Exhibition dates: 7th January – 2nd July 2023
Curated by Madeleine Schuppli and Yasmin Afschar
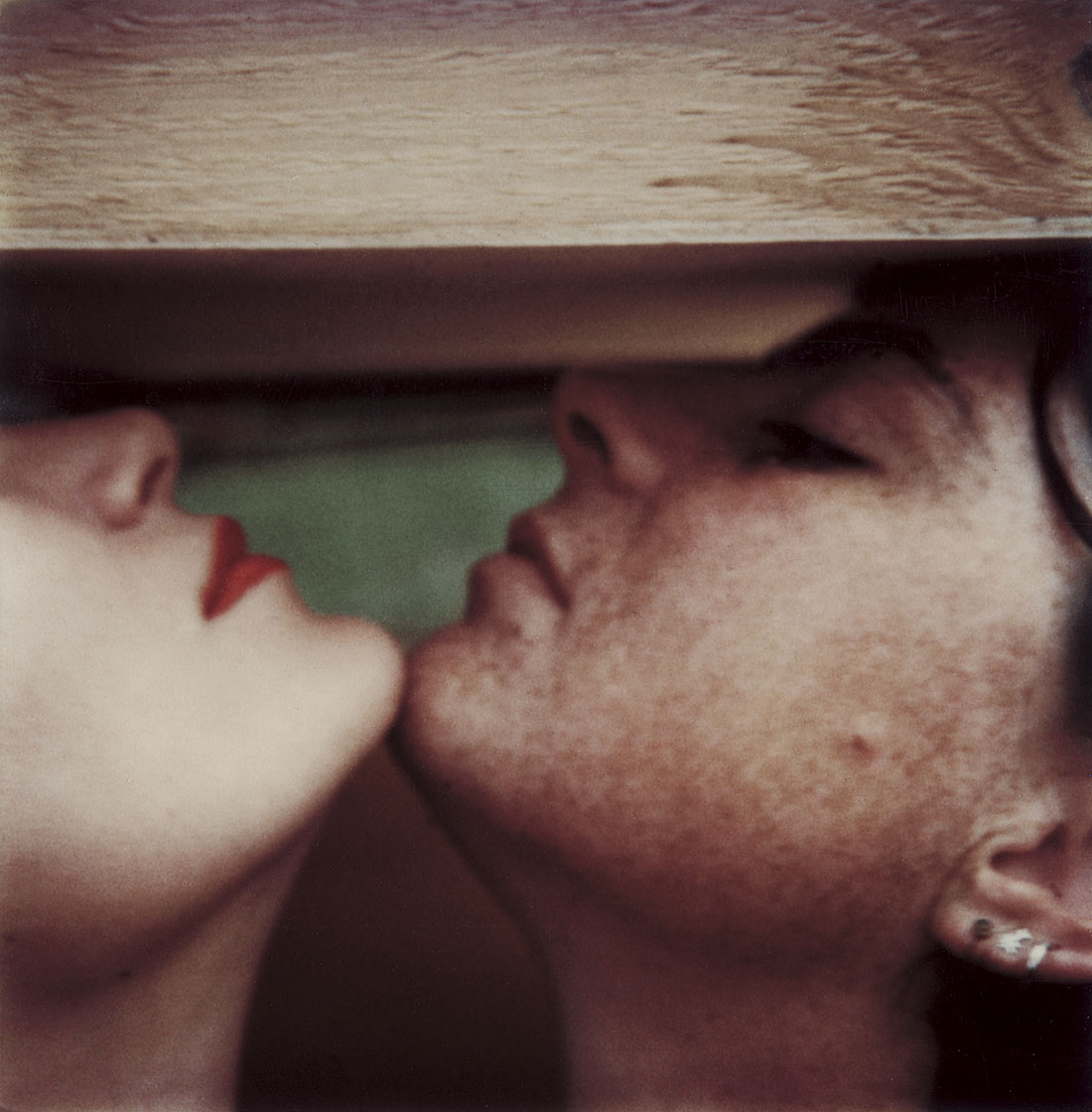

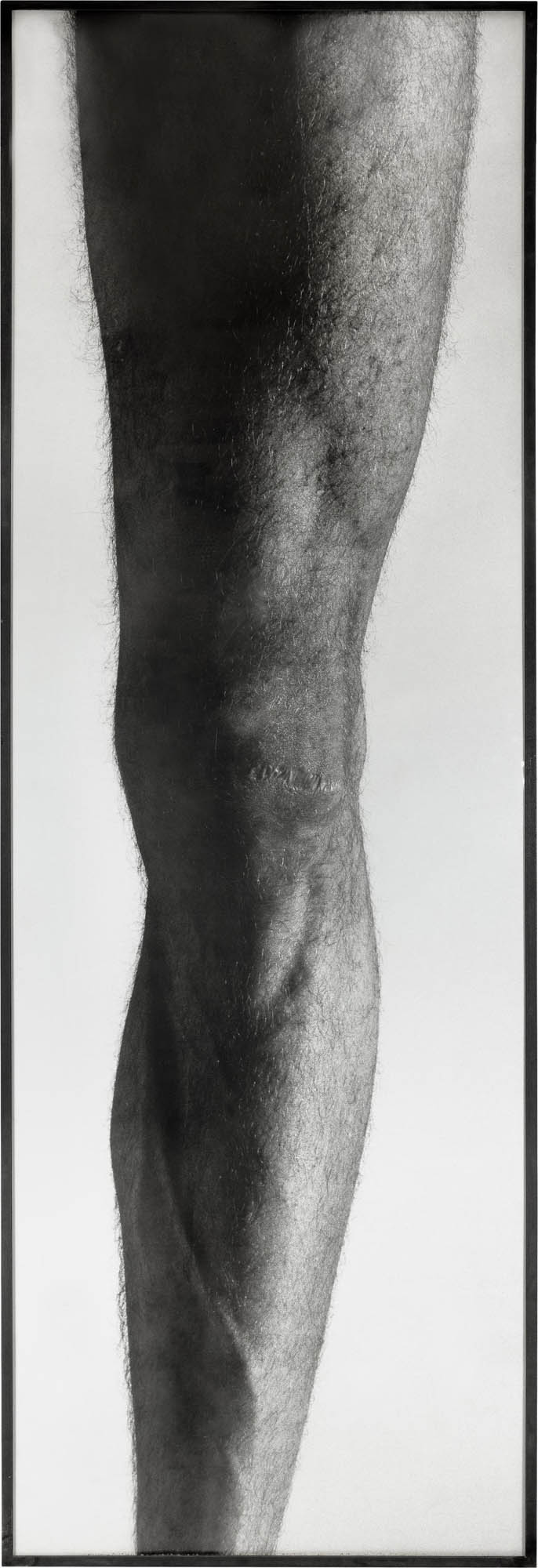
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1980
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
100 x 100cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
who am I who I am
I love artists who push the boundaries of seeing / being, body / Self, self / spirit.
Artists who see and feel the world in unique and tantalising – excites the senses or desires of (someone) – ways.
Hannah Villiger is one such artist.
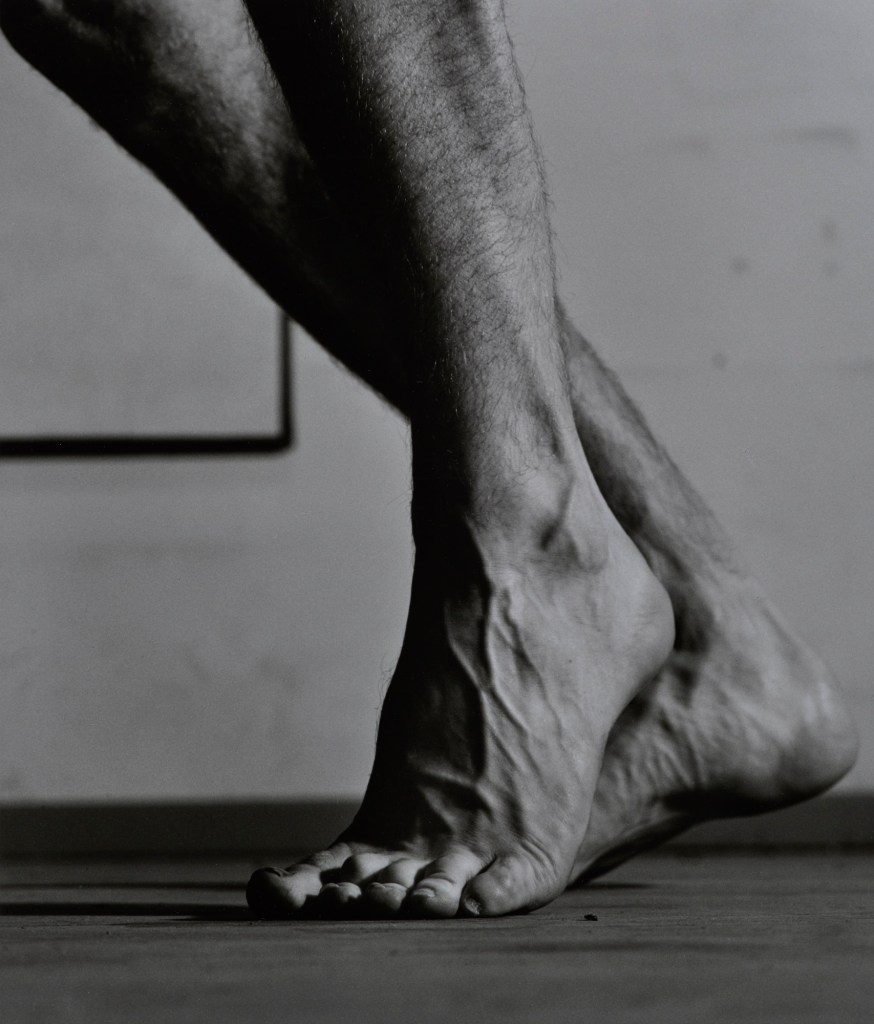
Her fragmentary, space-related assemblages (Works or Blocks) investigate the representation of the female body, “its classification in the media, questions of surface, space and body, and the objectification of the body. In Villiger’s work, the skin – where humans enter a dialogue with their environment – is a setting for highly topical questions of gender and ethnicity, as well as vulnerability and healing. The body was the artist’s primary working material. We encounter it abstracted or deconstructed; it can be human, but also of plant or artificial origin.” (Exhibition text)
But more than that, it is the conceived ‘idea in the mind’ strangeness of Villiger’s out of body gridded experiences… that promote in the viewer an acknowledgement of the physicality, touch, and emotion of actually living and feeling in the human body and beyond. Touch your skin, run your hands over the shape of your mouth, feel your ears, raise your foot, look at your reflection. Marvel at the bodies distortion, energy, spirit. For there is only one you. “I listen to my naked, bare body, the outside of it, the inside of it, traversing it.”
You are unique. An individual, unique, sentient animal. A human – being.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to Museum Susch for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“With my Polaroid camera I listen to my naked, bare body, the outside of it, the inside of it, traversing it. Thus I create images that I can correct immediately.”
Hannah Villiger
“The longest distance between the camera and any body part is between raised arm and my toes. I always trigger the camera myself, sometimes without looking through the viewfinder. I tilt the camera to an angle of 90, 180, 270 degrees. I turn myself – literally – upside down.”
Hannah Villiger. On My Book Envy
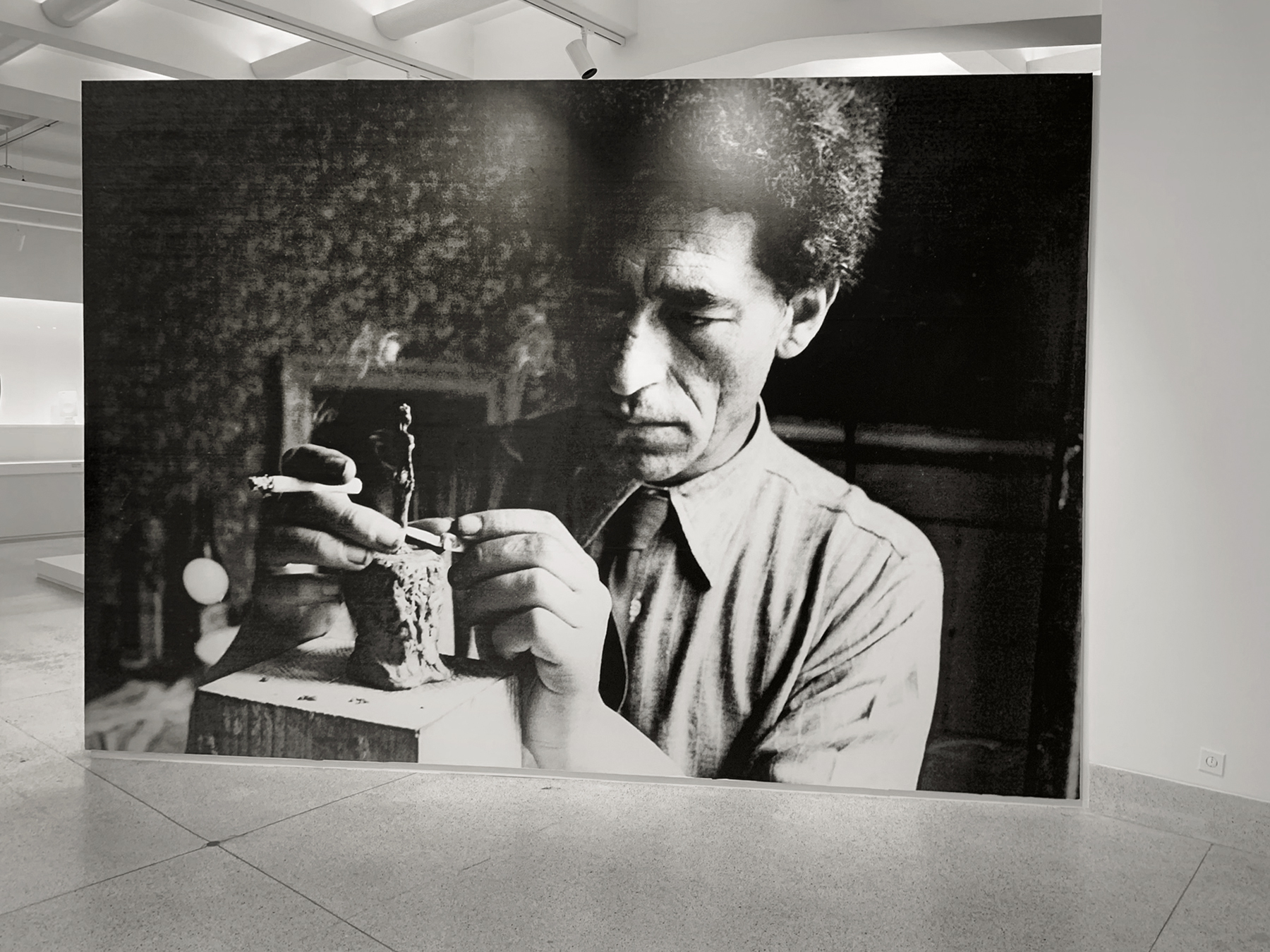
Hannah Villiger (1951-1997) was an extraordinary voice in the late 20th-century contemporary art, but her work came to an abrupt end with her untimely death. She became known above all for her photographic works based on the body.
Muzeum Susch is hosting the largest presentation of Hannah Villiger’s oeuvre in fifteen years. Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me offers new perspectives on the work of this important Swiss artist. Villiger’s large-format works based on Polaroid photographs make a lasting contribution to the genre of the self-image within art history. At the same time, her explorations of the body can be discussed against the background of numerous contemporary themes. Her oeuvre spans from the drawings she made in the 1970s to the black-and-white photographs and works with the Polaroid camera that she created from the 1980s onwards. These fragmentary close-ups of her own body, greatly enlarged via an internegative and mounted on aluminium, are presented individually or assembled into space-related ensembles. The results are unlimited possibilities of at times spectacular views of the body. The exhibition expands the view of Villiger to include contemporary themes and issues. The focus is on the representation of the female body, one’s own perspective, as well as that of others, on the human physique, its classification in the media, questions of surface, space and body, and the objectification of the body. In Villiger’s work, the skin – where humans enter a dialogue with their environment – is a setting for highly topical questions of gender and ethnicity, as well as vulnerability and healing. The body was the artist’s primary working material. We encounter it abstracted or deconstructed; it can be human, but also of plant or artificial origin. Although Villiger’s early death brought her oeuvre to an abrupt end, her works point unwaveringly to the present.
