Exhibition dates: 31st July – 8th November, 2015
Curators: Dr Mikhail Dedinkin, Deputy Head of the Western European Art Department at the Hermitage, working Dr Ted Gott, Senior Curator of International Art at the National Gallery of Victoria
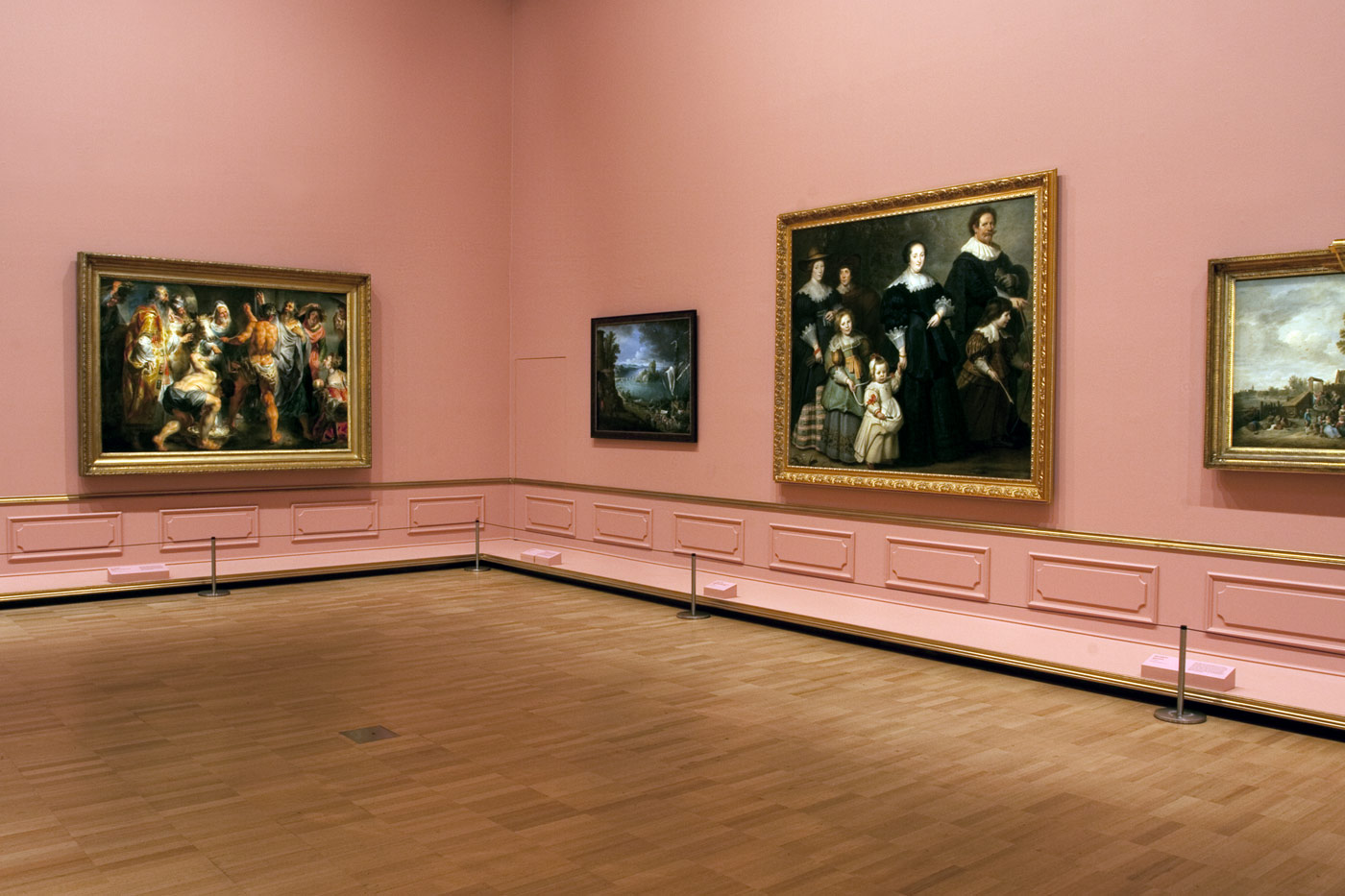
Installation view of room 1 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne featuring Alexander Roslin (Swedish 1718-93) Portrait of Catherine II 1776-77
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
A scintillating exhibition at NGV International which showcases one of the world’s greatest art collections. Exhibition design is outstanding (particularly the floor tiling), as are the Da Vinci, Titian, Rembrandt, van Dyck, Rubens and Flemish still life. Among my favourites is a small Watteau Savoyard with a Marmot (1716) which is absolutely still, delicate and exquisite: I thought of the photographs of Atget, his street sellers, when I saw this painting; and Frans Snyders’ tour-de-force Concert of birds (1630-40) which has such presence.
Well done to the curators, the Hermitage Museum and the NGV for staging such a magnificent exhibition.
Marcus
Many thankx to the National Gallery of Victoria for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image. All photographs © Dr Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria.
Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great showcases one of the world’s greatest art collections. Featuring works by artists including Rembrandt, Rubens, Velázquez and Van Dyck, the exhibition offers a dazzling array of works including the finest group of Dutch and Flemish art to come to Australia.
This exclusive Melbourne exhibition will also highlight the innovation and vision of Catherine the Great, whose inexhaustible passion for education, the arts and culture heralded a period of enlightenment in the region. The extraordinary works sourced and commissioned by Catherine during her thirty-four year reign, created the foundations for the Hermitage today – considered to be one of the world’s greatest treasure houses of art and decorative arts. The exhibition will offer audiences an immersive experience, recreating the rich atmosphere of the Hermitage to showcase these exquisite works.
German-born Catherine the Great (Catherine II) came to power in 1762, aged thirty-three, and ruled Russia for the next thirty-four years, until her death in 1796. She saw herself as a Philosopher Queen, a new kind of ruler in the Age of Enlightenment. Guided by Europe’s leading intellectuals, she modernised Russia’s economy, industry and government, drawing inspiration both from Antiquity and contemporary cultural and political developments in Western Europe. A fluent speaker of Russian, French and German, Catherine was largely self-educated, independent, idealistic and visionary.
While her reign was not always peaceful, Catherine sought to bring order, stability and prosperity to the vast Russian Empire. Her ideals of abolishing serfdom and ensuring the equality of all citizens under the law were ahead of her time, and strongly resisted by the nobility of the day; however, she achieved numerous other reforms, including the introduction of paper money and modernisation of Russia’s education system. French philosopher Denis Diderot, who visited St Petersburg in 1773, described an audience with Catherine as being ‘more like study than anything else: she is a stranger to no subject; there is no man in the Empire who knows her nation as well as she’.
Room 1 Catherine the collector
Between 1762 and 1796, the years of her reign, Catherine the Great oversaw a period of cultural renaissance in Russia. The world of ideas in which she was deeply involved from an early age found tangible expression in the material world the Empress later created around herself. The great complexes of imperial buildings Catherine constructed reflected her informed interest in both Classical and Chinese culture.
Catherine not only assembled a collection of Old Master paintings equal in scale and quality to leading European collections, but also paid considerable attention to the acquisition of contemporary art. While the richness and technical perfection of her diverse collections of decorative arts aimed to dazzle and please, they also had the more practical purpose of raising standards of artistic production in Russia. The fact that more than 400 exemplary works of art from her personal collection, including paintings, sculptures, drawings, porcelain, silver and precious gems, are seen here for the first time in Australia is cause for celebration.
Installation views of room 1 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne featuring Alexander Roslin (Swedish 1718-1793) Portrait of Catherine II 1776-1777
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Installation views of room 1 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne featuring in the last three photographs, the Sèvres Cameo Service. Cameo Service 1778-1779. Sevres Porcelain Factory (manufacturer) France, est. 1756. The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg.
