Exhibition dates: 7th May – 21st August, 2016
Curator: Susan van Wyk
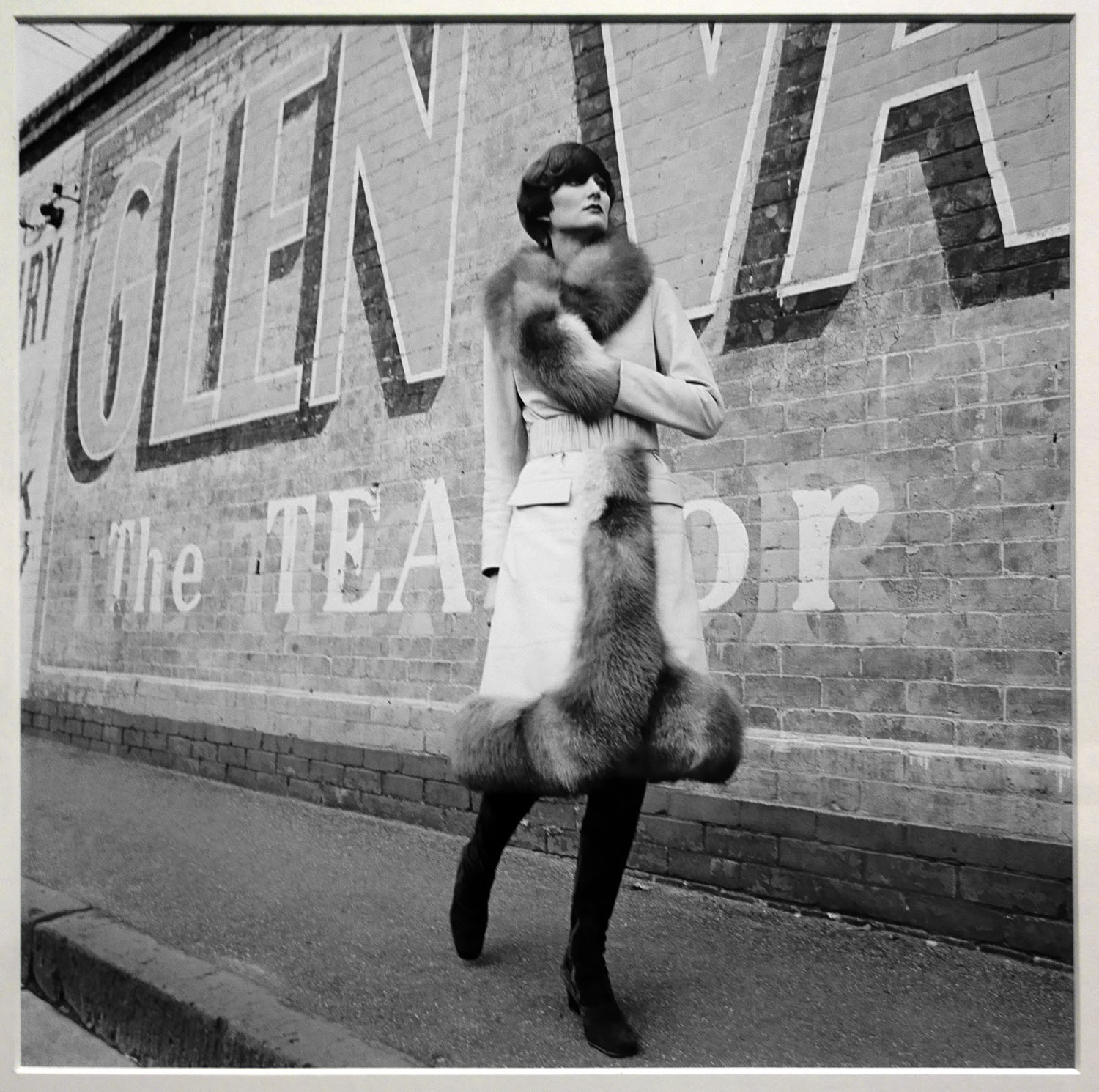

