Exhibition dates: 3rd March – 11th June, 2023
Curated by Alistair O’Neill, professor of Fashion History and Theory at Central Saint Martins (University of the Arts London)
Please note: This exhibition includes photographs showing nudity and sexually suggestive scenes. There is no age restriction for visitors to the exhibition. We are leaving the decision to visit to the discretion of parents, guardians and carers.
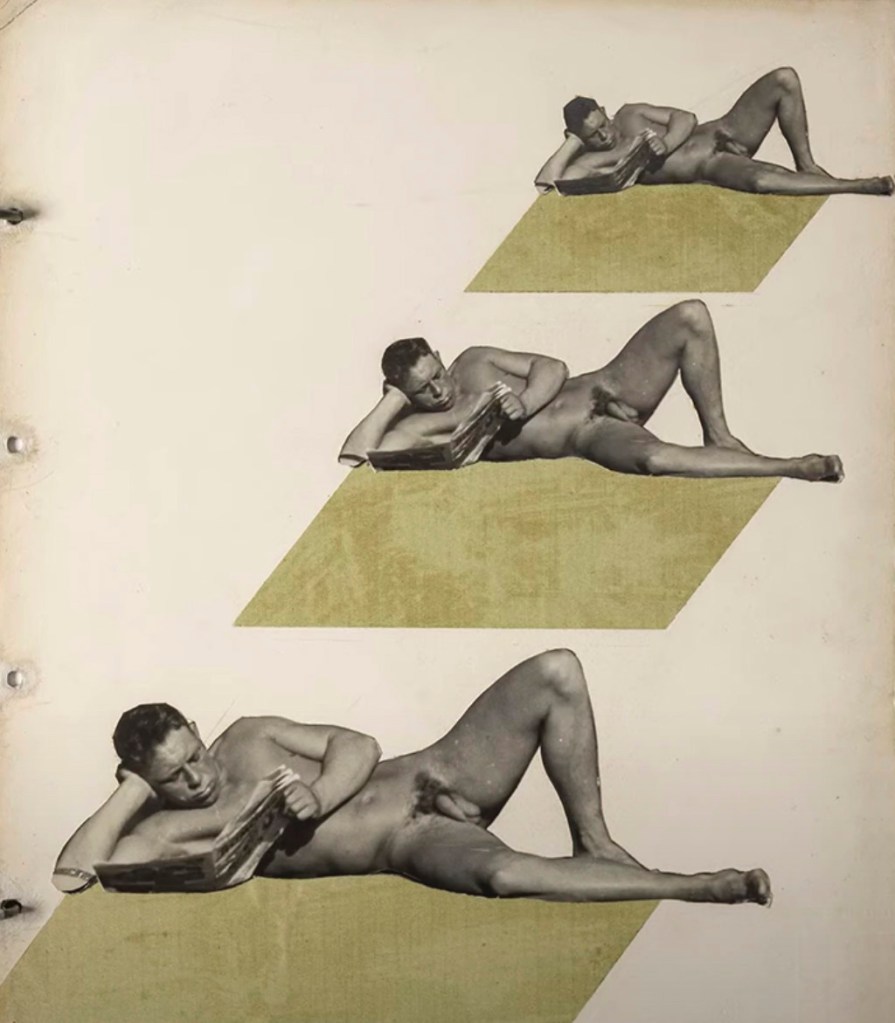
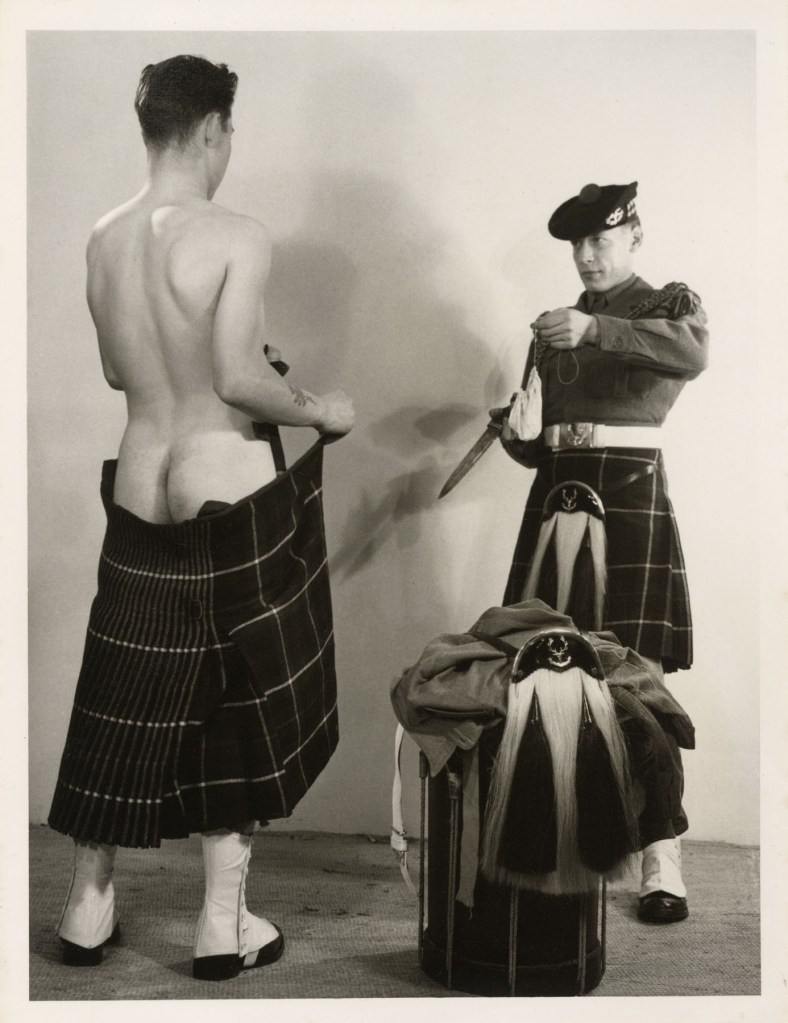
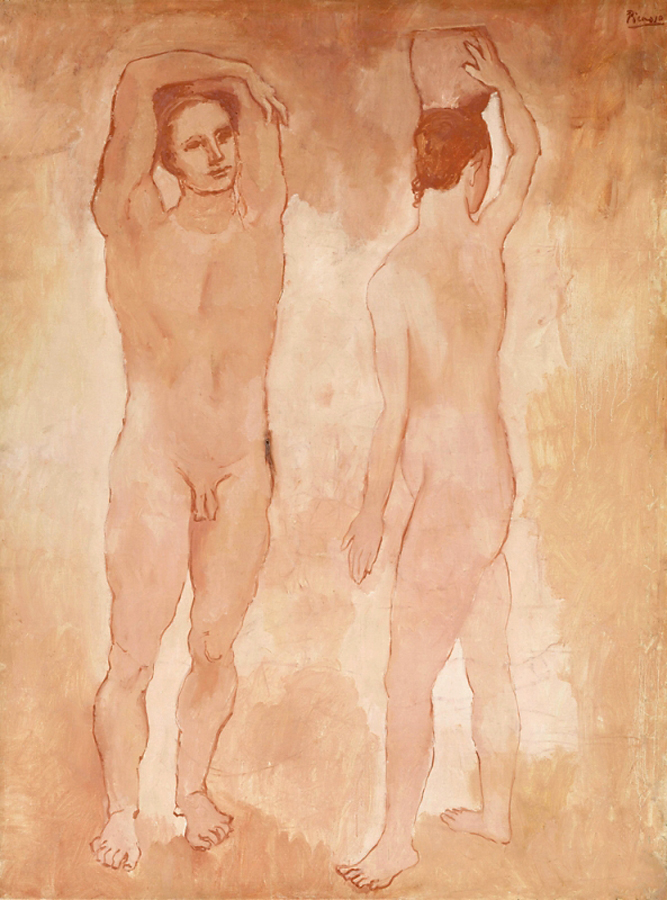
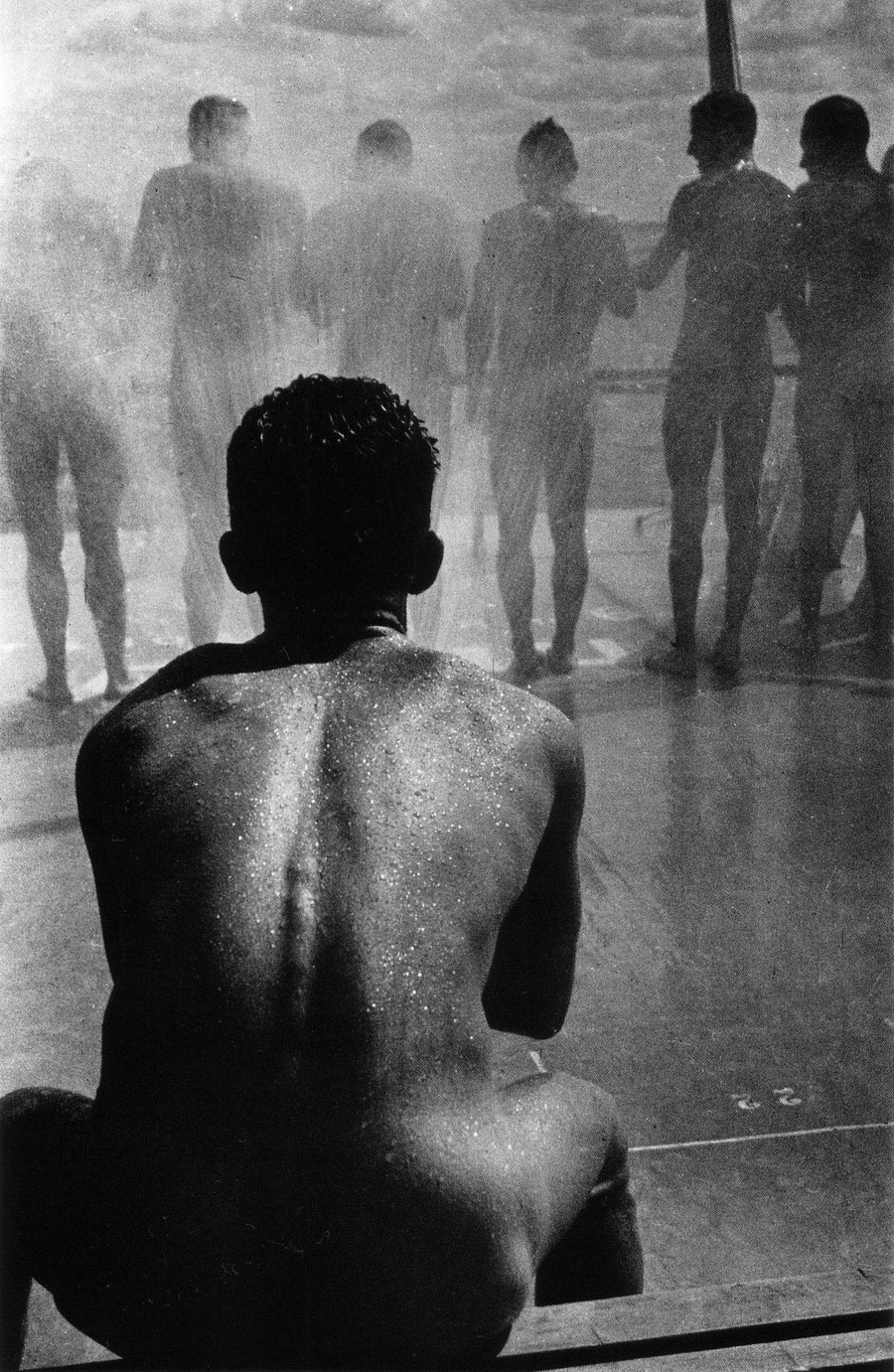
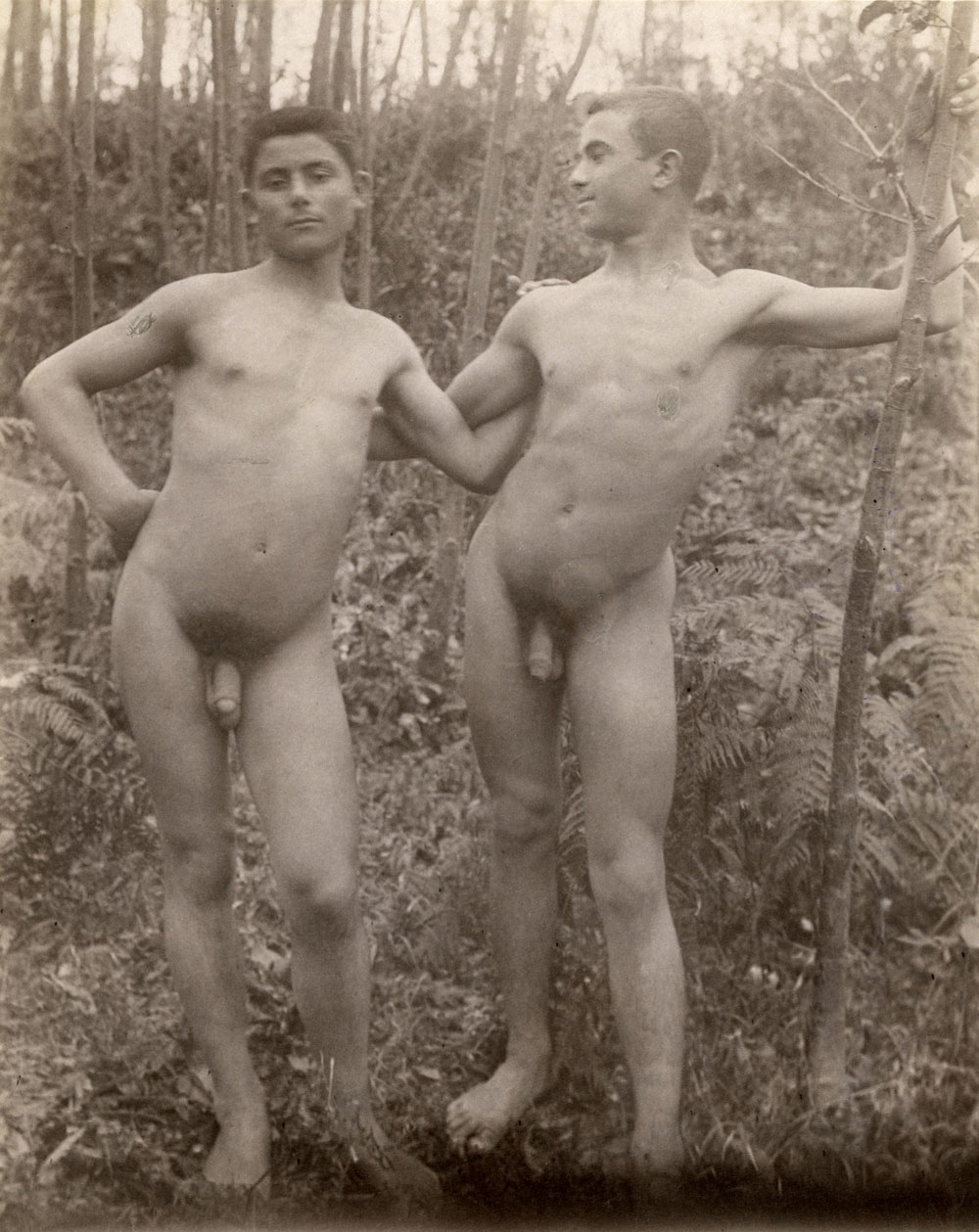
Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Highgate Men’s Pond Album
1933
Courtesy Aberystwyth University School of Art Museum and Galleries
Nothing hard to see here…
This looks to be a fascinating exhibition albeit with not a single erect penis on show and about half the exhibition showing flaccid examples. The photographs seem particularly asexual. Hardly any of them are what you would call “erotic”, except perhaps the photographs from the earliest album in this posting, Keith Vaughan’s Highgate Men’s Pond Album (1933, above and below). For me, the most sexual photographs are the “rough trade” such as the skins and carnies… an archetype which has existed for centuries.
My Phd research titled Presing the Flesh: Sex, Body Image and the Gay Male (1997-2001) examined in part the history of the male body in photography, including photos of ephebes (young men), the muscular mesomorphic body as featured in the physique magazines and gay male pornography. My history of the male body in photography can be found in the Historical Pressings chapter while the Bench Press chapter investigates the ‘Cult of Muscularity’, the development of gym culture, its ‘masculinity’, ‘lifestyle’, and the images used to represent it.
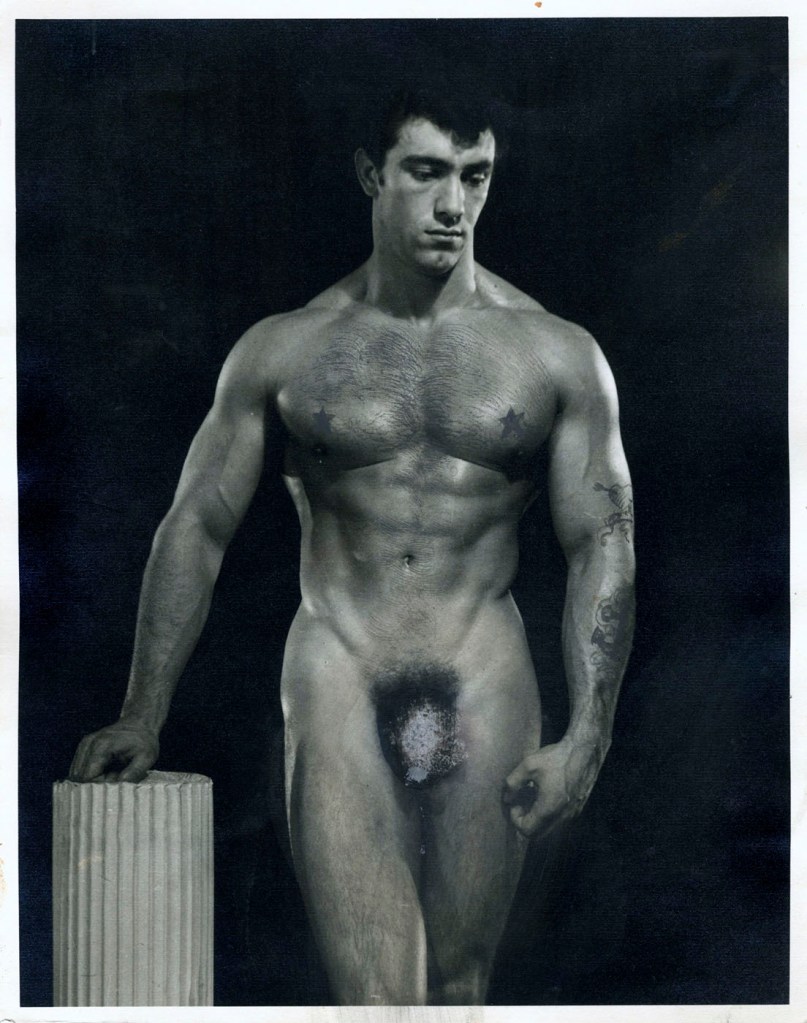
Much as gay men had to speak ‘Polari’ (gay slang language) when going to pubs such as the Salisbury on St Martin’s Lane in London in the 1970s so that those around us could not understand what we were saying, so physique or ‘beefcake’ magazines of the 1950s and 1960s relied heavily on the iconography of classical Rome and Greece to legitimise and hide from unknowing eyes (in plain sight) their homo-erotic overtones. Use was made of columns, drapery, and sets that presented the male body as the contemporary equivalent of idealised male beauty of ancient times.
Conversely, during my Phd I visited the Kinsey Institute and examined their M2M photographic collection where it was fascinating to see men having sex with each in photographs dating back from the Victorian era to the 1960s, most men with erect penises posed in a variety of intimate positions, situated in both indoor and outdoor urban settings. There were also black and white and colour physique photographs taken indoors and outdoors of the models having sex with each other. See my notes on the images of photographers such as Russ Warner, Al Urban, Lon of New York, Bob Mizer, Charles Renslow and Bruce of Los Angeles held in the Collection at the Kinsey Institute.
While Simon in his excellent post on the exhibition notes that there was a delicate balancing act in the photographs in their subtle aesthetics of constraint and tact and a “self-imposed restraint which made ‘physique photographs’ walk such an exciting fine line between factual depiction of male anatomy and objects of lust from the 1930s to the 80s,” behind the scenes the models were getting boners and having sex all over the place. Purely for private consumption in their day, none of these photographs are ever shown (as in this exhibition) or published today and hardly anyone knows about them. The limp, flaccid penis is all that we get to see for fear of offence and/or moral outrage… for what was covert activity at the time (with a wide underground circulation) is kept impotent today.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to The Photographers’ Gallery for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“I think the interest is not so much in the images, per se, as in their variety, and also in the extraordinary density and complexity of the clandestine networks of gay photographers, subjects, printers, publishers and distributors which the wall labels describe and explain. That’s interesting social history.
And then, when you lay the complex mesh of legal and cultural and visual parameters over the images you get, as it were, another layer of complexity beyond the images themselves; you get to see them as varying visual strategies and approaches and sublimations of very powerful male urges of desire and sexuality.”
Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
American physique photography“The bodies in the ‘beefcake’ magazines of the 1950’s tend to be bigger than that of the ephebe, even when the models were quite young in some cases. As the name ‘beefcake’ implies, the muscular mesomorphic shape was the attraction of these bodies – perfectly proportioned Adonis’s with bulging pectorals, large biceps, hard as rock abdomens and small waists. The 1950’s saw the beginning of the fixation of gay men with the muscular mesomorph as the ultimate ideal image of a male body. The lithe bodies of young dancers and swimmers now gives way to muscle – a built body, large in its construction, solid and dependable, sculpted like a piece of rock. These bodies are usually smooth and it is difficult to find a hirsute body11 in any of the photographs from the physique magazines of this time. According to Alan Berube in his book, Coming Out Under Fire,
