Exhibition dates: 25th October, 2020 – 28th February, 2021
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
For a few brief moments, rebels with a cause
This is one of my favourite photo essays of all time. The story Davidson tells of this male-orientated Brooklyn gang and its culture through his photographs is one of brotherhood, friendship, rivalry, love, longing, agony, depression and death at a time of utter poverty and rock ‘n roll rebellion. He produced “unflinchingly honest images of these American youths.” Now, all these years later, the photographs possess a powerful nostalgia for the era mixed with the desolation of destroyed lives and lost youth.
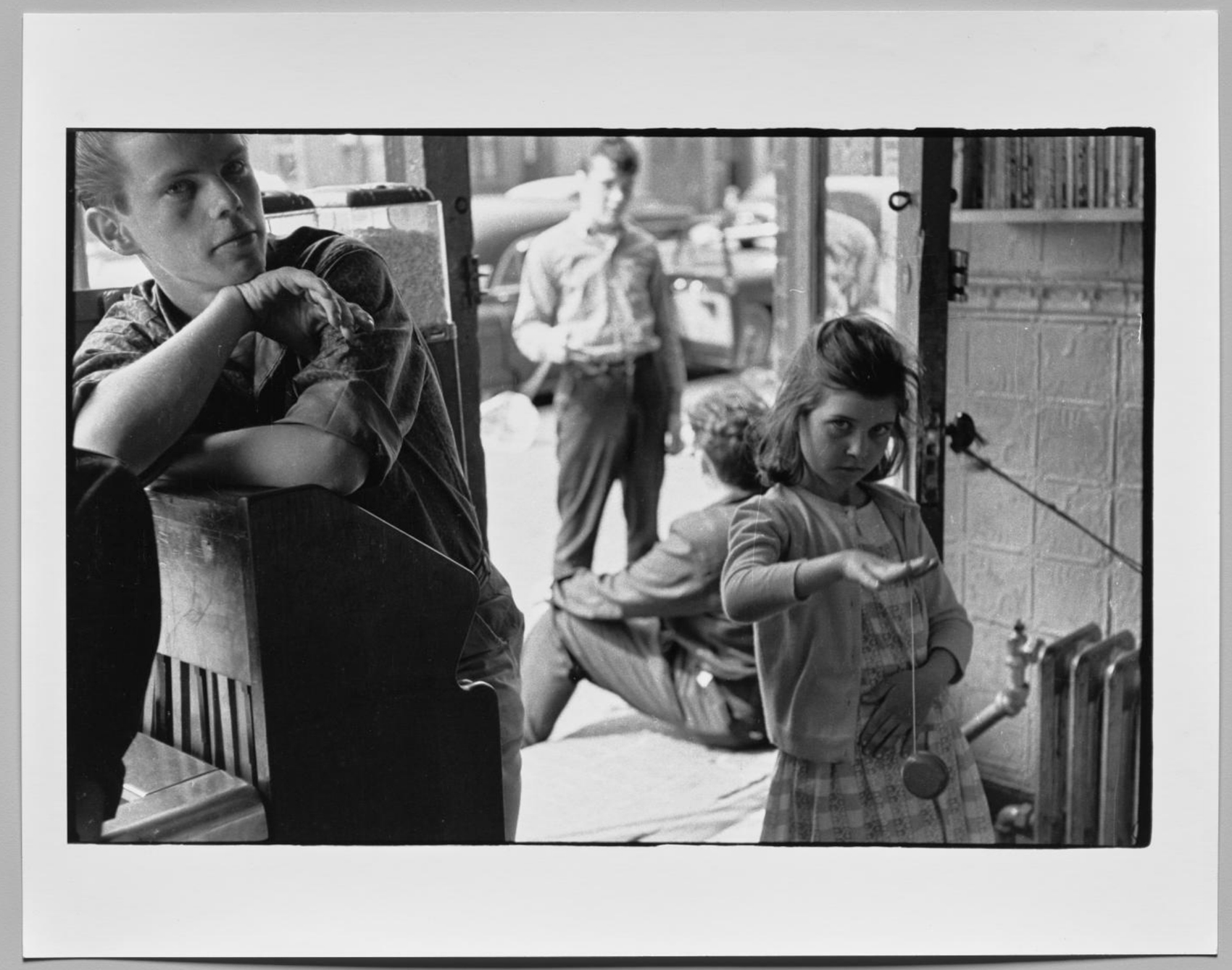
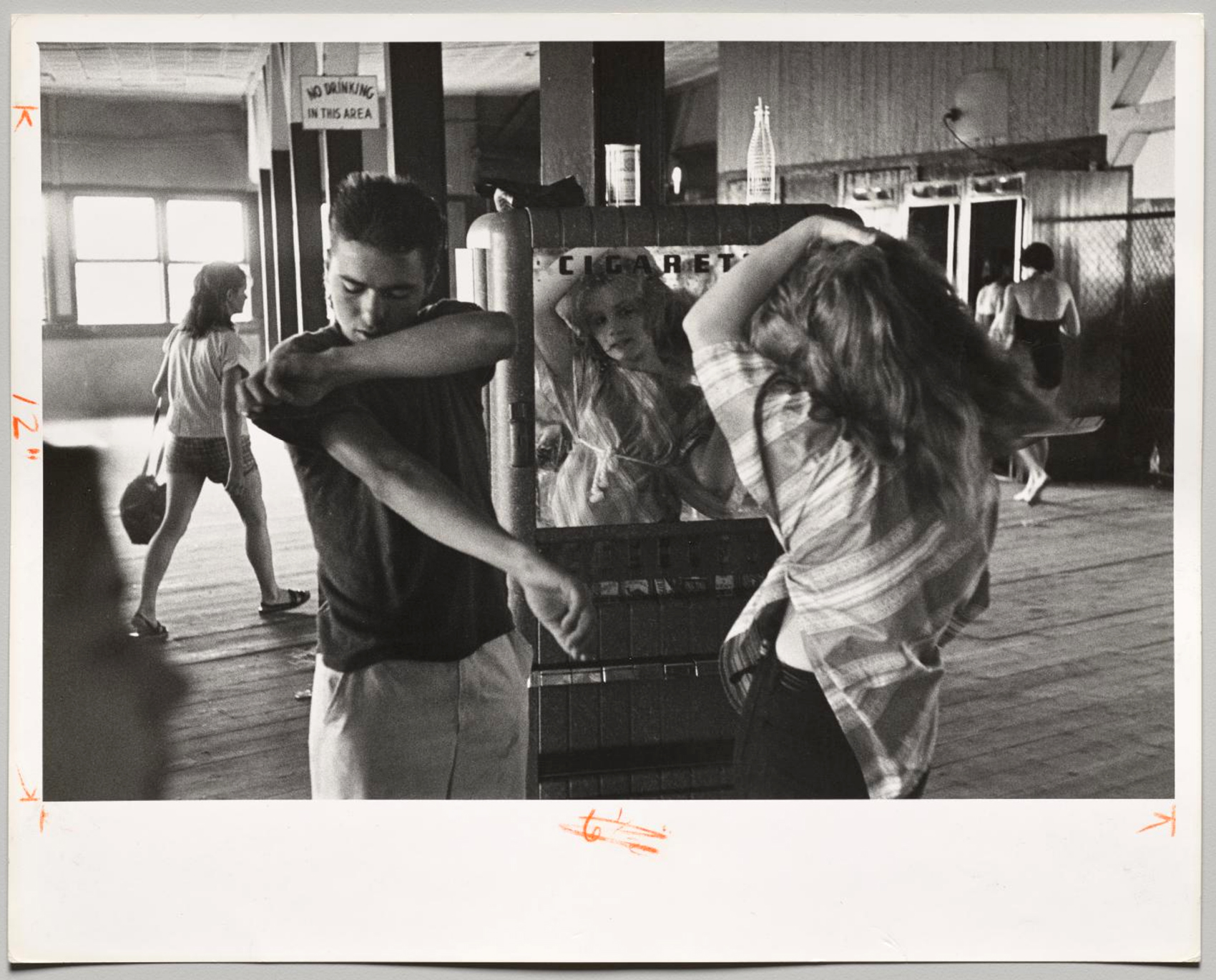
Davidson gets under the skin of his subjects, embeds himself firmly in their milieu. The subjects allow him to photograph their most intimate moments, seemingly free from worry or anxiety. There is an insouciance to their attitude, a knowing insouciance. In one photograph inside Helen’s Candy Store, Bob Powers stares directly and disarmingly at the camera while the girl playing with the yo-yo and the youth in the background also stare directly into the lens, forming a strong compositional triangle of the gaze. Powers said he was voted “most likely to die before I was 21 years old.” He lived with his seven siblings and alcoholic parents in a three-bedroom apartment that had a coal-powered cookstove and no hot water or central heating.
There is a dark undertone to the narrative. While there are moments of joy and happiness, you can sense the isolation and despair of these disaffected youths. Cathy O’Neal, seen in front of a cigarette machine at Coney Island, committed suicide by shotgun. Jimmie and his family were wiped out by drugs. Junior Rice became a heroin dealer. Lefty od’d in bed at 19. “He was the first in the group to die from a drug overdose… within a few years, drugs would claim the lives of many in the gang and in the neighbourhood.” In picturing their lives, the photographs gather moments (in time), enunciating how the gang members railed against the conformity and materialism of 1950s America whilst imbibing its rebellious iconography. Only occasionally does the artist pull back to show us the wider picture, the context of the action, with photographs of New York skyscrapers seen in the distance and the Statue of Liberty.
Davidson does not let his spontaneity slip. He is informed, aware, absent (but present) in all of these photographs waiting for that special moment. In the photograph above, a bird-like creature swoops down on something invisible on the ground. In informal yet tightly focused photographs – of sunbathing or walking the boardwalks of Coney Island, gang members fixing their hair, rolling up their sleeves, dead beat(s) in the back of the bus, making out in the back seat of a car, walking in the park or hooning around on the Metro – Davidson is there to capture the off-beat moments of gang existence and the members relationship to each other.
Through a superb eye, a feeling, a sensibility and connection towards the gang members desperation and isolation, universally acknowledged by the photographer himself, Davidson sets them all on the path to immortality. Do not forget, these photographs seem to be saying. For a few brief moments these people did exist, their lives were valuable, these rebels with a cause.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to the Cleveland Museum of Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
One of Davidson’s best-known series, Brooklyn Gang was inspired by a news story he read about a teenage gang called the Jokers.
Davidson contacted the Jokers, one of Brooklyn’s roughest gangs, through their social worker. In the summer of 1959, Davidson roamed the streets of New York with these teens, loitered in stores that the Jokers called their own, and sunbathed with them on the beach at Coney Island. Eventually they allowed him to photograph even their most intimate, private moments. He responded by producing unflinchingly honest images of these American youths.
Gang membership was exclusively male, but the members’ girlfriends appear frequently in Davidson’s photographs. Some of the pictures depict the teenagers exploring lust and love and the boys struggling to define and prove their masculinity. Looking back at the series in 1998, Davidson said that he felt “the reason that body of work has survived is that it’s about emotion. That kind of mood and tension and sexual vitality, that’s what those pictures were really about.”