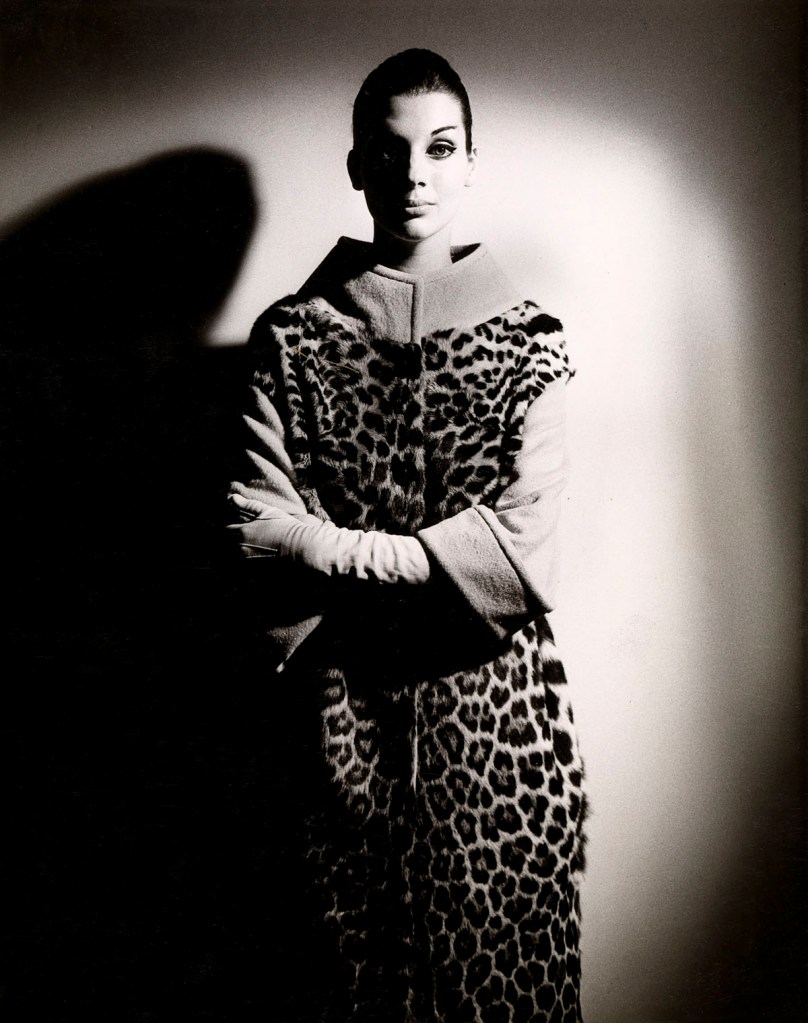
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Lisal of Melbourne) (installation view)
1971, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
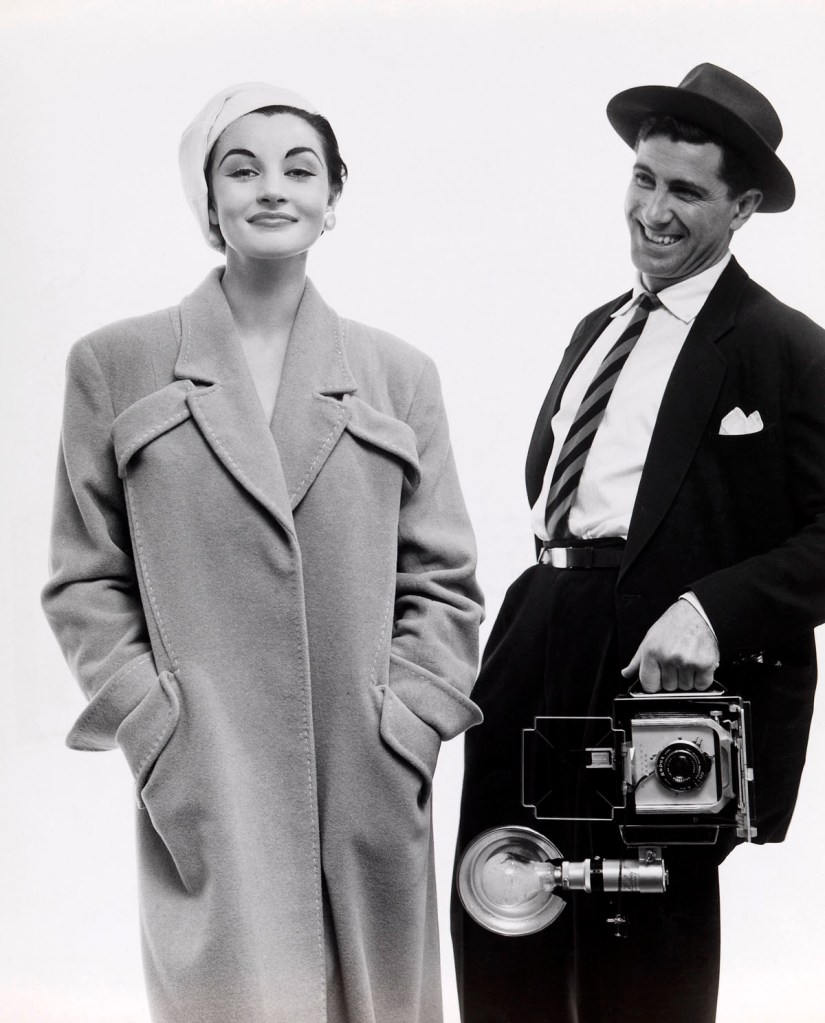
To be frank, this handsomely installed exhibition of the work of Australian fashion photographer Henry Talbot is a bit of a let down. The images look terribly dated, and while historically they have some significance in terms of the time and context from which they emerged – the movement towards en plein air photography, taking the model from the studio to the street – most of the photographs are not very good. The prints are either commercial vintage prints with all their faults (dust, scratches, poor printing, over exposure, lack of burning in etc.) evidencing a lack of care and attention to detail, or modern inkjet reproductions from original negatives and even then some of the printing is poor: for example, the hair of the model in Fashion illustration for Blunden Wool, models Joan Crellin and Bruce Anderson (1961, below) is completely blown out with no detail retained in the highlights. Some of the angles in his images (the positioning of the figure) are just off, the cropping of the negatives (the space above and below the figure) often does not work and framing of the prints is also less than exemplary. But we must remember Talbot was a commercial photographer from the 1960s and that’s just what these photographs are: commercial fashion photographs that fulfil a client brief.
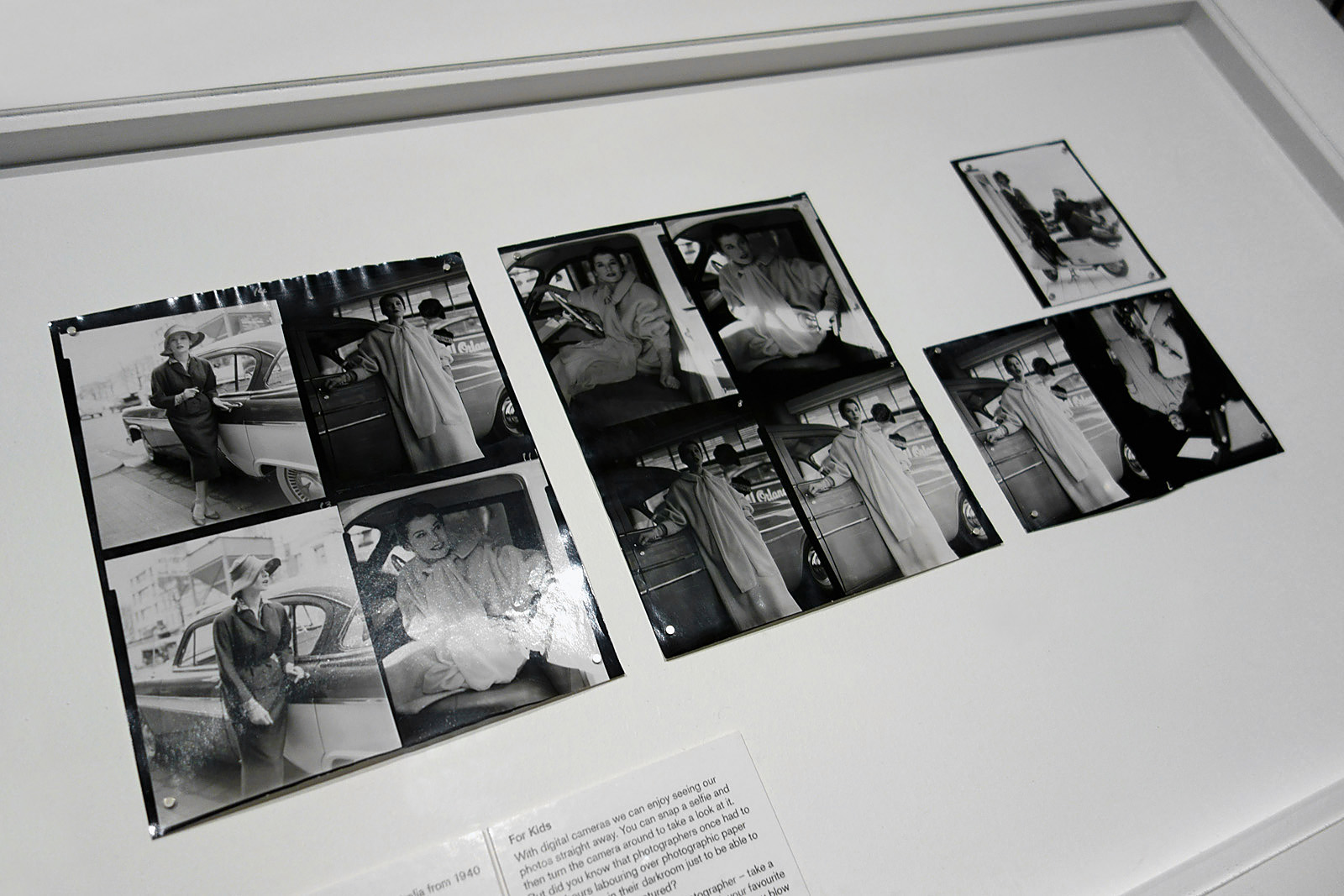
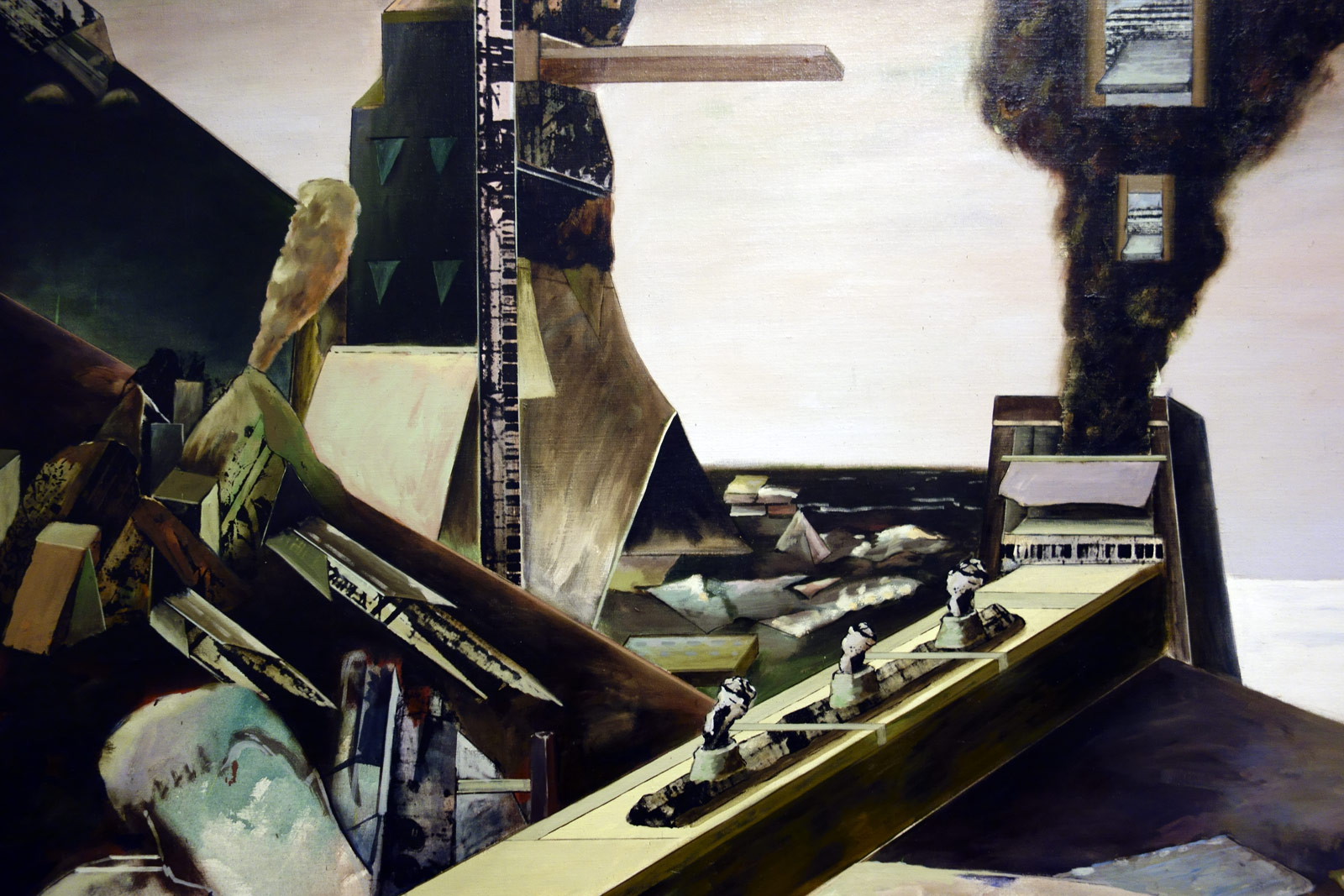
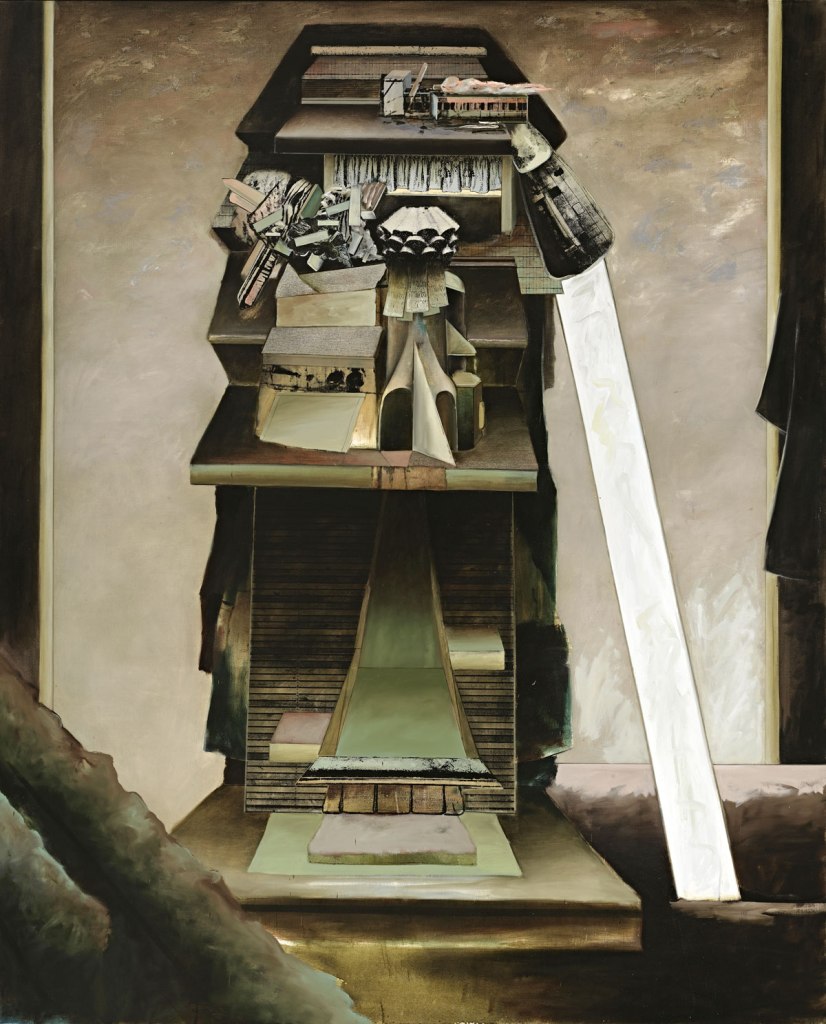
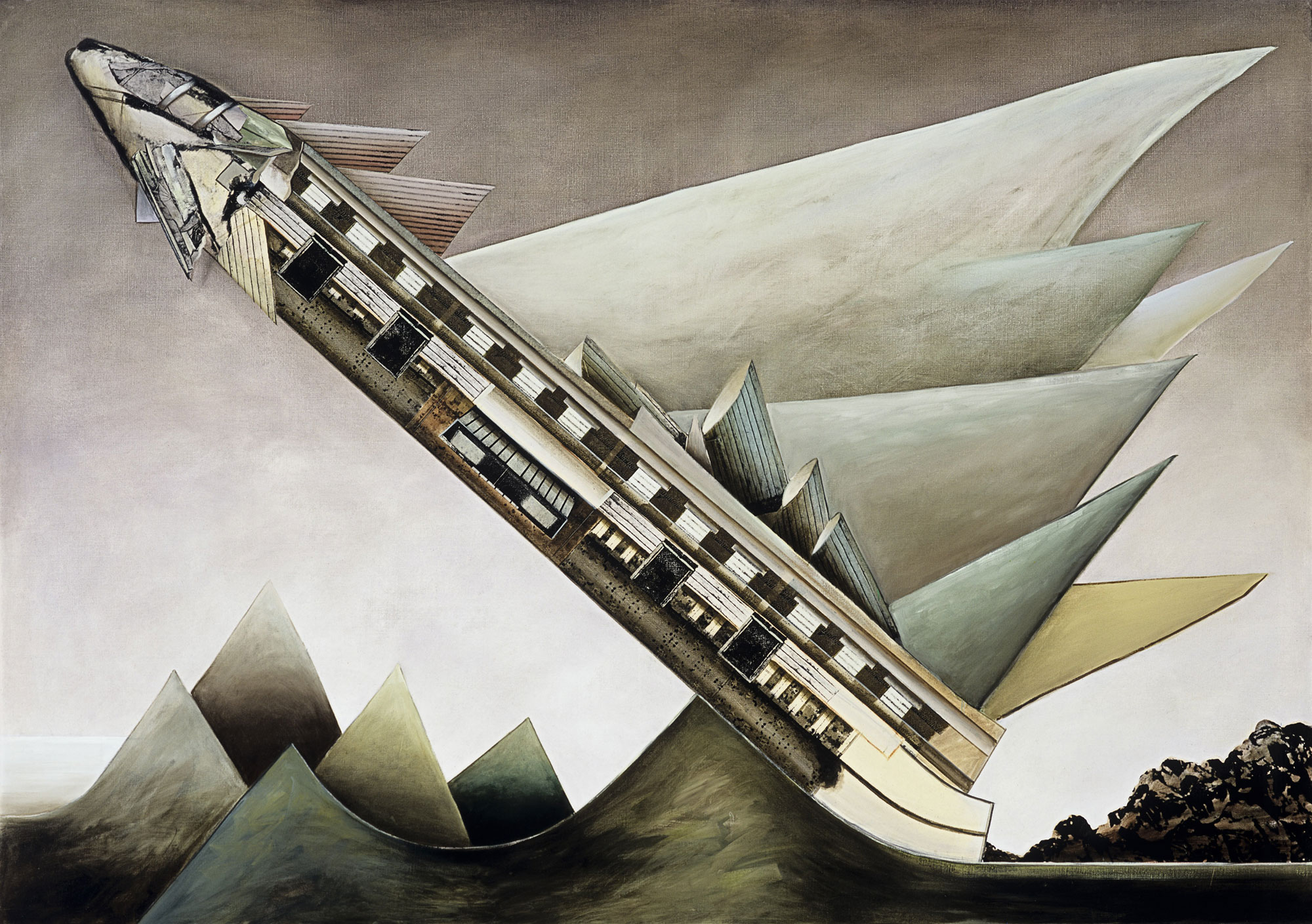
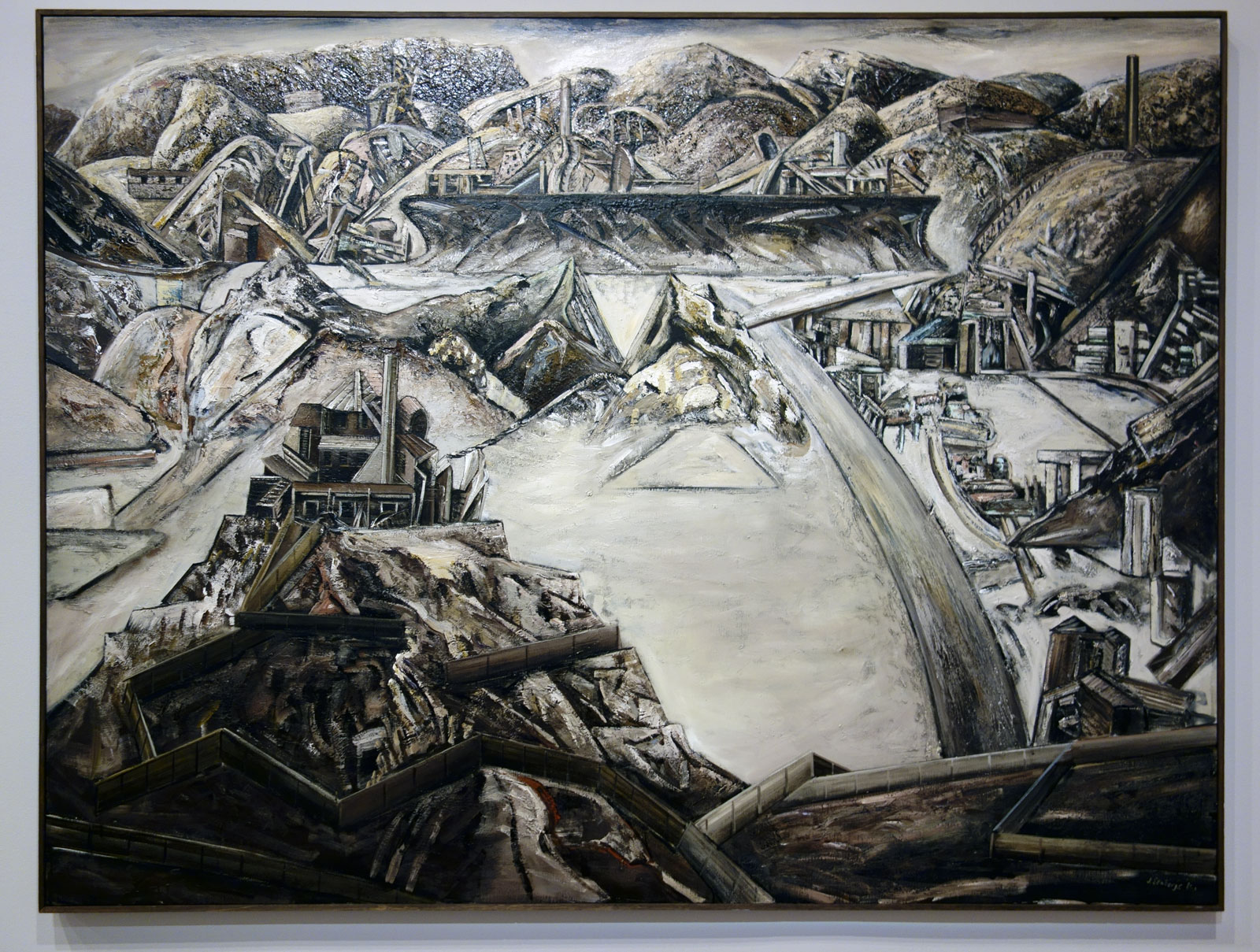
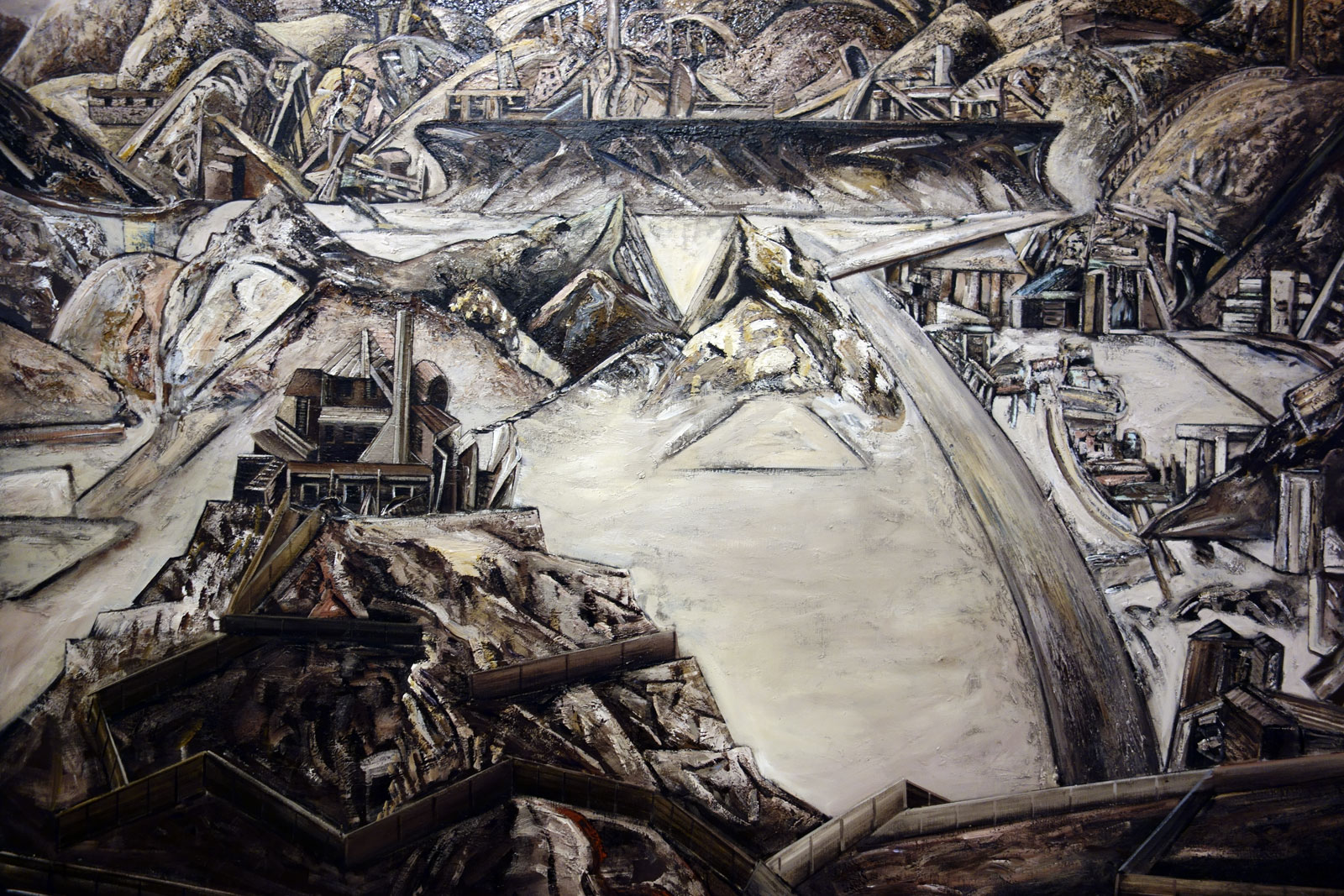
Talbot was no experimenter. Too often his images are really basic, a basic visualisation, and he has a fixed idea for a shot and goes with that idea and variations of it, even when it is evident that the photograph is not working. Any photographer worth their salt would recognise such a situation and be flexible enough to change it up but with Talbot this does not happen. Positioning his model centrally, he usually uses low depth of field so that everything falls out of focus behind. In this sense he still seems to possess a studio mindset. While professing his love of free-moving fashion, his photographs seem stilted and conformist, even as they are taken out of doors. His proof sheets are evidence of a “team” oriented focus in order to fulfil a client brief, but in these very proof sheets we see uneven exposures and severe cropping into the frame to get the final image. And while he was more romantic than the hard edged Helmut Newton, his photographs only ever project a surface and rarely show any true emotion. Without doubt his best two photographs are Fashion illustration for Fibremakers, model Maggi Eckardt (1966, below) taken at the Altona Petrochemical Company. The photographs are a symphony of form, movement and light. They possess a “feeling” a lot of his other photographs simply cannot, and do not, contain.
There is no catalogue to the exhibition so this posting will have to serve historically to document the exhibition and Talbot’s work. Thus, there is an in depth interview included with Australian curator, artist and photography collector Joyce Evans who ran Church Street Photographic Centre in Melbourne from 1976 and who showed Talbot’s work in her gallery. It is all very well that I have an opinion on the work but what I write needs to be an informed opinion, and the interview with Joyce provides valuable background with regard to the people, the era and the context from which these photographs emerged. One thing noted in the conversation is that Talbot photographed strong, independent women like Janice Wakeley and Maggie Taberer… something that is not mentioned at all in the wall text and press release that accompanies the exhibition. I would have thought it vital that a curator would have linked the presence of these independent women in fashion photography to the work of art photographers such as Australian artist Carol Jerrems who published her seminal book A Book About Australian Women in 1975.
Another insight into the times is provided by a friend Ian Lobb who knew Talbot:
“People said he was good, and he charged enough, but he just thought he was having fun, fun with a certain quality. I don’t think he had any grand ideas about his talent, but he was quite prepared to sell a print or sell his time if someone wanted to pay. Henry knew the fun he was having wasn’t going to last beyond his life. And now, it is weird and very country town that his work should be regurgitated. His work looks poor because people are making him into something he wasn’t.
There is a seminal incident that can help with the context of the Henry Talbot, Athol Shmith and Helmut Newton generation. Athol Shmith was giving a print critique at Prahran, and someone had left a glass of fixer on the shelf of the room. Athol finished his critique and drank it. Rushed to hospital of course. But think of that from all its angles. The world in which these photographers worked and the stories from those times reveal a world that was flying by the seat of its pants – just.”
Talbot is a solid photographer, no more. While the exhibition gives some sense of depth to the quality of work that was coming out of Melbourne at that time, perhaps it would have been best to let sleeping dogs lie.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the National Gallery of Victoria for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image. Some installation photographs as noted © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria. All the rest as noted taken by Brooke Holm for the National Gallery of Victoria.
In conversation with Australian curator, artist and photography collector Joyce Evans about the Australian photographer Henry Talbot
17/07/2016
MB: Just before we started this conversation you said to me Joyce that Talbot was a gentle man. Can you explain what you meant by that please?
JE: I use the word gentle in comparison to his one-time partner Helmut Newton, who I found to be an aggressive man.
MB: So they were in partnership together before Newton left for Europe
JE: Yes
MB: So Talbot was intelligent, he knew his field and understood the history of the genre that he was working in, he could speak well, and was well liked both by clients, models and the society in which he worked.
JE: Well, he was not a superficial person. When he spoke he researched things properly, he had the depth of knowledge which came from a sort of European intellect. This intellect was broadly read, and he was also a person that listened.
MB: And he was also a good teacher as well…
JE: In his commercial work, Henry photographed his women (as far as I could see), with the idea of having a client, and he was displaying clothes on the women, which was part of the old tradition. In an environment where, if you wanted to make a living, that’s what you had to do. If he had been, however, in a place like New York – which was avant-garde as compared to Melbourne, which was not avant-garde – he may well have gone the same way as Helmut Newton. The very big difference, though, is in the personality of the two men.
Helmut Newton went out and he was an aggressive man. He had charm, but it was an aggressive charm, it wasn’t a gentle charm. He had intelligence and he knew how to handle his women so that he got aggression out of his women, that’s what he wanted.
MB: Whereas Talbot was doing it for a job?
JE: Talbot A was doing it for a job and B, he had a gentle nature. He was not an aggressive man and actually if you look at those photographs you can see that he liked the women that he photographed and he lived in an environment where fashion was still, fairly soft, in many ways. You can see in things like the swimwear industry and the sports industry there was quite a lot of Australian independence, but he, combined with Athol Shmith in Melbourne, took his models out into the street, they interacted with the environment, and he did not depend on the studio.
MB: When I look at his photographs they are quite modernist, they are quite clean, but his vision seems to me to be quite limited… in the sense that he uses a central female figure (sometimes two central figures), low depth of field, out of focus background. And then you look at the proof sheets and you can see that he is not an experimenter. From shot to shot there is a slight change in angle of a hand or the tilt of a head but he really doesn’t push the boundaries of what he is trying to say with the image. He has his set idea (for the shot, for the location) and then he does slight variants in the proof sheet towards that idea. Very rarely do you get a feeling, a sense of atmosphere in his images – of the outdoors in the sense of the outdoors enveloping the model. The models seem to be isolated within their environment…
JE: But who does what is asked of him, at that time? You can compare him to Avedon or Athol Shmith, but you cannot compare him to today. You cannot ask someone to work outside of his own time. You can ask him to lead in his own time and the leading that occurred at that time, by both Shmith and Talbot, was that they took models out into the city and the environment and away from the studio. This was something that Avedon did and these two photographers did also. The big argument is, did Talbot do it effectively? Who chose his proofs? Which ones got published?
MB: But also, a quite organised and restricted view of the world, even though he was pushing the boundaries by taking fashion photography outdoors, he still seems to be in a studio mindset when he was outside.
JE: What you did in those days, is that you would do the shoot, you would come in with your proof sheets, and the art director would go over it with the red crayon with the team – it tended often to be team work. So he’s working to a brief …. and you are the instrument of the team. The art director sets everything up and you do the shoot. Now, when you get a name like Talbot had, you could start to begin to influence what the art director was doing. Now, how much and when and at what time and what effect – I really don’t know.
MB: Did he photograph strong women? You mentioned Maggie Taberer and Janice Wakeley.
JE: Maggie Taberer and Janice Wakeley – both educated women, well read women – Talbot would have chosen his own models and they were two of his favourites. Or been offered models, depending on the control of the art director and what they desired.
MB: Today, all we can do is try and understand the history of these photographs, and the time and context from which they emerged. From today’s standpoint they look rather dated and stilted.
JE: You have to see them from a decade earlier, looking at fashion photography in Australia from the 1930s and 1940s to see what was happening. The 1930s fashion stuff was very very largely in the studio. Very little of it was en plein air.
MB: But that doesn’t negate his aesthetic choices to shoot with so low a depth of field that the context of the outdoors becomes more or less irrelevant. Yes, you have the images of the oil refinery behind with the movement of the women, in my opinion some of his best photographs, that are more romantic in feel… and these tend to work better than other more prosaic shots.
JE: He was more of a romantic than Newton was. Newton was very hard edged and he managed to get that extra particular something out of his women…
MB: Even in his Melbourne images?
JE: Well, we don’t know Newton’s Melbourne images, because he has denied them all.
MB: Yes exactly, that’s the thing.
JE: Thinking about Talbot, he was part of a movement. He wasn’t the leader of it or the only one, but he was part of the early evolution of the movement.
MB: Does that mean his photographs stand up to scrutiny today?
JE: I have this feeling that when you only look at the top of the cake, you don’t know what the cake is all about. I don’t know whether I would put him as the fairy on top of the cake or one of the really nice pieces of icing. I think that Athol Shmith is a stronger photographer.
MB: What about the Australian photographer Bruno Benini? I find him incredibly strong in terms of his style, his lighting.
JE: My understanding of Bruno is that he is a decade younger that Talbot…
MB: So 1950s?
JE: Yes I think so
MB: So he has a more classical influence…
JE: It’s not that, he’s like John Eaton is to Pictorialism, he’s a very good photographer – but he’s not a groundbreaker, he’s not of the beginning of Pictorialism. I think Benini is a very good fashion photographer and I think he is working on other people’s shoulders. I think Athol Shmith is stronger and if I had a choice about having to show one, but I like the fact that we have shown Talbot, because it gives some sense of depth to the quality of work that was coming out of Melbourne. Places like Sportscraft were exceptionally good at encouraging talent, both in design and in photography.
MB: All I can do is understand the history and the context and what was going on at the time and then, as I was thinking the other day, all I can write is what I see.
JE: Compare this… Athol Shmith had Bambi. Bambi was the most exquisite women you would ever find in your whole life. I remember her when I was a teenager, me and my girlfriend were both sitting in a room and she was there, both in our late teens / early 20s, and I remember saying to my friend that I feel as though I have ten feet – and I am so clumsy when I look at her. She is so beautiful. Now Janice Wakeley was also a stunning looking women as was Maggie Taberer. But the number one model with Athol was Bambi and then there were really other top people that he had. And he, I think, had a much broader base to work with – not only his models, but his clientele was broader. Talbot was predominantly clothing as compared to Shmith who did a whole stack of things other than fashion. His love of music, he did a lot of musicians, he did some amazing portraiture. Shmith did H.G. Wells etc…
MB: His breadth was greater than Talbot. My concern with Talbot is 1/ the dating of the images, and 2/ his aesthetic choices when taking those photographs which may be a team decision but, the fact that he didn’t experiment that much. When looking at his proof sheets there are only slight changes to the positioning of the model…
JE: He’s got an idea and he goes for it.
MB: And that just really shows a lack of flexibility in his vision.
JE: No, I don’t think so I just think that it shows that he knows what he wants and that’s it.
MB: I think that is where we differ.
JE: He is very professional. How many shots of a person do you make at a time?
MB: I work on a ratio of 10 to 1, so if you take 10 shots you will get one, possibly two excellent shots. Talbot must have been thinking I need one good shot and he kept shooting and shooting, even though some of his exposures are poor, even though he radically crops the full frame image to get the final shot. It shows he was not as confident as you think about getting the shot, because he is hedging his bets with his in camera framing, relying on cropping later.
JE: He knows he wants her getting this feeling, and he goes bang, bang, bang, head turned slightly, arm down slightly and that’s it… and he knew what he wanted at the beginning and then he just saw the variations to fine tune it. And that’s what every photographer tends to do.
MB: And that’s where I really think there is a problem with his photography. Most of his images don’t really work – and yet he never recognised that fact at the time, when he was taking or setting up the shot, that it was not working. Any good photographer worth his salt, worth his previsualisation of the shot, must know how to adapt and be flexible enough to change on the run. He didn’t recognise that they weren’t working and change the idea. That’s the problem I have with him. It shows a fixed mindset in terms of not being able to see through the viewfinder when a shot is not working.
JE: That’s another story…
MB: Let’s leave it there. Thank you Joyce so very much for your thoughts.
“Well man, this is 1966 and in this game you have to be open to, and live, contemporary influences to a certain degree. The younger generation is very strong in fashion – very much in command. They’re spending a great deal of money in the garment industry, so fashion is geared to the young. There is, of course, in this “with it” idea itself, certain conformity to non-conformity, to a non-conformity standard. But, as a photographer, you must accept this idea as far as you can and that probably reflects to some extent in your own behaviour and dress.”
Henry Talbot, 1966
“I always tried to show models in a free-moving fashion. I avoided stiff poses and I tried to keep up with what the great fashion photographers overseas were doing”
Henry Talbot
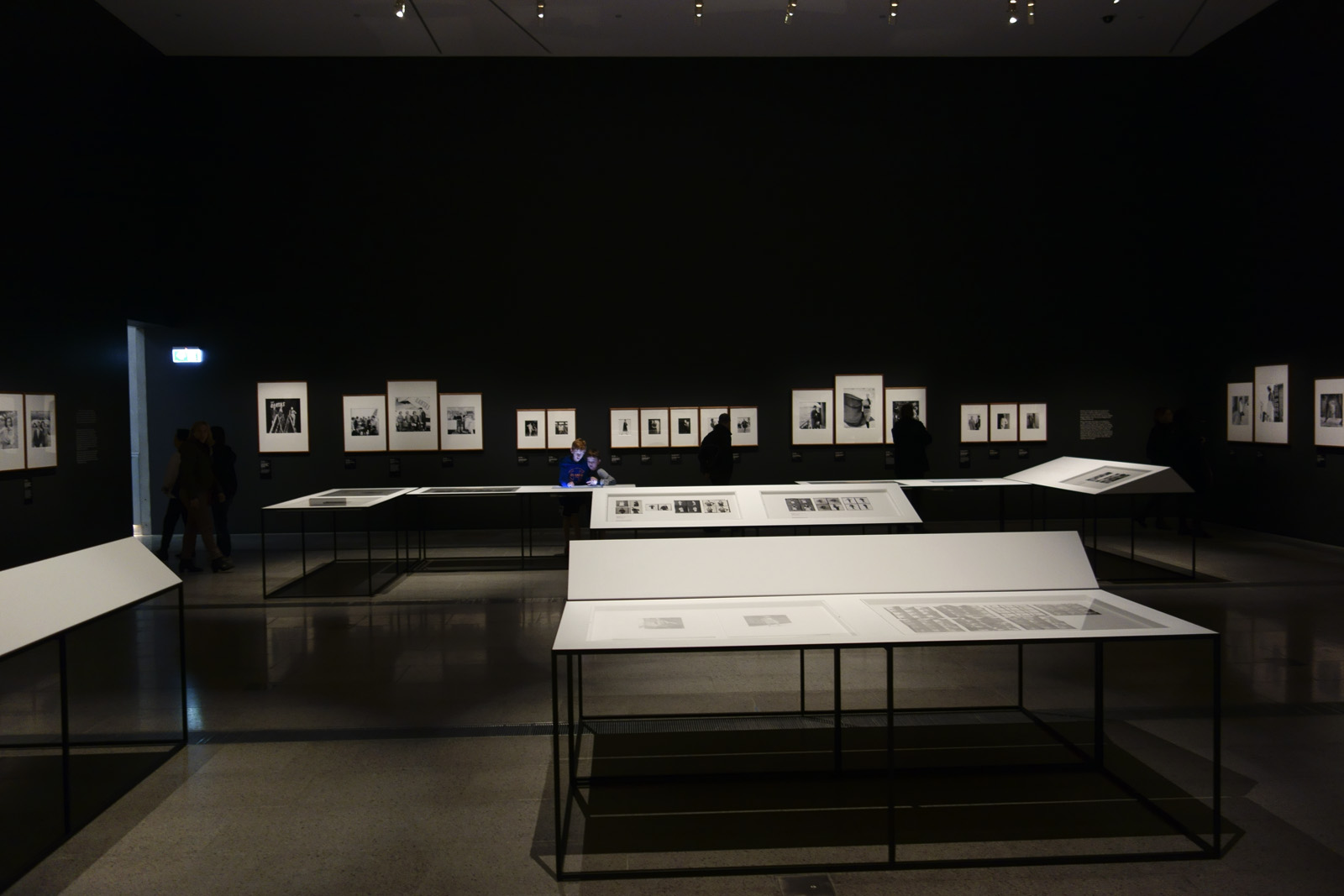
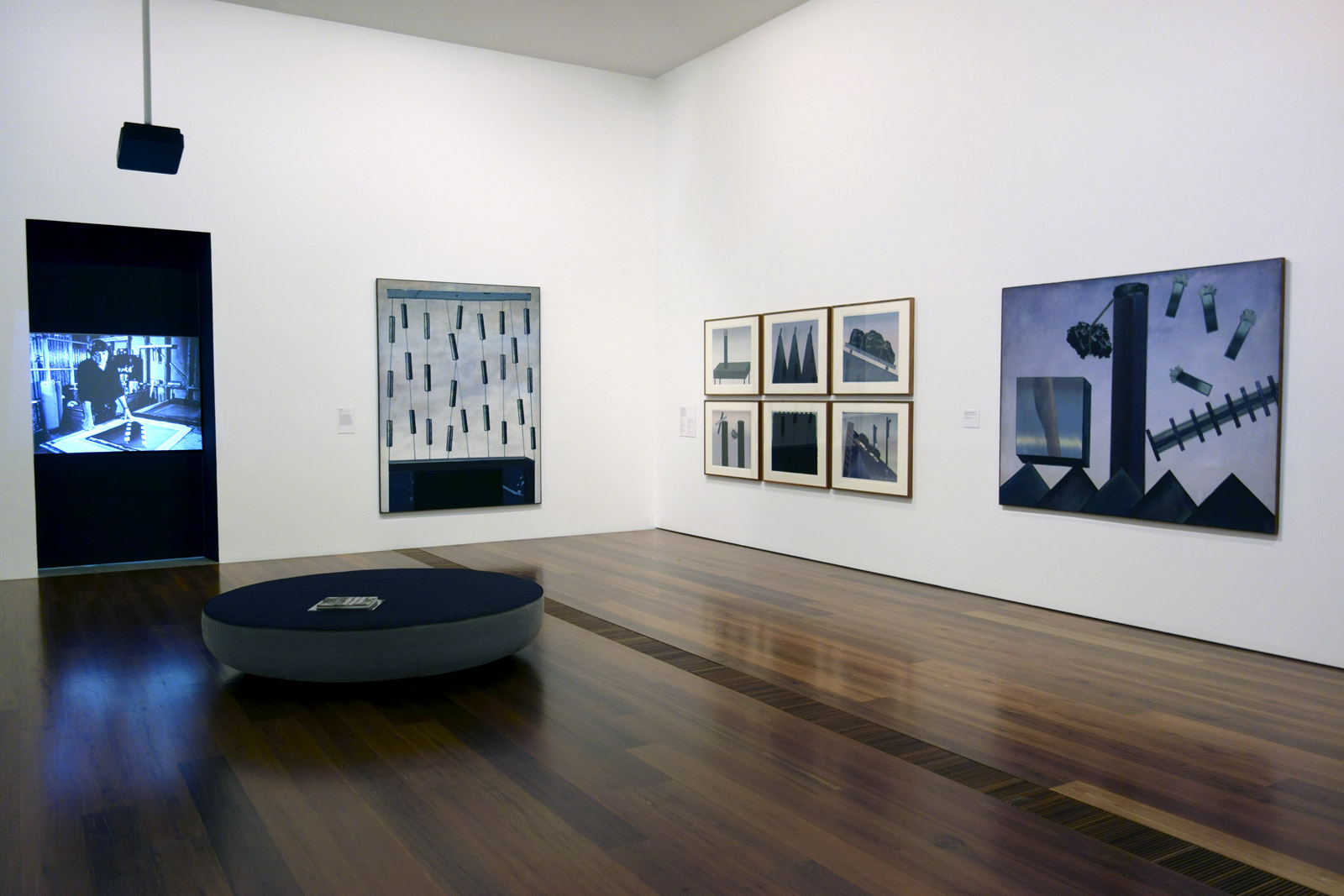
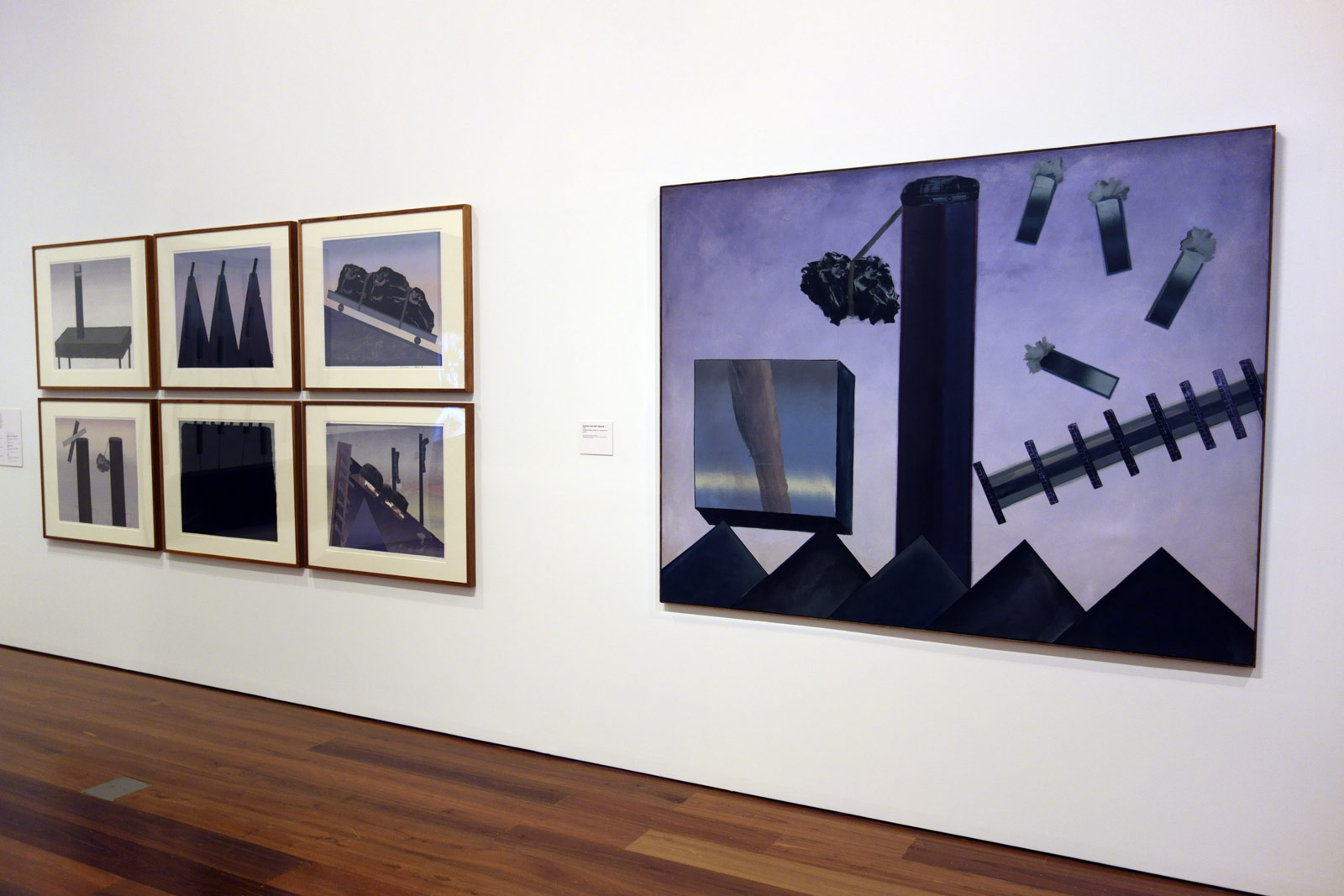
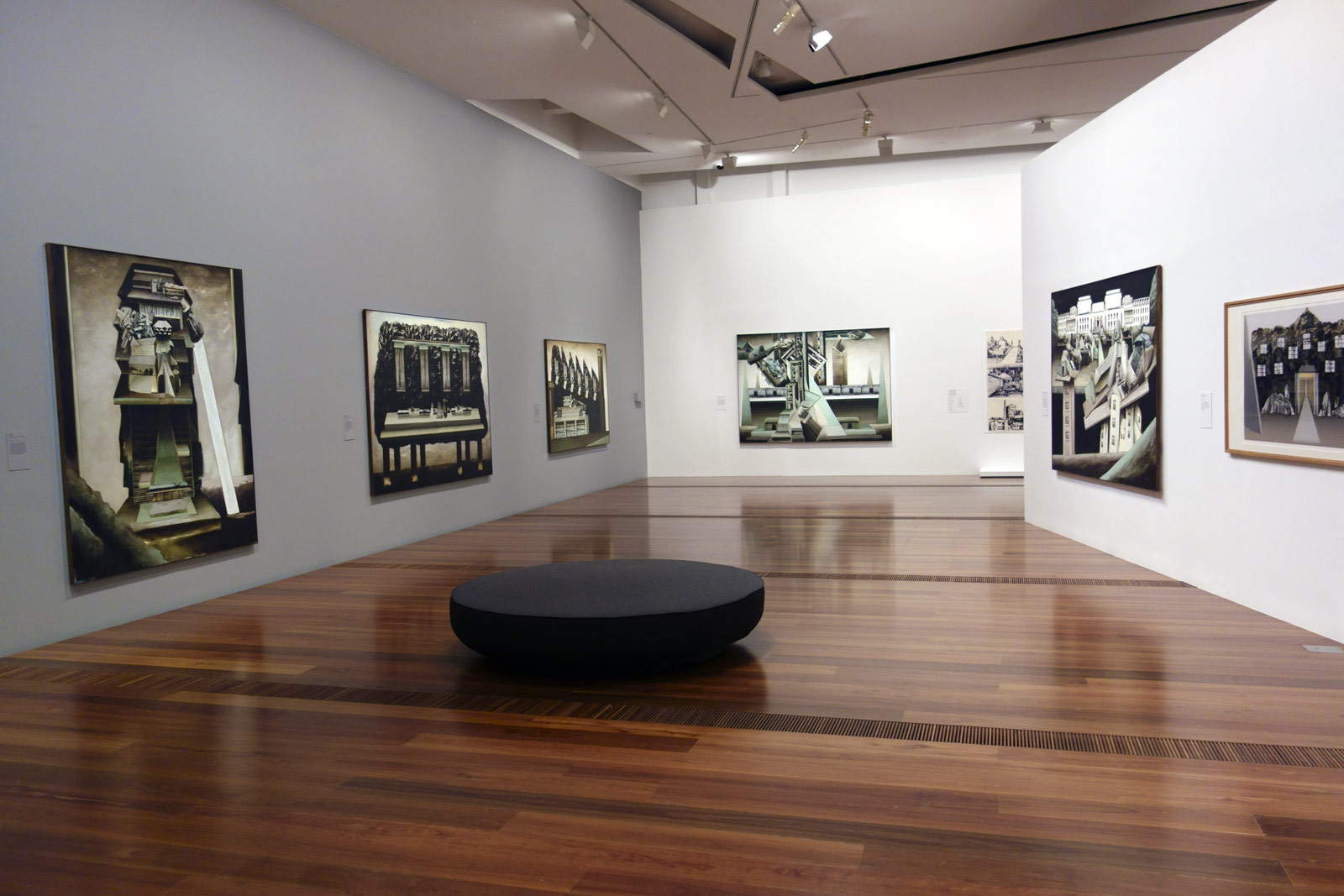
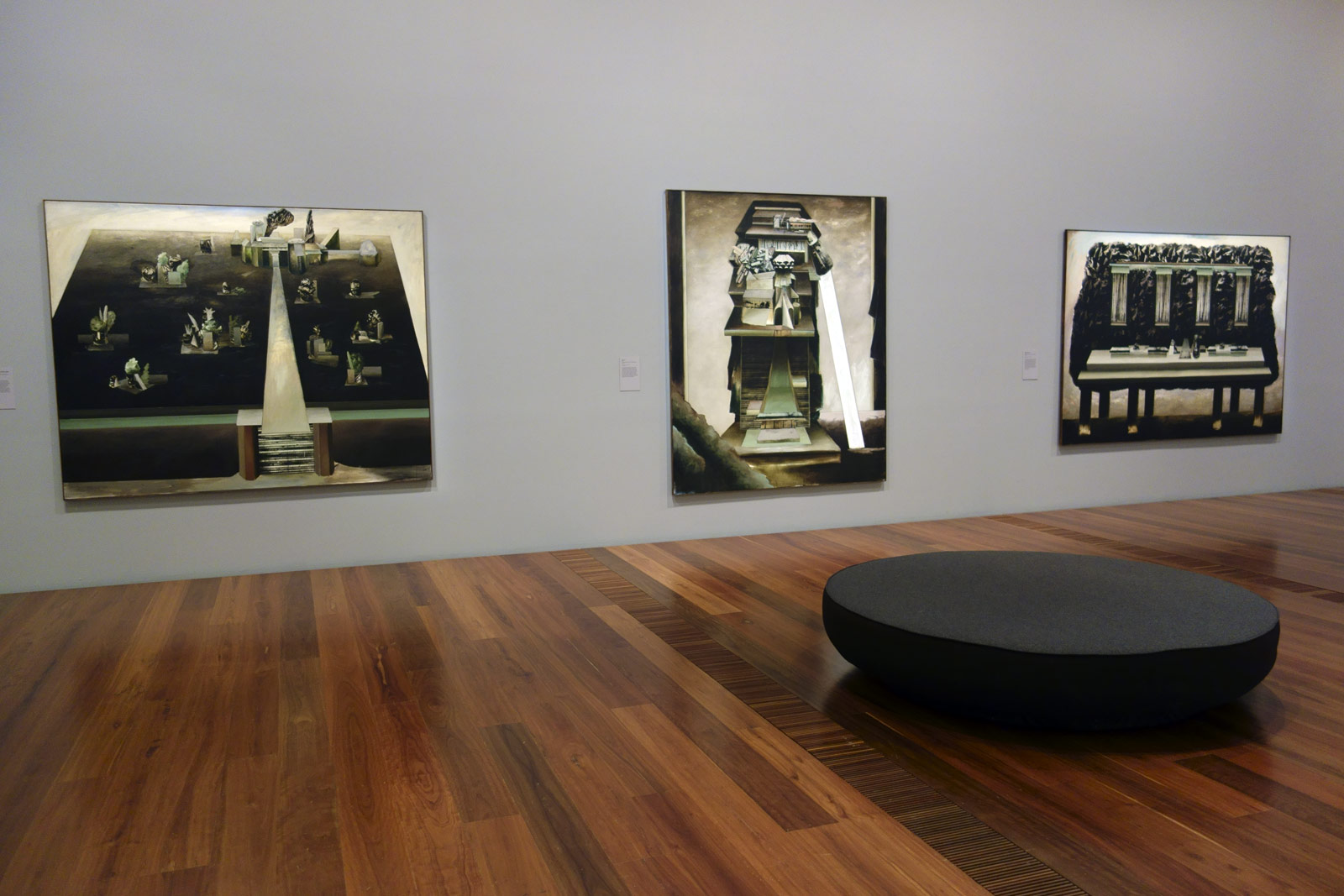
Installation views of the exhibition Henry Talbot: 1960s Fashion Photographer at The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia, Melbourne
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
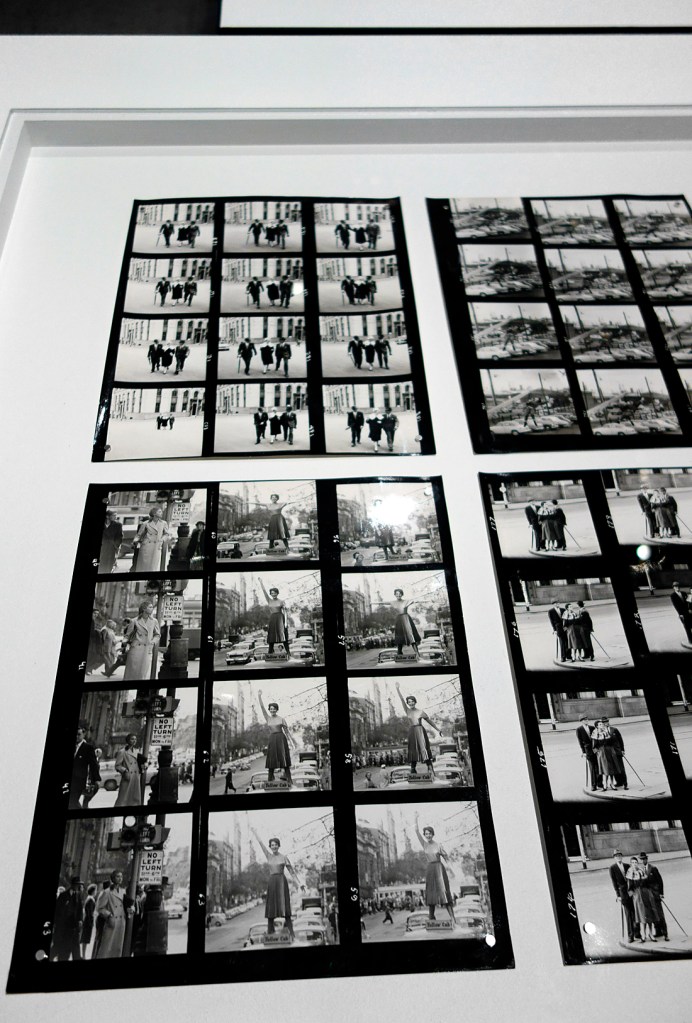