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
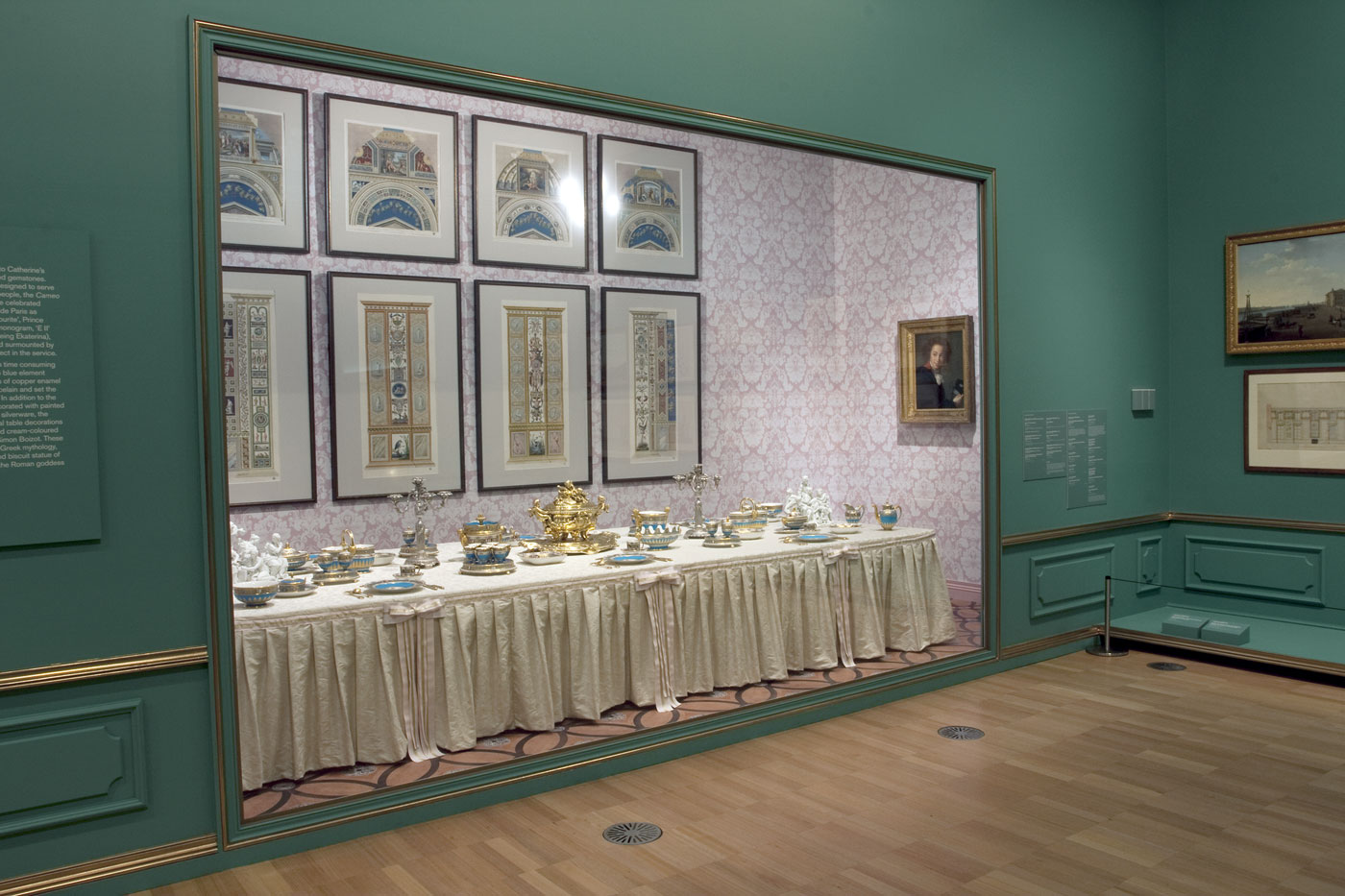
Sèvres Cameo Service
The Sèvres Cameo Service (1778-1779) relates to Catherine’s great passion for collecting engraved gemstones. Comprising 797 individual pieces designed to serve dinner, dessert and coffee to sixty people, the Cameo Service was commissioned from the celebrated Sèvres porcelain manufactory outside Paris as a present for Catherine’s court ‘favourite’, Prince Grigory Potemkin. The Empress’s monogram, ‘E II’ (the Russian version of her name being Ekaterina), woven from garlands of flowers and surmounted by a crown, adorned almost every object in the service.
Production of the service was both time consuming and labour-intensive. The exquisite blue element alone – made from separate layers of copper enamel that gradually seeped into the porcelain and set the pure colour – required five firings. In addition to the hundreds of porcelain objects decorated with painted and sculpted cameos and related silverware, the service also included grand central table decorations fashioned from biscuit, or unglazed cream-coloured porcelain, by the sculptor Louis-Simon Boizot. These decorations illustrated tales from Greek mythology, and were presided over by a grand biscuit statue of Catherine the Great as Minerva, the Roman goddess of wisdom and the arts.
Installation views of room 1 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Exhibition passageway
Installation view of passageway video of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Room 2 Italian art
When Catherine the Great began collecting European art, opportunities to acquire fine Italian Old Master paintings were already severely limited. Demand from wealthy collectors was high and the marketplace was saturated with misattributed works, some of which inevitably made their way to the Hermitage and other great collections.
Despite this, Catherine achieved great success collecting sixteenth and seventeenth century paintings, particularly from Venice, including great paintings by Titian, Paris Bordone and the enigmatic Lorenzo Lotto. These are complemented by fine examples of Roman and Florentine paintings, such as the famous Female nude (Donna nuda), by an artist very close to Leonardo da Vinci. This select group of paintings beautifully illustrate developments in figurative art, portraiture and religious art in Italy from the sixteenth to the eighteenth century.
In the early years of her reign, Catherine the Great acquired en masse several large collections of drawings representing all the main European schools. This set the foundations for the current Hermitage Museum’s outstanding Cabinet of Drawings. In terms of quality, Catherine’s acquisitions of Italian drawings were of the highest standard. The majority of these date from the mid sixteenth to late eighteenth centuries and include many rare and precious works.
Installation view of room 2 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne showing at centre, Domenico Fetti (Italian 1589-1623) Portrait of an actor 1620s
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
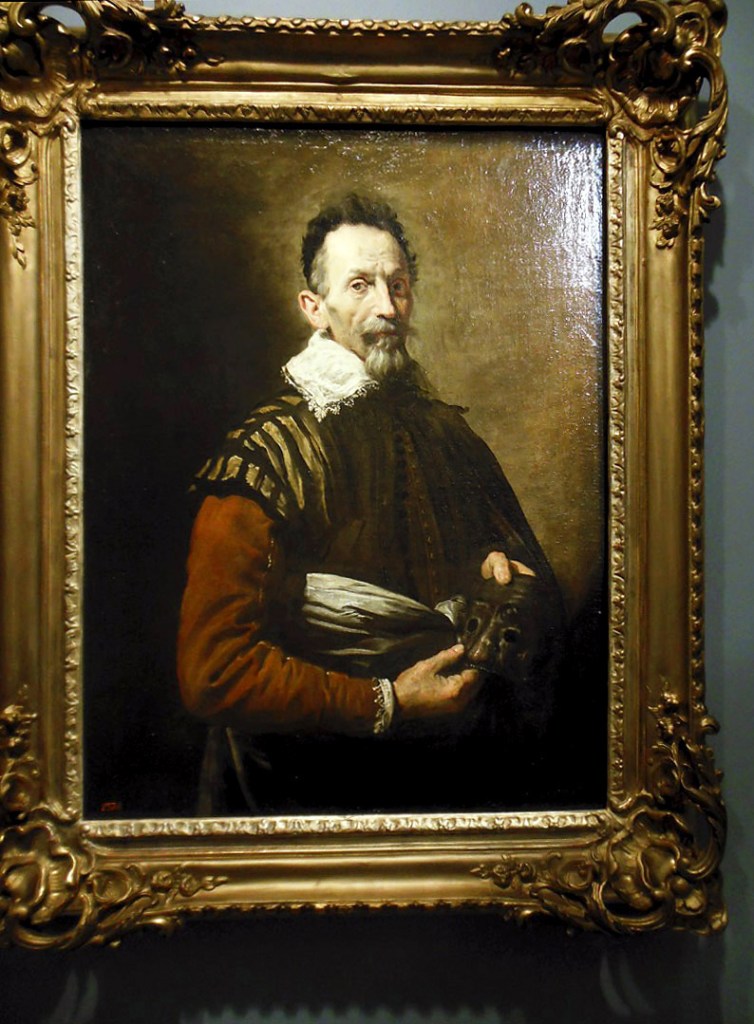

Domenico Fetti (Italian, 1589-1623)
Portrait of an actor (installation view)
1620s
Oil on canvas
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Domenico Fetti was court painter to Gerdinand II Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, when he made this striking portrait of an actor. It is though to be Tristano Martinelli who made his fame working in the commedia dell’arte tradition. It is believe that Marinelli created and popularised the standard roll of the Harlequin in theatre. Fetti himself was involved with the theatre in both Mantua and Venice.
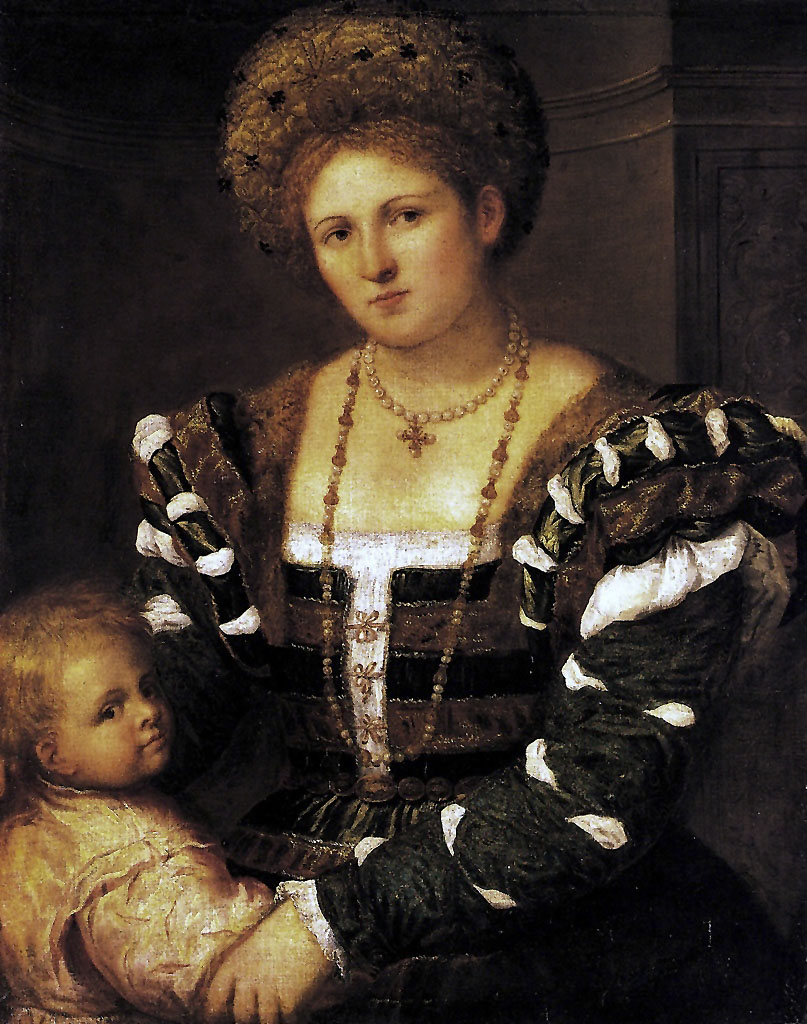
Installation view of room 2 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne featuring at centre, Paris Bordone (Italian 1500-1571) Portrait of a lady with a boy Mid 1530s
Photo: Marcus Bunyan

Paris Bordone (Italian, 1500-1571)
Portrait of a lady with a boy (installation view)
Mid 1530s
Oil on canvas
97cm (38.1 in) x 77cm (30.3 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
This work by Venetian artist Paris Bordone is a typical example of formal Renaissance portraiture. Bordone’s main aim was to show the high social standing of the sitters, so he painted their luxurious costumes in great detail. He draws our attention to the sumptuous sleeves of this woman’s dress, the headgear resembling a turban, as well as her opulent jewellery. Bordone was one of Titian’s most talented pupils whose work is characterised by a level of precision not often present in his master’s work. This painting entered the Hermitage as a work by Giorgione.