“The post-war growth and commercialization of gay male erotica in the form of mail-order 8 mm films, photographic stills, and physique magazines were developed in part by veterans and drew heavily on World War II uniforms and iconography for erotic imagery.”12
Looking through images from the 1940s in the collection at The Kinsey Institute, I did find that uniforms were used as a fetish in some of the explicitly erotic photographs as a form of sexual iconography. These photographs of male2male sex were for private consumption only. I found little evidence of the use of uniforms as sexual iconography in the published photographs of the physique magazines. Here image composition mainly featured classical themes, beach scenes, outdoor and studio settings. …As the 1950s turned into the 1960s other stereotypes became available to the photographers – for example the imagery of the marine, the sailor, the biker, the boy on a tropical island, the wrestler, the boxer, the mechanic. The photographs become more raunchy in their depiction of male nudity.
In the 1950s, however, classical aspirations were never far from the photographers minds when composing the images as can be seen in the undated photograph Jim Stevens by Lon of New York in London taken from a book called ‘Art in Physique Photography’.14 This book, illustrated with drawings of classical warrior figures by David Angelo, is subtitled: ‘An Album of the world’s finest photographs of the male physique’.
Here we observe a link between art and the body. This connection was used to confirm the social acceptability of physique photographs of the male body while still leaving them open to other alternative readings. One alternative reading was made by gay men who could buy these socially acceptable physique magazines to gaze with desire upon the naked form of the male body. It is interesting to note that with the advent of the first openly gay pornography magazines after the ruling on obscenity by the Supreme Court in America in the late 1960s,15 classical figures were still used to justify the desiring gaze of the camera and viewer upon the bodies of men. Another reason used by early gay pornography magazines to justify photographs of men having sex together was that the images were only for educational purposes! …
As social morals relaxed in the age of ‘free love’, physique photographers such as Bob Mizer from Athletic Model Guild produced more openly homo-erotic images. In his work from the 1970s full erections are not prevalent but semi-erect penises do feature, as do revealing “moon” shots from the rear focusing on the arsehole as a site for male libidinal desires. A less closeted, more open expression of homosexual desire can be seen in the photographs of the male body in the 1970s.17 What can also be seen in the images of gay pornography magazines from the mid 1970s onwards is the continued development of the dominant stereotypical ‘ideal’ body image that is present in contemporary gay male society – that of the smooth, white, tanned, muscular mesomorphic body image.
Marcus Bunyan. “Historical Pressings,” from Presing the Flesh: Sex, Body Image and the Gay Male. PhD thesis, RMIT University, 2001
A Hard Man is Good to Find! celebrates a clandestine visual culture of men’s bodies that emerged in the post-war period, during a time when making and distributing such images was a criminal offence.
This exhibition highlights key areas of London which were a focus for men seeking out men to photograph. It maps out a territory of risk and possibility across Highgate, between Chelsea and Wellington Barracks, in Soho, Brixton, Portobello and Euston. Catalogues, print ordering sheets, personal albums, magazines and publications explore how these photographs were circulated, exchanged and shared.
While the 1955 Wolfenden Report and the 1967 Sexual Offences Act marked the partial decriminalisation of gay sexual activity, prompting gay liberation and the fight for social equality; any depiction of male nudity which suggested homosexuality remained subject to the 1857 Obscene Publications Act.
Including work by John S. Barrington, Cecil Beaton, Guy Burch, Basil Clavering, Rotimi Fani-Kayode, Bill Green, David Gwinnutt, Angus McBean, Patrick Procktor, Ajamu X and many more.
Whilst this is an exhibition of queer pictures, it is important to note that not all the photographers or models can be claimed as queer subjects. It also acknowledges that language evolves and while queer is employed today for its inclusivity, the reclaiming of the derogatory term can sit uneasily for the generation subjected to it; the term homosexual can be similarly problematic for a younger generation.
As a number of the works are historical documents, it has not been possible to identify all individuals represented in the exhibition. We welcome any amendments or additions.
Text from The Photographers’ Gallery website
A Hard Man is Good to Find! Interview with exhibition curator Alistair O’Neill
Alistair O’Neill, professor of Fashion History and Theory at Central Saint Martins (University of the Arts London) talks about curating the exhibition A Hard Man is Good to Find! – a bold new exhibition charting over 60 years of queer photography of the male physique.

