Exhibition dates: 31st October, 2014 – 19th April, 2015
Curator: Sarah Montross, Senior Curator at the deCordova Sculpture Park and Museum
Charles “Teenie” Harris (American, 1908-1998)
Three men and three women, seated as couples in banquette in bar or restaurant advertising “Fried Shrimp Plate $.85” and “1/4 Fried Chicken $.70”
c. 1959; printed 2001
Silver gelatin print
Gift of Arlette and Gus Kayafas
Another fun posting to add to the archive!
Marcus
Many thankx to the deCordova Sculpture Park and Museum for allowing me to publish some of the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Charles “Teenie” Harris (American, 1908-1998)
Photographer taking picture of Muhammad Ali (Cassius Clay) possibly in Carlton House Hotel, Downtown
1963; printed 2001
Silver gelatin print
Gift of Arlette and Gus Kayafas
Charles “Teenie” Harris photographed the African-American community of his hometown of Pittsburgh, primarily for the Pittsburgh Courier, the preeminent national African-American newspaper (c. 1930-1960). Photographing community members, visiting political figures, athletes, and entertainers, Harris set out to balance negative views of African-Americans and their communities. Nicknamed “One-Shot,” Harris photographed confidently and with ease, rarely asking his subjects to pose more than once. The resulting 80,000 negatives make up one of the largest collections of photographs of a black urban community in the United States. Harris’ artistic output helps define photography as a tool for preserving the past, his photographs serving as invaluable documentation of the spirit of a particular time, place, and people.
Prefiguring the paparazzi images of celebrities that pervade contemporary media, Harris’ photographs of singer / actress Lena Horne and boxer Cassius Clay (Muhammad Ali) capture his famous subjects in relaxed settings that humanise them. Furthermore, Harris’ photograph of Clay shows the boxer having his portrait taken by another photographer, giving Harris’ image of a photograph-in-process an even greater behind-the-scenes feel.
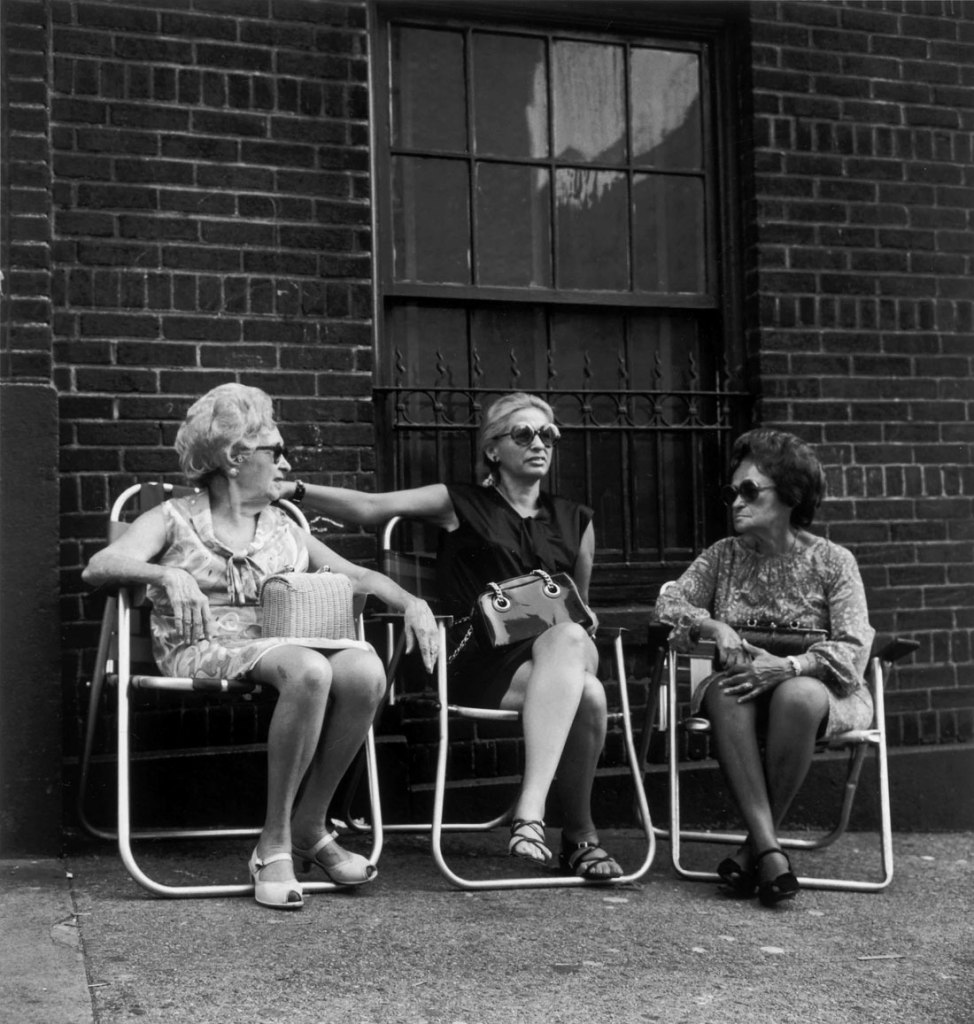