Paris Bordone (Italian 1500-1571)
Portrait of a lady with a boy
Mid 1530s
Oil on canvas
97cm (38.1 in) x 77cm (30.3 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Public domain
Installation view of room 2 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne showing at left in the bottom image, Domenico Capriolo (Italian c. 1494-1528) Portrait of a young man 1512 and to the right, Lorenzo Lotto (Italian c. 1480-1556) The Rest on the Flight into Egypt with Saint Justine 1529-1530
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Portrait of a young man by the Venetian master Domenico Capriolo captures the intellectual values of Renaissance art. Everything that surrounds this youth speaks of his interests, such as the church that indicates his piety; the statue of Venus that reveals his passion for Antiquity; and the folder (containing verses or drawings) that illustrates the richness of his inner world. The painting is dated 1512 and the artist’s name symbolised by a medallion containing a Capreolus, or deer, which is a play on his name. Such allusions were common in Renaissance art and would have been readily understood by his contemporaries.
Lorenzo Lotto (Italian c. 1480-1556)
The Rest on the Flight into Egypt with Saint Justine (installation views)
1529-1530
Oil on canvas
82cm (32.2 in) x 133cm (52.3 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Lorenzo Lotto is a much admired sixteenth-century Venetian artist. The Rest on the Flight into Egypt with Saint Justine has the typical dynamism of Lotto’s work, achieved not only through the poses, gestures and movement of the foliage, but also through his intense colour palette and the juxtaposition of resonant blues with red and yellow tones. Here, the Holy Family has been joined by Saint Justine of Padua, martyred in 304 AD, identifiable through her attribute of a sword piercing her breast. Justine was a very popular subject for artists of Northern Italy.
Lorenzo Lotto (Italian c. 1480-1556)
The Rest on the Flight into Egypt with Saint Justine
1529-1530
Oil on canvas
82cm (32.2 in) x 133cm (52.3 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Public domain
Installation view of room 2 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne showing Leonardo da Vinci (school of) Female nude (Donna Nuda) Early 16th century
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
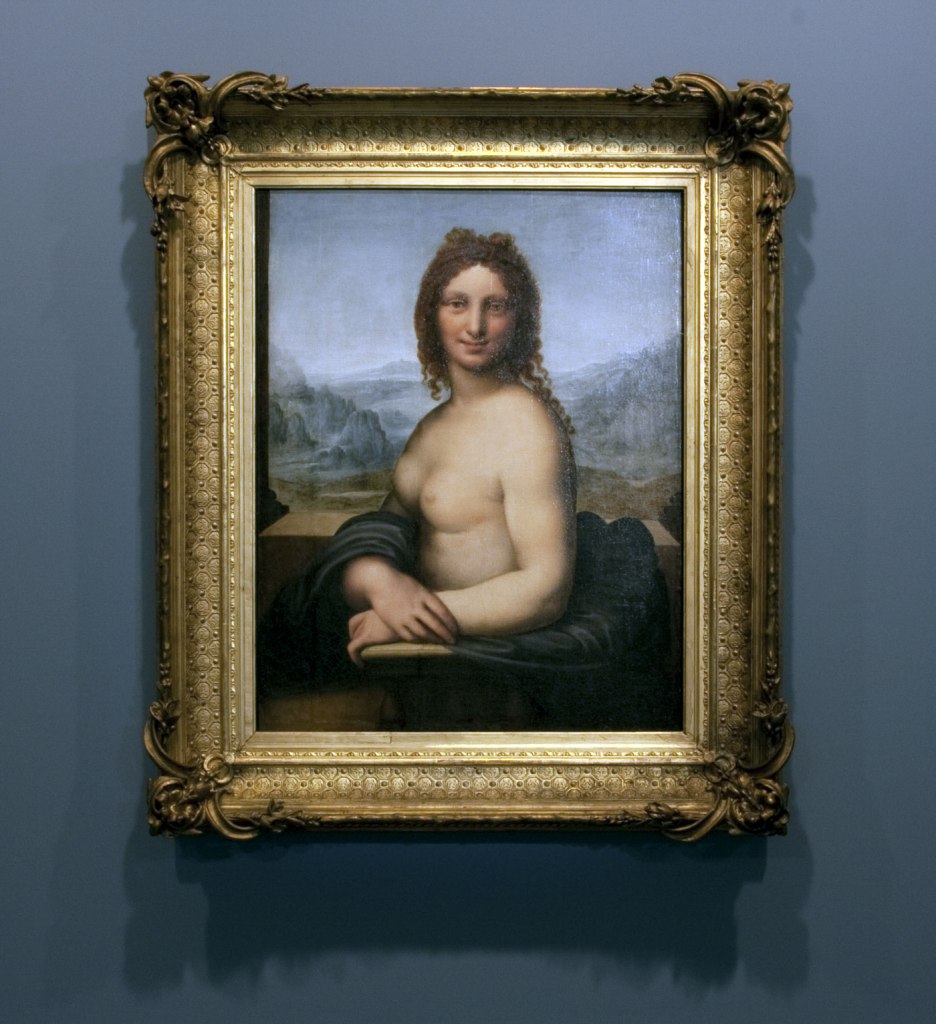

Leonardo da Vinci (school of)
Female nude (Donna Nuda) (installation view)
Early 16th century
Oil on canvas
86.5cm (34 in) x 66.5cm (26.1 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
This painting entered the Hermitage collection as a work by Leonardo da Vinci, but is now widely accepted to be by one of his close followers, possibly his pupil Salai. Perhaps more important is that it may be a close copy of a lost painting by Leonardo. Female nude (Donna Nuda) also shares some of the qualities of the famous Mona Lisa c. 1503-1519, in the Louvre Museum, Paris; namely the repetition of the pose, the position of the hands and the landscape setting seen behind a stone ledge in front of which the figure is set. This is the most refined of numerous variants of this composition in existence.
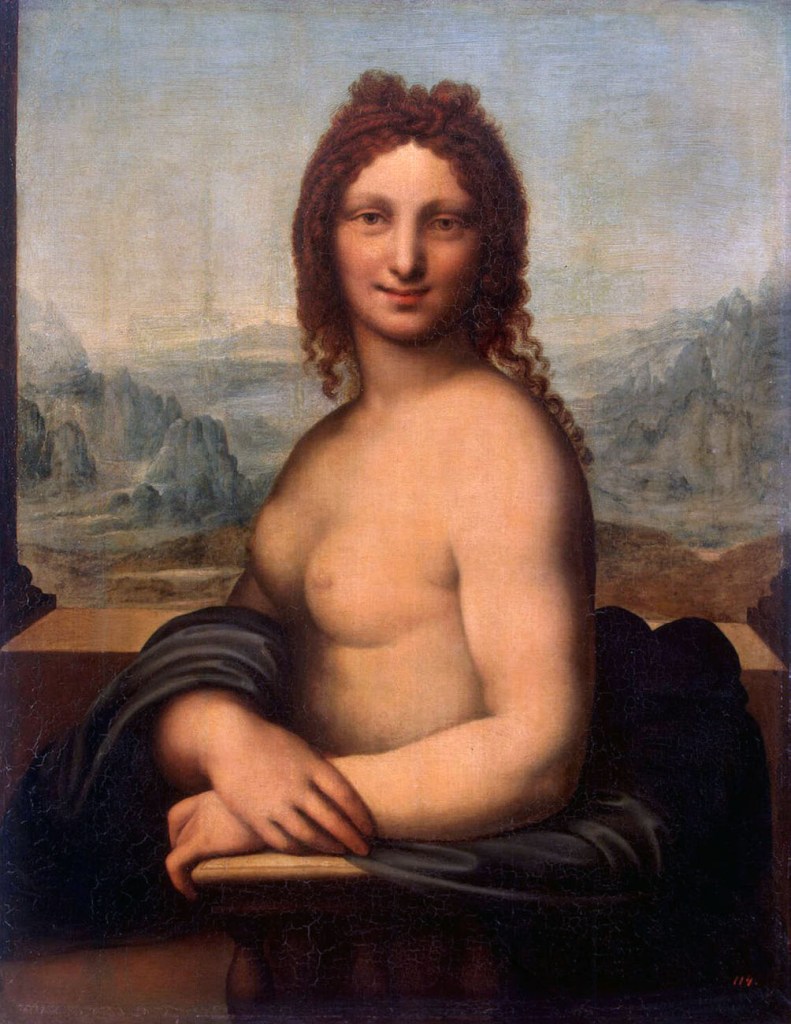

Leonardo da Vinci (school of)
Female nude (Donna Nuda)
Early 16th century
Oil on canvas
86.5cm (34 in) x 66.5cm (26.1 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Public domain
Room 3 Flemish art
In the seventeenth century, Flanders comprised the Catholic-dominated Southern Netherlands or ‘Spanish’ Austrian Netherlands, an area larger than modern Belgium. Thanks in large part to the talents of artist Peter Paul Rubens, the Flanders or ‘Flemish’ school in this era became very prestigious. While chiefly a painter, Rubens had far-reaching stylistic influence on many visual art forms, from prints to silverware and architecture. Every leading artist of seventeenth-century Flanders studied in, passed through or was connected with Rubens’s studio.
