The Chanel Legend exhibition dates: 28th February – 18th May 2014
New Women exhibition dates: 28th February – 27th July 2014
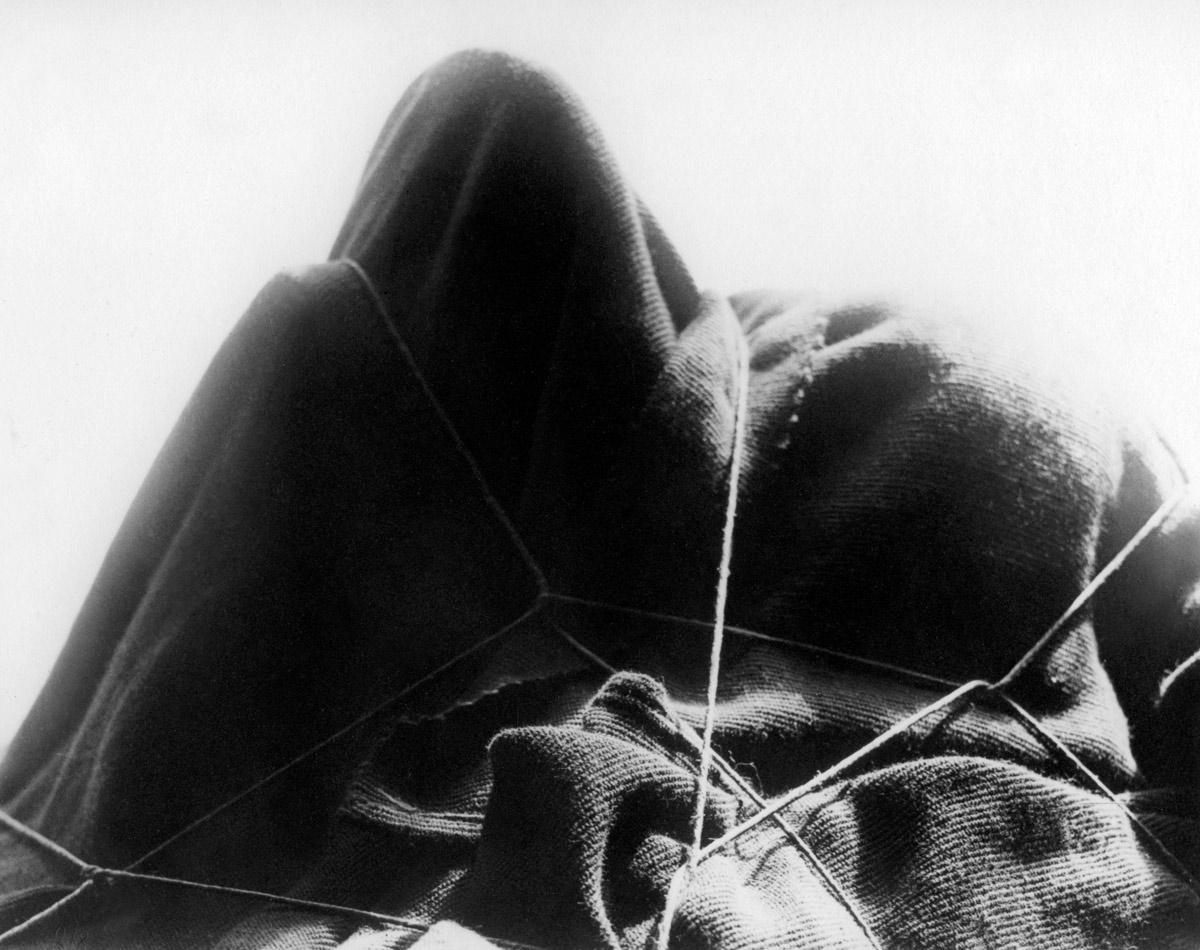
Yva (German, 1900-1944)
Silk stockings
Nd
Silver gelatin print
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg
Yva (26 January 1900 – 31 December 1944) was the professional pseudonym of Else Ernestine Neuländer-Simon who was a German Jewish photographer renowned for her dreamlike, multiple exposed images. She became a leading photographer in Berlin during the Weimar Republic. When the Nazi Party came to power, she was forced into working as a radiographer. She was deported by the Gestapo in 1942 and murdered, probably in the Majdanek concentration camp during World War II.
Do you feel like a new woman?
Do you feel like a god?
You, in the oft mentioned (ten times in the accompanying texts) LBD (Little Black Dress) or Chanel Suit (ten times as well)
It’s like the ten commandments.
And ~ on we go… say after me,
“Sashay! Shantay!”
PS some of the photos ain’t half bad tho!
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
‘Sleeping with the Enemy, Coco Chanel and the Secret War’ written by Hal Vaughan further solidifies the consistencies of the French intelligence documents released by describing Coco as a “vicious anti-Semite” who praised Hitler.
World War II, specifically the Nazi seizure of all Jewish-owned property and business enterprises, provided Chanel with the opportunity to gain the full monetary fortune generated by Parfums Chanel and its most profitable product, Chanel No. 5. The directors of Parfums Chanel, the Wertheimers, were Jewish. Chanel used her position as an “Aryan” to petition German officials to legalise her claim to sole ownership.
