Exhibition dates: 18th October 2013 – 9th February 2014
Participating artists: Vito Acconci / Bas Jan Ader / Luc Andrié / Lynda Benglis / Luciano Castelli / Martin Disler / VALIE EXPORT and Peter Weibel / Gelitin / Pascal Häusermann / Alexis Hunter / Cathy Joritz / Jesper Just / Jürgen Klauke / Frantiček Klossner / Elke Silvia Krystufek / Marie-Jo Lafontaine / Peter Land / Littlewhitehead / Sarah Lucas / Urs Lüthi / Manon / Paul McCarthy / Tracey Moffatt / Josef Felix Müller / Ursula Palla / Adrian Piper / Anne-Julie Raccoursier / Ugo Rondinone / Carole Roussopoulos / Rico Scagliola and Michael Meier / Sylvia Sleigh / Nedko Solakov / Megan Francis Sullivan / Sam Taylor-Johnson / Costa Vece / William Wegman / Silvie Zürcher.
PLEASE NOTE: THIS POSTING CONTAINS ART PHOTOGRAPHS OF MALE NUDITY AND MALE SEXUAL AROUSAL – IF YOU DO NOT LIKE PLEASE DO NOT LOOK, FAIR WARNING HAS BEEN GIVEN
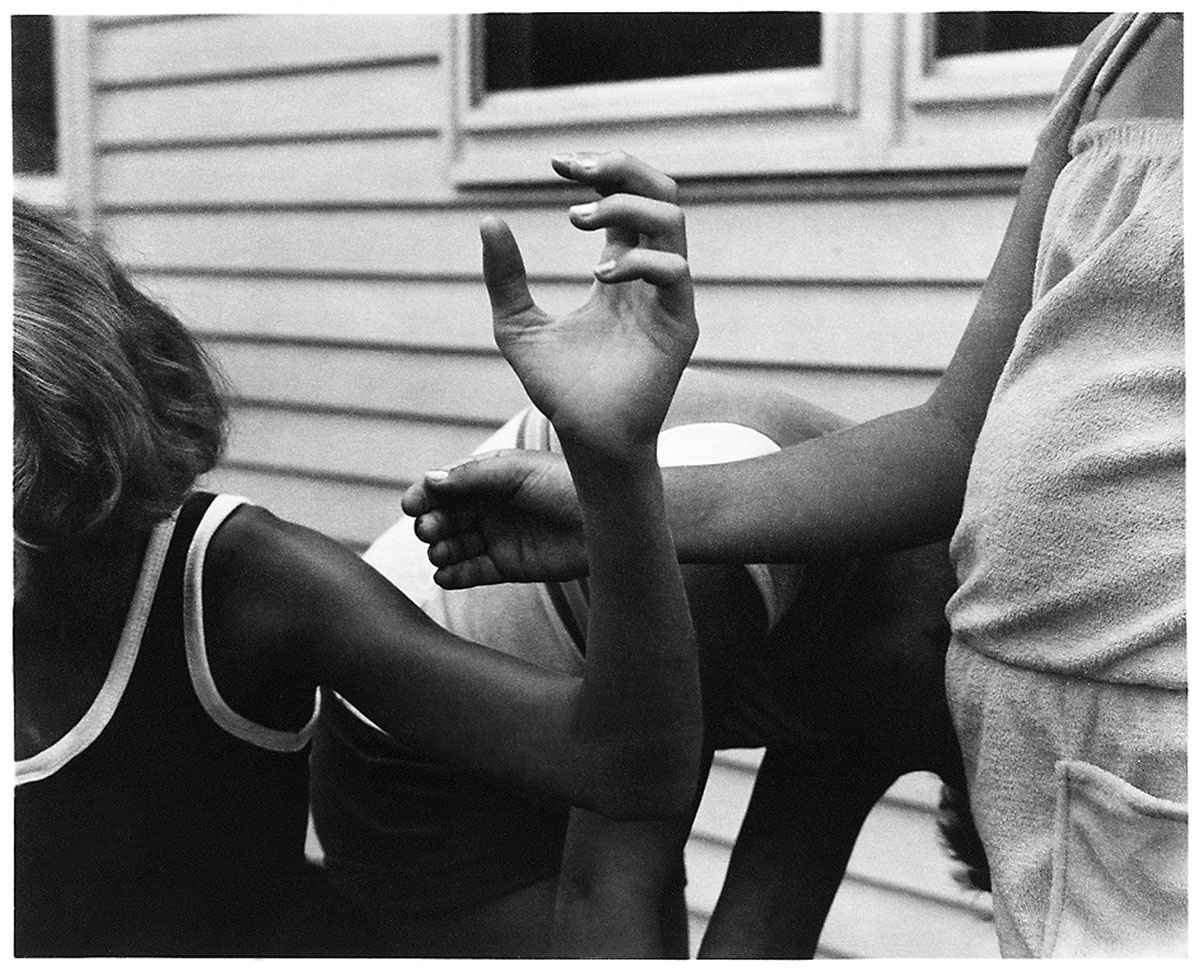
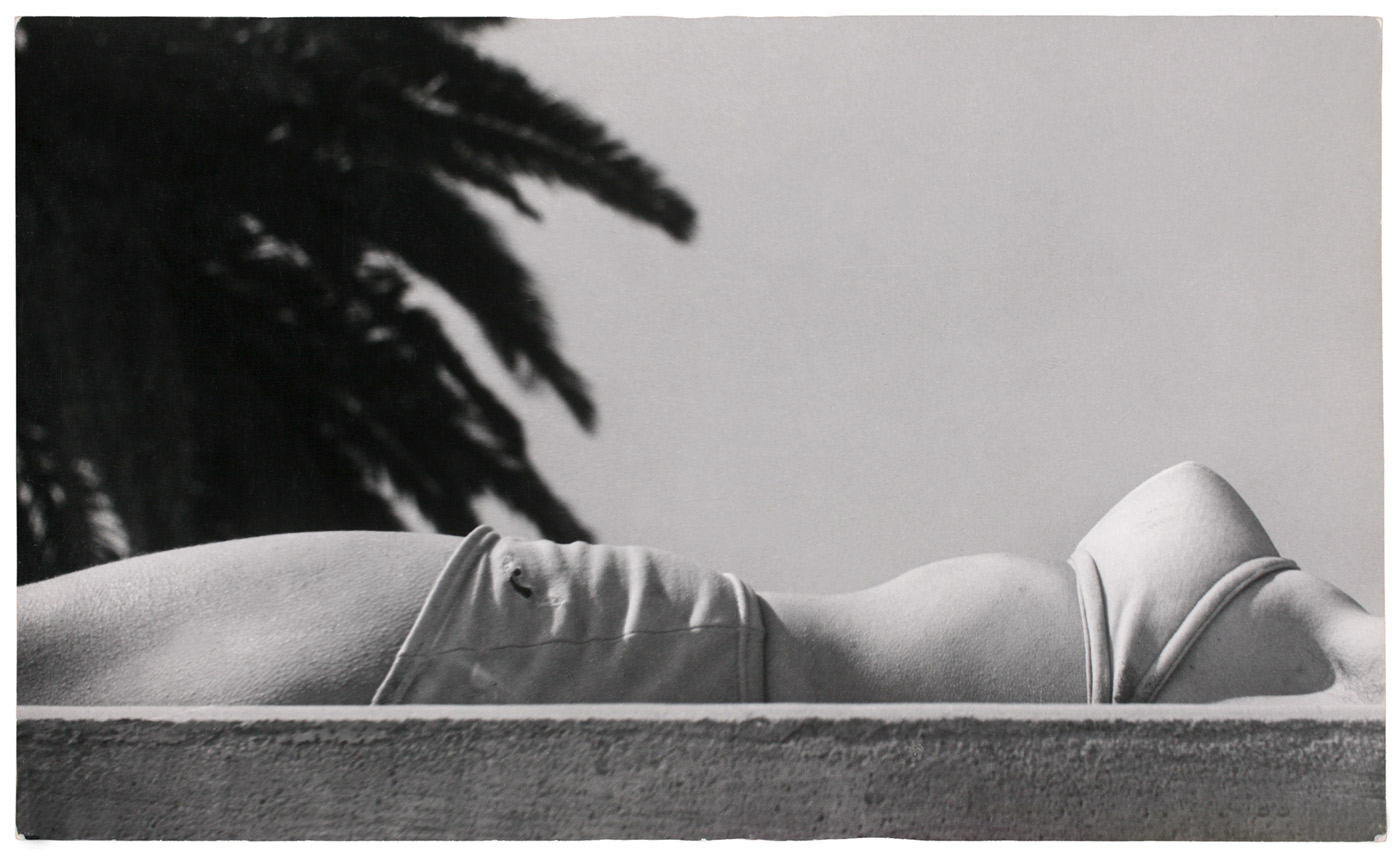
Alexis Hunter (New Zealand, b. 1948)
Approach to Fear: XVII: Masculinisation of Society – exorcise
1977
10 Colour photographs, mounted on two panels, both 25 x 101cm
Courtesy of Richard Saltoun Gallery
© 2013 ProLitteris, Zürich
(From the section Experiments)
The Cult of Muscularity
“… muscularity is a key term in appraising men’s bodies … this comes from men themselves. Muscularity is the sign of power – natural, achieved, phallic.”
Richard Dyer. Only Entertainment. London: Routledge, 1992, p. 114
“The formation of ‘The Cult of Muscularity’ (Elliott Gorn. The Manly Art. London: Robson Books, 1986) in the last decade of the 19th century was a reaction to the perceived effeminisation of heterosexual masculinity. The position of the active, heroic hetero-male was under attack from the passivity of industrialisation, from the expansion of women’s rights and their ability to become breadwinners, and through the naming of deviant sexualities that were seen as a threat to the stability of society. By naming deviant sexualities they became visible to the general public for the first time, creating apprehension in the minds of men gazing upon the bodies of other men lest they be thought of as ‘pansies’. (Remember that it was in this decade the trials of Oscar Wilde had taken place in England after he was accused of being a sodomite by The Marquis of Queensbury. It is perhaps no coincidence that the rules that governed boxing, a very masculine sport in which a man could become a popular hero, were named after his accuser. By all accounts he was a brute of a man who despised and beat his son Lord Alfred Douglas and sought revenge on his partner, Oscar Wilde, for their sexual adventures). Muscles became the sign of heterosexual power, prowess, and virility. A man had control over his body and his physical world. His appearance affected how he interacted with this world, how he saw himself, and was seen by others, and how closely he matched the male physical ‘ideal’ impacted on his own levels of self-esteem. The gymnasium became a meeting point for exercise, for health, for male bonding, and to show off your undoubted ‘masculinity’…”