A diplomat and court insider, Rubens operated on an international stage. His art was correspondingly monumental; characterised by large forms modelled with loose brushstrokes in glowing, brilliant colours. Rubens’s pupil Anthony van Dyck and collaborator Cornelis de Vos led the way in bringing new naturalism to portraiture. While they catered to different markets (van Dyck to the nobility and de Vos to a rich merchant class) their mutual influence is apparent.
Flanders was a nation built on trade, and Flemish artists travelled widely, especially to Italy. From Italy they brought back new pictorial trends, such as the theatrical naturalism of Caravaggio. Flemish artists excelled in naturalistic effects, which they applied even to traditionally humble subjects, such as still lifes and animal pictures, seen to brilliant effect in the art of Frans Snyders and David Teniers II.

Installation views of room 3 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne showing in the centre in the bottom photograph, Peter Paul Rubens and workshop (Flemish 1577-1640) The Adoration of the Magi, c. 1620 at centre
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Rubens painted the subject of the Adoration of the Magi (Matthew 2:1) more often than any other episode from Christ’s life. Rendered at life-sized scale, this painting combines the humility of Christ’s birth with splendid, worldly pageantry. Three Kings from the East are shown crowding into Christ’s stable (portrayed as a cave, in an allusion to Christ’s later interment) wearing gold- embroidered silks and satins, and offering gifts. The eldest king, Caspar, kneels before Christ with gold; behind him is Melchior, with frankincense; and Balthazar with myrrh, used for embalming. With the help of his studio, Rubens produced more than sixty altarpieces during his career.
Installation views of room 3 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Peter Paul Rubens (Flemish 1577-1640)
Roman Charity (Cimon and Pero) (installation view)
c. 1612
Oil on canvas
141cm (55.5 in) x 180cm (70.8 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St Petersburg
Acquired from the collection of Count Cobenzl, Brussels, 1768
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Roman Charity (Cimon and Pero) depicts a story told by the Roman historian Valerius Maximus in his Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX (Nine Books of Memorable Deeds and Sayings), written around 30 AD. The story involves Cimon, an old man awaiting execution in prison who was not given food. Cimon’s daughter Pero visited him, and suckled him at her breast like a child. Pero’s nourishing of Cimon was considered an outstanding example of paying honour to one’s parents.
Peter Paul Rubens (Flemish 1577-1640)
Roman Charity (Cimon and Pero)
c. 1612
Oil on canvas
141cm (55.5 in) x 180cm (70.8 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St Petersburg
Acquired from the collection of Count Cobenzl, Brussels, 1768
Public domain
Room 4 Dutch art
The Hermitage holds the finest collection of Dutch art outside the Netherlands. While Peter the Great (1672-1725) had a passion for Dutch art and acquired some notable masterpieces, Catherine the Great established the depth and breadth of this extraordinary collection, beginning in 1764 with her first acquisitions. In that year Catherine purchased 317 paintings that had been assembled for Frederick II of Prussia by the German merchant Johann Ernst Gotzkowsky. Among this substantial group were more than 100 Dutch paintings by the most notable masters.
In 1769 Catherine purchased the collection of Count Heinrich von Brühl, which included spectacular landscapes by Jacob van Ruisdael, Isaack Jansz. van Ostade and Aert van der Neer, as well as four Rembrandt portraits, including the wonderful Portrait of a scholar, 1631. For the rest of her life Catherine continued to add outstanding Dutch works to her rich collection.Although the paintings and drawings from the Dutch school included here are only a fragment of the extensive and diverse collection assembled by Catherine the Great, they reveal her artistic preferences and taste.
Installation views of room 4 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne with Rembrandt Harmensz van Rijn (Dutch 1606-1669) Portrait of a scholar 1631 at centre
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Rembrandt painted Portrait of a scholar shortly after moving from his native Leiden to Amsterdam in 1630. He had already established a growing reputation in Leiden and was enticed to the capital by the art dealer Hendrick van Uylenburgh, father of his future wife Saskia. Once completing the move, Rembrandt rapidly became the city’s leading artist, mainly on account of dazzling portraits such as this early masterpiece. He then secured the most prestigious commissions from wealthy and powerful citizens of Amsterdam.
Room 5 French taste
The Russian aristocracy spoke French and modelled their manners and style on those of the French Court. Catherine followed the vast intellectual strides of the French philosophes with passionate interest. She also embraced the arts, luring French artists, architects and craftsmen to St Petersburg.
Catherine relied on agents and advisors in France and Germany to identify and acquire works of art on her behalf. In this way she acquired the collection of Paris banker Louis Antoine Crozat, Baron de Thiers and other important bodies of work in France. Her holdings of French art came to encompass works by Renaissance masters as well as seventeenth-century landscapes and history paintings.
Catherine also acquired examples of work of her own century by Rococo artists such as Antoine Watteau. The playful, erotic and at times wistful art of Watteau’s generation gave rise to the intimate and worldly art of François Boucher, whose pictures Catherine also purchased. The Empress collected modern masterpieces created in reaction to French courtly and decadent styles. Her paintings by Jean-Baptiste Siméon Chardin are premier examples of a new, moralising directness in ambitious French art.
Catherine’s buying in France was not limited to French art. Also in this room are paintings by great German, Spanish and Italian masters that were acquired in Paris from prestigious collections under the direction of Catherine’s French advisors.
Installation views of room 5 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
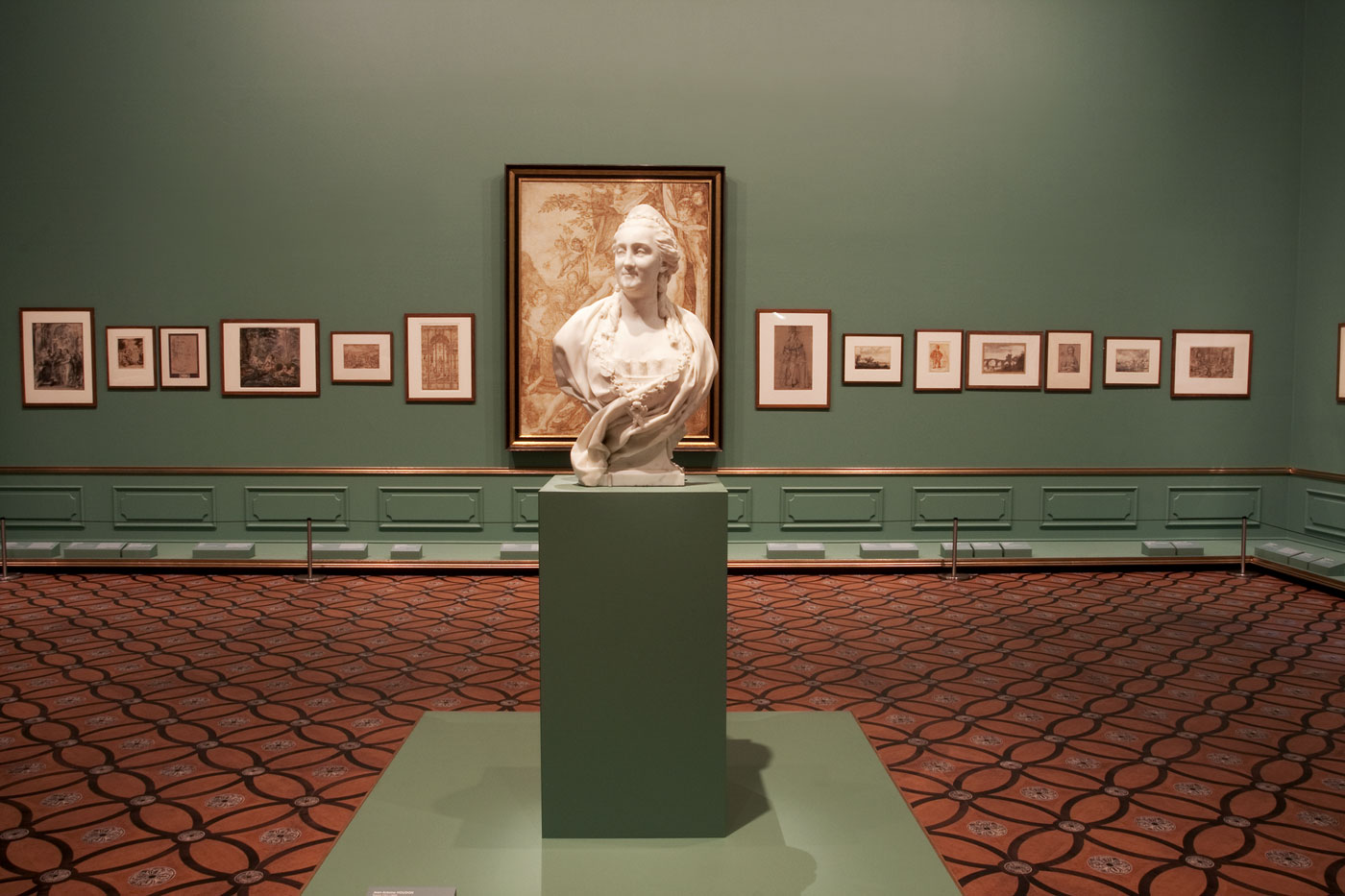
Room 6 Catherine and the world
For Catherine the Great, collecting art was part of a wider economic and diplomatic program designed to stimulate economic and cultural activity at home and abroad. At a meeting in December 1762 with the Moscow Senate, Catherine suggested that consuls be stationed in Spain, Holland and England not only to promote maritime trade but also to source luxury goods and works of art as examples for Russian artists and manufacturers to aspire to.
