Exhibition dates: 9th Dec 2022 – 10th April 2023
Curator: Dr. Markus Bertsch
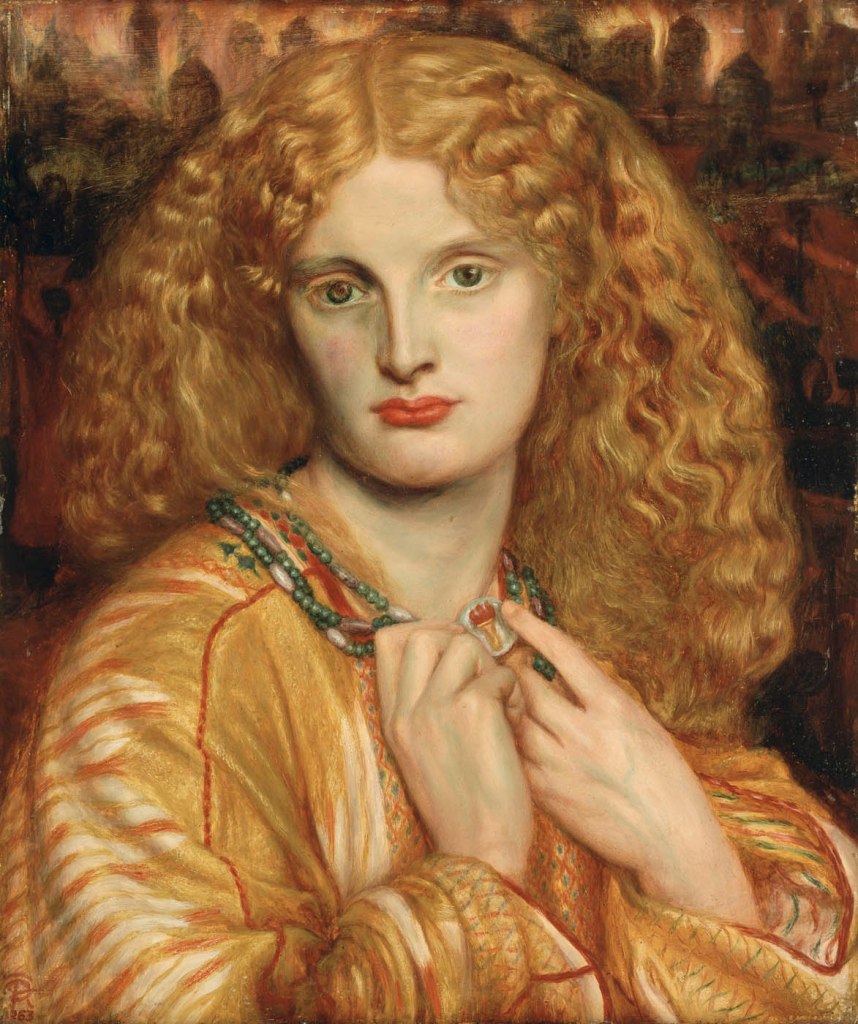

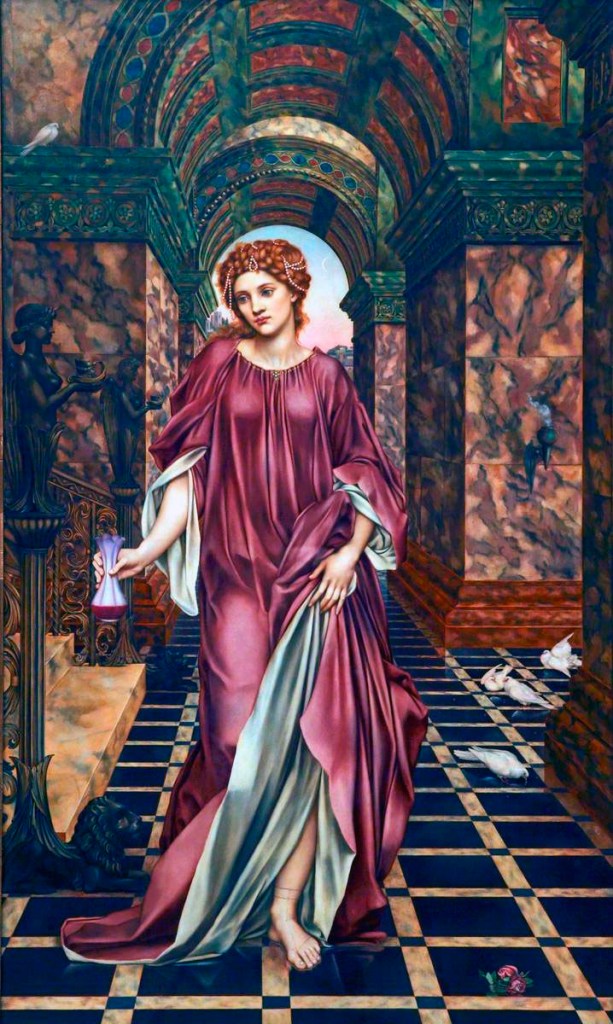
Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1828-1882)
Helen of Troy
1863
Oil on mahogany
32.8 x 27.7cm
© Hamburger Kunsthalle / bpk
Foto: Elke Walford
What a fascinating and inspired concept for an exhibition!
In order to understand the myth and construction of the femme fatale stereotype the exhibition investigates, through art and representation, concepts such as sexuality and its demonisation, the male and female gaze, white ideals of beauty, racism, Orientalism, anti-Semitism, power relations, hate, non-binary gaze, gender roles, myth and religion and black feminism. Such areas of breath are needed to examine the myth of the femme fatale.
I just wish the media images had included some photographs from the interwar avant-garde period by photographers such as Claude Cahun, Dora Maar, Eva Besnyö, Ilse Bing, Lotte Jacobi, Yva, Grete Stern, Ellen Auerbach, Aenne Biermann and Florence Henri for example – all of whom photographed the “New Woman” of the 1920s, an image which embodied an ideal of female empowerment based on real women making revolutionary changes in life and art. I hope the exhibition contains images by some of these photographers.
“The femme fatale is a myth, a projection, a construction. She symbolises a visually coded female stereotype: the sensual, erotic and seductive woman whose allegedly demonic nature reveals itself in her ability to lure and enchant men – often leading to fatal results. It is this likewise dazzling and clichéd image, long dominated by a male and binary gaze, that is in the focus of the exhibition Femme Fatale. Gaze – Power – Gender at the Hamburger Kunsthalle. Beyond exploring a range of artistic approaches to the theme from the early 19th century to the present, the show aims to critically examine the myth of the femme fatale in its genesis and historical transformation.” (Text from the Hamburger Kunsthalle website)
Dr Marcus Bunyan
PS. I have added further images and bibliographic information about the artists to the posting.
Many thankx to the Hamburger Kunsthalle for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
The male gaze places women in the context of male desire, essentially portraying the female body as eye candy for the heterosexual man. By valuing the desires of the male audience, the male gaze supports the self-objectification of women.
According to the Theory of Gender and Power (Robert Connell), the sexual division of power reproduces inequities in power between men and women which are maintained by social mechanisms such as the abuse of authority and control in relationships.
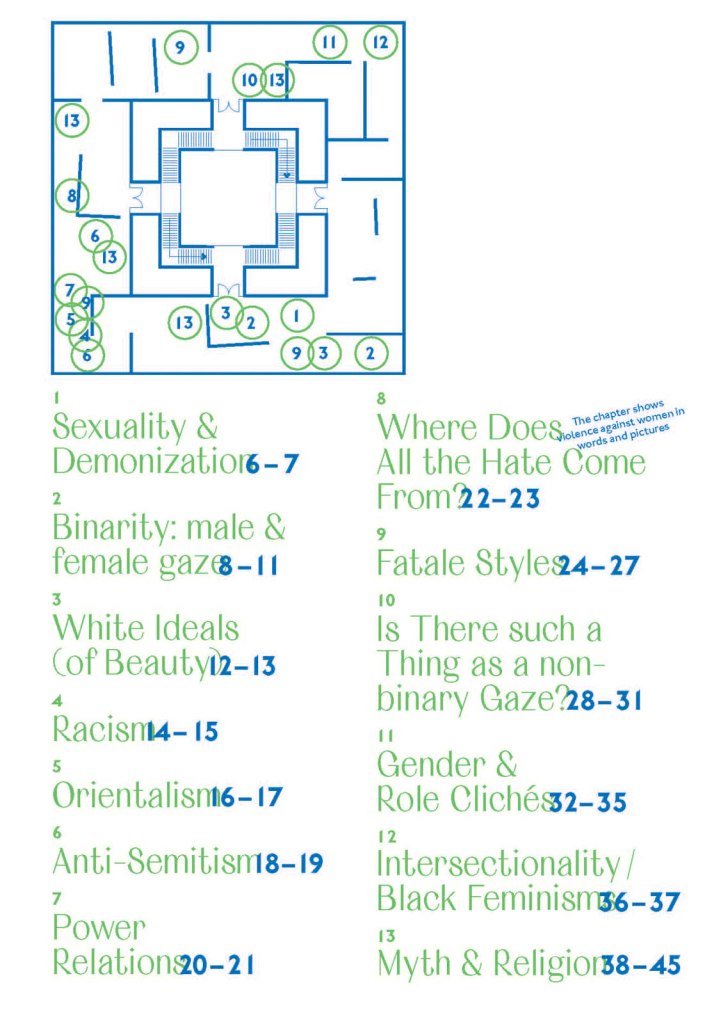
Pages from Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition Femme Fatale. Gaze – Power – Gender showing in the bottom posting, the room layout with sections to the exhibition
The femme fatale is a myth, a projection, a construction. She symbolises a visually coded female stereotype: the sensual, erotic and seductive woman whose allegedly demonic nature reveals itself in her ability to lure and enchant men – often leading to fatal results. It is this likewise dazzling and clichéd image, long dominated by a male and binary gaze, that is in the focus of the exhibition Femme Fatale. Gaze – Power – Gender at the Hamburger Kunsthalle. Beyond exploring a range of artistic approaches to the theme from the early 19th century to the present, the show aims to critically examine the myth of the femme fatale in its genesis and historical transformation.
The “classical” image of the femme fatale feeds above all on biblical and mythological female figures such as Judith, Salome, Medusa or the Sirens, who were widely portrayed as calamitous women in art and literature between 1860 and 1920. Characteristic of the femme fatale figure is the demonisation of female sexuality associated with these narratives. Around 1900, the femme fatale image was frequently projected onto real people, mainly actors, dancers or artists such as Sarah Bernhardt, Alma Mahler or Anita Berber. What is striking here is the simultaneity of important achievements of women’s emancipation and the increased appearance of this male-dominated image of women. In the sense of a counter-image that playfully picks up on aspects of the femme fatale figure, the New Woman, an ideal emerging well into the 1920s, also becomes important for the exhibition. A decisive caesura was set in the 1960s by feminist artists concerned with deconstructing the myth of the femme fatale – along with the corresponding viewing habits and pictorial traditions. Current artistic positions, in turn, deal with traces and appropriations of the archetypic image or establish explicit counter-narratives – often with reference to the #MeToo movement, questions of gender identities, female corporeality and sexuality, and by addressing the topic of the male gaze.
To investigate the constellations of gaze, power and gender that are constitutive for the image of the femme fatale and its transformations over time, the exhibition has assembled around 200 exhibits spanning a broad range of media and periods. On display will be paintings by Pre-Raphaelite artists (including Evelyn de Morgan, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, John William Waterhouse) alongside Symbolist works (such as Fernand Khnopff, Gustave Moreau, Edvard Munch and Franz von Stuck), works of Impressionism (including Lovis Corinth, Max Liebermann, Édouard Manet, Max Slevogt), of Expressionism and New Objectivity (Dodo, Jeanne Mammen, Gerda Wegener, among others). The featured positions of the early feminist avant-garde (including VALIE EXPORT, Birgit Jürgenssen, Ketty La Rocca, Maria Lassnig, Betty Tompkins) along with current works based on queer and intersectional feminist perspectives (Nan Goldin, Mickalene Thomas, Zandile Tshabalala, among others), build a bridge all the way to the present.
Text from the Hamburger Kunsthalle website
Chapters of the exhibition

Carl Joseph Begas (German, 1794-1854)
Die Lureley
1835
Oil on canvas
124.3 × 135.3cm
© Begas Haus – Museum für Kunst und Regionalgeschichte Heinsberg
Dangerous waters – Lorelei and her ‘fatal’ sisters
During the Romantic era, the element of water was often associated with the idea of dangerous femininity. The figure of Lorelei, in particular, was widely and diversely interpreted in numerous works of art, music and literature. Clemens Brentano laid the foundation for the legend of Lorelei with his ballad Zu Bacharach am Rheine…, written in 1801. Here, for the first time, a female figure was linked to the Lorelei – a large slate rock on the bank of the river Rhine that was known for producing an unusual echo. The broad popular appeal of this legend began with the publication of Heinrich Heine’s poem Die Lore-Ley in 1824 and continued to grow throughout the century. Although neither Brentano nor Heine stylised Lorelei as a femme fatale, many 19th-century artistic representations of this myth reduced the female figure to her siren-like, demonic qualities. The legend of Lorelei also has a remarkable resonance in contemporary art: in her video work “das Schöne muss sterben!”, for example, Gloria Zein transfers the narrative into the urban present, giving it an ironic twist and reflecting critically on the power of beauty; Aloys Rump traces the myth that surrounds this famous rock in the Rhine back to its material origins, exposing the Lorelei legend as pure invention and projection.
Aestheticized, demonized, sexualized: the femme fatale in the Victorian age
The 19th-century image of the femme fatale was largely shaped by the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. This group of English artists around Dante Gabriel Rossetti and Edward Burne-Jones was founded in 1848. Drawing on ancient myths and works of English literature, the Pre-Raphaelites (as they were later known) established a very specific ideal of beauty. Their depictions above all featured female figures to whom destructive or even fatal qualities had traditionally been attributed, such as Lilith, Medea, Circe and Helen of Troy. The Pre-Raphaelites deliberately emphasised the contrast between the subjects’ mythological demonisation and their visualisation as sensual beings of ethereal beauty. Later artists who were influenced by the Pre-Raphaelites created increasingly eroticised depictions of women, portraying them as both an ideal and a vision of fear. John William Waterhouse’s painting of Circe, for example, explicitly links her power to her both enchantingly and threateningly seductive nature. John Collier’s highly sexualised interpretation of Lilith, meanwhile, presents the mythic figure primarily as an object of male desire. This white, Victorian ideal of femininity and beauty, along with its (re-)presentation in a museum context, is reflected by Sonia Boyce in her video installation Six Acts. This work emerged from a critical intervention she performed at Manchester Art Gallery in 2018.
Sexuality & Demonisation
The term femme fatale originally describes a sensual, erotically seductive woman who puts men in danger and plunges them into their misfortune – not seldom with deadly consequences. In his painting Lilith, John Collier also illustrated such a prototype of a femme fatale. Here, the woman’s body is excessively sexualised and her sexuality demonised. This narrative also suggests: a woman’s lust is something dangerous. Even today, women are often morally condemned when they live out their sexuality openly. How can that be? Female lust is declared taboo, while male lust is celebrated? That is indeed problematic. However: the figure of the femme fatale is by now often appropriated by women as an instrument for self-empowerment.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition

John William Waterhouse (1849-1917)
Circe offering the cup to Ulysses
1891
Oil on canvas
148 cm × 92cm
© Gallery Oldham
John William Waterhouse RA (6 April 1849 – 10 February 1917) was an English painter known for working first in the Academic style and for then embracing the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood’s style and subject matter. His artworks were known for their depictions of women from both ancient Greek mythology and Arthurian legend.
Born in Rome to English parents who were both painters, Waterhouse later moved to London, where he enrolled in the Royal Academy of Art. He soon began exhibiting at their annual summer exhibitions, focusing on the creation of large canvas works depicting scenes from the daily life and mythology of ancient Greece. Many of his paintings are based on authors such as Homer, Ovid, Shakespeare, Tennyson, or Keats. Waterhouse’s work is displayed in many major art museums and galleries, and the Royal Academy of Art organised a major retrospective of his work in 2009.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Binarity: male & female gaze
What is the male gaze actually all about?
The male gaze refers to the concept of a predominant masculine perspective; it represents the systematic use of male control in our society and its impact on us. The term was coined by feminist film theorist Laura Mulvey who in the 1970s drew attention to how women in films were mostly portrayed as objects catering to the fantasies of heterosexual males. It was soon applied to other genres such as fashion, literature, music and art – and widely adopted in the everyday world. Whether in film, advertising, in novels, on the street, at school, during training or at university: the male gaze is omnipresent. It condemns, objectifies, defines standards and ideals, oppresses and classifies: male= active, female=passive. We all grew up with the phenomenon and are confronted with it on an everyday basis. As a result, all of us, including women and non-binary people, have more or less internalised it. Whether consciously or unconsciously, especially these groups tend to see themselves through a kind of mirror, anticipating the male gaze. But: understanding the male gaze also means being able to unlearn it.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
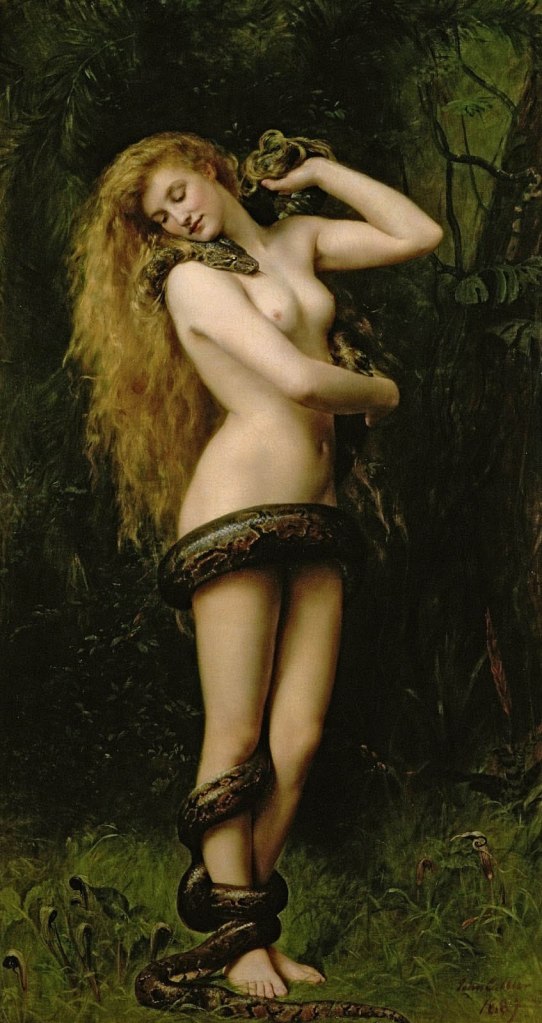

John Collier (English, 1850-1934)
Lilith
1887
Oil on canvas
194 × 104cm (76 × 41 in)
Atkinson Art Gallery and Library, Southport, Merseyside, England
© The Atkinson
Public domain
Lilith is an 1889 painting by English artist John Collier, who worked in the style of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. The painting of the Jewish mythic figure Lilith is held in the Atkinson Art Gallery in Southport, England. It was transferred from Bootle Art Gallery in the 1970s.
Collier portrayed Lilith as a golden-haired, porcelain-skinned beautiful nude woman who fondles on her shoulder the head of a serpent, coiled around her body in a passionate embrace. Against the background of a dark, brown-green jungle, stands a naked female figure, whose pale skin and long blond hair falling down her back form a stark contrast with the forest. The head position and gaze of Lilith are turned away from the viewer, concentrating on the snake’s head resting on her shoulder. The snake encircles her body in several coils, starting around its closely spaced ankles, past the knee, to her lower abdomen, where it thereby conceals. Lilith supports the snake’s body with her hands in the area of her upper body, so that the snake’s head can lie over her right shoulder up to her throat. Lilith’s head is bent towards the snake, her cheek nestles against the animal. The brown tones of the snake’s body stand out in contrast with the pale woman’s body, but take up the colour scheme of the surrounding jungle. Collier presented his painting inspired by fellow painter and poet Dante Gabriel Rossetti’s 1868 poem Lilith, or Body’s Beauty, which describes Lilith as the witch who loved Adam before Eve. Her magnificent tresses gave the world “its first gold,” but her beauty was a weapon and her charms deadly.
The magazine The British Architect described the work in 1887: “Here is a nude woman, whose voluptuous, round form is most gracefully represented, surrounded by a great serpent, the thickest part of which crosses it horizontally and cuts it in half; her head slides down her chest and she seems to be pulling it in tighter coils. The background is a coarse kind of green, repulsive and abominable.”
Text from the Wikipedia website
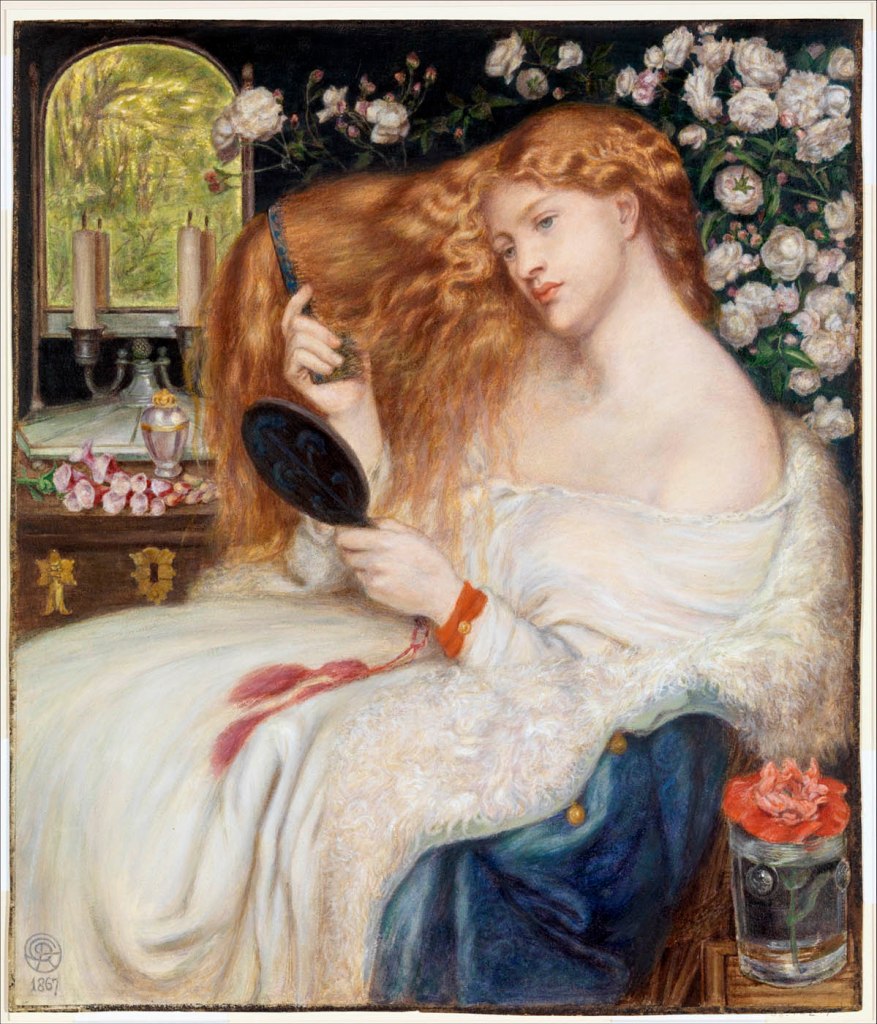

Dante Gabriel Rossetti (British, London 1828 – 1882 Birchington-on-Sea)
Henry Treffry Dunn (British, Truro 1838 – 1899 London)
Lady Lilith
1867
Watercolour and gouache
20 3/16 X 17 5/16 in. (51.3 x 44cm)
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, Rogers Fund, 1908
© The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
Fascinated by women’s physical allure, Rossetti here imagines a legendary femme fatale as a self-absorbed nineteenth-century beauty who combs her hair and seductively exposes her shoulders. Nearby flowers symbolise different kinds of love. In Jewish literature, the enchantress Lilith is described as Adam’s first wife, and her character is underscored by lines from Goethe’s Faust attached by Rossetti to the original frame, “Beware … for she excels all women in the magic of her locks, and when she twines them round a young man’s neck, she will not ever set him free again.” The artist’s mistress, Fanny Cornforth, is the sitter in this watercolour, which Rossetti and his assistant Dunn based on an oil of 1866 (Delaware Art Museum).
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
Lady Lilith is an oil painting by Dante Gabriel Rossetti first painted in 1866-1868 using his mistress Fanny Cornforth as the model, then altered in 1872-1873 to show the face of Alexa Wilding. The subject is Lilith, who was, according to ancient Judaic myth, “the first wife of Adam” and is associated with the seduction of men and the murder of children. She is shown as a “powerful and evil temptress” and as “an iconic, Amazon-like female with long, flowing hair.” …
A large 1867 replica of Lady Lilith, painted by Rossetti in watercolour, which shows the face of Cornforth, is now owned by New York’s Metropolitan Museum of Art. It has a verse from Goethe’s Faust as translated by Shelley on a label attached by Rossetti to its frame:
“Beware of her fair hair, for she excels
All women in the magic of her locks,
And when she twines them round a young man’s neck
she will not ever set him free again.”
Text from the Wikipedia website
White Ideals (of Beauty)
Apparently, the ideal is the white woman. She is thought to be pure, innocent and therefore endearing. This racist idea reaches from colonial times all the way to the present day. In 2022 alone, it can be found in several social media trends. One of them is the clean girl look on TikTok.
But what is behind all this and who is the trend actually for? The clean girl aesthetic gone viral is rather minimalistic: simple clothes, subtle make-up with delicate lip gloss and small gold creole earrings. With this look, young women want to represent themselves as so-called “girl bosses”, meaning women who have everything under control. This, however, is no more than a male fantasy. It has nothing to do with real people. The clean girl image also reinforces perceptions of which kind of women are more socially accepted. Namely, those who, like the clean girl, have “smooth and porcelain-like skin”. This Eurocentric ideal of beauty can already be detected in the nineteenth-century work Lady Lilith by Dante Gabriel Rossetti. Lady Lilith‘s skin is ivory white; she is combing her hair smooth, which is still wavy at the hairline. In the clean girl look hair is also straight, usually tied into a tight braid or chignon. Curly hair is excluded – and along with it especially Black people with Afro hair. Their natural appearance is thus portrayed as dirty in contrast to the allegedly pure clean girl look – a racist narrative that continues to try to position Black women in particular as inferior in society. Whereas, some of those characteristics appearing in the clean girl look originally were appropriated from Black Culture and then minimised: big gold creoles and gel-combed hairdos are just two of many examples. The clean girls with the most TikTok views represent this kind of standard beauty: thin, white and wearing expensive clothes. On the social media schoolyard, they are the ones who are considered as cool. But what they are doing while they are at it is bowing to racist, classist ideals that need to be made visible and discussed.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition

Evelyn de Morgan (English, 1855-1919)
Medea
Nd
Oil on canvas
148 × 88cm
© Williamson Art Gallery and Museum, Birkenhead; Wirral Museums Service
Purchased 1927
Evelyn De Morgan (30 August 1855 – 2 May 1919), née Pickering, was an English painter associated early in her career with the later phase of the Pre-Raphaelite Movement, and working in a range of styles including Aestheticism and Symbolism. Her paintings are figural, foregrounding the female body through the use of spiritual, mythological, and allegorical themes. They rely on a range of metaphors (such as light and darkness, transformation, and bondage) to express what several scholars have identified as spiritualist and feminist content.
De Morgan boycotted the Royal Academy and signed the Declaration in Favour of Women’s Suffrage in 1889. Her later works also deal with the themes of war from a pacifist perspective, engaging with conflicts like the Second Boer War and World War I.
Text from the Wikipedia website
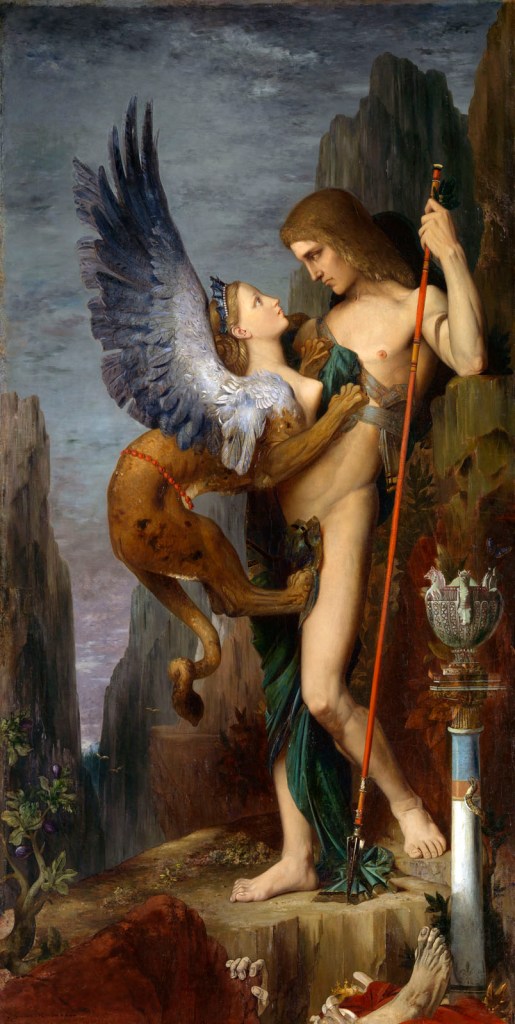

Gustave Moreau (1826-1898)
Oedipus and the Sphinx
1864
Oil on canvas
206 x 104.8cm
© The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
Bequest of William H. Herriman, 1920
Racism
Racism means that people are subjected to depreciation exclusion or even to experiencing violence due to their origin, skin colour or religion. Racism comes in many forms. There is, for example, anti-Muslim, anti-Black or anti-Asian racism which is particularly directed against these groups. While such group based hostility was formerly justified above all by the “wrong” religious affiliation, from the 16th century on, allegedly scientific explanations became established. People were divided into different “races” from the time white people started enslaving Black people to then exploit them for economic profit in the new colonies. Today, most people are aware that there is no such thing as different “human races”. Instead, it is the different “social background” or “culture” that now is often used as an argument to racially stigmatise people. The ‘others’ may be described as ‘primitive’ and ‘uncultivated’, sometimes exoticised or sexualised. Men are portrayed as libidinous, women as erotic and, quite often, as their victims. The Indian postcolonialism theorist Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak critically pinpointed this colonial perspective with the sentence: “White men are saving brown women from brown men.” This ironic statement emphasises the sense of civilisational superiority of white colonisers who saw themselves as “saviours”, but often came to the country as rapists and, on top of that, oppressed the female population in their countries of origin.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
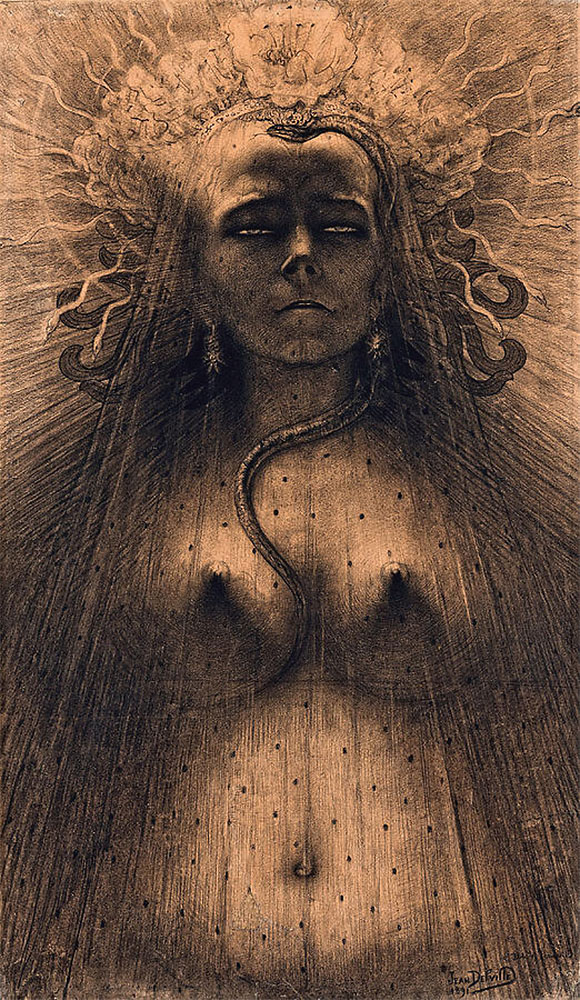

