Exhibition dates: 17th October 2017 – 21st January 2018
Curator: Sérgio Mah, Universidade NOVA, Lisboa
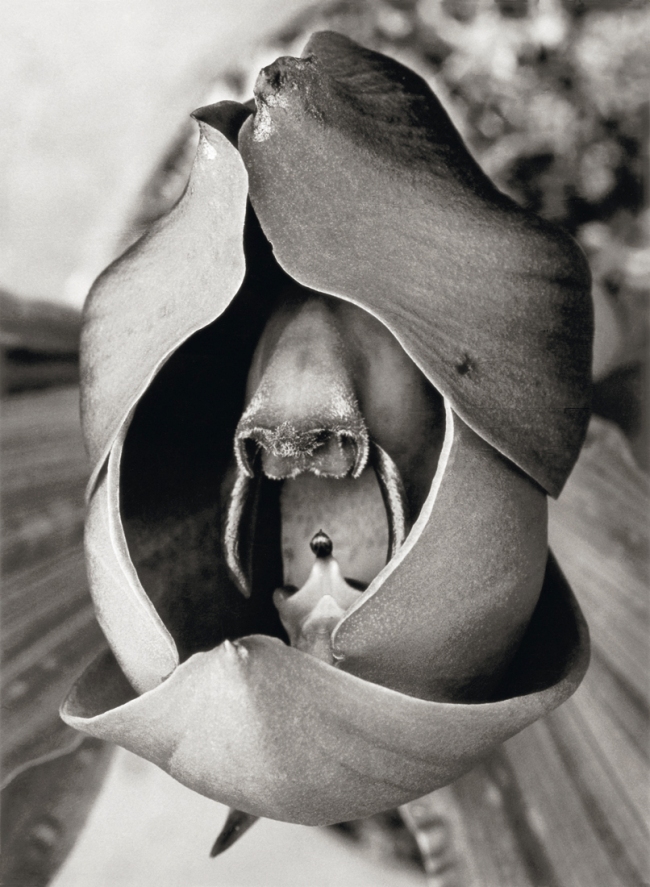
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Stapelia variegata, Asclepiadaceae
1923
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde. Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Experiencing the image
“[Walter Isaacson] describes the photographs, of which 7200 … miraculously survive today, as the greatest record of curiosity, because his “cross-disciplinary brilliance whirls across every page, providing a delightful display of a mind dancing with nature”. Renger-Patzsch delighted in seeing patterns in nature, so he would juxtapose a photograph of the branching arteries of the heart with the roots of a sprouting tree.”1
A mind dancing with nature.
Of course, the original quote (which I have altered) was talking about Leonardo da Vinci… but the same enquiring mind, the same display can be seen in the work of Albert Renger-Patzsch. His was a mind entranced by the nature of technology, and the technology, the structure of nature. However, he is ambivalent about the benefits of industrialisation even as he photographed it in ‘New Objectivity’ style – that is, supposedly free from emotion and subjectivity.
No writing about his work can put it better than this quote from when this exhibition was at Fundación MAPFRE in Madrid:
“Technical precision and exact representation of the subject; psychological contention and rejection of pictorial stylisation and expressionism; a keen sense of composition with attention to details, structures and forms; a sharp and clear construction of the image: these were some of the fundamental premises of a tendency that understands photography as a privileged medium to promote an artistic and simultaneously perceptive shift.
Renger-Patzsch’s work amalgamates a great number of photographic subjects, typologies and genres. In a historical period marked by deep political tension and significant social and economic change, his work allows the viewer to envision a unique worldview, a platform of intersections and re-appreciations between the domains of nature and technology.”
The only point I would not support in this quotation are these words, “psychological contention and rejection of pictorial stylisation and expressionism.”
Of course, “through the disconcerting simplicity of the photographs Renger-Patzsch highlights the phenomenological and psychological aspects that are part of experiencing the image,” but he does so not through a REJECTION of pictorial stylisation and expressionism (and all the baggage that those words embody), but through an INTENSIFICATION of a different form of pictorial style which forces? the image to emit a new form of expression. That is, the object is just its surface and is captured, instantly, by the camera in this perceptive shift.
