March 2016
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Untitled [Spectators massing for the Grand Review of the Armies, 23-24 May 1865, at the side of the crepe-draped U.S. Capitol, flag at half mast following the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln]
1865
The Grand Review of the Armies, Washington, 23-24 May, 1865
Location
Pennsylvania Avenue, Northwest, Washington, D.C.
Participants
George Gordon Meade
Army of the Potomac
William T. Sherman
Army of the Tennessee
Army of Georgia
In this, the second of three consecutive postings on nineteenth century photography, I compare and contrast the photographs that Alexander Gardner and Mathew Brady took of the official celebrations that marked the close of the American Civil War: The Grand Review of the Armies held over two hot days in Washington, 23-24 May, 1865.
In the last post, Dark Fields of the Republic: Alexander Gardner Photographs, 1859-1872, we examined the establishment of the rivalry between Brady and Gardner. The latter had been assistant to Brady for many years including the first two years of the war, before setting up his own studio in Washington, only a few blocks from the studio of his former employer.
In this post we have a chance to compare the styles of the photographers side-by-side, an experience almost unique in the annals of early photography: two great photographers taking images of the same event, possibly at the same time (they could have been photographing on different days, it being a two day event). It is fascinating to compare the placement of the camera by each artist and the feeling that they wanted to convey in the representation of the event.
In the image Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry] (1865, below), Gardner places the camera at head high level and fills the foreground with a melee of swirling men on horses, the blurred movement of such belying the length of the exposure. In this photograph the Presidential reviewing stand beyond is of secondary importance for the photographer, compared to the atmosphere, the “air” that he creates with skirmish happening in front the camera.
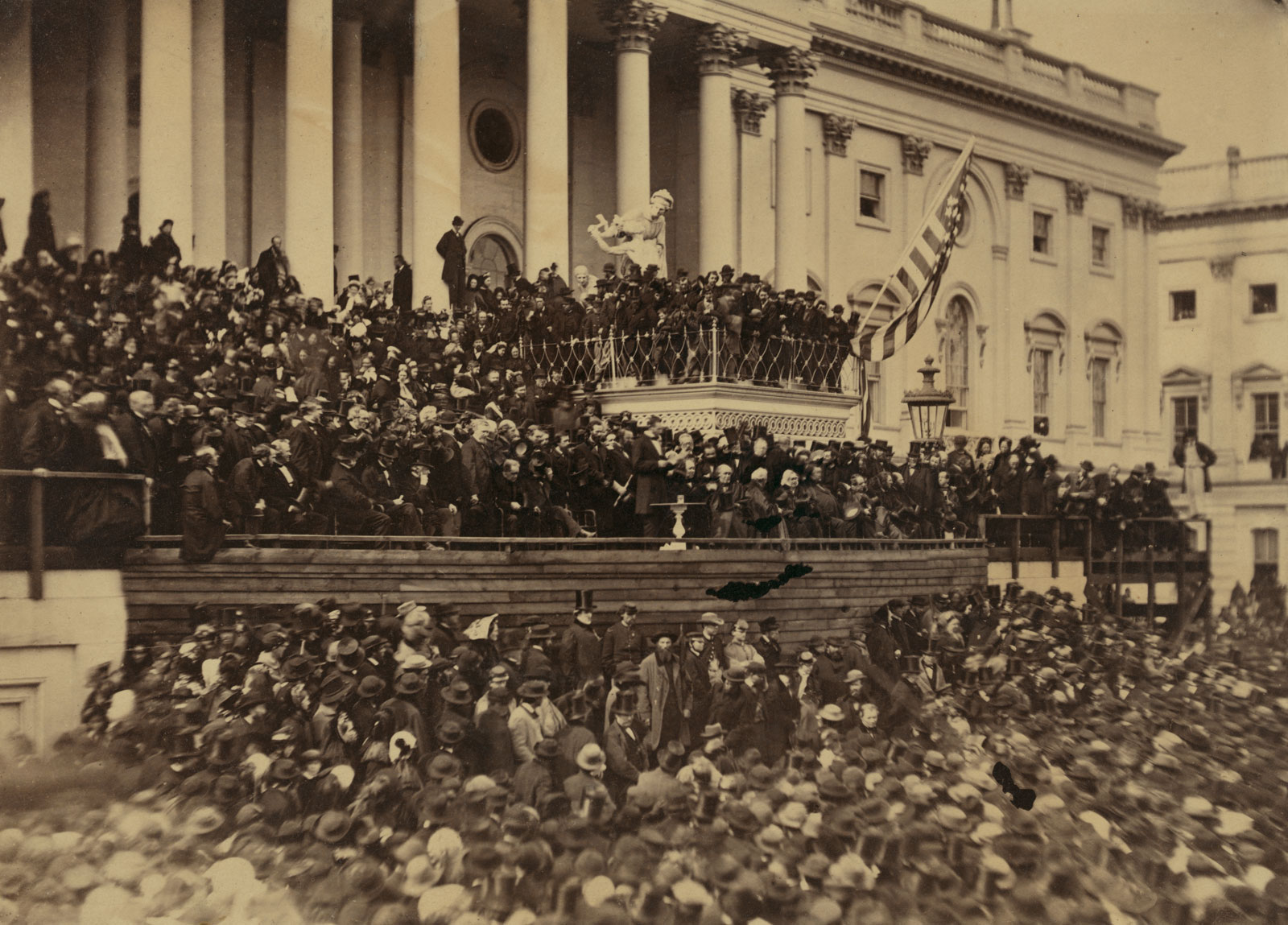
By contrast, Brady positions his camera high up above the crowd looking down on the spectacle in his image Reviewing Stand in Front of the Executive Mansion, Washington, D.C., May, 1865 (below), layering his image with four separate delineations: the crowd in front which grounds the image; the blur of the soldiers, wonderfully previsualised by Brady using the length of his exposure; the bulk of the Reviewing Stand; and the trees and sky beyond.
There is no right or wrong here, for they are both strong images. For a feeling of atmosphere, the surging and swirling of horses, then the Gardner is most effective but for me, the Brady is the more successful image in imparting the magic and cultural significance of the event. The reviewing stand still has a strong presence but it is the sea of blurred bodies that carries you along with the marching armies.
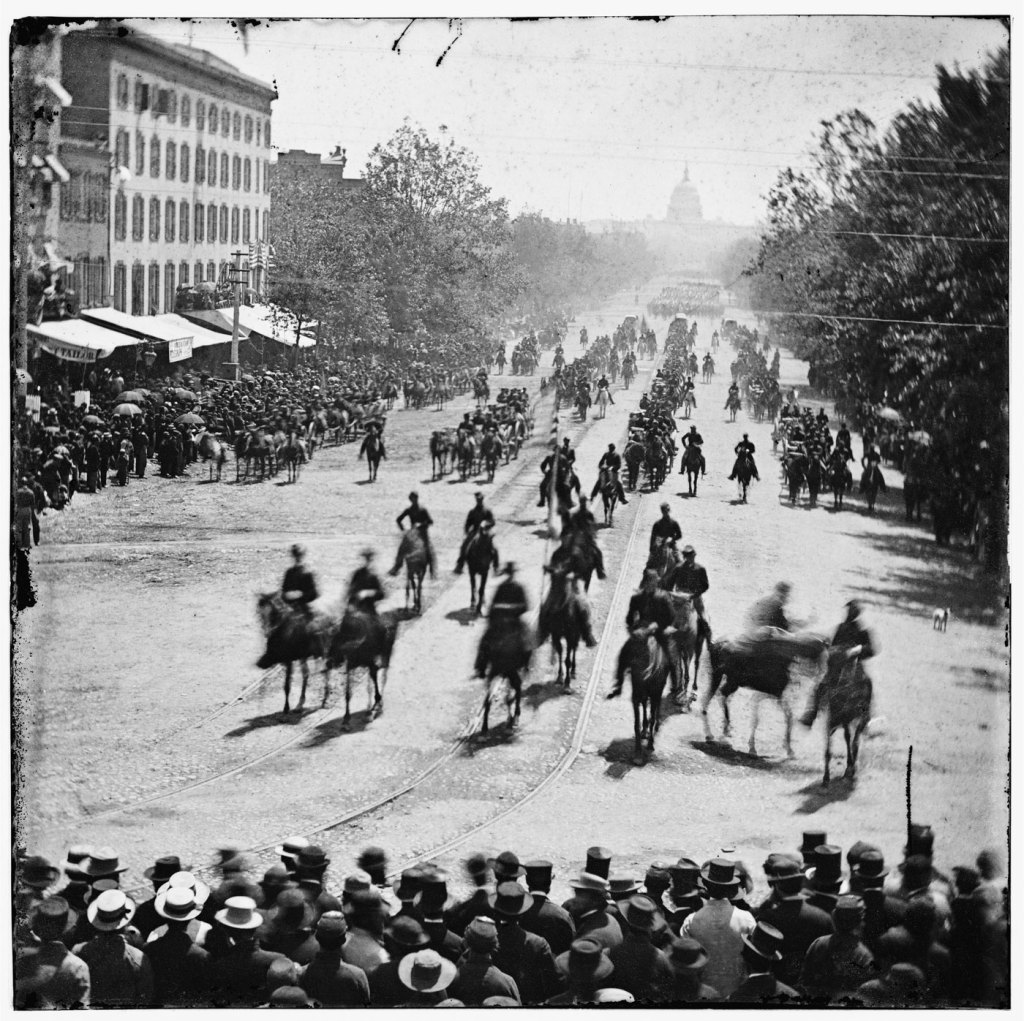
We can compare another two camera positions used by both artists, this time as they photographed the armies as they marched down Pennsylvania Avenue. In all of Gardner’s photographs of this location his camera is obliquely offset to the avenue and slightly above the crowd so that we, the viewer, only get a glimpse of the Capitol building in the distance through the dust raised by the horses hooves. There is no vanishing point in these images and the oblique perspective allows Gardner to give the viewer a wonderful sense of the scale of the Review, as wagons stretch away into the distance, as bayonets flash in the sun. Imagine the smell of such a scene, of horse shit, of sweating men in thick uniforms, the crowd with umbrellas open to protect them from the heat of the May day sun.
