Exhibition dates: 8th May – 27th September, 2009
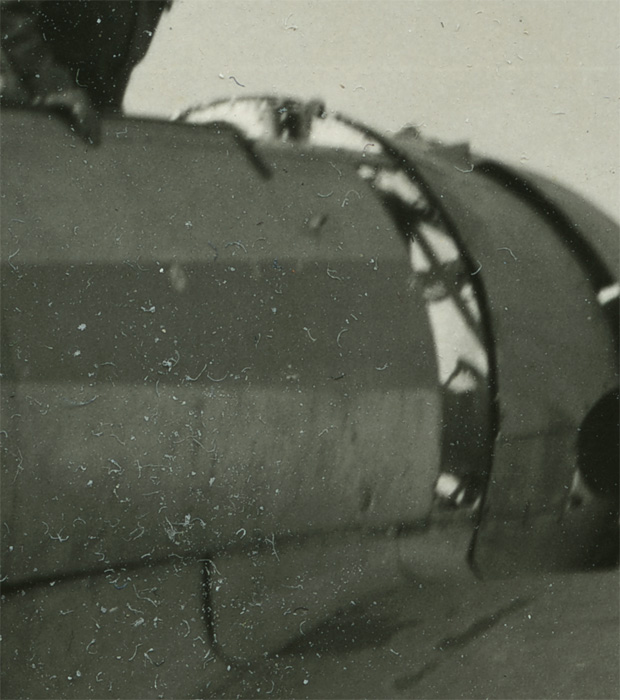
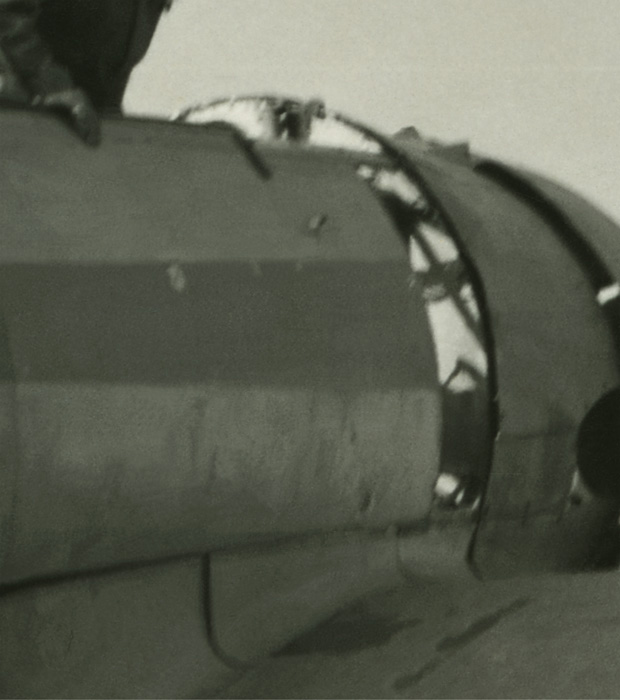
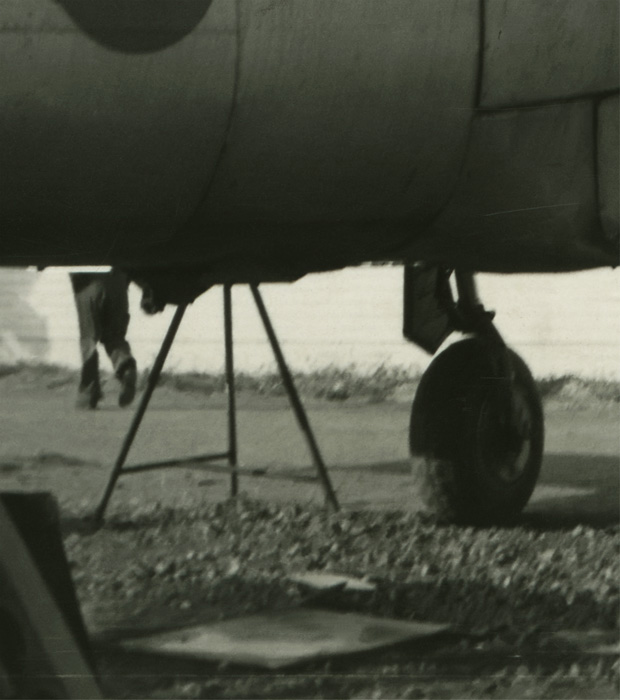
NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Skylab (photographer)
Three Skylab 2 crewmen demonstrate effects of weightlessness
1973
Type C photograph
40.5 x 49.9cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1980
A small but fun show at NGV International, Melbourne that is drawing in the crowds. A selection of beautiful, breathtaking images from NASA really takes you into space. I had a great time researching and finding some of the images from the exhibition on the NASA Image and Video Library website!
Dr Marcus Bunyan
.
Many thankx to the National Gallery of Victoria for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Once a photograph of the Earth, taken from outside, is available, we shall, in an emotional sense, acquire an additional dimension … and a new idea as powerful as any in history will be let loose.”
Sir Fred Hoyle, 1948
“Every great advance in science has issued from a new audacity of the imagination.”