“On 5 May 1941, she wrote to the government administrator charged with ruling on the disposition of Jewish financial assets. Her grounds for proprietary ownership were based on the claim that Parfums Chanel “is still the property of Jews” and had been legally “abandoned” by the owners”. …
Chanel was not aware that the Wertheimers, anticipating the forthcoming Nazi mandates against Jews had, in May 1940, legally turned control of Parfums Chanel over to Félix Amiot, a Christian French businessman and industrialist. At war’s end, Amiot returned “Parfums Chanel” to the hands of the Wertheimers.
During the period directly following the end of World War II, the business world watched with interest and some apprehension the ongoing legal wrestle for control of Parfums Chanel. Interested parties in the proceedings were cognisant that Chanel’s Nazi affiliations during wartime, if made public knowledge, would seriously threaten the reputation and status of the Chanel brand. Forbes magazine summarised the dilemma faced by the Wertheimers: [it is Pierre Wertheimer’s worry] how “a legal fight might illuminate Chanel’s wartime activities and wreck her image – and his business.”
Text from the Wikipedia website
Aenne Biermann (German, 1898-1933)
Self-Portrait with silver ball
1931
Silver gelatin print
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe, Hamburg
Aenne Biermann (March 8, 1898 – January 14, 1933), born Anna Sibilla Sternfeld, was a German photographer of Ashkenazi origin. She was one of the major proponents of New Objectivity, a significant art movement that developed in Germany in the 1920s.
Major exhibitions of her work include the Munich Kunstkabinett, the Deutscher Werkbund and the exhibition of Folkwang Museum in 1929. Other important exhibitions include the exhibition entitled Das Lichtbild held in Munich in 1930 and the 1931 exhibition at the Palace of Fine Arts (French: Palais des Beaux Arts) in Brussels.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Horst P. Horst (German-American, 1906-1999)
Coco Chanel
1937
Silver gelatin print
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg
Horst Paul Albert Bohrmann (August 14, 1906 – November 18, 1999), who chose to be known as Horst P. Horst, was a German-American fashion photographer. …
Horst is best known for his photographs of women and fashion, but is also recognised for his photographs of interior architecture, still lifes, especially ones including plants, and environmental portraits. One of the great iconic photos of the Twentieth-Century is “The Mainbocher Corset” with its erotically charged mystery, captured by Horst in Vogue‘s Paris studio in 1939. Designers like Donna Karan continue to use the timeless beauty of “The Mainbocher Corset” as an inspiration for their outerwear collections today. His work frequently reflects his interest in surrealism and his regard of the ancient Greek ideal of physical beauty.
His method of work typically entailed careful preparation for the shoot, with the lighting and studio props (of which he used many) arranged in advance. His instructions to models are remembered as being brief and to the point. His published work uses lighting to pick out the subject; he frequently used four spotlights, often one of them pointing down from the ceiling. Only rarely do his photos include shadows falling on the background of the set. Horst rarely, if ever, used filters. While most of his work is in black & white, much of his colour photography includes largely monochromatic settings to set off a colourful fashion. Horst’s colour photography did include documentation of society interior design, well noted in the volume Horst Interiors. He photographed a number of interiors designed by Robert Denning and Vincent Fourcade of Denning & Fourcade and often visited their homes in Manhattan and Long Island. After making the photograph, Horst generally left it up to others to develop, print, crop, and edit his work.
One of his most famous portraits is of Marlene Dietrich, taken in 1942. She protested the lighting that he had selected and arranged, but he used it anyway. Dietrich liked the results and subsequently used a photo from the session in her own publicity.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Boris Lipnitzki (French born Ukraine, 1887-1971)
Coco Chanel
1937
© Getty Images
Boris Lipnitzki (1887-1971) was a Ukrainian-born French photographer of the arts; ballet, fashion, cinema, visual art, writing and music.
Haim Efime Boris Lipnitzki (or Lipnitzky) was born into a Jewish family in Oster, in Chernihiv Province of the Russian Empire (now Ukraine) on 4 February 1887. He died in Paris on 6 July 1971, aged 84, and is buried in Pere Lachaise cemetery.
Lipnitzki first worked for a photographer in Odessa, then opened his own studio in Pultusk. He arrived in Paris in the early 1920s. There, he established a studio at 40 rue du Colisée, where he photographed many of the artistic personalities of the 20th century from the 1920s-1960s, as well as picturing them in their own surroundings. His friendship with fashion designer Paul Poiret, with whom he would stay to photograph in Biarritz, provided an entrée into these circles.
His subjects included Maurice Ravel, René Hubert, Albert Camus, Blaise Cendrars, Jean Cocteau, Otto Preminger, Igor Strawinsky, Arthur Honegger, Leonid Massine, Serge Lifar, Paul Poiret, Coco Chanel, Olga Spessivtseva, Nyota Inyoka, Tamara Karsavina, Serge Gainsbourg, Les Six, Marc Chagall, Pablo Picasso, as well as Josephine Baker of whom in 1926 he made a famous series of nude photographs.
Text from the Wikipedia website
New Women
In the 1920s Coco Chanel chiefly influenced the type of the “new woman”. She established skirts that reached just below the knee, encouraged women to wear trousers and represents functional ladies wear. In the photographs by among others Yva, Franz Roth, Lotte Jacobi and Hein Gorny presented here, women show legs in silk stockings, wear cropped hair, drive motorbikes or automobiles and play tennis or go into baths. In this period women begin to take charge of their lives. Being a photographer offered the opportunity to express this new notion of the self in images and in life. The special display of the Photography Department coincides with the exhibition The Chanel Legend.