Jean Delville (Belgian, 1867-1953)
The Idol of Perversity (L’idole de la perversite)
1891
Jean Delville, The Idol of Perversity (L’idole de la perversite), 1891. Delville was a Belgian symbolist painter, author, poet and Theosophist, studying mystical and occultist philosophies. Such philosophies concentrate mainly on seeking the true origins of the universe, specifically of the divine and natural kind, believing that knowledge of ancient pasts offers a path to true enlightenment and salvation. Delville was the leading patron of Belgian Idealist movement, specifically in art circa the 1890s, having a belief system that upheld art to higher standards of substance, believing that it should express higher spiritual truth, based on principles of Ideal, or spiritual Beauty. …
The goal of the living body is to spiritualise itself and to refine our material selves, meaning to elevate ourselves to the level of not requiring or wanting things that are just of material value. Without a spiritual path or goal, men and women that walk the earth become slaves to their material possessions, forever destined to succumb to the desires, passions, greed, and egotistic need to always seek power over one another. Under this belief, the physical world we live in becomes the land of Satan, and those without a spiritual goal become merely his slaves. According to Delville, the first step to true enlightenment is to gain power over earthly temptations, such as promiscuity and erotic temptation. Truly enlightened soul is one that can use the power of his mind to rise above the temptations of, what was believed “unquenched bestial desires of a woman”. In late nineteenth century femme fatale embodied the kind of misogynistic idea that women were lower on the evolutionary scale, and female sex was that of animalistic, monstrous and aggressive, hence, the femme fatale characterisation, meaning that women’s grotesque sexual desires led men away from their spiritual goals, and thus driving them to live a life in sin, forever slaves to the Devil. In this painting Delville portrays the femme fatale as an almost demonic entity, with the bellow angel as to show her looming over the viewer, with an almost phallic snake, reminiscent of Franz von Stuck’s Sin, slithering between her pointed breasts. This image is a direct representation of Delville’s esoteric ideologies of material versus spiritual.
Art Universal. “Jean Delville, The Idol of Perversity (L’idole de la perversite), 1891,” on the Art Universal website August 8, 2017 [Online] Cited 03/03/2023
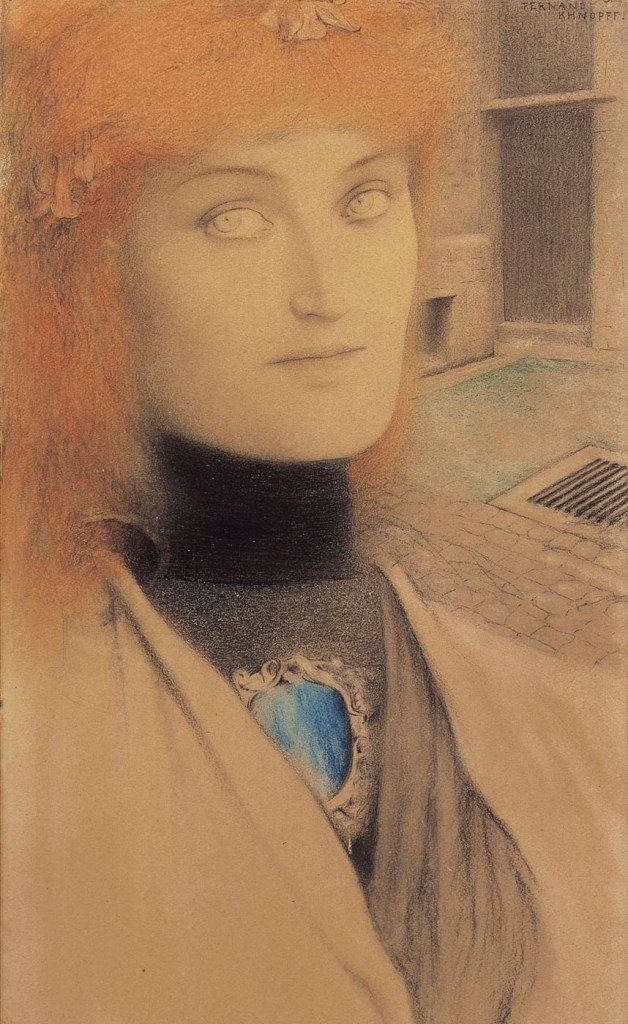
Fernand Khnopff (1858-1921)
Who Shall Deliver Me? (Christina Georgina Rossetti)
1891
Conté pen and coloured pencil on paper
21.9 x 13cm
© The Hearn Family Trust
Enigmatic images – the femme fatale in Symbolist art
Fantastical scenarios, imaginary dream worlds and psychological depths are the defining characteristics of Symbolism, a cultural movement that flourished throughout Europe from the 1880s onwards. The image of the femme fatale is also omnipresent in Symbolist art, but in these depictions, the female subjects often have an enigmatic, other-worldly appearance and their meaning is ambiguous. As the epitome of the cliché of ‘female mystery’, the sphinx is a prominent motif in Symbolist art. The image of this malevolent creature – a hybrid of woman, lion and bird – was strongly influenced by Gustave Moreau’s Oedipus and the Sphinx, an important early work by the painter. Moreau’s orientalised and eroticised interpretation of Salome as an ornamental figure also shaped the perception of her as a femme fatale. A similar composition featuring a vision of John the Baptist’s floating head is found in Odilon Redon’s Apparition. His figures, however, are even further removed from objective representation and concrete corporeality. These kinds of mystifying depictions were also interpreted and elaborated by other Symbolist artists, above all in Belgium and the Netherlands. In Fernand Khnopff’s subtle drawings, the femme fatale appears as a mysterious, ambiguous projection, addressing the themes of stereotypical femininity and androgyny.
Focussing on the body – interpretations of the femme fatale in Munich
In contrast to the enigmatic dream worlds of French and Belgian Symbolism, the depictions of femmes fatales by artists of the Munich School focus more explicitly on women’s bodies. Carl Strathmann’s large-format interpretations of Gustave Flaubert’s historical novel Salammbô, which was frequently adapted in France, place the titular female figure in an ornamental Art Nouveau setting that is typical of the period. Franz von Stuck and Franz von Lenbach, on the other hand, focus on concrete physical realities; while their paintings are set in mythological and biblical contexts, they are mainly aimed at representing nudity. In Stuck’s interpretation of the Sphinx, for example, the subject is no longer depicted as a hybrid creature, but is a purely human, naked woman. Only the posture of the nude, who is reduced to her physicality and sensuality, recalls a sphinx. This kind of sexualization in images of femmes fatales often involves constructing a supposed ‘otherness’ of the depicted subject. Through the incorporation of orientalising elements and antisemitic attributions such as the stereotype of the ‘beautiful Jewess’, female subjects – above all Judith and Salome – are presented as alluring and desirable, but are at the same denigrated as ‘other’.
Orientalism
Turbans, veils, sabres, teacups, palm trees, colourful carpets and nude women in harems – this cliché-ridden image of the ‘Orient’ was spread in the West and was a major theme especially in nineteenth-century painting. In 1978, the Palestinian-American literature professor Edward Said published a book entitled Orientalism in which he characterised this image as a Western invention. By describing the ‘Orient’, meaning roughly those regions now called North Africa and the Near and Middle East, as ‘alien’ and ‘backward’, the West was able to present itself as culturally superior. This, at the same time, made it easier to justify imperialist ambitions to subjugate and exploit these regions. Orientalism has been typified by rejection and attraction alike: the people and customs of the region are portrayed as irrational, lazy and dishonest just as much as sensual, pleasure-oriented and seductive. A widespread symbol of this in painting was the figure of the “Odalisque”, a white slave girl, preferably drawn naked in the bath. She strikingly exemplifies the kind of fantasies that (mainly) white European men would live out in their depictions of the Orient: at once a ‘chaste’ victim of ‘Oriental’ tyrants and a ‘sinful’ seductress of Western conquerors. Many of these Orientalist clichés have survived to this day and can also be found, in anti-Muslim racisms, for example.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition

Bruno Piglhein (1848-1894)
Egyptian Sword Dancer
1891
Oil on canvas
138 × 89cm
Private collection
© Courtesy Kunkel Fine Art, München
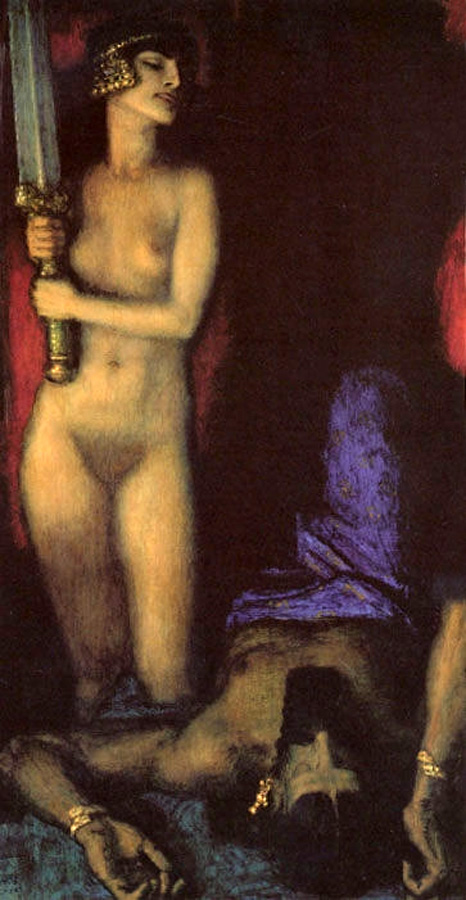

Franz Von Stuck (German, 1863-1928)
Judith and Holofernes
1926
Oil on canvas
157 × 83cm
Staatliche Schlösser, Gärten und Kunstsammlungen Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Schwerin
© Staatliche Schlösser, Gärten und Kunstsammlungen Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Staatliches Museum Schwerin
Foto: Elke Walford
Anti-Semitism
The term anti-Semitism describes a hostile attitude towards Jews. It manifests itself in various forms, from prejudice, to insults, to violence. Anti-Semitism, which has existed for thousands of years, is the oldest known form of group-specific hatred of people, regardless of gender. Its worst manifestation was during German National Socialism under Adolf Hitler when over six million Jewish people were murdered between 1933 and 1945 in Europe. What distinguishes anti-Semitism from other forms of discrimination is the idea of a cultural and economic superiority of the group being attacked, unlike, for example, racism or Islamophobia, where the counterpart is usually devalued. Instead of labelling Jews as backward, in stereotypes they often appear as representatives of a modern and sophisticated worldview, which is, however, portrayed as ‘decadent’ and ‘threatening’. Conspiracy theories also often contain anti-Semitic elements, as it is imagined that all Jewish people are wealthy, influential and well-connected and thus able to act as secret ‘string-pullers’ in international affairs. Anti-Semitic prejudices often refer to categories such as wealth and power, sexuality or external characteristics.
Visually, anti-Semitic body stereotypes are sometimes expressed through the depiction of large, crooked noses (‘hooknose’), bulging lips, narrow eyes, hunched posture, bowlegs and flat feet. Somewhat more subtle, but no less problematic, is the stereotype of the “beautiful Jewess”. This cliché image from art and literature around 1900 often showed Jewish women as smart, beautiful and seductive, but at the same time marked them as ‘foreign’ and ‘different’, for example, based on orientalising elements such as jewellery, etc.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition

Antonin Idrac (French, 1849-1884)
Salammbô
1882
Plaster
Height: 182cm (71.6 in); width: 53 cm (20.8 in); depth: 71cm (27.9 in)
Musée des Augustins
Public domain
Carl Strathmann (German, 1866-1939)
Salammbô
1894
Mixed media on canvas
187.5 x 287cm
Strathmann’s curious work occupies an intermediate position between the art of painting and the crafts. His paintings are strange concoctions studded with colored glass and artificial gems, foreshadowing similar extravagances by the Viennese Jugendstil painter Gustav Klimt. In Strathmann’s painting Salammbô, inspired by Flaubert’s novel, the Carthaginian temptress reclines on a carpet spread out on a flower-strewn meadow. Swathed in veils whose design is as complex as that of the harp beside her head, she submits to the kiss of the mighty snake that encircles her. Lovis Corinth described how Strathmann, while working on the large picture, gradually covered the originally nude model with “carpets and fantastic garments of his own invention so that in the end only a mystical profile and the fingers of one hand protruded from a jumble of embellished textiles. … coloured stones are sparkling everywhere; the harp especially is aglitter with fake jewels.” According to Corinth, Strathmann knew “how to glue and sew” these on the canvas “with admirable skill.”
Anonymous. “Carl Strathmann, Salammbô,” on the Dark Classics website 12/05/2011 [Online] Cited 01/03/2023
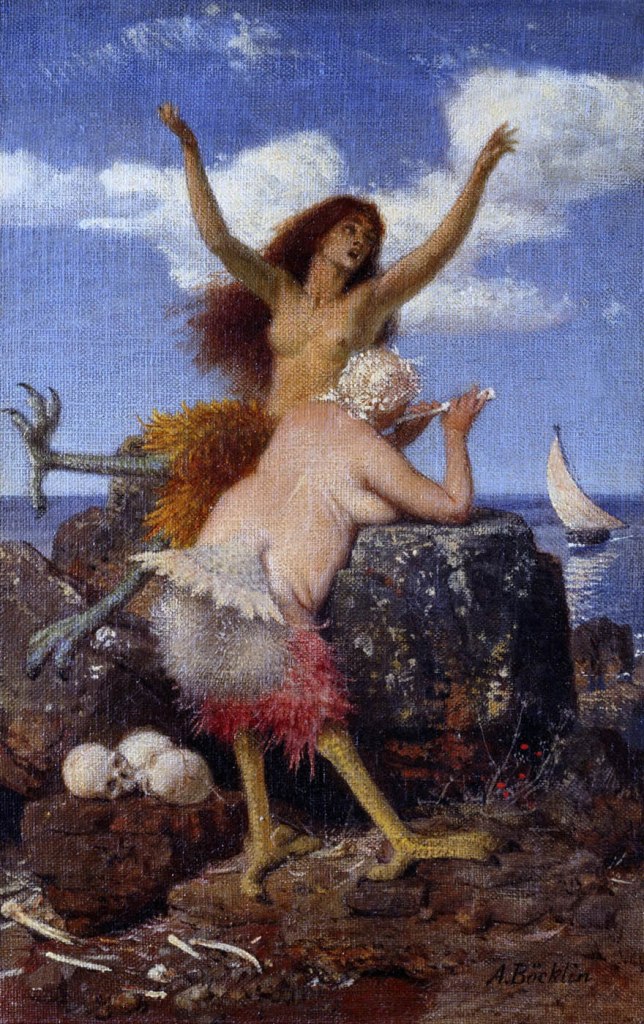

Arnold Böcklin (Swiss, 1827-1901)
Sirens
1875
Tempera on canvas
Height: 46cm (18.1 in); width: 31cm (12.2 in)
Alte Nationalgalerie
Public domain
Arnold Böcklin (16 October 1827 – 16 January 1901) was a Swiss symbolist painter. …
Influenced by Romanticism, Böcklin’s symbolist use of imagery derived from mythology and legend often overlapped with the aesthetic of the Pre-Raphaelites. Many of his paintings are imaginative interpretations of the classical world, or portray mythological subjects in settings involving classical architecture, often allegorically exploring death and mortality in the context of a strange, fantasy world.
Böcklin is best known for his five versions (painted 1880 to 1886) of the Isle of the Dead, which partly evokes the English Cemetery, Florence, which was close to his studio and where his baby daughter Maria had been buried. An early version of the painting was commissioned by a Madame Berna, a widow who wanted a painting with a dreamlike atmosphere.
Clement Greenberg wrote in 1947 that Böcklin’s work “is one of the most consummate expressions of all that is now disliked about the latter half of the nineteenth century.”
Text from the Wikipedia website
Franz Von Stuck (German, 1863-1928)
Sphinx
1904
Oil on canvas
83 × 156.5cm
© Loan from the Federal Republic of Germany as a permanent loan to the Hessian State Museum in Darmstadt
Foto: Wolfgang Fuhrmannek, HLMD
Franz Ritter von Stuck (February 23, 1863 – August 30, 1928), born Franz Stuck, was a German painter, sculptor, printmaker, and architect. Stuck was best known for his paintings of ancient mythology, receiving substantial critical acclaim with The Sin in 1892. In 1906, Stuck was awarded the Order of Merit of the Bavarian Crown and was henceforth known as Ritter von Stuck. …
Stuck’s subject matter was primarily from mythology, inspired by the work of Arnold Böcklin. Large forms dominate most of his paintings and indicate his proclivities for sculpture. His seductive female nudes are a prime example of popular Symbolist content. Stuck paid much attention to the frames for his paintings and generally designed them himself with such careful use of panels, gilt carving and inscriptions that the frames must be considered as an integral part of the overall piece.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Gustav Adolf Mossa (French, 1883-1971)
The Satiated Siren (Die gesättigte Sirene)
1905
Oil on canvas
81 × 54cm
Musée des Beaux-Arts, Nizza
© VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2022
Foto: Michel Graniou
Gustav-Adolf Mossa (28 January 1883 – 25 May 1971) was a French illustrator, playwright, essayist, curator and late Symbolist painter. …
Symbolist paintings
Mossa’s decade long Symbolist period (1900-1911) was his most prolific and began as a reaction to the recent boom of socialite leisure activity on the French Rivera, his works comically satirising or condemning what was viewed as an increasingly materialistic society and the perceived danger of the emerging New Woman at the turn of the century, whom Mossa appears to consider perverse by nature.
His most common subjects were femme fatale figures, some from Biblical sources, such as modernised versions of Judith, Delilah and Salome, mythological creatures such as Harpies or more contemporary and urban figures, such as his towering and dominant bourgeoise woman in Woman of Fashion and Jockey. (1906). His 1905 work Elle, the logo for the 2017 Geschlechterkampf exhibition on representations of gender in art, is an explicit example of Mossa’s interpretation of malevolent female sexuality, with a nude giantess sitting atop a pile of bloodied corpses, a fanged cat sitting over her crotch, and wearing an elaborate headress inscribed with the Latin hoc volo, sic jubeo, sit pro ratione voluntas (What I want, I order, my will is reason enough).
Many aspects of Mossa’s paintings of this period were also indictive of the decadent movement, with his references to Diabolism, depictions of lesbianism (such as his two paintings of Sappho), or an emphasis on violent, sadistic or morbid scenes.
Though these paintings are the subject of most present day exhibitions, scholarly articles and books on the artist, they were not released to the public until after Mossa’s death in 1971.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Inverted images – the femme fatale turns grotesque
In the late 19th century, artists began using exaggeration and caricature to highlight the grotesque, bizarre and absurd qualities of the femme fatale motif, suggesting that the traditional image of the wickedly seductive enchantress had become redundant. While these inverted images of the femme fatale illustrate the constructed nature of this concept, they in turn employ clichés of demonic femininity. Arnold Böcklin gives an ironic, grotesque twist to a popular artistic motif in his painting Sirens, where the typically emphasised seductiveness of the hybrid creatures appears to have the opposite effect. In Gustav-Adolf Mossa’s The Satiated Siren, meanwhile, the siren’s outstanding feature is her bloodthirsty instinct. In Carl Strathmann’s almost humorously exaggerated depiction of the Head of Medusa, on the other hand, Medusa’s petrifying gaze is no longer intended to shock the viewer. Although ancient myths still provided the subject matter for these interpretations, they were increasingly losing their exemplary function and could often only be transposed to the present in a grotesque guise. Aubrey Beardsley’s illustrations after Oscar Wilde’s play Salome (1893) were highly influential; while these also contained some vividly macabre motifs, the unmistakable ornamental aesthetic of defined lines and flat spatial planes made them appear less frightening.
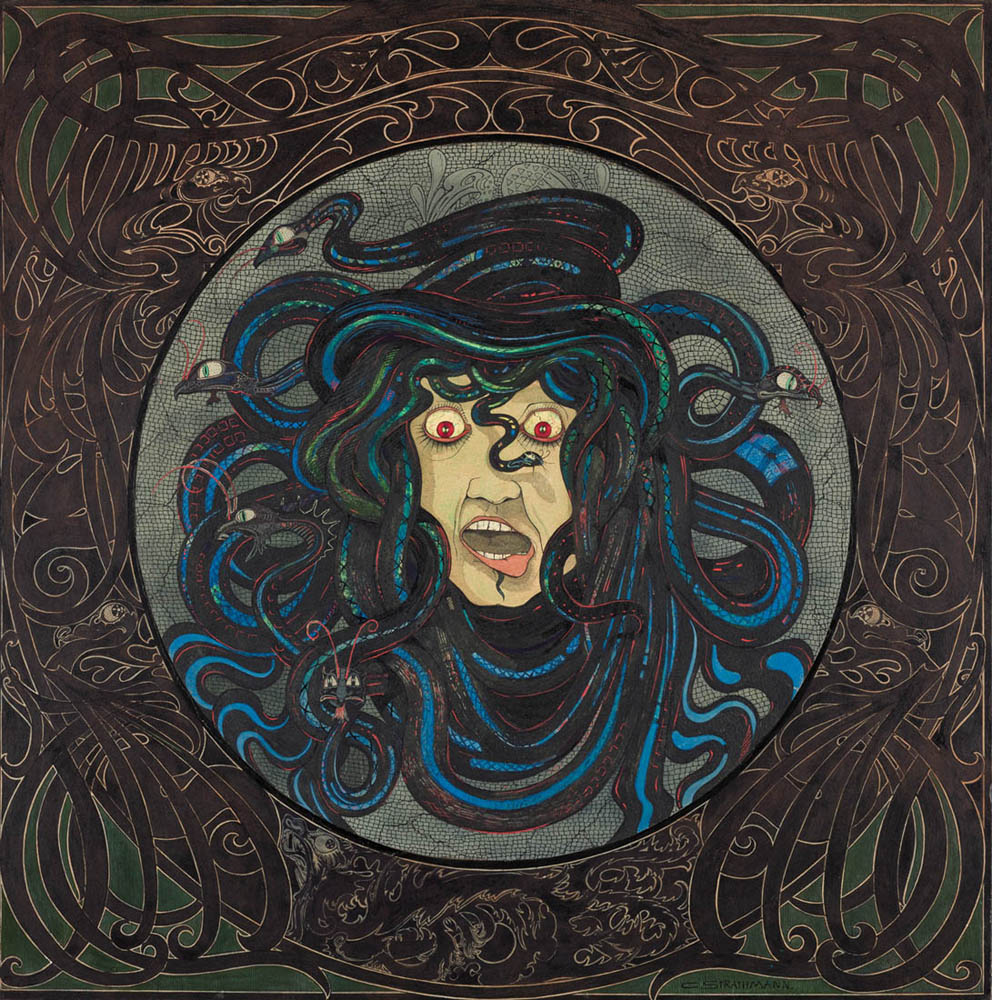

Carl Strathmann (German, 1866-1939)
Head of Medusa
c. 1897
Watercolour and ink
69.8 cm x 69.5cm
Münchner Stadtmuseum, Sammlung
CC BY-SA 4.0
Carl Strathmann (11 September 1866, Düsseldorf – 29 July 1939, Munich) was a German painter in the Art Nouveau and Symbolist styles.
His father, also named Carl Strathmann, was a merchant and manufacturer, who later served as consul in Chile. His mother, Alice, was originally from Huddersfield, England, and was an art enthusiast. From 1882 to 1886, he studied at the Kunstakademie Düsseldorf, with Hugo Crola, Heinrich Lauenstein and Adolf Schill. After being dismissed for a “lack of talent”, he enrolled at the Grand-Ducal Saxon Art School, Weimar where, from 1888 to 1889, he studied in the master class taught by Leopold von Kalckreuth.
When Kalckreuth left, he did as well; moving to Munich, where he lived a Bohemian lifestyle as a free-lance artist, and met the painter Lovis Corinth, who became a lifelong friend and associate. In 1894, he painted one of his best known works: “Salammbô”, inspired by a novel of the same name by Gustave Flaubert. In this monumental painting (6 x 9 feet) Salammbô, a high priestess of the Carthaginians, is shown caressing a snake, as part of a ritual sacrifice. Many were horrified, calling it a “sadistic fantasy”. The scandal made him immediately famous.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Aubrey Beardsley (British, 1872-1898)
The Toilette of Salome (second version)
1893
Please note: This drawing may not be in the exhibition but Beardsley’s drawings of Salome are mentioned in the exhibition text (below)

Aubrey Beardsley (British, 1872-1898)
J’ai baisé ta bouche Iokanaan
1892-1893
Please note: This drawing may not be in the exhibition but Beardsley’s drawings of Salome are mentioned in the exhibition text (below)

Aubrey Beardsley (British, 1872-1898)
John and Salome
1893
Please note: This drawing may not be in the exhibition but Beardsley’s drawings of Salome are mentioned in the exhibition text (below)
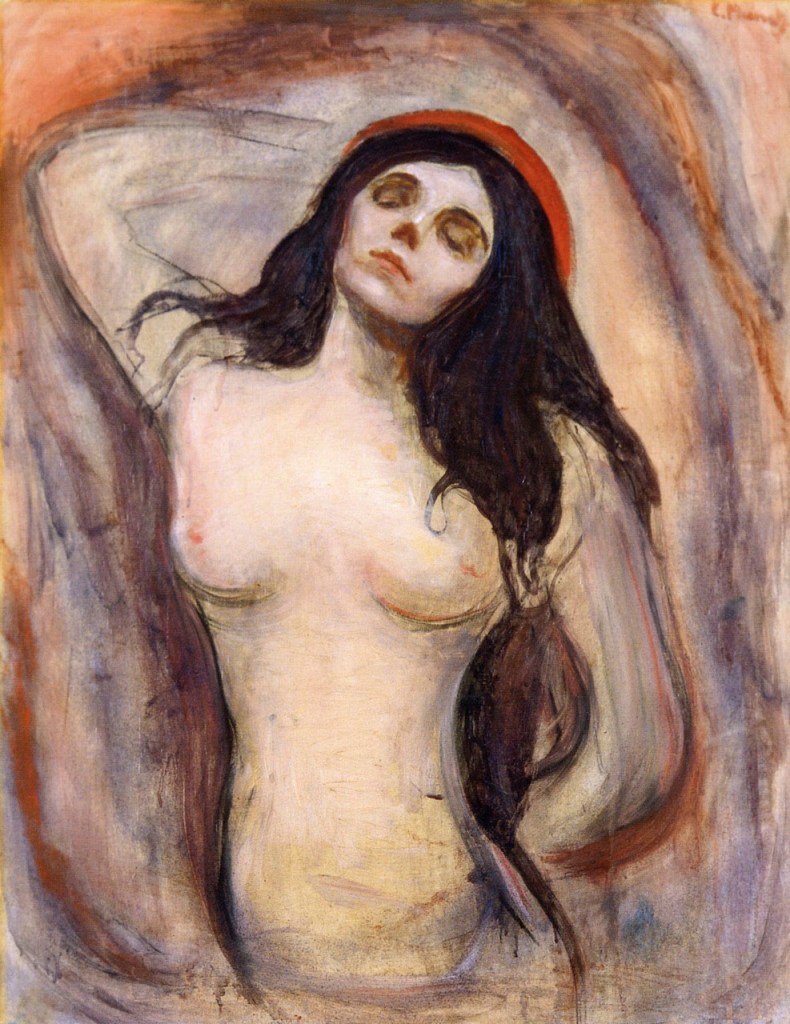

Edvard Munch (Norwegian, 1863-1944)
Madonna
1895
Oil on canvas
90 × 71cm
Hamburger Kunsthalle, permanent loan of the Stiftung Hamburger Kunstsammlungen, acquired 1957
© SHK / Hamburger Kunsthalle / bpk
Public domain
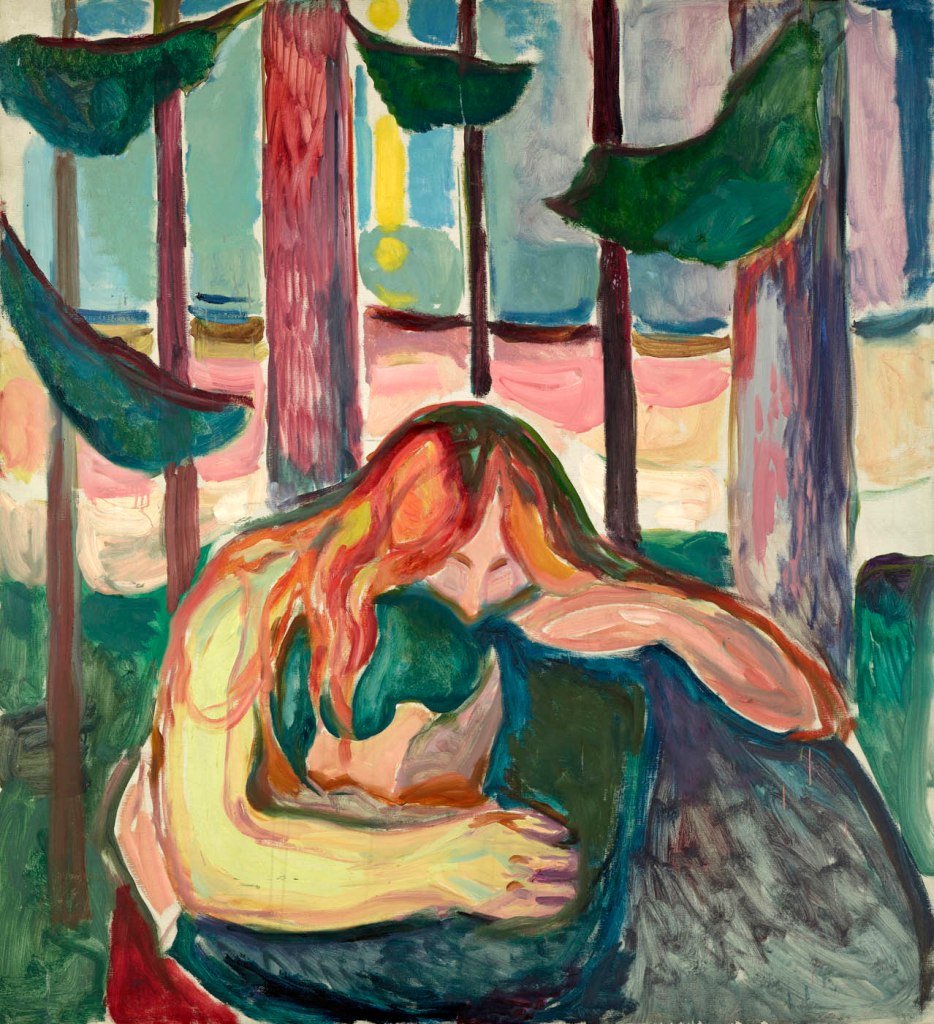