The development of ‘The Cult of Muscularity’ may also have parallels in other social environments which were evolving at the turn of the century. For example, I think that the construction of the muscular mesomorphic body can be linked to the appearance of the first skyscrapers in cities in the United States of America. Skyscrapers were a way increasing visibility and surface area within the limited space of a crowded city. One of the benefits of owning a skyscraper like the Chrysler Building in New York, with its increased surface area, was that it got the company noticed. The same can be said of the muscular body. Living and interacting in the city, the body itself is inscribed by social interaction with its environment, its systems of regulation and its memories and historicities (his-tor-i-city, ‘tor’ being a large hill or formation of rocks). Like a skyscraper, the muscular body has more surface area, is more visible, attracts more attention to its owner and is more admired. The owner of this body is desired because of his external appearance which may give him a feeling of superiority and power over others. However this body image may also lead to low self-esteem and heightened body dissatisfaction in the owner (causing anxiety and insecurity in his identity) as he constantly strives to maintain and enhance his body to fulfil expectations he has of himself.
Of course, body image is never a static concept for the power of muscular images of the male body resides in their perceived value as a commodity. This value is reinforced through social and moral values, through fluid personal interactions, and through the desire of self and others for a particular type of body image; it is a hierarchical system of valuation. It relies on what type of body is seen as socially desirable and ‘beautiful’ in a collective sense, even though physical attractiveness is very much a personal choice.”
Dr Marcus Bunyan. Excerpt from “Bench Press,” in Pressing the Flesh: Sex, Body Image and the Gay Male, PhD thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, 2001.
Many thankx to the Kunstmuseum Bern for allowing me to publish the art work in the posting. Please click on the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Ugo Rondinone (Switzerland, b. 1962)
I Don’t Live Here Anymore
1998
C-prints between Alucobond and Plexiglas
Each 180 × 125cm
Kunstmuseum Bern, purchased with the donation of an Art Lover
(From the section Masculinity as Masquerade)
Digitally manipulates photos of women depicted in various suggestive poses, replacing their features with his own in a sufficiently consistent way for the image to retain its erotic content. By slipping into different bodies, he tests his own body and appearance, and he raises the issue of reality. The artist can only offer his own, man-made version.