Text from the Museum Susch website
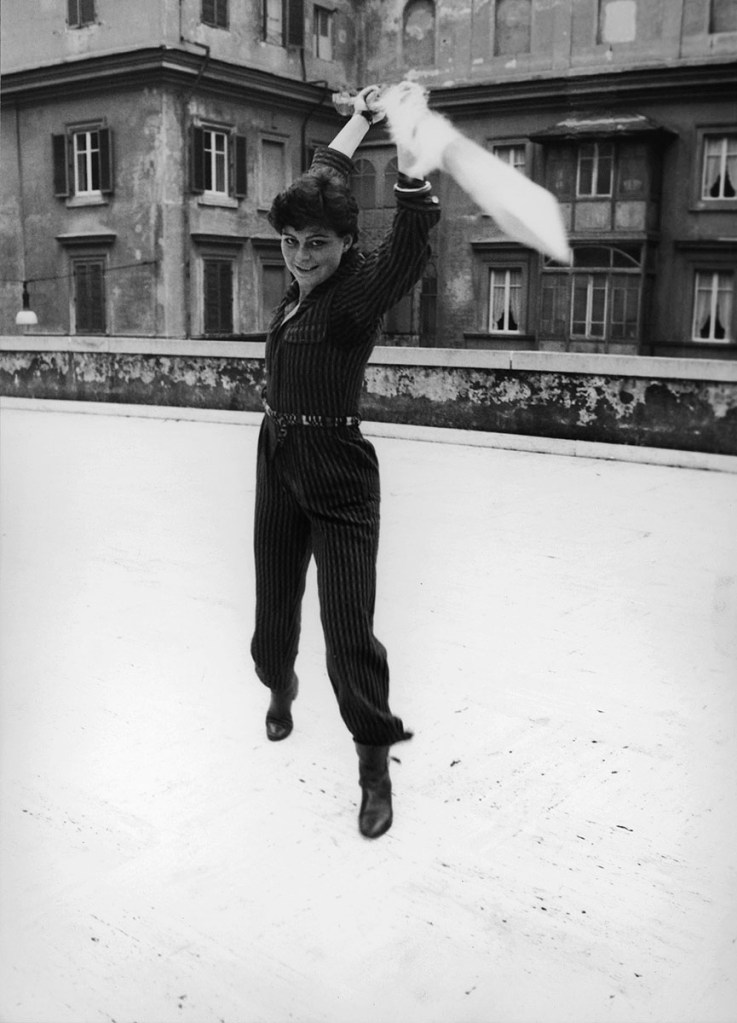

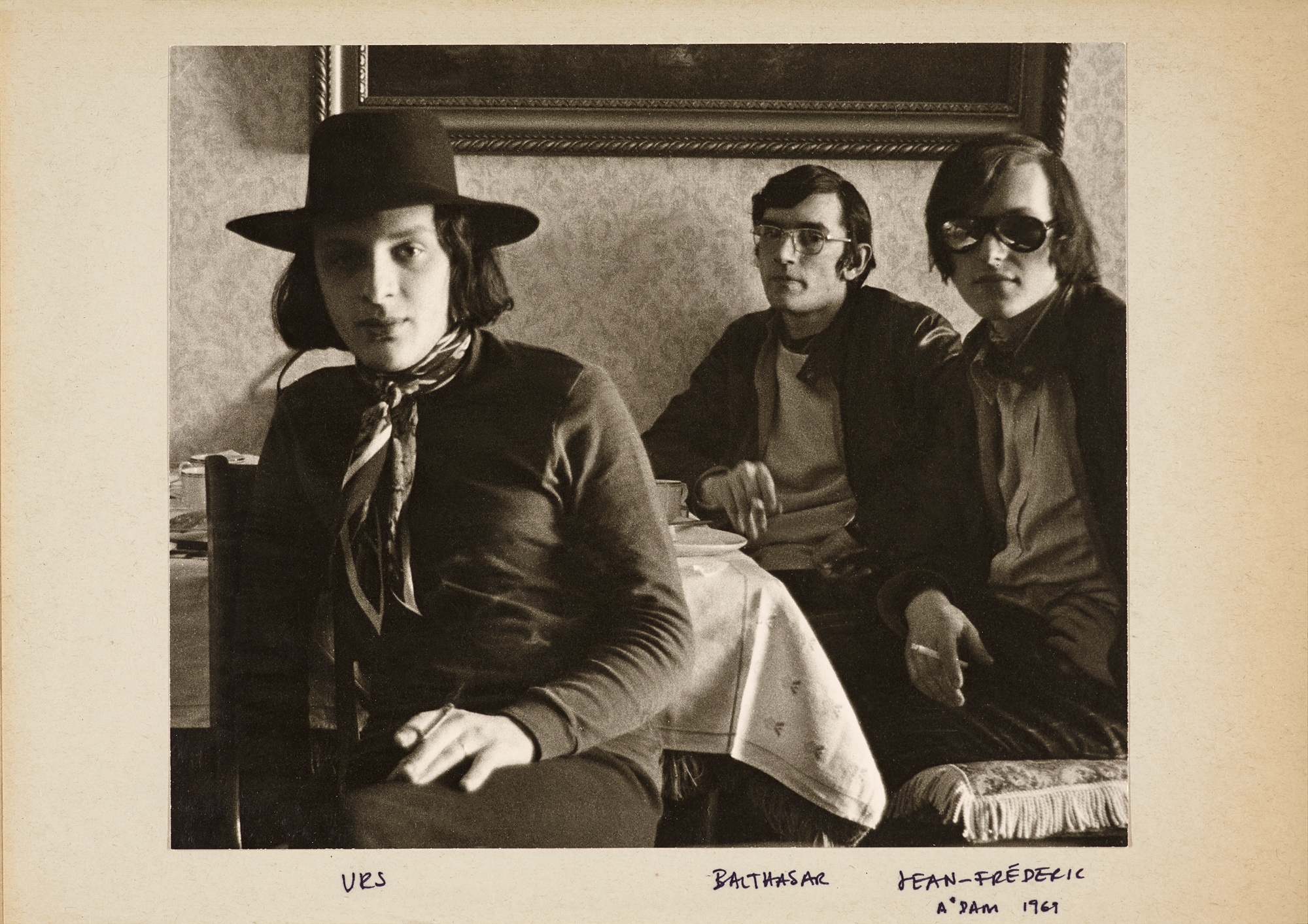
Trix Wetter
Portrait of Hannah Villiger
1976, Rome
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger

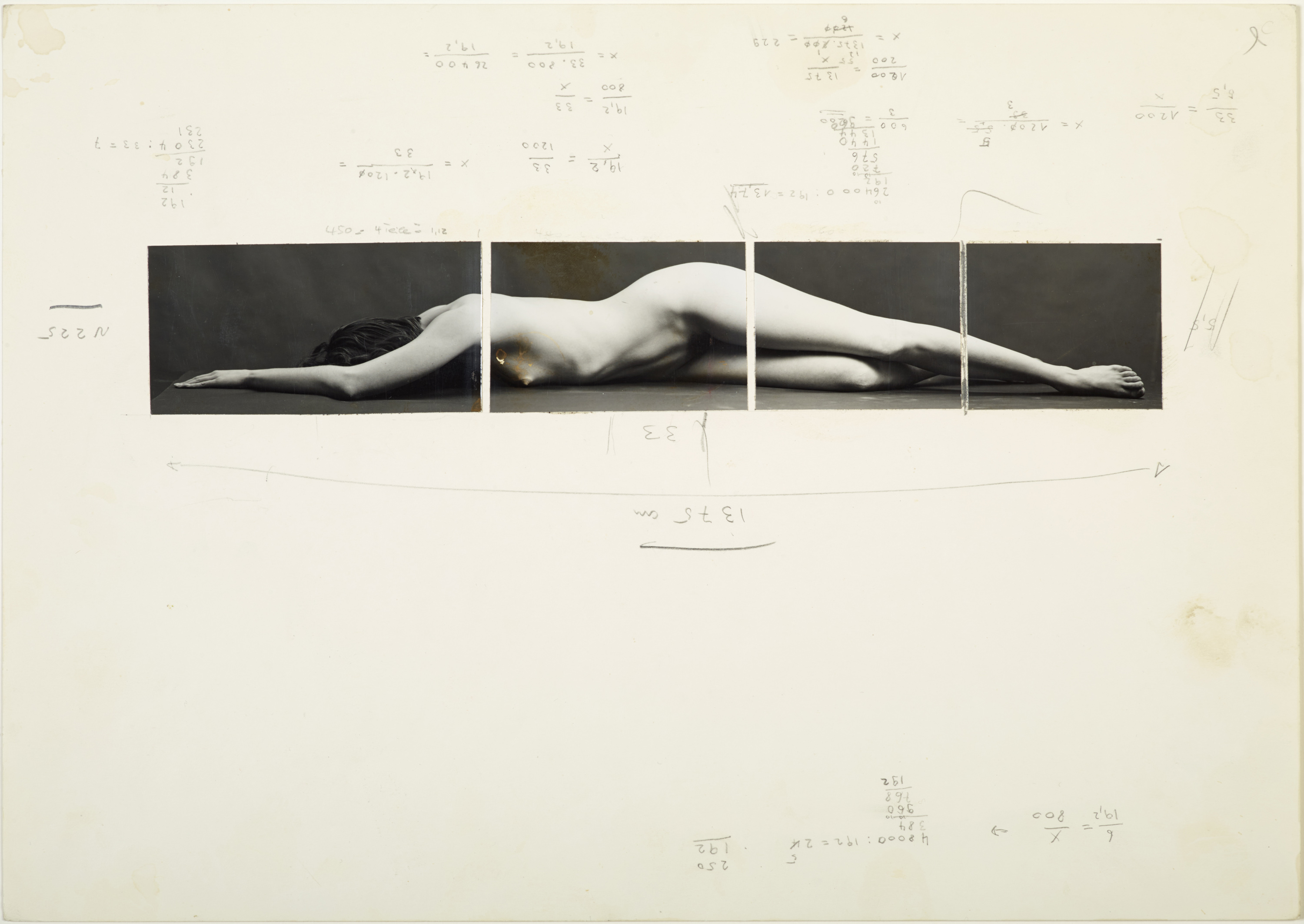
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1976
Four black and white photographs
61 x 51cm / 40.5 x 33.5cm each
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
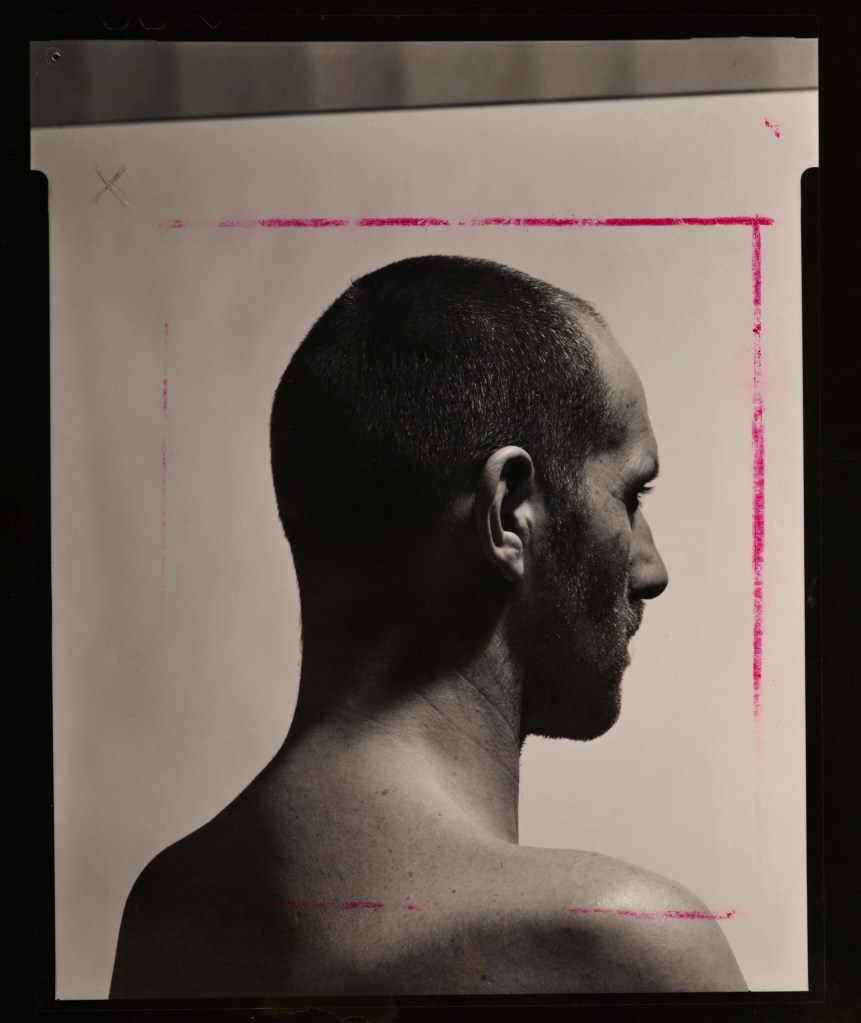
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1976
black and white photograph
70 x 100cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1976
68 x 97cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1980
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
99.5 x 99.5cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
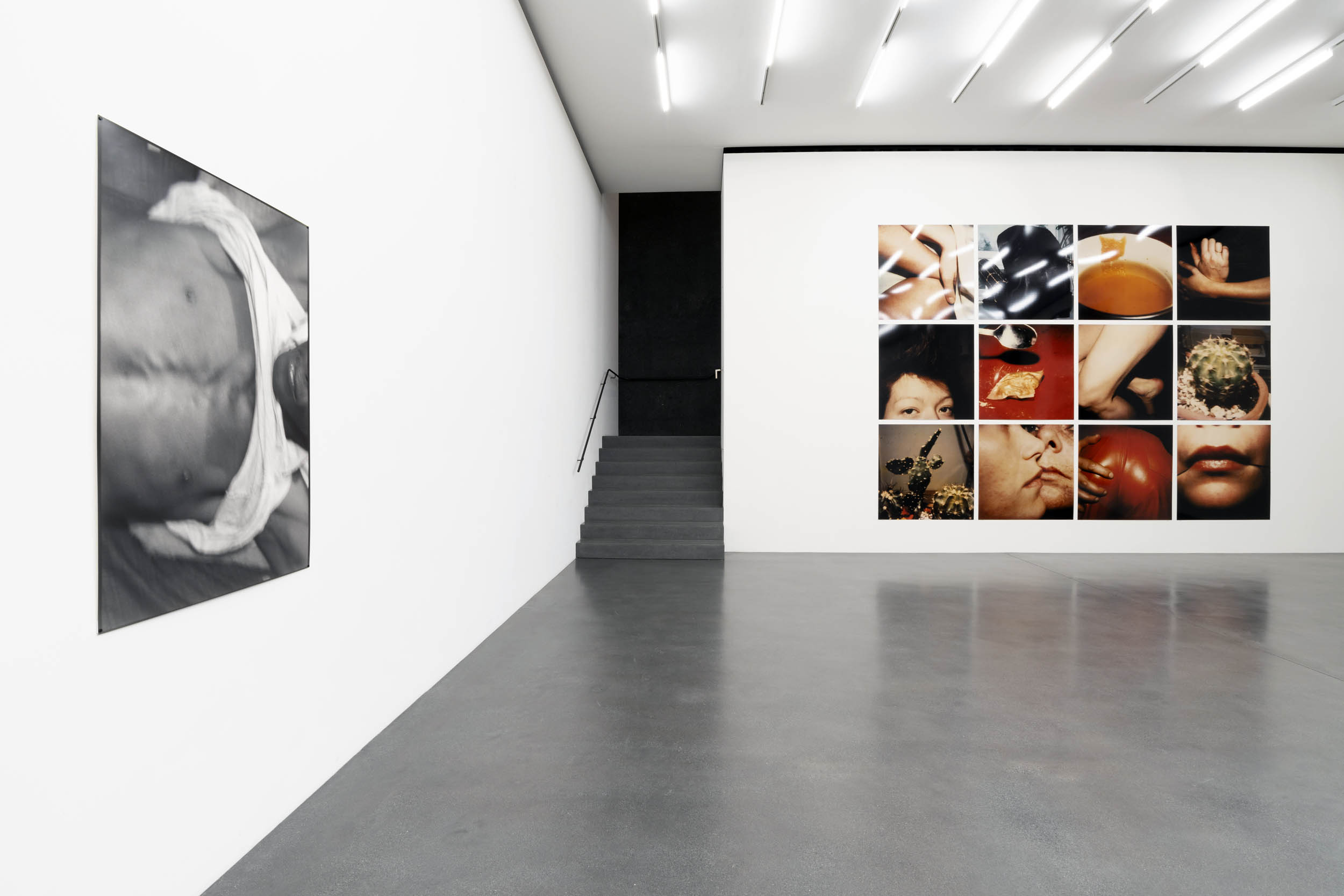
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left Hannah Villager’s Block (1997); and at right, Work (1980-1981, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
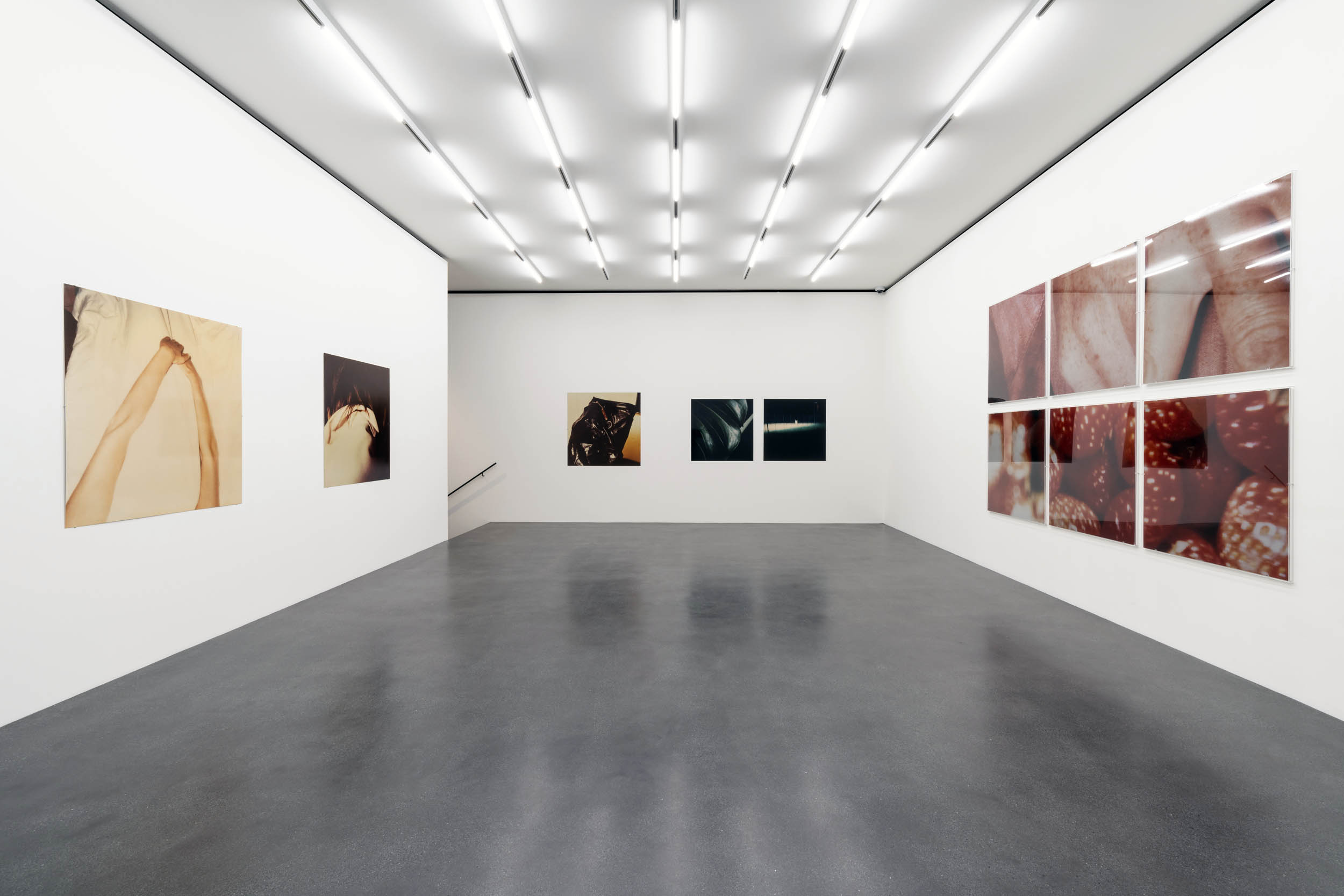
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left Hannah Villiger’s Work (1987, below); and at right, Work (1980-1981, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1987
Black and white photograph
127.5 x 86.5cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
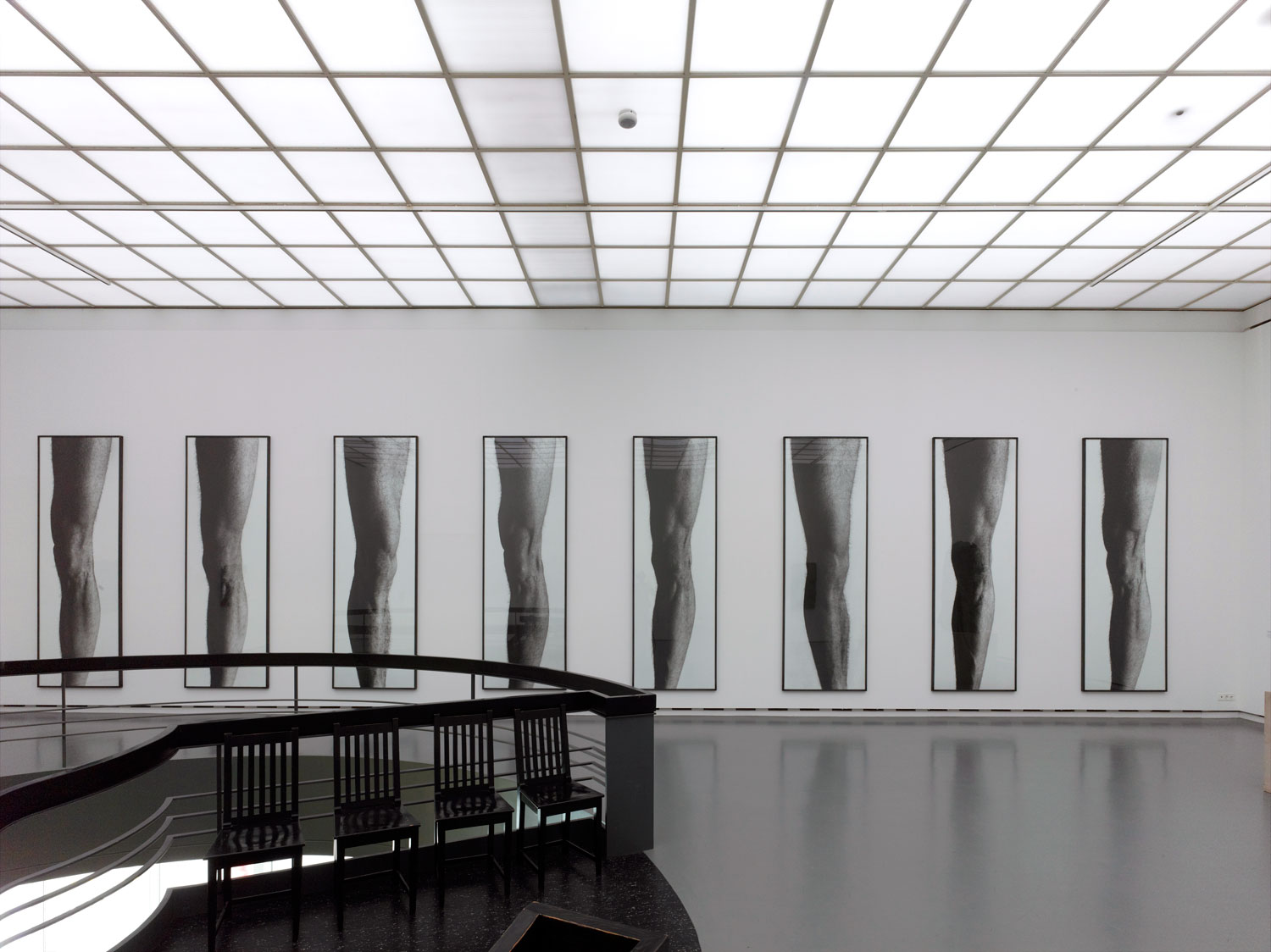
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1980-1981
C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium (12 pieces)
355 x 475cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left Hannah Villiger’s Work (1981, below); and at right, Work (1982, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1981
Two C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
Each 38 x 38cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Running from 4 January to 2 July 2023, Muzeum Susch presents Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me, a comprehensive survey dedicated to the Swiss artist Hannah Villiger (1951-1997) with contributions from contemporary artists Alexandra Bachzetsis, Lou Masduraud (b. 1990) and Manon Wertenbroek (b. 1991).
The exhibition Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me offers new perspectives on the work of this important Swiss artist. Hannah Villiger’s (1951-1997) large-format works based on Polaroid photographs make a lasting contribution to the genre of the self-image within art history. At the same time, her explorations of the body can be discussed against the background of numerous contemporary themes.
Muzeum Susch is hosting the largest presentation of Hannah Villiger’s work in fifteen years. The exhibition spans her oeuvre, from the drawings she made in the 1970s to the black-and-white photographs and works with the Polaroid camera that she created from the 1980s onwards. These fragmentary close-ups of her own body, greatly enlarged via an internegative and mounted on aluminium, are presented individually or assembled into space-related ensembles. The results are unlimited possibilities of at times spectacular views of the body. On display are vintage prints, existing though often still unknown individual works, as well as so-called blocks, large-format assemblages of up to fifteen square picture panels. Some of these will be shown for the first time in the exhibition in Susch.