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
Collection of proof sheets (installation view)
1958-1972
Gelatin silver photographs
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Blunden Wool, models Joan Crellin and Bruce Anderson) (installation view)
1961, printed 2016
Photographed on location at the National Gallery of Victoria
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Blunden Wool, models Joan Crellin and Bruce Anderson) (installation view)
1961, printed 2016
Photographed on location at the National Gallery of Victoria
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Blunden Wool, models Joan Crellin and Bruce Anderson) (installation view)
1961, printed 2016
Photographed on location at the National Gallery of Victoria
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
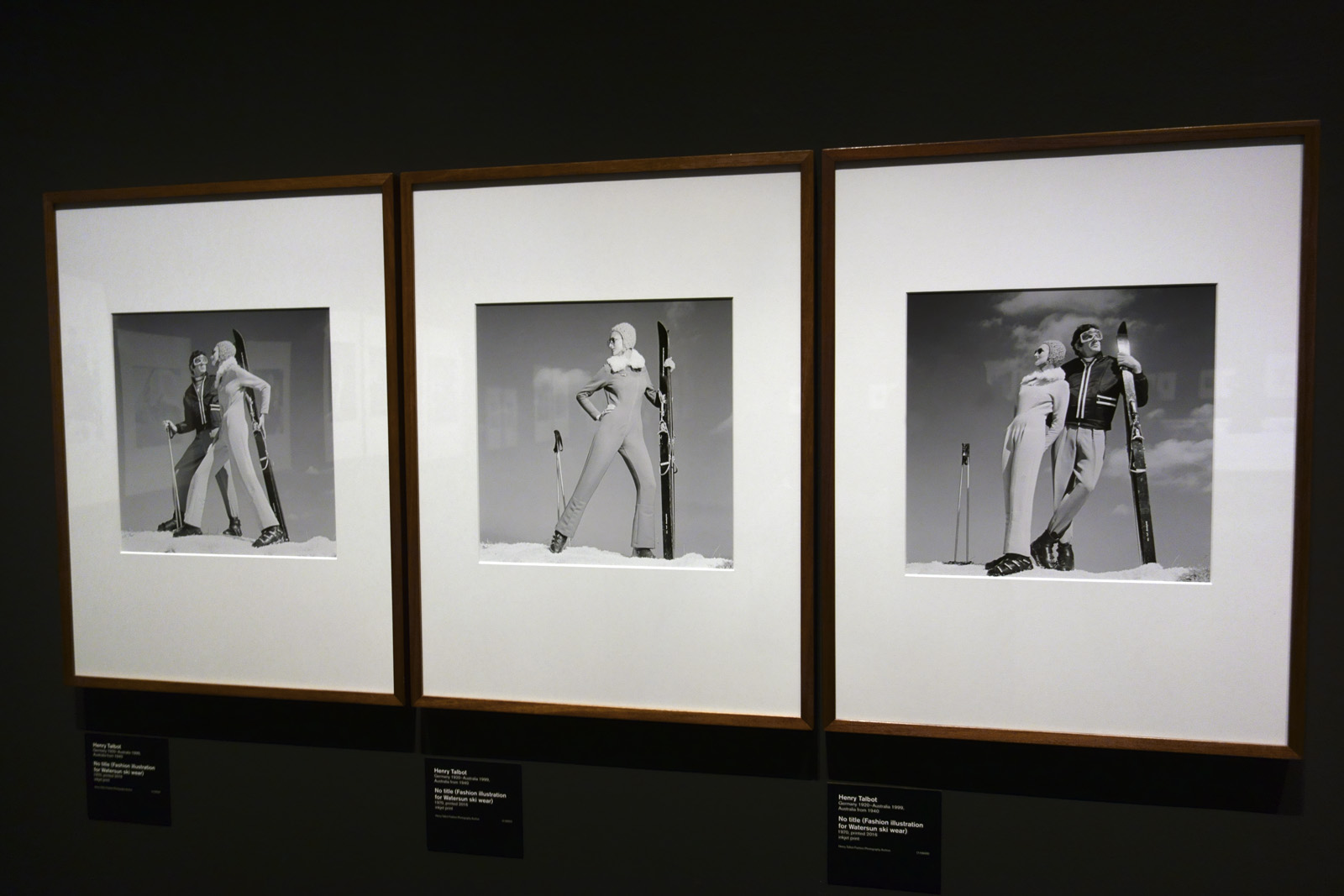
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Watersun ski wear) (installation view)
1970, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Watersun ski wear) (installation view)
1970, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Watersun ski wear) (installation view)
1970, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
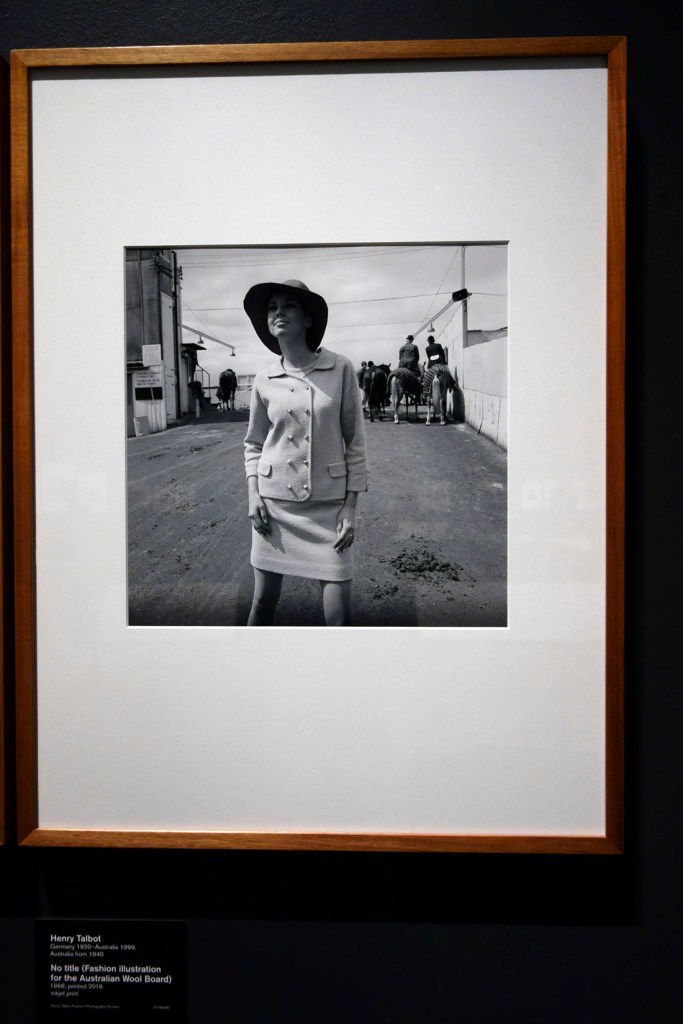