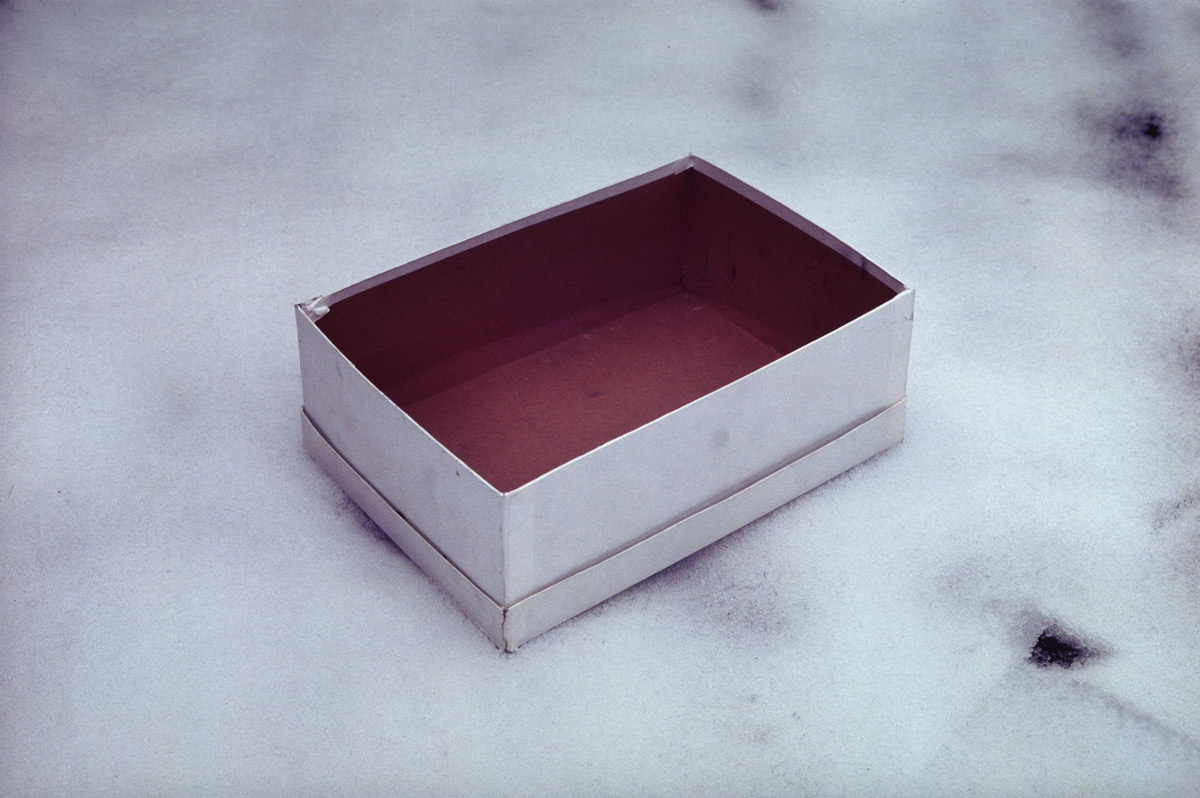
Lynda Benglis (American, b. 1941)
Artforum Advertisement in: Artforum, November 1974, Vol. 13, No. 3, S. 3-4
1974
26.7 × 26.5 × 0.5cm
Bayerische Staatsbibliothek, München
(From the section Experiments)
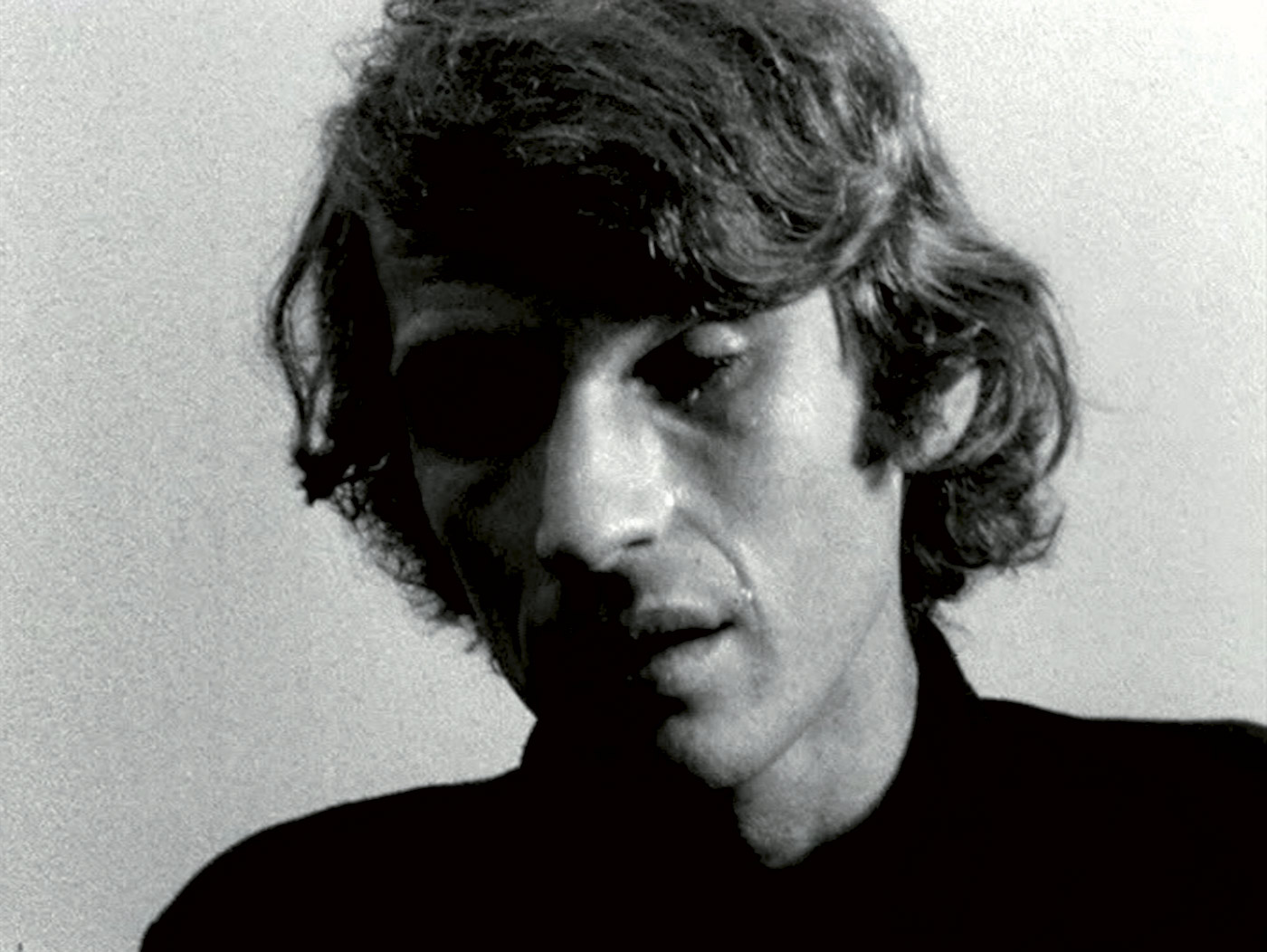
Peter Land (Danish, b. 1966)
Peter Land d. 5. maj 1994
1994
Colour video
Time, 25 Min.