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
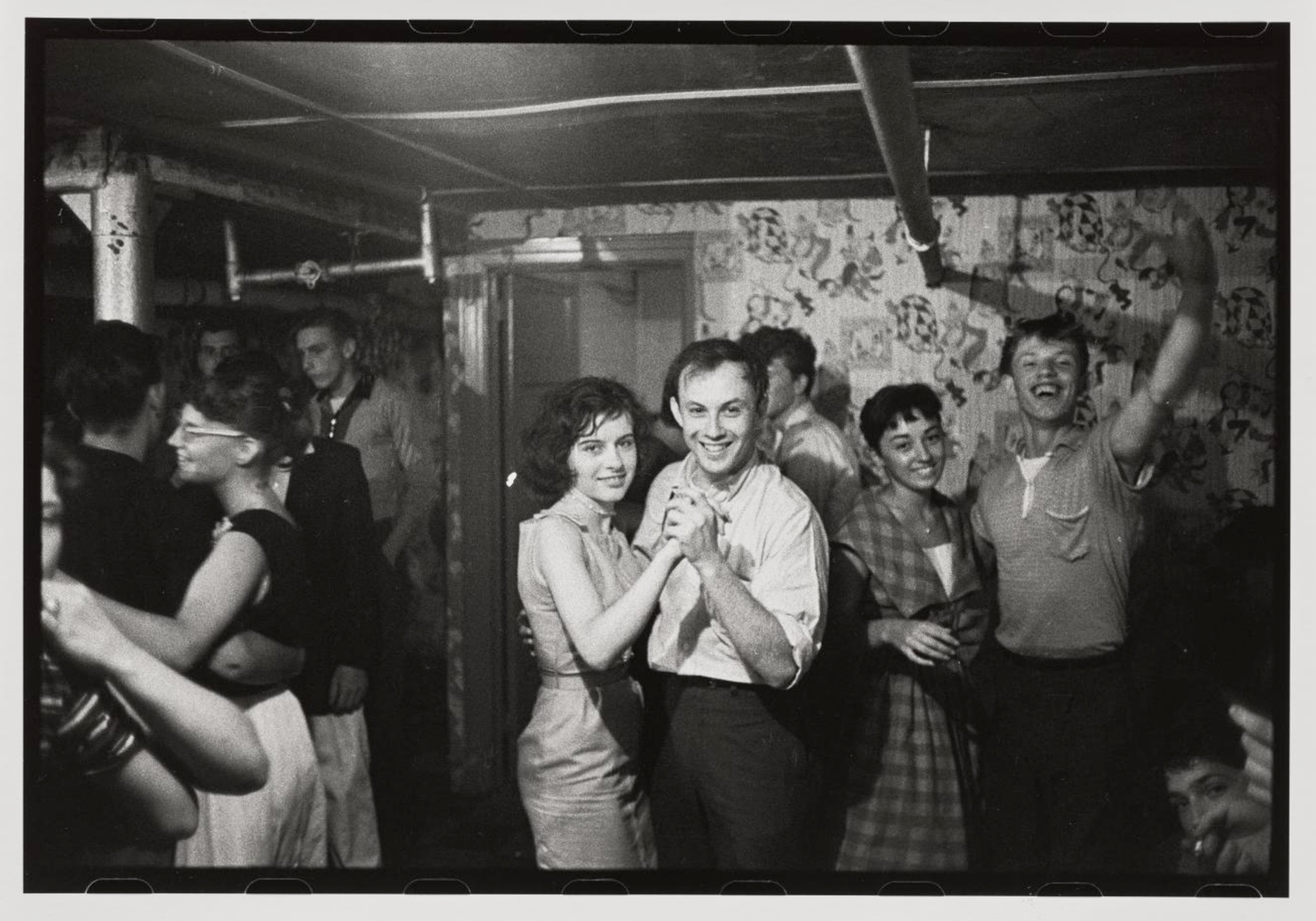
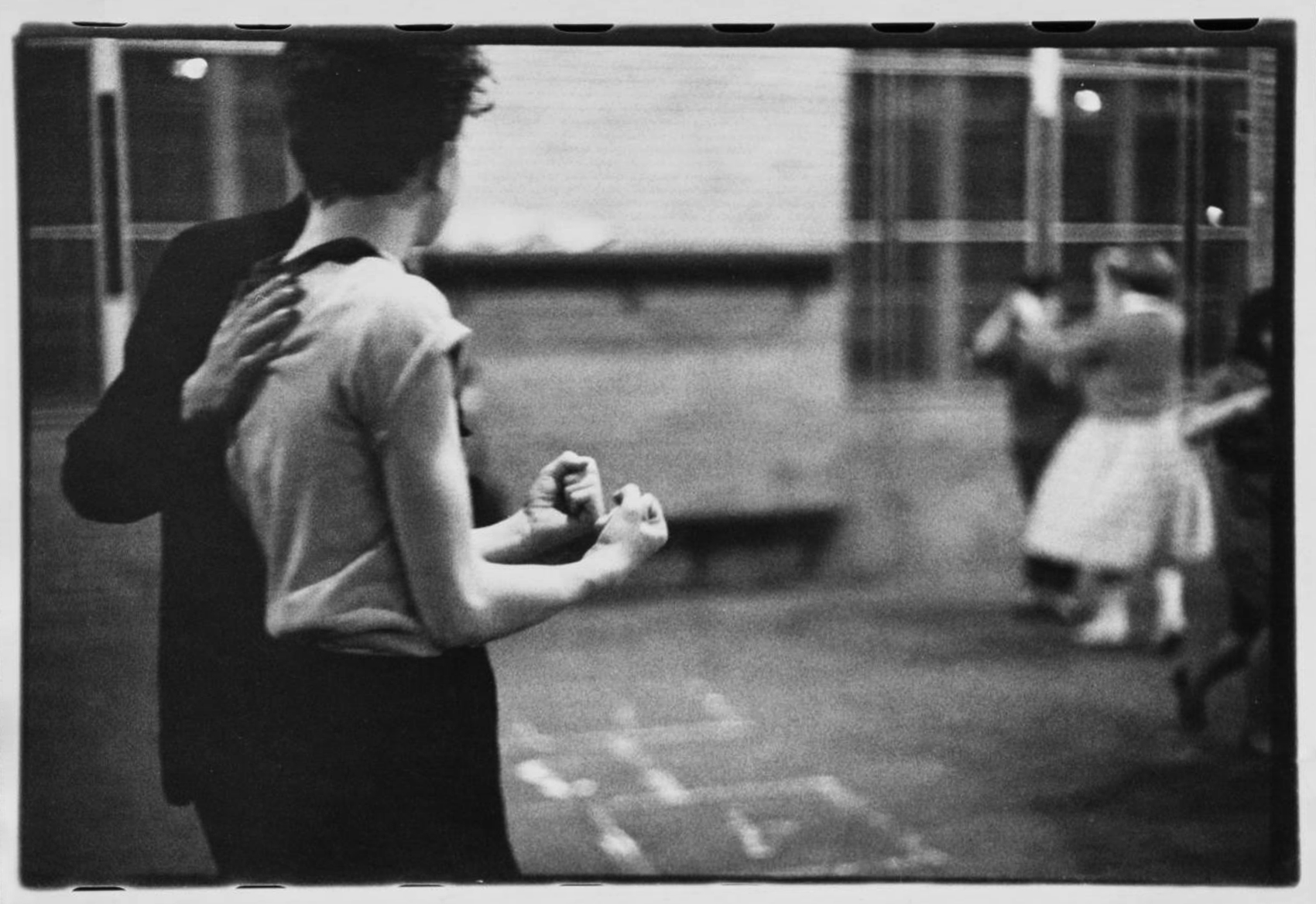
The pleasures and agonies of teenage romance are captured in Bruce Davidson’s photographs of the gang’s dance parties, which were held variously in Brooklyn’s Prospect Park, at a neighbourhood school, and in members’ homes. The basement wallpaper seen here – with its fairy-tale figures, including horses, queens, knights, marionettes, and jokers – suggests a domestic setting. The event could have been a farewell party for an older gang member going off to join the army, which was a common occurrence.
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 20.3 x 25.4cm (8 x 10 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Image: 16 x 23.9cm (6 5/16 x 9 7/16 in.)
Paper: 20.3 x 25.2cm (8 x 9 15/16 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
This rooftop view in Park Slope, Brooklyn, was taken from a building in the gang’s “turf,” which was a block anchored by the intersection of 17th Street and 8th Avenue. Davidson spent the summer hanging out with the gang and photographing them. Describing his process, the artist said, “I stay a long time. … I am an outsider on the inside.” Park Slope, now one of New York’s most desirable neighbourhoods, was then a poor, mostly Irish area.

Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Image: 21.9 x 14.6cm (8 5/8 x 5 3/4 in.)
Paper: 25.1 x 20.2cm (9 7/8 x 7 15/16 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
Davidson contacted the Jokers, one of Brooklyn’s roughest gangs, through their social worker. In the summer of 1959, Davidson roamed the streets of New York with these teens, loitered in stores that the Jokers called their own, and sunbathed with them on the beach at Coney Island. Eventually they allowed him to photograph even their most intimate, private moments. He responded by producing unflinchingly honest images of these American youths.
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
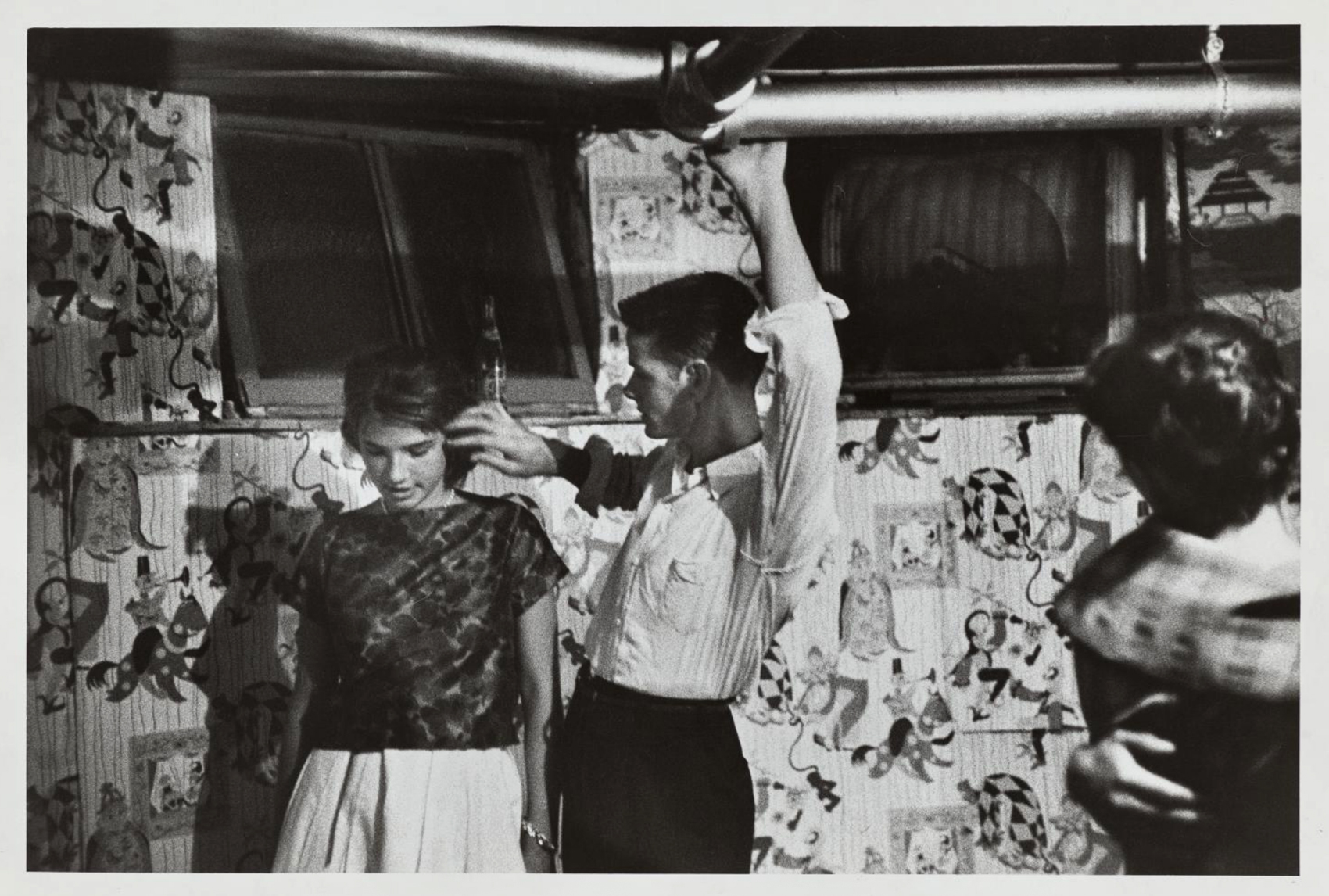
The pleasures and agonies of teenage romance are captured in Bruce Davidson’s photographs of the gang’s dance parties, which were held variously in Brooklyn’s Prospect Park, at a neighbourhood school, and in members’ homes.