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for the Australian Wool Board) (installation view)
1968, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
“There is little an Australian fashion photographer can do that has not been done overseas, and often better. But one thing they do not have is our Australian environment. I use it a great deal because the idea makes it possible to come up with something uniquely different.”
Henry Talbot 1966
“The striking and youthful fashion of 1960s Melbourne is the starring subject of more than eighty photographs by fashion photographer Henry Talbot, many of which have never been exhibited before. Showcasing the shifting face of fashion from a time that has captured popular imagination, many of the images have never been seen since their original publication 50 years ago and offer an insight into the styles and attitudes of the 1960s. The photographs on display have been carefully selected from an extraordinary archive of 35,000 negatives that Talbot gifted to the NGV in the 1980s.
“Henry Talbot’s photography captures the exuberance and changing times of a generation. His modern photographs depict an emerging youth culture and offer an insider’s look into a thriving cultural scene during the 1960s,” said Tony Ellwood, Director, NGV.
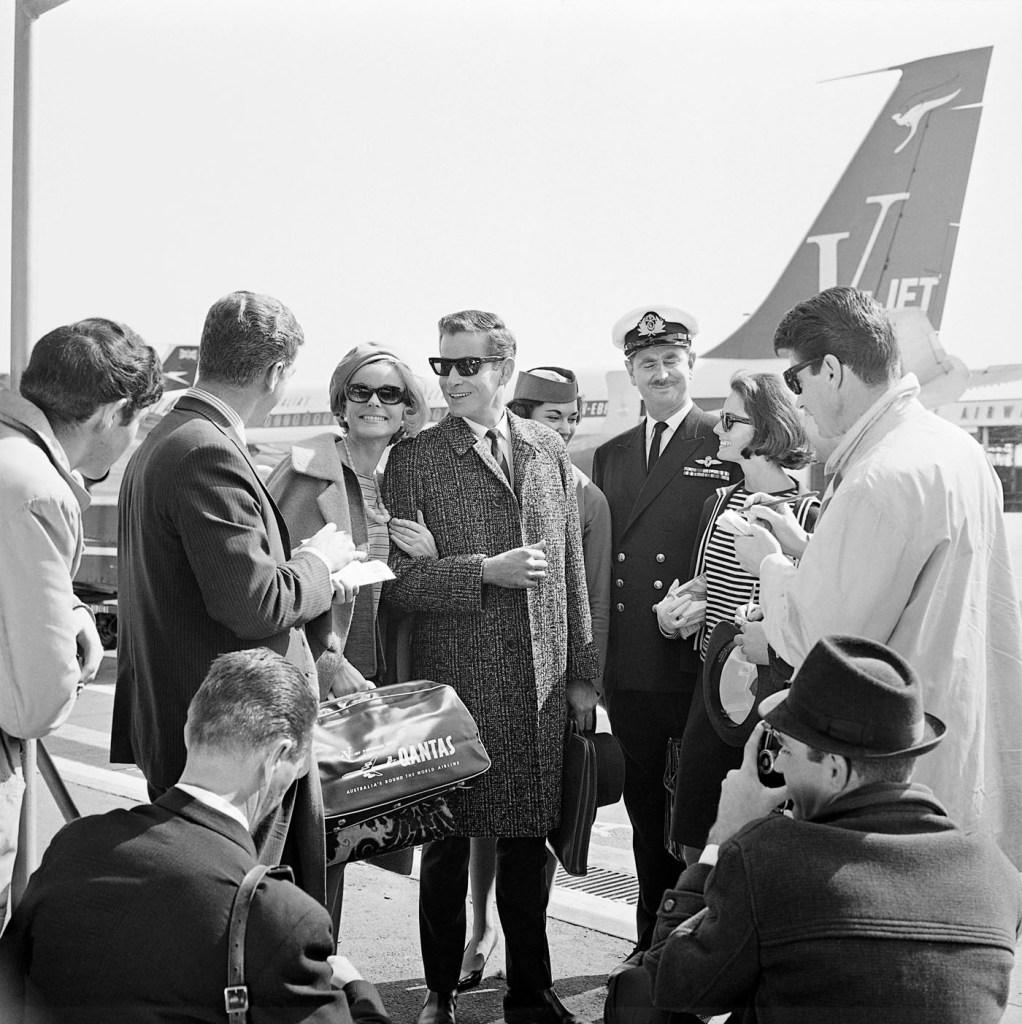
A European émigré artist from Germany, Talbot brought an invigorating internationalism to Australian photography and partnered with Helmut Newton. Their Flinders Lane studio was very successful enterprise and secured major clients including the Australian Wool Board and Sportscraft. It was during the 1960s that Talbot established his place as a dynamic force in Australian fashion photography and his work was regularly published in Australian Vogue.
The exhibition includes some of Talbot’s beautiful fashion spreads from 1960s Australian Vogue, providing a visual history that chronicles the magazine’s first decade in Australia. The photographs will be presented alongside a display of early edition Australian Vogue magazines, including those in which Talbot’s photographs originally appeared, offering an insight into the aspirational fashion and lifestyle choices of Australians living in this era. Talbot’s photography also highlights the public’s affinity with uniquely Australian brands, such as Qantas and Holden. Fast cars and air travel were aspirational luxury experiences in the 1960s and, as a result, airports, planes and brand new cars were the glamorous setting for many of Talbot’s photographs, demonstrating his astute understanding of current trends and consumer culture.
From an outback sheep station, to lamp-lit streets of Melbourne, Australian cityscapes and landscapes also provided the backdrop to some of Talbot’s most arresting photographs. Shot on location around Melbourne, these photographs showcase Talbot’s adventurous style and ability to transform 1960s Melbourne into scenes that looked like Paris, London, New York – a testament to his ‘international eye’. A photographer with an astute vision, Talbot also ingeniously transformed Altona Petrochemical Company into an intergalactic, futuristic setting that captured the public’s fascination with space travel during the ‘space race’ of the 1960s. This exciting suite of images demonstrates the ways in which space travel permeated popular culture, including space-age fashion trends.
The exhibition will open during the NGV’s landmark 200 Years of Australian Fashion exhibition and together, these two exhibitions will offer a comprehensive and fresh new look at Australian fashion in the 1960s.”
Press release from the National Gallery of Victoria
Henry Talbot (Australian born Germany, 1920-1999)
Henry Talbot was born in Germany in 1920. As a young man he studied graphic design and photography in Berlin and Birmingham. After leaving Germany in 1939, he arrived in Australia in 1940. Following a period of internment, Talbot then served in the Australian army. In the postwar years he left Australia, travelling to South America and Europe, before returning to Melbourne in 1950. At the time Melbourne was the most important centre of fashion in Australia because of the abundance of textile and garment manufacturing in Flinders Lane; boutiques in the Paris End of Collins Street, and major department stores around the city.
Talbot worked in some of the leading Melbourne photographic studios and quickly established a reputation as a major fashion photographer in Melbourne. In 1956 he was invited to go into partnership with Helmut Newton. Newton was already renowned for his innovate fashion images and this partnership offered Talbot recognition for his talent in this field. In 1973 Talbot closed his studio, and ten years later presented the NGV with what is now known as the Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive. Works in this exhibition at taken from this remarkable collection, comprising 35,000 black-and-white negatives, photographs and contact prints.
Wall text
Installation view of the National Gallery of Victoria’s Henry Talbot: 1960s Fashion Photographer exhibition at NGV Australia at Federation Square with at left, No title (Fashion illustration, model Janice Wakely) (1961, below) (installation view)
Photo: Brooke Holm
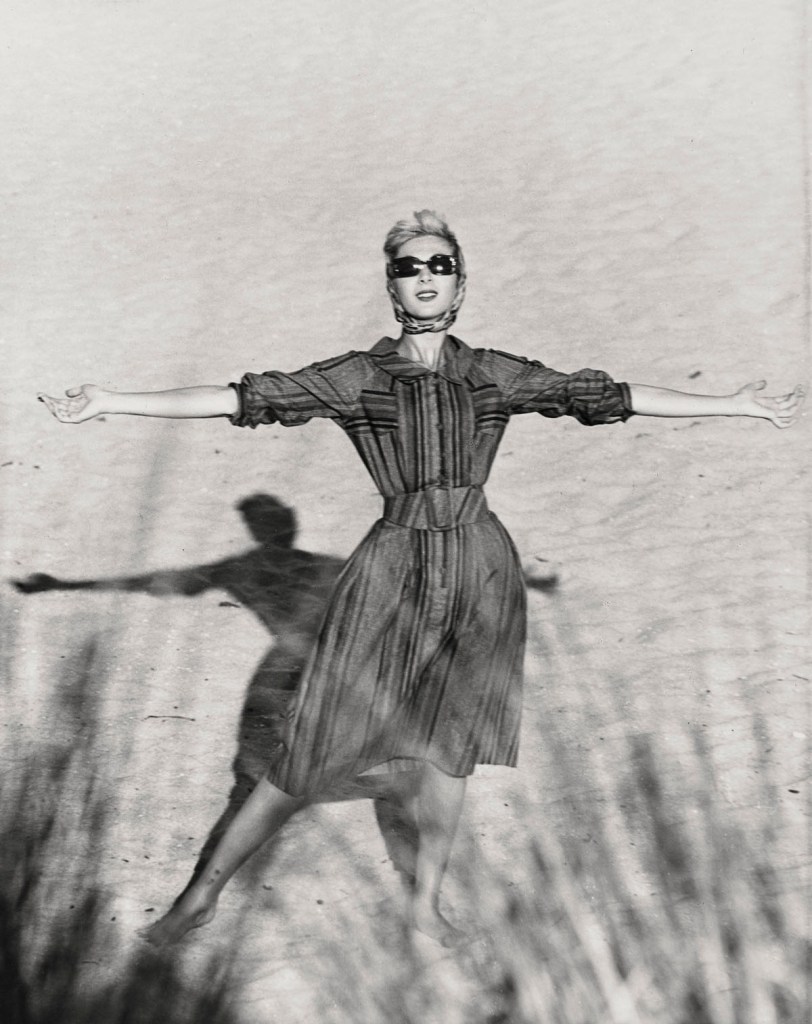

