Exhibition dates: 21st February – 29th June 2014
Exhibition artists
Public Intimacy presents
~ Photography by Ian Berry, Ernest Cole, David Goldblatt, Terry Kurgan, Sabelo Mlangeni, Santu Mofokeng, Billy Monk, Zanele Muholi, Lindeka Qampi, Jo Ractliffe, and Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
~ Video works by William Kentridge, Donna Kukama, Anthea Moys, and Berni Searle
~ Painting and sculpture by Nicholas Hlobo and Penny Siopis
~ Puppetry by Handspring Puppet Company
~ Publications, prints, graphic works, and public interventions by Chimurenga, ijusi (Garth Walker), Anton Kannemeyer, and Cameron Platter
~ Performances by Athi-Patra Ruga, Kemang Wa Lehulere, and Sello Pesa and Vaughn Sadie with Ntsoana Contemporary Dance Theatre

Santu Mofokeng (South Africa, 1956-2020)
Opening Song, Hand Clapping and Bells
1986
From the series Train Church
Pigment print
9 13/16 x 13 3/4 in. (25 x 35cm)
© Santu Mofokeng
Continuing my fascination with South African art and photography, here is another exhilarating collection of work from an exhibition jointly arranged between SFMOMA and the Yerba Buena Center for the Arts, San Francisco. This art has so much joy, life, movement and “colour”. I particularly like The Future White Women of Azania series by Athi-Patra Ruga, who presented his work at the 55th Venice Biennale in the African pavilion. Thank god not another rehashed colonial image, even though he is working with the tropes of myth and the history of Africa as a contemporary response to the post-apartheid era.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
Many thankx to SFMOMA and Yerba Buena Center for the Arts for allowing me to publish the installation photographs in the posting. Most of the other photographs were gathered from the internet. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
“Disrupting expected images of South Africa, the 25 contemporary artists and collectives featured in Public Intimacy eloquently explore the poetics and politics of the everyday. This collaboration with Yerba Buena Center for the Arts presents pictures from SFMOMA’s collection of South African photography alongside works in a broad range of media, including video, painting, sculpture, performance, and publications – most made in the last five years, and many on view for the first time on the West Coast. Coinciding with the 20th anniversary of democracy in South Africa, Public Intimacy reveals the nuances of human interaction in a country still undergoing significant change, vividly showing public life there in a more complex light.”
Text from the SFMOMA website

Santu Mofokeng (South Africa, 1956-2020)
Leading in Song, Johannesburg – Soweto Line
1986
From the series Train Church
Pigment print
9 13/16 x 13 3/4 in. (25 x 35cm)
© Santu Mofokeng

Santu Mofokeng (South Africa, 1956-2020)
Hands in Worship, Johannesburg – Soweto Line
1986
From the series Train Church
Pigment print
9 13/16 x 13 3/4 in. (25 x 35cm)
© Santu Mofokeng
These images, by the South African photographer Santu Mofokeng, ostensibly depict scenes of segregated transport during apartheid. Yet in their composition they evoke something more: the rhythms and textures of everyday life. Taken from within and among a crowd of commuters, the pictures seem to sway with the velocity of the train carriage. Shards of light blur the edges of figures, interplaying with shifting shadows as passengers move in unison. Titled “Train Church,” Mofokeng’s series was made during a few weeks in 1986, and in South Africa it became veritably synonymous with his name. Mofokeng, who died in January, at the age of sixty-three, was a photographer whose body of work – both images and text – waded through themes of history and land, memory and spirituality, and helped shape the course of South African photography.
Oluremi C. Onabanjo. “How Santu Mofokeng Shaped South African Photography,” on The New Yorker website February 24, 2020 [Online] Cited 10/04/2021.

Santu Mofokeng (South Africa, 1956-2020)
Supplication, Johannesburg – Soweto Line
1986
From the series Train Church
Pigment print
9 13/16 x 13 3/4 in. (25 x 35cm)
© Santu Mofokeng
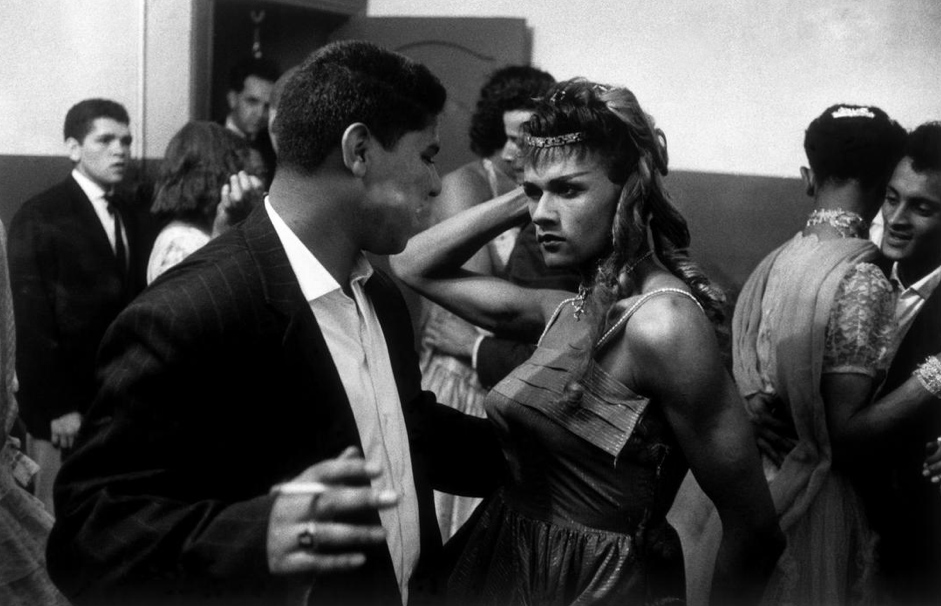

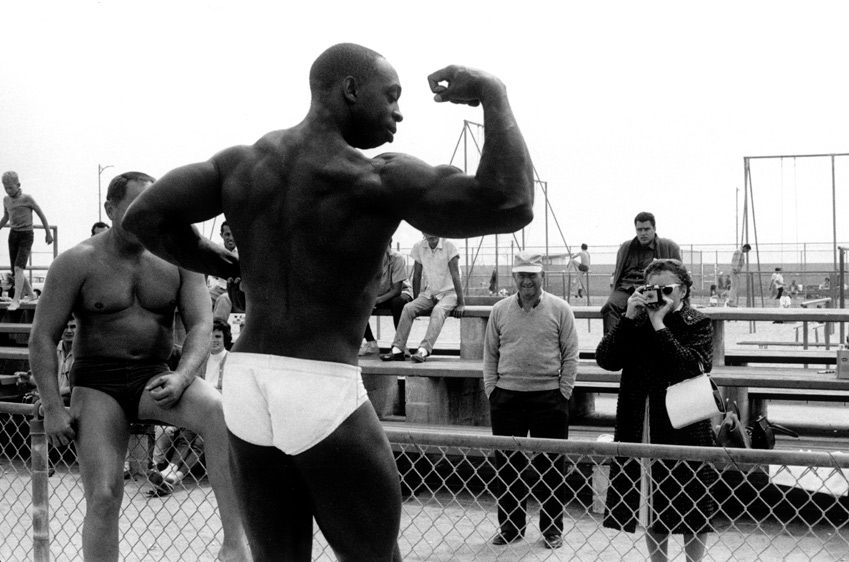
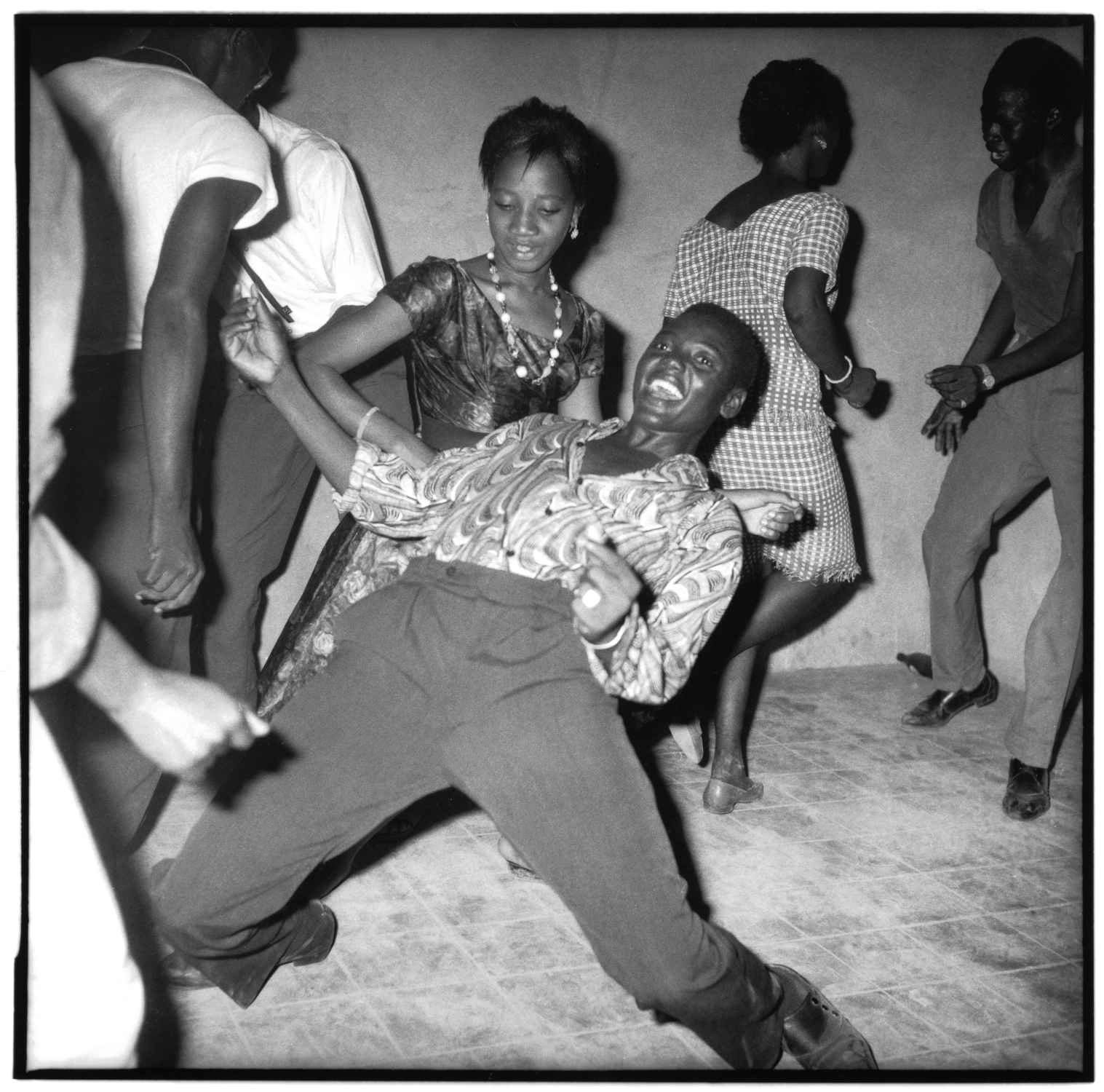
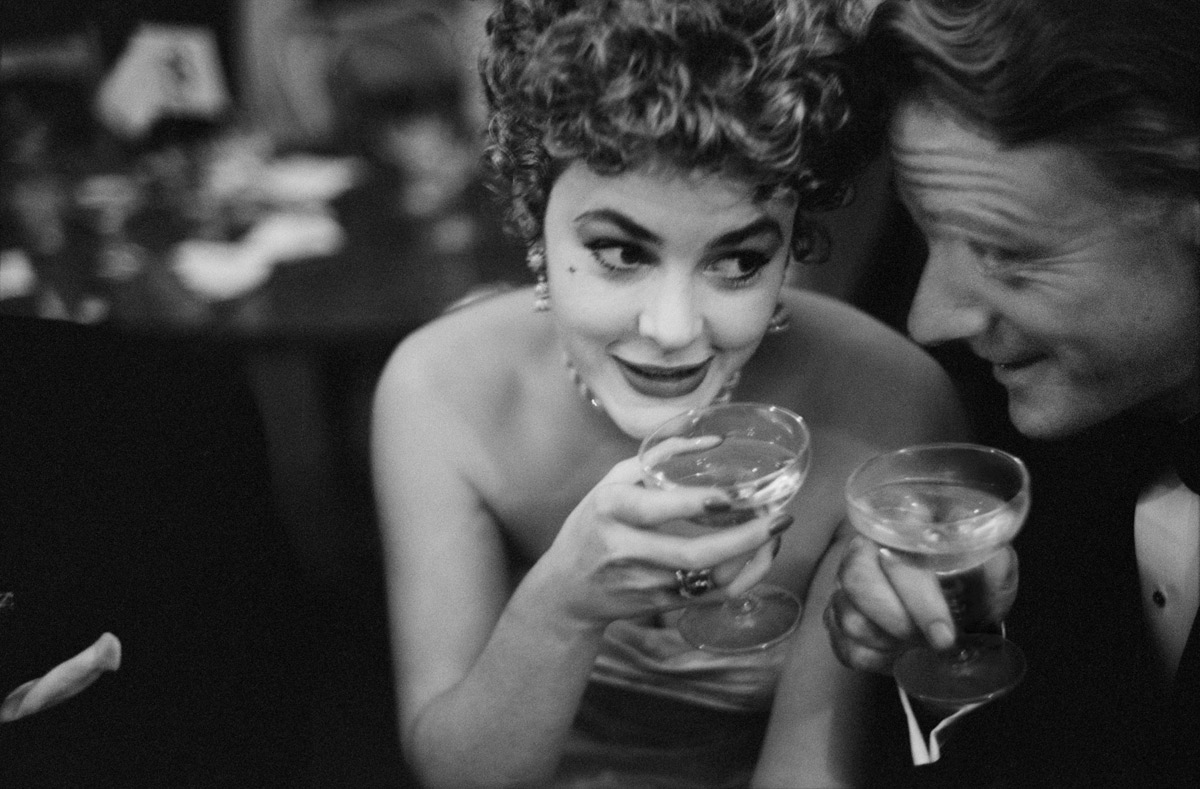
Ian Berry (British, b. 1934)
Guests at a ‘moffie’drag party
Cape Town, South Africa, 1960
Silver gelatin photograph
Ian Berry was born in Lancashire, England. He made his reputation in South Africa, where he worked for the Daily Mail and later for Drum magazine. He was the only photographer to document the massacre at Sharpeville in 1960, and his photographs were used in the trial to prove the victims’ innocence.
He moved to South Africa in 1952, where he soon taught himself photography. He worked under the tutelage of Roger Madden, a South African photographer who had been an assistant to Ansel Adams. After some time as an amateur photographer, Berry began photographing communities and weddings. During this period he met Jürgen Schadeberg, also a European immigrant and photographer. Schadeberg was offered a position with the new African Sunday newspaper eGoli but declined, suggesting Berry apply for the position instead. After working there only 10 months, the newspaper closed, and Berry began working for the Benoni City Times, but he soon became more interested in freelance work.
Berry returned to Great Britain and traveled for some time but returned to South Africa in the early 1960s and worked for the Daily Mail. Later Tom Hopkinson, previously editor of the British Picture Post, hired Berry to work for Drum magazine. He was in Sharpeville on 21 March 1960, when a peaceful protest turned violent, leading to the deaths of 69 people and the wounding of 178 others by police. There were no other photographs documenting the events, and Berry’s were entered into evidence in the court proceedings proving that the victims had done nothing wrong. Berry was invited by Henri Cartier-Bresson to join Magnum Photos in 1962 when he was based in Paris; five years later he became a full member. In 1964 he moved to London and began working for Observer Magazine. He has since traveled the globe, documenting social and political strife in China, Republic of Congo, Czechoslovakia, Ethiopia, Israel, Ireland, Vietnam, and the former Soviet Union. He has contributed to publications including Esquire, Fortune, Geo, Life, National Geographic, Paris-Match, and Stern.
Text from the Wikipedia website
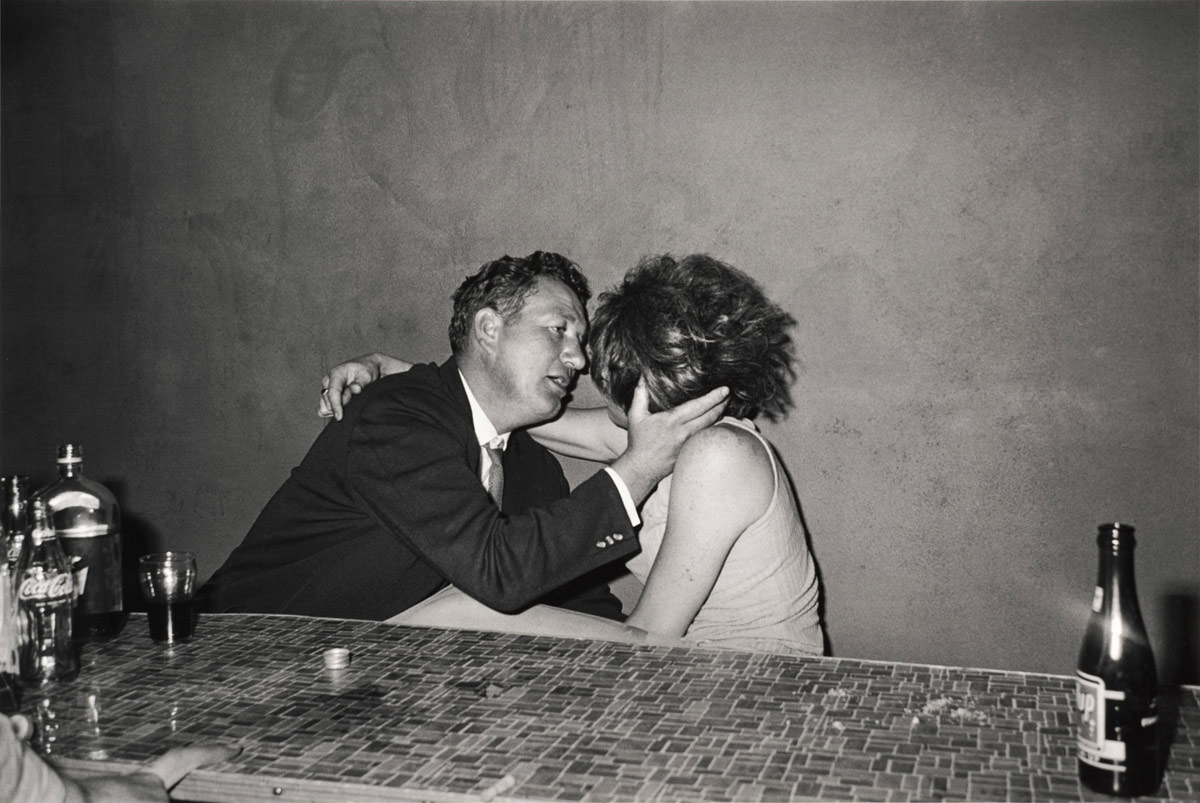