Can you imagine seeing these photographs in the 1920s, having never seen anything like them before? They would have been revolutionary, in their rendering of the surface of the object and nothing more. Placing the camera directly before the object which requires nothing else but itself… the eye of the snake, the darkness of a tree trunk, the ordering of shoemakers’ irons. But then he finishes his ode to life, Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful), with his version of Albrecht Dürer’s Praying Hands (c. 1508). I suspect that the idea the Renger-Patzsch was working with is that beauty is truth, and truth is beauty.
In contemporary society, have we lost the ability to see these photographs as he intended, with a child-like innocence? Was he saying, this is objective, do you agree? Or does the poetic intensity in the life of things refuse to be stilled?
For me, these photographs are not e/motion-less, they are the very essence of a reality rendered wonderful in my eyes.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
1/ Paraphrase of Tina Allen. “Prophetic Polymath,” on Leonardo da Vinci by Walter Isaacson in Weekend Australian Review January 6-7 2018, p. 14
Many thankx to Jeu de Paume for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Albert Renger Patzsch / Trailer
Independently of the role he played in New Objectivity – an artistic movement that appeared in Germany at the beginning of the 1920s – Albert Renger-Patzsch (1897-1966) is today considered one of the most important and most important figures / influences in the history of 20th century photography.
The exhibition pays tribute to this extraordinary photographer and allows us to rediscover the posterity of a work that invites us to reflect on the nature of photography and on its artistic and speculative potential in the context of contemporary art and culture.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Albert Renger-Patzsch (1897-1966), who produced a huge body of work spanning four and half decades, was one of the most influential photographers of the New Objectivity movement that emerged in Germany in the mid 1920s. His work helped to establish photography as a unique and important medium within modern art. Renger-Patzsch revived realism in photography, adopting an approach that was characterised by formal and technical rigour and a rejection of expressionism and pictorial stylisation. He had a highly developed sense of composition, and his attention to detail, structure and form resulted in images with sharp, clear compositions. For Renger-Patzsch, photography was a medium that made possible new forms of artistic imagery, while being perfectly in step with a period marked by industrialisation and the spread of technology. By highlighting the medium’s unique properties and the creative possibilities of documentary photography, Renger-Patzsch forged a unique role for photography within the arts of his time.
His original, simple images combine extraordinary realism and documentary value with poetic and phenomenological resonance, giving them great power. Renger-Patzsch was a highly prolific photographer who explored a wide range of subjects and genres. This exhibition highlights the invaluable legacy of this extraordinary photographer, whose work provides an ideal context for reflecting on the specificities and relevance of photography within the field of contemporary art and culture.
– The Design of Nature
– From Vernacular Landscape to the Modern City
– The vision of things
– Landscapes of the Ruhr: the Topography of a Transformation
– Industrial Objects and Architecture: Geometry and Series
– The Destiny of Nature
Sérgio Mah
The Design of Nature
During the initial phase of his career, Albert Renger-Patzsch produced a series of photographs depicting plants and flowers for the collection Die Welt der Pflanze (The World of Plants), coordinated by Ernst Fuhrmann as part of his biosophical studies.
The first two volumes in the series, both published in 1924, were Orchideen (Orchids) and Crassula. Renger-Patzsch worked within the general parameters of the book, reproducing fragments of nature with as much objectivity and clarity as possible. He produced a large number of photographs distinguished by their great technical and compositional rigour, including systematic close-ups of plants and flowers. In 1923, Renger-Patzsch wrote his first text, “Pflanzenaufnahmen” (Plant photographs), setting out his views on photography and its extraordinary capacity for capturing nature. Among the images and arguments in the text he outlines some of the key principles that would underpin his photography: attention to detail and emphasis on the formal, structural and material aspects of nature, as well as, correspondingly, a reiterative affirmation of the intrinsic qualities of photography – realism, objectivity, neutrality – and its unique role in expanding our perception of reality.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Catasetum trindentatum, Orchidaceae
1922-1923
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Brasilianischer Melonenbaum von unten gesehen (Brazilian melon tree seen from below)
1923
Galerie Berinson, Berlin
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
From Vernacular Landscape to the Modern City
In 1927, Albert Renger-Patzsch published his most ambitious book to date, Die Halligen (The Halligen Islands), with images of the islands in the Wadden Sea, on the northern coast of Germany.
