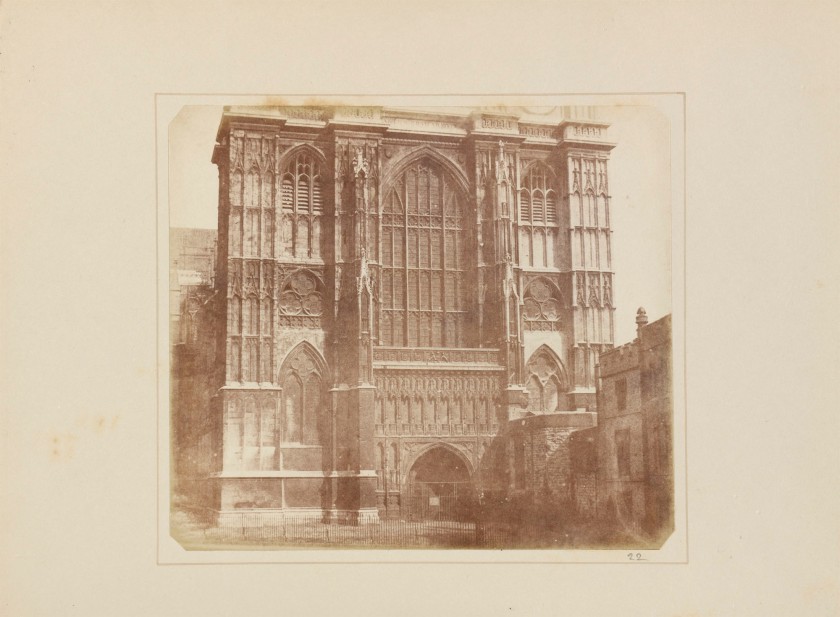
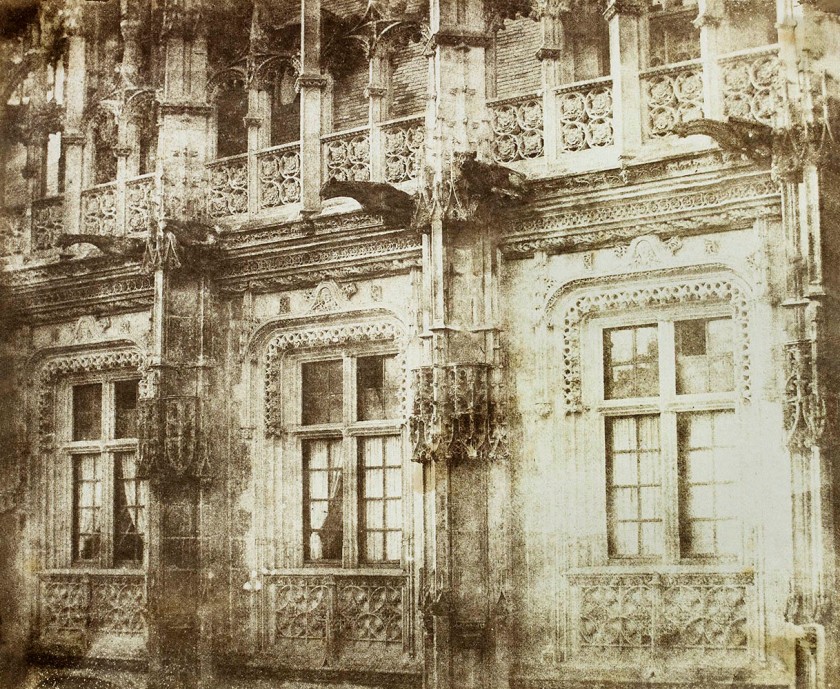
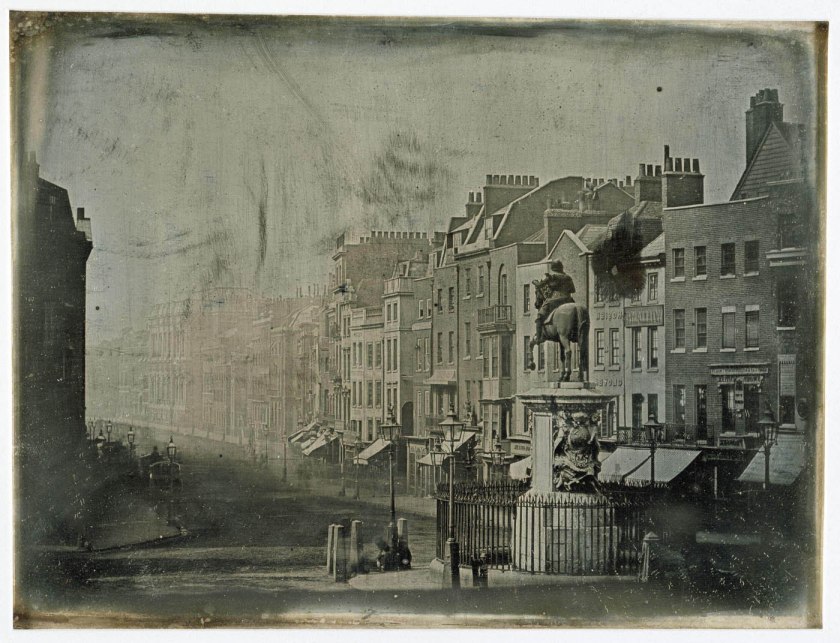










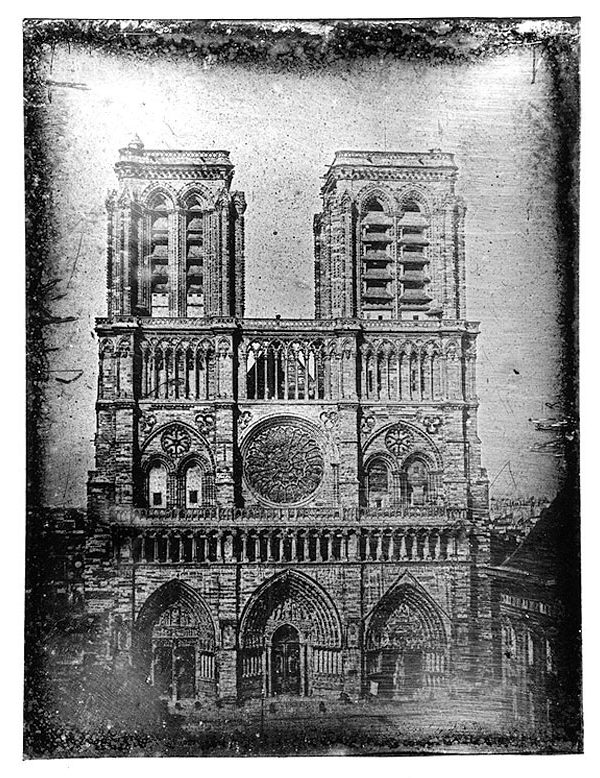