Courtesy Galleri Nicolai Wallner
(From the section Crisis and Criticism)
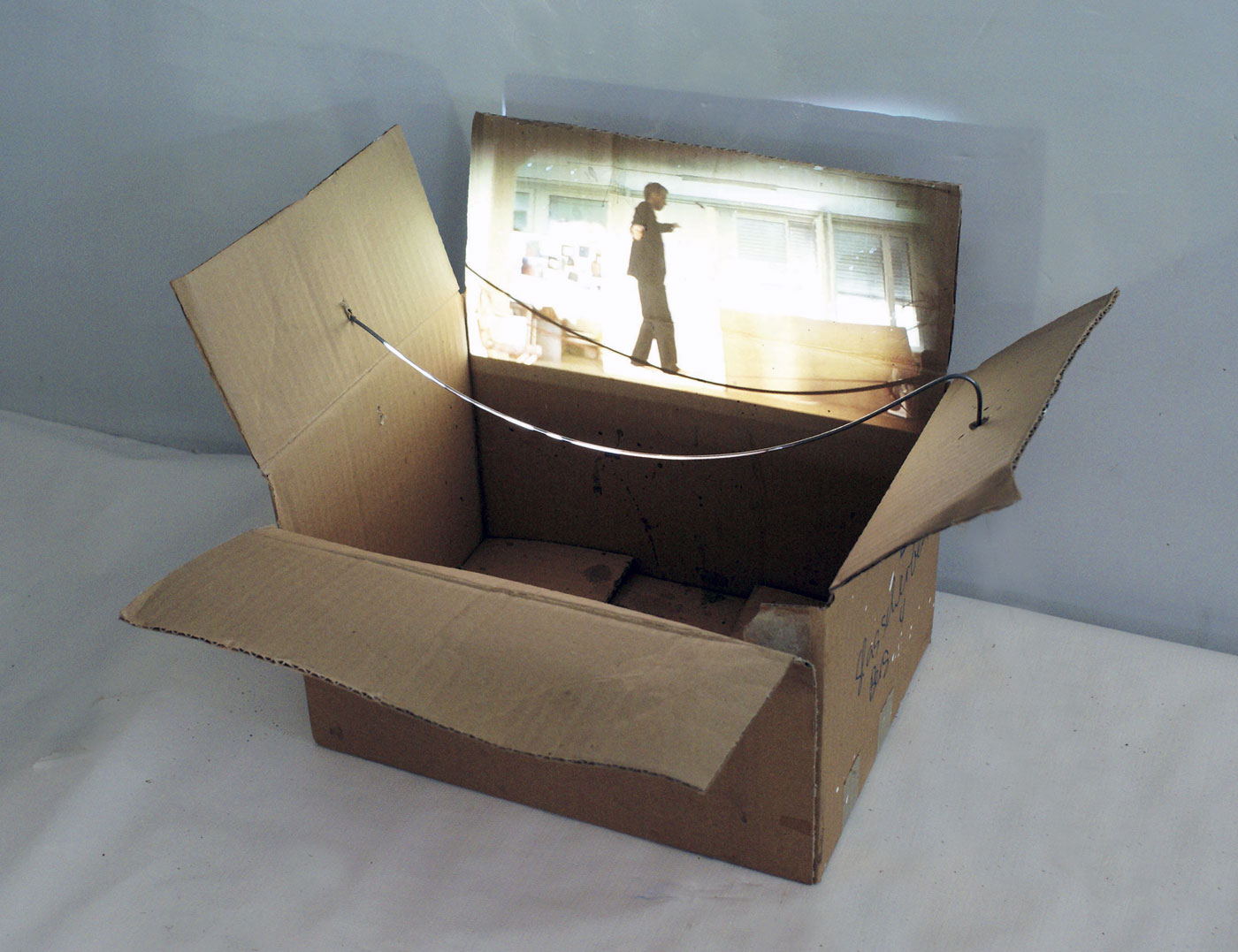
Ursula Palla (Switzerland, b. 1961)
balance
2012
Colour video installation
Time, 8 Min.
Courtesy the artist
(From the section Crisis and Criticism)
Masculinity under scrutiny
This themed group exhibition is our contribution to the discussion on new role definitions of the male gender, a topic that has long been on the agenda of academia and popular culture. Works by artists of both sexes will address the issue of how contemporary art stages male role models and masculinity, critically scrutinising the content of the same.
Who or what makes a man? How do men define themselves in art since feminism; how do they reflect on their gender and the portrayal thereof? Whereas the preferred angle of engaging with female artists is still today via “gender”, this is still a novel angle for looking at male artists. And as feminist art has finally become an established entity in major institutions, it is time to take a closer look at the art produced by men about men. The Sexual Revolution as well as the feminist and gay movements did not have only one side to them: they likewise impacted the roles of men and transformed images of masculinity. The exhibition therefore explores how contemporary Western artists of both sexes have, since the 1960s, invented new notions of masculinity or shattered existing ones. It does this with some 45 installations, some of which are large and extensive.
With this exhibition, the Kunstmuseum Bern is addressing a topic that, until now, has hardly been tackled in a museum context: the “normal” white heterosexual male, hitherto the ultimate measure for everything we consider characteristically human, is now facing a crisis. The exhibition and catalogue draw on the reflections and insights gained from masculinities studies to throw light on the consequences of the contemporary male crisis and how it is reflected in art, making the extent of the crisis visually palpable.
The works selected for the show have been divided up into six sections. These sections explore what “normal” might be and what the new nuances inherent in being “male” are today. The prescribed tour of the exhibition begins with the chapter on “Strong Weaknesses” and then proceeds through the sections focusing thematically on “Experiments”, “Emotions”, “Eroticism”, “Critique and Crisis”, and “Masculinity as Masquerade”. This route follows, at the same time, a roughly chronological order. The show is accompanied by a rich fund of educational programs with tours of the exhibition, discussions of artworks with invited guests, as well as a film program in collaboration with the cinema Kino Kunstmuseum, and not least, workshops for schools.
Text from the Kunstmuseum Bern website
Tracey Moffat (Australian, b. 1960)
Heaven (3 stills)
1997
Colour video
Time, 28 Min.
© 2013 ProLitteris, Zürich
(From the section Eroticism)
Male to the Hilt: Images of Men
The exhibition The Weak Sex – How Art Pictures the New Male zeroes in on the evolution of male identity since the 1960s. On view are works by 40 artists regardless of gender who question masculinity and stage it anew. The Kunstmuseum Bern seeks to foster dialogue in the exhibition and is therefore increasing its focus on social media. For the first time our visitors can respond to issues raised by an exhibition immediately on location…
The whole spectrum of art media and male images
The exhibition is presenting works that cover the entire range of media used by artists, including paintings, drawings, photographs, films, videos, sculptures and performance-installations. Artists of all ages are represented in the exhibition, enabling it to highlight images of men in all age groups. Each of the artworks questions social norms, who or what a man is, while orchestrating masculinity in novel ways and reflecting on what it means to be a “man”. The artworks in the show take up the theme of masculinity or male emotions – as discussed in society in general or as openly demonstrated by men today: as weeping sport heroes, the disadvantaged position of divorced fathers, overstrained top managers or criminal youths.
Of strong weaknesses, eroticism and the male in crisis
The exhibition is divided into six sections that explore key aspects of masculinity studies and thus simultaneously follow a loose art-historical chronological thread. The introductory section takes up the theme of “Strong Weaknesses” with representations of men weeping or expressing fear. The second section “Experiments” scrutinises the exciting events that took place in conjunction with the social movements of the 1960s and 1970s. The section “Emotions” presents male emotionality in intensely stirring artistic orchestrations. The section “Eroticism” take us through a selection of artworks that investigate men as objects of desire. The last two sections of the exhibition “Crisis and Critique” and “Masculinity as Masquerade” investigate traditional male images and give us an account of the potential of new gender orientations.