The exhibition expands the view of Villiger to include contemporary themes and issues. The focus is on the representation of the female body, one’s own perspective, as well as that of others, on the human physique, its classification in the media, questions of surface, space and body, and the objectification of the body. In Villiger’s work, the skin – where humans enter a dialogue with their environment – is a setting for highly topical questions of gender and ethnicity, as well as vulnerability and healing. The body was the artist’s primary working material. We encounter it abstracted or deconstructed; it can be human, but also of plant or artificial origin. Although Villiger’s early death brought her oeuvre to an abrupt end, her works point unwaveringly to the present.
The undiminished relevance of Villiger’s work is underscored by the inclusion of works by the contemporary artists Alexandra Bachzetsis, Lou Masduraud and Manon Wertenbroek. These younger women artists present thematically related works – distributed throughout the entire exhibition – in dialogue with Villiger and at the same time represent strong contemporary positions. The artists have been selected based on their exploration of similar themes to those of Villiger. Bachzetsis in collaboration with Julia Born presents This Side Up, a video installation of the artist moving in all directions in a confined space, much like the way Villiger writhes, turns and shapes her own body under the eye of her Polaroid camera. Masduraud presents Petrifying basin (kisses with the nymphs), a sculptural installation and small wall objects that playfully and sensually rethink organic life and anchors mythological traditions in the present day. And finally, Wertenbroek presents a selection of objects addressing the boundaries between the skin and surrounding world and reflects on themes such as unveiling and veiling.
On the exhibition and Hannah Villiger, Muzeum Susch’s found Grazyna Kulczyk says, “Female artists are no longer afraid to document their bodies being destructed due to illness or ageing – often the artworks become projects showing chronicles of pain. Observing and recording their own bodies has become a form of manifesto for female artists, reclaiming the subjectivity of the body. Female artists have painted, photographed and sculpted themselves. In this way, the shame of nakedness or imperfection has often become a point of pride. Hannah Villiger, through photographs of her body, become the body’s conscious sculptor.”
The exhibition is accompanied by a monograph on the latest research on Hannah Villiger’s practice and influence. Villiger is often likened to an artist’s artist, which has inspired the editors to invite artists who knew her to contribute texts, including Katja Schenker, Beat Streuli, and Claudia and Julia Müller. The book, part of a series of monographs by Muzeum Susch and Skira, will be published in March 2023.
Hannah Villiger (1951-1997) grew up as the fourth of five children in Cham (CH). After completing her studies at the School of Applied Arts in Lucerne, Villiger spent a period travelling and living between Toronto, Rome, Montefalco and Switzerland until she finally settled in Basel in 1977. In Basel, she produced her first black-and-white photographs as well as wood and Plexiglas objects. In 1980 Villiger fell ill with open tuberculosis and spent a month isolated in the Basel Cantonal Hospital, followed by a stay in a sanatorium in Davos. Despite her poor health, Villiger continued to create and exhibit her work. From 1981 to 1982 she undertook a world road-trip with Susan Wyss, with whom she had been in a relationship since 1975. In the early 1980s, Villiger began to use Polaroid cameras primarily to explore her body, serving as a working material, and increasingly moved away from the classic black-and-white and colour photographs. In 1988 in Paris, she met Mouhamadou Mansour (“Joe”) Kébé, with whom she had a son with in 1991. Between 1992 and 1997, Villiger taught at the Basel School of Art and Design. She died of heart failure in 1997.