His photographs featured a number of subjects: landscapes, portraits, architectural motifs and everyday activities. These subjects encapsulated the relationship between local ways of life (genuine, deep-rooted, traditional) and the physical and symbolic characteristics of this peculiar area. This vernacular reality contrasted with the rampant industrialisation that was transforming many of the great urban centres in Germany.
Over the ensuing years, Renger-Patzsch published Lübeck (1928) and Hamburg (1930), books that highlight the emerging characteristics of the modern city, the coexistence of different historic periods and the intersection between historical culture and the impact of industrialisation. In these photographs the photographer’s interest in combining documentary objectives with the creative potential of a modern vision is evident in his use of close-cropped, asymmetrical compositions and innovative perspectives, alternating between general shots and a focus on details. He displays sensitivity to the formal and structural aspects of reality, rejecting the atavistic influence of painting in order to embrace the possibilities of a “new vision” governed by photography.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Krabbenfischerin (Shrimp fisherwoman)
1927
Centre Pompidou, Musée national d’art moderne – Centre de création industrielle, Paris. Acquisition en 1979
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
The vision of things
In 1928, Albert Renger-Patzsch’s best-known book was published, Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful), although the photographer would have preferred the title Die Dinge (Things).
It exemplifies the principles and characteristics of the photographer’s work: a desire to represent the immanent substance of an object/subject while demonstrating photography’s capacity for recording reality. In this respect, representing the unique character of a particular thing was also a way of affirming the unique character of photography.
The book encompasses a wide range of subjects and elements from the photographer’s world. It is an anthology of photographs taken since the beginning of his career, including several images produced for the books Die Welt der Pflanze, Die Halligen and Lübeck. Photographic genres are equally diverse, spanning portrait, landscape, still life and architectural images. The subjects are presented in an evolving thematic and conceptual sequence: first nature, plants, animals, people and landscapes; next, the manmade world of objects, architecture, the city, machines, and industrial structures and spaces. In this way a worldview is organised, a context of intersections and reappraisals, between nature and technology, between the sacred and the profane, between historical heritage and modernity.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Ritzel and Zahnräder, Lindener Eisen-und Stahlwerke (Sprockets and gears, Lindener Eisen-und Stahlwerke factory)
1927
Albert Renger-Patzsch. Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann and Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Bügeleisen für Schuhfabrikation, Faguswerk Alfeld (Shoemakers’ irons, Fagus factory, Alfeld)
1928
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on the book Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful)
Like other artists of his time, Renger-Patzsch was especially keen on exploring the formal analogies between the things of nature and industrial things. Industry led to mass production and the manufacture of standardised objects, exemplified in this image. This contrasts with other images from Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful), such as Gebirgsforst im Winter (Mountain forest in winter) (below), which capture repetition in nature.
Renger-Patzsch identifies a coherence, a parity, between nature and culture as non-antagonistic doHands. He suggests a measure of naturalness in technology, and a measure of rationality in nature. For the photographer the emphasis on industrial seriality also allowed him to underscore the seriality of photography itself (as a means of technical reproduction), thus demonstrating the unique, mediating condition of this medium for visual reproduction in the connection between the natural world and the world of modern industry.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Gebirgsforst im Winter (Fichtenwald im Winter)
(Mountain forest in winter (spruce forest in winter))
1926
Galerie Berinson, Berlin
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Natterkopf (Head of an adder)
1925
Galerie Berinson, Berlin
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on the book Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful)
Painstaking attention to detail is a central feature of Renger-Patzsch’s photography, as demonstrated by several images in Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful). Resorting to pronounced close-ups or subsequent reframing, the photographer breaks down and isolates the vision of certain things, thereby providing a fresh perspective: in this case, the image of a serpent’s head surrounded by a section of its body.
The close-up framing allows him to accentuate the two-dimensionality of the image, the part being more suggestive than the whole. This is a realistic, objective vision, but one aimed at creating a tension between the concrete nature of the motif and its abstract character.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Hände (Hands)
1926-1927
Collection Ann und Jürgen Wilde
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on the book Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful)
This is the hundredth and last image of Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful). It shows a pair of hands joined together, isolated from the rest of the body, rising over a black background in a gesture heavy with symbolic, meditative and spiritual fervour.