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Highgate Men’s Pond Album (detail)
1933
Courtesy Aberystwyth University School of Art Museum and Galleries
Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Highgate Men’s Pond Album (detail)
1933
Courtesy Aberystwyth University School of Art Museum and Galleries
Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Highgate Men’s Pond Album
1933
Courtesy Aberystwyth University School of Art Museum and Galleries

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Highgate Men’s Pond Album, front cover
1933
Courtesy Aberystwyth University School of Art Museum and Galleries
Highgate men’s pond has a history of accommodating physical culturists and queer men as swimmers and sunbathers. At the age of 21, artist Keith Vaughan purchased a Leica camera and set up a darkroom in his bedroom. One of his first projects was a photobook he designed and made charting the climbing temperature of a summer’s day at the pond. This is the first time the album has been exhibited.
Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Highgate Men’s Pond Album
1933
Courtesy Aberystwyth University School of Art Museum and Galleries

Keith Vaughan (British, 1912-1977)
Highgate Men’s Pond Album (detail)
1933
Courtesy Aberystwyth University School of Art Museum and Galleries
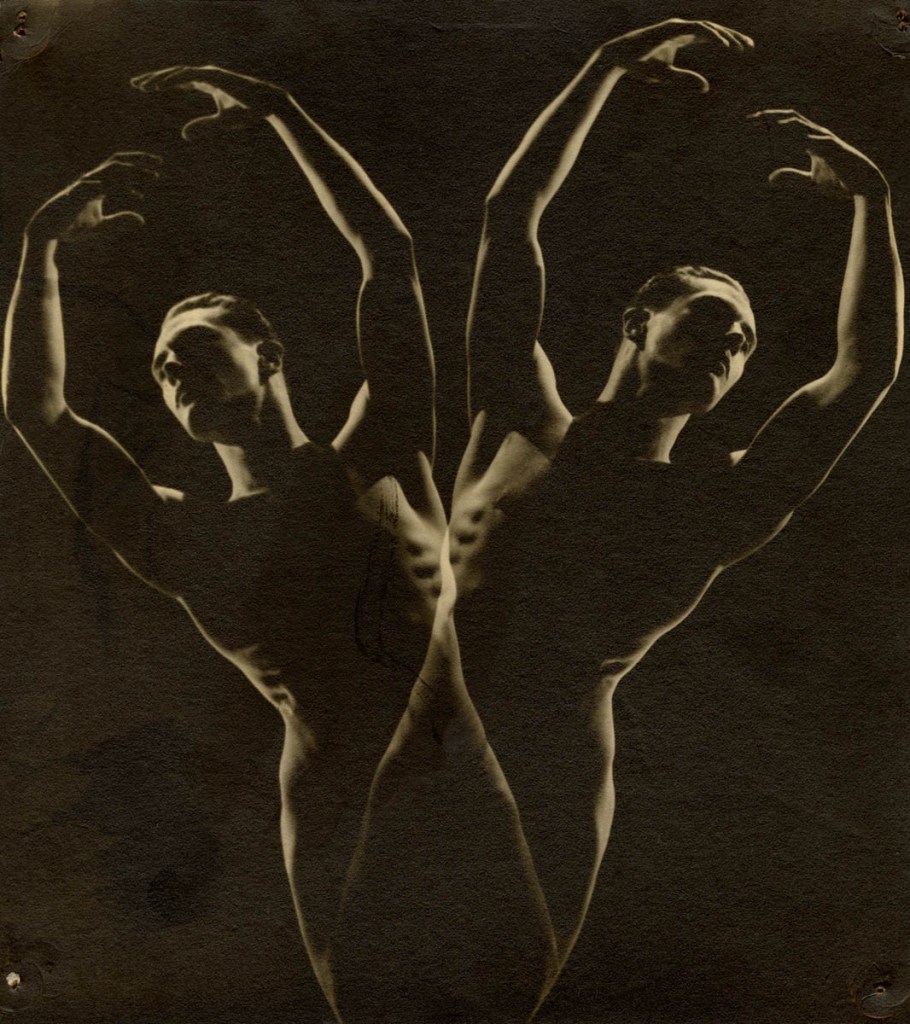
Angus McBean (Welsh, 1904-1990)
David Dulak
1946
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
In a study of Dulak taken in Angus McBean’s Covent Garden studio, an idealised diptych of the naked dancer is created from controlled lighting and double exposure. It was taken after McBean was released from prison, having served two years’ hard labour for gross indecency. During the Blitz, McBean relocated his studio to Bath and it was raided by police in 1941.
Between Chelsea and Wellington Barracks
I.e. Pimlico, an area of boarding houses and rented rooms, an enclave of queer life. Angus McBean opened his photographic studio on Belgrave Road in 1935.
Montague Glover had served in the First World War where he was awarded a medal. He went on to practice as an architect with photography on the side. His military career gave him easy access to the barracks where he recruited like-minded Guards to return to his studio or rented rooms and pose in less than full uniform. Squaddies available for gay sex were known as ‘a bit of scarlet’.
Wall text from the exhibition on Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
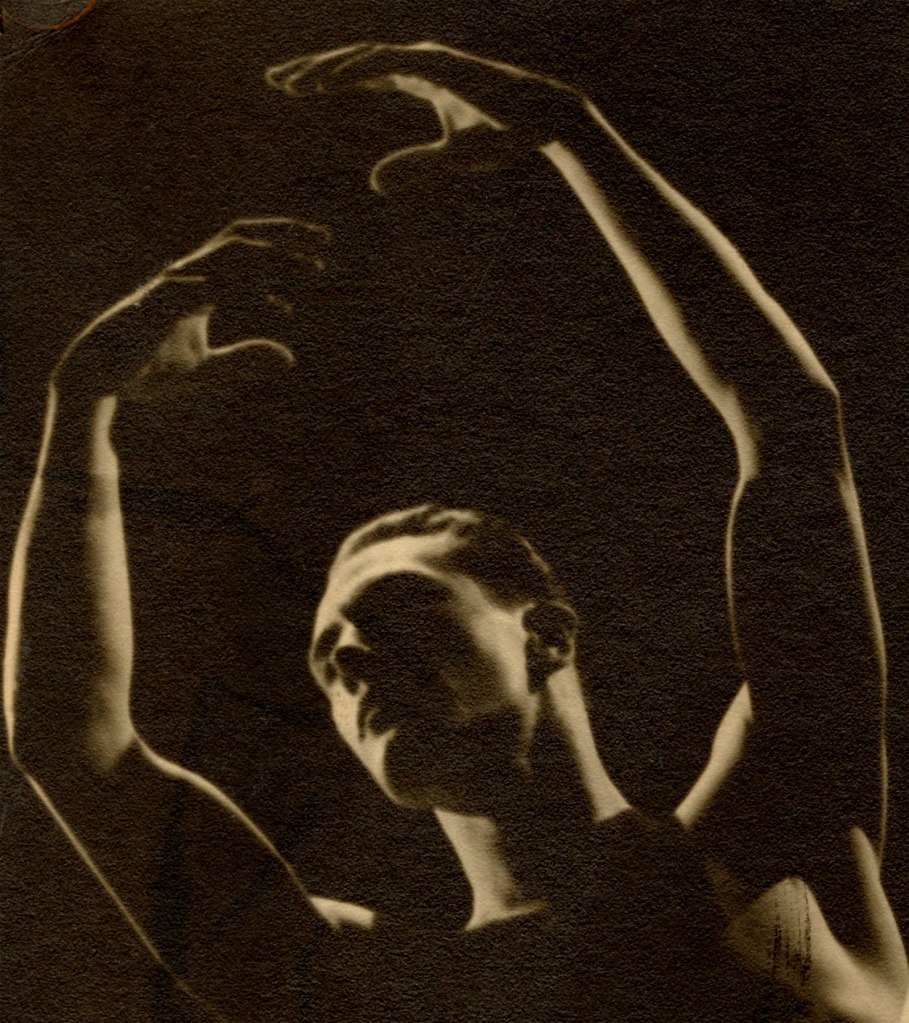