Text from the Museum Susch website
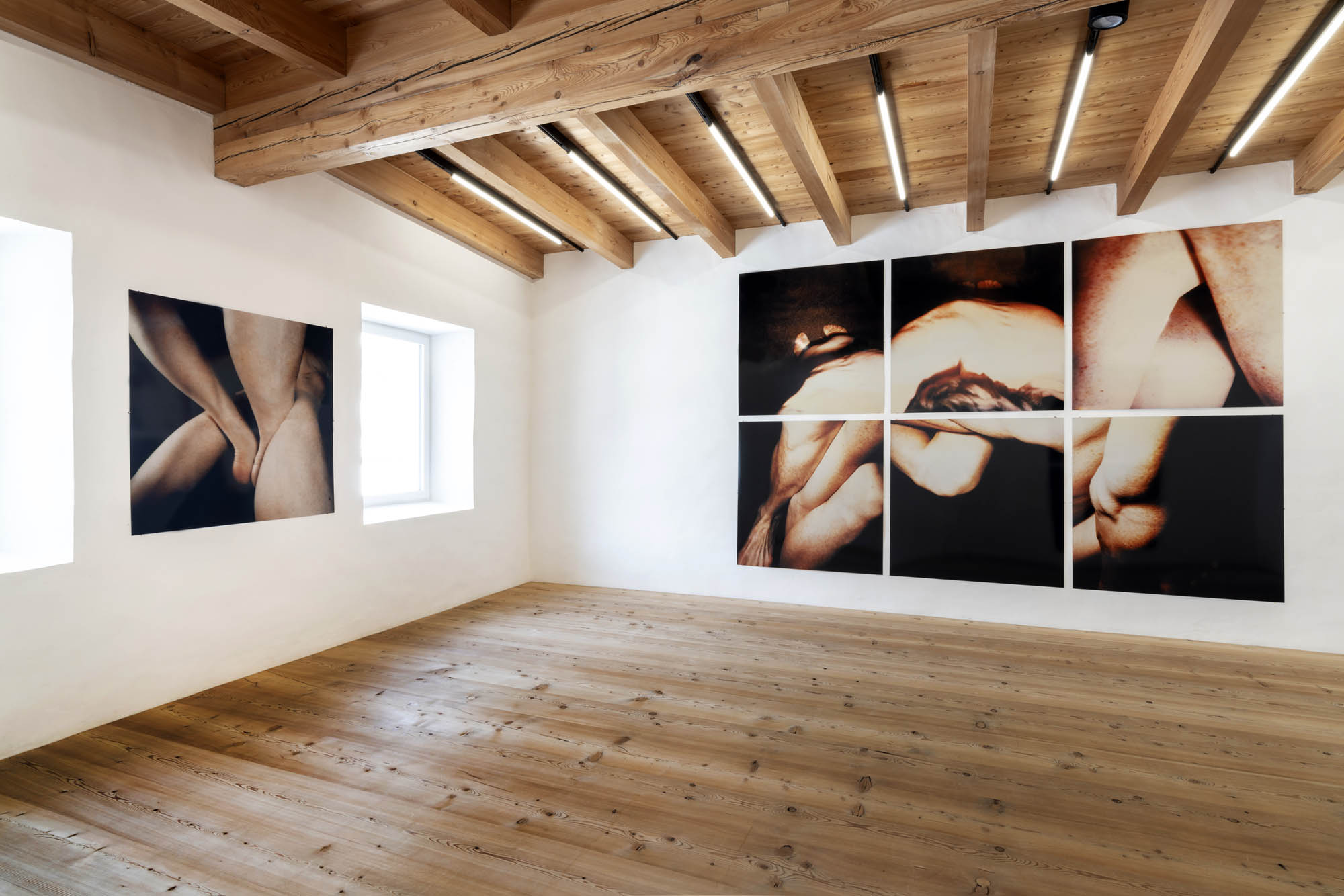
Installation views of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left in the bottom image, Hannah Villiger’s Work (1982, below); and at right, Sculpting (1983, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
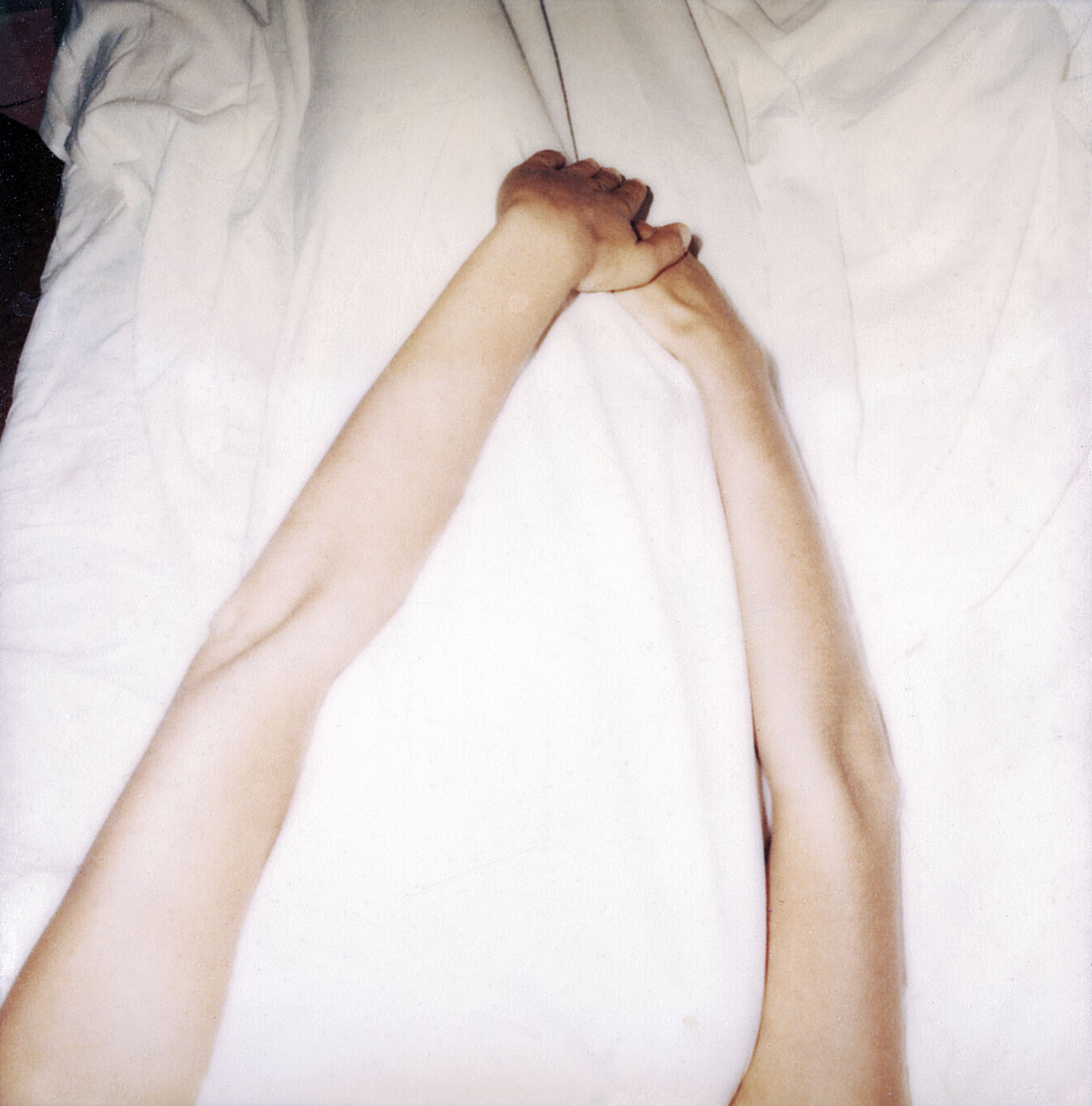
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Work
1982
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
125 x 123cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculpting
1983
Six C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
222 x 322cm
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Courtesy of Collection Pictet
Installation views of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing in the bottom image at left, Sculptural (1984-85, below); at centre, Sculptural (1984-85, below); and at right, Sculptural (1984-85, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
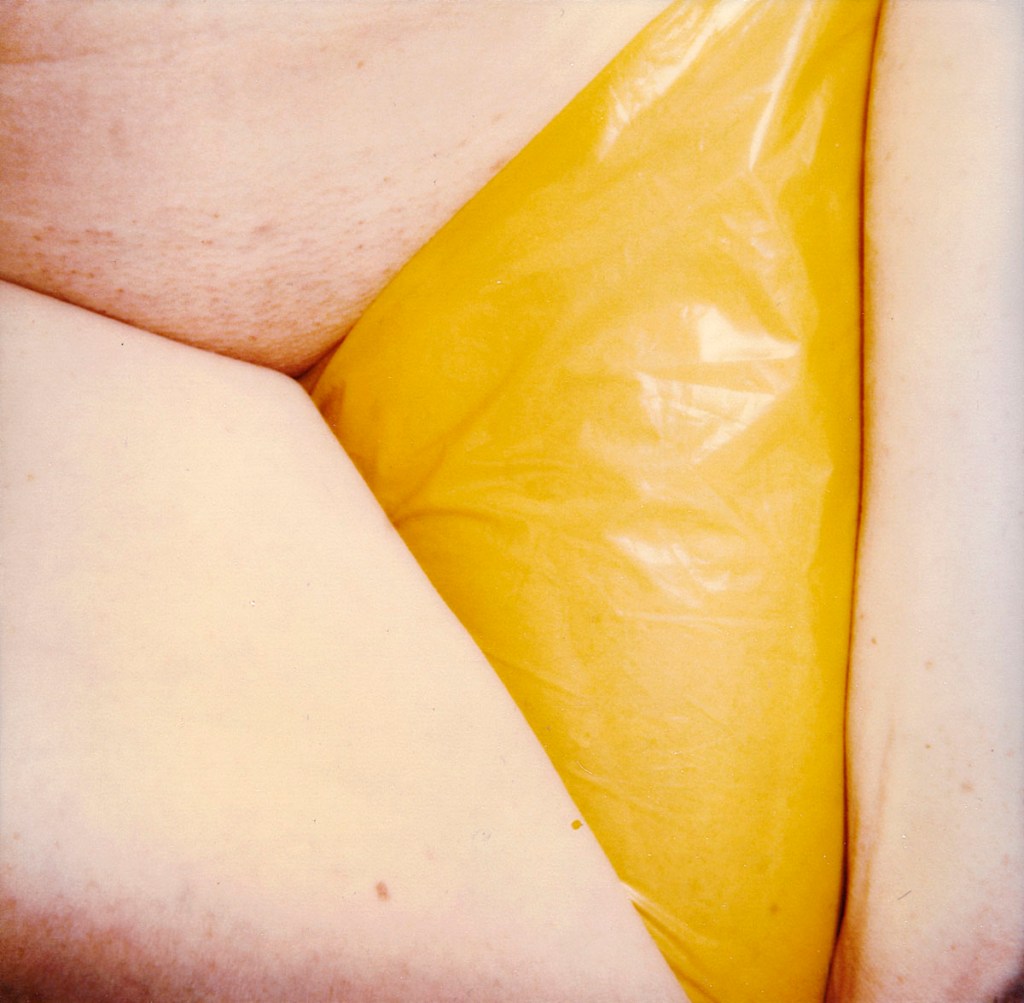

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculptural
1984-85