Aware that photography was increasingly becoming mundane and banal, and that the experience of attention was crumbling in the face of the accelerating transformation of reality, in Die Welt ist schön Renger-Patzsch offers an imaginary world where modern subjects can be reconnected with the things surrounding them via the mediation of a diffuse and calm temporality, the temporality of tradition and myth. A symptom of this vision is precisely the closing image of the book.
“To do justice to modern technology’s rigid linear structure, to the lofty gridwork of cranes and bridges, to the dynamism of machines operating at one thousand horsepower – only photography can do that. […] The absolutely correct rendering of form, the subtlety of tonal gradation from the brightest light to the darkest shadow, impart to a technically expert photograph the magic of experience.”
Albert Renger-Patzsch, “Ziele”, ‘Das Deutsche Lichtbild’, Berlin, 1927
“There is an urgent need to examine old opinions and look at things from a new viewpoint. There must be an increase in the joy one takes in an object, and the photographer should become fully conscious of the splendid fidelity of reproduction made possible by this technique.”
Albert Renger-Patzsch, “Die Freude am Gegenstand,” ‘Das Kunstblatt’, Berlin, 1928
“[…] the eye is subjective; it views with pleasure the essential things and completely overlooks what is unimportant. The camera, on the other hand, has to reproduce the entire image in focus and in a particular size. It will see the essential and the inessential with equal clarity.”
Albert Renger-Patzsch, in ‘Meister der Kamera erzählen wie sie wurden und wie sie arbeiten’, Halle (Saale), 1937
“[…] the eye is not isolated in its perception of the world. Rather its connections to the brain and the support of our senses in experience heat, cold wind, noise, smells and so on create an extraordinarily compact image of the world, whose plasticity and density are perhaps intensified by a particularly appropriate emotional state. Photography reduces this colourful world into a black-and-white rectangle. It is obvious that this most unpretentious of art forms requires the greatest reliability of taste, ability for abstraction, fantasy and concentration.”
Albert Renger-Patzsch, in ‘Meister der Kamera erzählen wie sie wurden und wie sie arbeiten’, Halle (Saale), 1937
The aim of this exhibition is to rediscover and pay tribute to the legacy of this unique photographer in the conviction that his work offers a context for encouraging reflection on the nature and artistic and speculative potential of photography within the framework of contemporary art and culture.
Of enormous simplicity and originality, Renger-Patzsch’s photography is notable for being based on a documentary style that prioritised realist sobriety and frankness as fundamental characteristics of photographic representation. In other words, his work offers a rigorous approach in technical and formal terms, in which the camera is only used to intensify our vision and aware of things. For Renger-Patzsch, this not only explained his photographic procedures but above all the potential for an aesthetic and conceptual identity for photography that visibly distanced itself from the Pictorialist legacy and from the hybrid experimentalism characteristic of the early 20th-century avant-gardes.
Both Renger-Patzsch’s photography and the various texts in which he set out his ideas reveal his determination to exploit the qualities inherent in the photographic medium. He stated that his aim was: “to use photographic means to create a photography that could exist through its own photographic nature.” In another text Renger-Patzsch wrote that,
“the eyes are not isolated from their perception of the world.
On the contrary, they are part of our senses and, by being connected to the brain, allow us to experience heat, cold, wind, noise, smell, and to rapidly construct a remarkably compacted image of the world, the plasticity and density of which also depend on our emotional states.
Photography reduces the world in colour to a rectangle in black and white. And logically, given that it is the least pretentious form of art, it requires rigorous taste, a capacity for abstraction, imagination and concentration.”
Such statements reveal that the exceptional quality of Renger-Patzsch’s work and thought is also notable for the way it conceives and expands the horizon and scope of the idea of documentary photography. As a result, the descriptive and objective qualities of photography are combined with and articulated by its aesthetic, poetic and phenomenological powers.
This retrospective aims to encompass the principal themes, periods and genres that define Renger-Patzsch’s photographic output through the identification of three moments that are fundamental for an understanding of his career: firstly, his early years, from his photographs of plants taken for Folkwang / Auriga publishers, to the profusion of themes and photographic eclecticism which would be decisive for the creation of his book Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful) of 1928. The period that began after his move to Essen was one of intense photographic creation on the Ruhr area, principally involving subjects associated with places, buildings and industrial objects. Finally, the years after World War II reveal a new interest in the themes of nature and landscape particularly trees and rocks.
