Exhibition dates: 24th July – 27th September 2015
Hotham Street Ladies (est. Australia 2007)
Dark tea (installation photo)
2015
Royal icing, butter cream icing, fondant, food dye, found objects
Dimensions variable
Courtesy of the artists
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
This is the best thematic group exhibition I have seen in Melbourne and surrounds this year.
Every piece in the exhibition is visually stimulating and intelligently constructed, all works combining to make an engaging exhibition. Nothing is superfluous, every work having something interesting to say, whether it is about the ceremony of tea drinking, colonisation, global warming, Stolen Generations or social mores. Congratulations must go to the curators and artists for their efforts.
Particular favourites where the Hotham Street Ladies Dark Tea (2015, below) made of royal icing, butter cream icing, fondant, food dye, and found objects; the many sculptural objects which form the backbone of the exhibition, especially the work of Sharon West and Penny Byrne; and the wonderful vintage photographs that are displayed in the foyer of the gallery.
Accompanying this exhibition is another excellent exhibition, Ways to draw: A selection from the permanent collection by Betty Churcher, on till 27th September as well. If you want a day out from Melbourne with lunch in Mornington, some seriously good art and a drive along the coast, you could do no better than visit the gallery in the next week. Highly recommended.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Mornington Peninsula Regional Art Gallery for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. All installation photographs © Marcus Bunyan and the Mornington Peninsula Regional Art Gallery. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Hotham Street Ladies (est. Australia 2007)
Dark tea (installation view details)
2015
Royal icing, butter cream icing, fondant, food dye, found objects
Dimensions variable
Courtesy of the artists
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Charles Blackman (Australian, 1928-2018)
Feet beneath the table
1956
Tempera and oil on composition board
106.5 x 121.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Presented through the NGV Foundation by Barbara Blackman, Honorary Life Benefactor, 2005
Charles Blackman first encountered Lewis Caroll’s book, Alice in Wonderland, through a talking book for the blind which his wife, Barbara was listening to. Her developing blindness resulted in telescopic vision, spatial disorientation and a shrinking visual field. She was also pregnant with their first child and her distorted body image also had parallels with Alice’s experiences. By painting Alice at the Mad Hatter’s tea party Blackman could express his wife’s feeling of bewilderment and disorientation.
E. Phillips Fox (Australian, 1865-1915)
The arbour
1910
Oil on canvas
190.5 x 230.7cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Felton Bequest 1916