Edvard Munch (Norwegian, 1863-1944)
Vampire in the forest
1916-1918
Oil on canvas
150 × 137cm
Munch Museet, Oslo
© Munchmuseet
Femme fatale, saint and vampire – the elevation and denigration of women in the art of Edvard Munch
Among the many images of the femme fatale that were created around 1900, Edvard Munch’s ambiguous, both positively and negatively connoted female figures occupy a place of their own. Existential questions and universal themes such as life, death, love, loss and grief are central to Munch’s art. Women are omnipresent in his compositions, appearing in a variety of roles and stereotypical depictions; at the same time, they are inseparably linked to the artist’s personal experience of life and love. The transfiguration of this experience often leads to the opposite extreme. Munch’s painting Madonna illustrates the contradictory aspects of his image of women: the depicted subject can be interpreted as a lustful femme fatale or as a saintly figure. The relationship and tension between the sexes is another leitmotif in Munch’s art. This is illustrated by his painting Vampire in the Forest, which leaves the viewer in doubt as to whether the depicted female figure is a loving woman or a bloodthirsty creature. Demonisations of femininity and female sexuality that threaten male existence appear throughout Munch’s oeuvre. They are as much an expression of his fears as of his self-stylisation as a victim – and once again reveal Munch’s image of the femme fatale to be a misogynistic projection.
Impressionist digressions – staged presentations from the theatrical to the nude
The theme of the femme fatale is even addressed in Impressionist art, which aimed to create immediate and realistic depictions rather than idealised representations. Here, however, the image was presented in very different ways. Lovis Corinth’s stage-like scenario shows a dramatically made-up, bare-breasted Salome bending over the head of John the Baptist. The abysmal aspect of her power is visualised above all through the sexualization of her body. The female figures in Max Liebermann’s interpretations of the biblical theme of Samson and Delilah, on the other hand, are far less eroticised. The choice of this subject – an unusual one for the artist – reveals his awareness of the popularity of the femme fatale motif. The lack of historicising details and focus on the strength of the austere-looking female figures, however, situate Liebermann’s stark images more decisively in the present than those of Corinth. The French sculptor Auguste Rodin also portrayed a femme fatale figure – but was evidently using this theme as a justification for an explicit nude. In his drawing, which takes its title from Gustave Flaubert’s novel Salammbô, the female subject is reduced to her sex: the reference to the fictional character is, therefore, merely a pretext.
Power Relations
Smash the Patriarchy! Free the Nipple!
Women and many non-binary people are confronted with various dress codes and rules of conduct in their everyday lives. The skirt should not be too short. Breastfeeding in public is taboo. A woman has to wear a bra in the office, otherwise there may be professional consequences. Above all, bodies perceived as female are being eroticised. The Free the Nipple movement is fighting against this. It’s a matter of choice: whether it’s a long or short skirt, bra or not – everyone decides for themselves. The breast perceived as female is also censored in social media.
The Free the Nipple movement has been criticised for not paying enough attention to the nuances concerning Black people and People of colour, for not pursuing an intersectional approach, but rather for primarily reflecting a white feminism.
Fighting for Female Freedom
In Spain, it was decided in May 2022 that catcalling should be banned. Catcalling? Many women experience obtrusive looks, being whistled at or hearing disrespectful comments about their appearance on the streets every day. Verbal sexual harassment is harmful and leaves its mark. Yet it still is often presented as an alleged compliment, also in films. In the 1968 performance Tapp- und Tastkino (Tap and Touch Cinema), VALIE EXPORT strapped a ‘scaled-down cinema’ in front of her bare chest. Passers-by had ‘public access’ for thirty seconds at a time during which they were allowed to touch her breasts. Interestingly, it was not VALIE EXPORT and her (upper) body that were thus exposed, but rather the passers-by who accepted this offer in public. Who is being embarrassed here and who is a voyeur? How are power and gaze relationships reversed here?
The Bechdel Test was introduced in 1985 by writer and cartoonist Alison Bechdel, namely with her comic dykes to watch out for. The test focuses on the stereotyping of women in film has only three rules:
1/ The movie has to have at least two women in it,
2/ Who talk to each other,
3/ About something other than a man.
Pretty simple criteria that don’t say much about whether a film is sexist!? Yet many films do not fulfil the criteria of the Bechdel Test.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
VALIE EXPORT (Austrian, b. 1940)
Tapp- und Tastkino (Tap and Touch Cinema)
1968
Video: Digibeta PAL, B/W, Sound, 1:08 min
© VALIE EXPORT / Courtesy Electric Arts Intermix (EAI), New York / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2022 / SAMMLUNG VERBUND, Wien
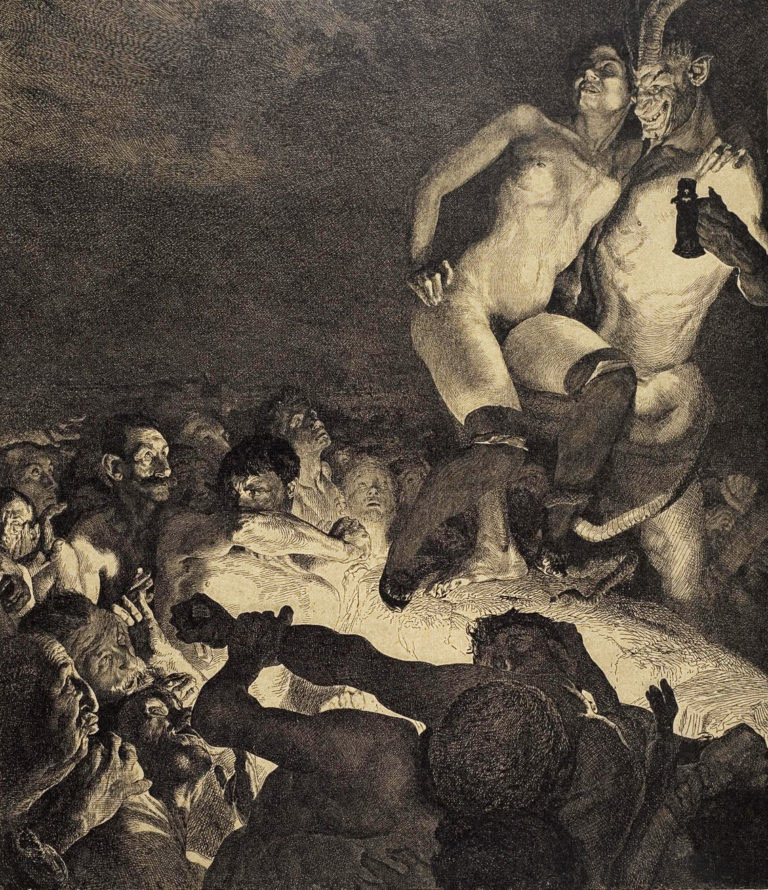

Otto Greiner (German, 1869-1916)
The Devil Showing Woman to the People
1898
From the five-part series Of Woman
Pen lithograph
70 × 55 cm
Museum der bildenden Künste, Leipzig
© bpk / Museum der bildenden Künste, Leipzig
Public domain
Otto Greiner (16 December 1869 – 24 September 1916) was a German painter and graphic artist. He was born in Leipzig and began his career there as a lithographer and engraver. He relocated to Munich around 1888 and studied there under Alexander Liezen-Mayer. Greiner’s mature style – characterised by unexpected spatial juxtapositions and a sharply focused, photographic naturalism – was strongly influenced by the work of Max Klinger, whom he met in 1891 while visiting Rome.
Where Does All the Hate Come From?
Hatecore
Misogyny is an attitude that refers to hatred of women (Ancient Greek: misos = hate, gyne = woman). It has existed for thousands of years all over the world. It can be seen in many historical works of art, in the extermination fantasies of Otto Greiner, for example, but also in our modern times. Since the emergence of the internet, misogyny has also increasingly manifested itself in the digital space, where people perceived as female are many times more likely than people perceived as male to be targeted, sexualised and threatened.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
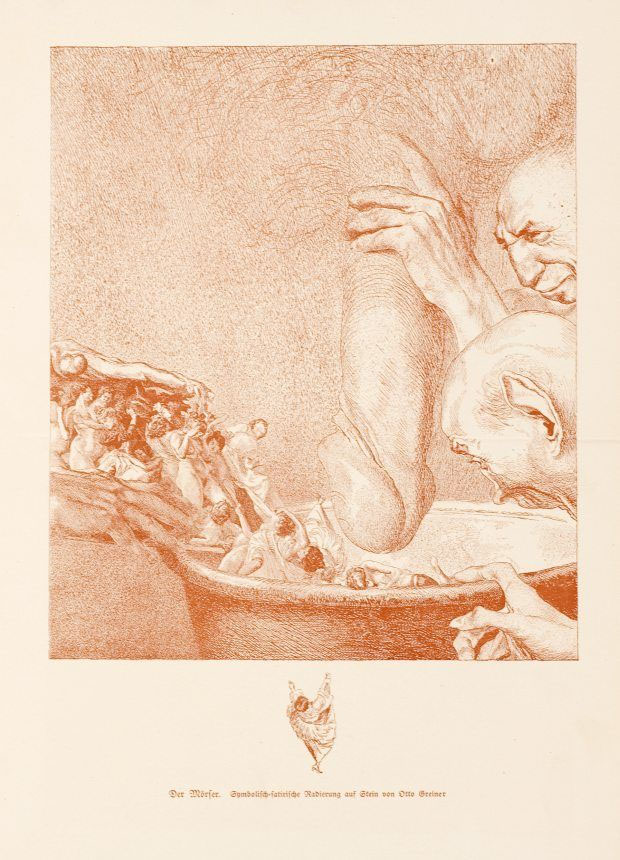
Otto Greiner (German, 1869-1916)
The Mortar
1900
From the five-part series Of Woman
Pen lithograph, crimson print
62 × 46cm
Museum der bildenden Künste, Leipzig
© bpk / Museum der bildenden Künste, Leipzig
Lovis Corinth (German, 1858-1925)
Salome II
1899/1900
Oil on canvas
127 × 147cm
Museum der bildenden Künste Leipzig
© bpk / Museum der bildenden Künste, Leipzig / Ursula Gerstenberger
Lovis Corinth (21 July 1858 – 17 July 1925) was a German artist and writer whose mature work as a painter and printmaker realised a synthesis of impressionism and expressionism.
Corinth studied in Paris and Munich, joined the Berlin Secession group, later succeeding Max Liebermann as the group’s president. His early work was naturalistic in approach. Corinth was initially antagonistic towards the expressionist movement, but after a stroke in 1911 his style loosened and took on many expressionistic qualities. His use of colour became more vibrant, and he created portraits and landscapes of extraordinary vitality and power. Corinth’s subject matter also included nudes and biblical scenes.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Max Liebermann (German, 1847-1935)
Samson and Delila
1902
Oil on canvas
151.2 x 212cm
© Städel Museum, Frankfurt am Main
Max Liebermann (20 July 1847 – 8 February 1935) was a German painter and printmaker, and one of the leading proponents of Impressionism in Germany and continental Europe. In addition to his activity as an artist, he also assembled an important collection of French Impressionist works.
The son of a Jewish banker, Liebermann studied art in Weimar, Paris, and the Netherlands. After living and working for some time in Munich, he returned to Berlin in 1884, where he remained for the rest of his life. He later chose scenes of the bourgeoisie, as well as aspects of his garden near Lake Wannsee, as motifs for his paintings. Noted for his portraits, he did more than 200 commissioned ones over the years, including of Albert Einstein and Paul von Hindenburg.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Becoming femme fatale: between projection and self-presentation
In the period around 1900, the image of the femme fatale was increasingly projected onto real people. A cult of female actors, dancers and artists emerged, above all in cities such as Paris, Vienna and Berlin. Femmes fatales were now also situated in the realm of theatre, cinema and variety entertainment. Male projection and active self-presentation both played their part in this development, and particular modern media served to disseminate corresponding depictions of women: Alfons Mucha’s posters of Sarah Bernhardt contributed significantly to the fact that in public perception, the image of Bernhardt as a person gradually merged with her theatrical roles – although the actress herself also cultivated her reputation as an eccentric figure. In the same way, many people in the public eye used the medium of photography to increase their popularity. Portrait photographs taken by Madame d’Ora, for example, were used to publicise Anita Berber and Sebastian Droste’s scandal-ridden show Dances of Vice, Horror and Ecstasy. The composer Alma Mahler was also among those who had their portraits taken at Atelier d’Ora. Her reputation as a femme fatale was, however, mainly shaped by Oskar Kokoschka. The painter developed an obsessive desire for Mahler during their affair and at the same time stylised her as a disastrous, destructive force – a demonisation that reached its climax in the destruction of a life-size fetish doll he had commissioned in his ex-lover’s likeness.

Madame d’Ora (Atelier d’Ora)
Anita Berber and Sebastian Droste
1922
From “The Dances of Vice, Horror and Ecstasy”
Dora Kallmus (Madame d’Ora) (Austrian, 1881-1963), Arthur Benda (German, 1885-1969)
Anita Berber and Sebastian Droste in their dance Märtyrer [Martyrs]
1922
Gelatin silver print
Albertina, Vienna
Dora Philippine Kallmus (20 March 1881 – 28 October 1963), also known as Madame D’Ora or Madame d’Ora, was an Austrian fashion and portrait photographer.
In 1907, she established her own studio with Arthur Benda in Vienna called the Atelier d’Ora or Madame D’Ora-Benda. The name was based on the pseudonym “Madame d’Ora”, which she used professionally. D’ora and Benda operated a summer studio from 1921 to 1926 in Karlsbad, Germany, and opened another gallery in Paris in 1925. She was represented by Schostal Photo Agency (Agentur Schostal) and it was her intervention that saved the agency’s owner after his arrest by the Nazis, enabling him to flee to Paris from Vienna.
Her subjects included Josephine Baker, Coco Chanel, Tamara de Lempicka, Alban Berg, Maurice Chevalier, Colette, and other dancers, actors, painters, and writers.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Arthur Benda (23 March 1885, in Berlin – 7 September 1969, in Vienna) was a German photographer. From 1907 to 1938 he worked in the photo studio d’Ora in Vienna, from 1921 as a partner of Dora Kallmus and from 1927 under the name d’Ora-Benda as the sole owner. …
In 1906, Arthur Benda met photographer Dora Kallmus, who also trained with Perscheid. When she opened the Atelier d’Ora on Wipplingerstrasse in Vienna in 1907, Benda became her assistant. The Atelier d’Ora specialised in portrait and fashion photography. Kallmus and Benda quickly made a name for themselves and soon supplied the most important magazines. The peak of renown was reached when Madame d’Ora photographed the present nobility in 1916 on the occasion of the coronation of Emperor Charles I as King of Hungary.
In 1921, Arthur Benda became a partner in Atelier d’Ora, which also ran a branch in Karlovy Vary during the season. In 1927 Arthur Benda took over the studio of Dora Kallmus, who had run a second studio in Paris since 1925, and continued it under the name d’Ora-Benda together with his wife Hanny Mittler. In addition to portraits, he mainly photographed nudes that made the new company name known in men’s magazines worldwide. A major order from the King of Albania Zogu I, who had himself and his family photographed in 1937 for three weeks by Arthur Benda in Tirana secured Arthur Benda financially. In 1938 he opened a new studio at the Kärntnerring in Vienna, which he continued to operate under his own name after the Second World War.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Anita Berber (10 June 1899 – 10 November 1928) was a German dancer, actress, and writer who was the subject of an Otto Dix painting. She lived during the time of the Weimar Republic. …
Her hair was cut fashionably into a short bob and was frequently bright red, as in 1925 when the German painter Otto Dix painted a portrait of her, titled “The Dancer Anita Berber”. Her dancer friend and sometime lover Sebastian Droste, who performed in the film Algol (1920), was skinny and had black hair with gelled up curls much like sideburns. Neither of them wore much more than low slung loincloths and Anita occasionally a corsage worn well below her small breasts.
Her performances broke boundaries with their androgyny and total nudity, but it was her public appearances that really challenged taboos. Berber’s overt drug addiction and bisexuality were matters of public chatter. In addition to her addiction to cocaine, opium and morphine, one of Berber’s favourites was chloroform and ether mixed in a bowl. This would be stirred with a white rose, the petals of which she would then eat.
Aside from her addiction to narcotic drugs, she was also a heavy alcoholic. In 1928, at the age of 29, she suddenly gave up alcohol completely, but died later the same year. She was said to be surrounded by empty morphine syringes.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Anita Berber (1899-1928), and to a lesser extent her husband / dance partner Sebastian Droste (1892-1927), have come to epitomise the decadence within Weimar era Berlin, their colourful personal lives overshadowing to a large extent their careers in dance, film and literature. Yet the couple’s daring and provocative performances are being re-assessed within the history of the development of expressive dance, and their extraordinary book ‘Tänze des Lasters, des Grauens und der Ekstase’ (‘Dances of Vice, Horror and Ecstasy’-1922), is a ‘gesamkunstwerk’ (total work of art) of Expressionist ideology largely unrecognised outside a devoted cult following.
The book
Berber and Droste chose to express themselves almost exclusively through the Expressionist / Modernist ethos, which was in itself filtered through the angst of Germany during the Weimar period.
Expressionism had been in existence before Weimar and, like many art movements, it had no formal beginnings, as opposed to a ‘school’ of artists who might band together under a common technique. It was fundamentally a reaction against the Impressionists who were seen by the Modernists as merely portrayers of ‘reality’ but who had failed to add anything of the artists own interior processes such as intuition, imagination and dream. This new wave of artists found inspiration in painters such as Van Gogh and Matisse but also drew from writers such as Rimbaud, Baudelaire, and the Symbolists, together with the philosophy of Nietzsche and Freudian psychology.
Expressionists believed the artist should utilise “what he perceives with his innermost senses, it is the expression of his being; all that is transitory for him is only a symbolic image; his own life is his most important consideration. What the outside world imprints on him, he expresses within himself. He conveys his visions, his inner landscape and is conveyed by them”. Herwert Walden: Erster Deutscher Herbstsalaon (1913).
The image is the poem as portrayed in the book by D’Ora. Interestingly, it is doubted whether the dance was performed (at least in Vienna) topless. Once again, this would indicate that the book is to be considered as its own specific entity. The poems cite their inspirations: artists Wassily Kandinsky, Marc Chagall, Pablo Picasso and Matthias Grünewald and authors lsuch as Villiers De L’Isle Adam, Edgar Allan Poe, Paul Verlaine, E.T.A. Hoffman and Hanns Heinz Ewers.
Lapetitemelancolie. “Madame d’ora – photography for Dances of Vice, Horror, & Ecstasy written and danced, by Anita Berber & Sebastian Droste, 1923,” on the La Petite Melancolie website 14/09/2015 [Online] Cited 01/03/2023

Jeanne Mammen (German, 1890-1976)
Man and Medusa
1910-1914
Watercolour, pencil and ink drawing
24.7 x 21cm
Stiftung Stadtmuseum Berlin
© VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2022
Reproduction: Dorin Alexandru Ionita, Berlin
The New Woman – a counter-image to the femme fatale?
Strongly influenced by their experiences during the First World War, the artists associated with the New Objectivity (Neue Sachlichkeit) movement focused on present-day themes and realities. Their works reflected a changing society and a new relationship between the sexes: women were no longer only active in the domestic roles of wife and mother, but were now also participating in political and social life outside the home, wearing clothes that would traditionally be read as masculine, and pursuing careers – as artists and office workers, but also as revue dancers, waitresses or sex workers. With their bobbed hair, painted red lips, trouser suits, hats and cigarettes, they represented a new ideal: the New Woman. The image of the New Woman was omnipresent in illustrated women’s magazines and satirical journals of the time. The artist Jeanne Mammen, whose early work was greatly inspired by Symbolism, articulated women’s growing self-awareness and a new understanding of sexuality and gender in her paintings, while Gerda Wegener’s portraits of Lili Elbe drew attention to the existence of gender identities beyond the binarism of male and female. The motif of the femme fatale was now countered by a contemporary, emancipated ideal of womanhood that replaced traditional gender roles and stereotypes.

Jeanne Mammen (German, 1890-1976)
She represents!
1928
(In: Simplicissimus, 32, Nr. 47)
Three-colour print on paper
38.5 × 28cm
Stiftung Stadtmuseum Berlin, Jeanne Mammen Stiftung
© VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2022
Reproduction: Mathias Schormann
Fatale styles
Garçonne style
Black top hat slanting one way, cigarette slanting the other, red lips, short hair, men’s suit, challenging pose: this is how Berlin artist Jeanne Mammen saw the “New Woman” in the wild 1920s, the “garçonne” (feminine form of the French “garçon”, boy). She got rid of the corset, and with it the expectations of how women should dress or behave.
Snakes
Snakes are the perfect accessory to signal danger and seduction at the same time. Pure sex appeal! Remember: in the Bible, it is the nasty snake that persuades Eve to nibble from the tree of knowledge, and afterwards Adam and Eve are suddenly ashamed of being naked but also find it somehow exciting … Women are called snakes when they are considered manipulative and use their sex appeal to seduce men who supposedly don’t really want that. The combination of the naked female figure and snakes is particularly popular in the 19th century, when women had hardly any social power or status, but started rebelling against that. Strange coincidence, isn’t it?
Long flowing hair
Long Flowing Hair is considered a symbol of absolute femininity and seduction par excellence in nineteenth-century paintings. If it is shaggy or even made of snakes (beware: Medusa head!), this is supposed to indicate that its wearer is morally depraved. Conversely, in the twentieth century, short hair usually stands for emancipation from outdated gender images and for a free, sometimes queer sexuality.
Mirrors
“Women see themselves being looked at,” wrote the English art critic John Berger. Women looking at themselves (narcissistically) in the mirror in paintings are meant to prove the vanity of the female sex. Yet these paintings rather prove the dominance of the male gaze that turns women into objects through its constant scrutiny or even surveillance. Some say that the mirror in the paintings has now been replaced by computer or smartphone screens, in which especially women are reflected for the male gaze on social media. Do you see it that way too?
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
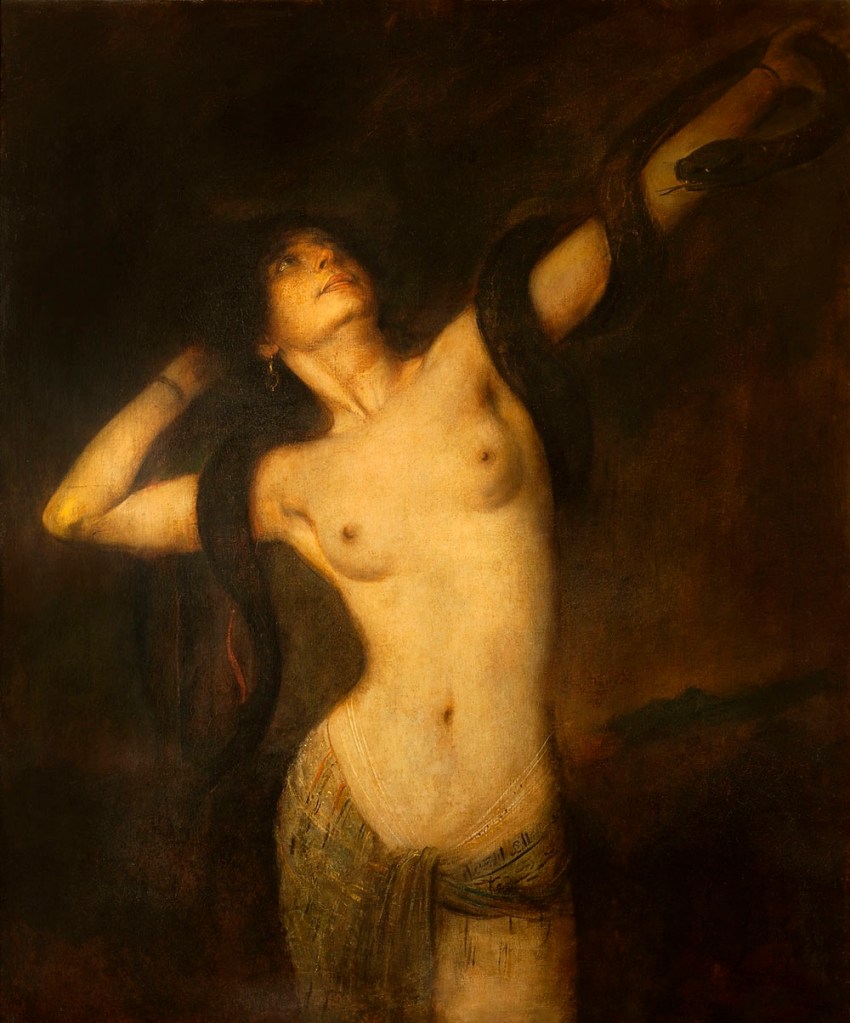
Franz von Lenbach (German, 1836-1904)
Serpent Queen
1894
Oil on canvas
123 × 106cm
Kunstsammlung Züll, Sankt Augustin
© Kunstsammlung Züll, Sankt Augustin
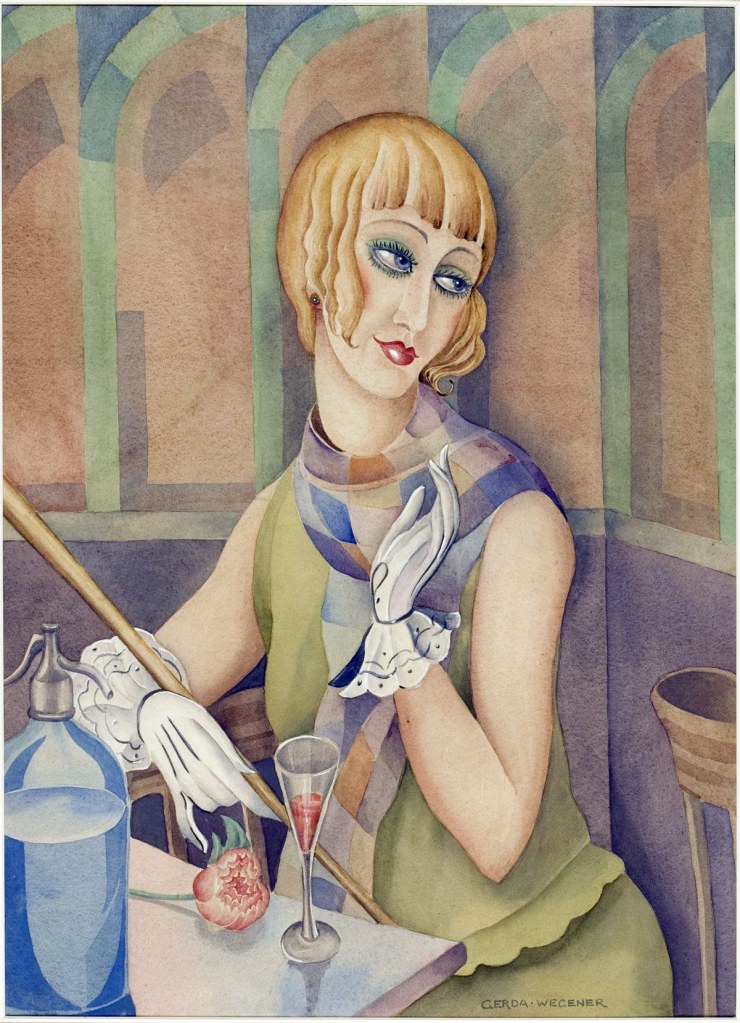

Gerda Wegener (Danish, 1886-1940)
Lili Elbe
c. 1928
Watercolour
Please note: This watercolour may not be in the exhibition but Wegener’s paintings are mentioned in the exhibition text (above)

Gerda Wegener (Danish, 1886-1940)
Lili with a Feather Fan
1920
Please note: This art work may not be in the exhibition but Wegener’s paintings are mentioned in the exhibition text (above)
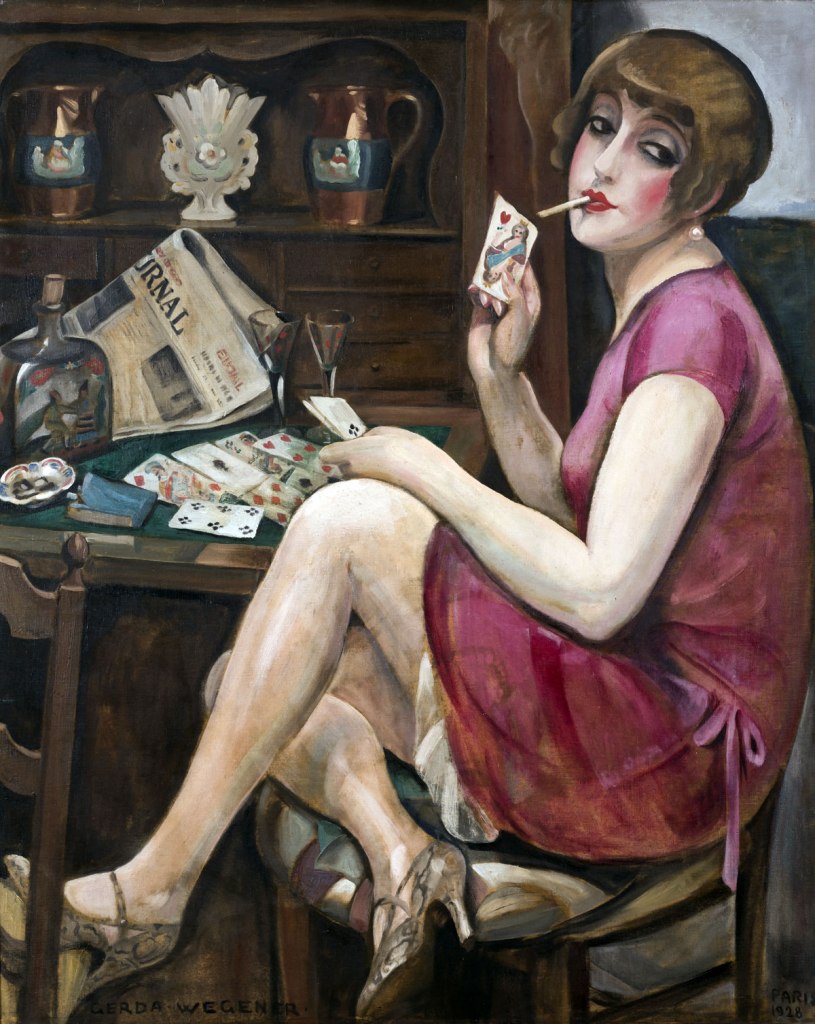

Gerda Wegener (Danish, 1885-1940)
Queen of Hearts (Lili)
1928
Please note: This art work may not be in the exhibition but Wegener’s paintings are mentioned in the exhibition text (above)
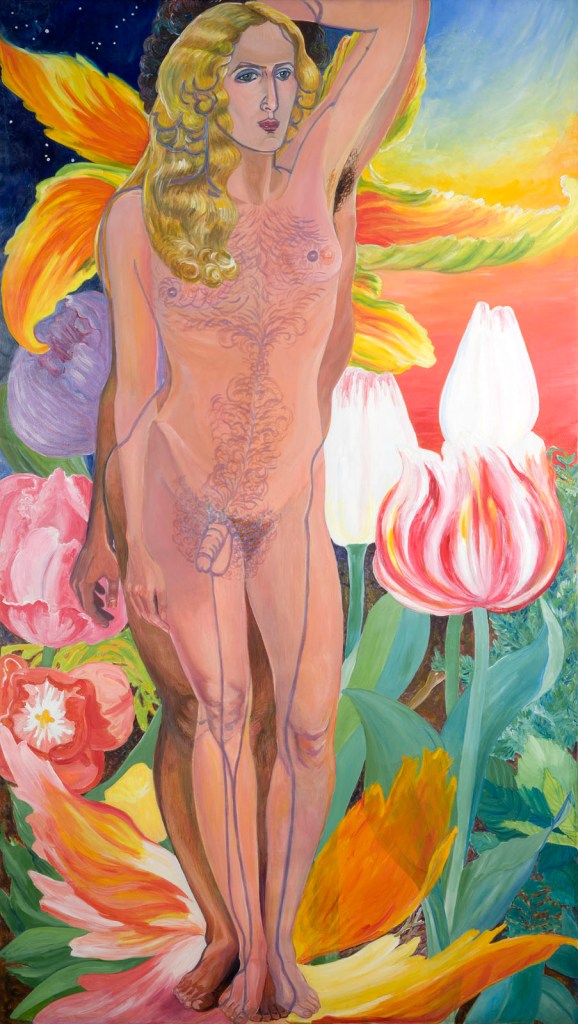