Through Catherine’s consuls and agents, such items began to flow into St Petersburg, steadily elevating that city into a vibrant centre of European culture. While her cultural sympathies were French, Catherine was also very curious about Britain – the economic success story of the age. She informed herself about Britain’s trade, commerce, manufacturing, philosophy and political system, and purchased works by modern British neoclassical masters, such as Joseph Wright of Derby and Joshua Reynolds. Examples of Spanish, Italian and German art were often not sourced in their own countries of origin but acquired as a part of larger collections.
Installation views of room 6 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne with the 1773 sculpture Catherine II by Jean-Antoine Houdon (French 1741-1826) at centre
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Room 7 The Walpole collection
In 1779 Catherine the Great acquired 198 paintings from a celebrated collection formed by Sir Robert Walpole, 1st Earl of Orford, Britain’s first prime minister. They were bought from the family estate, Houghton Hall, and sold by Walpole’s grandson, George Walpole, 3rd Earl of Orford, who approached the Russian ambassador to Britain directly about the sale. At more than £40,000, the price was high, but the transaction was concluded in only two months. Attempts were made to keep this famous collection in Britain, to no avail.
The Walpole collection was outstanding in quality, and significantly enhanced the Hermitage’s range of Flemish and Italian works. The Russian ambassador to Great Britain, Alexey Musin-Pushkin, who organised the valuable purchase, wrote to Catherine the Great: ‘The greater part of the nobility here are displaying general dissatisfaction and regret that these paintings are being allowed out of this country, and are setting in train various projects to keep them here … No little assistance comes from Lord Orford’s zealous desire to unite [the collection for] the gallery of Your Imperial Majesty, rather than to sell it to parliament itself or, least of all, to divide it through sale to different individuals’.
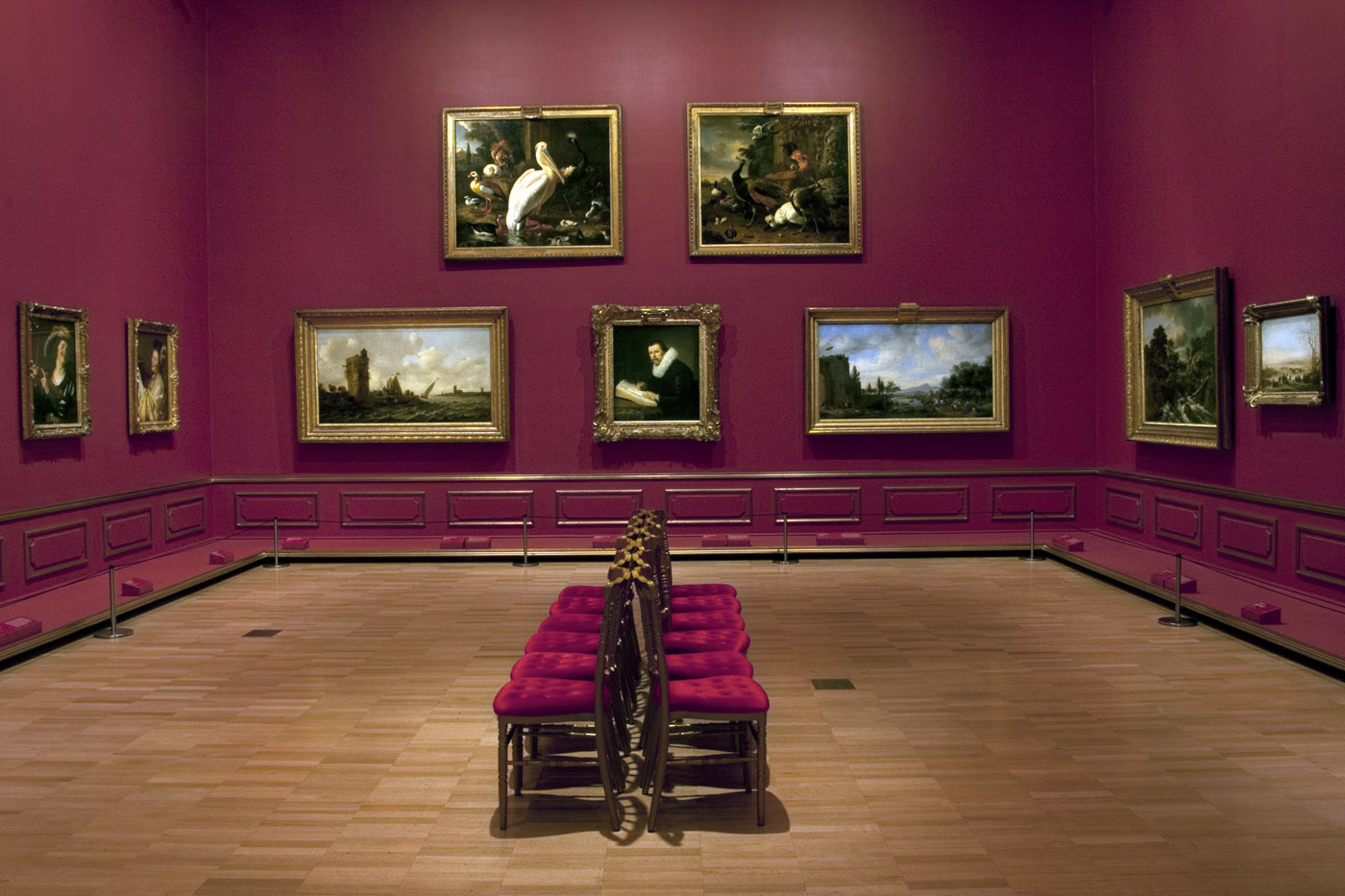
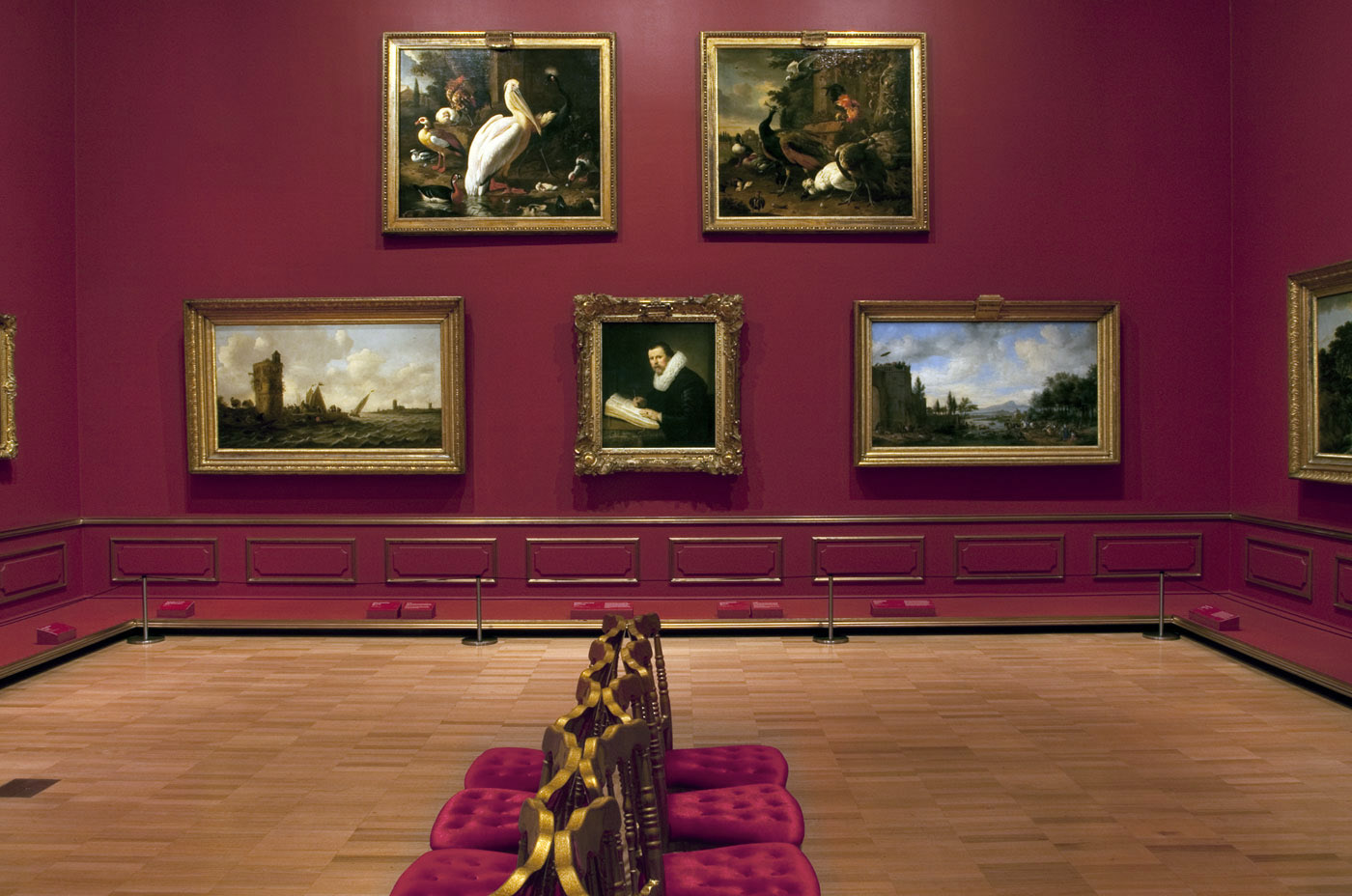
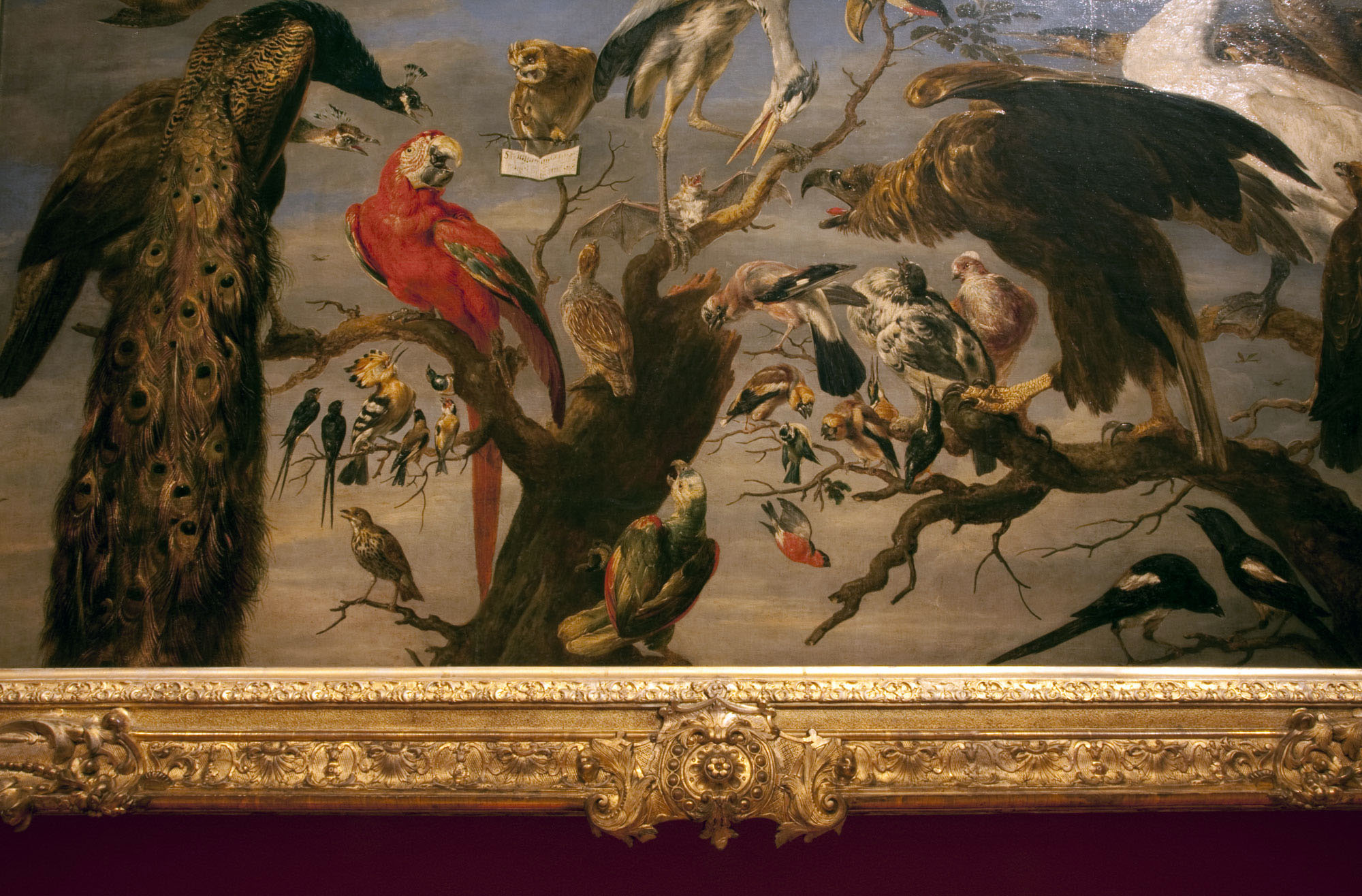
Installation views of room 7 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne showing in the bottom image, Frans Snyders (Flemish 1579-1657) Concert of birds, 1630-1640 at right and Frans Snyders (Flemish 1579-1657) Cook at a kitchen table with dead game, c. 1636-1637 at second left
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Frans Snyders (Flemish 1579-1657)
Concert of birds (installation view)
1630-1640
Oil on canvas
137cm (53.9 in) x 240cm (94.4 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St Petersburg
Acquired from the collection of Sir Robert Walpole, Houghton Hall, 1779
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
