Exhibition dates: 2nd March – 4th September 2023
![Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975) [Berenice Abbott] 1929-1930 Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975) [Berenice Abbott] 1929-1930 from the exhibition 'Berenice Abbott's New York Album, 1929' at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, March - Sept 2023](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/11.-walker-evans-berenice-abbott.jpg?w=650)
Walker Evans (American, 1903-1975)
[Berenice Abbott]
1929-1930
Gelatin silver print
16.9 x 11.8cm (6 5/8 x 4 5/8 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1997
© Walker Evans Archive, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Abbott appraises the camera with cool assurance in this portrait, made just after her return from Paris to New York. Her gamine-short hair and bare face affect a chic nonchalance that intrigued Evans. Describing her to a friend after their first meeting, he wrote: “You would like Berenice Abbott, with her hair brushed forward and her woozy eyes.” Her work likewise impressed the young photographer, then finding his footing in the field. Evans’s picture betrays admiration for his new acquaintance, whose burgeoning career offered a model for his own.
American visionary
What a wonderful photographer Berenice Abbott developed into and what a debt of gratitude we owe her for saving the archive of French photographer Eugène Atget whose photographs initially influenced her urban(e) style.
“Abbott felt the changing city [New York] needed an equivalent to the French photographer Eugène Atget (1857-1927), who had documented Paris during a critical period of transition in the late 19th and early 20th centuries with what Abbott called “the shock of realism unadorned.””
It is interesting to analyse Abbott’s New York photographs in relation to Atget. In photographs such as the grouping on Album Page 9: Fulton Street Fish Market and Lower East Side, Manhattan (1929, below) there is an almost symbiotic relationship between Atget’s photographs of street Petits Métiers (trades and professions) and those of Abbott. “The subjects were not sensational, but nevertheless shocking in their very familiarity,” she said of seeing Atget’s photographs in Man Ray’s studio in 1926. Similarly, we can recognise in Abbott’s grouping in Album Page: City Hall Park and Brooklyn Bridge Vicinity, Manhattan (1929, below) and Pingpank Barbershop, 413 Bleecker Street, Manhattan (1938, below) an affinity with Atget’s photographs of architectural details of door handles and the front of shops.
A step away from Atget’s aesthetic are Abbott’s photographs such as Brooklyn Bridge, With Pier 21, Pennsylvania R.R. (1937, below), West Street (1936, below) and Henry Street from Market, Looking West, Manhattan (1935, below) where the foreground of each photograph mimics Atget’s photographs of Old Paris whilst the soaring background of skyscrapers and bridges is all modernist New York, the near / far of the picture plane becoming old / new. Abbott chronicled “the changing aspect of the world’s great metropolis. … Its hurrying tempo, its congested streets, the past jostling the present.”
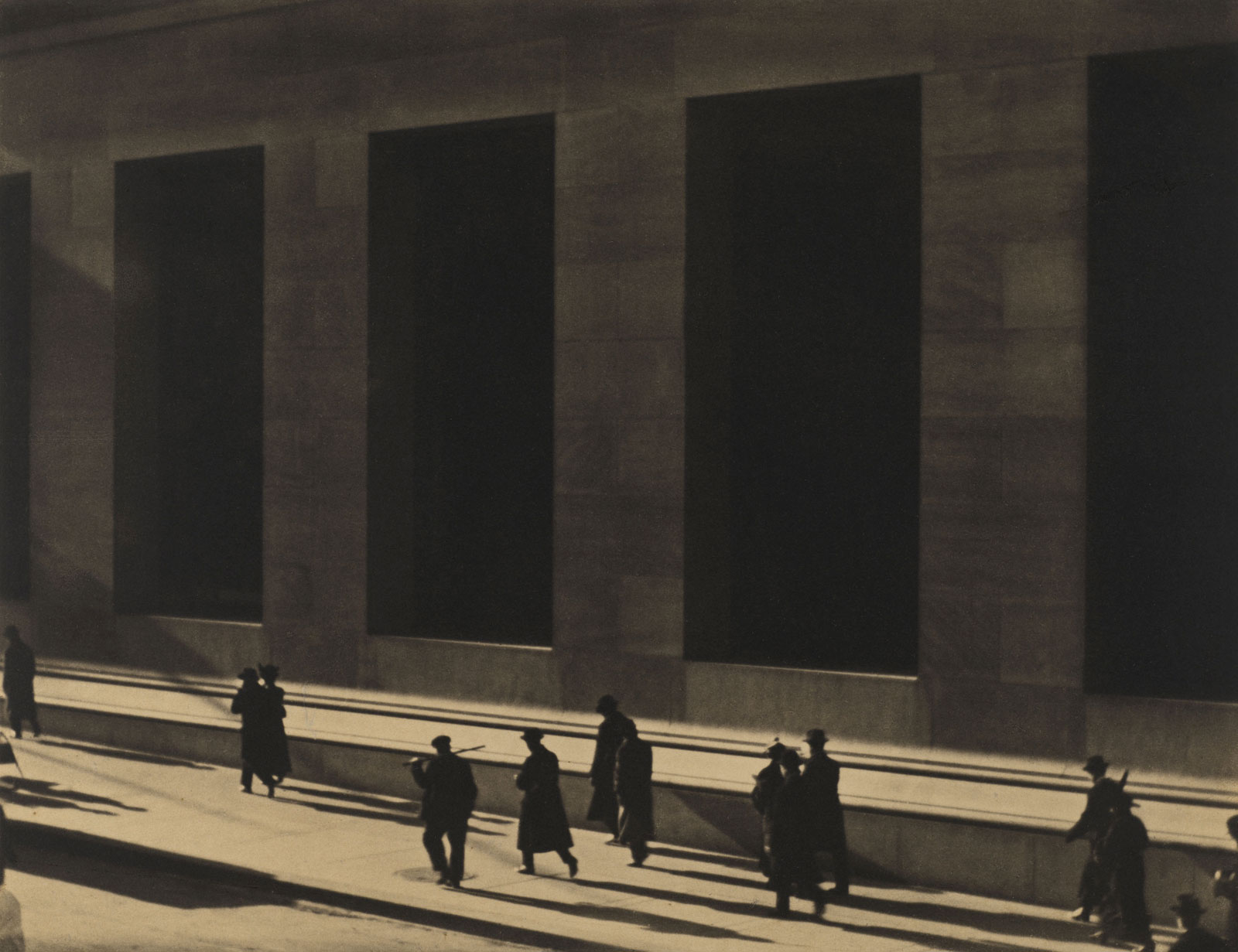
Still further away from Atget’s aesthetic are Abbott’s photographs grouped in Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan (1929, below) where the artist uses with the chiaroscuro (the treatment of light and shade) within the canyons of skyscraper New York – and modernist almost constructivist photographs such as Canyon, Broadway and Exchange Place (1936, below) and Manhattan Bridge, Looking Up (1936, below) where the artist plays with pictorial perspective by pointing her camera skywards.
Finally, there are Abbott’s photographs that bear no relation to those of Atget, where Abbott as an artist has stepped out of the older artist’s shadow and developed her own artistic signature. Those wonderfully abstract and enigmatic photographs at lower left and right in Album Page 5: Pier 17, South Street Seaport, Manhattan push the boundaries of 1930s photographic language. In other glorious photographs such as The El at Columbus and Broadway (1929, below) and The El, 2nd and 3rd Avenue Lines, Bowery and Division Street, Manhattan (1936, below) Abbott captured the random disorder of urban activity with a focused intensity of vision that produces magical images… and by that I mean, images that transport you into other spaces, other states of being. Her dadaist poet Tristan Tzara put it this way: “We leave with those leaving arrive with those arriving / leave with those arriving arrive when the others leave.”
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Metropolitan Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
In January 1929, after eight years in Europe, the American photographer Berenice Abbott (1898-1991) boarded an ocean liner to New York City for what was meant to be a short visit. Upon arrival, she found the city transformed and ripe with photographic potential. “When I saw New York again, and stood in the dirty slush, I felt that here was the thing I had been wanting to do all my life,” she recalled. With a handheld camera, Abbott traversed the city, photographing its skyscrapers, bridges, elevated trains, and neighbourhood street life. She pasted these “tiny photographic notes” into a standard black-page album, arranging them by subject and locale.
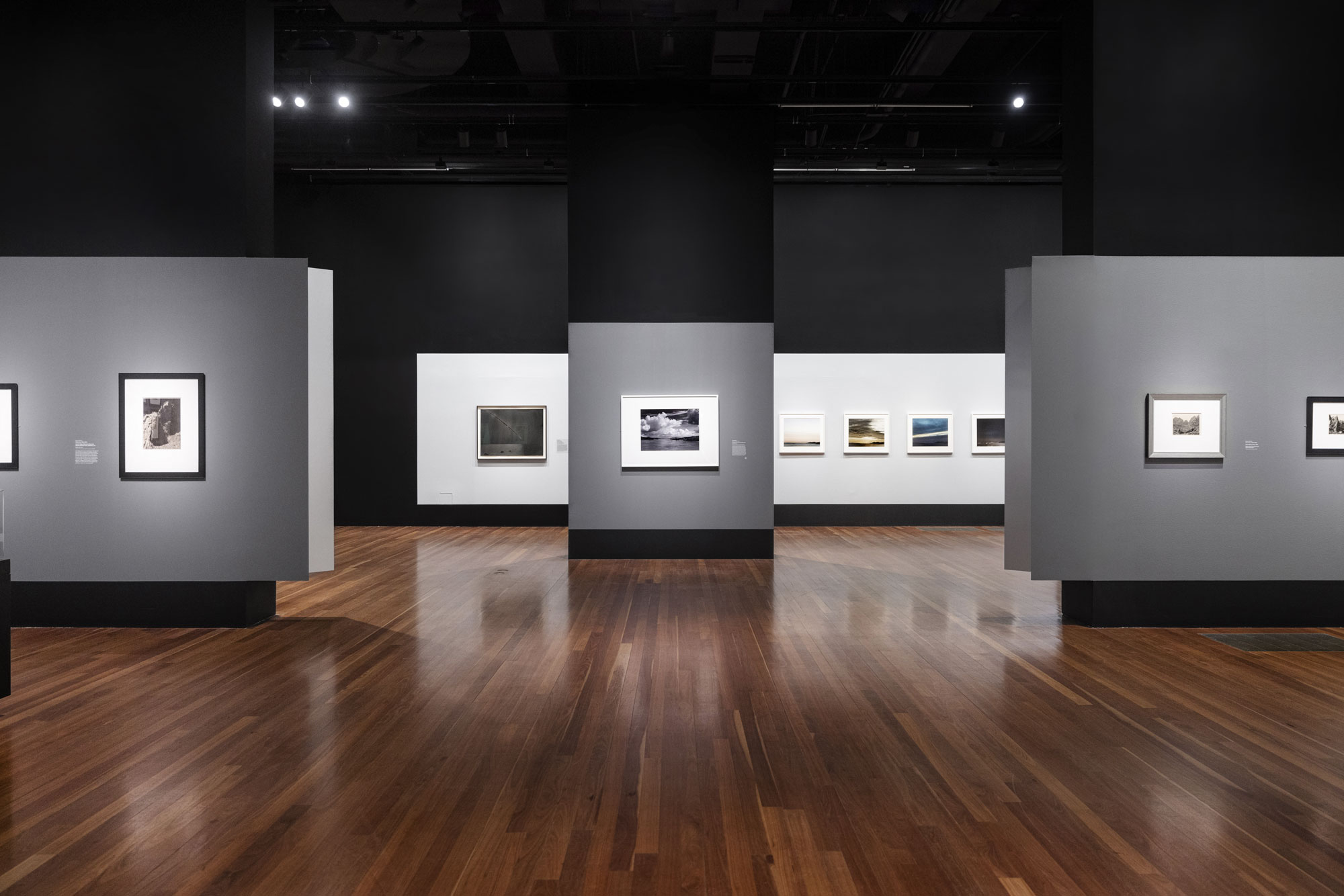
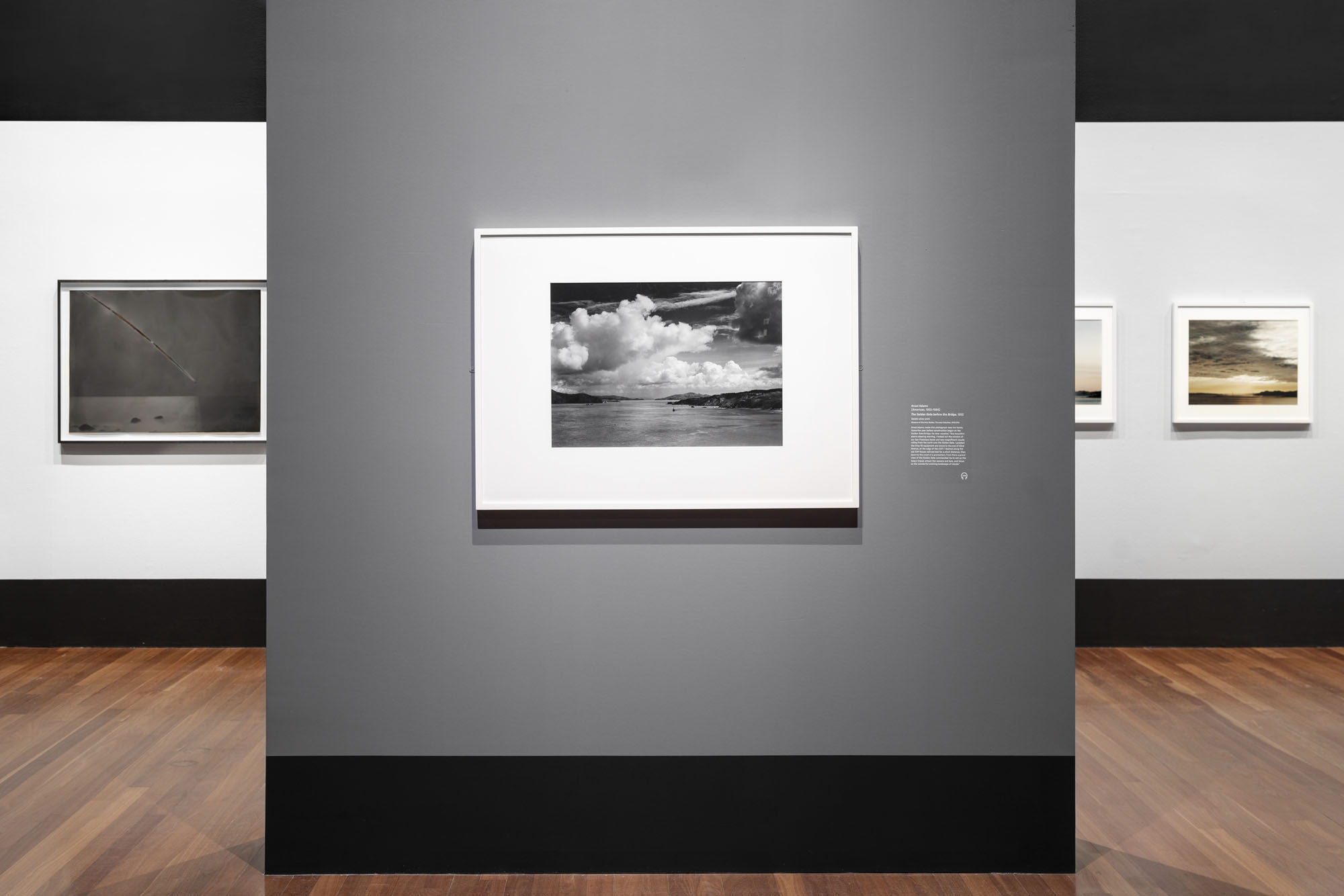
Consisting of 266 small black-and-white prints arranged on thirty-two pages, Abbott’s New York album marks a key turning point in her career – from her portrait work in Paris to the urban documentation that culminated in her federally funded project, Changing New York (1935-1939). Berenice Abbott’s New York Album, 1929 presents a selection of unbound pages from this unique album, shedding new light on the creative process of one of the great photographic artists of the twentieth century. For context, the exhibition also features views of Paris by Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927), whose extensive photographic archive Abbott purchased and publicised; views of New York City by her contemporaries Walker Evans, Paul Grotz, and Margaret Bourke-White; and photographs from Changing New York. The exhibition is made possible by The Robert Mapplethorpe Foundation, Inc.
Text from the Metropolitan Museum of Art website
MAP
This map charts some of the locations across Manhattan that Berenice Abbott photographed in her New York Album (1929). As the album bears almost no notations, identifying the exact sites depicted in the photographs had to be done through visual recognition of streets, buildings, and other urban landmarks.
Some of the iconic places Abbott photographed, such as the main branch of the New York Public Library and Trinity Church on Wall Street, haven’t changed much since 1929. Others, such as the city’s four elevated train lines and Harlem’s famed Lafayette Theater, have vanished completely. Several sites have gone through multiple transformations within the past century. The National Winter Garden Theater on Houston Street and Second Avenue opened in 1912 as a cinema and vaudeville theatre. By the time Abbott photographed it in 1929, it had been converted to a burlesque house; today, it’s a Whole Foods. The map is an invitation to explore Abbott’s photographs beyond the confines of the Museum’s galleries, and, like the artist herself, to cherish New York as a vibrant metropolis that is, and always has been, defined by change.
For their invaluable help with the historical research, The Met is grateful to the Jones Family Research Collective: former Manhattan Borough Historian Celedonia “Cal” Jones; his daughter, Diane Jones Randall; and his son, Kenneth Jones. Explore Abbott’s 1929 images of New York here with images of each album page.

Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Eugène Atget
1927
Gelatin silver print
4 3/8 × 3 5/16 in. (11.1 × 8.4cm)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Maria Morris Hambourg, in honour of John Szarkowski, 2020
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
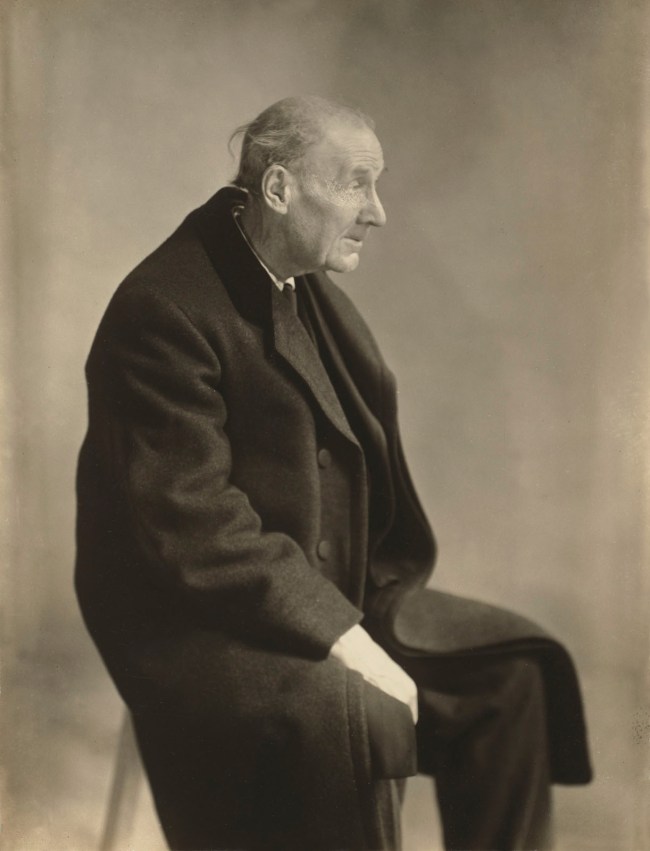
Born in Ohio, Berenice Abbott moved to Paris and in 1923 became Man Ray’s darkroom assistant. In 1927 she made this photograph of Atget, the renowned documentarian of the streets of Paris and an unwitting hero of the surrealists; when she returned to his apartment to deliver a print of her portrait, Abbott learned of the elderly artist’s death. The unfortunate circumstance put in motion a process that led to Abbott’s purchase of Atget’s archive of five thousand photographs and one thousand negatives, the first (1930) monograph on Atget (edited by Abbott), and the collection’s eventual acquisition by MoMA in 1968.
In the spring of 1927, Abbott invited Atget to sit for a portrait in her Paris studio. She made only three exposures that day: a standing pose, a frontal view, and this profile view. Unfortunately, Atget never saw the photographs. When Abbott arrived at his apartment a few months later to deliver the proofs, she found that the elderly photographer had died suddenly. This portrait was used as the frontispiece in the first book devoted to his work, Atget, Photographe de Paris (1930), displayed in the case nearby.

Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
James Joyce
1926
Gelatin silver print
23.3 x 17.4cm (9 3/16 x 6 7/8in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gilman Collection, Purchase, Ann Tenenbaum and Thomas H. Lee Gift, 2005
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
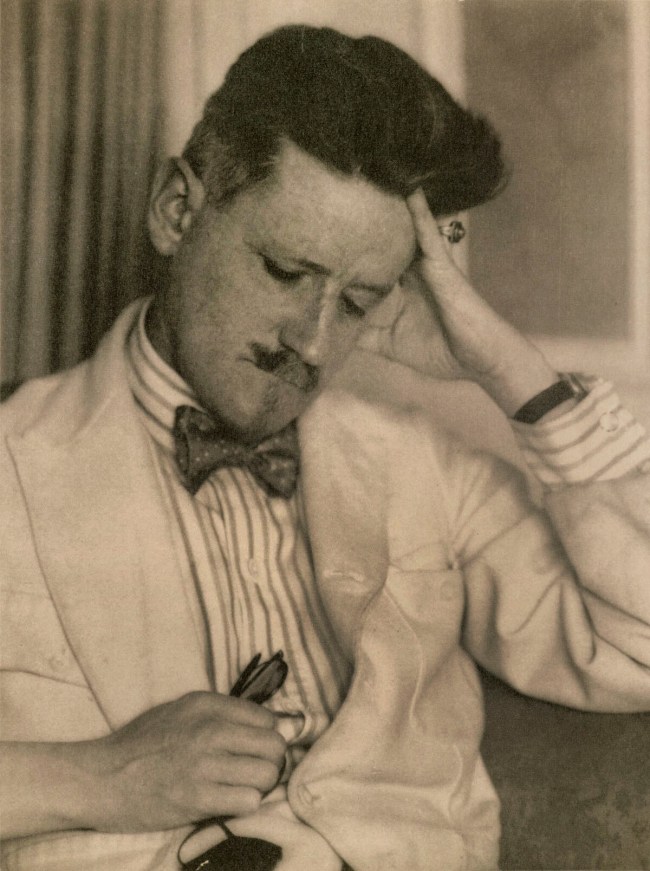
Berenice Abbott opened a photographic portrait studio in Paris in 1926 after having worked for three years as an assistant to Man Ray, whom she had met in New York. Although her Paris portraits are indebted stylistically to Man Ray’s, she brought to them a sympathetic eye that was very much her own. Her portraits of women are notable for their empathic understanding of her subjects, but she reached a depth of expression in her photographs of James Joyce (1882-1941). Abbott photographed Joyce on two occasions, the first in 1926 at his home, the second in 1928 at her studio, as was her more customary practice. In spite of Abbott’s annotation on the back of the print, this portrait belongs to the earlier session, when Joyce was photographed both with and without the patch over his eye, worn because of his sadly degenerating sight. For this particular exposure Joyce removed the patch and held it, with his glasses, in his right hand; his forehead still bears the diagonal impression of the ribbon. This intimate portrait, with its softly diffused lighting, suggests the complex, introverted character of Joyce’s imagination. It is with good reason that Abbott’s are considered the definitive portraits of the author of “Ulysses” and “Finnegan’s Wake.”

Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Djuna Barnes
1925
Gelatin silver print
22.6 x 17.1cm (8 7/8 x 6 3/4 in.)
Purchase, Joyce and Robert Menschel Gift, 1987
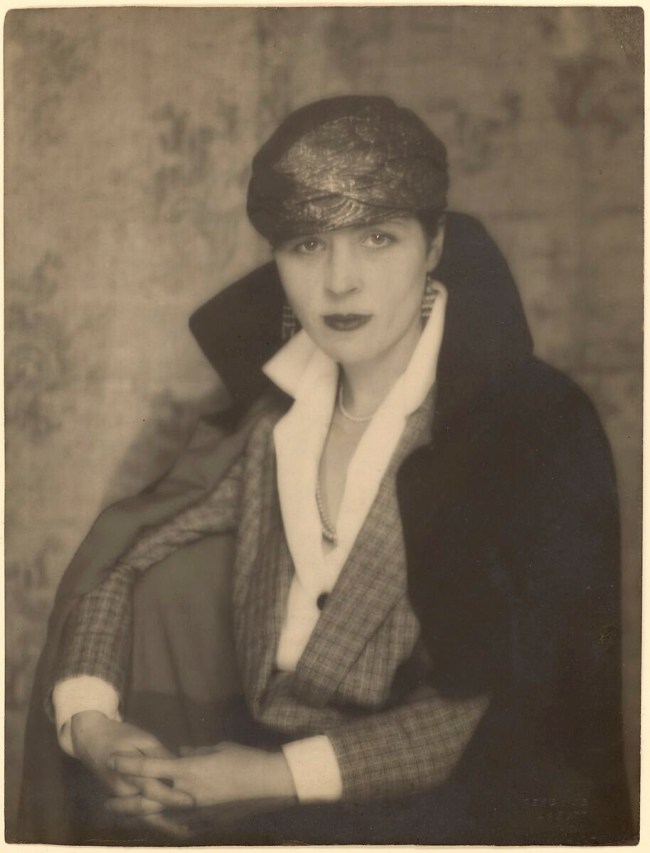
Abbott lived with the American writer Djuna Barnes when she moved from Ohio to Greenwich Village in 1918, and the two women remained friends, and occasional romantic rivals, throughout their lives. In this portrait, made in Man Ray’s Paris studio, Barnes is elegantly attired and addresses the camera with a smouldering gaze above a slight smile. A decade later, Barnes would publish Nightwood (1936), a classic of lesbian fiction inspired by her tormented affair with the American artist Thelma Wood (1901-1970), who also had a brief relationship with Abbott.

Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Buddy Gilmore, Paris
1926-1927
Gelatin silver print
23.1 x 17.2cm (9 1/8 x 6 3/4 in.)
Purchase
Gift of the Polaroid Corporation and matching funds from the National Endowment for the Arts, 1981
Gilmore was an American jazz drummer known for his acrobatic dexterity and energetic solos. After seeing him perform at Zelli’s, a nightclub in Paris, Abbott invited him to her studio to pose for this action portrait with his drum set. “I was simply crazy about his playing,” she recalled.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Fifth Avenue, Nos. 4, 6, 8
1936
Gelatin silver print
19.2 x 24.4cm (7 9/16 x 9 5/8 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Ford Motor Company Collection, Gift of Ford Motor Company and John C. Waddell, 1987
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
In 1929, after eight years in Paris, Abbott returned to America, bringing with her an immense collection of photographs by Eugène Atget and the ideas of European modernist photographers. Her first pictures of New York show the modernist influence in the sharply angled viewpoints and tendency toward abstraction. By the mid-1930s, however, Atget emerged as the stronger influence, as Abbott’s style became more straightforward and documentary.
In 1935 Abbott embarked on a series documenting New York funded by the Federal Art Project, and during the next four years she made hundreds of images of the city’s monuments and architecture. Ninety-seven of these, including “Fifth Avenue, Nos. 4, 6, 8,” were published in “Changing New York” (1939). The caption for this picture informs us that “No. 8 was once the home of the art collection which formed a part of the original Metropolitan Museum of Art.” It was built in 1856 for John Taylor Johnston, president of the Central Railroad of New Jersey. A leading collector of American art, Johnston was a founder of The Met and was elected its first president in 1870.
The New York Album
Abbott sailed for New York in January 1929, hoping to find an American publisher for a proposed book of Atget’s photographs and to promote her own portrait work. She brought with her a new handheld Curt Bentzin camera, thinking she might make some views of the city to sell to publishers in Europe. Inspired by the towering skyscrapers that had reshaped the American metropolis in the 1920s, Abbott pointed her camera up, down, and at skewed angles, creating dynamic compositions with sharp contrasts of light and shadow. She wandered all over Manhattan, photographing storefronts in Harlem, construction sites in midtown, and street vendors and tenement buildings in Chinatown and on the Lower East Side. She paid special attention to the city’s transportation infrastructure: bridges, elevated train lines, railroad terminals, ships docked on the waterfront.
Without access to a darkroom, Abbott had her negatives processed and printed at local drug stores and commercial labs. She pasted the little prints onto the pages of a standard photo album, creating a kind of sketchbook of subjects and themes. When The Met acquired it between 1978 and 1984, the album had already been disbound. Abbott reconstructed the sequence of the first eleven pages displayed here for a publication in 2013; the order of the remaining pages is unknown.
Changing New York
Abbott’s New York album laid the groundwork for her ambitious documentary project Changing New York (1935-1939). Comprising more than 300 negatives and a wealth of research, the project was funded by the Federal Art Project of the Works Progress Administration, a government program dedicated to supporting unemployed artists during the Great Depression. Aided by a team of researchers, field assistants, and darkroom technicians, Abbott chronicled “the changing aspect of the world’s great metropolis. … Its hurrying tempo, its congested streets, the past jostling the present.” She returned to many of the locations she visited in 1929, but the new photographs, made with a large-format view camera like the one Atget used, are more straightforward and less influenced by the jazzy, sharp-angled style of European modernism. The project culminated in a book, published in 1939, featuring ninety-seven photographs with captions by Abbott’s companion, the art critic Elizabeth McCausland. The photographs were widely exhibited and complete sets of the final images were distributed to high schools, libraries, and other public institutions throughout the New York area.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan]
1929
Gelatin silver prints
Images: approx. 2 1/4 × 3 1/4 in. (5.7 × 8.2cm), and the reverse
Album Page: 10 × 13 in. (25.4 × 33cm), irregular
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Emanuel Gerard, 1984
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan] 1929 (detail) Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan] 1929 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/abbott-album-page-financial-district-b.jpg?w=1024)
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan] (detail)
1929
Gelatin silver prints
Images: approx. 2 1/4 × 3 1/4 in. (5.7 × 8.2cm), and the reverse
Album Page: 10 × 13 in. (25.4 × 33cm), irregular
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Emanuel Gerard, 1984
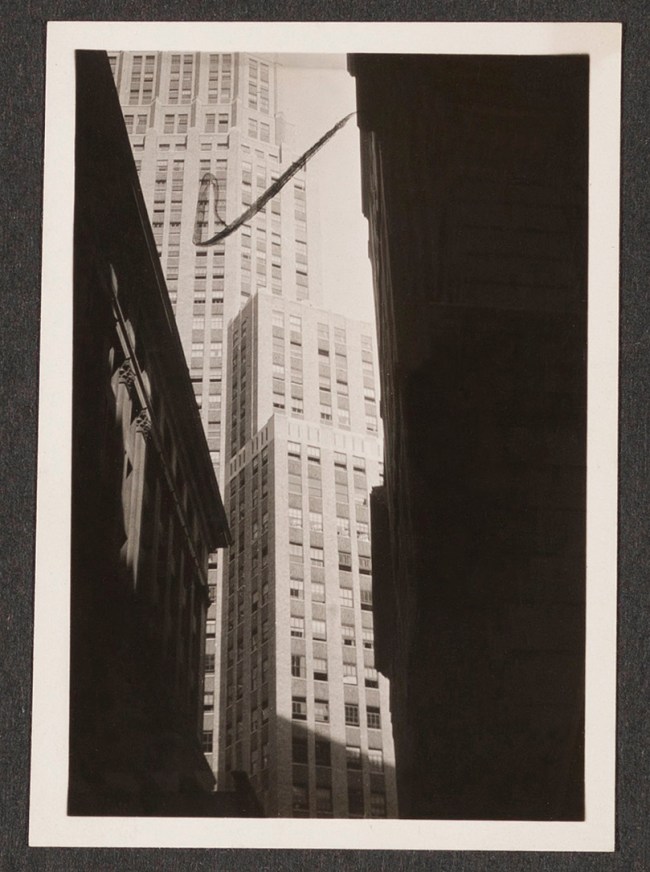
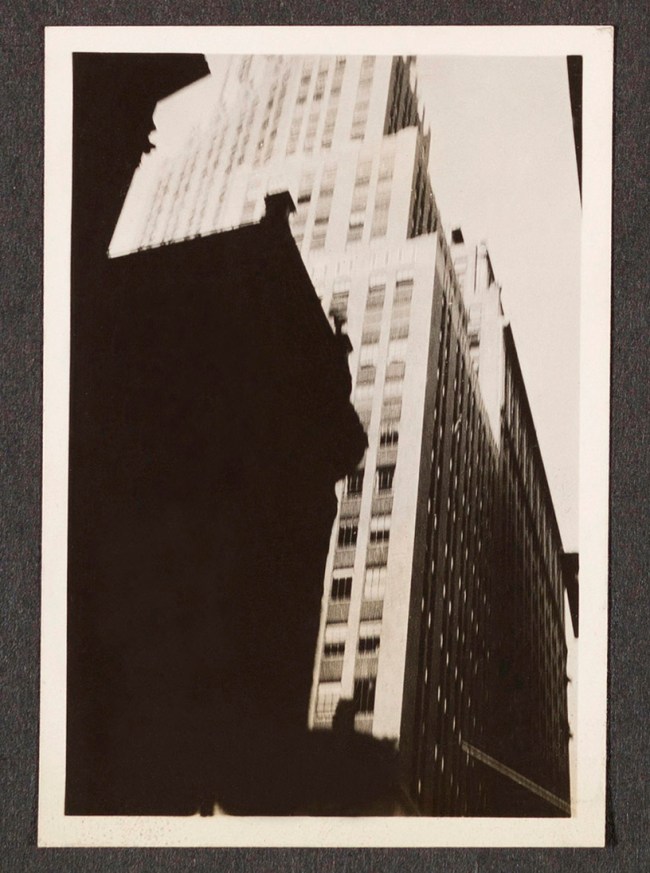
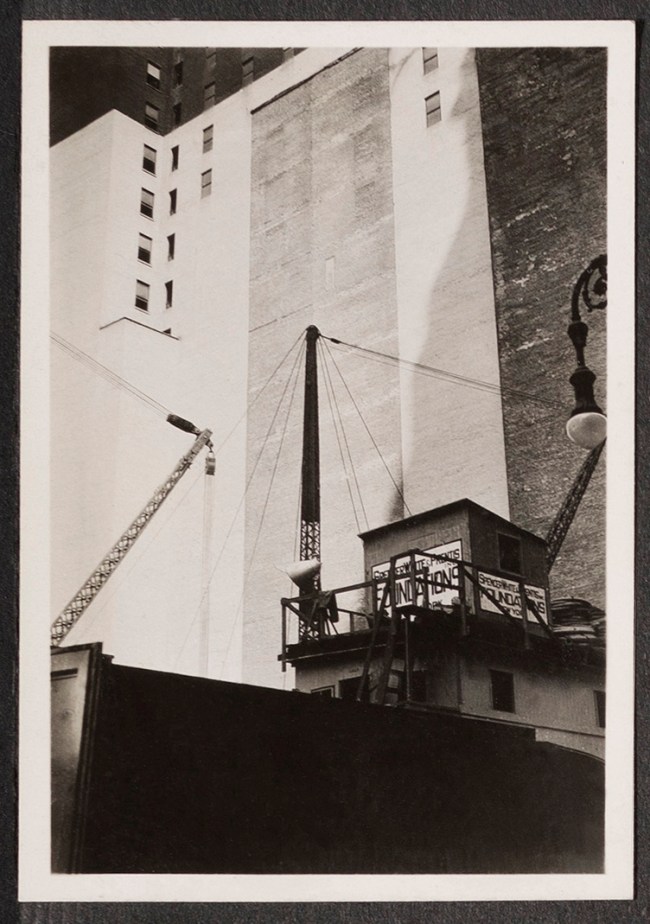





Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan] (details)
1929
Gelatin silver prints
Images: approx. 2 1/4 × 3 1/4 in. (5.7 × 8.2cm), and the reverse
Album Page: 10 × 13 in. (25.4 × 33cm), irregular
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Emanuel Gerard, 1984
If you were an American artist or writer in the 1920s, Paris was where you wanted to be. Springfield, Ohio-born photographer Berenice Abbott (1898-1991) arrived there in 1921 by way of New York, and by early 1929 she had managed to establish herself in the French capital’s flourishing interwar avant-garde scene – first working as an assistant to Man Ray and later taking her own celebrated portraits of luminaries such as James Joyce and Djuna Barnes. She even changed the spelling of her name from “Bernice” to the more Gallic “Berenice.”
Yet somehow this magnet for culturally minded expatriates lost its hold on Abbott the moment she set foot in Lower Manhattan – on a messy January day, no less – at the beginning of what was supposed to be a short trip back to the United States. She had lived in New York once, just eight years before, but in her absence the city had been scaled up: new skyscrapers were rising, the population was exploding, and every block, it seemed, was abuzz with commerce and construction. (The market crash of October 1929 was still many months away). Suddenly, Paris was passe. “When I saw New York again, and stood in the dirty slush,” she later recalled, “I felt that here was the thing I had been wanting to do all my life.”
“Berenice Abbott’s New York Album, 1929,” a small but inspiring show at the Metropolitan Museum, channels the exhilaration Abbott felt upon arriving in the city. The exhibition’s focus is a disbound scrapbook with seven to nine photographs per page, all taken over the course of that year, as Abbott paced the streets (and piers, bridges and train platforms) with a hand-held camera and a compulsion to capture New York’s unruly, cutthroat modernity.
With its 32 pages of small contact prints processed at drugstores and commercial labs (or as Abbott called them, “tiny photographic notes”), the album can be seen as a rough draft of her well-known Works Progress Administration project of the 1930s, “Changing New York.” (Several examples from this later series are in the Met show, including a disconcertingly ethereal view of Seventh Avenue taken from the top of a 46-story building in the garment district.) But Abbott’s “New York Album” is a fascinating artwork in its own right, an adrenalized and ambitious alignment of artist and subject.
Abbott felt the changing city needed an equivalent to the French photographer Eugène Atget (1857-1927), who had documented Paris during a critical period of transition in the late 19th and early 20th centuries with what Abbott called “the shock of realism unadorned.” She had come to New York as part of an impassioned effort to promote Atget’s oeuvre, one that included purchasing the photographer’s archive after his death and making her own prints from his glass-plate negatives; in the “New York Album” she goes further, becoming, in effect, his heir.
The Met’s exhibition incorporates several Atget photographs from the museum’s collection, including one that Abbott was known to admire; it shows an early automobile garage in the Fifth Arrondissement, with a Renault parked in a cobblestoned courtyard. A similar appreciation for the collision of the newfangled with the outmoded can be seen throughout Abbott’s “New York Album,” in shots of skyscrapers looming over rows of tenements and, in one more subtle and almost surreal case, an overhead view of an equine statue photographed from the Ninth Avenue El.
Although the album is not strictly organized by location, it has a distinct cartography. Abbott gravitated to certain neighborhoods that, for her, showed the face of the new city emerging. Many of them were in lower Manhattan; multiple pages are devoted to the Lower East Side, where she was drawn to storefronts and their simultaneously poetic and transactional signage, and the Financial District, where she often pointed her camera skyward to exaggerate the intimidating height of new corporate towers.
Unlike peers such as Walker Evans, she did not take much of an interest in the human subject – or, at least, in individuals. To her, the city was a human construction and humanity was implicit in every part of it. “You’re photographing people when you’re photographing a city,” she explained in a documentary film about her life. “You don’t have to have a person in it.”
As Abbott’s biographer has noted, she was influenced by the French literary movement of Unanimism, which emphasized collective consciousness and expression. You can sense this especially in her shots of the city’s elevated train system, which revel in the formal modernism of all that interlaced steel and cast iron without losing sight of its function of moving millions of people.
As an extension of the exhibition, the Met has created a helpful digital map that identifies some of the subjects in Abbott’s album and updates them with present-day photographs (a collaboration between the Met curator of photography who organized the exhibition, Mia Fineman, and the Jones Family Research Collective, led by the Manhattan borough historian emeritus, Celedonia Jones, until his death last April). It reveals, for example, that the site of a burlesque theater on Houston Street photographed by Abbott is now a Whole Foods.
Visitors to the exhibition can spend a lot of time testing their own knowledge of the city’s geography, but the pleasures of the show have more to do with the drive and dynamism behind the pictures. “Berenice Abbott’s New York Album, 1929” takes us back to an invigorating moment in the history of the metropolis, captured on the fly by an emergent modern artist.
During her upbringing in Ohio, Abbott had planned to be a journalist – she attended Ohio State University’s School of Journalism before turning to art – and it’s clear from her photography that she never lost that instinct for wanting to be where the story was. In those early months of 1929 she recognized that New York was the big story; looking at her “New York Album” gives us hope that it could be again.
Karen Rosenberg. “Berenice Abbott Captured Manhattan in the Throes of Heady Change,” on the New York Times website August 16, 2023 [Online] Cited 21/08/2023
Unanimism
Unanimism (French: Unanimisme) is a movement in French literature begun by Jules Romains in the early 1900s, with his first book, La vie unanime, published in 1904. It can be dated to a sudden conception Romains had in October 1903 of a ‘communal spirit’ or joint ‘psychic life’ in groups of people. It is based on ideas of collective consciousness and collective emotion, and on crowd behaviour, where members of a group do or think something simultaneously. Unanimism is about an artistic merger with these group phenomena, which transcend the consciousness of the individual. Harry Bergholz writes that “grossly generalising, one might describe its aim as the art of the psychology of human groups”. Because of this collective emphasis, common themes of unanimist writing include politics and friendship.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Album Page: Madison Square Park, Third Avenue and Ninth Avenue Elevated Train Lines, Manhattan]
1929
Gelatin silver prints
Images: 5.3 x 7.8cm (2 1/16 x 3 1/16 in.)
Sheet: 6.4 x 8.7cm (2 1/2 x 3 7/16 in.)
Album Page: 25.4 x 30.3cm (10 x 11 15/16in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Emanuel Gerard, 1978
In 1921 Ohio-native Abbott left New York to study in Paris. Returning to the city in 1929, she found it transformed and ripe with photographic potential. Following the model of the French photographer Eugène Atget, whose street views of Paris she admired, Abbott ventured around New York photographing seemingly incidental, but often profound, scenes that captured the city’s changing character. This page of small-scale photographs is one example of many of similar album pages in the Metropolitan’s collection. Assembled by Abbott, the album from which they derive comprised a kind of photographer’s sketchbook for subjects and themes.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Album Page: City Hall Park and Brooklyn Bridge Vicinity, Manhattan]
1929
Gelatin silver print
Album Page: 25.4 x 33.2 cm (10 x 13 1/16 in.), irregular
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Emanuel Gerard, 1981
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Album Page 5: Pier 17, South Street Seaport, Manhattan]
1929
Gelatin silver prints
Images: approx. 5.6 x 8.2cm (2 1/4 x 3 1/4 in.), and the reverse
Album Page: 25.3 x 30.5cm (9 15/16 x 12 in.), irregular
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Emanuel Gerard, 1982
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Album Page 9: Fulton Street Fish Market and Lower East Side, Manhattan]
1929
Gelatin silver print
Images: approx. 5.6 x 8.2cm (2 1/4 x 3 1/4 in.), and the reverse
Album Page: 25.3 x 30.5 cm (9 15/16 x 12 in.), irregular
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Emanuel Gerard, 1981
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Sumner Healy Antique Shop, 942 3rd Avenue near 57th Street, Manhattan]
1930s, printed 1936
Gelatin silver print
8 1/8 × 9 15/16 in. (20.6 × 25.2cm)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Phyllis D. Massar, 1971
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
In 1935 Abbott embarked on a series of photographs documenting New York City. Funded by the Federal Art Project, during the next four years she made hundreds of images of the city’s monuments and architecture, including this one of Sumner Healey’s shop. Attracted to the “extraordinary montage of antiques” – anchored by a ten-foot-tall figurehead of Mars from an eighteenth-century battleship – Abbott also captured the owner’s cat, seemingly trapped on either side by the decorative dogs flanking the store’s entrance. Healey died soon after Abbott made this photograph, and the shop closed two years later.

Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Pingpank Barbershop, 413 Bleecker Street, Manhattan
1938
Gelatin silver print
24.5 × 19.7cm (9 5/8 × 7 3/4 in.)
Twentieth Century Photography Fund, 2013
With its subtle interplay of reflection and interior, this slightly oblique view of a barbershop window reveals the influence of Atget’s photographs of Parisian storefronts. When Abbott made this image, August Pingpank was eighty-seven and was said to be the oldest barber in New York City. He lamented to Federal Art Project researchers that he would soon have to retire due to the invention of the safety razor: “It’s different now with men shaving themselves every morning at home.”
Berenice Abbott’s New York Album, 1929 presents selections from a unique unbound album of photographs of New York City created by American photographer Berenice Abbott (1898-1991), shedding light on the creative process of one of the great artists of the 20th century. Consisting of 266 small black-and-white prints arranged on 32 pages, the album is a kind of photographic sketchbook that offers a rare glimpse of an artist’s mind at work. In addition to some 25 framed album pages, the exhibition features photographs from The Met collection of Paris streets by Eugène Atget, whose archive Abbott purchased and promoted; views of New York by her contemporaries Walker Evans and Margaret Bourke-White; and selections from Abbott’s grand documentary project, Changing New York (1935-1939).
“Berenice Abbott’s groundbreaking work in photography continues to inspire and captivate audiences today, nearly a century after she first began documenting the world around her,” said Max Hollein, Marina Kellen French Director of The Met. “Abbott’s insightful and powerful images provide a window into the New York of the past, while also reminding us of the city’s enduring vitality and resilience.”
Born in Ohio, Abbott moved to New York City in 1918 and to Paris in 1921. She learned photography as a darkroom assistant in Man Ray’s studio and soon established herself as a prominent portraitist of the Parisian avant-garde. Through Man Ray, Abbott met the ageing French photographer Eugène Atget, whose documentation of Paris and its environs struck her as a model of modern photographic art. Following Atget’s sudden death in 1927, she purchased his archive of some 8,000 prints and 1,500 glass negatives and set about promoting his work through exhibitions and publications.
In January 1929, after eight years in Europe, Abbott boarded an ocean liner to New York City for what was intended to be a short visit. Upon arrival, she found the city transformed and ripe with photographic potential. “When I saw New York again, and stood in the dirty slush, I felt that here was the thing I had been wanting to do all my life,” she recalled. Inspired by Atget, Abbott traversed the city with a handheld camera, photographing its skyscrapers, storefronts, bridges, elevated trains, and neighbourhood street life. She pasted these “notes” into a standard black-page album, arranging them by subject and locale. As the immediate precursor to her 1930s WPA project, Changing New York, Abbott’s New York album marks a key moment of transition in her career: from Europe to America and from studio portraiture to urban documentation. The exhibition will be accompanied by an online feature that identifies, for the first time, the locations of many of the photographs in the album.
Berenice Abbott’s New York Album, 1929 is organised by Mia Fineman, Curator in the Department of Photographs, with assistance from Virginia McBride, Research Assistant in the Department of Photographs, both at The Met.
Press release from the Metropolitan Museum of Art
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
The El at Columbus and Broadway
1929
15.0 x 20.3cm (5 15/16 x 8 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Ford Motor Company Collection, Gift of Ford Motor Company and John C. Waddell, 1987
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Following her eight years of expatriate life in Paris, Abbott saw New York with European eyes. In this view, made shortly after her return, she captured the random disorder of urban activity as handily as her friend the dadaist poet Tristan Tzara, who put it this way: “We leave with those leaving arrive with those arriving / leave with those arriving arrive when the others leave.”
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [The El, 2nd and 3rd Avenue Lines, Bowery and Division Street, Manhattan] 1936 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [The El, 2nd and 3rd Avenue Lines, Bowery and Division Street, Manhattan] 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/abbott-the-el-2nd-and-3rd-avenue-lines-bowery-and-division-street-manhattan.jpg?w=650)
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[The El, 2nd and 3rd Avenue Lines, Bowery and Division Street, Manhattan]
1936
Gelatin silver print
Image: 9 11/16 × 7 5/8 in. (24.6 × 19.3cm)
Sheet: 9 7/8 × 7 15/16 in. (25.1 × 20.1cm)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Gift of Phyllis D. Massar, 1971
Manhattan’s elevated (El) train lines fascinated Abbott when she first photographed the city in 1929. Seven years later, she used her large-format camera to capture this shadowed vista beneath the El in Chinatown. “I was right in the middle of the street on a little island,” she recalled. “This was one of the occasions when it was downright dangerous to document New York, with traffic whizzing by on both sides, but it was very important to get in exactly the right position to make the photograph work.”
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Manhattan Bridge] 1936 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Manhattan Bridge] 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/abbott-manhattan-bridge.jpg?w=650)
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Manhattan Bridge]
1936
Gelatin silver print
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Phyllis D. Massar, 1971
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
The Brooklyn Bridge was New York’s first and most famous, but Abbott favoured the all-steel Manhattan Bridge, completed in 1909. She made this photograph on the southern pedestrian walkway; the vibrations of the suspension bridge required a fast shutter speed to avoid blur. “I seem to veer toward waterfronts,” she later said. “As Melville wrote in Moby Dick, the heart of a port city is around its waterfront, and by nature I seem to head right there. Perhaps I should have been a sailor – boats and bridges have always fascinated me.”
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Seventh Avenue Looking South from Thirty-fifth Street, New York] 1935 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Seventh Avenue Looking South from Thirty-fifth Street, New York] 1935](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/abbott-seventh-avenue-looking-south-from-thirty-fifth-street.jpg?w=650)
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
[Seventh Avenue Looking South from Thirty-fifth Street, New York]
1935
Gelatin silver print
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Phyllis D. Massar, 1971
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Abbott made this overhead view of skyscrapers in the garment district from atop the forty-six-story Nelson Tower on Seventh Avenue. The roof of the original Pennsylvania Station, demolished in 1962, can be seen in the lower right corner.
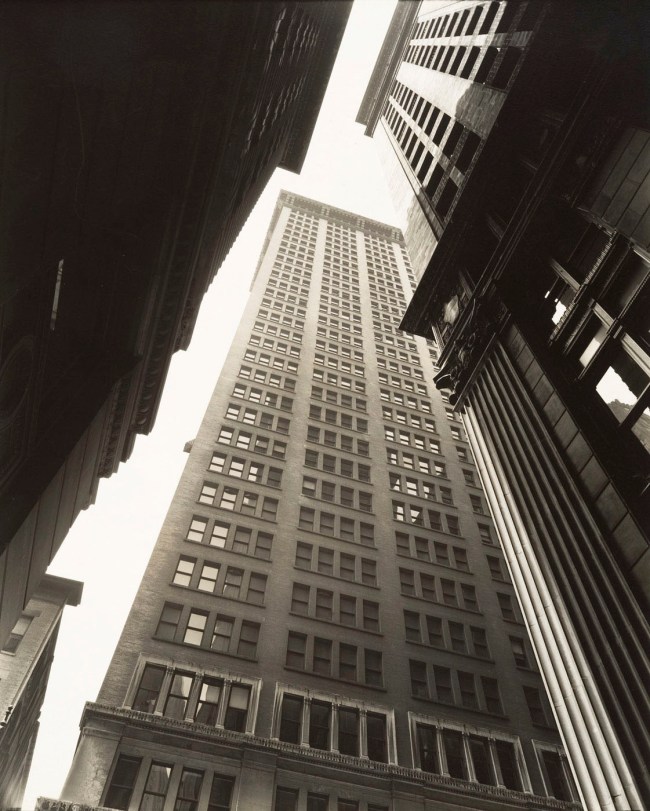

Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Canyon, Broadway and Exchange Place
1936
Gelatin silver print
23.8 x 19.3cm (9 3/8 x 7 5/8 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1991
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
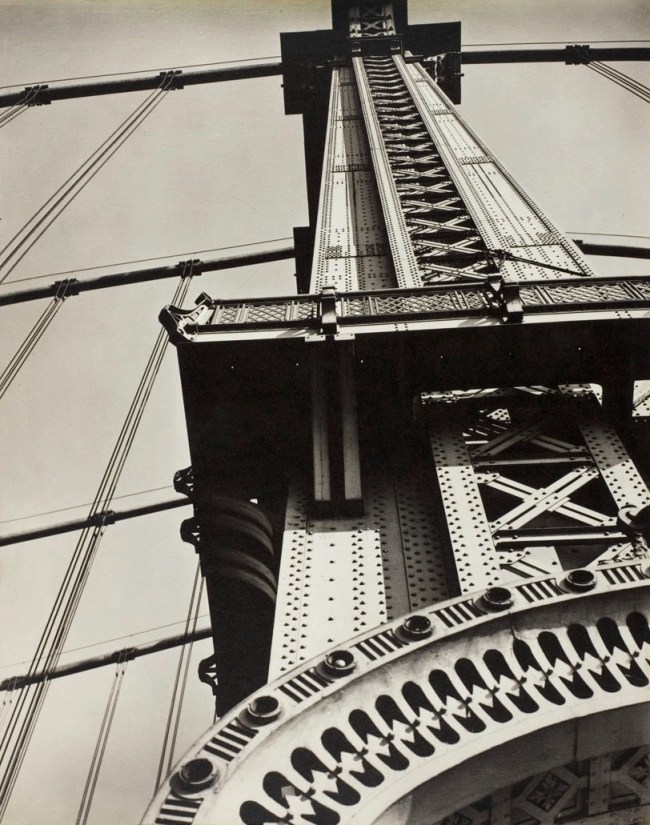

Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Manhattan Bridge, Looking Up
1936
Gelatin silver print
24.5 x 19.4cm (9 5/8 x 7 5/8 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Phyllis D. Massar, 1971
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Brooklyn Bridge, With Pier 21, Pennsylvania R.R.
1937
Gelatin silver print
19.4 x 24.4cm (7 5/8 x 9 5/8 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1991
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
West Street
1936
Gelatin silver print
19.1 x 24cm (7 1/2 x 9 7/16 in. )
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Jane and Mark Ciabattari, 2000
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Henry Street from Market, Looking West, Manhattan
1935
Gelatin silver print
19.2 x 24.2cm (7 9/16 x 9 1/2 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Joyce F. Menschel, 2012
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Automat, 977 Eighth Avenue, Manhattan
1936
Gelatin silver print
Image: 19.4 x 24.6cm (7 5/8 x 9 11/16 in.)
Sheet: 22 x 25.3cm (8 11/16 x 9 15/16 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gift of Joyce F. Menschel, 2011
© Berenice Abbott / Commerce Graphics Ltd. Inc.
During the Depression, Horn & Hardart’s chain of “waiterless restaurants” served as many as eight hundred thousand freshly prepared meals a day to customers in New York and Philadelphia. With its clean lines, polished chrome details, and mechanical efficiency, the Automat struck Abbott as “an extremely American artefact.” New York’s first Automat opened in Times Square in 1912, but Abbott chose to document the branch at Columbus Circle, popular as a nighttime gathering spot for musicians and cabaret patrons.
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)

Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Printer: Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Street Musicians
1898-1999, printed 1956
Title page from the portfolio 20 Photographs by Eugène Atget (1856-1927), 1956
Published by Berenice Abbott, New York Gelatin silver print from glass negatives David Hunter McAlpin Fund, 1956
In 1956 Abbott produced a portfolio of twenty new prints from Atget’s glass-plate negatives and offered it by subscription to museums, libraries, and private collectors. This photograph of an organ grinder and exuberant female singer belongs to a series of photographs devoted to the rapidly vanishing street trades, or petits métiers, of Paris.
![Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) [Atget's Work Room with Contact Printing Frames] c. 1910 Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927) [Atget's Work Room with Contact Printing Frames] c. 1910](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/atgets-work-room-web1.jpg?w=650)
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
[Atget’s Work Room with Contact Printing Frames]
c. 1910
Albumen silver print from glass negative
20.9 x 17.3cm (8 1/4 x 6 13/16 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1990
This straightforward study by Atget of his own work room offers a rare glimpse of the inner sanctum of an auteur éditeur, as he described his profession. On the table are the wooden frames the photographer used to contact print his glass negatives; at right are several bins of negatives stacked vertically; below the table are his chemical trays; on the shelves above are stacks of paper albums – a shelf label reads escaliers et grilles (staircases and grills). Atget used these homemade albums to organise his vast picture collection from which he sold views of old Paris to clients.

Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
15, rue Maître-Albert
1912
Gelatin silver print from glass negative
23.2 x 17.6 cm (9 1/8 x 6 15/16 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Rogers Fund, 1991
Creative Commons CC0 1.0
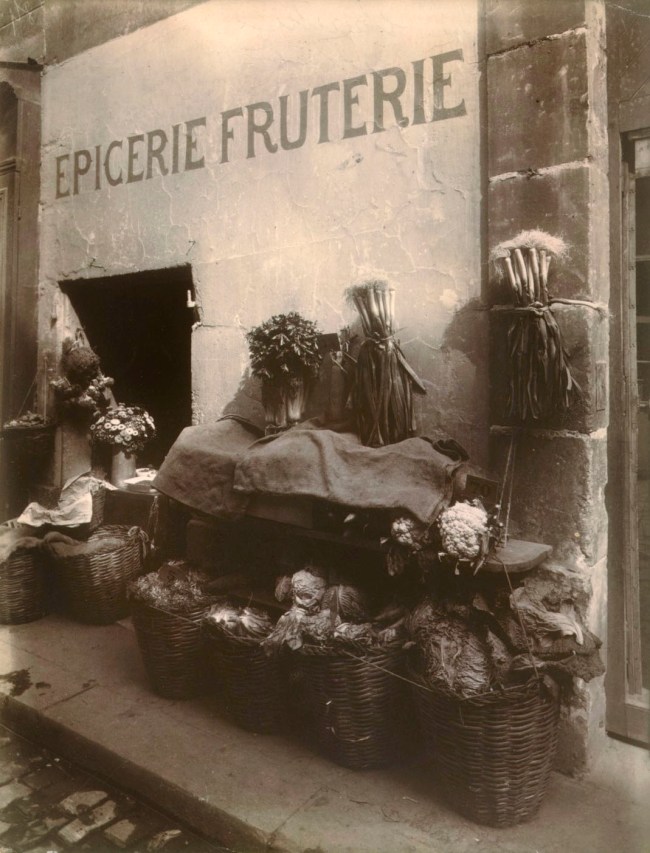
Eloquent testimony to Atget’s keen regard for the expressions of common folk, this photograph was part of a self-assigned survey of storefronts and commercial signs. Atget ennobled the little grocery with its modest façade and rudimentary display (covered for lunch hour against the midday heat) and framed it simply, thus withdrawing it from the predictable realm of the picturesque.
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Courtyard, 7 Rue de Valence, 5th arr.
1922
Gelatin silver print from glass negative
Image: 17.2 x 22.7cm (6 3/4 x 8 15/16 in.)
Mount: 36.7 x 28.7cm (14 7/16 x 11 5/16 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Gilman Collection, Purchase, Ann Tenenbaum and Thomas H. Lee Gift, 2005
Atget found his vocation in photography in 1897, at the age of forty, after having been a merchant seaman, an itinerant actor, and a painter. He became obsessed with making what he termed “documents” of Paris and its environs, and with compiling a visual compendium of the architecture, landscape, and artefacts that distinguish French culture and its history. By the end of his life, Atget had amassed an archive of over 8,000 negatives that he had organised into such categories as Parisian Interiors, Petits Métiers (trades and professions), and Vehicles in Paris.
The subject of this photograph is an early automobile garage occupying a timeworn courtyard near the intersection of rue Mouffetard and rue Monge in the fifth arrondissement. Although Atget’s interest was primarily in the texture of old Paris – not the city’s new promenades and modern monuments – he did make a few studies of automobiles, signs of modern times, beginning in 1922. Beside a pair of motorcycles rests an early-model Renault touring car, probably dating from 1908. It, too, may be a relic: its four-cylinder engine lies beside it.
Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Printer: Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Fête du Trône
1925, printed c. 1929
Matte gelatin silver print from glass negative
23.4 x 17cm (9 3/16 x 6 11/16 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1999
Abbott made new contact prints from Atget’s glass-plate negatives, experimenting with various photographic papers and processes to try to approximate the clarity and detail of Atget’s own prints. Sometime early in 1930, Walker Evans visited Abbott’s studio in New York’s Hotel des Artistes, where she stored her vast Atget archive. Deeply affected by the French photographer’s work, Evans left that day with four of Abbott’s Atget prints: this one, Boutique, Marché aux Halles (displayed to the right), and two others. Although Atget’s work was never exhibited during his lifetime, his soulful documentation of Paris had a profound impact on both Abbott and Evans, and contributed to the emergence of a documentary style in twentieth-century American art photography.
Learning from Atget
When Abbott met Eugène Atget in 1926, he had been photographing Paris for thirty years. Working with a large wooden-view camera, Atget made what he modestly called “documents” of the city, compiling a vast visual archive of Parisian streets, courtyards, gardens, shop windows, architectural details, apartment interiors, and tradespeople. Atget’s studio was on the same street in Montparnasse as that of Man Ray, who purchased several dozen of his photographs, publishing four of them in the journal La Révolution surréaliste. Abbott was instantly captivated by Atget’s photographs when she encountered them in Man Ray’s studio. “Their impact was immediate and tremendous,” she recalled. “There was a sudden flash of recognition – the shock of realism unadorned. The subjects were not sensational, but nevertheless shocking in their very familiarity.” In 1927 Abbott persuaded Atget to sit for a portrait in her own studio on the rue du Bac. Months later, following his sudden death at age seventy, she purchased his archive of some 8,000 prints and 1,500 glass negatives and set about promoting his work through exhibitions, publications, and sales of the prints, a selection of which are on display here. When she moved to New York in 1929, Abbott brought the archive with her, and eventually sold it to the Museum of Modern Art in 1968.
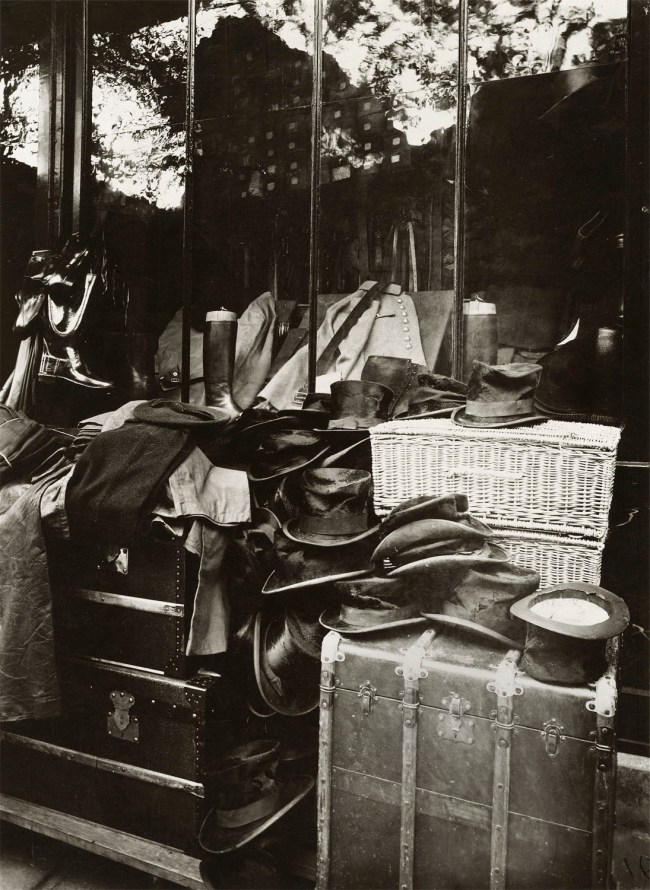

Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Printer: Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991)
Boutique, Marché aux Halles, Paris
1925, printed c. 1929
Matte gelatin silver print from glass negative
23.1 x 17cm (9 1/8 x 6 11/16 in. )
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Purchase, The Horace W. Goldsmith Foundation Gift, through Joyce and Robert Menschel, 1999
Creative Commons CC0 1.0
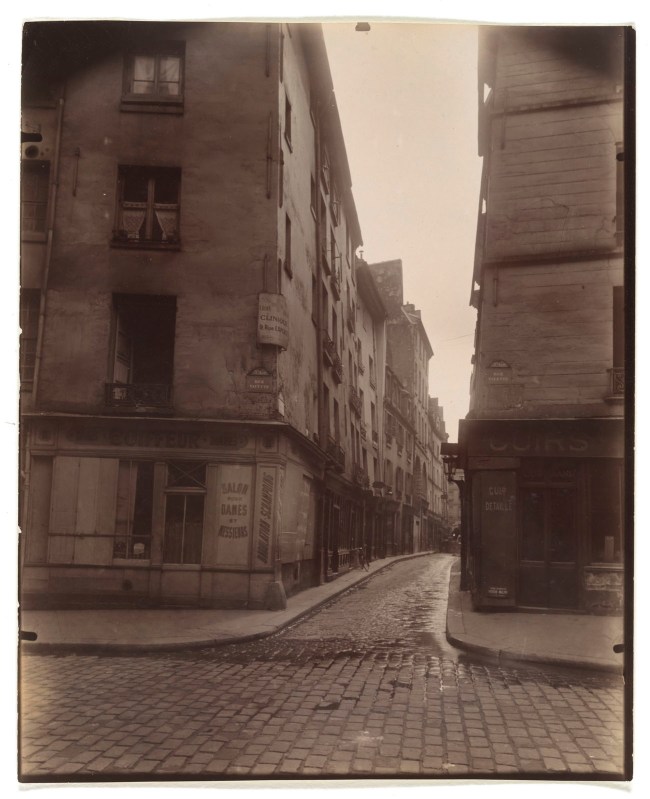

Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Rue Laplace and Rue Valette, Paris
1926
Gelatin silver print from glass negative
Image: 22 x 17.6cm (8 11/16 x 6 15/16 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Elisha Whittelsey Collection, The Elisha Whittelsey Fund, by exchange, 1970
Creative Commons CC0 1.0
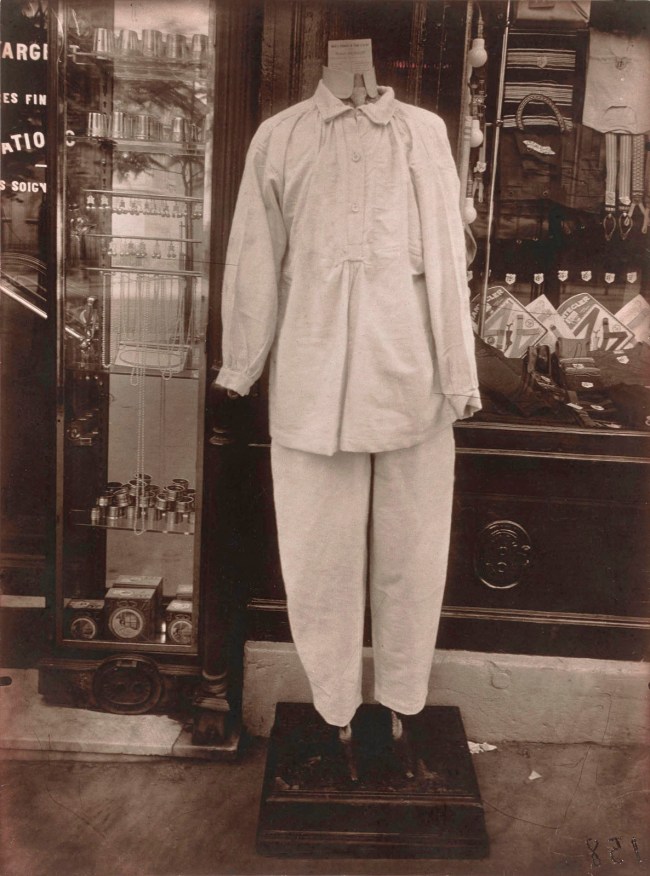

Eugène Atget (French, 1857-1927)
Avenue des Gobelins
1927
Gelatin silver print from glass negative
36.8 x 28.6cm (14 1/2 x 11 1/4 in.)
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Purchase, Rogers Fund, and Joyce and Robert Menschel and Harriette and Noel Levine Gifts, 1994
In this headless mannequin, clothed in a simple white uniform, Atget recognised a modern version of the commedia dell’arte clown Gilles, depicted by the eighteenth-century painter Jean Antoine Watteau, for example. It was for the type of transforming vision seen in this picture, which is among the very last in Atget’s lifelong exploration of Paris, that the artist’s work was so enthusiastically embraced by the Surrealists.
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
1000 Fifth Avenue at 82nd Street
New York, New York 10028-0198
Phone: 212-535-7710
Opening hours:
Thursday – Tuesday 10am – 5pm
Closed Wednesday