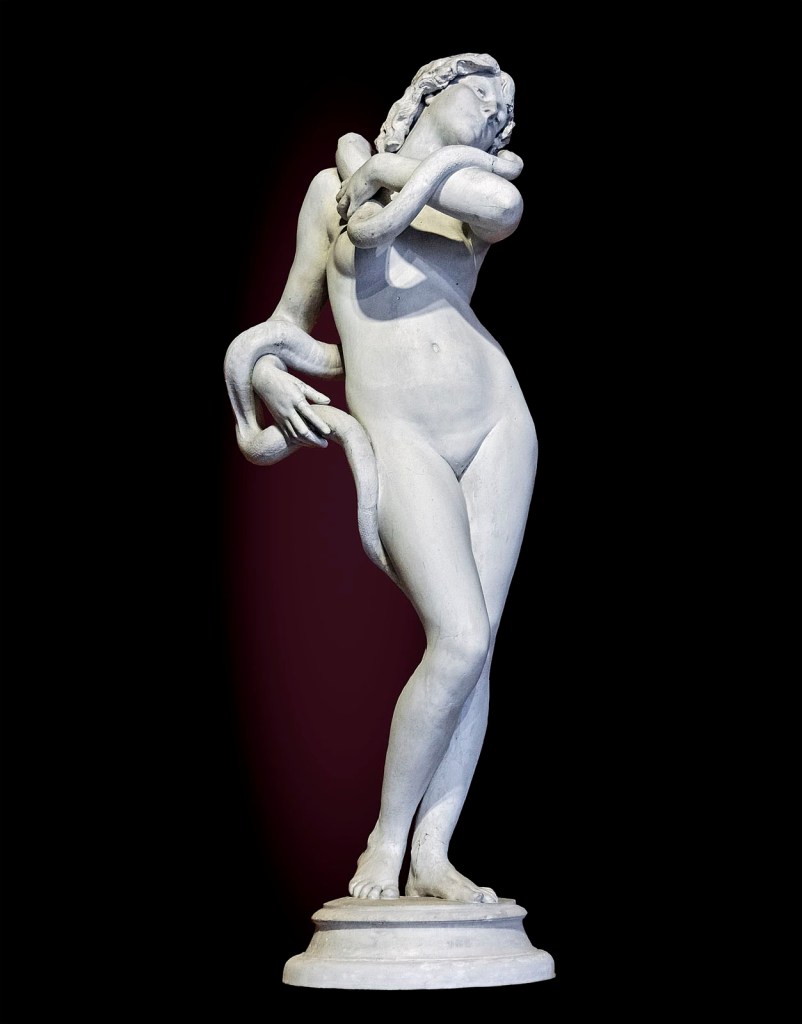
Sylvia Sleigh (American born Wales, 1916-2010)
Lilith
1967
Acrylic on canvas
274.6 × 152.4cm
Rowan University Art Gallery, Glassboro, New Jersey
© Estate of Sylvia Sleigh
Foto: Karen Mauch Photography/Rowan University Art Gallery
Is There such a Thing as a non-binary Gaze?
The non-binary gaze does not exist! As long as we are living in a society dominated by men, there can be no non-binary gaze. Because it is not our own gender identity that decides how we look at others, but the system in which we live. And that, all over the world, is still patriarchy. So as long as we are living in social structures in which humanity is divided binarily into male and female, we cannot escape this gaze. For this, it does not matter where on the gender scale we locate ourselves, whether we characterise ourselves as male, female, non-binary or whatever. To have a female gaze, we would have to live in matriarchy. Therefore, under the global domination of male capitalist structures, there can be no queer, no trans (siehe LGBTQIA), no Black Gaze, because all these identities continue to be marginalised and discriminated against. Gazes, especially in art, are always connected with power, with external determinations, with conditioning. There can be no non-binary gaze for the sole reason that it would not classify living beings into different sexes, would not categorise them. In the required non-binary form of society – which would be interested in the equality of the different – this form of exercising power would not even exist.
But there would still be gazing wouldn’t there? Or does it mean that for that reason alone there can be no non-binary gaze?
The non-binary gaze is the future!
The male gaze divides people into men and women, into those who look and those who are looked at, into the active and the passive, into subjects and objects. The non-binary gaze abolishes “gender” as a distinguishing feature altogether because it has no interest in this type of category. Neither living beings nor anything else like colours, styles or smells are assigned to a single gender, but exist only for and from themselves. Individual features such as lipstick, stubble or breasts are not read as indicators of gender, but are perceived impartially and without this filter in their specific properties, such as shape, colour, structure etc. Therefore, this gaze does not exert any power, because it does not classify and evaluate what is being looked at into any existing categories. It does not look from top to bottom, not from bottom to top, not at individual parts or the overall view, but it does all this simultaneously with everyone, the gazers as well as those gazed at. The non-binary gaze has the power to destabilise our entire world order, because qualities and characteristics can now be perceived in a completely new way, without prejudices and evaluations. For this concerns not only human bodies but all forms of being that we can imagine.
Actually, it is interesting that we not only classify people, but also, for example, shapes – angular vs round – or smells – tart vs sweet – according to gender.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition

Maria Lassnig (Austrian, 1919-2014)
Woman Power
1979
Oil on canvas
182 x 126cm
Albertina Wien – The ESSL Collection
© VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2022
Foto: Peter Kainz
Deconstructing, appropriating and retelling: abolishing the image of the femme fatale
The fight against the traditional image of the femme fatale began at the latest with the emergence of feminist art in the 1960s: feminist avant-garde artists challenged such outdated notions of women and began creating their own new narratives of femininity, sexuality and physicality. Self-portraiture and self-presentation, especially in the medium of photography, takes on a particular significance in the creation of self-empowering images of one’s own body. Female artists find many different ways to deal with the clichéd image of the femme fatale. Deconstructive approaches by artists such as Ketty La Rocca have contributed a great deal to dismantling this image, as have ironic and subversive appropriations by the likes of Birgit Jürgenssen. Other female artists reimagine the mythological figures who were long depicted as femmes fatales, presenting them, as Francesca Woodman did, in subtly restaged scenarios; depicting them as powerful goddesses – as seen, for example, in the works of Mary Beth Edelson; or, like Sylvia Sleigh, situating them outside the boundary of binary gender. Arresting representations of female corporeality, meanwhile, such as those created by Maria Lassnig and Dorothy Iannone, provide positive images that leave the narrative of demonic, deadly female sexuality far behind them.
Gender & Role Clichés
What does gender mean?
Gender describes the social, lived, perceived sex of a person. Gender is an English term, but is also used in German, precisely when it comes to social characteristics and gender identity. Gender is not limited to what is assigned to us at birth on the basis of physical characteristics (sex) but rather refers to socially constructed attributes, opportunities and relationships.
The teacher who says to you: “Well, your handwriting doesn’t look like that of a girl.” The colour pink is for girls and women, just like dresses and skirts; the colour blue and trousers are for boys and men. The latter should not cry, that would be weak. So, better for them to suppress their feelings? But then there is the saying “Boys will be boys”, meaning that’s just the way they all are. Boys are seen as wild and rebellious, girls as calm and understanding. But these are not biological traits; it’s the way we were brought up in a system of patriarchy. So, boys are allowed to get away with more, while girls are expected to put up with a lot of things. Role stereotypes hurt and reduce us all and press us into categories. Because they say: all people in a group should behave in the same way – which is pretty absurd.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
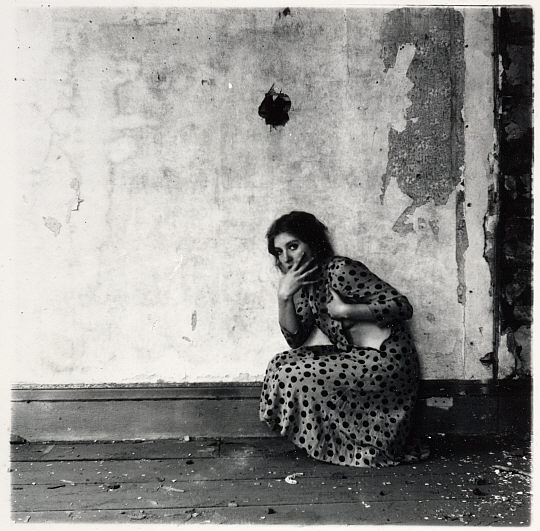

Francesca Woodman (American, 1958-1981)
Untitled, 1975-1980
1975-1980
Gelatin silver print
Please note: This image may not be in the exhibition but Woodman’s photographs are mentioned in the exhibition text (above)
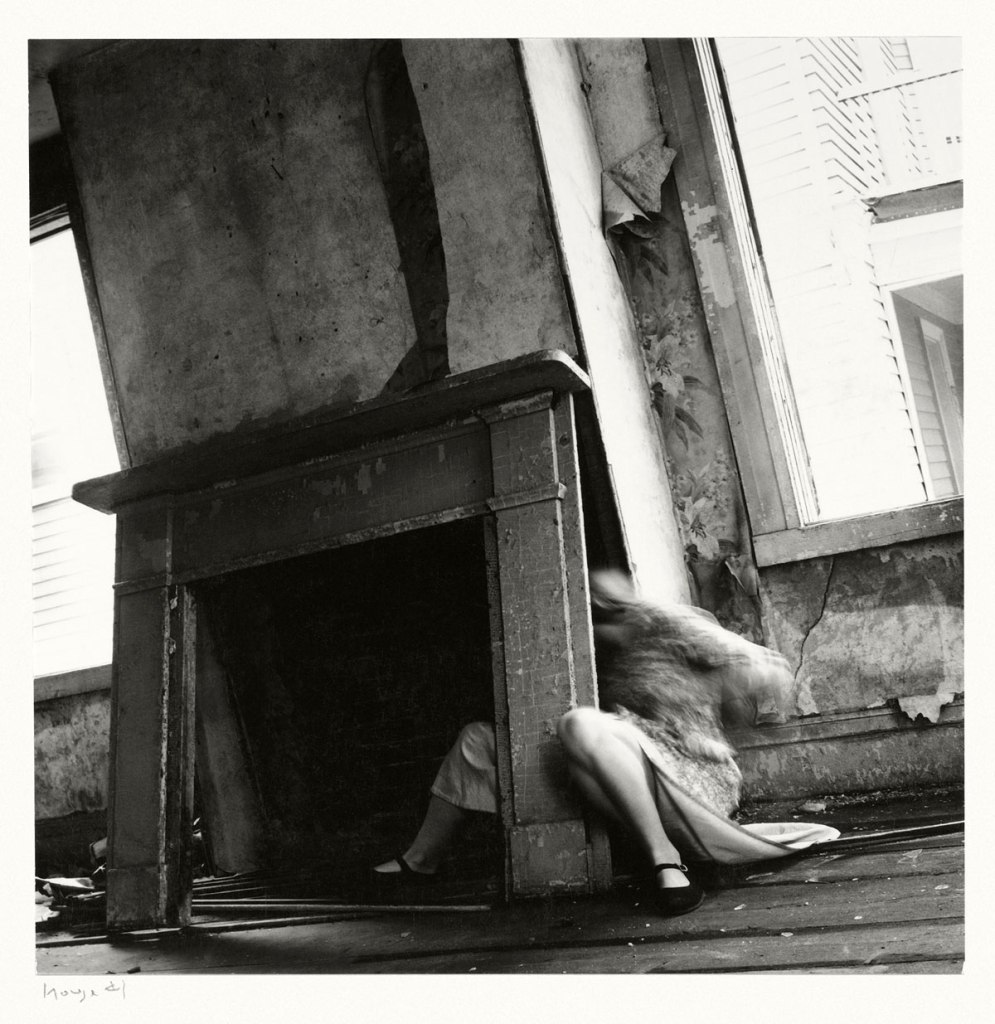

Francesca Woodman (American, 1958-1981)
House #4
Providence, Rhode Island, 1976
Gelatin silver print
Please note: This image may not be in the exhibition but Woodman’s photographs are mentioned in the exhibition text (above)
Nan Goldin (American, b. 1953)
C performing as Madonna, Bangkok
1992
Archival pigment print, ed. #2/25
76.2 × 114.3cm
Courtesy of the artist and Marian Goodman Gallery, New York
© Nan Goldin
The varied afterlife of the femme fatale: contemporary (counter-)images
Nowadays there is no single, unambiguous vision of the femme fatale, and the counter-images are equally multifaceted. Artists examine traces of the clichéd concept, explore representations and adaptations of the femme fatale trope, reflect on the male gaze in art history, and consider gender identity, female physicality and sexuality from intersectional and queer feminist perspectives. In Jenevieve Aken’s work, for example, the ‘super femme fatale’ is a positively connoted, liberated (identificatory) figure who defies the constraints of a patriarchal society. Nan Goldin’s photographs show drag queens appropriating iconic figures who have long been stylised as femmes fatales, such as Marilyn Monroe or Madonna. In a similar way, Goldin’s video works place the mythological figures of Salome and the Sirens in new contexts. Betty Tompkins’ series of images highlight the fact that female sexuality is still being demonised today; her complex combinations of words and images reveal the continuities in a violently patriarchal art field, up to and including the #MeToo movement. Important counterpoints are also provided by artists such as Mickalene Thomas and Zandile Tshabalala, who deal with female beauty, physicality and sexuality through critical engagement with a white art canon.
Text from the Hamburger Kunsthalle website
Insectionality / Black Feminisms
Black women who are simply portrayed leading their everyday lives, without being reduced to their suffering or racial trauma experiences – unfortunately, this is a rarely shown image. The woman in the painting Lounging 1: G fabulous [below] is unmistakably depicted as Black. Next to her is a soft bathrobe. She is relaxing in a room with pompous wallpaper, on a fluffy carpet in front of a glamorous couch. Her material possessions, together with the fact that she is resting, are markers of luxury. For in the system of white supremacy, Black women are expected to live in a “hustle and grind culture”, where they continually have to prove themselves and try twice as hard as their white counterparts. Resting as a form of resistance is thus understood as a counter-movement and a radical political practice against social injustice. The slogan “rest is resistance” became famous on social media through the organisation The Nap Ministry. Though the woman in Lounging 1: G fabulous is nude, she is not depicted in a voyeuristic or sexist way – as Black women are in many works of European and American art history. The power of the gaze no longer lies with a voyeur, but in this case emanates from the sitter. Despite her nakedness, the image is in no way about conforming to a male gaze. The woman in the work simply shows herself as she is.
Likewise, Jenevieve Aken’s series The Masked Woman [below] is about self-fulfilment. Her self-portrayals show everyday scenes from the life of a woman in Nigeria who has decided against the role of the subordinate housewife. Instead, she leads a contented solo life as a “super femme fatale” – as she writes herself. A decision for a lifestyle that is not nearly as socially prestigious as living in a bourgeois nuclear family. Both works create new self-designations and show how extensive and multi-layered Black female identities are.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
Zandile Tshabalala (South African, b. 1999)
Lounging 1: G fabulous
2021
Acrylic and mixed media on canvas
120 × 200cm
Courtesy Privatsammlung Saskia Draxler und Christian Nagel
© Zandile Tshabalala / Privatsammlung Köln / Galerie Nagel Draxler Berlin / Köln / München
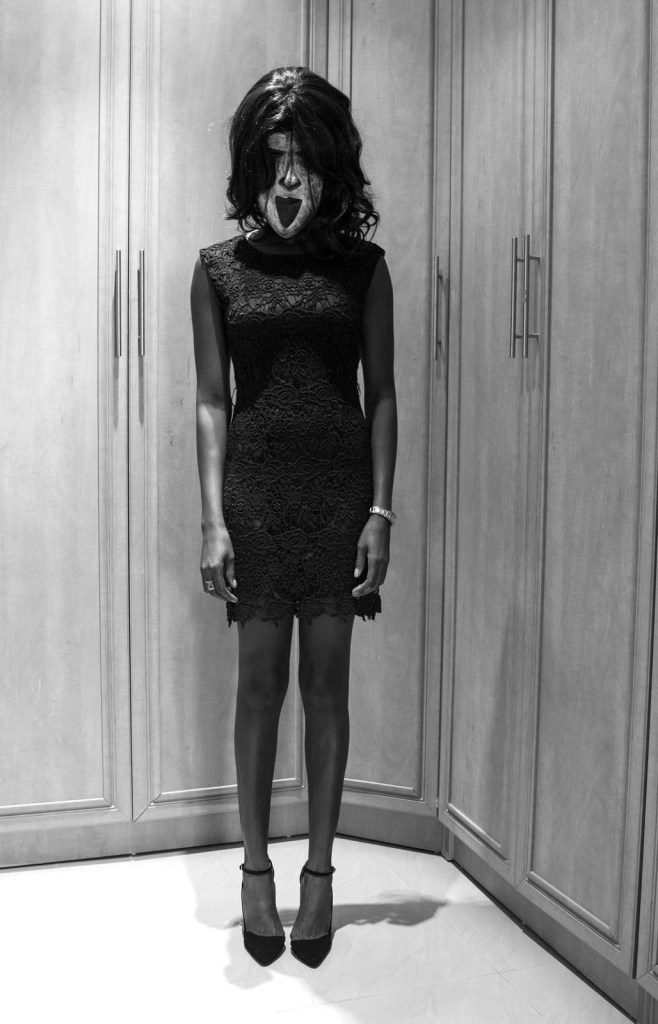

Jenevieve Aken (Nigeria, b. 1989)
The Masked Woman
2014
Photographs seven-part series
Courtesy of the artist
© Jenevieve Aken
The Masked Woman is a self-portrait series that explores representation of gender in Nigeria society through a performative lens. It attempts to avert the overarching male gaze by facing it head on with the artist’s own actions and choices. The images portray the solitary lifestyle of the “super femme fatale” character, choosing to achieve pleasure and contentment through self-fulfilment that not dictated by the subservient role as a house wife or defined through a man’s affection. While depicting a confident and sexually free woman, the subject’s mask and body language also suggest a nuanced tone of isolation which speaks to her stigmatization in a society that has limiting and strictly defined roles of what the proper woman should be. By diverting the status-quo and exercising freedom of choice, such women are perceived as extreme, eccentric, and outside of polite society in Nigeria. The series personifies a growing number of independent, professional women in Nigeria who at once assert their autonomy while also being ostracized by cultural norms. Rather than waiting for the narrative to be told from the outside, I choose to give birth to my own freedom, in hope that it will inspires other women in Nigeria to express their independence and free-will.
Jenevieve Aken. “The Masked Woman,” on the Jenevieve Aken website Nd [Online] Cited 04/03/2023
Jenevieve Aken (born 1989) is a Nigerian documentary, self-portrait and urban portrait photographer, focusing on cultural and social issues. Her work often revolves around her personal experiences and social issues surrounding gender roles. …
The Masked Woman
This is a black and white, self-portrait series meant to depict women and their social roles in Nigerian culture. The images depict the peace and self-fulfilment of a woman without the stigmatised overarching views of women in a Nigerian culture. The images also explore how women can feel constrained by the stereotypes of what a “proper women” should act like in society. These photos are meant to exemplify women who have broken these stigmas but feel isolated by the norms of the society. In this series Aken hopes to inspire Nigerian women to practice their freedom regardless of external stereotypes.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Myth & Religion
Lilith
Lilith was the first in various respects. Apparently, not only the Adam’s first wife who lived equally with him in the Garden of Eden, but also the first feminist, because she simply flew away when he demanded submission from her. Conveniently, as recorded in older Babylonian accounts, she was a hybrid being and had wings. Others imagined her as a hybrid between a woman and a serpent. Unfortunately, as a woman who was sexually independent, she evidently did not have a good image among the patriarchy, for she was said to bring sickness and death, to seduce and kill men, be infertile and kill newborn babies with the poisonous milk from her breast. In Jewish feminist theology, however, she stands for wisdom and strength because she was the first being to convince God to tell her his name – granting her unlimited power.
Judith
Judith is described in the Old Testament as a beautiful, wealthy and, besides this, pious widow who defended her Jewish homeland against the seizure by the Assyrian general Holofernes. She saved her mountain village of Bethulia by trusting in God completely and impressing Holofernes with her charm and wise speeches, so that she was able to sneak into his confidence. On the 40th day of the occupation, there was a celebration in Judith’s honour at which Holofernes got so drunk that Judith was able to cut off his head with her sword. The Assyrians left in horror and Judith retired to her quiet widowhood. Thanks to her deed, the overall trust in God was so great that no one could shake the Israeli community for a long time. In the Western world, the figure of Judith was often used as a motif in art, from the nineteenth century onwards with an increasingly eroticising, orientalising and anti-Semitic undertone. Judy Chicago, on the other hand, showed her as a feminist icon in her famous installation Dinner Party in the 1970s.
Medusa
Today, Medusa is mainly known for her extravagant hairstyle consisting exclusively of live snakes. How did this come about? There exist several variants of her story in Greek mythology, but the best known says that Pallas Athena happened to witness her husband Poseidon raping the beautiful Medusa. Instead of helping her and imprisoning him, she disfigured the rape victim forever by conjuring up: snakes on her head, pigs’ teeth, scaly skin, arms made of bronze and a tongue hanging out. Anyone who caught sight of her would henceforth turn to stone in horror. The artistic representation of the terrifying snake’s head has fascinated artists since ancient times, and even today it plays a role in films, games or even the logo of the Versace fashion label. It appears to be the perfect antithesis to the Western ideal of women – evil, tough and ugly – and, according to some research, could represent the transition from matriarchy to patriarchy, which went hand in hand with the demonisation of female strength.
Salome
Salome, who features prominently in the New Testament, albeit without being named, became famous for a dance: she danced so impressively and seductively at a feast that her powerful stepfather Herod assured her that he would grant her any wish in return. Her mother Herodias whispered in her ear what she wanted: the head of her adversary John the Baptist, who had publicly criticised the illegitimate marriage between her and Herod and thus humiliated her. The cut-off head was presented on a platter. In the nineteenth century, art was obsessed with this female figure, generally depicted as a lightly to barely clothed vamp who, because of her enthralling sex appeal, could only cost men their lives.
Madonna
When it comes to the idealisation of femininity, nearly everything conceivable in Christian societies comes together in the image of the Madonna figure. Since the first appearance of Madonna portraits from the second century onwards, the Mother of God has been painted as an absolute symbol of a pure, innocent and self-sacrificing femininity, typically one including and suggesting motherliness. Mostly, she is shown in these pictures with the little Child Jesus in her arms or lap. The figure Mater dolorosa, meaning Mother of Sorrows, refers to the pain of childbirth and the lifelong care of a child (particularly a divine one). But there are also other, sometimes surprising expressions and variations of these representations: for example, the Madonna lactans, a nursing Madonna with visible breast, the Black Madonnas or Madonnas with a body-encompassing, almond-shaped corona shaped like a vulva.
However, a Madonna is not always staged in a supernatural, maternal manner. She can also be depicted somewhere between the extremes of ‘saint’ or ‘whore’.
Doing Feminism – With Art! booklet to the exhibition
Franz von Stuck (German, 1863-1928)
Head of Medusa
c. 1892
Pastel on paper
26.5 × 32.5cm
Private collection
Courtesy Kunkel Fine Art, München
© Privatsammlung

Gustave Moreau (French, 1826-1898)
The Apparition
After 1875
Oil on canvas
142 × 103cm
Paris, Musée Gustave Moreau
© bpk I RMN – Grand Palais I René-Gabriel Ojéda

Edvard Munch (Norwegian, 1863-1944)
Madonna
1895
Oil on canvas
90 × 71cm
Hamburger Kunsthalle, permanent loan of the Stiftung Hamburger Kunstsammlungen, acquired 1957
© SHK / Hamburger Kunsthalle / bpk
Public domain

Birgit Jürgenssen (Austrian, 1949-2003)
Birgit Jürgenssen Untitled (Olga)
1979
SX 70 Polaroid
10.5 x 8.7cm
© Birgit Jürgenssen, Estate Birgit Jürgenssen / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2022; Courtesy Galerie Hubert Winter
Foto: pixelstorm
Birgit Jürgenssen (1949-2003) was an Austrian photographer, painter, graphic artist, curator and teacher who specialised in feminine body art with self-portraits and photo series, which have revealed a sequence of events related to the daily social life of a woman in its various forms including an atmosphere of shocking fear and common prejudices. She was acclaimed as one of the “outstanding international representatives of the feminist avant-garde”. She lived in Vienna. Apart from holding solo exhibitions of her photographic and other art works, she also taught at the University of Applied Arts Vienna and the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna.
Text from the Wikipedia website
With the epoch-spanning exhibition Femme Fatale: Gaze – Power – Gender, the Hamburger Kunsthalle is dedicating itself for the first time to diverse artistic treat-ments of the dazzling and clichéd image of the femme fatale. The stereotype of the erotic and seductive woman who holds men in her thrall, ultimately leading them to their downfall, has long been shaped by the male gaze and by a binary understanding of gender. The show will focus on various artistic manifestations of this theme dating from the early nineteenth century to the present while critically examining its origins and transformations: What historical changes and subsequent appropriation processes has the image of the femme fatale undergone? What role does it still play today? How do contemporary artists negotiate the gaze, power and gender constellations this image evokes in an effort to shift our perspective? The exhibition explores these questions based on some 200 exhibits across diverse media. On display are paintings by Pre-Raphaelite artists (Evelyn de Morgan, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, John William Waterhouse) as well as works of Symbolism (Fernand Khnopff, Gustave Moreau, Franz von Stuck), Impressionism (Lovis Corinth, Max Liebermann), Expressionism and New Objectivity (Dodo, Oskar Kokoschka, Jeanne Mammen, Edvard Munch, Gerda Wegener). Early feminist avant-garde artists (VALIE EXPORT, Birgit Jürgenssen, Maria Lassnig, Betty Tompkins), alongside recent works taking intersectional and (queer) feminist approaches (Jenevieve Aken – Philipp Otto Runge Foundation Fellow, Nan Goldin, Mickalene Thomas, Zandile Tshabalala) build a bridge to the present day. Among the paintings, drawings, prints, photographs, sculptures, installations and video works on view are a wealth of high-ranking international loans as well as major works from the collection of the Hamburger Kunsthalle. Highlights include Gustave Moreau’s major Symbolist work Oedipus and the Sphinx (1864), Edvard Munch’s painting Vampire in the Forest (1916-1918), Sonia Boyce’s much-discussed video installation Six Acts (2018), and Nan Goldin’s recent video works Sirens (2019-2021) and Salome (2019).
The “classical” image of the femme fatale was inspired mainly by biblical, mythological and literary figures (such as Judith, Salome, Medusa, Salambo and the Sirens) that were associated in art between 1860 and 1920 with the notion of mortal danger. Combining the feminine ideal with ominous portents, these pictures, often featuring stylised protagonists, convey a demonisation of female sexuality. Around 1900, this female image was increasingly projected onto real people, in particular actors, dancers and artists (such as Sarah Bernhardt, Alma Mahler and Anita Berber). Striking in this context is the simultaneous advancement of women’s emancipation and an upsurge in images of the femme fatale. The exhibition therefore also takes a look at the ideal of the New Woman that emerged in the 1920s as a counter-image that subtly takes up aspects of the femme fatale. Equally telling is the caesura that feminist artists brought about starting in the 1960s by radically deconstructing the myth and, with it, entrenched points of view and pictorial traditions. Contemporary artistic positions in turn address questions of gender identity, female corporeality and sexuality as well as the #MeToo movement and the male gaze. They track the traces and transformations of the image of the femme fatale or in other cases establish explicit counter-narratives.
The exhibition is accompanied by a particularly extensive art education programme: In addition to a diverse range of guided tours including livestreams of curator talks, a chatbot module will debut that lets visitors enter into a dialogue with six femme fatale figures from the art-works on view. A text-based dialogue system using artificial intelligence playfully tells background stories about the works and their artists. Developed jointly with the Stadtteilschule am Hafen, this module specifically addresses a younger target group. The Hamburger Kunsthalle is also offering audio descriptions for the first time. For selected exhibits, supplementary tactile copies are provided, which give people with visual impairments a way of accessing the exhibition independently by feeling contours. More audio tours are available in the Hamburger Kunsthalle app: for adults in German and English, for children from 8 years and older, and in simple language (both German). On the 4th Thursday of each month, a Salon fatal will dedicate itself to socially relevant topics that tie into the exhibition such as sexuality and the construction of beauty ideals. The salon will take the form of a reading, performance, panel discussion, concert or workshop, featuring changing guests. In cooperation with the Hamburger Kunsthalle, the Metropolis Kino is showing a film series on the theme of the femme fatale – from silent films to recent productions.
A free companion booklet, produced in collaboration with Missy Magazine, opens up intersectional and (queer) feminist perspectives on the show. The exhibition theme will also be explored in interdisciplinary depth in the accompanying catalogue (Kerber Verlag), scheduled for publication in early 2023. The catalogue will be available for 39 euros in the museum shop or for the bookstore price of 50 euros at http://www.freunde-der-kunsthalle.de.
Press release from Hamburger Kunsthalle
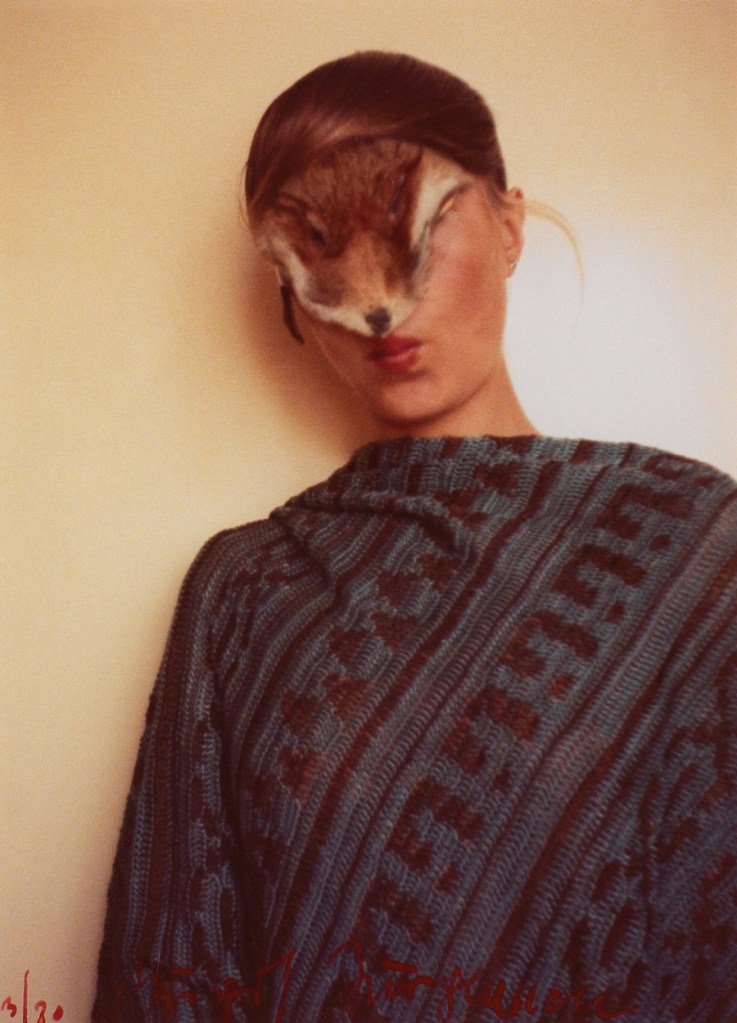

Birgit Jürgenssen (Austrian, 1949-2003)
Untitled (Self with pelts)
1974/1977
Blickmacht
The exhibition Femme Fatale: Gaze – Power – Gender is dedicated to the myth of seductive, ominous femininity – and its deconstruction. This is an extract from Ina Hildburg-Schneider in conversation with the exhibition organisers Markus Bertsch and Ruth Stamm translated from the German by Google Translate:
Do the artists of the time deal with their fears of the early emancipatory movements in the 19th century by depicting the femme fatale?
Stamm: I believe that the picture has something to do with a growing women’s movement in the 19th century, which became more and more institutionalised from 1865 – right up to women’s suffrage. This is exactly the time when the classic femme fatale images are created. But that’s not all. There are also a number of other aspects, further emancipation movements, but also associated fears and projections. Orientalism and anti-Semitism in particular play a role in the femme fatale image.
Bertsch: And the self-perception of the man has also been very different over time. This is often overlooked. There is the age of decadence in France, in which the male artist sees himself as frail and in this way stylises himself as the victim of the apparently overpowering women. Whether this is a firm conviction or a staging remains to be seen. The structure was immensely complex and allowed very different, sometimes contradictory readings of the femme fatale.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the role models for depicting the femme fatale changed. Now the works of art show “real” women. Who do you think of first?
Bertsch: I’m thinking of Sarah Bernhardt, Alma Mahler, Anita Berber. Suddenly living people were referred to as “femmes fatales”. They sometimes even adopted the characteristics of a femme fatale themselves – or, as in the case of Alma Mahler, they were the product of an obsession. Yes, Oskar Kokoschka went particularly far with his admiration for Alma Mahler. This is documented by a photo series in the exhibition.
Stamm: Kokoschka had a fetish doll made by the doll maker Hermine Moos after Alma Mahler, according to his very specific, sometimes explicitly physical ideas. However, his wish for a doll that was as lifelike as possible was not fulfilled – the result disappointed him greatly. The photos in our exhibition show the doll, which served as his model many times, draped in various poses. After Kokoschka had created a number of paintings and drawings based on the doll, some of which brought life to life, the story ended with its violent destruction. Ultimately, in this way, Kokoschka got rid of the figure of Mahler, which he stylised, obsessively sought out and at the same time demonised.
Is the First World War a turning point in the history of the motif?
Bertsch: I think so. Everything that was previously present as a mythical reference dissolves, and art faces the current political and social realities more strongly. Certain images of femininity are being phased out. The classic type of femme fatale is eroding and disappearing.
The “New Woman” developed in the interwar period – is she the female interpretation of the femme fatale?
Stamm: The New Woman was not a concrete antithesis to the femme fatale, but a new, quite stylised, emancipated image of women that developed with the growing women’s movement. In fact, this ideal was only lived by very few women from rather elitist circles who could afford it. The “type of woman” with bob haircuts and cigarettes that accompanies this has been reflected all the more in art and of course offers a completely different narrative than the femme fatale.
Jeanne Mammen is one of the early 20th century artists on display. She was educated in Paris and Brussels. Some of the sheets shown were created there. Can she create a “Homme fatale” with the heart stabber (Herzensstecher)?
Bertsch: She definitely does. The Herzensstecher is a figure that already fascinated me in the 2016 exhibition in Frankfurt, and that can be read as a counterpart to the overpowering femme fatale motif. Mammen is a very independent artist who brought together many spheres of influence in her work and had important teachers in Brussels in Jean Delville and Fernand Khnopff, both of whom are represented in our exhibition. Both of them addressed the relationship between the sexes in their art and in some cases already created androgynous figures. Mammen dealt productively with this symbolist heritage, but created independent, deviating images of masculinity and, above all, of femininity.
Markus Bertsch heads the 19th Century Collection at the Hamburger Kunsthalle and is curator.
Ruth Stamm is project assistant for the exhibition Femme Fatale: Gaze – Power – Gender.
Ina Hildburg-Schneider is an art historian and has been an editor at the Friends of the Kunsthalle since 2022.
Ina Hildburg-Schneider. “Blickmacht,” on the Freunde Der Kunsthalle website Nd [Online] Cited 03/03/2023