![Alonzo Chappel (American, 1828-1887)(engraver) 'Thomas Chalmers: Likeness from a daguerreotype by Claudets [sic]' 1873 Alonzo Chappel (American, 1828-1887)(engraver) 'Thomas Chalmers: Likeness from a daguerreotype by Claudets [sic]' 1873](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2023/02/chappel-thomas-chalmers.jpg?w=650&h=897)
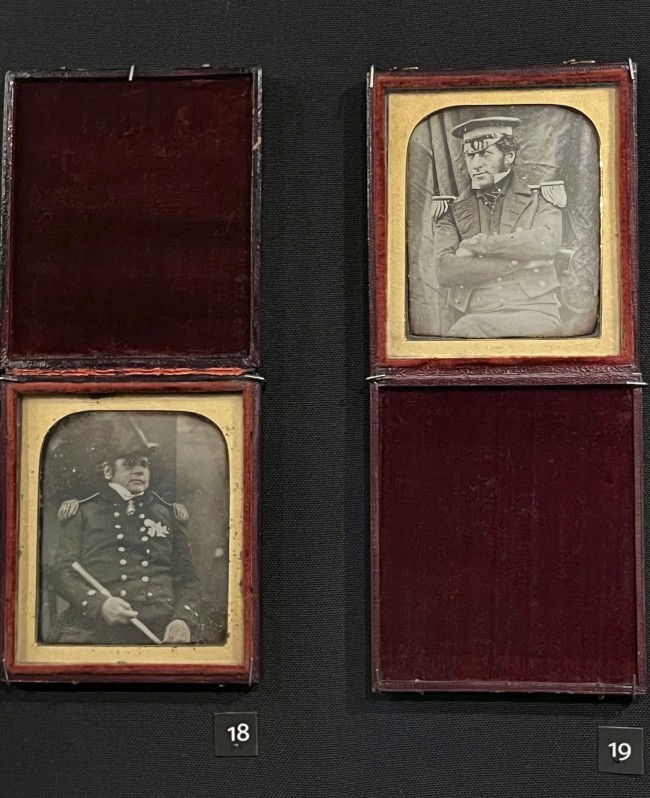
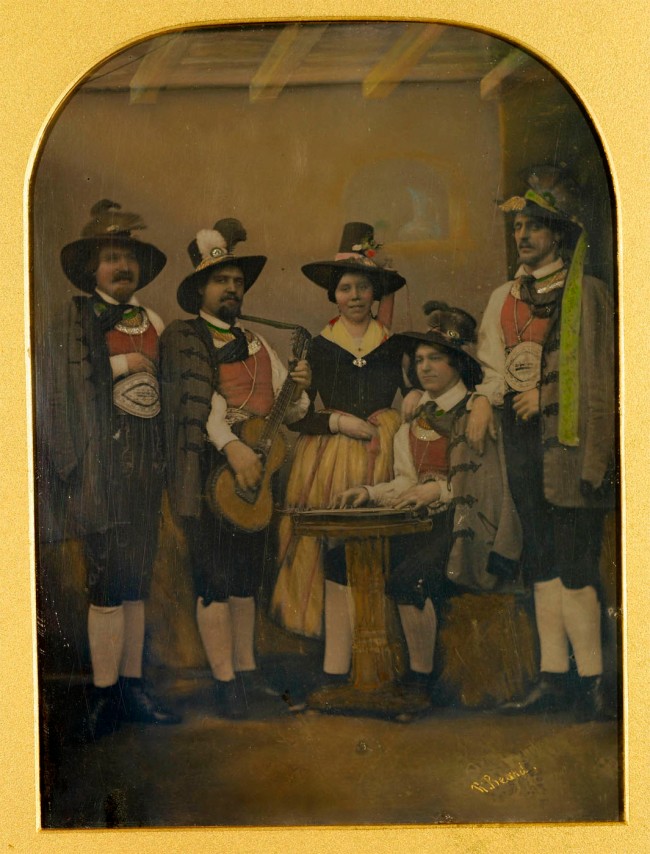