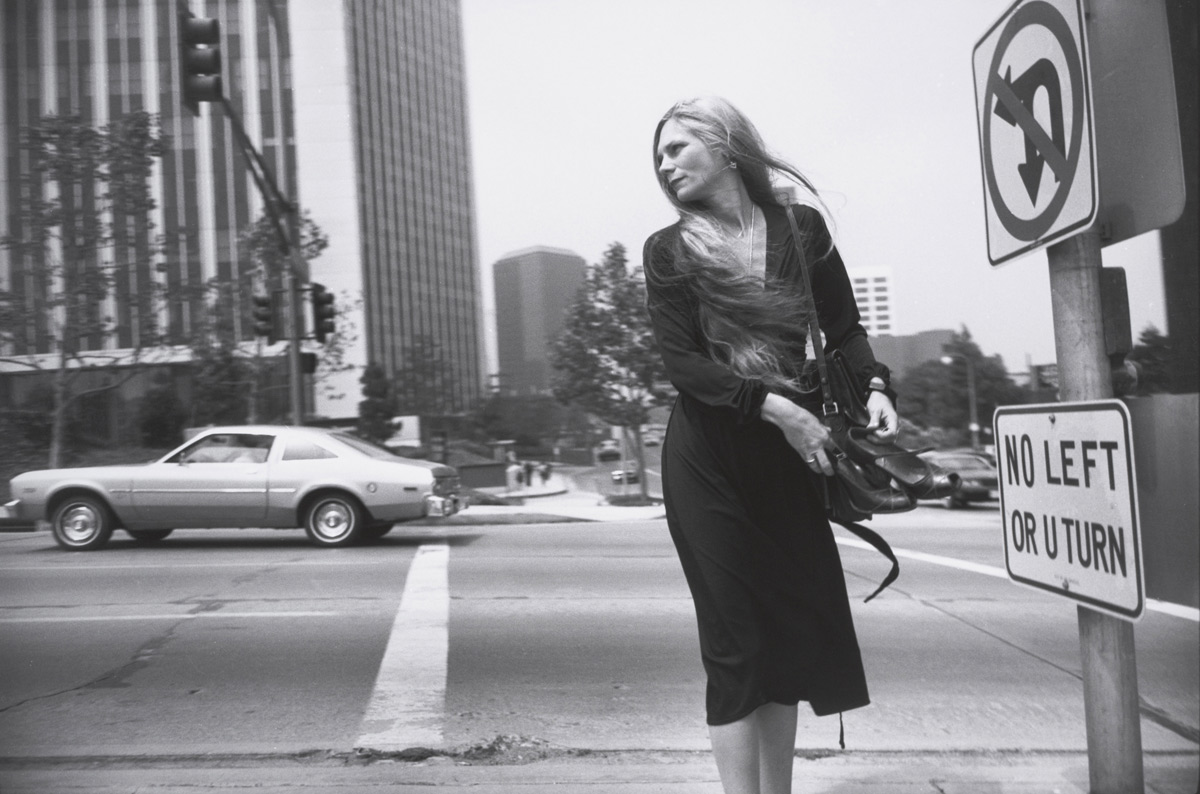
Billy Monk (South African, 1937-1982)
The Catacombs, 30 September 1967
1967, printed 2011
Gelatin silver print
10 1/16 x 14 15/16 in. (25.56 x 37.94 cm)
Collection SFMOMA, Accessions Committee Fund purchase
© Estate of Billy Monk
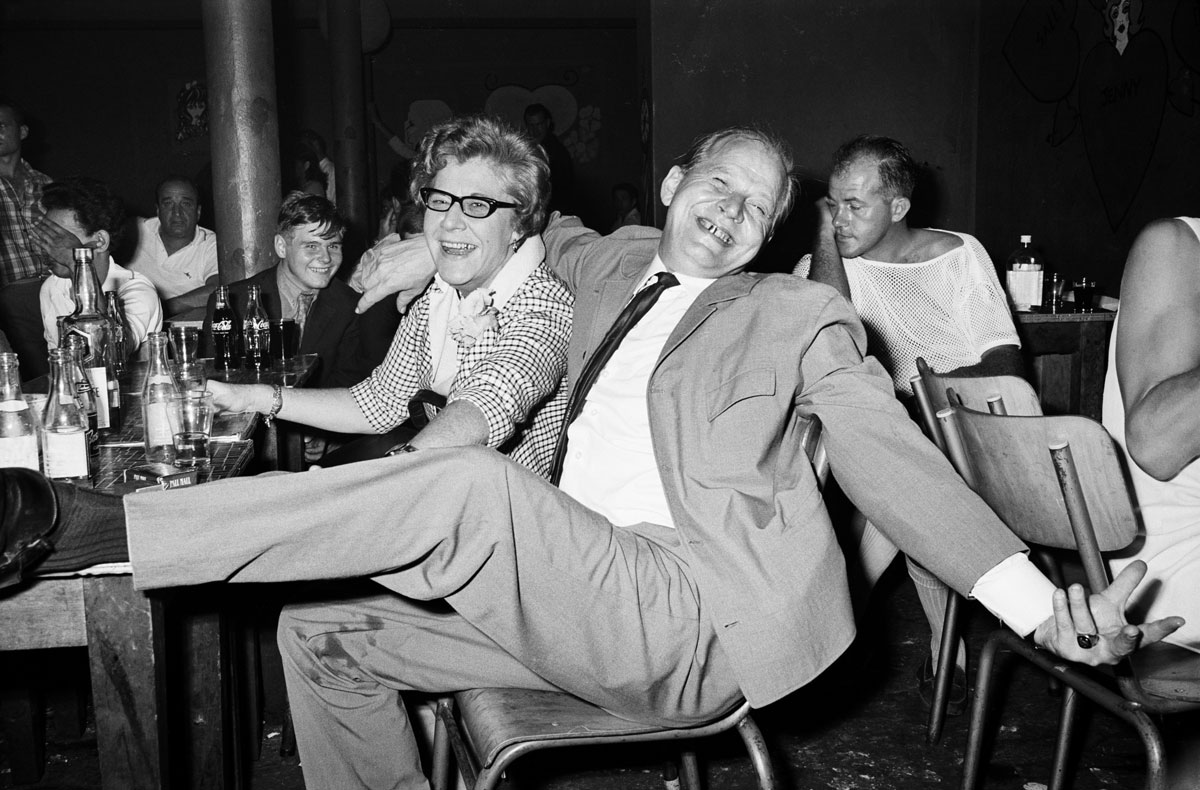

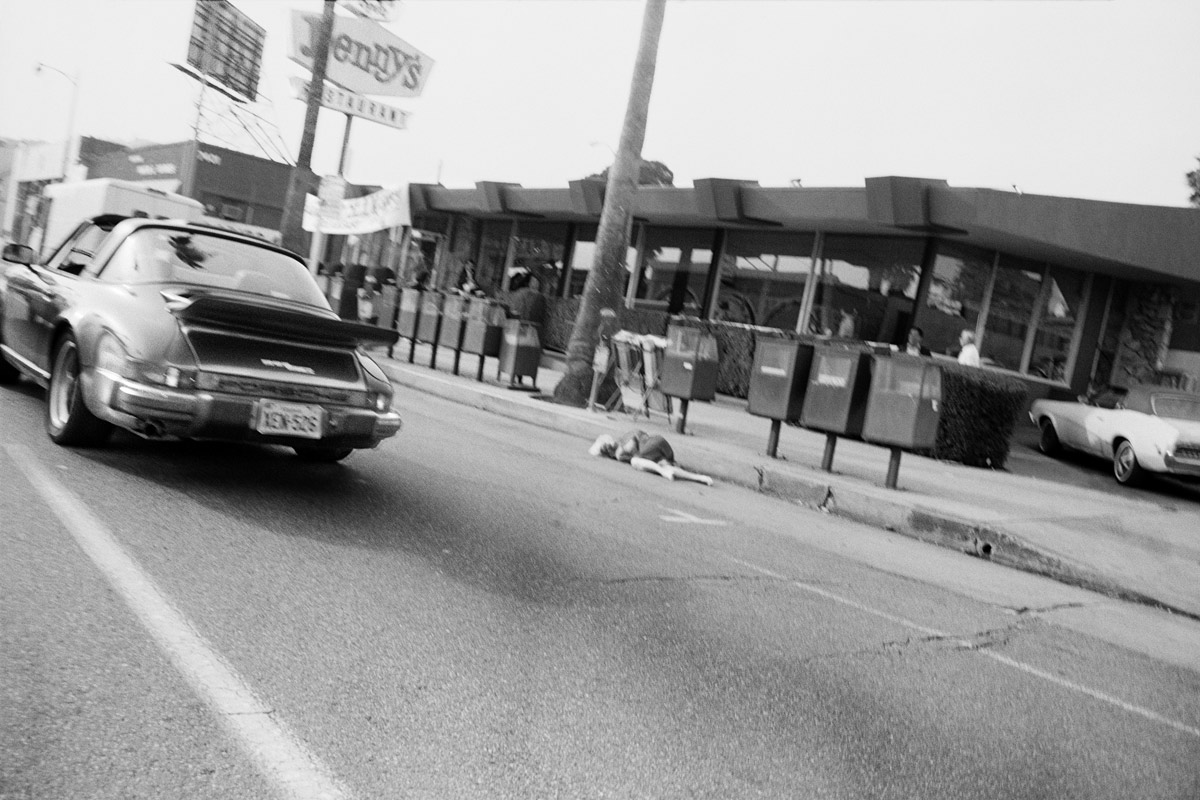
Billy Monk (South African, 1937-1982)
The Catacombs, 5 February 1968
1968, printed 2011
Gelatin silver print
11 x 16 in. (27.94 x 40.64cm)
Courtesy of Stevenson, Cape Town and Johannesburg
© Estate of Billy Monk
William John Monk (died 31 July 1982) was a South African, known for his photographs of a Cape Town nightclub between 1967 and 1969, during apartheid. In 2012 a posthumous book was published, Billy Monk: Nightclub Photographs. …
When Monk’s work as a bouncer did not work out he took up photography. Still working in The Catacombs, he began to make his living taking pictures of the diverse clientele in a seedy bar. He used a Pentax camera, with a 35 mm focal-length lens, a small flash and Ilford FP4 film. Monk stopped taking pictures in 1969. His photographs show a variety of the underbelly of Cape Town life at the time – ranging from old men with young wives and gay couples, to midgets and mixed race relationships, he shows a side of life under apartheid that is rarely seen elsewhere.
Discovery of his work
Monk’s work was discovered in 1979 by Jac de Villiers, when he moved into Monk’s old studio. Not only were they already well constructed by the photographer, they were also impeccably annotated with dates and names, which made curation a simple and enjoyable process. The first exhibition of Monk’s work took place at the Market Gallery in Johannesburg in 1982 – and although Monk could not attend the event it was subject to much critical acclaim.
Apartheid
Monk was working during apartheid in South Africa – a time when the colour of your skin was indicative of where you could live, work, who you could marry, and where you could drink. The underground lifestyle of The Catacombs allowed for dissent. Monk chose to take pictures originally as a way of making money, by selling them to his clients.
His photographs reveal a variety of clientele. Some are sloppy, some are neat and put together. Many of the women are heavily made up with short dresses, and almost all the photographs are highly sexually charged. The photographs reveal much of what was not allowed under apartheid rule – specifically a variety of same sex and mixed race couples.
Text from the Wikipedia website
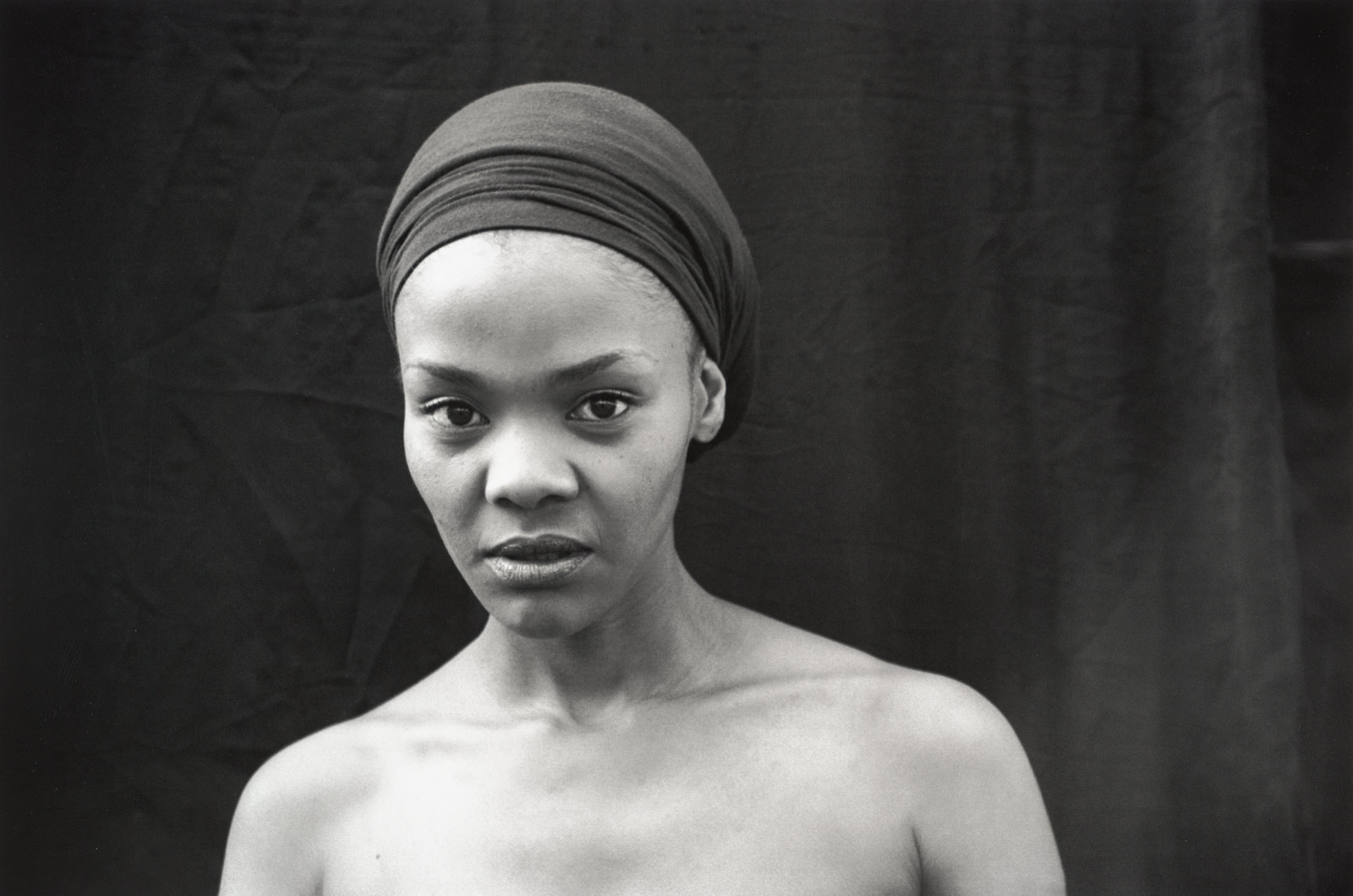