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
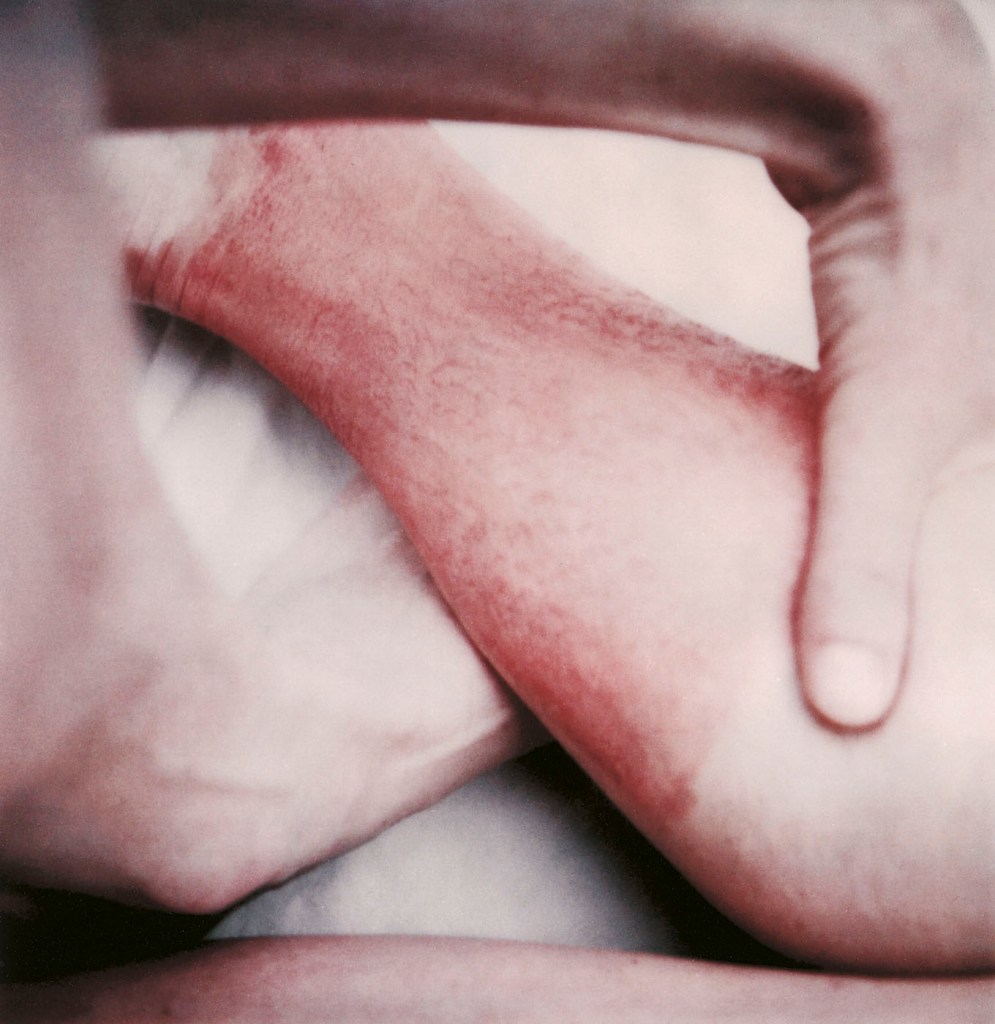
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculptural
1984-85
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculptural
1984-85
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Installation views of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at centre, Block XVI (1989, below); and at right, Sculptural (1988-89, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
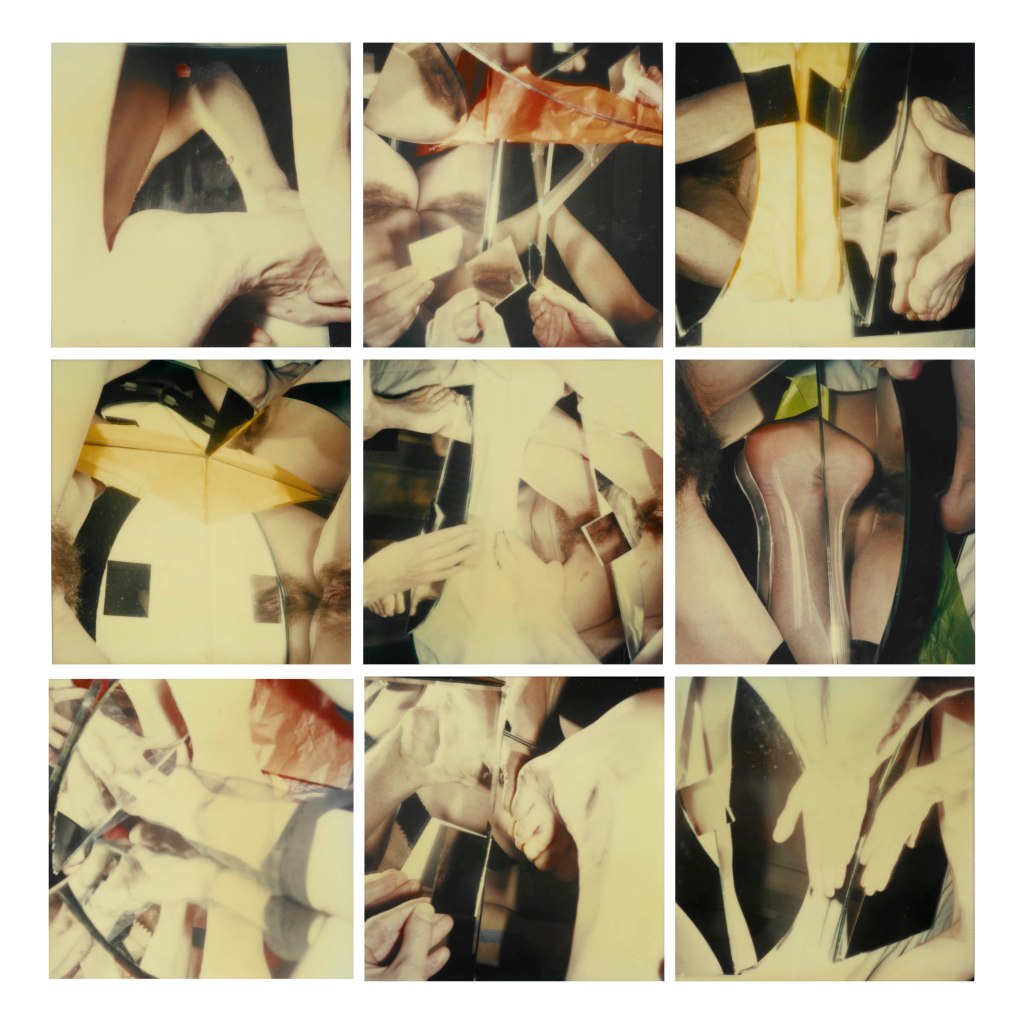
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block XVI
1989
Nine C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
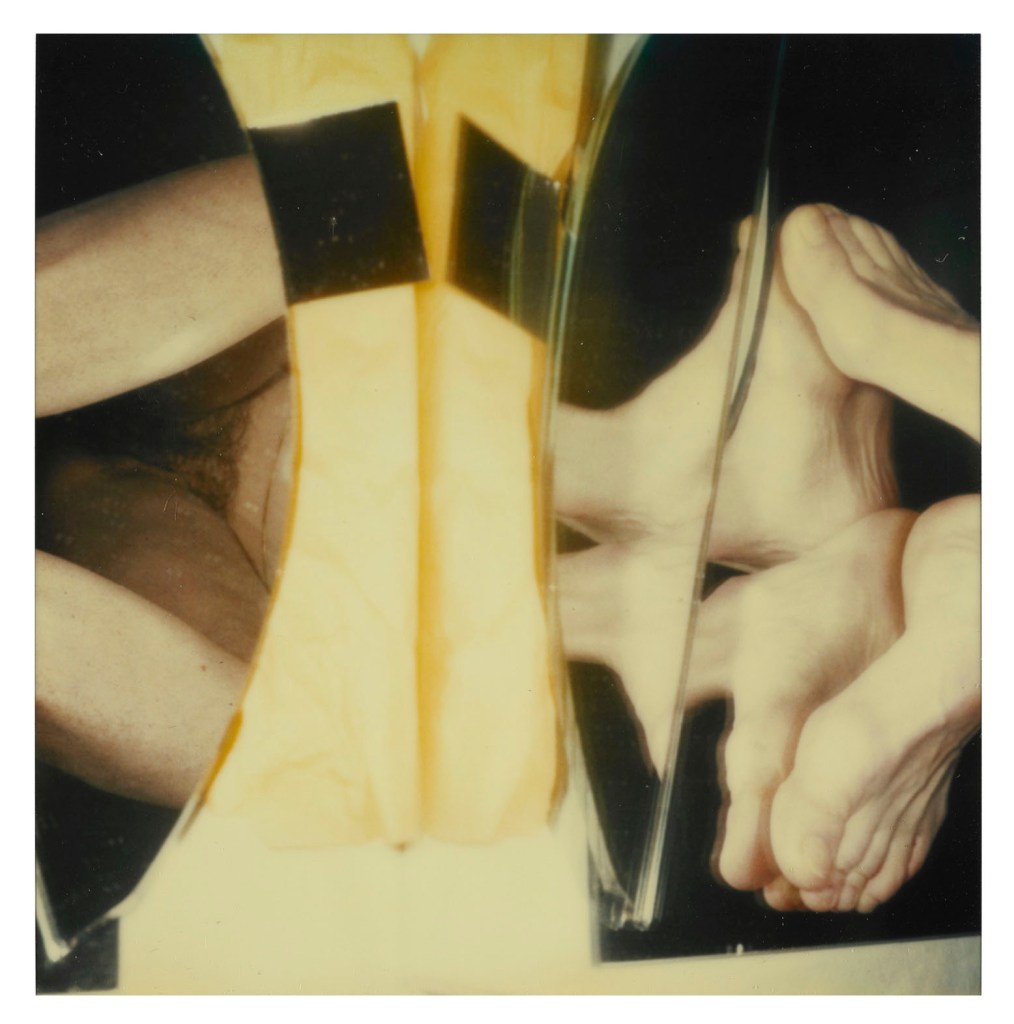
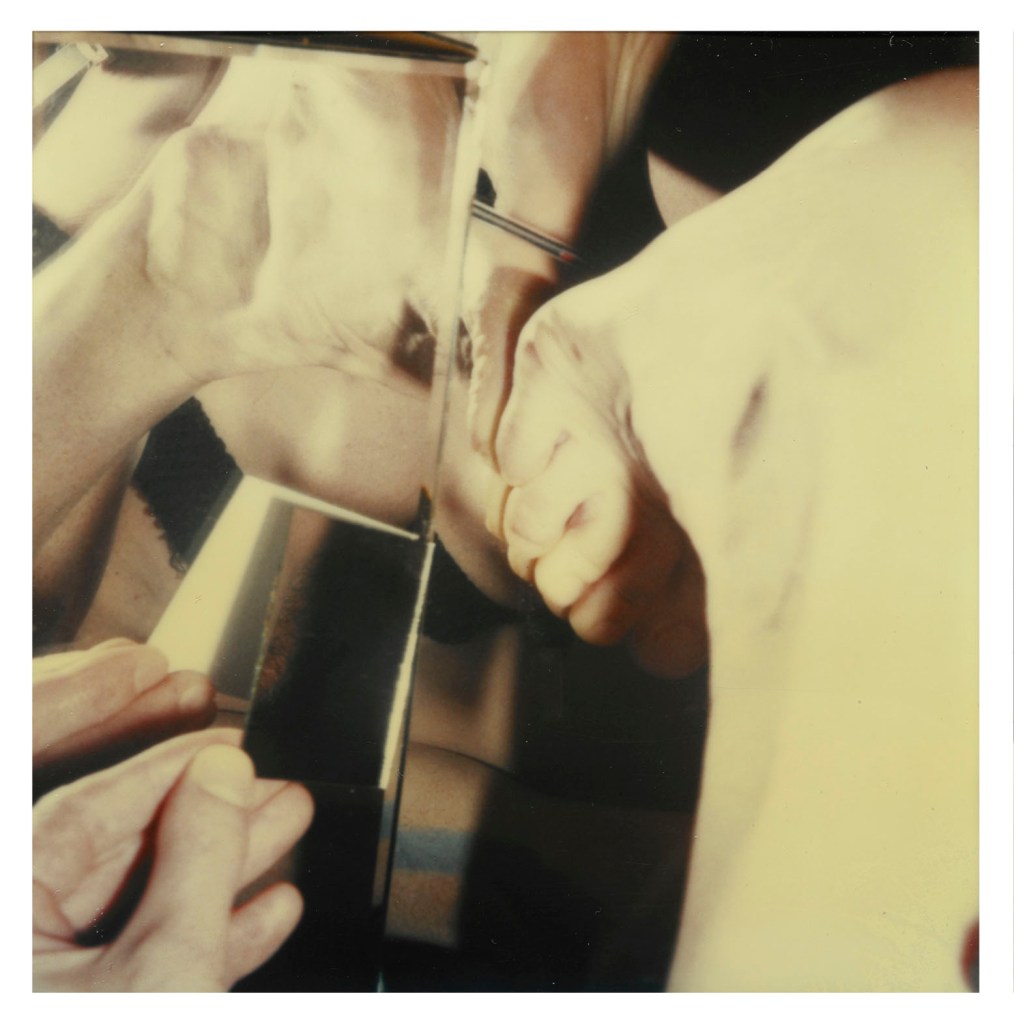
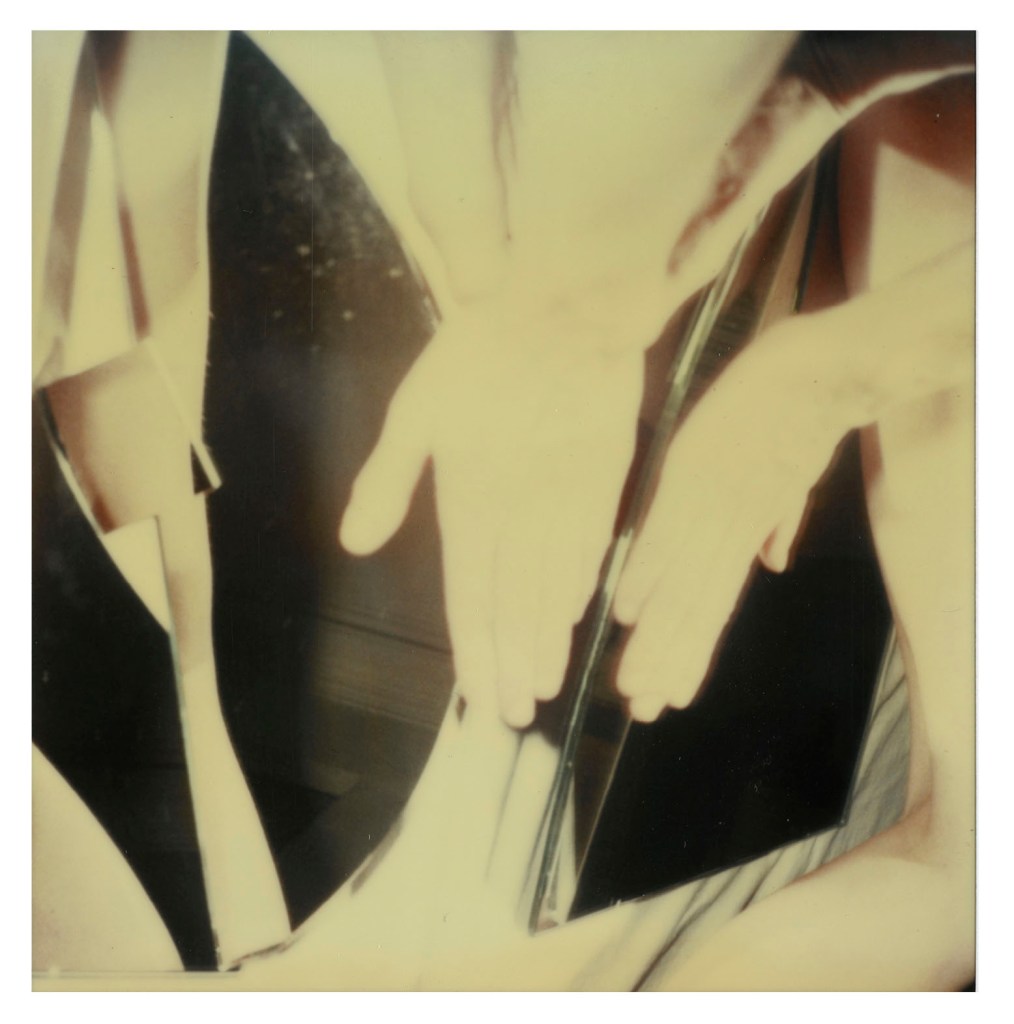



Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block XVI (details)
1989
Nine C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
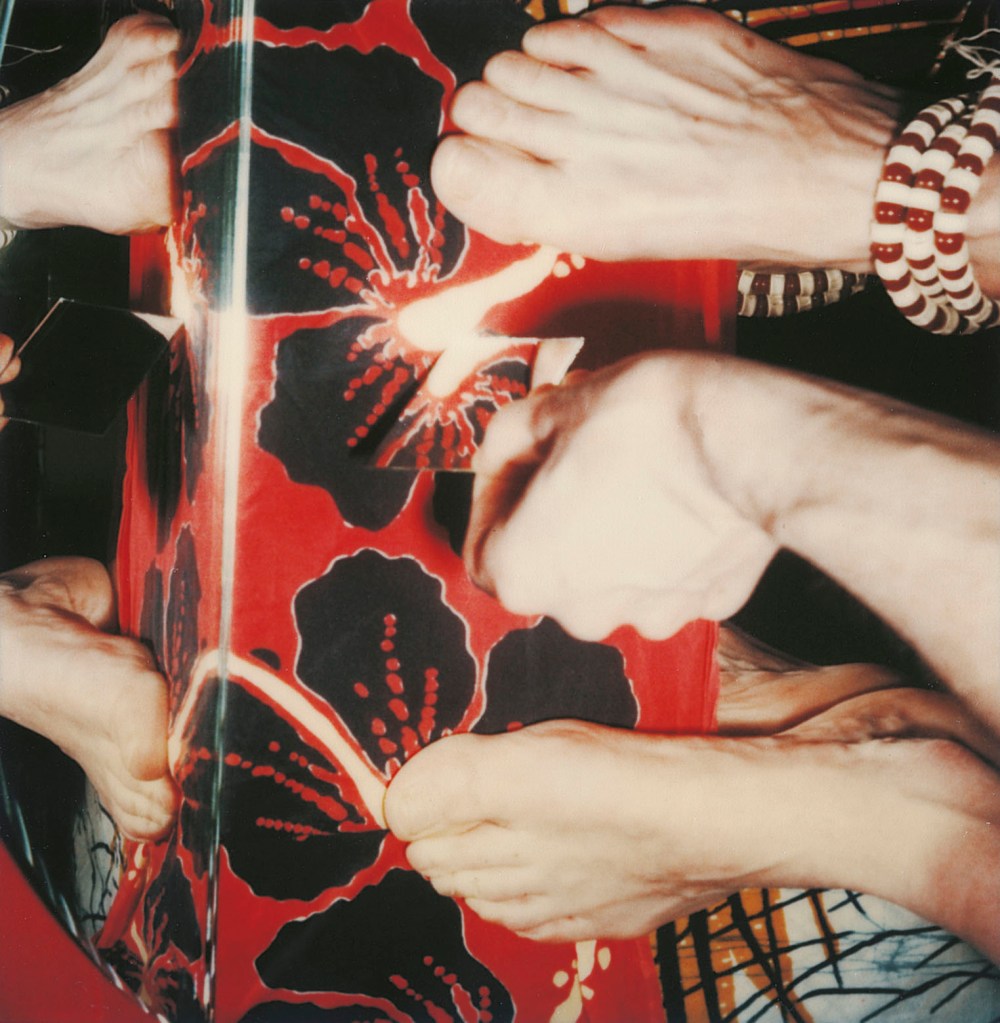

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculptural
1988-89
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculptural