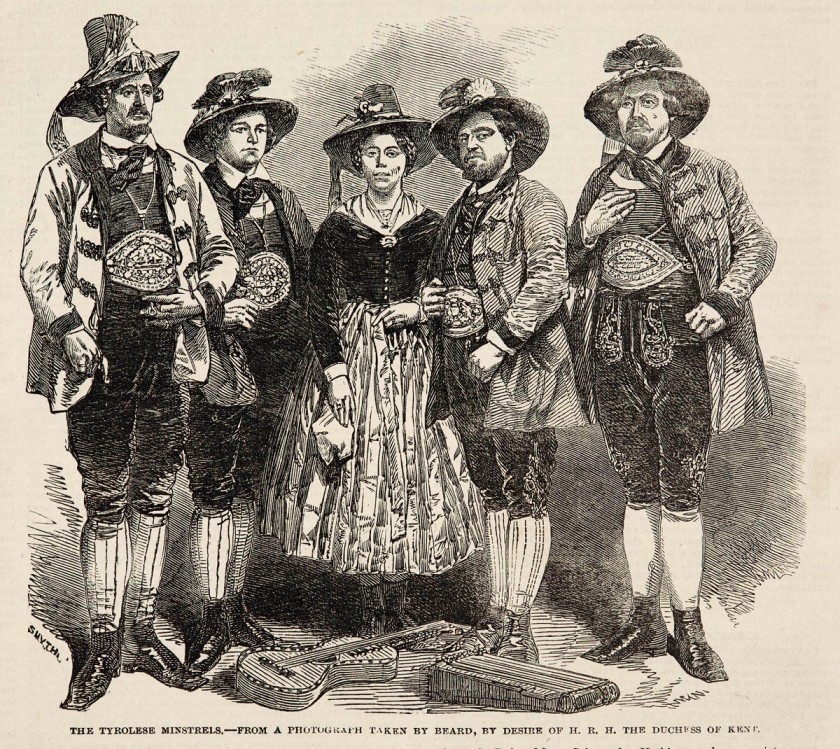
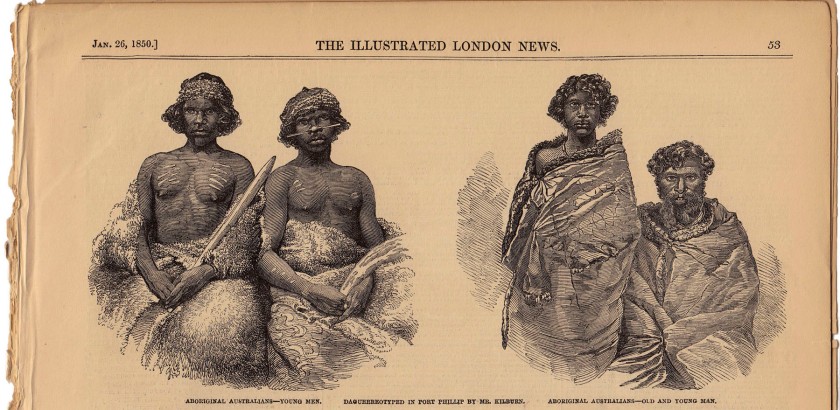
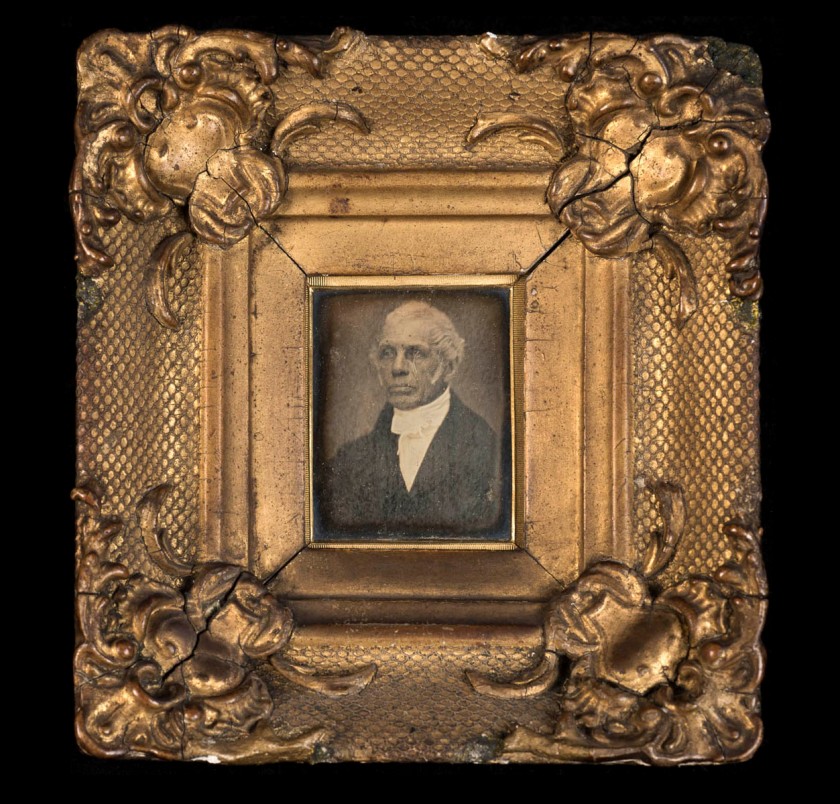
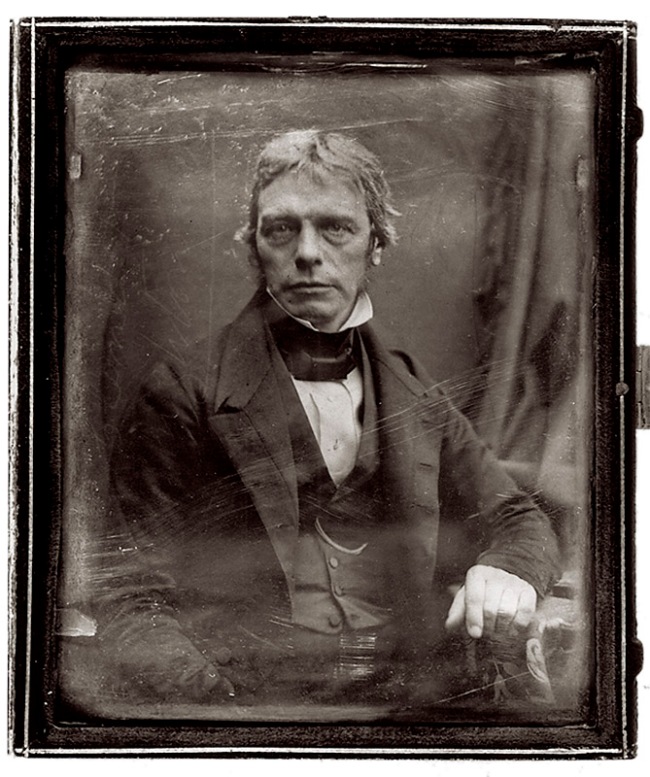
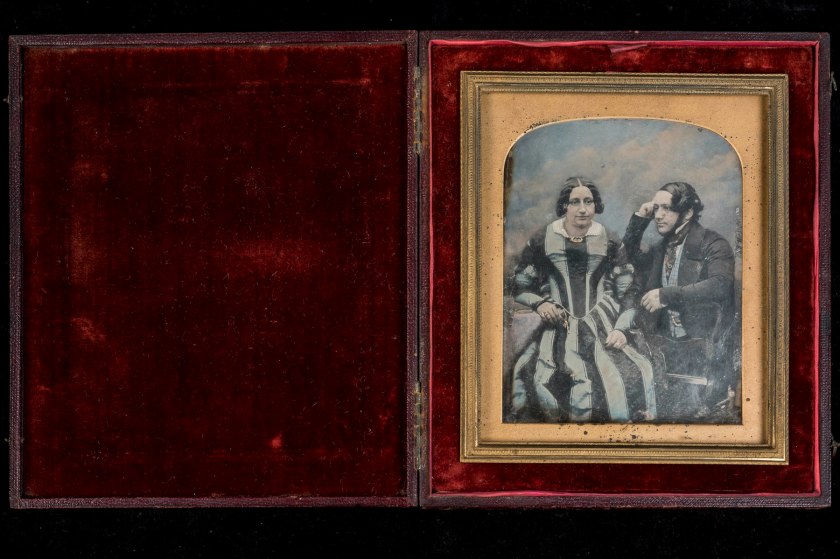