Angus McBean (Welsh, 1904-1990)
David Dulak (detail)
1946
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
“… by the time of the 1939 National Register he was 35 and living in a Hertfordshire cottage with three other men; his 19 year old photographer’s assistant, a 21 year old theatre clerk, and a 26 year old builder’s carpenter. Because of the London Blitz McBean moved to Bath where he set up a studio in his ground floor flat in Kingston House, Pierrepont Street, which soon became a meeting place for gay men, including servicemen who were stationed nearby.
On 13 November 1941 Bath police raided the flat and arrested McBean and a 16 year old youth. This began a chain of arrests using evidence from letters, diaries and statements to the police. It also resulted in one, and possibly two, suicides.
McBean and five other men were tried “on grave charges” at Winchester Assizes in March 1942 in front of Bristol born and former Clifton College pupil Lord Chief Justice Thomas Inskip, 1st Viscount Caldecote. All six men were found guilty and sent to prison with McBean receiving a 4 year sentence of hard labour for three charges of gross indecency. On hearing the sentence McBean collapsed in the dock. Others convicted were: 25 year old Lt. Tom Gill, in civilian life an actor, who received 15 months in prison; 18 year old Theodore Parker who was found in possession of 36 love letters from Gill and was sent to borstal for three years; 28 year old Arthur Sigmund Politzer, a well known artist and glass designer serving with the Field Security Police who received a 20 month prison sentence; 21 year old Eric Hughes, a civil servant sentenced to three years Borstal; and 22 year old Brian Ball, a soldier stationed in Surrey and sentenced to 15 months imprisonment.
Two other lives were ended by the case, though neither was charged. Alan Farr, a 30 year old Admiralty electrical fitter and draughtsman had been interviewed twice by police in the week after the raid about connections with McBean. On 16 December 1941 a Detective Inspector called at Farr’s office to escort him to the police station, probably to be charged. On the pretext of visiting the cloakroom before leaving, Farr shot himself and died instantly. Also mentioned during the trial was 18 year old Allan Patrick Nottingham, already on probation for indecency charges in Portsmouth, who may have been the catalyst for the initial discovery of Bean’s circle. A week after the trial, the Bath Chronicle of 21 March 1942 reported that Nottingham had been found in a crashed car on the Wiltshire Downs and had died shortly after in Swindon Hospital.
Jonathan Rowe. “Angus McBean,” on the Out Stories Bristol website 2021 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023

Angus McBean (Welsh, 1904-1990)
David Dulak
Ballet, January 1946
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
Dulak was a dancer, found by physique photographer John S Barrington in 1938 on Charing Cross Road. Barrington introduced him to theatre photographer Angus McBean; this study featured on the cover of Richard Buckle’s progressive dance journal, Ballet.
The Photographers’ Gallery presents A Hard Man is Good to Find! – a bold new exhibition charting over 60 years of queer photography of the male physique, on display from 2 March to 11 June 2023.
Bringing together more than 100 works, the exhibition centres on queer photographs of men’s bodies, produced in London in the twentieth century. While the 1955 Wolfenden Report and the 1967 Sexual Offences Act marked the partial decriminalisation of gay sexual activity, prompting gay liberation and the fight for social equality; any depiction of male nudity which suggested homosexuality remained subject to the 1857 Obscene Publications Act, which made making or distributing such images a criminal offence.
A clandestine visual culture emerged, regulated by laws which enforced homosexuality as invisible. In turn, it directly fed the defiant, overt visuality of gay men’s bodies that emerged in the post-war period. The tension between invisibility and visibility was negotiated through ideas about the male body drawn from art, physical culturists, and pornography – both home-grown and imported.
Taking a novel approach, the exhibition highlights key areas of London which were a focus for men seeking out men to photograph. It maps out a territory of risk and possibility across Highgate, between Chelsea and Wellington Barracks, in Soho, Brixton, Portobello and Euston. Within each site it is possible to locate artists of all persuasions, creating work about queer sensibilities and men’s bodies in radical ways. Catalogues, print ordering sheets, personal albums, magazines and publications are also included in the exhibition to explore how these photographs were circulated, exchanged and shared. Drawing together photographs produced for commercial, as well as creative and personal purposes, A Hard Man is Good to Find! dissolves hierarchies, creates non-linear historical narratives and brokers unlikely adjacencies.
Covering the 1930s to early 1990s, many works are exhibited here for the firsttime including Keith Vaughan’s Highgate Men’s Pond album, a modernist photo collage made in 1933; ‘The Portobello Boys’, an anonymous and striking portfolio of young men taken in the late 1950s and early 1960s in North Kensington. A set of archetypes, ‘The Londoners’, documented in the late 1960s by Anthony C Burls (trading as Cain of London) and Martin Spenceley’s street portraits of subcultural men photographed in Euston in the 1980s.
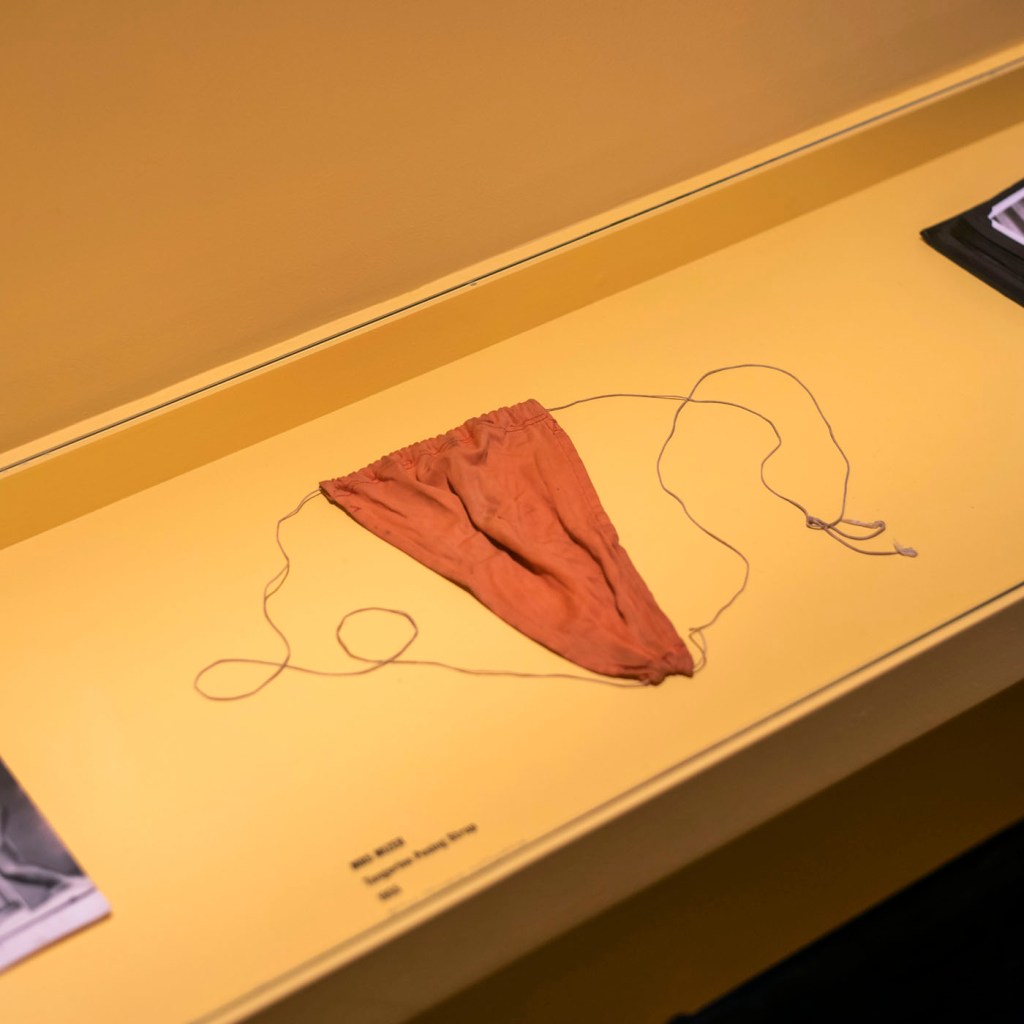
The hinge of this history is the posing pouch, a modest fabric covering for the male genitals developed by gay physique photographers to show as much of the male body as possible. Its origins lie in the US, in the Athletic Model Guild established by Bob Mizer in 1945, although there is evidence of it being worn for sunbathing in London in the early 1930s. An original 1950s posing pouch will on display in the exhibition. Employed to circumvent the ban on full nudity (which included the postal system), the pouch was also painted on mail order reproductions so that customers could rub them off once received in the post. The sighting and dematerialising of the posing pouch is key to thinking through how such images were consumed, and how queer erotics were discursively constructed from imaginative forms of resistance to power and oppression.
The exhibition includes works by: John S Barrington, Cecil Beaton, Guy Burch, Basil Clavering (trading as Royale), Rotimi Fani-Kayode, Bill Green (trading as Vince), David Gwinnutt, Paul Hawker, Angus McBean and Ajamu X.
Press release from the Photographers’ Gallery
Installation view of the exhibition A Hard Man is Good to Find! at The Photographers’ Gallery, London
Mrs Mizer
Tangerine Posing Strap
1955
Miles Chapman Collection
In 1945 Bob Mizer started the Athletic Model Guild, a model agency for bodybuilders for the film industry. In 1951 he launched a quarterly magazine, Physique Pictorial. For his photoshoots Mizer developed the skimpiest possible garment which dwindled down to the posing pouch. The exhibition explains that the earliest versions were sewn for him by his mother who, nonetheless, strongly disapproved of his sexuality. …
Slightly spoiling the effect, there is a small mention of the photographic evidence that this kind of super-minimalist covering was, in fact, being worn by sunbathing men in London in the early 1930s. Still. American has to be shoehorned in somehow. [see photographs by Keith Vaughan at the top of the posting]
Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
Bill Green (Vince)
catalogue sheet 31949
June 1949
Bill Green set up Vince Studio at 46 Manchester Street, Marylebone in 1946, specialising in photographs of bodybuilders. Prints could be ordered from catalogue sheets advertised in the classifieds of Health and Strength magazine. His catalogue sheets always had a gutter in the middle so they could be folded for discreet posting without creasing any image.
“Vince” had originally been the pseudonym of Bill Green, a photographer for men’s magazines, who shot wrestlers and bodybuilders naked but for nifty briefs he had cut down from chainstore trunks. These were so unlike available mens’ underwear that models and readers wanted to buy them. Green obliged by mail order, later adding to his catalogue the black sweater get-up of intellectual Paris and unshrunk Levis; in 1954 he set up in the Soho premises – described by Richard Benson of the Face magazine as “a CS Lewis of a wardrobe for young men” – they passed through its door into somewhere far out.
Vince and his boys supplied flagrant colour, untweedy texture, tight fit and low cut to a theatrical and artistic clientele, and many followers of camp. But these were not the only customers for that “certain ambiguity”: pink hipsters walked out of the shop on heteros, too.
Veronica Horwell. “John Stephen,” on The Guardian website Mon 9 Feb 2004 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
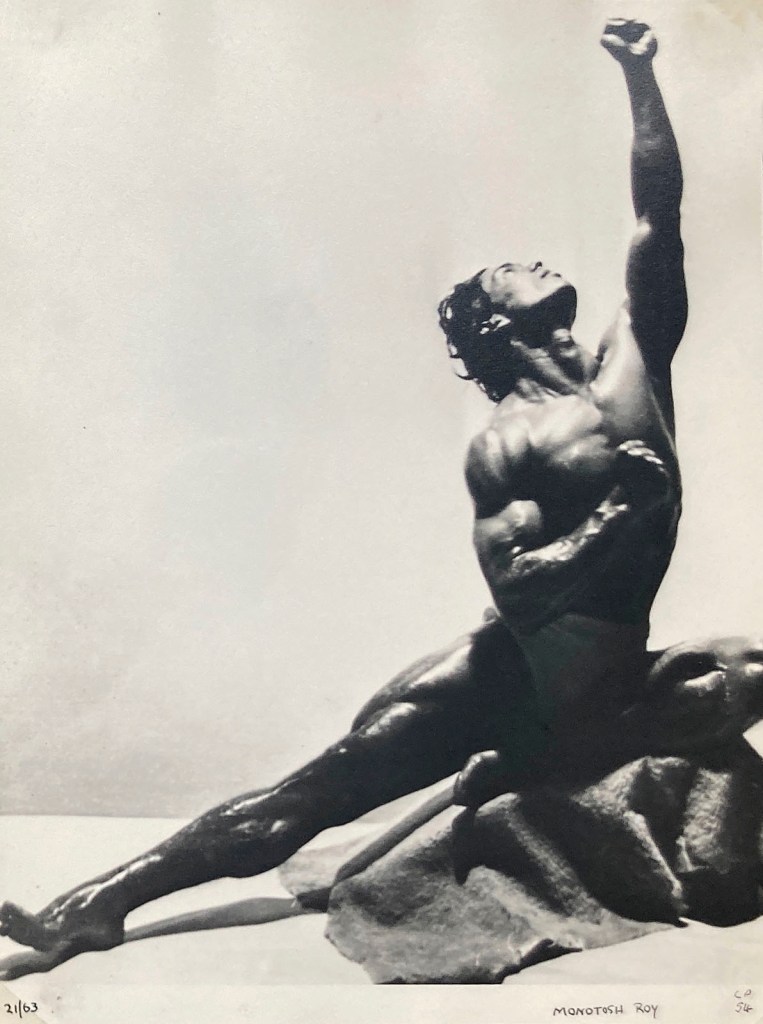