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Image: 16.1 x 24.1cm (6 5/16 x 9 1/2 in.)
Paper: 20.2 x 25.3cm (7 15/16 x 9 15/16 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
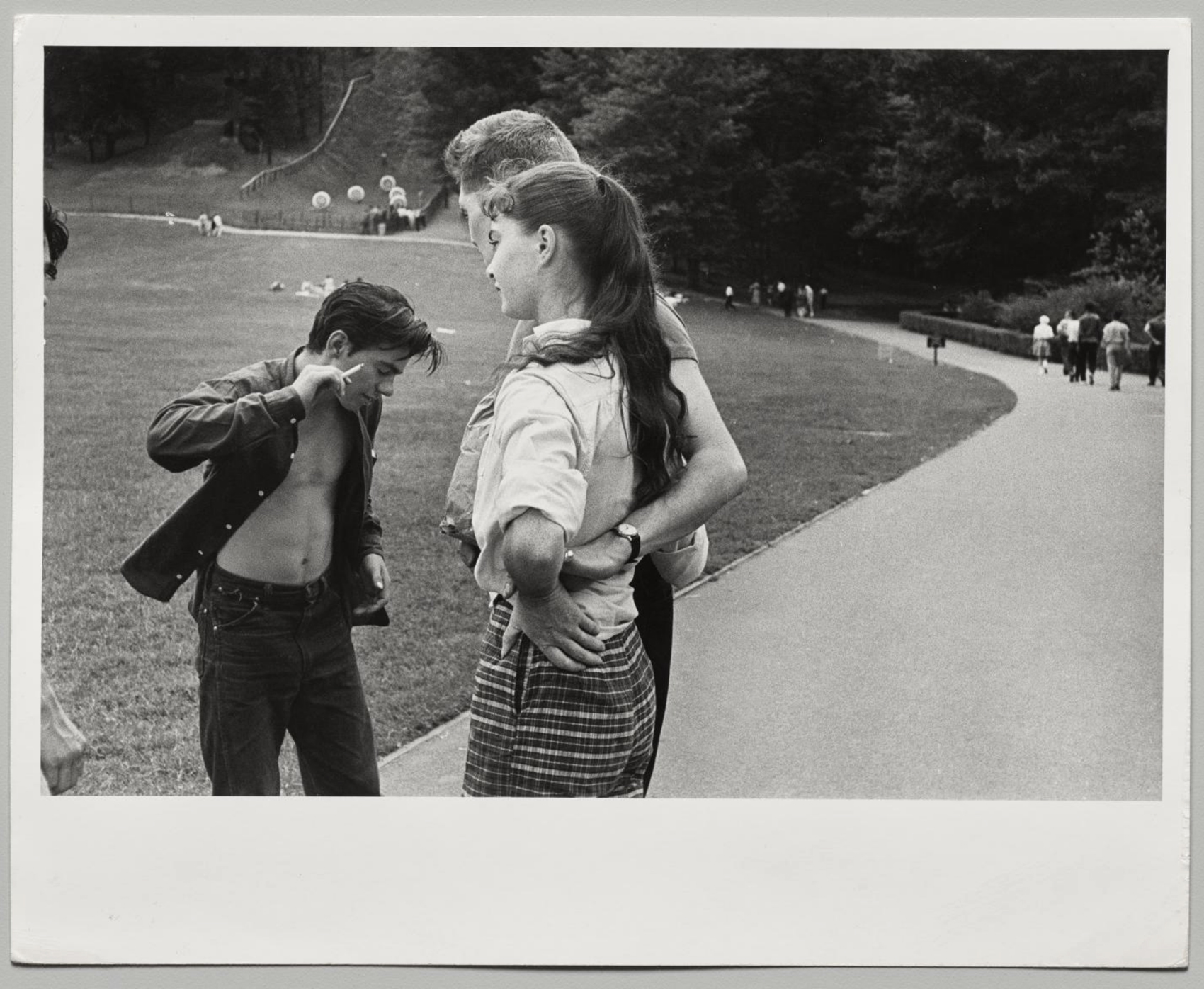
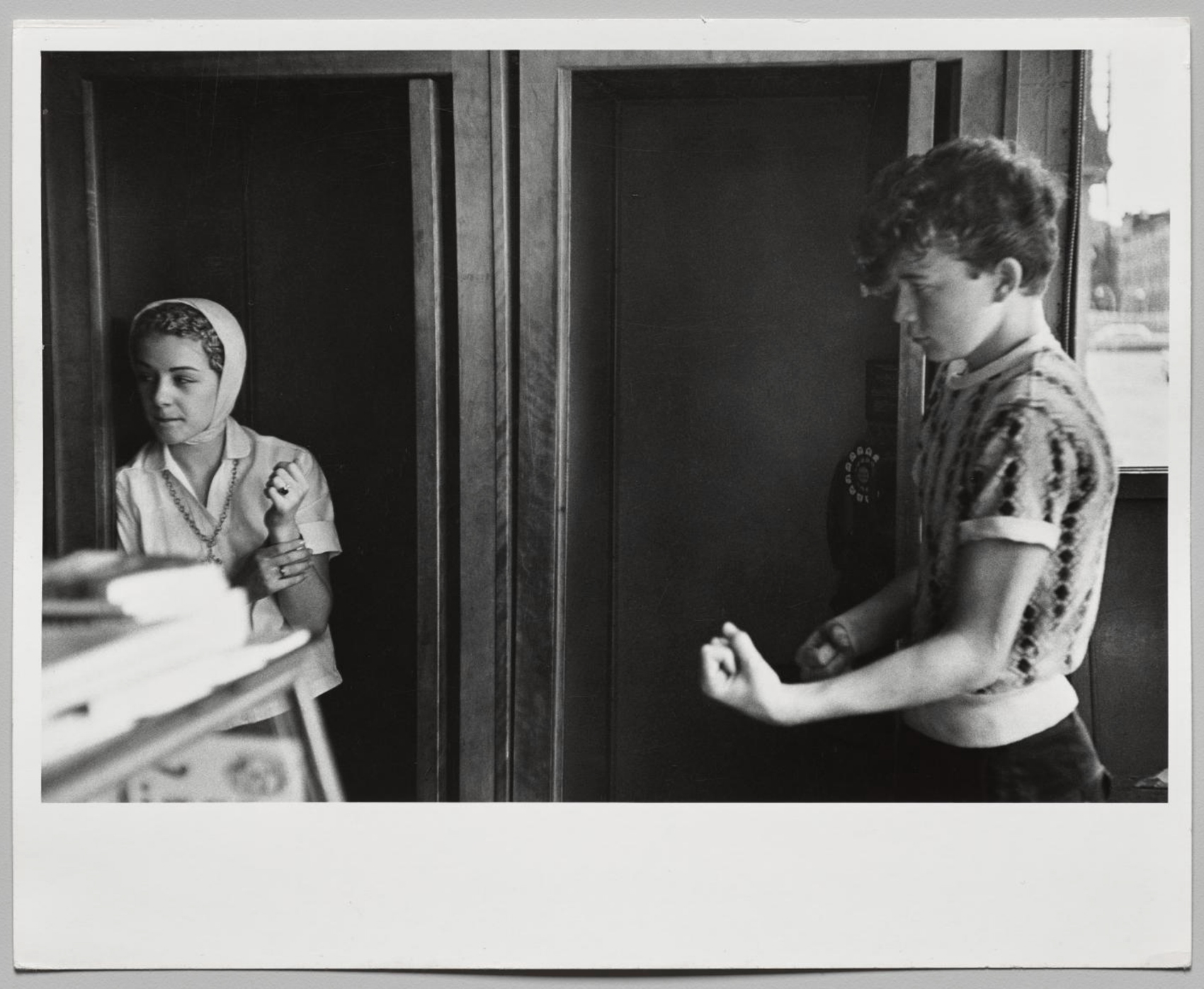
Childhood pastimes like playing yo-yo were a thing of the distant past for 15-year-old Bob Powers, a Joker seen here leaning against a fixture in Helen’s Candy Store. He had already been in and out of the court system numerous times by 1959. Powers stabbed someone when he was 12 and had been incarcerated for bringing zip guns (homemade firearms) and chains to school, where, Powers said, he was voted “most likely to die before I was 21 years old.”

Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
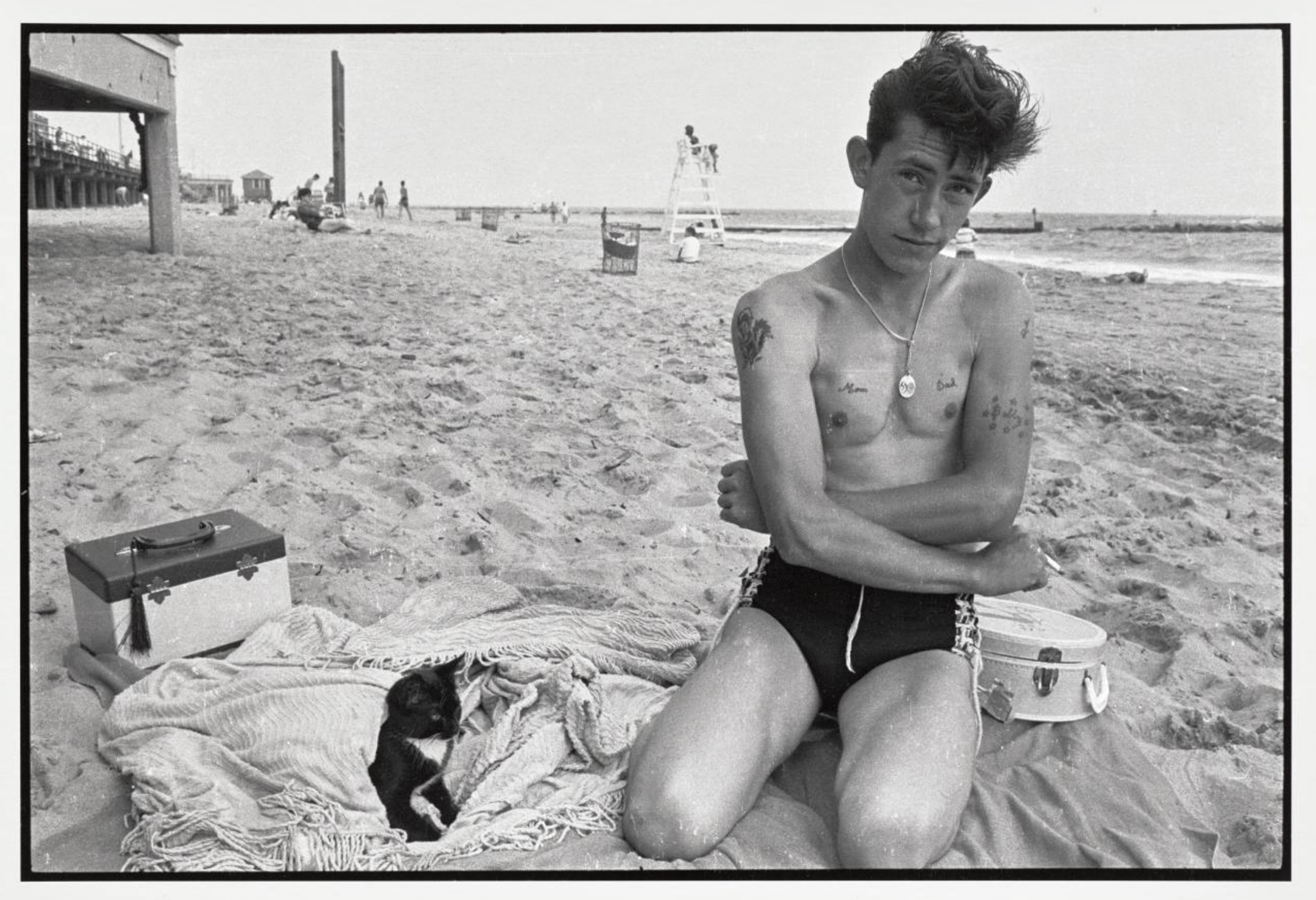
The gang members, most of whom were 15 or 16 years old, thought tattoos made them look older and might help them get served at bars. Tattoos were also a demonstration of masculinity and a rite of passage. Bob Powers, seen here at age 15 displaying his first tattoo, recalled years later that “the first time you get a tattoo it’s scary. I was sitting back with a cigarette like it’s nothing. Meanwhile, it was killing me. … I got ‘Bobby’ with stars around it. … They said, ‘Get your name.’ … I hated it forever.”

Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 61 x 50.8cm (24 x 20 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
One of the gang members – Bob Powers – suggested that Davidson follow him to a rooftop on the gang’s block. “I remember thinking,” said Davidson, “‘This kid’s going to throw me off the roof and then rob me,’ but he’s pointing down at the stickball game (an informal form of baseball played in the street) and saying, ‘Get that,’ and saying: ‘Oh, there’s the Statue of Liberty. You can see it through all these television antennas.'”
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6 cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
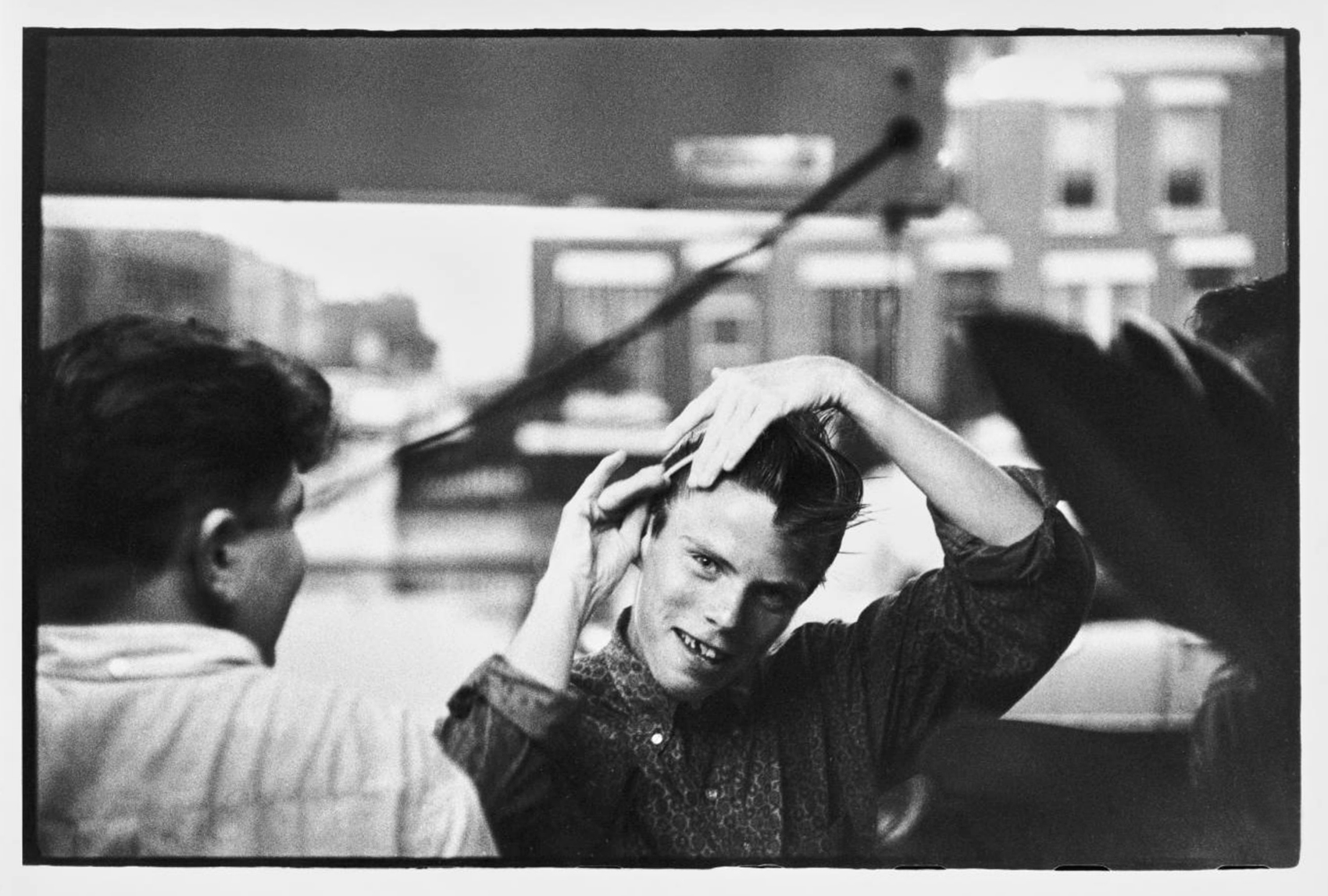
The gang members were very concerned with their appearance, although they did not have much money to spend on grooming or clothes. “If you see a picture of me,” said former gang member Bob Powers, “the broken tooth, my teeth were green because I didn’t go to the dentist. We never had any money even though my father worked. … We used Vaseline petroleum jelly to make our hair stick like iron in a pompadour. We combed our hair constantly, wore sunglasses, and all thought we were Marlon Brandos.”
The Jokers’ slicked-back pompadours … and their clothing echoed the greaser style, a rebellious youth subculture that was promoted by cinematic antiheroes of the era. Role models included Marlon Brando’s portrayal of a motorcycle gang member in The Wild One (1953) and James Dean as a troubled teen in Rebel without a Cause (1955). The “bad boy” image flouted the aspirational role model of the time, the upwardly mobile white-collar worker in a business suit and short haircut.

Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
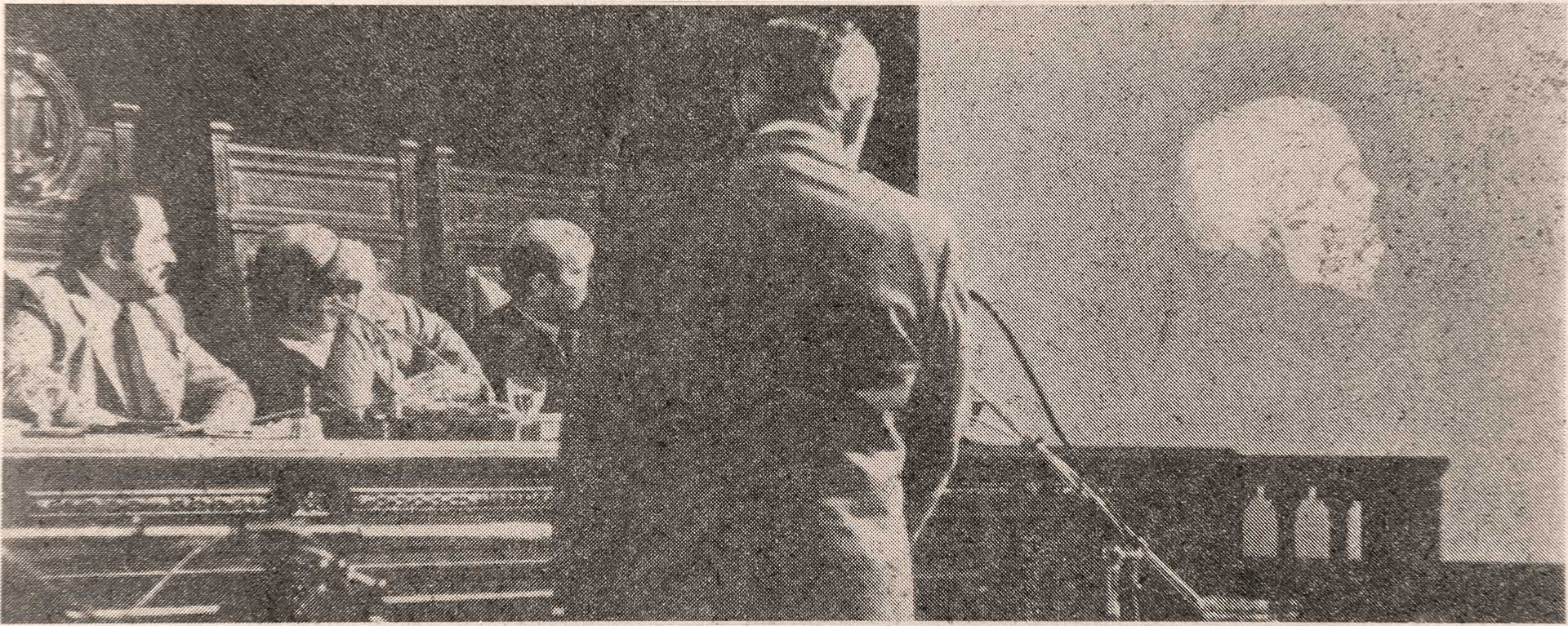
Petey, a Jokers member who looks out the second-story window here, was injured in that fight. Petey’s best friend, fellow Jokers member Bob Powers, walks by the house. Housing in the gang’s neighbourhood, the then-impoverished Park Slope, Brooklyn, was overcrowded and rundown. Powers lived with his seven siblings and alcoholic parents in a three-bedroom apartment that had a coal-powered cookstove and no hot water or central heating.