Zanele Muholi (South Africa, b. 1972)
Nomonde Mbusi, Berea, Johannesburg
2007
From the Faces and Phases series
Gelatin silver print
23 13/16 in. x 34 1/16 in. (60.5 cm x 86.5cm)
Courtesy of the artist and Stevenson, Cape Town and Johannesburg
© Zanele Muholi
Zanele Muholi, born 1972
Muholi’s work addresses the reality of what it is to be LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender) in South Africa. She identifies herself as a visual activist, dealing with issues of violation, violence and prejudice that she and her community face, despite South Africa’s progressive constitution.
In Faces and Phases, she sets out to give visibility to black lesbians and to celebrate the distinctiveness of individuals through the traditional genre of portraiture. The portraits are taken outdoors with a hand-held camera to retain spontaneity and often shown in a grid to highlight difference and diversity. In the series Beulahs, she shows young gay men, wearing Zulu beads and other accessories usually worn by women, who invert normative gender codes in both costume and pose. At the same time her photographs evoke tourist postcards and recycled stereotypes of Africans and recall traditional anthropological and ethnographic iconography.
“Faces and Phases, is a group of black and white portraits that I have been working on from 2006 until now – it has become a lifetime project. The project is about me, the community that I’m part of. I was born in the township: I grew up in that space. Most of us grew up in a household where heterosexuality was the norm. When you grow up, you think that the only thing that you have to become as a maturing girl or woman is to be with a man; you have to have children, and also you need to have lobola or “bride price” paid for you. For young men, the expectation for them is to be with women and have wives and procreate: that’s the kind of space which most of us come from. We are seen as something else by society – we are seen as deviants. We’re not going to be here forever, and I wanted to make sure that we leave a history that is tangible to people who come after us.”
Zanele Muholi, interviewed by Tamar Garb, South Africa, 2010.
Text from the V&A website