1988-89
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger

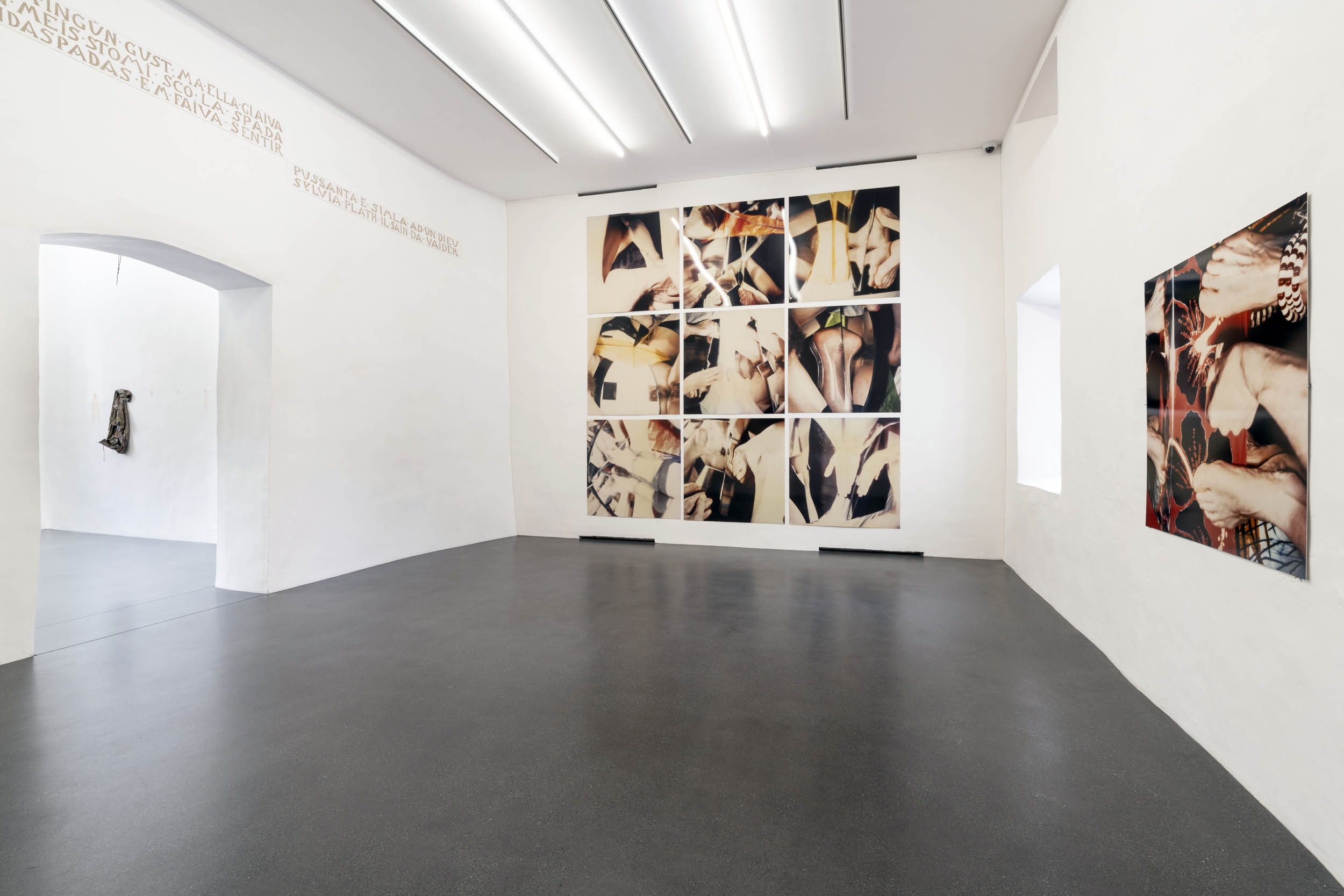
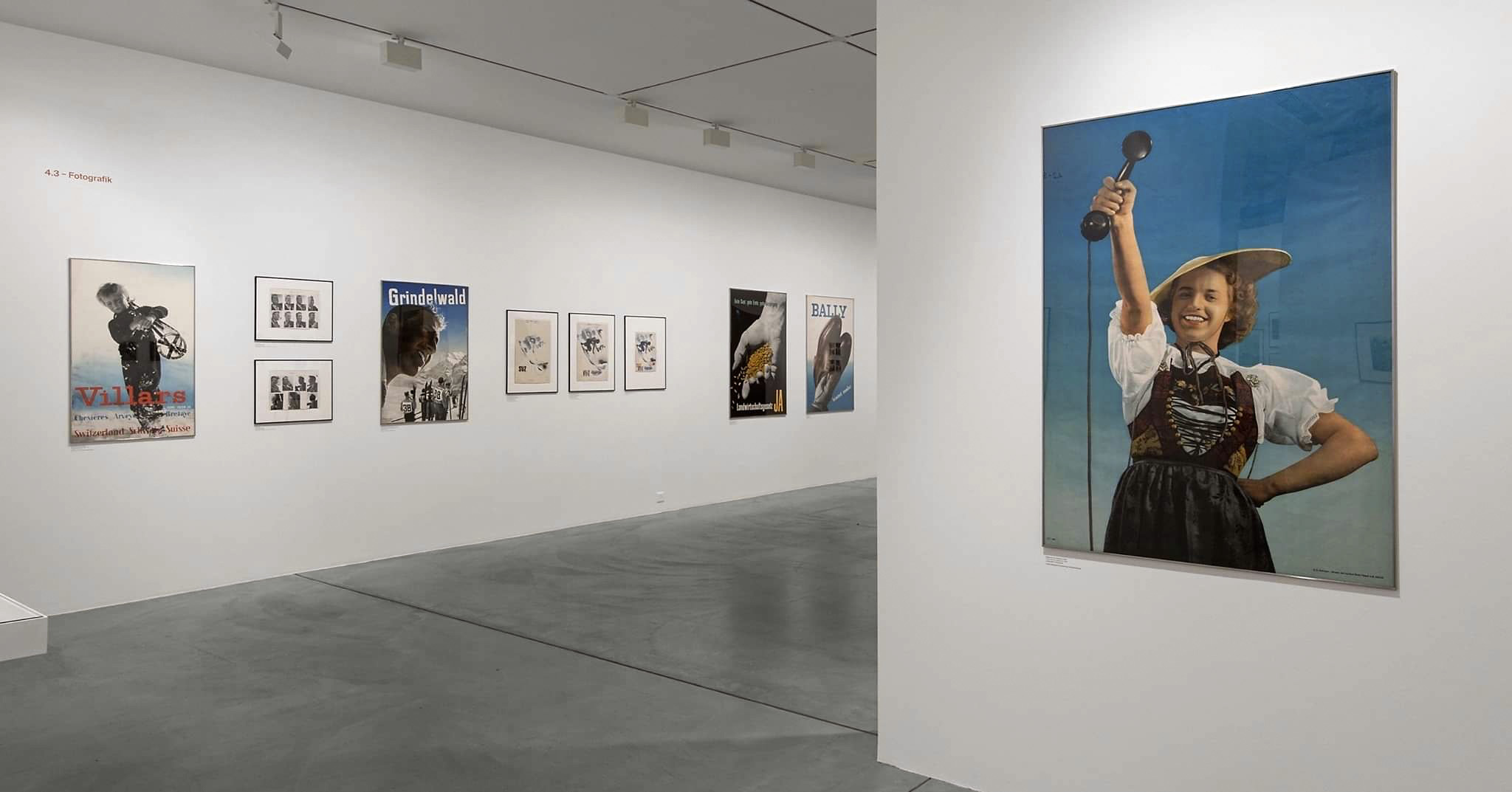
Installation views of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
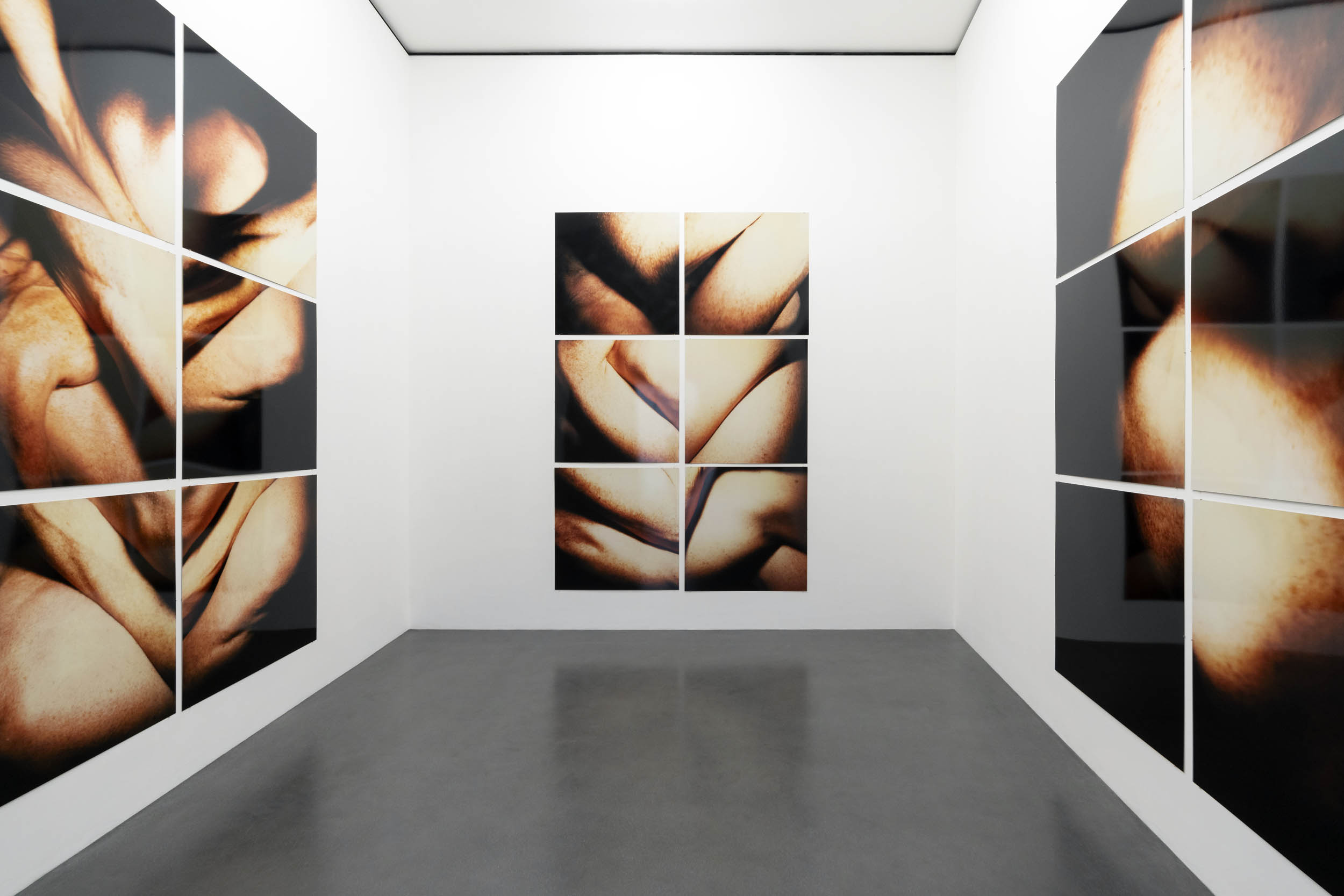
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left Block XIII (1989, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing Block XIII (1989, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block XIII
1989
Fifteen C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
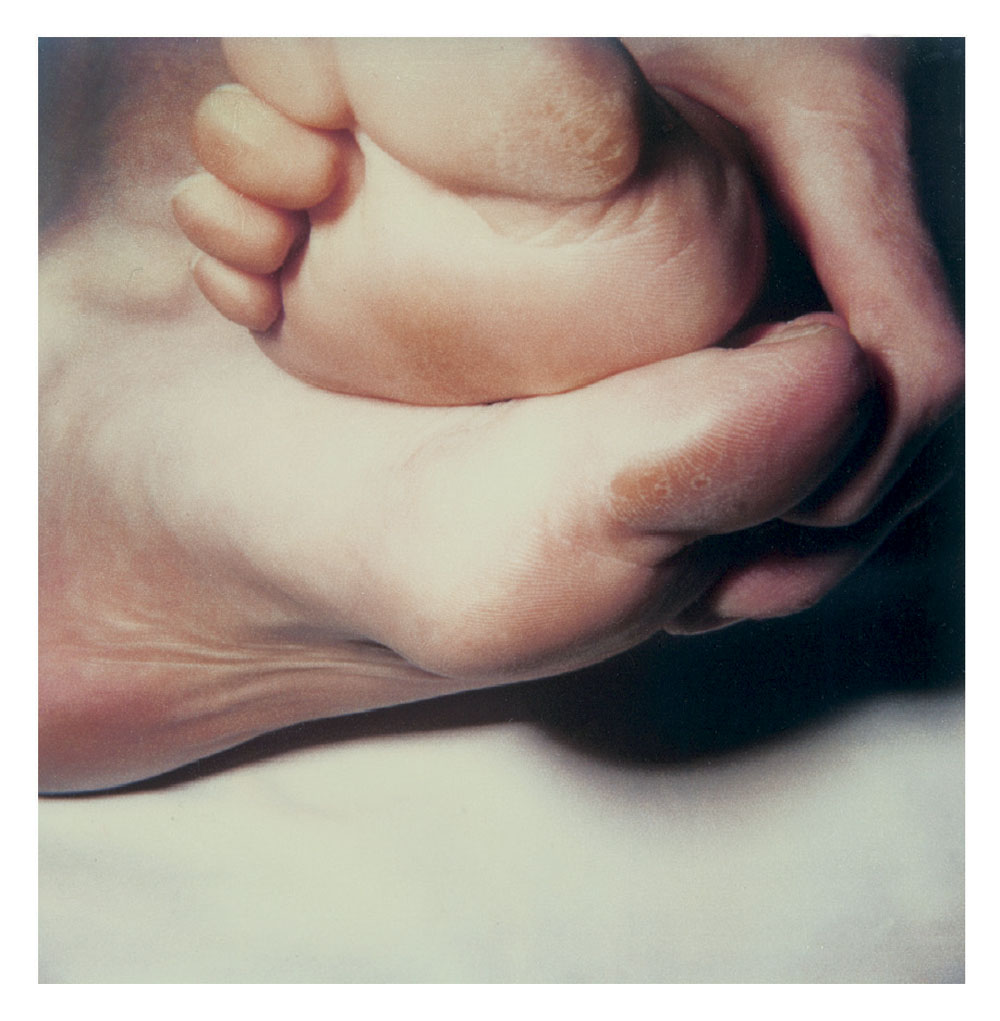
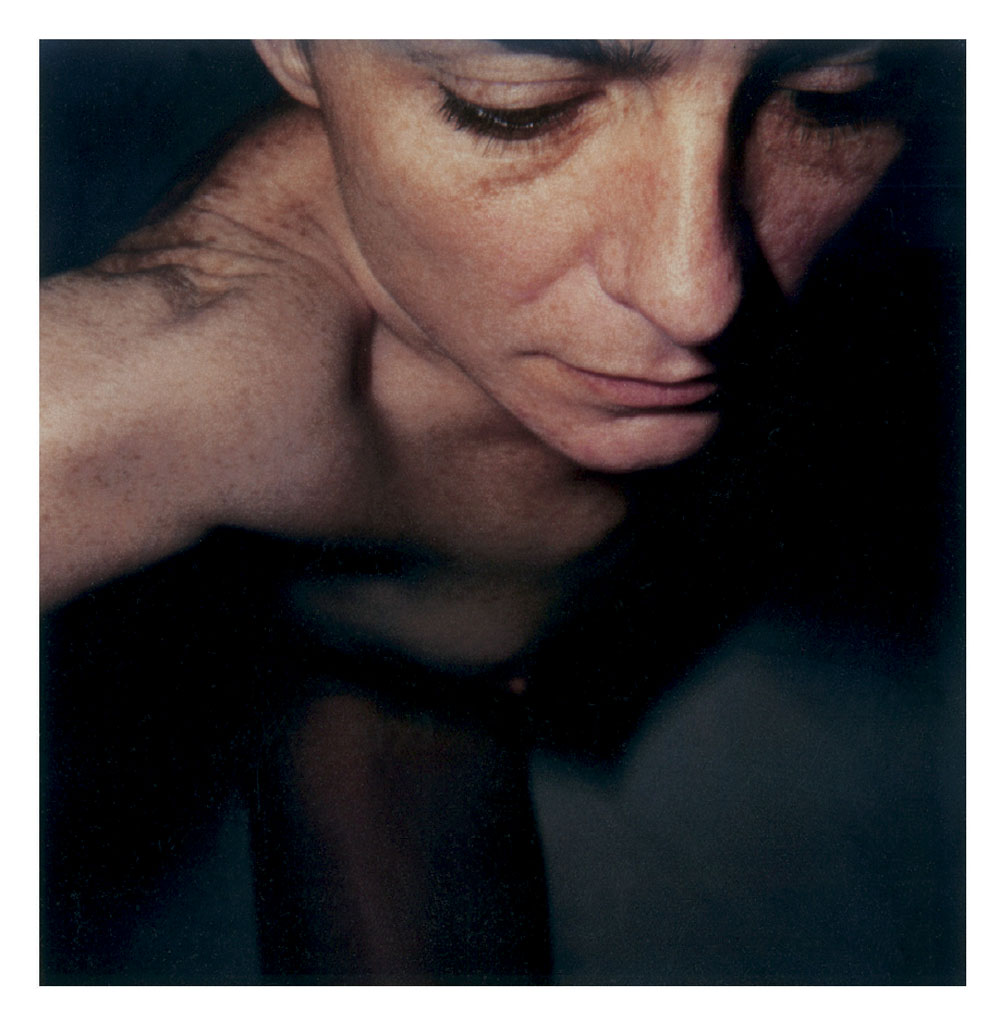
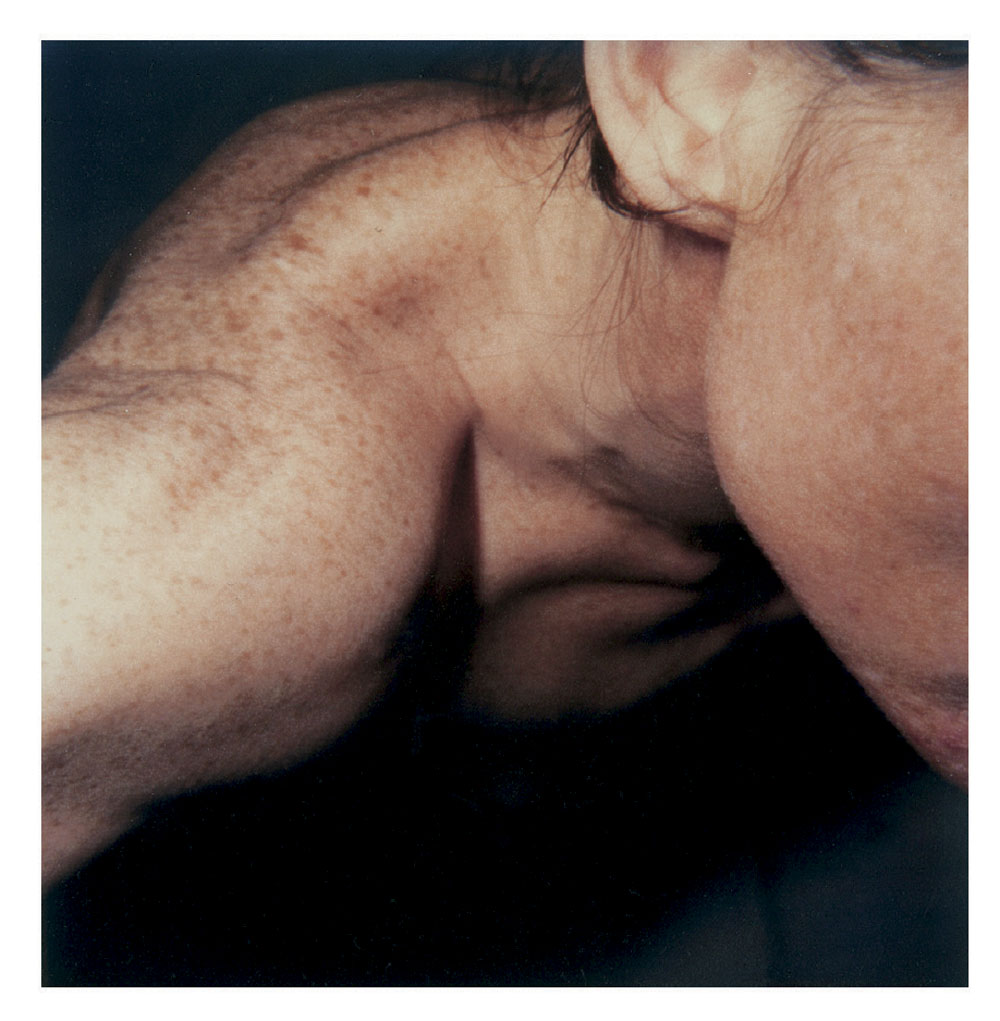
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block XIII (details)
1989
Fifteen C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
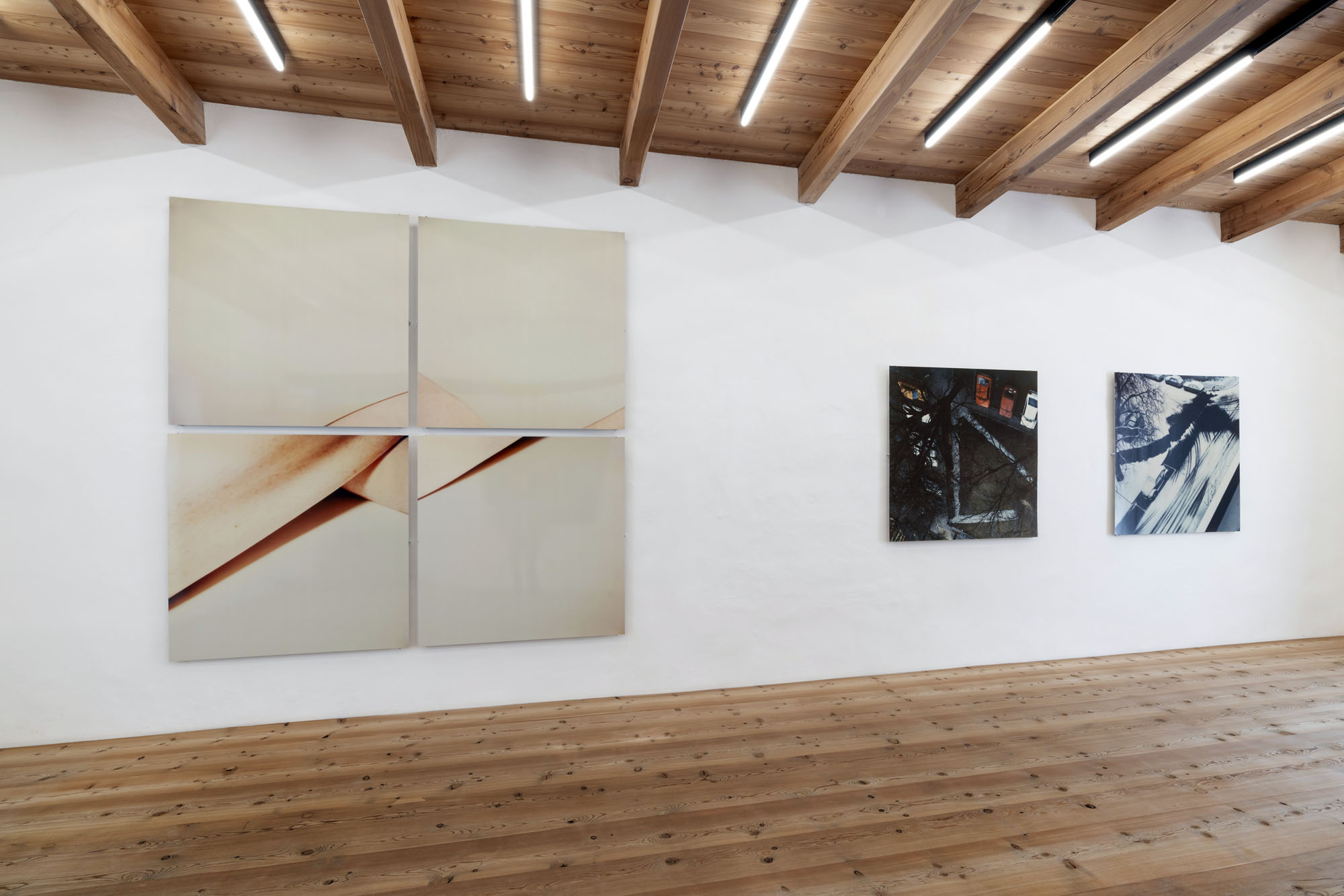
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left, Sculptural (1990-91, below); and at right, Block XXX (1993-1994)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
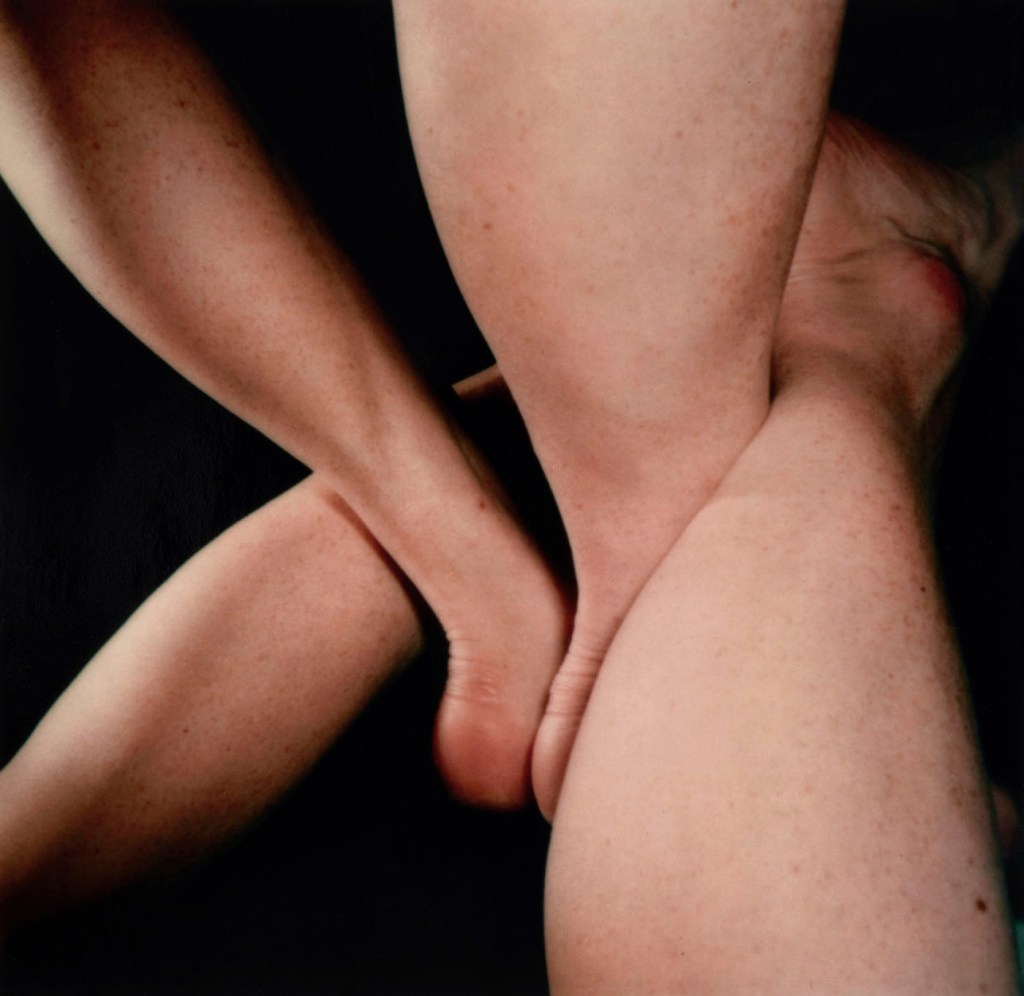