One of the most highly respected and influential American documentary photographers of the past half century, Bruce Davidson spent several months photographing the daily lives of a teenage street gang for his 1959 series Brooklyn Gang. A new exhibition in the Cleveland Museum of Art’s Mark Schwartz and Bettina Katz Photography Gallery, Bruce Davidson: Brooklyn Gang features 50 black-and-white photographs from that series, which are part of a recent anonymous gift to the museum of extensive selections from the artist’s archives. The exhibition is on view now through February 28, 2021.
Brooklyn Gang was Davidson’s first major project after joining the distinguished photo agency Magnum and was the fruit of several months spent immersing himself in the daily lives of the Jokers, one of the many teenage street gangs worrying New York City officials at the time. He recorded the teenagers’ pleasures and frustrations as they attempted to define masculinity and mimic adult behaviour. The photographs reflect the group’s camaraderie but also their alienation from societal norms. While many officials and commentators at the time saw the gangs as evidence of social deterioration resulting from poverty, others regarded them as the most visible manifestations of a socially disengaged generation of males – rebels without a cause.
“Bruce Davidson: Brooklyn Gang presents an intimate portrayal of the teens’ lives,” said William Griswold, director of the Cleveland Museum of Art. “Davidson was an outsider, but one who spent so much time with the gang that he became, as he liked to say, ‘an outsider on the inside.’ Davidson offered an independent look at the lives of these disadvantaged youths; this view of society was quite different from the age of visual and social homogenisation of the 1950s presented in mainstream magazines such as Life and Look and predicts the social turmoil of the 1960s.”
The images reflect the time Davidson spent with the teens hanging out on street corners and in the local candy store and accompanying them to the beach at Coney Island with their girlfriends. Included are several sets of variant images, affording a rare glimpse into Davidson’s working process.
“Despite a more than ten-year age difference, Davidson describes recognising his own repression in his subjects and feeling a connection to their desperation,” said Barbara Tannenbaum, the CMA’s chair of prints, drawings, and photographs and curator of photography.
Press release from the Cleveland Museum of Art
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 40.6 x 50.8cm (16 x 20 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
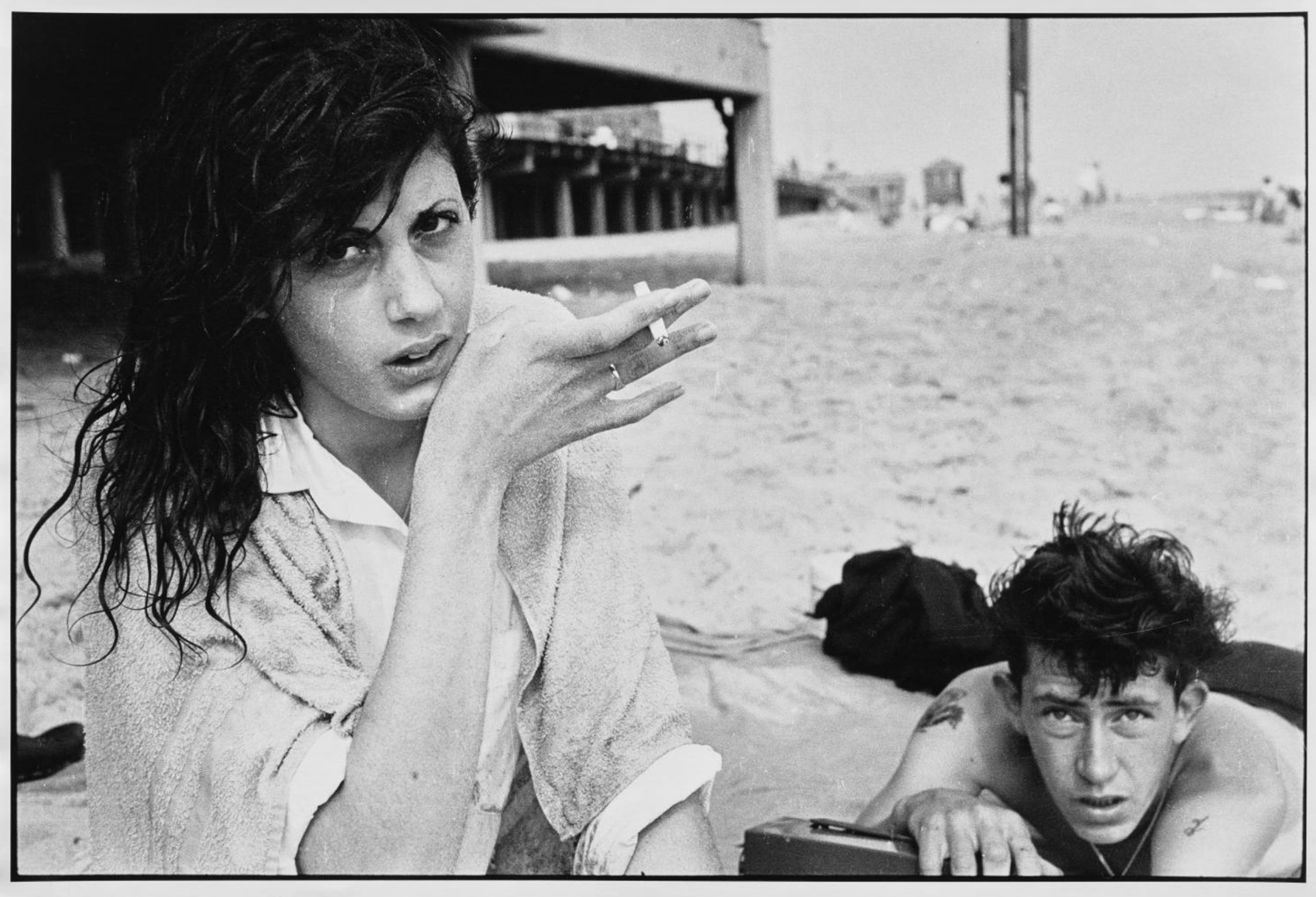
The museum owns several groups of images from the series taken during the same shoot at Coney Island. They provide a rare glimpse of the artist’s selection process (see 2018.688, 2018.696, 2018.697, 2018.701, 2018.706, and 2018.735). The size of these prints, and the fact that the artist printed them long after they were shot, suggest he considered all four images worthwhile. In an exhibition print, the white marks on the woman’s cheek here, made by dust on the negative, would have been covered up with ink or dye, a process known as spotting. This may be a work print, made to aid in decisions on exactly how to print this picture. It has become one of the better-known images from Brooklyn Gang.
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 20.3 x 25.4cm (8 x 10 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
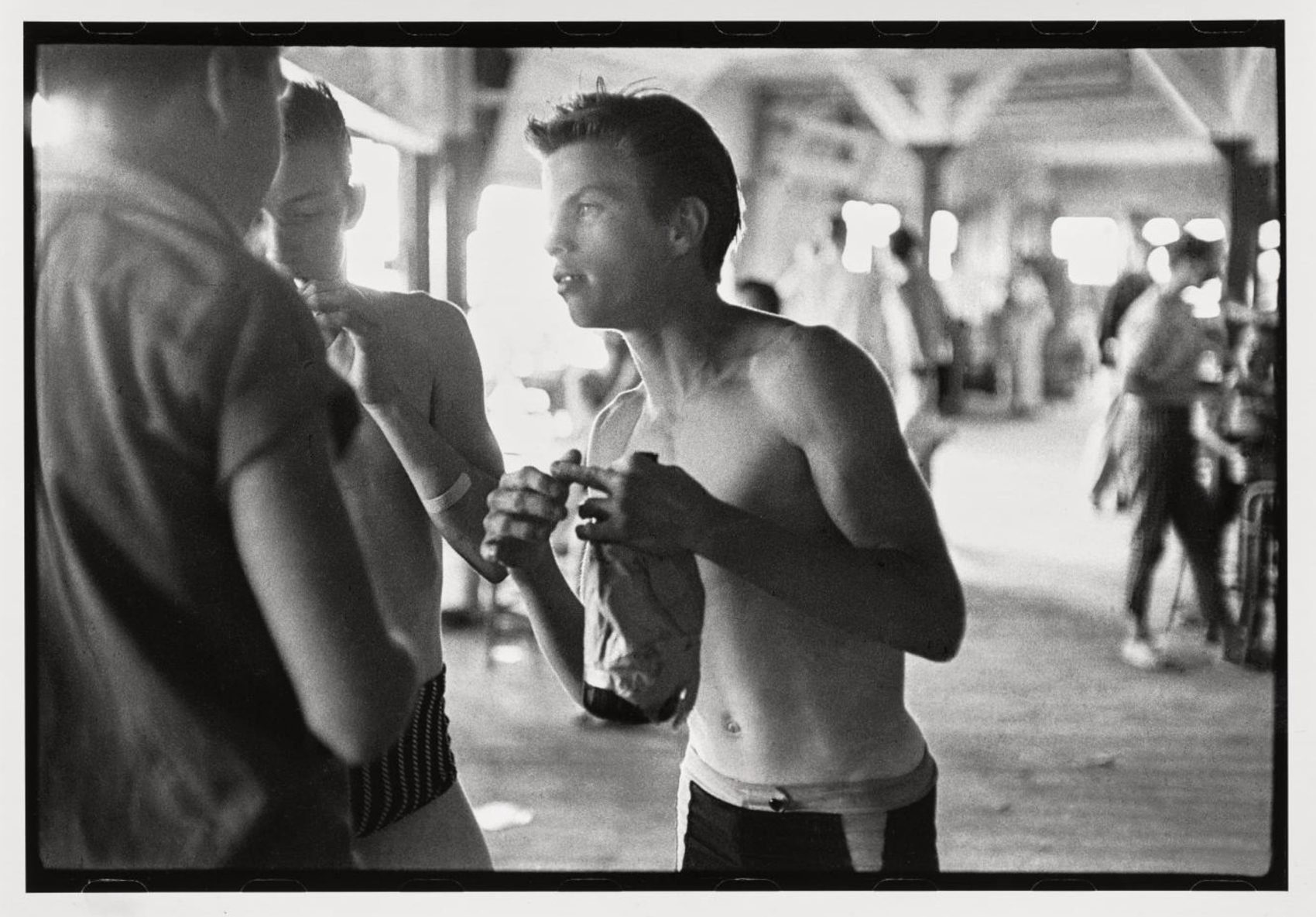
In this photograph, gang member Bob Powers talks with friends in one of the many Coney Island bathhouses where people could change, shower, or swim in pools. “We’d come down on a Friday and sometimes we’d stay the whole weekend till Monday, down on the beach, me, Lefty, Junior,” Powers recalled. “The girls would stay too… We would light fires and bury all the cans of beer. I remember stealing cars and driving down there. We’d drive the car under the boardwalk and bring it right onto the bay and leave it there.”