By contrast, in Brady’s stereocard and image Grand Review, Pennsylvannia Avenue, May, 1865 (both below), the artist positions his camera high up above the crowd with a view directly down Pennsylvania Avenue with the Capitol building clearly seen in the distance. In one image, Brady grounds his composition with the serried ranks of bystanders at the bottom of the image, while in the stereocard he allows the lines of advancing horses to lead the eye of the viewer back into the interior of the image. Again, there is no right or wrong to either approach and they both have elements to commend them. In this instance, I like the approach that Gardner has taken: the position of the camera is more intimate, and you really get a feeling of getting down and dirty in amongst the crowds at the event, viewing the bounteous strength of the army as it disappears into the hazy distance.
In general, having extensively viewed the photographs of each artist of this event, I can say that Mathew Brady seems to be the more inventive of the two artists. In the last two photographs in the posting, Brady’s Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865] (below) he does something that Gardner never did: photograph the reviewing stand from the reverse angle (as the cavalry march blearily away); and photograph the reviewing stand in the dying light, after the parade was over for the day. This is the most poignant image, focusing as it does on the empty wooden stands and the tree in front of it, not the reviewing stand. Brady could have easily moved further up the road but he pulls back and lets our eyes play over the empty scene.
Of course there is always a danger to presume that these differences have always been there. One photographer may have bitterly forced the other into taking a particular vantage point, considering that they may have been within shouting distance of each other. However, it is evident these two artists had a clear opinion of where history was going and only got reinforcement from their subject matter on these opinions. Today, we live in murky times – we can see everywhere – where nothing can be trusted in its appearance… it is a swamp. How different the “view” seemed to Brady and Gardner (mankind / war / peace / great men / great ideas) compared to the nexus in which we live today.
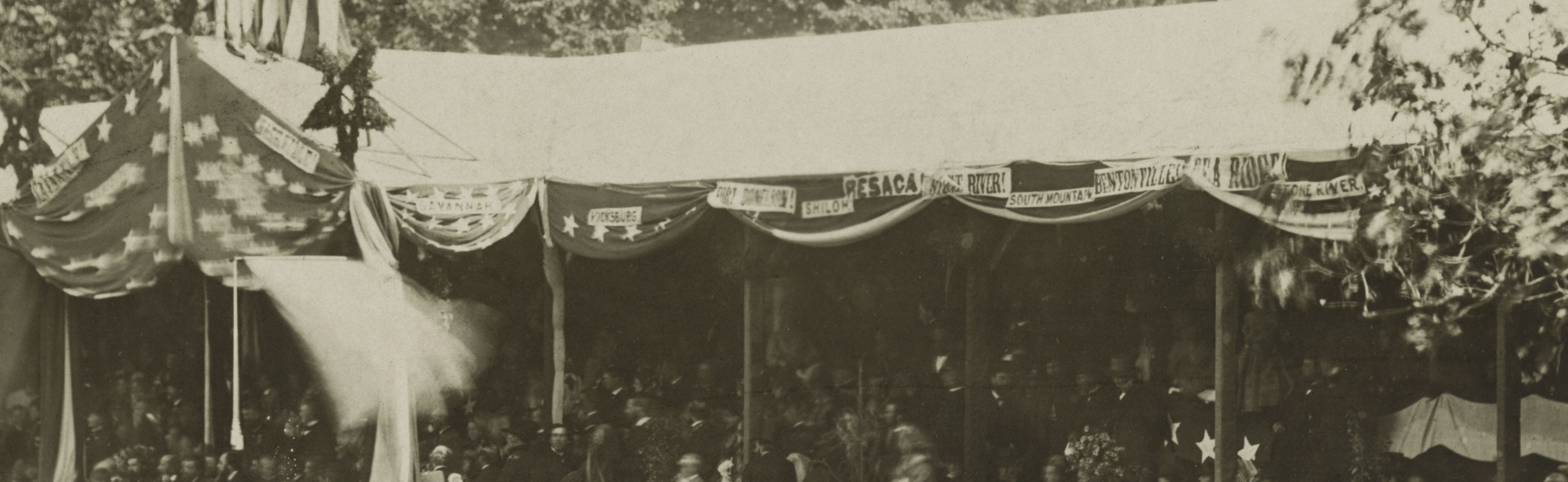
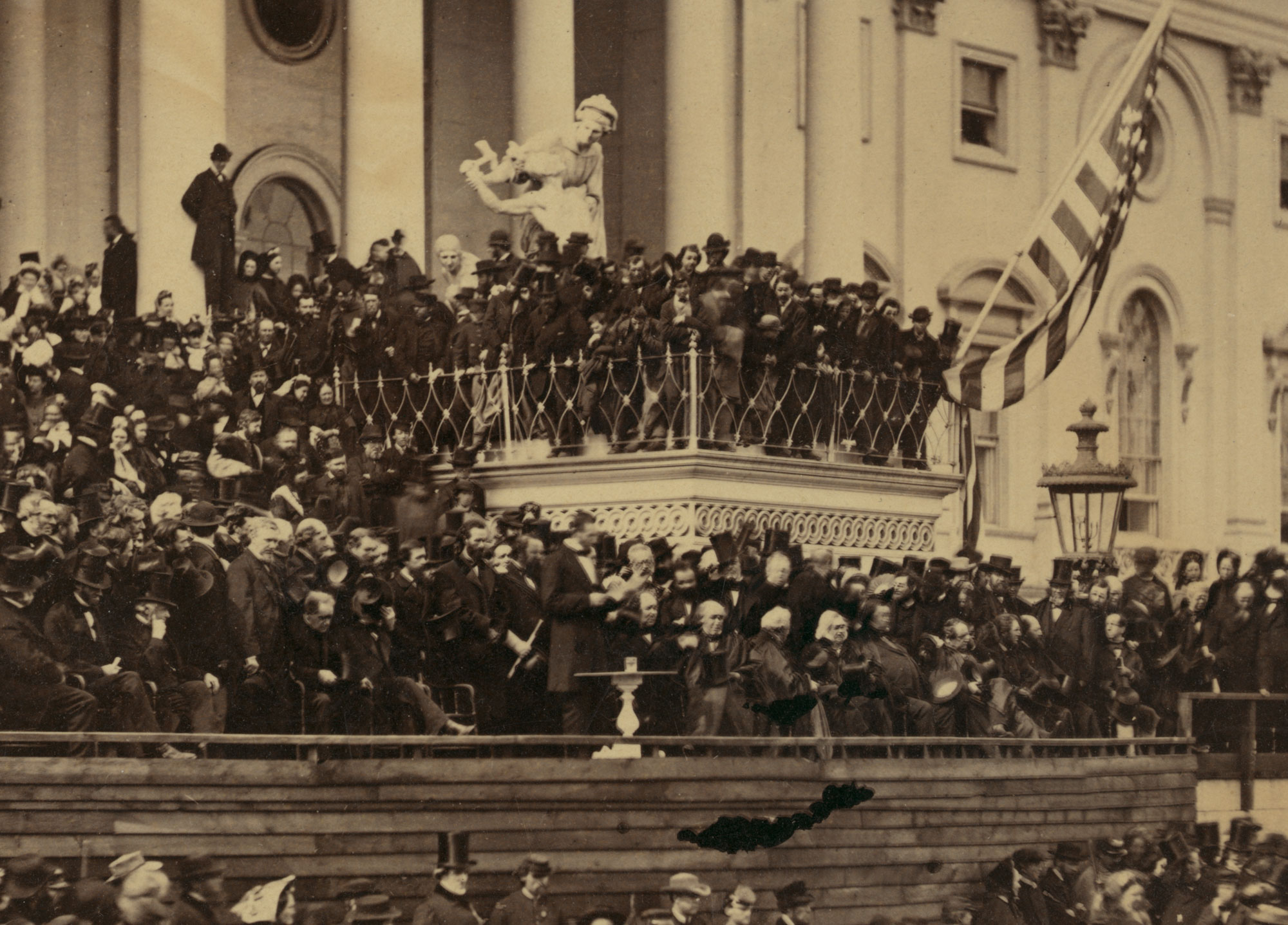
Finally, I note that other cultural markers of significance can be seen in one of Brady’s photographs. These are the names of the battles that appear on the canopy of the Presidential reviewing stand (see Reviewing Stand in Front of the Executive Mansion, Washington, D.C., May, 1865, details below).
Elsevime (?)
Savannah
Vicksburg
Fort Donelson
Shiloh
Resaca
… River!
South Mountain
Bentonville
Pea Ridge
Stone River
These are not the names of the major battles that we remember as being the most important and mythical today: Gettysburg, Bull Run, Antietam, Atlanta. I was fascinated by these battles appearing on the Presidential Reviewing Stand, so I have included research and colour lithographs on each battle. At the time these engagements were obviously thought worthy of high honour even as now they fade from our memory.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
The Grand Review of the Armies: Twelve Alexander Gardner Albumens
“Beginning with the surrender of Gen. Robert E. Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia on April 9, 1865, the Civil War was coming to an end. Two and a half weeks later, on April 26, Gen. Joseph E. Johnston surrendered his Army of Tennessee to Gen. William T. Sherman. On May 10, President Andrew Johnson declared that armed resistance had essentially come to an end. The very same day down in Georgia, Confederate President Jefferson Davis, on the run since early April, was captured. As the conflict was winding down, the armies in the field were making their way back to the nation’s capital which was still in mourning from the death of President Lincoln one month earlier. President Johnson felt a change was needed in Washington and ordered a grand military parade through the streets.
Three armies – the Army of the Potomac, the Army of the Tennessee, and the Army of Georgia – participated in the Grand Review of the Armies on May 23 and 24, 1865, as thousands lined the streets. Prominent Washington photographer, Alexander Gardner, formerly the staff photographer for the Army of the Potomac under Gen. George B. McClellan, documented the procession.
Each photograph measures 3.75″ x 2.75″ and is affixed to an Alexander Gardner mount to an overall size of 9.25″ x 7.75″. Each photograph is surrounded by an ornate border, below which is printed: “Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review. Washington, D.C., May 23 and 24, 1865.” Five of the images show the review stand of the president, adorned in patriotic décor, where President Johnson, politicians, and prominent citizens of Washington sat to watch the parade. An additional five images show the soldiers, consisting of cavalry, infantry, and a wagon train, headed up Pennsylvania Avenue (in two of the photographs, the dome of the Capitol Building can be seen at the end of the street). The remaining two images show soldiers on the march and civilians in wagons and on horseback moving down unidentified streets.