David Goldblatt (South Africa, 1930-2018)
Woman smoking, Fordsburg, Johannesburg
1975
Pigment inkjet print
23 5/8 in. x 29 1/2 in. (60 cm x 75cm)
Collection SFMOMA, Accessions Committee Fund purchase
© David Goldblatt
David Goldblatt HonFRPS (29 November 1930 – 25 June 2018) was a South African photographer noted for his portrayal of South Africa during the period of apartheid. After apartheid had ended he concentrated more on the country’s landscapes. What differentiates Goldblatt’s body of work from those of other anti-apartheid artists is that he photographed issues that went beyond the violent events of apartheid and reflected the conditions that led up to them. His forms of protest have a subtlety that traditional documentary photographs may lack: “[M]y dispassion was an attitude in which I tried to avoid easy judgments. … This resulted in a photography that appeared to be disengaged and apolitical, but which was in fact the opposite.”
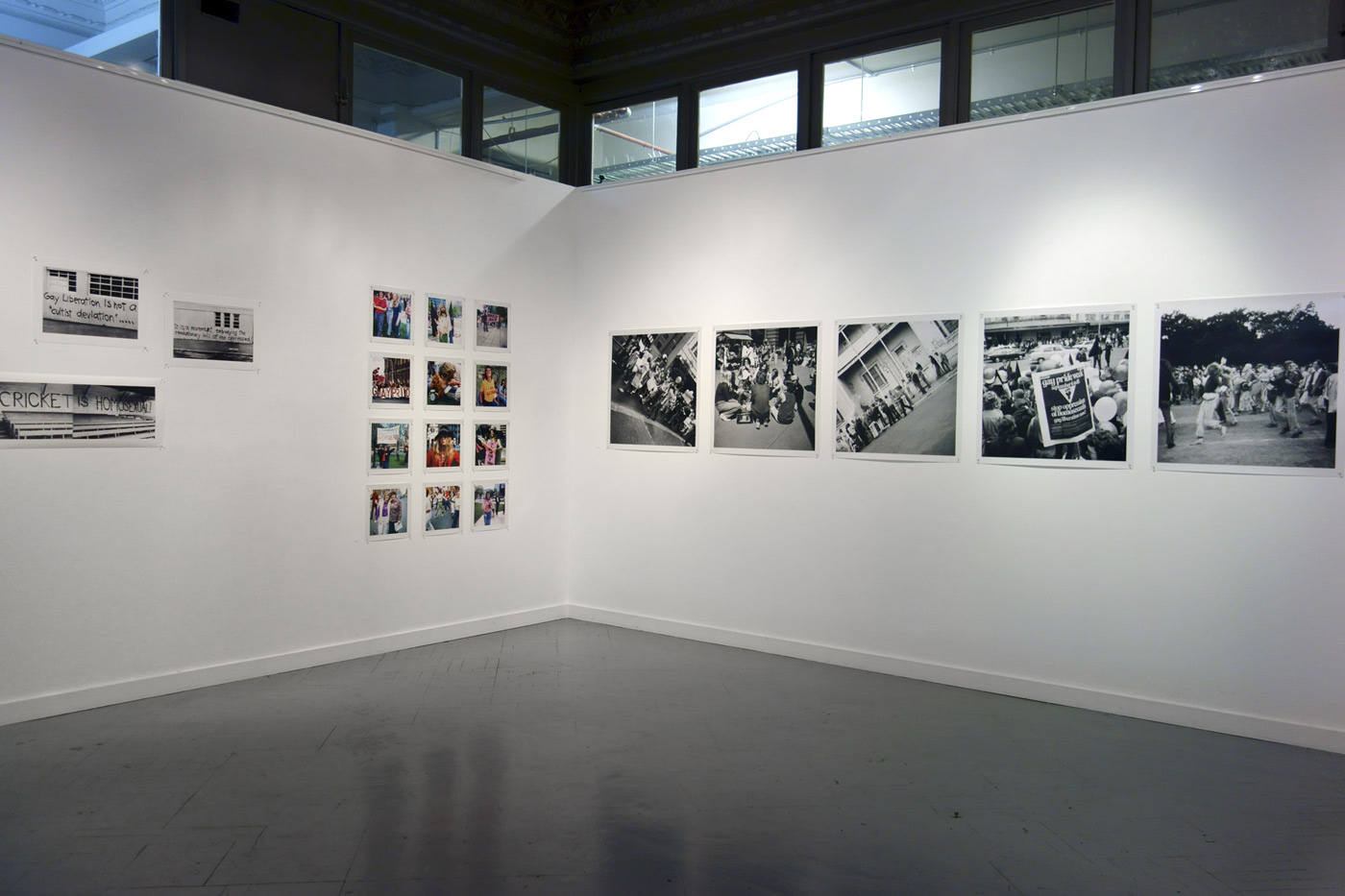
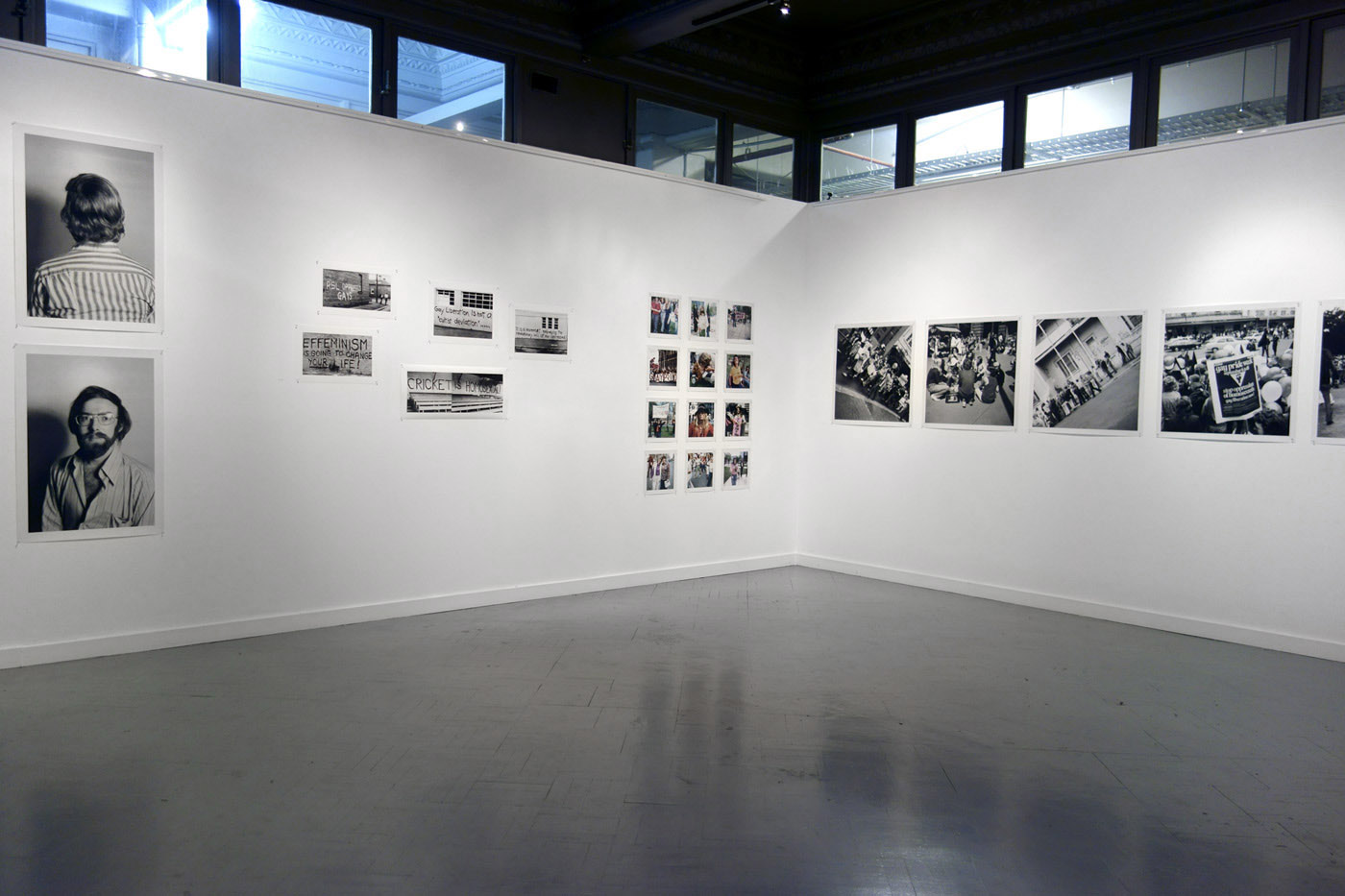
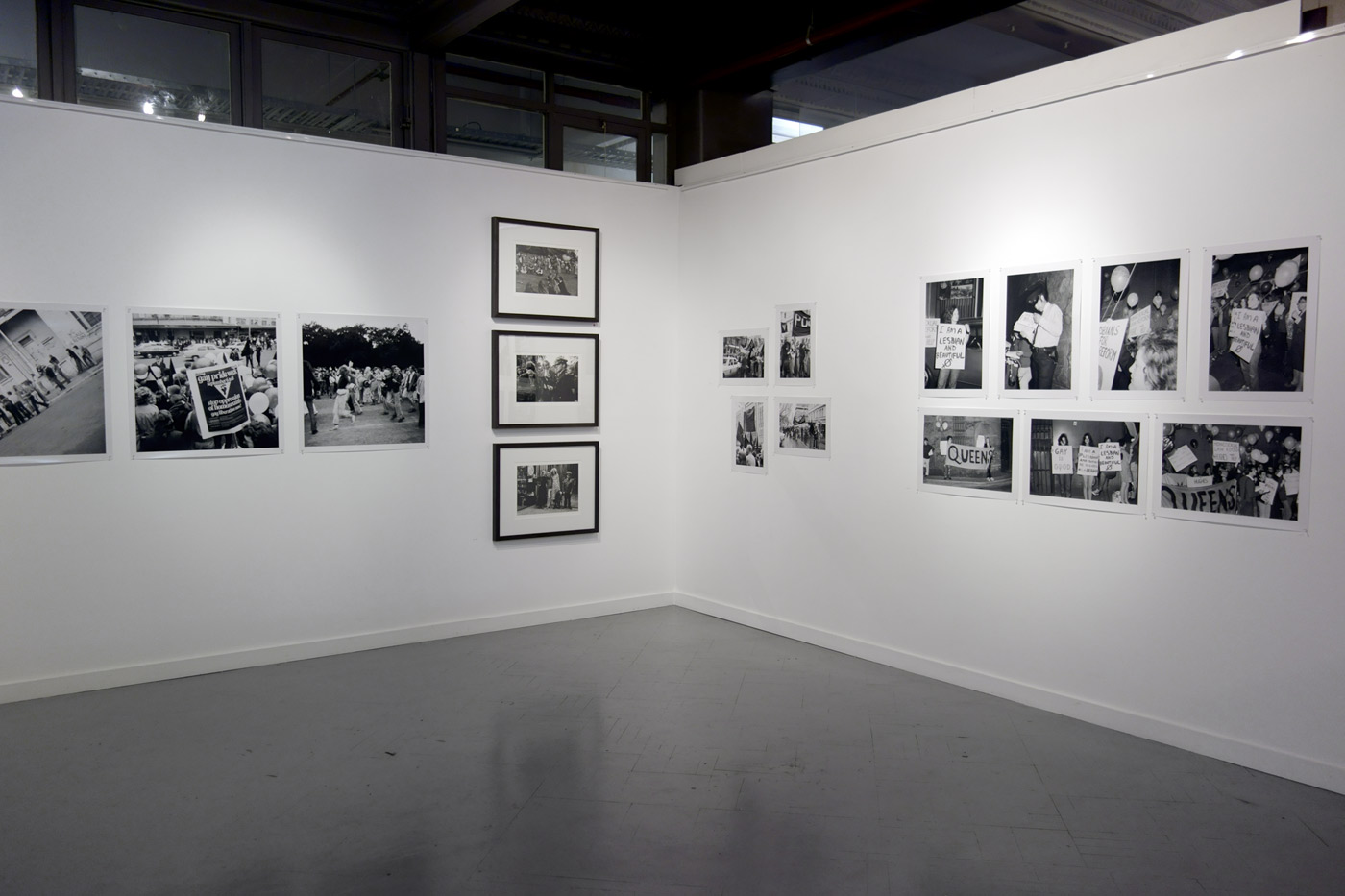
Jointly organised by the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA) and Yerba Buena Center for the Arts (YBCA), Public Intimacy: Art and Other Ordinary Acts in South Africa brings together 25 artists and collectives who disrupt expected images of a country known through its apartheid history. The exhibition features an arc of artists who look to the intimate encounters of daily life to express the poetics and politics of the “ordinary act,” with work primarily from the last five years as well as photographic works that figure as historical precedents. On view at YBCA February 21 through June 29, 2014, Public Intimacy presents more than 200 works in a wide range of mediums, many of them making U.S. or West Coast debuts.
The exhibition joins SFMOMA’s important and growing collection of South African photography with YBCA’s multidisciplinary purview and continued exploration of the Global South. Significant documentary photography is paired with new photographs and work in other mediums, including video, painting, sculpture, performance, and publications, to reveal the multifaceted nuances of everyday life in a country still undergoing significant change. Coinciding with the 20th anniversary of democracy in South Africa, Public Intimacy looks at the way artists imagine present and future possibilities in South Africa. A new orientation emerges through close-up views of street interactions, portraiture, fashion and costume, unfamiliar public actions, and human imprints on the landscape.
The exhibition’s three curators – Betti-Sue Hertz, director of visual arts at YBCA; Frank Smigiel, associate curator of public programs at SFMOMA; and Dominic Willsdon, Leanne and George Roberts Curator of Education and Public Programs at SFMOMA – developed the show after visits to South Africa, where they met with artists, curators, and critics. The exhibition – and a companion publication to be published in fall 2014 – grew out of this research.
“Although South Africa’s political history remains vital to these artists and is important for understanding their work, Public Intimacy offers a more subtle view of the country through personal moments,” said Hertz. “It goes against expectations in order to reveal the smaller gestures and illuminate how social context has affected artists and how they work.”
“The familiar image of contemporary South Africa as a place of turmoil is, of course, not the whole story,” added Willsdon. “The art in this exhibition restages how those violent incidents fit in the broader realm of human interactions – a way of showing public life there in a more complex light.”
“Another central aspect of the exhibition is live performance,” said Smigiel. “Three major live works will unfold both in and outside the gallery context, offering a way to situate and reframe San Francisco through the lens of what artists are producing in South Africa.”
Public Intimacy is part of SFMOMA’s collaborative museum exhibitions and extensive off-site programming taking place while its building is temporarily closed for expansion construction through early 2016. As neighbours across Third Street in San Francisco, YBCA and SFMOMA have partnered in the past on various performance and exhibition projects, but Public Intimacy represents the deepest collaboration of shared interests to date between the two institutions. It also brings together SFMOMA’s approach to curating live art and YBCA’s multidisciplinary interest in exhibitions, social practice, and performances.
Exhibition highlights
While the exhibition explores new approaches to daily life in post-apartheid South Africa, it also makes visible the continued commitment of artists to activism and contemporary politics. Beginning with photographs from the late 1950s and after, the exhibition includes vital moments in the country’s documentary photography – from Ian Berry’s inside look at an underground drag ball to Billy Monk’s raucous nightclub photos – each capturing a moment of celebration within different social strata of South African society. Ernest Cole’s photographs of miners’ hostels and bars and Santu Mofokeng’s stirring photographs of mobile churches on commuter trains reveal everyday moments both tender and harsh.
David Goldblatt’s photographs depict the human landscape in apartheid and after, providing the genesis of the idea of “public intimacy.” Over decades of photographs in urban, suburban, and rural locations, Goldblatt has chronicled the changing nature of interpersonal engagement in South Africa. At the same time, they provide a historical backdrop and visual precedent for other artists in the exhibition, including Zanele Muholi and Sabelo Mlangeni.
Muholi has won several awards for her powerful photographic portraits as well as her activism on behalf of black lesbians in South Africa. Although best known for her photographs – in particular her Faces and Phases series – Muholi continuously experiments with an expanded practice including documentary film, beadwork, text, and her social-action organisation Inkanyiso, which gives visibility to conditions facing lesbians of colour in her country. “Sexual politics has been looked at less than racial politics in South Africa, but in many ways, the two have always been intertwined,” said Willsdon.
Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse bring another perspective to the upheavals of life in the city of Johannesburg with works from their Ponte City (2008-10) series, comprised of photographs, video, and a publication offering various views of this centrally located and iconic 54-story building. The works illustrate the struggles facing many native and immigrant South Africans in the years following the dissolution of apartheid, including stalled economic growth and social opportunities.
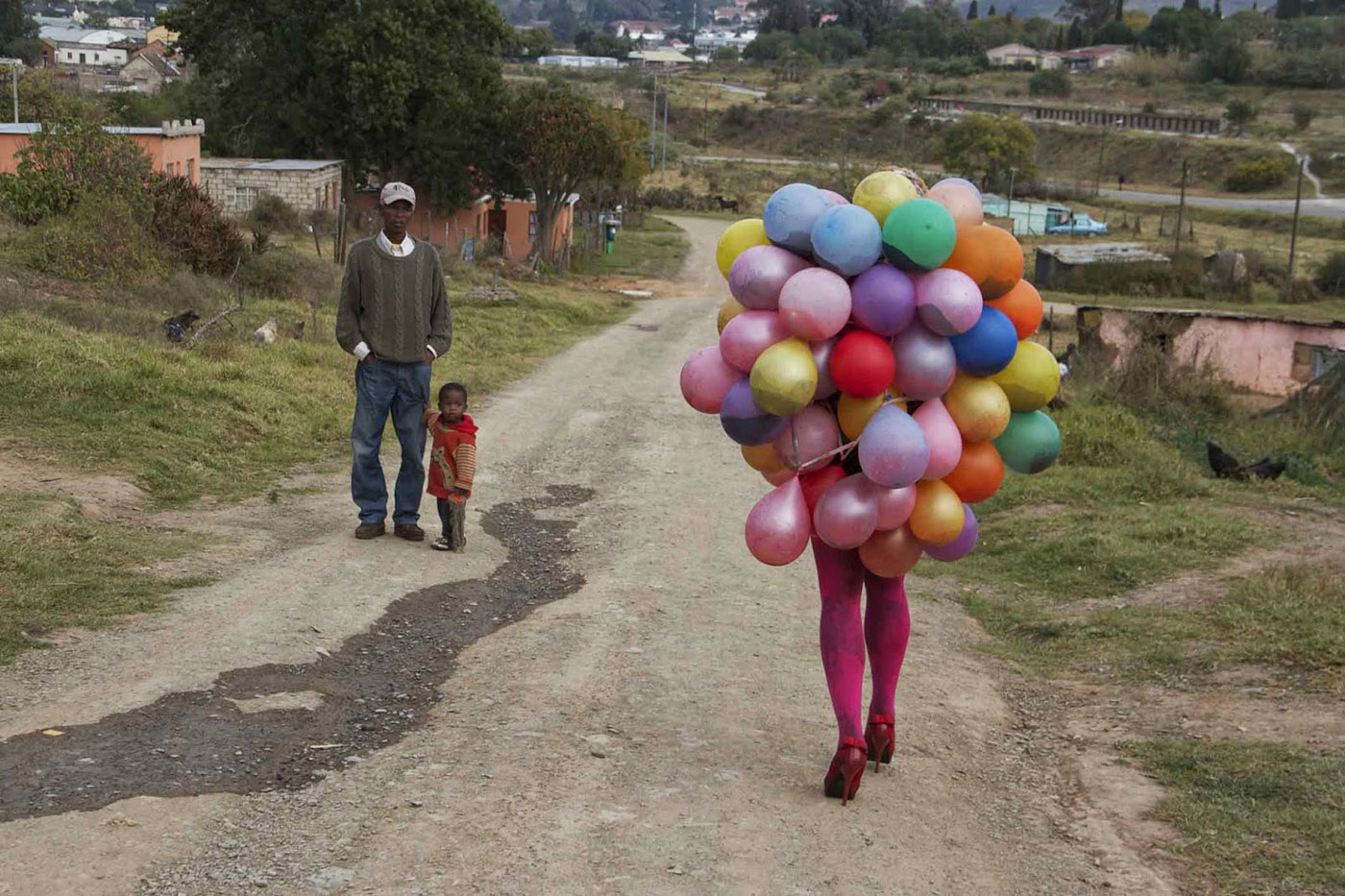
In contrast to the daily realities pictured in photographic works in the exhibition, Athi-Patra Ruga’s ongoing performance series The Future White Women of Azania (2010-present) features fantastical characters – usually played by the artist – whose upper bodies sprout colourful balloons while their lower bodies pose or process in stockings and high heels. Ruga’s Azania is a changing utopia, and Smigiel notes the shift: “The balloons are filled with liquid, and as the figure moves through the streets, they start popping, so the character dissolves and reveals a performer, and the liquid spills out and into a rather sloppy line drawing.” A new iteration of the series, The Elder of Azania, will premiere in the YBCA Forum during the exhibition’s opening weekend.
Chimurenga, an editorial collective working at the intersection of pan-African culture, art, and politics produces publications, events, and installations. Founded in 2002 by Ntone Edjabe, the collective has created the Chimurenga Library, an online archiving project that profiles independent pan-African paper periodicals from around the world. Expanding upon this concept, their presence in Public Intimacy will have two elements: a text and media resource space in YBCA’s galleries and an intervention at the San Francisco Public Library main branch that will explore the history of pan-African culture in the Bay Area, scheduled to open in late May.
Providing one of the most personally vulnerable moments in the exhibition, Penny Siopis’s series of 90 small paintings on enamel, Shame (2002), provokes a visceral reaction. With red paint reminiscent of blood and bruises, Siopis mixes colour and text in an attempt to convey emotion rather than narrative. While she is interested in the guilt and embarrassment most frequently associated with shame, she also looks at the possibility for empathy that emerges from traumatic experiences.
In all of these works, explains Hertz, “We are looking at how art and activism align, but we’re also interested in how politics is embedded in less obviously political practices, such as Sabelo Mlangeni’s photographs of mining workers’ hostels, Penny Siopis’s powerful painting series about human vulnerability, or Nicholas Hlobo’s large-scale, organically shaped sculptures made primarily of rubber.
Text from the SFMOMA website
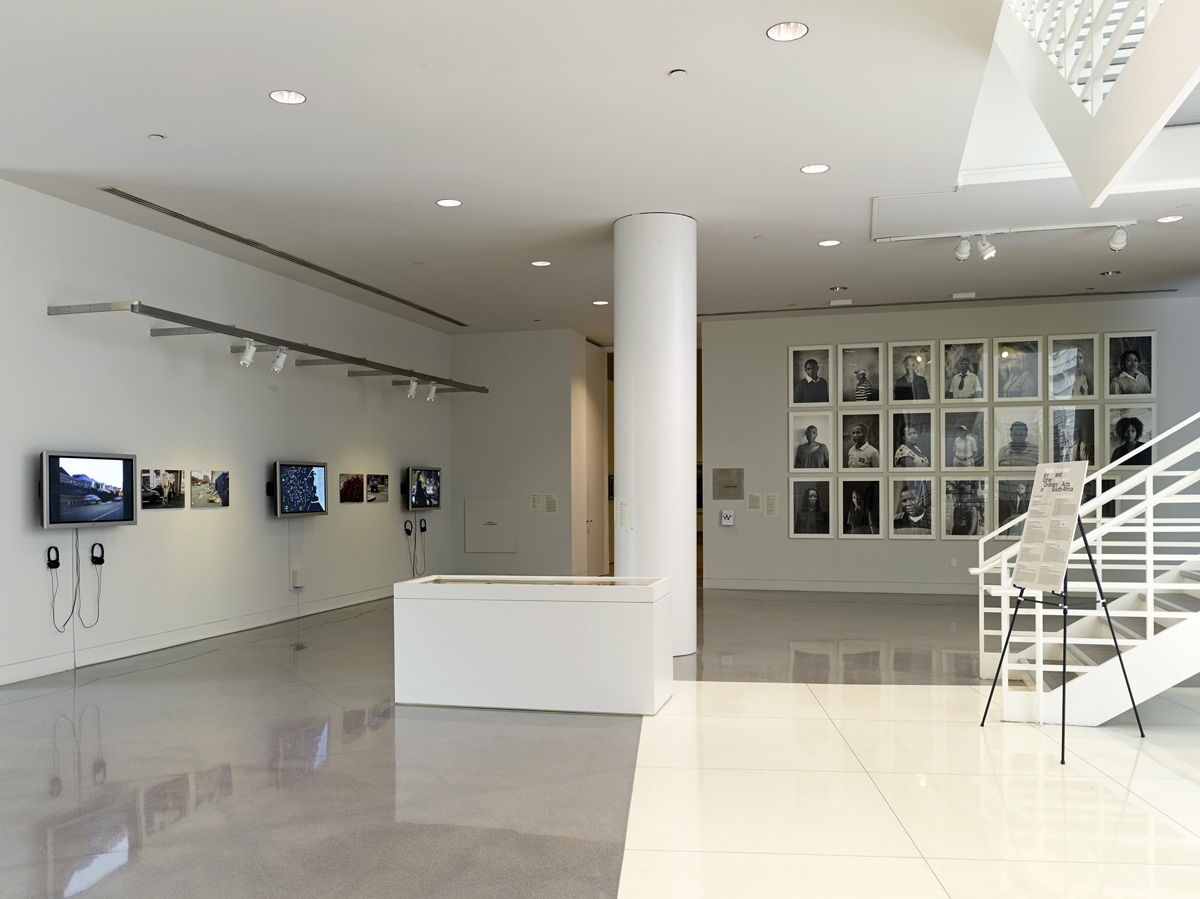
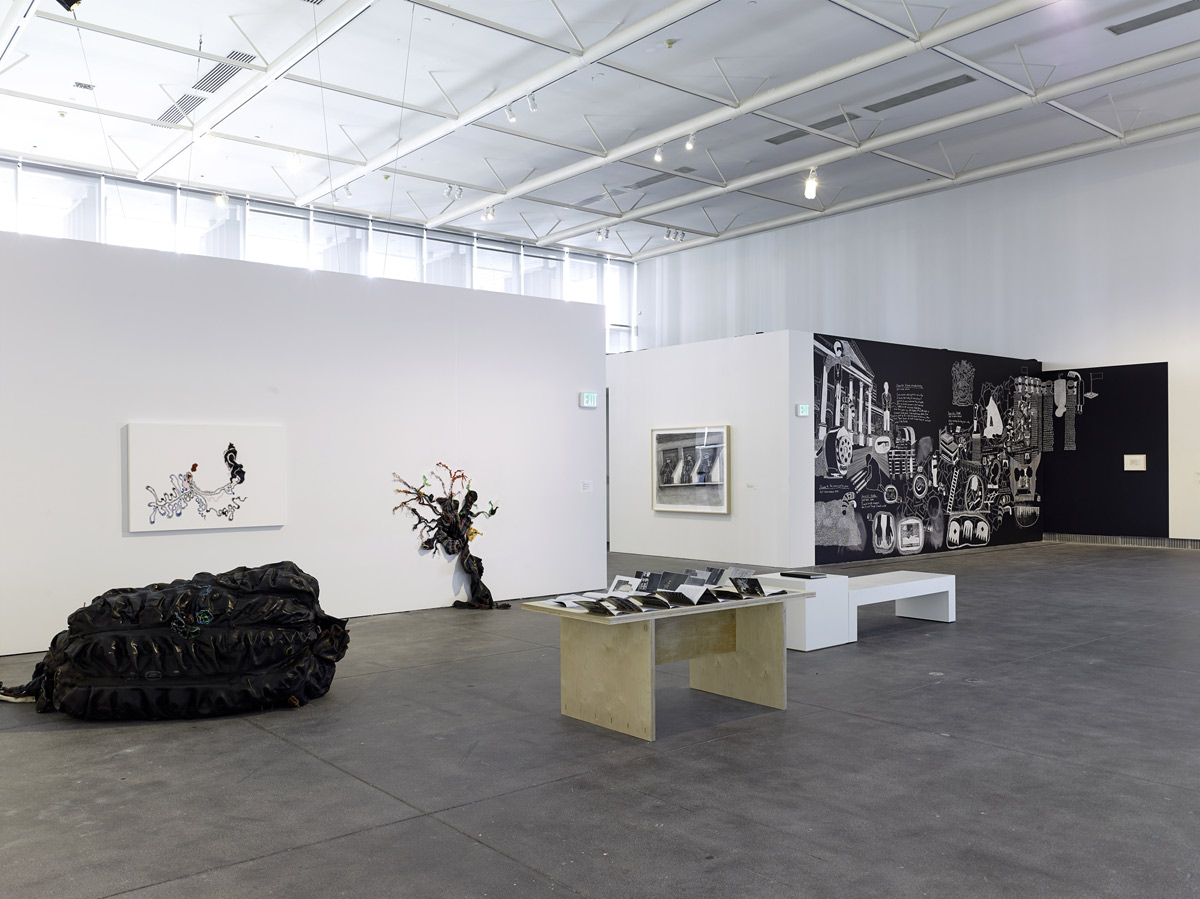
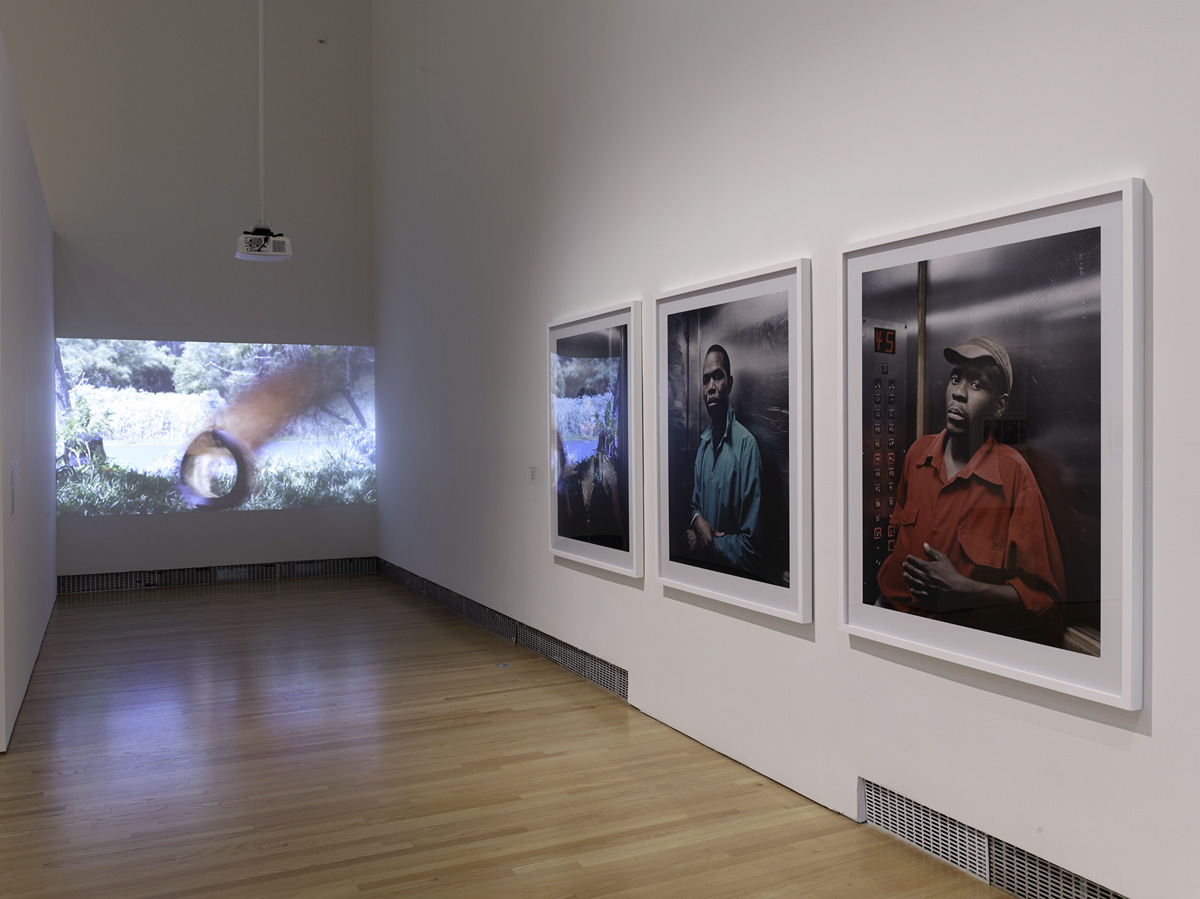
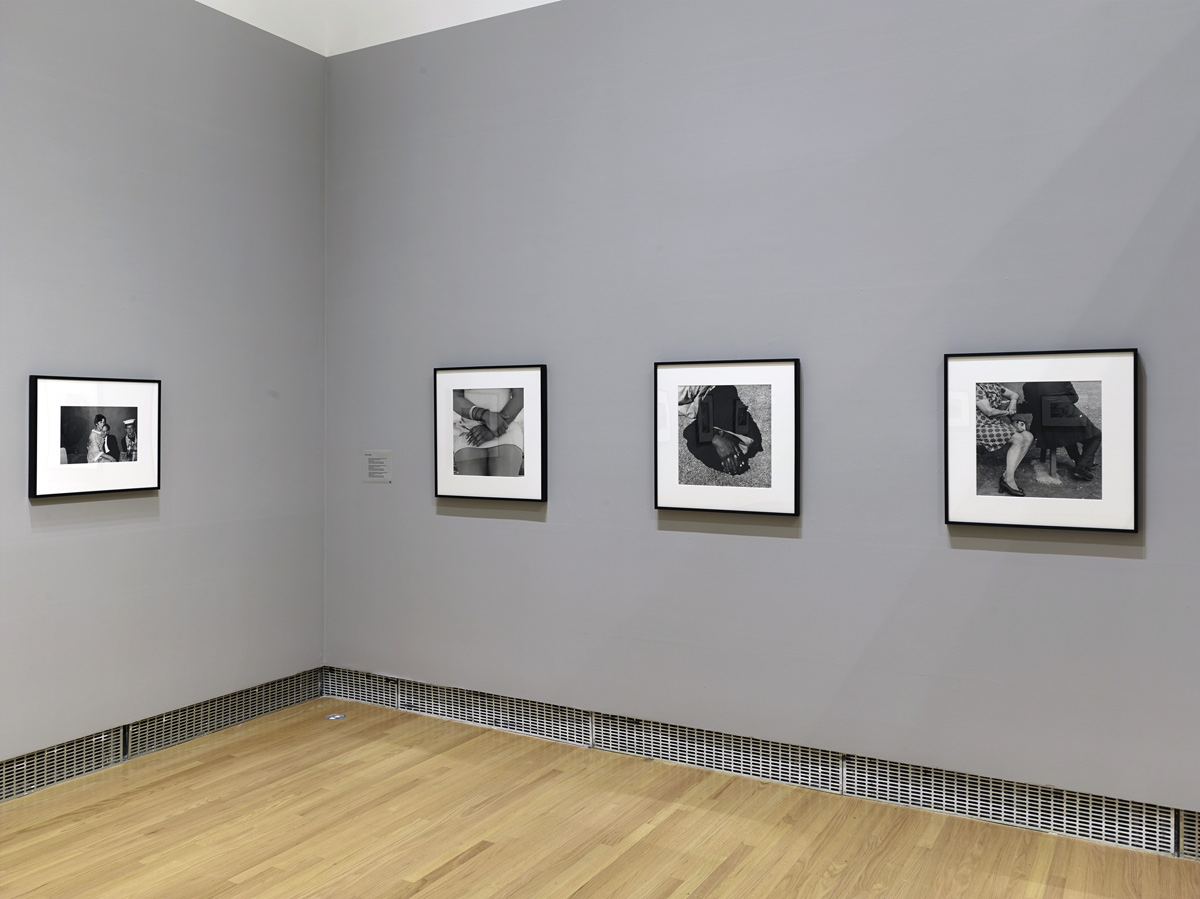
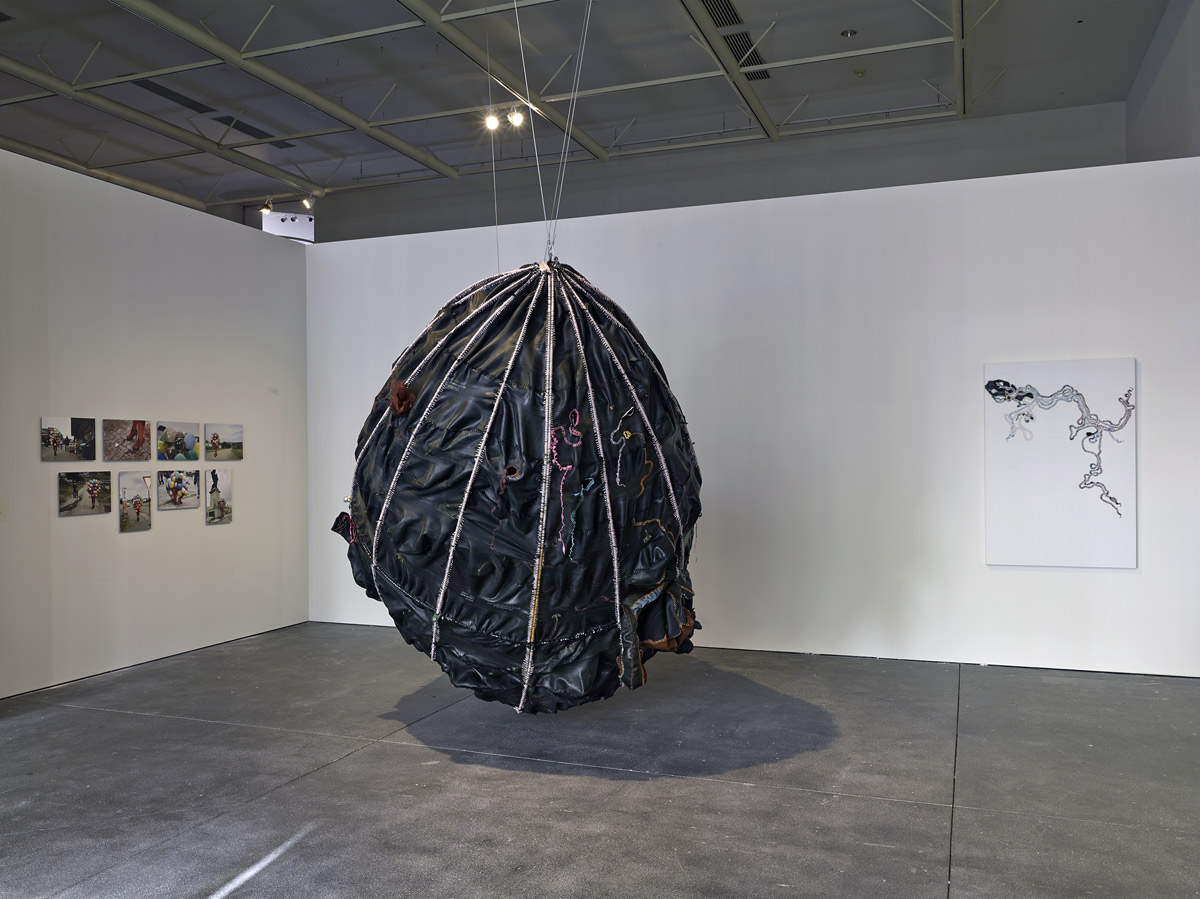