Melbourne born E. Phillips Fox, described as ‘one of the greatest of Australia’s Impressionist painters and the most gifted of her colourists’1 went to Paris in 1887 to study at the Ecole des Beaux Arts where he encountered the work of the French Impressionists. He remained in Paris for several years but made frequent trips back to Melbourne to visit his family. The Arbour was painted in Paris in Fox’s garden but is based upon observations of family life in his brother’s garden in Malvern. The depiction of an elegant family taking tea al fresco is a study of refined gentility. The Arbour was exhibited at both the Royal Academy and the Paris Salon exhibitions and was regarded by Fox as the finest thing he had done.2 At the time the painting was much admired for its ‘subtle lights ad shadow’3 and his exemplary ‘use of delicate colour and refined harmonies.’4
1/ Courier Mail, 12 May 1949
2/ Sydney Morning Herald, 13 October 1913
3/ Sydney Morning Herald, 13 October 1913
4/ Le Courrier Australien, Sydney, 15 April 1949
Clare Humphries (Australian, b. 1973)
Some things were out in the open
2007
Pigment print on Hahnemühle photo rag paper (ed. 3/5)
63 x 62cm
Courtesy of the artist
Adam Hill (Blak Douglas) (Australian, b. 1970)
Not everyone’s cup of tea
2009
Synthetic polymer paint on canvas
150 x 260cm
National Gallery of Australia, Canberra Purchased 2009
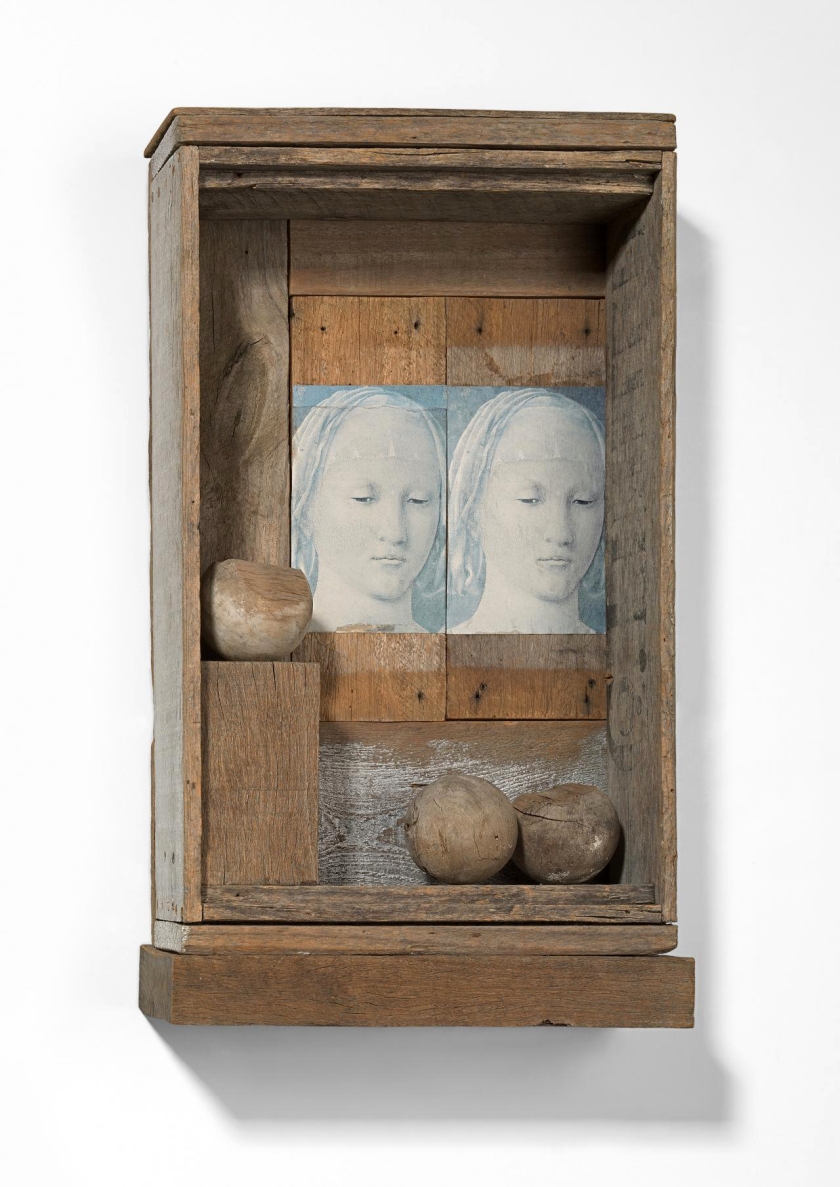
Kendal Murray (Australian, b. 1958)
Exceed speed, mislead, concede
2011
Mixed media assemblage
18 x 24 x 14cm
Courtesy of the artist and Arthouse Gallery, Sydney
Penny Byrne (Australian, b. 1965)
Tea for two in Tuvalu
2011
Vintage porcelain figurine, vintage, Action man accessories, vintage coral, glass fish, epoxy resin, epoxy putty, retouching medium, powder pigments
15 x 19cm
Private Collection
Penny Byrne (Australian, b. 1965)
Tea for two in Tuvalu (installation view)
2011
Vintage porcelain figurine, vintage, Action man accessories, vintage coral, glass fish, epoxy resin, epoxy putty, retouching medium, powder pigments
15 x 19cm
Private Collection
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
This piece was inspired by an underwater cabinet meeting held in 2009 by Maldives President Mohammed Nasheed in a campaign to raise awareness for activity on climate change. The thirty minute meeting was held six metres below sea level and was attended by eleven cabinet members calling upon all countries to cut their emissions to halt further temperature rises.
Polynesian island nation of Tuvalu, located in the Pacific Ocean midway between Hawaii and Australia, experienced a severe drought in 2011. A state of emergency was declared and rationing of fresh-water took place which restricted households on some of the islands to two buckets of fresh water per day. Tuvalu is also especially susceptible to changes in sea level and it is estimated that a sea level rise of 20 to 40 centimetres in the next 100 years could make Tuvalu uninhabitable.
Kate Bergin (Australian, b. 1968)
The hunt for a room of one’s own
2012
Oil on canvas on board
75 x 101cm
Private Collection
Kate Bergin draws upon Dutch and Flemish seventeenth century tradition of still life painting to comment on our attitudes to animals. Bergin stages the scene on a crumpled white tablecloth upon which a large fox, based on a taxidermy fox she bought on eBay, regally sits centre stage. Meticulously rendered native birds, including a honeyeater, finch and triller, are based on photographs of specimens from the Melbourne Museum Collection. They flit about unperturbed by the introduced predator. Teaspoons, representing the impulse for collecting, entangle the fox and bird. Together with a teapot and cup, precariously placed, they contribute to the overarching sense of impending chaos.