Within a week of the review, the armies of the Republic began to disband and the men began their return home.”
Text from the Heritage Auctions website
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-b.jpg)
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand] (and detail)
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review.
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
A Grand Review, Presidential Reviewing Stand
The Presidential Reviewing stand in front of the White House on Pennsylvania Avenue during the Grand Review of the victorious Union armies in Washington, DC, May 23 and 24 of 1865. It is occupied by President Andrew Johnson and his cabinet, Generals Ulysses S. Grant and William T. Sherman and other military officers. President Johnson and General Grant are clearly visible seated next to each other in the front row.
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry] (and detail)
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review.
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Reviewing Stand in Front of the Executive Mansion, Washington, D.C., May, 1865
1865, printed early 1880s
Albumen silver print
Sheet and image: 6 1/2 x 9 in. (16.5 x 22.9 cm)
Smithsonian American Art Museum
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Reviewing Stand in Front of the Executive Mansion, Washington, D.C., May, 1865
1865, printed early 1880s
Albumen silver print
Library of Congress Prints and Photographs
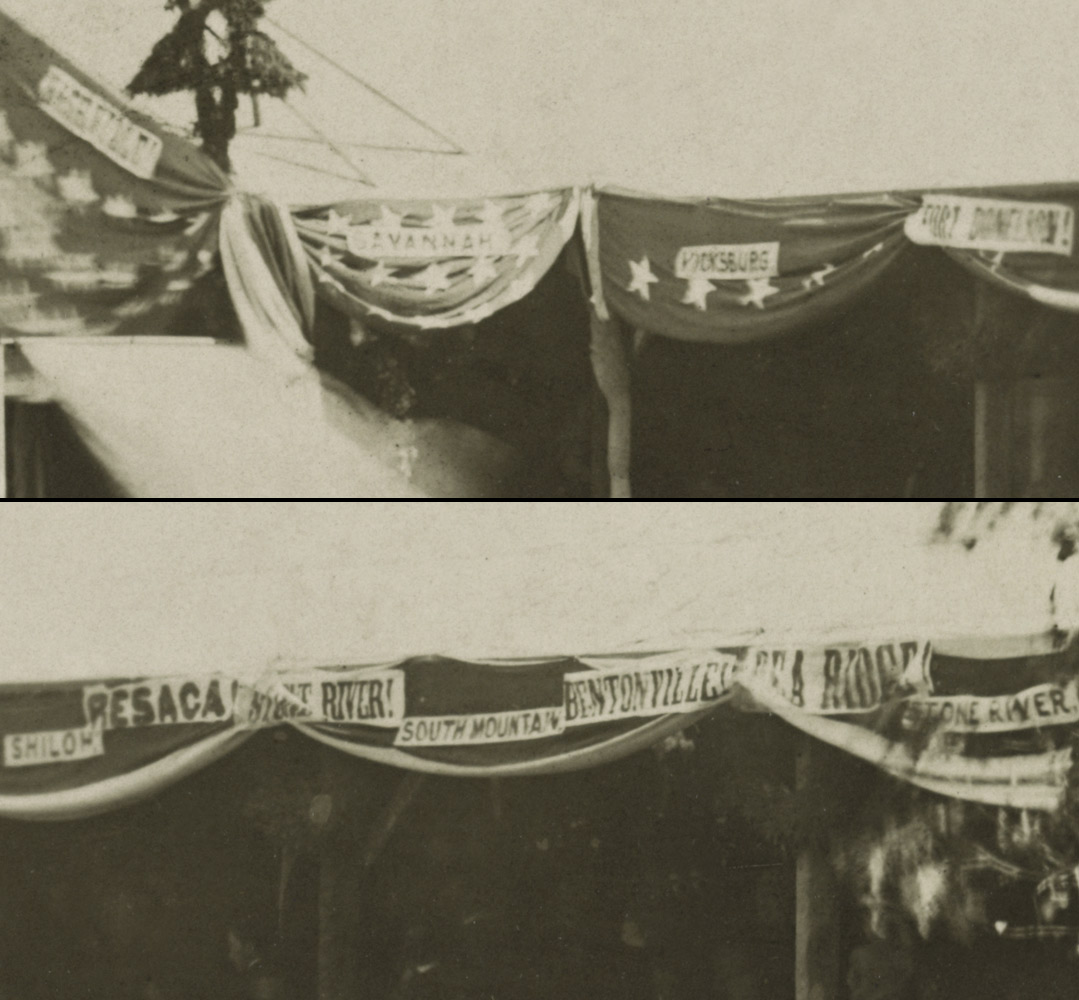
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Reviewing Stand in Front of the Executive Mansion, Washington, D.C., May, 1865 (detail of name of battles)
1865, printed early 1880s
Albumen silver print
Library of Congress Prints and Photographs
Elsevime (?)
Savannah
Vicksburg
Fort Donelson
Shiloh
Resaca
… River!
South Mountain
Bentonville
Pea Ridge
Stone River
Savannah
Throughout the war whites feared that the city was vulnerable to Union attack. Yet when the end came in late 1864, it originated not from the sea, but from the Georgia interior, as General William Tecumseh Sherman led his massive army southeast from Atlanta, sweeping through a largely defenseless state and entering Savannah on the morning of December 21, 1864. The night before, Confederate forces, several thousand strong, had staged an ignominious retreat across the Savannah River to South Carolina. The weary city, blacks and whites alike, rejoiced at the sight of U. S. troops marching down the Bay, the street running parallel to the river and showcasing the city’s largest warehouses and merchants’ offices. Truly, Sherman had liberated the city-and not only for black people, for most of the city’s whites were thoroughly sick of the carnage, and of the conflict that had robbed them of so much and turned their world upside down.
Jacqueline Jones. “Savannah in the Civil War”
Siege of Vicksburg
The Siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate Army of Vicksburg led by Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton into the defensive lines surrounding the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi.
When two major assaults (May 19 and 22, 1863) against the Confederate fortifications were repulsed with heavy casualties, Grant decided to besiege the city beginning on May 25. With no reinforcement, supplies nearly gone, and after holding out for more than forty days, the garrison finally surrendered on July 4. This action (combined with the surrender of Port Hudson to Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks on July 9) yielded command of the Mississippi River to the Union forces, who would hold it for the rest of the conflict.
The Confederate surrender following the siege at Vicksburg is sometimes considered, when combined with Gen. Robert E. Lee’s defeat at Gettysburg by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade the previous day, the turning point of the war. It cut off the states of Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas from the rest of the Confederacy, as well as communication with Confederate forces in the Trans-Mississippi Department for the remainder of the war.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Kurz and Allison (American publisher, founded 1880)
Siege of Vicksburg – 13, 15, & 17 Corps, Commanded by Gen. U.S. Grant, assisted by the Navy under Admiral Porter – Surrender, July 4, 1863
1888
Lithograph, colour
Kurz and Allison were a major publisher of chromolithographs in the late 19th century. Based at 267-269 Wabash Avenue in Chicago, they built their reputation on large prints published in the mid-1880s depicting battles of the American Civil War. In all, a set of 36 battle scenes were published from designs by Louis Kurz (1835-1921), himself a veteran of the war. Kurz, a native of Salzburg, Austria, had emigrated to the United States in 1848.
While the prints were highly inaccurate and considered naive fantasies like Currier and Ives prints, they were still sought after. They did not pretend to mirror the actual events but rather attempted to tap people’s patriotic emotions.
Text from the Wikipedia website
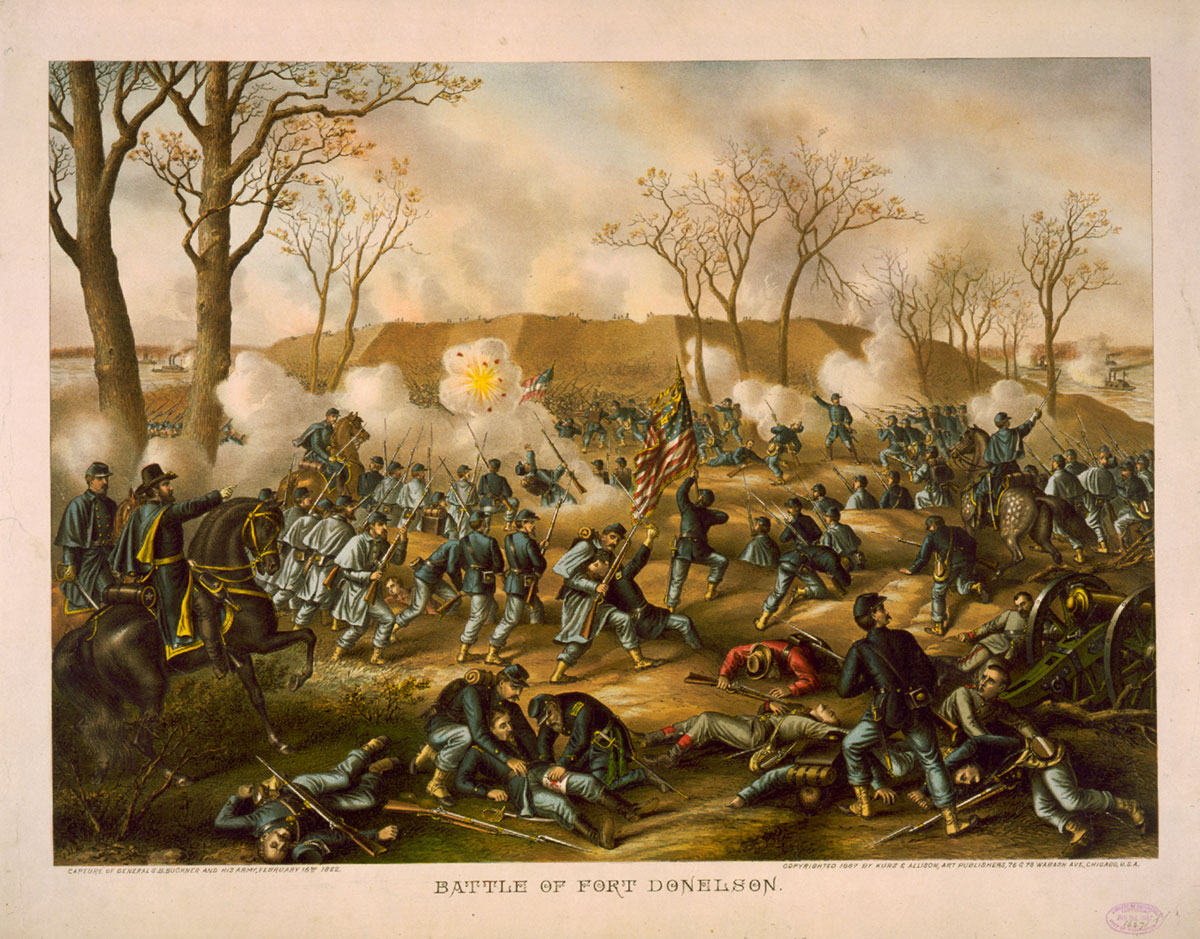
Fort Donelson
The Battle of Fort Donelson was fought from February 11 to 16, 1862, in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. The capture of the fort by Union forces opened the Cumberland River, an important avenue for the invasion of the South. The success elevated Brig. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant from an obscure and largely unproven leader to the rank of major general, earning him the nickname “Unconditional Surrender” Grant in the process (using his first two initials, “U.S.”).