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration, model Janice Wakely)
1961
Gelatin silver photograph
24.3 x 19.3cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Working with the right model was as important to the success of Talbot’s images as choosing the right location. Like most photographers he had his favourite models, and often worked with Janice Wakely, Maggie Tabberer, Helen Homewood, Maggi Eckardt and Margot McKendry.
Talbot’s philosophy was simple, as he explained it in 1995: “I’ve always held that if you can establish a definite emotional rapport with a model you’re halfway toward producing good photographs. My own favourite method of fashion working is to explain roughly what I am after then leave the model more or less free to interpret the garment she’s to show. A good model will absorb and become part of what she is wearing almost completely. Whilst shooting away I may suggest minor changes, the model senses what I’m after, and then really good shots happen.”
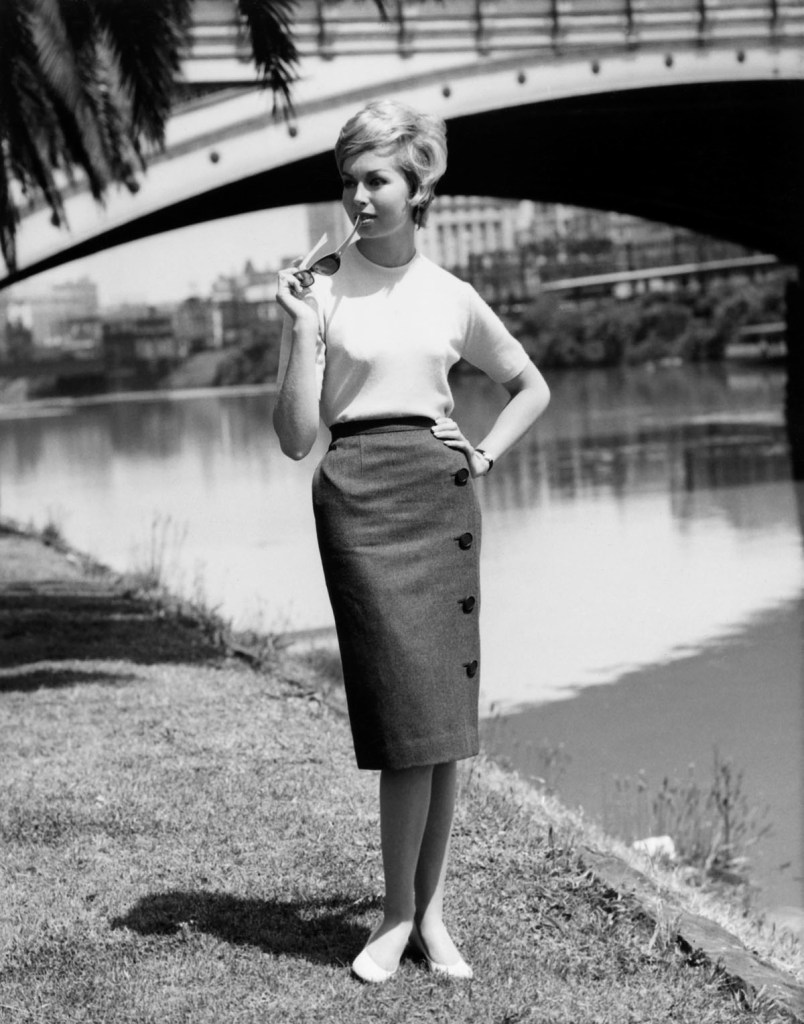

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Sportscraft on location Yarra River near Princes Bridge)
1961
Gelatin silver photograph
24.4 x 19.0cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
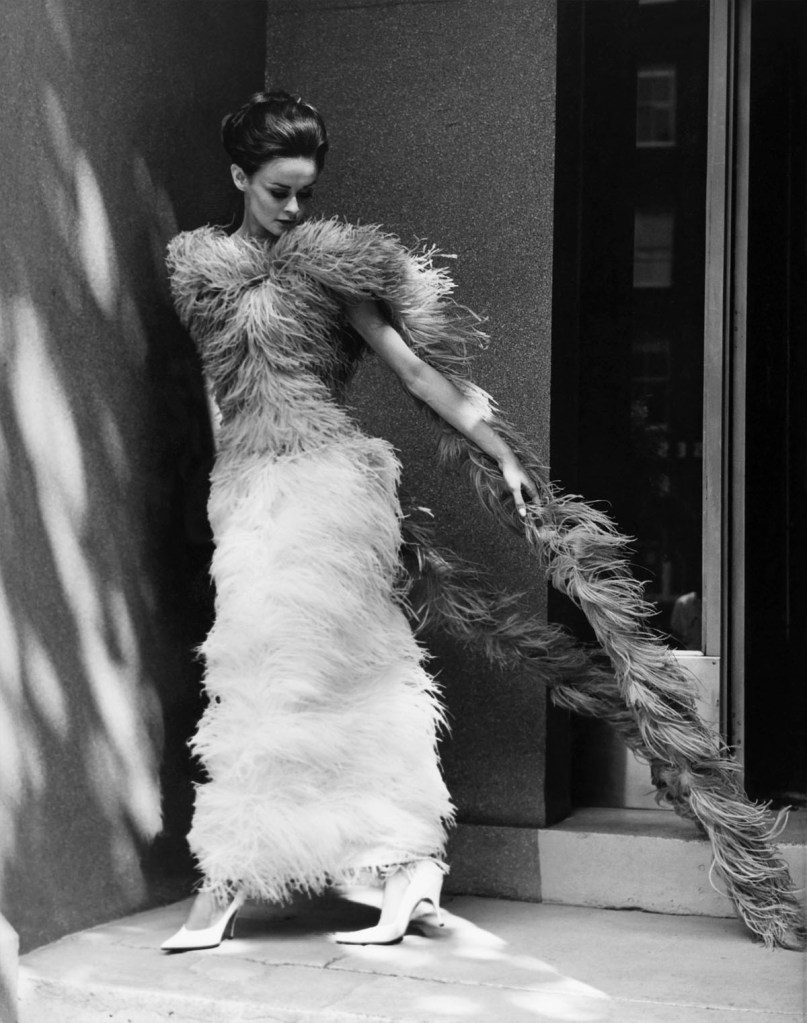

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration model wearing long feather dress)
1961-1966
Gelatin silver photograph
24.2 x 19.4cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
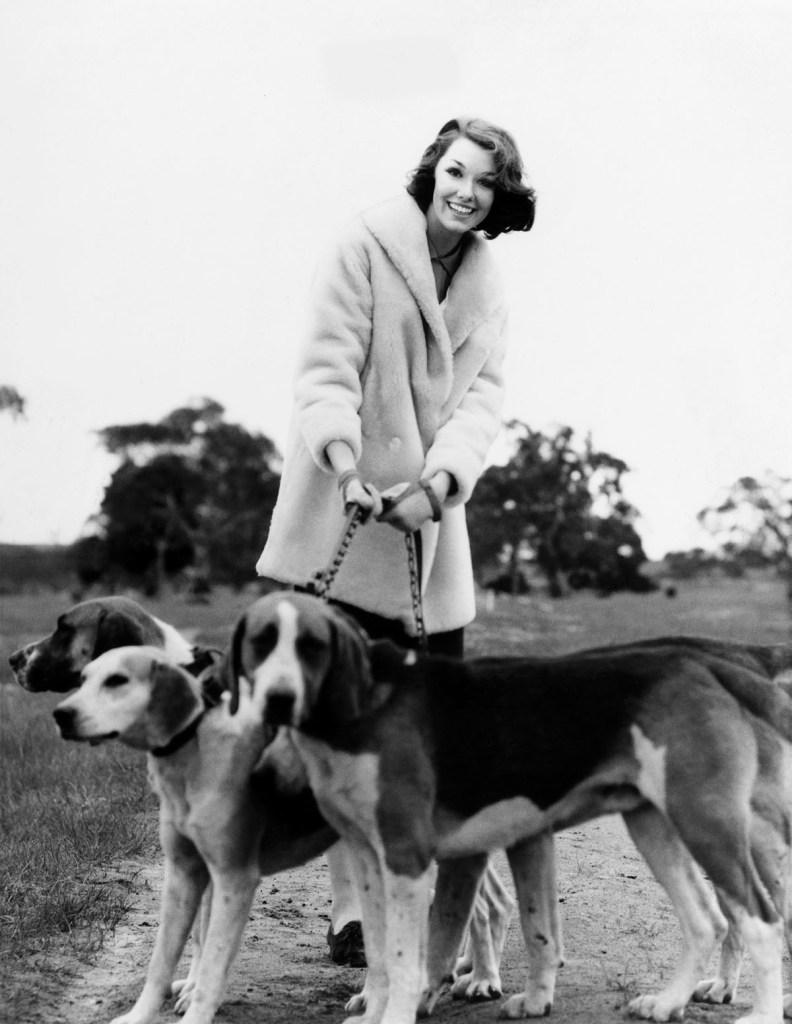