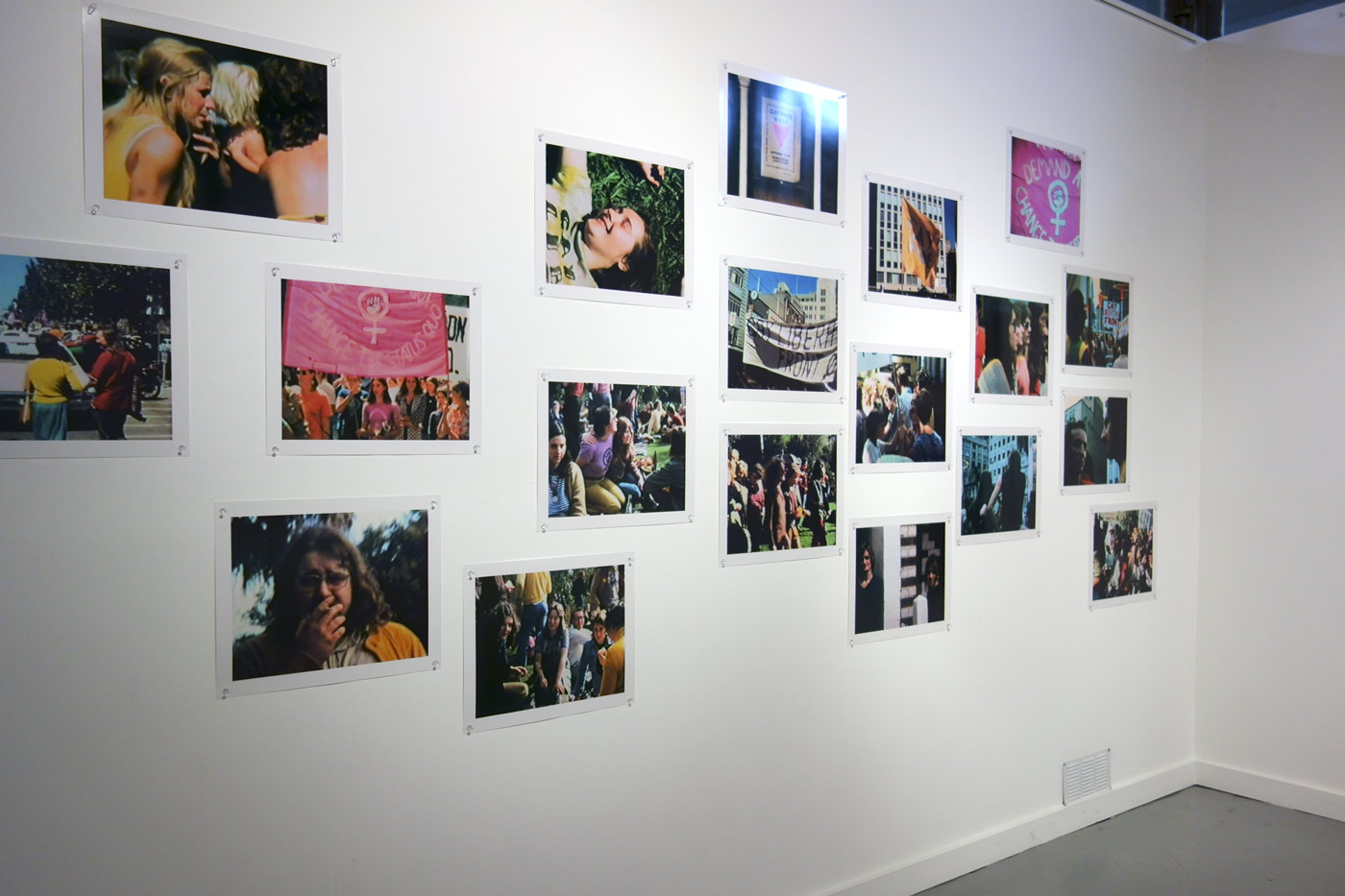
Installation views of the exhibition Public Intimacy: Art and Other Ordinary Acts in South Africa at the Yerba Buena Center for the Arts, San Francisco with, in the last photo, Nicholas Hlobo, Umphanda ongazaliyo (installation view), 2008; rubber, ribbon, zips, steel, wood, plaster; ICA Boston; © Nicholas Hlobo; photo: John Kennar.
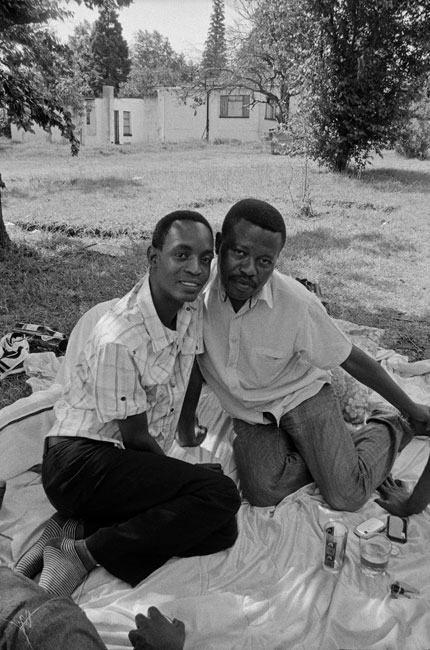