The battle followed the capture of Fort Henry on February 6. Grant moved his army 12 miles overland to Fort Donelson on February 12 and 13 and conducted several small probing attacks. (Although the name was not yet in use, the troops serving under Grant were the nucleus of the Union’s Army of the Tennessee.) On February 14, U.S. Navy gunboats under Flag Officer Andrew H. Foote attempted to reduce the fort with naval gunfire, but were forced to withdraw after sustaining heavy damage from Donelson’s water batteries.
On February 15, with their fort surrounded, the Confederates, commanded by Brig. Gen. John B. Floyd, launched a surprise attack against Grant’s army, attempting to open an avenue of escape. Grant, who was away from the battlefield at the start of the attack, arrived to rally his men and counterattack. Despite achieving a partial success and opening the way for a retreat, Floyd lost his nerve and ordered his men back to the fort. On the following morning, Floyd and his second-in-command, Brig. Gen. Gideon J. Pillow, panicked and relinquished command to Brig. Gen. Simon Bolivar Buckner (later Governor of the Commonwealth of Kentucky), who agreed to accept the unconditional surrender terms offered by Grant.
Grant was courteous to Buckner following the surrender and offered to loan him money to see him through his impending imprisonment, but Buckner declined. The surrender was a humiliation for Buckner personally, but also a strategic defeat for the Confederacy, which lost more than 12,000 men, 48 artillery pieces and much equipment, as well as control of the Cumberland River, which led to the evacuation of Nashville. This army was the first of three Confederate armies that Grant would capture during the war. (The second was John C. Pemberton’s at the Siege of Vicksburg and the third Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia at Appomattox). Buckner also turned over considerable military equipment and provisions, which Grant’s hungry troops needed badly. More than 7,000 Confederate prisoners of war were eventually transported from Fort Donelson to Camp Douglas in Chicago; others were sent elsewhere throughout the North. Buckner was held as a prisoner at Fort Warren in Boston until he was exchanged that August.
The casualties at Fort Donelson were heavy primarily because of the large Confederate surrender. Union losses were 2,691 (507 killed, 1,976 wounded, 208 captured/missing), Confederate 13,846 (327 killed, 1,127 wounded, 12,392 captured/missing).
Text from Wikipedia website
Kurz and Allison (American publisher, founded 1880)
Battle of Fort Donelson – Capture of General S.B. Buckner and his army, February 16th 1862
c. 1887
Lithograph, colour

L. Prang & Co. (American publisher, founded 1860)
Thulstrup, Thure de, (1848-1930), artist
Battle of Shiloh, April 6-7, 1862
c. 1888
Chromolithograph
Louis Prang (American, 1824-1909)
Louis Prang (March 12, 1824 – June 15, 1909) was an American printer, lithographer, publisher, and Georgist. …
In 1856, Prang and a partner created a press, Prang and Mayer, to produce lithographs. The company specialised in prints of buildings and towns in Massachusetts. In 1860, he bought out his partner, creating L. Prang & Company and began work in colour printing of advertising and other forms of business materials. The firm became quite successful, and became known for war maps, printed during the American Civil War and distributed by newspapers. …
In June 1886, Prang published a series of prints under the title Prang’s War Pictures: Aquarelle Facsimile Prints. These became popular and helped inspire a genre of such prints, particularly the series issued by Kurz and Allison. However, Prang aimed at a more modern and individual treatment, as opposed to the panoramic style of Kurz and Allison, and before them, Currier and Ives.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Shiloh
The Battle of Shiloh, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, was a major battle in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, fought April 6-7, 1862, in southwestern Tennessee. A Union army under Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant had moved via the Tennessee River deep into Tennessee and was encamped principally at Pittsburg Landing on the west bank of the river. Confederate forces under Generals Albert Sidney Johnston and P. G. T. Beauregard launched a surprise attack on Grant there. The Confederates achieved considerable success on the first day, but were ultimately defeated on the second day.
On the first day of the battle, the Confederates struck with the intention of driving the Union defenders away from the river and into the swamps of Owl Creek to the west, hoping to defeat Grant’s Army of the Tennessee before the anticipated arrival of Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell’s Army of the Ohio. The Confederate battle lines became confused during the fierce fighting, and Grant’s men instead fell back to the northeast, in the direction of Pittsburg Landing. A position on a slightly sunken road, nicknamed the “Hornet’s Nest”, defended by the men of Brig. Gens. Benjamin M. Prentiss’s and W. H. L. Wallace’s divisions, provided critical time for the rest of the Union line to stabilise under the protection of numerous artillery batteries. Gen. Johnston was killed during the first day of fighting, and Beauregard, his second in command, decided against assaulting the final Union position that night.
Reinforcements from Buell and from Grant’s own army arrived in the evening and turned the tide the next morning, when the Union commanders launched a counterattack along the entire line. The Confederates were forced to retreat from the bloodiest battle in United States history up to that time, ending their hopes that they could block the Union advance into northern Mississippi.
In the immediate aftermath of the battle, Northern newspapers vilified Grant for his performance during the battle on April 6. Reporters, many far from the battle, spread the story that Grant had been drunk, falsely alleging that this had resulted in many of his men being bayoneted in their tents because of a lack of defensive preparedness. Despite the Union victory, Grant’s reputation suffered in Northern public opinion. Many credited Buell with taking control of the broken Union forces and leading them to victory on April 7. Calls for Grant’s removal overwhelmed the White House. President Lincoln replied with one of his most famous quotations about Grant: “I can’t spare this man; he fights.” Sherman emerged as an immediate hero, his steadfastness under fire and amid chaos atoning for his previous melancholy and his defensive lapses preceding the battle. Today, however, Grant is recognised positively for the clear judgment he was able to retain under the strenuous circumstances, and his ability to perceive the larger tactical picture that ultimately resulted in victory on the second day.
The two-day battle of Shiloh, the costliest in American history up to that time, resulted in the defeat of the Confederate army and frustration of Johnston’s plans to prevent the joining of the two Union armies in Tennessee. Union casualties were 13,047 (1,754 killed, 8,408 wounded, and 2,885 missing); Grant’s army bore the brunt of the fighting over the two days, with casualties of 1,513 killed, 6,601 wounded, and 2,830 missing or captured. Confederate casualties were 10,699 (1,728 killed, 8,012 wounded, and 959 missing or captured). The dead included the Confederate army’s commander, Albert Sidney Johnston; the highest ranking Union general killed was W. H. L. Wallace. Both sides were shocked at the carnage. None suspected that three more years of such bloodshed remained in the war and that eight larger and bloodier battles were yet to come.
Text from Wikipedia website
Resaca
The Battle of Resaca was part of the Atlanta Campaign of the American Civil War. The battle was waged in both Gordon and Whitfield counties, Georgia, May 13-15, 1864. It ended inconclusively with the Confederate Army retreating. The engagement was fought between the Military Division of the Mississippi (led by Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman) on the side of the Union and the Army of Tennessee (Gen. Joseph E. Johnston) for the Confederates.
Johnston had withdrawn his forces from Rocky Face Ridge to the hills around Resaca. On May 13, the Union troops tested the Confederate lines to pinpoint their whereabouts. The next day full scale fighting occurred, and the Union troops were generally repulsed except on the Confederate right flank where Sherman did not fully exploit his advantage. On May 15, the battle continued with no advantage to either side until Sherman sent a force across the Oostanaula River, at Lay’s Ferry, using newly delivered Cumberland pontoon bridges and advanced towards Johnston’s railroad supply line. Unable to halt this Union turning movement, Johnston was forced to retire.
Unable to halt the Union turning movement caused by Sherman’s crossing of the Oostanaula, Johnston was forced to retire, burning the railroad span and a nearby wagon bridge in the early morning of May 16. After the Union repaired the bridges and transported more men over, they continued in the pursuit of the Confederates, leading to the Battle of Adairsville on May 17. There were 6,100 combined casualties: 3,500 for the Union and 2,600 for the Confederacy.
Text from Wikipedia website
Kurz and Allison (American publisher, founded 1880)
Battle of Resaca – May 13-15, 1864
c. 1889
Lithograph, colour
Robert Knox Sneden (American, 1832-1918)
The Battle of Crampton’s Gap : 5 miles south of Turner’s Gap, South Mountain, Md. September 14th 1862
1862-1865
A regional view of South Mountain in Frederick County, Md., showing the location of Crampton’s Gap in relation to Sharpsburg, Middletown, Burkittsville, and Brownsville, Md. Illustrates the position of Confederate forces (Anderson’s division commanded by Lafayette McLaws) and the Unions VI Corps, 1st and 2nd divisions during this engagement, part of the larger Antietam, or Maryland Campaign.