Including around 154 photographs, this is one of the largest retrospectives on the artist to date and undoubtedly the one to bring together the largest number of works by Renger-Patzsch from institutional and private collections: the Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde / Pinakothek der Moderne München (Munich), the Museum Folkwang (Essen), the Ludwig Museum (Cologne), the Galerie Berinson (Berlin), the Centre Georges Pompidou (Paris).
Press release from Jeu de Paume
Highlights of the exhibition
Author of a monumental oeuvre created over four and a half decades, Albert Renger-Patzsch (1897-1966) was the leading photographer of the New Objectivity movement that appeared in German art in the mid 1920s.
Renger-Patzsch was a prolific photographer and his oeuvre encompasses a variety of themes, types and genres. This exhibition covers the most important stages in Renger-Patzsch’s career, from his first photographs of plant details, urban scenes and industrial subjects to his later landscape work. In total the exhibition features more than 150 photographs, mostly vintage prints from the most important collections in Germany.
Renger-Patzsch devoted himself to creating a new photographic realism, characterised by an extreme simplicity and originality. He created a modern visual language that was imbued with a poetic resonance and helped to redefine the photographic image. For Renger-Patzsch, photography was the most appropriate medium for carrying out a change that was simultaneously artistic and perceptual, i.e., the possibility of a new kind of image that reflected the changes of the 1920s and 1930s, a period marked by industrialisation and the spread of technology.
Albert Renger-Patzsch is the author of one of the seminal books in the history of photography, Die Welt ist schön (The World is Beautiful), which was published in 1928. This work reveals the full scope of Renger-Patzsch’s approach, which was to capture the unique character of each concrete thing in order to affirm also the unique character of photography.
Renger-Patzsch produced an exceptional body of work on the theme of industrial architecture, which he helped to turn into a genre in itself. He exerted a decisive influence on generations of photographers, not least Bernd and Hilla Becher. This exhibition sets out to highlight the vital legacy of this extraordinary photographer. In so doing, it sheds light on the important role of photography within the context of contemporary art and culture.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Landstraße bei Essen (Country road near Essen)
1929
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Landscapes of the Ruhr: the Topography of a Transformation
In 1929, Renger-Patzsch relocated to Essen, in the Ruhr, Germany’s leading industrial region and one the photographer was familiar with.
Two years earlier, he had produced the first images in an ambitious project focusing on the landscapes of the Ruhr, which he would work on until 1935. In this realm of contrasts, he became particularly interested in spaces that were between cities, between the urban and the rural, landscapes that displayed the process of change that the region was undergoing due to industrialisation and the development of public infrastructure.
The works reflect a change in Renger-Patzsch’s photographic vision: the compositions are widened, in some cases into large panoramic views. The images now focus on a multiplicity of elements and explore interpretative relationships and associations. His preference for more open images that include the surroundings of objects, rather than just close-ups, reflects a more inclusive objectivity. Some images include people, usually seen from afar. These figures are set in particular socio-spatial contexts and help to highlight the enormous disparity in scale between the human figure and the new industrial complexes. Vertical and horizontal elements, close up and in the distance, are combined and juxtaposed. The relationship between different planes, between foreground and background, is intensified in order to show how industry has shaped the landscape, turning it into a heterogeneous and paradoxical landscape (in historical and social terms).
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Landschaft bei Essen und Zeche “Rosenblumendelle” (Landscape near Essen with the Rosenblumendelle colliery)
1928
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Zeche “Victoria Mathias” in Essen (Colliery “Victoria Mathias” in Essen)
1929
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich. © Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on the Ruhr
In the photographs of the Ruhr, the landscape emerges as a genre in which disparate elements are combined and contrasted, a way of exploring the boundaries between the rural and industrial worlds, the city and the periphery.
One of the most extraordinary examples from this period is the 1928 image Landschaft bei Essen und Zeche “Rosenblumendelle” (Landscape near Essen with the Rosenblumendelle colliery) (above). This photograph that seems to result from the collage of two layers (two regions, two realities), bringing together the idyllic serenity of the rural world, in the foreground, and the massive and disproportionate character of the new industrial complexes in the background, as the fatal destiny of the modern world.