An important place in Flemish seventeenth-century painting is occupied by two specific genres: animal painting and the still life. One of the most important animal and still-life painters was Frans Snyders, a very close collaborator of Peter Paul Rubens who often painted still-life details and animals on the master’s canvases. Snyders’s superb skill as a painter of animals is revealed by Concert of birds, based on a subject from Aesop’s Fables. It shows a gathering of feathered creatures screeching and singing under the direction of an owl seated on a dried branch in front of an open music score.
Frans Snyders (Flemish 1579-1657)
Concert of birds
1630-1640
Oil on canvas
137cm (53.9 in) x 240cm (94.4 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St Petersburg
Acquired from the collection of Sir Robert Walpole, Houghton Hall, 1779
Public domain
Frans Snyders (Flemish 1579-1657)
Concert of birds (installation view detail)
1630-1640
Oil on canvas
137cm (53.9 in) x 240cm (94.4 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St Petersburg
Acquired from the collection of Sir Robert Walpole, Houghton Hall, 1779
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Frans Snyders (Flemish 1579-1657)
Cook at a kitchen table with dead game (installation view detail)
c. 1636-1637
Oil on canvas
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Frans Snyders was the son of the owner of one of Antwerp’s largest wine and eating houses. His dramatically realistic still lifes celebrate the exotic variety of rare fowls available at Antwerp’s markets. Images of dead animals being prepared for a banquet were understood in Snyder’s time as lessons in Christian morality. Many Dutch and Flemish still lifes featuring the sacrifice of an animal for the table functioned as allusions to Christ’s Passion and the transience of the flesh.
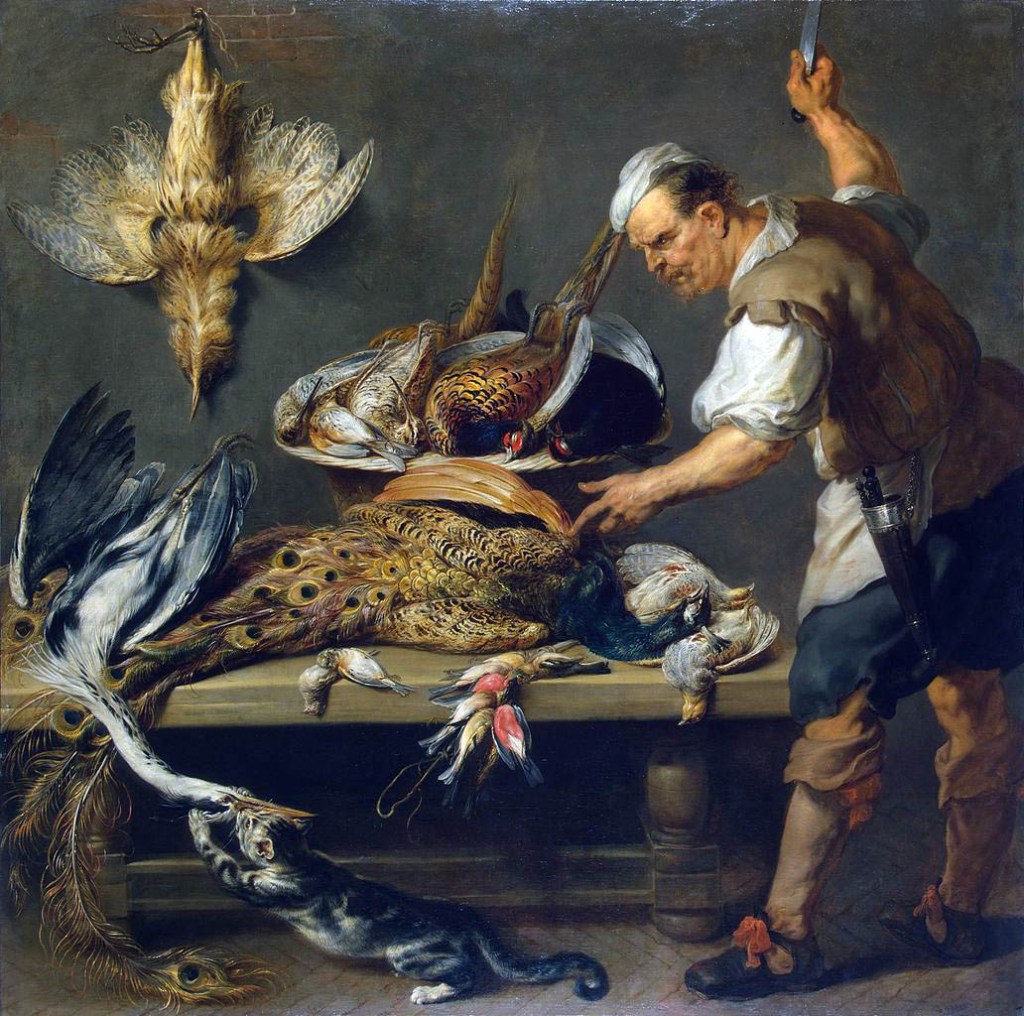

Frans Snyders (Flemish 1579-1657)
Cook at a kitchen table with dead game
c. 1636-1637
Oil on canvas
171cm (67.3 in) x 173cm (68.1 in)
The State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg
Public domain
Installation views of room 7 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne showing at left in the bottom image, Anthony van Dyck (Flemish 1599-1641) Portrait of Philadelphia and Elizabeth Wharton, 1640
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
This is one of the most charming portraits of children paint by van Dyck, who had particular talent for such works. It is one of a group of family portraits commissioned from can Dyck by Philip, Lord Wharton in the late 1630s. Van Dyck worked in England for approximately ten ears and brought a new standard of elegance and style to English portraiture. He largely conveyed this through his flair for painting lavish costumes and sumptuous fabrics, a sensibility he carried through to his portraits of children.