Sabelo Mlangeni (South Africa, b. 1980)
Couple Bheki and Sipho
2009
From the series Country Girls
Gelatin silver print
40 x 30cm
Courtesy the artist and Stevenson, Cape Town and Johannesburg
© Sabelo Mlangeni
Figures & Fictions: Sabelo Mlangeni from Victoria and Albert Museum on Vimeo.

Anton Kannemeyer (South Africa, b. 1967)
D is for dancing ministers
2006
From the series Alphabet of Democracy
Lithograph on Chine Collé
22 1/16 x 24 in. (56 x 61cm)
Courtesy the artist and Stevenson, Cape Town and Johannesburg
© Anton Kannemeyer
Anton Kannemeyer (born 1967) is a South African comics artist, who sometimes goes by the pseudonym Joe Dog.
Anton Kannemeyer was born in Cape Town. He studied graphic design and illustration at the University of Stellenbosch, and did a Master of Arts degree in illustration after graduating. Together with Conrad Botes, he co-founded the magazine Bitterkomix in 1992 and has become revered for its subversive stance and dark humour. He has been criticised for making use of “offensive, racist imagery”. Kannemeyer himself said that he gets “lots of hate mail from white Afrikaners”.
His works challenge the rigid image of Afrikaners promoted under Apartheid, and depict Afrikaners having nasty sex and mangling their Afrikaans. “X is for Xenophobia”, part of his “Alphabet of Democracy”, depicts Ernesto Nhamwavane, a Mozambican immigrant who was burnt alive in Johannesburg in 2008. Some of Kannemeyer’s works deal with the issues of race relations and colonialism, by appropriating the style of Hergé’s comics, namely from Tintin in the Congo. In “Pappa in Afrika”, Tintin becomes a white African, depicted either as a white liberal or as a racist white imperialist in Africa. In this stereotyped satire, the whites are superior, literate and civilised, and the blacks are savage and dumb. In “Peekaboo”, a large acrylic work, the white African is jumping up in alarm as a black man figure pokes his head out of the jungle shouting an innocuous ‘peekaboo!’ A cartoon called “The Liberals” has been interpreted as an attack on white fear, bigotry and political correctness: a group of anonymous black people (who look like golliwogs) are about to rape a white lady, who calls her attackers “historically disadvantaged men”.
Text from the Wikipedia website
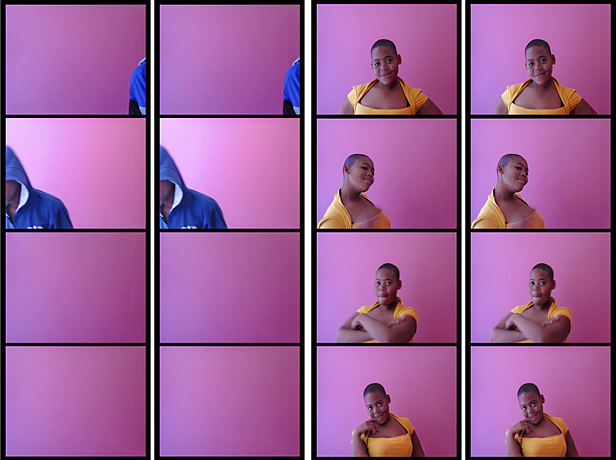

Terry Kurgan (South Africa, b. 1958)
Hotel Yeoville
2012
Digital print on bamboo hahnemulle paper
Courtesy the artist
© Terry Kurgan

Penny Siopis (South Africa, b. 1953)
Untitled from the series Shame
2002
Paint on enamel
© Penny Siopis
Siopis established herself as one of the most talented and challenging artists in South Africa and beyond, by working across painting, installation and film, bringing together diverse references and materials in ways that disturb disciplinary boundaries and binaries.
Concepts of time run through all her work often manifesting in the actual physical changes of her materials; in her early cake paintings oil paint is made to be unnaturally affected by gravity, age and decay; in her films using archival footage time is marked as much by the effects of age on the celluloid as by the historical period caught in the sweep of the camera; in her accumulations of found objects in her installations, ideas of the heirloom come to the fore with her ongoing conceptual work Will (1997- ) – in which she bequeaths objects to beneficiaries – being the ultimate time piece only becoming complete on her death; her glue and ink paintings index flux as they record the material transformation that happens when viscous glue matter reacts with pigment, gravity, the artist’s bodily gestures, and the drying effects of the air.
Siopis sees her art practice as ‘open form’, operating as an intimate model in which the physical changes of her materials can be extrapolated into a larger ethics of personal and political transformation. According to Achille Mbembe this quality marks her interest in process as a perpetual state of becoming and entails “the crafting of an unstable relation between form and formlessness, in the understanding that the process of becoming proceeds in ways that are almost always unpredictable and at times accidental.”
Shame paintings
Siopis began the Shame paintings in 2002 and they became a key feature of her exhibition Three Essays on Shame (2005), an intervention in the museum of Sigmund Freud, once his house, in London. It was part of a project that marked the centenary of Freud’s groundbreaking publication Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality. Responding to Freud, Siopis’ installation consisted of three parts located in Freud’s study (with the famous couch), dining room and bedroom and titled Voice, Gesture and Memory. The small paintings shown in a grid in this room were presented as a frieze in the Memory section of the original exhibition. The artist invokes this exhibition here through the arrangement of some of the objects from the installation on a table reminiscent of that in Freud’s dining room, where she had placed Baubo, one of Freud’s objects from his collection of antiquities. Baubo is a small terracotta figurine who gestures to her genitalia in a provocative way, an act some have interpreted as a show of shame that speaks of both vulnerability and empowerment.
In the installation Siopis also evoked a complex dialogue between Freud’s ideas and her personal experiences by inserting references (voice recordings and objects) to the traumatic proceedings of the South African Truth and Reconciliation Commission and colonial and apartheid history. Once again she was interested in binding the traces of human vulnerability and the dramatic effects of sweeping historical narratives.
In this body of work Siopis manipulates thick and gooey lacquer gel paint, used in home-craft to create stained glass and coloured mirror effects on surfaces. For her it is a physical process that moulds anxiety into form. It translates the result of childhood trauma that we know as shame onto a painted surface. Through the reflective qualities of the medium Siopis blends the bodily sensation with the experience of being looked at, both of which define shame. The use of language in the form of ready-made rubber stamped clichés that clash with the raw power of this familiar emotion further underscores the ‘unspeakable’ character of the experience.
Text from the Wikipedia website
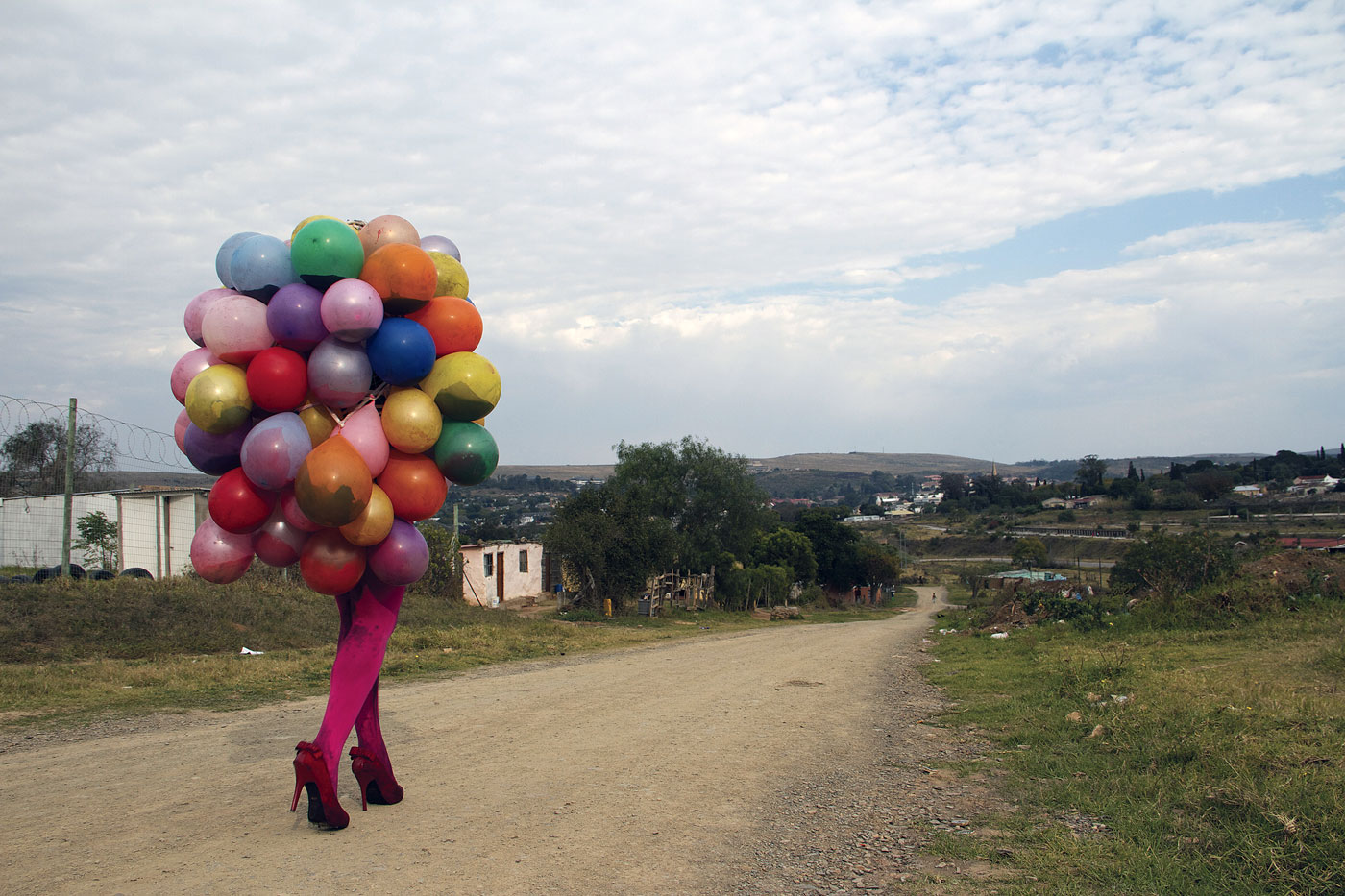