At the centre is a road, a metaphor for history, mediating two different realities and suggesting the dilemma between tradition and modernity – a dilemma that highlights Renger-Paztsch’s ambivalent and paradoxical stance towards industrialisation.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Kauper, Hochofenwerk Herrenwyk, Lübeck (Cowper, blast furnace Herrenwyk, Lübeck)
1927
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich. © Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Industrial Objects and Architecture: Geometry and Series
From the late 1920s onwards, Renger-Patzsch produced numerous works following commissions from architects and industrial companies.
At this time, the expansion of the press and advertising, boosted by industry, was having a big impact on art, providing an abundance of work opportunities for artists and photographers.
Photographs of industrial objects and buildings lent themselves to rigorous, carefully calculated compositions. In many cases, the viewer’s perception is guided by planimetric compositions, which are sometimes orthogonal, sometimes diagonal. His architectural photographs combine structural and formal aspects with a desire to record the functional reality of industrial complexes. His images of objects are characterised by their attention to detail and a desire to give aesthetic meaning to each of the objects photographed through meticulous graphic composition.
However, Renger-Patzsch emphasises the repetitive, standardised nature of the objects – aspects inherent to mass production. For him, the theme of technology was further confirmation of how photography differed from painting and provided the most suitable medium for representing the new reality – technical, material and spatial – of modern industrialisation.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Ein Knotenpunkt der Fachwerkbrücke Duisburg-Hochfeld (A node from the latticework bridge in Duisburg-Hochfeld)
1928
Vintage gelatin silver print
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / VEGAP, Madrid 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Zeche “Heinrich-Robert”, Turmförderung, Pelkum bei Hamm (Headframe at the Heinrich-Robert colliery in Pelkum, near Hamm)
1951
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Zeche “Graf Moltke”, Gelsenkirchen-Gladbeck (Graf Moltke colliery, in the Gladbeck district of Gelsenkirchen)
1952-1953
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Zeche “Katharina”, Schacht Ernst Tengelmann, Essen-Kray (Katharina colliery, Ernst Tengelmann well, in the Kray district of Essen)
1955-1956
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich. © Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on architecture
Throughout his career, Renger-Patzsch created a huge number of photographs of industrial architecture. Its emergence as an artistic genre owes much to him, and his legacy exerted a decisive influence on generations of future photographers, including Bernd and Hilla Becher.
The perspective and the composition accentuate the geometry of the vertical, horizontal and diagonal lines. The photographer seeks to highlight the significance of a building designed according to strict functional and rational principles. In doing so, Renger-Patzsch reveals a correspondence between method and object in the sense that precision, objectivity and the documentary value of photography were in harmony with the rationality, coherence and functionality of the new industrial and modern architecture.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Jenaer Glas (Zylindrische Gläser) (Jena glass (cylinders))
1934
Museum Folkwang, Essen
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on series
For Renger-Patzsch commercial commissions also provided opportunities for a personal and creative approach to photography. This image is part of a commission from the Jenaer Glaswerke Schott company, for whom he photographed several sets of laboratory objects in glass (recipients, flasks, tubes, jars). In this particular image Renger-Patzsch arranges eight glass beakers, all with the same cylindrical shape but of differing dimensions, on a reflecting surface and photographs them from a slightly elevated angle. The larger items are placed to the rear. The objects overlap with each other. The mirroring effect of the base creates the impression that the glassware is floating, especially at the centre of the image where the smaller cylinder (on which the manufacturer’s logo can be read) is the focal point. In their simple, standardised shape, and their transparency, the objects create a choreography of light, shadows and reflections, an experiment with the possibilities of looking at objects and reconfiguring their shapes.
The Destiny of Nature
In 1944, a large part of his archives at the Folkwang Museum were destroyed in an Allied bombing raid. With his family, Renger-Patzsch moved to the rural area of Wamel, close to Soest. He began to work on a new theme, returning to natural subjects, although now with an emphasis on landscape.
The photographer seemed to find among the trees, forests, rocks and craggy scenes a vital energy. These images suggest a diffuse sense of time contrasting with the linear nature of history and immune to the contingencies of modernity and the devastating consequences of war. In this final phase of his life, Renger-Patzsch published Baüme (Trees) in 1962 and Gestein (Rocks) in 1966, two volumes that exemplify the conceptual and aesthetic bases of this renewed, revitalised view of nature. Both books include essays by the writer and philosopher Ernst Jünger, with whom the photographer maintained an intense and regular correspondence for over twenty years.
