Exhibition dates: 3rd April – 8th June 2014
Ponch Hawkes (Australian, b. 1946)
Rennie Ellis photographing at the Gay Liberation march, Elizabeth Street, Melbourne, 1973
1973
Silver gelatin photograph
© Ponch Hawkes
In researching photographs for the upcoming exhibition Out of the closets, onto the streets: Gay Liberation photography 1971-73 I came across this photograph taken by Ponch Hawkes of the Gay Liberation march that was part of Gay Pride week in 1973. Ponch had never seen this image before until I scanned the negative. And there, front and centre as always, is Rennie Ellis capturing the action… What a special find and a wonderful photograph by Ponch!
We Are Family
This is FAB, one of the best experiences I have had this year at an exhibition in Melbourne. You know you are having a good time when you laugh out loud at so many photographs, sharing the experience of the artist as though you had been there. As indeed I had, for in many cases the clubs pictured in Rennie Ellis’ photographs are the ones I went to.
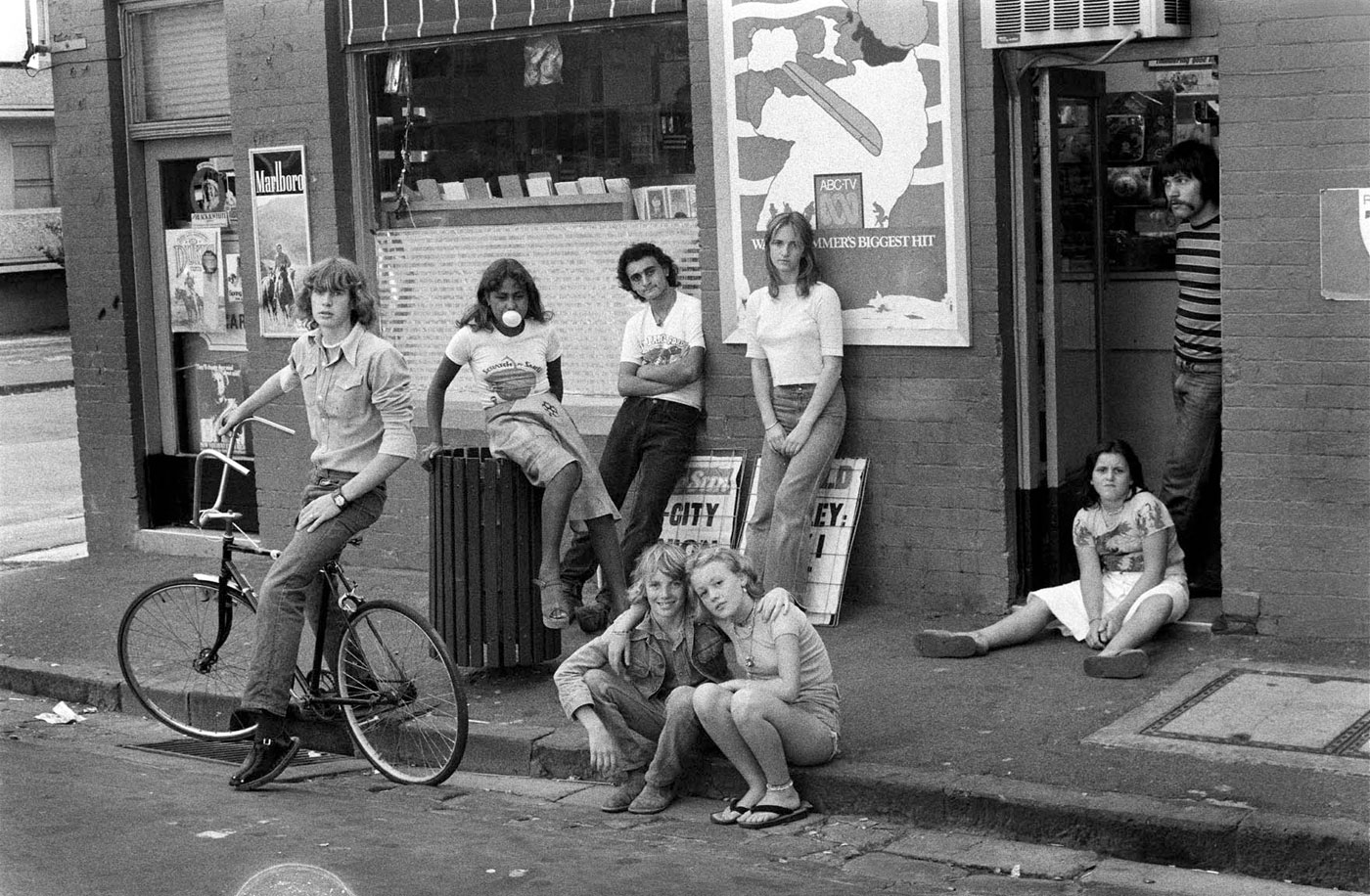
I remember: Wednesday nights at Inflation in the late 80s, where to satisfy licensing restrictions you had to be served a “meal” so that you could drink alcohol (Dining Out, Inflation, 1980 below). The famous Razor Club (1986-1992), based at the Light Car Club of Australia’s clubrooms on the corner of Queens Road and Roy Street, opposite the Albert Park Lake and golf course. “It was Melbourne’s version of Studio 54, the hedonistic, off-the-wall New York disco of the late ’70s – both places notoriously hard to get into but once inside a wonderland of celebrities, freaks, transvestites and fantastic music free from the tyranny of genre.” Once on a big party night the gang of us tried to get in but the queue was so long it was impossible – so I went down the side, climbed up the drain pipes past the ladies loo, and up to the first floor balcony where someone pulled me over – completely off my face, just to get my friends in. Zu Zu’s, Cadillac Bar, 397, Commerce Club, Tasty, Freakazoid, Dome, Baseline, Hardware Club, The Peel and so many parties you could poke a stick at – what a time we had!
There to capture it all – affectionately, non-judgementally – was Rennie Ellis. He wasn’t like Diane Arbus, who thrust her camera as an outsider at people, waiting for a reaction. He was always part of the action because he was part of the family. He was a humanist photographer in the true sense of the word, for he loved photographing human beings, their social relations and their habitats, whatever that might be – sunning, partying, boozing, smoking, picking up. He referred to himself as a “people perv.”
Ellis had an eloquently clumsy eye, and for the type of baroque photographs he took this is a great thing. No perfect framing, no perfect tension points within the image, no regular alignment of horizontals, verticals or diagonals – just instinctual images taken in a split second, with his own particular brand of humour embedded in them. And always with this slight eccentricity in his vision. Look at the image of Dancing People, Razor Club (1991, below) and notice the odd hand poking in at the left hand side and the attitude of the dancers, or Fully equipped, Albert Park Beach (c. 1981, below), with the angle of the three cigarettes, the drink and the bottle of sun tan lotion strapped to the hip – FIERCE!
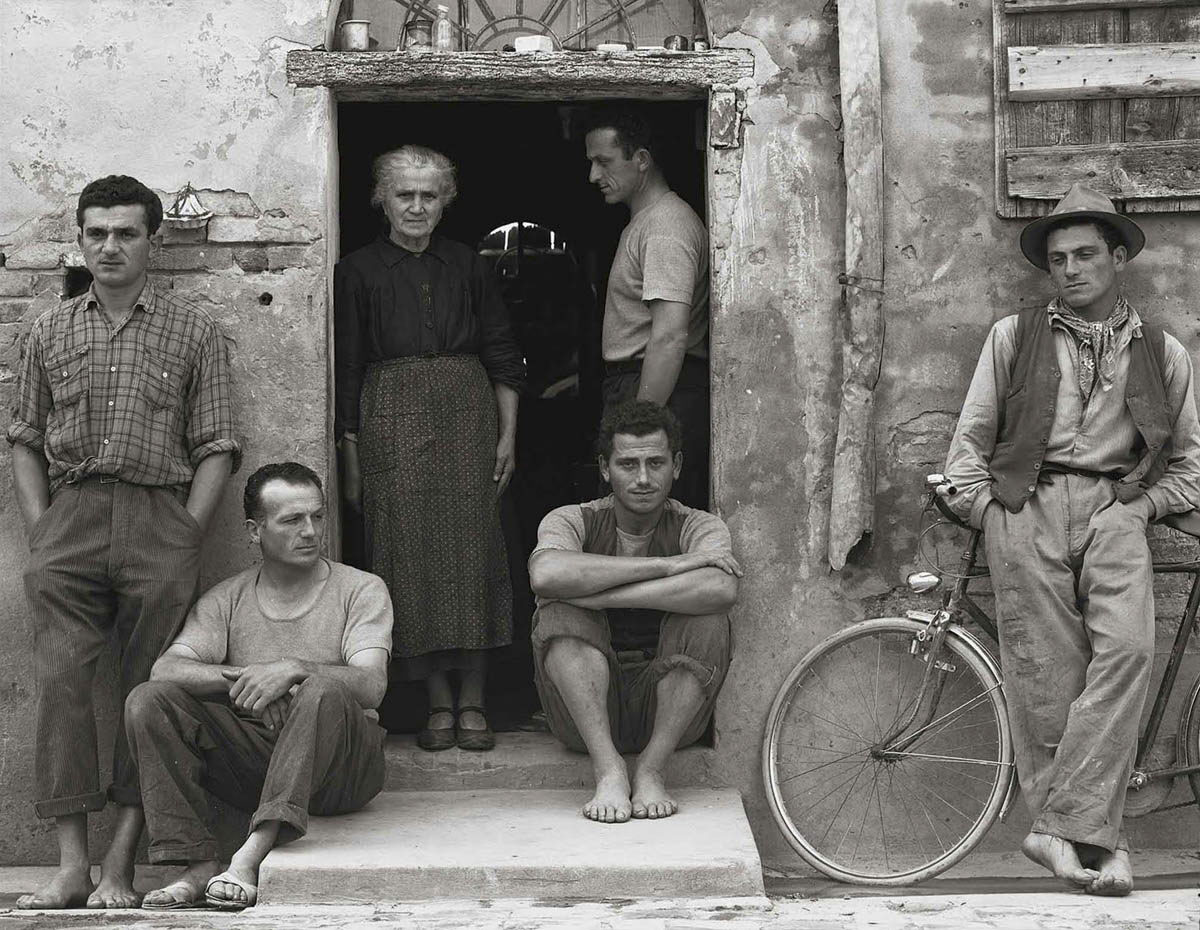
But he was not averse to understanding the structure of his images either, as can be seen by my comparison between the tight, formal structure of Paul Strand’s The Family, Luzzara, Italy (1953, below) and the looser, more natural gathering in Ellis’ The Gang, Windsor (1976, below); or the influence of other artists on his work, for example Norman Lindsay in his My Bare Lady, The Ritz, St Kilda (1977, below). Ellis also liked to push and pull at the pictorial plane; he liked to use pairs of people; he was not afraid of out of focus elements in the foreground of his images; he used chiaroscuro; and his use of light is always excellent. Above all, there is a consistency to his vision that never falters – a concatenation of images that is his style?