Dorothy Iannone (American, 1933-2022)
The Statue Of Liberty
1977
ColoUr silkscreen on paper
32 9/10 × 23 3/5 in (83.5 × 60cm)
Dorothy Iannone (August 9, 1933 – December 26, 2022) was an American visual artist. Her autobiographical texts, films, and paintings explicitly depict female sexuality and “ecstatic unity.” She lived and worked in Berlin, Germany. …
The majority of Iannone’s paintings, texts, and visual narratives depict themes of erotic love. Her explicit renderings of the human body draw heavily from the artist’s travels and from Japanese woodcuts, Greek vases, and visual motifs from Eastern religions, including Tibetan Buddhism, Indian Tantrism, and Christian ecstatic traditions like those of the seventeenth-century Baroque. Her small wooden statues of celebrities with visible genitals, including Charlie Chaplin and Jacqueline Kennedy, especially display with the artist’s interest in African tribal statues.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Mickalene Thomas (b. 1971)
Racquel: Come to me
2016
Rhinestones, acrylic, enamel and oil on wooden panel
274.6 × 213.7 × 5.1cm
Whitney Museum of American Art, New York;
Proposed gift from Rachel and Jimmy Levin © 2022
Digital image Whitney Museum of American Art / Licensed by Scala / VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2022
Glossary
Ableism
The term is derived from the English word “able” and denotes discrimination based on physical abilities. People whose bodies are deemed less “able” due to a disability or impairment, are socially and spatially excluded and devalued. An ableist society adopts a ‘healthy’ body as the norm and sees all others as (negative) aberrations. Ableism is, for example, when a person in a wheelchair is dependent on the help of others because buildings aren’t constructed barrier-free. Or when blind students at universities or educational institutions don’t have full access to all teaching materials.
Antisemitism
Hostile attitude toward Jews. It presents in various forms – from prejudice and verbal abuse to violence and murder. The gravest manifestation of antisemitism was German Nazism under Adolf Hitler, when between 1933 and 1945 more than six million Jewish people were murdered.
BIPoC
BIPoC is a political self-designation and short form for Black, Indigenous and People of Color. The short form BIPoC combines the communities referred to but also underlines their different experiences. Because of this, the term is sometimes used as an alternative for the term People of Color, to make Black people and indigenous identities explicitly visible and to emphasise that not all People of Color have the same experiences.
Black
Black is capitalised and is the politically correct and self-chosen term for Black people. The capital B emphasises social-political positioning within a society principally dominated by white people. The term Black is therefore not about biological characteristics but about socio-political affiliations. Black people are diverse and have completely diverse skin tones. As such, the term is more about highlighting the collective experiences that Black people have in this system and to emphasise their ongoing resistance.
Black Culture
The term Black Culture describes Black popular culture which deals mainly with entertainment, pleasure as well as knowledge and which is expressed via aesthetic codes and genres. It represents the identity and politics of Black cultures according to their beliefs, experiences and values. Although Black Culture encompasses all Black people worldwide, US-American Black pop culture is given the most attention.
Cis- and Transgenderism
Cis and trans are Latin words. Trans means “across” or “beyond” and, in relation to gender, refers to a person who does not identify with the sex assigned to them at birth and who experience themselves “beyond” it. Cis is, in a sense, the opposite. It can be translated as “on this side of” and indicates that someone lives within the boundaries of their assigned sex.
Classism
When recipients of state benefits are depicted as unwilling to work and unintelligent, this is an example of classism. Or when a working-class child is laughed at in university for not knowing certain trends or foreign words. Because people are not only discriminated against due to their gender and skin colour, but also because of the social and economic class they were brought up in. The term classism is even older than sexism and racism, the terms often associated with it: it was already in use in the 19th Century. Those who are poor and / or have less education due to a lack of resources are devalued in a classist society and have more difficulty accessing institutions seen as elitist.
Colonialism
Colonialism refers to a process of subjugation: one group of people goes to another group of people and imposes on it its rules, laws, language, customs, or religions in order to exploit it economically and culturally. When we speak of colonialism today, we mostly mean the process which began with the colonisation of the American continent by Europe’s ruling classes from the 15th century onwards and its negative consequences (such as racism, slavery, and exploitation) which can be still felt today.
Discrimination
Discrimination means the use of supposedly unambiguous distinctions to justify and rationalise unequal treatment. As a result of this unequal treatment, the persons discriminated against experience social disadvantages. Discrimination is an extensive system of social relationships, in which the discriminatory distinctions operate. Discrimination can therefore not be understood as a consequence of individual qualities. A by now very well known example for discrimination on a structural level is the Gender Pay Gap. This is the gap between the salaries of men and women as well as non-binary people for equal work. In 2022, women in Germany are still paid 18 percent less in terms of (gross) hourly wage than men.
Drag
The best-known examples are drag queens. A drag queen portrays, in a performative and artistic way, the appearance and behaviour of women, or rather femininity, a drag king the demeanour and outward appearance of men. This play with (exaggerated) femininity or masculinity is hence a show which is independent from the gender of the performer. The most famous drag practice is the embodiment of drag queens. These are often performed by queer men.
Empowerment
Mostly used as self-empowerment, it means to turn a disempowered situation into a more empowered one through certain actions. Often, this is a group process, for example, racially and sexually discriminated people who unite and fight for their cause and thus gain more confidence and, at best, more rights. This process may also take place symbolically, for example when young girls feel “empowered” by the encouraging writings of a feminist.
Eurocentrism
Eurocentrism means a view of the world that renders European history and so-called European principles as the primary measure of value. The term eurocentrism consequently makes evident global power relations and colonial historical thinking.
Feminism
Feminism is a social movement, which has already undergone several waves with different priorities, for example the achievement of women’s suffrage in the first wave or the legal equality of men and women in the second wave. While in the past many feminists assumed essentialist gender conceptions, meaning a clear distinction between only two genders – female and male – contemporary feminism is more inclusive. Often it no longer speaks of women but uses the term FLINTA*, which encompasses Female, Lesbian, Intersex, Trans and Agender and, with the asterisk, all others who identify as feminine. Earlier feminists had often focused on the concerns of middle-class, white, western women. But as part of an intersectional consideration of feminism, queer, PoC, trans and many more feminist voices have gained influence in recent decades. Initially, feminism was understood as the liberation of women from the patriarchy, but today it ideally refers to engagement for a world in which all forms of oppression, discrimination and exploitation will be abolished.
Gender and sex
Gender describes the social, lived, perceived sex of a person. Gender is an English term, but is also used in German, precisely when it comes to social characteristics and gender identity. Gender is not limited to what is assigned to us at birth on the basis of physical characteristics but rather refers to socially constructed attributes, opportunities and relationships.
Heteronormativity
When at day care little girls and boys, who are friends, are asked if they want one day to marry each other, this is an example of heteronormativity: a worldview in which heterosexuality is seen as the norm, as ‘normal’ and so what is desirable for everyone. A heteronormative society divides people into the binary categories of men and women, values men as more important and tends to be hostile towards queerness.
Hustle-Culture/Grind-Culture
Hustle-Culture/Grind-Culture describes a lifestyle, in which an aspiration to success and high-performance take priority. Long working hours and little rest are seen as the benchmarks of success.
Imperialism
Derived from the Latin word “imperium”, it means to pursue extended political and economic power outside one’s own (national) borders. By means of military or economic strategies, but also with the aid of culture and education, it is attempted to gain control over other countries or regions.
Intersectionality
The term intersectionality was coined in 1989 by lawyer, scholar and civil rights activist Kimberlé Williams Crenshaw. It is about the intersection and interaction of social identities and connected systems of oppression. Intersectionality focuses on the fact that people are often disadvantaged or benefit from several characteristics at once. Social, ethnic background, social and economic status as well as gender can be examples of such interconnected categories. A person may be Black and a woman, hence experiences racism and sexism. A white woman, on the other hand, experiences sexism too but benefits from her white privileges. Intersectional feminism therefore aims to recognise and make visible the multi-layered perspectives of people who experience overlapping forms of oppression.
LGBTQIA*
LGBTQIA* is an English-language collective term for ways of living and loving outside the heterosexual norm, which is now being used around the world. It is short form for Lesbian, Gay, Bi, Trans, Queer, Inter and Asexual. The asterisk stands for further identities that are perhaps not or not completely included therein, to leave no one out.
The male gaze
The male gaze is the concept of the male stare and stands for how systematically male control is applied and functions in our society. The term was coined by the feminist film theorist Laura Mulvey, who in the 1970s, brought attention to the fact that women in films were mostly represented as objects of male heterosexual fantasy.
Misogyny
Misogyny literally means “hatred of women” (from the ancient Greek: “misos” = “hate”, “gyne” = “woman”) and has been prevalent around the globe for thousands of years as a derogatory to murderous attitude towards about 50% of the world’s population.
(Non-) Binarity
If something is binary, it functions like a two-part system: there is always only the one and the other, like the two sides of a coin. Both mutually define each other. A binary gender system assumes that there are only men and women, and that everyone must belong to one of these two categories. Non-Binarity (NB) breaks up this rigid structure. Non-binary people, sometimes also called enbies (from NB), identify neither as man nor woman.
Objectification
Objectification describes the dehumanising treatment of certain people as things, hence as objects. The most common example is sexist objectification by men, who reduce women to sex-objects.
Orientalism
The term Orientalism exposes how the world has been divided into two parts: on the one side there is the supposedly modern, enlightened West, the ‘Occident’, which sees itself as the centre and protagonist of world events. The ‘Orient’ finds itself on the other side, depicted by the West as ‘backward’ and ‘unmodern’, yet at the same time as ‘exotic’ and ‘sensual’. According to the Palestinian-American literary scholar Edward Said, who published his influential book titled Orientalism in 1978, the ‘Orient’ was invented by Europeans in order to better dominate and exploit these regions.
Othering
With othering, a usually more powerful group, or individual, dissociates itself from another group characterising it as ‘alien’ and ‘different’, thus devaluing it and connoting it negatively. The group higher up in the power structure thus discriminates against the people described as ‘different’ who cannot defend themselves against these attributions.
Patriarchy
Patriarchy is a social system predominantly controlled and shaped by hetero-cis men. This means men determine the gender roles within society. Everything in the patriarchy is geared towards cis-men and they profit highly from such a system. Patriarchal structures are firmly established everywhere in our society. For example, for many in a heterosexual relationship it is still a given that the woman takes parental leave after a pregnancy to take care of the child while the father continues to work. Another example of patriarchal structures: the man is supposed to propose marriage. And after the wedding, the woman takes his name. A man’s power is thus always paramount, though emotions are denied to men. To cry, to be shy or insecure, or to take parental leave after the birth of a child – according to the patriarchy this is not how ‘real’ men behave. In this way men too are restricted by the patriarchy’s toxic masculinity.
People of Color
The term People of Color, PoC for short, is a self-designation and does not describe, like the terms Black and white, any particular skin tones. It is a matter of a position in society and an umbrella term for communities that experience marginalisation due to racism. The experienced racist discriminations vary and are far-reaching. To be asked every day “where are you from?” or be told “but your English is very good” are examples of this, as well as not being invited for a job interview because of one’s name or being threatened or attacked on the train.
Queer
If something is “queer” in English, it is actually peculiar or odd. Since the end of the 19th Century the word has been used derogatively for people who felt sexually attracted to their own gender. From the 1980s, this negative meaning was consciously and provocatively reversed by activists and the term was used positively. Today, many people who do not love heterosexually and / or live cisgendered, describe themselves as queer.
Racism
If people have to endure marginalisation or even violence because of their origin or their appearance, for example because of their skin colour or their religion, that is racism. Racism can take on many forms – for example anti- Muslim, anti-Black, or anti-Asian racism, that particularly targets these groups.
Sexism
Sexism is the discrimination against people because of their sex. “Blonde jokes”, unequal pay for equal work or unwanted wolf-whistles on the street – these are all examples of sexism. Since we still live in patriarchal societies in which men dominate, sexism affects people perceived as female. But men too can be restricted by patriarchal gender stereotypes such as “boys don’t cry” or “men don’t know about babies.”
Stereotyping
Stereotyping is the generalisation of a group of people. In the process, individuals and the differences between them are not considered. Instead, all people in this group are reduced to the same, often negative, characteristics.
Stigmatisation
Stigmatisation is a distinctly negative demarcation from other individuals or groups within a society. This may happen in interpersonal relationships, such as bullying in school, or on a structural level, when for example People of Color repeatedly experience rejection when searching for apartments, or when people with specific therapy experience are denied civil servant status. In this last case, derogatory characteristics are attributed to a mentally ill person by large sections of society, denying them full social acceptance.
White
White is the socio-politically correct description for white people. It is not a biological term, rather a position in society. The terms Black, PoC and BIPoC are capitalised because they are self-chosen terms. The term white, on the other hand, is written in lower case and often in italics. The call for concrete labelling of white, hence white people and white privileges, became louder through antiracist movements. Because being white, from a white perspective, is generally the norm. In this way, being white is often made invisible, while all non-white people are made visible and portrayed as supposedly ‘different’.
White Supremacy
White Supremacy is the ideology that white people, and all their ideas, actions and opinions are superior to those of BIPoC. White Supremacy is a self-sustaining system in that it marginalises People of Color though colonialism, exploitation and repression and so guarantees white people a continuous position of power.
This accompanying glossary is a cooperation between Missy Magazine and Hamburger Kunsthalle. It is published on the occasion of the exhibition.
Glossary
Concept and Realisation: Sonja Eismann, Melanie Fahden, Selvi Göktepe, Josephine Papke, Ruth Stamm, Andrea Weniger
Authors: Sonja Eismann, Josephine Papke
Editors: Nanda Bröckling, Melanie Fahden, Selvi Göktepe, Ruth Stamm, Andrea Weniger
English translation: Matthew Burbridge
Hamburger Kunsthalle
Glockengießerwall 20095 Hamburg
Phone: +49 (0)40-428 131 204
Opening hours:
Tuesdays to Sundays 10am – 6pm
Thursdays 10am – 9pm
Closed Mondays