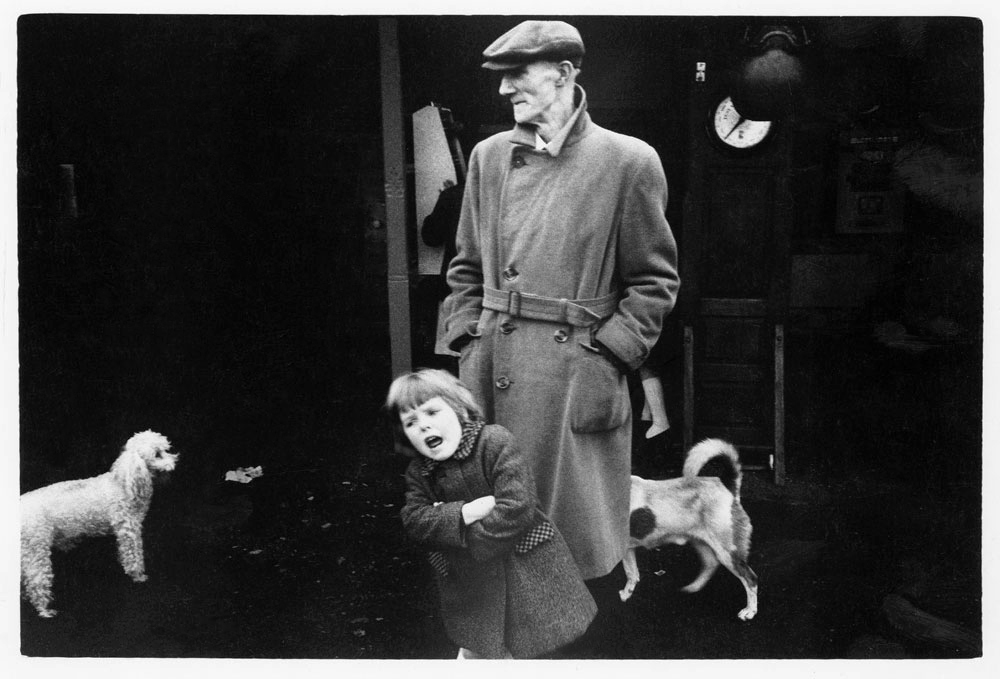
Jules Aarons (American, 1921-2008)
Untitled (Bronx), from the portfolio In The Jewish Neighborhoods 1946-76
c. 1970; printed 2003
Silver gelatin print, printer’s proof II
Gift of Arlette and Gus Kayafas
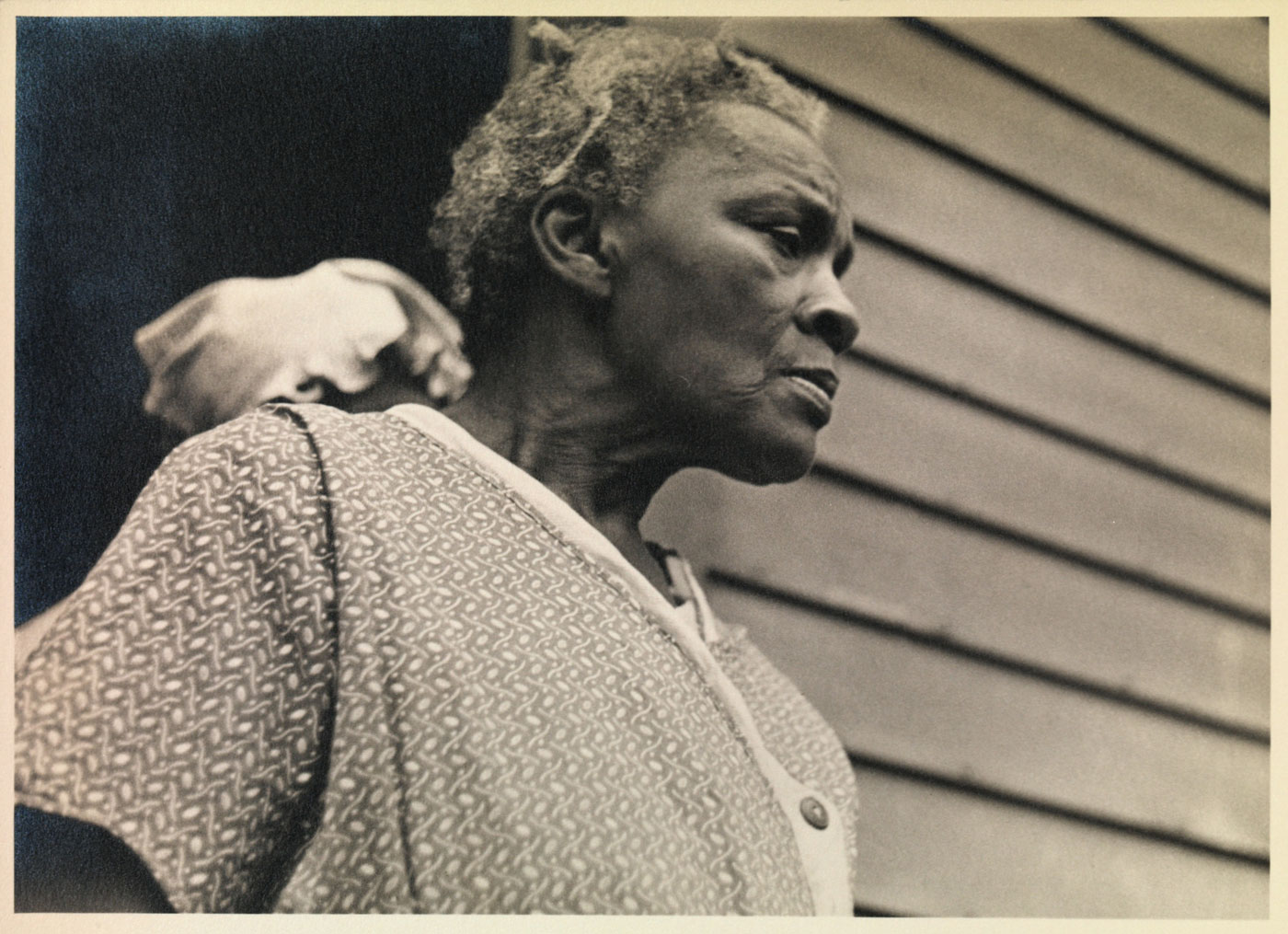
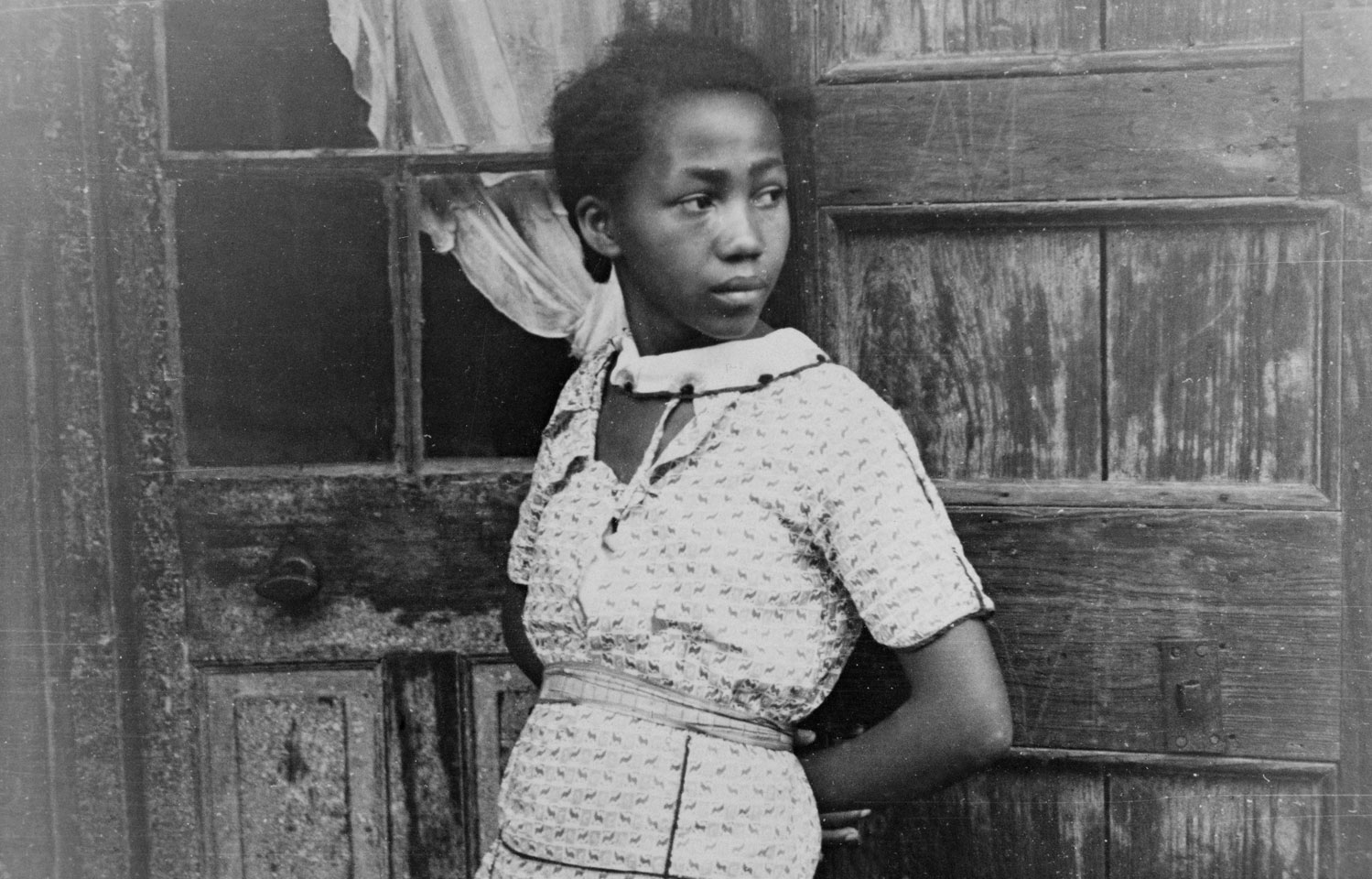
Jules Aarons was one of the most respected and prolific American social documentary photographers in the twentieth century. His street photography captured personal moments in the public eye within the urban neighbourhoods in which he lived: the Bronx, where he was born and raised, and Boston, where he spent the majority of his adult life. Shot with his twin lens Rolleiflex camera held at waist-level, Aarons’ images are casual, intimate, and lively. Although the artist did not personally know his subjects, his work does not exhibit the detachment found in earlier forms of social documentary photography. His deep associations with the places and people he photographed imbue his images with a warmth and familiarity.
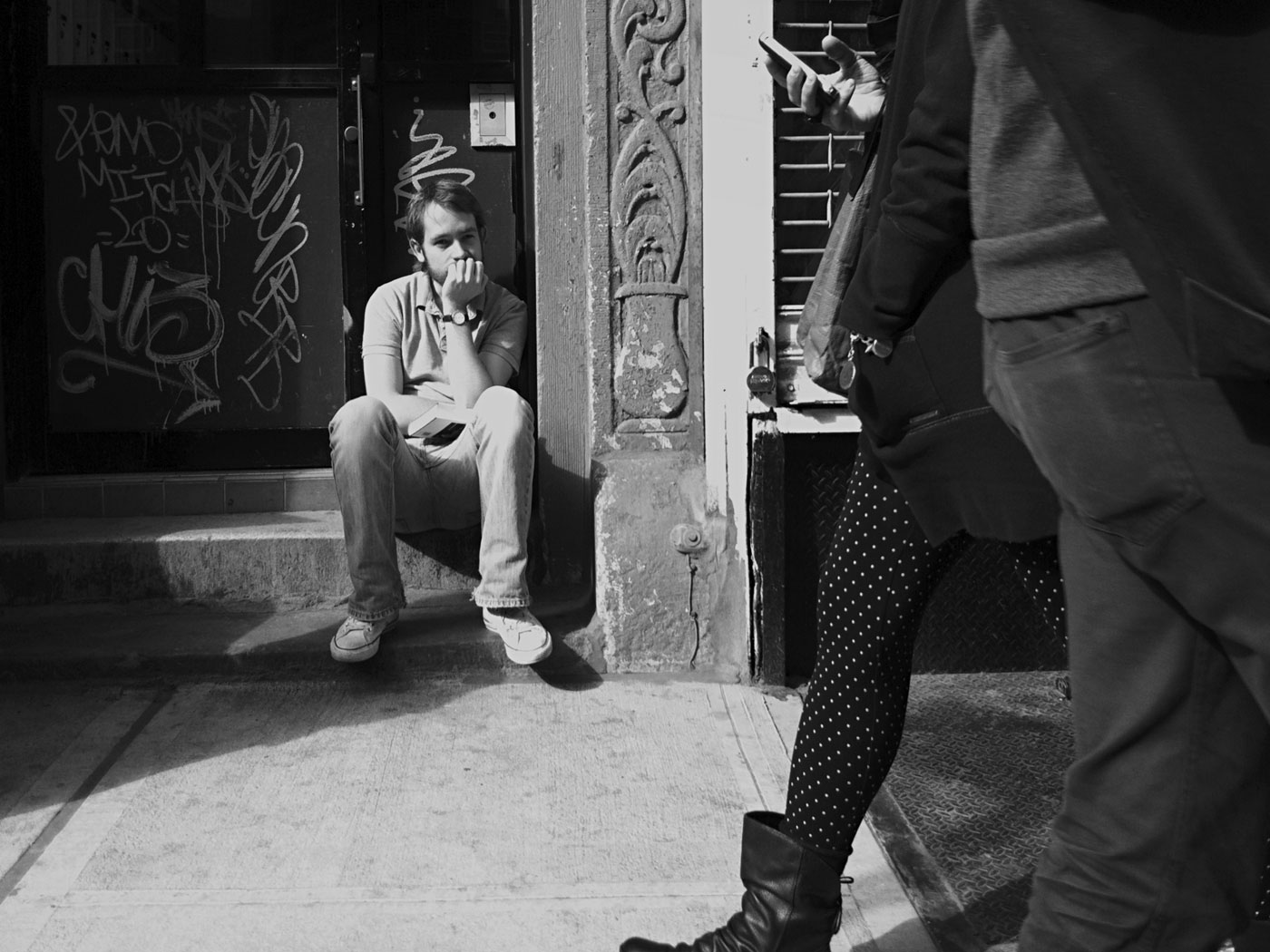
Greg Schmigel (American, b. 1969)
Subway Triptych
2011
Digital photographic prints
Courtesy of the artist
Greg Schmigel (American, b. 1969)
An Afternoon in the Sun
2012
Digital photographic prints
Courtesy of the artist
Greg Schmigel (American, b. 1969)
Ideal Hosiery
2013
Digital photographic prints
Courtesy of the artist
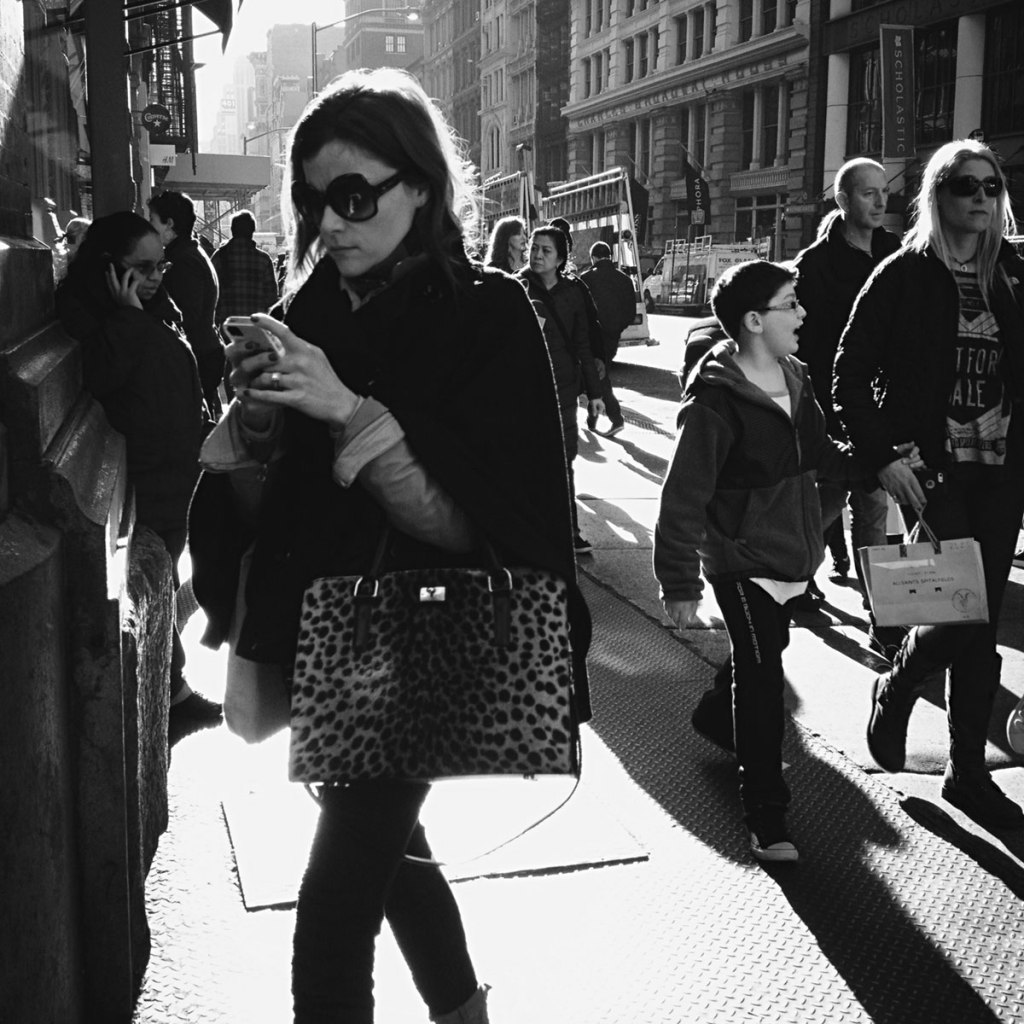