This is not just nostalgia. These are bloody good images, and Ellis takes these insightful type of images over and over again – the excesses of hedonism, the influences of wealth, the see-and-be-seen syndrome, things erotic and bizarre and, most importantly, enduring friendships. He photographs what he sees with a love and affection for his subject matter. None of this “staged” vernacular photography that I recently featured in an exhibition at the Art Gallery of New South Wales. This is the real deal. A friend said to me recently, “Ah, but you know, he never did in depth photo-essays like Mary Ellen Mark did of the circus, for example.” To which I have a one word reply: BULLSHIT. His whole oeuvre is a huge photo-essay on the human race, specifically the construction of Australian identity as evidenced in sections like portraits, gangs, sharpies, Aboriginals, Kings Cross, Social Documentary, Decadence, Graffiti, Life’s a Parade, Life’s a Beach etc…
When you look at his photography it would seem to me that his images dissolve the barriers between image / subject / viewer. It’s a strange phenomena to feel so connected to a person’s work. It’s the journey that he takes us on, that we went on too – not so much the destination but the rejoicing in this journey… of company, of environment, friends, places – the joy of being human. He was allowed entry into these public/private spaces because he earned our trust. He lived with the people, and they allowed him to take a bit of their life with him – as a photographic memory, to be retold and relived in the present, allowing us all to relive those times and places. It’s the love, trust, humour and anticipation of the journey that make Ellis’ images truly unique in the history of Australian photography.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Manuela Furci, Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive and the Monash Gallery of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Dancing People, Razor Club
1991
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Robyn Dean (Australian)
Marcus dancing at an unknown club, Melbourne
c. 1991-1992
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Dining Out, Inflation
1980
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
SISTER SLEDGE – WE ARE FAMILY (1979) OFFICIAL VIDEO
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Fitzroy extrovert
1974
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
40.5 x 50.8cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Dino Ferrari, Toorak Road
1976
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Bon Scott and Angus Young, Atlanta, Georgia
1978
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Ronald Belford “Bon” Scott (9 July 1946 – 19 February 1980) was a Scottish-born Australian rock musician, best known for being the lead singer and lyricist of Australian hard rock band AC/DC from 1974 until his death in 1980.
Angus McKinnon Young (born 31 March 1955) is a Scottish-born Australian guitarist best known as a co-founder, lead guitarist, and songwriter of the Australian hard rock band, AC/DC. Known for his energetic performances, schoolboy-uniform stage outfits, and popularisation of Chuck Berry’s duckwalk, Rolling Stone magazine ranked Young as the 24th greatest guitarist of all time.
AC/DC’s popularity grew throughout the 1970s, initially in Australia, and then internationally. Their 1979 album Highway to Hell reached the top twenty in the United States, and the band seemed on the verge of a commercial breakthrough. However, on 19 February 1980, Scott died after a night out in London. AC/DC briefly considered disbanding, but the group quickly recruited vocalist Brian Johnsonof the British glam rock band Geordie. AC/DC’s subsequent album, Back in Black, was released only five months later, and was a tribute to Scott.
Text from the Wikipedia website
AC/DC – Highways to Hell (Official Video)
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
At the Pub, Brisbane
1982
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
The Gang, Windsor
1976
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Paul Strand (American, 1890-1976)
The Family, Luzzara, Italy
1953
Silver gelatin photograph
The photographer Rennie Ellis (1940-2003) is a key figure in Australian visual culture. Ellis is best remembered for his effervescent observations of Australian life during the 1970s-90s, including his now iconic book Life is a beach. Although invariably inflected with his own personality and wit, the thousands of social documentary photographs taken by Ellis during this period now form an important historical record.
The Rennie Ellis Show highlights some of the defining images of Australian life from the 1970s and ’80s. This is the period of Gough Whitlam and Malcolm Fraser, Paul Keating and Bob Hawke; AC/DC and punk rock; cheap petrol and coconut oil; Hare Krishnas and Hookers and Deviant balls.
This exhibition of over 100 photographs provides a personal account of what Ellis termed ‘a great period of change’. Photographs explore the cultures and subcultures of the period, and provide a strong sense of a place that now seems worlds away, a world free of risk, of affordable inner city housing, of social protest, of disco and pub rock, of youth and exuberance.
Text from the MGA website
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
My son Josh learns to swim
1972
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
My Bare Lady, The Ritz, St Kilda
1977
Digital C Type photograph
Fuji Crystal Archive print
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Norman Lindsay (Australian, 1879-1969)
The Olympians
Nd
Oil on canvas
Collection of Hamilton Art Gallery
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Richmond fans, Grand Final, MCG
1974
Chromogenic print
40.5 x 50.8 cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Interesting to note that Ellis must have been shooting both black and white and colour film during the VFL Grand Final of 1974. He must have had two cameras with him (this is more likely than swapping between films in the same 35mm camera) to shoot the photograph above in colour and the black and white image of Robbie McGhie (1974, below).
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Mr Muscleman, Albert Park Beach
c. 1986
Chromogenic print
26.7 x 40.7cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Fully equipped, Albert Park Beach
c. 1981
Digital C Type photograph
Fuji Crystal Archive print
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Don and Patrizia, St Kilda Beach
1985
Chromogenic print
40.5 x 50.8cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Berlin Party, Inflation, Melbourne
1980
Digital C Type photograph
Fuji Crystal Archive print
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Rennie Ellis book covers: Decade: 1970-1980 (left) and Decadent: 1980-2000 (right)
Decade: 1970-1980 is a photography book showcasing Rennie Ellis’ (1940-2003) contribution to photography and social history. With an introduction by film maker and Rennie contemporary Paul Cox and an essay by academic Susan Van Wyk, Decade highlights Ellis as one of Australia’s most important chroniclers of the 1970s. The photographs, predominantly black and white, are drawn from a core selection originally made by Rennie from his own unpublished book, supplemented by other significant and iconic images from 1970 to 1980 drawn from the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive and the State Library of Victoria Rennie Ellis collection. Many of the photographs are accompanied by extended captions written by Rennie himself, published here for the first time. Decade explores the cultures and sub-cultures of the seventies: the political upheavals, alternative lifestyles and counter culture, the women’s movement, gay liberation, the new religions and cults, pop festivals, Vietnam and other protests, massage parlours, the disco scene, the blossoming of Australia’s film industry, the new sexual freedom, Aboriginal rights, street festivals, the new theatre, fashion, drugs and the emergence of a decadent and hedonistic society that would later characterise the 1980s.
Decadent: 1980-2000 is a photography book showcasing Rennie Ellis’ (1940-2003) contribution to photography and social history. It is a fascinating snapshot of the wild, opulent, sometimes tacky and always decadent 1980s in Australia by a true original. With an introduction by photographer and Rennie contemporary William Yang and an essay by photographer and art critic Robert McFarlane, Decadent highlights Ellis as one of Australia’s most important chroniclers of the 1980s. The photographs, both colour and black and white, are drawn from the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive and the State Library of Victoria Rennie Ellis collection. Decadent explores the rise of the hedonism that we now associate with the 1980s. Ellis’ boundary-pushing, racy and sometimes voyeuristic works capture a society that seems to be revelling in its abandonment of the politically charged 1970s documented in Decade.
About the Author
No other photographer has documented – in such depth – the life and times in Australia, throughout the 1970s until his death in 2003, with such insight into the human condition as Rennie Ellis. His non-judgmental approach was his ‘access-to-all-areas’ pass. Ellis used his camera as a key to open the doors to the social arenas of the rich and famous and to enter the underbelly of the nightclubs, bearing witness to the indulgences and excesses. In today’s post-Henson era, these captured moments offer an intimate access to an Australia tantalisingly, but sadly, now almost out of reach.
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Robert McGhie, Grand Final, MCG
1974
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
50.8 x 40.5cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Robert ‘Robbie’ McGhie is a former Australian rules football player who played in the VFL between 1969 and 1972 and again in 1979 for the Footscray Football Club, from 1973 to 1978 for the Richmond Football Club and in 1980 and 1981 for the South Melbourne Football Club. His height was 192 cm and he weighed 85.5 kg. He played 46 games for Footscray, 80 games for Richmond and 16 games for South Melbourne. He was a Richmond Premiership Player 1973, 1974 (the year this photograph by Rennie Ellis was taken at the Grand Final).