![Installation view of the exhibition 'Documentary Genealogies: Photography 1848-1917' at the Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid showing at left rear, pages from Carl Dammann's '[Races of Mankind]: Ethnological Photographic Gallery of the Various Races of Men' 1876 Installation view of the exhibition 'Documentary Genealogies: Photography 1848-1917' at the Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid showing at left rear, pages from Carl Dammann's '[Races of Mankind]: Ethnological Photographic Gallery of the Various Races of Men' 1876](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/documentary-genealogies-installation-d.jpg)
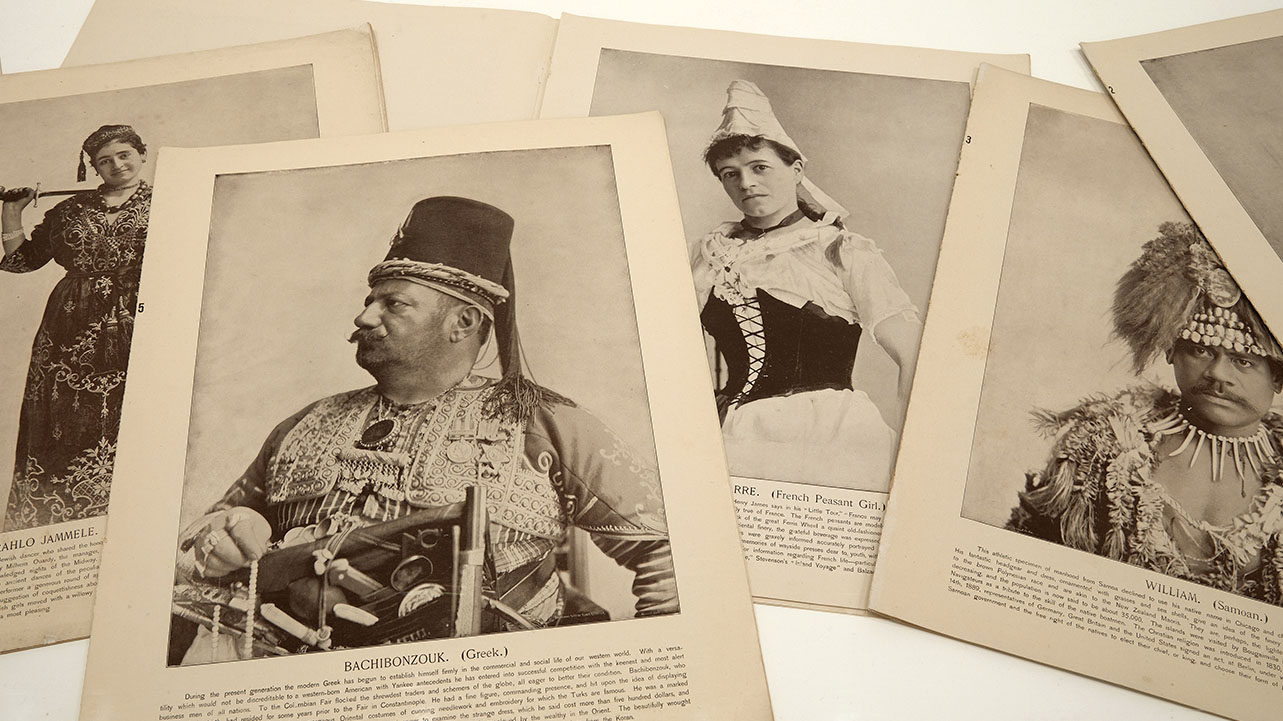
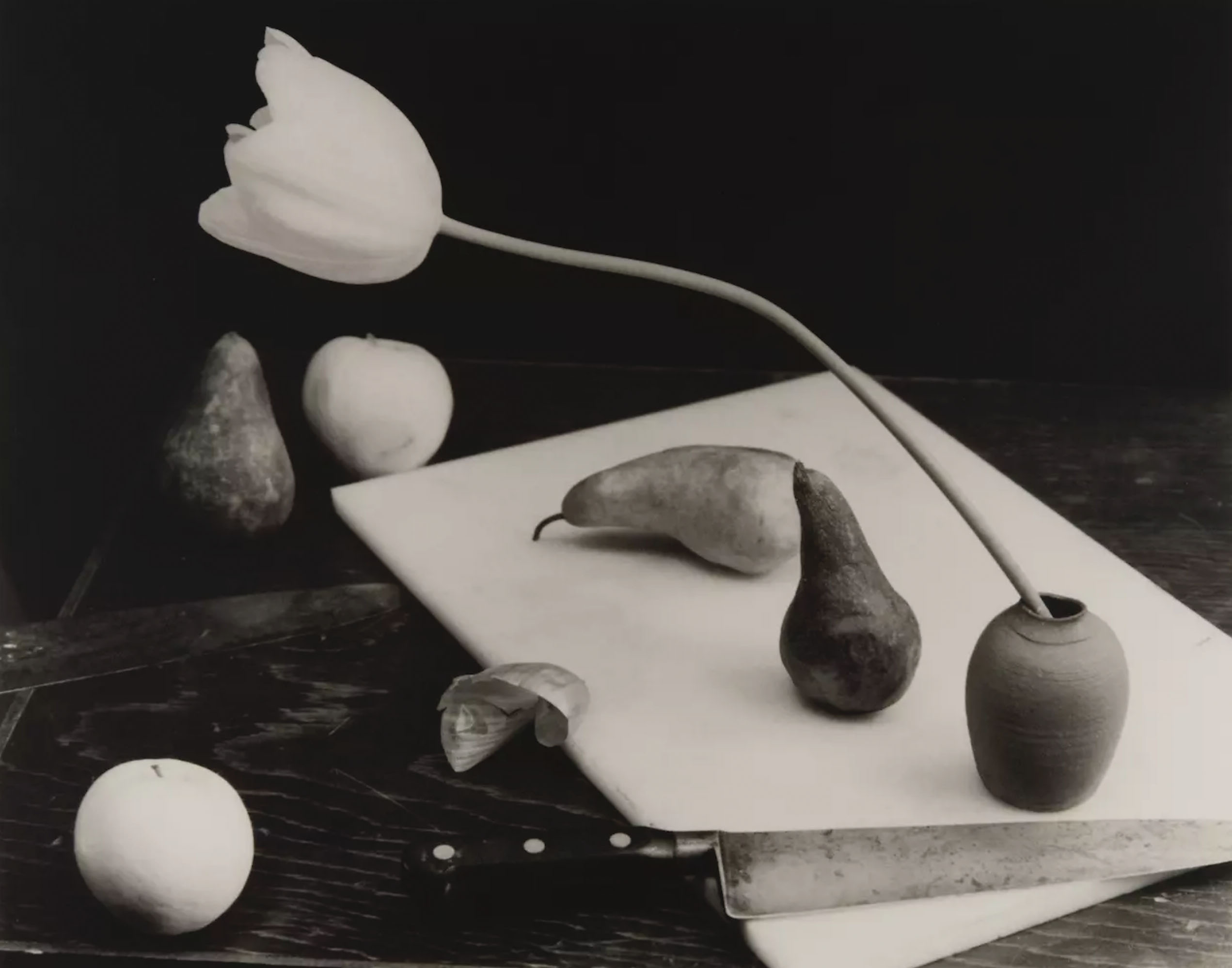
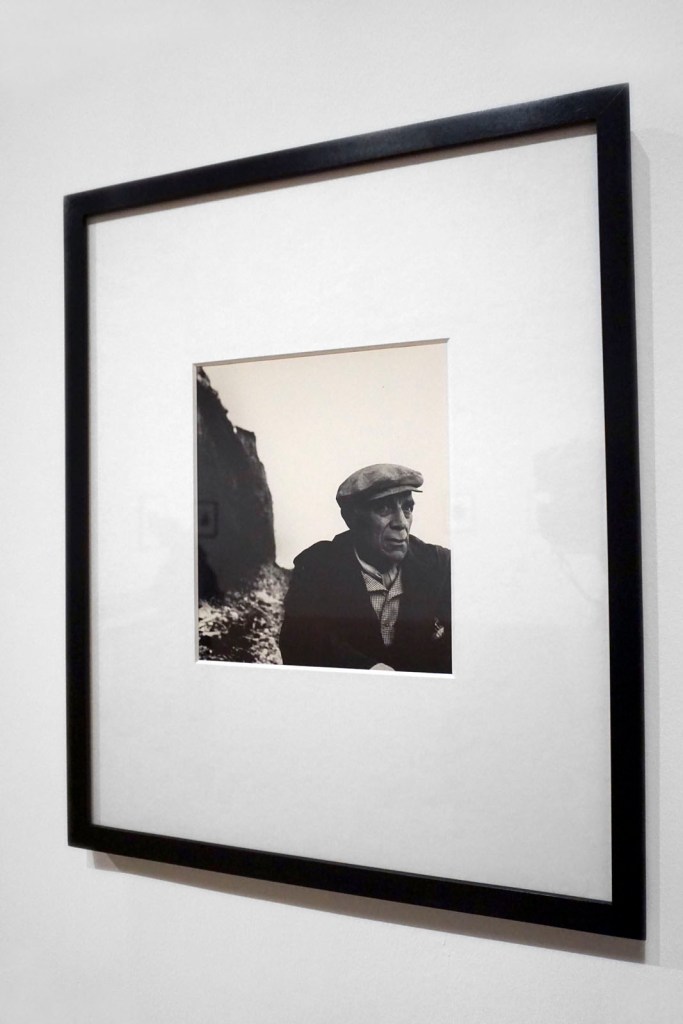
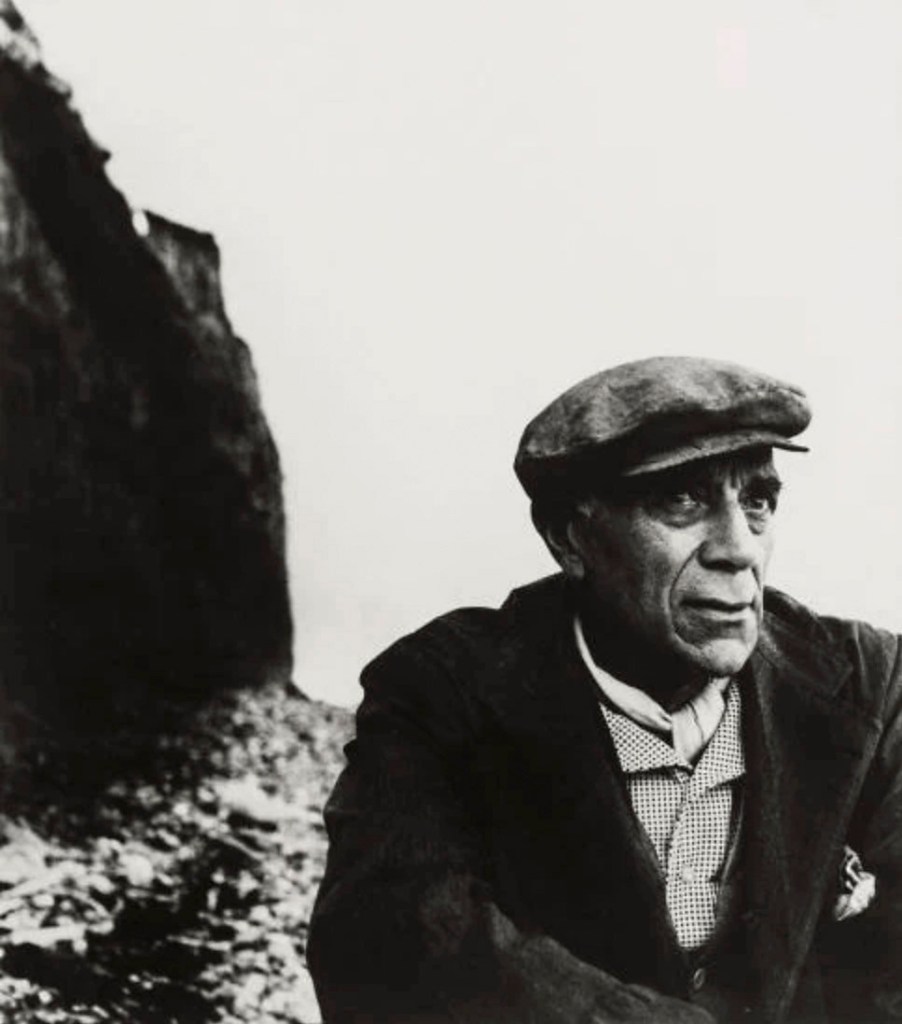
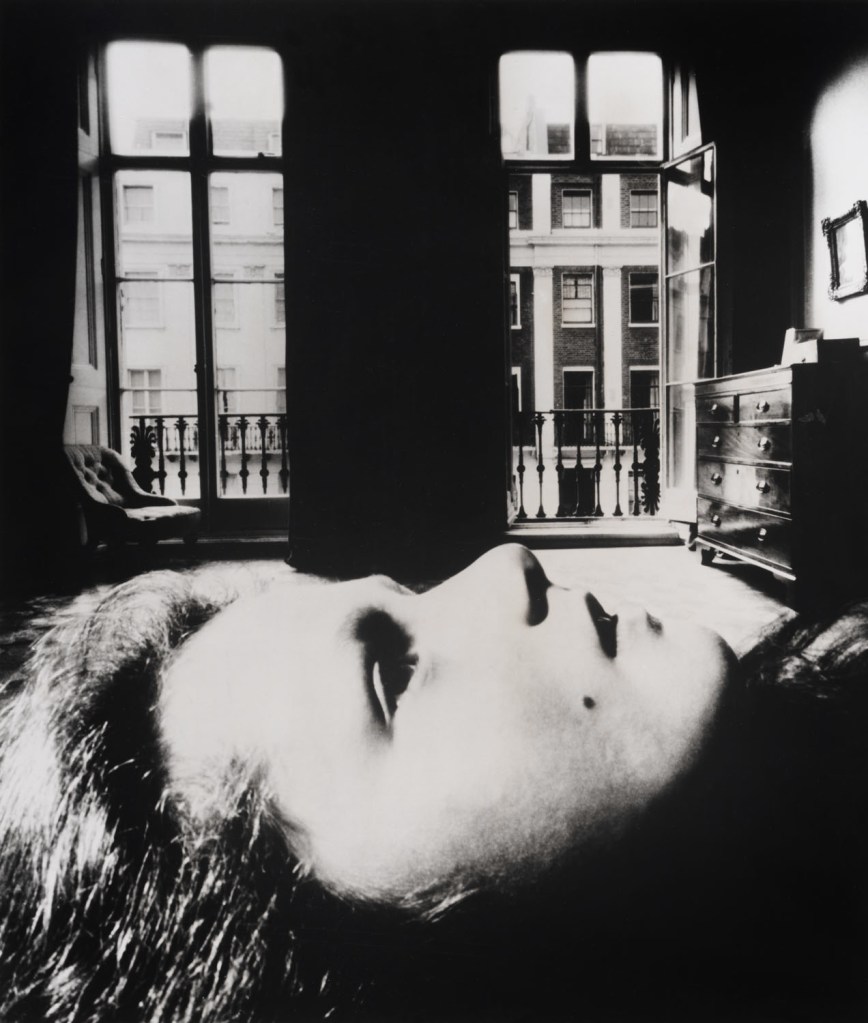
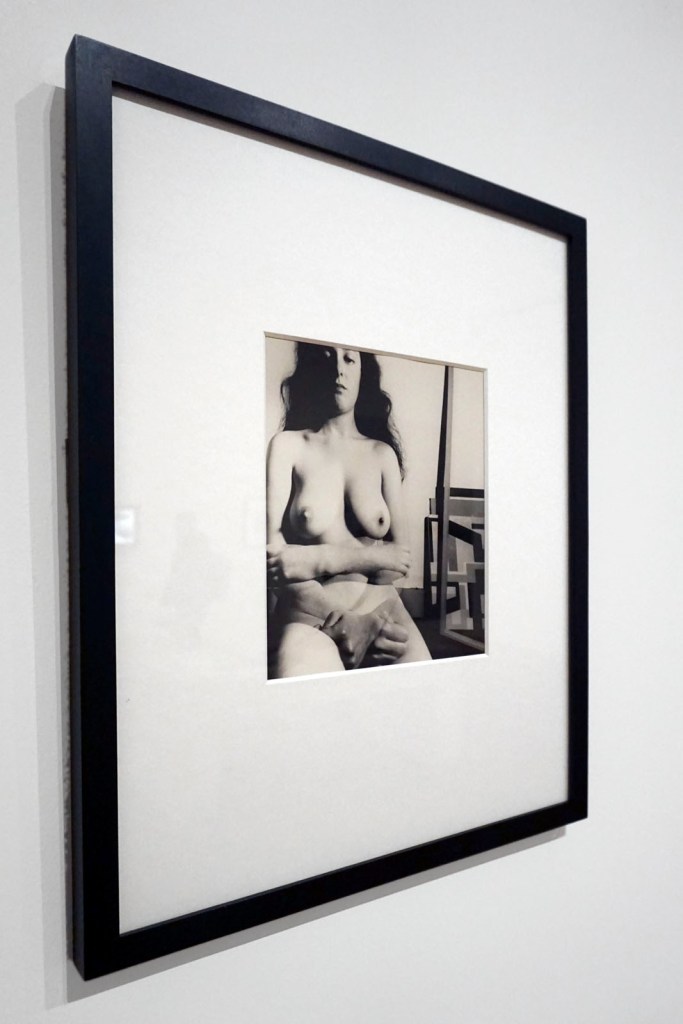
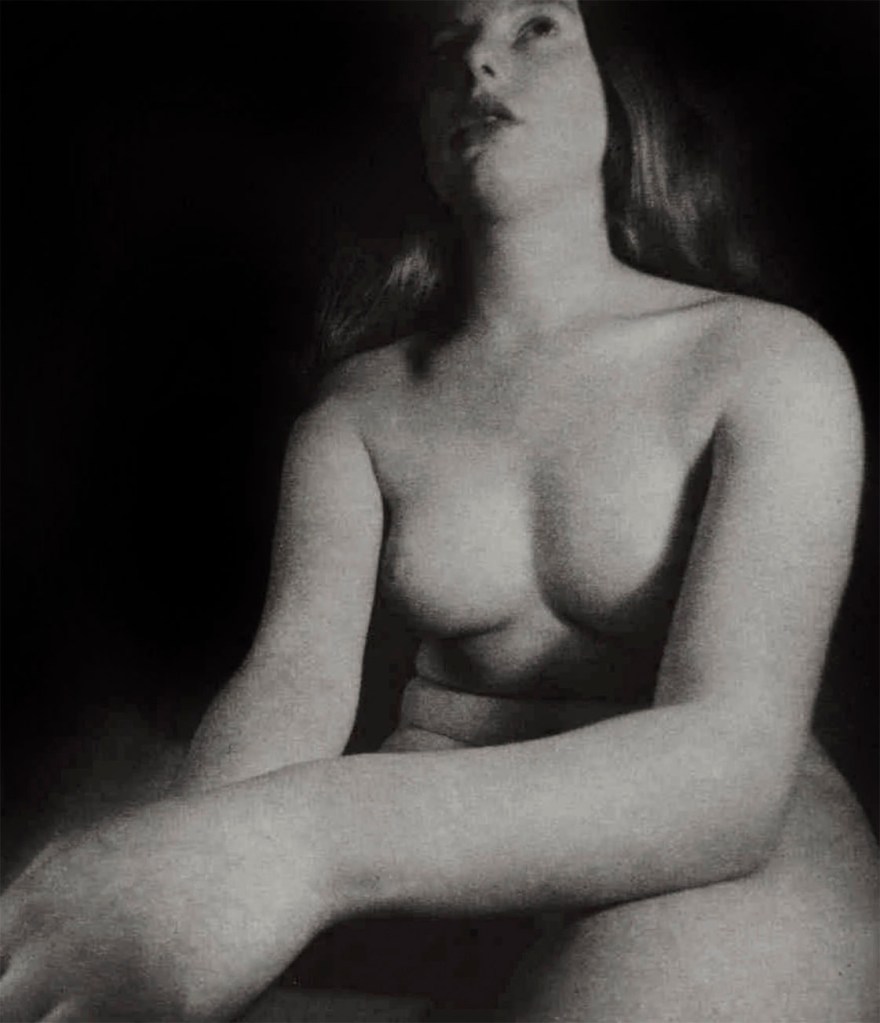
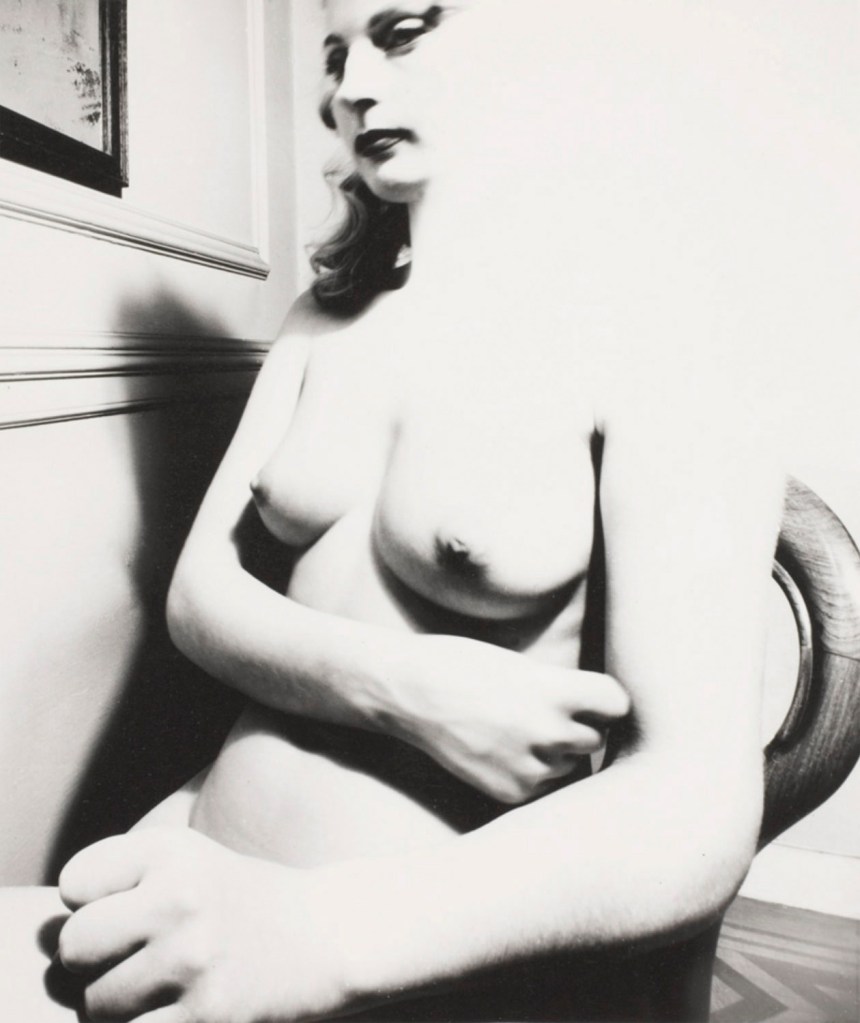
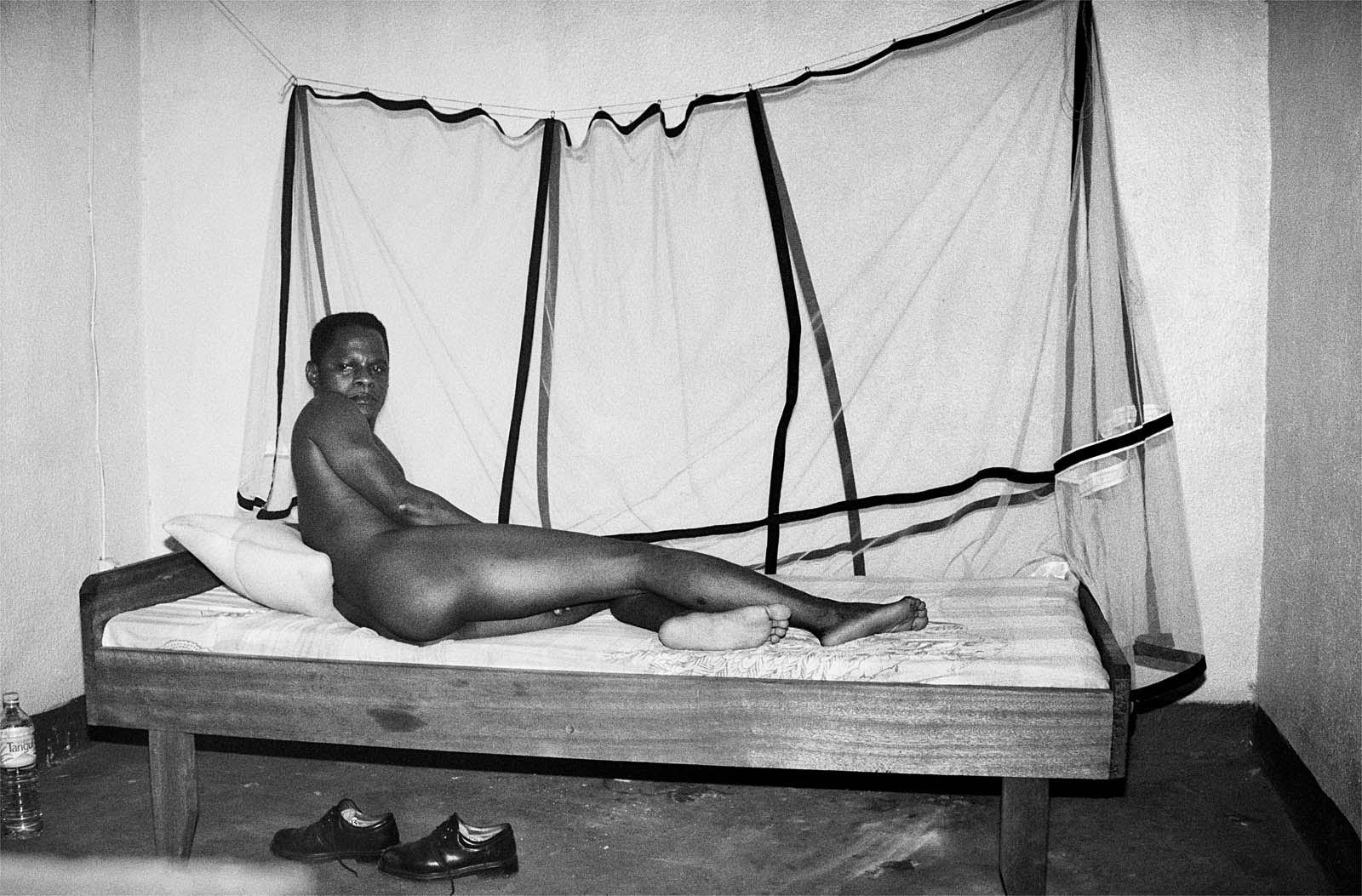
