Exhibition dates: 11th December, 2015 – 24th April, 2016
Curator: Max Delany, Senior Curator of Contemporary Art at the NGV
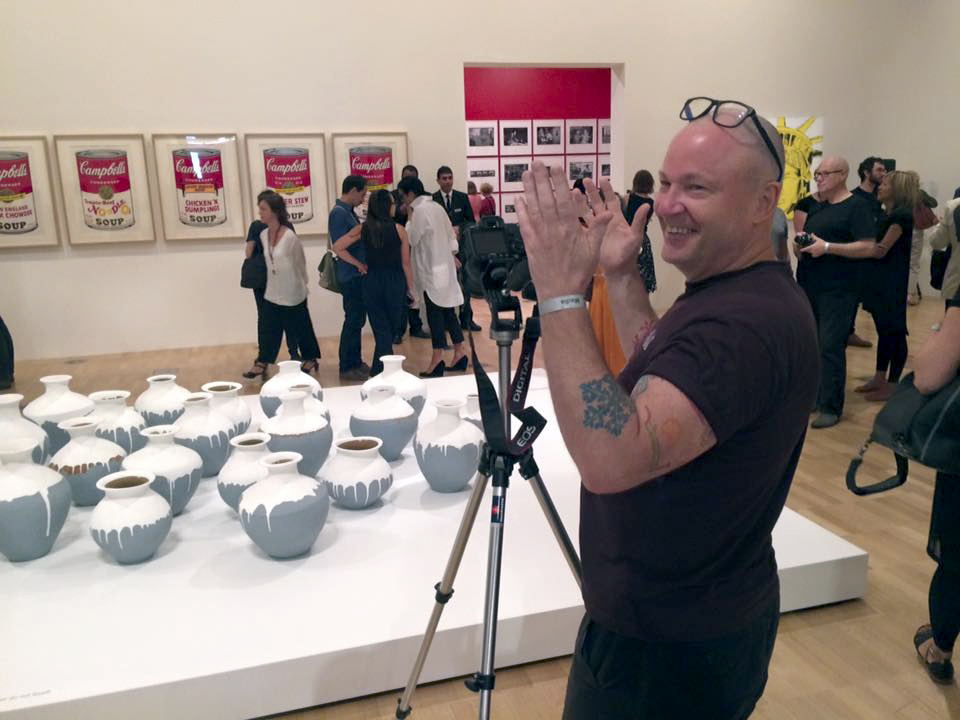
Marcus photographing the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria
Photo: Nick Henderson
A monster posting of installation images of the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, in chronological order. Thoughts to follow. See my review of the exhibition.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the National Gallery of Victoria for allowing me to take and publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image. All photographs © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria.
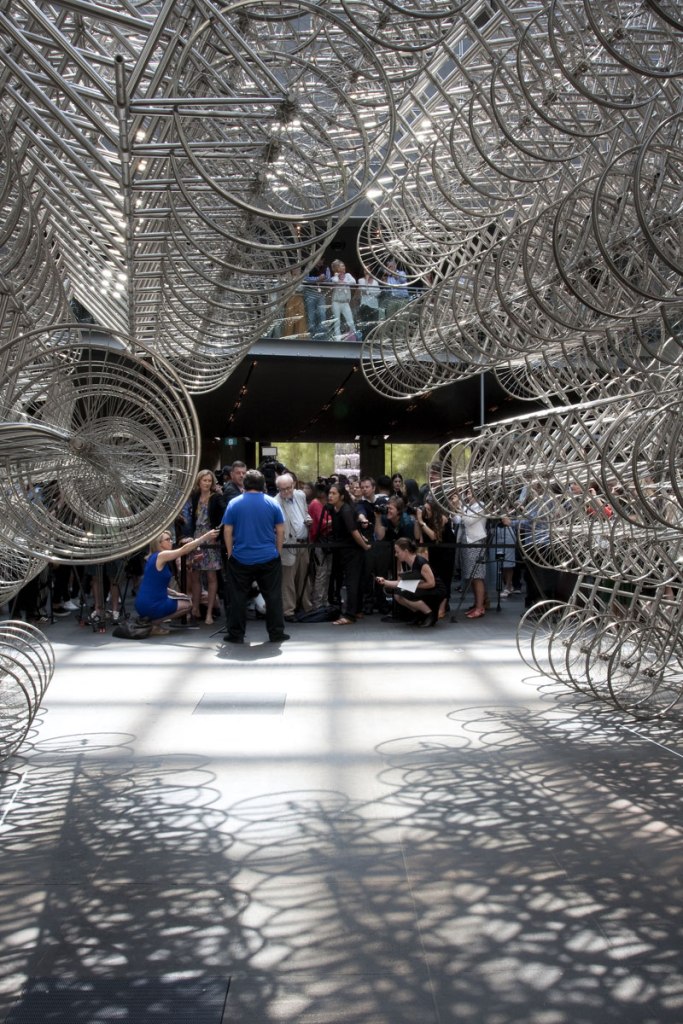

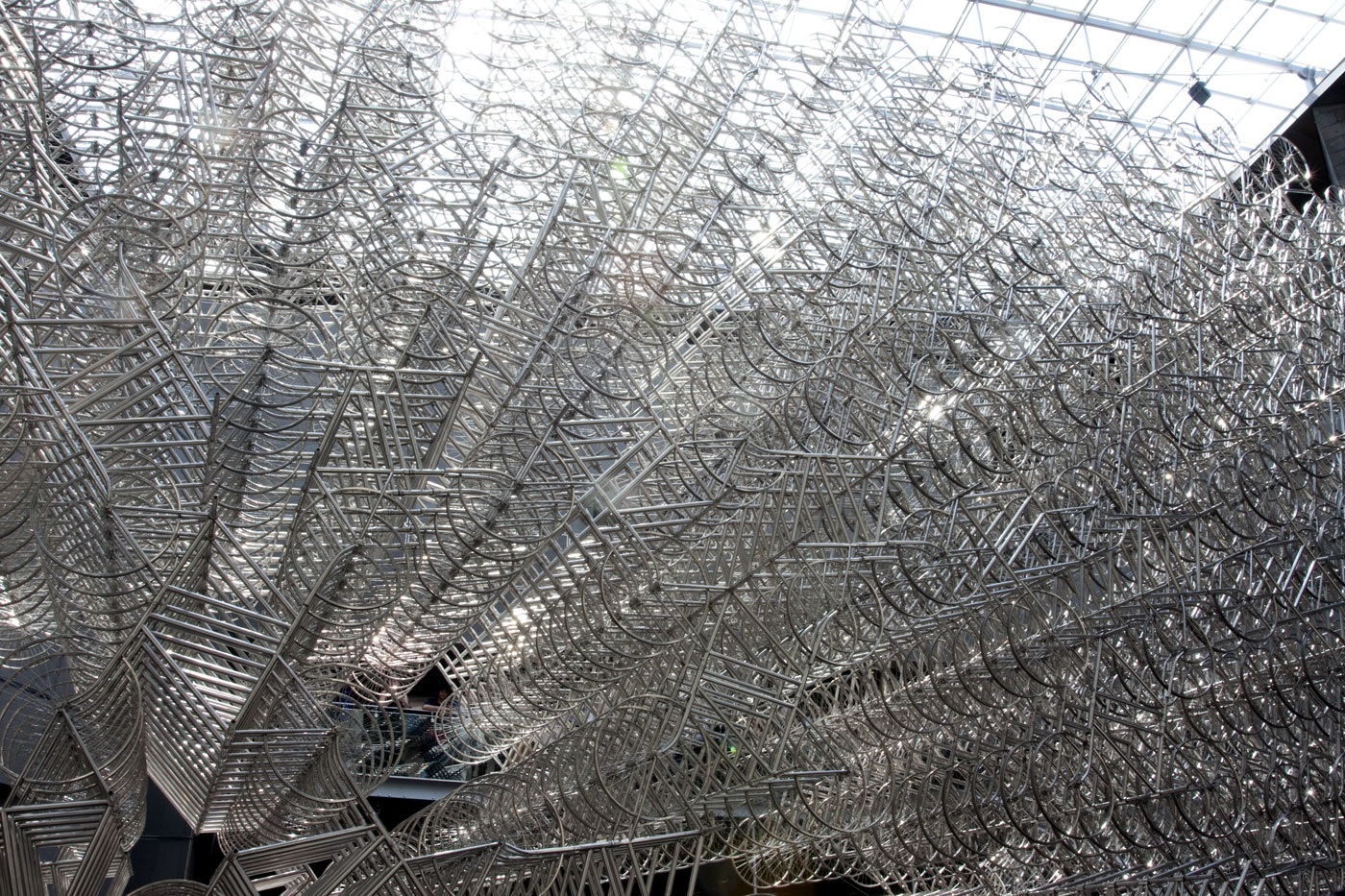
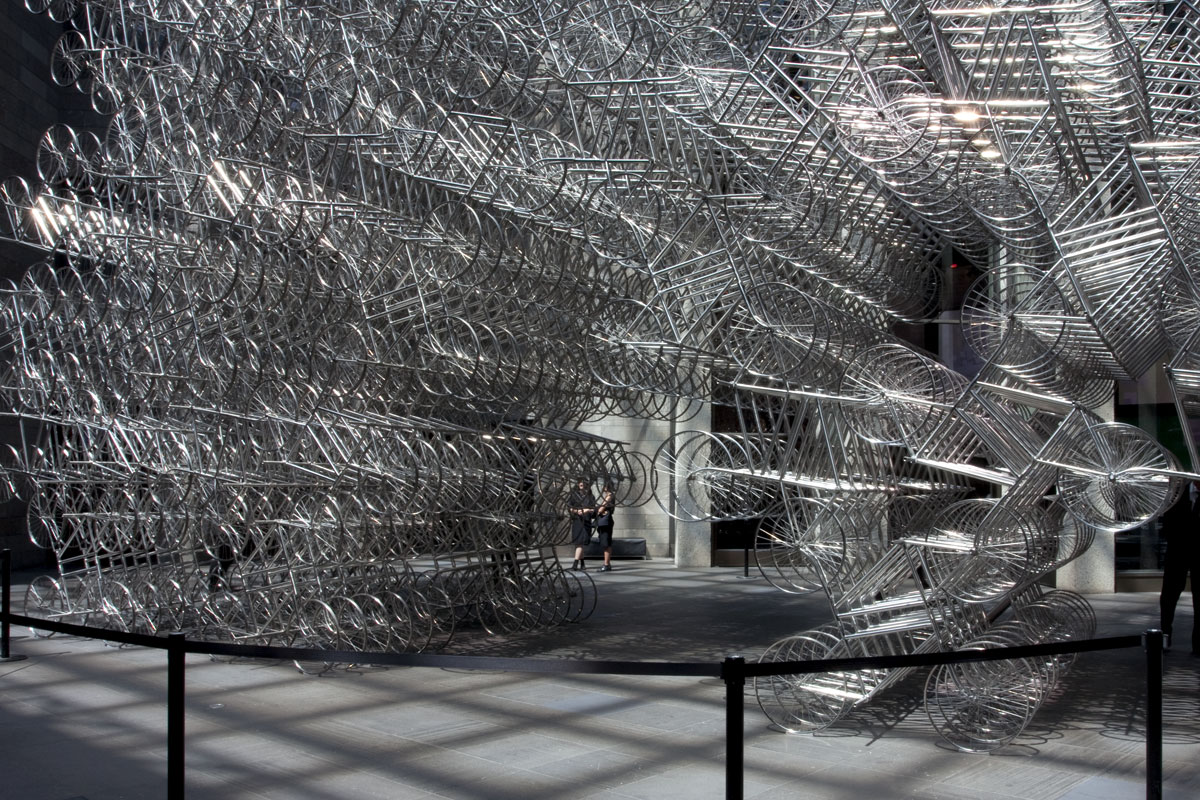
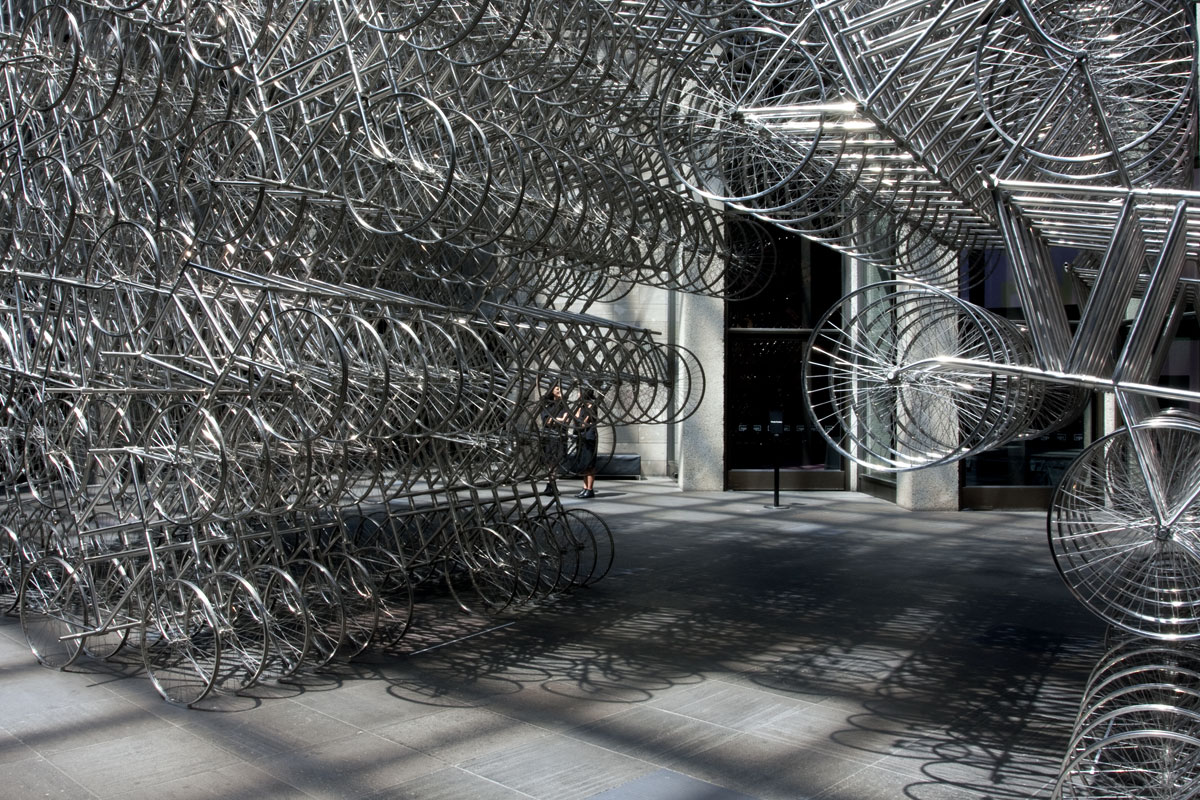
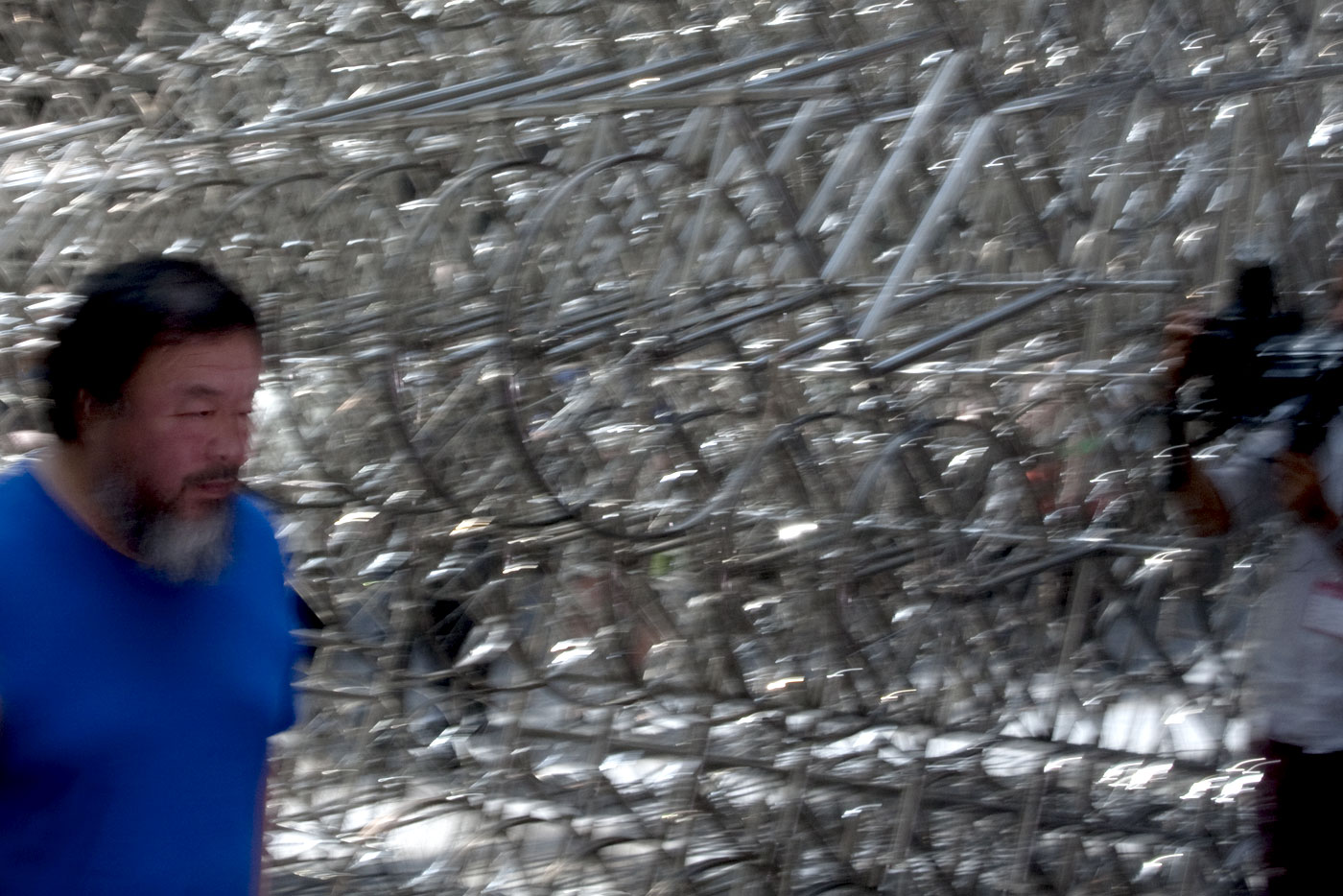
Ai Weiwei talking to the media in front of his installation Forever Bicycles (2015) at the opening of the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
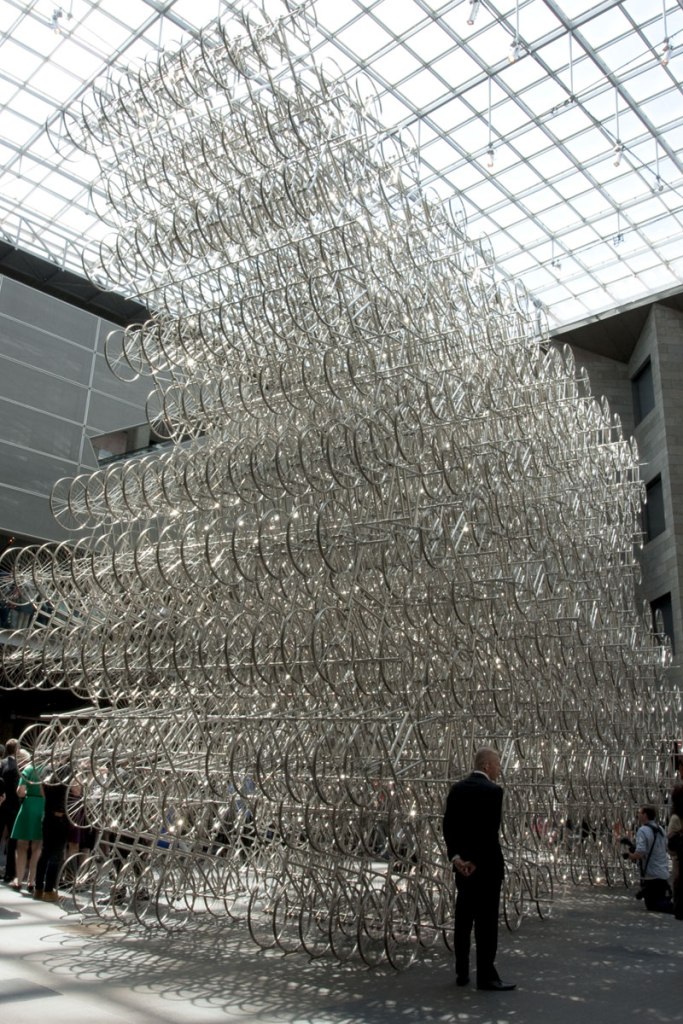
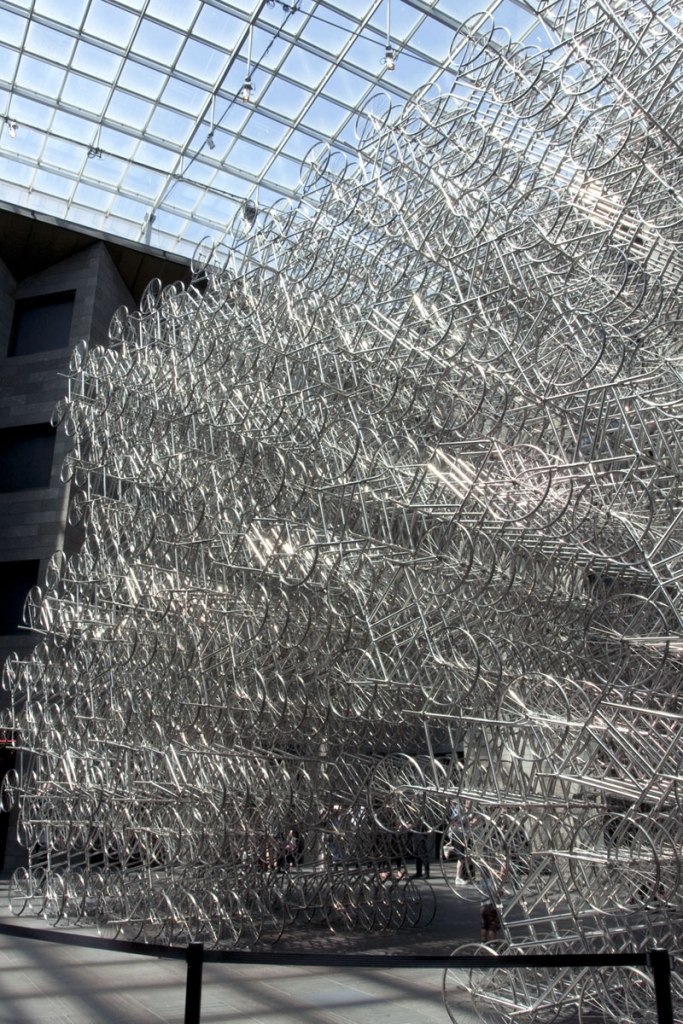


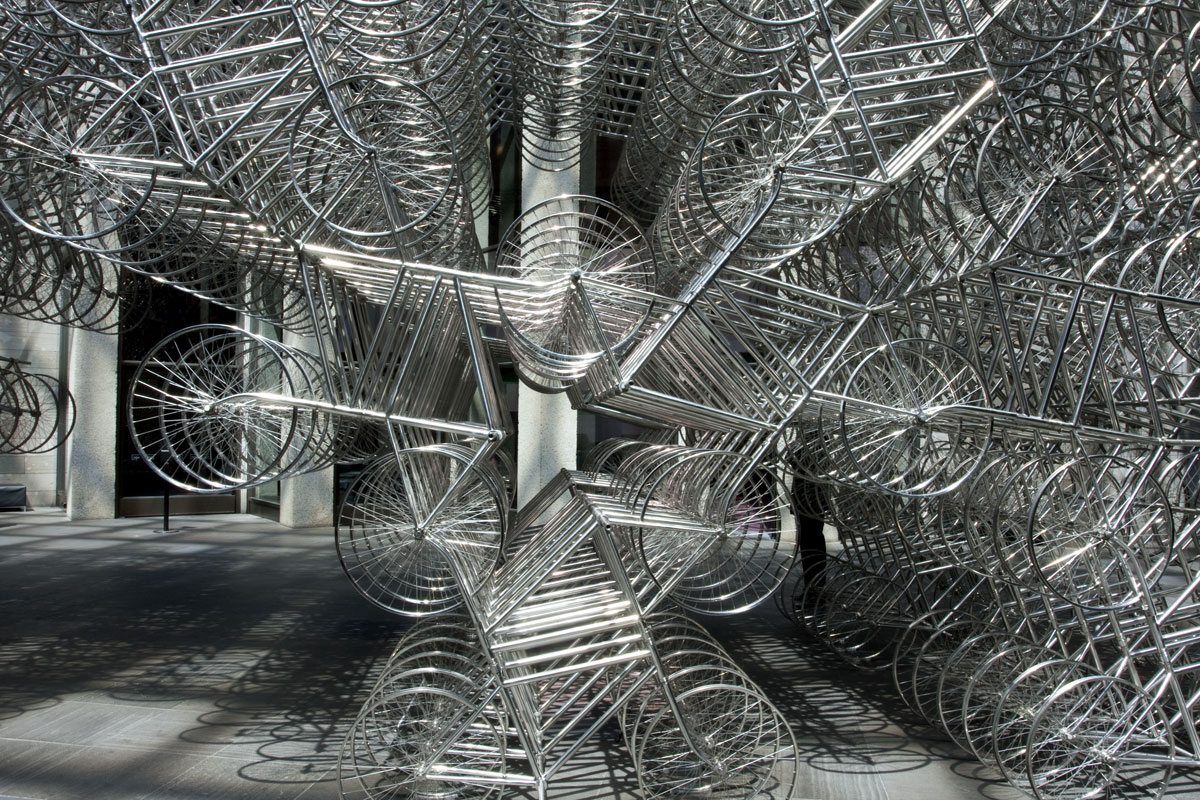
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Forever Bicycles (installation details)
2015
Stainless steel bicycle frames
Courtesy Ai Weiwei and Lisson Gallery, London
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
The assembly and replication of readymade bicycles in Ai’s Forever Bicycles series, ongoing since 2003, promotes an intensely spectacular effect. ‘Forever’ is a popular brand of mass-produced bicycles manufactured in China since the 1940s and desired by Ai as a child. Composed from almost 1500 bicycles, this installation suggests both the individual and the multitude, with the collective energy of social progress signalled in the assemblage and perspectival rush of multiple forms.
Forever Bicycles disconnects the bicycles from their everyday function – reconfiguring them as an immense labyrinth-like network. The multi-tiered installation also achieves an architectural presence, much like a traditional arch or gateway to the exhibition.