![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan] 1929 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 1: Financial District, Broadway and Wall Street Vicinity, Manhattan] 1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/07.-berenice-abbott-album-page-1-financial-district-broadway-and-wall-street-vicinity-manhattan-1929.jpg)
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page: Madison Square Park, Third Avenue and Ninth Avenue Elevated Train Lines, Manhattan] 1929 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page: Madison Square Park, Third Avenue and Ninth Avenue Elevated Train Lines, Manhattan] 1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/abbott-album-page-madison-square-park-third-avenue-and-ninth-avenue-elevated-train-lines-manhattan.jpg)
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page: City Hall Park and Brooklyn Bridge Vicinity, Manhattan] 1929 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page: City Hall Park and Brooklyn Bridge Vicinity, Manhattan] 1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/06.-berenice-abbott-album-page-city-hall-park-and-brooklyn-bridge-vicinity-manhattan-1929.jpg)
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 5: Pier 17, South Street Seaport, Manhattan] 1929 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 5: Pier 17, South Street Seaport, Manhattan] 1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/08.-berenice-abbott-album-page-5-pier-17-south-street-seaport-manhattan-1929.jpg)
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 9: Fulton Street Fish Market and Lower East Side, Manhattan] 1929 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Album Page 9: Fulton Street Fish Market and Lower East Side, Manhattan] 1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/09.-berenice-abbott-album-page-9-fulton-street-fish-market-and-lower-east-side-manhattan-1929.jpg)
![Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Sumner Healy Antique Shop, 942 3rd Avenue near 57th Street, Manhattan] 1930s, printed 1936 Berenice Abbott (American, 1898-1991) [Sumner Healy Antique Shop, 942 3rd Avenue near 57th Street, Manhattan] 1930s, printed 1936](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/abbott-sumner-healy-antique-shop.jpg)
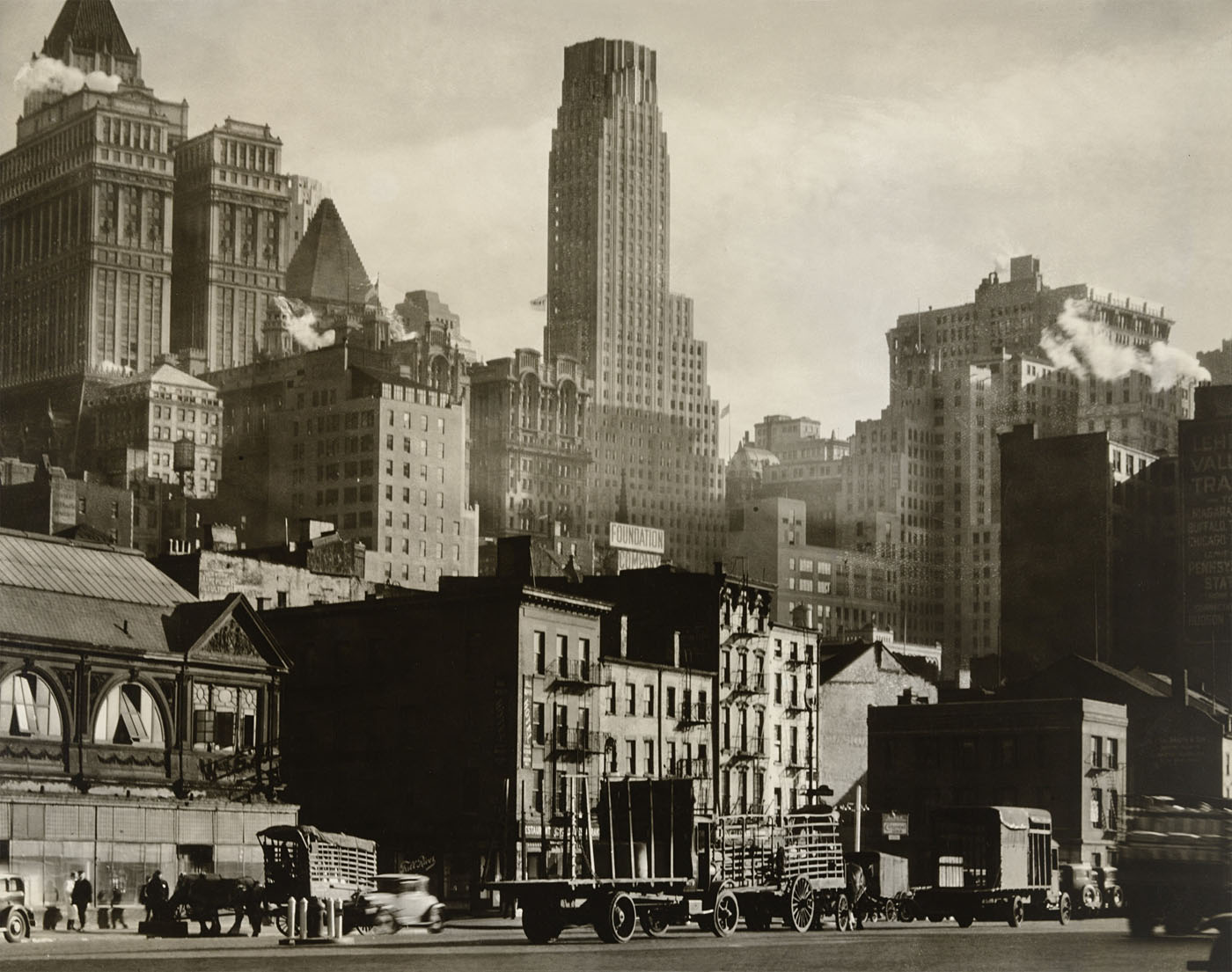
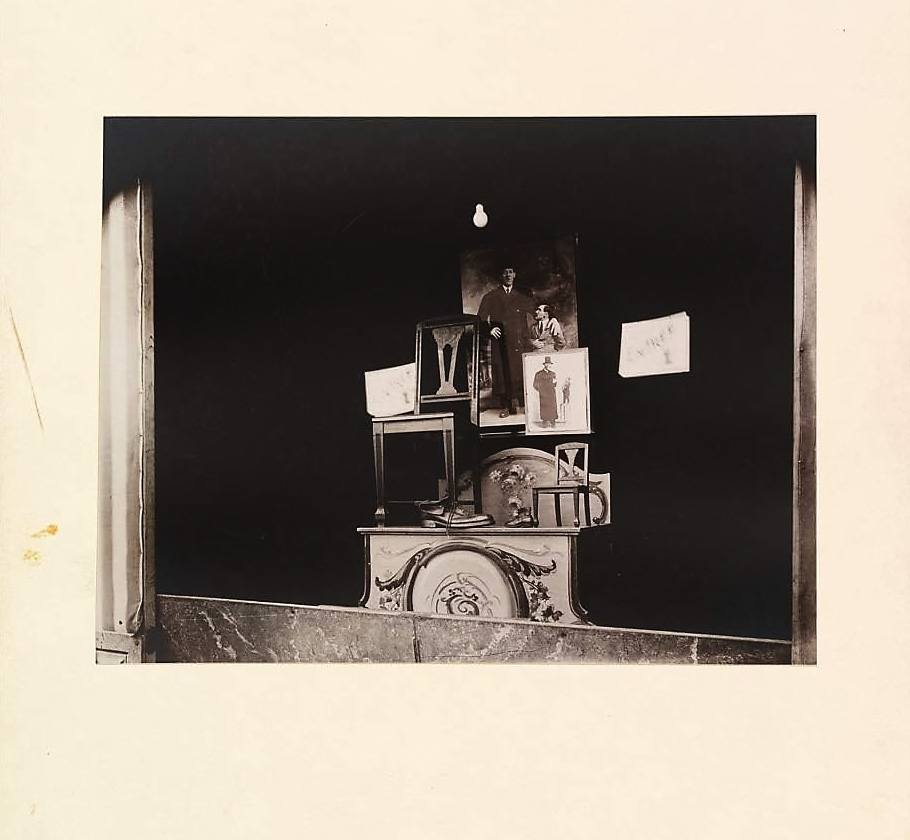







![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Boulevard de Clichy, Paris' [Boulevard de Clichy, París] 1951 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Boulevard de Clichy, Paris' [Boulevard de Clichy, París] 1951 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/03.-id40_p.jpg)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Aubervilliers, France' [Aubervilliers, Francia] 1947 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Aubervilliers, France' [Aubervilliers, Francia] 1947 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/02.-id37_p.jpg?w=801)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Concentric Circles, Construction Site, New York' [Círculos concéntricos, obra, Nueva York] 1952 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Concentric Circles, Construction Site, New York' [Círculos concéntricos, obra, Nueva York] 1952 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/11.-id737_p.jpg)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Manhole, Times Square, New York' [Tapa de alcantarilla, Times Square, Nueva York] 1954 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Manhole, Times Square, New York' [Tapa de alcantarilla, Times Square, Nueva York] 1954 from the exhibition 'Louis Stettner' at Fundación MAPFRE Recoletos Room (Madrid), June - August, 2023](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/08.-id68_p-b.jpg?w=689)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Brooklyn Promenade, Brooklyn, New York' [Brooklyn Promenade, Brooklyn, Nueva York] 1954 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Brooklyn Promenade, Brooklyn, New York' [Brooklyn Promenade, Brooklyn, Nueva York] 1954](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/09.-id1_p.jpg)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Nancy Listening to Jazz, Greenwich Village, New York' [Nancy escuchando jazz, Greenwich Village, Nueva York] 1958 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Nancy Listening to Jazz, Greenwich Village, New York' [Nancy escuchando jazz, Greenwich Village, Nueva York] 1958](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/10.-id4211_p.jpg?w=744)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Woman Holding Newspaper, New York' [Mujer sujetando un periódico, Nueva York] 1946 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Woman Holding Newspaper, New York' [Mujer sujetando un periódico, Nueva York] 1946](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/01.-id1732_p.jpg)
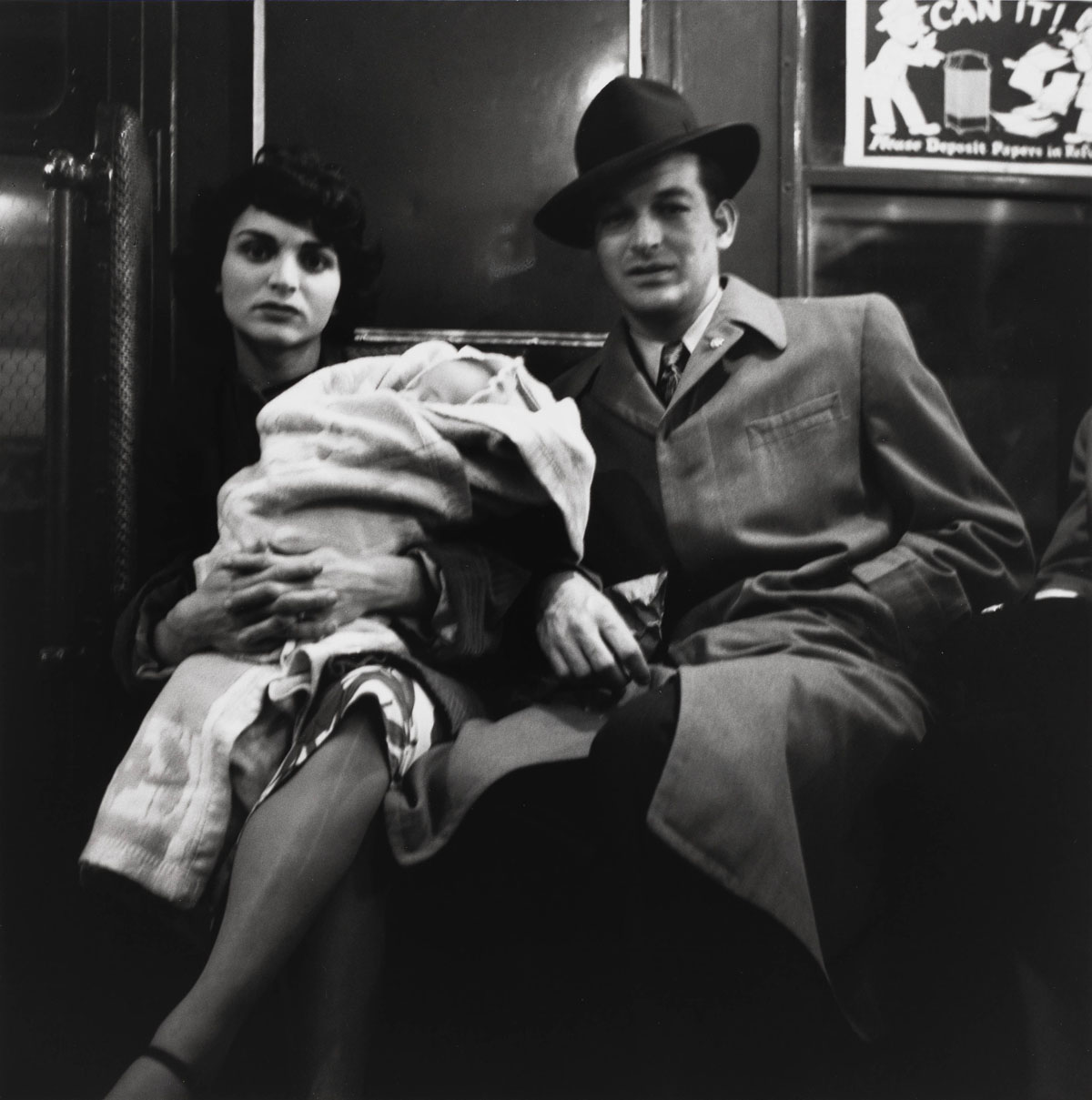