Robert Knox Sneden (American, 1832-1918)
Robert Knox Sneden (1832-1918) was an American landscape painter and a map-maker for the Union Army during the American Civil War. He was a prolific illustrator and memoirist documenting the war and other events. …
Civil War
Sneden left Brooklyn in 1861 to enlist in the 40th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment, or the Mozart Regiment, of the Army of the Potomac. He served as a quartermaster when his regiment camped near Leesburg Turnpike. Starting from January 12, 1862, Sneden served on Samuel P. Heintzelman’s III Corps staff, at first, as a draughtsman on map work, later, as a topographical engineer. On March 22, 1862, Sneden embarked with Heintzelman for the Peninsula Campaign, participating in the Battle of Williamsburg, Battle of Seven Pines, Battle of Savage’s Station, and Battle of Glendale. Returning to Northern Virginia, he took part in the Second Battle of Bull Run. He was assigned to the defenses of Washington, D.C., first in Alexandria, Virginia, then at Arlington House.
In October, 1863, after the Battle of Bristoe Station, he was assigned to David B. Birney’s division, participating in the Battle of Kelly’s Ford. He was assigned to the staff of general William H. French, during the abortive Battle of Mine Run.
Prisoner-of-War
On November 27, 1863, Sneden was captured by Confederate rangers under John S. Mosby and became a prisoner-of-war for the next thirteen months. In November 1863, he was held at a tobacco warehouse next to Libby Prison, where he suffered from typhoid fever. On February 22, 1864, after a prison escape, prisoners were shipped to a new camp in Georgia. Sneden was placed in the notorious Andersonville Prison, but continued making clandestine drawings. Altogether, he sketched scenes of prison life in Savannah and Millen, Georgia, and in Florence and Charleston, South Carolina. On December 11, 1864, he was exchanged at Charleston.
Text from the Wikipedia website
South Mountain
The Battle of South Mountain – known in several early Southern accounts as the Battle of Boonsboro Gap – was fought September 14, 1862, as part of the Maryland Campaign of the American Civil War. Three pitched battles were fought for possession of three South Mountain passes: Crampton’s, Turner’s, and Fox’s Gaps. Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, commanding the Union Army of the Potomac, needed to pass through these gaps in his pursuit of Confederate General Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia. Despite being significantly outnumbered, Lee’s army delayed McClellan’s advance for a day before withdrawing.
By dusk, with Crampton’s Gap lost and his position at Fox’s and Turner’s Gaps precarious, Lee ordered his outnumbered forces to withdraw from South Mountain. McClellan was now in position to destroy Lee’s army before it could concentrate. Union casualties of 28,000 engaged were 2,325 (443 killed, 1,807 wounded, and 75 missing); Confederates lost 2,685 (325 killed, 1560 wounded, and 800 missing) of 18,000. The Battle of South Mountain was an important morale booster for the defeat-stricken Army of the Potomac. The New York World wrote that the battle “turn[ed] back the tide of rebel successes” and “the strength of the rebels is hopelessly broken.” Lee contemplated the end of his Maryland campaign. However, McClellan’s limited activity on September 15 after his victory at South Mountain condemned the garrison at Harpers Ferry to capture and gave Lee time to unite his scattered divisions at Sharpsburg for the Battle of Antietam on September 17.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Bentonville
The Battle of Bentonville (March 19-21, 1865) was fought in Bentonville, North Carolina, near the town of Four Oaks, as part of the Carolinas Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the last battle between the armies of Union Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman and Confederate Gen. Joseph E. Johnston.
As the right wing of Sherman’s army under command of Maj. Gen. Oliver O. Howard marched toward Goldsborough, the left wing under command of Maj. Gen. H. W. Slocum encountered the entrenched men of Johnston’s army. On the first day of the battle, the Confederates attacked the XIV Corps and routed two divisions, but the rest of Sherman’s army defended its positions successfully. The next day, as Sherman sent reinforcements to the battlefield and expected Johnston to withdraw, only minor sporadic fighting occurred. On the third day, as skirmishing continued, the division of Maj. Gen. Joseph A. Mower followed a path into the Confederate rear and attacked. The Confederates were able to repulse the attack as Sherman ordered Mower back to connect with his own corps. Johnston elected to withdraw from the battlefield that night.
As a result of the overwhelming enemy strength and the heavy casualties his army suffered in the battle, Johnston surrendered to Sherman little more than a month later at Bennett Place, near Durham Station. Coupled with Gen. Robert E. Lee’s surrender earlier in April, Johnston’s surrender represented the effective end of the war.
During the battle, the Confederates suffered a total of nearly 2,600 casualties: 239 killed, 1,694 wounded, and 673 missing. About half of the casualties were lost in the Army of Tennessee.[30] The Union army lost 194 killed, 1,112 wounded, and 221 missing, for a total of 1,527 casualties. The wounded were treated at the house of John Harper, with several of the wounded who died being buried next to the Harper family cemetery.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Kurz and Allison (American publisher, founded 1880)
Battle of Pea Ridge, Ark., March 6-8, 1862
c. 1889
Chromolithograph
56 x 71.8cm (sheet)
Pea Ridge
The Battle of Pea Ridge (also known as the Battle of Elkhorn Tavern) was a land battle of the American Civil War, fought on March 6-8, 1862, at Pea Ridge in northwest Arkansas, near Garfield. Union forces led by Brig. Gen. Samuel R. Curtis moved south from central Missouri, driving Confederate forces into northwestern Arkansas. Maj. Gen. Earl Van Dorn reorganised the Confederate army and launched a counter-offensive, hoping that a victory would enable the Confederates to recapture northern Arkansas and Missouri. In a two–day battle, Curtis held off the Confederate attack on the first day and drove Van Dorn’s force off the field on the second day. The outcome of the battle essentially cemented Union control of Missouri and northern Arkansas. The battle was one of the few during the war in which a Confederate army outnumbered its Union opponent.
Federal forces reported 203 killed, 980 wounded and 201 missing for a total of 1,384 casualties. Of these, Carr’s 4th Division lost 682, almost all in its action on the first day, and Davis’ 3rd Division lost 344. Both Asboth and Carr were wounded but remained in command of their divisions. Van Dorn reported his losses as 800 killed and wounded, with between 200 and 300 prisoners, but these are probably too low. A more recent estimate is that the Confederates suffered approximately 2,000 casualties in the Battle of Pea Ridge. These losses included a large proportion of senior officers. Generals McCulloch, McIntosh, and William Y. Slack were killed or mortally wounded, and Price wounded. Among colonels, Hébert was captured, and Benjamin Rives was mortally wounded, with two other colonels captured and one wounded.
Text from the Wikipedia website
Kurz and Allison (American publisher, founded 1880)
Illustration of the Battle of Stones River, which occurred on December 31, 1862 and January 2-3, 1863. Commanding the forces were General Rosecrans for the Union and General Bragg for the Confederacy. General Rosecrans (left) rallies his troops at Stones River
1891
Lithograph, color
Stones River
The Battle of Stones River or Second Battle of Murfreesboro (in the South, simply the Battle of Murfreesboro), was fought from December 31, 1862, to January 2, 1863, in Middle Tennessee, as the culmination of the Stones River Campaign in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. Of the major battles of the Civil War, Stones River had the highest percentage of casualties on both sides. Although the battle itself was inconclusive, the Union Army’s repulse of two Confederate attacks and the subsequent Confederate withdrawal were a much-needed boost to Union morale after the defeat at the Battle of Fredericksburg, and it dashed Confederate aspirations for control of Middle Tennessee.
Union Maj. Gen. William S. Rosecrans’s Army of the Cumberland marched from Nashville, Tennessee, on December 26, 1862, to challenge General Braxton Bragg’s Army of Tennessee at Murfreesboro. On December 31, each army commander planned to attack his opponent’s right flank, but Bragg struck first. A massive assault by the corps of Maj. Gen. William J. Hardee, followed by that of Leonidas Polk, overran the wing commanded by Maj. Gen. Alexander M. McCook. A stout defense by the division of Brig. Gen. Philip Sheridan in the right center of the line prevented a total collapse and the Union assumed a tight defensive position backing up to the Nashville Turnpike. Repeated Confederate attacks were repulsed from this concentrated line, most notably in the cedar “Round Forest” salient against the brigade of Col. William B. Hazen. Bragg attempted to continue the assault with the corps of Maj. Gen. John C. Breckinridge, but the troops were slow in arriving and their multiple piecemeal attacks failed.
Fighting resumed on January 2, 1863, when Bragg ordered Breckinridge to assault the well-fortified Union position on a hill to the east of the Stones River. Faced with overwhelming artillery, the Confederates were repulsed with heavy losses. Aware that Rosecrans was receiving reinforcements, Bragg chose to withdraw his army on January 3 to Tullahoma, Tennessee.
Total casualties in the battle were 24,645: 12,906 on the Union side and 11,739 for the Confederates. Considering that only about 76,400 men were engaged, this was the highest percentage of killed and wounded of any major battle in the Civil War, higher in absolute numbers than the infamous bloodbaths at Shiloh and Antietam earlier that year. Four brigadier generals were killed or mortally wounded: Confederate James E. Rains and Roger W. Hanson; Union Edward N. Kirk and Joshua W. Sill.