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration model wearing a three-quarter length coat)
1961-66
Gelatin silver photograph
25.0 x 19.1cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
‘Forsaking city airs for cool country breezes, she previews the three day event at Oaklands Hunt Club which will finish the Melbourne Cup season, wearing a three-quarter oat of palest blue pearl lamb.’
Descriptive caption, 1966
Installation view of the National Gallery of Victoria’s Henry Talbot: 1960s Fashion Photographer exhibition at NGV Australia at Federation Square
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration) (installation view)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
40.7 x 40.6cm (image)
67.4 x 61.1cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration) (installation view)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
40.7 x 40.6cm (image)
67.4 x 61.1cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration) (installation view)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
50.9 x 50.8cm (image)
72.4 x 61.0cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Photo: Brooke Holm

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
40.7 x 40.6cm (image)
67.4 x 61.1cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
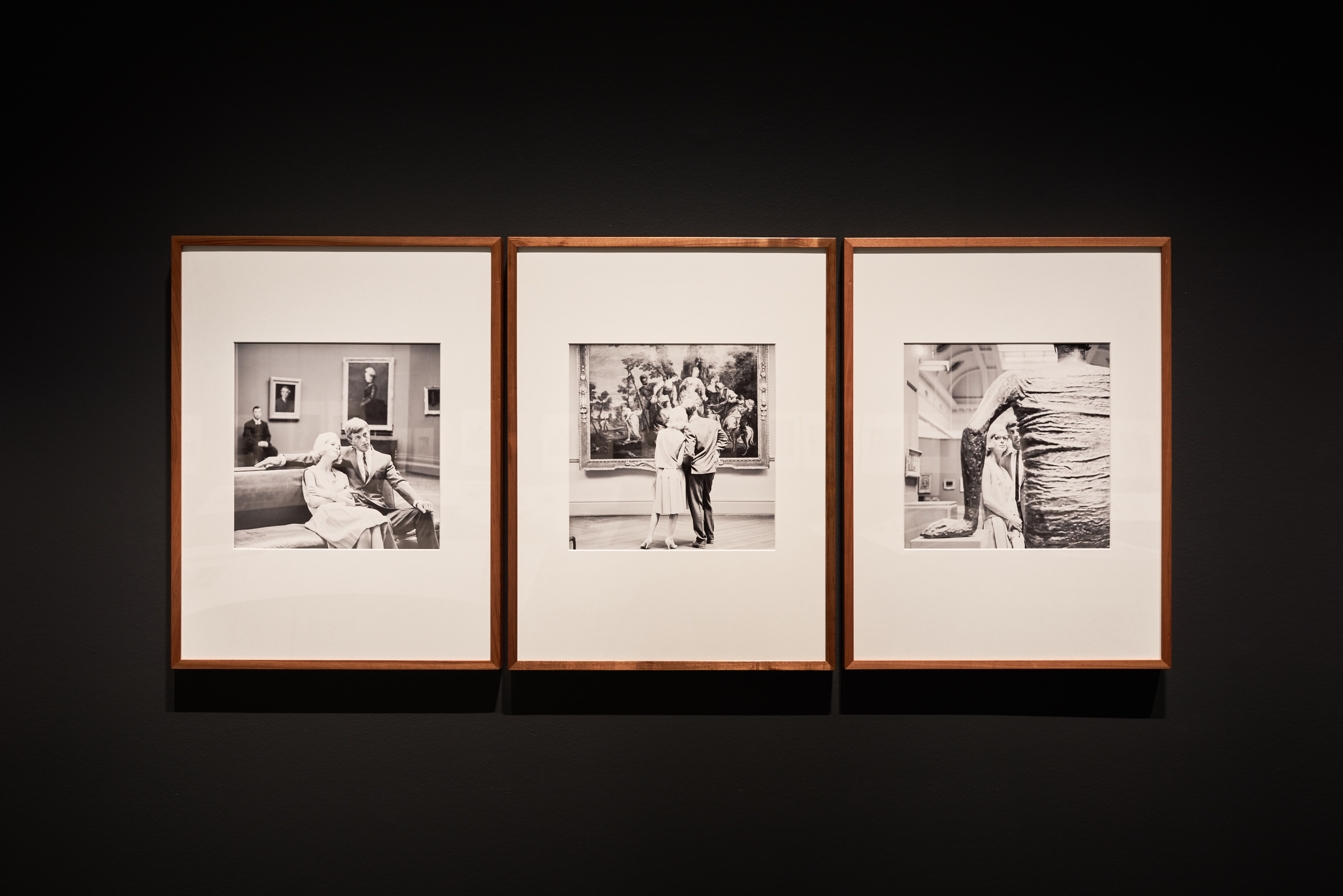
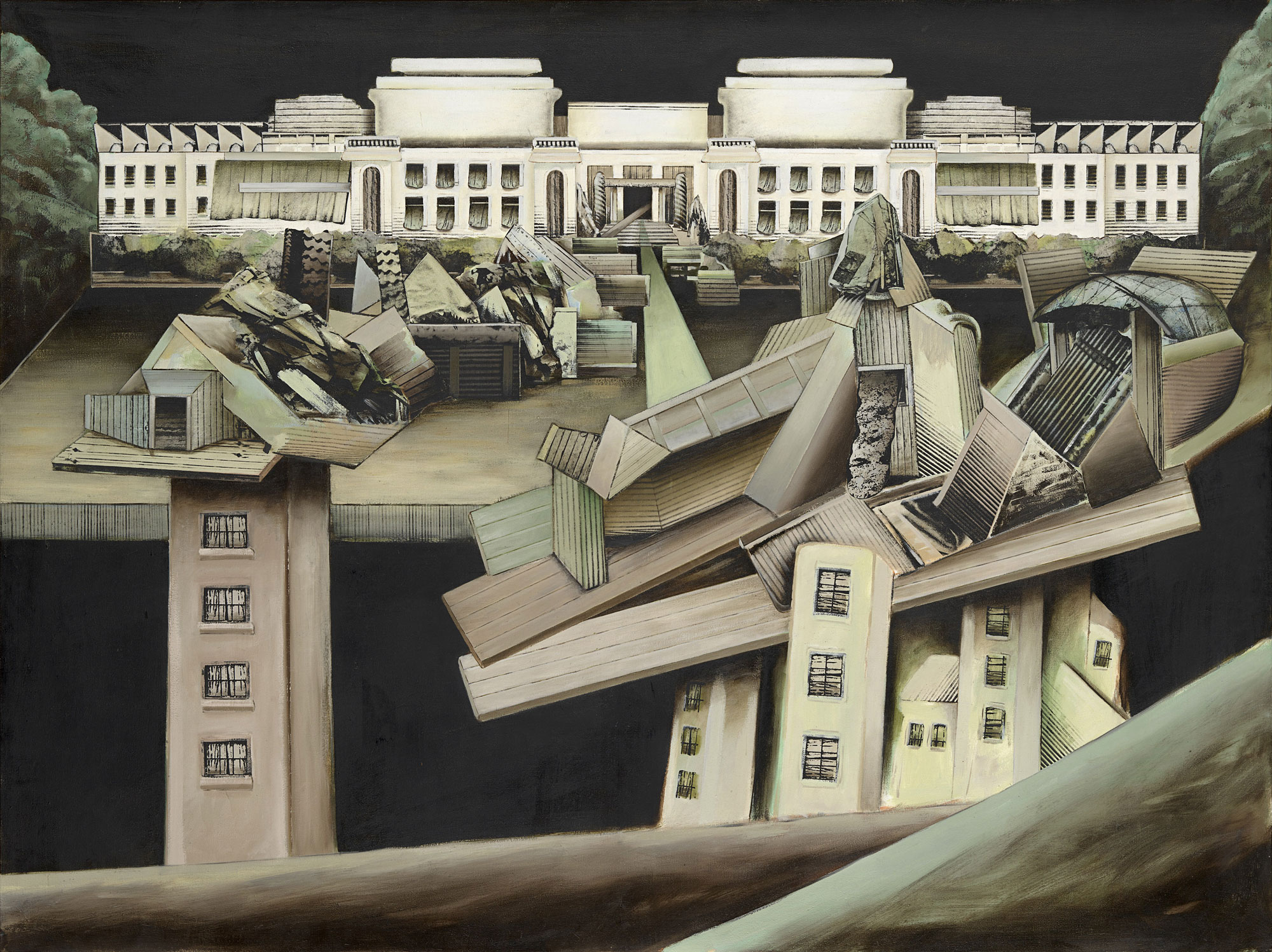
The locations used by Talbot were an important aspect of his image making; they played a significant role in the implicit narratives he constructed in his fashion photography. Talbot’s work, like most fashion photographs, presents an aspirational ideal. In his case a picture of the modern woman – at an opening night; arriving at the airport; on the streets of London; visiting an art gallery; or in a beatnik coffee bar – who looks effortlessly up to date and glamorous because she has bought the perfect garment.
Despite Talbot’s assertion that using Australian settings gave his work an edge, some of his most successful photographs artfully disguise the familiar streets of Melbourne. The streets of the city are transformed in Talbot’s photographs to look like Fifth Avenue, New York or Hyde Park in London.
Wall text

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
50.8 x 50.3cm (image and sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
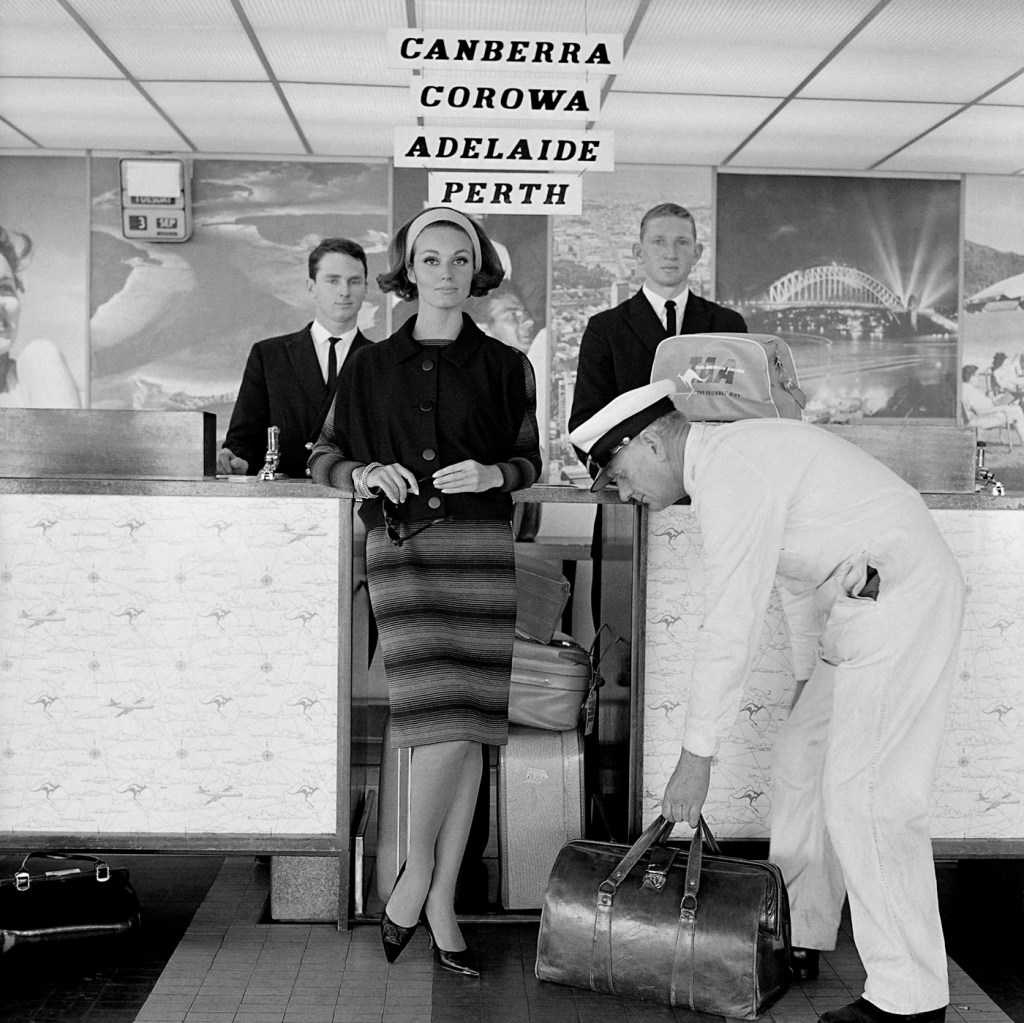

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
50.9 x 50.8cm (image)
72.4 x 61.0cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
The 1960s was a period of social turbulence, when youth-led movements changed the world. In Australia it was a time of prosperity: employment rates were high and, for many, the opportunities seemed boundless. The fashions of the day, including mini skirts and hipster pants, reflected the “youthquake” that was shaking up the status quo. Photography studios made the transition to the 1960s by creating images with a fresh, contemporary edge, and increasingly worked on location rather than in the studio.
Henry Talbot began to work in fashion photography in the 1950s, but it was in the 1960s that he established himself as a leading force in Melbourne’s fashion industry. He worked for designers and manufacturers, department stores and boutiques, as well as on the job for the Australian Wool Bureau, taking photographs that showed Australian fashion to the world.
Wall text

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Classweave Fabric, models Uschi Huber, Ellen Neudal and Heather Ceembruger)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
50.9 x 50.8cm (image)
72.5 x 61.1cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
‘The magic carpet revisited: Classweave takes to the air. Classweave deny weaving the magic carpet, but [the] chic three disagree, find Classweave fabrics magic. Feel like flying,and choose Qantas.’
Advertising copy, Australian Vogue, 1963
Installation view of the National Gallery of Victoria’s Henry Talbot: 1960s Fashion Photographer exhibition at NGV Australia at Federation Square
Photo: Brooke Holm
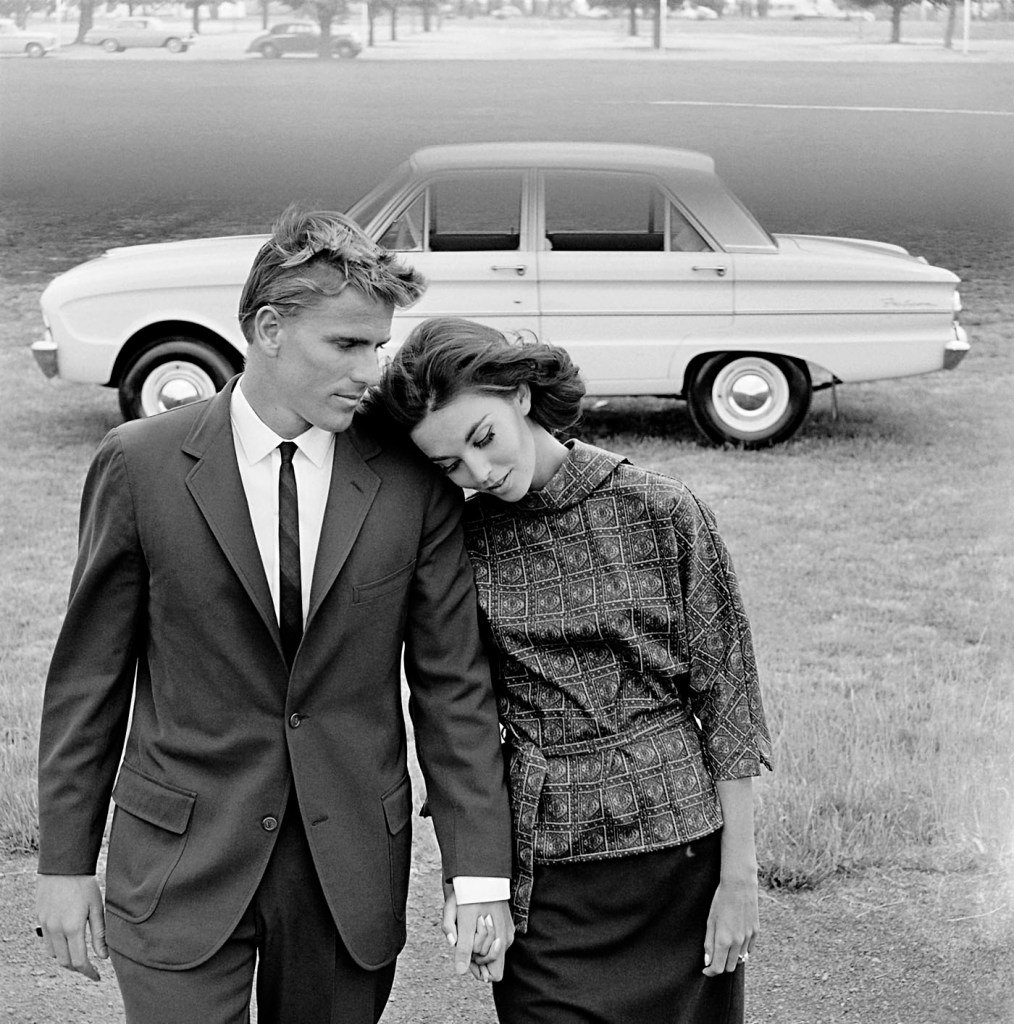