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 50.8 x 61cm (20 x 24 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
Shown here on the Coney Island boardwalk, from left to right, are gang members Junior Rice, Bob Powers, and Lefty, who “was a pretty tough guy in the gang and then he went to jail for about a year,” according to Powers. “He came out and he just lost it. He wasn’t the same guy. Something happened and nobody knew what. … We protected him a bit, but he caught a couple of bad beatings and lost his reputation. He ate a lot of pills one night and never woke up. His mother found him dead. OD’d in bed at 19. He was the first in the group to die from a drug overdose.”
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Image: 16.1 x 24.1 cm (6 5/16 x 9 1/2 in.)
Paper: 20.2 x 25.3 cm (7 15/16 x 9 15/16 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
This print is vintage – made soon after the picture was shot – and its 8 x 10-inch size was typical of the period and preferred for making reproductions for magazines and books. As photography began gaining acceptance into the gallery and museum world in the 1980s, larger prints became the norm. The museum also owns an unusually large print of the same image, made in the 1990s or 2000s, which was created to be exhibited in galleries and museums. The two may look the same on the computer screen, but do not feel the same when viewed in real life.
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Image: 15.8 x 24.1 cm (6 1/4 x 9 1/2 in.)
Paper: 20.1 x 25.4 cm (7 15/16 x 10 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
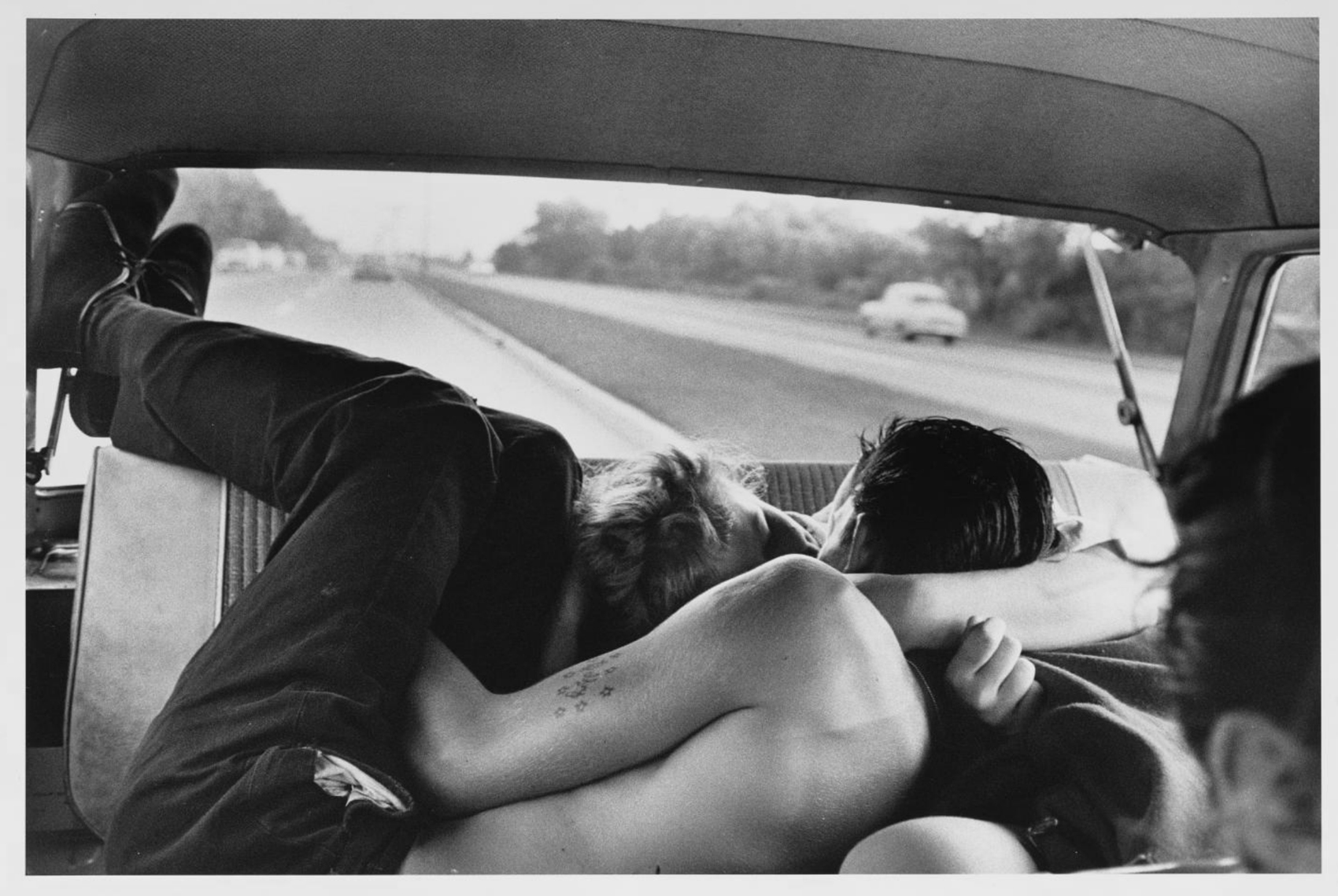
After a day at the beach at Coney Island, the teens “would take the long bus ride back to their neighbourhood,” remembered Bruce Davidson. “As they sat in the rear of the bus, the sunlight burned through the windows, giving them an angelic glow. They would drift into their dreams and awake alert to the mean streets awaiting them.”
Bruce Davidson
Barbara Tannenbaum
Curator of Photography
A hot topic in the 1950s, gangs were avidly analysed by sociologists, the press, and artists. Gordon Parks’s photographs of a young black Harlem gang leader were published in Life magazine in 1948. The musical West Side Story, which pitted a Polish gang against a Puerto Rican one, debuted on Broadway in 1957. The following year, a seven-part series in the New York Times analysed the social, economic, and psychological causes of this juvenile delinquency.
In the summer of 1959, Bruce Davidson went to Brooklyn to meet and photograph a teenage street gang called the Jokers. Davidson’s series Brooklyn Gang provided an in-depth view into the daily activities of an Irish and Polish gang whose turf was a block in the impoverished Park Slope neighbourhood. The Jokers were teenagers who were mostly students at the neighbourhood Catholic school or dropouts. They shoplifted and fought with members of rival gangs in rumbles that involved bricks, bats, knives, and occasionally zip (homemade) guns.
At age 25, Davidson was an outsider to them. He had been raised in a Jewish family in suburban Chicago and held an MFA in photography from Yale University. His images were being published in major magazines, and he had just joined Magnum, a distinguished, artist-run photographic agency. The Jokers’ role models were the greasers, a rebellious youth subculture promoted by cinematic antiheroes such as Marlon Brando’s motorcycle gang member in The Wild One (1953) and James Dean’s troubled teen in Rebel without a Cause (1955). The gang members’ “bad boy” image, replete with Vaseline-slicked pompadours and blue-collar clothing, flouted the era’s aspirational role model of an upwardly mobile white-collar worker in a business suit and short haircut.
Davidson did not sport a pompadour, but making a living as a freelance photojournalist was itself a rebellion against the nine-to-five office world. He spent the summer with the Jokers, hanging out on street corners, in the local candy store, and on the beach at Coney Island. His images reflect their alienation and anxieties but also their camaraderie. The boys explore male bonding rituals and act out their visions of maleness and adulthood. They may roughhouse, but gang ethics dictated that they were not to hurt each other. Real violence was reserved for rival gangs and, like their criminal acts, was not shown by Davidson.
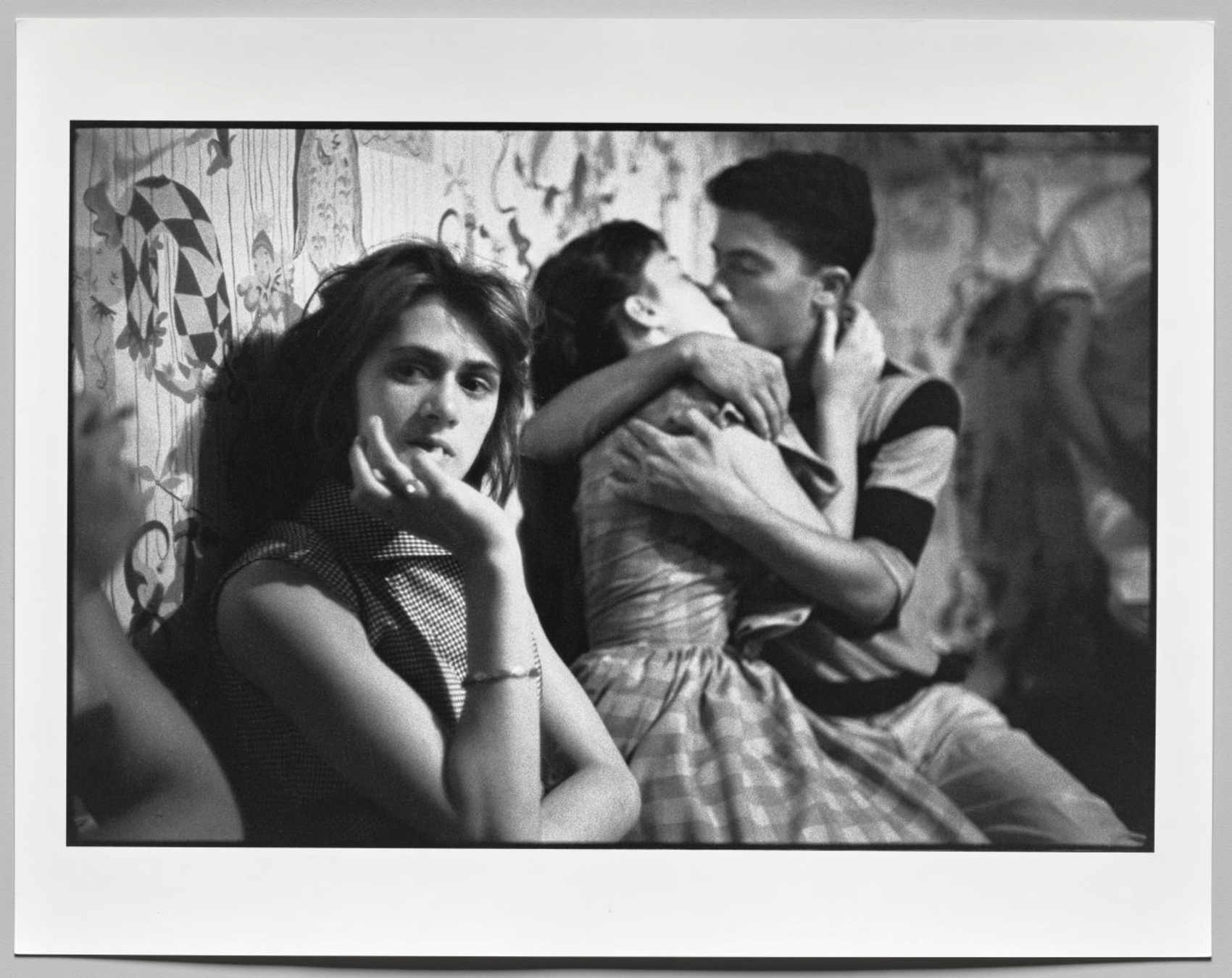
He did capture the teens’ early experiences with lust and love. The Lothario in the back seat of a car is Lefty, of whom Bob Powers, a gang member who wrote a memoir 40 years later, remarked, “We never thought he was good-looking, but all the girls loved him.” This well-known image of Lefty is joined in the exhibition by three others from that same make-out session. Together they form an almost cinematic progression. Several other groups of related images of events are also included in the exhibition. These rare glimpses into the artist’s shooting and editing processes are all drawn from the recent anonymous gift to the museum of 367 works from Davidson’s archive, selections that span his 70-year career.