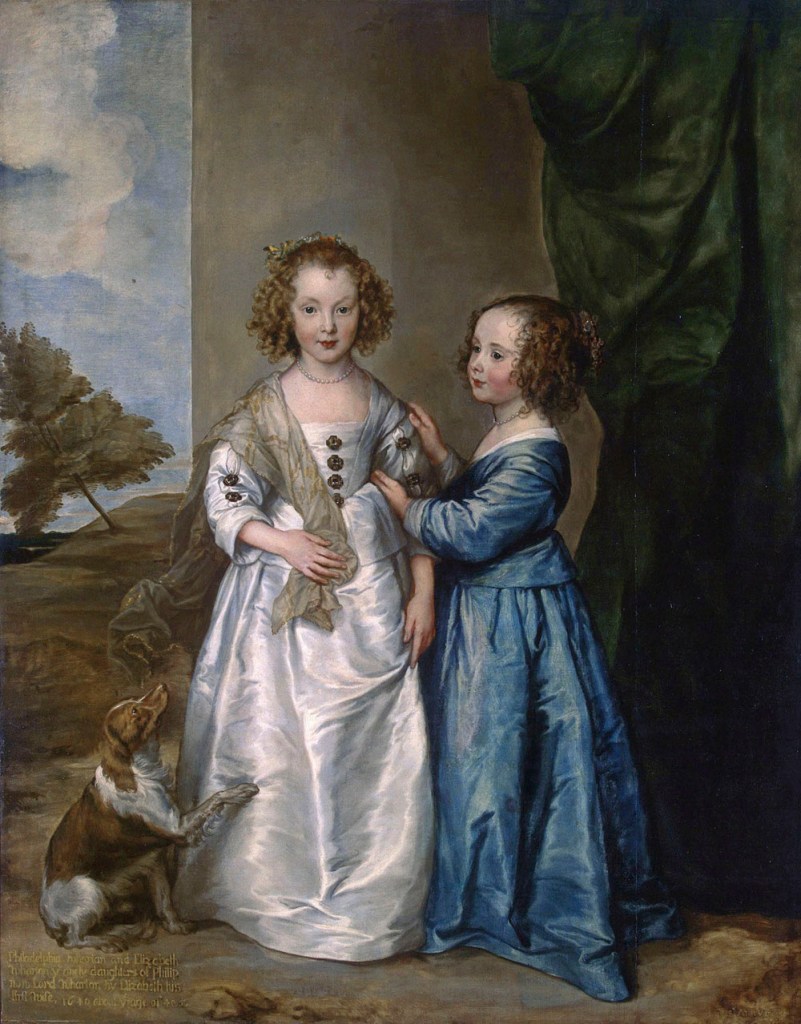

Anthony van Dyck (Flemish 1599-1641)
Portrait of Philadelphia and Elizabeth Wharton
1640
Oil on canvas
162cm (63.7 in) x 130cm (51.1 in)
Hermitage Museum
Public domain
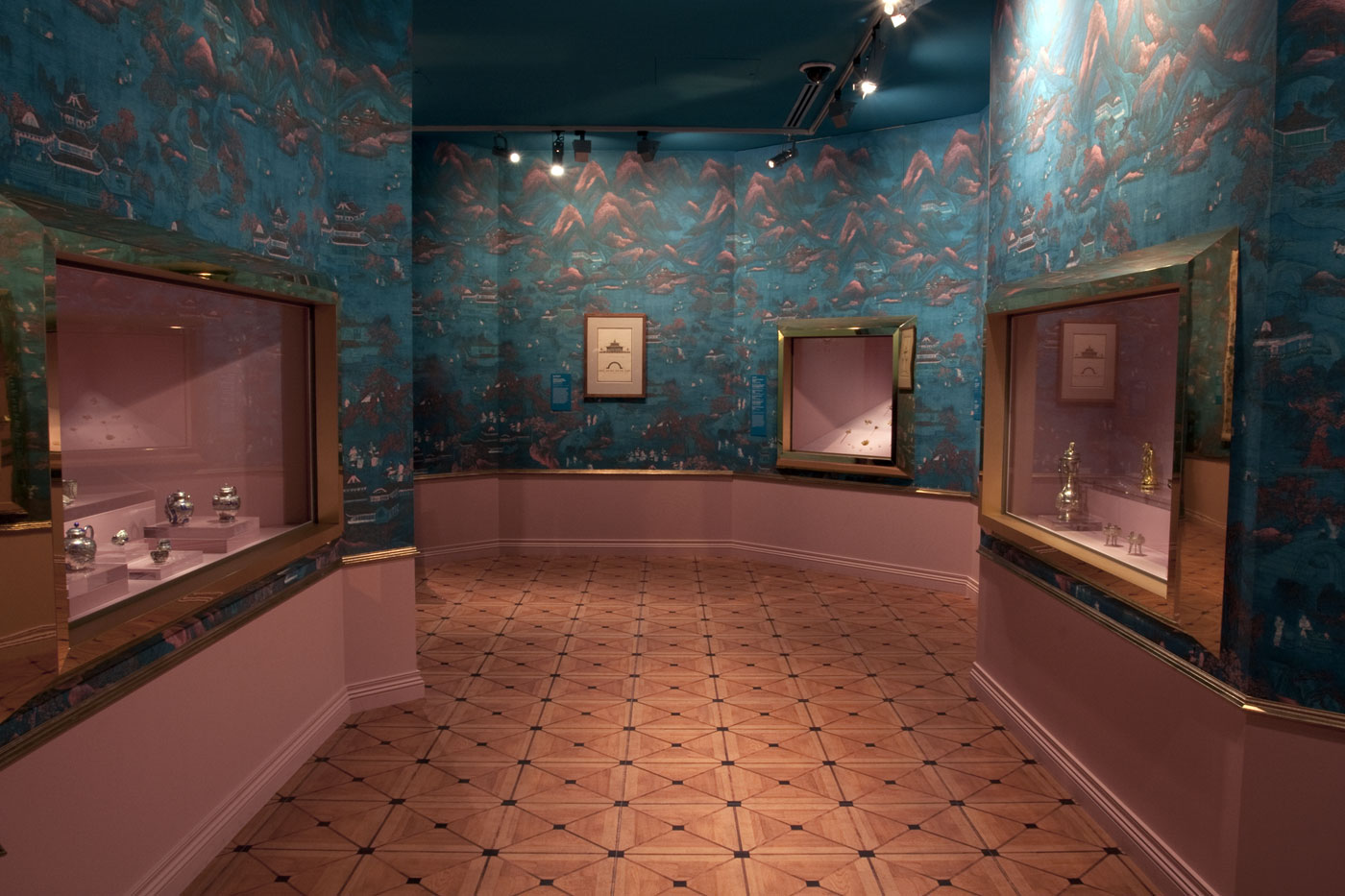
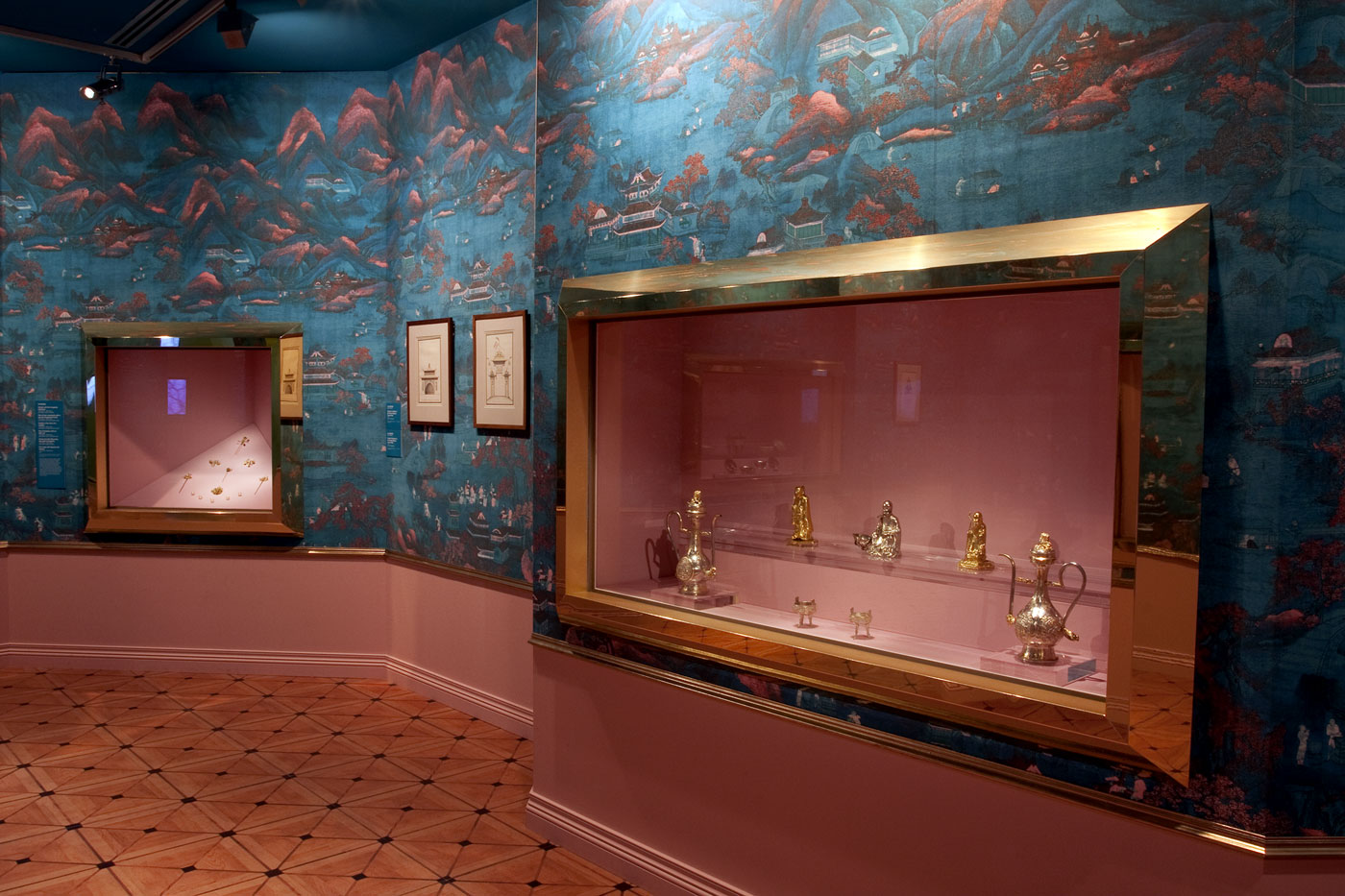
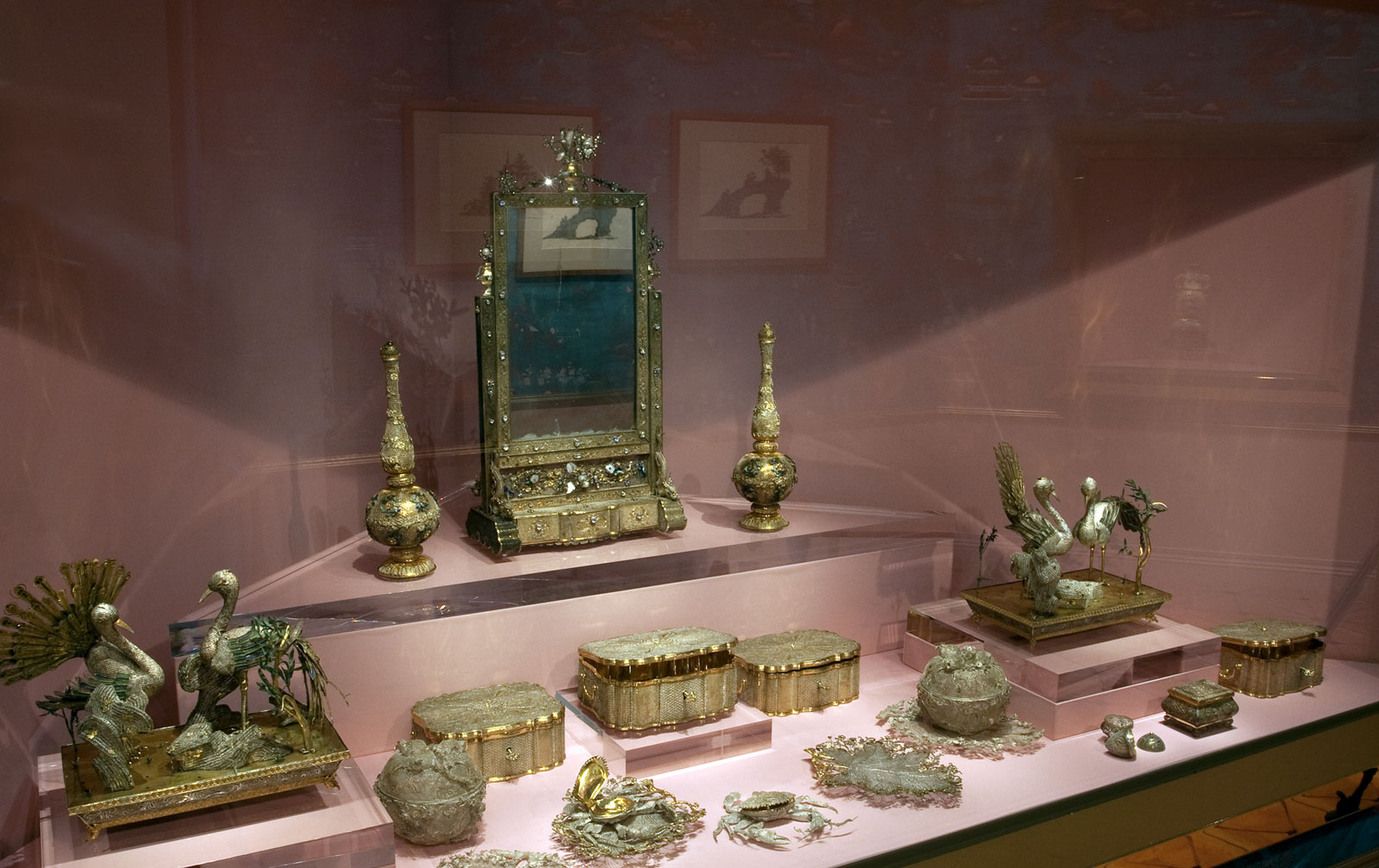
Room 8 China
Eighteenth-century Enlightenment fascination with the East, particularly China, is reflected by Catherine the Great’s architectural and landscaping works completed in St Petersburg and at her summer and winter palaces, as well as by her collecting of Oriental curiosities and philosophical texts. Russian interest in China can be traced to the reign of the Romanov tsars in the seventeenth century, when several missions brought back Chinese treasures and goods to the Russian Court. Importantly, in 1689 the first treaty between Russia and China was signed at Nerchinsk, outlining the border between the countries and rules about caravan trade.
Like many educated people of her time, Catherine was fascinated by the concept of the enlightened ruler thought to be found in China, such as the Kangxi Emperor (reigned 1662-1722), Yongzhèng Emperor (reigned 1723-35), and Qianlong Emperor (reigned 1736-95). One of her regular and most influential correspondents was French philosopher Voltaire, who praised the Celestial Kingdom, its monarchs and men of wisdom; only in China, he thought, was a man’s life, honour and property truly protected by law. Such a clear link between Catherine’s desire for justice and order in Russia and general perceptions of good Chinese government, combined with the Enlightenment fashion for curiosities of all kinds, led to great Russian interest in China in the second half of the eighteenth century.
Installation views of room 8 of the exhibition Masterpieces from the Hermitage: The Legacy of Catherine the Great at NGV International, Melbourne