![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Train Station Near Málaga, Spain' [Estación de tren cerca de Málaga, España] 1951 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Train Station Near Málaga, Spain' [Estación de tren cerca de Málaga, España] 1951](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/05.-id74_p.jpg?w=675)


![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Tony, "Pepe and Tony, Spanish Fishermen", Ibiza, Spain' [Tony, "Pepe y Tony, pescadores españoles", Ibiza, España] 1956 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Tony, "Pepe and Tony, Spanish Fishermen", Ibiza, Spain' [Tony, "Pepe y Tony, pescadores españoles", Ibiza, España] 1956](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/04.-id4569_p.jpg?w=669)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Commuters, Evening Train, Penn Station, New York' [Volviendo del trabajo en el tren de la tarde, Penn Station, Nueva York] 1958 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Commuters, Evening Train, Penn Station, New York' [Volviendo del trabajo en el tren de la tarde, Penn Station, Nueva York] 1958](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/06.-id179_p.jpg?w=684)
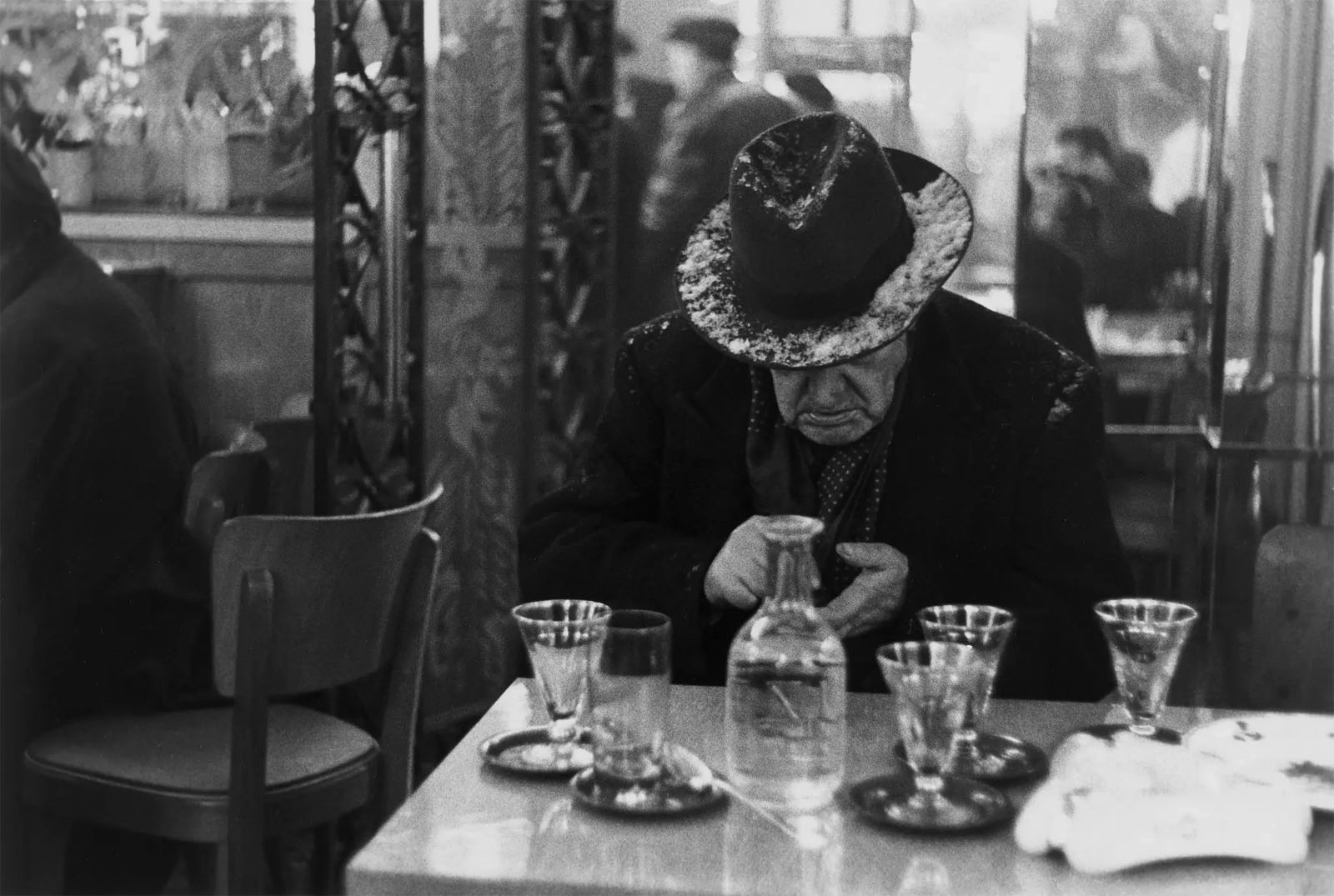
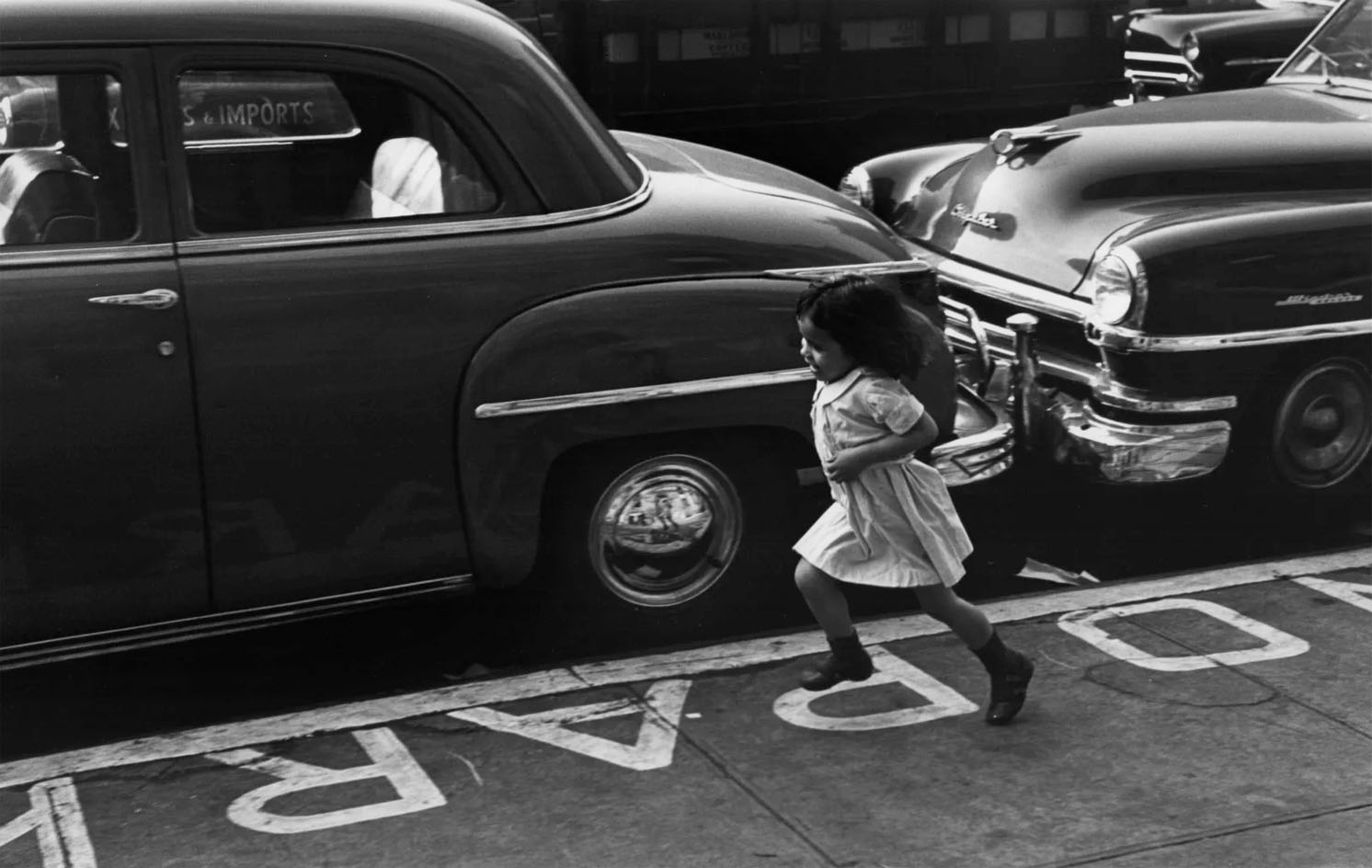
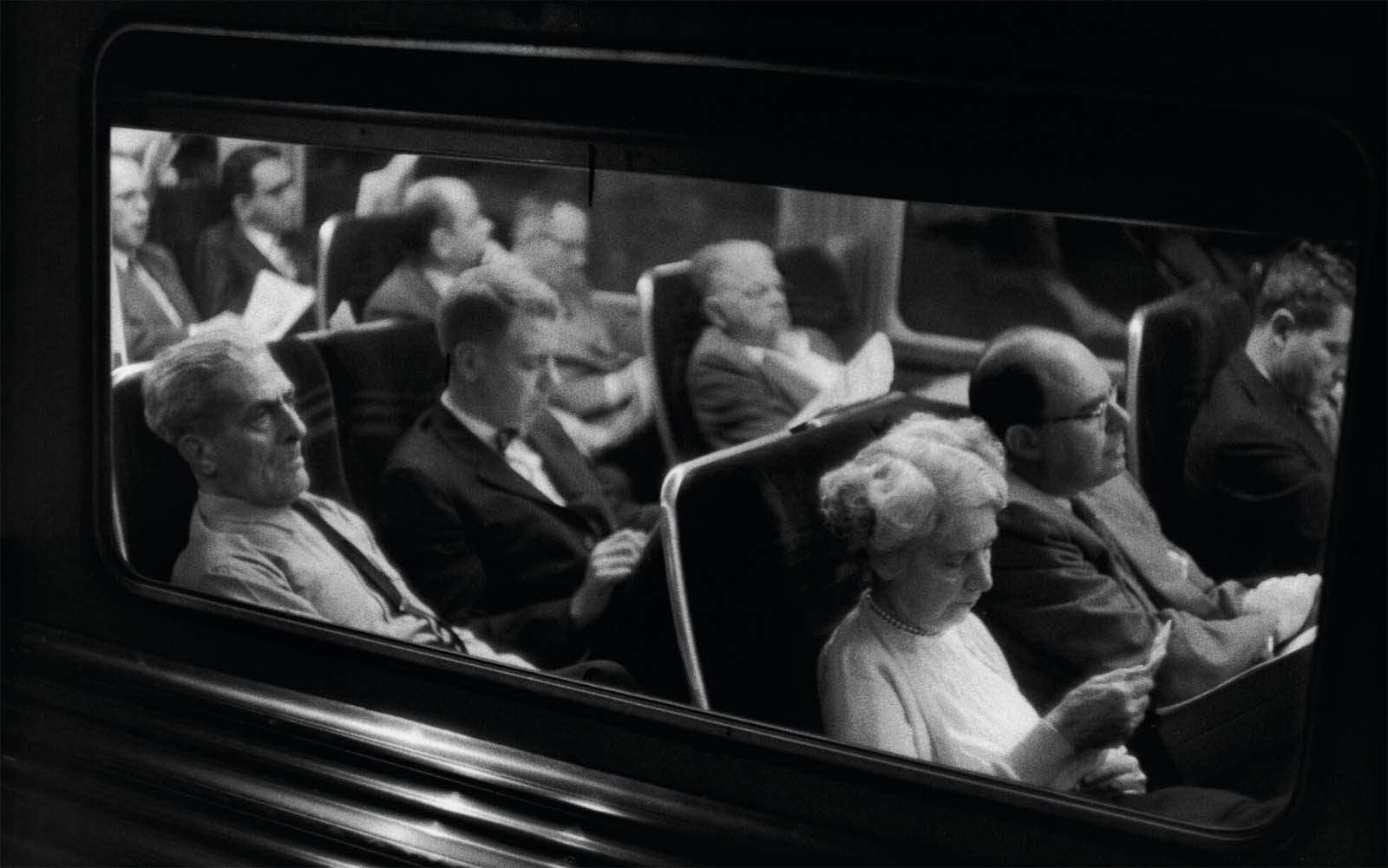
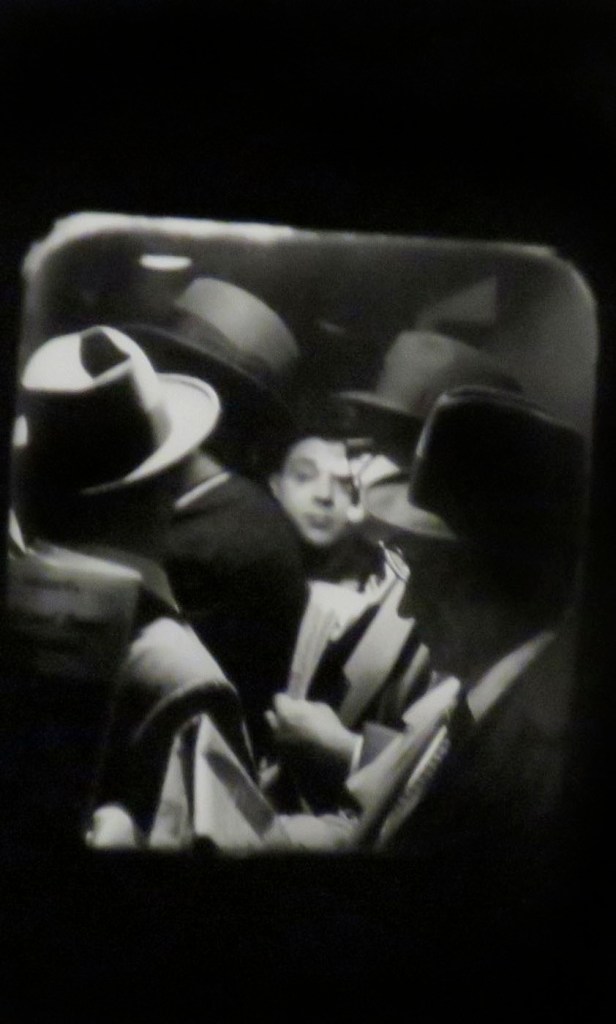