Press release from the Kunstmuseum Bern website
Bas Jan Ader (born Winschoten, Netherlands, 1942, died 1975 presumably on the high seas. Lived in California, USA, as of 1963)
I’m Too Sad to Tell You
1970-1971
16mm, s/w
Time, 3:34 Min.
Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen, Rotterdam
(From the section Strong Weaknesses)
Sylvia Sleigh (born Llandudno, Wales, Great Britain, 1916; died New York, USA, 2010)
Paul Rosano in Jacobson Chair
1971
Oil on canvas
131 x 142cm
Courtesy The Estate of Sylvia Sleigh & Freymond-Guth Fine Arts Zürich
(From the section Eroticism)
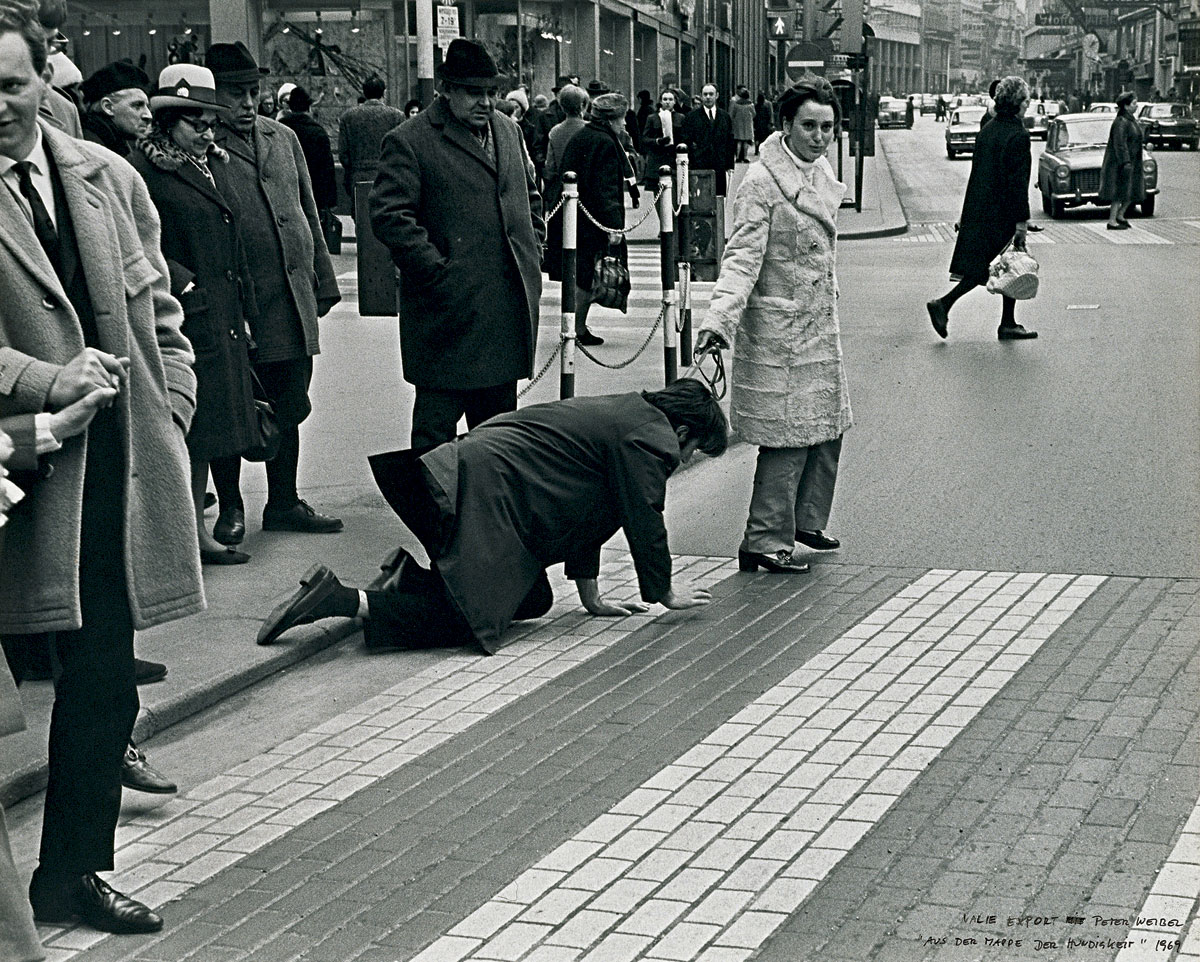
Peter Weibel (Austrian, b. 1944) with Valie EXPORT (Austrian, b. 1940)
Peter Weibel Aus der Mappe der Hundigkeit (Peter Weibel From the Underdog File)
1969
Documentation of the action
5 s/w photographs, 40.4 x 50 cm / 50 x 40.4cm
Sammlung Generali Foundation
Vienna Foto: Josef Tandl
© Generali Foundation © 2013 ProLitteris, Zürich
(From the section Experiments)
Gelitin
Ständerfotos – Nudes (Standing Photos – Nudes)
2000
Series of 15 Lambda prints
Various dimensions
(From the section Eroticism)
Gelitin
Ständerfotos – Nudes (Standing Photos – Nudes)
2000
Series of 15 Lambda prints
Various dimensions
(From the section Eroticism)
Austrian artists’ collective with Wolfgang Gantner, Ali Janka, Florian Reither, and Tobias Urban. Apparently became acquainted at a summer camp in 1978. Changed their name from Gelatin to Gelitin in 2005.
Those who lived through their childhood and youth as members of the baby-boomer generation in the period of the late nineteen-fifties to the mid-seventies, as we did, received a clear view of the world along the way. It was the Cold War. There were precise dividing lines, and it was possible to completely separate good and evil, right and wrong, from one other. The division of roles between men and women was regulated in a way that was just as self-evident. For many children of this time, it was natural that the father earned the money while the mother was at home around the clock and, depending on her social position, went shopping and took care of the laundry herself, or left the housework to employees in order to be able to dedicate herself to “nobler” tasks such as, for instance, beauty care. Family and social duties were clearly distributed between husband and wife: the “strong” sex was responsible for the material basics of existence and for the social identity of the family. The “weak” or also fair sex, in contrast, was responsible for the “soft” factors inside: children, housekeeping, and the beautification of the home. The year 1968 did away with bourgeois concepts of life. Feminism and emancipation anchored the equality of men and women in law. And since the nineteen-sixties, art has also dealt intensively and combatively with feminism and gender questions.