Ai Weiwei at the opening of the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
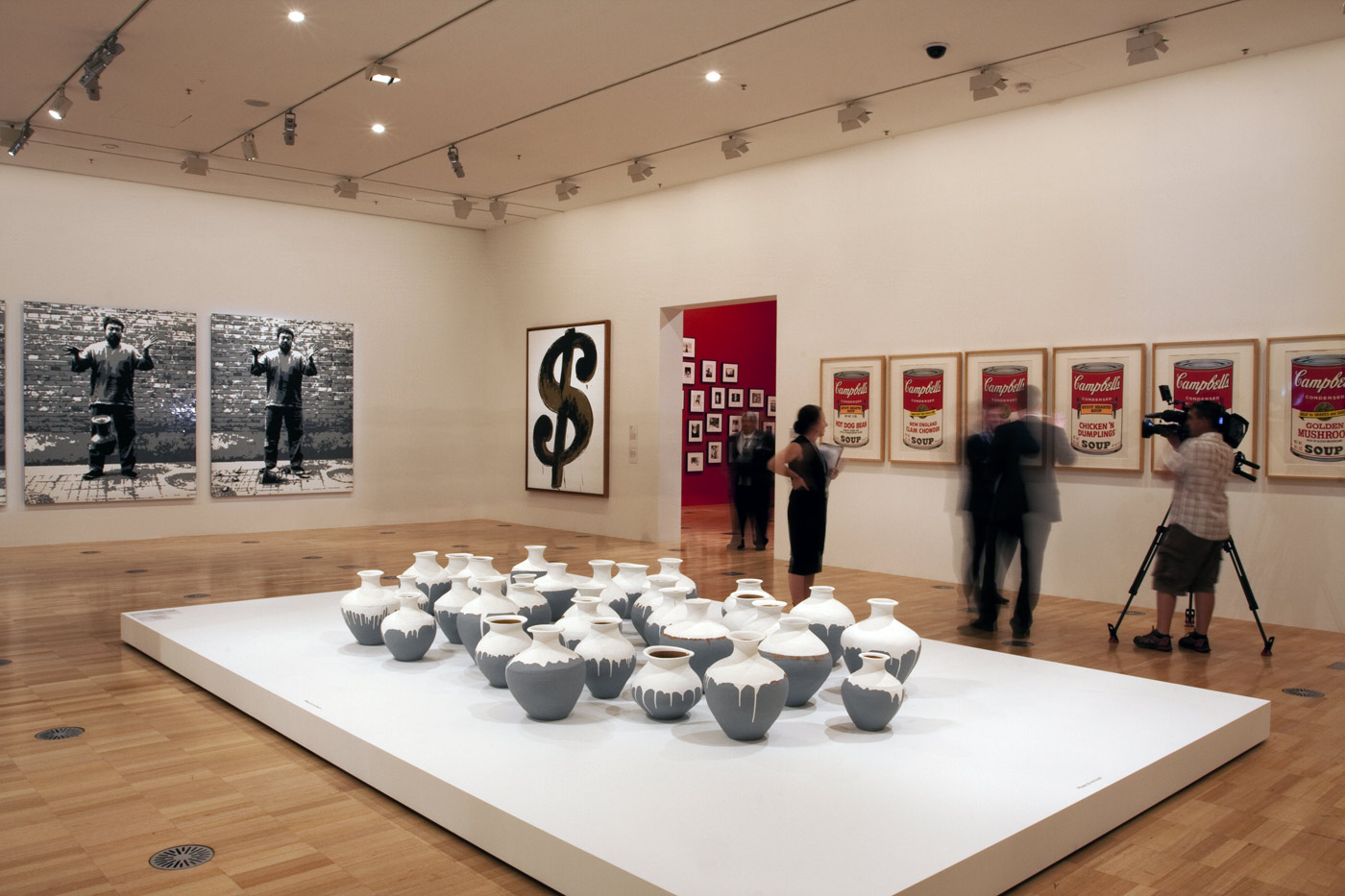
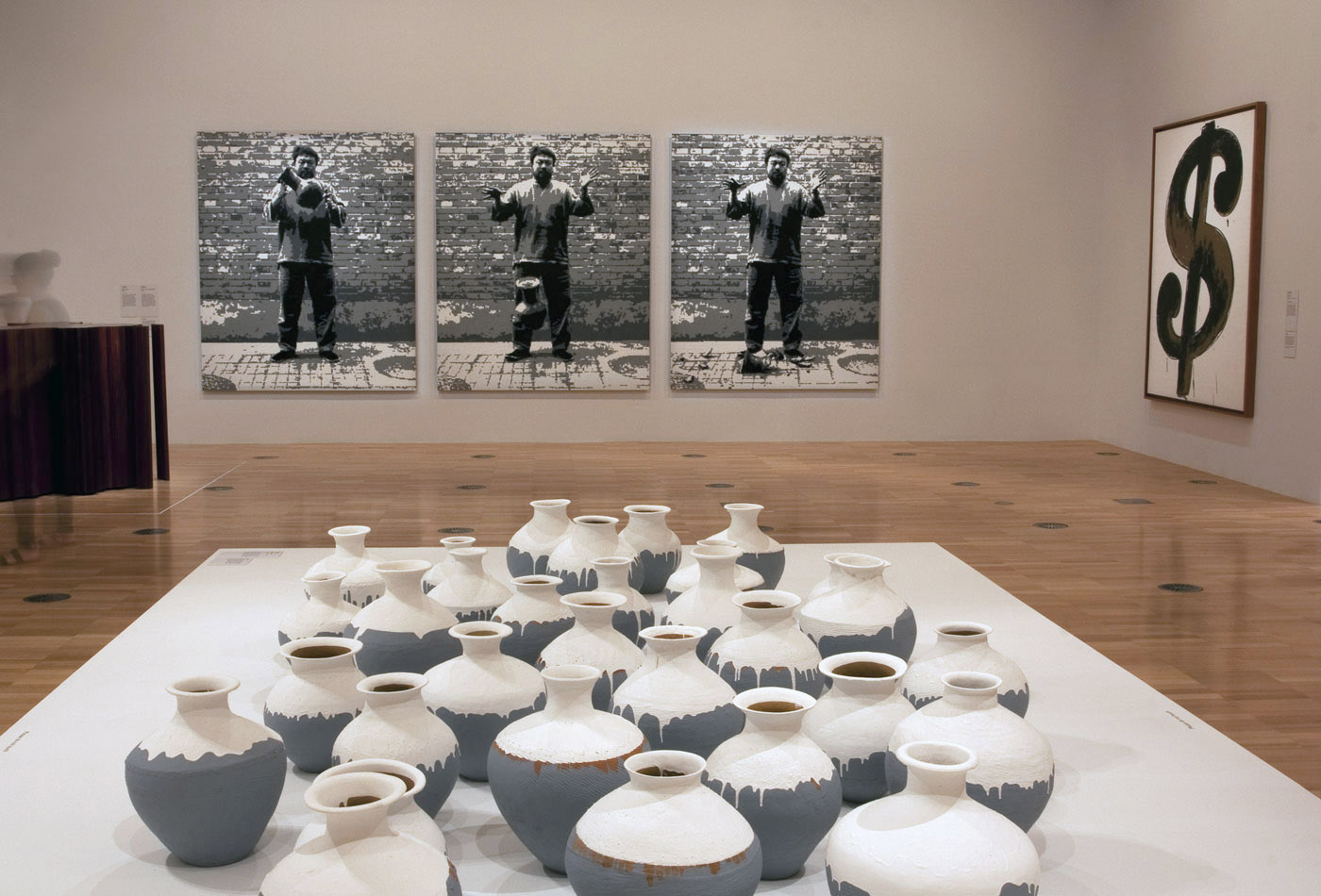
Installation view of the first room including Andy Warhol’s Dollar Sign (1981) and screen prints from his Campbell’s Soup II series (1969), with Ai Weiwei’s Dropping a Han Dynasty Urn (2015) made of LEGO-style plastic bricks at back left with, on the floor, his Coloured Vases (2015).
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
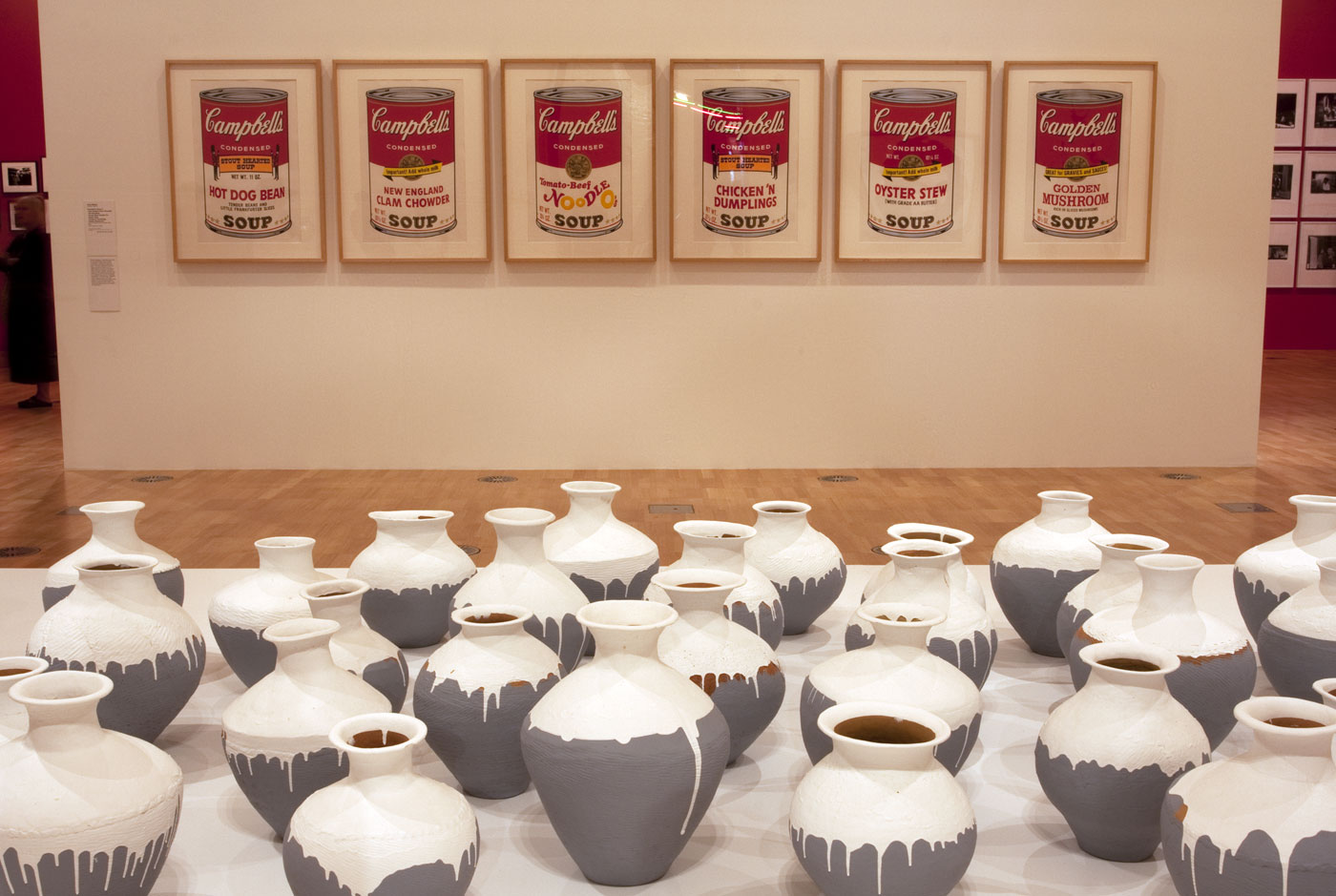
Installation view of the first room including Andy Warhol’s screen prints from his Campbell’s Soup II series (1969), with Ai Weiwei’s Coloured Vases (2015, detail)
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Installation view of the first room including Andy Warhol’s Dollar Sign (1981), with Ai Weiwei’s Dropping a Han Dynasty Urn (2015) made of LEGO-style plastic bricks, with on the floor his Coloured Vases (2015, detail)
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
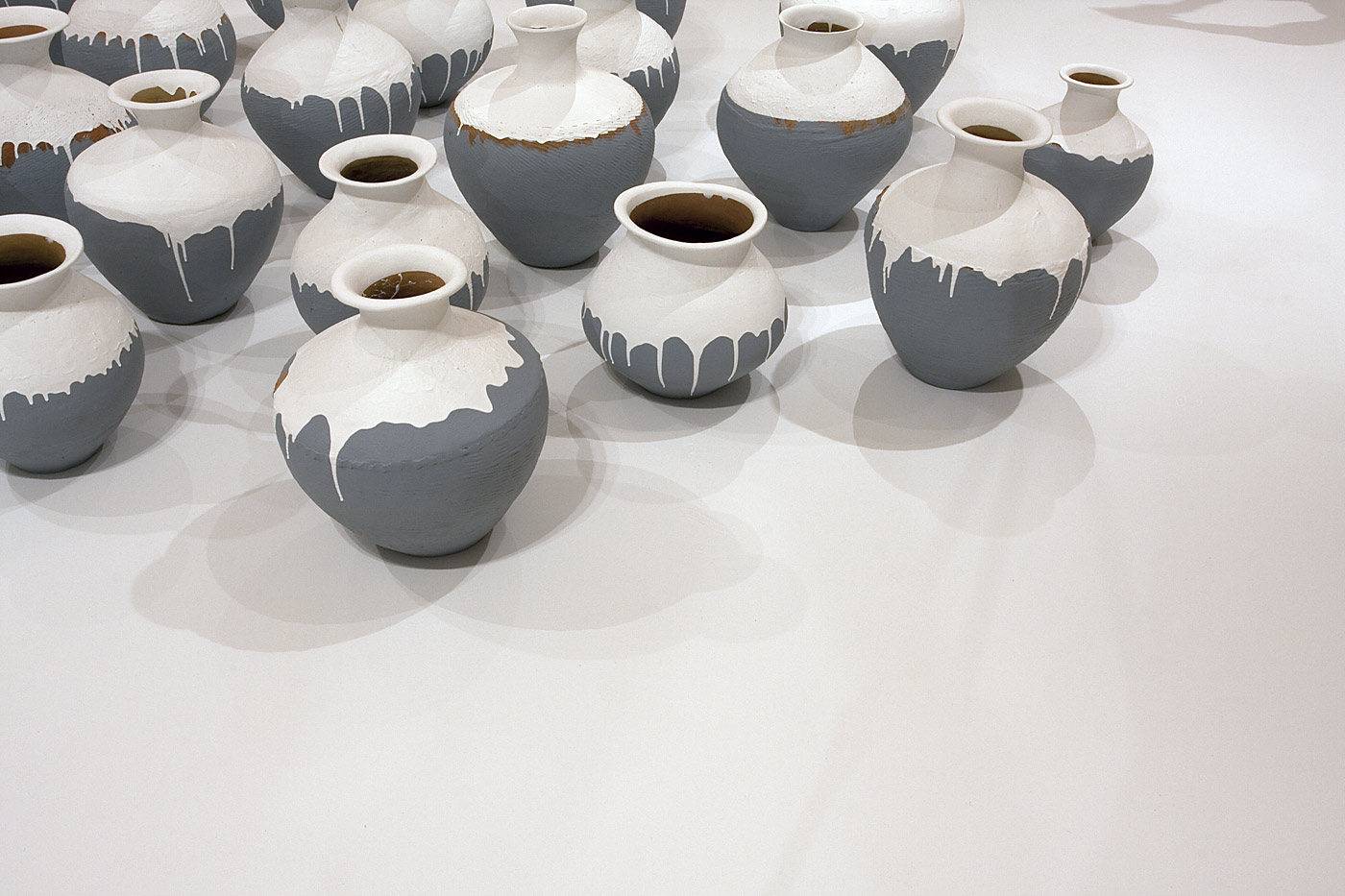
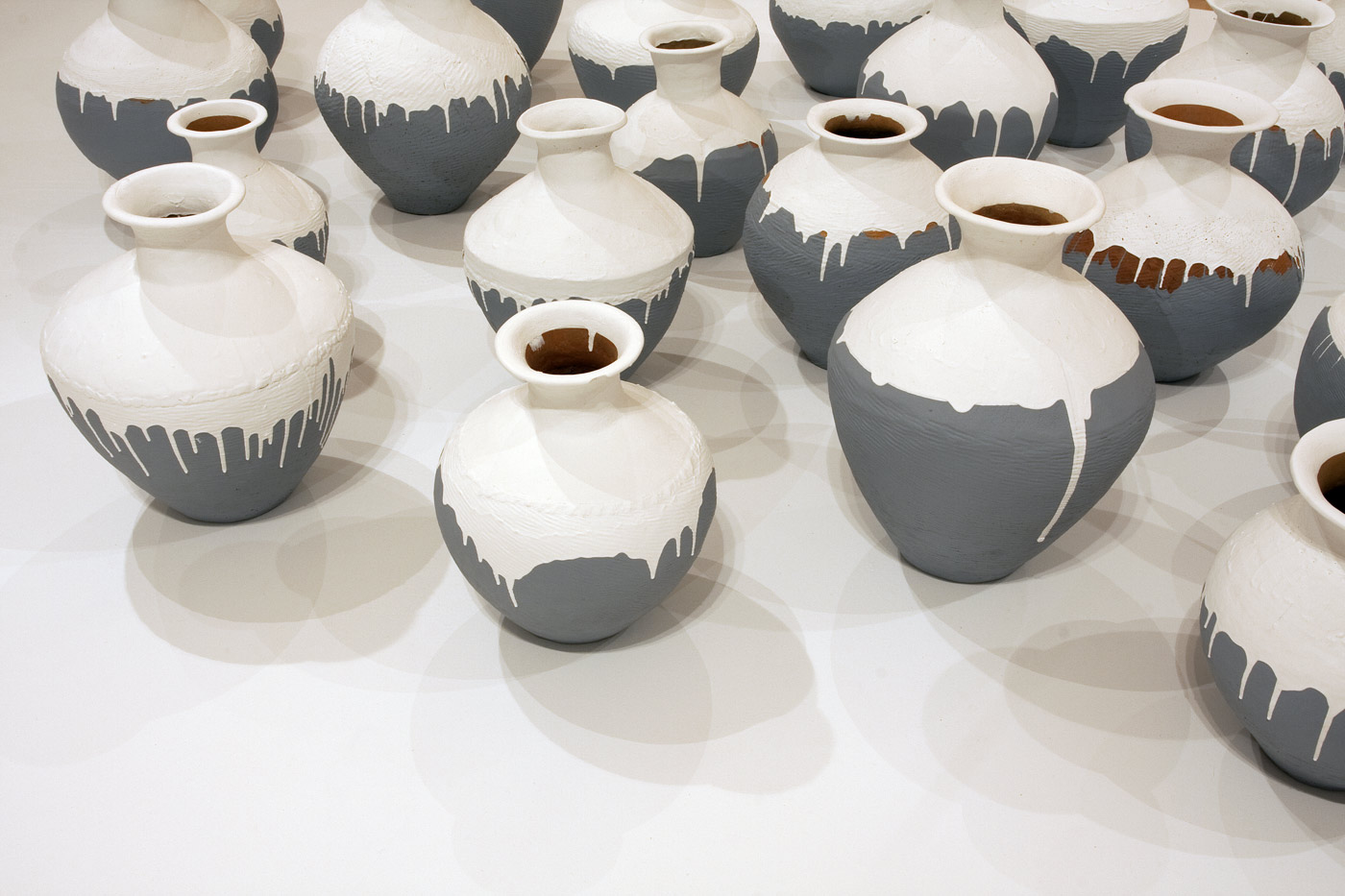
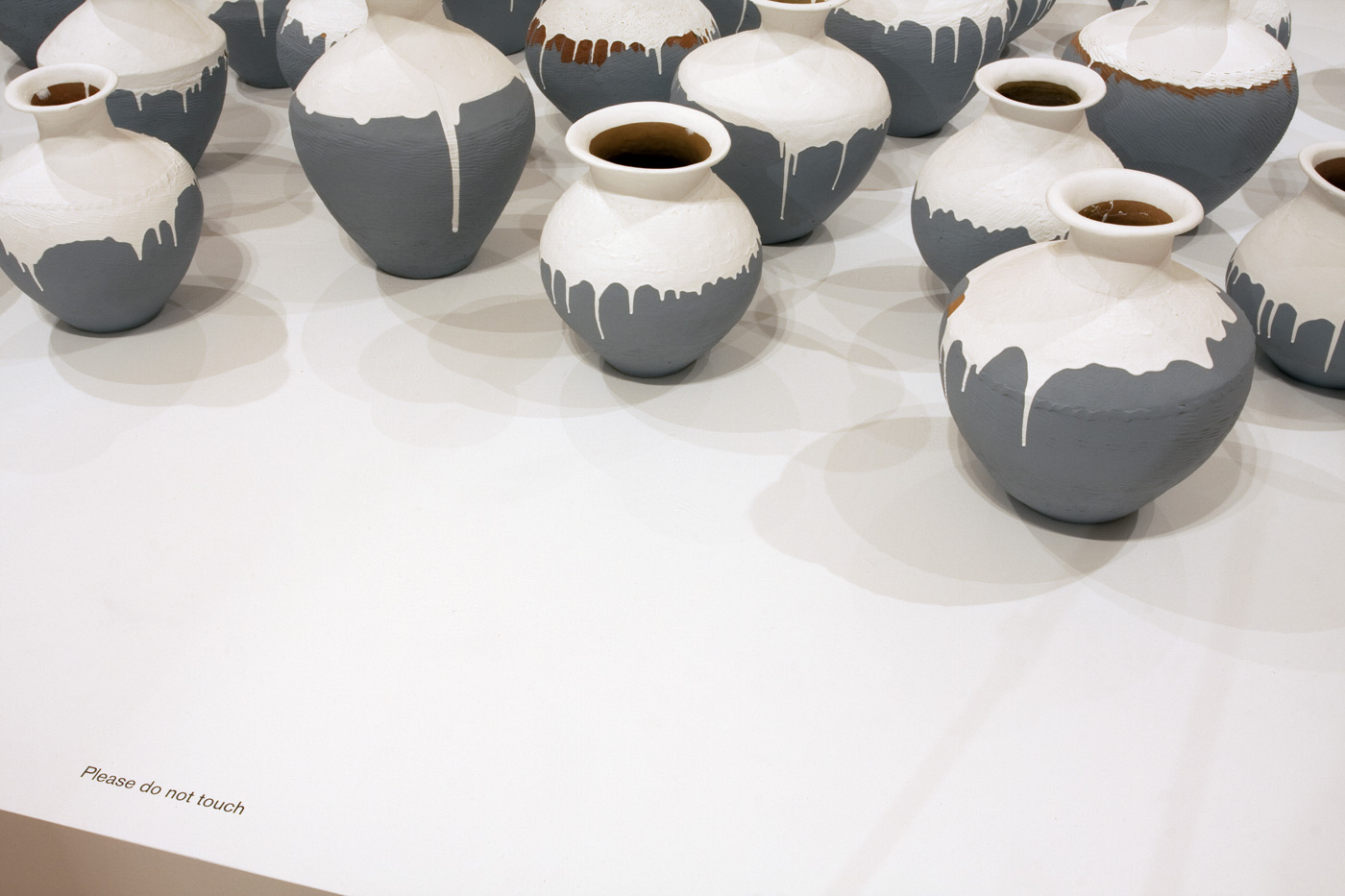
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Coloured Vases (installation details)
2015
Synthetic polymer paint, Neolithic earthenware jars
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
In Ai’s series of Coloured Vases, ongoing since 2006, Neolithic and Han dynasty urns are plunged into tubs of industrial paint to create an uneasy confrontation between tradition and modernity. In what might be considered an iconoclastic form of action painting, Ai gives ancient vessels a new glaze and painterly glow, appealing to new beginnings and cultural change through transformative acts of obliteration, renovation and renewal.