![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Woman with White Glove, Penn Station, New York' [Mujer con guante blanco, Penn Station, Nueva York] 1958 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Woman with White Glove, Penn Station, New York' [Mujer con guante blanco, Penn Station, Nueva York] 1958](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/07.-id461_p.jpg?w=683)



![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Aluminum Foundry, Soviet Union' [Fundición de aluminio, Unión Soviética] 1975 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Aluminum Foundry, Soviet Union' [Fundición de aluminio, Unión Soviética] 1975](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/13.-id648_p.jpg?w=686)
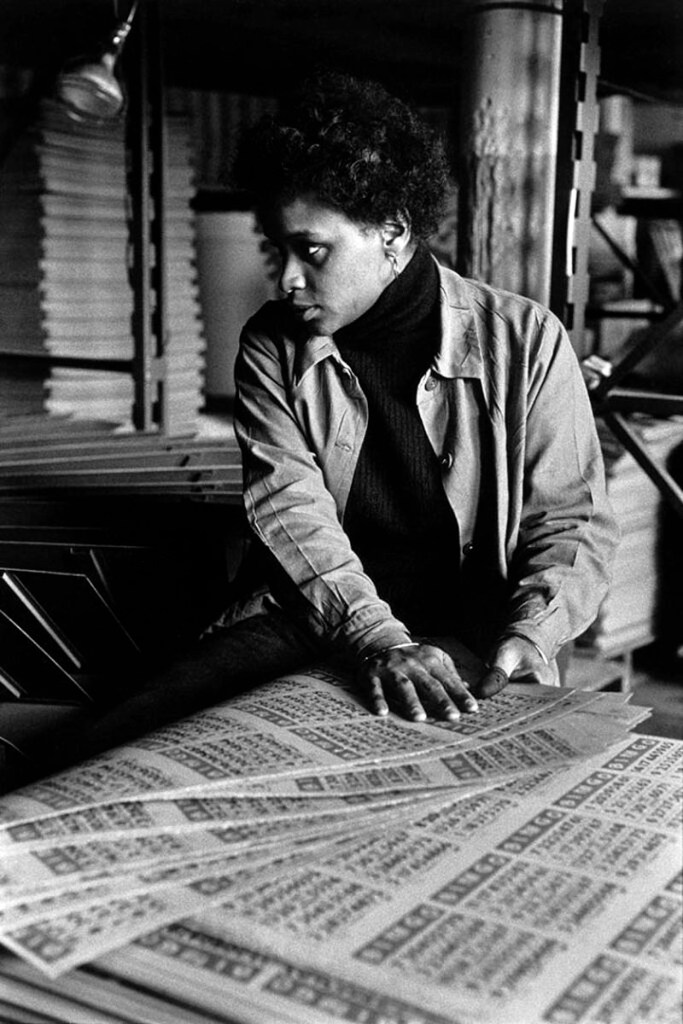





![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Assembly Line Worker, Long Island City, New York' [Trabajadora en cadena de montaje, Nueva York] 1972-1974 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Assembly Line Worker, Long Island City, New York' [Trabajadora en cadena de montaje, Nueva York] 1972-1974](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/12.-id96_p-1.jpg?w=691)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Demonstrators on March in Support of United Farm Workers, New York' [Manifestantes en una marcha de apoyo a la Unión de Campesinos, Nueva York] 1975-1976 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Demonstrators on March in Support of United Farm Workers, New York' [Manifestantes en una marcha de apoyo a la Unión de Campesinos, Nueva York] 1975-1976](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/14.-id1307_p.jpg?w=685)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Self-Portrait, Santiago, Chile' [Autorretrato, Santiago de Chile] 2000-2001 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Self-Portrait, Santiago, Chile' [Autorretrato, Santiago de Chile] 2000-2001](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/16.-id1627_p.jpg)
![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Women from Texas, Fifth Avenue, New York' [Mujeres de Texas, Fifth Avenue, Nueva York] 1975 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Women from Texas, Fifth Avenue, New York' [Mujeres de Texas, Fifth Avenue, Nueva York] 1975](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/15.-id145_p.jpg?w=694)
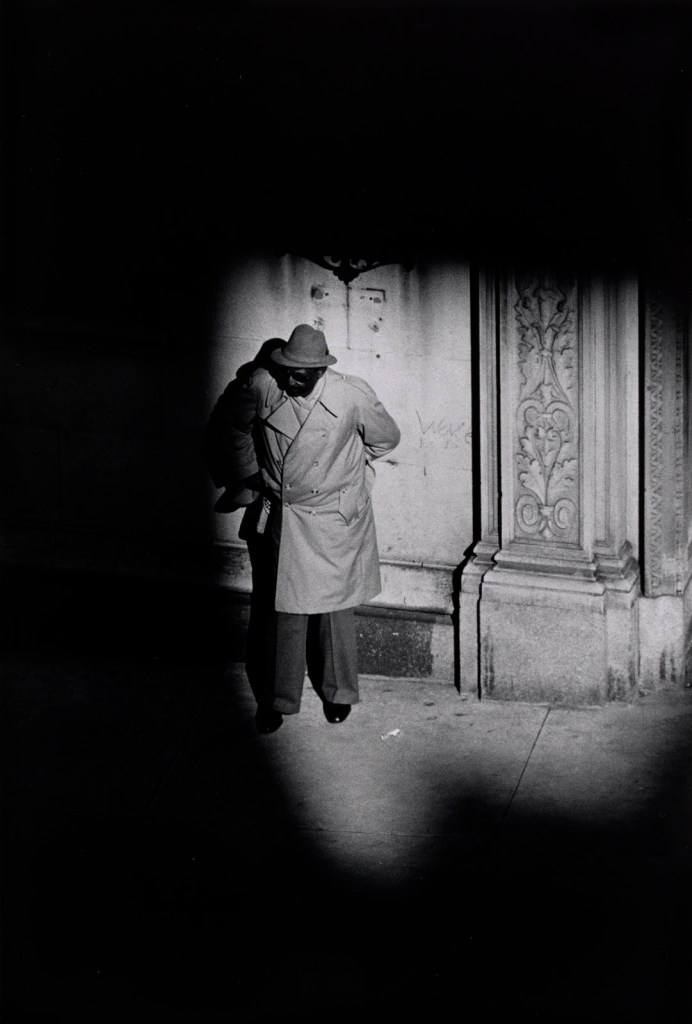

![Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Jardin du Luxembourg, Paris' [Jardin du Luxembourg, París] 1997 Louis Stettner (American, 1922-2016) 'Jardin du Luxembourg, Paris' [Jardin du Luxembourg, París] 1997](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/17.-id2978_p.jpg)
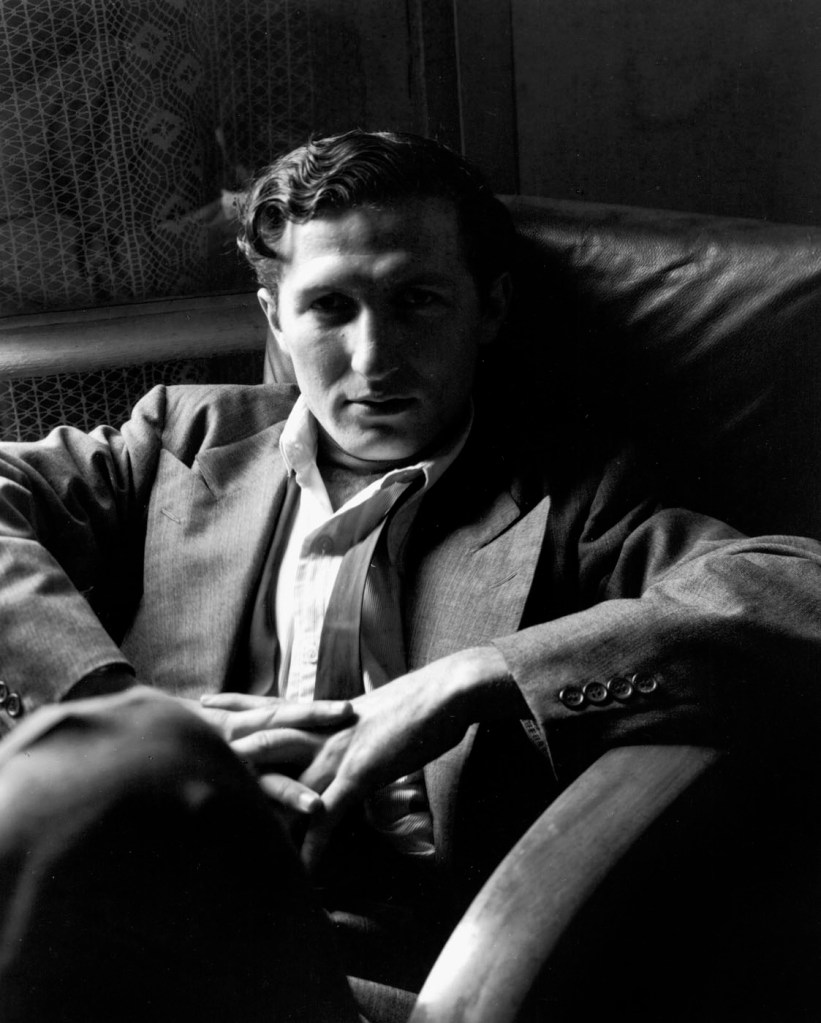
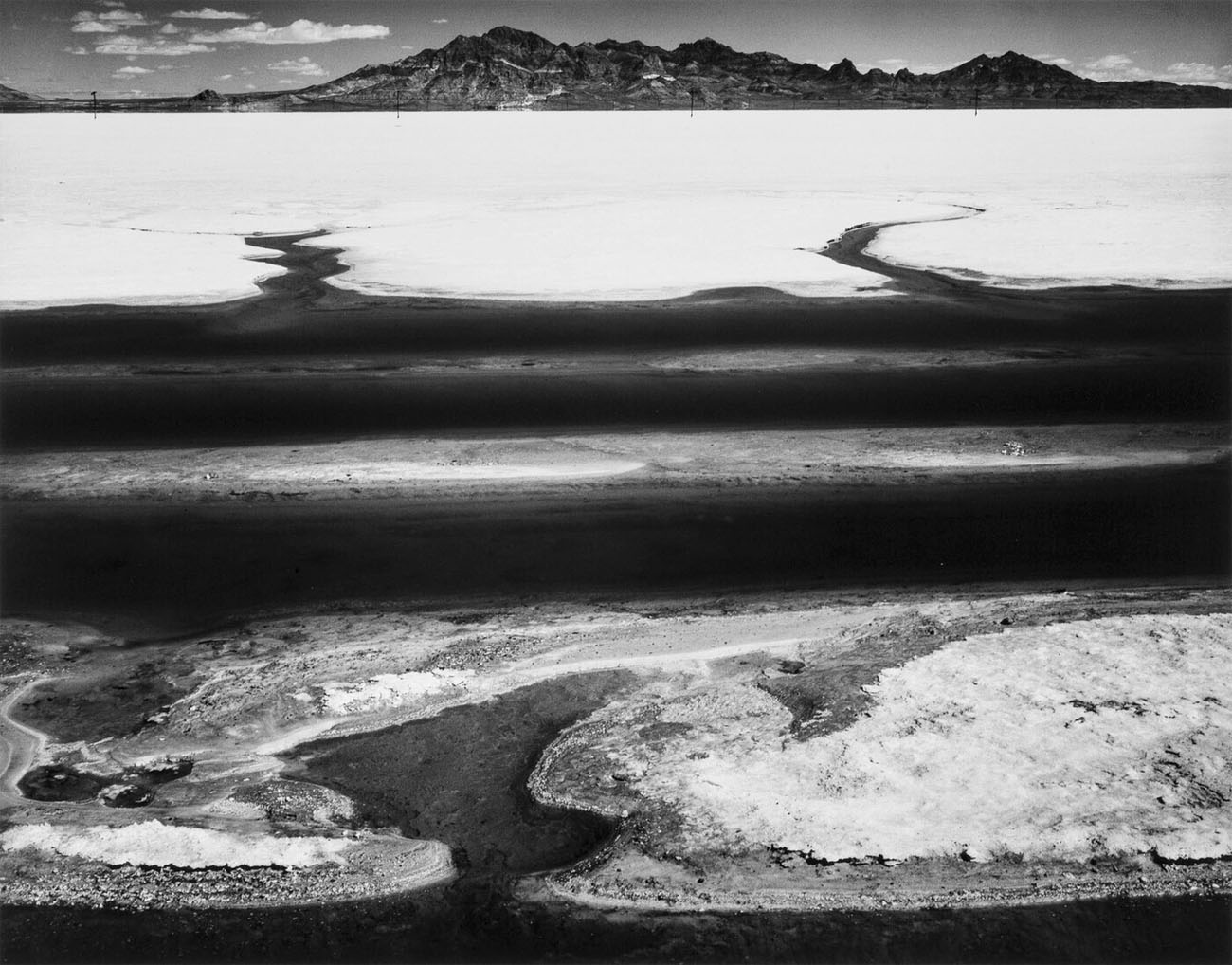





































































































































































































































![Life Magazine (1883-1972) '[Harlem Gang Leader opening spread]' 1948 Life Magazine (1883-1972) '[Harlem Gang Leader opening spread]' 1948](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/15_p.-96_97-harlem-gang-leader-opening-spread.jpg)










































You must be logged in to post a comment.