The Chanel Legend
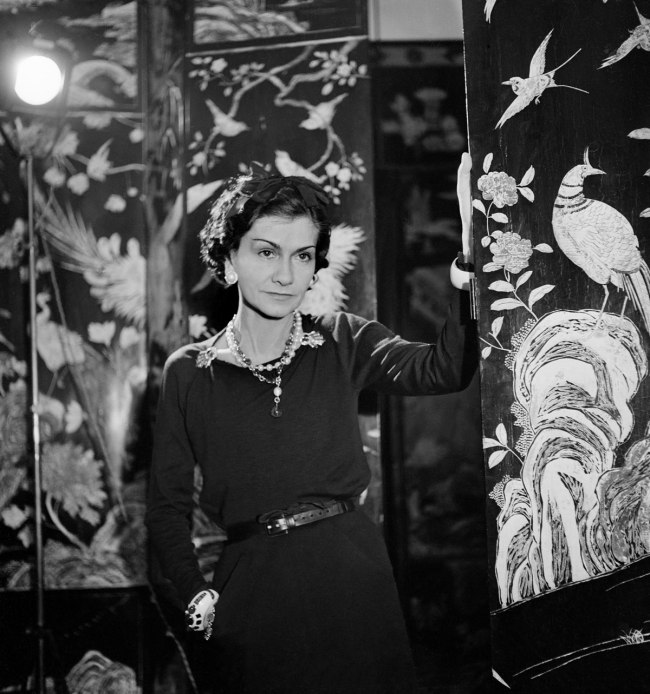
Coco Chanel (1883-1971) is one of the most eminent couturières of the twentieth century. She already appears as an advocate of simple, comfortable clothes in the years just after 1910, thus helping to pave the way for a style which has retained its major importance in the fashion world till today. Such outstanding fashion classics as the “little black dress”, the Chanel Suit and the Chanel handbag are inseparably linked with her person. Since her start-up in 1913, Chanel has built up an international and, till the present day, astoundingly successful fashion empire. It is not until 1983, in the shape of Karl Lagerfeld, that a personality with anything like her charisma and influence becomes her successor. Coco – her real name was Gabrielle – Chanel launched her perfume Chanel N° 5, whose overwhelming commercial success guaranteed her a financial independence which was to last all her life, at the beginning of the 1920s. She combined fashion jewellery and genuine gemstones with surefooted confidence and had herself portraited by celebrity photographers such as Man Ray or Horst P. Horst.
The Chanel Legend investigates why it is that the person of Coco Chanel and the brand she established have attracted such huge attention up to and including the present. It will turn the spotlight both on the fashion designer’s biography and the image which she created for herself, as well as the brilliant achievement of Karl Lagerfeld (b. 1933) in combining this legacy with the fluctuating currents of contemporary taste since 1983. The exhibition shows a total of more than 200 objects from eminent collections, including women’s suits, accessoires, jewellery, advertising graphic, historical photographs and over 75 fashion magazines spanning a period from 1920 to1971. Besides more than 54 original garments, among them 38 created by Coco Chanel, and some 50 jewellery creations, over 35 adaptions of the Chanel classics can be seen for the first time, which in their own individual way give us a new appreciation of the “Chanel Legend”.
The exhibition approaches the “Chanel Legend” in three chapters. The first documents, with 38 original garments, accessoires and more than 50 items of fashion jewellery from the period between 1925 and 1971 the fashion designer’s oeuvre. Designs for evening and day wear and the perfume Chanel N° 5, of which an original flacon is on show, belong to Chanel’s pre-Second World War creative phase. After her return to Paris in 1954, Chanel continued to lead her firm up to her death in 1971. The exhibition shows, among other items from this period, some 10 garments which Chanel designed for the actress and singer Marlene Dietrich, including day wear and garments for representative occasions. On top of this, a large quantity of pieces of fashion jewellery can be seen, supplemented by original photographs.
The second chapter throws light on the Chanel classics, which have retained their fascination till today. Thus historical original examples of the Chanel Suit are juxtaposed with some 20 different adaptations of it, including models from other fashion houses, unknown ateliers and garment manufacturers. The procession of “lookalikes” and “distant cousins” by no means comes to an end with Chanel’s lifetime, but integrates aspects of contemporary fashion. A selection of the endless variations on the theme of the “little black dress” from the 1920s till the present will also be on show, some of them by designers such as Yves Saint Laurent, Max Heyman and Issey Miyake or Nina Ricci. They should by no means be seen as just copies of Chanel models. The short black dress was in keeping with the modern, dynamic lifestyle of the 1920s. Later the “little black dress” is an indispensable requisite in every woman’s wardrobe and, in the Fifties and Sixties, the epitome of Parisian chic.
In the third section, the focus is on Karl Lagerfeld’s creations for the House of Chanel. He succeeded in modernising the brand without sacrificing the features which were typical for it. The exhibition shows in particular items which quote the Chanel classics, or pay homage to his revered predecessor in some of their details. This selection, too, is complemented by fashion jewellery. The development comes full circle here, since Lagerfeld’s present winter collection for 2013-14 playfully quotes references to Coco Chanel’s legendary initial phase in the 1920s. More than 100 historical fashion magazines spanning a period from 1920 to 1971 can also be seen in the exhibition, including an issue of the American Vogue dated 1st October 1926 in which the “little black dress” is shown. Magazines were the most important medium for the propagation and reception of Chanel’s fashion. Visitors can leaf through them on the tablet computers provided.