The photographs in Baüme and Gestein are the logical corollary to Renger-Patzsch’s extraordinary trajectory. The images are less graphic, in part due to the fact that they depict forms that are apparently disordered, uncontrollable and unpredictable. Nevertheless, through the disconcerting simplicity and sobriety of these photographs, Renger-Patzsch also highlights the phenomenological and psychological aspects that are part of experiencing the image.
Nature can thus be seen as a subject that allows the viewer to experience a primal gaze. This is the condition for a vision simultaneously concrete, poetic and metaphysical that leads to a rediscovery of nature, its destiny, its silence, its rhythms, forms and forces.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Buchenwald (Beech forest)
1936
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Das Bäumchen (The little tree)
1928
Galerie Berinson, Berlin
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on vertical landscape
This is one of Renger-Patzsch’s best-known and most outstanding photographs. This landscape with a tree in the middle heralds his later work. Because of its links to the history of painting, landscape was not a central theme of New Objectivity. In this image Renger-Patzsch chose a vertical landscape, a less usual format than the horizontal landscape. It is a hybrid image in the sense that it combines the tree as the central motif (leafless and reduced to its branch structure) with a panoramic view of a vast landscape. Of particular note is the way the photographer explores the different planes within the image, playing with depth and distance, with the foreground, where the tree stands and the background of the endless landscape. The differences between near and far are diluted on the two-dimensional surface of the image.
Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966)
Mechanismus der Faltung (Fold mechanism)
1962
Albert Renger-Patzsch Archiv / Stiftung Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Pinakothek der Moderne, Munich
© Albert Renger-Patzsch / Archiv Ann und Jürgen Wilde, Zülpich / ADAGP, Paris 2017
Focus on geology
Rocks and geological phenomena became of great interest to Renger-Patzsch in the latter phase of his career as a photographer, during which he travelled to France, Norway, Northern Ireland, Italy, Sweden and several parts of Germany to take the photographs published in Gestein (Rocks). In the book, the images are strategically interspersed with text by geologist and palaeontologist Max Richter and an essay by writer and philosopher Ernst Jünger.
Renger-Patzsch photographed the rocks and layers of rock as evidence of the slower phenomena of nature, but also as metaphors for time and history. This image, taken on the coast of Brittany, shows a series of geological folds, a phenomenon that occurs when different forces cause the planar rock sheets to curve or fold. The photographic precision and objectivity of the image, along with the stunning (peculiar, expressive, pictorial) appearance generated by tectonic forces on the surface of the rock, create a vision that combines figuration and abstraction.
Jeu de Paume
1, Place de la Concorde
75008 Paris
métro Concorde
Phone: 01 47 03 12 50
Opening hours:
Tuesday: 11.00 – 21.00
Wednesday – Sunday: 11.00 – 19.00
Closed Monday



![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Brasilianischer Melonenbaum von unten gesehen [Brazilian melon tree seen from below]' 1923 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Brasilianischer Melonenbaum von unten gesehen [Brazilian melon tree seen from below]' 1923](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-brasilianischer-melonenbaum.jpg?w=650&h=846)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Krabbenfischerin [Shrimp fisherwoman]' 1927 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Krabbenfischerin [Shrimp fisherwoman]' 1927](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-krabbenfischerin.jpg?w=650&h=882)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Ritzel and Zahnräder, Lindener Eisen-und Stahlwerke [Sprockets and gears, Lindener Eisen-und Stahlwerke factory]' 1927 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Ritzel and Zahnräder, Lindener Eisen-und Stahlwerke [Sprockets and gears, Lindener Eisen-und Stahlwerke factory]' 1927](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-ritzel-und-zahnracc88der.jpg?w=840)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Bügeleisen für Schuhfabrikation, Faguswerk Alfeld [Shoemakers' irons, Fagus factory, Alfeld]' 1928 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Bügeleisen für Schuhfabrikation, Faguswerk Alfeld [Shoemakers' irons, Fagus factory, Alfeld]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-bugeleisen-fur-schuhfabrikation.jpg?w=650&h=874)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Gebirgsforst im Winter (Fichtenwald im Winter)' [Mountain forest in winter (spruce forest in winter)] 1926 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Gebirgsforst im Winter (Fichtenwald