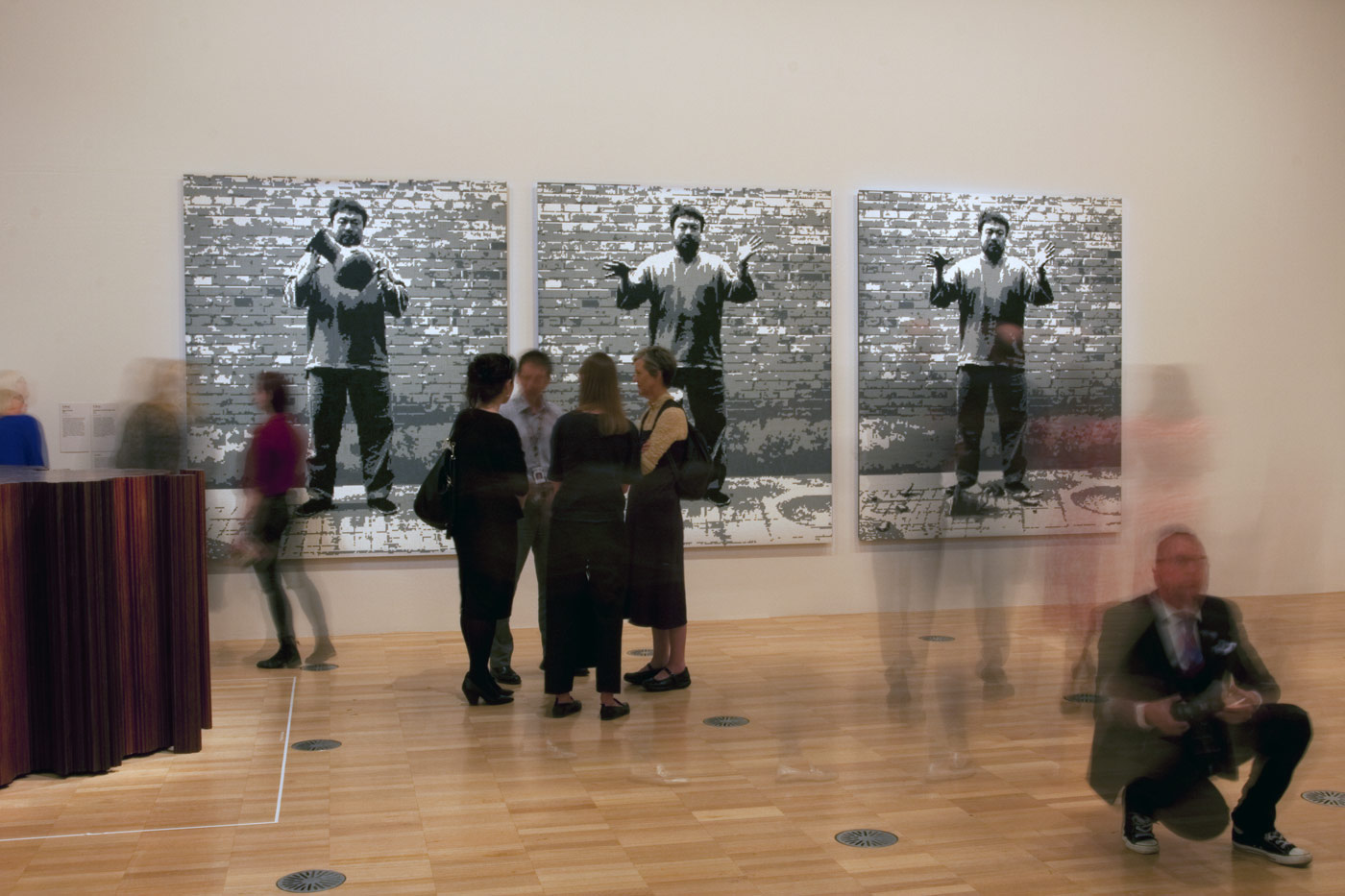

Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Dropping a Han Dynasty Urn (installation views)
2015
Plastic
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
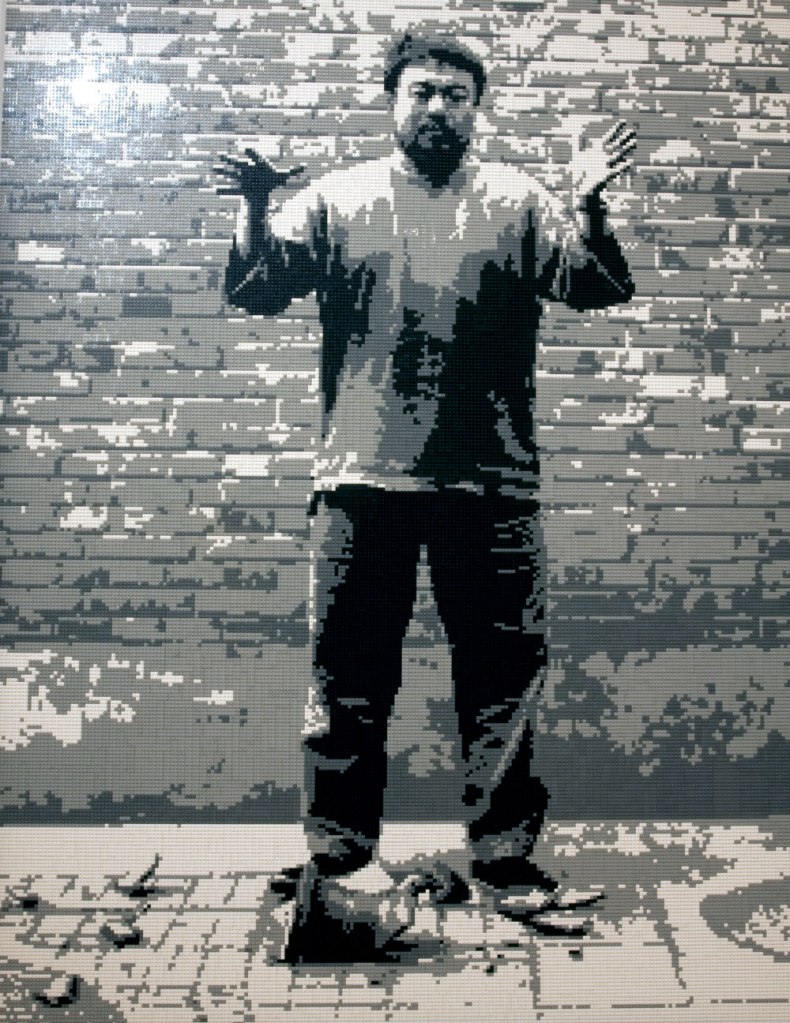

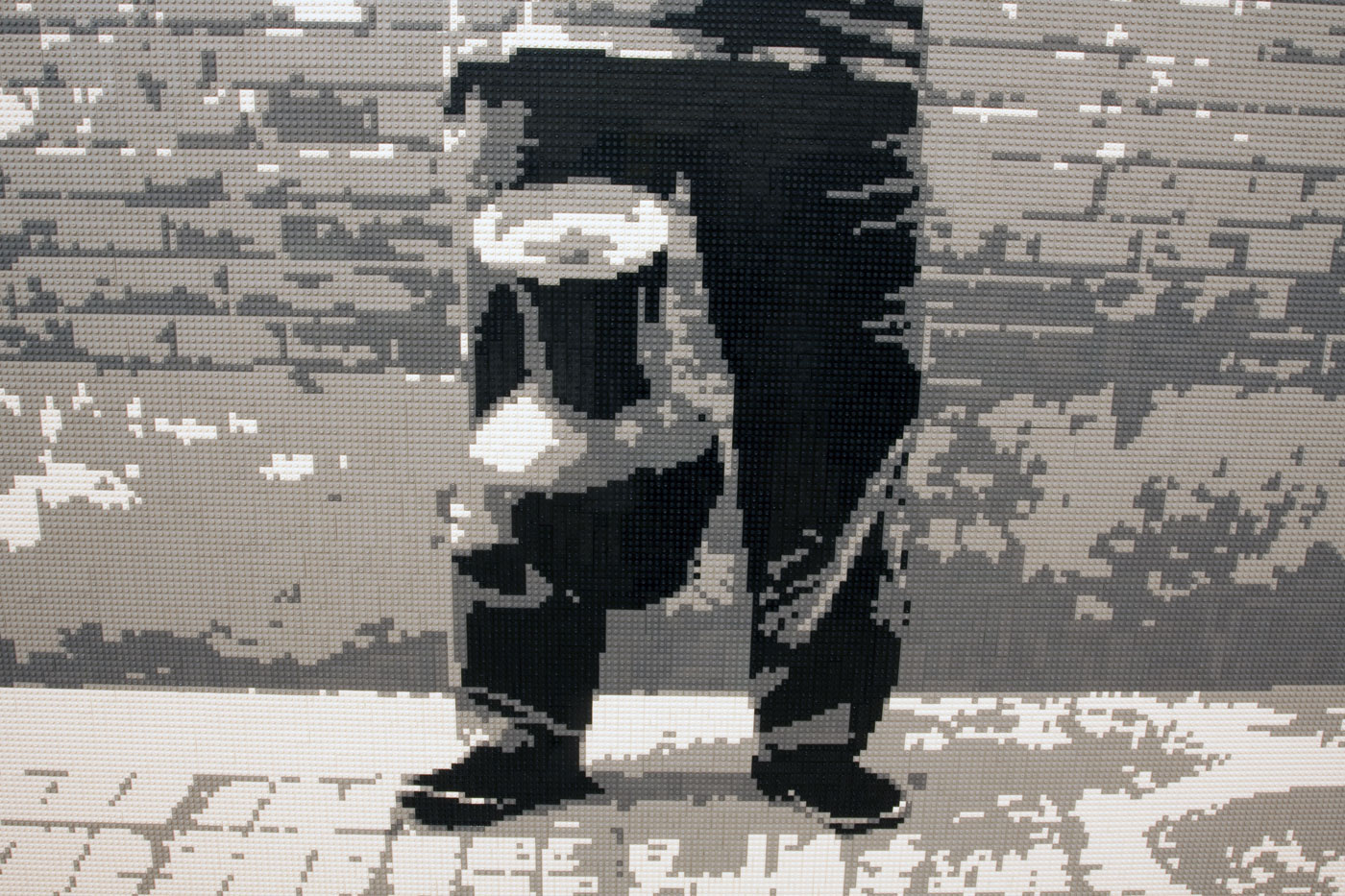
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
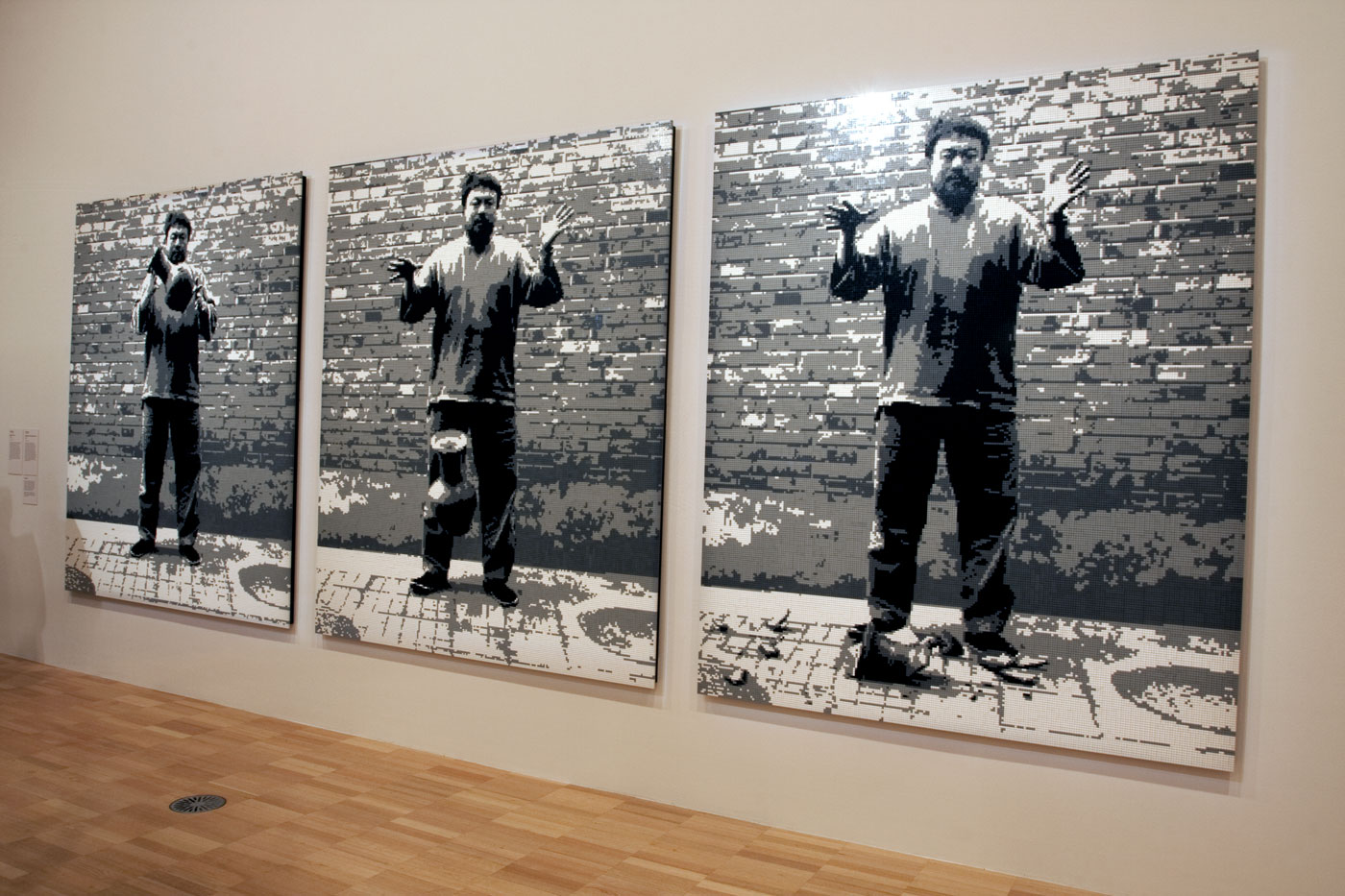
Dropping a Han Dynasty Urn (installation details)
2015
Plastic
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Ai’s photographic triptych Dropping a Han Dynasty Urn, 1995, which shows the artist holding, releasing and smashing a Han dynasty vase, is one of the artist’s most iconic works and demonstrates his critical engagement with China’s violent cultural tradition. Drawing attention to the desecration of cultural heritage, the artist’s performative action is presented matter-of-factly, with the viewer left to contemplate the event and what might be salvaged from the destruction. Ai has recreated the image here in children’s building blocks, in pixelated form, attesting to the distribution of images by digital technologies.
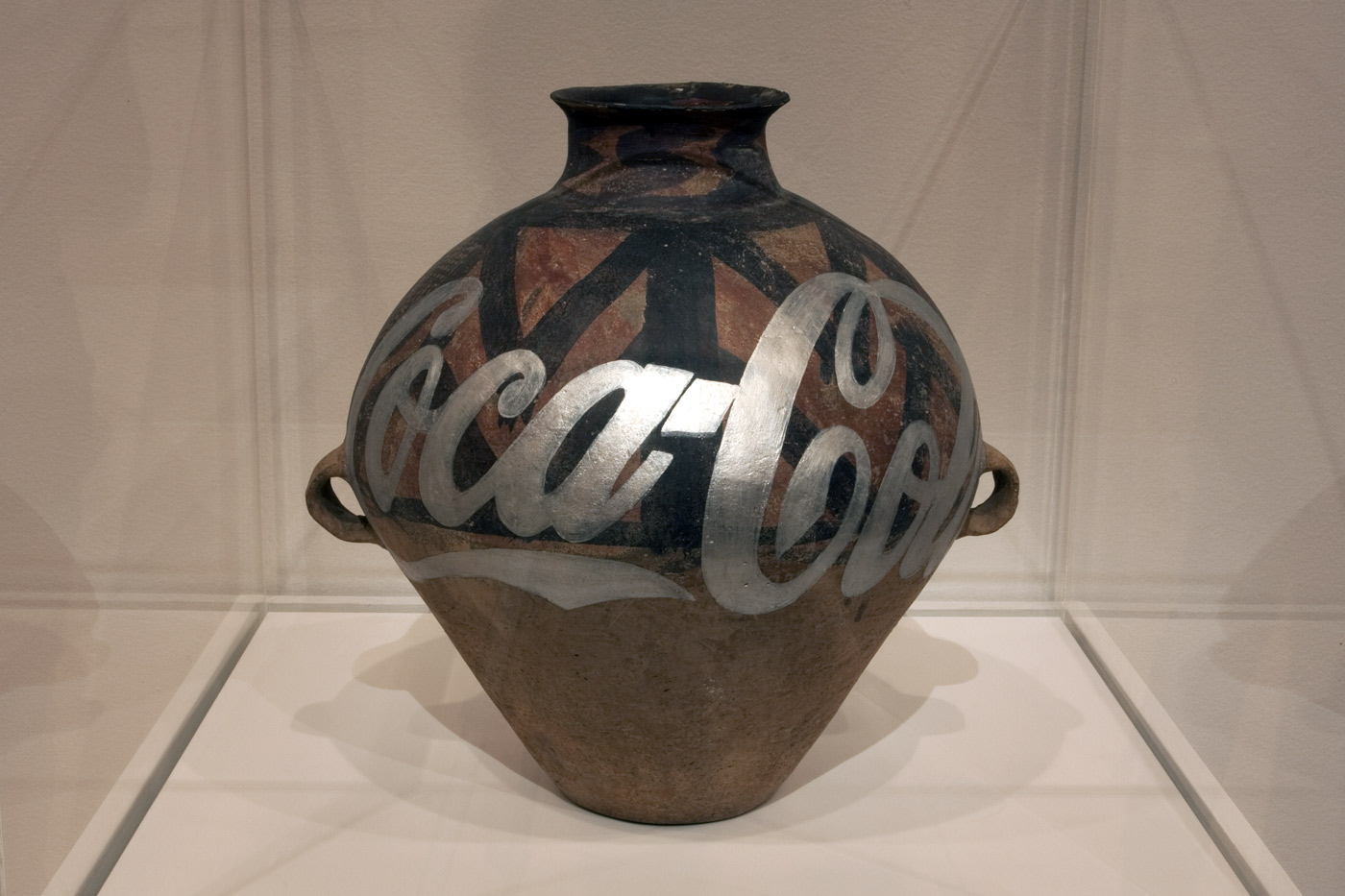
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Neolithic Pottery with Coca-Cola Logo (installation view)
2007
Metallic paint, earthenware jar
Collection of Larry Warsh, New York
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Bringing together a readymade cultural artefact (after Marcel Duchamp) and pop-cultural imagery (after Andy Warhol), Ai’s painted Neolithic vase presents a rich albeit uneasy confrontation of elements. The Coca-Cola logo – emblem of American capitalism and brand identity – adorns an ancient, revered Chinese artefact. In branding a unique handcrafted object with a product of mass-consumption, Ai delivers a nuanced cultural comment, candidly invoking the conflicted contemporary identity of Chinese cultural heritage, socialist government and capitalist economics.
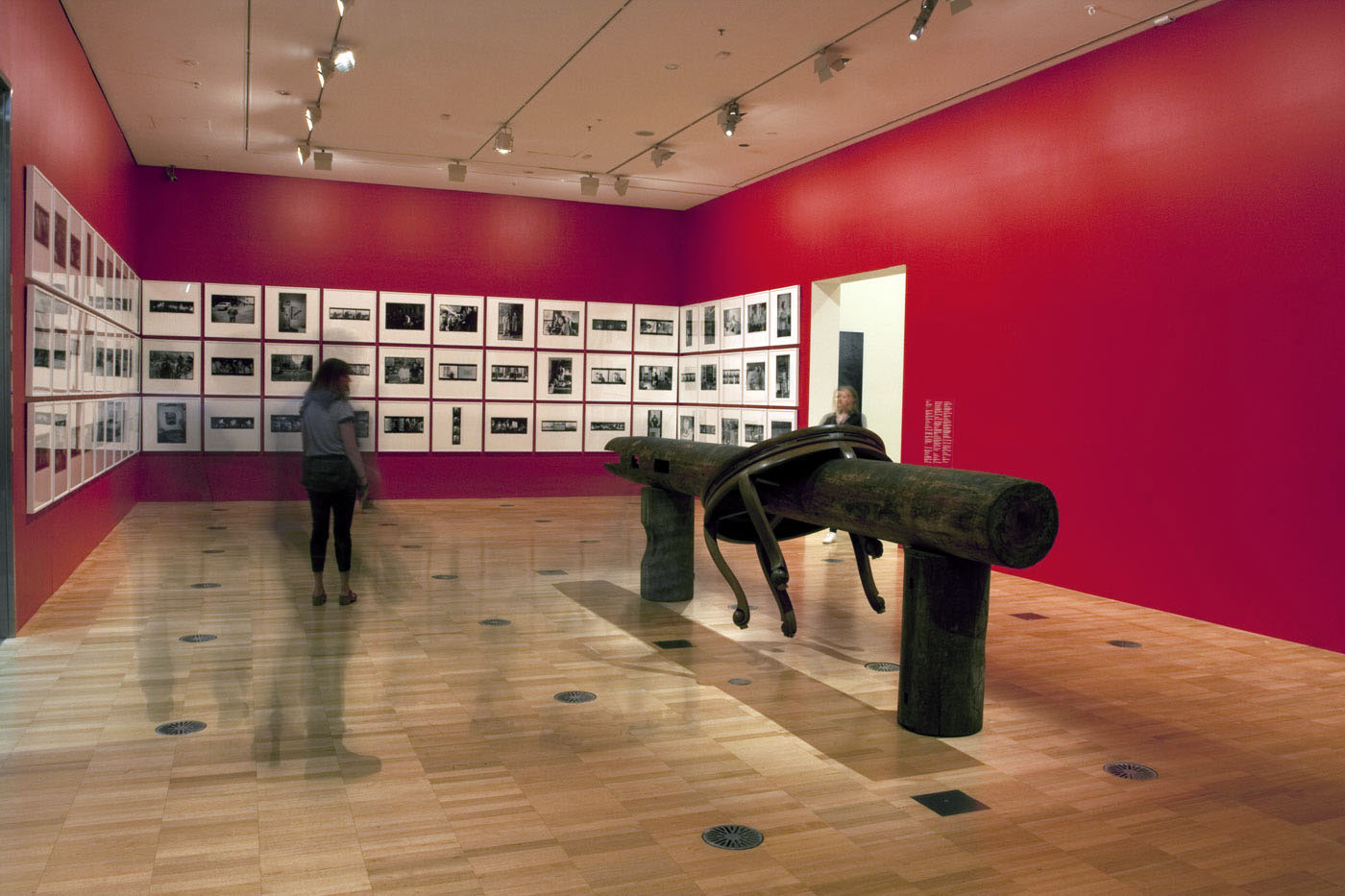
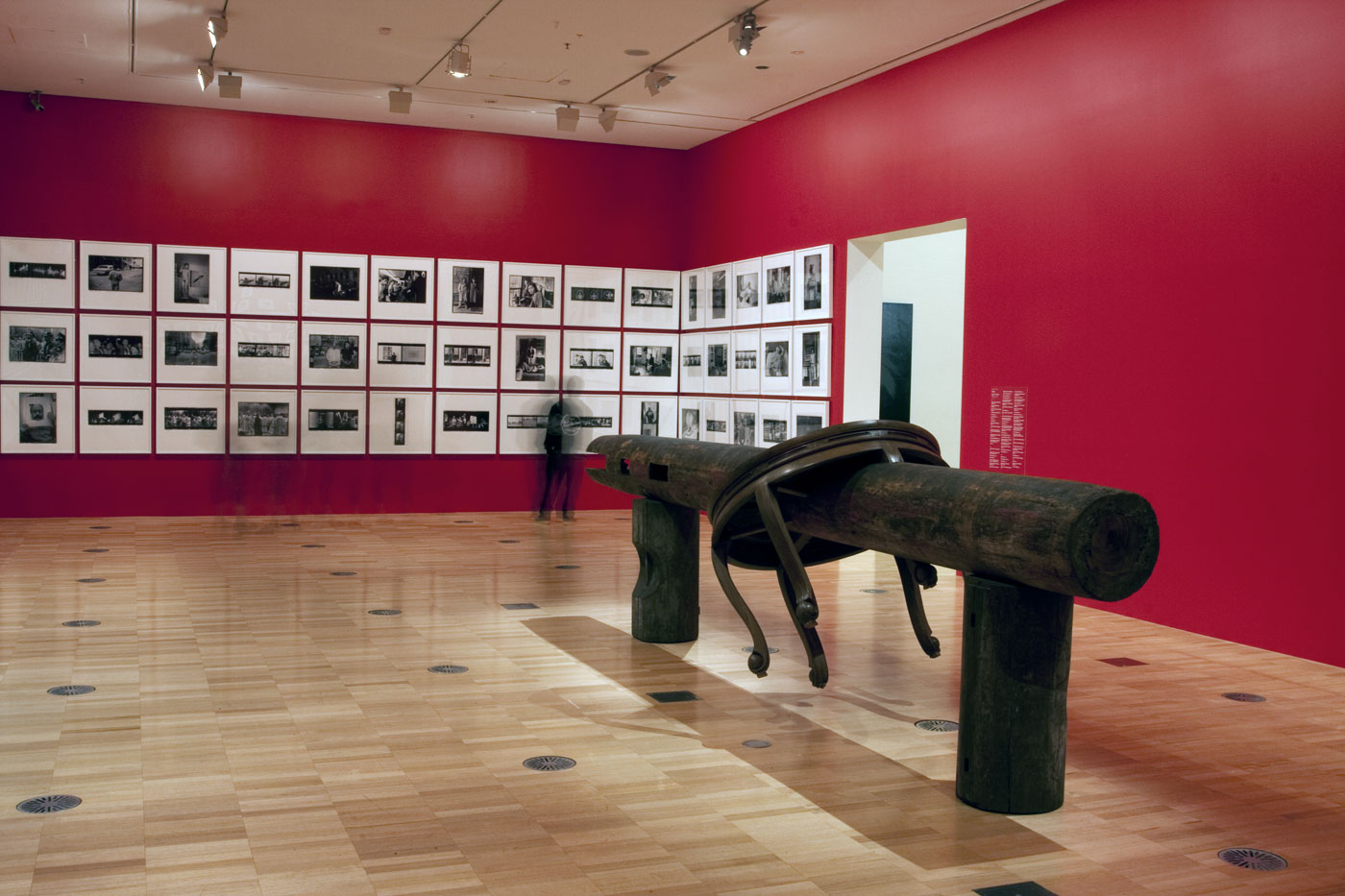
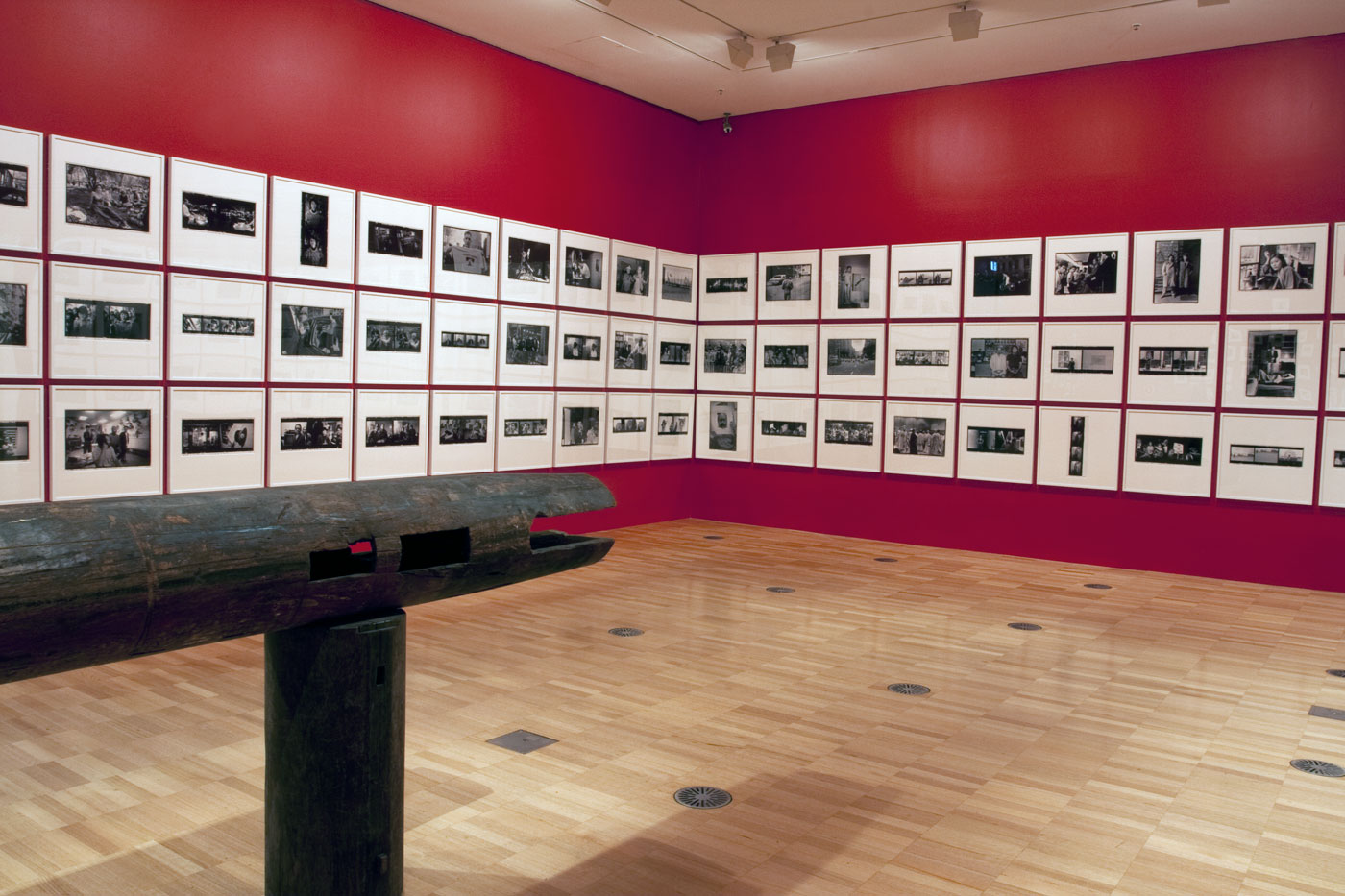
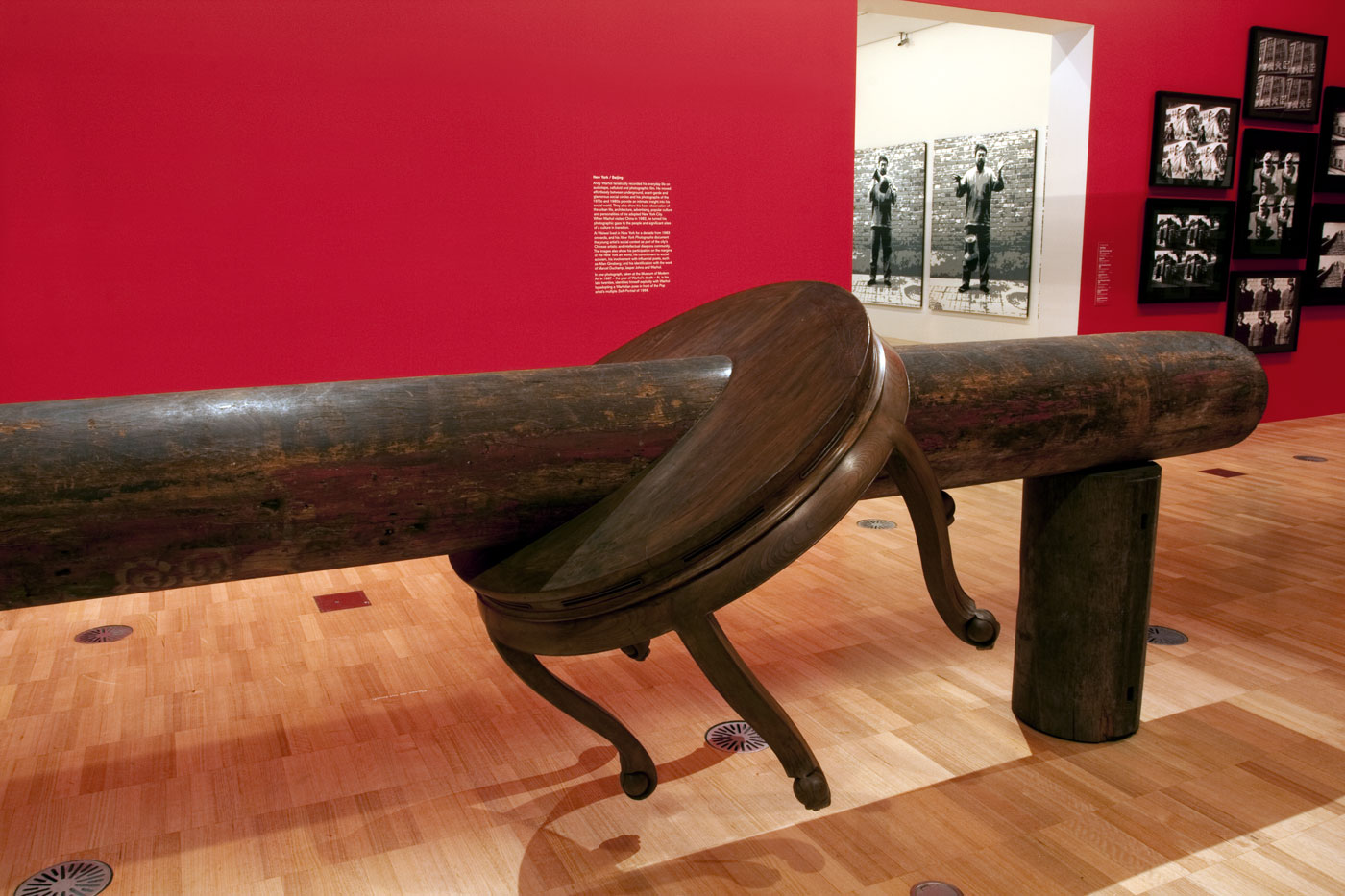
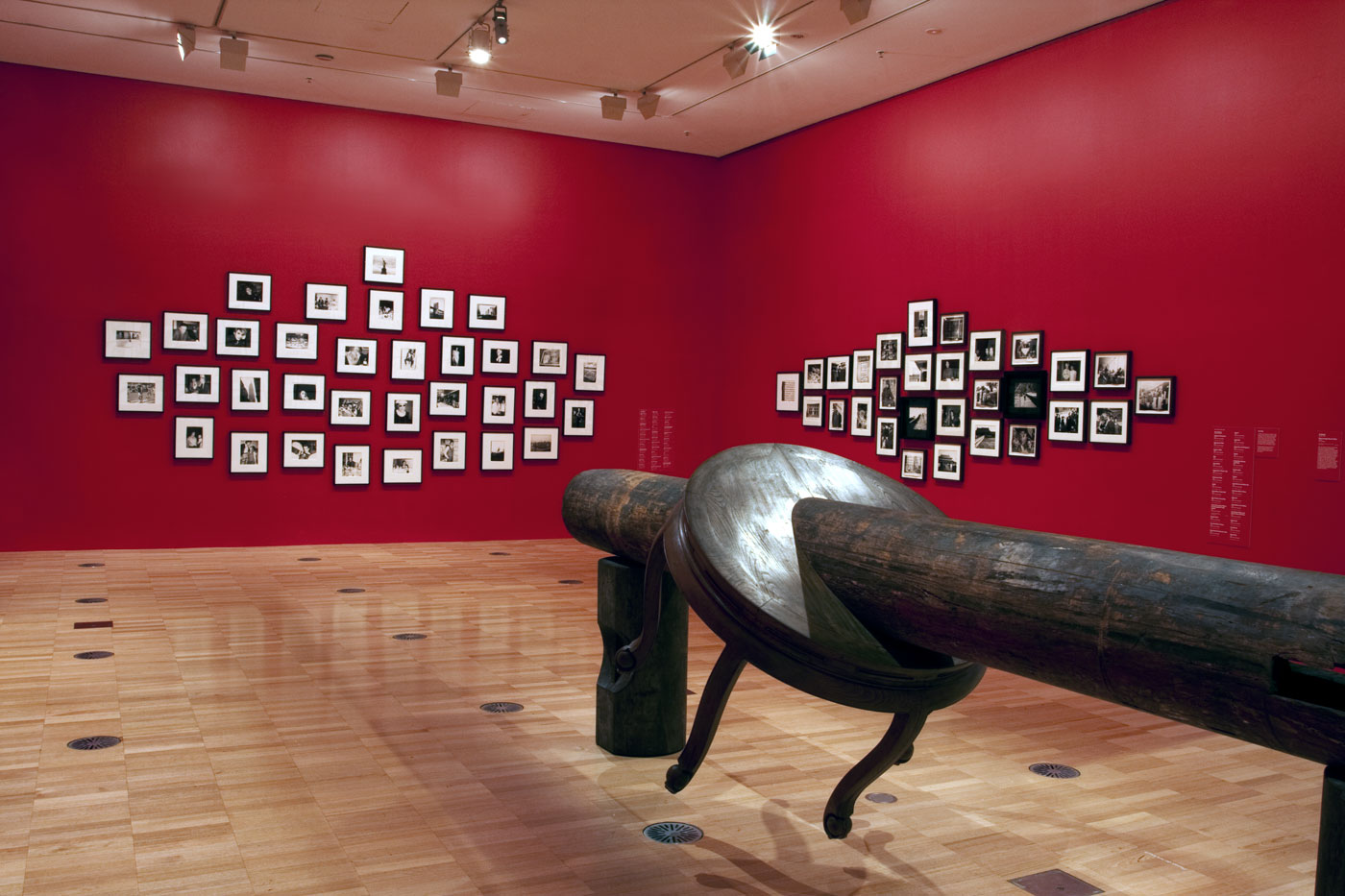
Installation views of second room including at centre, Ai Weiwei’s Pillar through Round Table (2004-2005) with Ai’s black and white photographs behind
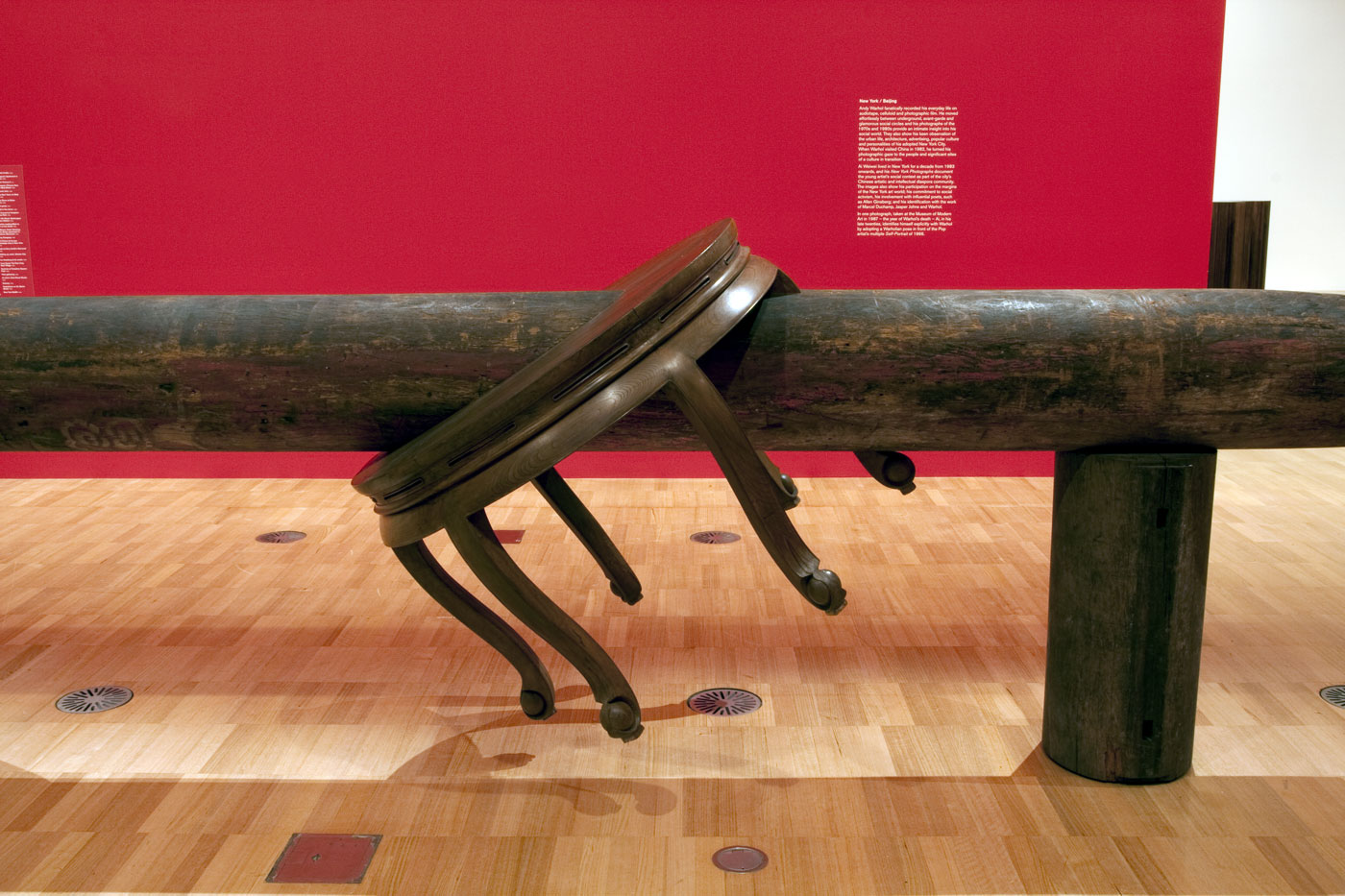
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Pillar through Round Table
2004-2005
Elm, ironwood
Queensland Art Gallery/Gallery of Modern Art, Brisbane, Purchased 2006
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Pillar through Round Table is constructed from a pair of elmwood half-tables bisected horizontally by an ironwood pillar. It is one of an extensive body of works by Ai composed of furniture and architectural fragments from the Qing dynasty period (1644-1911) which have been dismantled and painstakingly reassembled with the assistance of highly skilled carpenters to create new and often confounding arrangements. Ai’s reinvention of historical forms serves to enliven traditional crafts and skills, while his disavowal of modern industrial production processes also acts as a counterpoint to contemporary models of productivity and efficiency in Chinese industrial production.
Installation views of Ai Weiwei’s Pillar through Round Table (2004-2005, details) with Ai’s black and white photographs at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Installation views of second room including, at centre, Ai Weiwei’s Pillar through Round Table (2004-2005) with a group of Andy Warhol’s black and white photographs behind at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
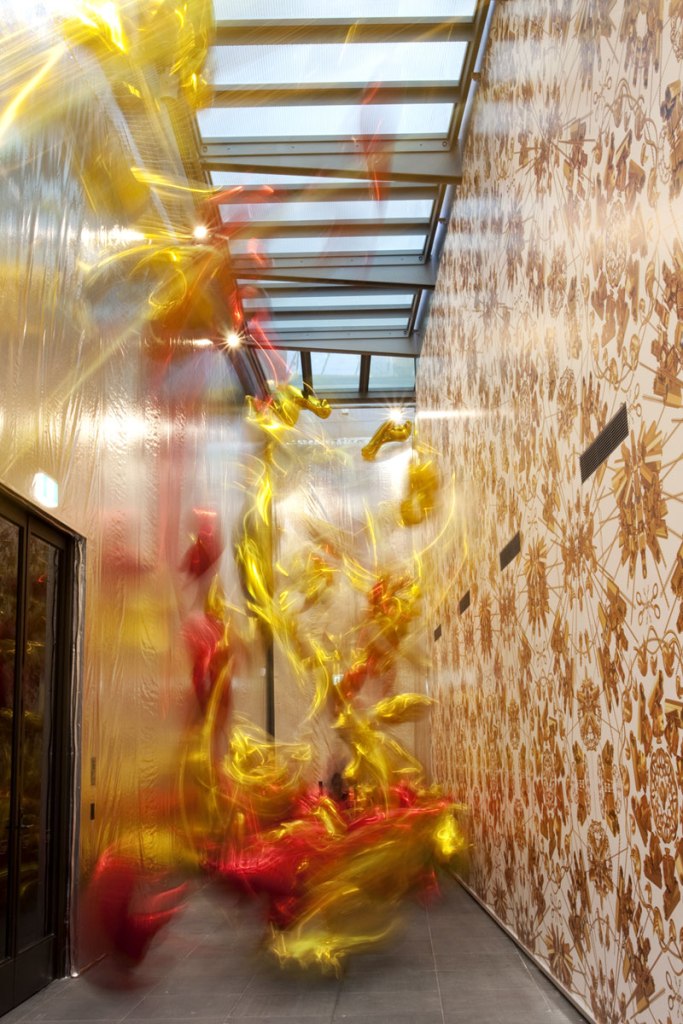
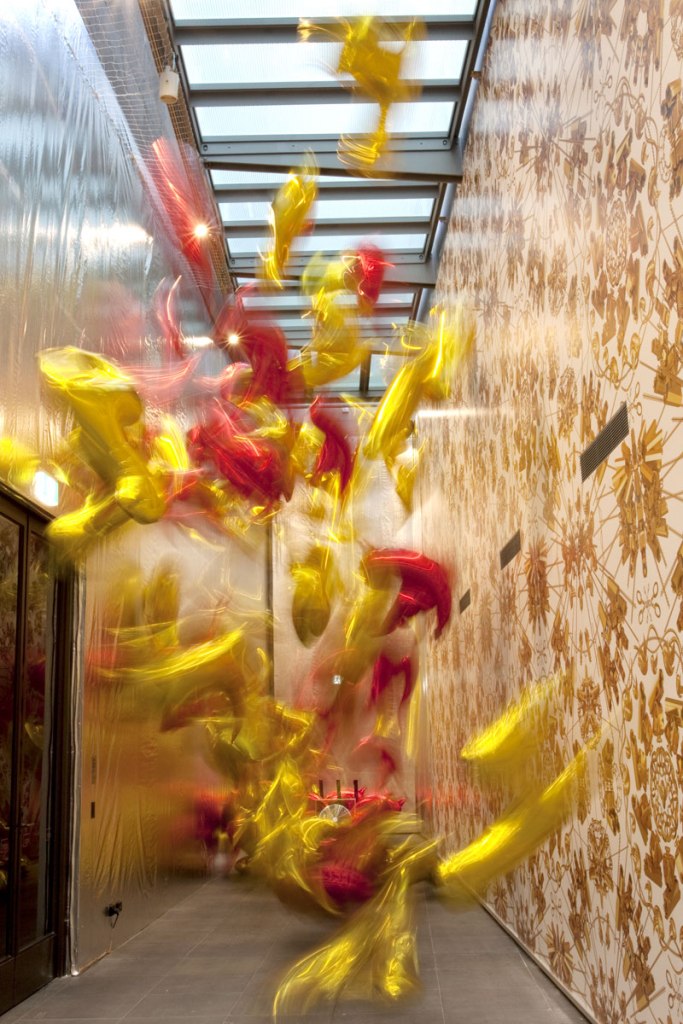