Davidson was careful not to pass judgment in his Brooklyn Gang photographs. The youngsters’ hairstyles, tattoos, and underage drinking, smoking, and sex were considered ruinous behaviour at the time. The memoirs of Bob Powers and the reminiscences of other members give the Jokers’ story a dark tone. The best-known image in the series, taken in front of a cigarette machine at Coney Island, shows Artie Giammarino, who later became a transit police detective, and Cathy O’Neal, whom the boys considered “beautiful like Brigitte Bardot.” Cathy is seen here at age 13 or 14, around the time she began dating the “coolest” of the gang, Junior Rice. At 14 she got pregnant. Though they were both under the legal age, they married. They later divorced, and Junior became a heroin dealer and user; within a few years, drugs would claim the lives of many in the gang and in the neighbourhood. Years after their divorce, Cathy committed suicide by shotgun.
Davidson would always remain an outsider to the gang, but his working process allowed for intimacy and trust to grow between the gang members and the photographer. By the end of the summer, Davidson realised that he and the Jokers were all considered outsiders in the conformist, materialistic 1950s. “I could see my own repression in them, and I began to feel a connection to their desperation,” he remembered. “I began to feel their isolation and even my own.”
Cleveland Art, Fall 2020
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 61 x 50.8cm (24 x 20 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
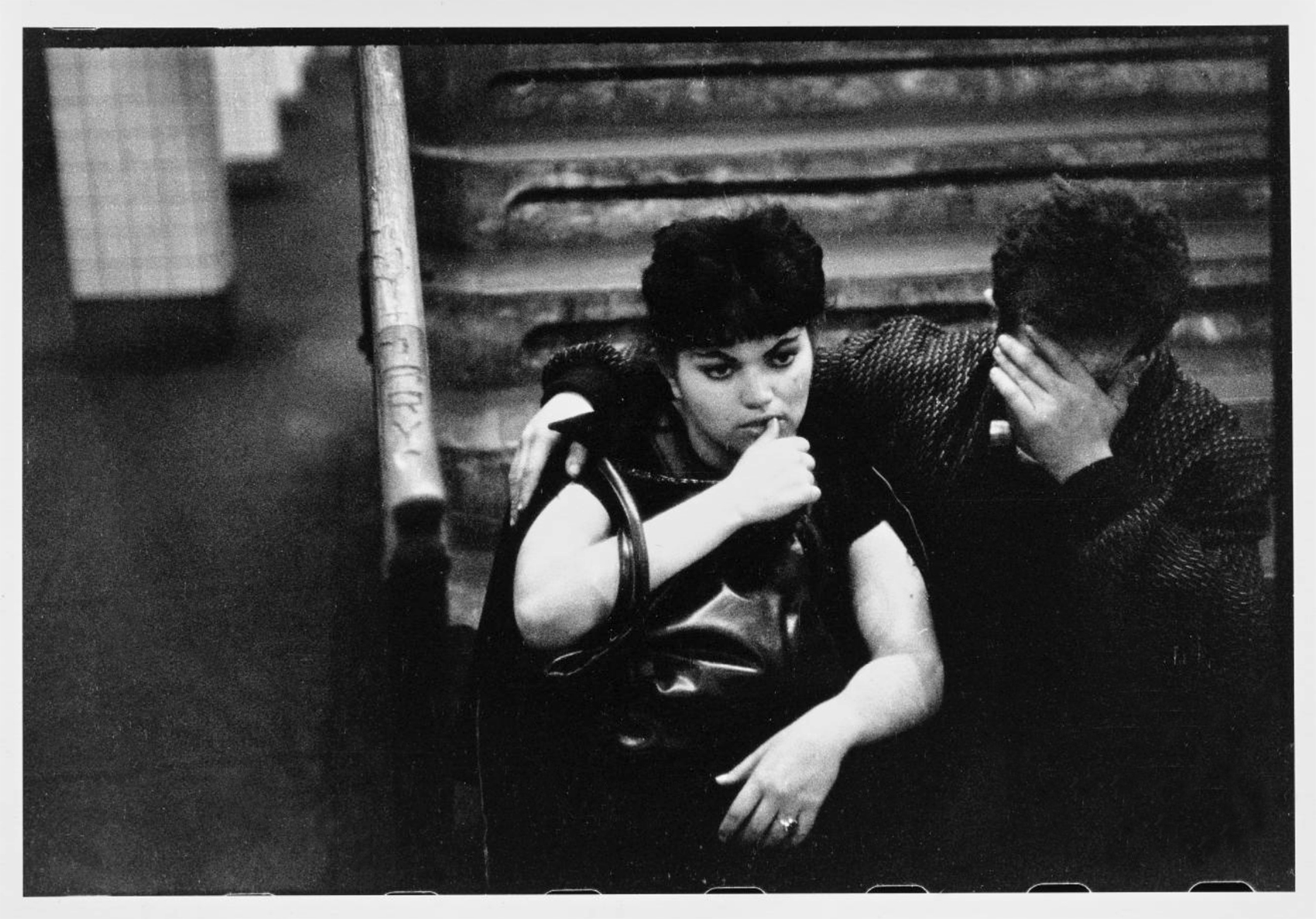
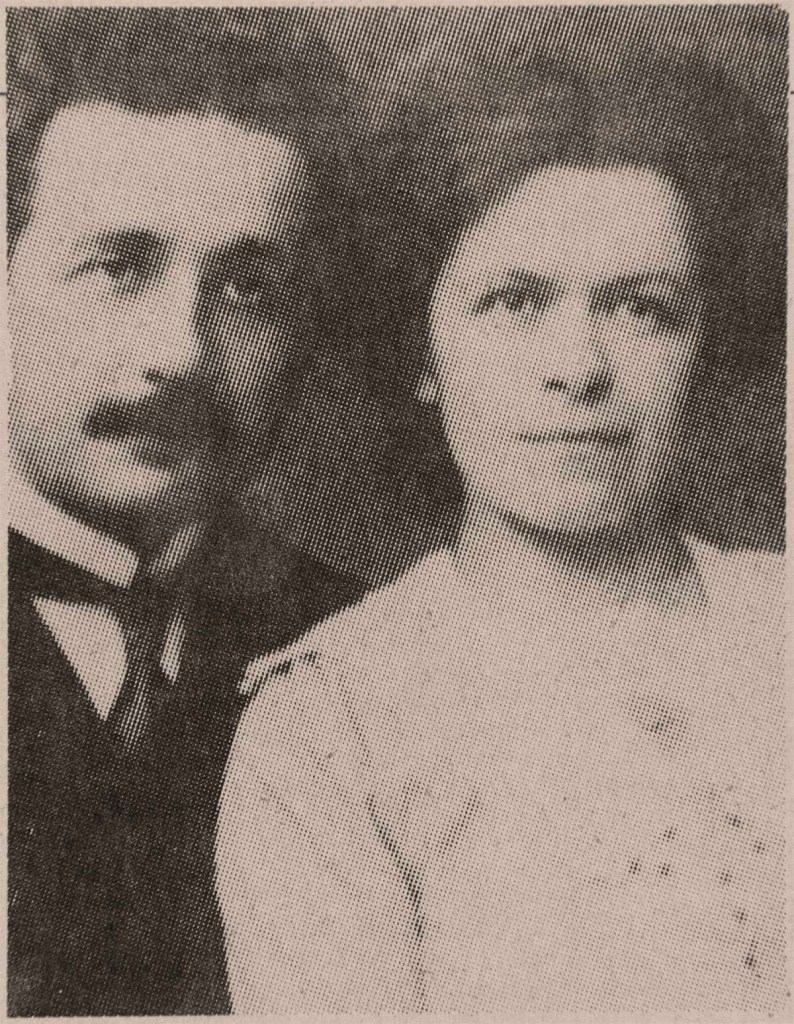
Although most of the gang members’ time was spent in their neighbourhood of Park Slope, Brooklyn, the Jokers sometimes took excursions. Few had access to cars, so most travel was by bus and subway. The subway fare of 15 cents – the equivalent of $1.33 today – would take them anywhere in New York City. Here a gang member and his girlfriend wait for a train on the neighbourhood subway platform. The beach at Coney Island was a favourite summer destination for the gang.
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 20.3 x 25.4cm (8 x 10 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
“We used to hang out in [Brooklyn’s] Prospect Park all the time,” recalled Jokers member Bob Powers. “We did a lot of drinking and sleeping overnight in the park. … The cops with their bats would push us along, tell us to move. We were very defiant. If we moved, we moved ten feet. Then they had to tell us to move another ten feet. We’d kind of like move around in a circle and come back to where we originally started. The cops were mean at that time, but then we weren’t the best of kids either.”
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 13.9 x 17.6cm (5 1/2 x 6 15/16 in.)
Image: 11.4 x 16.9cm (4 1/2 x 6 5/8 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
The Jokers roughhoused and fought among themselves but were not allowed to hurt each other. Real violence was reserved for those in other gangs or occasionally for civilians. “Did we fight with chains and pipes and knives? Yeah,” gang member Bob Powers reminisced years later. “Did people get stabbed? Yeah, people got stabbed. And people got their heads cracked open with bats.”
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 20.3 x 25.4cm (8 x 10 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 27.9 x 35.6cm (11 x 14 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
The gang member making out in the back seat of a car on the way home from Coney Island is Lefty, identifiable by his tattoo. “We always wondered why the girls liked him,” recalled Jokers member Bob Powers. “We never thought he was good-looking, but all the girls loved him. It was amazing.”
Bruce Davidson (American, b. 1933)
Untitled
1959
Gelatin silver print
Paper: 61 x 50.8cm (24 x 20 in.)
Gift of an anonymous donor
© Bruce Davidson/Magnum Photos
Jimmie, an older member of the gang, watched over the younger members with his brother Johnny. In 1998, Jokers member Bob Powers recalled, “Later, the whole family, all six of them … died, wiped out, mostly from drugs. It’s amazing because at this particular time, if you see Jimmie, he’s like the ‘Fonz,’ like James Dean – handsome. He was good-looking, he had the women, and he was always working on cars.”
