February 2011
It is with much sadness that I note the death of respected Australian photographer and teacher Dr John Cato (1926-2011). Son of Australian photographer Jack Cato, who wrote one of the first histories of Australian photography (The Story of the Camera in Australia (1955)), John was apprentice to his father before setting up a commercial studio with Athol Shmith that ran from 1950-1971. Dr Cato then joined Shmith at the fledgling Prahran College of Advanced Education photography course in 1974, becoming head of the course when Shmith retired in 1979, a position he held until John retired in 1991.
I was fortunate enough to get to know John and his vivacious wife Dawn. I worked with him and co-curatored his retrospective with William Heimerman, ‘…and his forms were without number’ at The Photographers’ Gallery, South Yarra, in 2002. My catalogue essay from this exhibition is reproduced below.
John was always generous with his time and advice. His photographs are sensitive, lyrical renditions of the Australian landscape. He had a wonderful ear for the land and for the word, a musical lyricism that was unusual in Australian photographers of the early 1970s. He understood how a person from European background could have connection to this land, this Australia, without being afraid to express this sense of belonging; he also imaged an Aboriginal philosophy (that all spirits have a physical presence and everything physical has a spiritual presence) tapping into one of the major themes of his personal work: the mirror held up to reveal an’other’ world – the language of ambiguity and ambivalence (the dichotomy of opposites e.g. black / white, masculine / feminine) speaking through the photographic print.
His contribution to the art of photography in Australia is outstanding. What are the precedents for a visual essay in Australian photography before John Cato? I ask the reader to consider this question.
It would be fantastic if the National Gallery of Victoria could organise a large exhibition and publication of his work, gathering photographs from collections across the land, much like the successful retrospective of the work of John Davis held in 2010. Cato’s work needs a greater appreciation throughout Australia because of it’s seminal nature, containing as it does the seeds of later development for Australian photographers. His educational contribution to the development of photography as an art form within Australia should also be acknowledged in separate essays for his influence was immense. His life, his teaching and his work deserves nothing less.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
‘… and his forms were without number’
John Cato: A Retrospective of the Photographic Work 1971-1991
This writing on the photographic work of Dr John Cato from 1971-1991 is the catalogue essay to a retrospective of his work held at The Photographers’ Gallery in Prahran, Melbourne in 2002. Dr Cato forged his voice as a photographic artist in the early 1970s when photography was just starting to be taken seriously as an art form in Australia. He was a pioneer in the field, and became an educator in art photography. He is respected as one of Australia’s preeminent photographers of the last century.
With the arrival of ‘The New Photography’1 from Europe in the early 1930’s, the formalist style of Modernism was increasingly adopted by photographers who sought to express through photography the new spirit of the age. In the formal construction of the images, the abstract geometry, the unusual camera angles and the use of strong lighting, the representation ‘of the thing in itself’2 was of prime importance. Subject matter often emphasised the monumentality of the factory, machine or body/landscape. The connection of the photographer with the object photographed was usually one of sensitivity and awareness to an external relationship that resulted in a formalist beauty.
Following the upheaval and devastation of the Second World War, photography in Australia was influenced by the ‘Documentary’ style. This “came to be understood as involved chiefly with creating aesthetic experiences … associated with investigation of the social and political environment.”3 This new movement of social realism, “… a human record intimately bound with a moment of perception,”4 was not dissimilar to Henri Cartier-Bresson’s ‘decisive moment’ (images a la sauvette) where existence and essence are in balance.5
The culmination of the ‘Documentary’ style of photography was The Family of Man exhibition curated by Edward Steichen that toured Australia in 1959.6 This exhibition, seen many times by John Cato,7 had a theme of optimism in the unity and dignity of man. The structure of the images in ‘Documentary’ photography echoed those of the earlier ‘New Photography’.
Max Dupain “stressed the objective, impersonal and scientific character of the camera; the photographer could reveal truth by his prerogative of selection.”8 This may have been an objective truth, an external vocalising of a vision that concerned itself more with exterior influences rather than an internal meditation upon the subject matter.