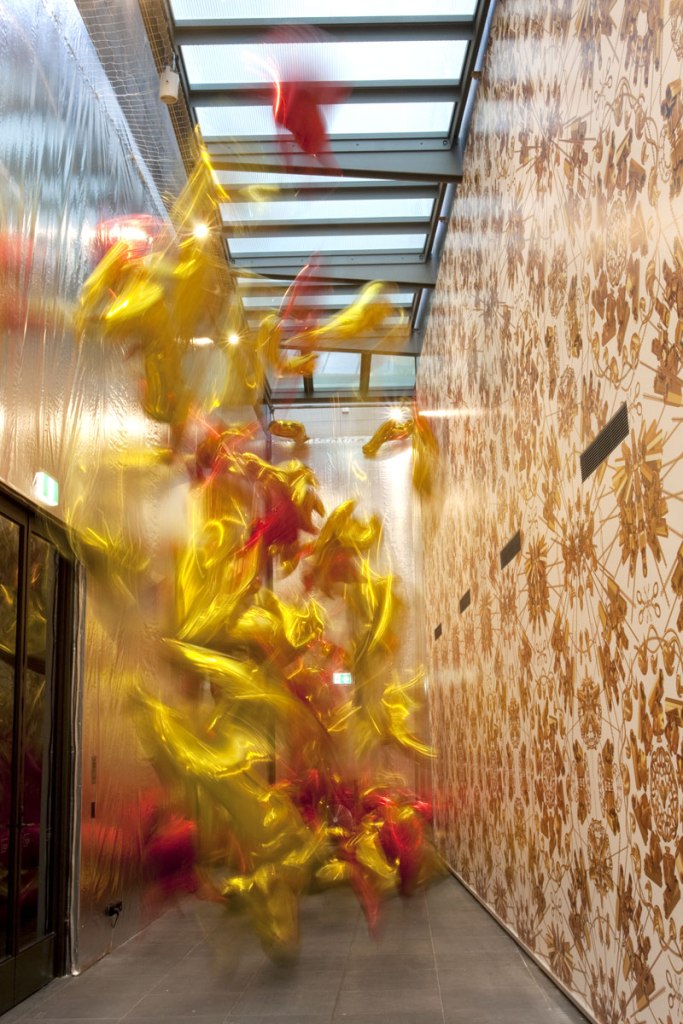



Passageway between second and third rooms at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
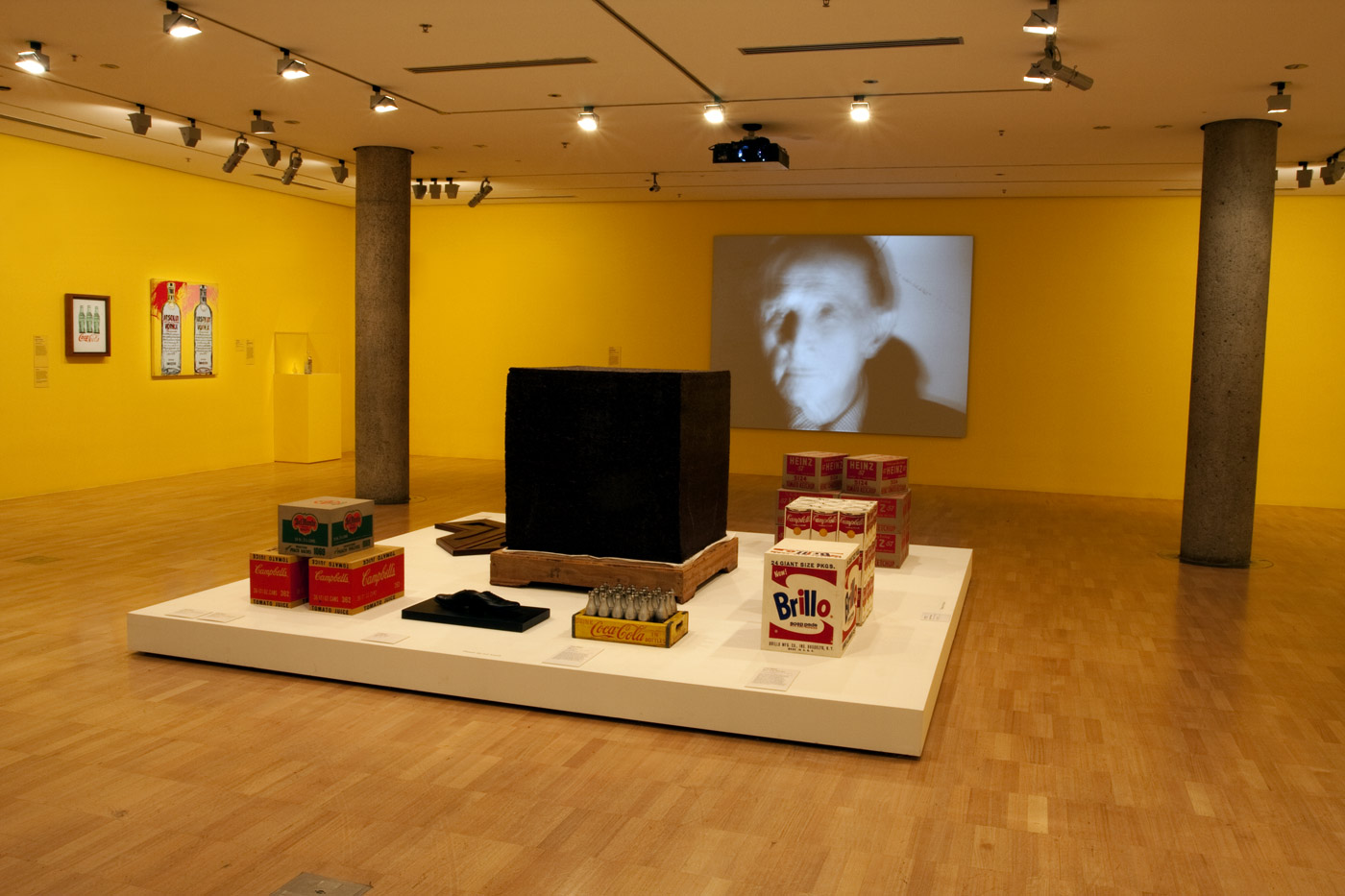
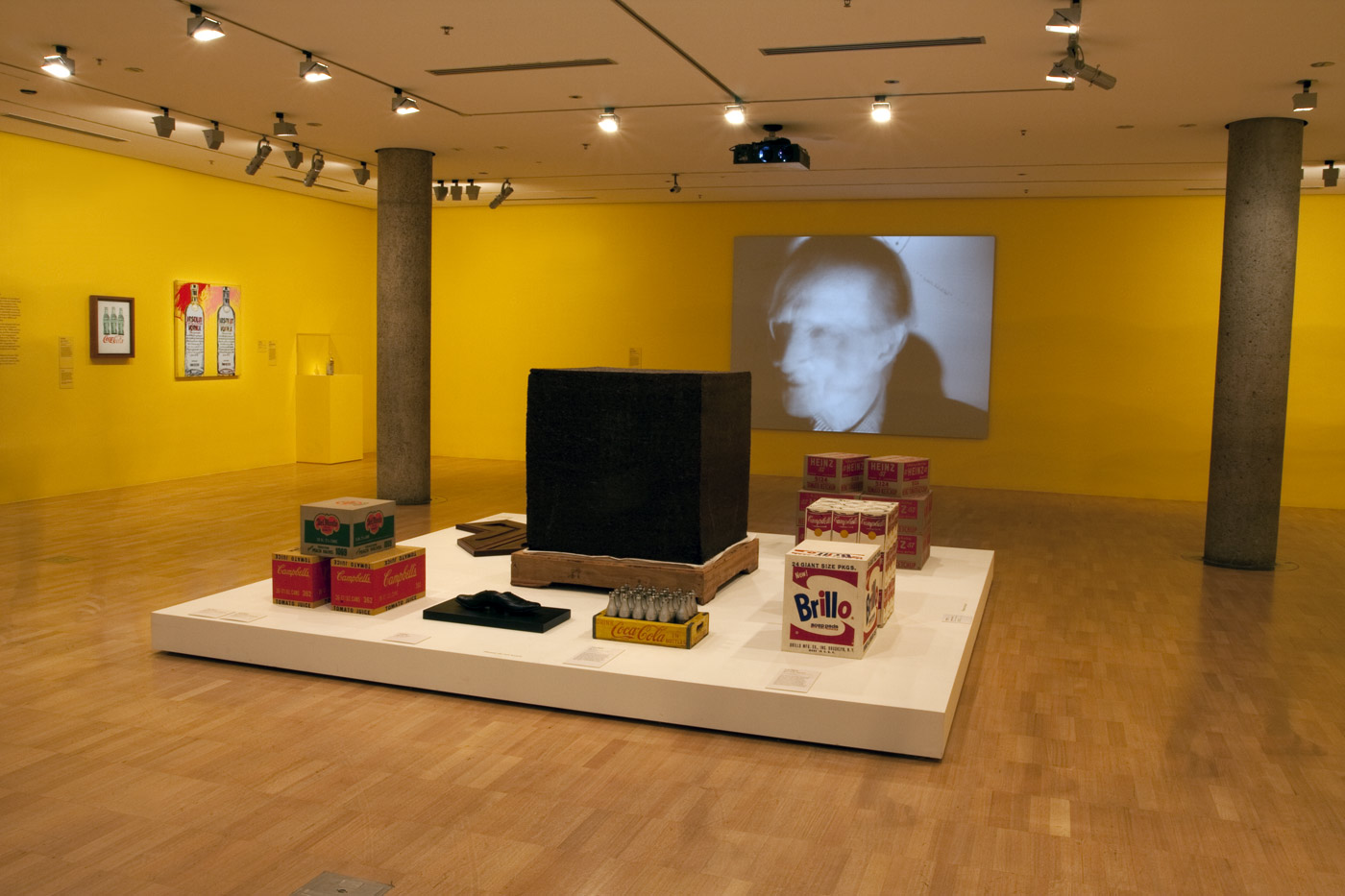
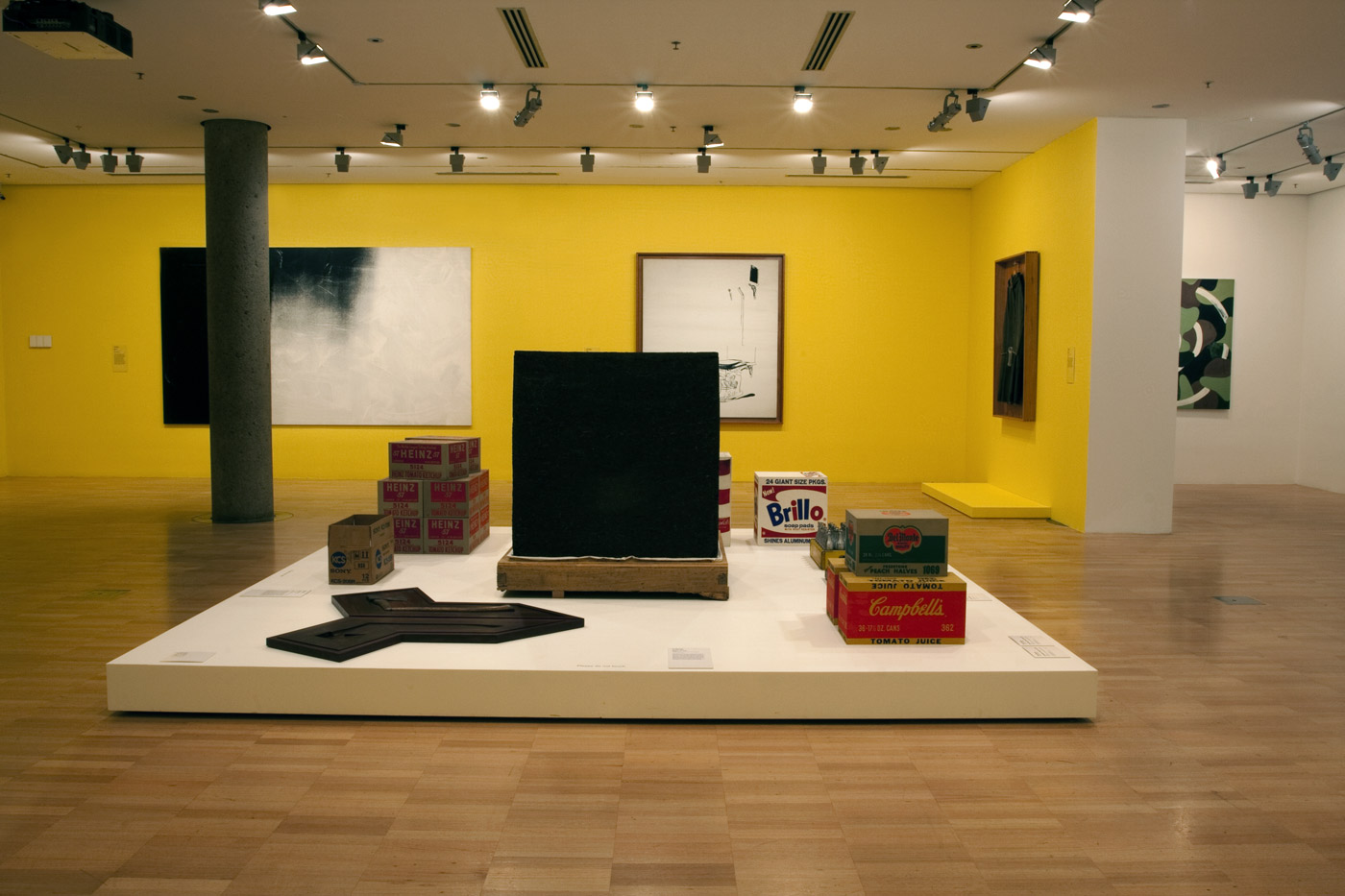
Installation views of the third room including at centre, Ai Weiwei’s Tonne of Tea (2006) and And Warhol’s Brillo Soap Pads Box (1964) at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Tonne of Tea
2006
Compressed pu’er tea, wood base
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
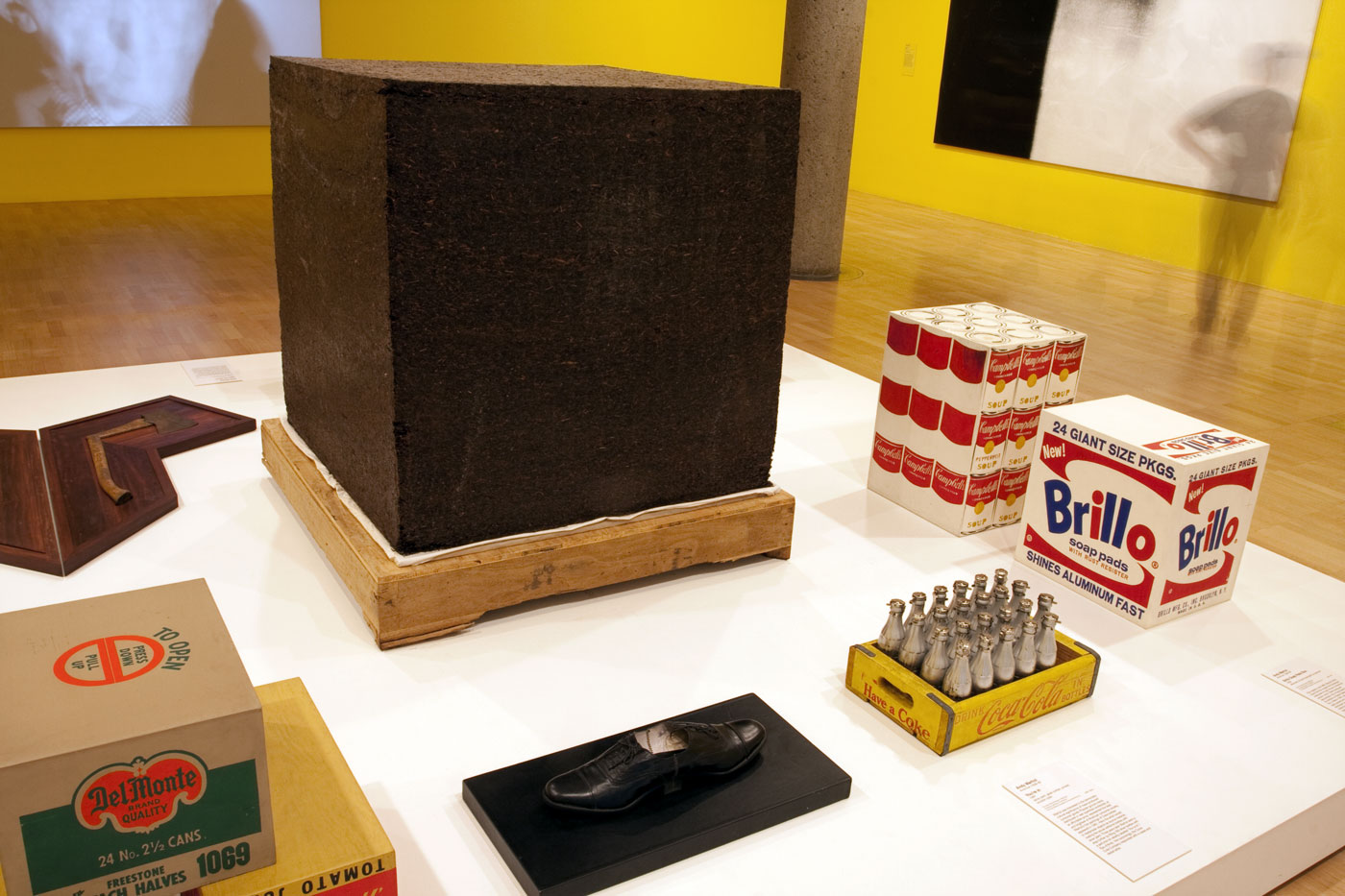
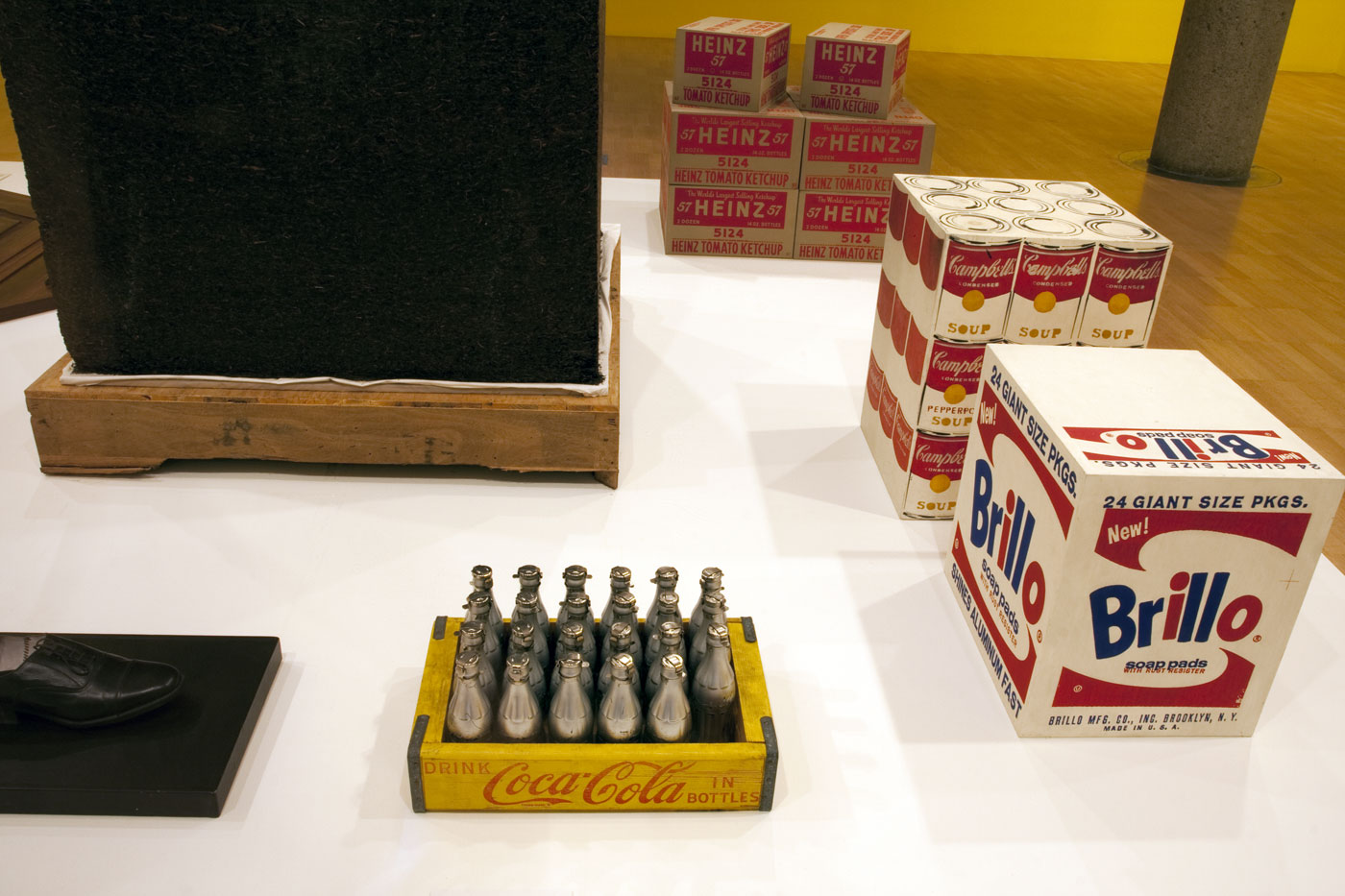
Ai’s Tonne of Tea is a readymade object redolent of the artist’s cultural context and heritage. Ai’s compressed cube of Pu’er tea – a staple of Chinese life, trade and custom – recalls not only the commercial aesthetics of Warhol’s Brillo Soap Pads Box but also the minimalist sculpture of postwar American artists such as Donald Judd, while introducing a specifically Chinese historical reference and cultural narrative into the readymade tradition.
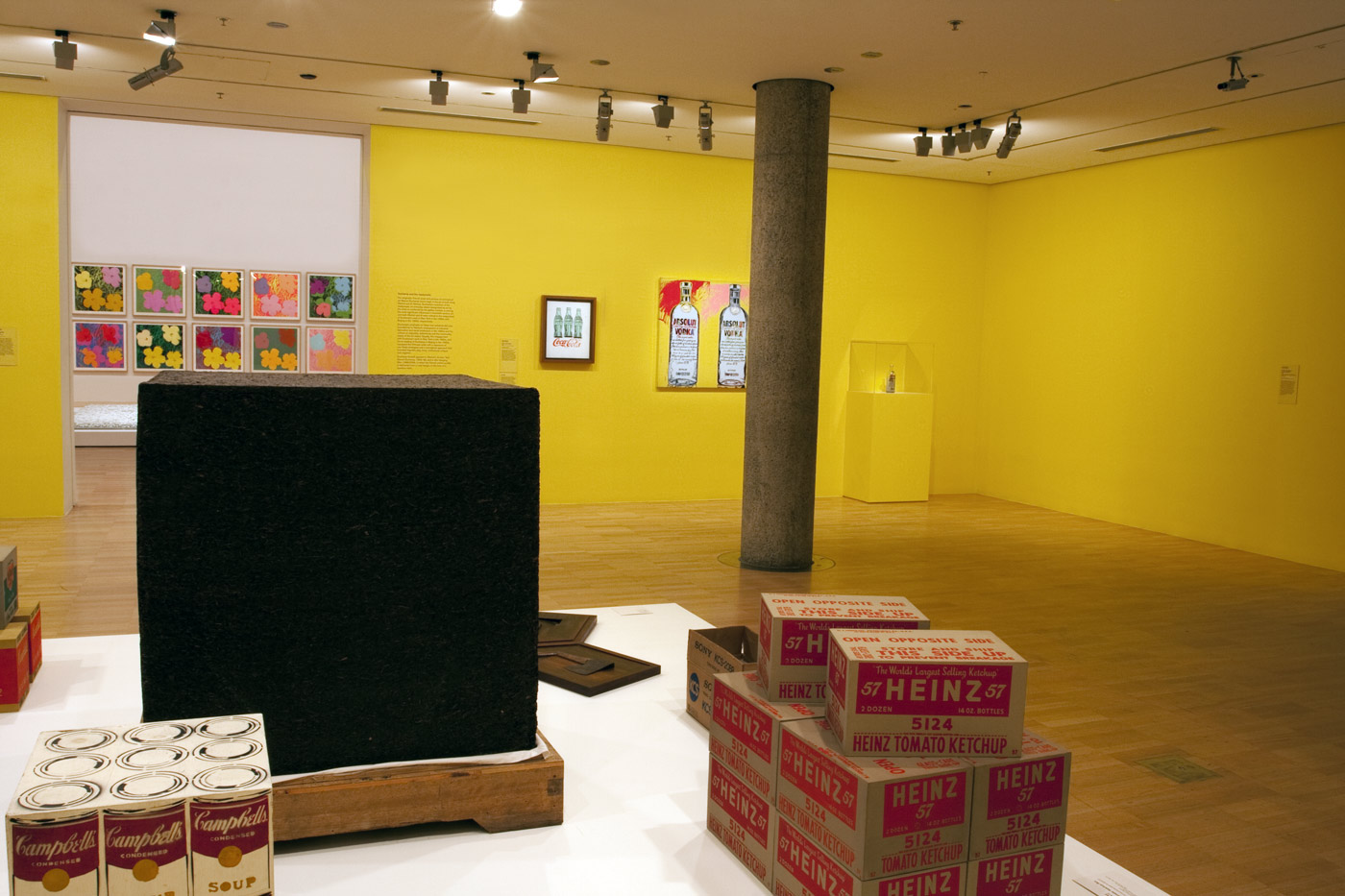

Installation views of the third room including Ai Weiwei’s Tonne of Tea (2006) and And Warhol’s Brillo Soap Pads Box (1964) and You’re in (1967) at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Brillo Soap Pads Box
1964
Silkscreen ink and house paint on plywood
The Andy Warhol Museum, Pittsburgh
Founding Collection, Contribution
The Andy Warhol Foundation for the Visual Arts, Inc.
First created in late 1963, Warhol’s Brillo Soap Pads Box recasts the Duchampian readymade through the lens of American popular culture. Warhol produced approximately 100 of these boxes for his exhibition at Stable Gallery, New York, in March 1964, where they were tightly packed and piled high in a display reminiscent of a grocery warehouse. Unlike Duchamp’s use of real objects as readymade works of art, Warhol’s Brillo Soap Pads Boxes are carefully painted and silkscreened to resemble everyday consumer items. For philosopher Arthur C. Danto, Warhol’s Brillo boxes marked the end of an art-historical epoch and represented a new model of how art could be produced, displayed and perceived.
Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
You’re in
1967
Spray paint, glass bottles, printed wooden crate
The Andy Warhol Museum, Pittsburgh
Founding Collection, Contribution
The Andy Warhol Foundation for the Visual Arts, Inc.
Warhol was interested in the democratic cultural significance of mass-produced consumer goods. Popular grocery items distributed in vast quantities worldwide, at an affordable price, represented the best and brightest of American consumer society. Warhol’s first paintings of Coke bottles appeared in 1961. Here the artist turned to readymade objects as source material, coating the actual softdrink bottles with silver paint. Three years later Warhol went a step further by filling 100 silver bottles with a perfume he rakishly labelled ‘You’re In’ / ‘Eau d’Andy’. Not surprisingly, the Coca-Cola Company responded with a cease and desist letter.
A major international exhibition featuring two of the most significant artists of the twentieth and twenty-first centuries – Andy Warhol and Ai Weiwei – opened at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne, on 11 December 2015.
Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei, developed by the NGV and The Warhol, with the participation of Ai Weiwei, explores the significant influence of these two exemplary artists on modern art and contemporary life, focussing on the parallels, intersections and points of difference between the two artists’ practices. Surveying the scope of both artists’ careers, the exhibition at the NGV presents over 300 works, including major new commissions, immersive installations and a wide representation of paintings, sculpture, film, photography, publishing and social media.