Text from press release from the Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg website
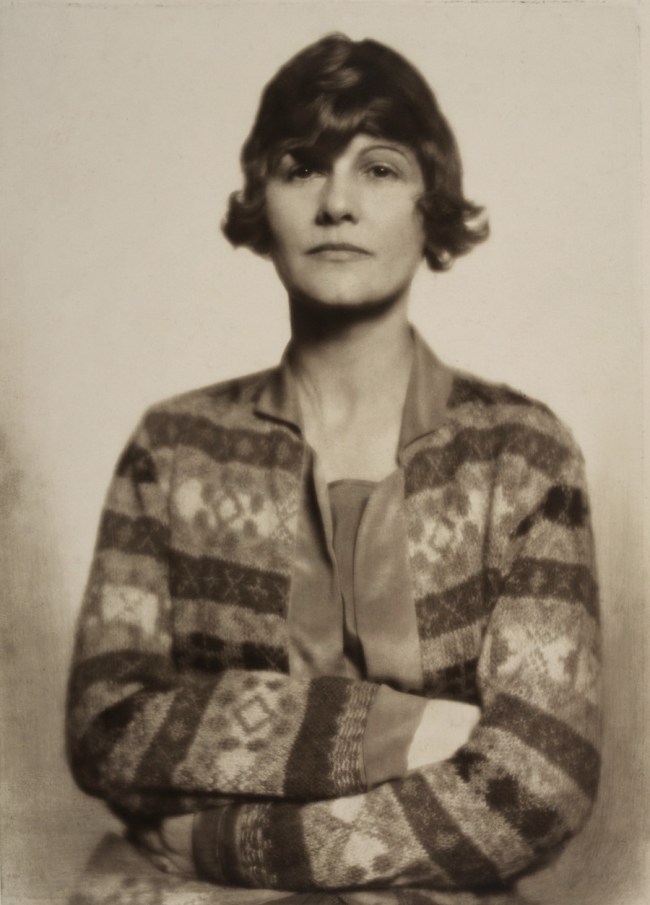
Aenne Biermann (German, 1898-1933)
Portrait of Anneliese Schiesser
1929
Silver gelatin print
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe, Hamburg
Hein Gorny (German, 1904-1967)
Portrait of a Woman
c. 1930/1972
Silver gelatin print, Reprint ofHeinrich Riebesehl
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe, Hamburg
Hein Gorny (1904-1967) was a highly versatile photographer. Self-taught, he had extensive, in-depth knowledge of photographic techniques and was specialised both in photographic and darkroom processes. He photographed a broad range of subject matter, including portraits, architecture, and animals as well as images used in industrial, commercial, and illustrational contexts. In addition he created experimental photographs, primarily working with macrophotography. Advertising photography was the field in which Hein Gorny carried out numerous commissions and was most well-known. He was primarily active in Hanover and Berlin. Hein Gorny is described by Heinrich Riebesehl as a “pioneer of modern commercial photography” in a catalogue published in conjunction with the Spectrum Photogalerie’s inaugural exhibition of 1972. He was masterful in his groundbreaking ability to fuse the photographic spirit of his time with the demands of advertising photography.
“Especially in his early work, the joy of experimentation and the openness to everything new and unusual is clearly visible. His positive attitude towards life, his carefree, almost exuberant way of using the medium of photography made him – consciously or unconsciously – adopt the taste of the times.” ~ Heinrich Riebesehl
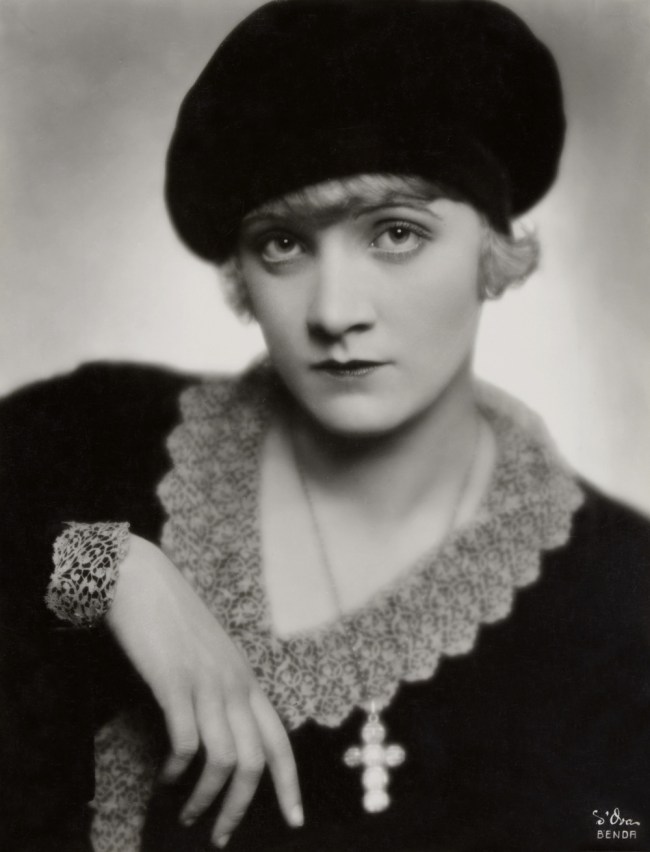
Atelier Benda/d’Ora
The actress Marlene Dietrich with beret
1927
Silver gelatin print
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg
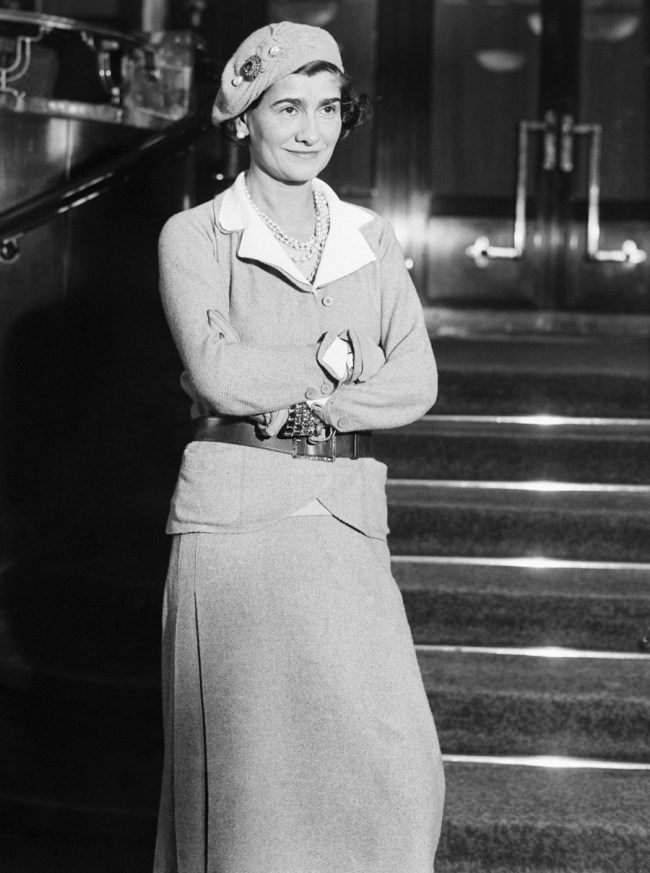
Madame D’Ora
The fashion designer Coco Chanel
about 1927
Silver gelatin print
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg
Dora Philippine Kallmus (20 March 1881 – 28 October 1963), also known as Madame D’Ora or Madame d’Ora, was an Austrian fashion and portrait photographer.
She became interested in the photography field while assisting the son of the painter Hans Makart, and in 1905 she was the first woman to be admitted to theory courses at the Graphische Lehr- und Versuchsanstalt (Graphic Training Institute). That same year she became a member of the Association of Austrian photographers. At that time she was also the first woman allowed to study theory at the Graphischen Lehr- und Versuchsanstalt, which in 1908 granted women access to other courses in photography.
In 1907, she established her own studio with Arthur Benda in Vienna called the Atelier d’Ora or Madame D’Ora-Benda. The name was based on the pseudonym “Madame d’Ora”, which she used professionally. D’ora and Benda operated a summer studio from 1921 to 1926 in Karlsbad, Germany, and opened another gallery in Paris in 1925. She was represented by Schostal Photo Agency (Agentur Schostal) and it was her intervention that saved the agency’s owner after his arrest by the Nazis, enabling him to flee to Paris from Vienna.
Her subjects included Josephine Baker, Coco Chanel, Tamara de Lempicka, Alban Berg, Maurice Chevalier, Colette, and other dancers, actors, painters, and writers.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Unknown photographer
Chanel
1931
© Corbis Images
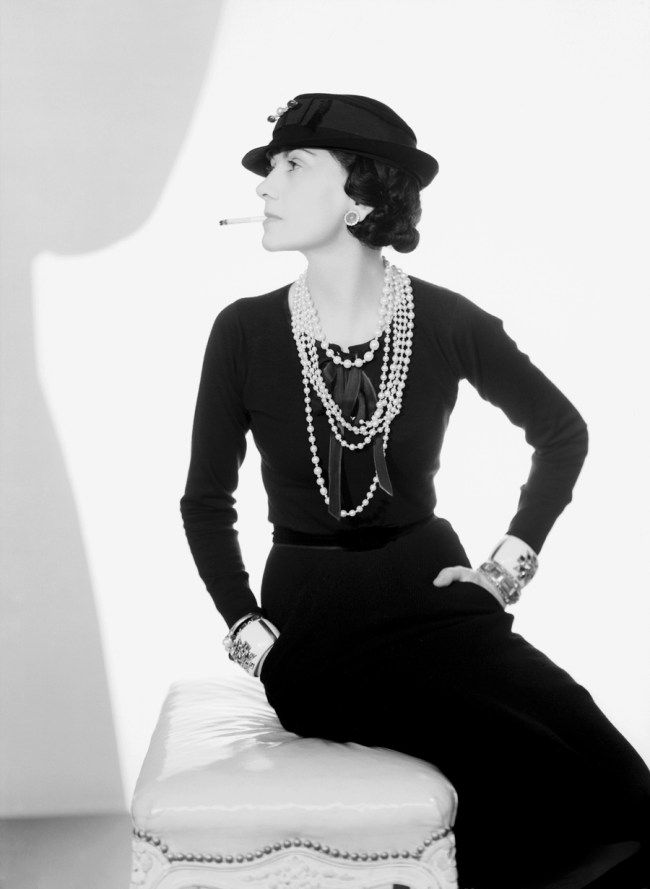
Man Ray (American, 1890-1976)
Chanel with cigarette
1935
© VG Bildkunst Bonn, 2014, and Man Ray Trust
Roger Schall (French, 1904-1995)
Ritz Apartment
Nd
© Roger Schall-Collection Schall
Roger Schall was a photographer during the interwar period, a contemporary of Brassaï. He excelled in photojournalism, in which he was one of the pioneers, as well as in the photographic disciplines of fashion and portraits. In the early 30s, the “revolution” Leica and Rolleiflex allowed him to fulfill his passion for images taken on the spot. Paris was his main exploration ground, where the night allowed him to capture and expose with strength and delicacy the particular shapes of a city made of diversities.