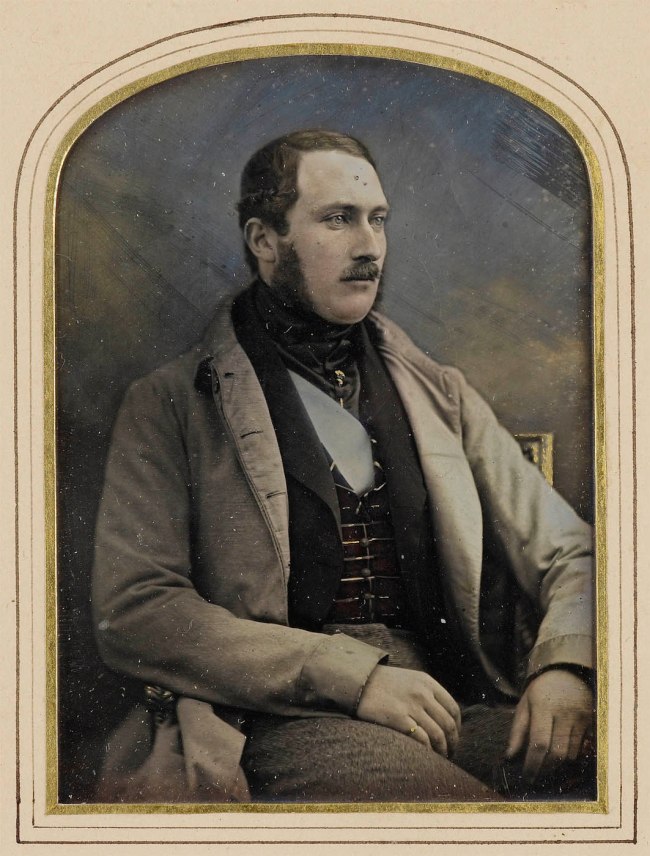
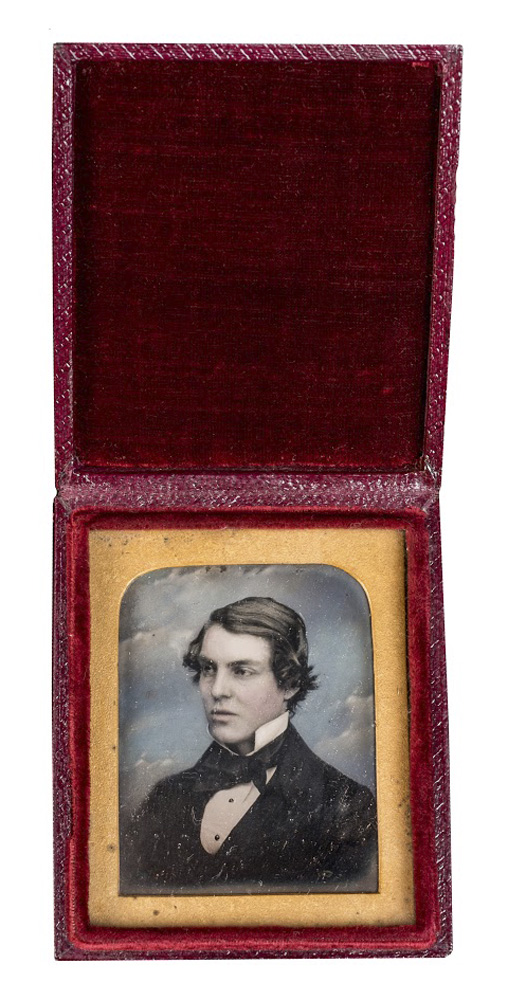
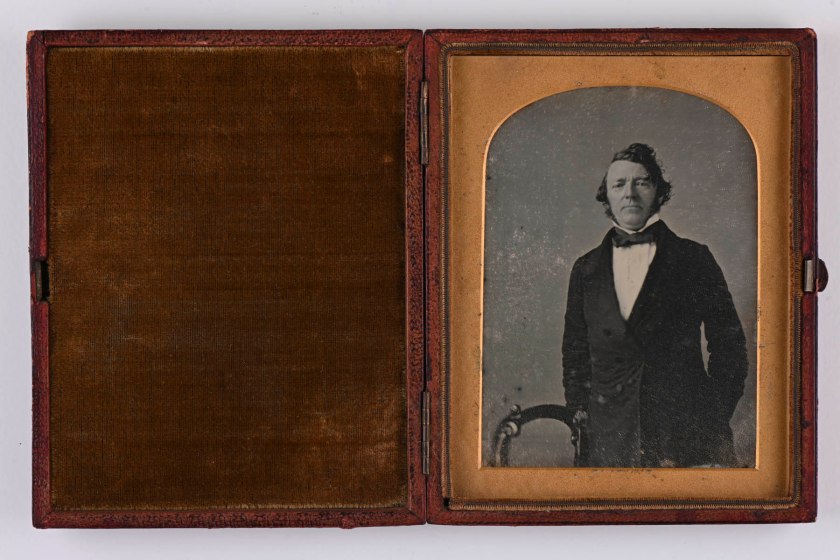
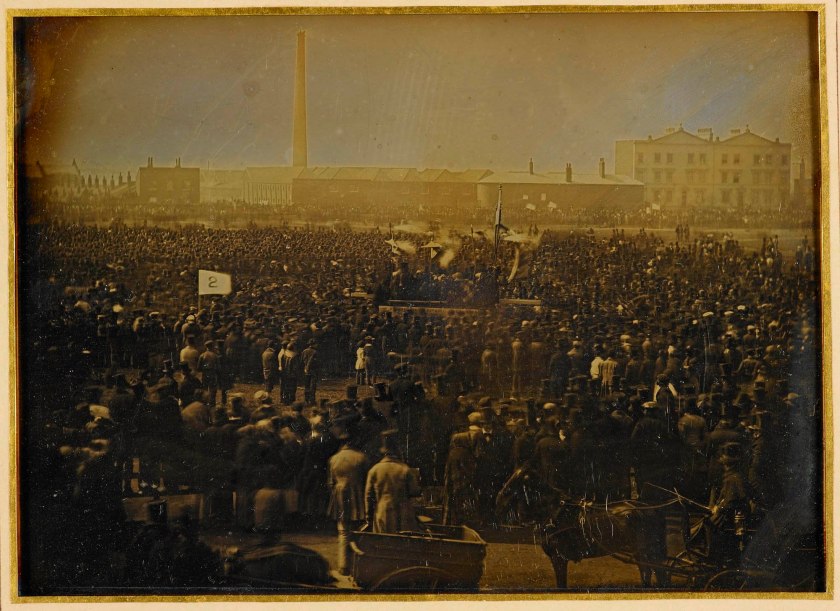
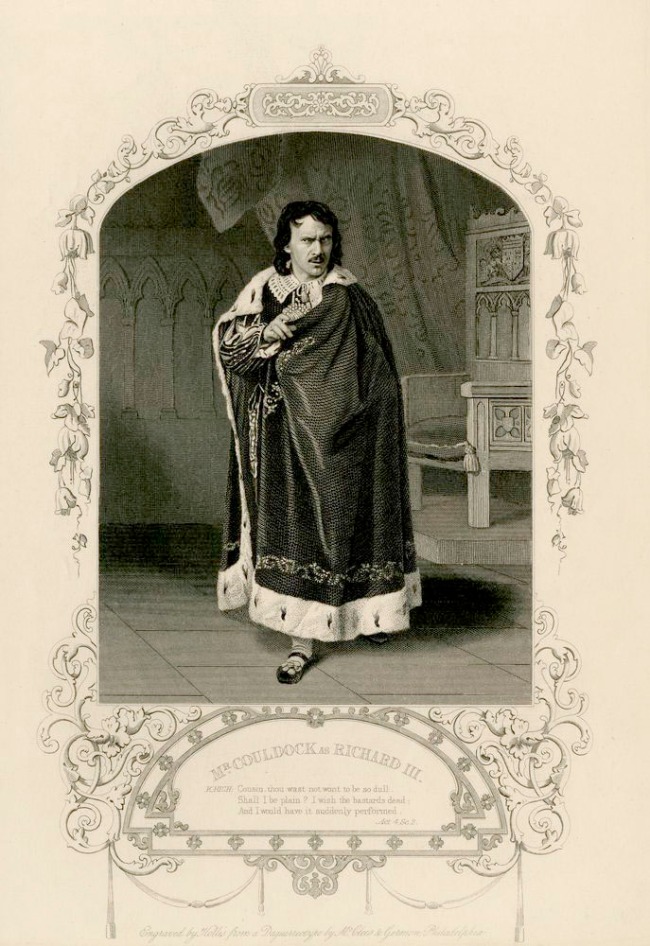