Both afternoon tea and the fox represent English upper class social mores and were introduced into the colonies following British settlement. The fox arrived in 1855, brought in for recreational hunting, and has been a major cause of native bird extinctions. Fox numbers are increasing in some areas further threatening the precarious balance between wild life and introduced species.
Sharon West (Australian, b. 1963)
Two Koori Tribesmen receive a gift of afternoon tea from local colonists (installation photo)
2014
Mixed media assemblage
15 x 46 x 30cm
Courtesy of the artist
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Heather Shimmen (Australian, b. 1957)
Tip me up (installation view)
2005
Linocut on paper and organza (ed. 7/30)
56 x 76cm
Courtesy of the artist and Australian Galleries, Melbourne and Sydney
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Trent Jansen (Australian, b. 1981)
Briggs family tea service (installation view)
2011
Slip cast porcelain, bull kelp, wallaby pelt, copper and brass
George (teapot) 22.5 x 20.5 x 13cm; Woretermoeteyenner (sugar bowl) 16 x 13.5 x 9cm; Dolly (milk jug) 12.5 x 12.5 x 8.5cm; John (teacup) 7 x 8.5 x 8cm; Eliza (teacup) 7.5 x 10.5 x 8cm; Mary (teacup) 10 x 9 x 6.5cm
Courtesy of Broached Commissions, Melbourne
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
The Briggs family tea service represents the marriage of George Briggs, a free settler, to Woretermoeteyenner of the Pairrebeenne people in Van Diemen’s Land and the four children they had together. Briggs arrived from Bedfordshire in 1791 and learned to speak the language of the local Pairrebeenne people, trading tea, flour and sugar fro kangaroo, wallaby and seal skins. It is understood that he became good friends with the leader of the Pairrebeenne people, Mannalargenna, and by 1810 he partnered his daughter Woretermoeteyenner. Their marriage meant she had to adapt to a way of life that merged her traditional cultural values with the ways of British settlers. The teapot and sugar bowl represent the parents while their first daughter, Doll Mountgarret Briggs is symbolised in the milk jug and the three cups each signify their other children John, Eliza and Mary.
The tea service is a hybrid design bringing together materials common to both cultures. To realise the set Jansen worked with Rod Bamford on the ceramic elements, Oliver Smith for the brass and copper and Vicki West, who uses the traditional methods of her Tasmanian Aboriginal ancestors, worked with the bull kelp components.
eX de Medici (Australian, b. 1959)
Blue (Bower-Bauer) (installation view)
1998-2000
Watercolour over black pencil on paper
114.0 x 152.8cm
National Gallery of Australia, Canberra Purchased 2004
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
eX de Medici (Australian, b. 1959)
Blue (Bower-Bauer) (installation view detail)
1998-2000
Watercolour over black pencil on paper
114.0 x 152.8cm
National Gallery of Australia, Canberra Purchased 2004
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
A turning point in eX de Medici’s career came in 1998 when she saw an exhibition of watercolours by Ferdinand Bauer comprising 2,000 rarely seen images of native flora and fauna made when Bauer was official artist on Matthew Flinder’s historic circumnavigation of Australia in 1801-1803. Previously working with tattoo imagery, Medici found the intricate works so compelling she decided to change course and ‘retrograde’ herself and explore watercolour as a medium.1
Referencing Australia’s Bower bird that adorns its nest with anything blue, Medici entangles the history of vanitas painting with commentary about the desire to seek permanence and affirmation in the accumulation of things. The broken willow pattern platter, upturned jugs and cups, amassed with so many other decorative and functional objects, are juxtaposed with skulls, fruit and flowers – symbols of mortality. A reaction to what she considered John Howard’s regressive politics at the time, the work ‘is a kind of a backhanded discussion about colonising our minds with retroactive ideas’.2
1/ Ted Gott. ‘eX deMedici an epic journey on a Lilliputian scale’ Art and Australia Vol. 40, No. 1, Spring 2002, p. 105
2/ eX deMedici in Paul Flynn. Artist Profile #5, March 2008, pp. 28-35.
Storm in a Teacup reflects upon tea drinking in Australia. Introduced by the British colonials, the afternoon tea party was an attempt to ‘civilise’ the land. Tea drinking became so popular in the colonies that by 1888 the amount of tea consumed per capita exceeded the amount consumed in England. Soon after, billy tea was to become an enduring symbol of the pioneering spirit, immortalised by Henry Lawson’s stories published under the title While the billy boils.