John Dewey, 1859-1952, American philosopher, psychologist and educational reformer
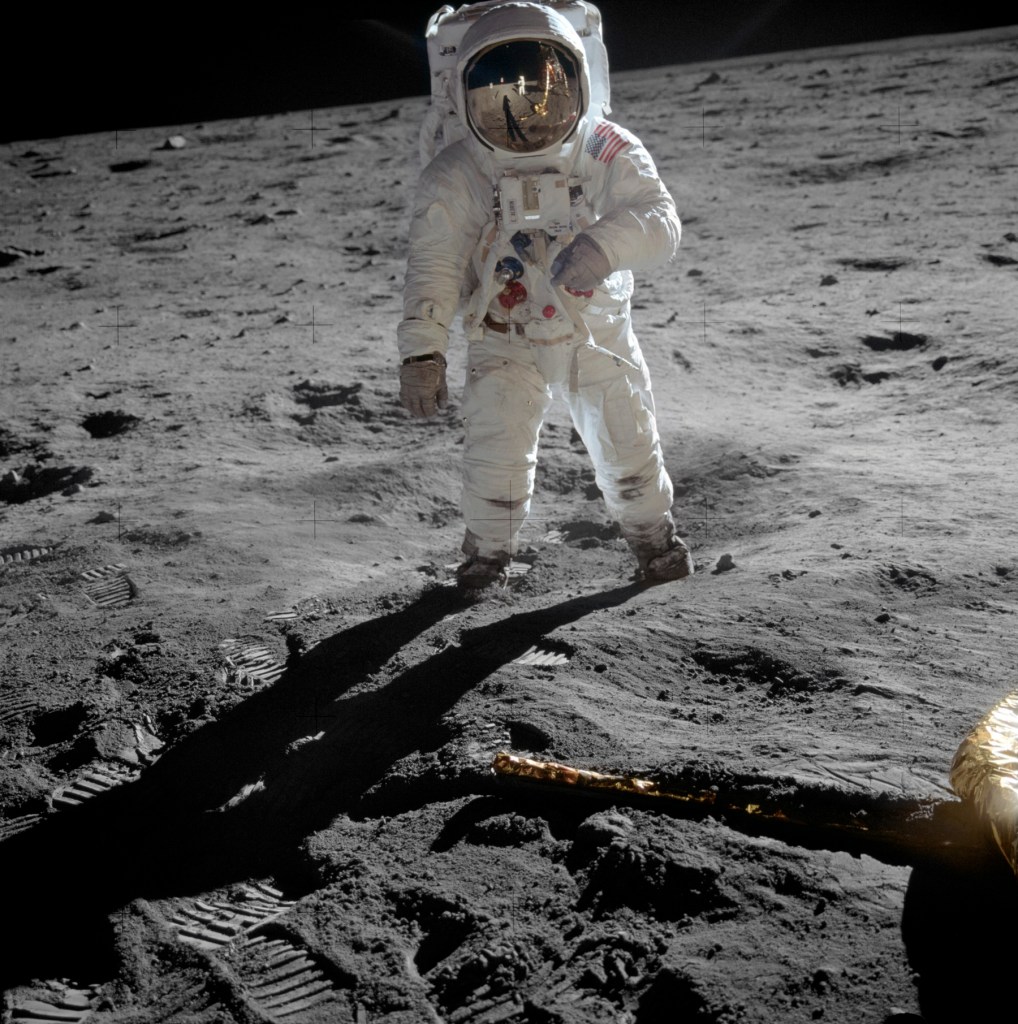

NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Neil Armstrong (American 1930-2012, photographer)
Astronaut Buzz Aldrin, lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the Moon near the leg of the Lunar Module (LM)
1969
Note the reflection of the shadow of the astronaut, the photographer and the leg of the LM in the visor of Buzz Aldrin.
Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module LM pilot, walks near the module as a picture is taken of him. Discolouration is visible on his boots and suit from the lunar soil adhering to them. Reflection of the LM and Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong is visible in Aldrin’s helmet visor. Image taken at Tranquility Base during the Apollo 11 Mission. Original film magazine was labeled S. Film Type: Ektachrome EF SO168 colour film on a 2.7-mil Estar polyester base taken with a 60mm lens. Sun angle is Medium. Tilt direction is Northeast NE.
Text from the NASA archives website
Astronaut Buzz Aldrin, lunar module pilot, stands on the surface of the moon near the leg of the lunar module, Eagle, during the Apollo 11 moonwalk. Astronaut Neil Armstrong, mission commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the lunar module to explore the Sea of Tranquility, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained in lunar orbit with the Command and Service Module, Columbia. This is the actual photograph [above] as exposed on the moon by Armstrong. He held the camera slightly rotated so that the camera frame did not include the top of Aldrin’s portable life support system (“backpack”). A communications antenna mounted on top of the backpack is also cut off in this picture. When the image was released to the public, it was rotated clockwise to restore the astronaut to vertical for a more harmonious composition, and a black area was added above his head to recreate the missing black lunar “sky”. The edited version [below] is the one most commonly reproduced and known to the public, but the original version, above, is the authentic exposure. A full explanation with illustrations can be seen at the Apollo Lunar Surface Journal.
Text from the Wikipedia website. Image from the NASA website.
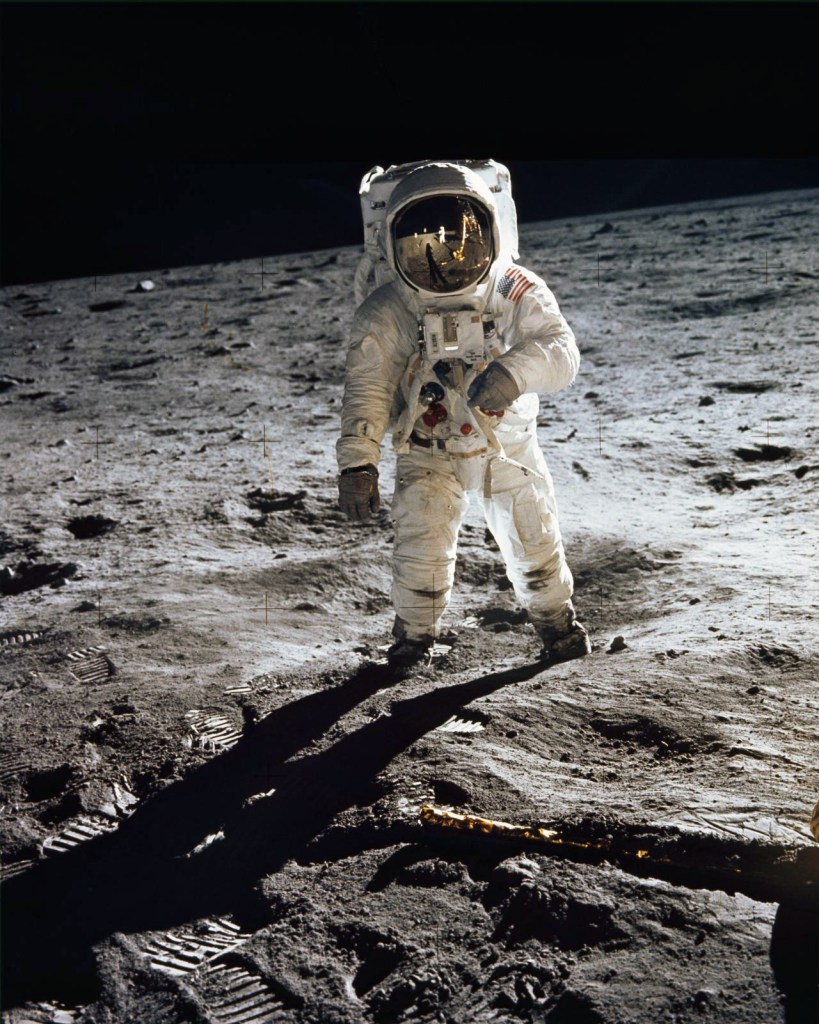

NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Neil Armstrong (American, 1930-2012 photographer)
Astronaut Buzz Aldrin, lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the Moon near the leg of the Lunar Module (LM)
1969
Colour transparency
50.8 × 40.6cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1980
In 1948, the British astronomer Sir Fred Hoyle speculated that “Once a photograph of the Earth, taken from outside, is available, we shall, in an emotional sense, acquire an additional dimension … and a new idea as powerful as any in history will be let loose.” Hoyle encapsulated the immense anticipation that was felt in the mid-twentieth century, when the idea of leaving Earth and viewing it from afar was on the verge of becoming reality.