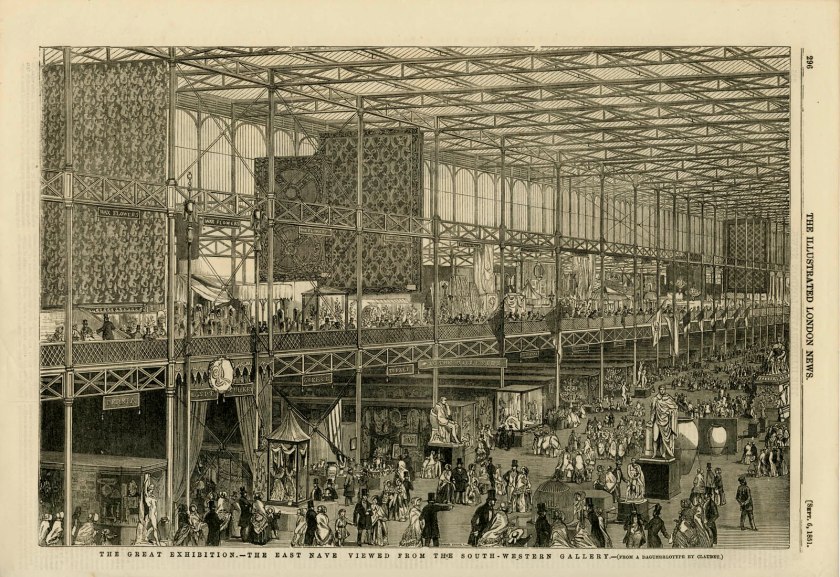
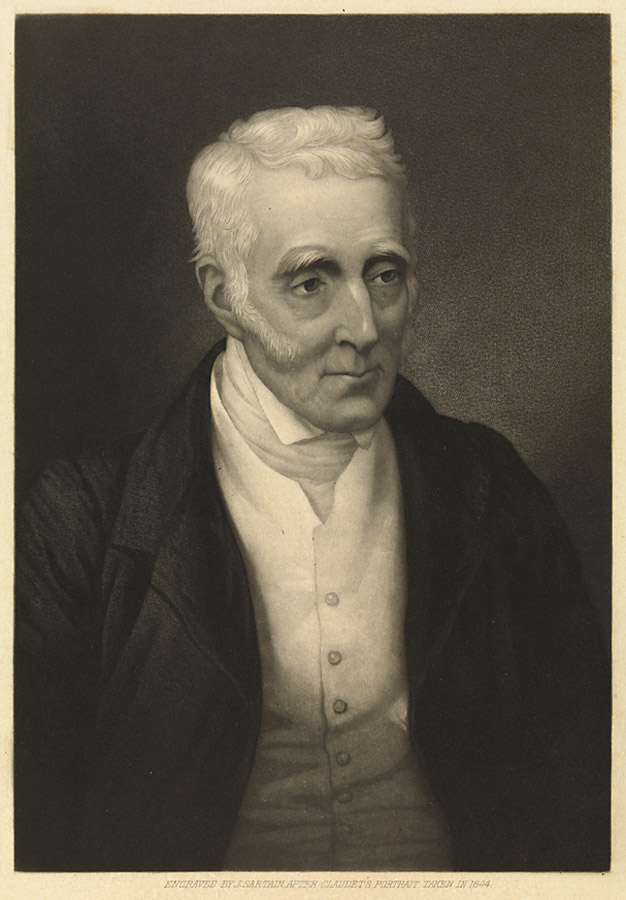
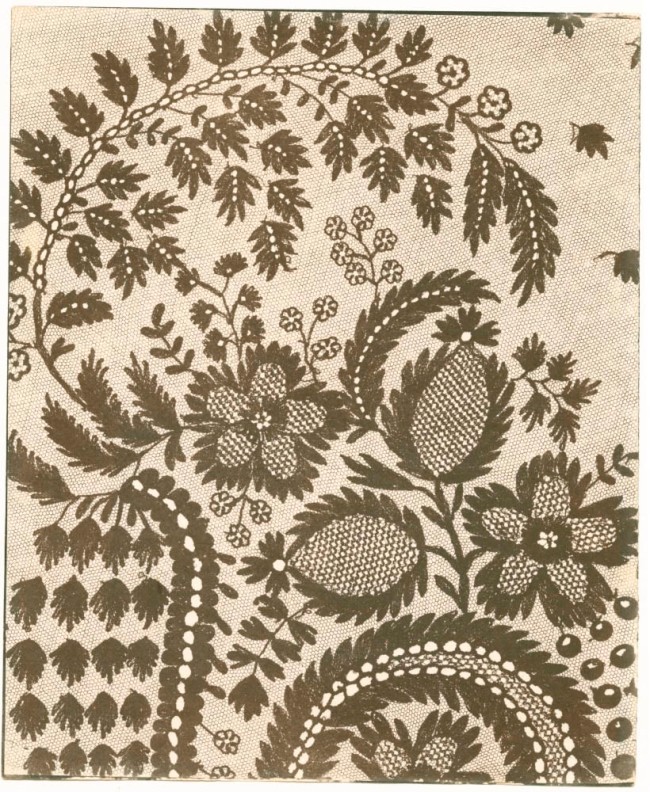
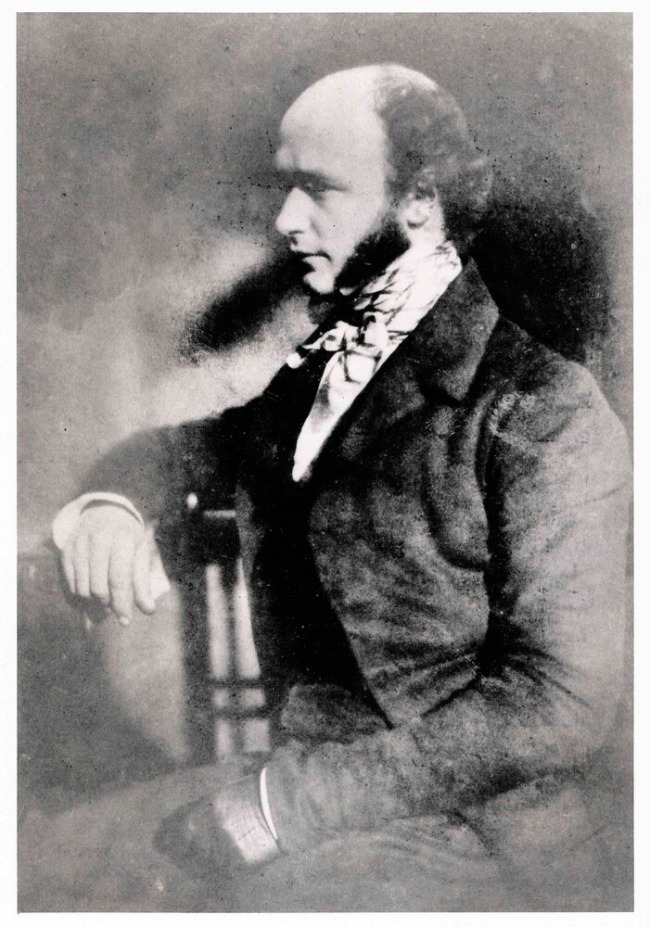
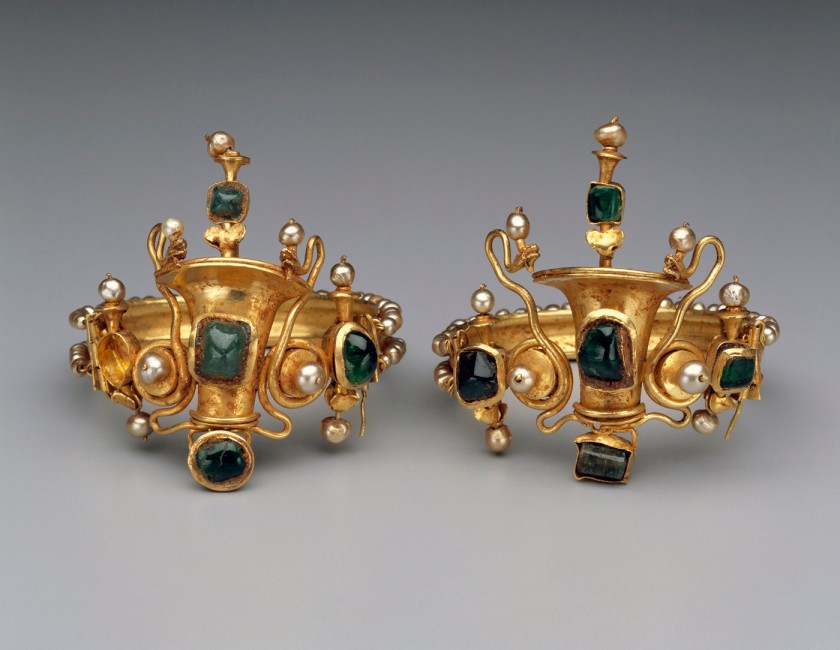