Greg Schmigel (American, b. 1969)
Late Day On Broadway
2012
Digital photographic prints
Courtesy of the artist
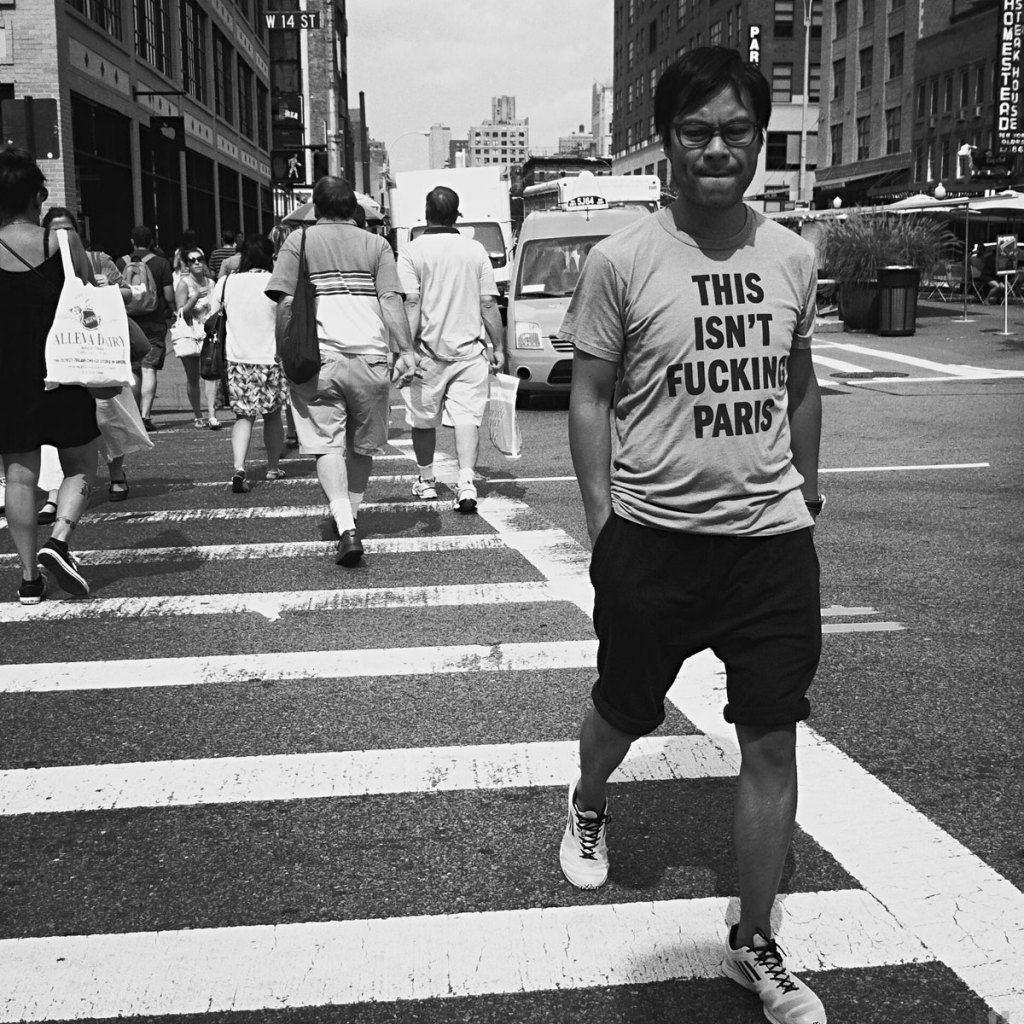

Greg Schmigel (American, b. 1969)
This Isn’t Fucking Paris
2012
Digital photographic prints
Courtesy of the artist
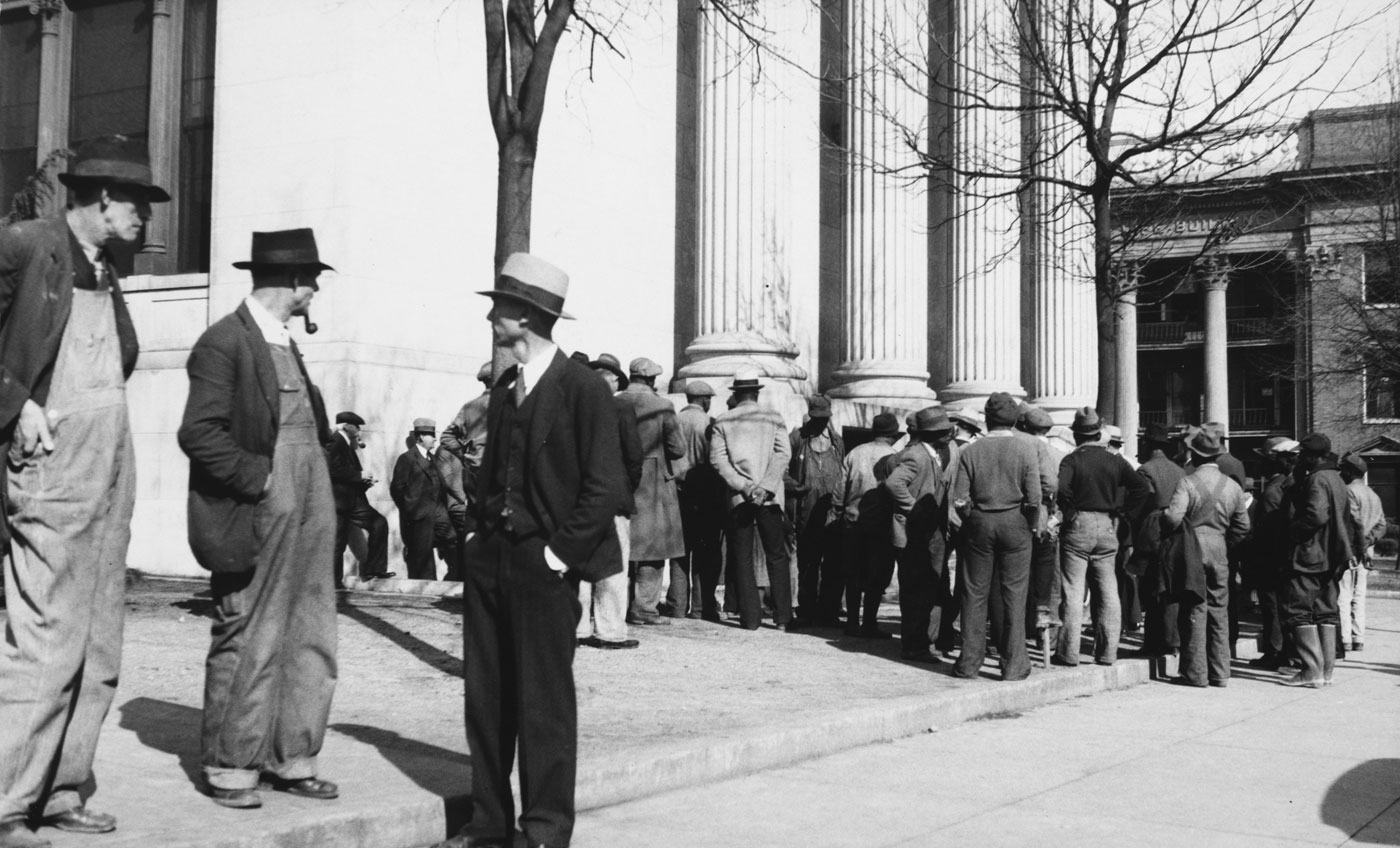
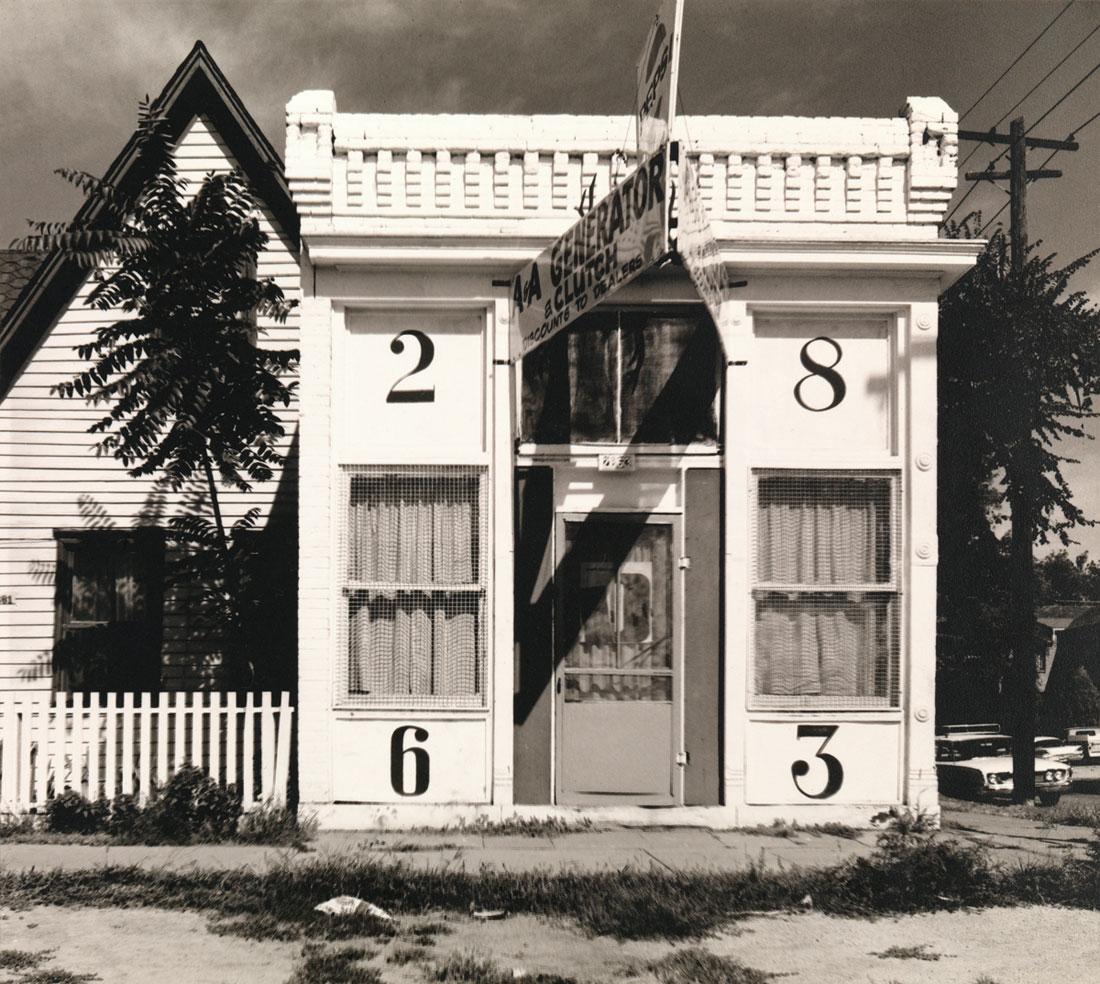
Greg Schmigel works in the vernacular of mid-twentieth century black and white street photography, capturing candid glimpses of everyday moments. While inspired by pioneering artists such as Jules Aarons, whose work is also on view in this gallery, Schmigel creates photographs with a decidedly twenty-first century quality. A mobile photographer since 2007, his device of choice is the most itinerant and convenient camera available: his iPhone. In his work, Schmigel emphasises that the production of a good photograph is due mainly to the eye of the photographer, and not necessarily dependent on the equipment he uses.
By producing black and white prints from his digital images, the artist casts a timeless aura over contemporary scenes. In photographs such as Ideal Hosiery, the faded signs of a New York City street corner provide an uncanny setting that could easily be found in a photograph taken many decades ago. In other images, however, the omnipresence of smartphones in the hands of pedestrians instantly signals the twenty-first century. In these photographs, Schmigel aptly captures the ironic isolation caused by the very technology created to increase interpersonal communication.
Presented at a time when the compulsion to digitally document and share human activity has increased exponentially, this exhibition features works from deCordova’s permanent collection that prefigure and inform current trends in social photography, as well as recent work by contemporary artists who utilise smartphones and social media to record the world around them. The Social Medium features work spanning from the mid-twentieth century to the present, and includes multiple photographic genres such as social documentary, street, society/celebrity, and portrait photography.
The Social Medium was largely inspired by a recent gift of one of Andy Warhol’s Little Red Books, which contains a set of colour Polaroids. With his camera, Warhol documented the events of his life – from glamorous celebrity parties to mundane occurrences. The arrival of these photographs, which record Warhol’s artistic and social milieu (or environment), created an opportunity to examine the work of other artists who also photograph social experience. Together, the images in this exhibition speak to the continued relevance of the photographic medium’s singular power to capture and preserve personal and societal histories, and provide a selective history of the camera’s role as an extension of memory and a tool that is at once a witness to and participant in human social activity.
Text from the deCordova Sculpture Park and Museum
Eugene Richards (American, b. 1944)
First Communion, Dorchester
1976
Silver gelatin print
Gift of the artist
Eugene Richards captures a specific, local community in which he was embedded, to offer us uncanny views of small-town America. In the 1970s, Richards returned to his native Boston neighbourhood and produced photographs such as First Communion, which would later comprise his seminal book, Dorchester Days (1978). Richards documented a small section of urban Boston at a time when racial tensions and economic decline were defining Dorchester along with swaths of American cities and towns in similar states of transition and decline. First Communion captures a moment that nods towards social frictions at large, where religious traditions and street life converge in ambiguously innocent tension.
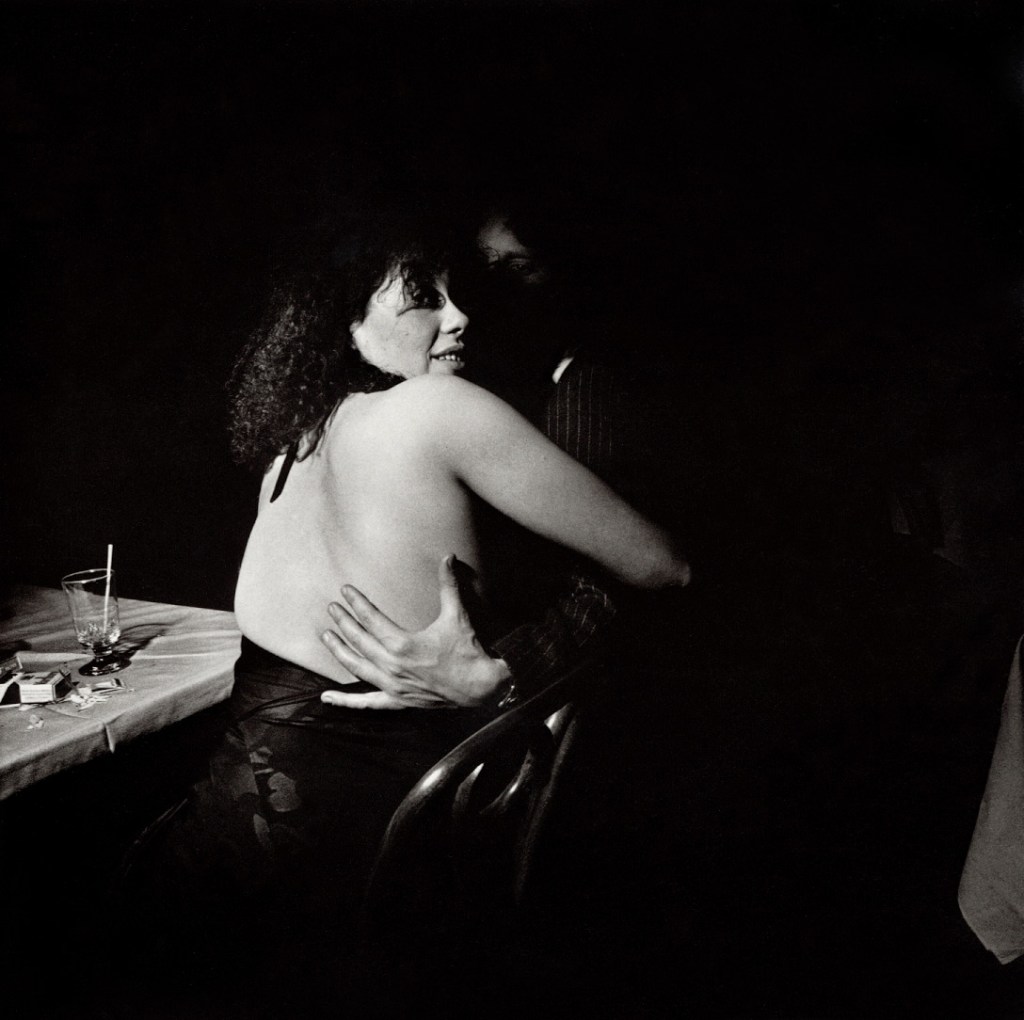