Rennie Ellis (Australian, 1940-2003)
Property of Hells Angels, Kings Cross
1970-1971
Selenium-toned gelatin silver print
50.8 x 40.5cm
Courtesy of the Rennie Ellis Photographic Archive
Invitation to The Rennie Ellis Show at the Monash Gallery of Art
Monash Gallery of Art
860 Ferntree Gully Road, Wheelers Hill
Victoria 3150 Australia
Phone: + 61 3 8544 0500
Opening hours:
Tue – Fri: 10am – 5pm
Sat – Sun: 10pm – 4pm
Mon/public holidays: closed











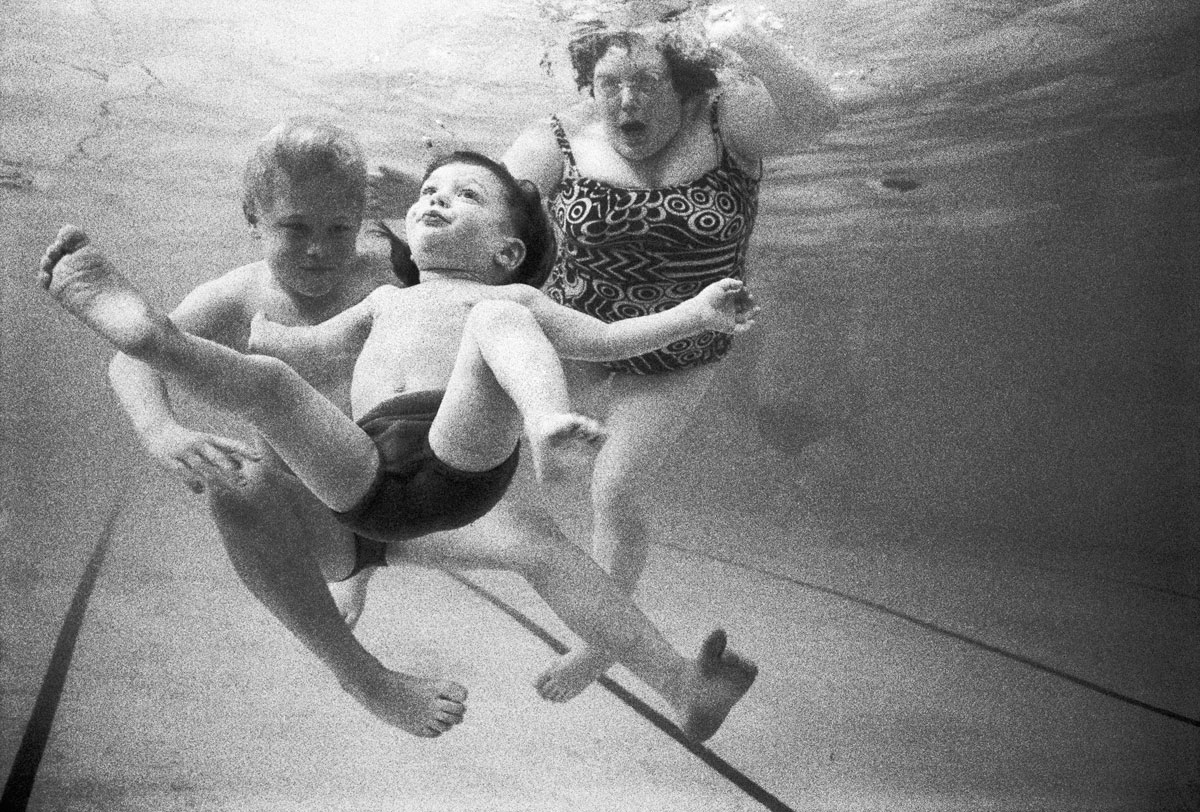
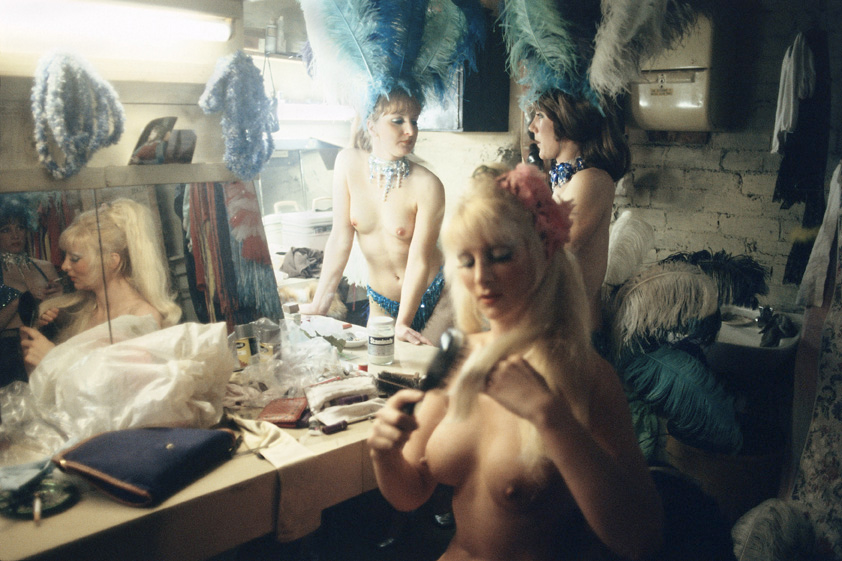


































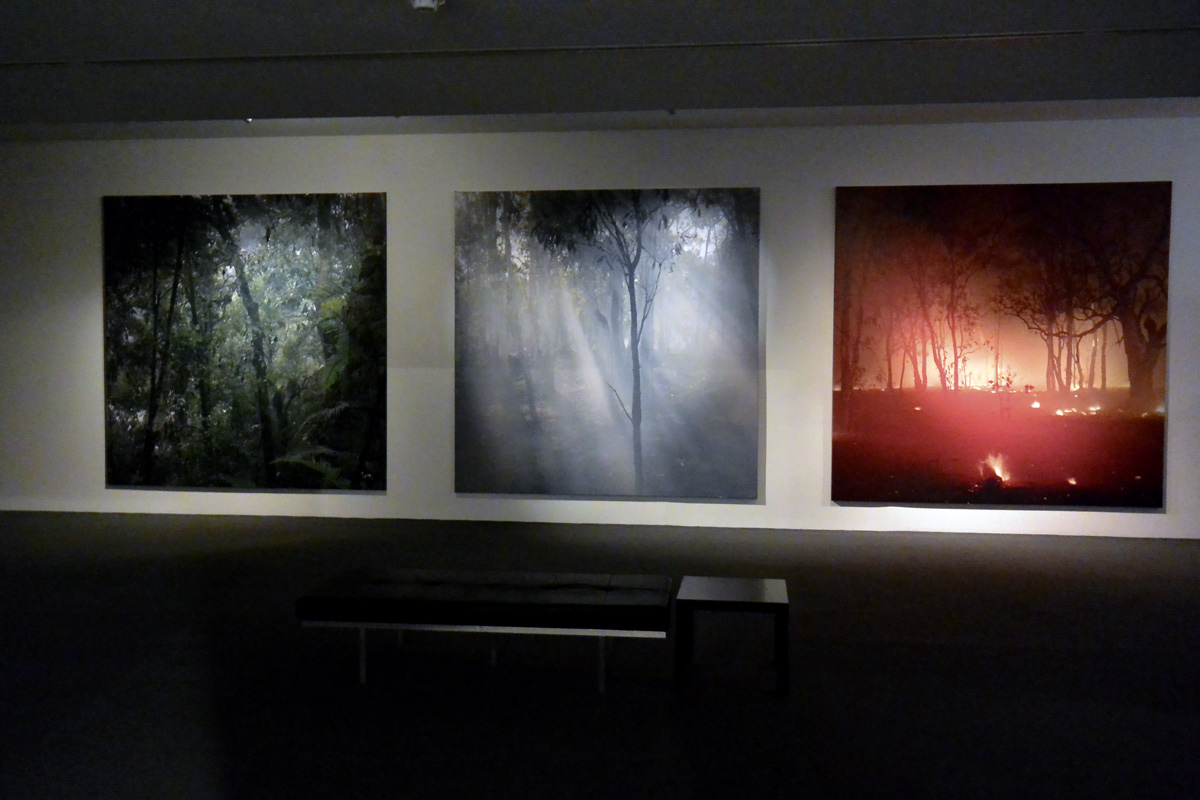
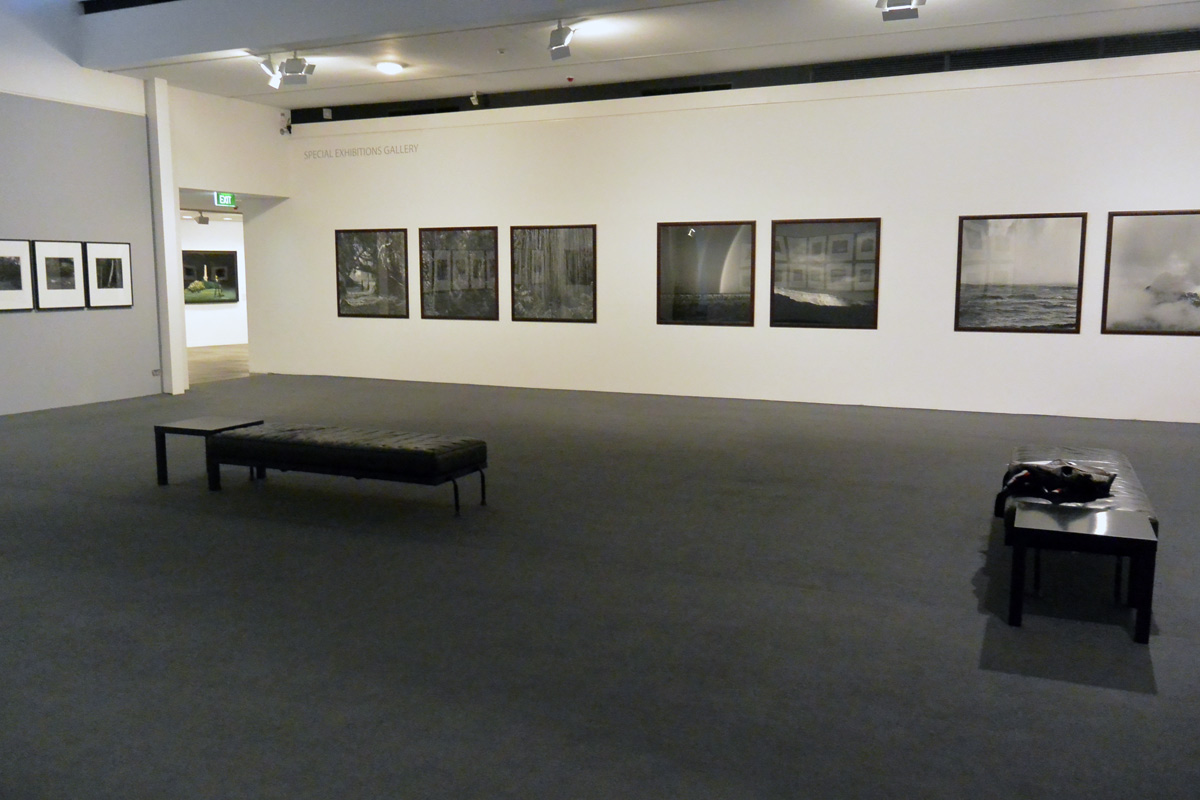
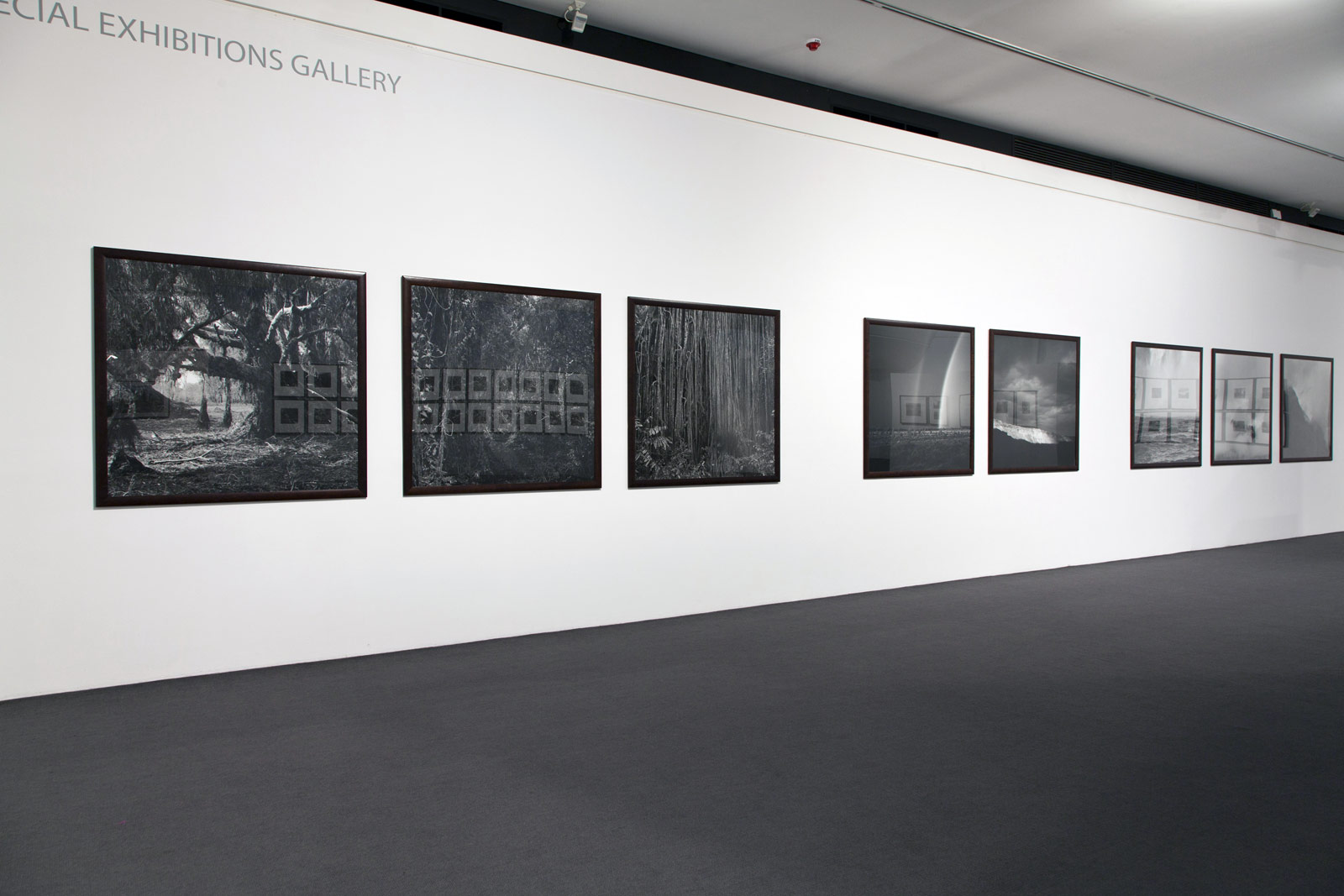