Text from the Artsper website [Online] Cited 25/03/2021
During World War II, Schall secretly documented the Nazi occupation of Paris. He also produced fashion photography for the fetish clothing company Diana Slip.
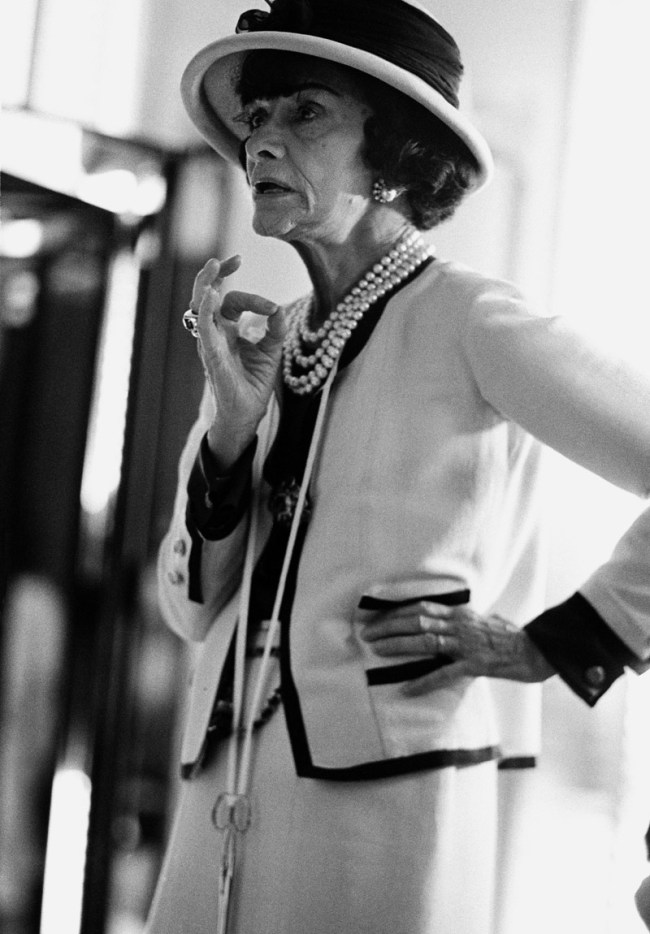
Douglas Kirkland (American, b. 1934)
Chanel im Atelier (Chanel in the studio)
1962
© Corbis Images
Coco Chanel
Gabrielle Chanel, who grew up in humble circumstances, opened her first Couture Salon in Paris in 1913, after she had already set up in business in 1908 as a modiste. In 1919 she moved to the Rue Cambon 31, which is still the address of the House of Chanel today. Coco Chanel’s first creative phase ended with the outbreak of war in 1939. Her fashion house stayed shut for 15 years before she dared a comeback in 1954, at the age of 70. The exhibition shows creations by Chanel from both periods. The “little black dress” becomes her trademark. Further models of day and evening wear show to what extent the fashion designer had her finger on the pulse of her time, and at the same time bear witness to the high quality of her models both in design and execution. In the 1950s and 1960s it is her women’s suits which cause a furore, first and foremost the “Chanel Suit”, which she first presented at a fashion show in 1957. Her celebrated quilted handbag, launched in February 1955 and called, simply, “2.55”, has long since attained the status of a classic and is a must in every collection of the luxury label. Her collections were always supplemented by matching fashion jewellery. Till today, Coco Chanel appears as an enigmatic and fascinating personality, and has been the theme of many films and books. Fierce controversy also surrounds her links to decision-makers of the Third Reich too, however, up to the present day.
The “little black dress” and suits by Chanel – their reception
he reception of Coco Chanel’s fashion and her style is already very widespread in her lifetime. A comparison with other contemporary couturiers reveals that Coco Chanel operated a very tolerant policy as regards the copyright for her models: The fashion designer allowed her models to be copied up to a certain point with her consent. For her, it was an acknowledgement of her eminence if women all over the world dressed in her style – an aspect whose influence on the “Chanel Legend” should not be underestimated, and which is investigated in this exhibition for the first time. In October 1926, the American Vogue magazine described a short black dress by Chanel as “The Chanel Ford – the frock that all the world will wear”. This drew a parallel between Chanel’s dress in its universality and modernity and one of the most important inventions of the time and prophesied a great future for it.