Larry Fink (American, 1941-2023)
N.Y.C. Club Cornich, from the portfolio 82 Photographs 1974 to 1982
1977; printed 1983
Silver gelatin print, 28/30
Gift of Diane and Eric Pearlman
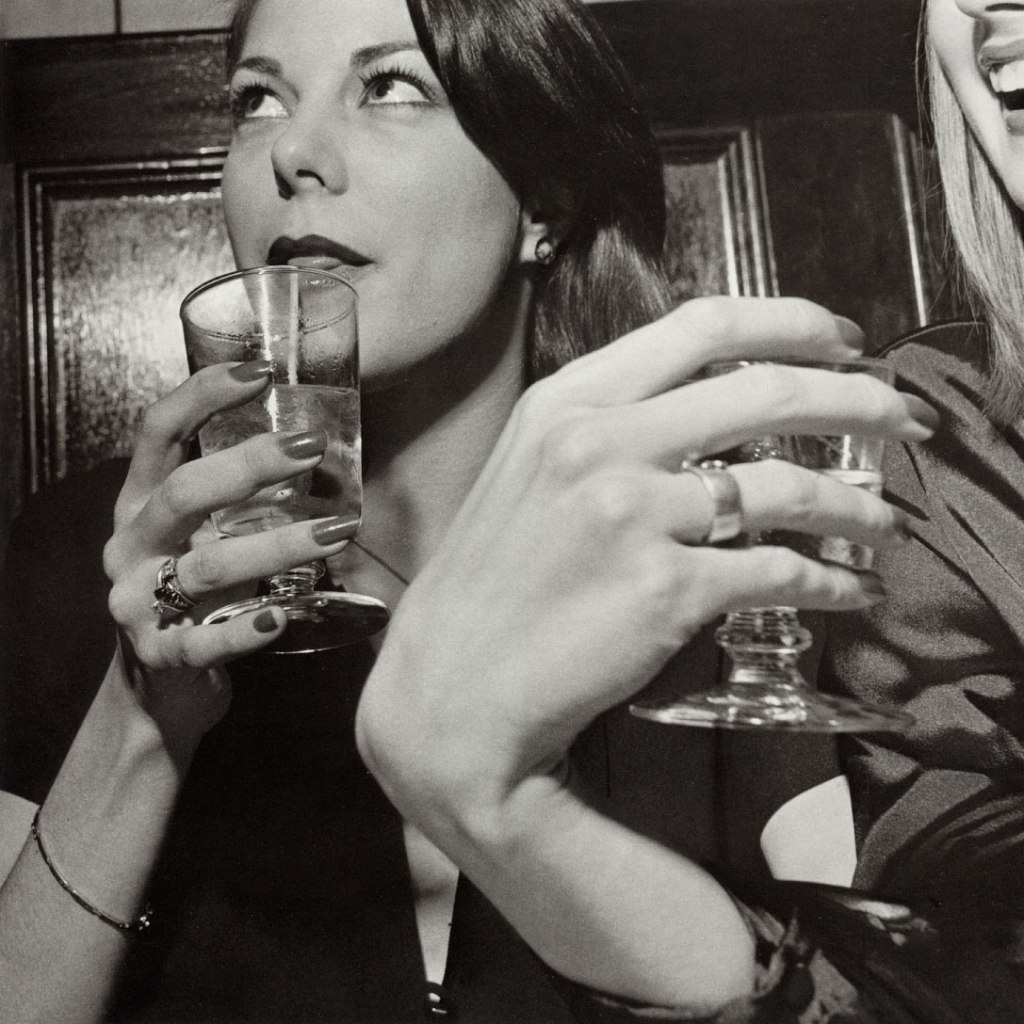