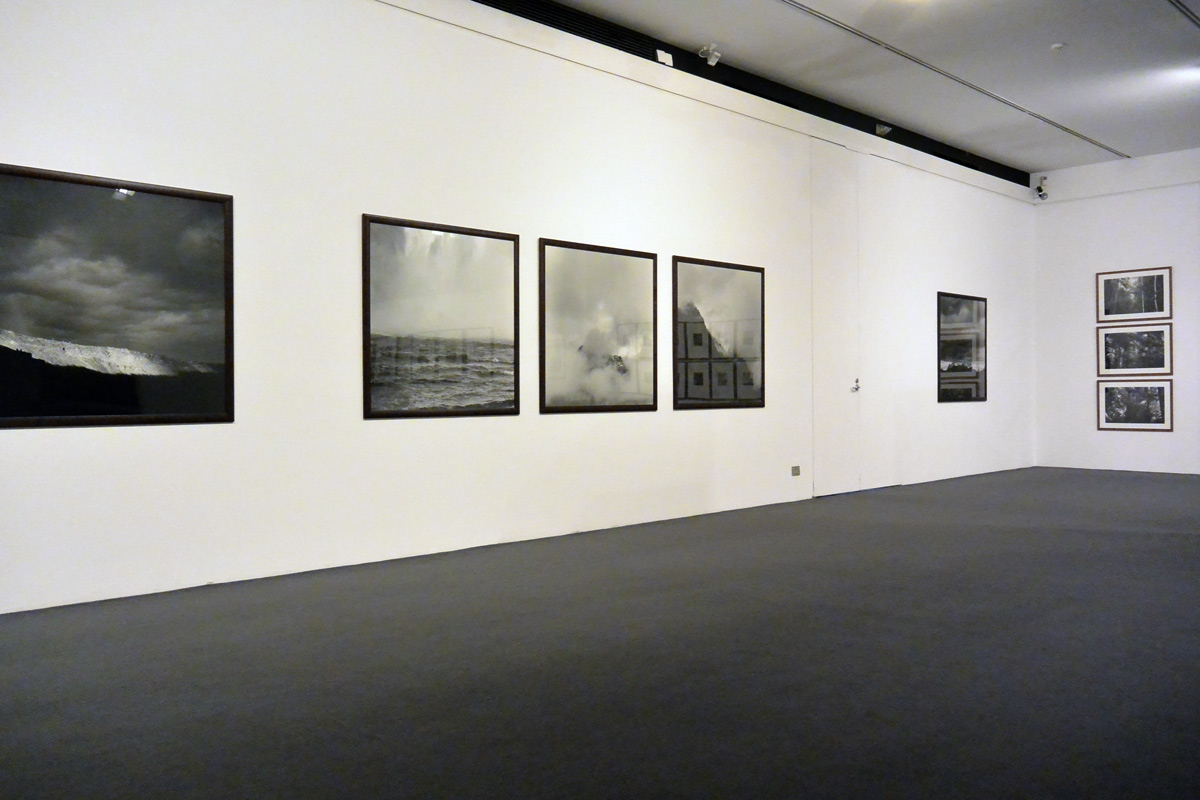
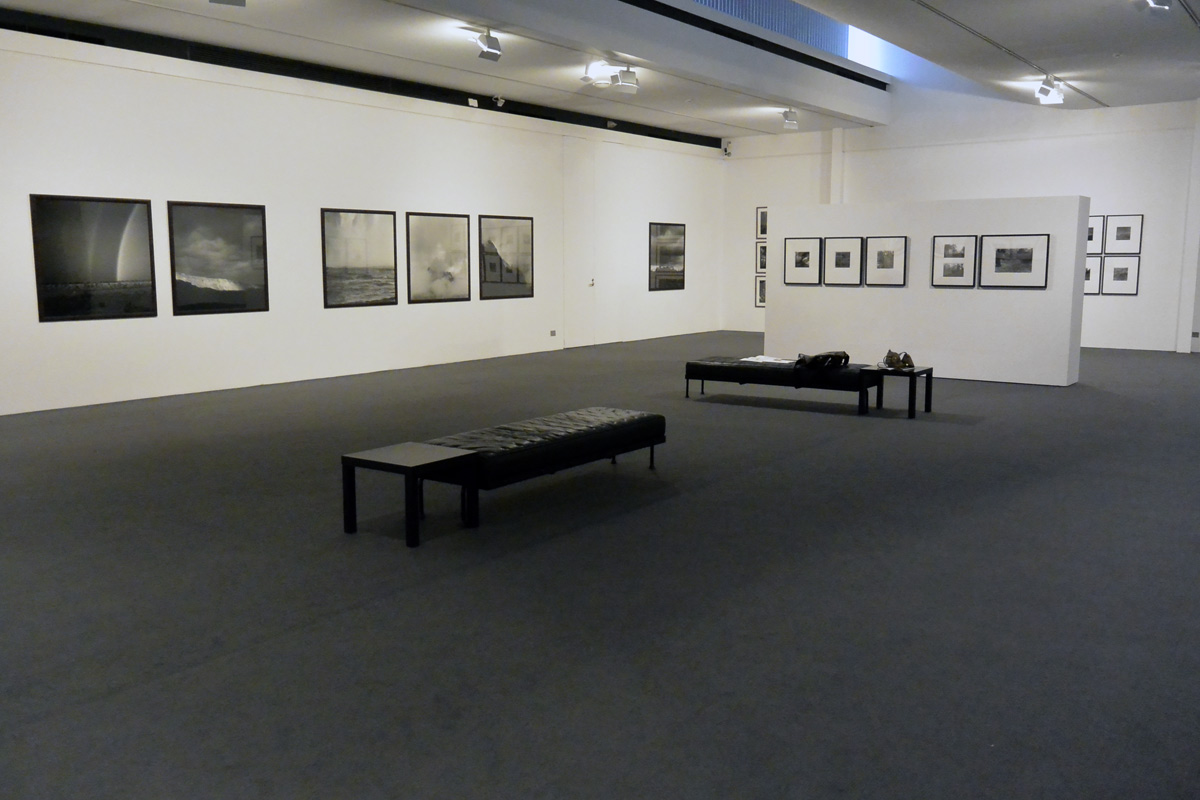
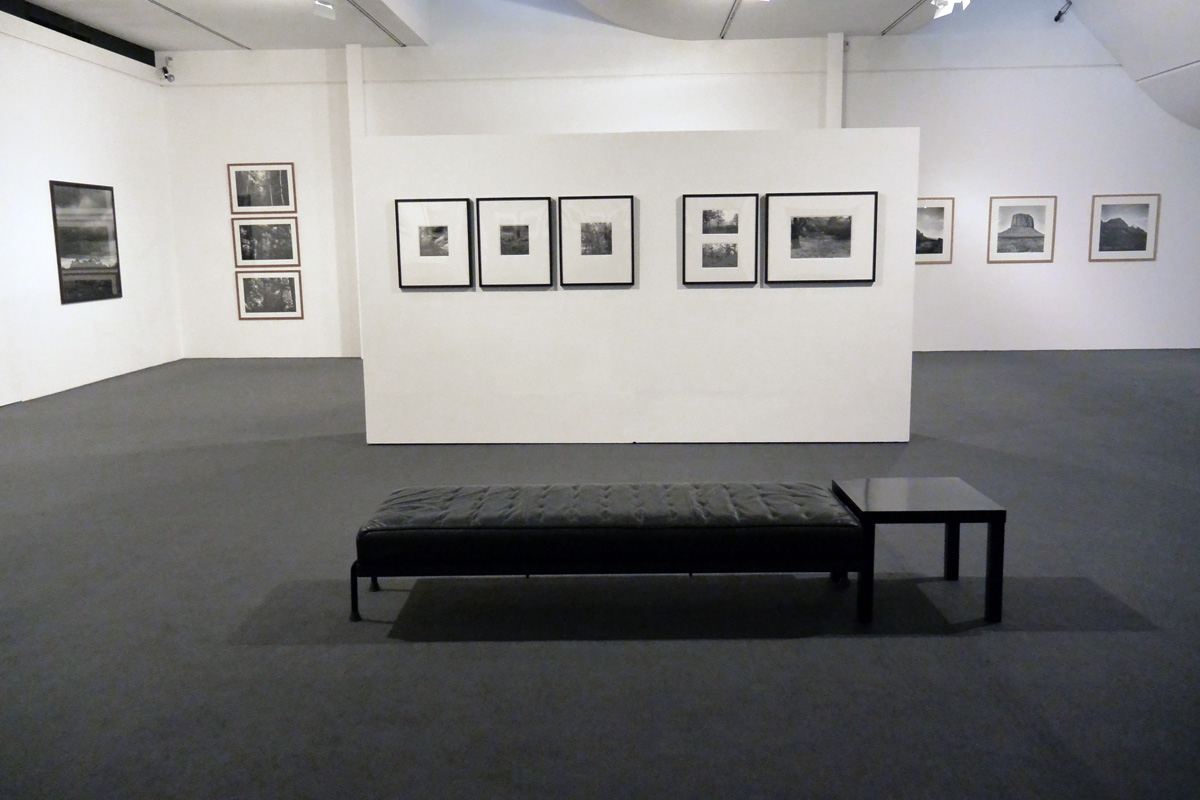
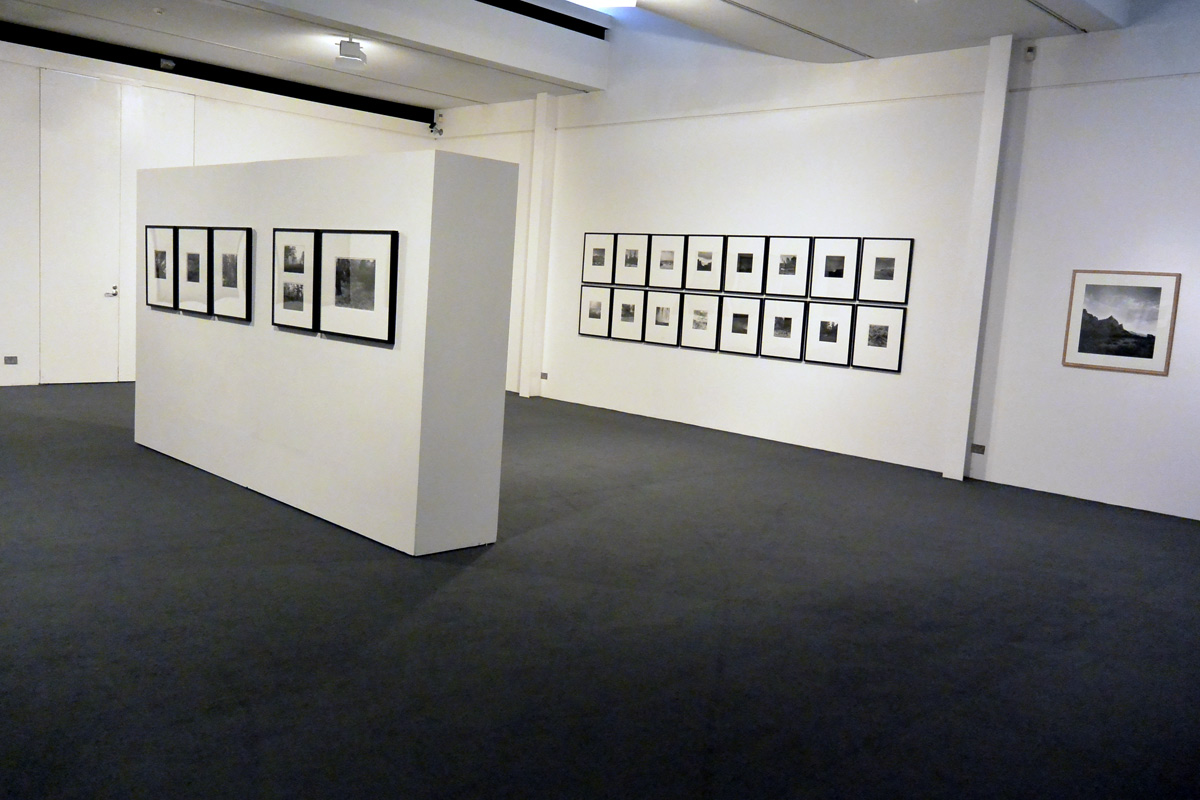
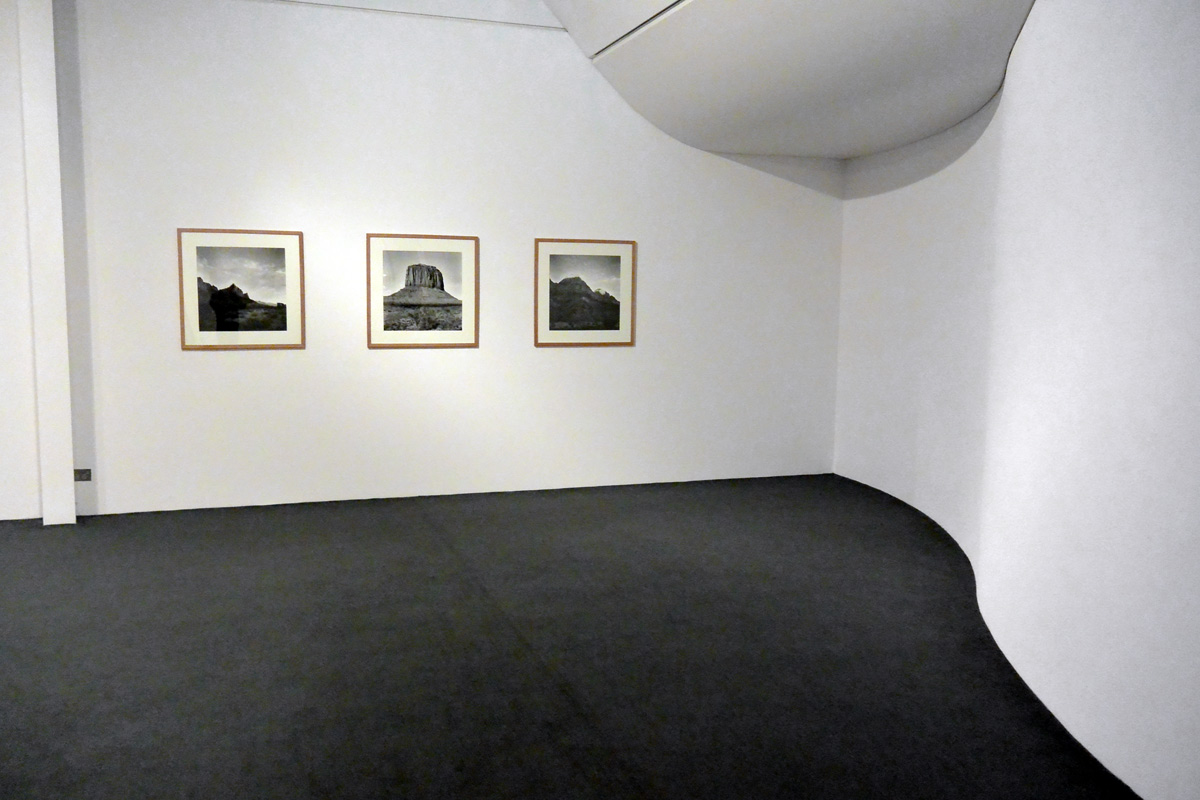
![Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Namandi spirit [Queensland, Australia]' 2002 Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Namandi spirit [Queensland, Australia]' 2002](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/tersappen_namandi_spirit_web.jpg?w=650&h=650)
![Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Cabbage trees [Queensland, Australia]' 2002 Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Cabbage trees [Queensland, Australia]' 