This is the birth of the “little black dress”. And although Chanel was not the first couturier to design simple black dresses for day wear it nevertheless remains inseparably linked with her name. Even the perhaps most celebrated “little black dress”, that worn by Audrey Hepburn in the film classic “Breakfast at Tiffany’s”, is often wrongly attributed to Chanel. The exhibition traces the development of the fashion classic from the 1920s till today. Another model which has gone down as an icon in fashion history is the “Chanel Suit” with its boxy, collarless jacket and often contrasting braided edgings. The term “Chanel Suit” is even quoted as a reference in the Duden. The exhibition shown here also document the fact that Coco Chanel produced a whole range of women’s suits which were adapted by other fashion houses or even home dressmakers. It is mostly no longer possible today to reconstruct whether individual models were made under licence or whether they were freely interpreted or simply copied. Irrespective of this, however, it is certain that all these models also made their contribution to the “Chanel Legend”.
Text from press release from the Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg website
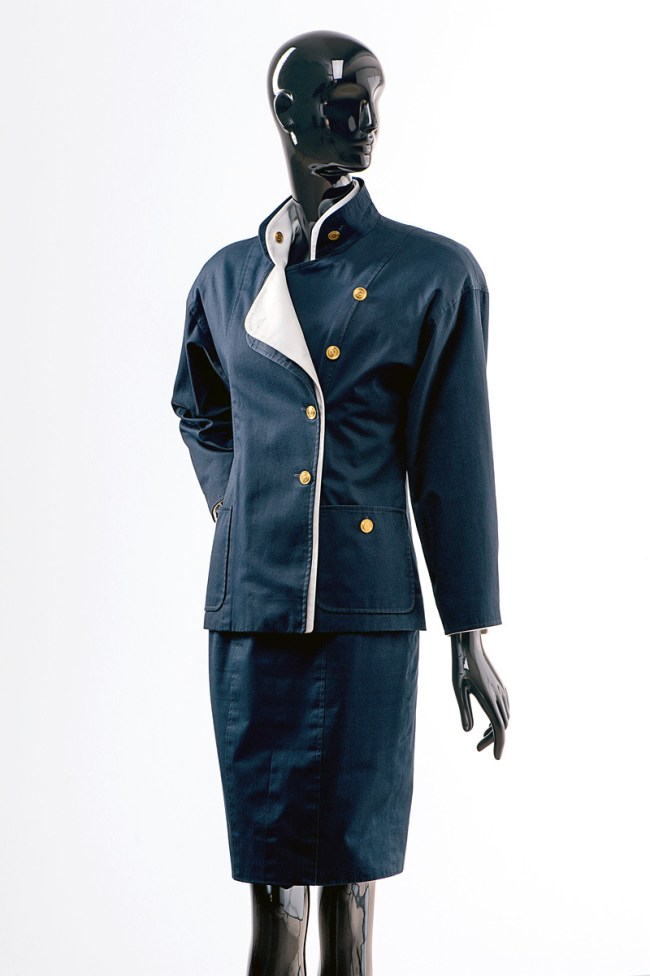
Gabrielle Chanel (French, 1883-1971)
Ensemble
1960s
Jahre Seidencloqué mit Lurex
Deutsche Kinemathek – Marlene Dietrich Collection, Berlin
© Draiflessen Collection, Mettingen, Fotografie von Christin Losta
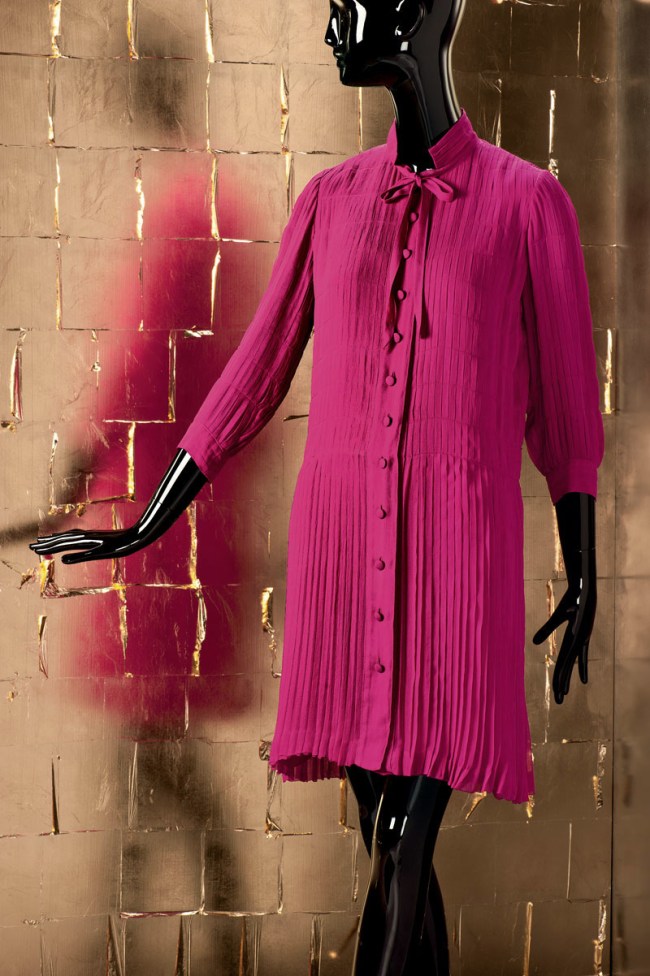
Gabrielle Chanel (French, 1883-1971)
Tageskleid/Day Dress
1960-62
Seiden-Crêpe de Chine
Gemeentemuseum, Den Haag
© Draiflessen Collection, Mettingen, Fotografie von Christin Losta
Gabrielle Chanel (French, 1883-1971)
Costume, C. H. Kuehne & Zn
Autumn / Winter 1966/67, licensed by Chanel
Silk brocade
Gemeentemuseum, Den Haag © Draiflessen Collection, Mettingen, Fotografie von Christin Losta
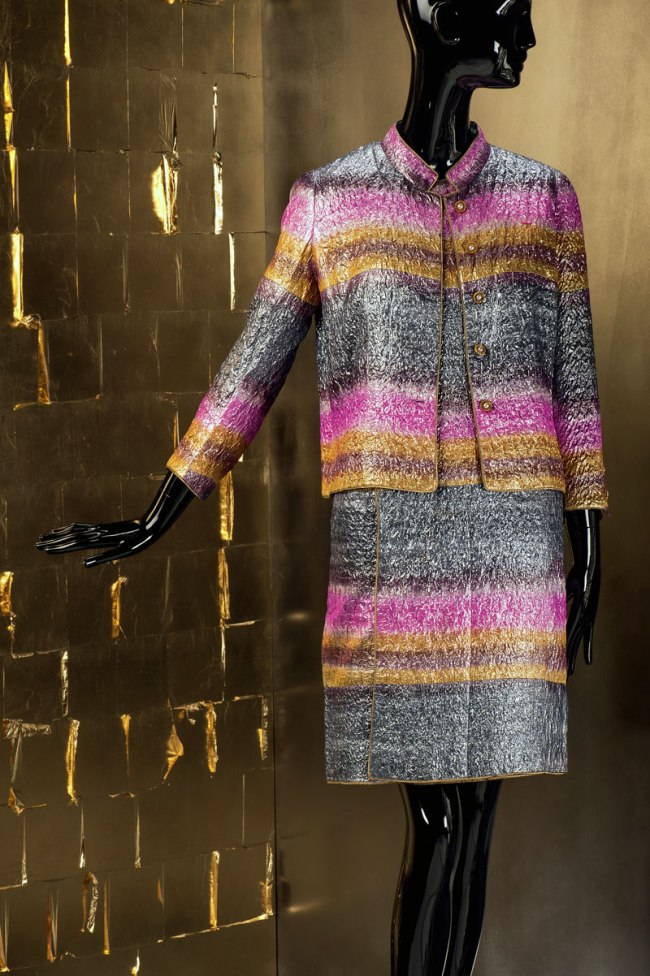
Karl Lagerfeld (German, 1933-2019)
Costume, Chanel Boutique
Autumn/Winter 1989/90
Wool tweed, Wool georgette