The exhibition explores modern and contemporary art, life and cultural politics through the activities of two exemplary figures – one of whom represents twentieth century modernity and the ‘American century’; and the other contemporary life in the twenty-first century and what has been heralded as the ‘Chinese century’ to come. Ai Weiwei commented, “I believe this is a very interesting and important exhibition and an honour for me to have the opportunity to be exhibited alongside Andy Warhol. This is a great privilege for me as an artist.”
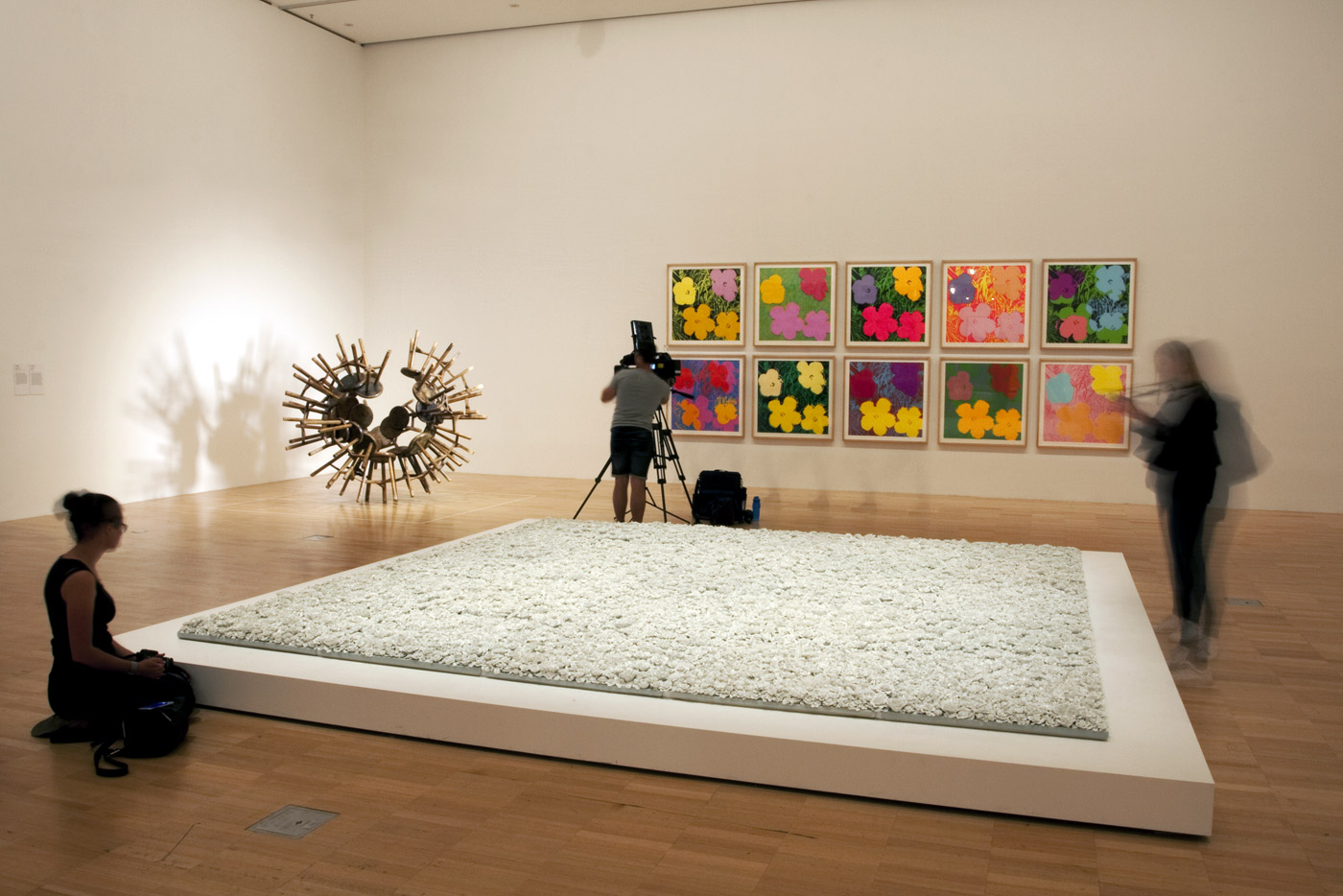
Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei premieres a suite of major new commissions from Ai Weiwei, including an installation from the Forever bicycles series, composed from nearly 1500 bicycles; a major five metre-tall work from Ai’s Chandelier series of crystal and light; Blossom 2015, a spectacular installation in the form of a large bed of thousands of delicate, intricately designed white porcelain flowers; and a room-scale installation featuring portraits of Australian advocates for human rights and freedom of speech and information.
Ai Weiwei lived in the United States from 1981 until 1993, where he experienced the works of Marcel Duchamp, Andy Warhol and Jasper Johns, among others. The Philosophy of Andy Warhol (From A to B & Back Again) was the first book that Ai Weiwei purchased in New York, and was a significant influence upon his conceptual approach. Ai Weiwei’s relationship to Warhol is explicitly apparent in a photographic self-portrait, taken in New York in 1987, in which Ai Weiwei poses in front of Warhol’s multiple self-portrait, adopting the same gesture.
Each artist is also recognised for his unique approach to notions of artistic value and studio production. Warhol’s Factory was legendary for its bringing together of artists and poets, film-makers and musicians, bohemians and intellectuals, ‘drag queens’, ‘superstars’ and socialites, and for the serial-production of silkscreen paintings, films, television, music and publishing.
The studio of Ai Weiwei is renowned for its interdisciplinary approach, post-industrial modes of production, engagement with teams of assistants and collaborators, and strategic use of communications technology and social media. Both artists have been equally critical in redefining the role of ‘the artist’ – as impresario, cultural producer, activist and brand – and both are known for their keen observation and documentation of contemporary society and everyday life.
Text from the National Gallery of Victoria
Installation view of the fourth room including, at centre, Ai Weiwei’s Blossom (2015) with his Grapes (2011) rear left, and Andy Warhol’s Flowers (Hand Coloured) (1974) on the wall behind at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
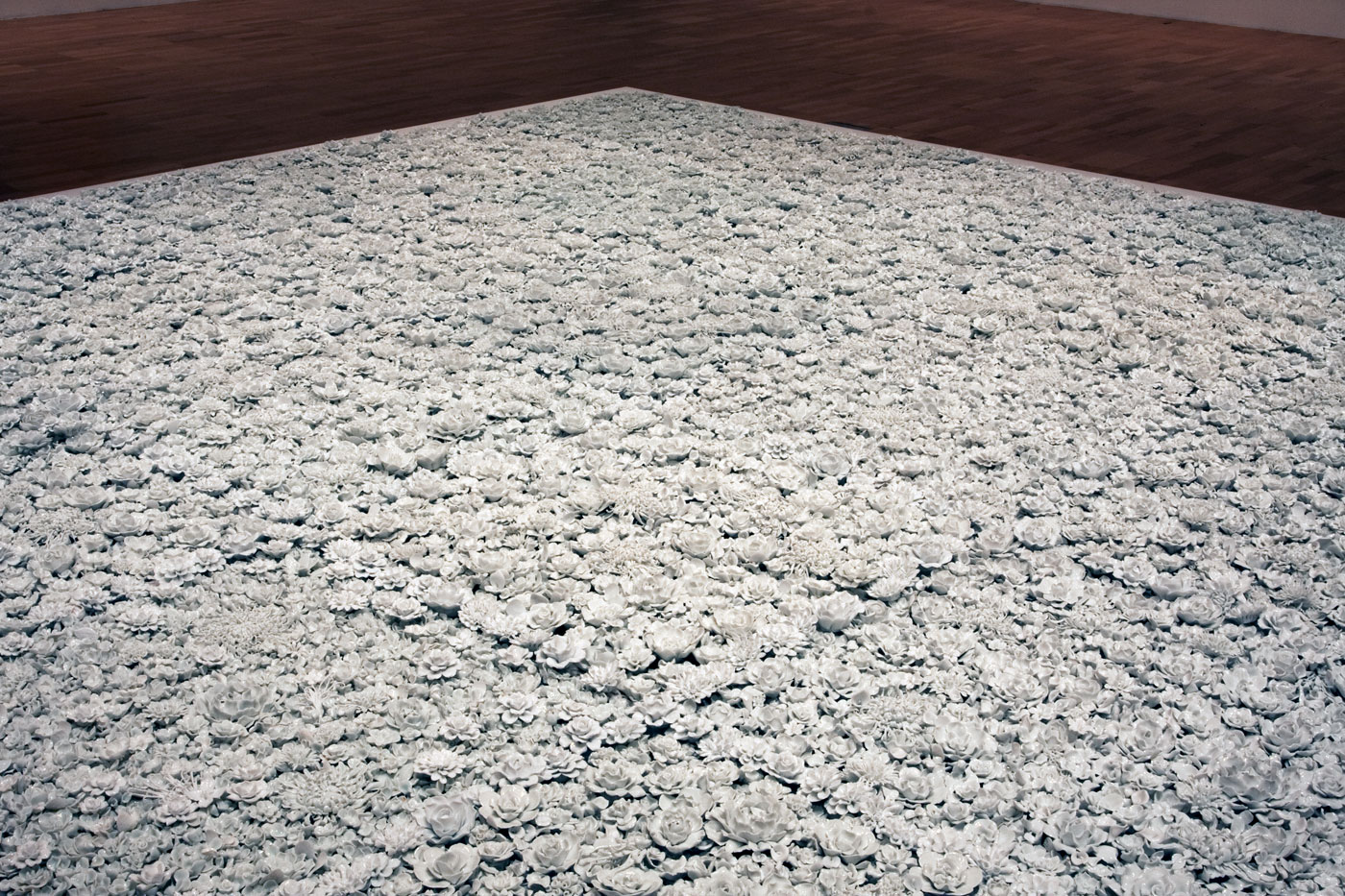
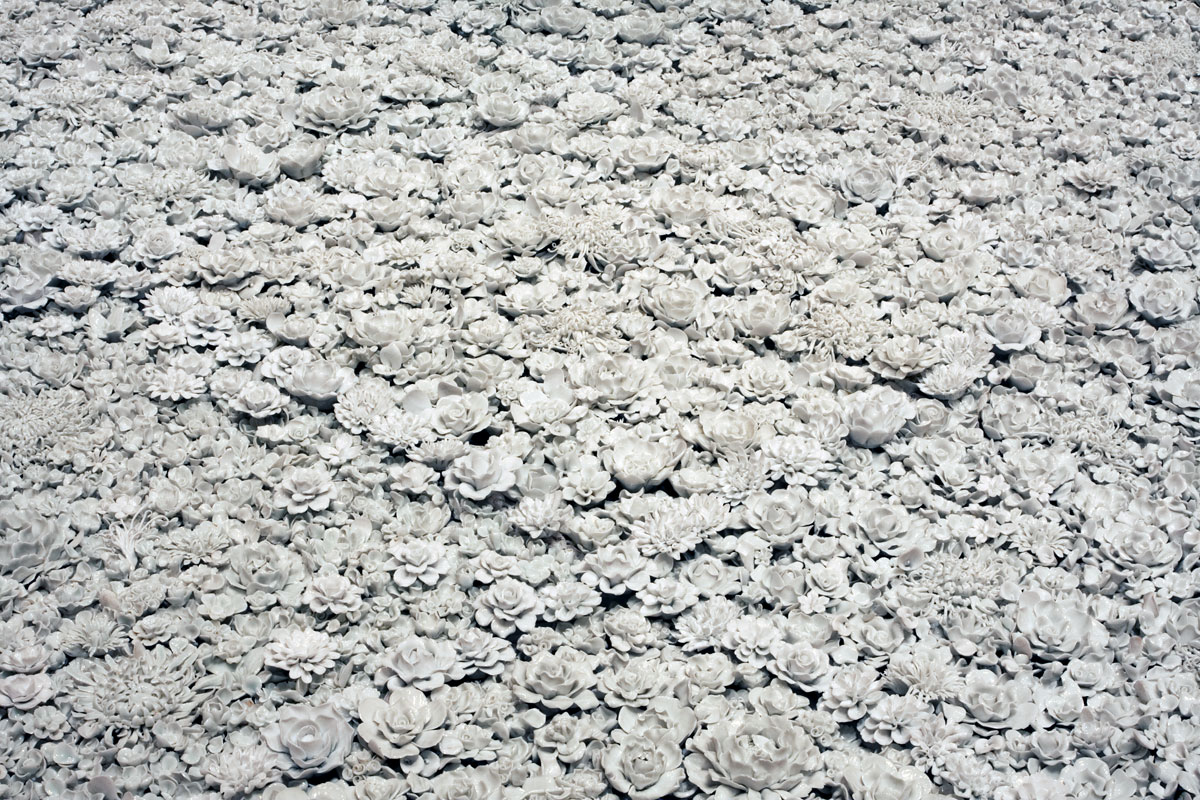
Blossom (installation view details)
2015
Porcelain
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Blossom is a new installation in the form of a garden bed, comprising thousands of flowers made from fine white porcelain. In response to the Flowers for Freedom movement which grew out of the artist’s With Flowers project, Blossom serves as a memorial to people who live in restricted conditions because of their fight for freedom of speech or human rights. The work was fabricated in collaboration with the finest craftspeople from Jingdezhen, whose predecessors once produced the highest quality porcelain for emperors of the past. Because of its size, the technical aspect of manufacturing this work was highly complex.