Text from Wikipedia website
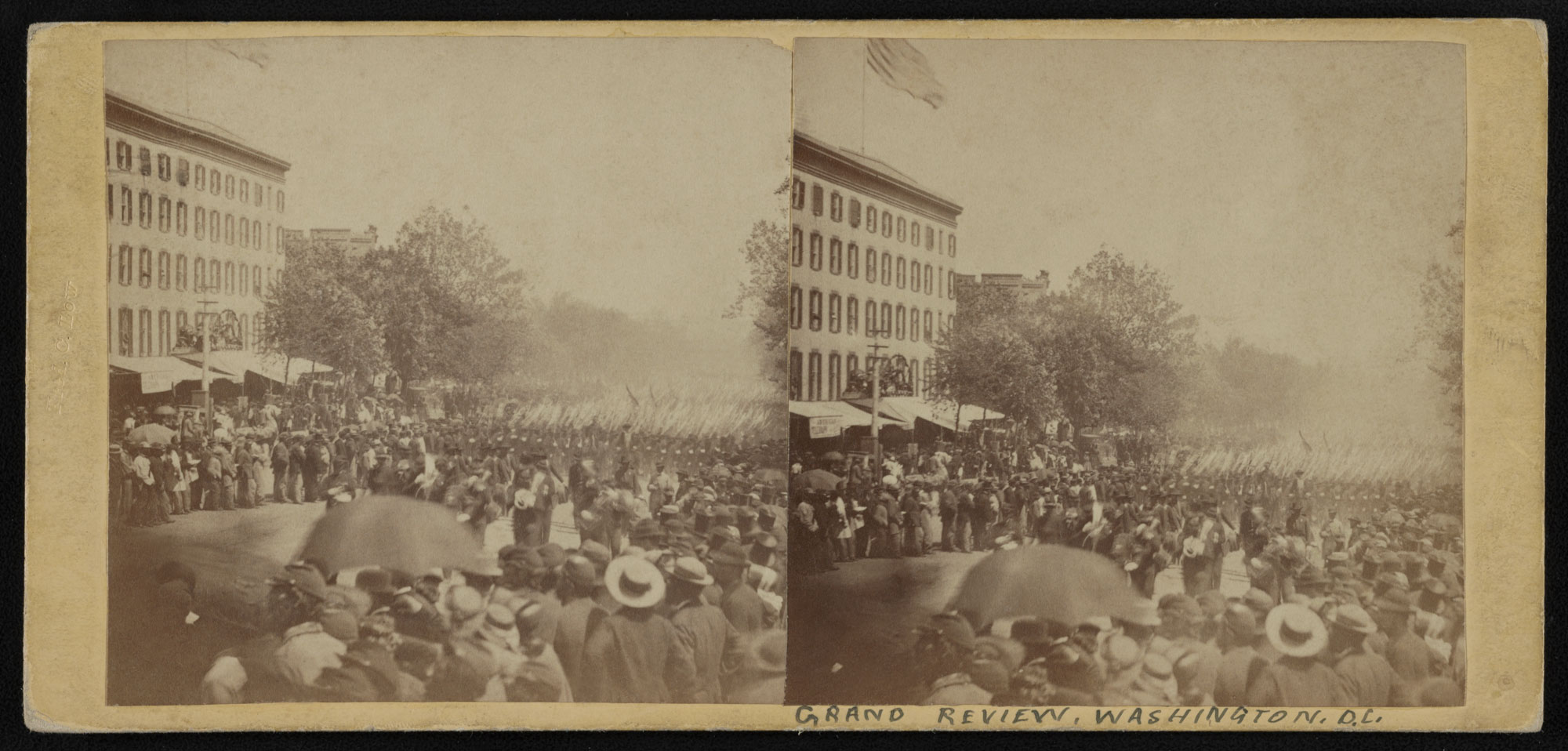
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Grand Review, Washington, D.C.
1865
Albumen photographs on Stereocard

Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Grand Review, Washington, D.C. (detail)
1865
Albumen photographs on Stereocard
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Grand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, May, 1865
1865
Stereocard

Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Grand Review, Pennsylvannia Avenue, May, 1865
1865
Civil War Slang
* indicates word is still in general use today
bark juice – alcohol
camp canard – army gossip
cracker line – supply line for moving troops
duds- clothes
greenbacks – money
*high-falutin – fancy
*in a huff – irritated or annoyed
knock into a cocked hat – to beat someone up
*let ‘er rip – to let something happen
lucifers – matches
not by a jug full – “no way”
*row – a fight
sawbones – surgeon
*skedaddle – run away
sparking – courting a girl
Sunday soldiers/parlor soldiers – bad soldiers, insult
*uppity – snobbish, arrogant
wallpapered – drunk
*forage – go through nearby farms for food
sacred soil – ground in Virginia
paper collar man – a rich man
vittles – food
fresh fish – new soldiers
bones – dice
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865] (and detail)
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865] (and detail)
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Over a Two-day period in Washington, D.C., May 23-24, 1865, the immense, exultant victory parade of the Union’s main fighting forces in many ways brought the Civil War to its conclusion. With the nation’s new president, Andrew Johnson, declaring on May 10 that all armed resistance was “virtually at an end,” plans commenced for the review. It would far eclipse the two victory celebrations held before the assassination of Abraham Lincoln and bring Washington out of its formal mourning period for the slain president.
William Tecumseh Sherman’s Army of Georgia, just finishing its 2,000-mile march through the heart of the Confederacy, arrived from North Carolina and bivouacked around the capital near George Gordon Meade’s Army of the Potomac. Though the two armies camped on opposite sides of the river, the troops met up with one another in the taverns and brothels of Washington, D.C., where the customary rivalries led to numerous fistfights. Sherman, concerned that Meade’s army would outshine his own in the upcoming parade, was not immune from the rivalry either, ordering some last-minute drilling and spit and polish sessions to whip his ragged troops into marching shape, Sherman knew they could not match the close-order discipline that the Army of the Potomac perfected.
The parade’s first day was devoted to Meade’s force, which, as the capital’s defending army, was a crowd favorite. May 23 was a clear, brilliantly sunny day. Starting from Capitol Hill, the Army of the Potomac marched down Pennsylvania Avenue before virtually the entire population of Washington, a throng of thousands cheering and singing favourite Union marching songs. At the reviewing stand in front of the White House were President Johnson, General-in-Chief Ulysses S. Grant, and top government officials. Leading the day’s march, General Meade dismounted in front of the stand and joined the dignitaries to watch the parade. His army made an awesome sight: a force of 80,000 infantrymen marching 12 across with impeccable precision, along with hundreds of pieces of artillery and a seven-mile line of cavalrymen that alone took an hour to pass. One already famous cavalry officer, George Armstrong Custer, gained the most attention that day-either by design or because his horse was spooked when he temporarily lost control of his mount, causing much excitement as he rode by the reviewing stand twice.
The next day was Sherman’s turn. Beginning its final march at 9 A.M. on another beautiful day, his 65,000-man army passed in review for six hours, with less precision, certainly, than Meade’s forces, but with a bravado that thrilled the crowd. Along with the lean, tattered, and sunburnt troops was the huge entourage that had followed Sherman’s on his march to the sea: medical workers, labourers, black families who fled from slavery, the famous “bummers” who scavenged for the army’s supplies, and a menagerie of livestock gleaned from the Carolina and Georgia farms. Riding in front of his conquering force, Sherman later called the experience “the happiest and most satisfactory moment of my life.”
For the thousands of soldiers participating in both days of the parade, it was one of their final military duties. Within a week of the Grand Review, the Union’s two main armies were both disbanded.
Anonymous. “Review of the Grand Armies,” on Shotgun’s Home of the American Civil War website Nd [Online] Cited 03/03/2016. No longer available online
On May 10, Johnson had declared that the rebellion and armed resistance was virtually at an end, and had made plans with government authorities for a formal review to honour the troops. One of his side goals was to change the mood of the capital, which was still in mourning following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln the month before at Ford’s Theater. Three of the leading Federal armies were close enough to participate in the procession. The Army of the Tennessee arrived via train. The Army of Georgia, also under the command of William T. Sherman, had just completed its Carolinas Campaign and had accepted the surrender of the largest remaining Confederate army, that of Joseph E. Johnston. It arrived from North Carolina in mid-May and camped around the capital city in various locations, across the Potomac River from the Army of the Potomac, fresh off its victories over Robert E. Lee in Virginia. It had arrived in Washington on May 12. Officers in the three armies who had not seen each other for some time (in some cases since before the war) communed and renewed acquaintances, while at times, the common infantrymen engaged in verbal sparring (and sometimes fisticuffs) in the town’s taverns and bars over which army was superior. Sherman, concerned that his Westerners would not present as polished an image as the eastern army, drilled his forces and insisted that uniforms be cleaned, buttons and brass shined, and that bayonets glistened.
At 9:00 a.m. on a bright sunny May 23, a signal gun fired a single shot and Maj. Gen. George Gordon Meade, the victor of Gettysburg, led the estimated 80,000 men of Army of the Potomac down the streets of Washington from Capitol Hill down Pennsylvania Avenue past crowds that numbered into the thousands. The infantry marched with 12 men across the road, followed by the divisional and corps artillery, then an array of cavalry regiments that stretched for another seven miles. The mood was one of gaiety and celebration, and the crowds and soldiers frequently engaged in singing patriotic songs as the procession of victorious soldiers snaked its way towards the reviewing stand in front of the White House, where President Johnson, general-in-chief Ulysses S. Grant, senior military leaders, the Cabinet, and leading government officials awaited. At the head of his troops, Meade dismounted when he arrived at the reviewing stand and joined the dignitaries to salute his men, who passed for over six hours.
On the following day at 10:00 a.m., Sherman led the 65,000 men of the Army of the Tennessee and the Army of Georgia, with an uncharacteristic semblance of military precision, past the admiring celebrities, most of which had never seen him before. For six hours under bright sunshine, the men who had marched through Georgia and those who had defeated John Bell Hood’s army in Tennessee now paraded in front of joyous throngs lining the sidewalks. People peered from windows and rooftops for their first glimpse of this western army. Unlike Meade’s army, which had more military precision, Sherman’s Georgia force was trailed by a vast crowd of people who had accompanied the army up from Savannah – freed blacks, labourers, adventurers, scavengers, etc. At the very end was a vast herd of cattle and other livestock that had been taken from Carolina farms.
Within a week after the celebrations, the two armies were disbanded and many of the volunteer regiments and batteries were sent home to be mustered out of the army.
Although there would be further guerrilla actions (particularly with respect to armed criminal factions, such as the James-Younger Gang) and racial violence in the South (including the rise of the Ku Klux Klan), military conflict between the North and the South had ended. The disbandment of the Union armies and the return home of fathers, brothers, and sons signalled to the population at large that they could begin their return to a normal life and that the end had come for the American Civil War.