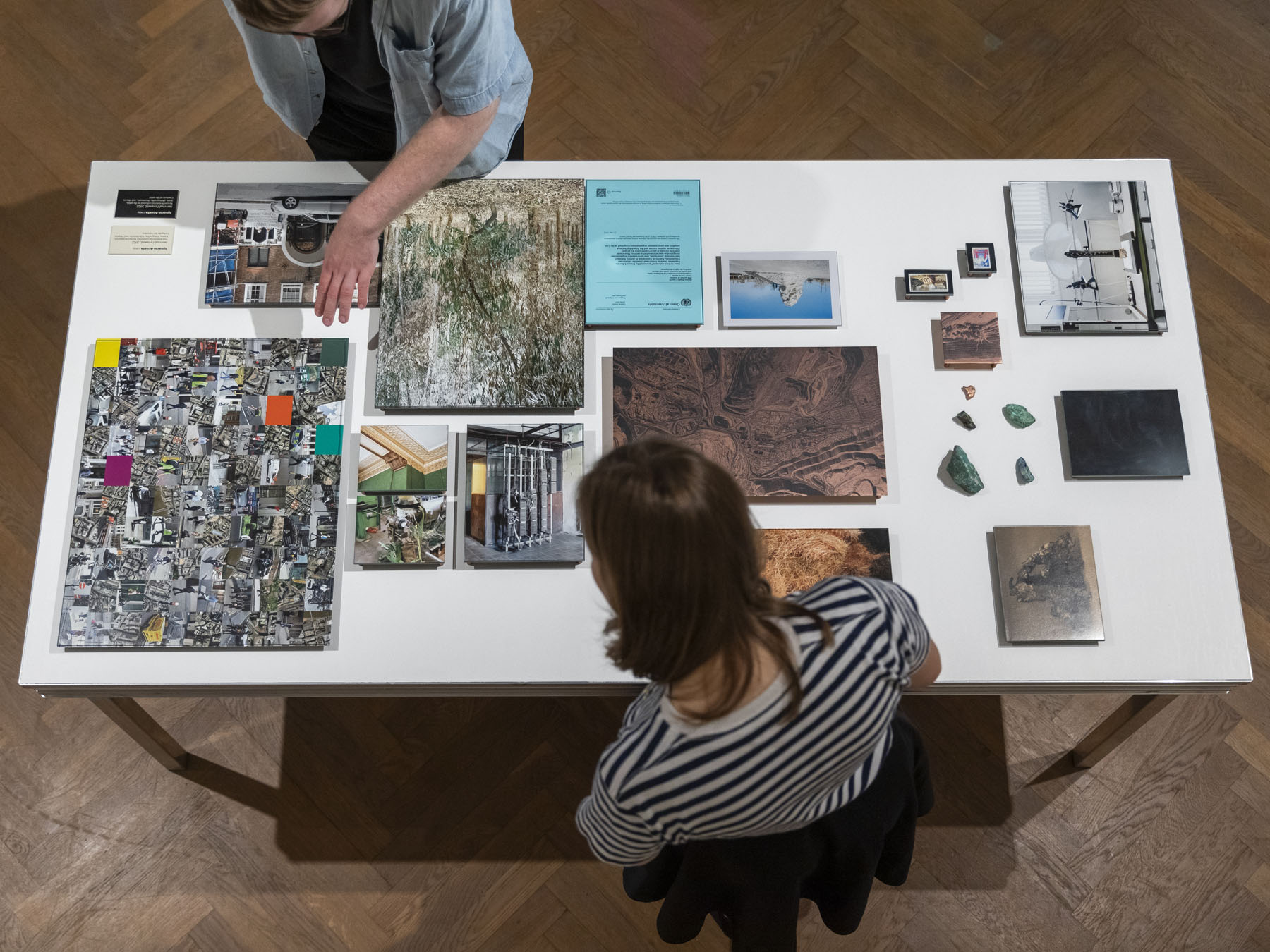
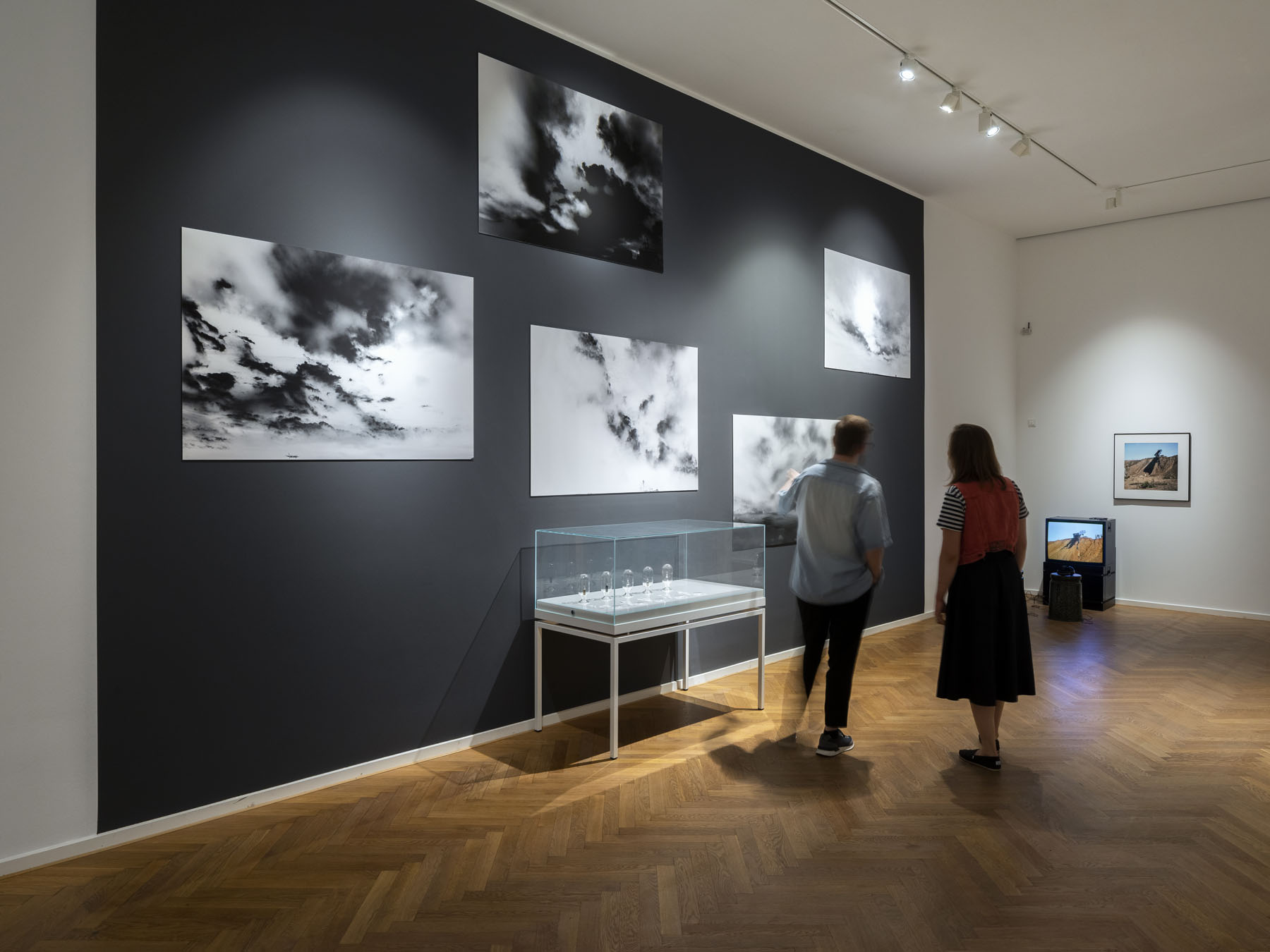
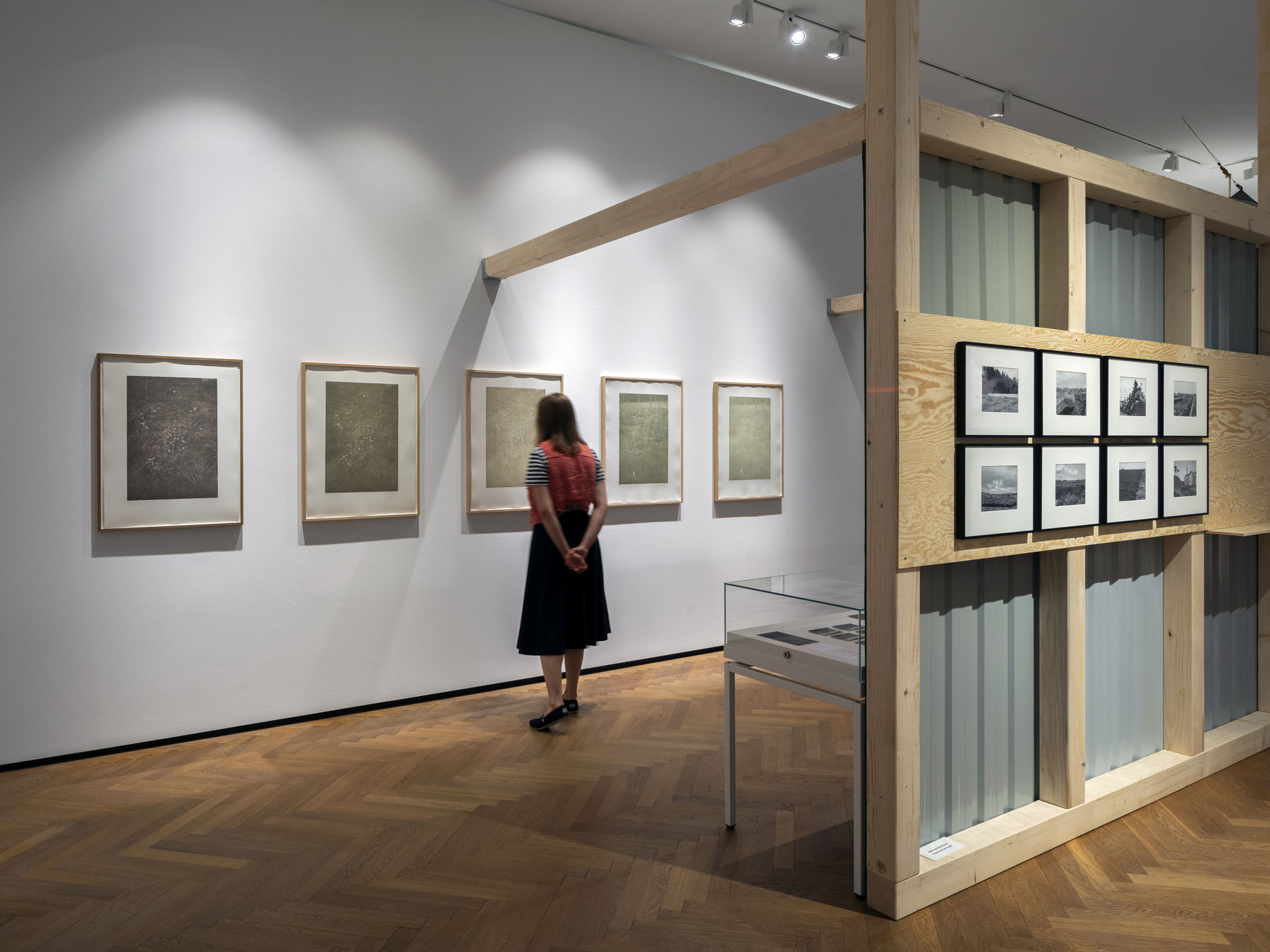
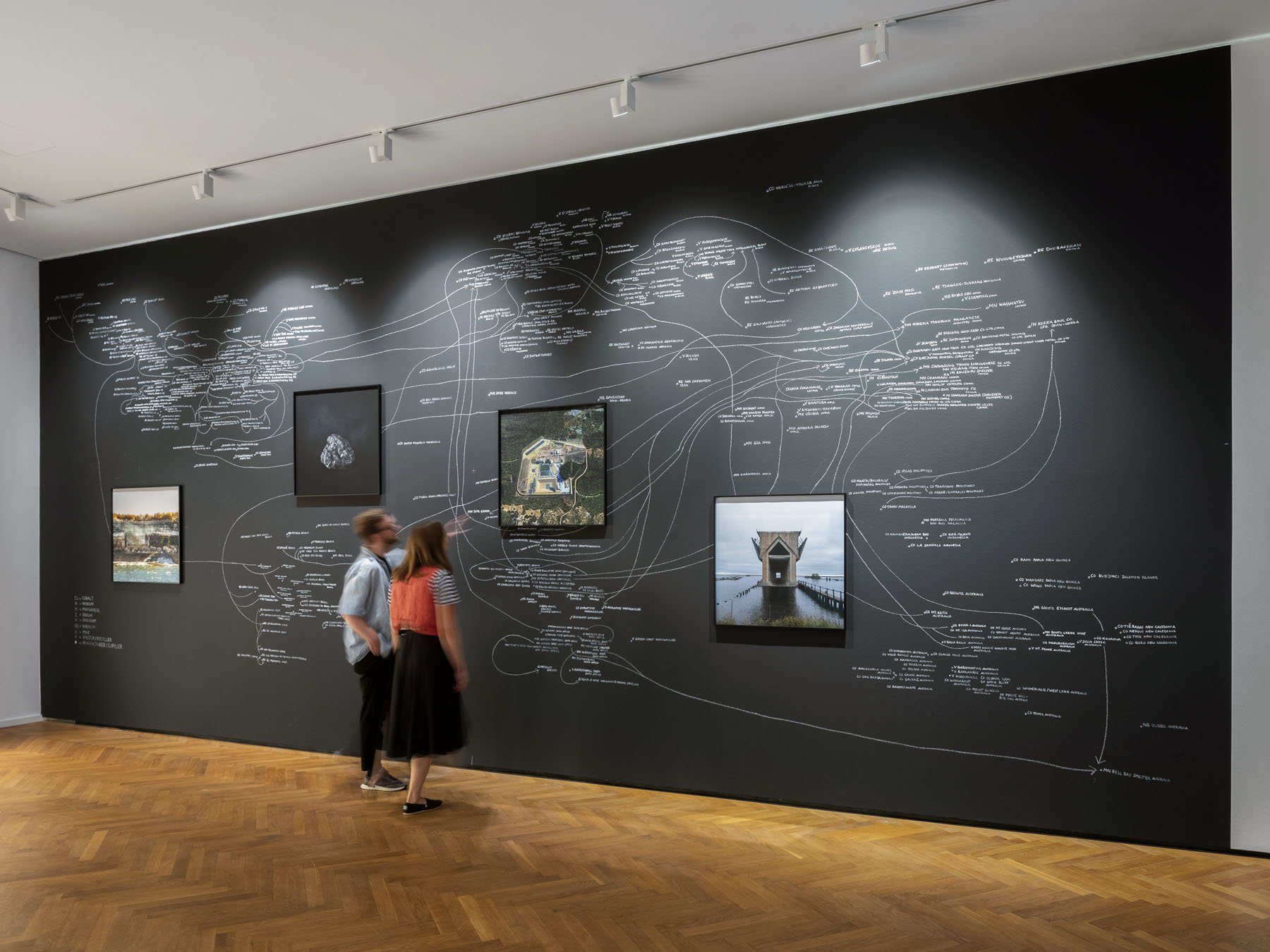
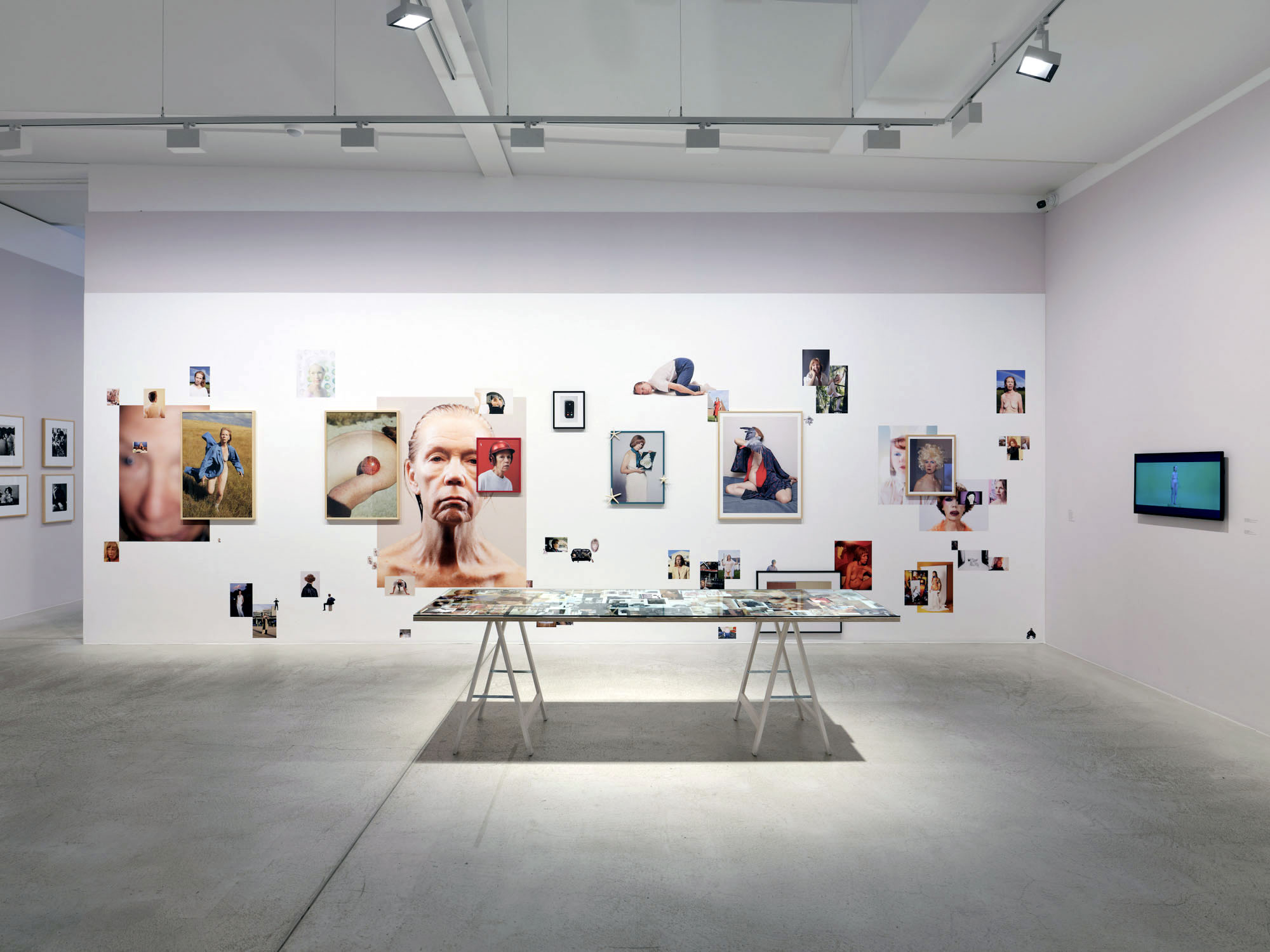
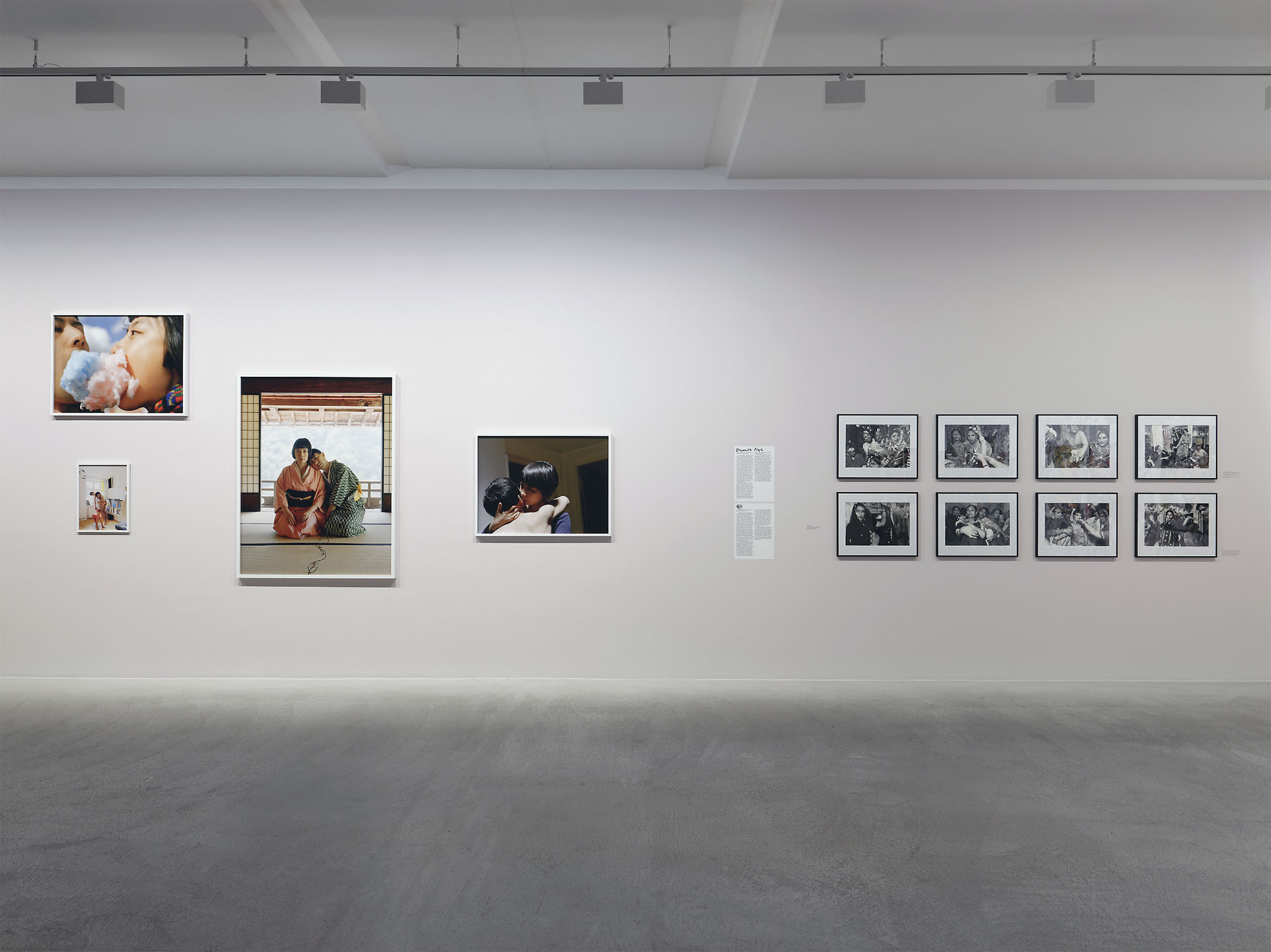
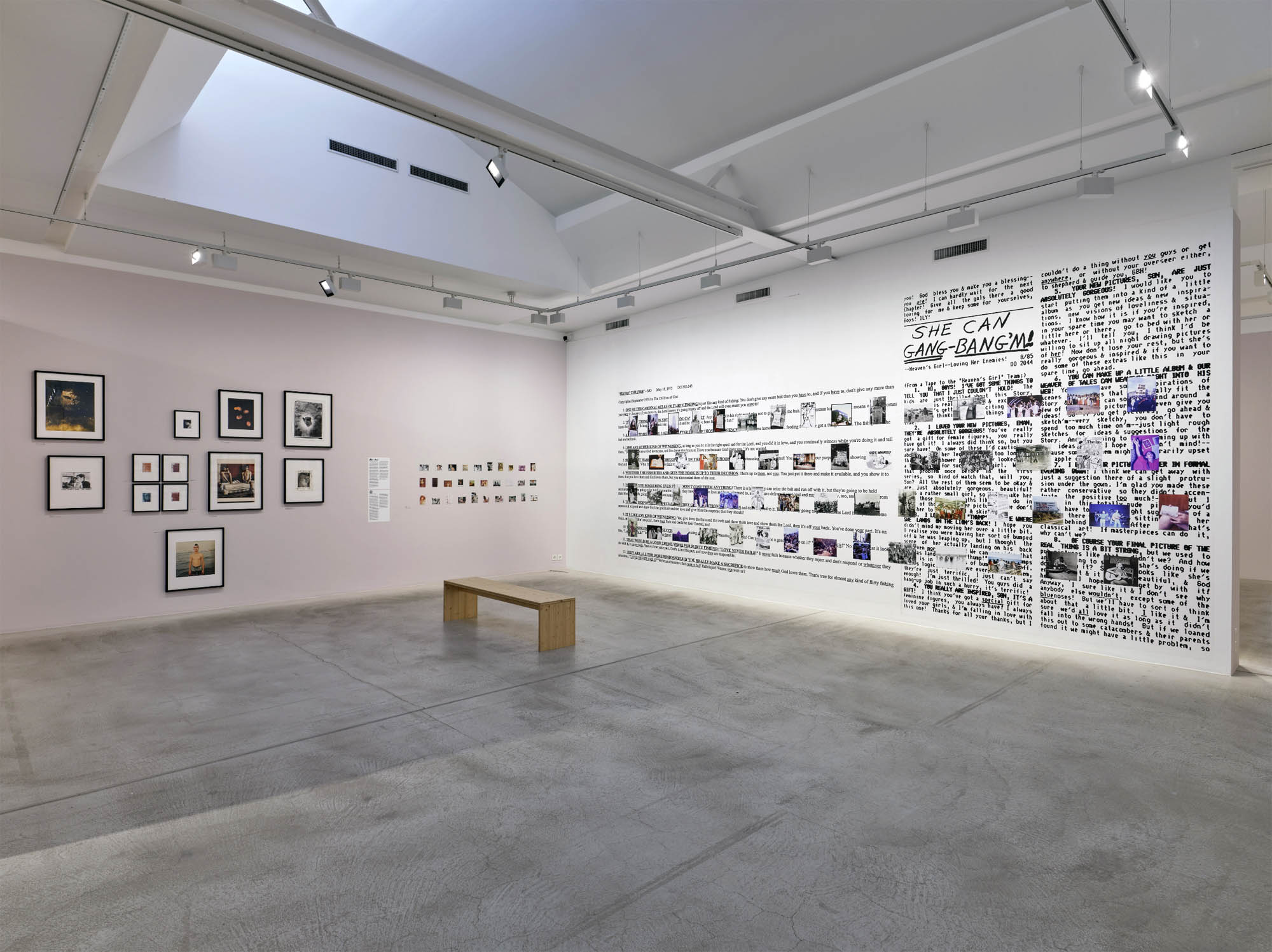
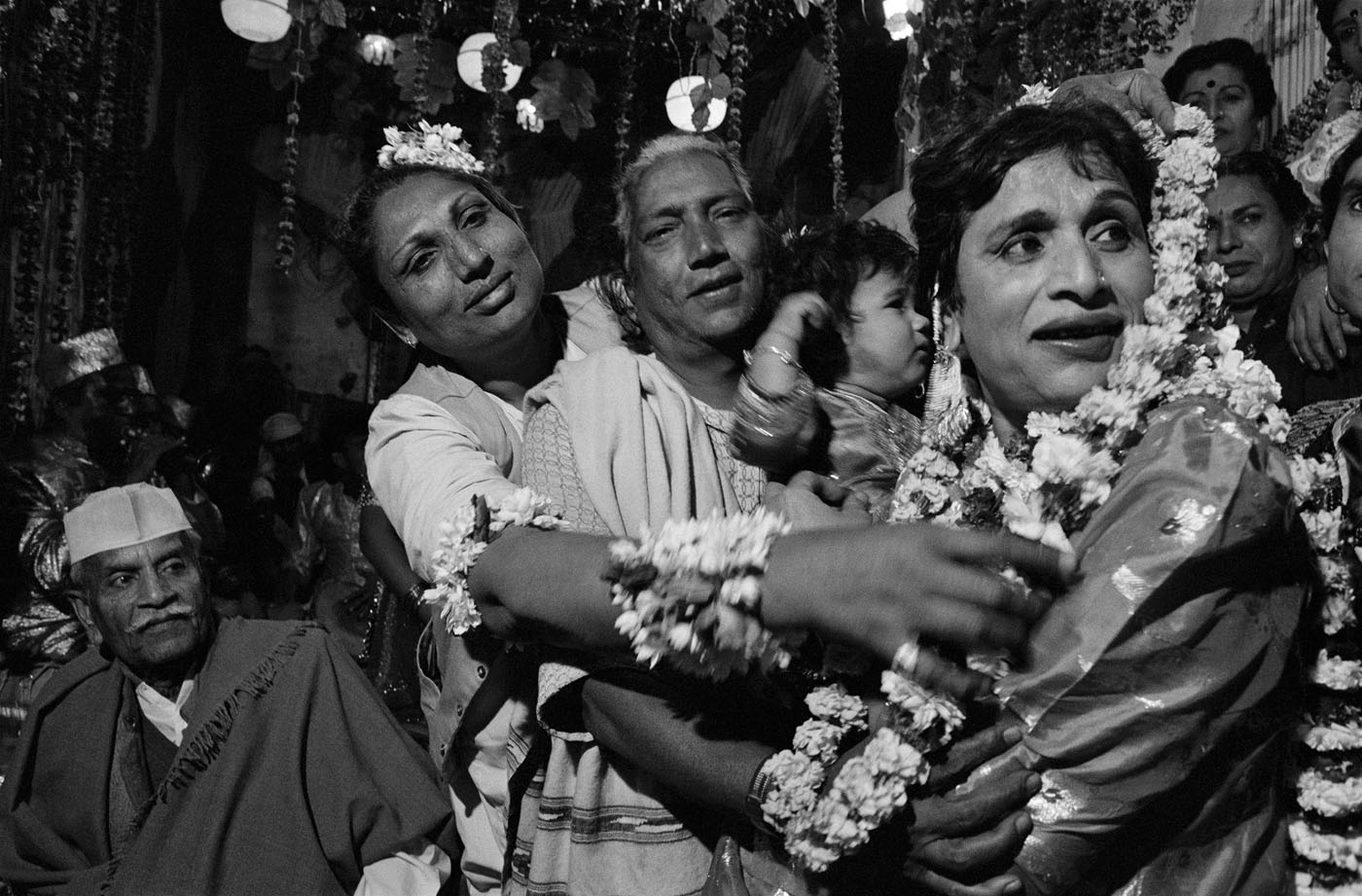
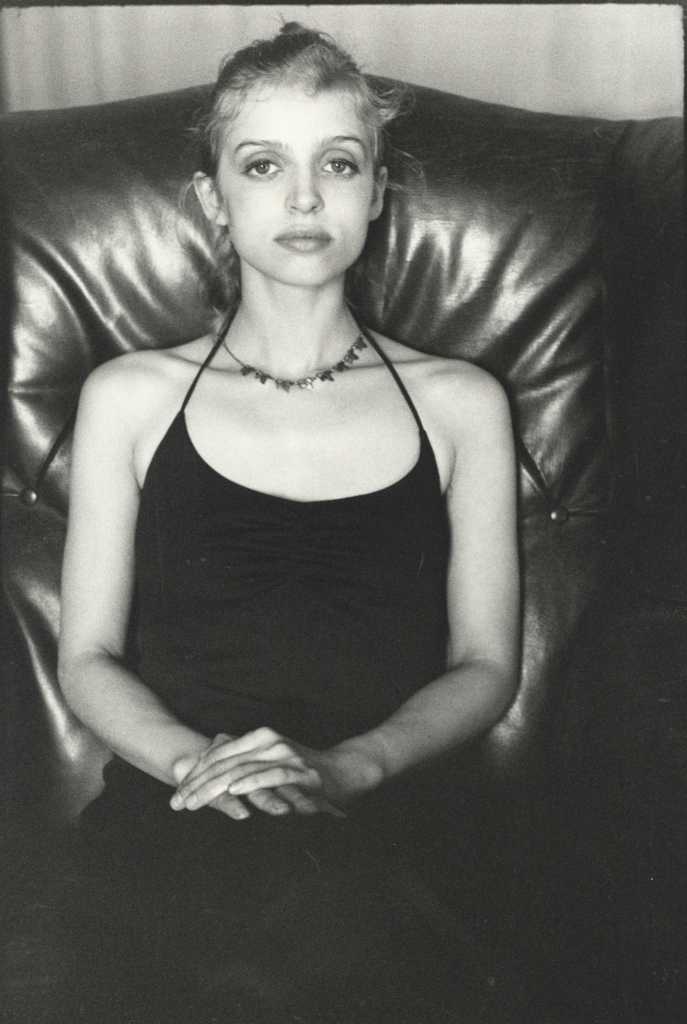
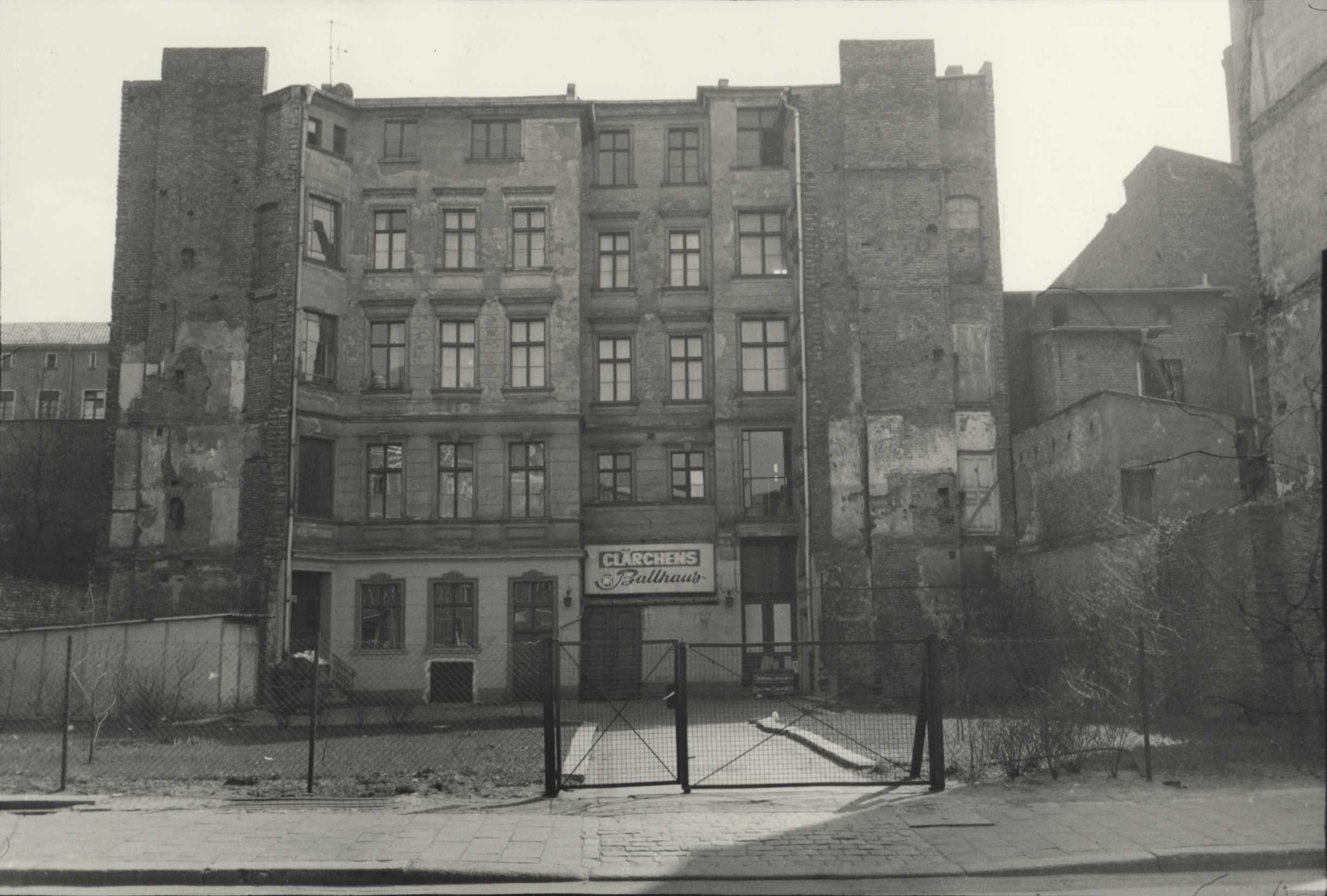
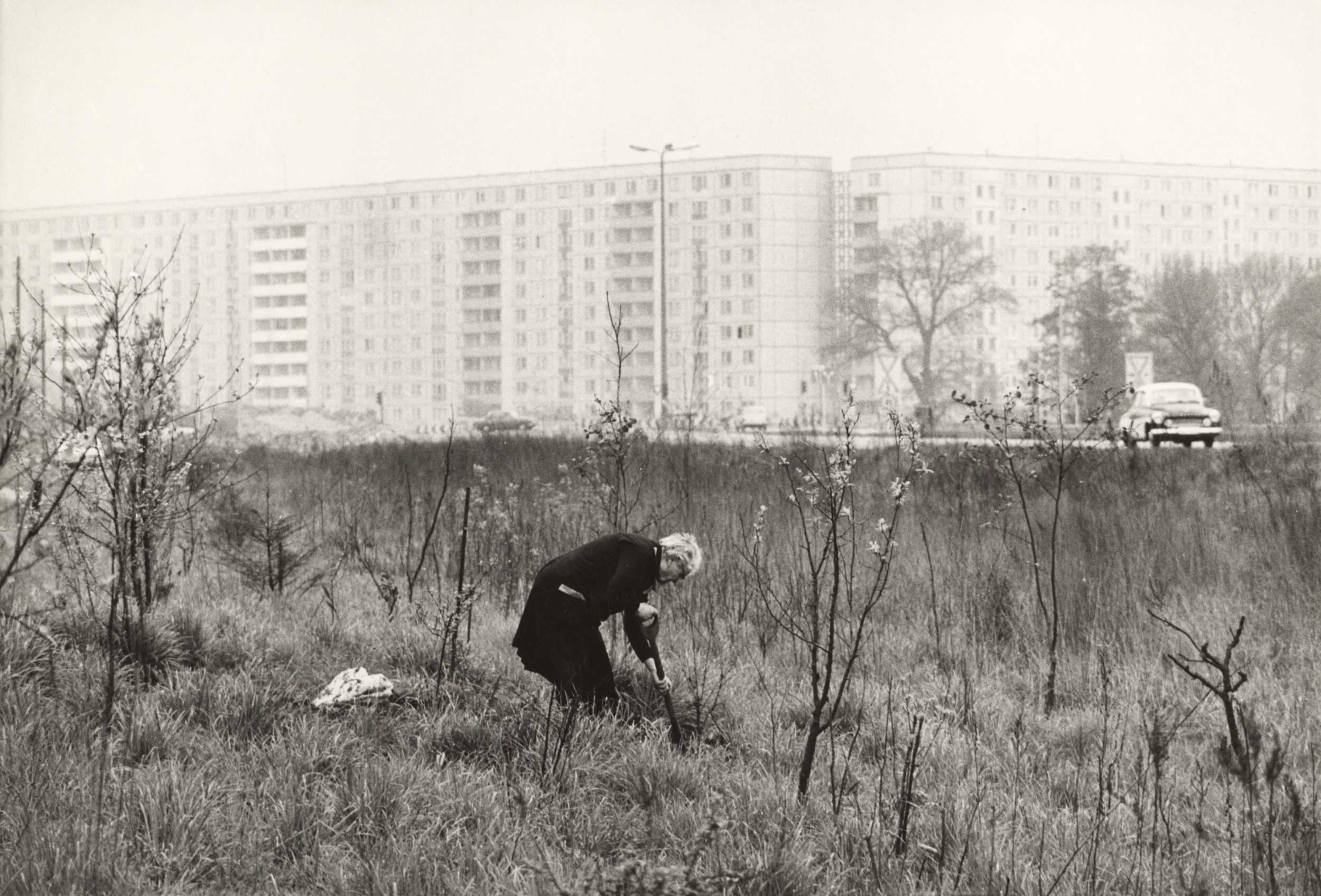
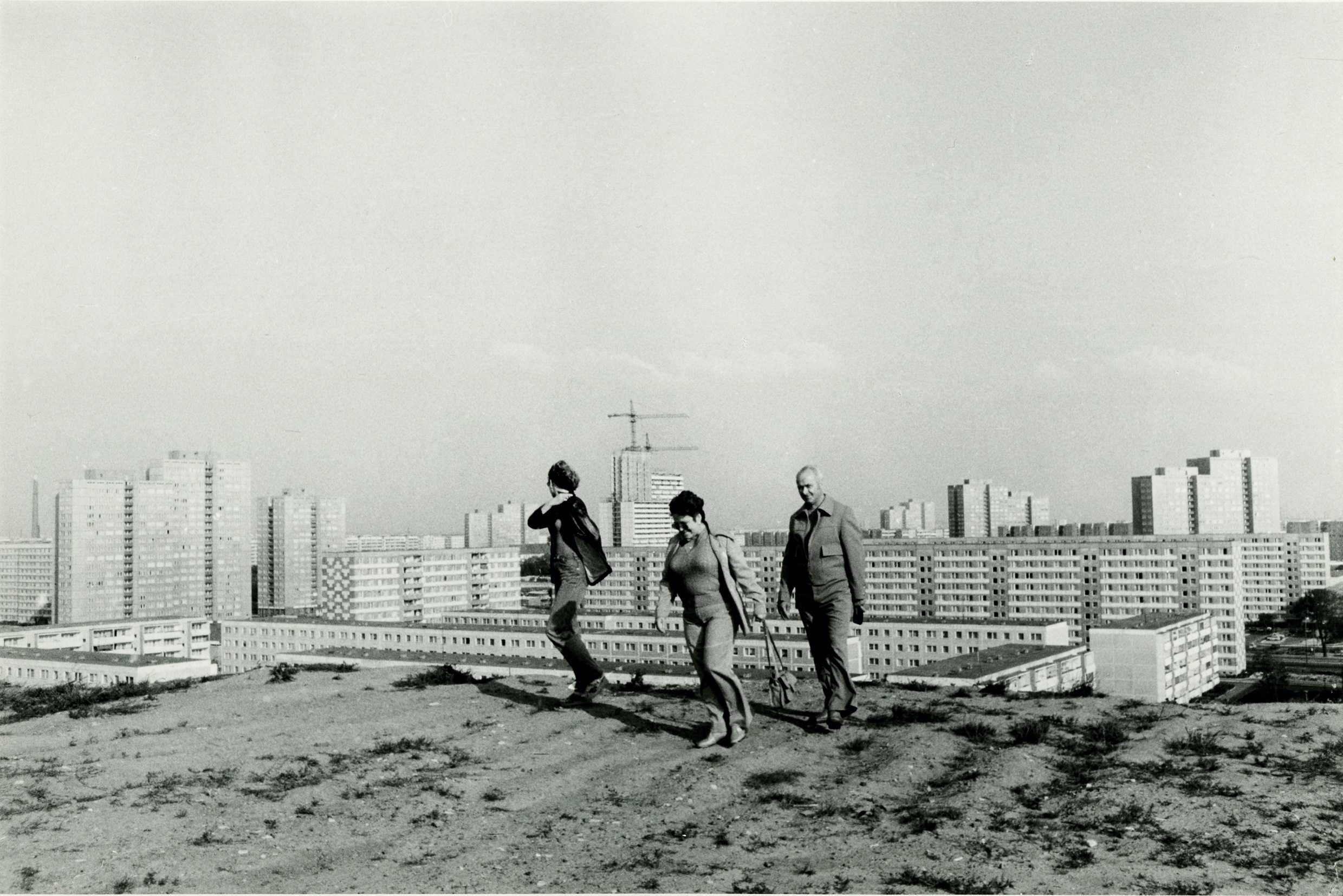
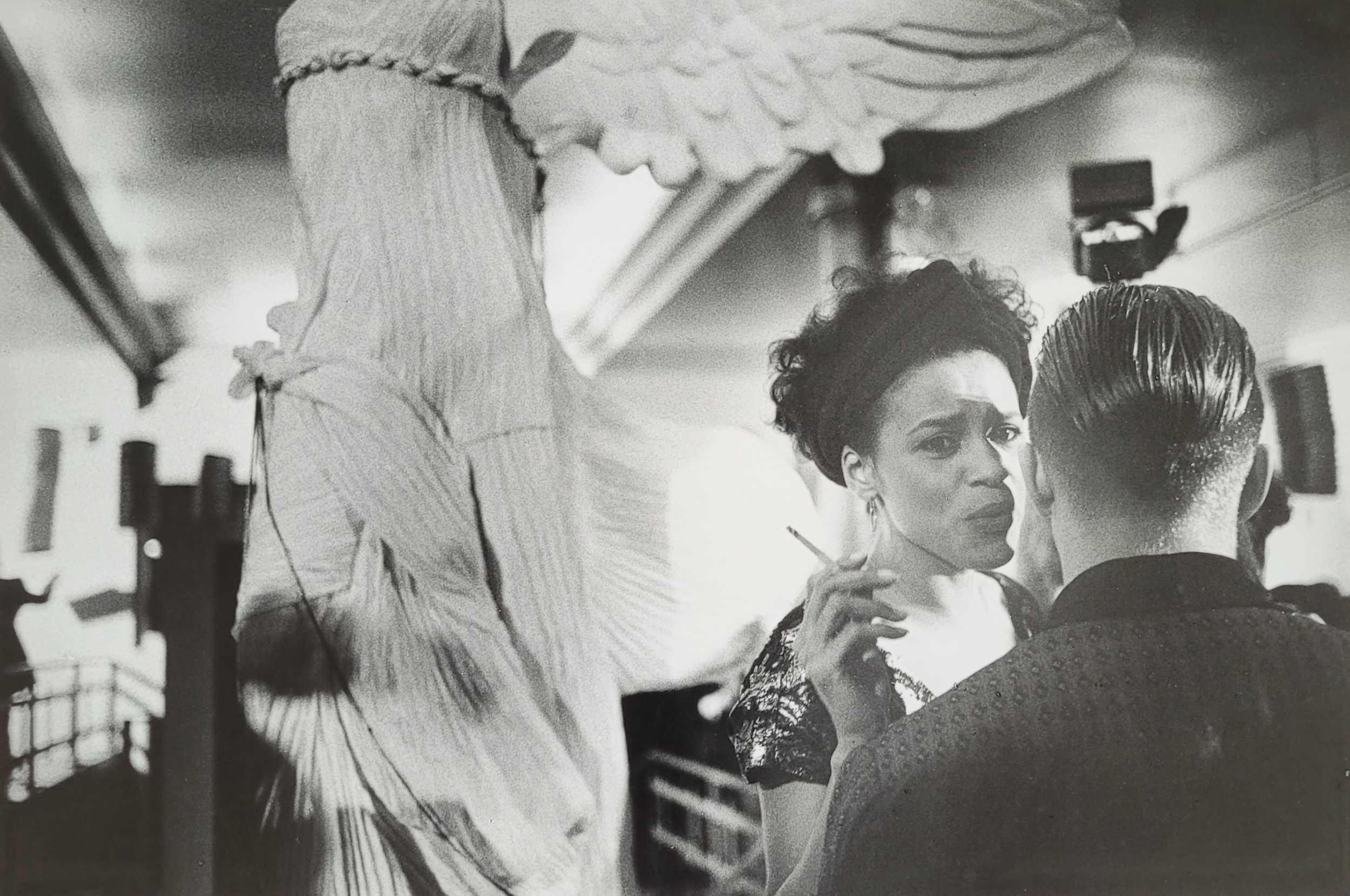
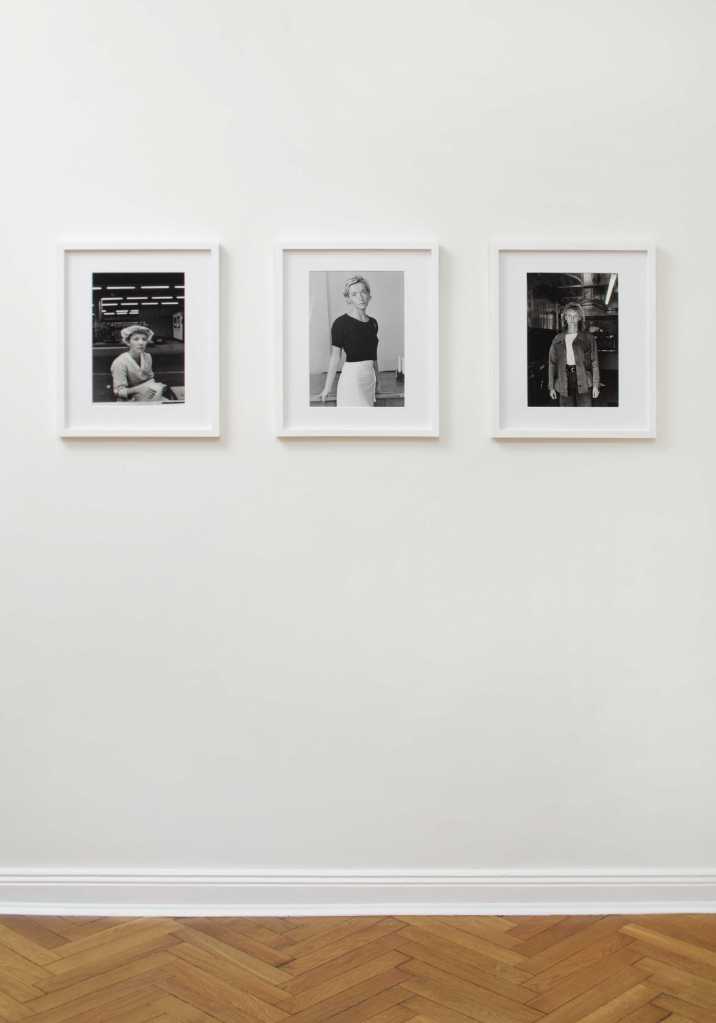
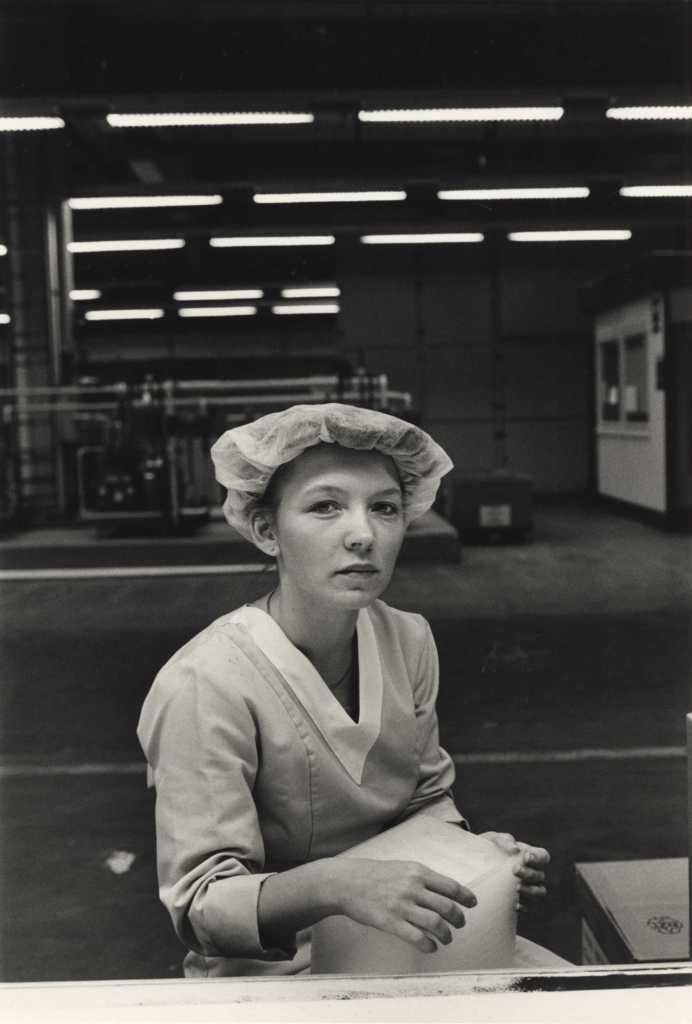
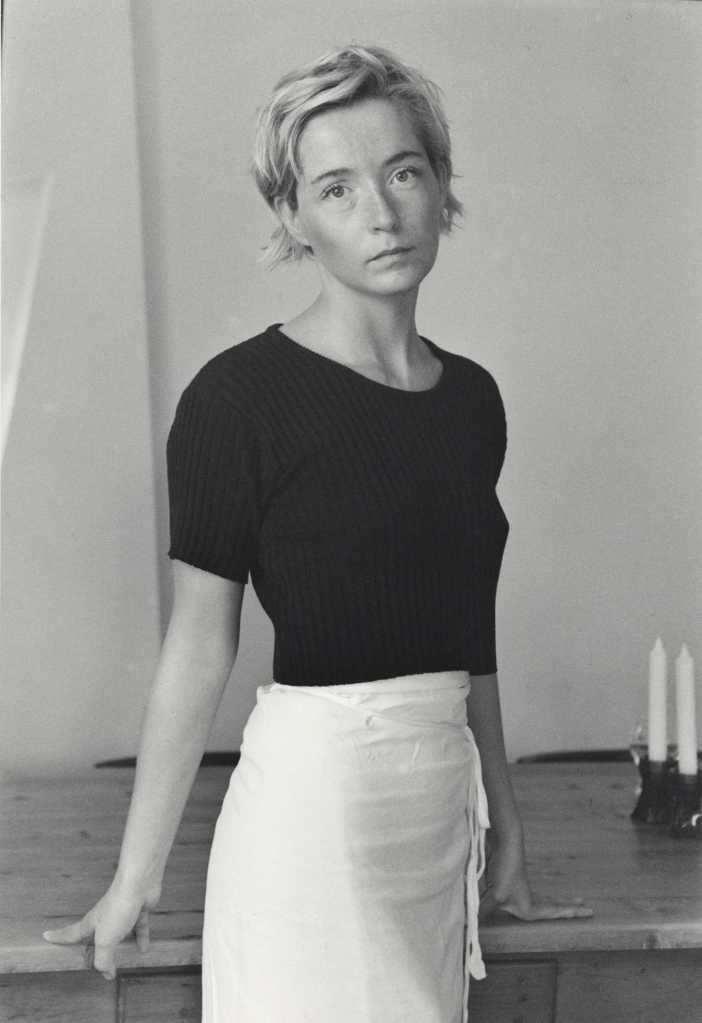
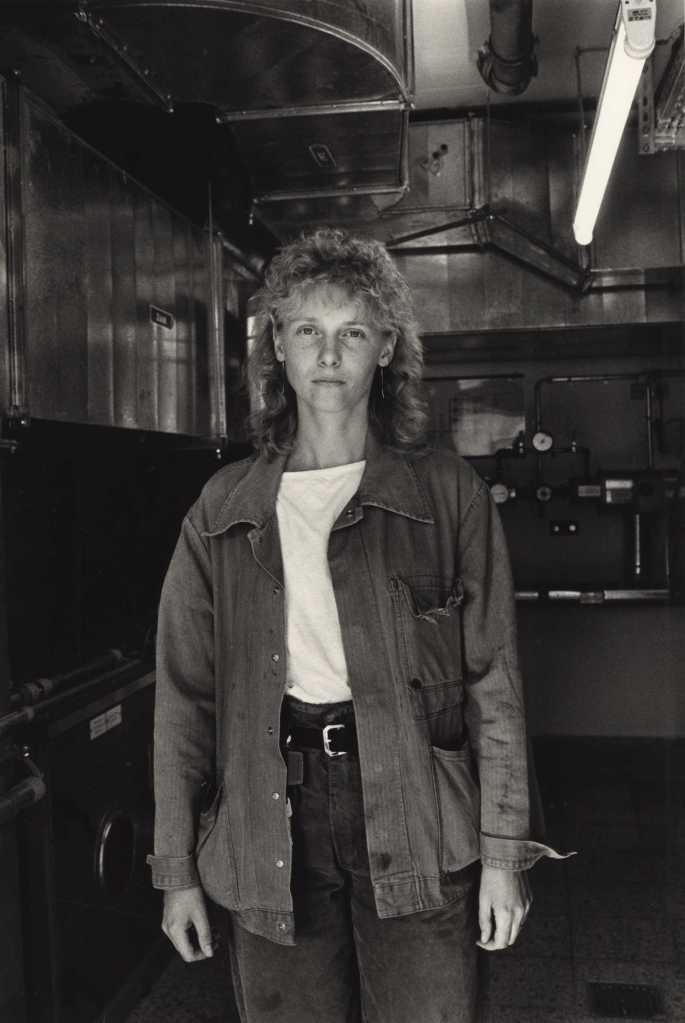
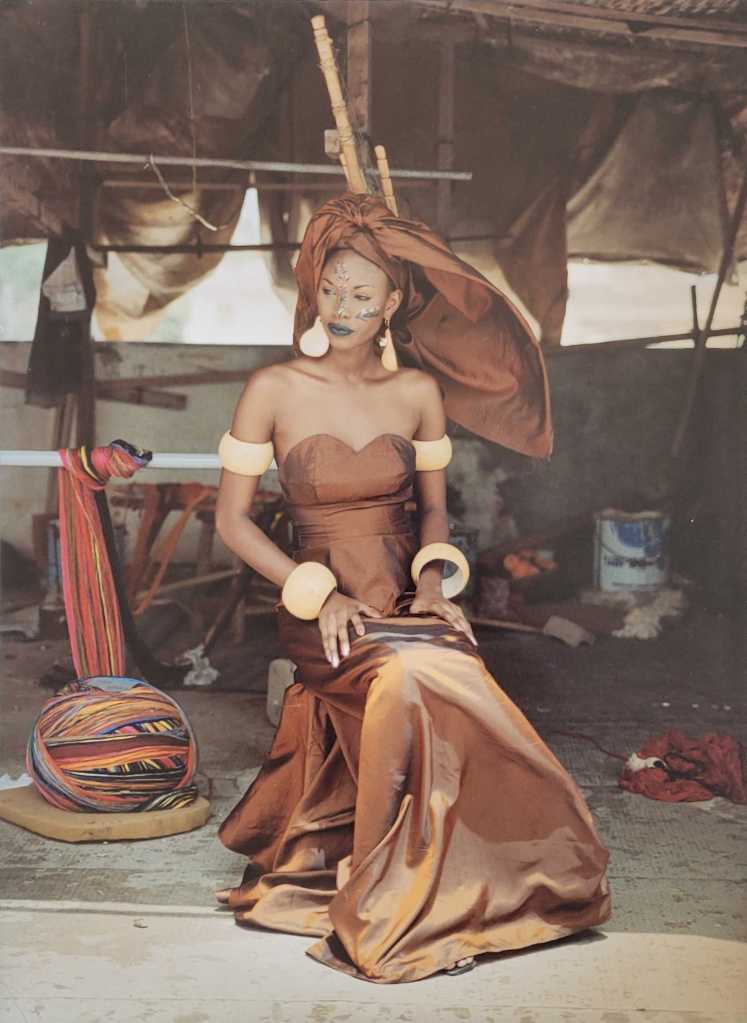
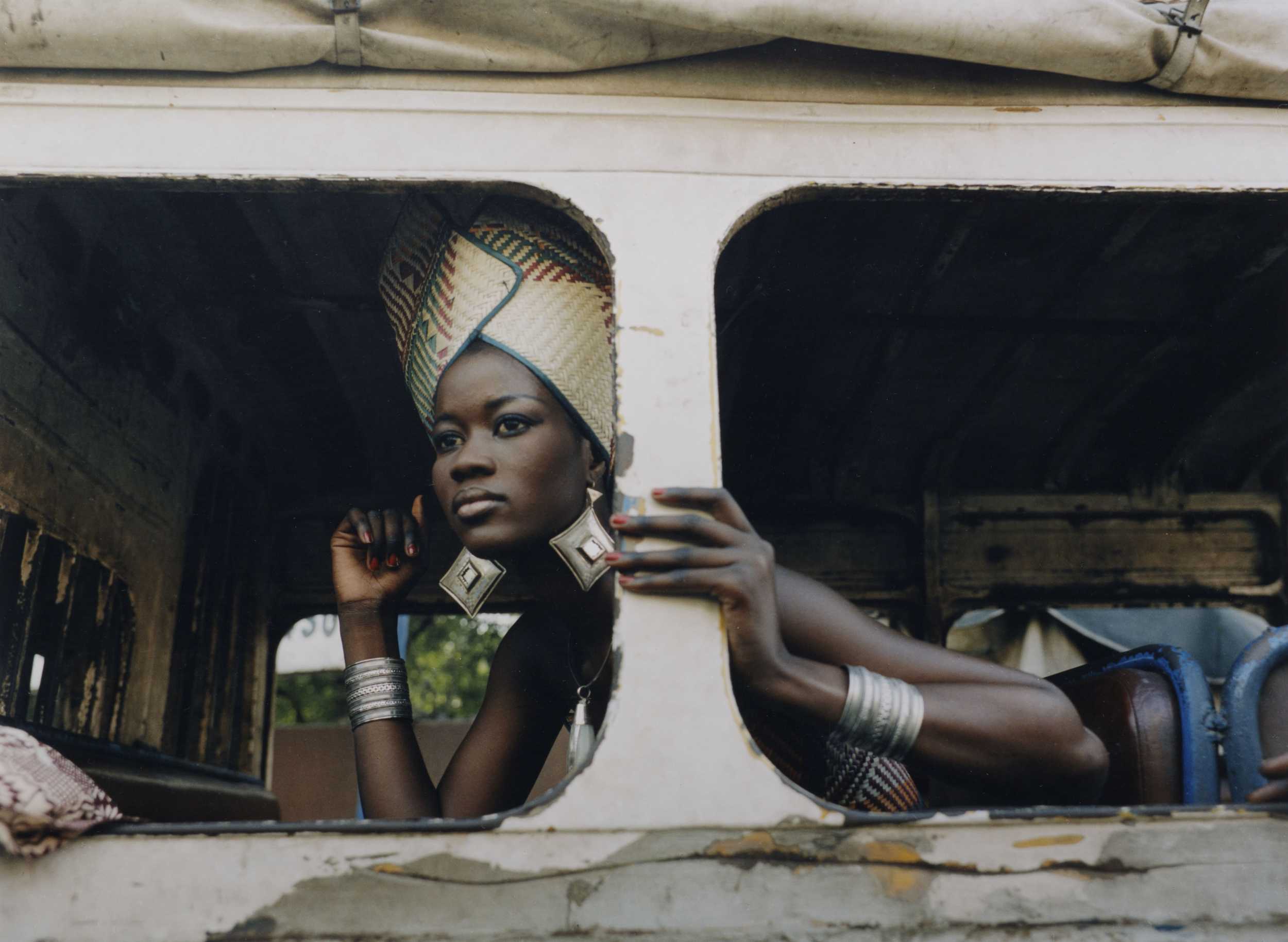
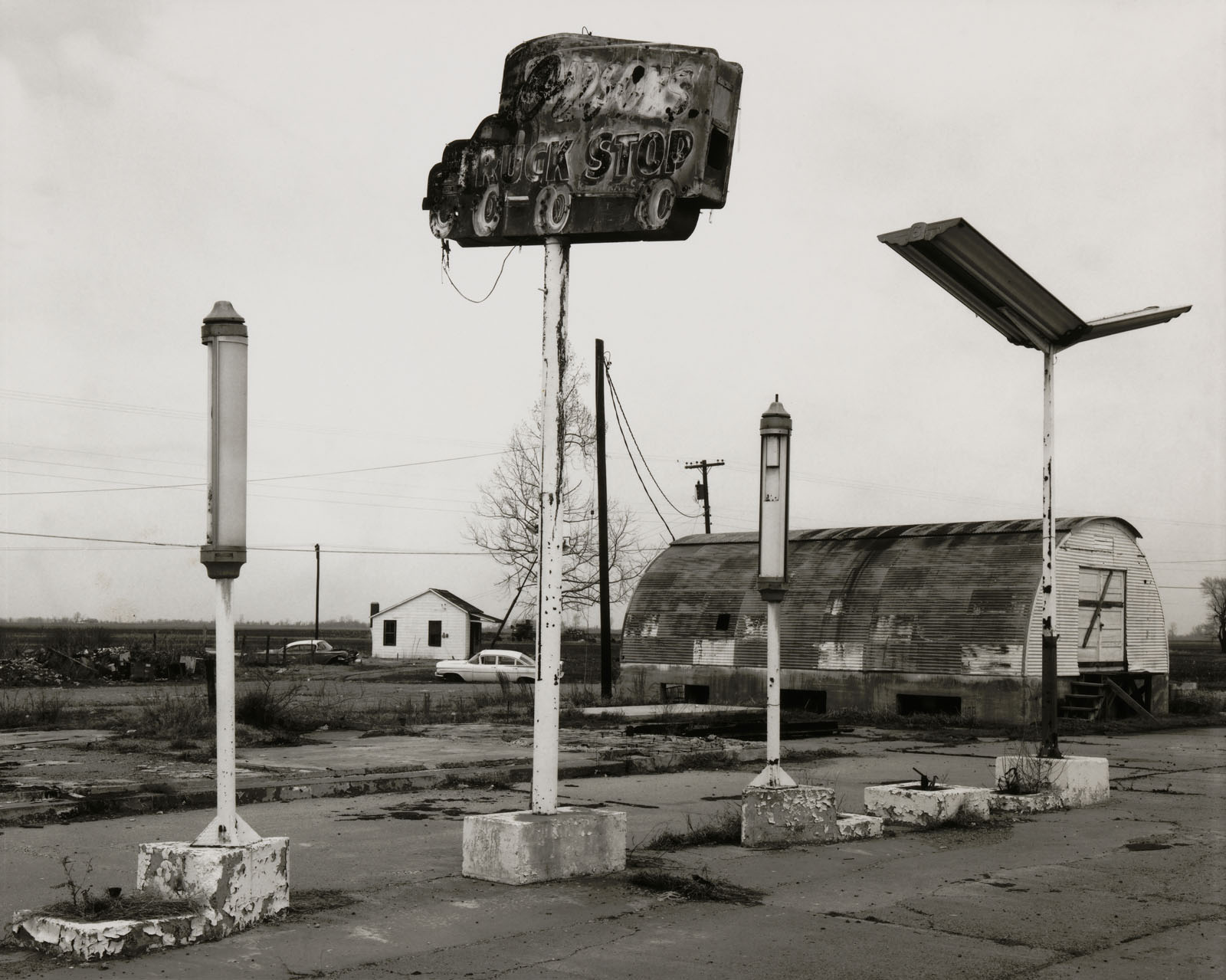
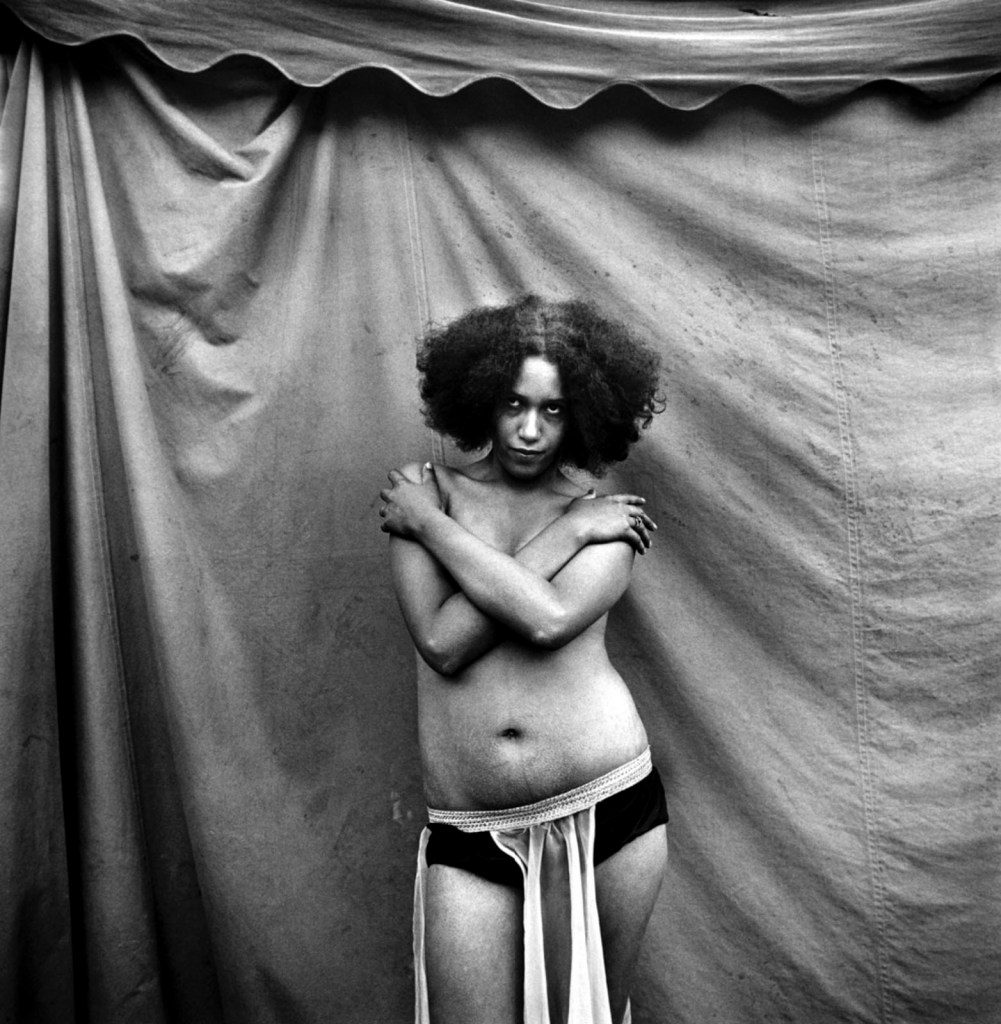
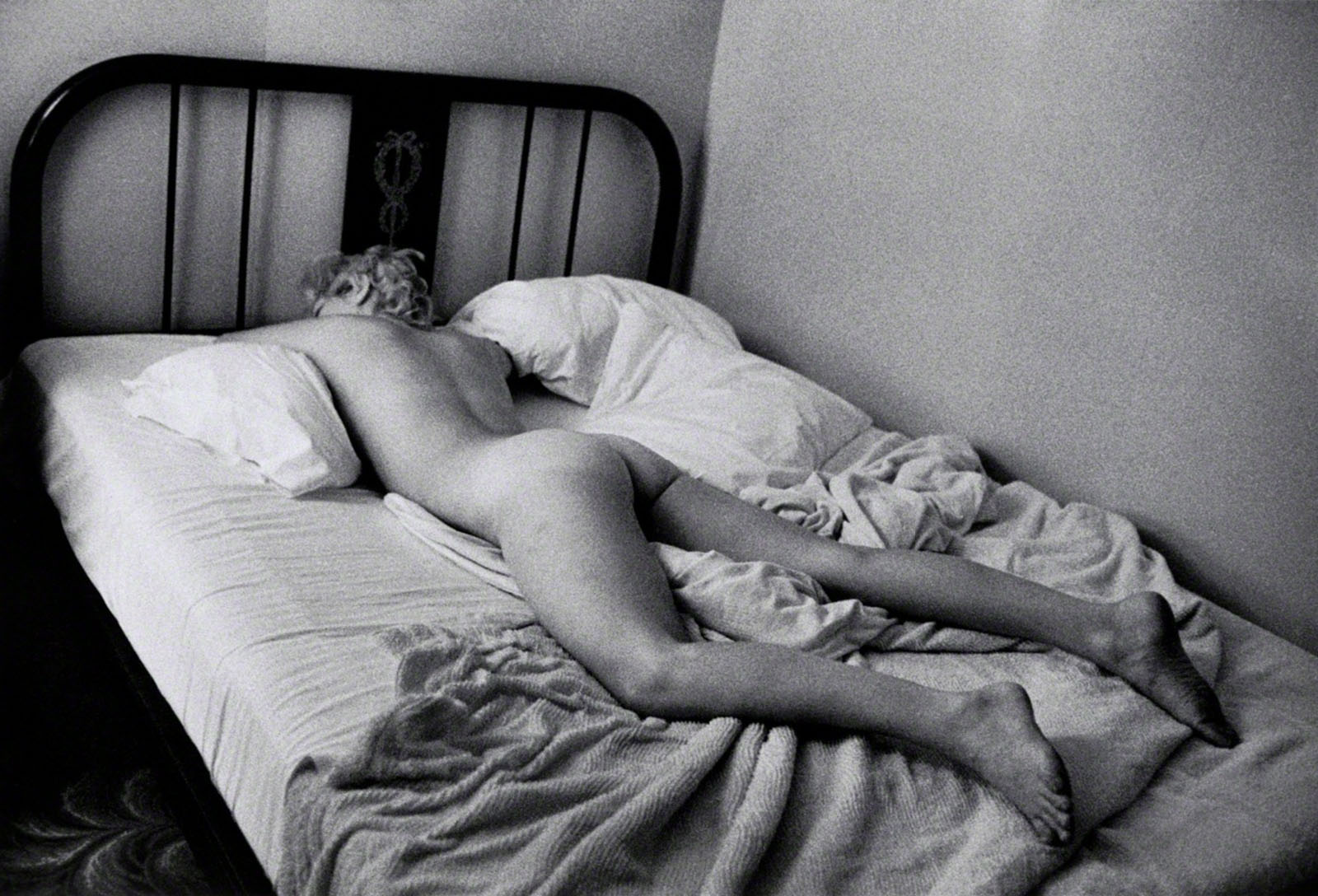
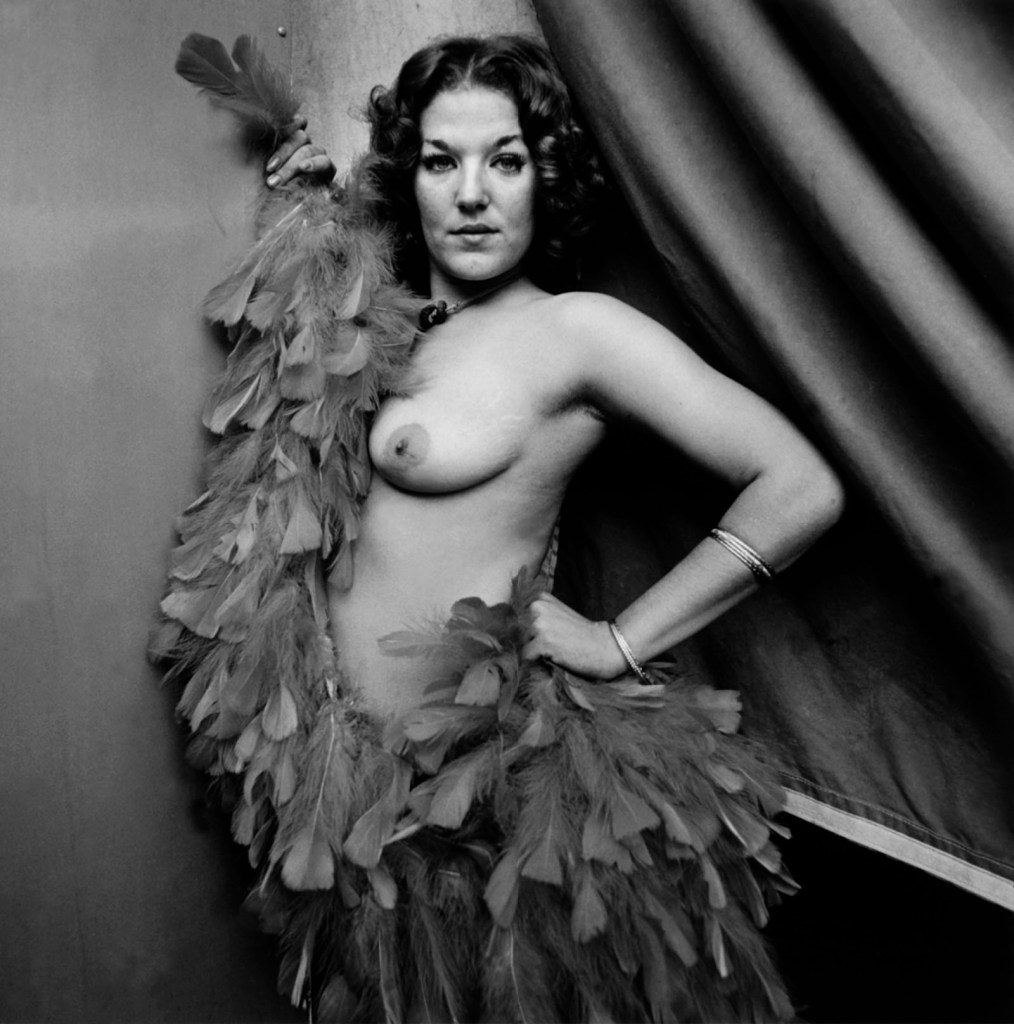
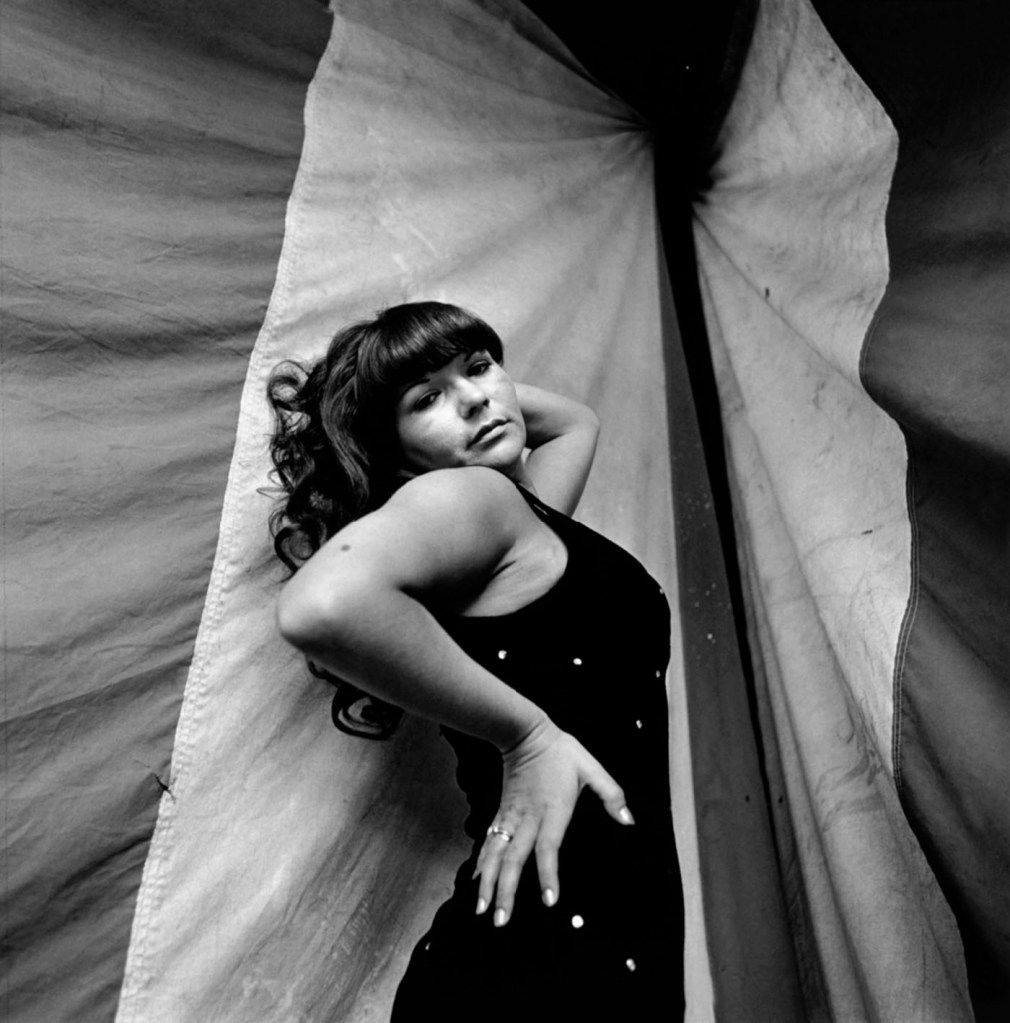




