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculptural
1990-91
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block XXX
1993-94
Six C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
Jacques Herzog und Pierre de Meuron Kabinett, Basel
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left, Block XXXV (1994, below); and at right, Place (1985, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
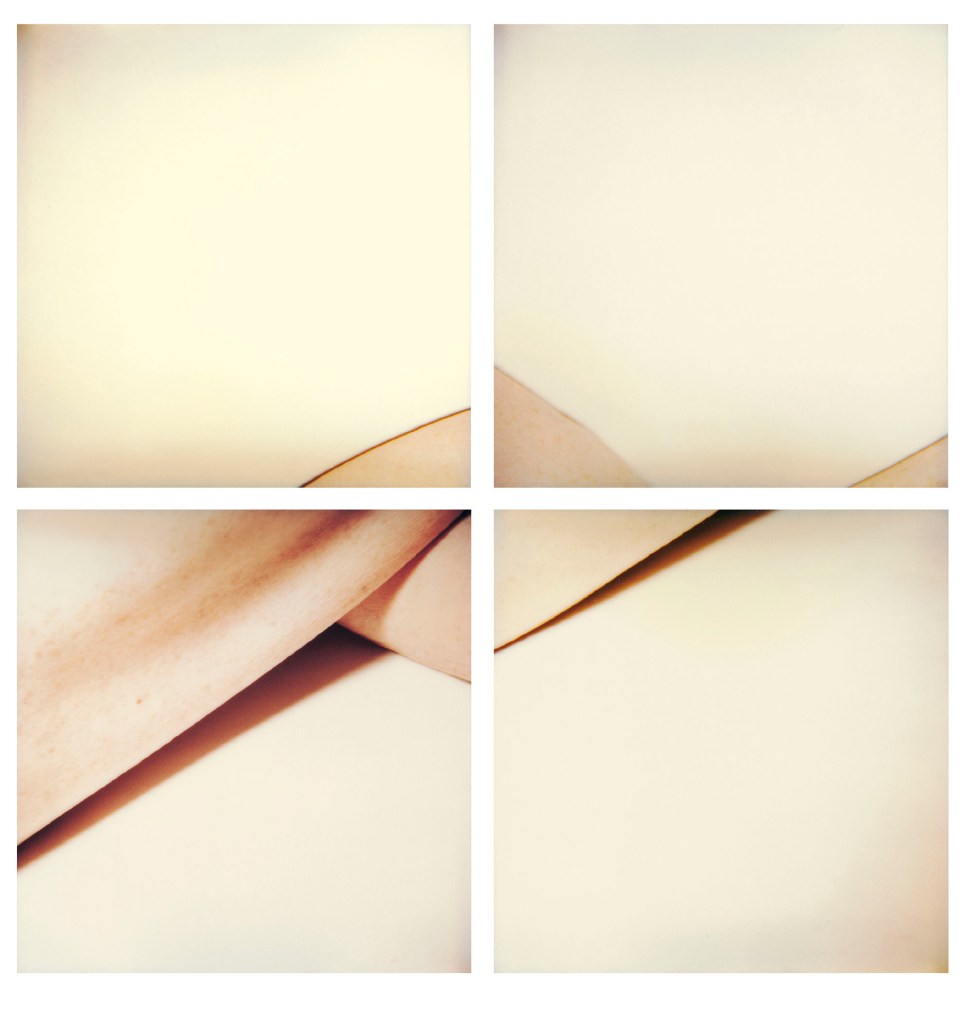

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block XXXV
1994
Four C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
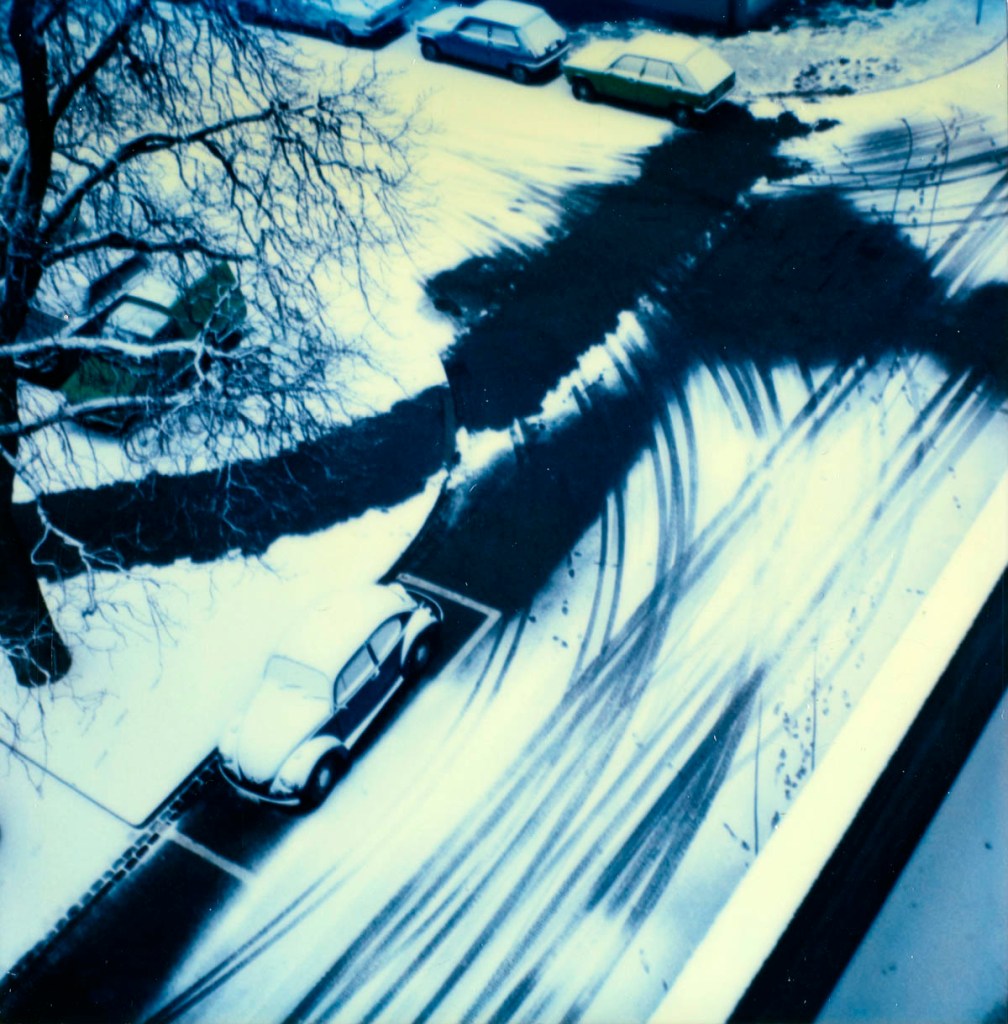

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Place
1985
C-print of a polaroid, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
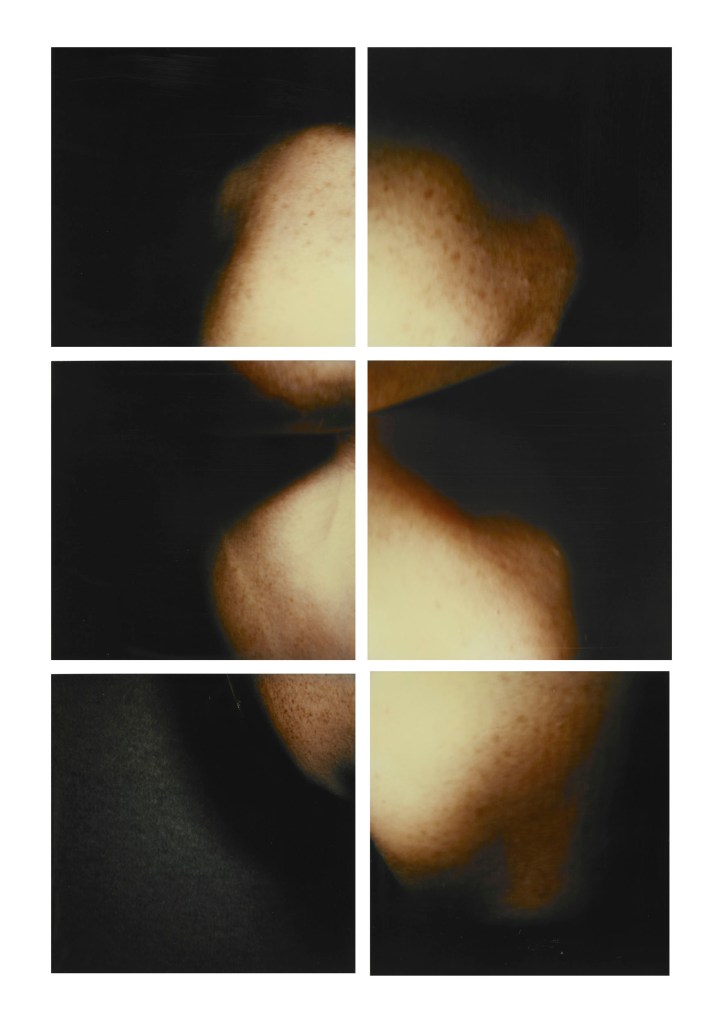
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Sculptural
1995
Six C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing the work Block (1996, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block
1996
Six C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