Beginning with elegant paintings of the afternoon tea table from E. Phillips Fox and Arthur Streeton, the exhibition goes on to explore the darker side of tea drinking and the social and environmental impacts of the humble cup of tea. Michael Cook’s Object (table), 2015, provides an alternative history to the narrative of colonialism while Sharon West and Adam Hill both use humour to subvert colonial understandings of the afternoon tea party as an occasion of refined gentility.
The humble cuppa has been around for thousands of years, but this exhibition explores how a popular beverage can impact on us culturally, socially, environmentally and politically. There is more to debate than just the proper way to make a cup of tea. Storm in a teacup explores far-reaching issues brewing from tea, including the imposition of one culture upon another – especially on the colonial frontier; the production of ceramics and the environmental impacts of porcelain and its production; gender stereotypes and socialisation through tea parties. The exhibition also reflects upon tea drinking ceremonies in Asia within a western Orientalist paradigm and tea drinking as an occasion for familial cohesiveness and disconnect.
Text from the Mornington Peninsula Regional Art Gallery
Mark James Daniel (Australian, 1867-1949)
Verandah, “Harefield” – afternoon tea
Feb 1900
Glass negative
8.5 x 11cm (quarter plate)
Collection of the State Library of Victoria
Michael J Drew (Australian, 1873-1943)
Group taking tea in a garden
between 1890 and 1900
Glass negative
12.2 x 16.5cm (half plate)
Collection of the State Library of Victoria
Rex Hazlewood (Australian, 1886-1968)
[Men drinking billy tea]
1911-1927
Silver gelatin print
Collection of the State Library of New South Wales
Anonymous photographer
Afternoon tea at “Vivaleigh”
1917
Gelatin silver print
12 x 16cm
Collection of the State Library of Victoria
James Fox Barnard (Australian, 1874-1945)
Lawn, Arylie, Hobart
c. 1900
Glass negative
8.5 x 11cm (quarter plate)
Collection of the State Library of Victoria
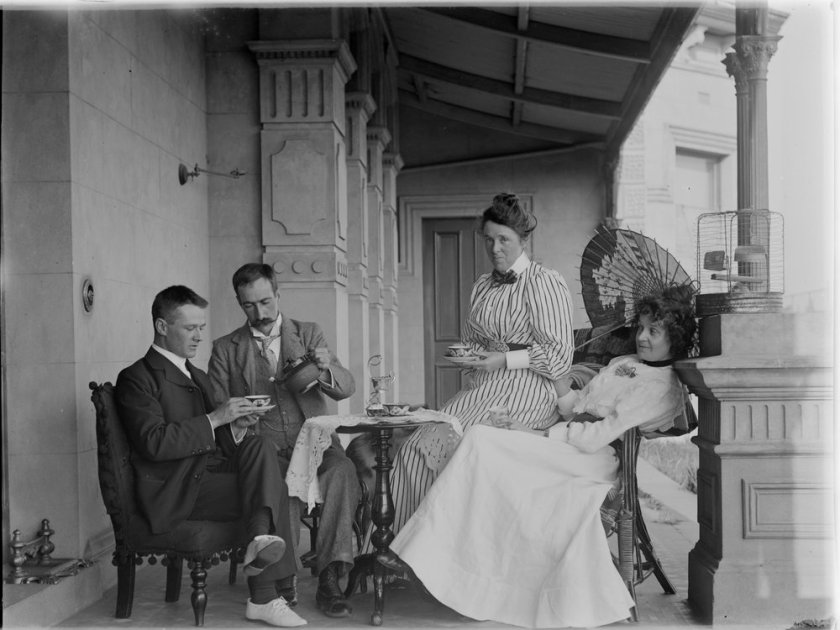
James Fox Barnard (Australian, 1874-1945)
[Tea on the verandah]
c. 1900
Glass negative
8.5 x 11cm (quarter plate)
Collection of the State Library of Victoria
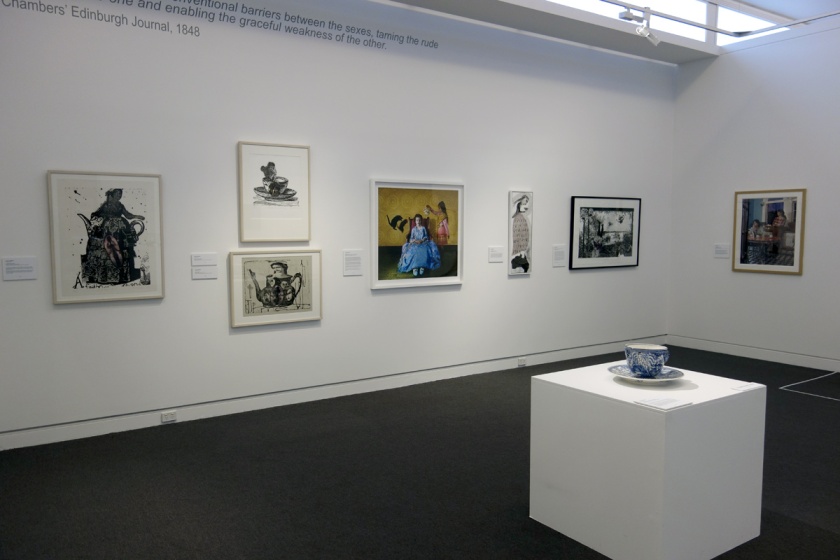
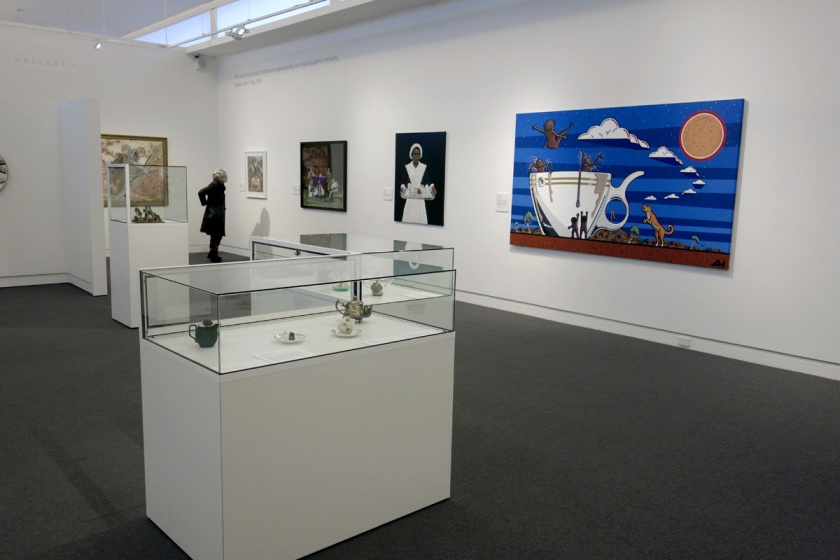