2002](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/terstappen_cabbagetrees_web.jpg?w=650&h=650)
![Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Full moon [France]' 1997 Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Full moon [France]' 1997](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/terstappen_fullmoon_france_web.jpg?w=650&h=650)
![Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Mountain [Brazil]' 1991 Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Mountain [Brazil]' 1991](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/terstappen_mountain_brazil_web.jpg?w=650&h=650)
![Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Mountain [Las Palmas, Spain]' 1992 Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Mountain [Las Palmas, Spain]' 1992](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/terstappen_portugal_web.jpg?w=650&h=650)
![Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Zion Park [USA]' 1996 Claudia Terstappen (Australian born Germany, b. 1959) 'Zion Park [USA]' 1996](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/terstappen_zion_park_web.jpg?w=650&h=650)
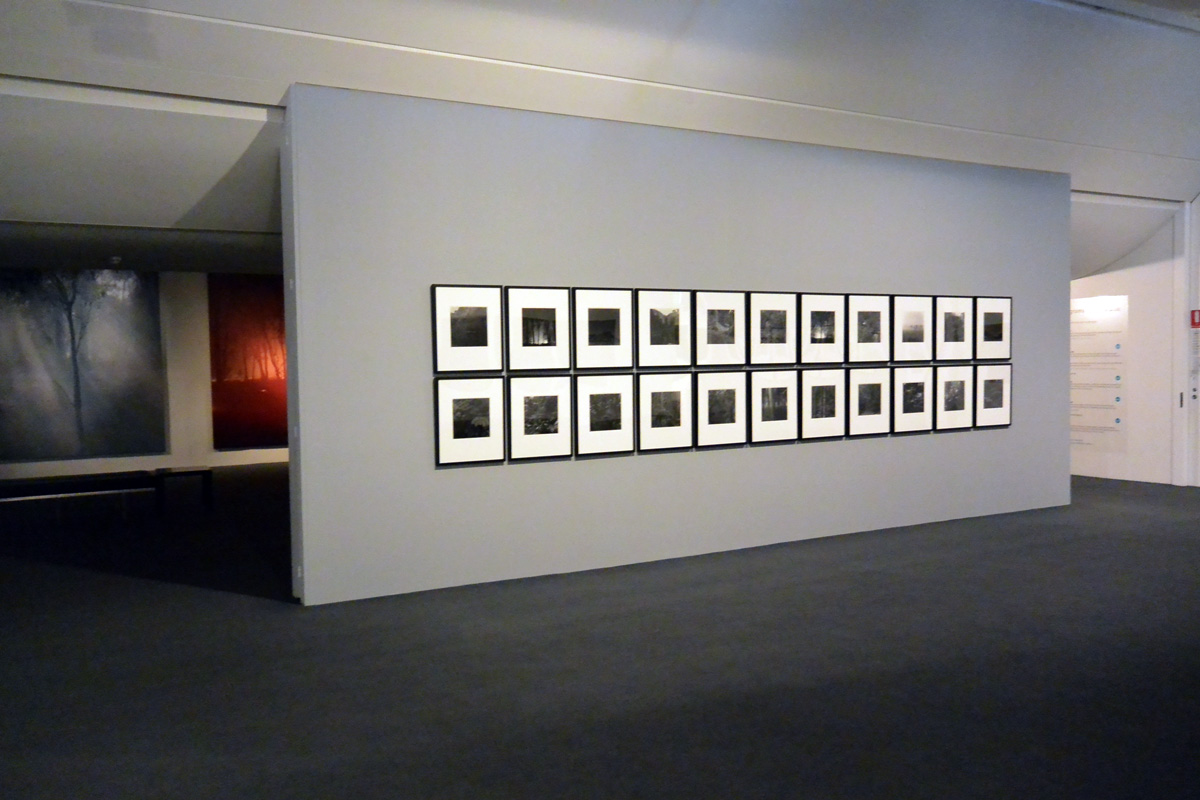
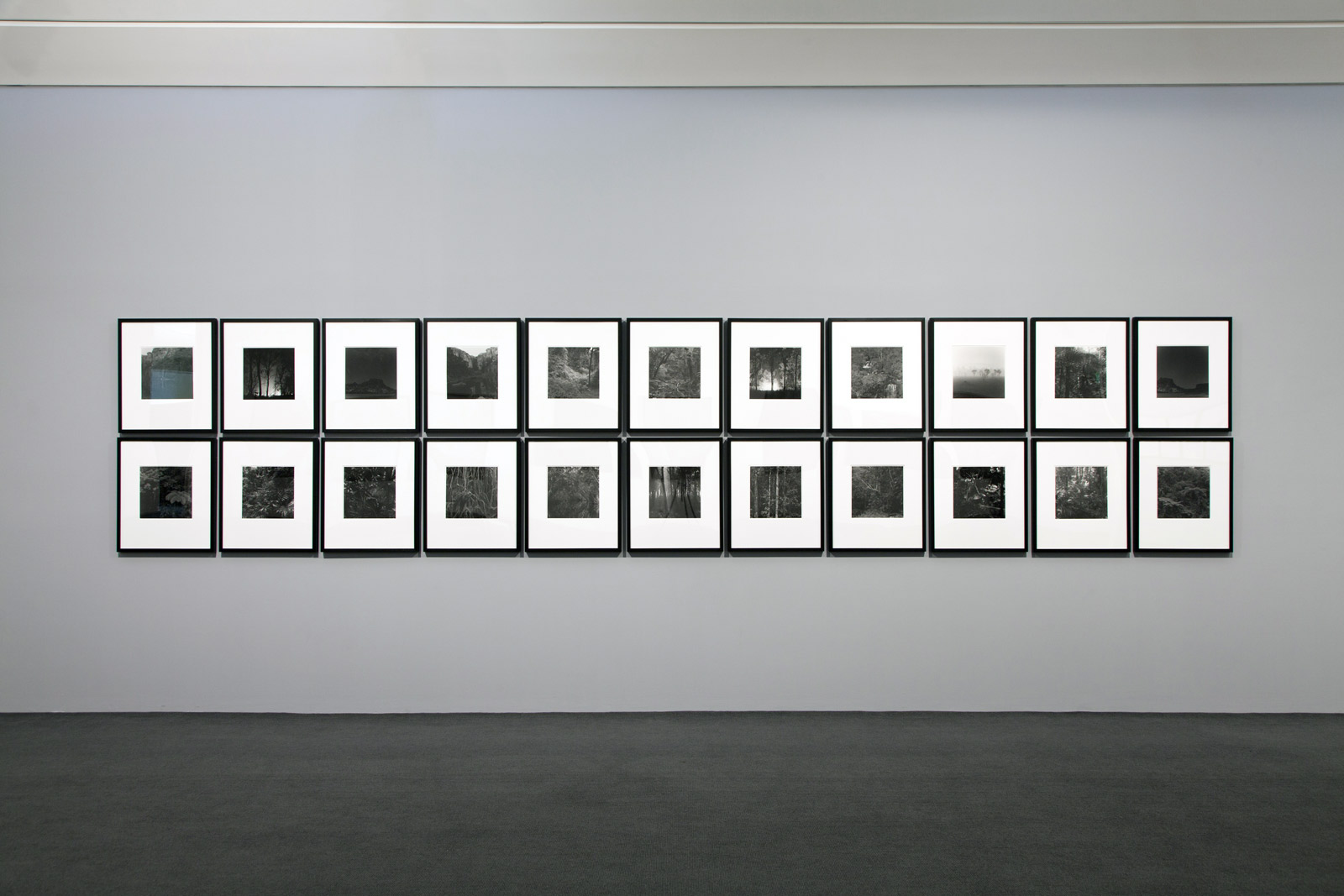
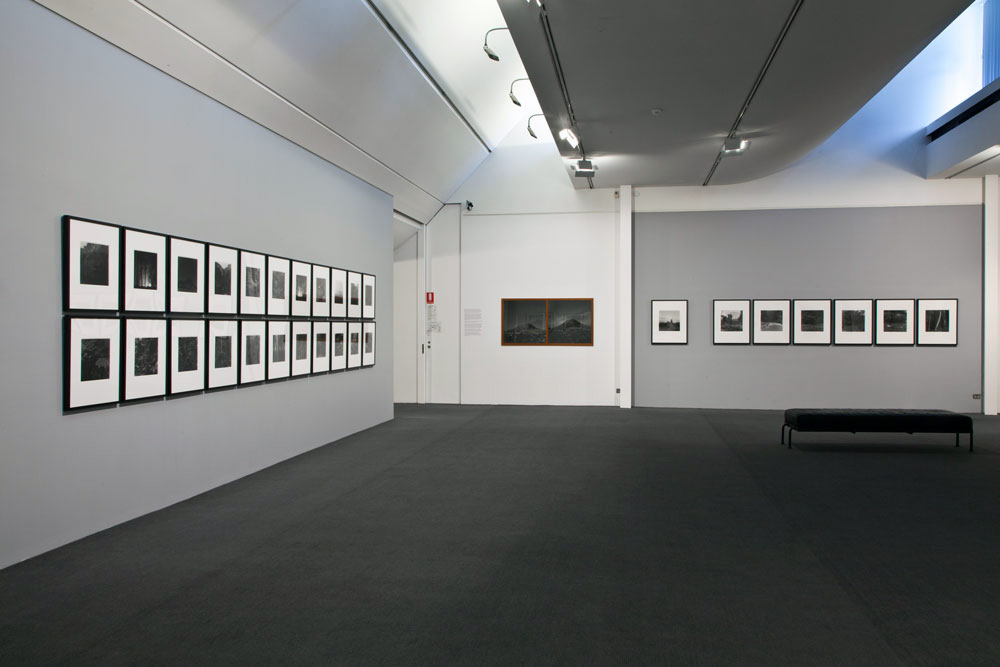
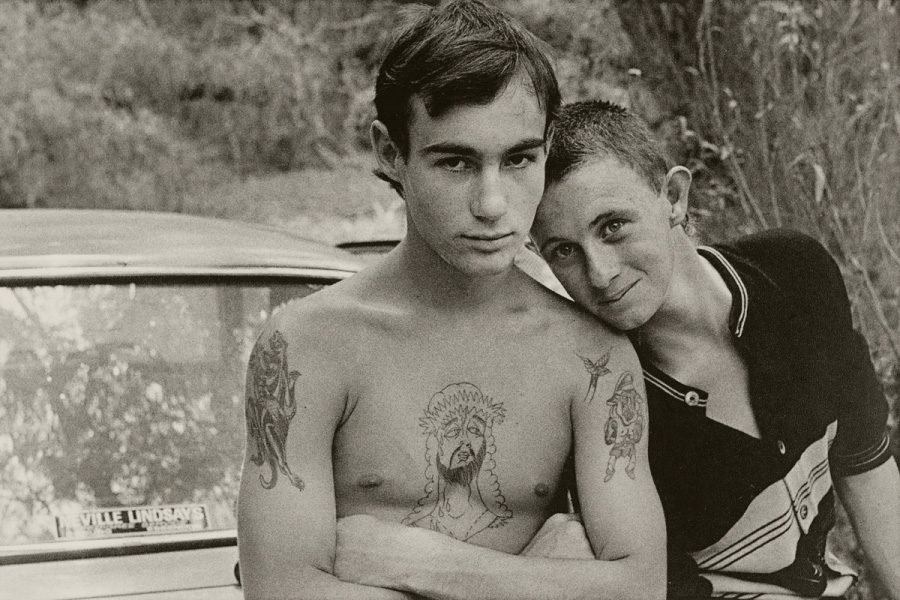
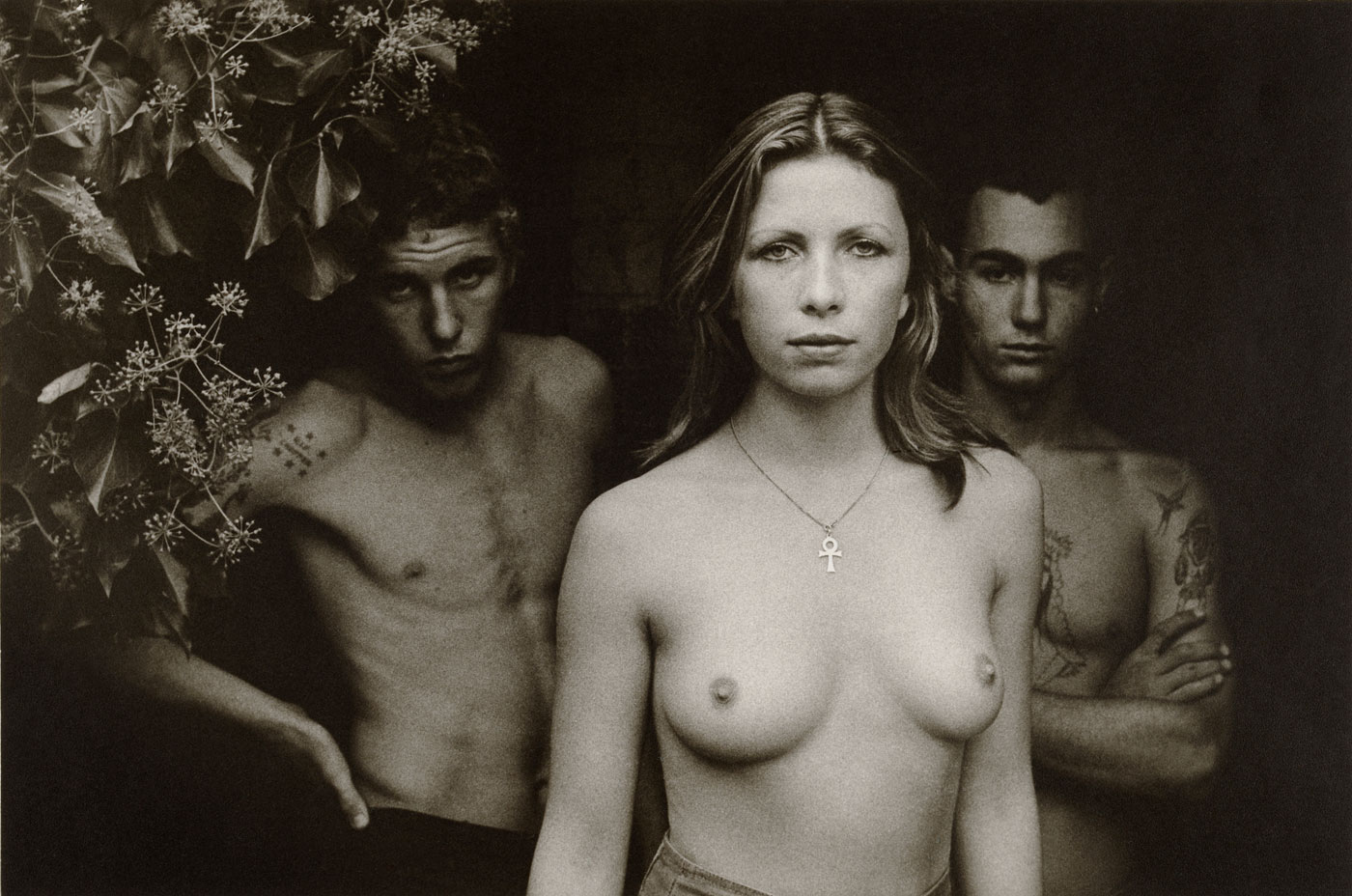
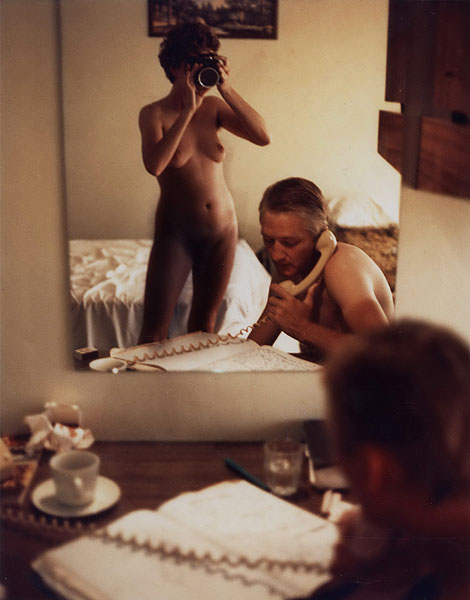