Text from the Wikipedia website
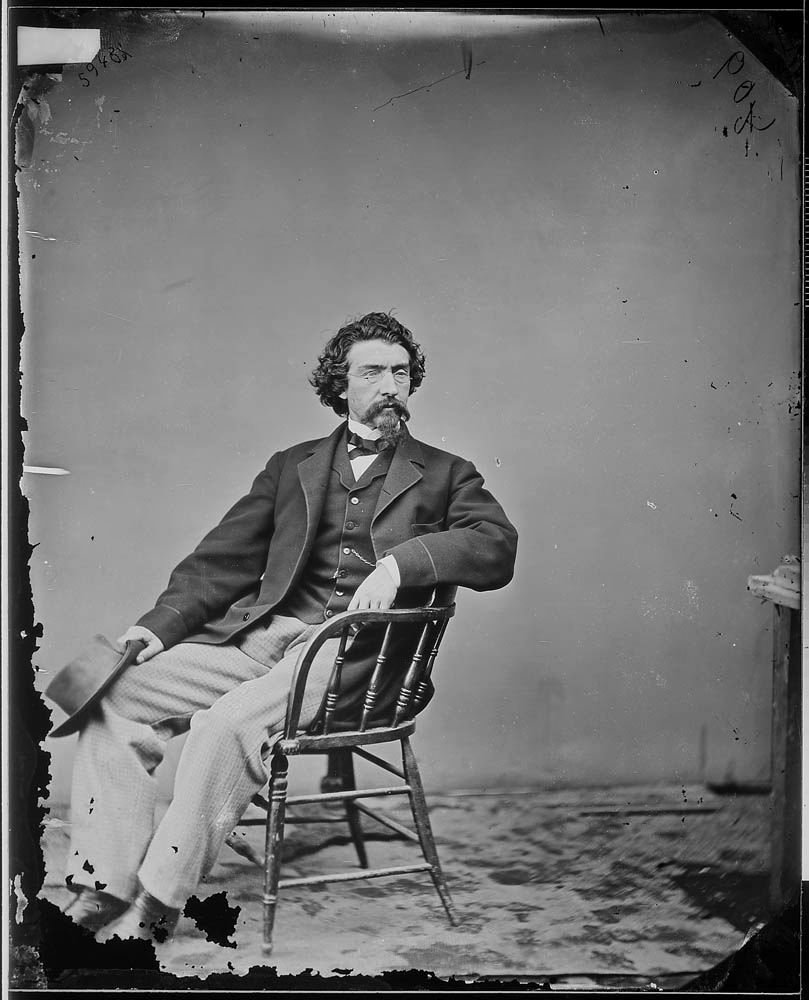

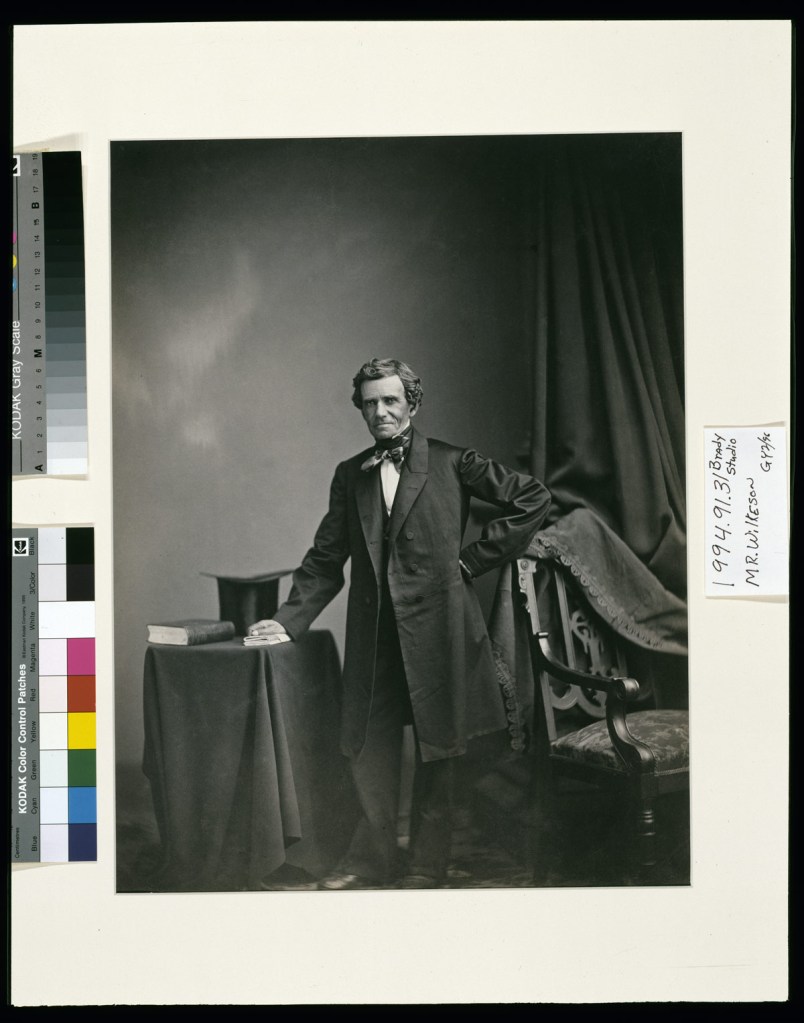
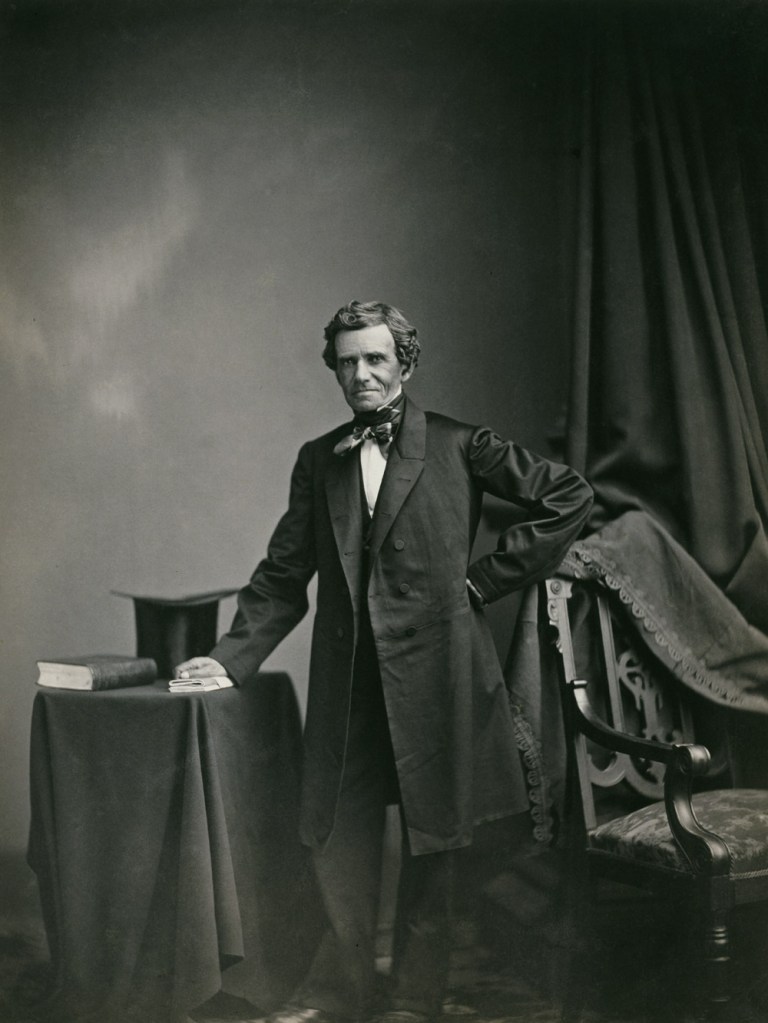
Matthew Brady (American, 1822-1896)
Self Portrait
c. 1861-1862

James Gardner (American, 1832 – ?)
Portrait of Alexander Gardner
1863
Albumen silver print
Alexander Gardner, shown here in an 1863 Albumen silver print, died at age 61 on Dec. 10, 1882 in his home on Virginia Avenue SW. He was buried two days later in Northeast Washington’s Glenwood Cemetery after a large, well-attended funeral that was noted by the press. Mathew B. Brady, his former employer and rival Civil War photographer, outlived him by almost 14 years. But Brady, who was in his early 70s, died penniless in New York City on Jan. 15, 1896. His body was shipped to Washington, where he was buried in Congressional Cemetery in his late wife’s family plot. He was placed in a grave already occupied by two relatives, after a funeral that cost $6. The two photography pioneers, who once had Washington studios blocks from each other, are now at rest just four miles apart.
Courtesy National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865] (and detail)
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865] (and detail)
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882)
Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865] (and detail)
From the folio Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review
1865
3.75″ x 2.75″
Albumen photograph on card
![Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/reviewing-stand-web.jpg?w=1024)
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]
1865
![Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 (detail) Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/reviewing-stand-detail.jpg?w=1024)
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865] (detail)
1865
Detail of the photograph of the reviewing stand in front of the White House shows a number of VIPs, including (left to right) Ulysses S. Grant, the blurred figure of Edwin Stanton, President Andrew Johnson, Wesley Merritt (as commander of the cavalry corps in Philip Sheridan’s absence, he sat next to the president as his corps passed), George Gordon Meade, Secretary of the Navy Gideon Welles, Postmaster William Dennison, William T. Sherman, and Quartermaster General Montgomery Meigs
Text from the Library of Congress
Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 – died New York City 1896)
Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]
1865
Presidential reviewing stand from the reverse angle. After the crowds have gone… exposure time can be gauged from the blurred figures.