Cleveland Museum of Art
11150 East Boulevard
Cleveland, Ohio 44106
Opening hours:
Tuesdays, Thursdays, Saturdays, Sundays 10.00am – 5.00pm
Wednesdays, Fridays 10.00am – 9.00pm
Closed Mondays

















































































































































































































![Ilse Bing (German, 1899-1998) '[Rue de Valois, Paris]' 1932 Ilse Bing (German, 1899-1998) '[Rue de Valois, Paris]' 1932](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/ilse-bing-rue-de-valois-paris-1932.jpg?w=804)

![Dora Maar (French, 1907-1997) '[Woman and Child in Window, Barcelona]' 1932-1934 Dora Maar (French, 1907-1997) '[Woman and Child in Window, Barcelona]' 1932-1934](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/dora-maar-woman-and-child-in-window-barcelona.jpg?w=768)












































































































































































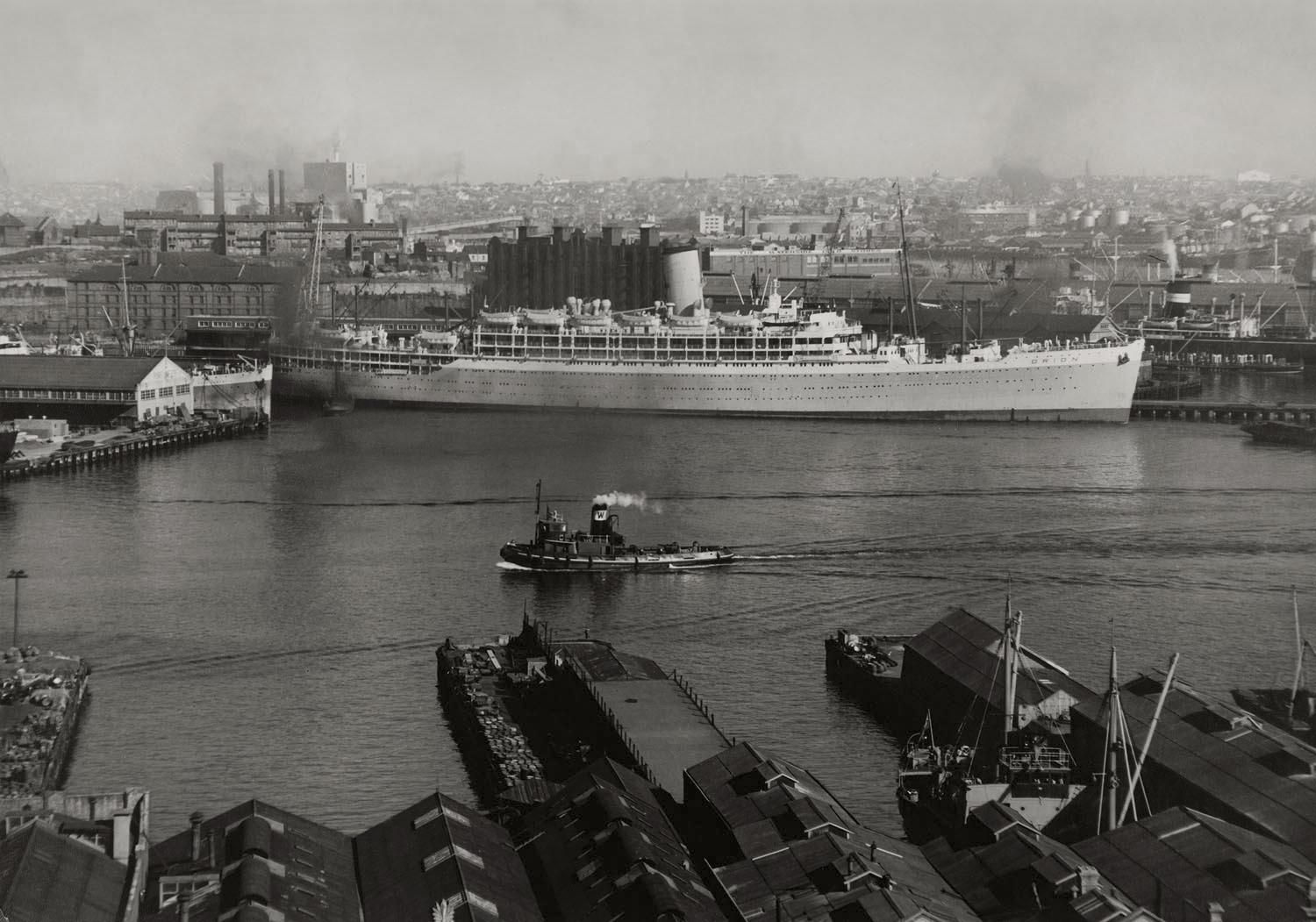
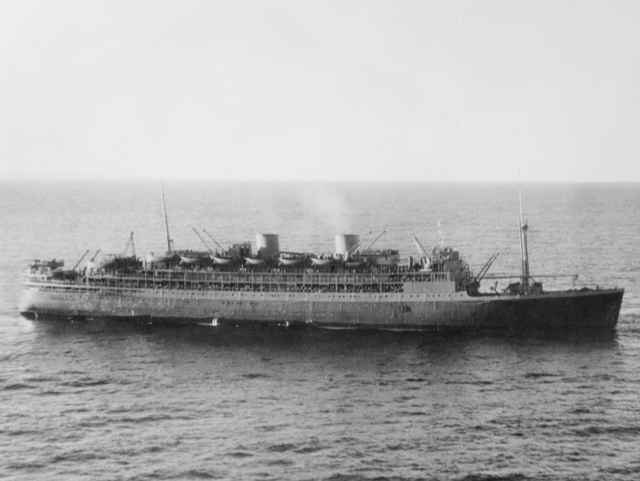
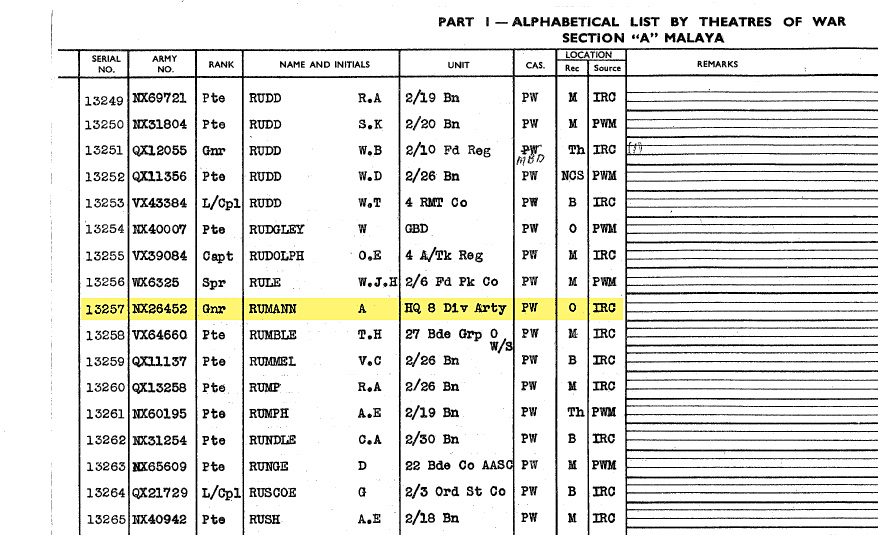
![Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941 Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-h.jpg?w=1024)
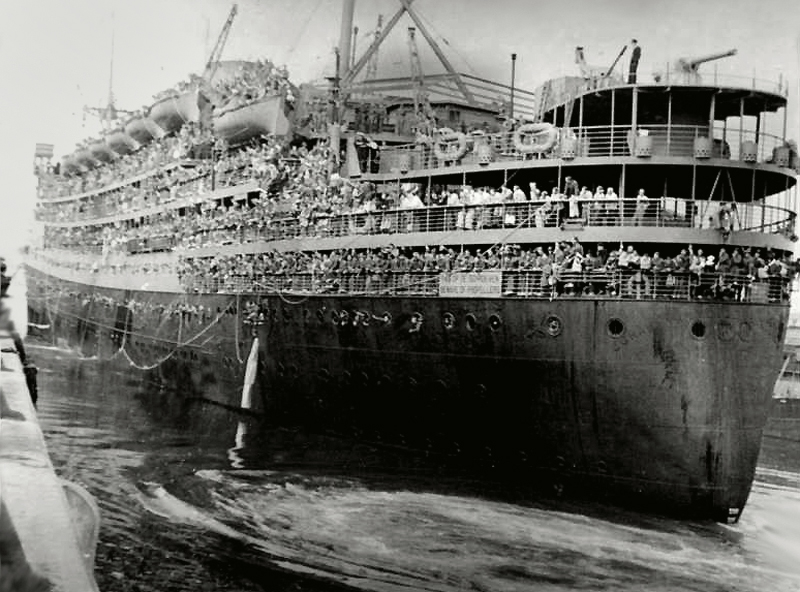


![Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941 Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-c.jpg?w=1024)
![Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941 Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-d.jpg?w=1024)
![Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941 (detail) Andrew Rumann (Australian, 1905-1974) 'Untitled [Departure from Circular Quay, Sydney for Fremantle and Singapore]' 1941 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-d-detail.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Encampment]' 1942-45 Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Encampment]' 1942-45](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-j.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Women standing in front of an American Red Cross sign]' 1942-45 Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Women standing in front of an American Red Cross sign]' 1942-45](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-i.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Post Exchange No. 2]' 1942-45 Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Post Exchange No. 2]' 1942-45](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-k.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Post Exchange No. 2]' 1942-45 (detail) Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Post Exchange No. 2]' 1942-45 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-k-detail.jpg?w=1022)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Taking out the rubbish]' 1942-45 Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Taking out the rubbish]' 1942-45](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-e.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [BKC*23]' 1942-45 Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [BKC*23]' 1942-45](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-f.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [BKC*23]' 1942-45 (detail) Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [BKC*23]' 1942-45 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-f-detail.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Transportation Corps US Army BKC*23]' 1942-45 Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Transportation Corps US Army BKC*23]' 1942-45](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-g.jpg?w=1024)

![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Transportation Corps US Army BKC*23]' 1942-45 (detail) Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Transportation Corps US Army BKC*23]' 1942-45 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-g-detail.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Embarkation]' 1942-45 Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Embarkation]' 1942-45](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-a.jpg?w=1024)
![Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Embarkation]' 1942-45 (detail) Anonymous photographer (Australian) 'Untitled [Embarkation]' 1942-45 (detail)](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/embarkation-a-detail.jpg?w=1024)
You must be logged in to post a comment.