Bill Green (Vince)
Monotosh Roy
c. 1950s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
Bill Green – ‘Vince Man’s Shop’
In the 1940s, Bill Green was a local photographer who specialised in artistic images of ‘muscle men’ and male wrestlers. His models wore fairly revealing (for the time) homo-erotic garments that were mainly designed by himself due to the lack of availability of commercial items. He decided to develop this business and by 1950 was selling them through mail-order catalogues appealing mainly to the gay community. Following European trips in the early Fifties he expanded his portfolio to include the ‘existentialist’ look that was popular in France and Italy and was the first to introduce British men to ‘Beatnik’-style fashions.
With the continued success of his mail-order business, and aware of its popularity with the gay community, he opened Vince Man’s Shop in 1954. The establishment was located in Newburgh Street, an intelligent business decision as this was right at the heart of London’s gay community and very close to Marshall Street Public Baths which was a well-known and popular meeting area for gay men. One of the earliest advertisements featured a muscular Sean Connery in a ‘matelot’ vest and skin-tight jeans.
His colourful and unconventional designs, which included velvet and silk materials and pre-faded denim, quickly widened its appeal by attracting younger members of the Bohemian and Thespian fraternities who frequented the West End of London. The window displays were provocative for the time, often featuring mannequins wearing outrageous fashions including briefs and pink hipster-style slacks, and his wide range of clientele included the likes of George Melly, Peter Sellers, Sean Connery, Pablo Picasso and even the King of Denmark!
The fashions in the establishment were not cheap, and were generally out of the normal price range of ordinary teenagers, but this brought a certain ‘respectability’ to the informality and flamboyance of new styles and were certainly one of the catalysts in the major changes that were to take place in the fashions appealing to young males in the Sixties. As the decade progressed, and ’boutiques’ started providing a progressively fast-moving outlet for cheap fashion clothing, Vince’s came under increasing financial pressure and the establishment was forced to move to a less expensive location in North London. Bill Green closed the shop for good in 1969, subsequently becoming the manager of a Soho restaurant.
Anonymous. “Carnaby Street,” on the Sixties City website Nd [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
Montosh Roy (1916-2014)
Monotosh Roy (1916-2014) was an Indian bodybuilder, who held the Mr. Universe title in Group III Amateur Division in 1951. Roy was the first Indian and Asian to be awarded the Mr. Universe title. …
In 1939, he competed in his first bodybuilding competition, but did not fare well. He resolved for success and engaged himself in further practice. In 1939, he won the East Indian Bodybuilding Championship. In 1947, he won the All India Bodybuilding Championship.
In 1951, Roy travelled to the United Kingdom and participated in the Mr. Universe competition. He won the Mr. Universe title in Group III Amateur Division category. The audience at the competition were mesmerised by his muscle display. They queued up for his autograph and even waited up to two and half hours for his autograph. Following his victory at the Mr. Universe competition, he was felicitated at the India House by the Indian High Commissioner.
After his return to India he acted as a trainer in many physical culture clubs. He used to train fitness and yoga to celebrities. He founded the Indian Bodybuilding Federation in 1958. He was also the founding member of Asian Bodybuilding Federation. He also taught at the Calcutta University and the Law College. He became a featured columnist in periodicals on health and fitness. He also wrote a few books on Yoga. He conducted bodybuilding programmes that were telecast in the Doordarshan. He set up several bodybuilding and yoga centres in Kolkata.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Bill Green (Vince)
Vince advertisement
Health and Strength, 29 May 1952
In 1951, Green was advertising posing briefs in the Daily Mirror. They were made by shortening and over-dyeing Marks & Spencer underwear. This advertisement was shot at the Serpentine Lido. In 1954, Green opened the first men’s fashion boutique, Vince Man’s Shop, on Fouberts Place, Soho; it was the start of the peacock revolution and Carnaby Street as a fashionable retail destination.

Bill Green (Vince)
Vince Man’s Shop catalogue, model Sean Connery
Spring/Summer 1957
Courtesy Alistair O’Neill Collection
Vince Man’s Shop was the first boutique to sell imported men’s fashion such as American workwear jeans and Italian suiting and shirting. It catered to homosexual men and benefited from its proximity to the Marshall Street gym, Soho’s coffee bars and Piccadilly Circus. The cover model here is aspiring actor Sean Connery, better known at the time as a bodybuilder and artist’s model
Cecil Beaton (British, 1904-1980)
‘Narcissus of 1967’ (Gervase Griffiths)
c. 1967
Gelatin silver print
Marylebone
‘The City of Quebec’ pub in Marylebone is supposed to be London’s oldest gay pub. It opened in 1946 and was popular with gay RAF men. Bill Green learned photography and wrestling in the RAF and in 1946 set up Vince Studio at 46 Manchester Street, soon establishing a name for ‘physique photography’. He advised beginners to use a little oil to help highlight the contours of male musculature.
In 1954 Green opened a men’s fashion boutique in Foubert’s Place, Soho. In 1956 his assistant, John Stephen, opened another fashion store. According to the exhibition’s curator, Alistair O’Neill, Professor of Fashion History and Theory at Central Saint Martins, these sparked ‘the peacock revolution’ in men’s fashion. They helped turn Carnaby Street into the centre of modern fashion.
Artist Patrick Prockter also had a studio on Manchester Street. He took photos as preparatory studies for paintings, especially of his boyfriend Gervase Griffiths. He cultivated an artistic circle which included painter David Hockney, fashion designer Ossie Clark, and physique model Peter Hinwood. The veteran photographer Cecil Beaton was attracted to this young group of openly queer men. The exhibition includes sets of colour photos of Griffiths on a beach, and two by Beaton which are among my favourites, not because they’re nude, camp or gay – simply because they’re beautiful.
Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023

Basil Clavering (British, 1910-1973) (Royale, Hussar, Dolphin)
Mail order Storyette print
late 1950s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
Basil Clavering ran the Cameo Royal cinema on the Charing Cross Road, and the Cameo Poly (now Regent Street Cinema). He built a studio in the basement of his home on Denbigh Street, Pimlico, with his friend, John Charles Pankhurst, both of whom had served in the navy. In their studio Basil & John recruited military men to model in authentic uniforms, and Clavering innovated the ‘storyette’ where the catalogue sheet of photos available to order would set out a narrative drama like film stills from a motion picture.