When astronauts and spacecraft began exploring our solar system, it was the photographs from these voyages which visualised the reality of the epic feats of science, engineering and human imagination. These photographs transcended a strictly scientific purpose and depicted scenes of unexpected and sublime beauty.
This exhibition brings together works from the permanent collection of the National Gallery of Victoria that depict space travel, seen in archival images from NASA, space allegories, and altered perceptions of reality inspired by ideas of science and space. These photographs also show a fascination with light, as both the means and the subject of the image.
The exhibition focuses largely on the 1960s and 1970s – an exciting time for the artistic and scientific exploration of worlds beyond our own. These were ‘light years’, in which people looked up to the skies and beyond, in a real and an imagined sense, and through photography discovered additional dimensions.
Text from the NGV International website
Ronnie Van Hout (New Zealander, b. 1962, worked in Australia 1998-)
Visitation
1992
from the Untitled series 1992
Gelatin silver photograph
31.8 × 47.3cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1996
© Ronnie van Hout
The work is from van Hout’s Untitled 1992 series. It comprises images made by photographing still life constructed from small scale models. The series is based upon B-grade 1950s and 1960s science fiction films. The photographs in the series show a single word, encapsulating an essential element of the story and constructed in 3-D text, placed within a barren / lunar model landscape.
Text from the National Gallery of Victoria website
In his Untitled series, 1992, Ronnie van Hout created models based on the mountains in New Zealand, shown as the sun was setting and they fell into silhouette, and placed a single word (‘rejoice’ or ‘visitation’) in the foreground. The influence of 1960s sci-fi aesthetics is clearly evident in the glowing lights, the desolate ground, and the potential for an otherworldly experience. As with much science fiction, van Hout’s photographs create ambiguous narratives that allude to alien visitation set in a mystical landscape.
Text from the NGV Education kit
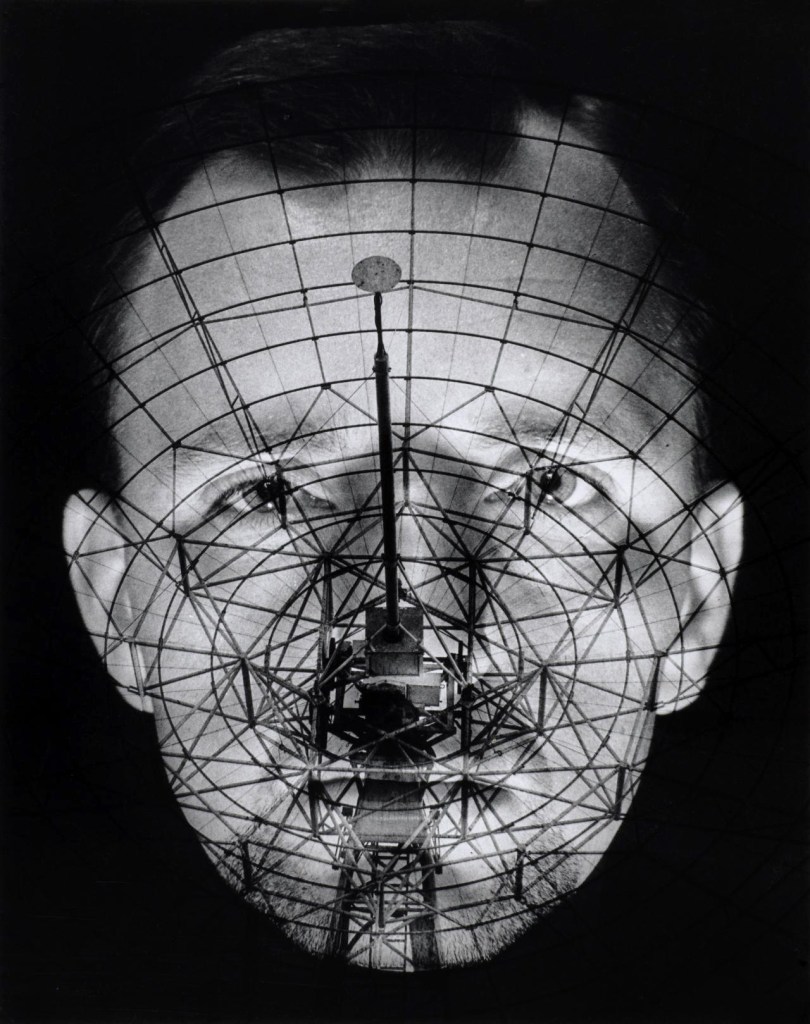

Raymond De Berquelle (Australian, b. 1933)
Where do you come from? Planet Earth (Self-portrait with radio telescope)
1968
Gelatin silver photograph
24.1 × 19.1cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, Victorian Foundation for Living Australian Artists, 2008