Larry Fink (American, 1941-2023)
N.Y.C. Club Cornich, from the portfolio 82 Photographs 1974 to 1982
1977; printed 1983
Silver gelatin print, 28/30
Gift of Diane and Eric Pearlman
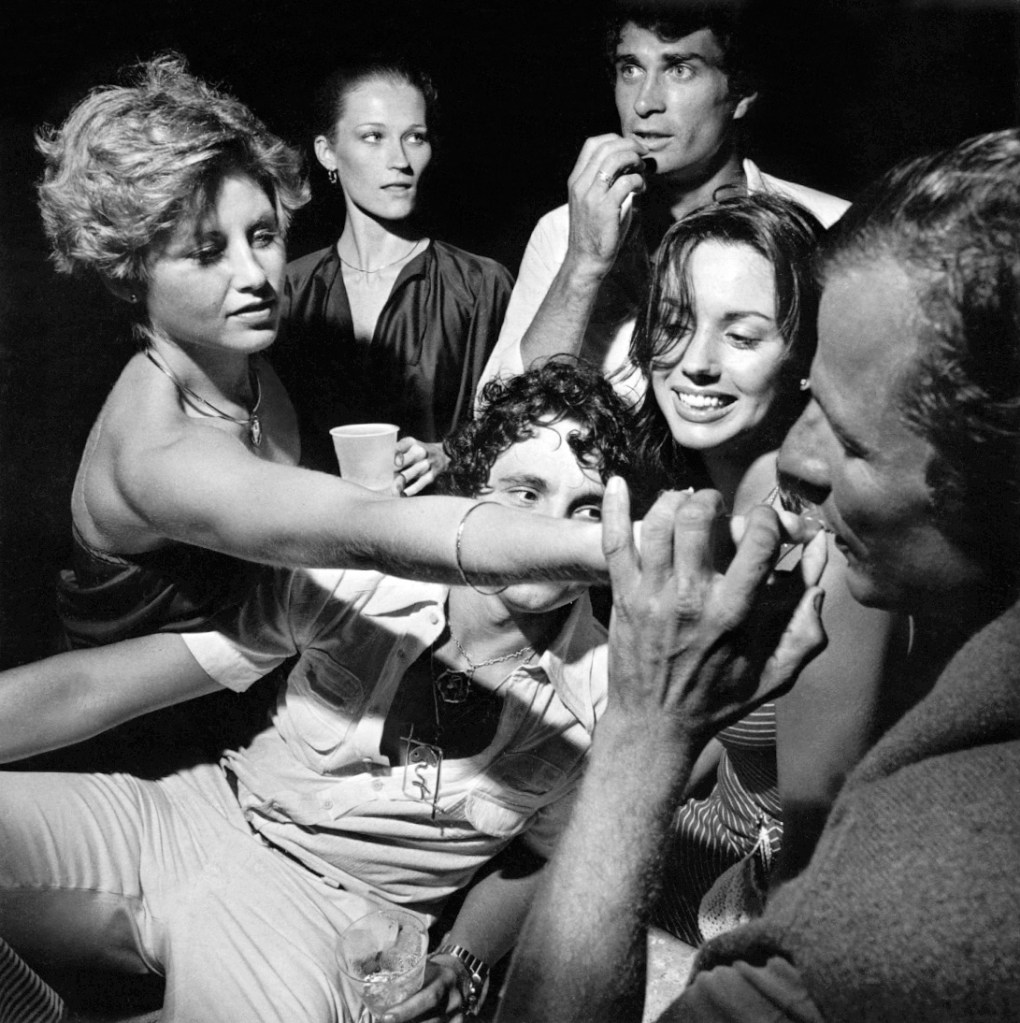

Larry Fink (American, 1941-2023)
Peter Beard’s, East Hampton, from the portfolio 82 Photographs 1974 to 1982
1982; printed 1983
Silver gelatin print, 28/30
Gift of Diane and Eric Pearlman
Larry Fink is a prominent American photographer who is best known for capturing images of high-profile social events. Fink’s images from the 1970s and 1980s capture individual vignettes within social gatherings, and nod to the development of documentary photography within the image-driven culture of the second half of the twentieth century. These photographs from Fink’s series 82 Photographs 1974 to 1982 and Making Out 1957-1980 depict scenes from clubs and parties in and around New York City. Fink’s subjects are caught off-guard by his camera, and their expressions provide windows into their weariness or giddy party euphoria. Capturing groups and individuals at surprisingly intimate and vulnerable moments, his photographs subtly reveal the disconnect often found between a subject’s public image and his or her inner self. For example, in Peter Beard’s, East Hampton, Fink captures a dynamic group of people in various levels of engagement with one another. While some are intertwined, others glance outward to the party beyond, having seemingly lost interest in the gathering at hand.
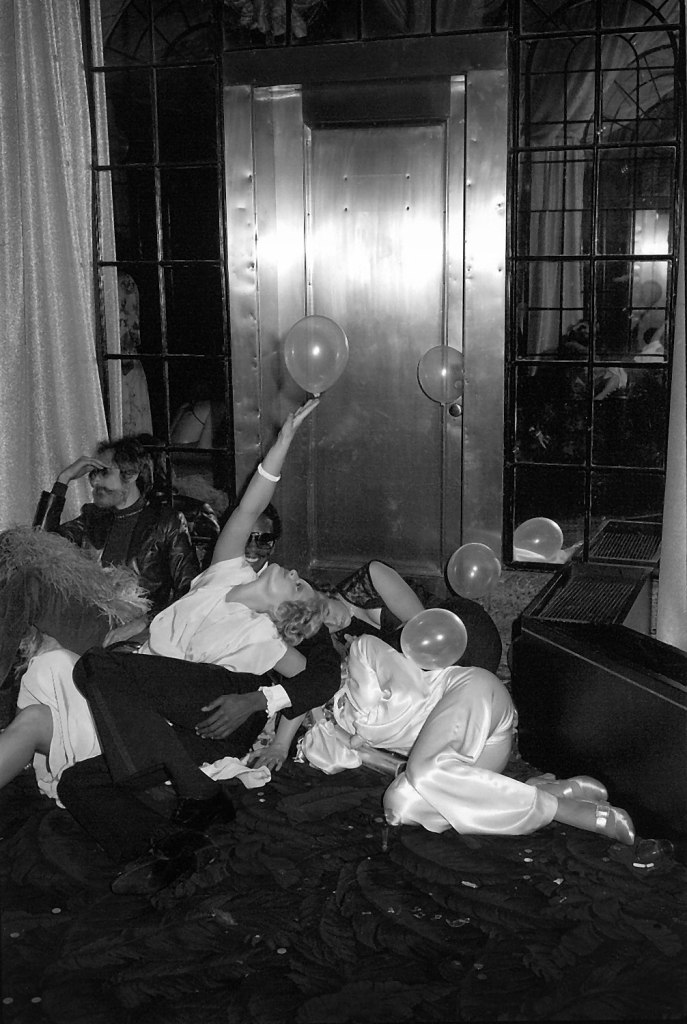

Tod Papageorge (American, b. 1940)
Studio 54
1977
Silver gelatin print
Gift of Pete and Constance Kayafas
In this photograph, Tod Papageorge captures revellers in gritty black and white, employing straightforward photography to show significant, poetic moments from everyday life. Highlighted by the timeless quality of a silver gelatin print, his photograph of partygoers at the infamous New York City nightclub, Studio 54, captures such a scene. Dramatic without arranging its subjects, Papageorge’s photograph freezes the precise moment just before the woman’s upstretched hand makes contact with balloon floating wistfully above her head.
Phillip Maisel (American, b. 1981)
Wall Photos, from the series A More Open Place
2010
Archival inkjet print
Courtesy of the artist

Phillip Maisel (American, b. 1981)
Profile Pictures (4702), from the series A More Open Face
2011
Archival inkjet print
Courtesy of the artist
Phillip Maisel’s photographs are layered, ethereal images that evoke the fleeting nature of memories. Though nostalgic in tone, these images derive from a very contemporary source. Setting long exposures on his camera, the artist captures the images appearing on his computer screen as he clicked through his friends’ Facebook albums. The resulting picture-of-pictures is twice removed from its source, emphasising the swollen state of image culture and the manner in which digital images are created, uploaded, and discarded at an ever increasing rate.
The title of these series derives from Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg, who noted that, through the social media platform, he was trying “to make the world a more open place.” Facebook and other sites have certainly achieved that; however, this extreme openness, the compulsion to over-share personal images and information, creates a paradox given the subsequent lack of privacy inherent in these activities. Maisel’s work comments on this contemporary phenomenon in which individuals willingly share images of their private memories in public venues. Furthermore, by reducing a collection of images to a single photograph, the artist manifests the compression of time and space in the internet age. This layering of images is also a form of erasure; each new image obscures the last, consistently degrading the significance of each individual picture and memory.
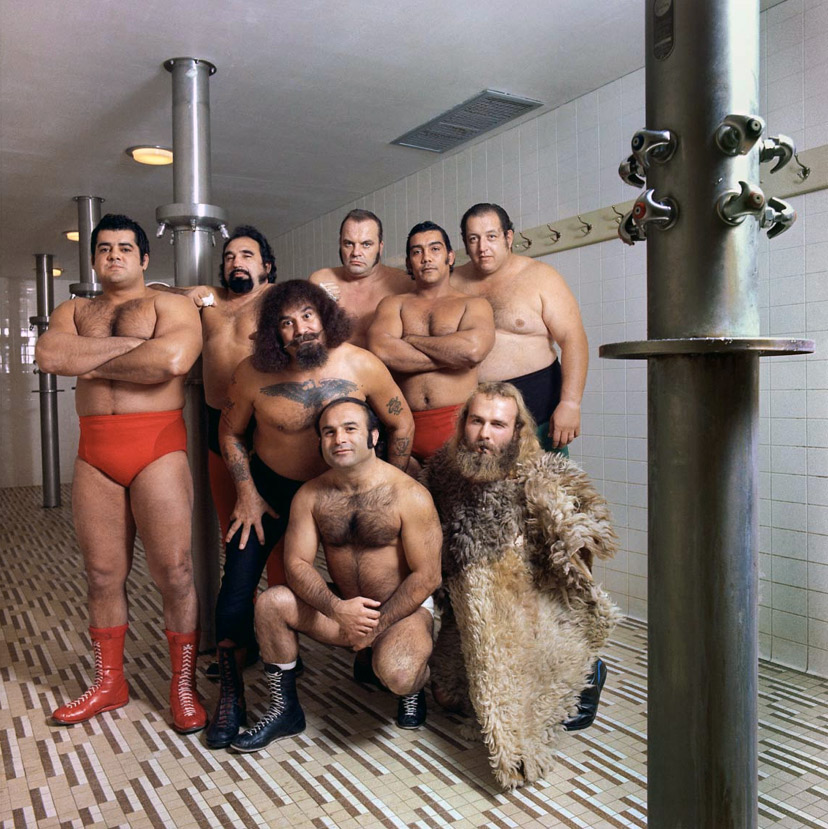