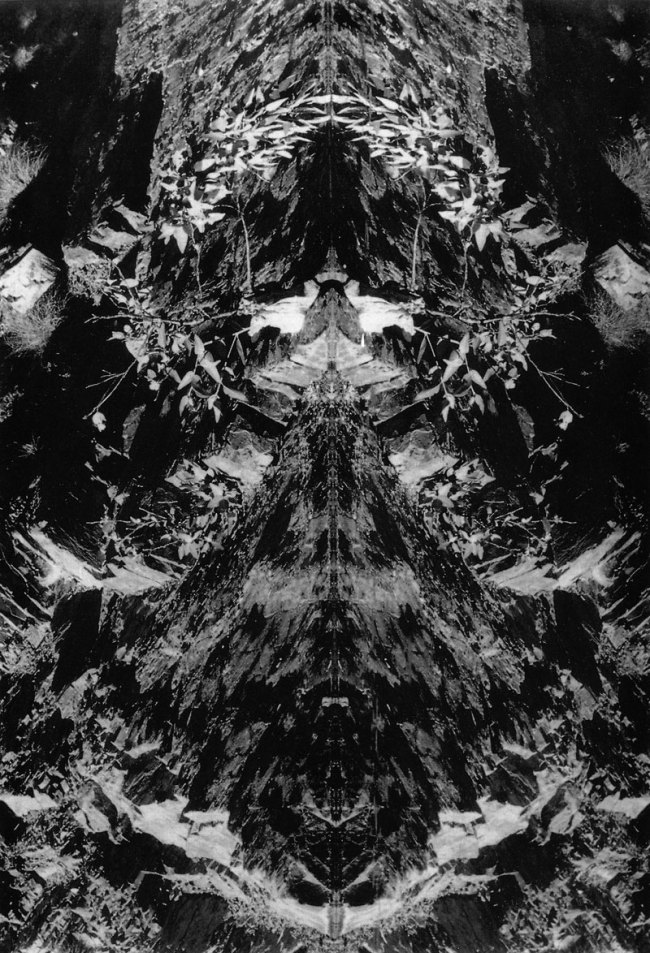

John Cato (Australian, 1926-2011)
Untitled from the series Essay I, Landscapes in a Figure
1971-1979
Silver gelatin photograph
In 1971, John Cato’s personal photographic work was exhibited for the first time as part of the group show Frontiers at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne.9 Earth Song emerged into an environment of social upheaval inflamed by Australian involvement in the Vietnam War. It provided a group of enthusiastic people who were beginning to be interested in photography as art, an opportunity to see the world, and photography, through a different lens. The 52 colour photographic prints in Earth Song, were shown in a sequence that used melodic line and symphonic form as its metaphoric basis, standing both as individual photographs and as part of a total concept.10
In the intensity of the holistic vision, in the connection to the subconscious, the images elucidate the photographers’ search for a perception of the world. This involved an attainment of a receptive state that allowed the cracks, creases and angles inherent in the blank slate of creation to become meaningful. The sequence contained images that can be seen as ‘acts of revelation’,11confirmed and expanded by supporting photographs, and they unearthed a new vocabulary for the discussion of spiritual and political issues by the viewer. They may be seen as a metaphor for life.
The use of sequence, internal meditation and ‘revelation’, although not revolutionary in world terms,12 were perhaps unique in the history of Australian photography at that time. During the production of Earth Song, John Cato was still running a commercial studio in partnership with the photographer Athol Shmith and much of his early personal work was undertaken during holidays and spare time away from the studio. Eventually he abandoned being a commercial photographer in favour of a new career as an educator, but found this left him with even less time to pursue his personal work.13
Earth Song (1970-1971) was followed by the black and white sequences:
| Tree – A Journey | 18 images | 1971-1973 | ||
| Petroglyphs | 14 images | 1971-1973 | ||
| Seawind | 14 images | 1971-1975 | ||
| Proteus | 18 images | 1974-1977 | ||
| Waterway | 16 images | 1974-1979 |
Together they form the extensive series Essay I, Landscapes in a Figure, parts of which are held in the permanent photography collection of the National Gallery of Victoria.14

John Cato (Australian, 1926-2011)
Untitled from the series Essay I, Landscapes in a Figure
1971-1979
Silver gelatin photograph
The inspiration for Essay I and later personal work came from many sources. An indebtedness to his father, the photographer Jack Cato, is gratefully acknowledged. Cato also acknowledges the influence of literature: William Shakespeare (especially the Sonnets, and As You Like It), William Blake, Walt Whitman (Leaves of Grass), Lewis Carroll (Through the Looking Glass), the Bible; and of music (symphonic form), the mythology of the Dreamtime and Aboriginal rock paintings.15 Each body of work in Essay I was based on an expression of nature, the elements and the Creation. They can be seen as Equivalents16 of his most profound life experiences, his life philosophy illuminated in physical form.
John Cato was able to develop the vocabulary of his own inner landscape while leaving the interpretation of this landscape open to the imagination of the viewer. Seeing himself as a photographer rather than an artist, he used the camera as a tool to mediate between what he saw in his mind’s eye, the subjects he photographed and the surface of the photographic negative.17 Photographing ‘in attention’, much as recommended by the teacher and philosopher Krishnamurti,18 he hoped for a circular connection between the photographer and the subject photographed. He then looked for verification of this connection in the negative and, eventually, in the final print.
Essay II, Figures in a Landscape, had already been started before the completion of Essay I and it consists of three black and white sequences:
| Alcheringa | 11 images | 1978-1981 | ||
| Broken Spears | 11 images | 1978-1983 | ||
| Mantracks | 22 images in pairs | 1978-1983 |
The photographs in Essay II seem to express “the sublimation of Aboriginal culture by Europeans”19 and, as such, are of a more political nature. Although this is not obvious in the photographs of Alcheringa, the images in this sequence celebrating the duality of reality and reflection, substance and shadow, it is more insistent in the symbology of Broken Spears and Mantracks. Using the metaphor of the fence post (white man / black man in Broken Spears) and contrasting Aboriginal and European ‘sacred’ sites (in pairs of images in Mantracks), John Cato comments on the destruction of a culture and spirit that had existed for thousands of years living in harmony with the land.