© Raymond de Berquelle
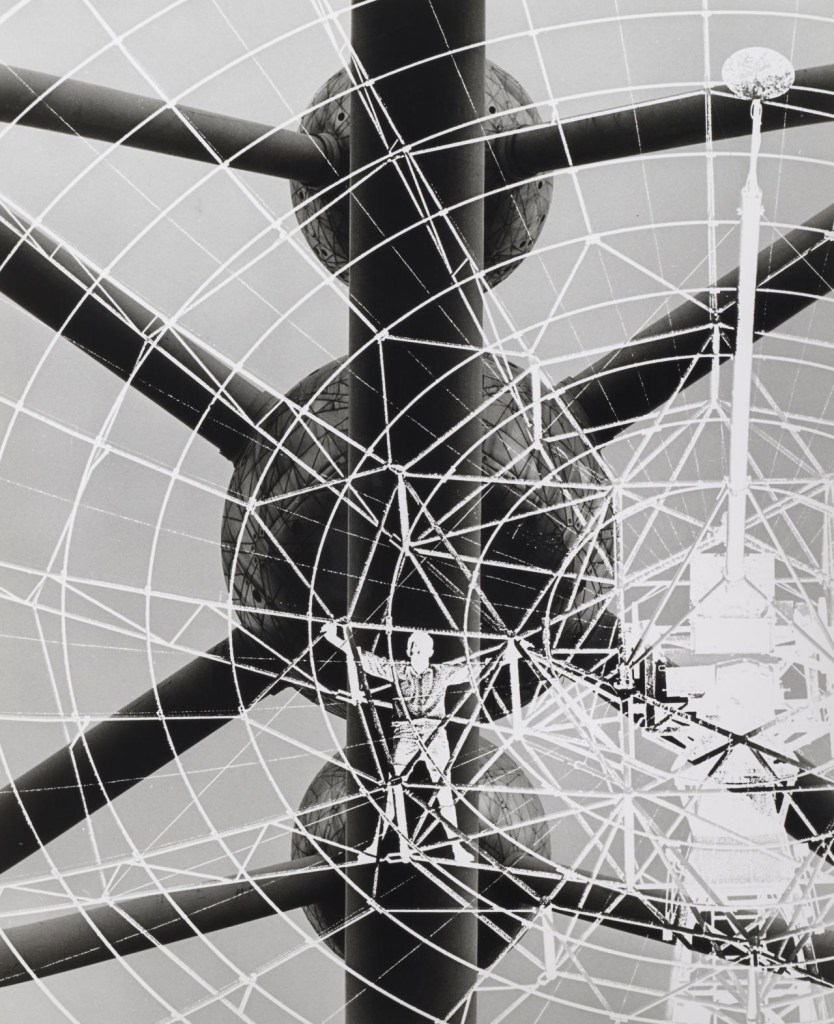

Raymond De Berquelle (Australian, b. 1933)
Space man
1963
Gelatin silver photograph
49.8 × 41.0cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1971
© Raymond de Berquelle
The photographs of Raymond de Berquelle reflect excitement about the possibilities of astronomy and a fascination for science fiction. The radio telescope was a particularly significant emblem of the exploration of the universe. The primary tool of astronomy, it allowed astronomers to see beyond visible light into the expansive electromagnetic spectrum. De Berquelle frequently visited observatories and radio telescopes, including the one at Parkes, outside Canberra, that was one of a network of radio antennas around the world used to receive images from the Apollo 11 Moon landing in July 1969.
To create the fantastical photograph, Space man, Raymond de Berquelle combined different negatives to construct an image that expressed both his expectations of astronomy and his vision of a man in space. De Berquelle describes the process as beginning with an unexpected vision:
[one day] a radio telescope appeared on the horizon with a human being clinging to it as if caught in its net. It was a technician [working on] the huge instrument. In the darkroom later on the negative appeared stronger than the positive image … and an earthy radio telescope technician became a space man.
Raymond de Berquelle in correspondence with Maggie Finch, 12 November 2008, quoted in Maggie Finch, Light Years: Photography and space (exh. cat.), National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, 2009, p. 18.
Text from the NGV Education kit
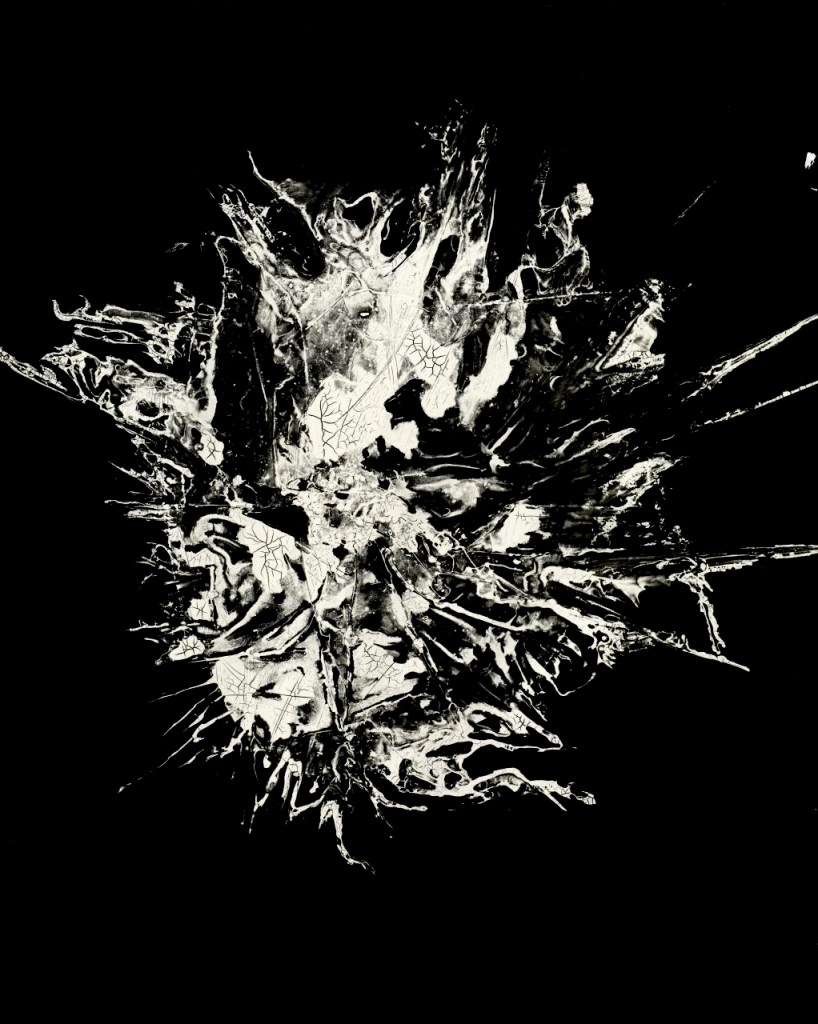
John Wilkins (Australian, 1946-2017)
Alien Icicle
c. 1970
Gelatin silver photograph on composition board
57.6 × 46.5cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1971
© John Wilkins
The photograms of John Wilkins reveal methods of abstraction and distortion (the hallmarks of psychedelia) to produce lush, exploding, organic forms. Wilkins uses the photogram technique to record the object (in this case, liquid) directly onto film, which was later enlarged and printed. Wilkins’s photographs resemble cosmic worlds, and he has described how the chemical patterns were directly influenced by the psychedelic patterns meant to simulate LSD trips that were projected onto the walls of nightclubs in the 1960s and 1970s. They possess a mysterious quality that transcends a distinction between art and science.