Basil Clavering (British, 1910-1973) (Royale, Hussar, Dolphin)
Photograph from Storyette EX FJSS
1950s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
“Clavering and Parkhurst’s work reflects in both imagery and subject matter the drawings of Tom of Finland (Touko Laaksonen, 1920-1991). Laaksonen met Clavering during a visit to London and Studio Hussar commissioned a series of 17 panel drawings from him entitled The Thieving Cowboy (1957). No other photographers of the time were extracting so much visual drama from the clothed male figure. Other physique photographers were viewing the legal restrictions of the time as a challenge, whereas Royale and Hussar embraced them as an opportunity to produce magnificent risqué images.
Clavering and Parkhurst both served in the Navy, and their experience and connection to their subject matter is evident in the way clothing and partial undress was depicted, reflecting an insider’s comprehension and understanding.
Many of the models were also active military personnel, who Clavering met in public houses close to Hyde Park and the Chelsea barracks. Consequently, the images are not simply of men dressing up in uniforms, but rather men fully aware of both the purpose and symbolism of the uniform.”
Extract from the Royale HUSSAR catalogue published by the Collection Of Male Erotic Art © June 2016

Basil Clavering (British, 1910-1973) (Royale, Hussar, Dolphin)
Photograph from Storyette EX FJSS
1950s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
Clavering was a successful businessman, and owned the Gala-Royale cinema chain. More as a hobby than anything else, he established a photographic studio in the basement of his Pimlico home, with his friend John Charles Parkhurst (1927-2000). Both men had served in the Navy, and they were drawn to the military men around the Hyde Park and Chelsea barracks, whom they paid to model for them.
The studio operated under two names, Royale and Hussar, and Clavering sold the photographs by mail order. The images are profoundly erotic, despite there being no frontal nudity. Models are occasionally depicted solo, but more often in groups, and scenarios involve uniform, military and naval discipline, wrestling, light bondage and spanking – somehow always in a mood of levity and playfulness. Clavering met Tom of Finland, and several images from a biker series echo the Finn’s work; in 1957 Studio Hussar even commissioned a series of drawings from him.
Text from the Bonhams website

Basil Clavering (British, 1910-1973) (Royale)
Untitled (Footballer)
1950s
Gelatin silver print
As far as I know this photograph is not in the exhibition but I like it!

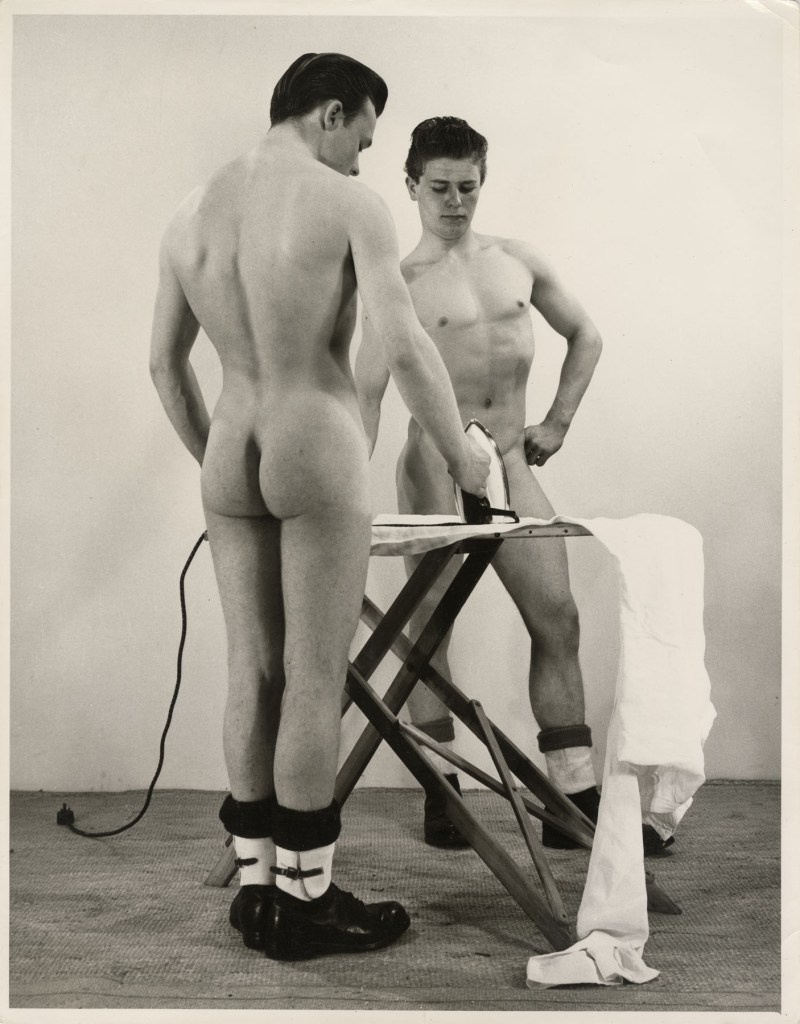
Paul Hawker
Spencer Churchill
1951
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
The Serpentine
In the 1950s British bodybuilding magazines catered for two audiences, straight bodybuilders and a gay readership. As well as the obvious photos and articles, in their back pages these magazines offered discreet mail order services for ‘original physique studies’. This section features the work of mail order publisher William Domenique (trading as Lon of New York) and gay erotic artist Bill Ward.
Paul Hawker came from Bristol, moved to London, and took photos of young men preening and parading at the Serpentine Open Air swimming pool, another well-known gay haunt. He is represented by some of the photos he took of his friend, body builder Spencer Churchill. Apparently Churchill was one of the first to adopt the American fashion for denim workware jeans as regular casual clothing.
Wall text from the exhibition on Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023

William Domenique (Lon of London)
Model Spencer Churchill print
Bill Ward adjusted print, 1955
© Estate of William Domenique (‘Lon of London’)/ Burch Collection
And once you knew, you could purchase. Lots of the images here skirt around the legality of the male nude by being available in bodybuilding magazines, or as a catalogue of physiques for fitness buffs to emulate at home. One amazing image shows Spencer Churchill tensed and glistening while wearing a posing pouch that you could scratch off to reveal the goods beneath. It’s a fascinating portrait of hidden mid-century male desire in London.
But there are ethical questions here too. John S Barrington pretended to be a Vogue photographer to persuade men to pose for him. That’s uncomfortable, exploitative and not really dealt with in the show. Also, lots of the subjects in the exhibition wouldn’t have considered themselves gay or queer either, so framing them anonymously in a queer context totally removes the sitters’ agency.
Then there’s the group of photos of young men lounging around in west London bedrooms and living rooms. They’re amazing images, totally unguarded and joyful, but they were purchased as a box of anonymous negatives from Portobello Antiques Market by Emmanuel Cooper. These men have had no say in their private nude moments being plastered across The Photographers’ Gallery decades after they were taken. This was a time when privacy not only mattered, but had a tangible impact on people’s lives, and this has taken the choice away from them.
So there are issues here and some tricky ethical moments, but there’s still a lot to like. At its best, this show is a celebration of the male form in London from a time when that was an incredibly dangerous thing to celebrate. The thing is, men are hot, always have been, and we should be very grateful that these days we can say that without getting put in prison.
Eddy Frankel. “‘A Hard Man Is Good to Find!’,” on the Time Out website 6 March 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023