Neal Slavin (American, b. 1941)
Capitol Wrestling Corporation, Washington, D.C ., from the portfolio Groups in America
1979
Color coupler print, 60/75
Gift of Stephen L. Singer and Linda G. Singer
Neal Slavin is acclaimed for his group portraits, which range from corporate associates to recreational cohorts to families. The photographs on display offer astute yet humorous studies of groups with specific shared interests that lay at the edges of societal norms. In Slavin’s images, no single member of the group pulls focus from the others and the ultimate personality of the portrait hinges upon the collective aura.
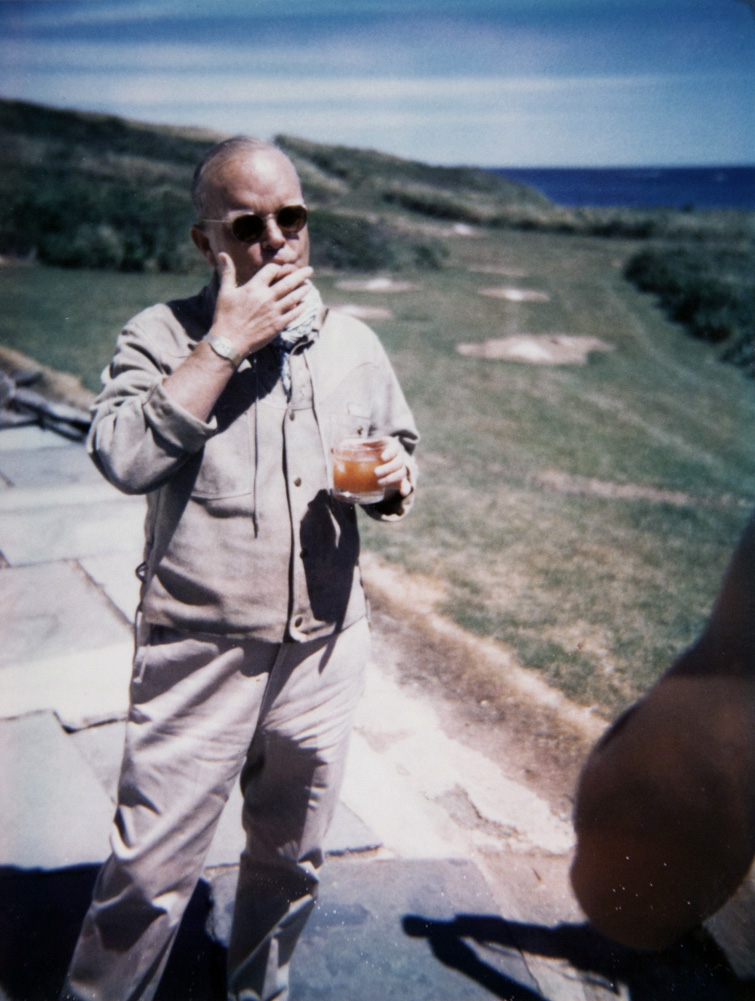
Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
The Little Red Book 128
1972
Twenty Polacolor Type 108 Polaroid prints
Gift of The Andy Warhol Foundation for the Visual Arts, Inc. 2014
Examples of Polaroids in book. 20 total.
During the 1970s and early 1980s, Andy Warhol used the Polaroid colour film camera. A then-novel technology which developed photographs in a matter of seconds, he employed it to document the events of his life – from the most glamorous celebrity parties to the most mundane and inconsequential occurrences. Warhol catalogued many of these photographs into small red Holston Polaroid albums, consequently known as Little Red Books. DeCordova’s Little Red Book 128, recently donated to the museum by The Warhol Foundation, features twenty photographs from a day in 1972 that Warhol shared with acclaimed writer Truman Capote, socialite Lee Radziwill and her family, and his business associates Vincent Fremont, Fred Hughes, and Jed Johnson. Consisting of both staged portraits and casual snapshots, the book is part paparazzi portfolio and part quaint family album.
Throughout the height of his fame, Andy Warhol was rarely without a camera in hand. The enigmatic artist often preferred social situations to be passively mitigated by his camera lens, rather than experienced physically and emotionally. In many ways, Warhol’s detachment mirrors a contemporary reliance on electronic forms of communication that limit human contact. Warhol once said, “In the future, everyone will be world – famous for 15 minutes.” Unsurprisingly, in all his work and in this collection of Polaroids, the artist blurs the lines between public / private and commoner / celebrity in a manner which is eerily prophetic of current social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, among others, which allow anyone and everyone to have their Warholian 15 minutes of fame, or perhaps even just 15 seconds of infamy.
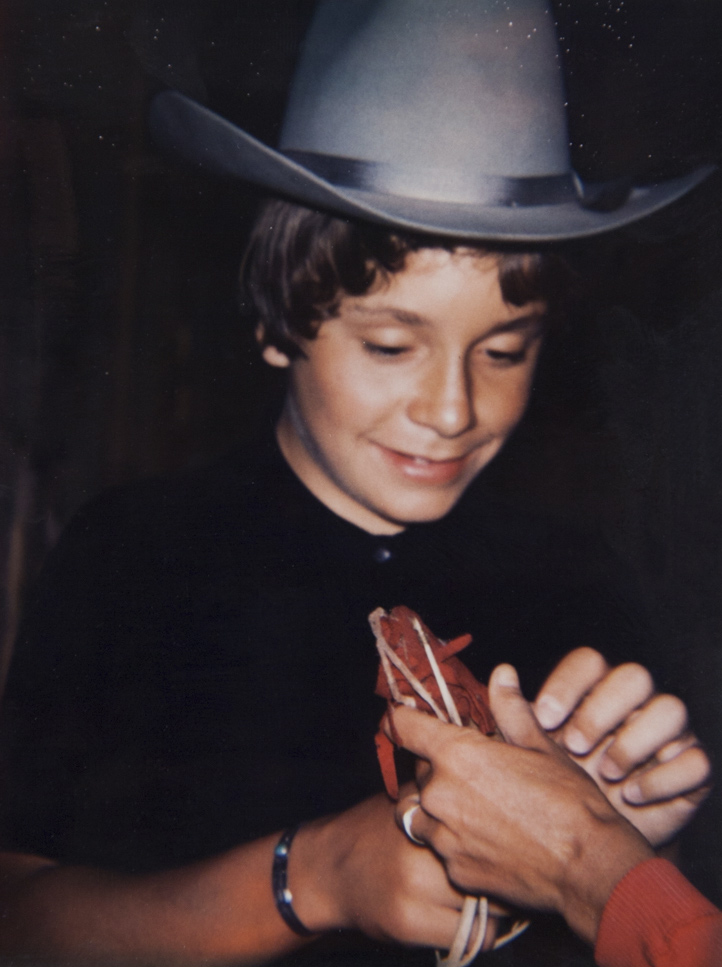

Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Anthony Radziwill
1972
Polacolor Type 108 Polaroid print
Prince Anthony Stanislaw Albert Radziwill (American, 1959-1999)
Prince Anthony Stanislaw Albert Radziwill (4 August 1959 – 10 August 1999) was an American television executive and filmmaker.
Born in Lausanne, Switzerland, Radziwill was the son of socialite / actress Caroline Lee Bouvier (younger sister of First Lady Jacqueline Lee Bouvier) and Polish Prince Stanisław Albrecht Radziwiłł. He married a former ABC colleague, Emmy Award-winning journalist Carole Ann DiFalco, on 27 August 1994 on Long Island, New York.
As a member of the Radziwills, one of Central Europe’s noble families, Anthony Radziwill was customarily accorded the title of Prince and styled His Serene Highness, although he never used it. He descended from King Frederick William I of Prussia, King George I of Great Britain, and King John III Sobieski of Poland. The family’s vast hereditary fortune was lost during World War II, and Anthony’s branch of the family emigrated to England, where they became British subjects.
Radziwill’s career began at NBC Sports, as an associate producer. During the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul, he contributed Emmy Award-winning work. In 1989, he joined ABC News as a television producer for Prime Time Live. In 1990, he won the Peabody Award for an investigation on the resurgence of Nazism in the United States. Posthumously, Cancer: Evolution to Revolution was awarded a Peabody. His work was nominated for two Emmys.
Around 1989 he was diagnosed with testicular cancer, undergoing treatment which left him sterile, but in apparent remission. However, shortly before his wedding, new tumours emerged. Radziwill battled metastasising cancer throughout his five years of marriage, his wife serving as his primary caretaker through a succession of oncologists, hospitals, operations and experimental treatments. The couple lived in New York, and both Radziwill and his wife tried to maintain their careers as journalists between his bouts of hospitalisation. During this period, Radziwill became especially close to his aunt Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis, who was also terminally ill with cancer. He died on 10 August 1999, and was survived by his sister, Anna Christina Radziwill.
Text from the Wikipedia website
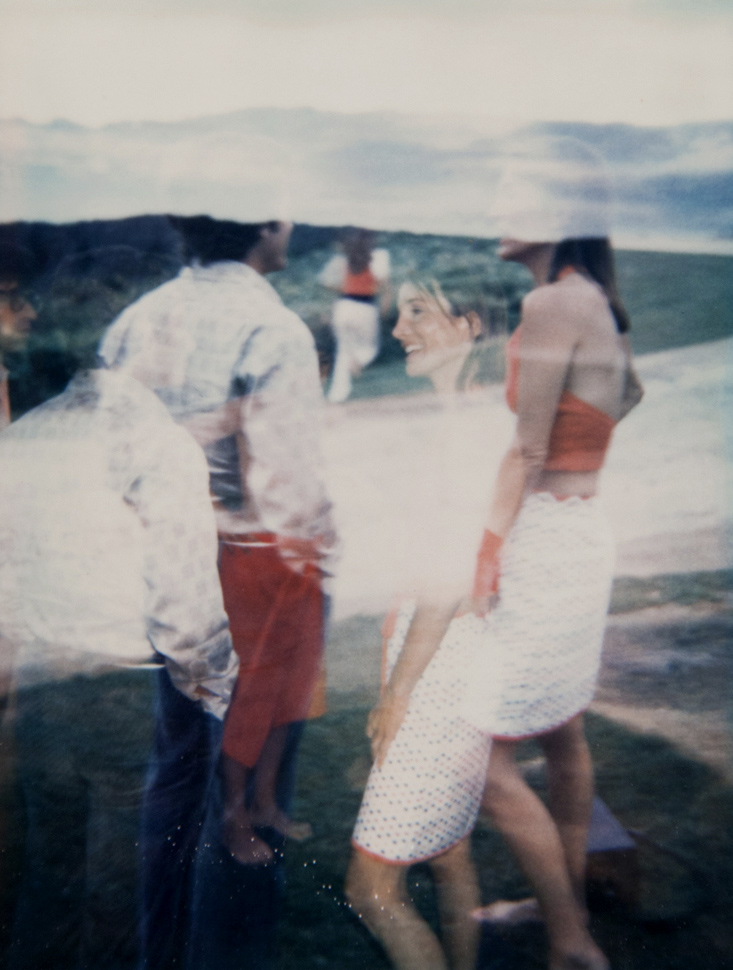

Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Lee Radziwill
1972
Polacolor Type 108 Polaroid print
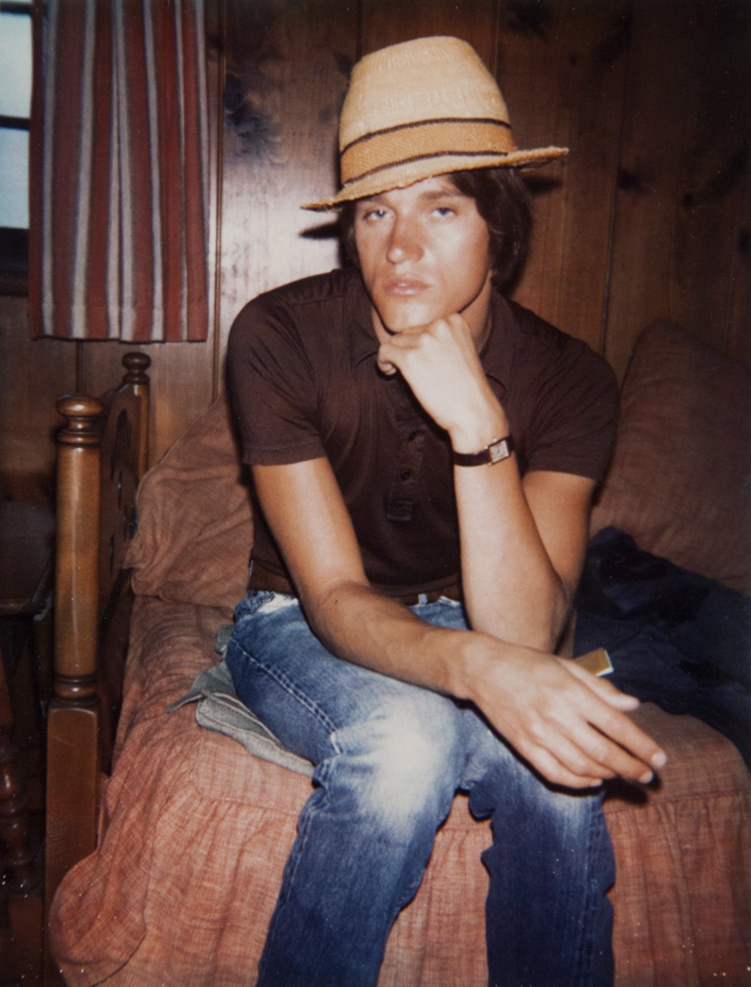

Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Jed Johnson
1972
Polacolor Type 108 Polaroid print
Jed Johnson (December 30, 1948 – July 17, 1996) was an American interior designer and film director. Initially hired by Andy Warhol to sweep floors at Warhol’s Factory, he subsequently moved in with Warhol and became his lover. As a passenger in the First Class cabin, he was killed when TWA Flight 800 exploded shortly after takeoff in 1996.

Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Truman Capote
1972
Polacolor Type 108 Polaroid print
deCordova Sculpture Park and Museum
51 Sandy Pond Rd, Lincoln, MA
01773, United States
Phone: +1 781-259-8355
Opening hours:
Summer
Every day
10am – 5pm




































![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Invierno en el patio' [Winter in the Courtyard] Paris, 1939 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Invierno en el patio' [Winter in the Courtyard] Paris, 1939](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/invierno-en-el-patio-web.jpg)



![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Subida a la catedral [Ascending to the Cathedral], Spanish Civil War' Barcelona 1938 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Subida a la catedral [Ascending to the Cathedral], Spanish Civil War' Barcelona 1938](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/subida-a-la-catedral-web.jpg)
![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Los Paraguas, mitin de la CNT' [Umbrellas, Meeting of the CNT], Spanish Civil War Barcelona, 1937 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Los Paraguas, mitin de la CNT' [Umbrellas, Meeting of the CNT], Spanish Civil War Barcelona, 1937](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/los-paraguas-mitin-de-la-cnt-web.jpg)



![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Untitled, Oda a la necrofília series [Ode to Necrophilia]' Mexico 1962 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Untitled, Oda a la necrofília series [Ode to Necrophilia]' Mexico 1962](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/necrophilia-web.jpg)
![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'El botellón' [The Bottle] Mexico, 1962 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'El botellón' [The Bottle] Mexico, 1962](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/el-botellc3b3n-web.jpg)