Since VALIE EXPORT walked her partner Peter Weibel on a leash like a dog in their public action that unsettled the public in 1968, legions of creators of art, primarily of the female sex, have questioned the correlations between the genders and undertaken radical reassessments. The formerly “strong” gender has thus long since become a “weak” one. Nevertheless, the exhibition The Weak Sex: How Art Pictures the New Male is not dedicated first and foremost to the battlefield of the genders. Nor is the gender question, which has so frequently been dealt with, posited in the foreground. The Weak Sex is instead dedicated to man as object of research. In what state does he find himself now that his classical role has been invalidated? How does he behave after the shift from representative external appearance to work within the family unit? And where does he stand in the meantime in the midst of so many strong women? What has become of the proud and self-assured man who once signed the school report cards with praise or reproach as head of the family? What has become of the XY species since then is presented – insightfully, sarcastically, and wittily – in the exhibition by Kathleen Bühler.
Part of the Preface to the exhibition by Matthias Frehner, Director of the Kunstmuseum Bern and Klaus Vogel, Director of the Deutsches Hygiene-Museum Dresden
Sam Taylor-Johnson (British, b. 1967)
Steve Buscemi
2004
From the series: Crying Men, 2002-2004
C-Print
99.2 x 99.2cm framed
Courtesy White Cube
© Sam Taylor-Johnson
(From the section Strong Weaknesses)
Sam Taylor-Johnson (British, b. 1967)
Gabriel Byrne
2002
From the series: Crying Men, 2002-2004
C-Print
86.2 x 86.2cm framed
Courtesy White Cube
© Sam Taylor-Johnson
(From the section Strong Weaknesses)
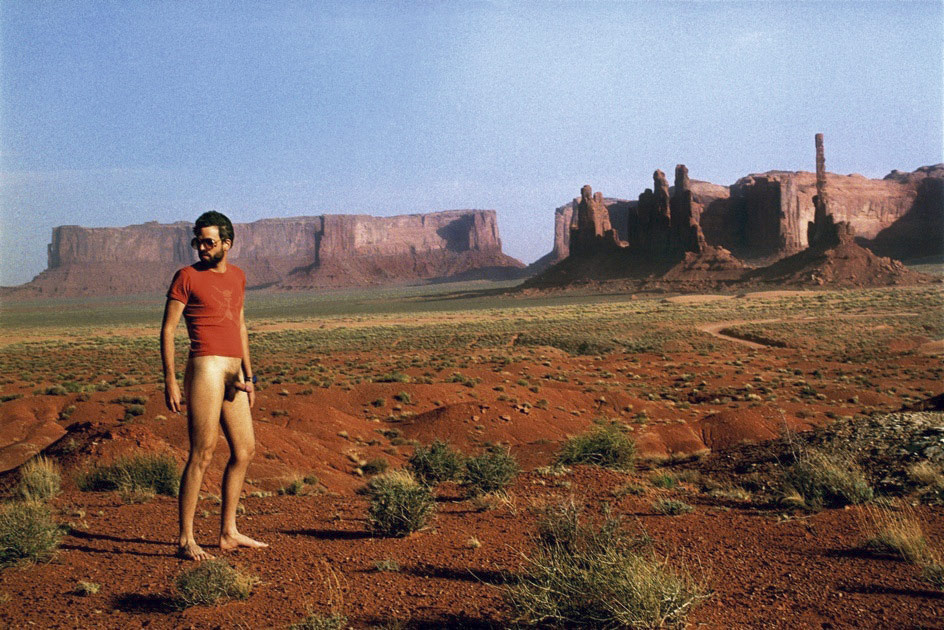
Costa Vece (Swiss, b. 1969)
Me as a Revolutionary, Dictator, Guerilla, Freedom Fighter, Terrorist, Jesus Christ
2007
Ultrachrome – Digitalprint
106 × 80cm
(From the section Crisis and Criticism)
Ugo Rondinone (Swiss, b. 1962)
I Don’t Live Here Anymore
1998
C-print between Alucobond and Plexiglas
180 × 125cm
Kunstmuseum Bern, purchased with the donation of an Art Lover
(From the section Masculinity as Masquerade)
Rico Scagliola & Michael Meier (Swiss, b. 1985; Swiss, b. 1982)
Nude, Leaves and Harp
2012
Floor Installation, HD Digital Print on Novilux traffic, dimensions variable
Ed. 1/5
Jürgen Klauke (Germany, b. 1943)
Rot
1974
Series of 7 photographs
Each 40 × 30cm
Kunstmuseum Bern
(From the section Experiments)
Stronger and Weaker Sexes: Remarks on the Exhibition
Kathleen Bühler Curator Kunstmuseum Bern
In 1908, the Genevan politician and essayist William Vogt wrote the book Sexe faible (The Weak Sex), in which he examines the “natural” weaknesses and inabilities of the female gender. Intended as a “response to absurd exaggerations and feminist utopias,”1 since then the catchy title has shaped the battle of the sexes as a dictum. Like Otto Weininger’s misogynistic study Geschlecht und Charakter (Sex and Character, 1903), Sexe faible is one of the texts from the turn of the previous century that justified the legal, political, and social subordination of women based on their anatomical and, according to the opinion of the author, thus also intellectual inferiority in comparison with men.2 The perception of women as the “weak sex” persisted tenaciously. It is first in recent years that this ascription has slowly been shifted to men, as for instance in the report by neurobiologist Gerald Huther called Das schwache Geschlecht und sein Gehirn (The Weak Sex and His Brain) published in 2009.
Polemics has long since yielded to statistics, and the most recent biological discoveries are gaining currency, such as the fact that male babies are already at risk in the womb because they lack a second X chromosome.3 This genetic “weakness” would apparently lead seamlessly to a social weakness, since males more frequently have problems in school, turn criminal, and die earlier.4 In addition to the findings on biologically based weaknesses also comes the social, economic, and political challenge, which has for some years been discussed as a “crisis of masculinity.” With this metaphor, “an attempt is made to apprehend all the changes that contribute to the fact that the dominance of the male gender, which was formerly consolidated to a large extent, … has lost the obviousness of being self-evident.”5 Nothing therefore demonstrates the transience of gender stereotypes more clearly, and one might rightly ask whether the earlier “weaknesses” might long since have come to be considered new “strengths.” The exhibition at the Kunstmuseum Bern takes up the thread that was already spun by the small but noteworthy exhibition in Switzerland Helden Heute (Heroes Today) in 2005.6 At that time, the focus was put on hero images in contemporary art and on society’s current need for strong men in art and politics.7 The current exhibition in Bern, in contrast, argues quite differently that specifically images of “weak” men best represent the social and cultural liberation movements of the twentieth and twenty-first centuries. The fact that men today are allowed to express their feelings publicly, as is shown for instance by the example of the exceptional Swiss athlete Roger Federer, or that they are staged by female artists as object of desire and no longer as subject of desire is a crucial innovation in the visualisation of gender identities. After various exhibitions in recent years were dedicated to gender relations, gender imprinting, or the social latitude in performative stagings of gender,8 the exhibition at the Kunstmuseum Bern focuses exclusively on men in contemporary art for the first time.9 It brings together the points of view of male and female artists who deal either with their own experiences with men and / or being a man, or with an examination of the images of men that are available. This exhibition has been long overdue.