In his imaging of an Aboriginal philosophy (that all spirits have a physical presence and everything physical has a spiritual presence) he again tapped one of the major themes of his personal work: the mirror held up to reveal an’other’ world. Cato saw that even as they are part of the whole, the duality of positive / negative, black / white, masculine / feminine are always in conflict.20 In the exploration of the conceptual richness buried within the dichotomy of opposites, Cato sought to enunciate the language of ambiguity and ambivalence,21 speaking through the photographic print.
The theme of duality was further expanded in his last main body of work, Double Concerto: An Essay in Fiction:
| Double Concerto (Pat Noone) | 30 images | 1984-1990 | ||
| Double Concerto (Chris Noone) | 19 images | 1985-1991 |
Double Concerto may be seen as a critique of the power of witness and John Cato created two ‘other’ personas, Pat Noone and Chris Noone, to visualise alternative conditions within himself. The Essay explored the idea that if you send two people to the same location they will take photographs that are completely different from each other, that tell a distinct story about the location and their self:
“For the truth of the matter is that people have mixed feelings and confused opinions and are subject to contradictory expectations and outcomes, in every sphere of experience.”22
This slightly schizophrenic confusion between the two witnesses is further highlighted by Pat Noone using single black and white images in sequence. Chris Noone, on the other hand, uses multiple colour images joined together to form panoramic landscapes that feature two opposing horizons. The use of colour imagery in Double Concerto, with its link to the colour work of Earth Song, can be seen to mark the closing of the circle in terms of John Cato’s personal work. In Another Way of Telling, John Berger states that …
“Photography, unlike drawing, does not possess a language. The photographic image is produced instantaneously by the reflection of light; its figuration is not impregnated by experience or consciousness.”23
But in the personal work of John Cato it is a reflection of the psyche, not of light, that allows a consciousness to be present in the figuration of the photographic prints. The personal work is an expression of his self, his experience, his story and t(his) language, is our language, if we allow our imagination to speak.
Dr Marcus Bunyan 2002
Footnotes
1/ Newton, Gael. Shades of Light: Photography and Australia 1839-1988. Sydney: Australian National Gallery, William Collins, 1988, p. 109
2/ Newton, Gael. Max Dupain. Sydney: David Ell Press,1980, p. 34
3/ Ibid., p. 32
4/ Greenough, Sarah (et al). On the Art of Fixing a Shadow: 150 Years of Photography. Boston: National Gallery of Art, Bullfinch Press, 1989, p. 256
5/ Ibid., p. 256
6/ Newton, Gael. Shades of Light: Photography and Australia 1839-1988. Sydney: Australian National Gallery, William Collins, 1988, p. 131
7/ Ibid., p. 131
8/ Newton, Gael. Max Dupain. Sydney: David Ell Press, 1980, p. 32
9/ Only the second exhibition by Australian photographers at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
10/ Shmith, Athol. Light Vision No.1. Melbourne: Jean-Marc Le Pechoux (editor and publisher), Sept 1977, p. 21
11/ Berger, John and Mohr, Jean. Another Way of Telling. New York: Pantheon Books, 1982, p. 118
12/ Hall, James Baker. Minor White: Rites and Passages. New York: Aperture, 1978
13/ Conversation with the photographer 29/01/1997, Melbourne, Victoria
14/ Newton, Gael. Shades of Light: Photography and Australia 1839-1988. Sydney: Australian National Gallery, William Collins, 1988, p. 135, Footnote 7; p. 149
15/ Conversation with the photographer 22/01/1997, Melbourne, Victoria
16/ Norman, Dorothy. Alfred Stieglitz. New York: Aperture, 1976, p. 5
17/ Ibid.,
18/ Krishnamurti. Beginnings of Learning. London: Penguin, 1975, p. 131
19/ Strong, Geoff. Review. The Age. Melbourne, 28/04/1982
20/ Conversation with the photographer 22/01/1997, Melbourne, Victoria
21/ The principal definition for ambiguity in Websters Third New International Dictionary is: “admitting of two or more meanings … referring to two or more things at the same time.”
That for ambivalence is “contradictory and oscillating subjective states.”
Quoted in Davis, Fred. Fashion, Culture and Identity. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1992, p. 21.
22/ Levine, Donald. The Flight From Ambiguity. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1985
23/ Berger, John and Mohr, Jean. Another Way of Telling. New York: Pantheon Books, 1982, p. 95




































You must be logged in to post a comment.