Installation photograph of the exhibition Storm in a Teacup at the Mornington Peninsula Regional Art Gallery
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Tea is the medium of many a complex and commonplace rituals. Adopted in a variety of ceremonies and customs across the globe, its unique and symbolic place in our lives is subtle and powerful. Whether a quick cuppa around the kitchen table or a lavish display of refined gentility; from billy tea to Asian tea-drinking ceremonies, tea has played an important role in international trade but more curiously in facilitating social cohesiveness.
Comprising approximately 50 works including painting, photography, sculpture and installation Storm in a Teacup features artists such as Chares Blackman, John Perceval, Emma Minnie Boyd, E. Phillips Fox and contemporary artists Stephen Bowers, Danie Mellor, Penny Byrne, Rosalie Gasgoigne, Matthew Sleeth, eX de Medici, Anne Zahalka, Polixeni Papapetrou and a mad tea party installation by Hotham Street Ladies.
Tea is said to have first been invented in China around 2700 BC, with the earliest records of tea consumption dating to 1000BC. Initially consumed as a medicinal drink, it became widely popular as a common beverage and traded across Asia and Europe during the 16th century. It was King Charles II’s wife Catherine of Portugal who is said to have brought the tea habit to Great Britain. Indeed, the afternoon tea party first became fashionable in the seventeenth century following Queen Catherine de Braganza’s fondness for serving the beverage at Whitehall in London. It wasn’t until the 18th century that it became widely consumed with tea smuggling bringing the tipple to the masses and later influenced the Boston Tea Party.
Tea drinking became a demonstration of social aspirations and grew in popularity giving rise to a subtle orchestration of manners, dress and serving paraphernalia which created new forms of commodity consumption. In the colonies of New South Wales and Victoria afternoon tea parties were a lavish display of settler understandings of refined gentility that were an attempt to signal allegiance to the values of the home country and ground the displaced community in their originating culture. In this respect the afternoon tea party expressed collective understandings of British identity and was a means of domesticating and civilising the alien terrain of the colonies.