Text from the NGV Education kit
Sir George F. Pollock (English born France, 1928-2016)
Energy bubble
1966
Cibachrome photograph
24.0 × 34.6cm irreg. (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by the National Gallery Society of Victoria, 1972
© George F. Pollock
“Light is the energy that maintains life on earth, through the plants’ marvellous process of photosynthesis: no light, no plants; no plants, no animals, and no us. This is the secret of life, and I want to celebrate this life-giving energy in images of, about, and made by light, in other words in photographs.”
Sir George Pollock, 2009
Space exploration opened up new ways of seeing and imagining the world and created new perceptions of our place in the universe.
Parallel to the exploration of outer space taking place under the auspices of science, explorations of space in other realms were contributing to new and altered perceptions of the world, and inspiring new forms of art and artmaking.
During the second half of the twentieth century, many artists rejected the illusionistic representation of three-dimensional space and form which had dominated western art for centuries and opted for a flattened pictorial space. In contrast to the closed compositions traditionally found in western art, artists such as Jackson Pollock (American, 1912-1956) worked with ‘open compositions’ which created the idea that the visual elements in an image extended beyond the confines of the picture space.
The mysterious world of ‘inner space’, including the subconscious, and the senses, was also important territory for exploration, especially within the ‘hippie’ subculture that emerged in the US in the mid-1960s. Psychedelic patterns, inspired by the hallucinations and mind-altering experiences produced by drugs such as LSD, and characterised by wild patterning and colours and dazzling light effects, had a significant effect on the art and popular culture of the period.
In 1962, English artist George Pollock commenced a conceptual photographic project comprising a series of abstract photographs that he called ‘vitrographs’. This term referred to the process of creating images by photographing pieces of glass that have been lit by a number of coloured lights. Pollock used pieces of cullet, the thick lumps of glass left in a kiln at the end of a melt.
By lighting the cullet from different angles and photographing the pieces at close range, Pollock was able to produce patterned, abstract images with an ethereal quality reminiscent of solar eruptions and the nebulae of outer space.
Pollock was influenced by scientific studies, particularly in the field of biology, as well as the literature of science fiction and the abstraction found in the art of surrealism and abstract expressionism. He was interested in using photography to reveal things that otherwise may have been overlooked.
Text from the NGV Education kit
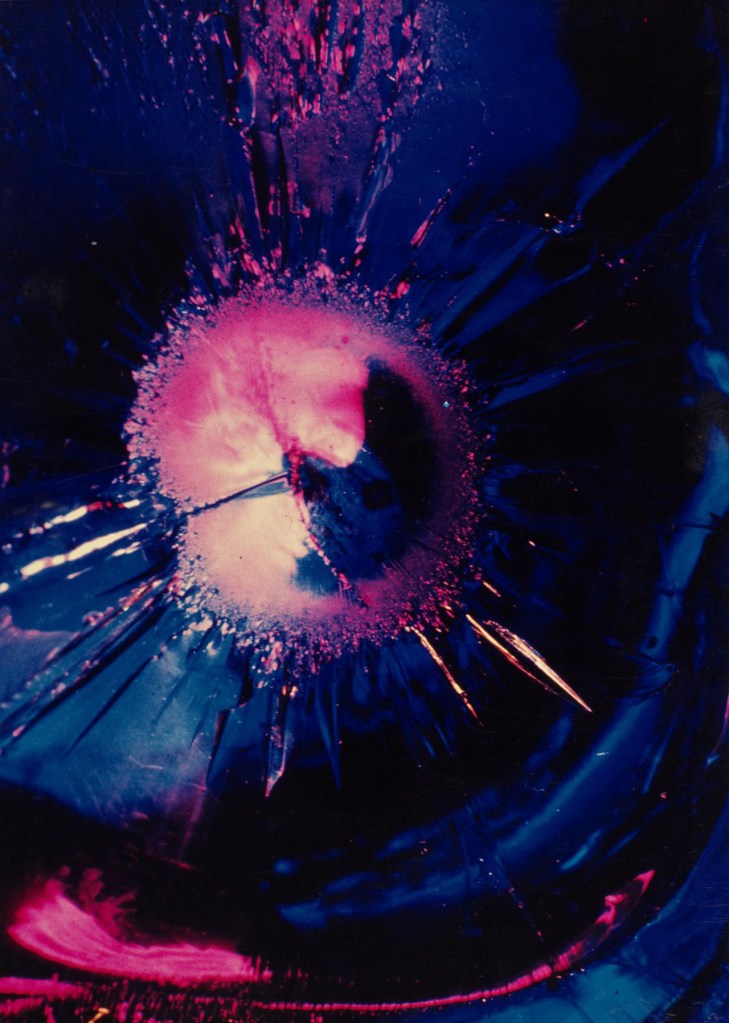

Sir George F. Pollock (English born France, 1928-2016)
Galactic event
1966
Cibachrome photograph
34.3 × 24.0cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by the National Gallery Society of Victoria, 1972
© George F. Pollock
A significant number of the works in Light Years: Photography and space have been acquired by the NGV from NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration). The United States government established NASA on 29 July 1958 as the agency responsible for the development of the nation’s new space program.