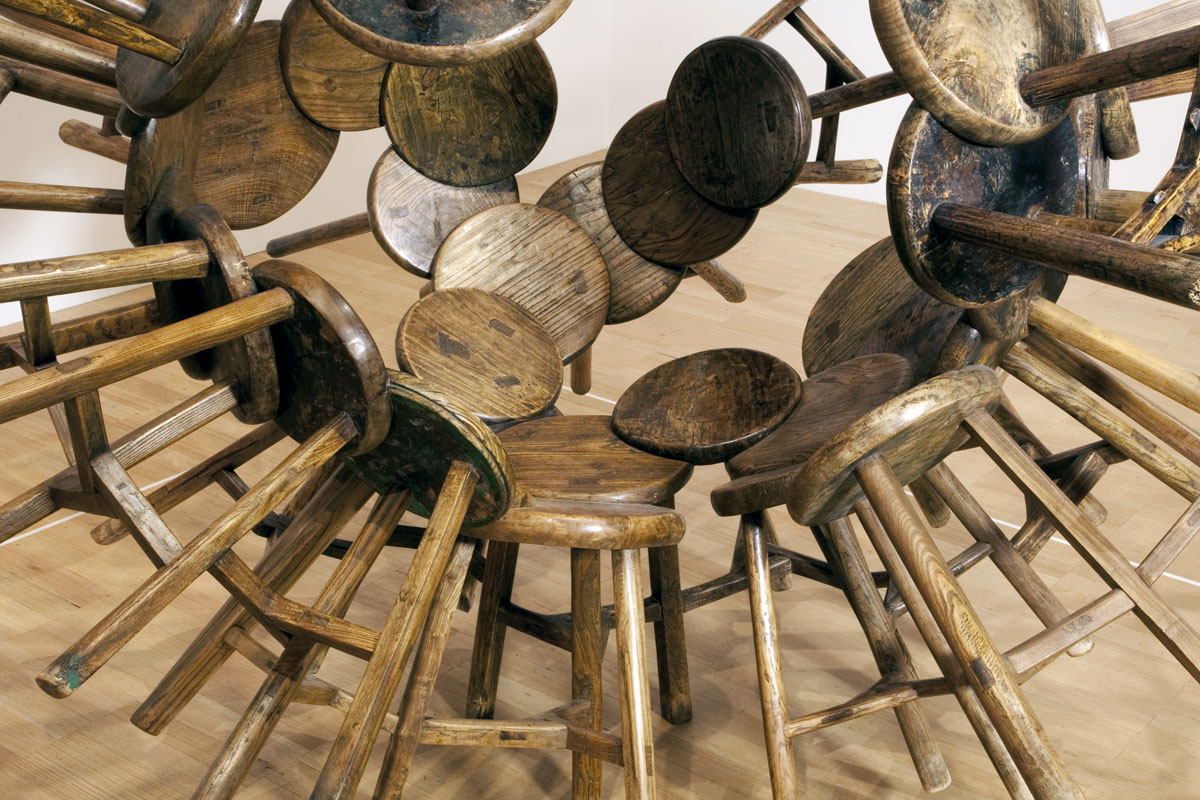
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
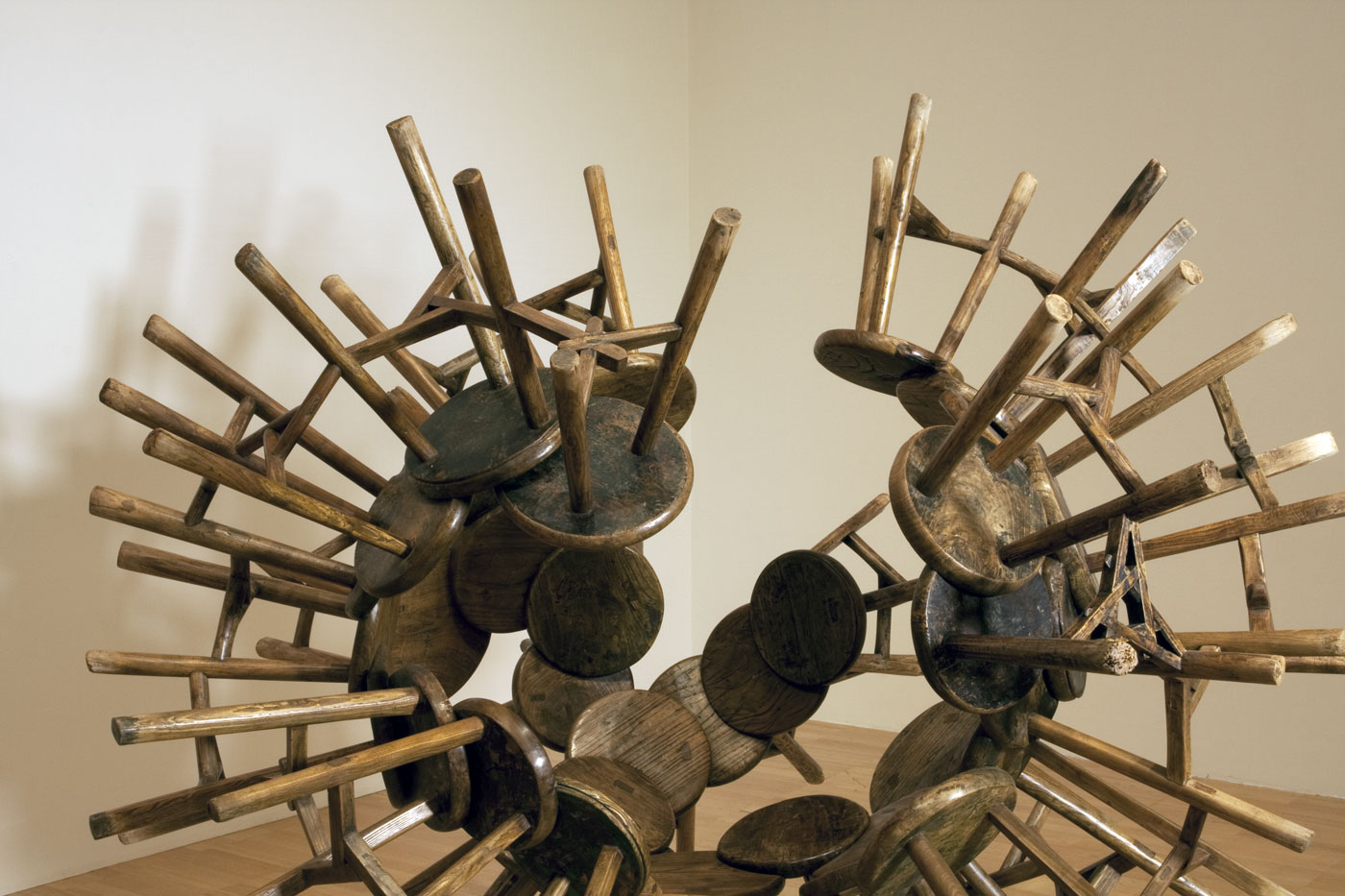
Grapes (installation view details)
2011
Qing Dynasty stools
Collection of Larry Warsh, New York
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
By reassembling Qing Dynasty furniture, which was constructed by traditional joinery techniques without glue or nails, Ai transforms the meaning and function of these cultural artefacts. Here he reconfigures a collection of wooden stools into a group resembling an organically formed cluster of grapes. The arrangement serves as a metaphor for the relationship between the individual and the collective, signifying the deferral of personal interests to those of the community and state characteristic of China’s socialist history. The linked structure of Grapes also recalls the idea of networks and communication, which are recurrent motifs in the Ai work. Manufactured by skilled craftsmen, this type of three-legged stool was used for centuries in China by all kinds of people – the rich and the poor, in towns and in the country. Every family had one, and they were passed on through many generations.
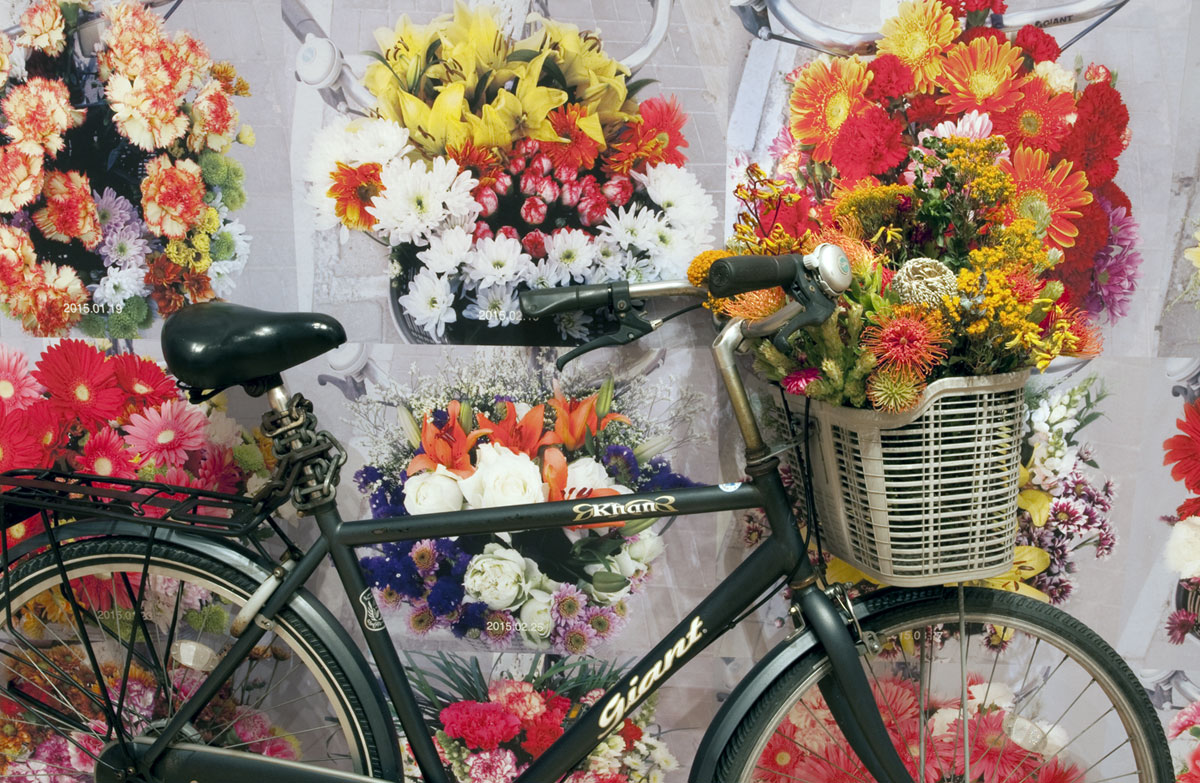

Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
With Flowers (installation view detail)
2013-2015
Bicycle, flowers, digital print on paper
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
In 2011 Ai was detained by Chinese authorities for eighty-one days without being charged. Upon his release, Ai’s passport was revoked and his studio placed under constant surveillance. With Flowers saw the artist place a fresh bunch of flowers in the basket of a bicycle outside his studio on a daily basis in a poetic protest against restriction on his right to travel. Images of the flowers were posted to Ai’s social media feeds, and an internet movement called Flowers for Freedom emerged. The project concluded upon the return of Ai’s passport in July 2015.
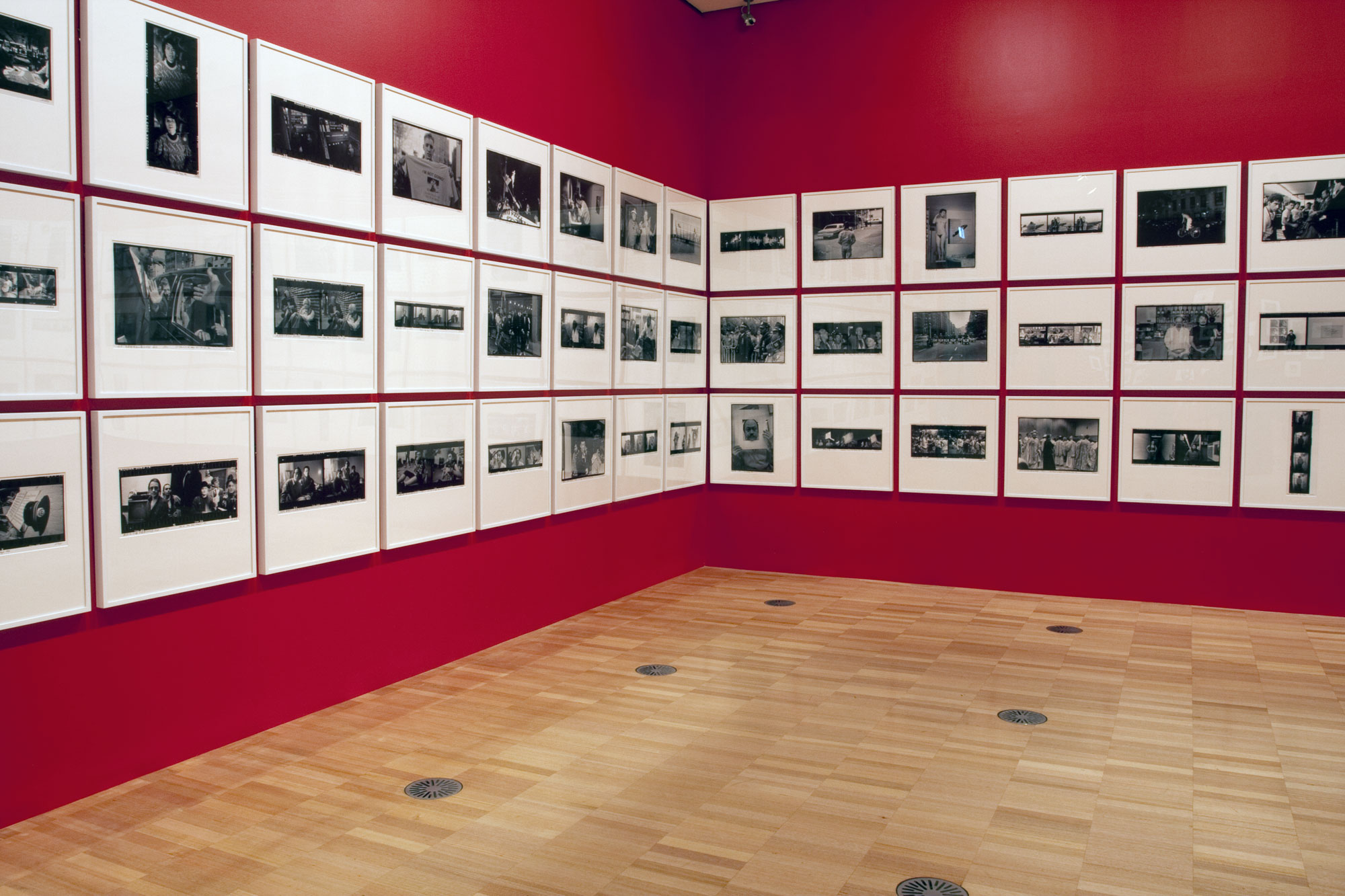
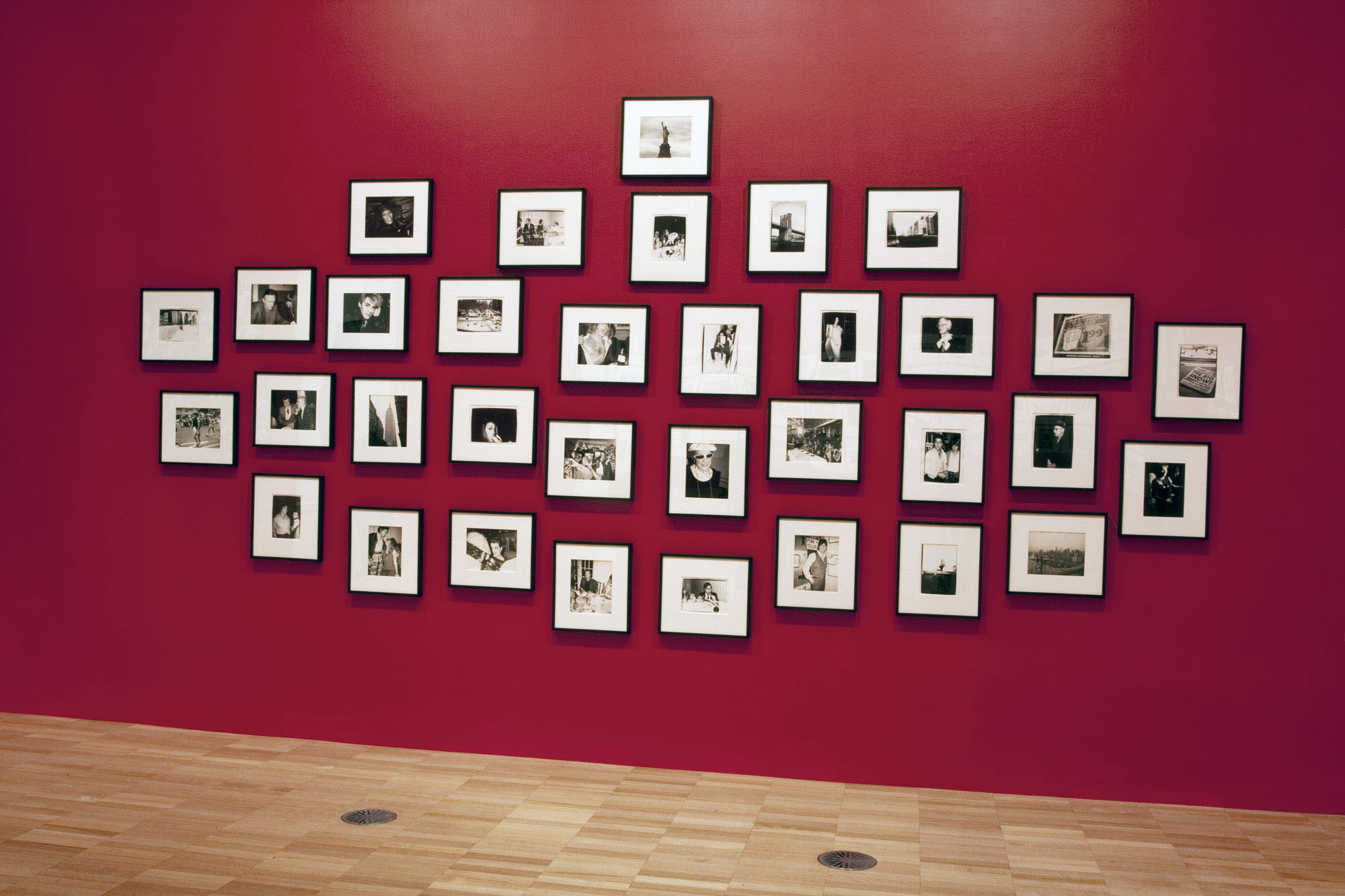
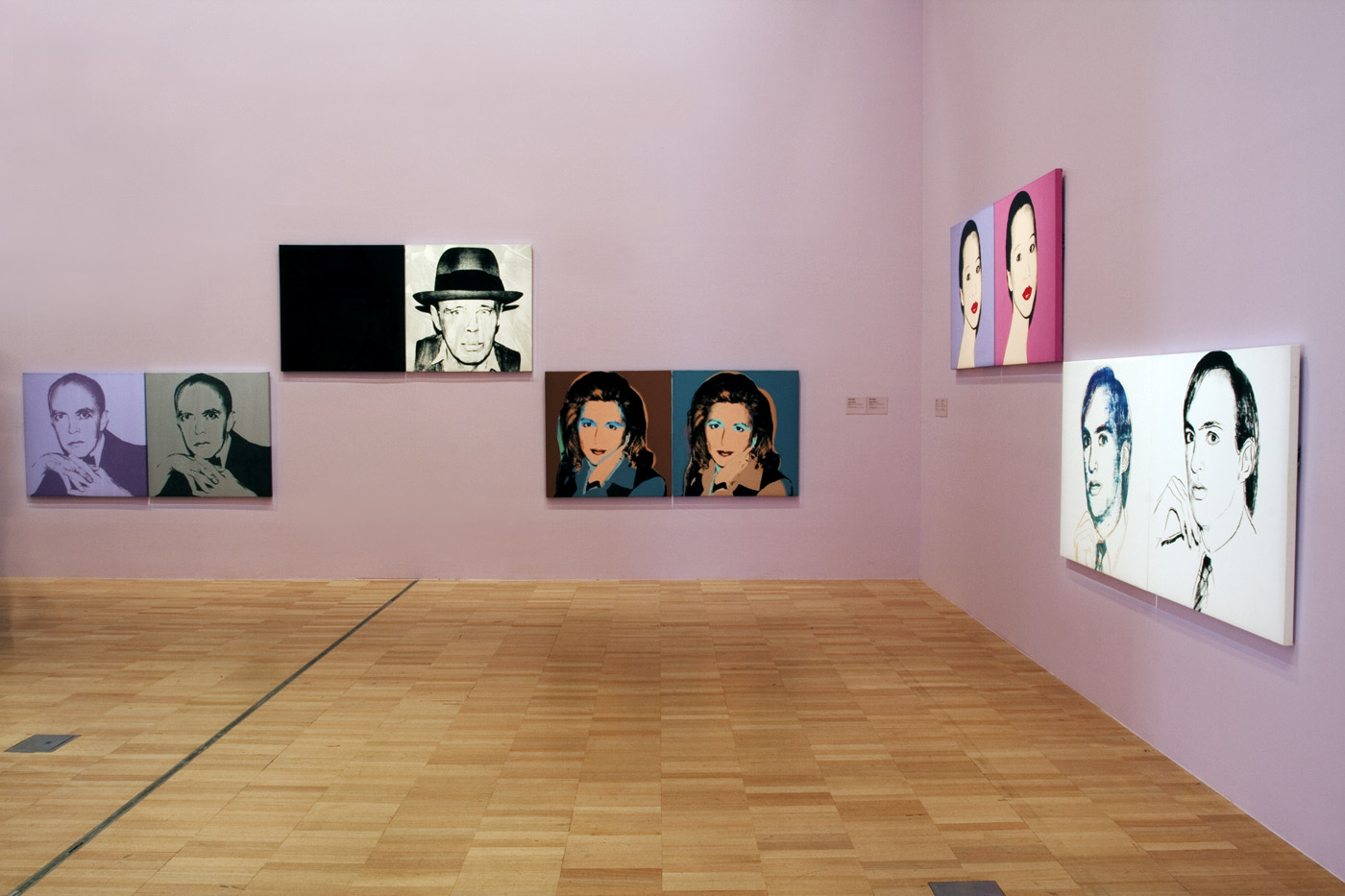
Installation view of part of the fifth room showing Andy Warhol’s portraits of friends and celebrities at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Letgo room (installation view details)
2015
Plastic
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Composed of more than three million plastic building blocks, Ai Weiwei’s Letgo room is a new installation featuring portraits of Australian activists and champions of human rights and freedom of speech. Ai has chosen people who represent grassroots community activism and advocacy within the fields of international law and academia, social welfare and the rights of Indigenous people, asylum seekers, sex workers and the gender nonspecific, among other cultural contexts. Each subject was asked to provide a one-line statement reflecting their philosophy and views to accompany his or her portrait.
The work attests to Ai’s longstanding commitment to liberty, manifested in his work as an artist, social commentator, activist and public intellectual. Letgo room was intended to be constructed from LEGO blocks; however, the LEGO company declined to provide a bulk order of their product due to the purported ‘political’ nature of the proposed work. Instead, the installation is composed of building blocks manufactured in China, continuing the artist’s exploration of the copy and fake.