Nonetheless, what first needs to be overcome is the perception that “gender” themes are a woman’s matter and that only marginalised positions have addressed their social gender. Hegemonic male types – thus men who, according to general opinion, embody the dominant masculine ideal most convincingly – have only been reflected in public through media for a relatively short time, even though the male gender is also a sociocultural construct, just like that of women, transgender, or inter-gender individuals.10 What comes to be expressed here is the invisibility of norms. As is generally known, it is those social groups that hold the most power that actually expose their own status the least. In Western cultural tradition, these are physically sound, white heterosexual men.11 They remain the norm unchallenged as a “blind spot” without their position of power and their power to make decisions ever becoming a focus. The masculine-heterosexual dominance succeeds in “remaining out of the question itself,” as the art historian Irit Rogoff has criticised, by subordinating all representations of the “other” to their own norm, including women, individuals with a different sexual orientation, and non-whites.12
The fact that male bodies are becoming visible today in the most unexpected places is demonstrated in a striking way by the work Nude, Leaves and Harp (2012) by Rico Scagliola and Michael Meier, which graces the entrance area to the exhibition in Bern. The artist duo incorporated detailed images of their naked, sculpted bodies into a palm and marble decor on the floor. The path to the exhibition literally leads over their nakedness. Two exhibitions in Austria were also recently dedicated to this new presence of the naked man,13 with numerous works documenting “the deconstruction of hegemonic models of masculinity – the look of desire at the male body as well as body cult and exploitation,” which is also a focus of the exhibition in Bern.14 However, while those responsible in Linz and Vienna assumed a distanced, art-historical perspective by taking an iconographic approach based on the selection of motifs or a chronological approach according to epoch, the exhibition in Bern favours a different perspective. It focuses on representations of masculinity in art since the nineteen-sixties while simultaneously taking the historical conditions of being a man into consideration by utilising central issues in masculinity research as a guide. What thus results is a logical division of the exhibition and this publication into six chapters.
The introductory chapter “Strong Weaknesses” revolves around the change in gender virtues and considers this based on the example of the weeping and fearful man. The chapter “Experiments” presents eccentric artistic stagings and socio-critical actions that were influenced by the sexual revolution. The chapter “Emotions” highlights the point in time at which men themselves increasingly cast aside the image of the successful and unflinching hero and explore men’s emotionality through doing so. The chapter “Eroticism” describes the change in gaze and position from the male subject to object of desire. The final two chapters “Crisis and Criticism” and “Masculinity as Masquerade,” in contrast, are dedicated to a younger generation of artists who deal out criticism of their “fathers” and also discover the arsenal of gender stagings and their utopian potential anew.
Footnotes
1/ Une riposte aux exagérations, aux absurdités et aux utopies du féminisme is the subtitle.
2/ Otto Weininger, Geschlecht und Charakter, 19th ed. (Leipzig and Vienna, 1920), p. 390. Both Weininger’s book and Vogt’s pamphlet, which saw signs of cultural decay in the women’s movement, are considered to be expressions of a growing antifeminism. The often-used term “weak sex” then also provided the title of a theatre piece by Edouard Bourdet in 1929, which was even filmed in 1933.
3/ “Männer – Das schwache Geschlecht und sein Gehirn: Peter Schipek im Gespräch mit Prof. Dr. Gerald Hüther,” p. 2 (accessed July 2013) No long available online.
4/ Carmen Sadowski, “Der Mann: das schwache Geschlecht,” Express.de, (accessed July 14, 2013) No longer available online.
5/ Michael Meuser and Sylka Scholz, “Krise oder Strukturwandel hegemonialer Männlichkeit?,” in In der Krise? Männlichkeiten im 21. Jahrhundert, ed. Mechthild Bereswill and Anke Neuber (Münster, 2011), p. 56. See also the text by Michael Meuser in this book.
6/ Helden Heute: Das Heldenbild in der zeitgenössischen Kunst, Centre Pasquart, Biel, 2005.
7/ Sociologists interpret this as a sign of need in times of social upheaval. See Dolores Denaro, in Helden Heute: Das Heldenbild in der zeitgenössischen Kunst, ed. Dolores Denaro, exh. cat. Centre Pasquart (Biel, 2005), p. 20.
8/ Oh boy! It’s a Girl, Kunstverein München, 1994; Féminin – Masculin, Centre Georges Pompidou, Paris, 1995; Rosa für Jungs: Hellblau für Mädchen, Neue Gesellschaft für Bildende Kunst, Berlin, 1999; Das achte Feld, Museum Ludwig, Cologne, 2006; to name but a few.
9/ To date, this has occurred only in smaller exhibition spaces, above all during the nineteen-eighties and nineties, and has remained practically undocumented. An exception in this respect was the exhibition Women’s Images of Men (1984) at the Institute of Contemporary Art, London, organised by Joyce Agee, Catherine Elwes, Jacqueline Morreau, and Pat Whiteread.
10/ Inge Stephan, “Im toten Winkel: Die Neuentdeckung des ‘ersten Geschlechts’ durch men’s studies und Männlichkeitsforschung,” in Männlichkeit als Maskerade: Kulturelle Inszenierungen vom Mittelalter bis zur Gegenwart, ed. Claudia Benthien and Inge Stephan (Cologne et al., 2003), p. 13.
11/ Richard Dyer, “Introduction,” in The Matter of Images: Essays on Representation, ed. Richard Dyer (London and New York, 1993), p. 4.
12/ Irit Rogoff, “Er selbst: Konfigurationen von Männlichkeit und Autorität in der Deutschen Moderne,” in Blick-Wechsel: Konstruktionen von Männlichkeit und Weiblichkeit in Kunst und Kunstge-schichte, ed. Ines Lindner et al. (Berlin, 1989), p. 141.
13/ Nude Men, Leopold Museum, Vienna, 2012-13; The Naked Man, Lentos Museum, Linz, 2012-13.
14/ Barnabàs Bencsik and Stella Rollig, “Vorwort,” in Der nackte Mann: Texte, exh. cat. Lentos Kun-stmuseum Linz and Ludwig Museum – Museum of Contemporary Art (Budapest, 2012), p. 7.