The 1950s and 1960s were a period of intense activity in space exploration, led by the US and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). The US and the Soviet Union emerged as the two most powerful forces in the world after the Second World War. During the Cold War that followed, these two superpowers competed for political, military and scientific dominance, fuelling a ‘space race’. The space race effectively began when the Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth, Sputnik 1, on 4 October 1957, and reached a milestone when NASA succeeded in landing humans on the moon on 20 July 1969 (in Australia, 21 July 1969).
The Apollo missions, in particular the Apollo 11 mission of 1969 that saw Neil Armstrong become the first man to step foot on the moon, have assumed enormous importance in the popular imagination in relation to space travel.
However, since the late 1950s NASA has been involved in many different projects, involving numerous manned and unmanned missions. These projects have ranged from exploring Earth’s orbit and mapping the lunar surface to penetrating greater and greater distances into space and exploring other planets in our solar system, including Mars, Mercury, Venus and Jupiter. These missions played a critical role in extending our knowledge of the solar system.
While information and photographs of the Russian space program were closely guarded and rarely released to the public, NASA strategically managed the publication of images drawn from its vast photographic archive, and this had a very positive impact on the public reception of the space program.
Interestingly, it was not a priority in the early days of NASA to take photographs during missions. However, the importance of photography was soon recognised and, along with rigorous flight training, astronauts who piloted the various space missions were given extensive photographic training. Unmanned probes were equipped with remotely operated cameras, allowing those back on Earth to see details of these voyages. Increasingly sophisticated technology, including advanced imaging techniques such as X-ray, ultraviolet and infrared photography, has also been employed to capture different phenomena.
The photographs in this exhibition include images taken on manned and unmanned space voyages, from the Gemini space walks of 1965 to the Pioneer missions of 1979.
While these space photographs clearly serve a documentary purpose and are a tool of scientific research, they have a unique beauty and evoke something of the mystery and wonder of space.
The NGV acquired the NASA space photographs in two groups, the first in 1971 and the second in 1980. The acquisition submission of 1980, prepared by the former Curator of Photography, Jennie Boddington, noted:
“Apart from the considerations of technology one cannot help but speculate on the philosophical and metaphysical questions which spring to mind when one sees so beautifully presented the form of nebulae which may be light years away from our small earth, or when we see spacemen performing strange exercises in a Skylab.”
Text from the NGV Education kit
NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
James McDivitt (American, 1929-2022, photographer)
Astronaut Edward H. White, Gemini 4, June 1965
1965
Type C photograph laminated on aluminium
39.0 × 49.1cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by Photimport, 1971
This photograph by astronaut James McDivitt is taken from inside the spacecraft on the Gemini 4 mission as it orbited Earth. It shows astronaut Edward White in his spacesuit and golden visor, ‘floating’ high above the Pacific Ocean. White is attached to the spacecraft by a twisting eight-metre tether and holds a manoeuvring unit. Below him is the extraordinary vision of the vivid blue curvature of Earth and, beyond, the black abyss of deep space.
Text from the NGV Education kit
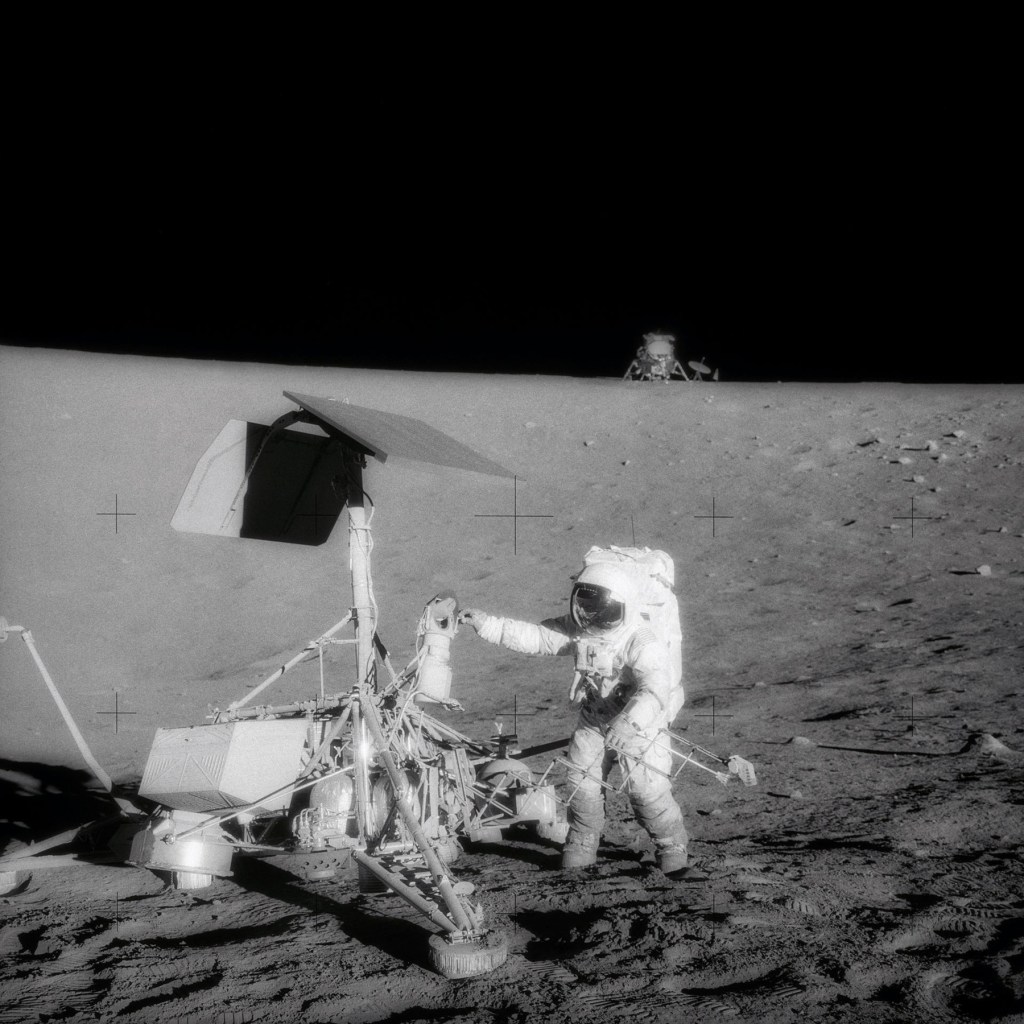
NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Apollo 12 (photographer)
View of two U.S. spacecraft on the surface of the moon, taken during the second Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA-2)
[Astronaut inspecting Surveyor 3, Unmanned craft resting on moon since April 1967]
1969
Gelatin silver photograph
49.0 × 39.0cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by Photimport, 1971
This unusual photograph, taken during the second Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA), shows two U.S. spacecraft on the surface of the moon. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) is in the background. The unmanned Surveyor 3 spacecraft is in the foreground. The Apollo 12 LM, with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean aboard, landed about 600 feet from Surveyor 3 in the Ocean of Storms. The television camera and several other pieces were taken from Surveyor 3 and brought back to Earth for scientific examination. Here, Conrad examines the Surveyor’s TV camera prior to detaching it. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended in the LM to explore the moon. Surveyor 3 soft-landed on the moon on April 19, 1967.