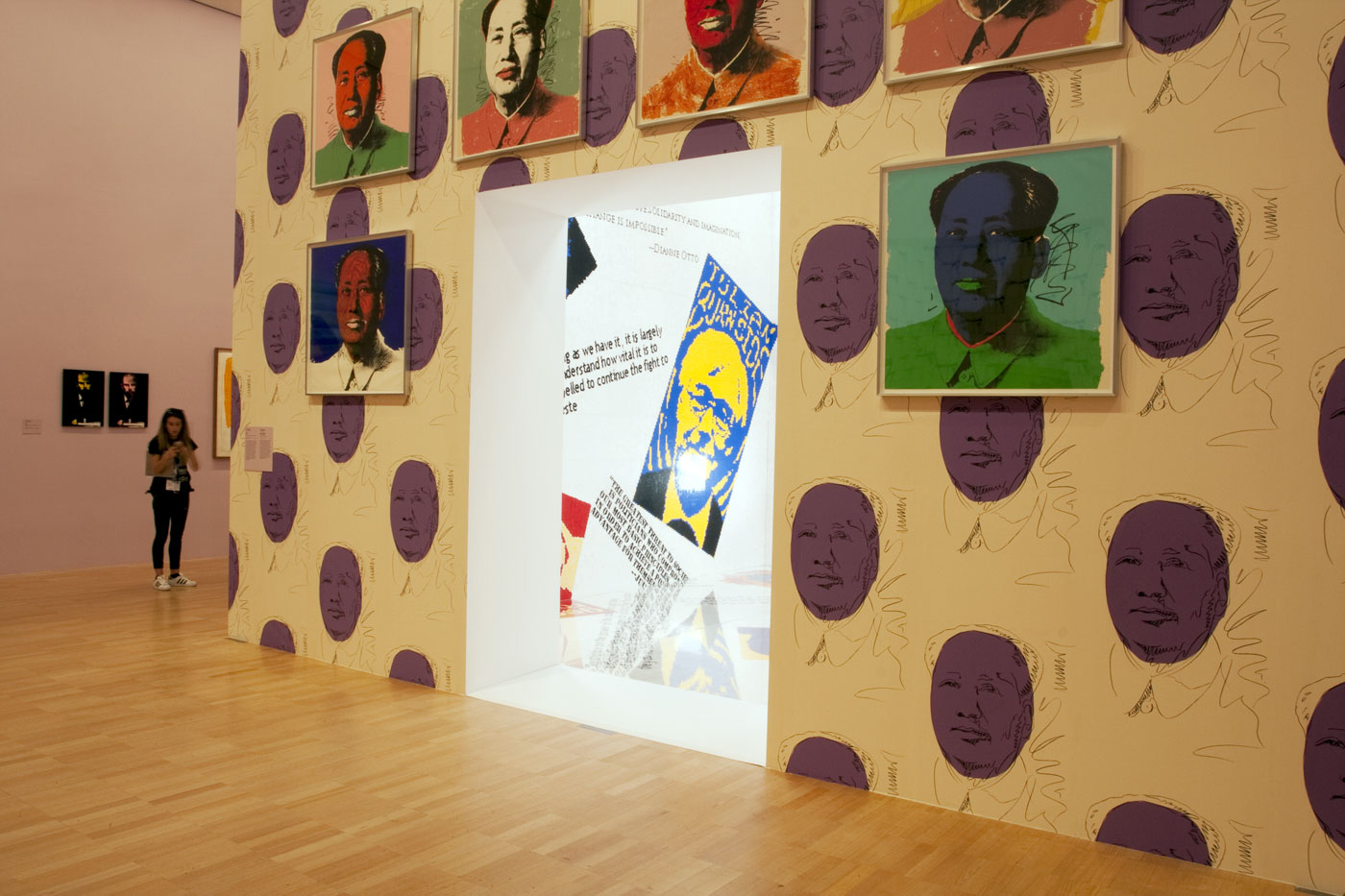

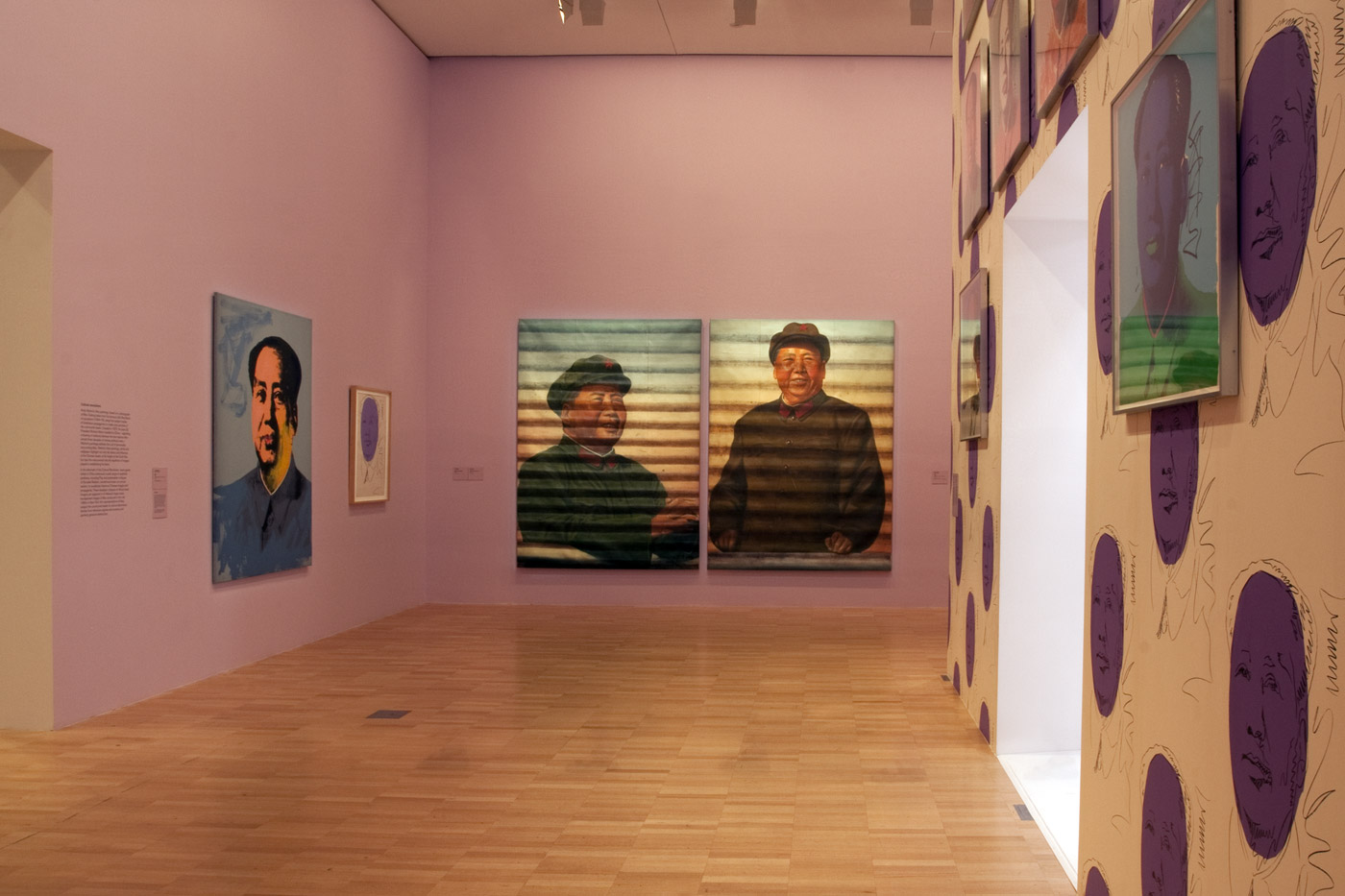
Installation view of part of the fifth room showing Andy Warhol’s silkscreen portraits of Mao (1972) hung on his Mao Wallpaper (1974, reprint 2015), on the exterior of Ai Weiwei’s Letgo room (2015) at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Andy Warhol (American, 1928-1987)
Mao
1972
Colour silkscreens on paper, ed. 162/250
National Gallery of Australia, Canberra
Purchased, 1973
The source image for Warhol’s numerous portraits of Mao Zedong is the frontispiece to the Chairman’s famous Little Red Book of quotations. Mao’s image was in the media spotlight in 1972, the year US President Richard Nixon travelled to China, and his official portrait could be seen on the walls of homes, businesses and government buildings throughout the country. It was also extremely popular among literary and intellectual circles in the West. Warhol’s repetition of the image as pop-cultural icon underlines the cult of celebrity surrounding Mao, and the ways in which the proliferation of images in media and advertising promotes consumer desire and identification.
Installation view of part of the fifth room showing, on the far wall, Ai Weiwei’s portraits of Mao: Mao (Facing Right) (1986) and Mao (Facing Forward) (1986) at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
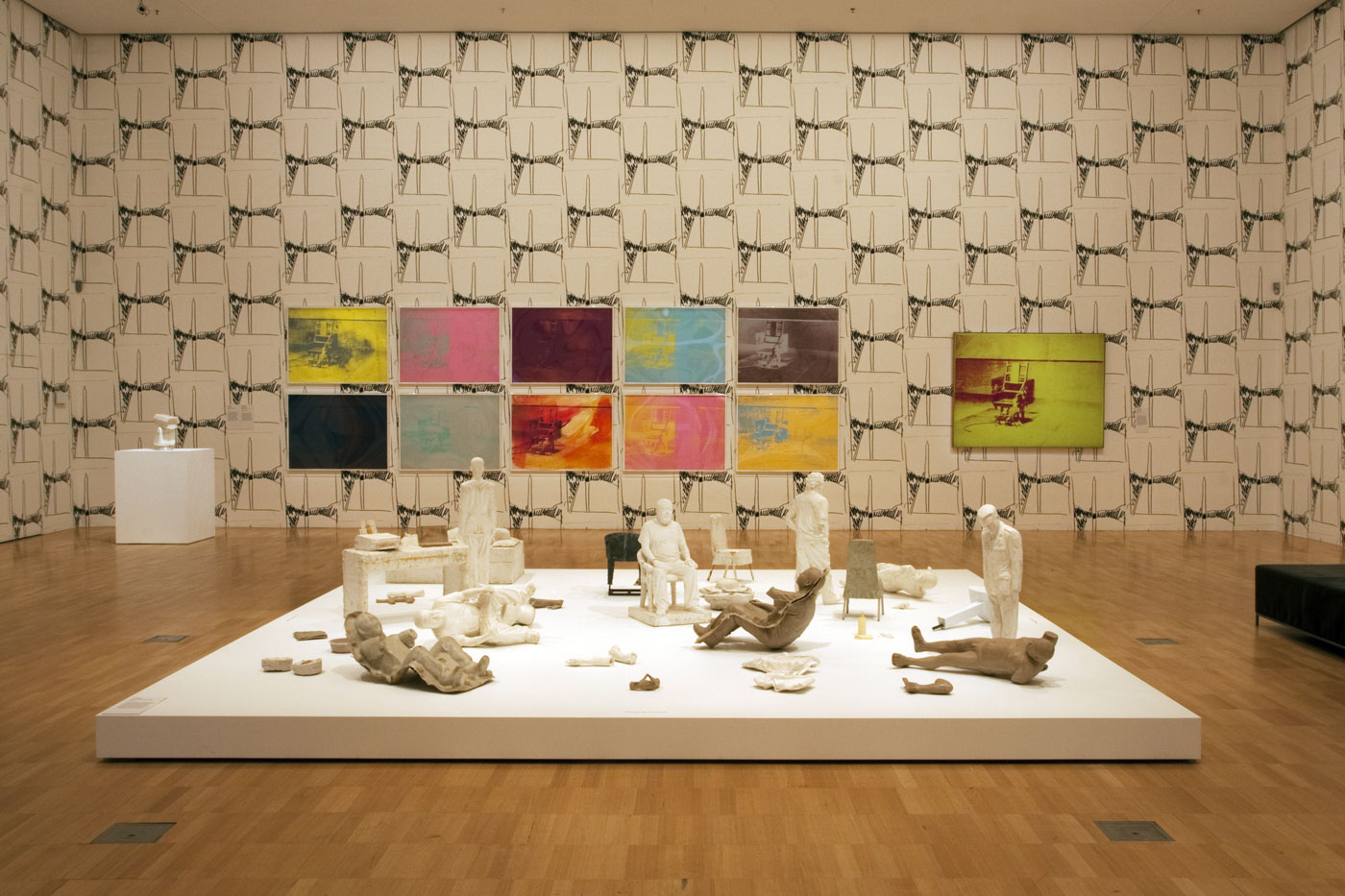
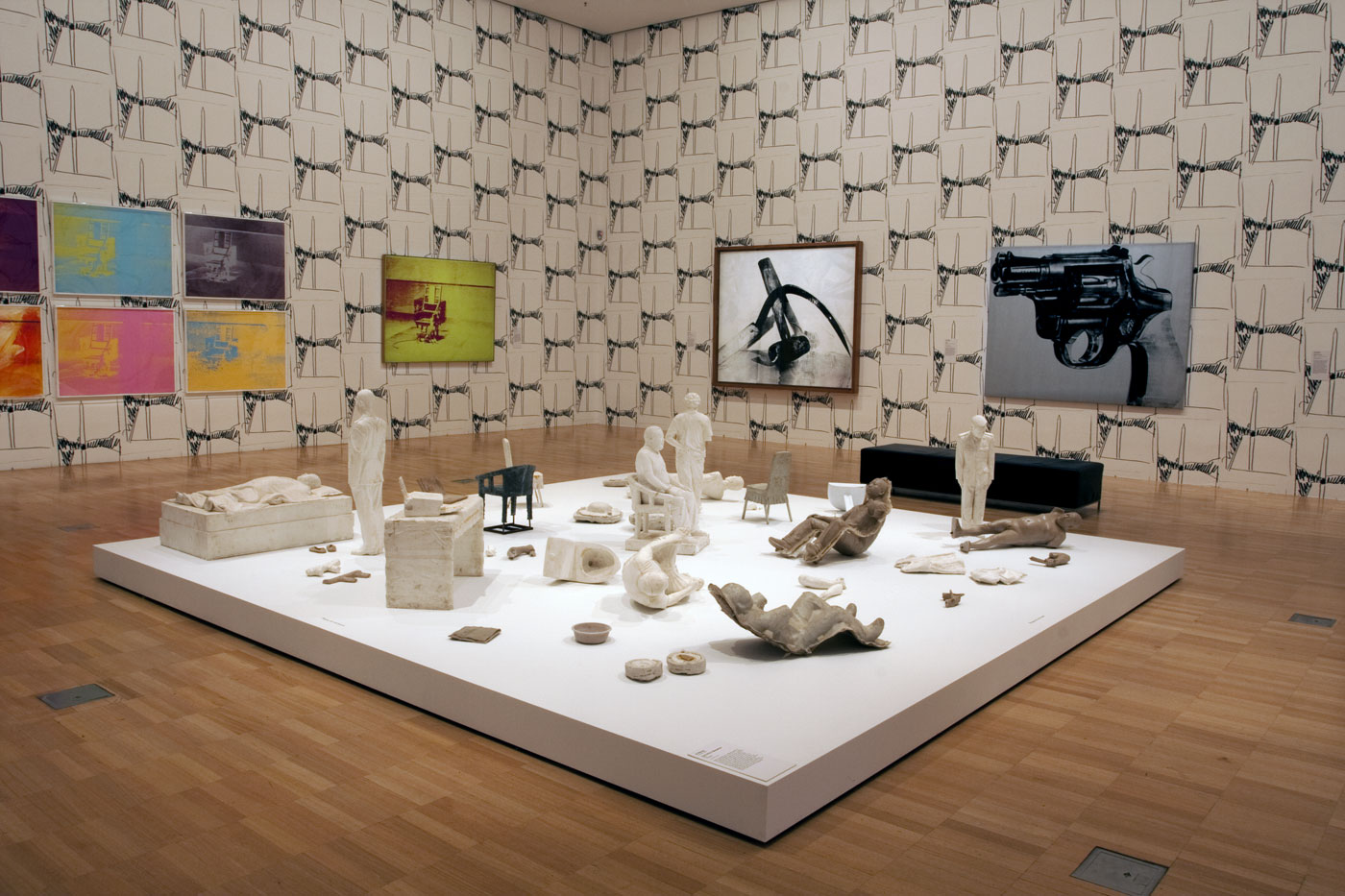
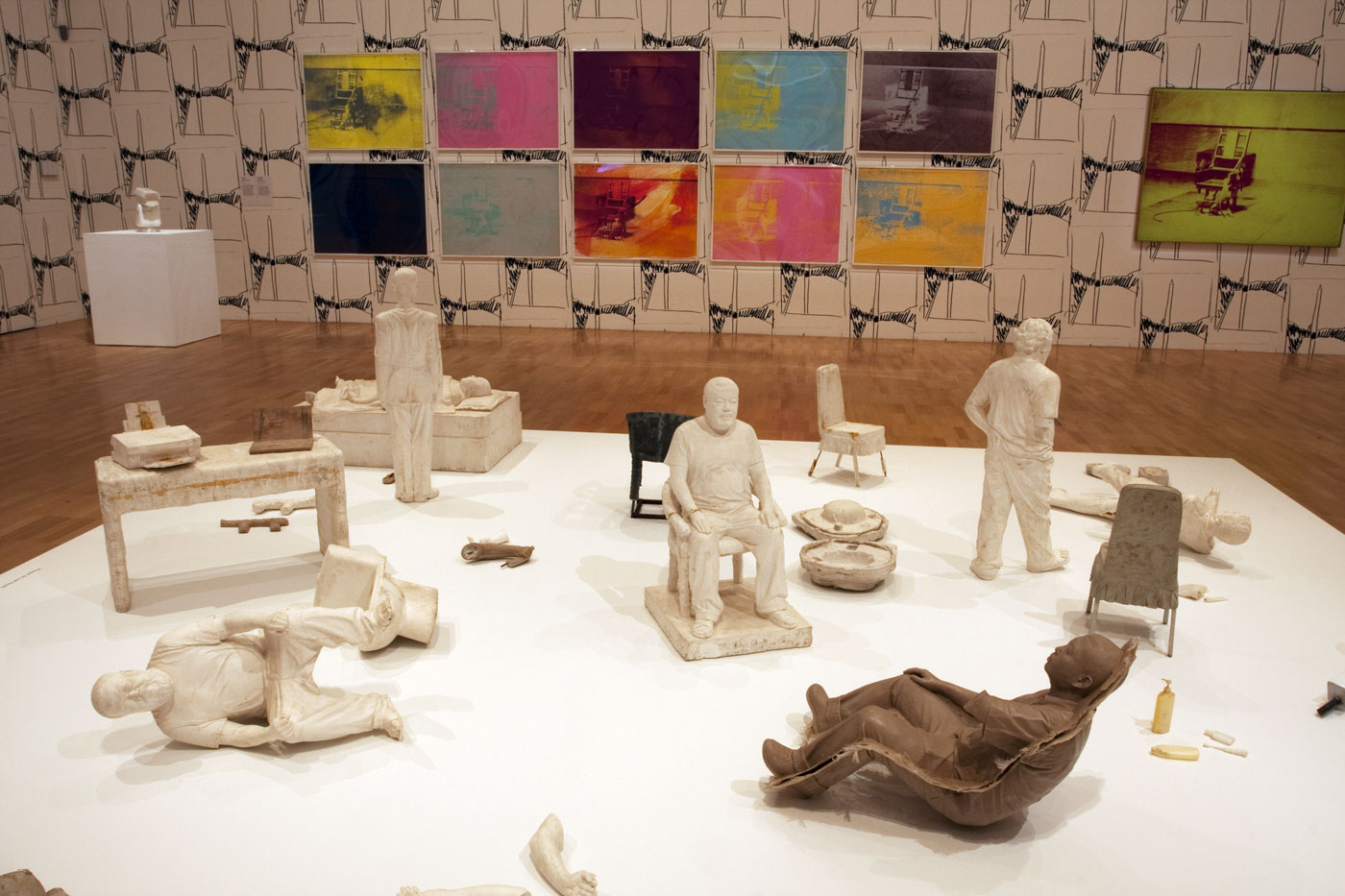
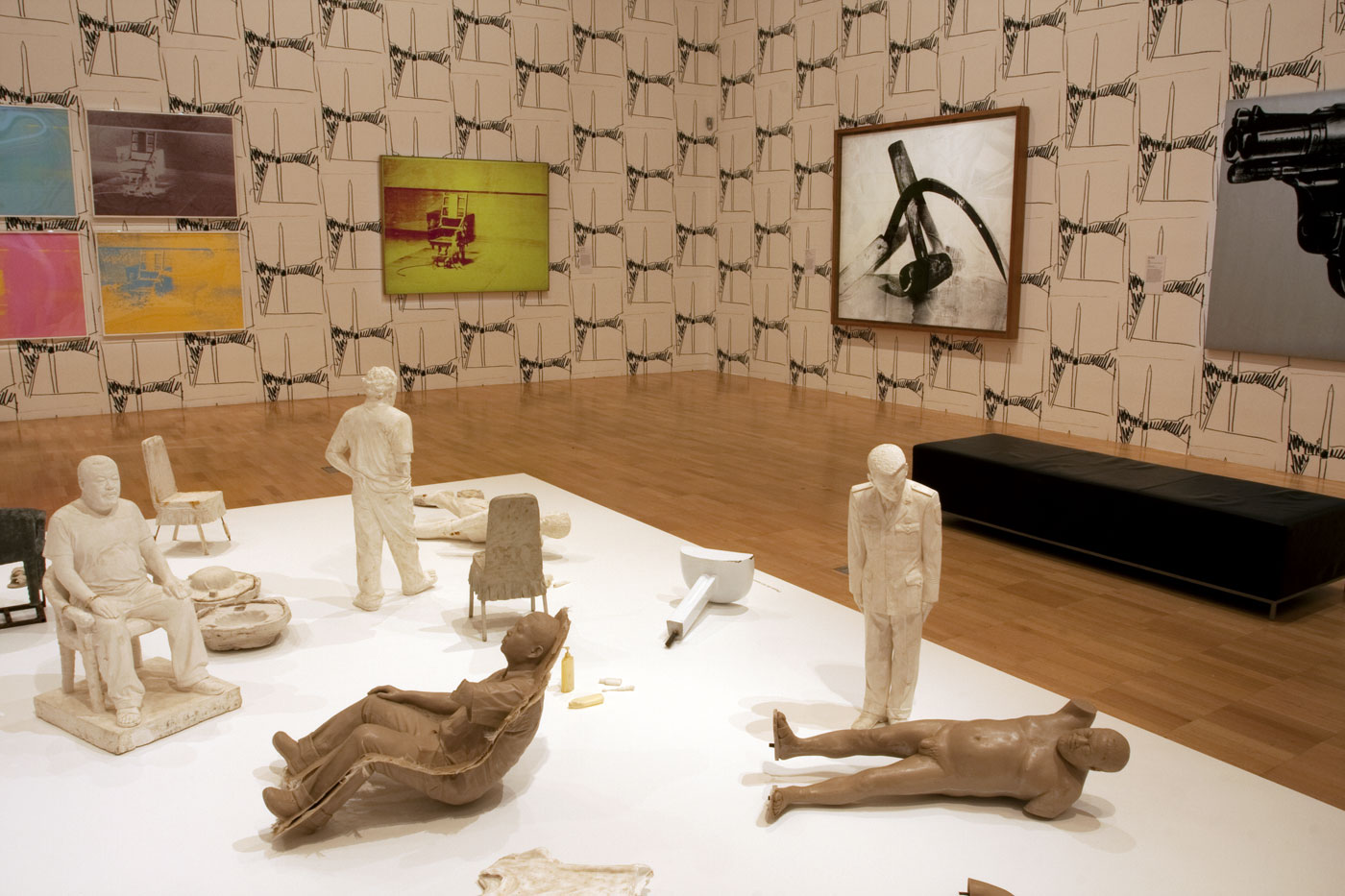
Installation view of the sixth room with, on the floor, Ai Weiwei’s S.A.C.R.E.D. Maquettes (2011) with Andy Warhol’s Electric Chairs (1971) silkscreens at left, and his Electric Chair (1967) painting at right, hung on Warhol’s Washington Monument Wallpaper (1974, reprint 2015) at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Installation view of the sixth room with, on the floor, Ai Weiwei’s S.A.C.R.E.D. Maquettes (2011) and Andy Warhol’s Gun (1981-82) paint and silkscreen ink on linen work on the wall behind at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
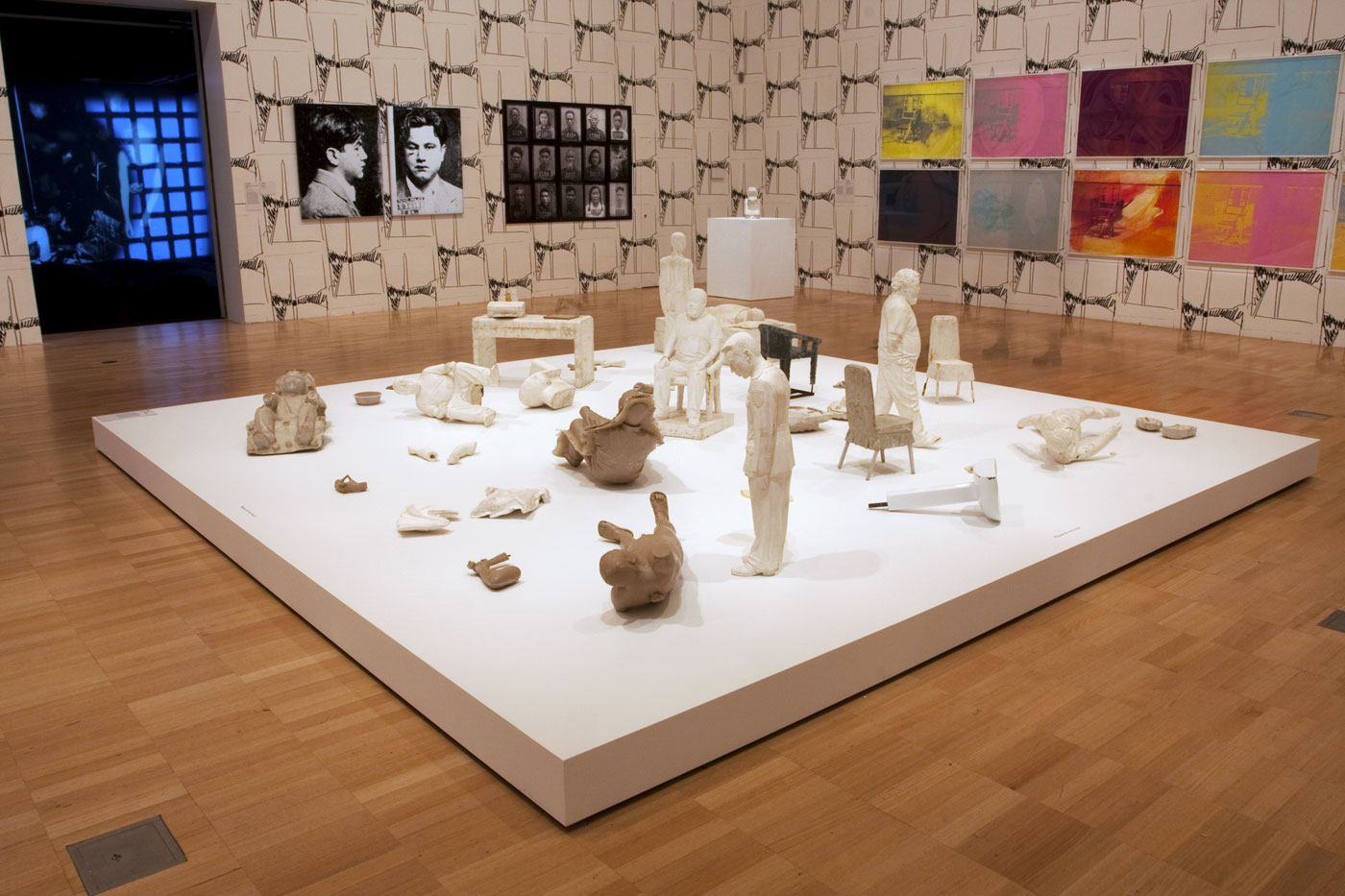

Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
S.A.C.R.E.D. Maquettes (installation view details)
2011
Fibreglass
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
These maquettes are sculptural models for Ai’s major installation S.A.C.R.E.D., a series of architecturally scaled dioramas depicting scenes from the detention cell where he was held without charge by the Chinese government for eighty-one days in 2011. The work consists of six parts to which its acronymic title refers: Supper, Accusers, Cleansing, Ritual, Entropy and Doubt. The maquettes serve as archaeological evidence of the denial of personal freedom and dignity that Ai and many other dissidents have experienced, and cast him in the dual roles of rebel and victim of oppression.