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Pelaco shirts and Ford Falcon, models Margot McKendry and Murray Rose)
1963, printed 2016
Inkjet print
41.0 x 40.6cm (image)
67.5 x 61.1cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
‘They’re going places, the Pelaco Pair – and riding the crest all the way. They live their life with a style and carefree assurance that many envy. They know and demand the best this modern world has to offer, a personal formula for success that shows in everything they do. You can see it in the clothes they wear (he doesn’t own a shirt that isn’t Pelaco; she collects Lady Pelaco, secretly feels they were created especially for her). You can see it in the cars they drive – always, a trim, taut, terrific Falcon.’
Advertising copy, Vogue Australia, April/May 1963
Murray Rose (Australian, 1939-2012)
Iain Murray Rose, AM (6 January 1939 – 15 April 2012) was an Australian swimmer, actor, sports commentator and marketing executive. He was a six-time Olympic medalist (four gold, one silver, one bronze), and at one time held the world records in the 400-metre, 800-metre, and 1500-metre freestyle (long course). He made his Olympic debut at the 1956 Summer Olympics as a 17-year-old and won three Olympic medals, all gold. Four years later, as a 21-year-old, he won three Olympic medals (one gold, one silver, one bronze) at the 1960 Summer Olympics.
At the age of 17, Rose participated in the 1956 Summer Olympics in Melbourne. He won the 400-metre and 1500-metre freestyle races and was a member of the winning team in the 4×200-metre freestyle relay. Winning three gold medals in his home country immediately made him a national hero. He was the youngest Olympian to be awarded three gold medals in one Olympic Games. Afterwards, Rose moved to the United States to accept an athletic scholarship at the University of Southern California where he received a Bachelor of Arts degree in Business/Communications.
He continued competing while at USC, and graduated in 1962. At the 1960 Summer Olympics in Rome, Italy, Rose again won an Olympic gold medal in the 400m freestyle, as well as a silver in the 1500m freestyle and a bronze in the 4 x 200m freestyle relay, bringing his haul to six Olympic medals. In addition to his Olympic medals, he won four gold medals at the 1962 Commonwealth Games in Perth, Australia. He eventually set 15 world records, including the world record in the 800-metre freestyle in 1962, which was not broken until Semyon Belits-Geiman set a new record in 1966. Rose continued to compete as a masters swimmer. During the 1960s, he also pursued an acting career, starring in two Hollywood films and making guest appearances on television shows.
In addition, Rose worked as an Australian sports commentator for the Nine Network, plus each of the major US networks, participating in seven consecutive Olympic Games.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Installation views of the National Gallery of Victoria’s Henry Talbot: 1960s Fashion Photographer exhibition at NGV Australia at Federation Square
Photos: Brooke Holm
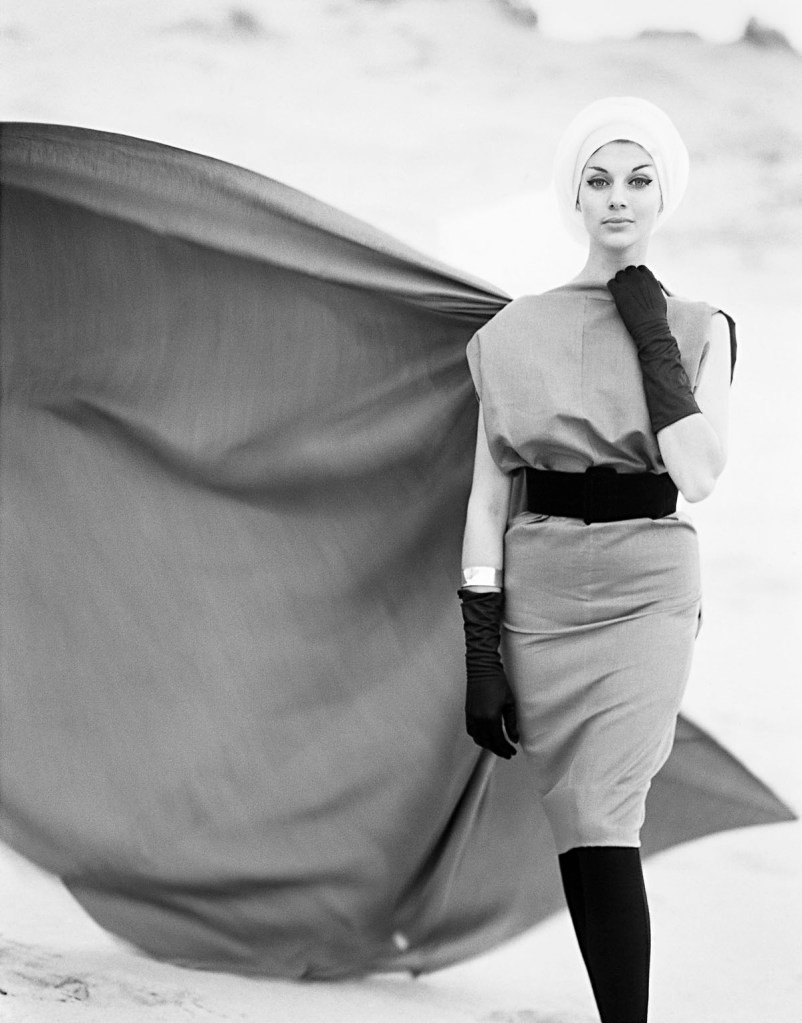

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration, model Maggie Tabberer)
(1960s), printed 2016
Inkjet print
61.2 x 47.4cm (image)
86.3 x 60.9cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive (119664)
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Maggie Tabberer (Australian, 1936-2024)
Maggie Tabberer AM (also known as Maggie T; born 11 December 1936 – died 6 December 2024) is a dual Gold Logie-winning Australian fashion, publishing and media / television personality. Maggie’s first modelling job was a one-off assignment at the age of 14, after a photographer spotted her at her sister’s wedding. She attended a modelling school in her early twenties, and at the age of 23 was discovered by photographer Helmut Newton, who mentored her and launched a highly successful modelling career. While living in Melbourne in 1960, she won ‘Model of the Year’, and moved to Sydney to take advantage of the modelling opportunities there, but she chose to end her modelling career at the age of 25 after she began to lose her slim figure.
Tabberer stayed well connected to the fashion industry, however. In 1967 she started a public relations company, Maggie Tabberer & Associates, which took on many fashion-related clients and assignments. In 1981, she launched a plus-size clothing label called Maggie T. A portrait of her by Australian artist Paul Newton was a finalist in the 1999 Archibald Prize.
Publishing work
Tabberer began working in publishing when she wrote a fashion column, “Maggie Says”, for Sydney’s Daily Mirror newspaper in 1963. She remained with the paper for sixteen years, until billionaire Kerry Packer asked her to become fashion editor of Australian Women’s Weekly magazine in 1981, and she soon became the public face of the magazine, frequently appearing on its cover and television advertising. Tabberer stayed with Women’s Weekly for fifteen years until 1996.
Television work
Tabberer began appearing on television in 1964, as the “beauty” on panel talk show Beauty and the Beast (the “beast” being the show’s host: Eric Baume until 1965, and then Stuart Wagstaff). Tabberer’s appearances on Beauty and the Beast made her a household name, and she began hosting her own daily chat show, Maggie, for which she won two consecutive Gold Logies, in 1970 and 1971. She was the first person to win back-to-back awards, although Graham Kennedy had already won three non-consecutive Gold Logies by 1970.
Since 2005, she has hosted her own television interview show, Maggie… At Home With on Australian pay TV channel Bio. (formerly The Biography Channel). On her show she “visits the homes of various Australian celebrities and elites to discuss their lives, careers, tragedies, and triumphs.”
Text from the Wikipedia website
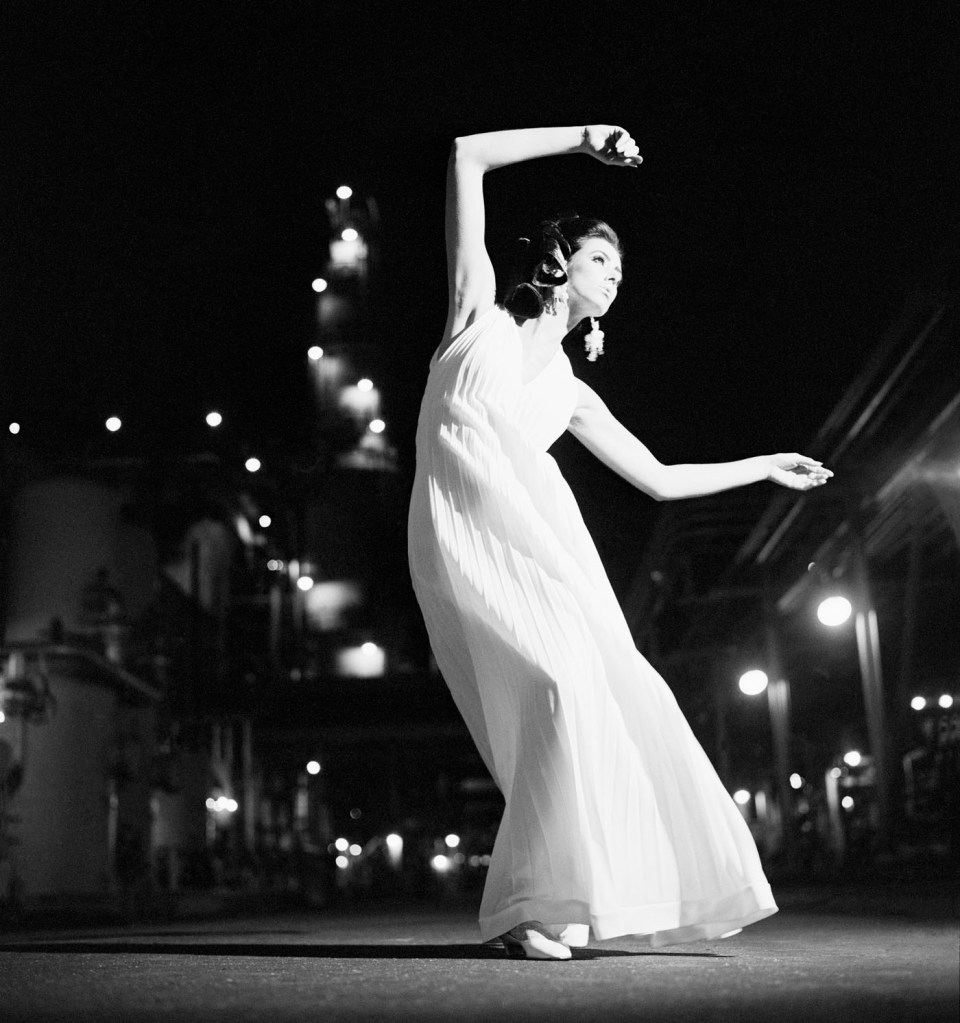

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Fibremakers, model Maggi Eckardt)
1966, printed 2016
Inkjet print
54.45 x 50.8cm (image)
72.5 x 61.0cm (sheet)
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Fibremakers, model Maggi Eckardt)
1966, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
“Fibres for fashions future. Its theme was fibres for the present and the future … pictures taken by Melbourne photographer Henry Talbot – a man who is as sophisticated as James Bond and always a jump ahead of ‘now’. The visiting ‘Venusians’ in Mr Talbot’s photographs (Maggi Eckardt and Jackie Holme) are gyrating at the Altona Petrochemical Company in Victoria.”
Australian Fashion News, March 1967
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Fibremakers, model Maggi Eckardt) (installation view)
1966, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Fibremakers, model Maggi Eckardt) (installation view)
1966, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Photo: Brooke Holm
Maggi had been brought up on Sydney’s northern beaches and went to a ladies’ college in Manly. She had the proud, sultry looks of a flamenco dancer. Her distinctive appearance limited her potential in Australian modelling but she was heaven-sent for elegant Parisian designers such as Balenciaga and Givenchy and was transformed through the worshipping lens of American photographer Richard Avedon into an international icon. After seven years overseas, Maggi returned to Sydney in 1972 to be embraced as a TV personality and high-profile fashion adviser to David Jones.
Text from Gerald Stone. “The six wives of Singo,” on The Sydney Morning Herald website July 27, 2002 [Online] Cited 09/10/2021
During the 1960s Maggi Eckhardt was one of the world’s most sought after models. Her modelling career began in 1958 when she was selected to model for celebrated British designer Norman Hartnell. He offered her a job in his London salon and she never looked back. The brunette beauty rapidly shot to international fame modelling top designer brands including Dior and Balenciaga. She posed for a string of famous photographers such as Richard Avedon and Helmut Newton and graced the covers of Australian and French Vogue.
Text from “Australia’s 25 top models named” on the News.com.au website [Online] Cited 17/08/2016. No longer available online
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Sportscraft) (installation view)
1967, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Sportscraft) (installation view)
1967, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Sportscraft) (installation view)
1967, printed 2016
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Photo: Brooke Holm
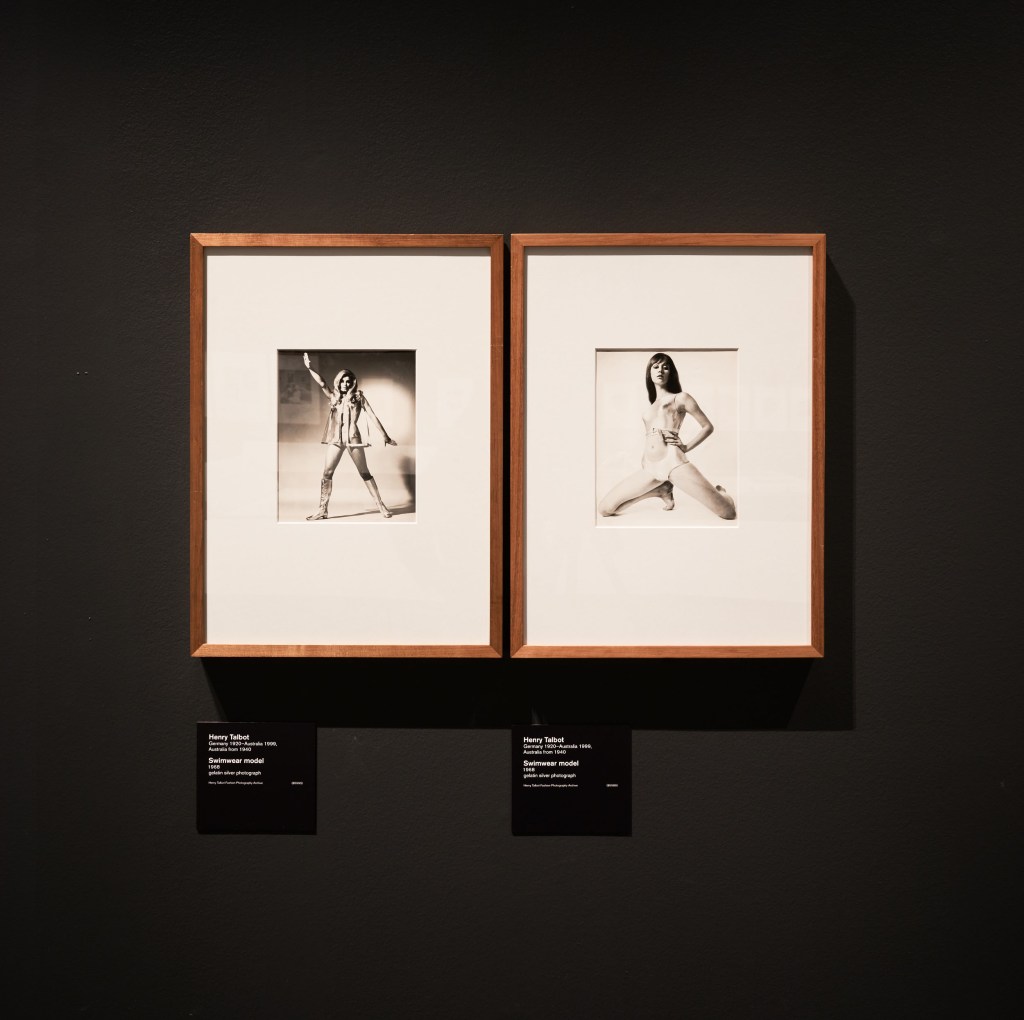

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
Swimwear model (installation view)
1968
Gelatin silver photograph
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
Swimwear model (installation view)
1968
Gelatin silver photograph
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Photo: Brooke Holm
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Blunden Wool, models Joan Crellin and Bruce Anderson) (installation view)
1961, printed 2016
Photographed on location at the National Gallery of Victoria
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Blunden Wool, models Joan Crellin and Bruce Anderson) (installation view)
1961, printed 2016
Photographed on location at the National Gallery of Victoria
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Blunden Wool, models Joan Crellin and Bruce Anderson) (installation view)
1961, printed 2016
Photographed on location at the National Gallery of Victoria
Inkjet print
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
Photo: Brooke Holm