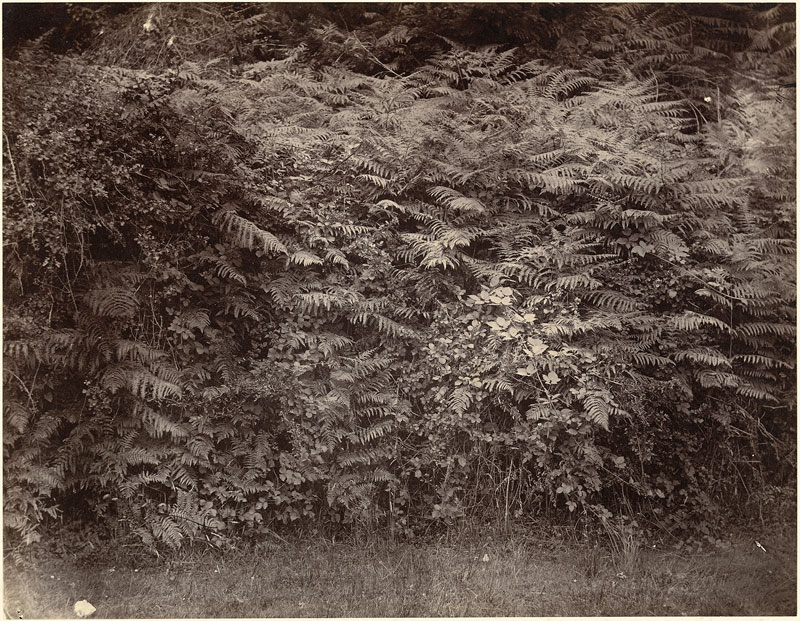
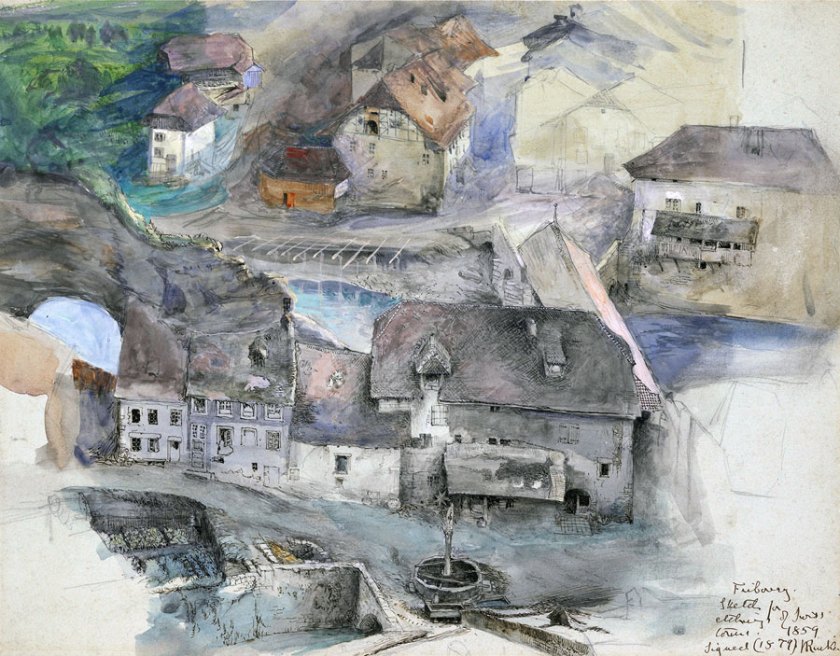
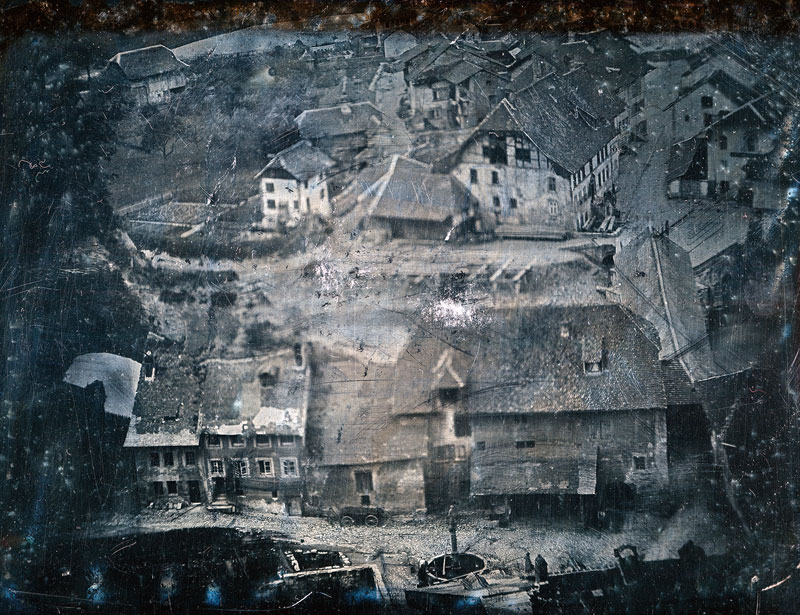
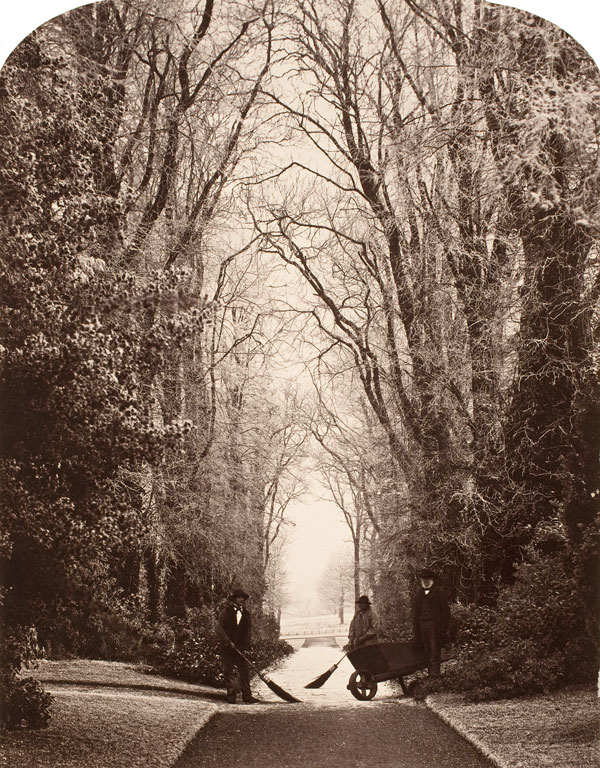