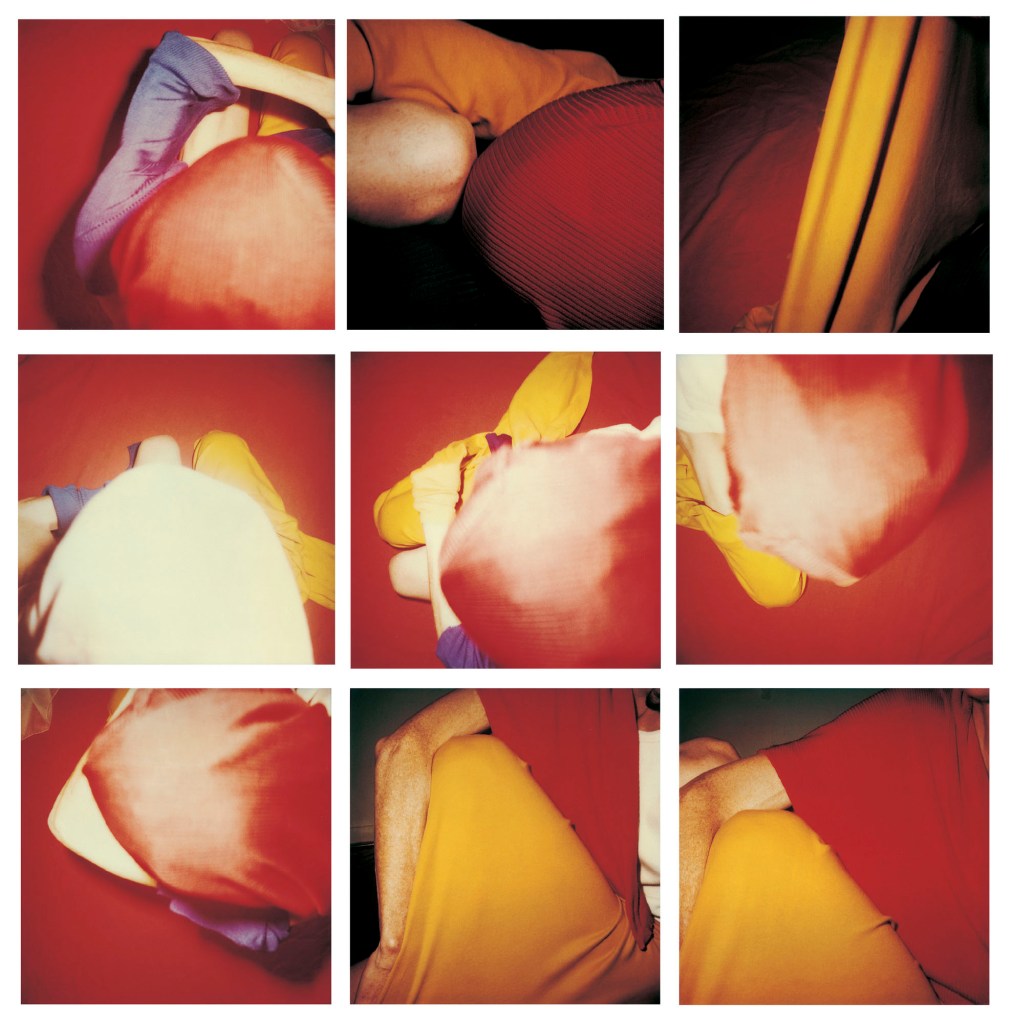
Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block
1997
Nine C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
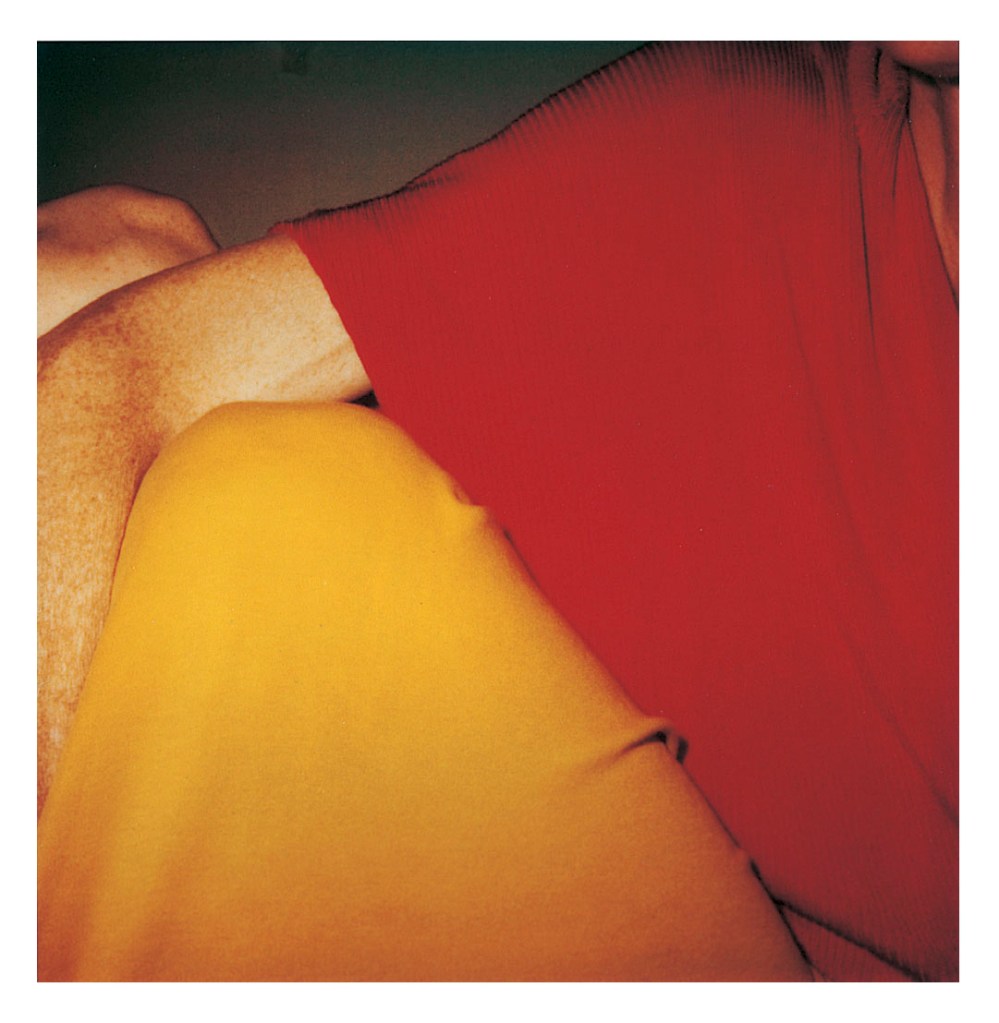
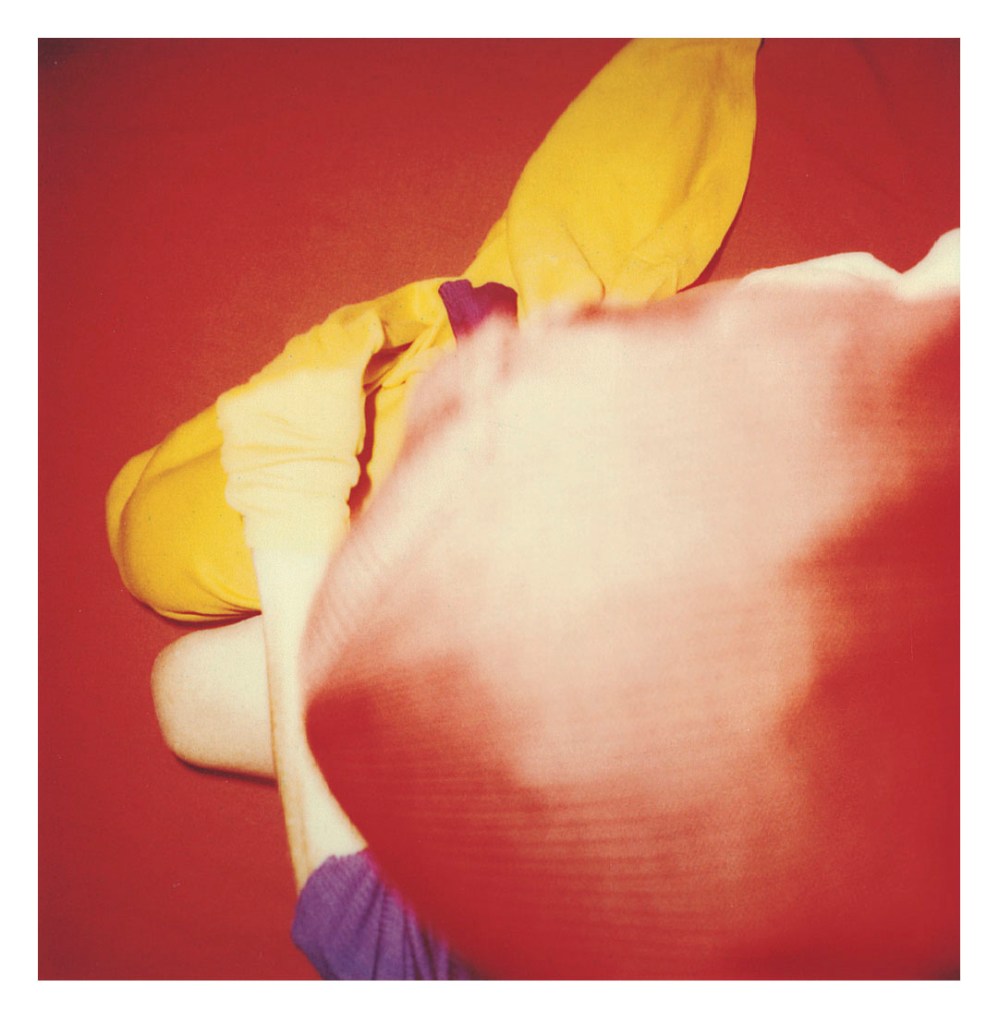

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
Block (details)
1997
Nine C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Installation view of Hannah Villiger: Amaze Me at Muzeum Susch showing at left, City (1997, below)
Courtesy: © Muzeum Susch / Art Stations Foundation
Photograph: Federico Sette
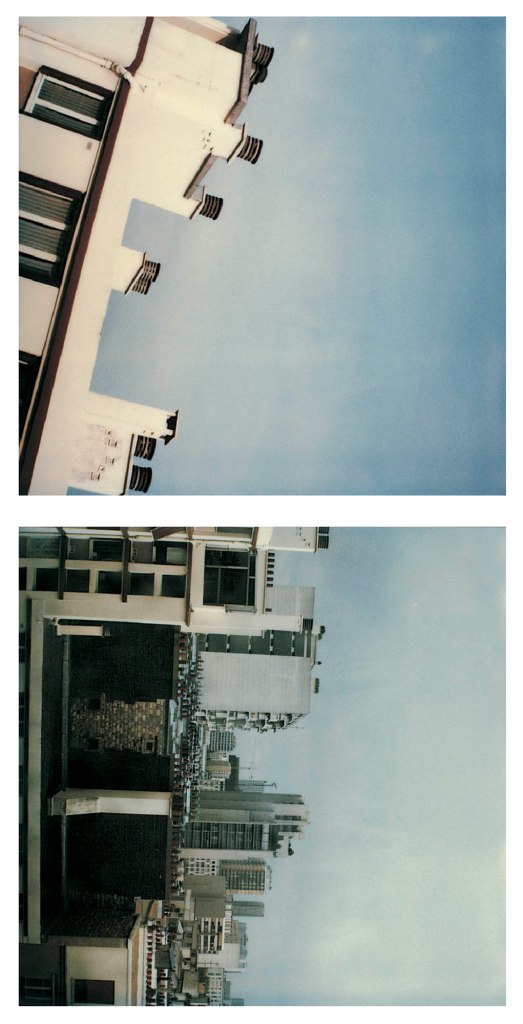

Hannah Villiger (Swiss, 1951-1997)
City
1997
Two C-prints of polaroids, mounted on aluminium
© Foundation The Estate of Hannah Villiger
Museum Susch
Surpunt 78
CH – 7542 Susch, Switzerland
Opening hours:
Wednesday: 11.00 – 17.00
Thursday: 11.00 – 17.00
Friday: 11.00 – 17.00
Saturday: 11.00 – 17.00
Sunday: 11.00 – 17.00



















































































































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.