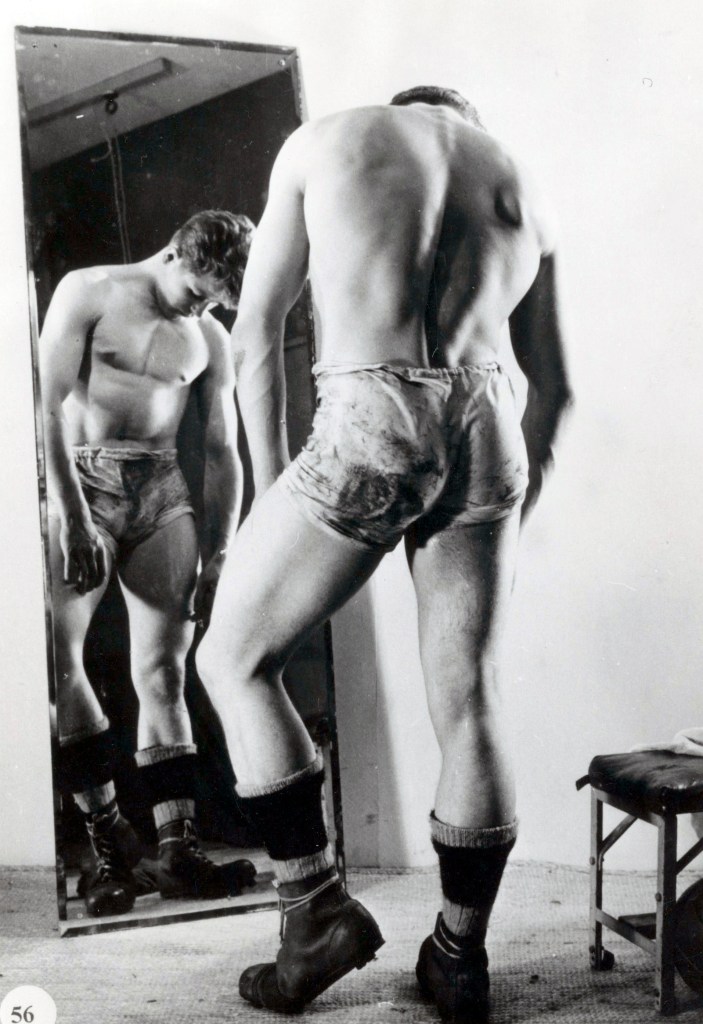
Anonymous photogapher
The Portobello Boys
Early 1960s
Courtesy Emmanuel Cooper Archive
The Bishopsgate Institute Special Collections and Archives
Emmanuel Cooper purchased a set of negatives from Portobello Antiques Market in the early 1980s. Cooper was a ceramicist, writer, art critic and gay rights activist. He called this anonymous body of work The Portobello Boys, as he believed they were taken in the north Kensington area in the late 1950s to mid-60s. Taken in an era before gay liberation, they document young men posing, in turns uncertainly and assertively, in states of undress.
Notting Hill
Became known after the war for its combination of bachelor housing and growing immigrant community. In the early 1980s ceramics artist Emmanuel Cooper picked up a set of negatives at Portobello Market. It turned out to be a set of studies of nude or partially clothed young men with an obvious queer vibe taken in the late 1950s and early 1960s in North Kensington. Cooper titled it ‘The Portobello Boys’ and arranged for its publication. They are surprisingly homely, unguarded, intimate studies of everyday life.
Wall text from the exhibition on Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
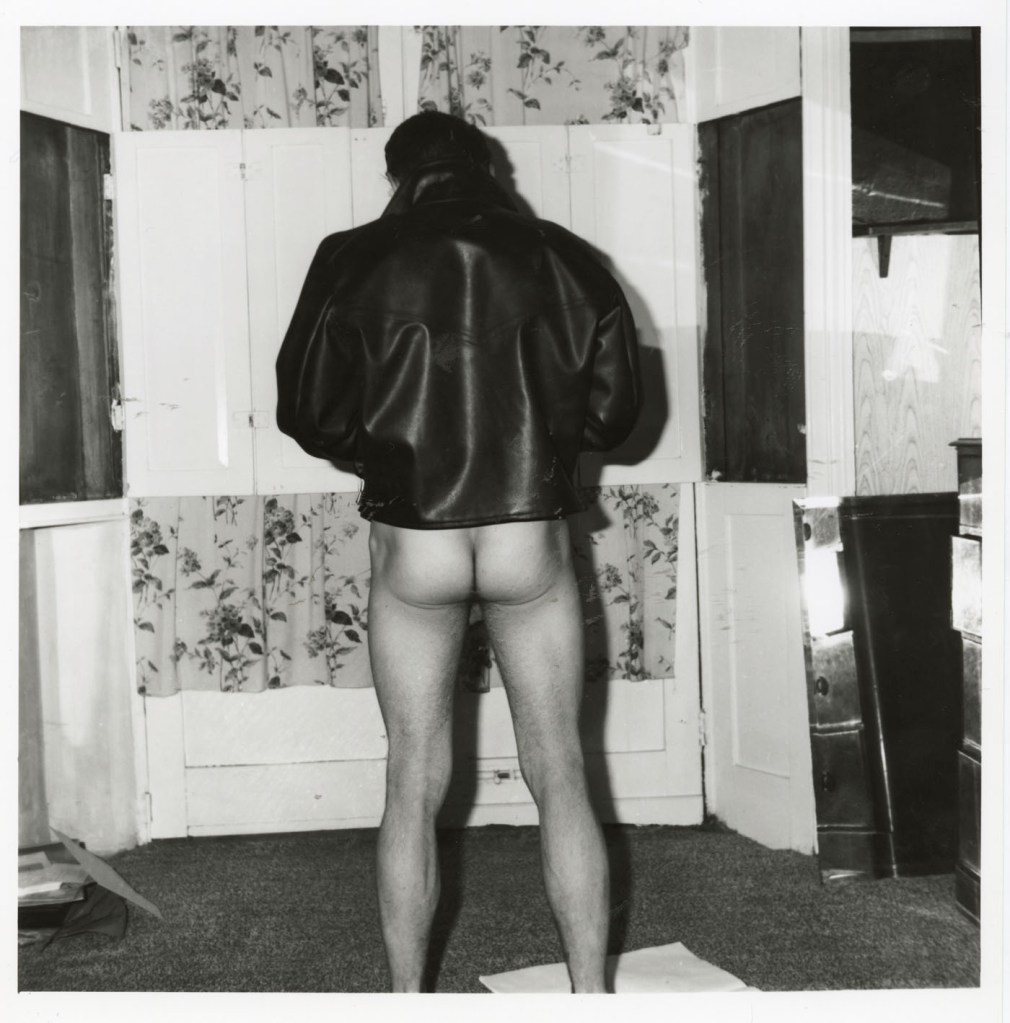
Anthony C Burls (Cain of London)
Catalogue sheet
c. 1968-1970
Guy Burch collection
Anthony C Burls was a photographer who engaged young men to model through street casting. He also ran a coffee shop at World’s End in Chelsea in the 1960s, took casual work at Battersea Funfair and regularly attended a gym in Brixton. He used these contexts to find working-class men to photograph.
White Brixton
Anthony C. Burls was an interesting character. In the 1960s he ran a coffee shop at the World’s End in Chelsea, got odd jobs working at funfairs, and attended a gym in Brixton. In all these settings he asked working class men if he could photograph them and the result is a series of full length, mostly fully clothed studies which I think I liked most out of the exhibition. He named the series ‘The Londoners: Official reports’, including not just the photos but the man’s job description and a pen profile. His first business address was Studio 200 on Railton Road, also home to the South London Gay Community Centre. …
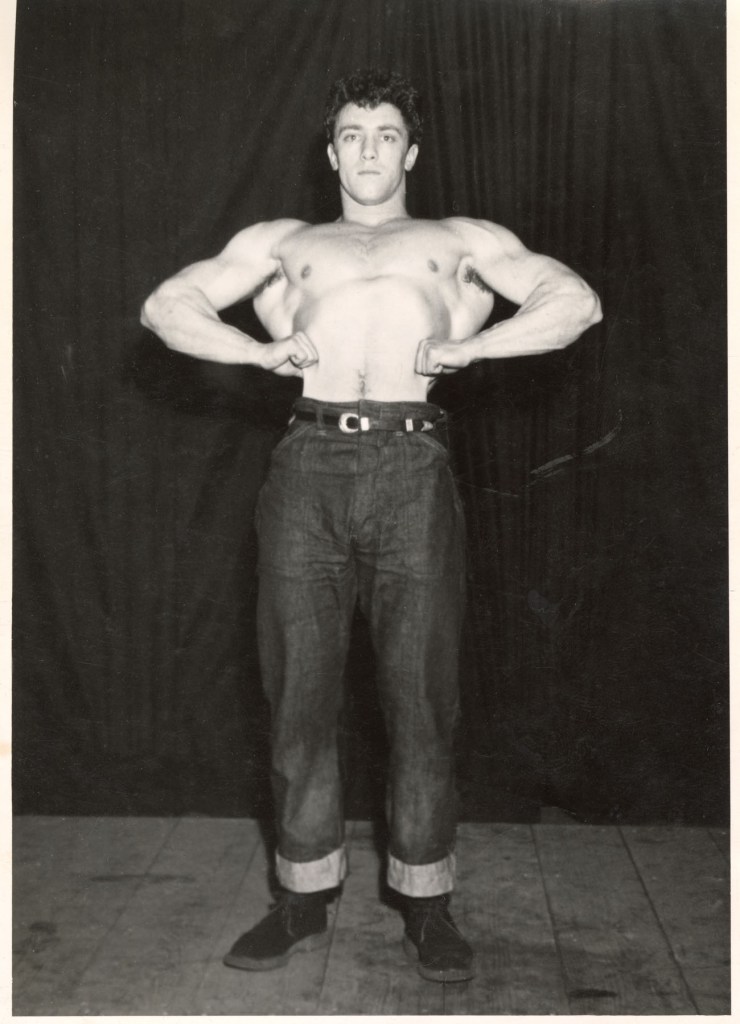
I liked Anthony C. Burls’ set of photos of the rough, dirty, tough-looking young men you get working at funfairs and such, swaggering among the dodgems in tight jeans, unbuttoned shirts and rocker brylcreemed hair. [see photograph at bottom of posting]
Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
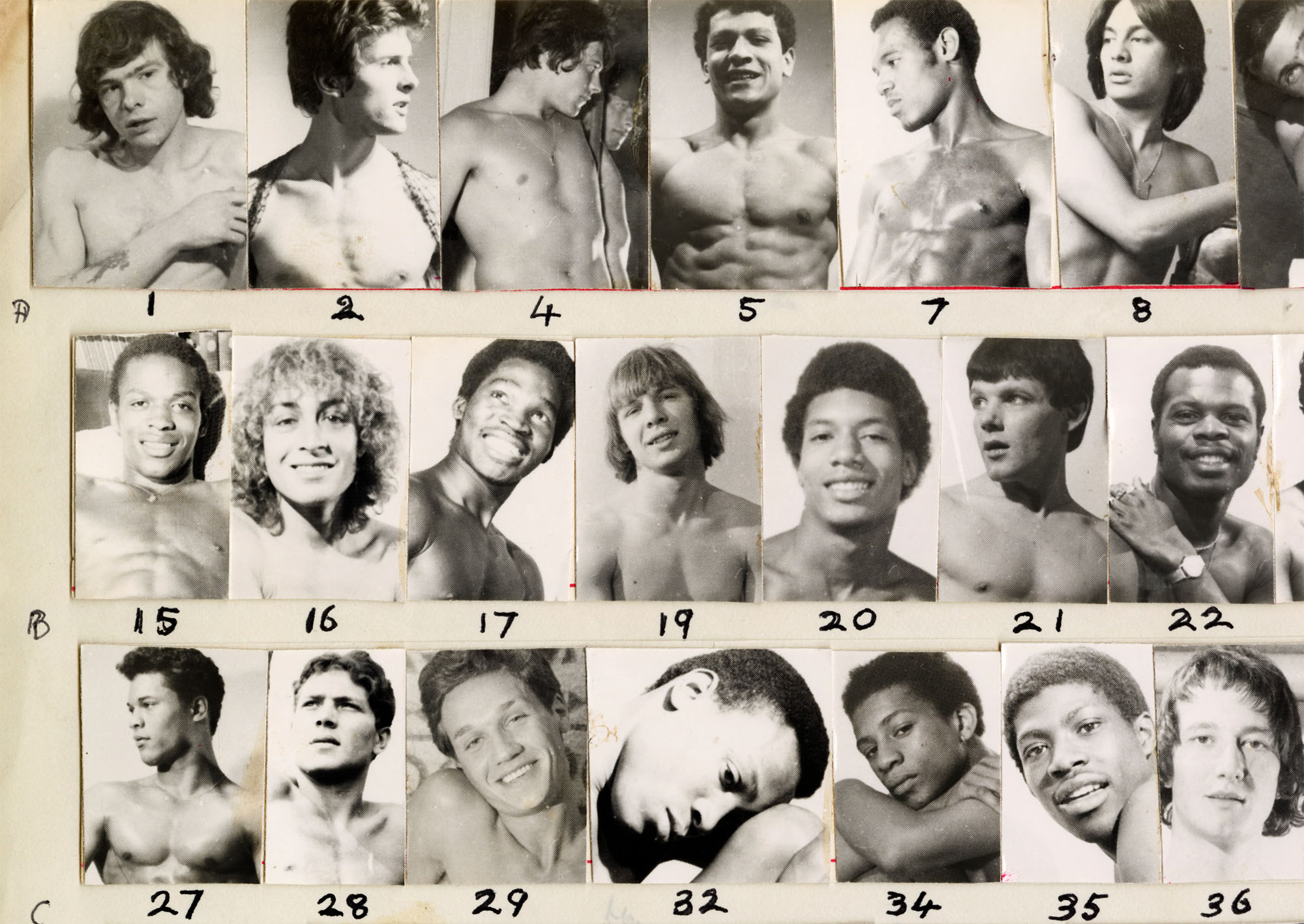
John S Barrington (British, 1920-1990)
John Hamill
c. 1966
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
John S. Barrington (1920-1991) was a British physique photographer and publisher. Barrington’s photos of nude or semi-nude men appeared widely in British and American physique magazines, sometimes under the pseudonym John Paignton. Barrington published many of his own physique magazines, including Male Model Monthly, the first in Britain. He also published a number of books related to photography and anthropometry. Barrington was a prolific artist and publisher, and by 1984 was said to have published more nude titles than any other individual in Europe or the United States.
Barrington had frequent sexual encounters with men throughout his life, particularly with the men who modeled for him, though he identified as heterosexual.
Barrington began photographing men in 1938 at the men’s bathing pond at Hampstead Heath. He studied at St Martin’s School of Art and L’Ecole des Beaux Arts in Paris. In addition to photography, Barrington was also a visual artist and sculptor.
Barrington began working as a physique photographer in 1948. In 1954, he began publishing Male Model Monthly, the first physique magazine in Britain. From 1954 until 1979, he would go on to publish many more physique magazines in Britain and the US, among the best-known being MAN-ifique, FORMosus, Superb Youth, and Youth in the Sun.
Barrington was known to select models in the “boy next door” mold, with average body types. His photographs were mostly taken outdoors, with models appearing in relaxed, natural poses.
In the 1950s and 1960s Barrington published books on anatomy and anthropometry, ostensibly for the benefit of artists.
Text from the Wikipedia website
John S Barrington (British, 1920-1990)
Catalogue sheet
c. 1970s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
John S Barrington (British, 1920-1990)
Catalogue sheet (details)
c. 1970s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
John S Barrington (British, 1920-1990)
Catalogue sheet
c. 1970s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
John S Barrington (British, 1920-1990)
Catalogue sheet (details)
c. 1970s
Courtesy Rupert Smith Collection
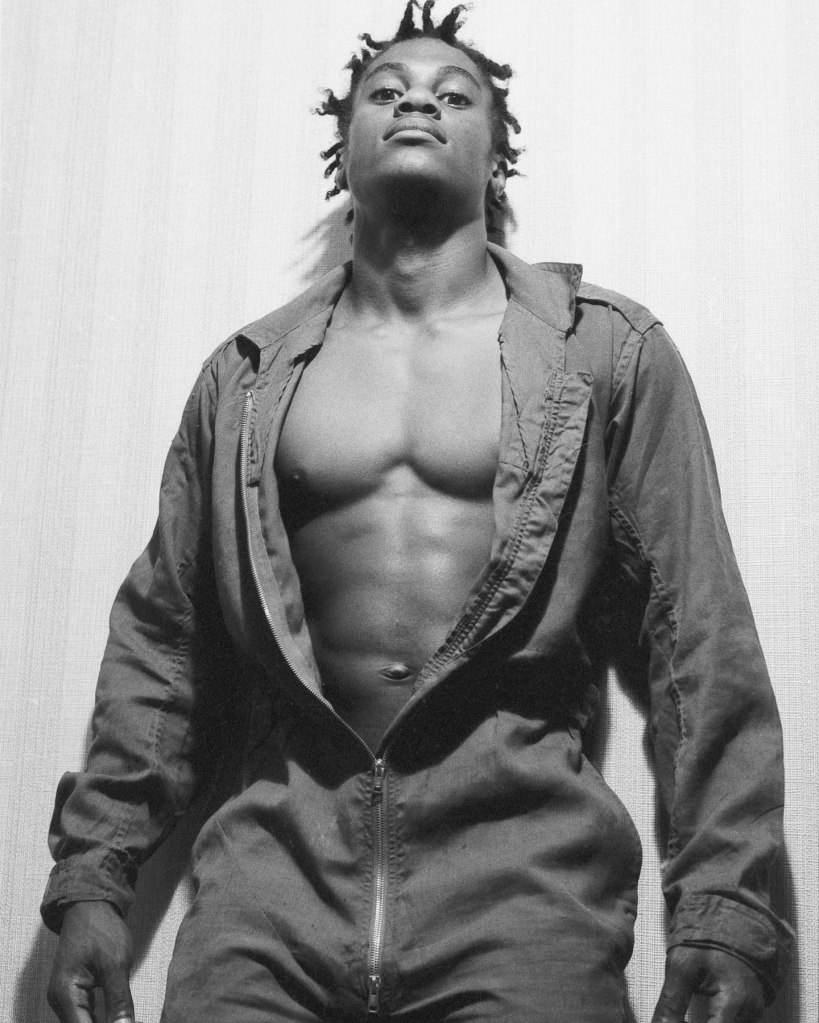