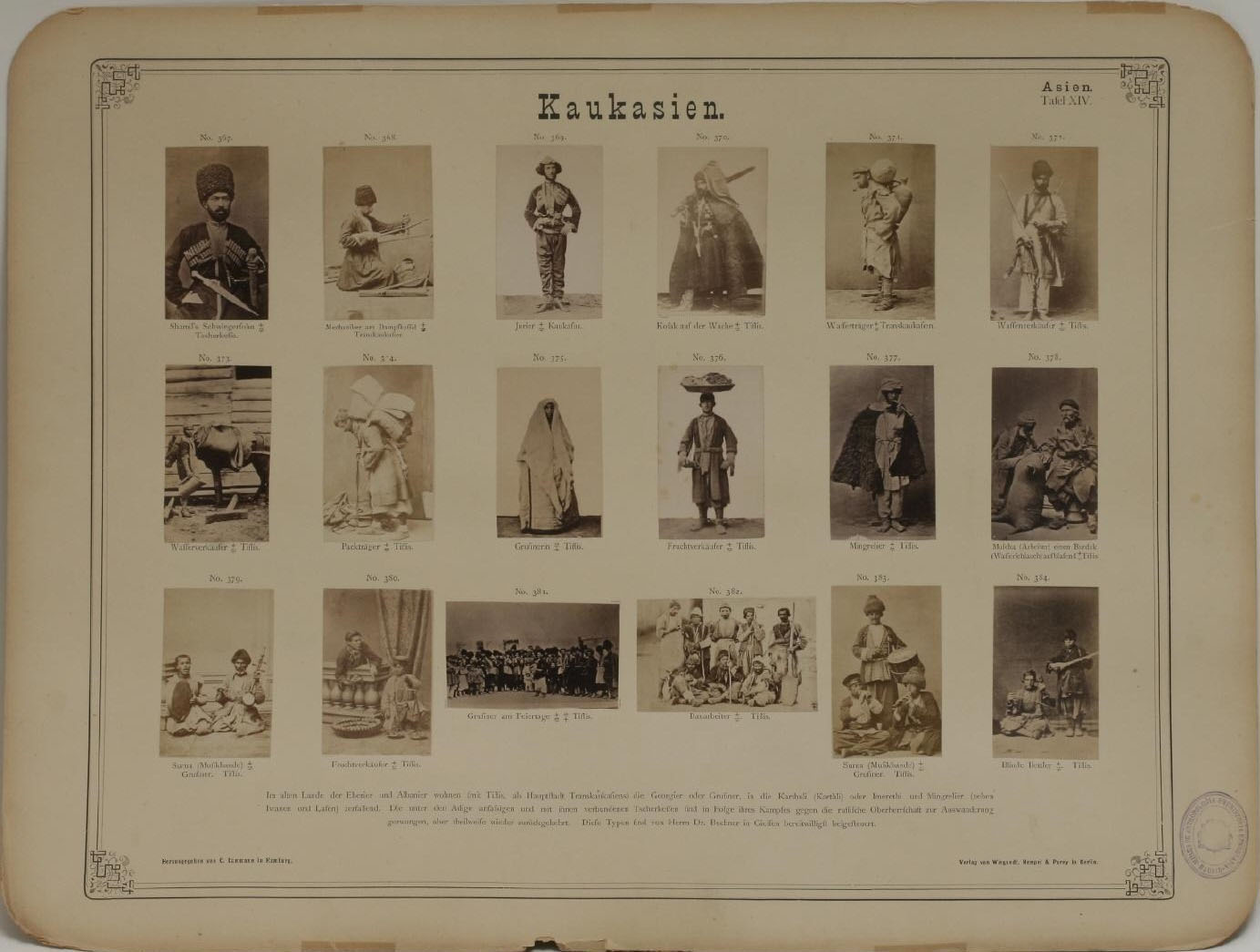











































































































































































































































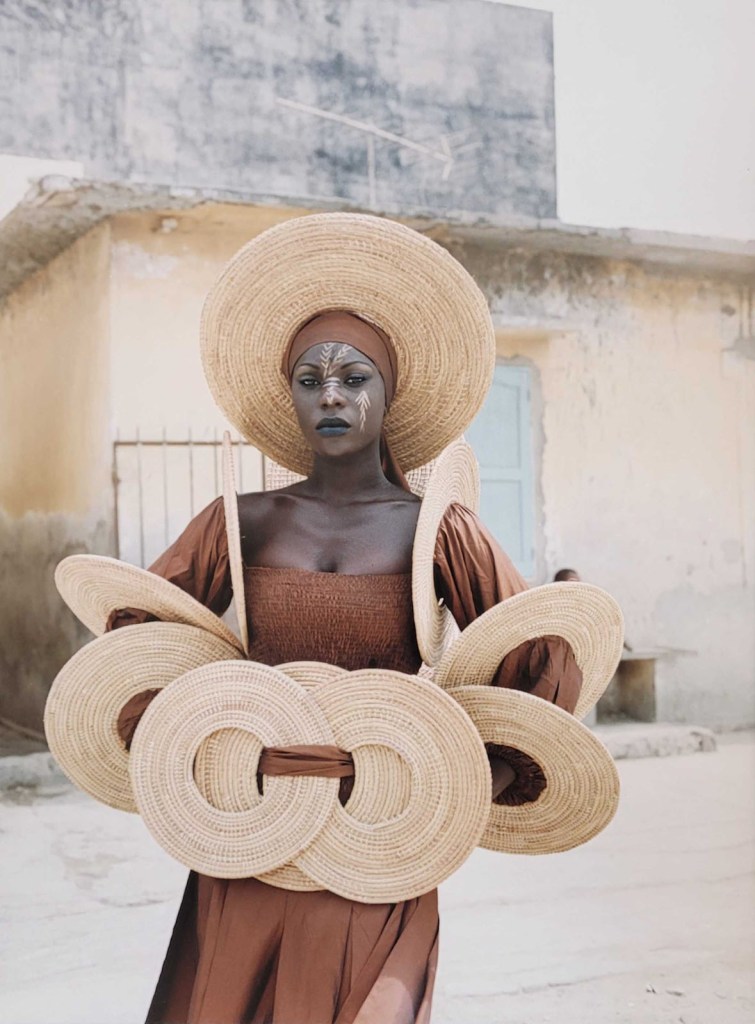











































































You must be logged in to post a comment.