im Winter)' [Mountain forest in winter (spruce forest in winter)] 1926](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-gebirgsforst-im-winter.jpg?w=650&h=874)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Natterkopf [Head of an adder]' 1925 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Natterkopf [Head of an adder]' 1925](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-natterkopf.jpg?w=840)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Hände [Hands]' 1926-1927 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Hände [Hands]' 1926-1927](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-hacc88nde.jpg?w=650&h=855)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Landstraße bei Essen [Country road near Essen]' 1929 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Landstraße bei Essen [Country road near Essen]' 1929](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-landstrac39fe-bei-essen.jpg?w=840)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Landschaft bei Essen und Zeche "Rosenblumendelle" [Landscape near Essen with the Rosenblumendelle colliery]' 1928 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Landschaft bei Essen und Zeche "Rosenblumendelle" [Landscape near Essen with the Rosenblumendelle colliery]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-landschaft.jpg?w=840)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Victoria Mathias" in Essen [Colliery "Victoria Mathias" in Essen]' 1929 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Victoria Mathias" in Essen [Colliery "Victoria Mathias" in Essen]' 1929](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-zeche-victoria-mathias.jpg?w=650&h=875)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Kauper, Hochofenwerk Herrenwyk, Lübeck [Cowper, blast furnace Herrenwyk, Lübeck]' 1927 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Kauper, Hochofenwerk Herrenwyk, Lübeck [Cowper, blast furnace Herrenwyk, Lübeck]' 1927](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-kauper.jpg?w=650&h=833)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Ein Knotenpunkt der Fachwerkbrücke Duisburg-Hochfeld [A node from the latticework bridge in Duisburg-Hochfeld]' 1928 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Ein Knotenpunkt der Fachwerkbrücke Duisburg-Hochfeld [A node from the latticework bridge in Duisburg-Hochfeld]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/albert-renger-patzsch-ein-knotenpunkt-der-fachwerkbrucc88cke-duisburg-hochfeld-1928-web.jpg?w=650&h=883)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Heinrich-Robert", Turmförderung, Pelkum bei Hamm [Headframe at the Heinrich-Robert colliery in Pelkum, near Hamm]' 1951 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Heinrich-Robert", Turmförderung, Pelkum bei Hamm [Headframe at the Heinrich-Robert colliery in Pelkum, near Hamm]' 1951](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-zeche-heinrich-robert.jpg?w=650&h=888)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Graf Moltke", Gelsenkirchen-Gladbeck [Graf Moltke colliery, in the Gladbeck district of Gelsenkirchen]' 1952-1953 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Graf Moltke", Gelsenkirchen-Gladbeck [Graf Moltke colliery, in the Gladbeck district of Gelsenkirchen]' 1952-1953](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-zeche-graf-moltke.jpg?w=650&h=894)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Katharina", Schacht Ernst Tengelmann, Essen-Kray [Katharina colliery, Ernst Tengelmann well, in the Kray district of Essen]' 1955-1956 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Zeche "Katharina", Schacht Ernst Tengelmann, Essen-Kray [Katharina colliery, Ernst Tengelmann well, in the Kray district of Essen]' 1955-1956](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-zeche-katharina.jpg?w=650&h=885)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Jenaer Glas (Zylindrische Gläser) [Jena glass (cylinders)]' 1934 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Jenaer Glas (Zylindrische Gläser) [Jena glass (cylinders)]' 1934](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-jenaer-glas.jpg?w=650&h=887)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Buchenwald [Beech forest]' 1936 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Buchenwald [Beech forest]' 1936](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-buchenwald.jpg?w=650&h=866)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Das Bäumchen [The little tree]' 1928 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Das Bäumchen [The little tree]' 1928](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-das-bacc88umchen.jpg?w=650&h=888)
![Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Mechanismus der Faltung [Fold mechanism]' 1962 Albert Renger-Patzsch (German, 1897-1966) 'Mechanismus der Faltung [Fold mechanism]' 1962](https://artblart.files.wordpress.com/2018/01/renger-patzsch-mechanismus-der-faltung.jpg?w=840)



































You must be logged in to post a comment.