Press release from the Mornington Peninsula Regional Art Gallery
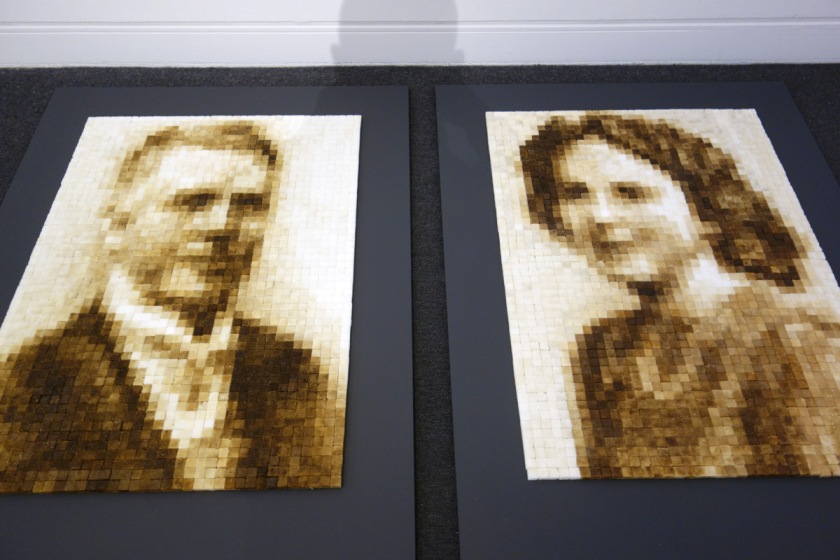
Clare Humphries (Australian, b. 1973)
Family confection II (installation views)
2015
Sugar cubes stained with coffee and tea
Dimensions variable
Courtesy of the artist
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
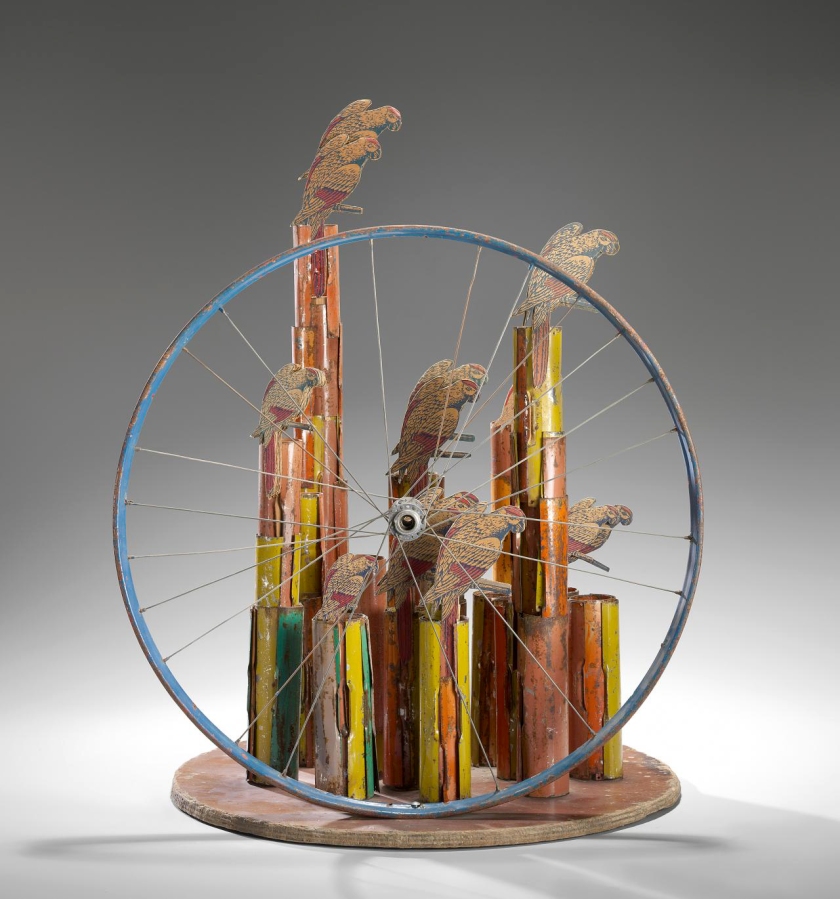
Giuseppe Romeo (Australian, b. 1958)
Subjective landscape, ‘Of consequence rather than reason’ (installation views)
2015
Found discarded objects, bitumen, paint
80 x 100 x 60cm
Courtesy of the artist
Photos: Marcus Bunyan
Guiseppe Rome asks the simple question: ‘What are you going to do with it all?’
Romeo recalls the tea sets his mother and aunts possessed and the ‘good set’ kept for special occasions that were rarely used. In this work a silver platter is the support for a silver cake stand upon which a teapot, creamer, sugar bowl and various serving implements jostle with items required to clean up the mess. The bat, ball and stumps are a reference to playing cricket which ‘became an excuse for a big afternoon tea party in England’. A ribbon of wire holds it all together ‘like a dream from Alice in Wonderland when nothing is as it seems’, while a tinkling melody from a music box is a lullaby that sends us in to a contented sleep.