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg
© Draiflessen Collection, Mettingen, Fotografie von Christin Losta
Karl Lagerfeld (German, 1933-2019)
Costume, Chanel Boutique
Spring/Summer 1986
Cotton poplin, cotton pique
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg
© Draiflessen Collection, Mettingen, Fotografie von Christin Losta
Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe Hamburg
Steintorplatz, 20099 Hamburg
Opening hours:
Tuesday to Sunday 11am – 6pm
Wednesday and Thursday 11am – 9pm





























































![Eugène Atget (French, Libourne 1857-1927 Paris) 'Untitled [Atget's Work Room with Contact Printing Frames]' c. 1910 Eugène Atget (French, Libourne 1857-1927 Paris) 'Untitled [Atget's Work Room with Contact Printing Frames]' c. 1910](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/atgets-work-room-web1.jpg?w=650&h=783)
![Eugène Atget (French, Libourne 1857–1927 Paris) 'Untitled [Atget's Work Room with Contact Printing Frames]' c. 1910 (detail) Eugène Atget (French, Libourne 1857–1927 Paris) 'Untitled [Atget's Work Room with Contact Printing Frames]' c. 1910 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/atget-workroom-detail-web.jpg)


![Marie-Charles-Isidore Choiselat (French, 1815-1858) Stanislas Ratel (French, 1824-1904) 'Untitled [The Pavillon de Flore and the Tuileries Gardens]' 1849 Marie-Charles-Isidore Choiselat (French, 1815-1858) Stanislas Ratel (French, 1824-1904) 'Untitled [The Pavillon de Flore and the Tuileries Gardens]' 1849](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/the-pavillon-de-flore-web.jpg)






![Edward J. Steichen (American born Luxembourg, Bivange 1879 - 1973 West Redding, Connecticut) 'Untitled [Brancusi's Studio]' c. 1920 Edward J. Steichen (American born Luxembourg, Bivange 1879 - 1973 West Redding, Connecticut) 'Untitled [Brancusi's Studio]' c. 1920](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/edward_steichen_brancusis_studio_1920-web.jpg?w=650&h=816)
















































You must be logged in to post a comment.