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration, model wearing cotton capri pants and cropped sleeveless top on location in Papua New Guinea)
1961-1966
Gelatin silver photograph
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
‘Discovering the hidden charms of New Guinea in the obvious attributes of Swiss cotton… she wears a cropped top and lean slack in sunny yellow, embroidered in diamond panels of white.’ Descriptive caption, 1966
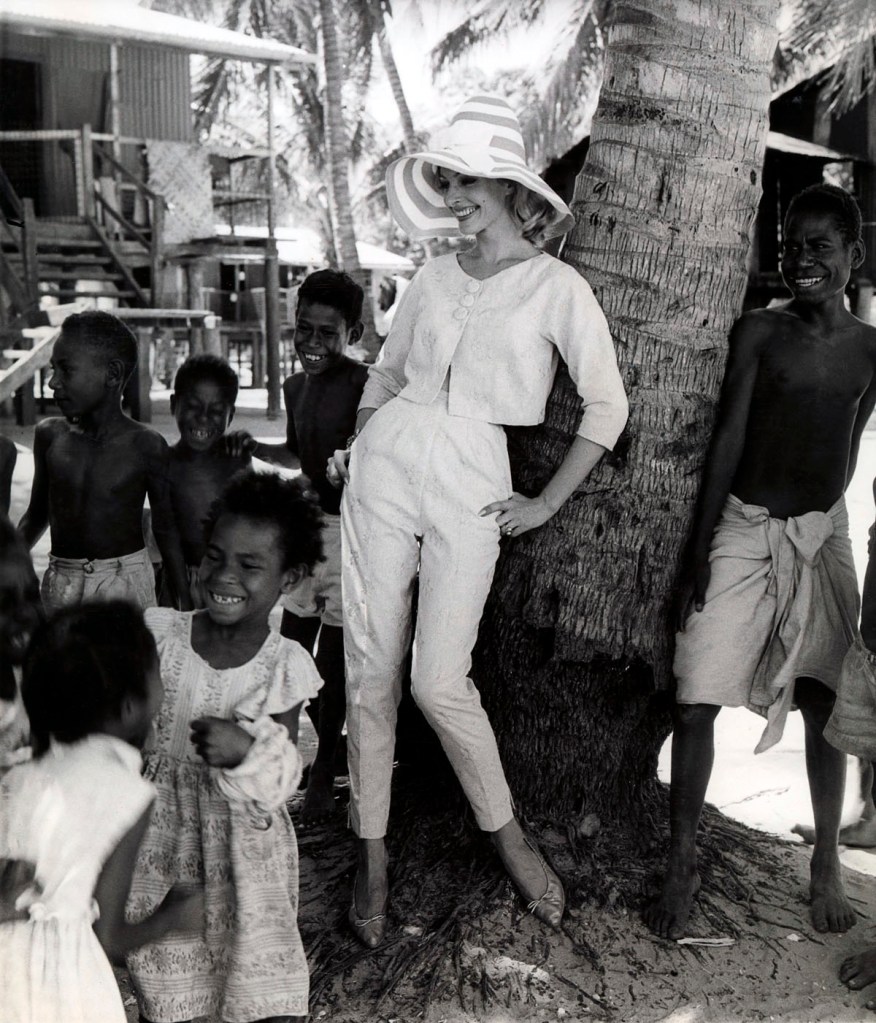

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration model wearing cropped pants and jacket, Papua New Guinea)
1961-1966
Gelatin silver photograph
22.4 x 19.1cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Stella Ricks, unknown model wearing coat and hat)
1960s
Gelatin silver photograph
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
‘Town and country, sport and travel are words enough to place this American style coat in the all-purpose group, and its colour is the outstanding feature – honey bamboo saddle stitched with white. Loose and casual it has fly-away cuffs on sleeves, hip, and breast pockets, and a tailored revere collar. By Stella Ricks.’ Descriptive caption, 1960s

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration model wearing plaid kilt style skirt, Spring Street, Melbourne)
1956-1960
Gelatin silver photograph
24.4 X 21.0cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
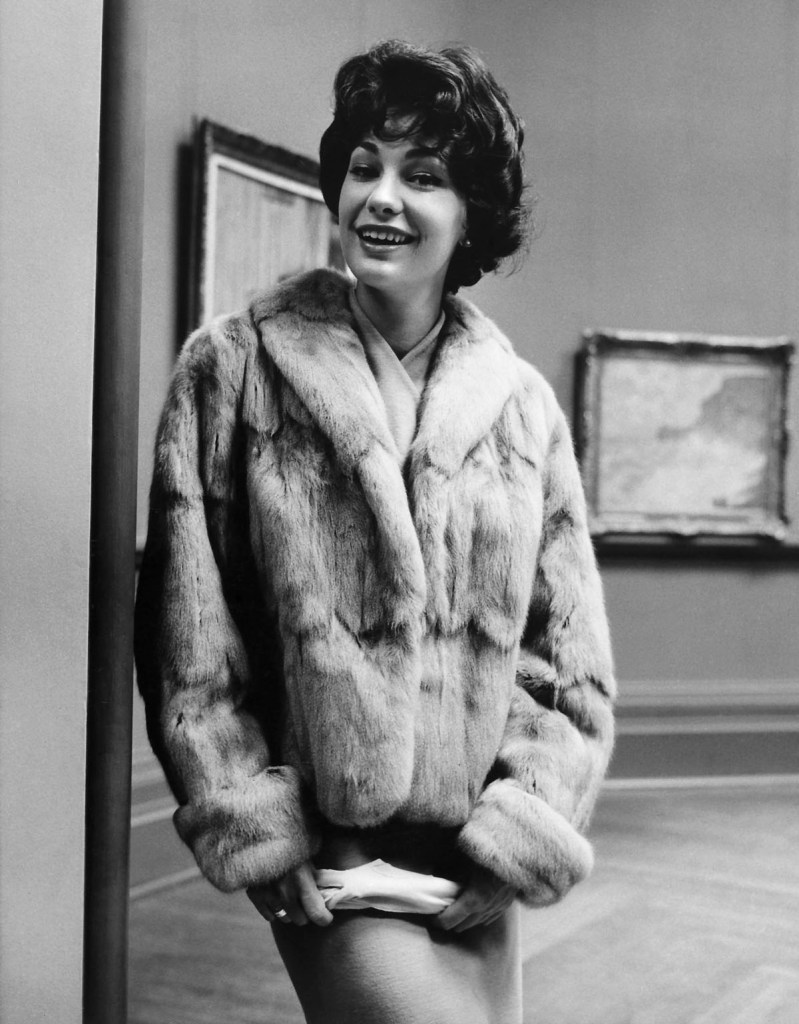

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration model wearing hip length fur jacket, photographed at the National Gallery of Victoria)
1960s
Gelatin silver photograph
24.3 x 19.1cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration, model Maggie Tabberer wearing ocelot coat)
1961-66
Gelatin silver photograph
24.0 x 19.0cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
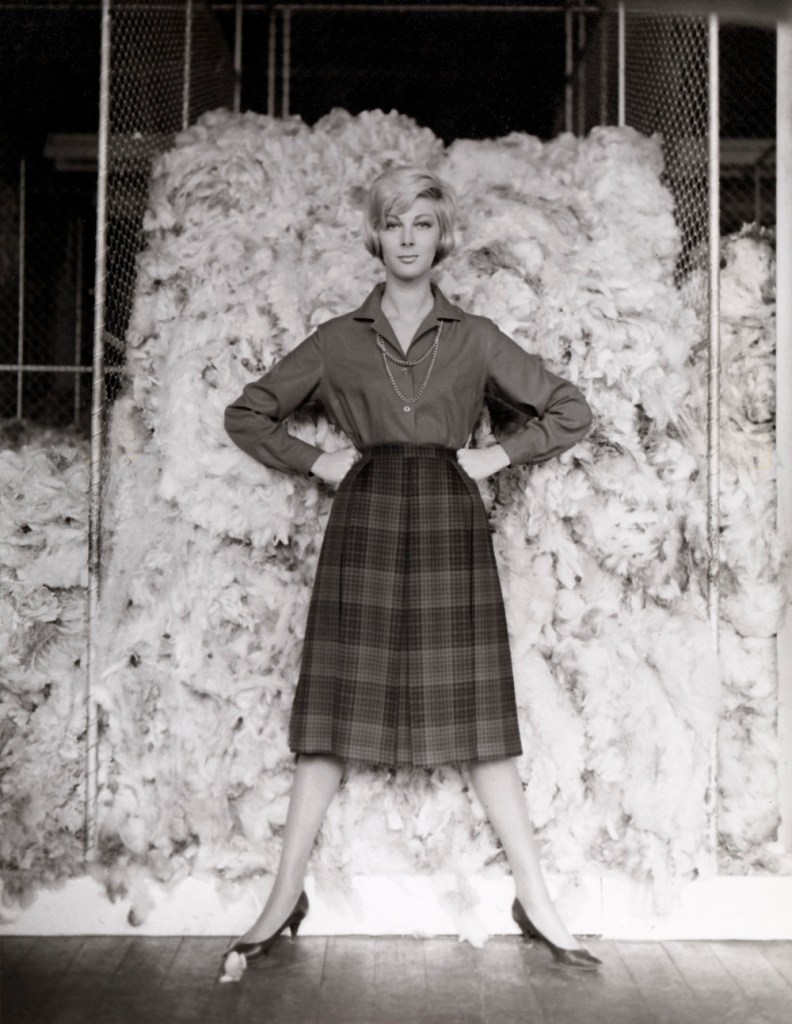

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration, model Janice Wakely standing in front of wool bale)
1961-66
Gelatin silver photograph
24.5 x 18.8cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Sportscraft, Treasury Gardens, Melbourne)
1960-61
Gelatin silver photograph
24.3 x19.1cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
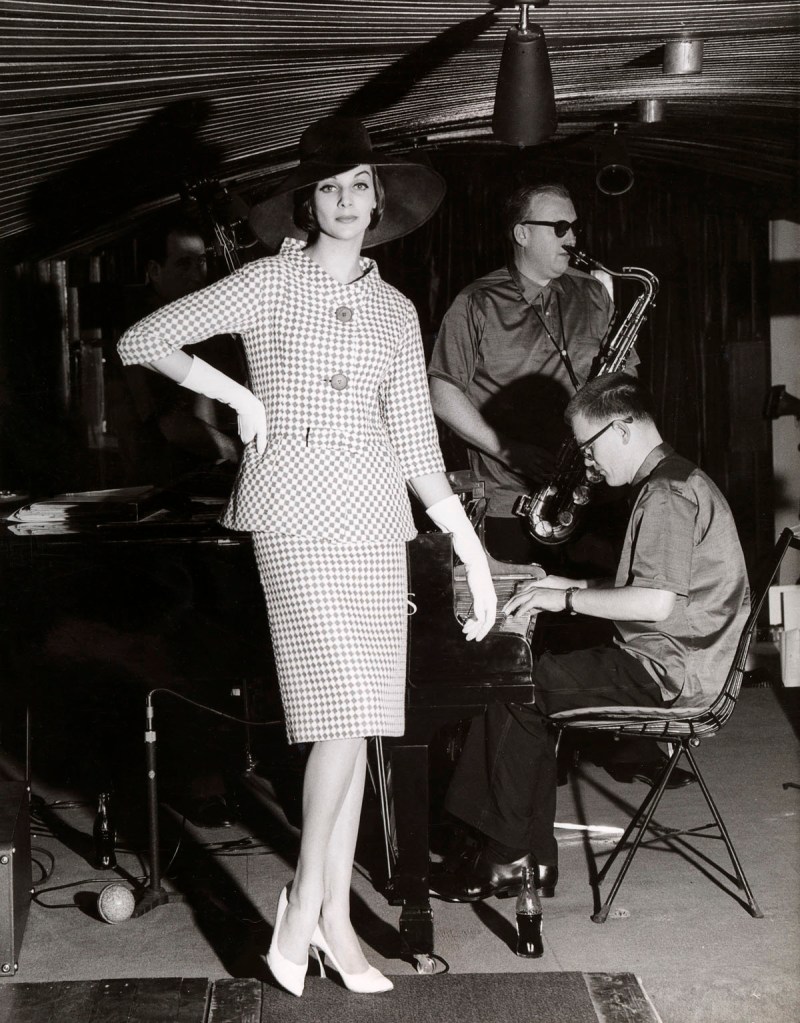

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration, model Maggie Tabberer)
1960
Gelatin silver photograph
24.4 x 19.1cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
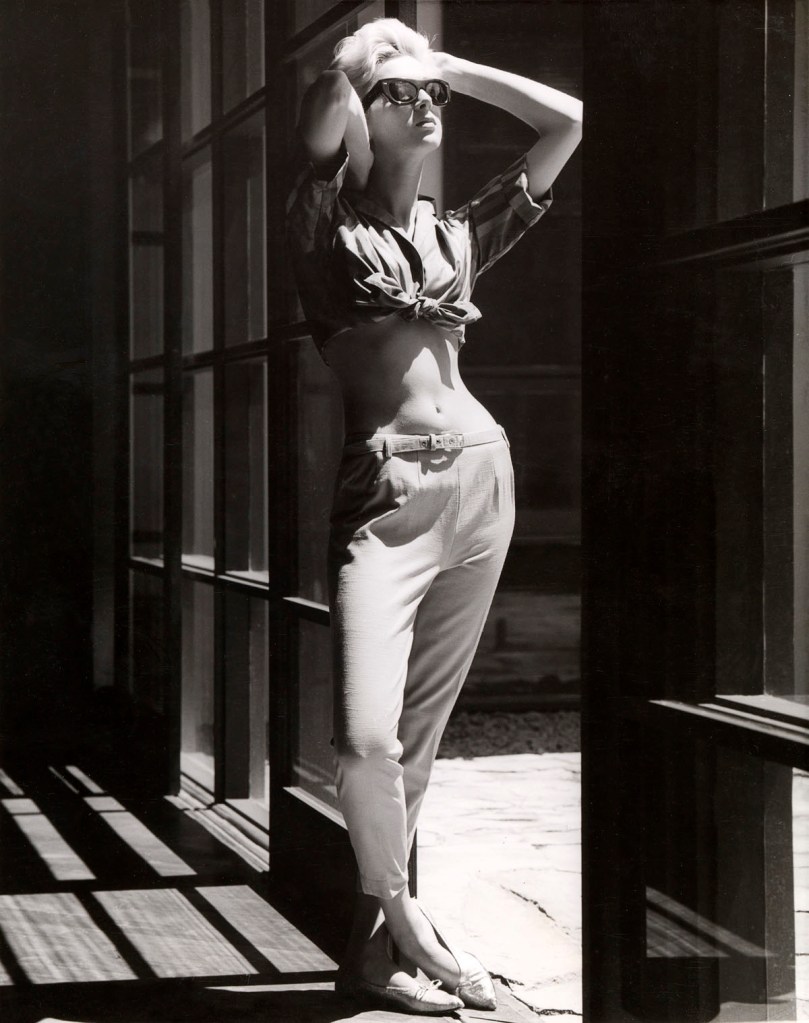

Henry Talbot (Germany 1920 – Australia 1999, Australia from 1940)
No title (Fashion illustration for Sportscaft, model Janice Wakely)
1956-61
Gelatin silver photograph
24.1 x 19.1cm
Henry Talbot Fashion Photography Archive
© Lynette Anne Talbot
Janice Wakely (Australian, 1935-2022)
Janice Wakely, fashion model and photographer, graduated from Sydney’s Mannequin Academy in 1952 and began her modelling career in Melbourne two years later. Dismissed as ‘too thin’ by various Australian agencies after working on a Department of Trade-sponsored fashion tour to New Zealand in 1956, she decamped for London. Within ten days, Wakely snared a shoot with Marie Claire in Paris and St Tropez; soon, she was dubbed ‘The Girl of the Moment’ with ‘The Look of 1958’.
The Australian Women’s Weekly reported that, in the competitive English market, her “fragile but tough and oh, so carefully casual” look had set her apart – for the time being – from “the thousands from Commonwealth countries who invade Britain each year to see something of the world before they settle down to marriage and the building of a home and family.”
Returning to Australia in 1958, Wakely commandeered the camera herself, proceeding to capture photographers such as Helmut Newton, Athol Shmith and Henry Talbot while they worked with models on location. During this time, Wakely maintained a strong presence in front of the camera. Photographed by Terence Donovan in London in 1960, in 1961 and 1962, she starred in the All-Australian Fashion Parades, was featured on the cover of The Women’s Weekly, was Model of the Year and wore the Gown of the Year.
Then, in 1963, she stepped down from the catwalk, establishing the Penthouse modelling agency and photographic studio in Flinders Lane, Melbourne with co-model Helen Homewood. After an overseas tour in 1965, Wakely returned to Melbourne and set up a studio with fashion photographer Bruno Benini, who, according to People magazine, had “given many other girls a helping hand up the ladder to success”.
Wakely commented in 1968 that “the Australian sense of fashion is appalling”.
Extract from “Treasure Trove: Janice Wakely, fashion icon,” on the ABC Canberra website 11 October, 2012 [Online] Cited 30/07/2016. No longer available online
The Ian Potter Centre: NGV Australia
Federation Square
Corner of Russell and
Flinders Streets, Melbourne
Opening hours:
Open daily 10am – 5pm


















































































































![Unknown photographer. '[A group of Aboriginal men at Coranderrk Station, Healesville]' Nd Unknown photographer. '[A group of Aboriginal men at Coranderrk Station, Healesville]' Nd](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/sixteen-aboriginal-men.jpg)
![Talma & Co. (1893-1932) 119 Swanston St. Melbourne 'Barak, Chief of the Yarra Yarra Tribe. [Barak drawing a corroboree]' c. 1895-1898 Talma & Co. (1893-1932) 119 Swanston St. Melbourne 'Barak, Chief of the Yarra Yarra Tribe. [Barak drawing a corroboree]' c. 1895-1898](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/william-barak-a.jpg?w=655)







![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Mantelpavian [Hamadryas Baboon]' c. 1925 from the exhibition 'The world is beautiful: photographs from the collection' at the National Gallery of Australia, Canberra, Dec 2015 - April 2016 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Mantelpavian [Hamadryas Baboon]' c. 1925 from the exhibition 'The world is beautiful: photographs from the collection' at the National Gallery of Australia, Canberra, Dec 2015 - April 2016](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/albert-renger-patzsch-baboon-web.jpg)





















































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.