Text from the NASA Image and Video Library website
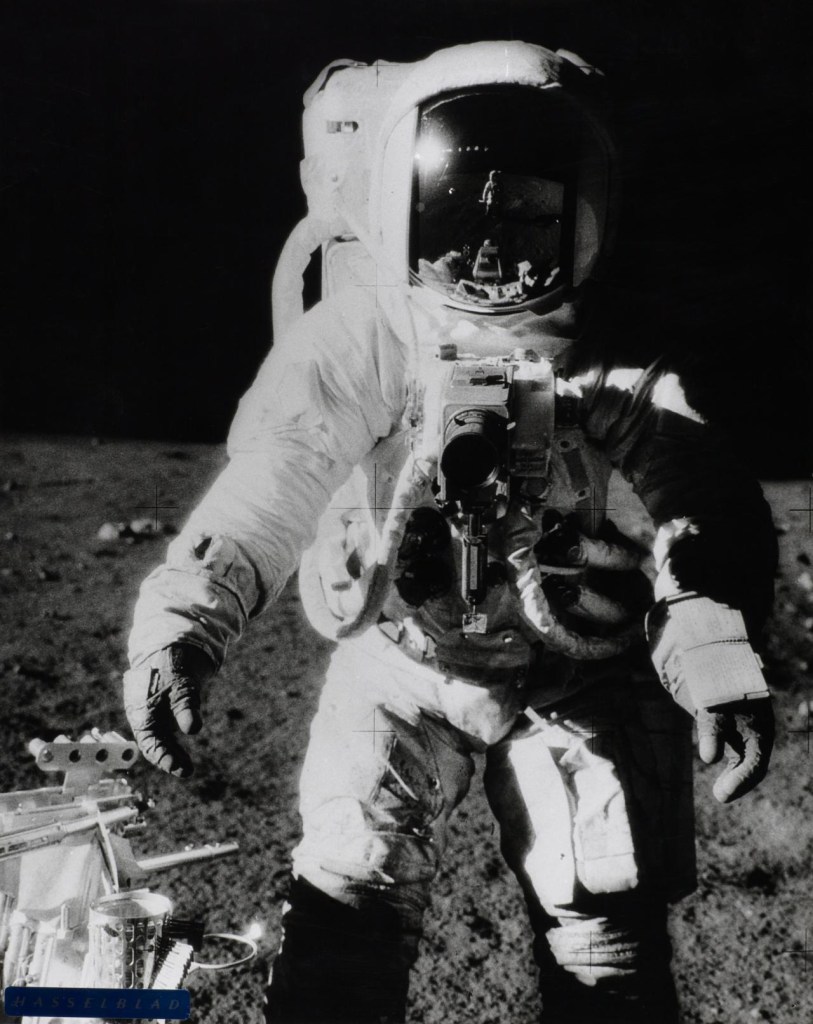

NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Charles Conrad (American, 1930-1999 photographer)
Astronaut Bean, Apollo XII, November 1969, on moon
1969
Gelatin silver photograph
49.0 x 39.0cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by Photimport, 1971

NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Apollo 8 crew (photographer)
The Earth showing Southern Hemisphere
1969
Type C photograph
48.9 × 38.9cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented by Photimport, 1971
Project Apollo (1968-1972) sent astronauts greater distances from Earth in the quest to land humans on the Moon. The further they travelled also, crucially, allowed for more complete photographic views of Earth. In this photograph, Earth is shown as a delicate, blue, cloud-covered dot hanging in infinite space.
The spectacle of Earth suspended in a black void had a profound effect on humanity. Earth was no longer seen to be our complete ‘world’ but was recognised as a small planet spinning in the solar system. As awareness of the vulnerability and limits of the planet grew, photographs such as this one formed a strong catalyst for environmental movements.
Photographs from the Apollo missions were also used to promote the inaugural Earth Day on 22 April 1970.