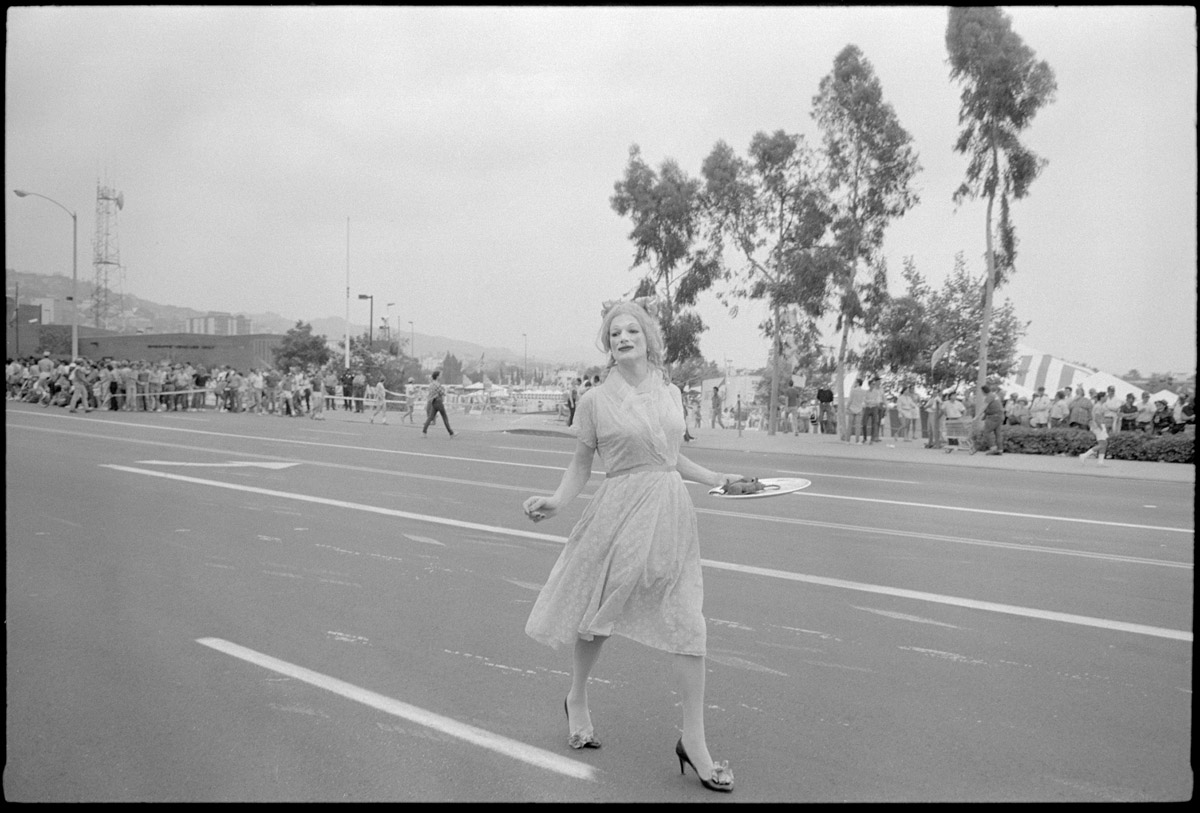
Athi-Patra Ruga (South Africa, b. 1984)
The Future White Women of Azania
2012
Performed as part of Performa Obscura in collaboration with Mikhael Subotzky
Commissioned for the exhibition Making Way, Grahamstown, South Africa
Photo: Ruth Simbao, courtesy Athi-Patra Ruga and WHATIFTHEWORLD/GALLERY

Athi-Patra Ruga (South Africa, b. 1984)
The Future White Women of Azania
2012
Performed as part of Performa Obscura in collaboration with Mikhael Subotzky
Commissioned for the exhibition Making Way, Grahamstown, South Africa
Photo: Ruth Simbao, courtesy Athi-Patra Ruga and WHATIFTHEWORLD/GALLERY
Athi-Patra Ruga (born in 1984) is a South African artist who uses performance, photography, video, textiles, and printmaking to explore notions of utopia and dystopia, material and memory. His work explores the body in relation to sensuality, culture, and ideology, often creating cultural hybrids. Themes such as sexuality, HIV/AIDS, African culture, and the place of queerness within post-apartheid South Africa also permeate his work. …
Future White Women of Azania (FWWoA, 2010-2016)
FWWoA consists of several works, including performance, tapestry, sculpture, video, and photography creating a saga. FWWoA is an allegory of post apartheid nationalism, where Ruga then becomes the “elder” or historian. Creating this constellationary history, drawing references from pre Xhosa history and post apartheid South Africa, tells the history of the non-dynastic line of queens who rule the lands of Azania. Ruga’s works are attentive to the demands for justice for his ancestors and the need for radical transformation in the future, to shatter the ideologies of “rainbowism”. By using Azania as the framework for a critical history of South Africa, FWWoA reveals the silencing of black voices that extends back to the first moments of colonial contact, while also addressing the impossible and unrealized ideologies of forgiveness, reconciliation and redemption practiced in a post apartheid South African.
Azania’s allegorical capacity derives from its status as a symbol of a liberated South Africa during the anti-apartheid struggle. However, the term has a specific history that complicates such dreams. The place name ‘Azania’ first appears in The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea (40 AD) to refer to the lands of southern and eastern Africa. By designating the lands of Africa as ‘Azania’, Ruga understands the label as one example in a long history of constructing Africa as uninhabited until European colonial contact.
Ruga’s tapestries in the FWWoA saga chronicles allegorical depictions of queens, maps, and other iconography of Azania. The struggles of the non-dynastic line of queens depicting signifiers of an Azanian national identity: national seal, crest, flower, maps, while also including Ruga’s long standing interest in popular culture. Taking inspirations from Gustave Eiffel’s ‘Statue of Liberty’ or Eugene Delacroix’s ‘Liberty Leading the People’, Ruga brings about the idea of objectifying the woman’s body as the conflict, but in his own work creates them as powerful but passive. In his work ‘The Lands of Azania’, Ruga reworks the map of Eastern Africa. Insetting a national animal, the saber-tooth zebra, the Azanian flag, and giving several countries new names. Throughout the geography of Azania he further explores the overlaps of exile and diaspora in the African and Jewish communities.
A narrative with five characters, a national flower, crest and animal including the rainbow coloured balloon characters. One of Ahti-Patra’s goals was to make a myth accessible even for children. A cute figure that has the capacity to be festive, create fanfare yet become disquieting when it violently pops and bleeds.
Text from the Wikipedia website

Athi-Patra Ruga (South Africa, b. 1984)
The Night of the Long Knives I
2013
Archival inkjet Print on Photorag Baryta
202 x 157cm
The Future White Woman of Azania is an ongoing series of performances first conceived in 2010 and evolving to engage new definitions of nationhood in relation to the autonomous body. In the enactment of the site-specific work commissioned for the 55th Venice Biennale, the performance takes the form of an absurdist funerary procession. The participants are the ABODADE – the sisterhood order of Azania and the central protagonist – The Future White Woman.
“Azania, as a geographic location, is first described in 1stCentury Greek records of navigation and trade, The Peryplus of the Erythrean Sea and is thought to refer to a portion of the East and Southern African coast. The word Azania itself is thought to have been derived from an Arabic word referring to the ‘dark-skinned inhabitants of Africa.’
Azania is then eulogised in the black consciousness movement as a pre-colonial utopian black homeland – this Promised Land, referenced in struggle songs, political sermons and African Nationalist speeches. In Cold War pop culture, Marvel Comics used Azania as a fictional backdrop to a Liberation story that bares a close resemblance to the situation that was Apartheid in Old South Africa… so it is at once a mythical and faintly factual place/state that this performance unfolds… Who are the Azanians for what it’s worth? It is in this liminal state that the performance unfolds…”
Seeking to radically reimage the potential of Azania and its inhabitants, the performance questions the mythical place that we mourn for and asks who its future inhabitants may be. Using the “Nation-Finding language of pomp and procession,” Ruga proposes a bold and iconoclastic break with the past Utopian promise of the elders and instead presents us with a new potential and hybridity.
Text from the Athi-Patra Ruga blog March 17, 2015 [Online] Cited 08/04/2021.
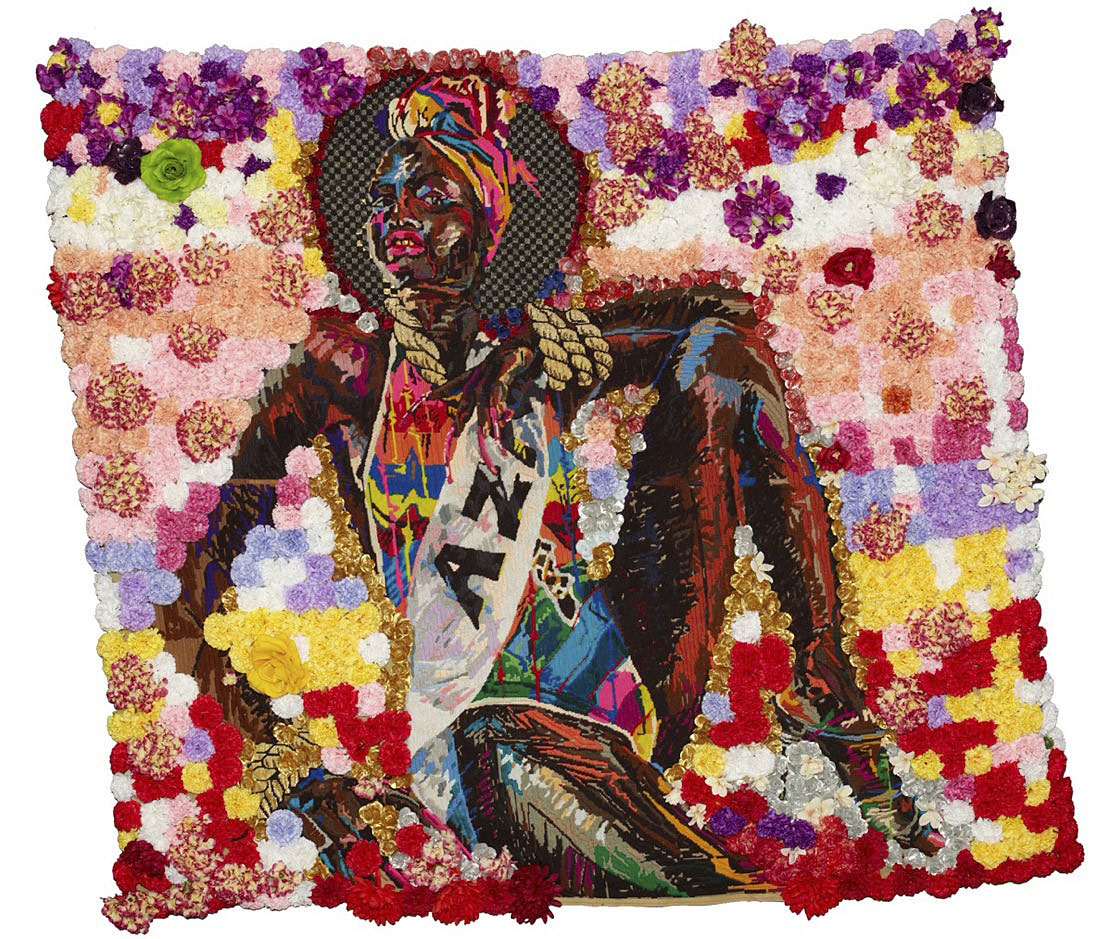

Athi-Patra Ruga (South Africa, b. 1984)
Uzuko
2013
Wool, thread and artificial flowers on tapestry canvas
200 x 180 cm
Athi-Patra Ruga is one of a handful of artists, working in South Africa today, who has adopted the tropes of myth as a contemporary response to the post-apartheid era. Ruga has always worked with creating alternative identities that sublimate marginalised experience into something strangely identifiable.
In The Future White Women of Azania he is turning his attention to an idea intimately linked to the apartheid era’s fiction of Azania – a Southern African decolonialised arcadia. It is a myth that perhaps seems almost less attainable now than when the Pan Africanist Congress (PAC) appropriated the name in 1965 as the signifier of an ideal future South Africa – then at least was a time to dream more optimistically largely because the idea seemed so infinitely remote.
But Ruga, in his imaginings of Azania, has stuck closer to the original myth, situating it in Eastern Africa as the Roman, Pliny the Elder, did in the first written record of the name. Here Ruga in his map The Lands of Azania (2014-2094) has created lands suggestive of sin, of decadence and current politics. Countries named Palestine, Sodom, Kuntistan, Zwartheid and Nunubia are lands that reference pre-colonial, colonial and biblical regions with all their negative and politically disquieting associations. However, in what seems like something of a response to the ‘politically’ embroidered maps of the Italian artist Alighiero e Boetti, Ruga infers that the politicisation of words are in a sense prior to the constructed ideology of the nation state.
What is more Azania is a region of tropical chromatic colours, which is populated with characters whose identities are in a state of transformation. At the centre of the panoply of these figures stands The Future White Woman whose racial metamorphosis, amongst a cocoon of multi-coloured balloons, suggests something disturbing, something that questions the processes of a problematic cultural assimilation. And it is here that the veracity of the myth of a future arcadia is being disputed if not entirely rejected.
To be sure, unlike Barthes’ suggestion in his essay ‘Myth Today’, Ruga is not creating myth in an act that depoliticises, simplifying form in order to perpetuate the idea of an erroneous future ‘good society’. Instead, placing himself in amongst the characters in a lavish self portrait Ruga imagines himself into the space of the clown or jester (much like the Rococo painter Watteau did in his painting ‘Giles’), into the space of interpreter as well as a cultural product of the forces outside of his own control.
Ruga’s Azania is a world of confusing transformations whose references are Rococo and its more modern derivative Pop. But whatever future this myth is foreshadowing, with its wealth, its tropical backdrop, its complicated and confusing identities, it is not a place of peaceful harmony – or at least not one that is easily recognisable. As Ruga adumbrated at a recent studio visit, his generation’s artistic approach of creating myths or alternative realities is in some ways an attempt to situate the traumas of the last 200 years in a place of detachment. That is to say at a farsighted distance where their wounds can be contemplated outside of the usual personalised grief and subjective defensiveness.
Statement from WHATIFTHEWORLD.com on the Empty Kingdom website [Online] Cited 20/06/2014. No longer available online

Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
Ponte City from Yeoville Ridge
2008
Lightjet chromogenic print
Courtesy the artists and Goodman Gallery
© Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse

Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
Ponte City, Johannesburg
2008
Lightjet chromogenic print
Courtesy the artists and Goodman Gallery
© Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
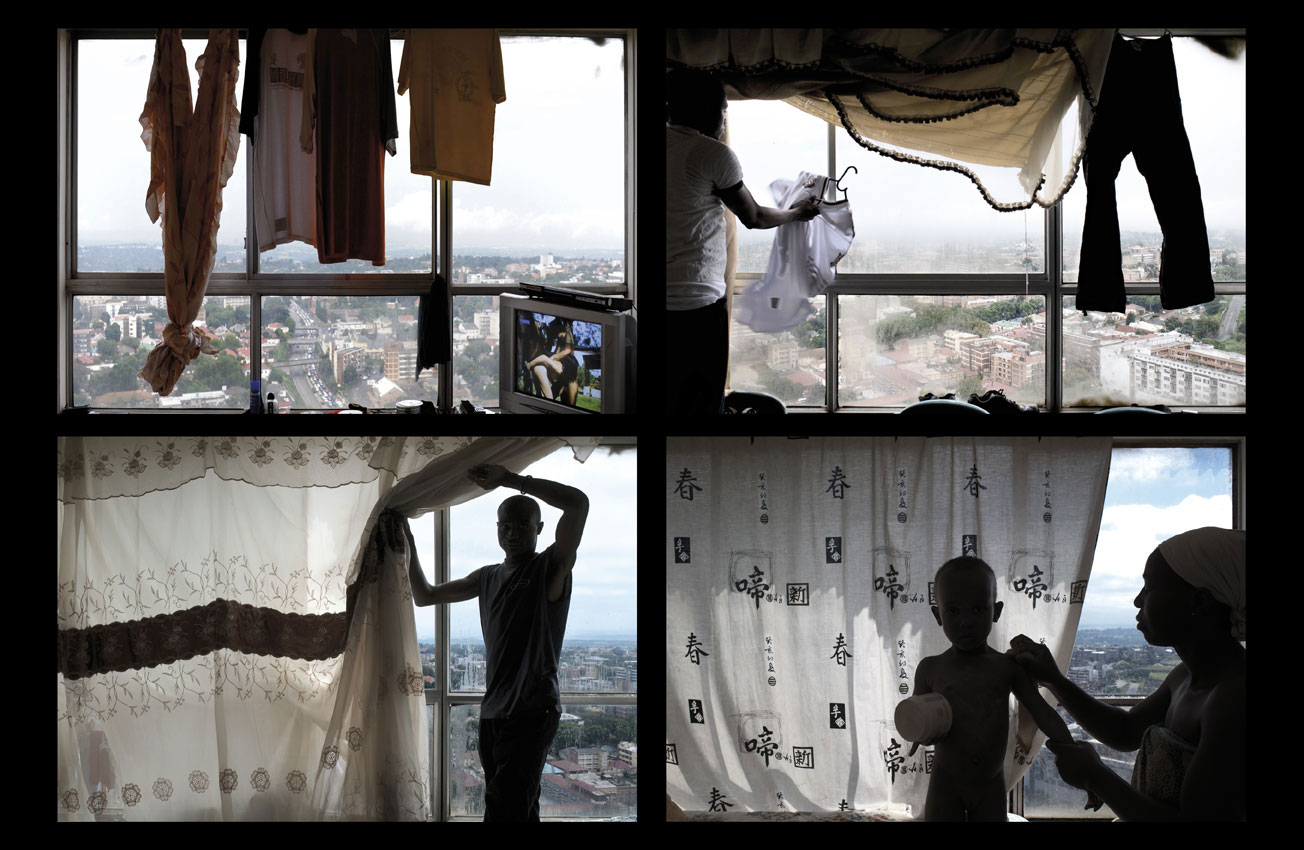

Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
Ponte City, Johannesburg
2008
Lightjet chromogenic print
Courtesy the artists and Goodman Gallery
© Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
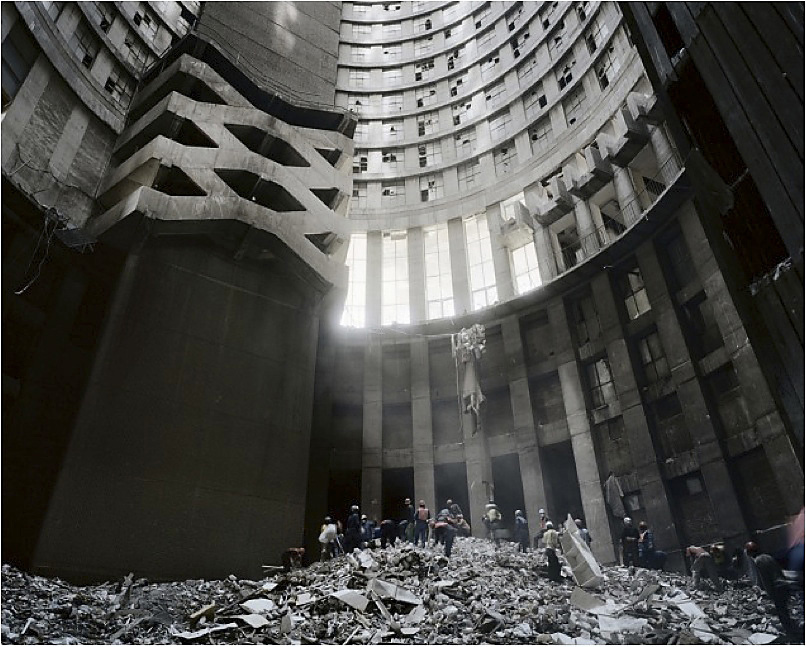

Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
Cleaning the Core, Ponte City, Johannesburg
2008
Lightjet chromogenic print
49 7/16 x 59 1/16 in. (125.5 x 150cm)
Courtesy the artists and Goodman Gallery
© Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
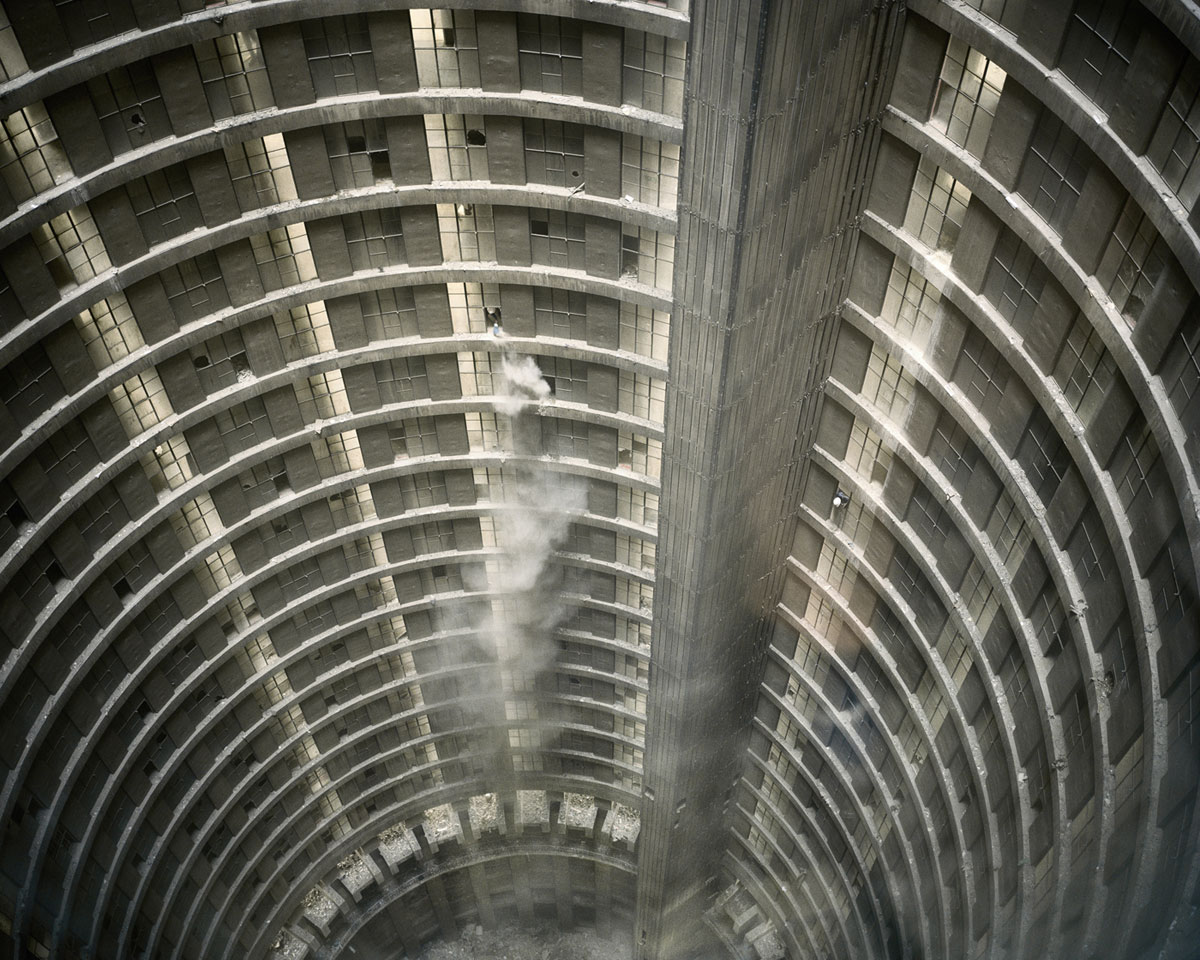

Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
Untitled I, Ponte City, Johannesburg
2008
Lightjet chromogenic print
Courtesy the artists and Goodman Gallery
© Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
Originally intended as a nuclear point in the upwardly mobile social cartography of Johannesburg’s Hillbrow, the 173 meter-high cylindrical apartment building Ponte City became an urban legend, and an essential part of visual renderings of the city. It was the conflicted spectacle of Ponte City that drew South African photographer, Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse, a British artist, to look more closely in rather than at the tower.

Mikhael Subotzky and Patrick Waterhouse
Lift Portrait 2, Ponte City, Johannesburg (0328)
2008
C-print mounted on Dibond
124 cm x 151.5cm
Yerba Buena Center for the Arts
701 Mission Street
San Francisco, CA 94103
Opening hours:
Sunday and Wednesday noon – 6.00pm
Thursday – Saturday noon – 8.00pm
Free First Tuesday of the month noon – 8.00pm
SFMOMA website
LIKE ART BLART ON FACEBOOK
Back to top


























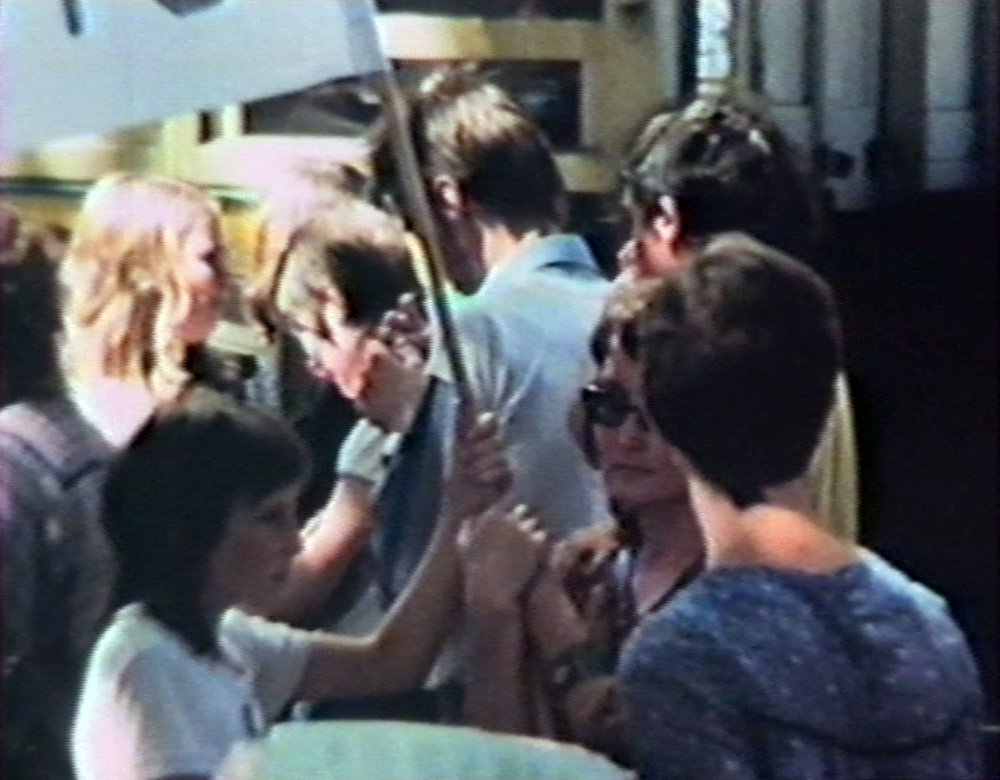














































































































































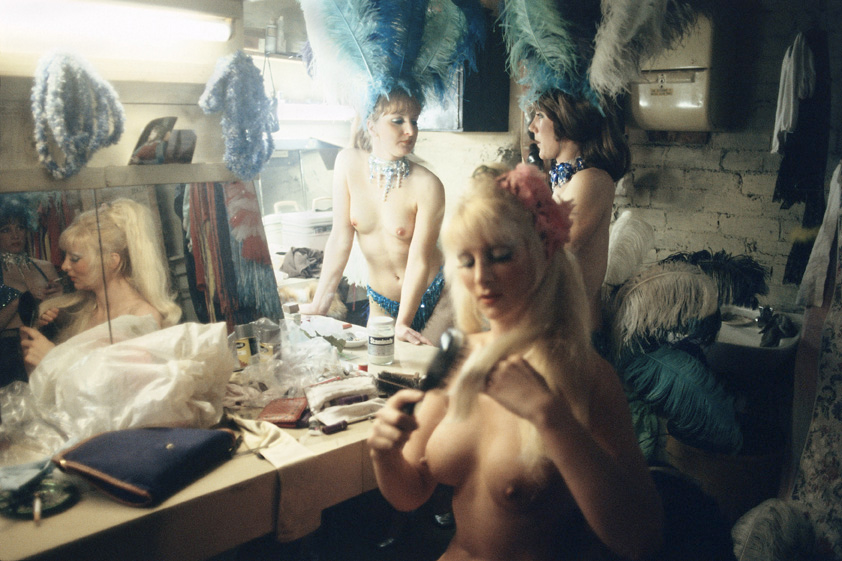










You must be logged in to post a comment.