Romeo coats the sculpture in bitumen then paints it entirely in white. The effect is reminiscent of excavated items from an ancient ruin, as if we are peering upon the remains from a modern day Pompeii – artefacts that have been covered in lava and buried. This work alludes to the ways in which we deceive ourselves and ‘attempt to keep it all together through consumption but ultimately we can’t’.
Samantha Everton (Australian, b. 1971)
Camellia
2009
From the series Vintage dolls 2009
Pigment print on rag paper (ed. AP2)
106 x 114cm
Courtesy of the artist and Anthea Polson Art, Queensland
Robyn Phelan (Australian, b. 1965)
Porcelain wall – ode to an obsession (installation view)
2010-2015
Porcelain, paper, clay, cobalt oxide, timber, pigment, Jingdezhen tissue transfer
240 x 122 x 42cm
Courtesy of the artist
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Robyn Phelan (Australian, b. 1965)
Porcelain wall – ode to an obsession (installation view detail)
2010-2015
Porcelain, paper, clay, cobalt oxide, timber, pigment, Jingdezhen tissue transfer
240 x 122 x 42cm
Courtesy of the artist
Robyn Phelan undertook a residency at the Pottery Workshop and Experimental Sculptural Factory of Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province in China in 2008. Jingdezhen is known as the porcelain capital because it has been the centre of China’s ceramic production, beginning in the fourteenth century Yuan Dynasty, where fine porcelain was first exported all over the world.
Deposits of kaolinite, a clay found at Mt Kaolin nearby which can sustain very high firing temperatures produced a superior white porcelain of increased strength and translucency. Items made from kaolinite were fired with cobalt landscape designs and were highly sought after by European collectors. Over the centuries, because of excessive mining, the mountain’s deposits have become depleted. Phelan’s work is a lament to the desecration of the mountain and a reminder of the potential destructiveness of consumer desire.
Penny Byrne (Australian, b. 1965)
‘Let’s forget about global warming’ said Alice ‘and have a cup of tea instead!’ (installation view)
2010
Vintage porcelain figurine, found toys, epoxy resin, epoxy putty, retouching medium, powder pigments
80 x 33cm
Williams Sinclair Collection
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Penny Byrne (Australian, b. 1965)
‘Let’s forget about global warming’ said Alice ‘and have a cup of tea instead!’ (installation view detail)
2010
Vintage porcelain figurine, found toys, epoxy resin, epoxy putty, retouching medium, powder pigments
80 x 33cm
Williams Sinclair Collection
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Penny Byrne’s reworked porcelain conversation piece was motivated by Republican Vice-Presidential nominee Sarah Palin’s cry to ‘drill, baby, drill’ during her campaign in 2008. A call for increase off-shore drilling of petroleum, including sites such as the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, Palin claimed ‘that’s what we hear all across the country in our rallies because people are so hungry for those domestic sources of energy to be tapped into’.1
In Byrne’s piece the patriotic figures gorge themselves, blithely overindulging without care to the wastage. The new Disney production of Alice in Wonderland directed by Tim Burton had just been released and this led Byrne to reflect upon the Mad Hatter’s tea party in which tea was drunk all day because time stood still and was stuck at tea-time.
1/ Transcript: The Vice-Presidential Debate, 2 October 2008. Reprinted in the New York Times, 23 May 2012.
Sharon West (Australian, b. 1963)
Joseph Banks’ tea party for a Botany Bay tribesman is ruined by flies and spiders
2014
Digital print on paper (ed. 2/5)
66 x 57cm (sheet)
Courtesy of the artist
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Sharon West’s recreation of an afternoon tea party is set in the early days of first contact. Joseph Banks was the botanist who sailed with Captain Cook on the Endeavour on the first voyage of discovery which mapped the east coast of Australia between 1768 and 1771. While ashore he made an extensive collection of native flora and fauna which was sent back to natural history museums in England. Banks was also instrumental in the British government’s decision to colonise the New South Wales settlement.
Rosalie Gascoigne (b. New Zealand 1917; arr. Australia 1943; d. Canberra 1999)
The tea party (installation view)
1980
Painted wood, celluloid, plastic, enamelled metal, feathers
83 x 35 x 20cm
Private collection
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Rosalie Gascoigne (b. New Zealand 1917; arr. Australia 1943; d. Canberra 1999)
The tea party (installation view detail)
1980
Painted wood, celluloid, plastic, enamelled metal, feathers
83 x 35 x 20cm
Private collection
Photo: Marcus Bunyan
Rosalie Gascoigne found the kewpie dolls amongst a large number of discarded things from an abandoned sideshow at the Bungendore dump in the summer of 1976. ‘I thought “Oh, those dollies, they’re having a … very joyful … picnic. They’re … in the paddock, they’ve got all these old things … they’ve sat down on the teapots and waved their wings around.”