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
NGV International
180 St Kilda Road
Opening hours for exhibition
10am – 5pm daily



























































![Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Horse and trap], Quandong' 1887 Unknown photographer. 'Untitled [Horse and trap], Quandong' 1887](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/quandong11.jpg)
![Unknown photographer. 'At Quandong [Horse, foal and cart]' 1887 Unknown photographer. 'At Quandong [Horse, foal and cart]' 1887](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/quandong9.jpg)


























































![Germaine Krull (European, 1897-1985) 'Étalage: les mannequins [Display: mannequins]' 1928 from the exhibition 'Germaine Krull (1897-1985) A Photographer's Journey' at Jeu de Paume, Paris, June - September, 2015 Germaine Krull (European, 1897-1985) 'Étalage: les mannequins [Display: mannequins]' 1928 from the exhibition 'Germaine Krull (1897-1985) A Photographer's Journey' at Jeu de Paume, Paris, June - September, 2015](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/gkrull_09-web.jpg)







![Germaine Krull (European, 1897-1985) 'Étude pour La Folle d’Itteville [Study for The Madwoman of Itteville]' 1931 Germaine Krull (European, 1897-1985) 'Étude pour La Folle d’Itteville [Study for The Madwoman of Itteville]' 1931](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/gkrull_14-web.jpg?w=767)






















































![Michael Riley (Australian, 1960-2004) 'Untitled' from the series 'Cloud [Feather]' 2000 Michael Riley (Australian, 1960-2004) 'Untitled' from the series 'Cloud [Feather]' 2000](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/riley-web.jpg)





















































You must be logged in to post a comment.