Urs Lüthi (Swiss, b. 1947)
Lüthi weint auch für Sie (Lüthi also cries for you)
1970
Offset printing on paper
85.5 x 58.6cm
Ed. 15/100
Kunstmuseum Bern Sammlung Toni Gerber (Schenkung 1983)
© Urs Lüthi
(From the section Experiments)
Luciano Castelli (Swiss, b. 1951)
Lucille, Straps Attractive
1973
Collage on cardboard
100 x 70cm
Kunstmuseum St. Gallen
© 2013 ProLitteris, Zürich
(From the section Experiments)
littlewhitehead (Craig Little, born Glasgow (UK), 1980. Blake Whitehead, born Lanark (UK), 1985)
The Overman
2012
Mannequin, towels, Boxing Glove, wooden base
120 x 120 x 120cm
Saatchi Collection, London Courtesy of the artist/Sumarria Lunn Gallery/Saatchi Collection
(From the section Crisis and Criticism)
Pascal Häusermann (Swiss, b. 1973)
Megalomania, No. 8
2009
Monotype, oil paint, shellac
43 x 29cm
Private Collection, Courtesy the artist
(From the section Crisis and Criticism)
Sarah Lucas (British, b. 1962)
Self Portrait with Knickers
1999
From Self Portraits 1990-1999
1999
Iris print on watercolour paper
80 x 60cm
© Sarah Lucas, courtesy Sadie Coles HQ, London
(From the section Masculinity as Masquerade)
Sarah Lucas (British, b. 1962)
Self Portrait With Skull
1996
From Self Portraits 1990-1999
1999
Iris print on watercolour paper
80 x 60cm
© Sarah Lucas, courtesy Sadie Coles HQ, London
(From the section Masculinity as Masquerade)
Sarah Lucas (British, b. 1962)
Smoking
1998
From Self Portraits 1990-1999
1999
Iris print on watercolour paper
80 x 60cm
© Sarah Lucas, courtesy Sadie Coles HQ, London
(From the section Masculinity as Masquerade)
Silvie Zürcher (Swiss, b. 1977)
Blue Shorts
2005-6
From the series I Wanna Be a Son
Collage
31.5 x 24.4cm
Courtesy Silvie Zürcher
(From the section Masculinity as Masquerade)
Kunstmuseum Bern
Hodlerstrasse 12
3000 Bern 7
Phone: +41 31 328 09 44
E: info@kunstmuseumbern.ch
Opening hours:
Tuesday: 10h – 21h
Wednesday to Sunday: 10h – 17h
Mondays: closed














































































![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Minotaur / Dictator' [Minotaure / Dictateur] The Minotaur or The Dictator Paris, c. 1937 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Minotaur / Dictator' [Minotaure / Dictateur] The Minotaur or The Dictator Paris, c. 1937](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/eblumenfeld14-web.jpg?w=650&h=813)

![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Marguerite von Sivers sur le toit du studio 9, rue Delambre' [Marguerite von Sivers on the roof of Blumenfeld’s studio at 9, rue Delambre] Paris, 1937 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Marguerite von Sivers sur le toit du studio 9, rue Delambre' [Marguerite von Sivers on the roof of Blumenfeld’s studio at 9, rue Delambre] Paris, 1937](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/eblumenfeld10-web.jpg?w=650&h=789)
![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Untitled [Natalia Pasco]' 1942 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Untitled [Natalia Pasco]' 1942](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/eblumenfeld12-web.jpg?w=650&h=812)
![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Voile mouillé' [Wet veil] Paris, 1937 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Voile mouillé' [Wet veil] Paris, 1937](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/eblumenfeld09-web.jpg?w=650&h=905)







![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'In hoc signo vinces [in this sign you will conquer]' 1967 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'In hoc signo vinces [in this sign you will conquer]' 1967](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/in-hoc-signo-vinces-in-this-sign-you-will-conquer-1967-web.jpg?w=650&h=823)

![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Untitled [Homme agenouillé avec tour]' [Kneeling man with tower] 1920 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Untitled [Homme agenouillé avec tour]' [Kneeling man with tower] 1920](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/eblumenfeld02-web.jpg?w=650&h=963)


![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Do your part for the Red Cross' [Soutenez la Croix-Rouge] 1945 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) 'Do your part for the Red Cross' [Soutenez la Croix-Rouge] 1945](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/blumenfeld_1-web.jpg?w=650&h=813)
![Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) Variant of the photograph published in Life Magazine entitled "The Picasso Girl" [The young woman of Picasso] (model: Lisette) c. 1941-1942 Erwin Blumenfeld (American-German, 1897-1969) Variant of the photograph published in Life Magazine entitled "The Picasso Girl" [The young woman of Picasso] (model: Lisette) c. 1941-1942](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/eblumenfeld15-web1.jpg?w=650&h=830)






















![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Barry Maurer, Hand on Gun], Los Angeles' c. 1961 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Barry Maurer, Hand on Gun], Los Angeles' c. 1961](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer6-web.jpg?w=650&h=817)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Larry Lamb, with Tumbleweed], Los Angeles' c. 1959 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Larry Lamb, with Tumbleweed], Los Angeles' c. 1959](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer8-web.jpg?w=650&h=817)



![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Ray Hornsby, Motorcycle], Los Angeles' c. 1957 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Ray Hornsby, Motorcycle], Los Angeles' c. 1957](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer9-web.jpg?w=650&h=821)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Ray Hornsby, with Skull Staff], Los Angeles' c. 1957 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Ray Hornsby, with Skull Staff], Los Angeles' c. 1957](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer10-web.jpg?w=650&h=816)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Ernie Rabb, Pointed Pistol], Los Angeles' c. 1957 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Ernie Rabb, Pointed Pistol], Los Angeles' c. 1957](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer11-web.jpg?w=650&h=817)


![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Larry Lamb, Profile with Chains], Los Angeles' c. 1959 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Larry Lamb, Profile with Chains], Los Angeles' c. 1959](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer13-web.jpg?w=650&h=816)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Dennis Schreffer, Wand Balance], Los Angeles' c. 1957 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Dennis Schreffer, Wand Balance], Los Angeles' c. 1957](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer14-web.jpg?w=650&h=827)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Dennis Schreffer with Portrait], Los Angeles' c. 1957 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Untitled [Dennis Schreffer with Portrait], Los Angeles' c. 1957](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer15-web.jpg?w=650&h=816)


![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, David Elliott. [Double-sided; This side Page 1 of SW series]' c. 1965 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, David Elliott. [Double-sided; This side Page 1 of SW series]' c. 1965](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer16-web.jpg?w=650&h=1022)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, David Elliott. [Double-sided; This side Page 2 of SW series]' c. 1965 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, David Elliott. [Double-sided; This side Page 2 of SW series]' c. 1965](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer17-web.jpg?w=650&h=1015)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, Ernie Rabb. [Double-sided; This side Page 57 of XT series]' c. 1957 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, Ernie Rabb. [Double-sided; This side Page 57 of XT series]' c. 1957](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer18-web.jpg?w=650&h=1019)
![Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, Ernie Rabb. [Double-sided; This side Page 58 of XT series]' c. 1957 Bob Mizer (American, 1922-1992) 'Athletic Model Guild Catalog Board, Ernie Rabb. [Double-sided; This side Page 58 of XT series]' c. 1957](https://artblart.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/bob_mizer19-web.jpg?w=650&h=1015)















































You must be logged in to post a comment.