For Gascoigne beauty existed in the most humble of objects and the wear and tear from use only added to the appeal. The enamel teapots were also found at various dumps and were a particular focus of her collecting.
‘I had a thing about enamelware because I see it as being elegant. People see the holes in it. I was collecting brown and white at the same time. To me it had a sort of elegance that a Dalmatian dog has, spotty, very elegant’.1
1/ Rosalie Gascoigne, excerpts from her correspondence, email communication with Martin Gascoigne, 13 March 2015
Julie Dowling (Australian, b. 1969)
Badimaya people, Western Australia
White with one
2003
Synthetic polymer paint and red ochre on canvas
121 x 100cm
Collection of Jane Kleimeyer and Anthony Stuart
Julie Dowling’s painting is a poignant reminder of the Stolen Generations and the plight of many young girls, forcibly removed from their families, who were brought up in government institutions and trained to be domestic servant to white families. Girls were targeted because women were considered the ‘uplifters’ or ‘civilisers’ of their communities and as future mothers their education into the values of white society was deemed essential to enable successful assimilation. Girls in service were supposed to receive a wage but often this was retained by their employer and not passed on. Dowling points out it is also a history of Stolen wages.
Michael Cook (Australian, b. 1968)
Bidjara people, south-west Queensland
Object (table)
2015
Inkjet print on Hahnemühle cotton rag (ed. 2/4 + 2AP)
140 x 99cm
Courtesy of the artist and THIS IS NO FANTASY + dianne tanzer gallery, Melbourne
Michael Cook’s photographic tableau ‘turns the table’ on racism. By depicting the body of a white woman as a functional object in service to others, Cook considers the dehumanisation and objectification of one race of people by another in the history of slavery.
The double portrait on the back wall is by Johann Zoffany from 1778, and features Dido Elizabeth Belle (1761-1804) who was born into slavery in the West Indies. The daughter of an African mother, her father was an English naval officer who left her to the care of his uncle, Lord William Murray, where she was raised as an equal with Murray’s niece. Murray was instrumental in outlawing slavery in the United Kingdom in 1772. In the painting Zoffany depicts the two women standing together, the niece affectionately reaching out to Belle. Hence Cook’s afternoon tea is also a reminder that prejudice and racial inequality can be surmounted.
Yenny Huber (b. Austria 1980; arr. Australia 2000)
Room No. 14
2006
Digital print on aluminium panel (ed. 1/6)
27.2 x 27.2cm
Warrnambool Art Gallery, Victoria
Underpinned by the belief that any one person is comprised of diverse, fragmentary and often illusory selves, Yenny Huber explores the various ego states that reside within. This photograph is a self portrait taken in a hotel room, but it is also an impersonation of an identity available to women. Tea-drinking was once described as ‘an infallible sign of an old maid’1 and in this work Huber offers us an image of a good Catholic girl, knees together, elbows in, sitting demurely on the couch sipping tea. It is an image of femininity constrained by the dictates of religion and outdated socially sanctioned ideals of respectable female behaviour.
1/ The Horsham Times, Victoria, 26 April 1898
Anne Zahalka (Australian, b. 1957)
Saturday 5.18 pm 1995
1995 (printed 1997)
Type C photograph (ed AP)
125 x 162cm
Art Gallery of New South Wales, Sydney Gift of the artist, 2011
Donated through the Australian Government’s Cultural Gifts Program
Mornington Peninsula Regional Art Gallery
Civic Reserve, Dunns Road, Mornington
Opening hours:
Tuesday – Sunday 11am – 4pm



















![Rex Hazlewood (Australian, 1886-1968) '[Men drinking billy tea]' 1911-1927 Rex Hazlewood (Australian, 1886-1968) '[Men drinking billy tea]' 1911-1927](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/hazelwood-billy-tea.jpg?w=840)


![James Fox Barnard (Australian, 1874-1945) '[Tea on the verandah]' c. 1900 James Fox Barnard (Australian, 1874-1945) '[Tea on the verandah]' c. 1900](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/barnard-tea-verandah.jpg?w=650&h=862)




































You must be logged in to post a comment.