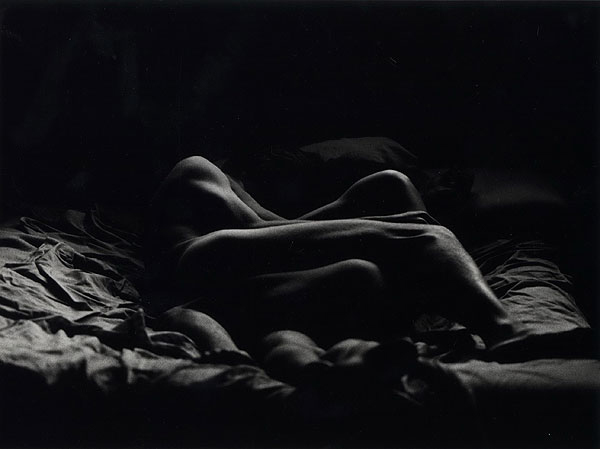
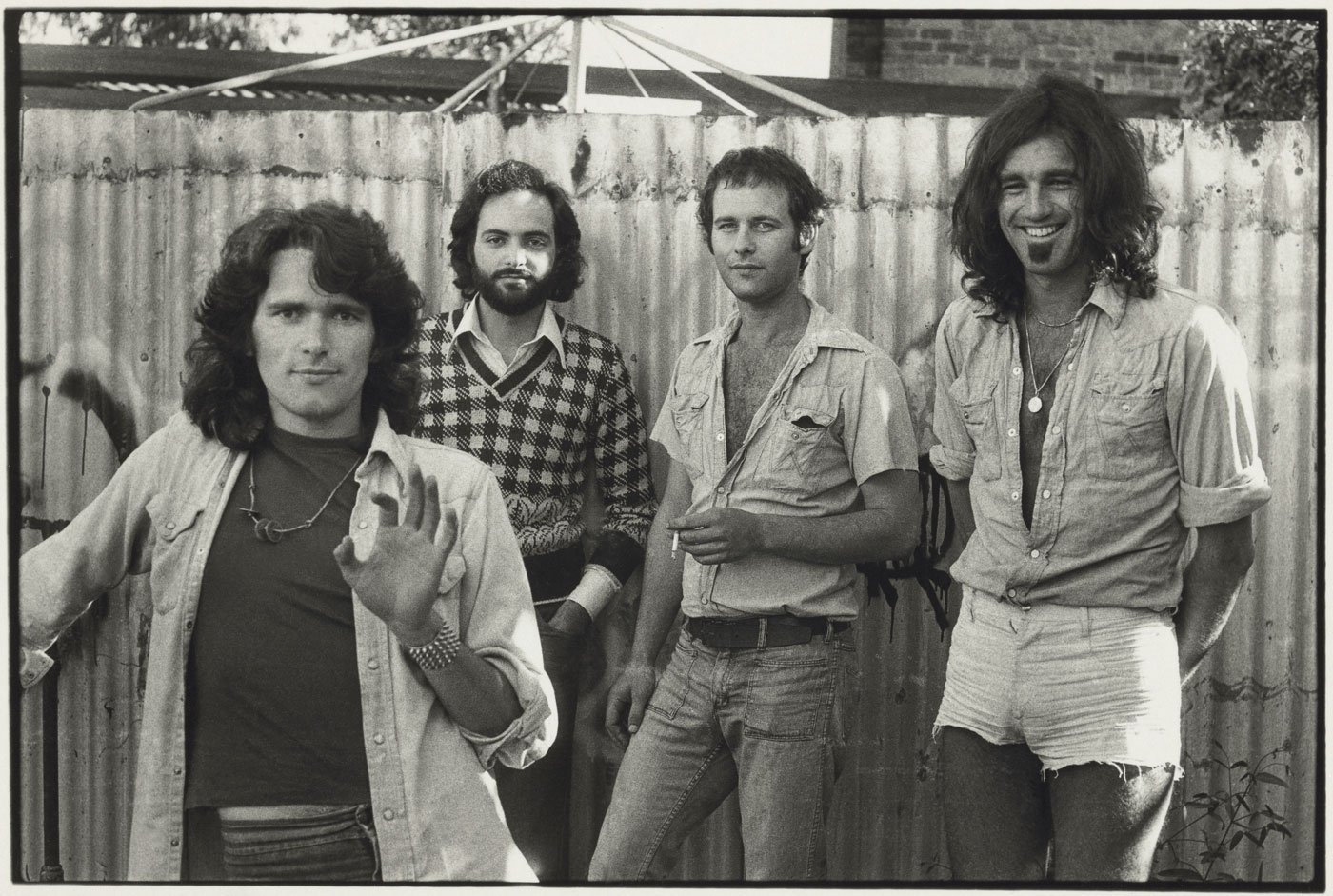
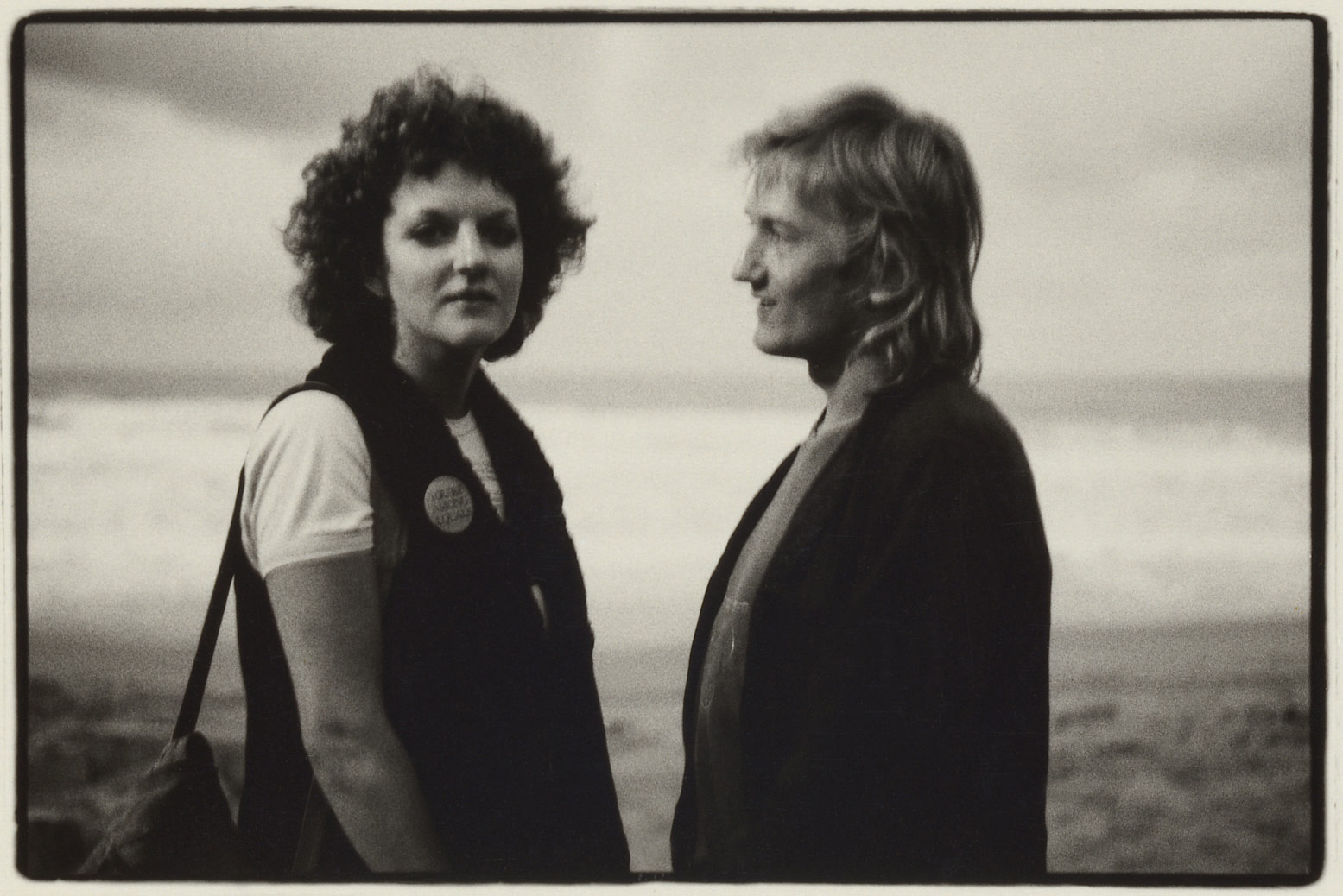







































![Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Butterfly behind glass [Red Symons from Skyhooks]' 1975 Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Butterfly behind glass [Red Symons from Skyhooks]' 1975](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/butterfly_174882_web.jpg)

![Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Performers on stage,' Hair', Metro Theatre Kings Cross, Sydney, January 1970 [Jim Sharman Director cast included Reg Livermore]' 1970 Carol Jerrems (Australian, 