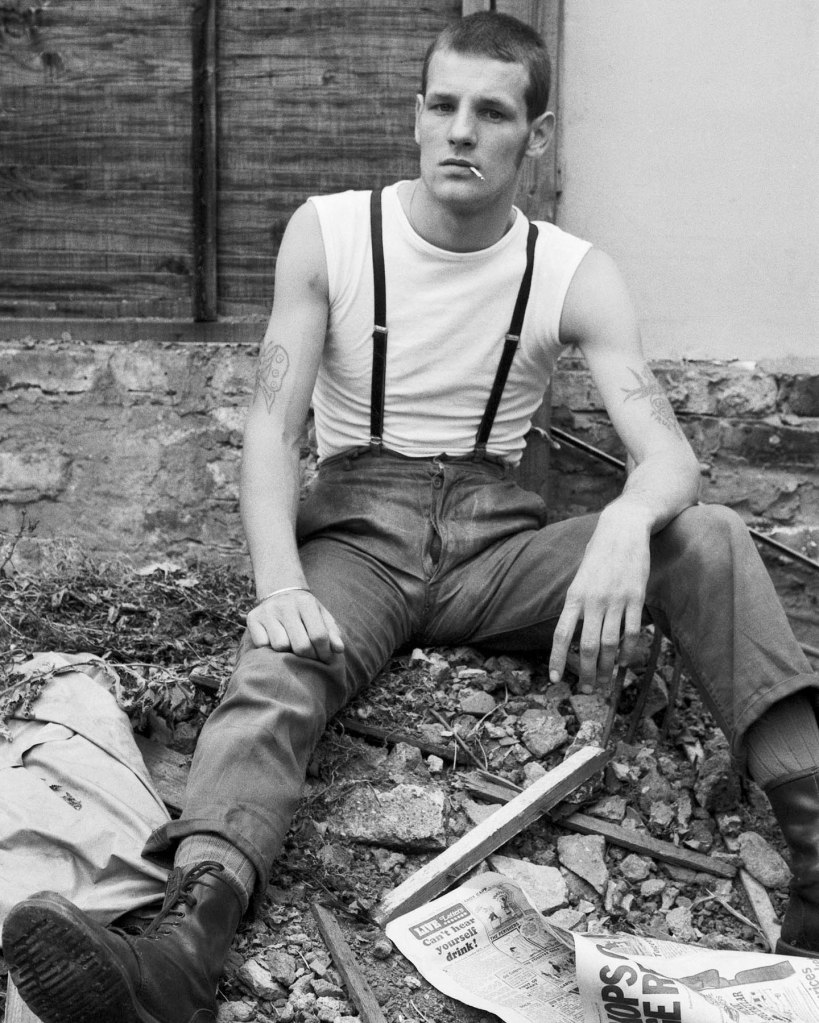
Martin Spenceley
Untitled
1980s
Courtesy of the Michael Carnes Collection
Martin Spenceley photographed young men in Euston in the 1980s, scouting for Teds, punks and skinheads, persuading them to pose by cheekily lying that he worked for Vogue America.
Martin Spenceley
Untitled
1980s
Courtesy of the Michael Carnes Collection
Rough trade!
The show is split into different geographical areas of London, each of which had a slightly different character, lending themselves to different types of man and images. We start in the bedsit land of Pimlico. In the 1950s this was home to many single young queer men as well as soldiers living in the two nearby army barracks. We see pictures of many of the young fit soldiers who liked being photographed to earn a little extra money.
We then move on to Hampstead Heath the famous cruising area and home to the men-only Highgate Men’s Swimming Pond. A good collection of sunbathing men from the 1930s is included here. Other areas of London shown include a selection of 1950s male physique photography shot in Marylebone and in Hyde Park and ‘The Portobello Boys,’ an interesting selection of men shot at home in Notting Hill and Portobello in the 1960s. This area of West London was very queer back then.
Then we head south of the river to Battersea and Brixton where pictures range from 1960s fairground and other workers through to queer artists and activists in the 70s and 80s.
Ris Fatah. “A HARD MAN IS GOOD TO FIND! a bold new exhibition charting over 60 years of queer photography of the male physique,” on the queerguru website Friday, March 24th, 2023 [Online] Cited 28/05/2023

Anthony C Burls (Cain of London)
The Young Londoners
late 1960s – early 1970s
“The show is structured through areas of London that were known for attracting queer communities and related imagemaking practices,” he explains.
“This might be open air sites where men could see and be seen, such as Highgate Men’s Pond or the Serpentine Lido, but it also includes areas that offered furnished rooms for rent that were popular with single gay men, such as Pimlico or Notting Hill.”
Interesting adjacencies are revealed, such as the fact that artist Patrick Procktor had a studio in Marylebone in the same street as physique photographer Bill Green (who traded under the name Vince).
Many of the works in the show are being exhibited at the gallery for the first time, including a set of archetypes, ‘The Londoners’, documented in the late 60s by Anthony C Burls (who traded as Cain of London) and Martin Spenceley’s street portraits, photographed in Euston in the 80s.
It also highlights fascinating historical objects such as an original 1950s posing pouch, which has its origins in the US Athletic Model Guild established by Bob Mizer in 1945, but was widely used by gay physique photographers to show as much of the male body as possible.
In bringing the show to life, O’Neill hopes to demonstrate how this fascinating pocket of queer history has gone on to influence visual culture more broadly. “The movement certainly informed the body consciousness of queer visual culture,” he says, “but I would argue that it’s intertwined history with the emergence of men’s fashion in the 1950s and 60s has played a significant role in contemporary queer style positions, both naked and dressed.”
Curator Alistair O’Neill quoted in Aimee Mclaughlin. “A queer photographic history of the male physique,” on the Creative review website 01/03/2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023

Anthony C Burls (Cain of London)
Untitled (Carnie)
1960s
As far as I know this photograph is not in the exhibition but I like it!
A secret history
All this explains why, as the tools of photography became cheaper and more widely available, from the 1920s and 30s onwards a clandestine visual culture emerged. During the 1930s stunning images of athletic male physiques could be associated with the general social trend towards hiking and healthy outdoor activities. During the Second World War photographers were encouraged to take photos of our brave boys looking butch and manly. After the war publishers gained more confidence but were still liable for arrest and confiscation of stock. It was only really in the later 1960s that, along with so many other social movement, gay men felt increasing confidence in depicting their lifestyles and objects of desire openly.
Throughout the period there is a continual interplay and overlap between licit and illicit ways of visualising the male body: the naked athlete trope ultimately derived from statues of ancient Greek and Roman men. Images of tough soldiers could walk a narrow line between being heterosexual propaganda and gay adoration. Young men sunbathing could be following European models of health and fitness. Models and precedents from heterosexual art and culture were continually being subtly reworked, the borderline between legal art and illegal ‘obscenity’ shimmered and wavered within individual images, different definitions of desire fight in single photographs.
Anyway, the repression gay photos were liable to be subject to at any moment explains why a good deal of this visual culture was underground or hidden. Some gay publications were subscription only, others were available as a sideline in otherwise ‘respectable’ book and art shops. In the 60s and 70s more magazines and specialist shops came out of the closet.
Simon. “A Hard Man is Good to Find! @ the Photographers Gallery,” on the Books and Boots website May 24, 2023 [Online] Cited 29/05/2023
The Photographers’ Gallery
16-18 Ramillies Street
London
W1F 7LW
Opening hours:
Mon – Wed: 10.00 – 18.00
Thursday – Friday: 10.00 – 20.00
Saturday: 10.00 – 18.00
Sunday: 11.00 – 18.00
































































You must be logged in to post a comment.