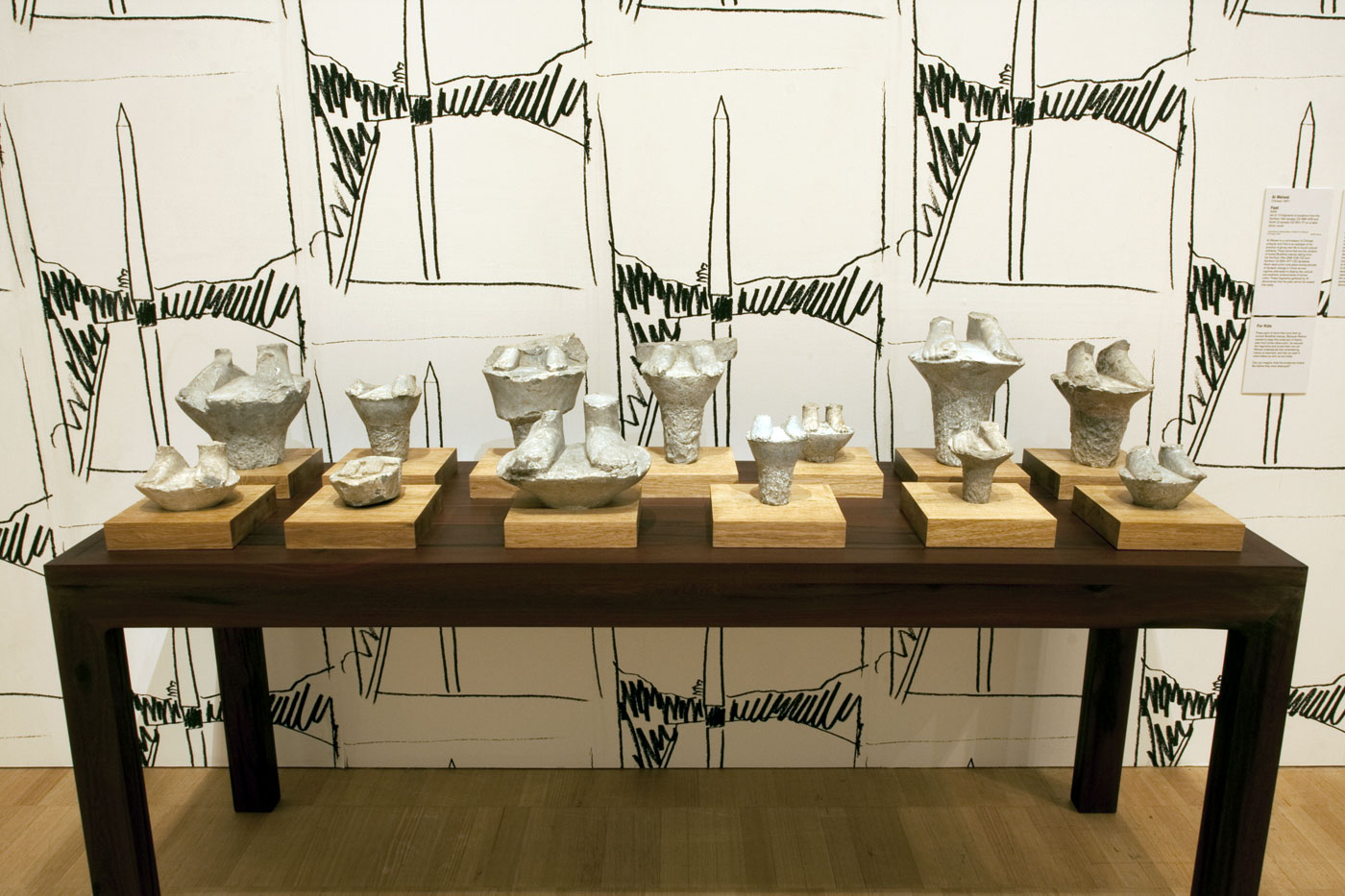
Installation view of Ai Weiwei’s Feet (2005) in the sixth room of the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Feet
2005
Set of 13 fragments of sculpture from the Northern Wei dynasty CE 386-535 and North Qi dynasty CE 550-77 on a table stone, wood
Queensland Art Gallery/Gallery of Modern Art, Brisbane
Purchased, 2006
Ai Weiwei is a connoisseur of Chinese antiquity and Feet is an example of his practice of giving new life to found cultural artefacts. These stone feet are the remains of looted Buddhist statues dating from the Northern Wei (386-535 CE) and Northern Qi (550-577 CE) dynasties. Much destruction took place during periods of dynastic change in China as new regimes attempted to destroy the cultural and aesthetic achievements of former rulers. These fragments gathered by Ai demonstrate that the past cannot be erased that easily.
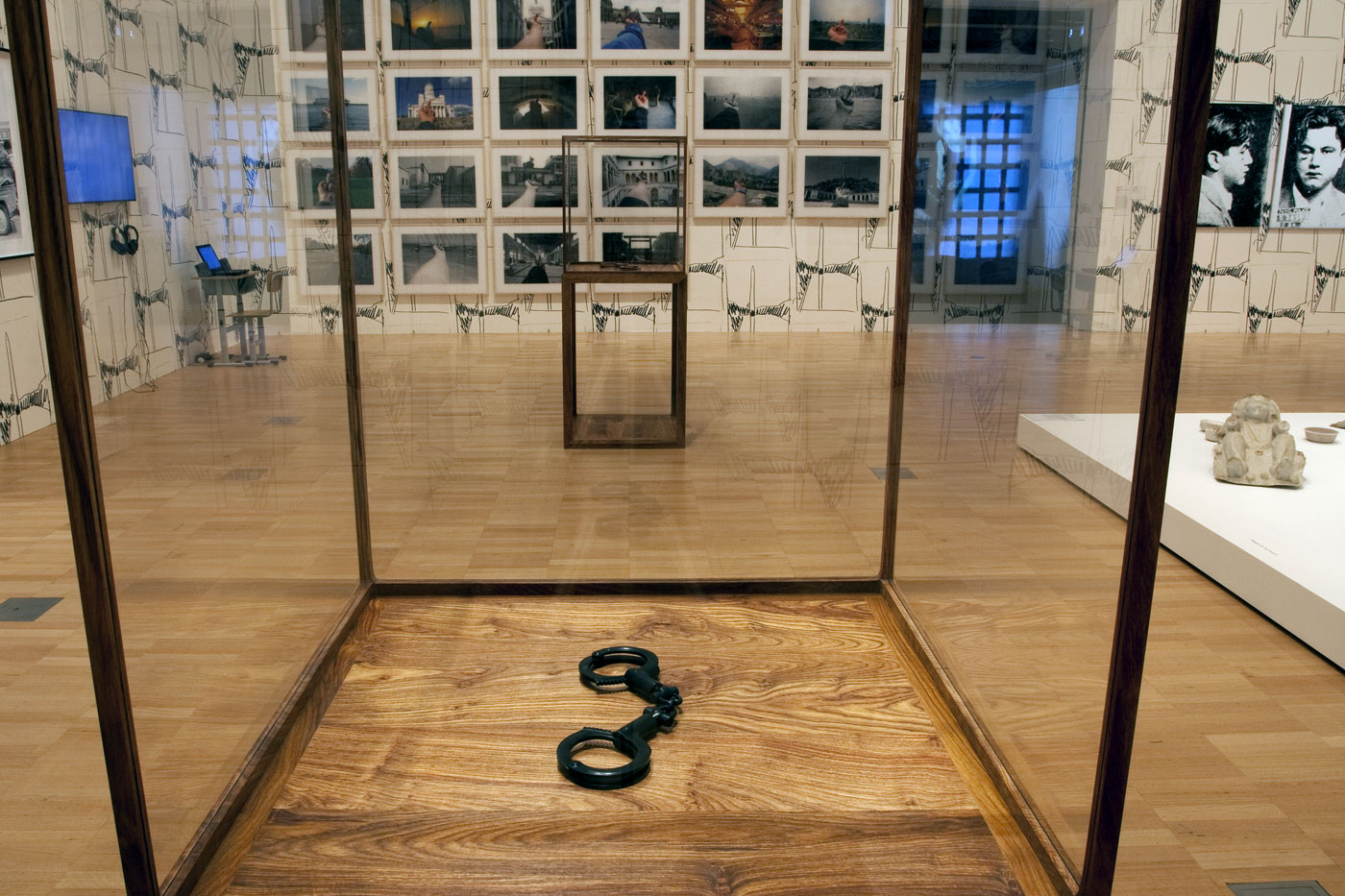
Installation view of Ai Weiwei’s Handcuffs (2015) in the sixth room of the exhibition with his Study of Perspective (1995-2011) series of photographs on the wall behind at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Handcuffs
2015
Jade
Ai Weiwei Studio, Beijing
This pair of handcuffs sculpted in jade – the most precious stones in Chinese culture – replicate those worn by Ai during his imprisonment in 2011. Historically, the wearing of jade was reserved for high-ranking members of the imperial family, and today wearing jade jewellery is still believed to bestow good health and protection upon the wearer. Here Ai recasts this material and its historical cultural connotations in relation to the containment of dissident political expression in contemporary China.
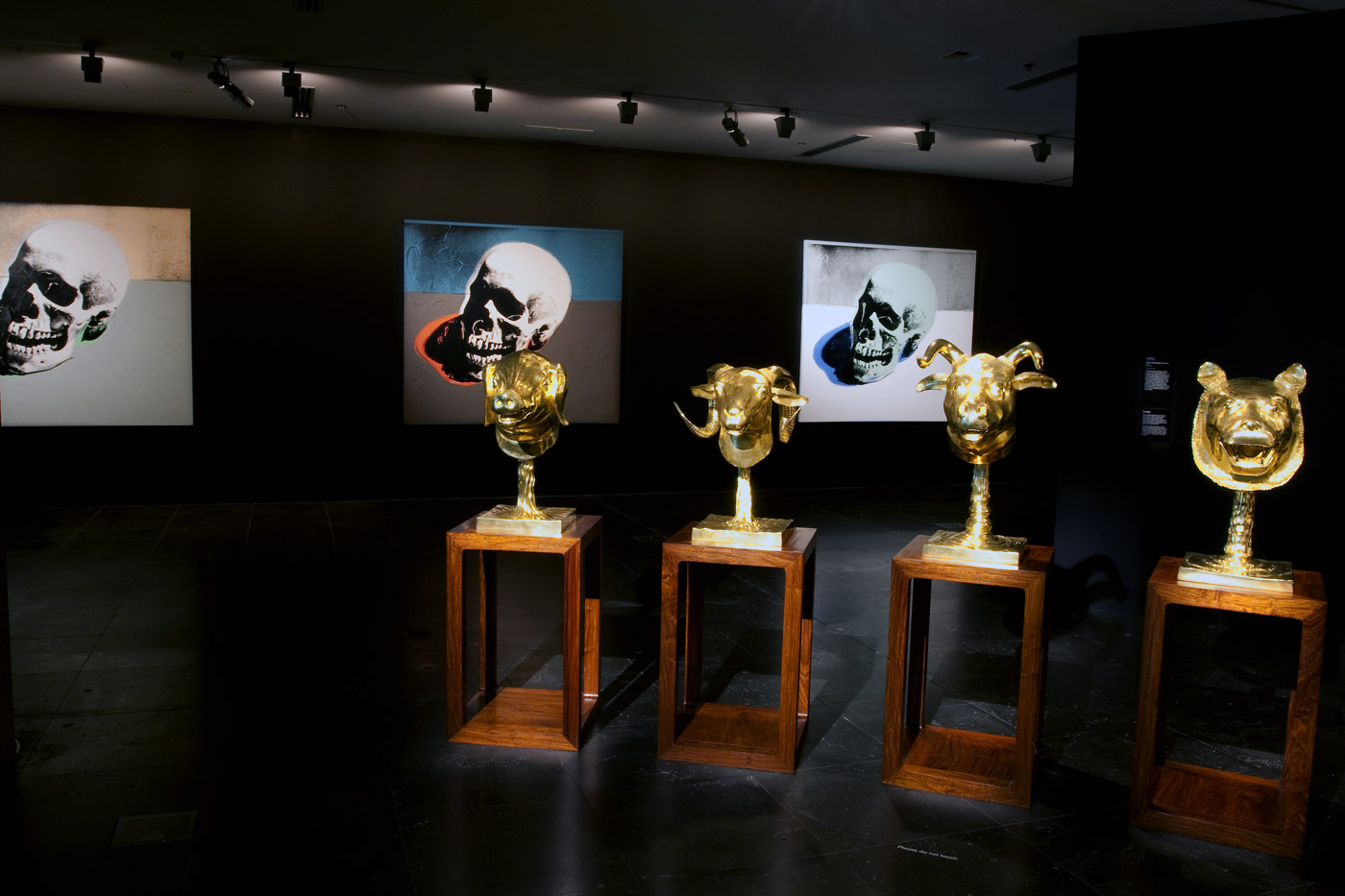
Installation view of the seventh room of the exhibition featuring part of Ai Weiwei’s Circle of Animals (in Gold) (2010), with Andy Warhol’s silkscreen skulls on the wall behind at the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
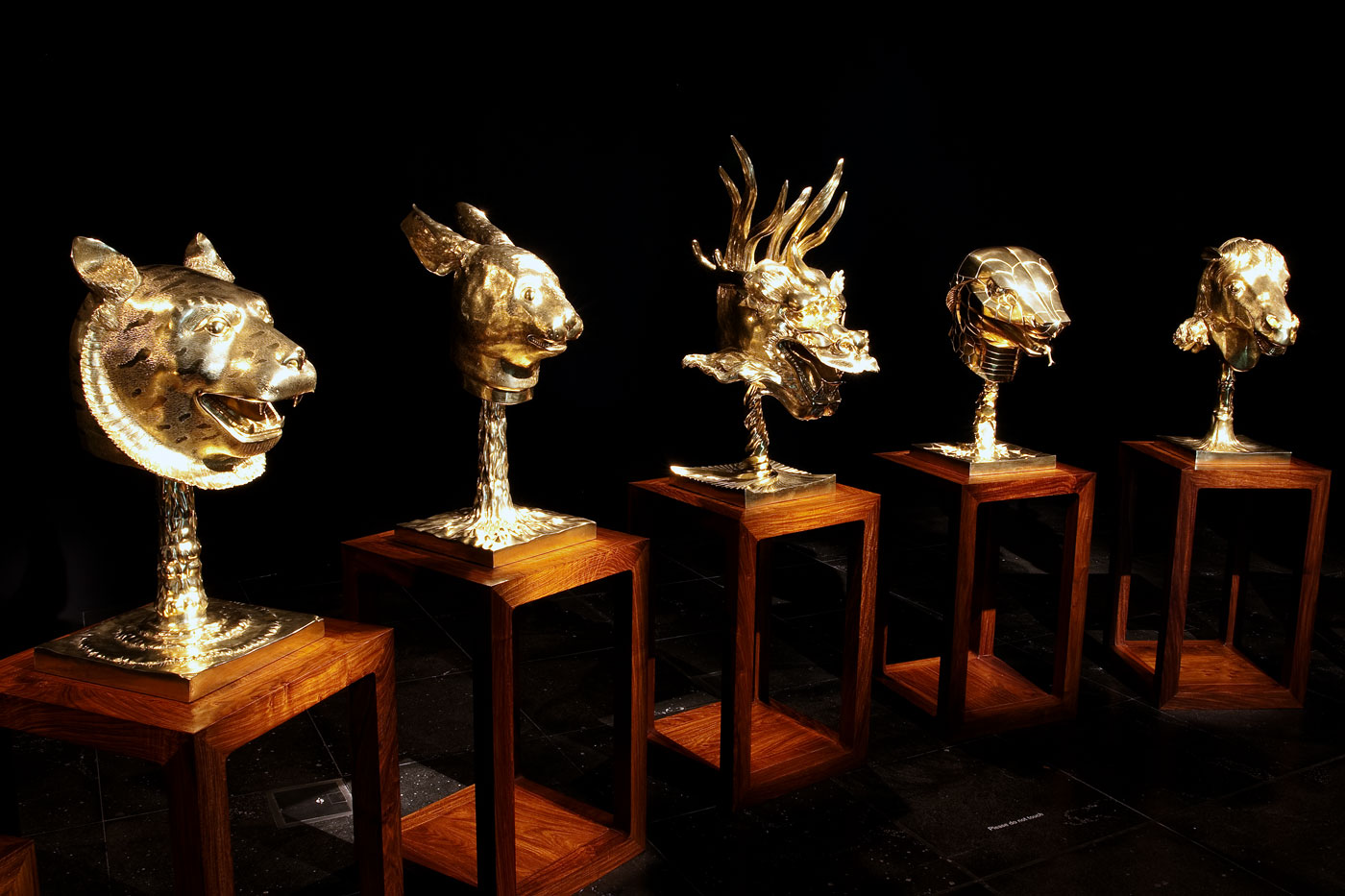
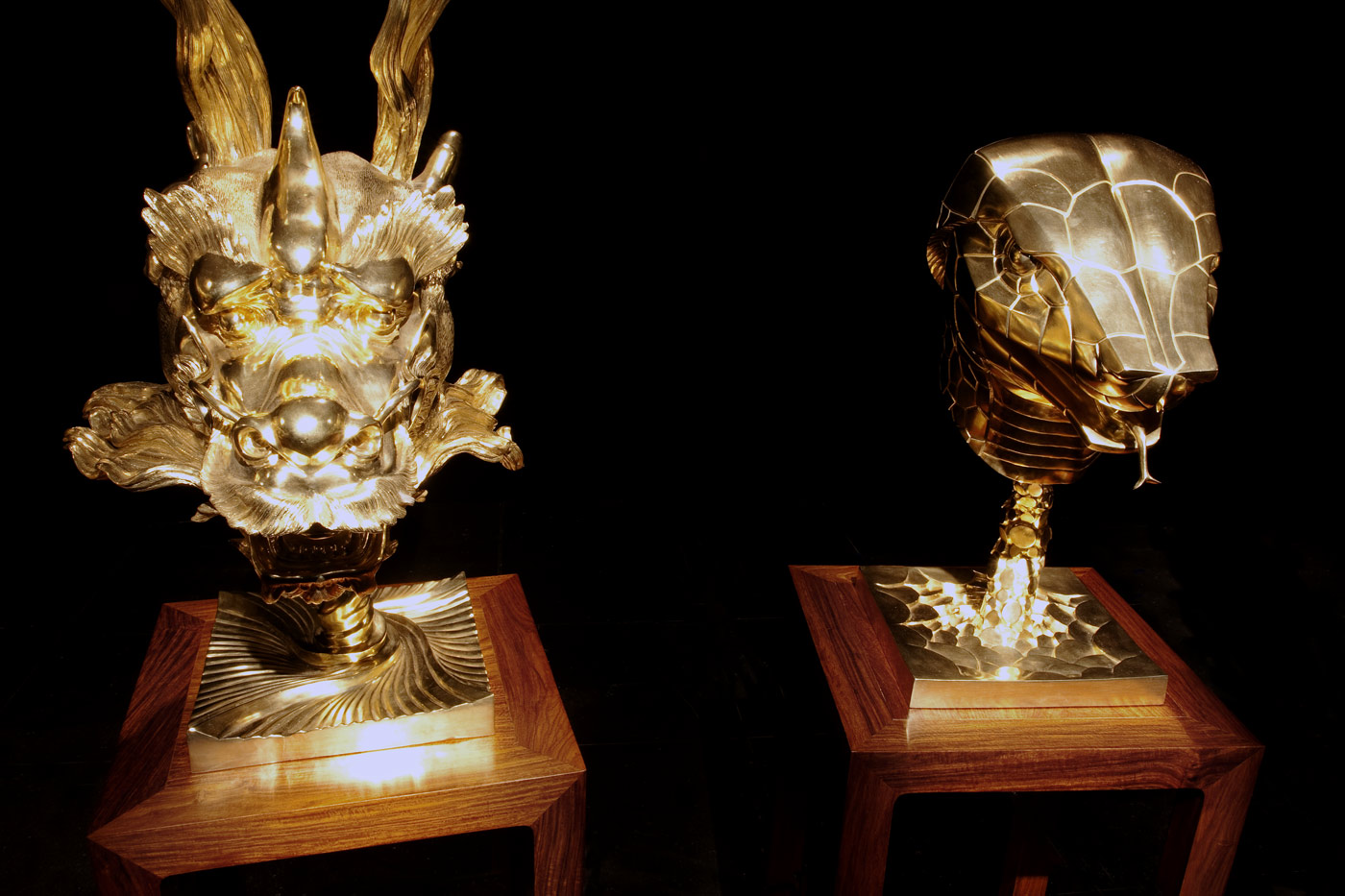
Ai Weiwei (Chinese, b. 1957)
Circle of Animals (in Gold) (installation view details)
2010
Gilt-bronze
Private collection, New York
Photos: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
Ai Weiwei’s Circle of Animals is based on twelve zodiac animal heads which functioned as a water clock-fountain in the European-style gardens of Yuanmingyuan palace, Beijing, designed in the eighteenth century by two European Jesuits for the Qing dynasty Emperor Qianlong. In 1860 Yuanmingyuan was ransacked by French and British troops and the heads were pillaged. In reinterpreting these objects, Ai focuses attention on the ethics of looting and repatriation, the role of the fake and the copy and power relations between China and the West.
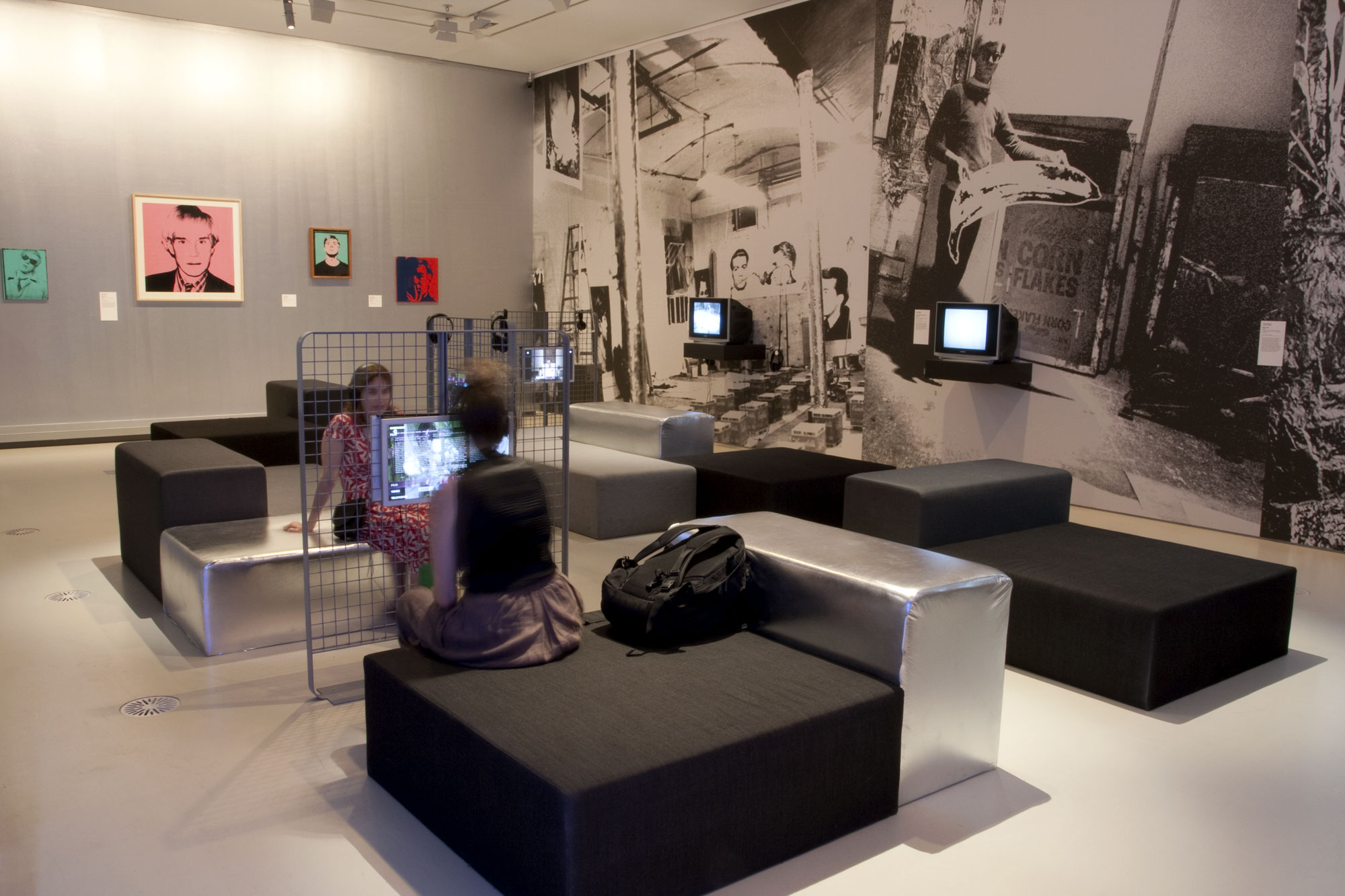
Installation view of part of room eight of the exhibition Andy Warhol | Ai Weiwei at the National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne. This room was based on interactivity with not much of interest photographically speaking, hence only one image.
Photo: © Marcus Bunyan and the National Gallery of Victoria
NGV International
180 St Kilda Road
Opening hours:
10am – 5pm daily










































































































































![Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Man on girders, Empire State Building]' c. 1931 Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Man on girders, Empire State Building]' c. 1931](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/man-on-girders-web.jpg?w=650)
![Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Steelworker touching the tip of the Chrysler Building]' c. 1931 Lewis Hine (American, 1874-1940) '[Steelworker touching the tip of the Chrysler Building]' c. 1931](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/steelworker-touching-the-tip-web.jpg?w=650)



















You must be logged in to post a comment.