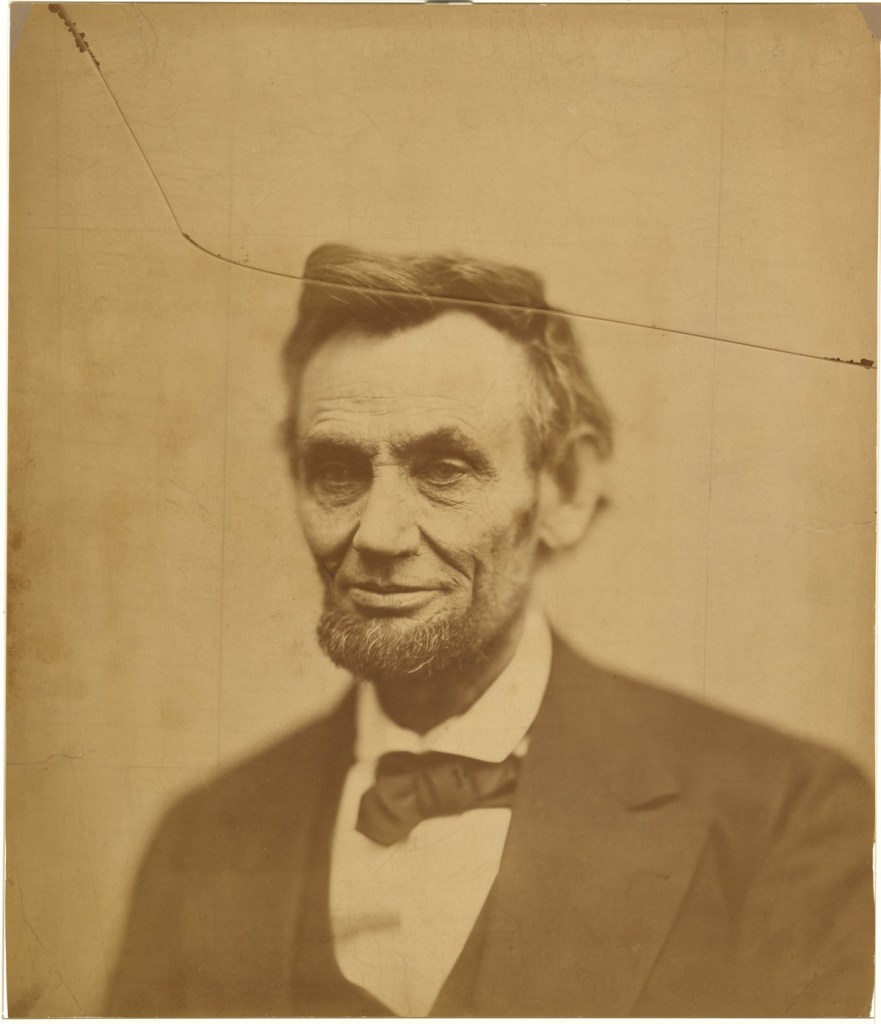
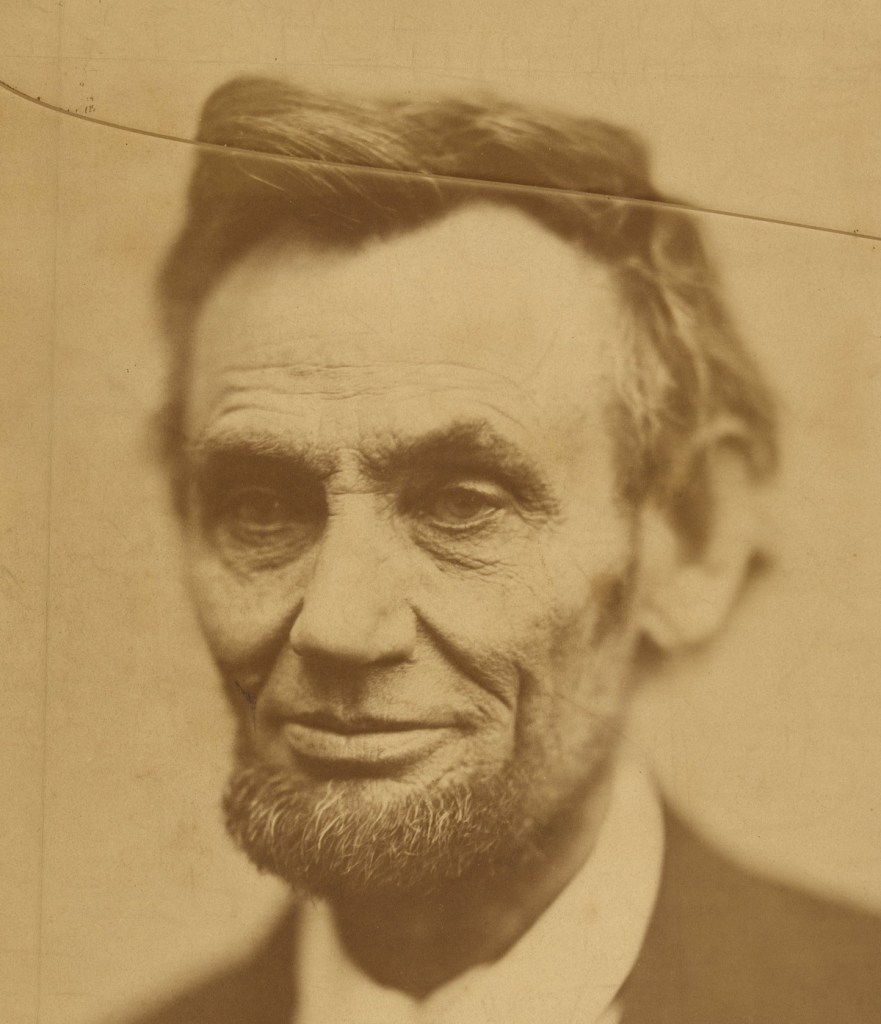
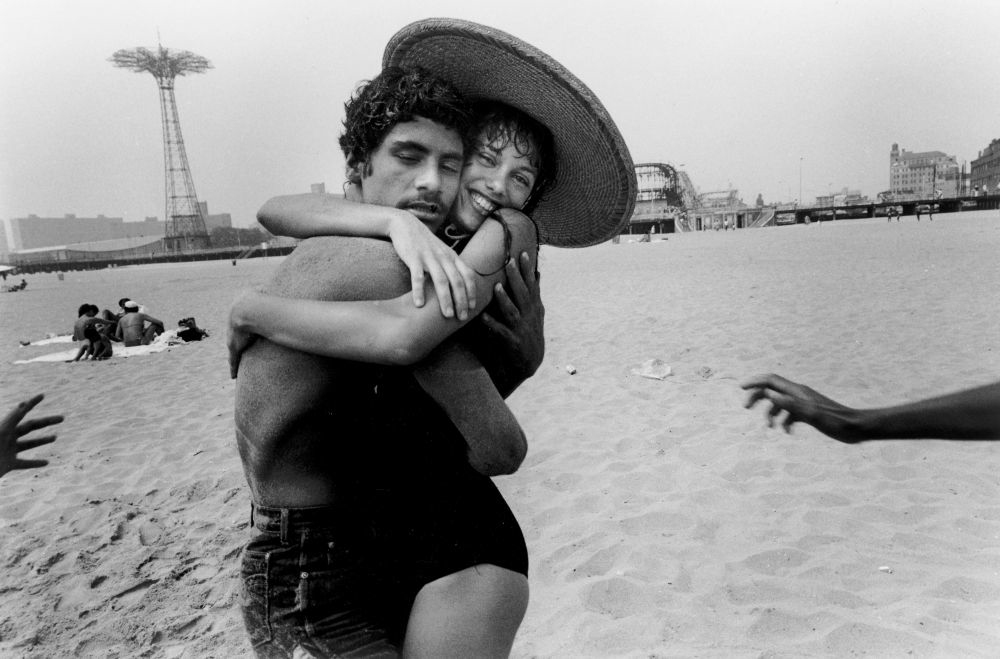
![Mathew B. Brady. 'Untitled [Spectators massing for the Grand Review of the Armies, 23-24 May 1865, at the side of the crepe-draped U.S. Capitol, flag at half mast following the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln]' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/matthew-brady-captured-spectators-massing-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-b-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand]," from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-b-detail.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-c-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-c-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. "Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand and mounted cavalry]," in the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-c-detail.jpg)












![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-d-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-d-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-d-detail.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-e-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-e-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-f-detail.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-f-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-f-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-g-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-g-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-h-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-h-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-i-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-i-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-i-detail.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-j-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-j-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-k-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-k-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner. 'Untitled [Gand Review, Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-k-detail.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-l-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-l-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-web.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-whole.jpg)
![Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail) Alexander Gardner (Scottish-American, 1821-1882) 'Untitled [Gand Review, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' from the folio 'Memories of the War. Illustrations of the Grand Review' 1865 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/memories-of-the-war-alexander-gardner-detail.jpg)
![Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865 Mathew B. Brady (born Lake George, NY 1823 - died New York City 1896) 'Untitled [Presidential reviewing stand, Washington, D.C., May, 1865]' 1865](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/brady-reviewing-stand.jpg)










































































































































































































































![Capt. Horatio Ross (British, 1801-1886) '[Dead stag in a sling]' c. 1850s - 1860s Capt. Horatio Ross (British, 1801-1886) '[Dead stag in a sling]' c. 1850s - 1860s](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/gm_05996801-web.jpg)
![Capt. Horatio Ross (British, 1801-1886) '[Dead stag in a sling]' c. 1850s - 1860s (detail) Capt. Horatio Ross (British, 1801-1886) '[Dead stag in a sling]' c. 1850s - 1860s (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/gm_05996801-detail.jpg)






![André Kertész (American born Hungary, 1894-1985) '[Wooden Mouse and Duck]' 1929 André Kertész (American born Hungary, 1894-1985) '[Wooden Mouse and Duck]' 1929](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/gm_04006701-web.jpg)
![Unknown maker (American) '[Dog sitting on a table]' c. 1854 Unknown maker (American) '[Dog sitting on a table]' c. 1854](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/gm_05620501-web.jpg)


![William Wegman (American, b. 1943) 'In the Box/Out of the Box [right]' 1971 William Wegman (American, b. 1943) 'In the Box/Out of the Box [right]' 1971](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/gm_32612201-web.jpg)
![William Wegman (American, b. 1943) 'In the Box/Out of the Box [left]' 1971 William Wegman (American, b. 1943) 'In the Box/Out of the Box [left]' 1971](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/gm_32612101-web.jpg)






















































You must be logged in to post a comment.