1949-1980) 'Performers on stage,' Hair', Metro Theatre Kings Cross, Sydney, January 1970 [Jim Sharman Director cast included Reg Livermore]' 1970](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/jerrems_performers-on-stage-hair-web.jpg?w=650&h=818)
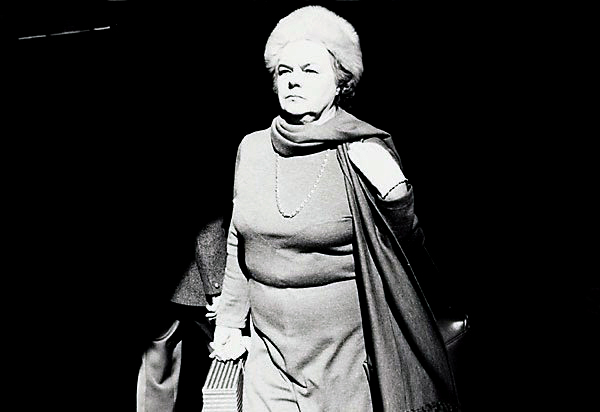
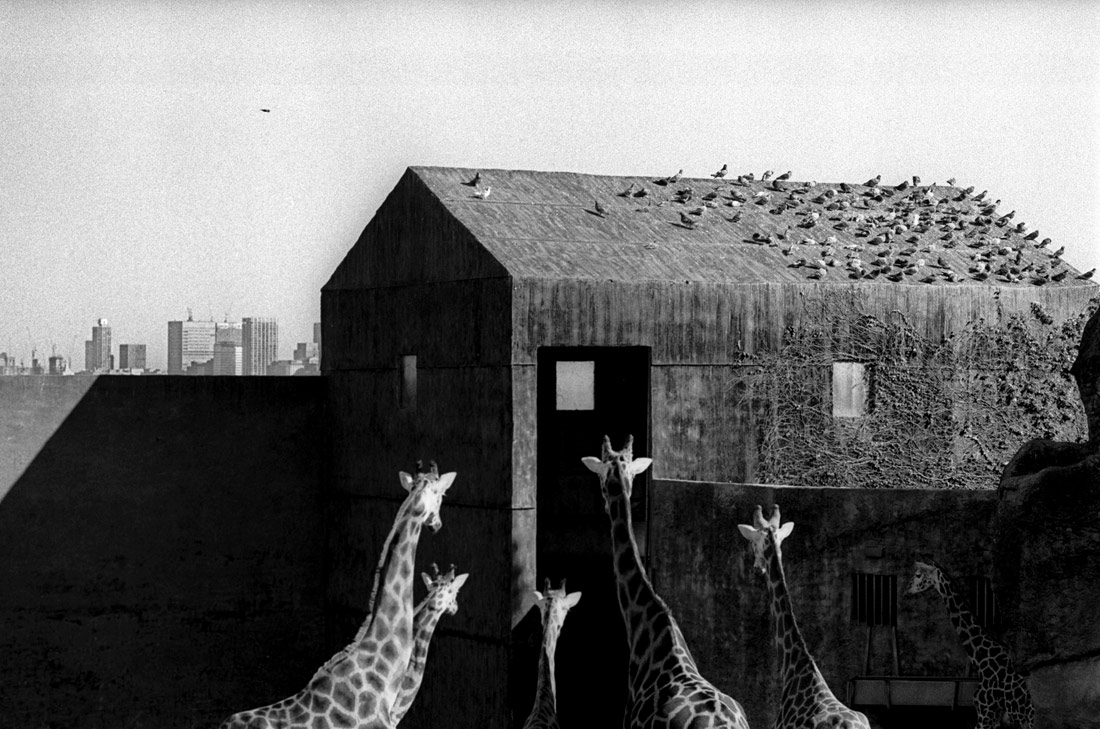

























































![Sue Ford (1943-2009) 'Untitled [Bliss at Yellow House, King's Cross, Sydney]' c. 1972–1973 Sue Ford (1943-2009) 'Untitled [Bliss at Yellow House, King's Cross, Sydney]' c. 1972–1973](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/008.jpg)







You must be logged in to post a comment.