Text from the NGV Education kit
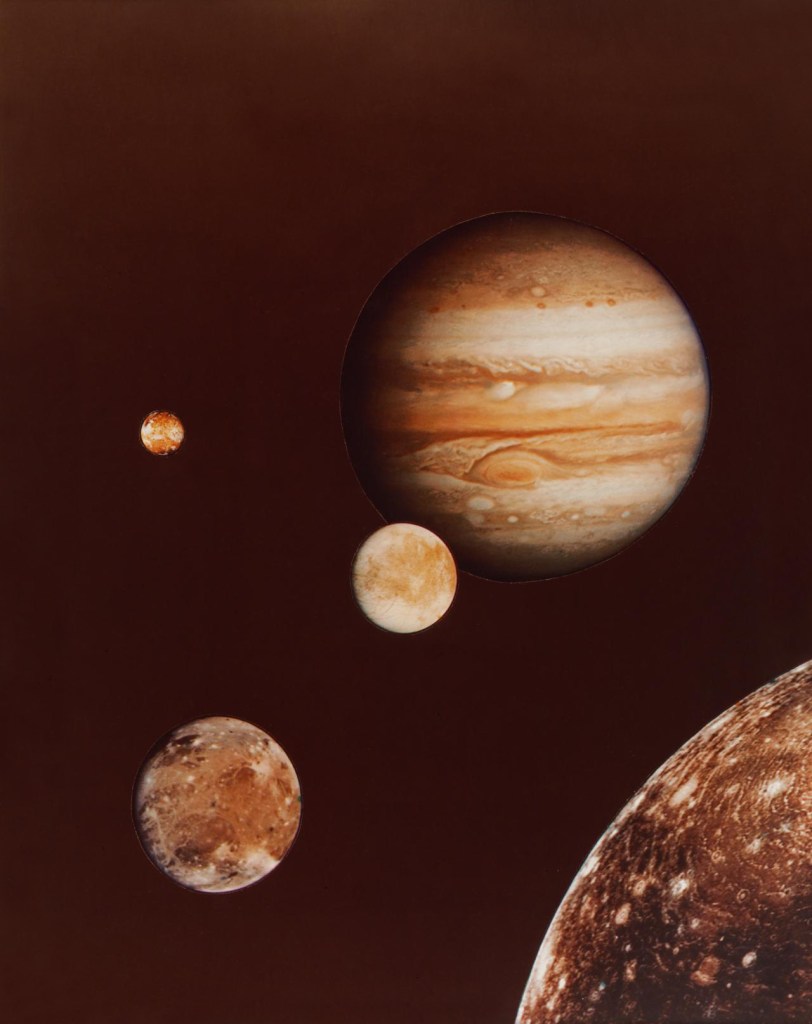

NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Voyager 1 (photographer)
Photo collage of Jupiter and its four largest moons; from early March Voyager I photos
1979
Type C photograph
51.0 x 40.5cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1980
While Jupiter had been studied through telescopes for centuries, the Voyager robotic probes that were launched into space in 1977 revealed new information about the planet and its moon system. In March 1979, the Voyager 1 mission took images of the four largest moons of Jupiter. These images were made into a photographic collage, so that the moons are seen in their relative positions (although not to scale). NASA’s arrangement of images in this montage (and others) essentially created an aesthetic rendering of scientific reality.
Text from the NGV Education kit
NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Pioneer 11 (photographer)
Image of Saturn and it’s moon Titan
1979
Type C photograph
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1980
Light Years: Photography and Space will feature around 50 works drawn entirely from the NGV Collection. Focusing largely on the 1960s and ’70s, the exhibition will include photographs taken during early NASA missions. The exhibition celebrates the International Year of Astronomy and the 40th anniversary of the first Moon walk.
Maggie Finch, Assistant Curator, Photography, NGV said that cameras were used to give form to both the fantasies and realities of space travel, revealing extra dimensions and animating space.
“The 1960s and ’70s were an exciting time for the artistic and scientific exploration of worlds beyond our own. They were ‘light years’ in which people looked up to the skies and beyond, in a real and an imagined sense, and through photography discovered additional dimensions. The photographs in ‘Light Years’ represent a giant leap forward in the collective journey into space. They retain the extraordinary sense of awe and wonderment that encapsulates our first encounters with a larger universe,” said Ms Finch.
A highlight of the exhibition is a collection of more than 30 NASA photographs, on display for the first time in over twenty years. Among the NASA selection are many celebrated space photographs, including the iconic image of Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin, Jr standing on the lunar surface, taken in 1969 by Neil Armstrong, the first man to step foot on the Moon.
These remarkable photographs will be on display alongside works by Sir George Pollock, John Wilkins Raymond de Berquelle, Dacre Stubbs, Val Foreman, Susan Fereday, Olive Cotton and Ronnie van Hout – artists who have been inspired by, and have responded to, the mysteries of space and science.
Frances Lindsay, Deputy Director, NGV said: “The photography from the NASA missions of the 1960s and ’70s has a fascinating yet nostalgic quality, particularly when one considers the advances in both science and photographic technology since that time. These early photographs of space changed our awareness and offered a new understanding of the Earth, the universe and our shared existence within it. Coinciding with the International Year of Astronomy and the 40th anniversary of the first Moon walk, this exhibition will delight viewers, providing a glimpse into another dimension,” said Ms Lindsay.
Press release from the National Gallery of Victoria
NASA, Washington, D.C. (United States est. 1958, manufacturer)
Skylab (photographer)
Solar Flare recorded by NASA Skylab, December 1973
1973
Colour transparency
50.8 × 40.6cm (image and sheet)
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Purchased, 1980
This photograph of the sun, taken on Dec. 19, 1973, during the third and final manned Skylab mission (Skylab 4), shows one of the most spectacular solar flares ever recorded, spanning more than 588,000 kilometres (365,000 miles) across the solar surface. The last picture, taken some 17 hours earlier, showed this feature as a large quiescent prominence on the eastern side of the sun. The flare gives the distinct impression of a twisted sheet of gas in the process of unwinding itself. Skylab photographs such quiescent features erupt from the sun. In this photograph the solar poles are distinguished by a relative absence of supergranulation network, and a much darker tone than the central portions of the disk. Several active regions are seen on the eastern side of the disk. The photograph was taken in the light of ionised helium by the extreme ultraviolet spectroheliograph instrument of the United States Naval Research Laboratory.
Text from the NASA Image and Video Library website
National Gallery of Victoria International
180, St. Kilda Road, Melbourne
Opening hours:
Daily 10am – 5pm
All NASA images are from the NASA Image and Video Library website







![William Kentridge (South African, b. 1955) 'Drawing for the film 'Stereoscope [Felix Crying]'' 1998-1999 from the exhibition 'William Kentridge: Five Themes' at San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA), March - May, 2009 William Kentridge (South African, b. 1955) 'Drawing for the film 'Stereoscope [Felix Crying]'' 1998-1999 from the exhibition 'William Kentridge: Five Themes' at San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA), March - May, 2009](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/04/kentridge2.jpg)




























































You must be logged in to post a comment.