![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Antonio Souza y su esposa Piti Saldivar' [Antonio Souza and his Wife Piti Saldivar] Mexico, 1959 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Antonio Souza y su esposa Piti Saldivar' [Antonio Souza and his Wife Piti Saldivar] Mexico, 1959](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/souza-web.jpg)
![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'José Horna elaborando la maqueta de la casa de Edward James' [José Horna Working on the Maquette for Edward James's House] Mexico, 1960 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'José Horna elaborando la maqueta de la casa de Edward James' [José Horna Working on the Maquette for Edward James's House] Mexico, 1960](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/josc3a9-horna-elaborando-web.jpg)
![Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Mujer y máscara' [Woman with Mask] Mexico, 1963 Kati Horna (Mexican born Hungary, 1912-2000) 'Mujer y máscara' [Woman with Mask] Mexico, 1963](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/woman-with-mask-web.jpg)
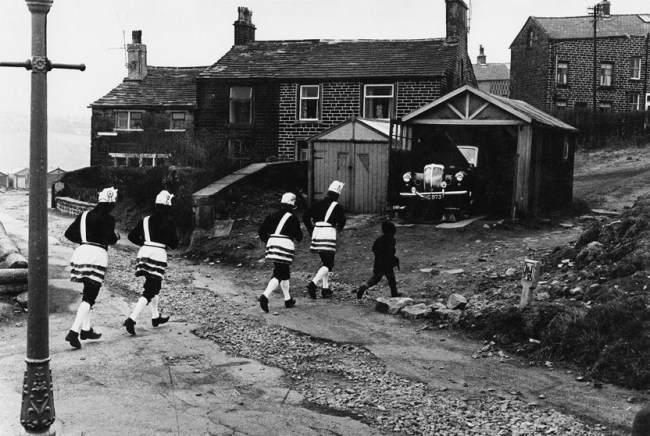
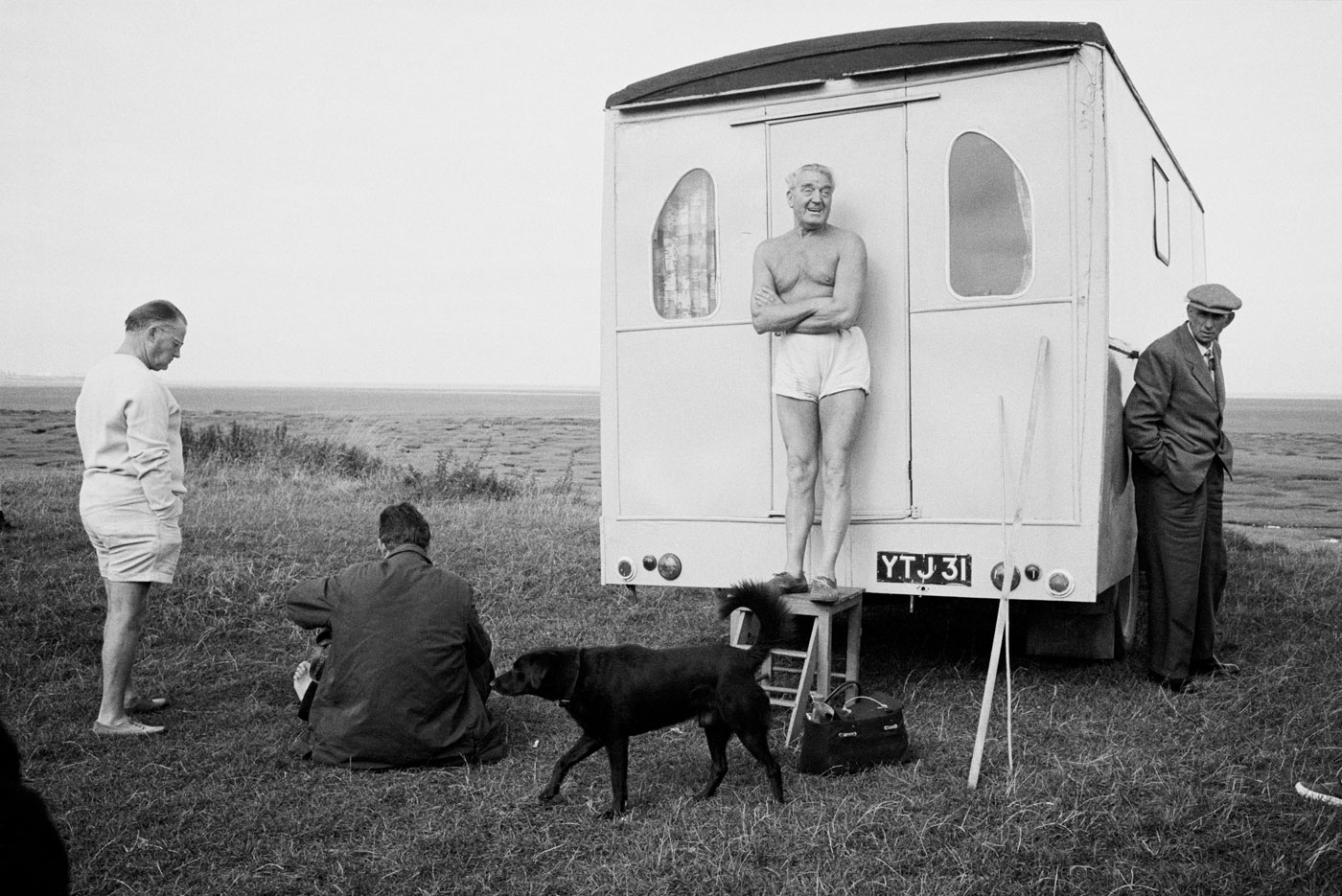
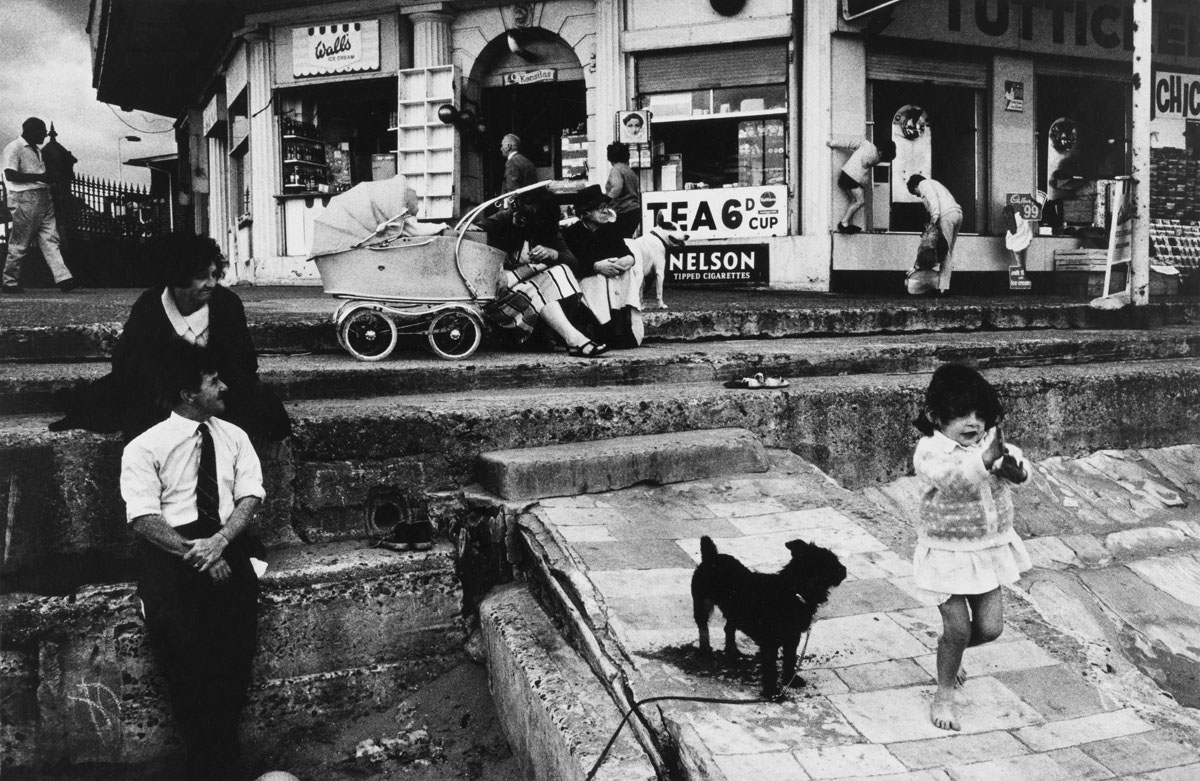
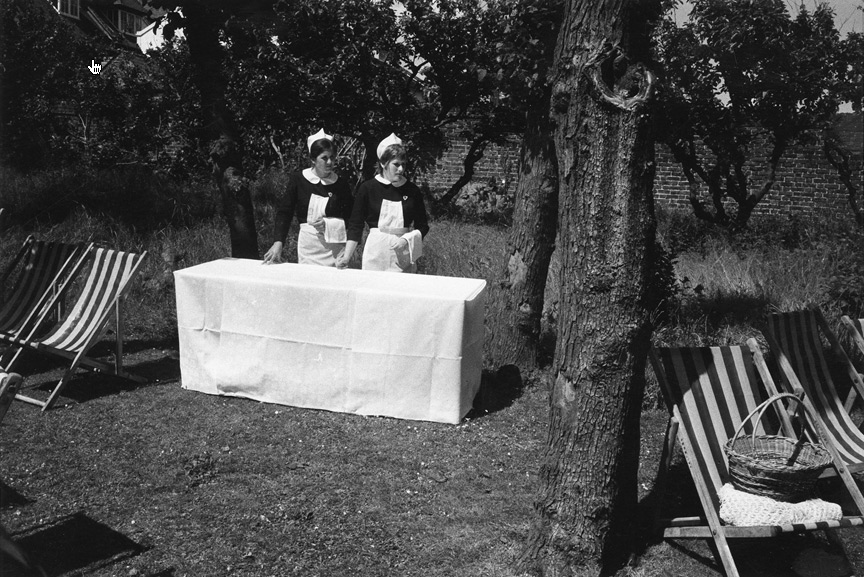
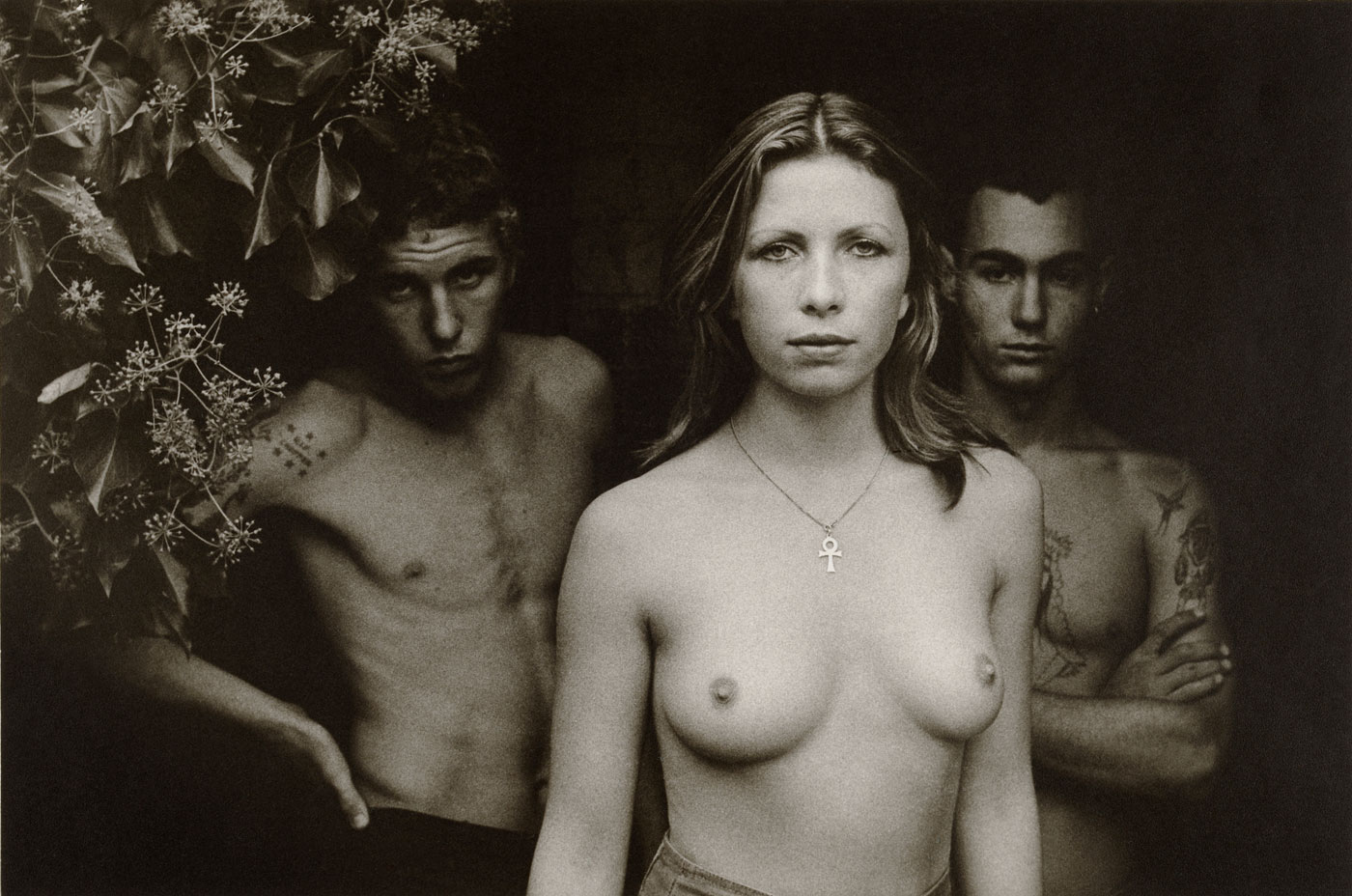
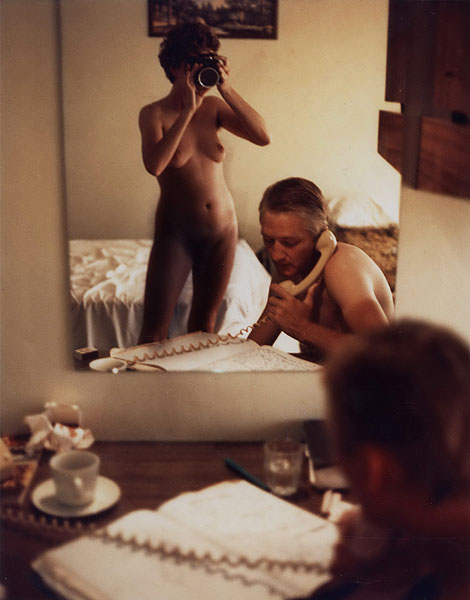
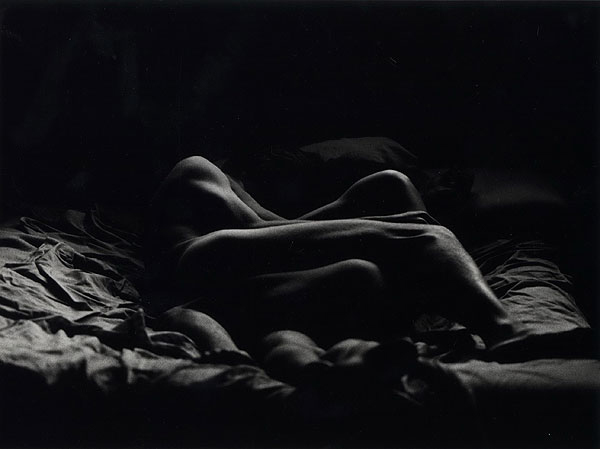
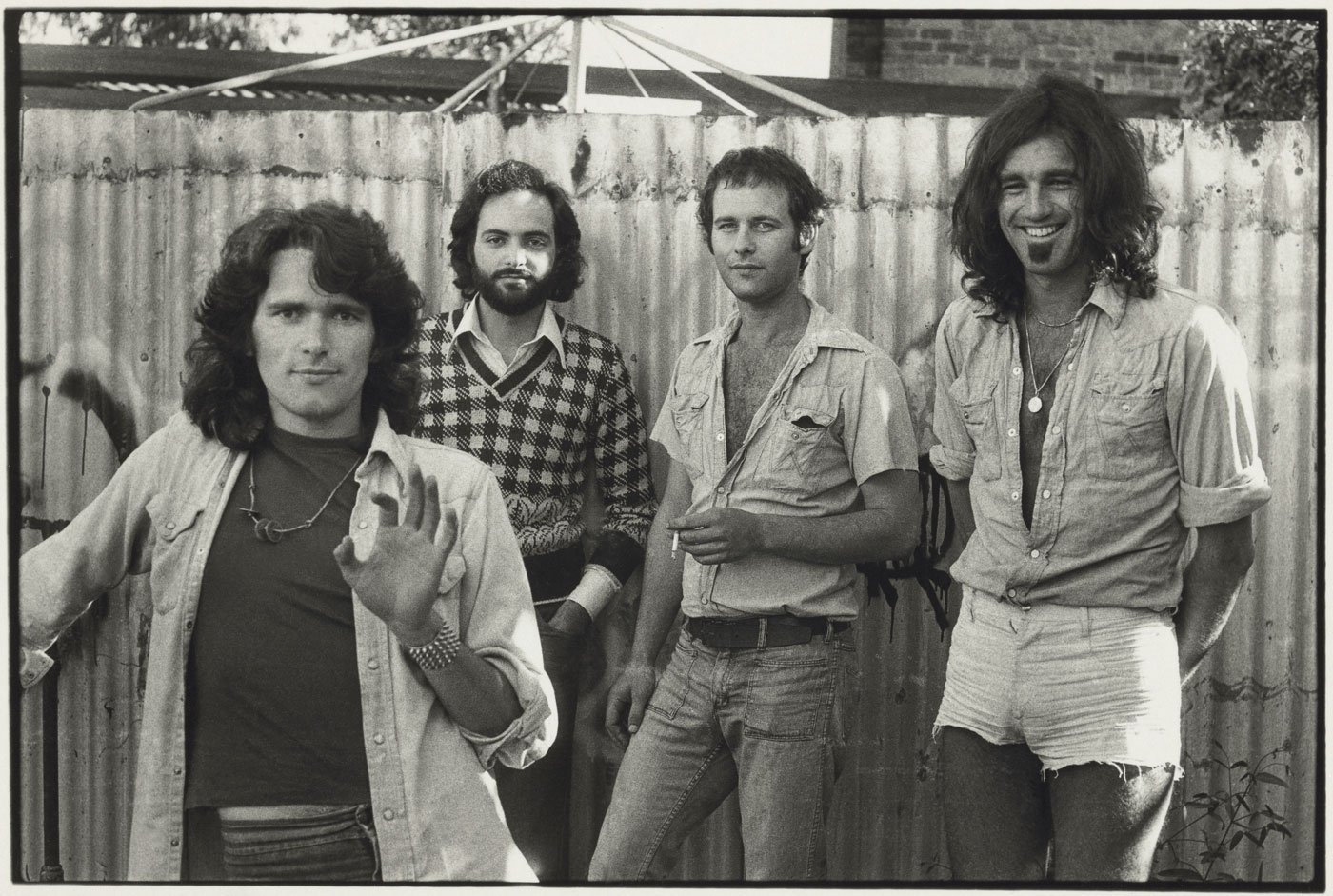























































































![Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Butterfly behind glass [Red Symons from Skyhooks]' 1975 Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Butterfly behind glass [Red Symons from Skyhooks]' 1975](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/butterfly_174882_web.jpg)

![Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Performers on stage,' Hair', Metro Theatre Kings Cross, Sydney, January 1970 [Jim Sharman Director cast included Reg Livermore]' 1970 Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Performers on stage,' Hair', Metro Theatre Kings Cross, Sydney, January 1970 [Jim Sharman Director cast included Reg Livermore]' 1970](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/jerrems_performers-on-stage-hair-web.jpg?w=650)


You must be logged in to post a comment.