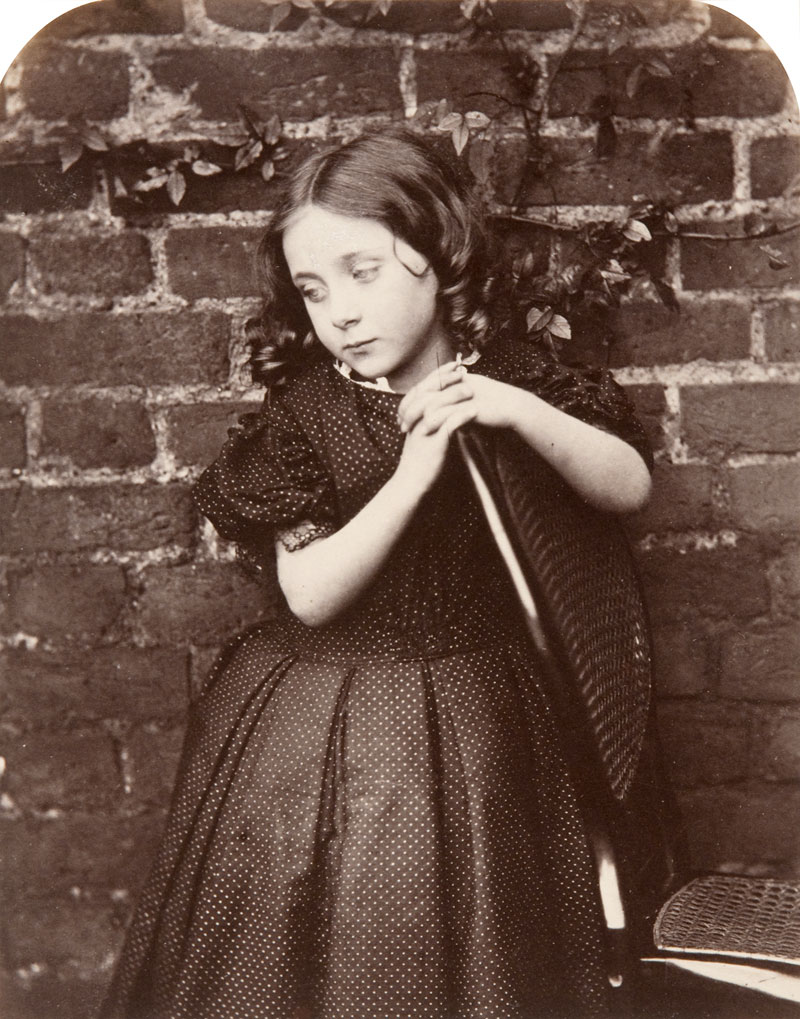
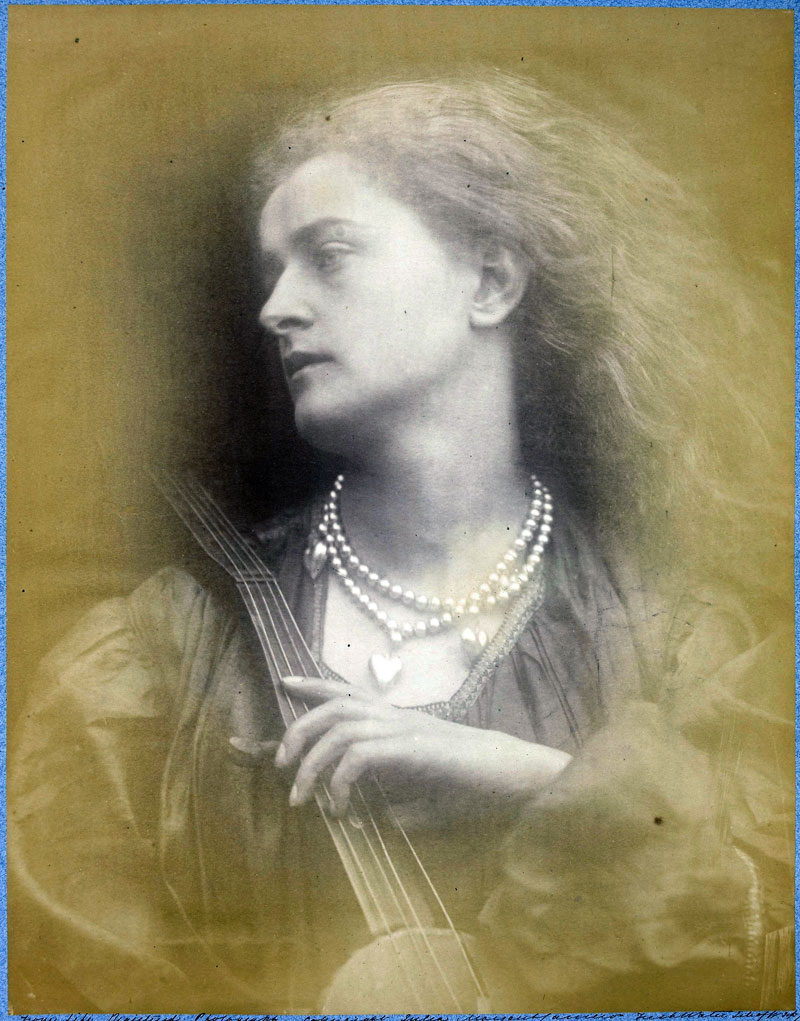













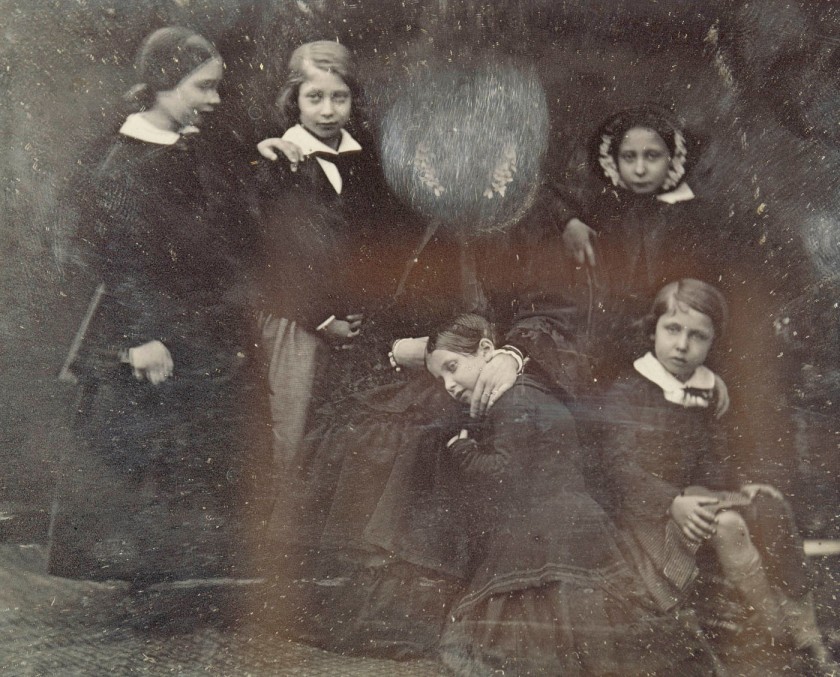































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.